An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul


Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
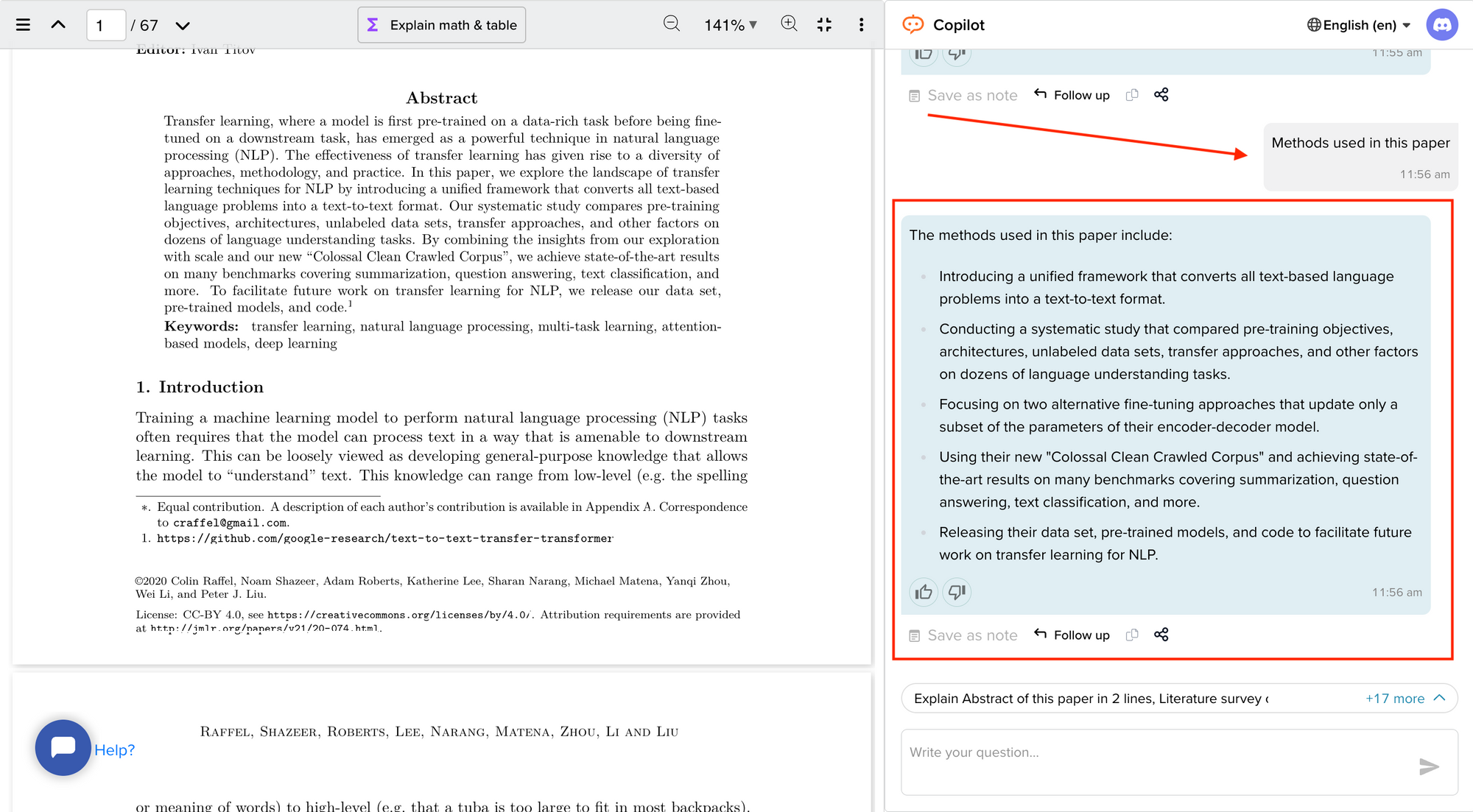
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Literature Review - A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
Curating and drafting a solid literature review section not only lends more credibility to your research paper but also makes your research tighter and better focused. But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye.
Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently synthesize and analyze a vast amount of information, identify key themes and trends, and uncover gaps in the existing research. Get real-time explanations, summaries, and answers to your questions for the paper you're reviewing, making navigating and understanding the complex literature landscape easier.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything from the definition of a literature review, its appropriate length, various types of literature reviews, and how to write one.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a collation of survey, research, critical evaluation, and assessment of the existing literature in a preferred domain.
Eminent researcher and academic Arlene Fink, in her book Conducting Research Literature Reviews , defines it as the following:
“A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have explored while researching a particular topic, and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.”
Simply put, a literature review can be defined as a critical discussion of relevant pre-existing research around your research question and carving out a definitive place for your study in the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews can be presented in multiple ways: a section of an article, the whole research paper itself, or a chapter of your thesis.
A literature review does function as a summary of sources, but it also allows you to analyze further, interpret, and examine the stated theories, methods, viewpoints, and, of course, the gaps in the existing content.
As an author, you can discuss and interpret the research question and its various aspects and debate your adopted methods to support the claim.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is meant to help your readers understand the relevance of your research question and where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. As a researcher, you should use it to set the context, build your argument, and establish the need for your study.
What is the importance of a literature review?
The literature review is a critical part of research papers because it helps you:
- Gain an in-depth understanding of your research question and the surrounding area
- Convey that you have a thorough understanding of your research area and are up-to-date with the latest changes and advancements
- Establish how your research is connected or builds on the existing body of knowledge and how it could contribute to further research
- Elaborate on the validity and suitability of your theoretical framework and research methodology
- Identify and highlight gaps and shortcomings in the existing body of knowledge and how things need to change
- Convey to readers how your study is different or how it contributes to the research area
How long should a literature review be?
Ideally, the literature review should take up 15%-40% of the total length of your manuscript. So, if you have a 10,000-word research paper, the minimum word count could be 1500.
Your literature review format depends heavily on the kind of manuscript you are writing — an entire chapter in case of doctoral theses, a part of the introductory section in a research article, to a full-fledged review article that examines the previously published research on a topic.
Another determining factor is the type of research you are doing. The literature review section tends to be longer for secondary research projects than primary research projects.
What are the different types of literature reviews?
All literature reviews are not the same. There are a variety of possible approaches that you can take. It all depends on the type of research you are pursuing.
Here are the different types of literature reviews:
Argumentative review
It is called an argumentative review when you carefully present literature that only supports or counters a specific argument or premise to establish a viewpoint.
Integrative review
It is a type of literature review focused on building a comprehensive understanding of a topic by combining available theoretical frameworks and empirical evidence.
Methodological review
This approach delves into the ''how'' and the ''what" of the research question — you cannot look at the outcome in isolation; you should also review the methodology used.
Systematic review
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research and collect, report, and analyze data from the studies included in the review.
Meta-analysis review
Meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects than those derived from the individual studies included within a review.
Historical review
Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, or phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and identify future research's likely directions.
Theoretical Review
This form aims to examine the corpus of theory accumulated regarding an issue, concept, theory, and phenomenon. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories exist, the relationships between them, the degree the existing approaches have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
Scoping Review
The Scoping Review is often used at the beginning of an article, dissertation, or research proposal. It is conducted before the research to highlight gaps in the existing body of knowledge and explains why the project should be greenlit.
State-of-the-Art Review
The State-of-the-Art review is conducted periodically, focusing on the most recent research. It describes what is currently known, understood, or agreed upon regarding the research topic and highlights where there are still disagreements.
Can you use the first person in a literature review?
When writing literature reviews, you should avoid the usage of first-person pronouns. It means that instead of "I argue that" or "we argue that," the appropriate expression would be "this research paper argues that."
Do you need an abstract for a literature review?
Ideally, yes. It is always good to have a condensed summary that is self-contained and independent of the rest of your review. As for how to draft one, you can follow the same fundamental idea when preparing an abstract for a literature review. It should also include:
- The research topic and your motivation behind selecting it
- A one-sentence thesis statement
- An explanation of the kinds of literature featured in the review
- Summary of what you've learned
- Conclusions you drew from the literature you reviewed
- Potential implications and future scope for research
Here's an example of the abstract of a literature review
Is a literature review written in the past tense?
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present perfect tenses.
How many sources for a literature review?
There are multiple approaches to deciding how many sources to include in a literature review section. The first approach would be to look level you are at as a researcher. For instance, a doctoral thesis might need 60+ sources. In contrast, you might only need to refer to 5-15 sources at the undergraduate level.
The second approach is based on the kind of literature review you are doing — whether it is merely a chapter of your paper or if it is a self-contained paper in itself. When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. In the second scenario, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
Quick tips on how to write a literature review
To know how to write a literature review, you must clearly understand its impact and role in establishing your work as substantive research material.
You need to follow the below-mentioned steps, to write a literature review:
- Outline the purpose behind the literature review
- Search relevant literature
- Examine and assess the relevant resources
- Discover connections by drawing deep insights from the resources
- Structure planning to write a good literature review
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review
As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications. You must be able to the answer below questions before you start:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What kind of sources should I analyze?
- How much should I critically evaluate each source?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or offer a critique of the sources?
- Do I need to include any background information or definitions?
Additionally, you should know that the narrower your research topic is, the swifter it will be for you to restrict the number of sources to be analyzed.
2. Search relevant literature
Dig deeper into search engines to discover what has already been published around your chosen topic. Make sure you thoroughly go through appropriate reference sources like books, reports, journal articles, government docs, and web-based resources.
You must prepare a list of keywords and their different variations. You can start your search from any library’s catalog, provided you are an active member of that institution. The exact keywords can be extended to widen your research over other databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Microsoft Academic
- Science.gov
Besides, it is not advisable to go through every resource word by word. Alternatively, what you can do is you can start by reading the abstract and then decide whether that source is relevant to your research or not.
Additionally, you must spend surplus time assessing the quality and relevance of resources. It would help if you tried preparing a list of citations to ensure that there lies no repetition of authors, publications, or articles in the literature review.
3. Examine and assess the sources
It is nearly impossible for you to go through every detail in the research article. So rather than trying to fetch every detail, you have to analyze and decide which research sources resemble closest and appear relevant to your chosen domain.
While analyzing the sources, you should look to find out answers to questions like:
- What question or problem has the author been describing and debating?
- What is the definition of critical aspects?
- How well the theories, approach, and methodology have been explained?
- Whether the research theory used some conventional or new innovative approach?
- How relevant are the key findings of the work?
- In what ways does it relate to other sources on the same topic?
- What challenges does this research paper pose to the existing theory
- What are the possible contributions or benefits it adds to the subject domain?
Be always mindful that you refer only to credible and authentic resources. It would be best if you always take references from different publications to validate your theory.
Always keep track of important information or data you can present in your literature review right from the beginning. It will help steer your path from any threats of plagiarism and also make it easier to curate an annotated bibliography or reference section.
4. Discover connections
At this stage, you must start deciding on the argument and structure of your literature review. To accomplish this, you must discover and identify the relations and connections between various resources while drafting your abstract.
A few aspects that you should be aware of while writing a literature review include:
- Rise to prominence: Theories and methods that have gained reputation and supporters over time.
- Constant scrutiny: Concepts or theories that repeatedly went under examination.
- Contradictions and conflicts: Theories, both the supporting and the contradictory ones, for the research topic.
- Knowledge gaps: What exactly does it fail to address, and how to bridge them with further research?
- Influential resources: Significant research projects available that have been upheld as milestones or perhaps, something that can modify the current trends
Once you join the dots between various past research works, it will be easier for you to draw a conclusion and identify your contribution to the existing knowledge base.
5. Structure planning to write a good literature review
There exist different ways towards planning and executing the structure of a literature review. The format of a literature review varies and depends upon the length of the research.
Like any other research paper, the literature review format must contain three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. The goals and objectives of the research question determine what goes inside these three sections.
Nevertheless, a good literature review can be structured according to the chronological, thematic, methodological, or theoretical framework approach.
Literature review samples
1. Standalone
2. As a section of a research paper
How SciSpace Discover makes literature review a breeze?
SciSpace Discover is a one-stop solution to do an effective literature search and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge. It is an excellent repository where you can find millions of only peer-reviewed articles and full-text PDF files. Here’s more on how you can use it:
Find the right information
Find what you want quickly and easily with comprehensive search filters that let you narrow down papers according to PDF availability, year of publishing, document type, and affiliated institution. Moreover, you can sort the results based on the publishing date, citation count, and relevance.
Assess credibility of papers quickly
When doing the literature review, it is critical to establish the quality of your sources. They form the foundation of your research. SciSpace Discover helps you assess the quality of a source by providing an overview of its references, citations, and performance metrics.
Get the complete picture in no time
SciSpace Discover’s personalized suggestion engine helps you stay on course and get the complete picture of the topic from one place. Every time you visit an article page, it provides you links to related papers. Besides that, it helps you understand what’s trending, who are the top authors, and who are the leading publishers on a topic.
Make referring sources super easy
To ensure you don't lose track of your sources, you must start noting down your references when doing the literature review. SciSpace Discover makes this step effortless. Click the 'cite' button on an article page, and you will receive preloaded citation text in multiple styles — all you've to do is copy-paste it into your manuscript.
Final tips on how to write a literature review
A massive chunk of time and effort is required to write a good literature review. But, if you go about it systematically, you'll be able to save a ton of time and build a solid foundation for your research.
We hope this guide has helped you answer several key questions you have about writing literature reviews.
Would you like to explore SciSpace Discover and kick off your literature search right away? You can get started here .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how to start a literature review.
• What questions do you want to answer?
• What sources do you need to answer these questions?
• What information do these sources contain?
• How can you use this information to answer your questions?
2. What to include in a literature review?
• A brief background of the problem or issue
• What has previously been done to address the problem or issue
• A description of what you will do in your project
• How this study will contribute to research on the subject
3. Why literature review is important?
The literature review is an important part of any research project because it allows the writer to look at previous studies on a topic and determine existing gaps in the literature, as well as what has already been done. It will also help them to choose the most appropriate method for their own study.
4. How to cite a literature review in APA format?
To cite a literature review in APA style, you need to provide the author's name, the title of the article, and the year of publication. For example: Patel, A. B., & Stokes, G. S. (2012). The relationship between personality and intelligence: A meta-analysis of longitudinal research. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 16-21
5. What are the components of a literature review?
• A brief introduction to the topic, including its background and context. The introduction should also include a rationale for why the study is being conducted and what it will accomplish.
• A description of the methodologies used in the study. This can include information about data collection methods, sample size, and statistical analyses.
• A presentation of the findings in an organized format that helps readers follow along with the author's conclusions.
6. What are common errors in writing literature review?
• Not spending enough time to critically evaluate the relevance of resources, observations and conclusions.
• Totally relying on secondary data while ignoring primary data.
• Letting your personal bias seep into your interpretation of existing literature.
• No detailed explanation of the procedure to discover and identify an appropriate literature review.
7. What are the 5 C's of writing literature review?
• Cite - the sources you utilized and referenced in your research.
• Compare - existing arguments, hypotheses, methodologies, and conclusions found in the knowledge base.
• Contrast - the arguments, topics, methodologies, approaches, and disputes that may be found in the literature.
• Critique - the literature and describe the ideas and opinions you find more convincing and why.
• Connect - the various studies you reviewed in your research.
8. How many sources should a literature review have?
When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. if it is a self-contained paper in itself, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
9. Can literature review have diagrams?
• To represent an abstract idea or concept
• To explain the steps of a process or procedure
• To help readers understand the relationships between different concepts
10. How old should sources be in a literature review?
Sources for a literature review should be as current as possible or not older than ten years. The only exception to this rule is if you are reviewing a historical topic and need to use older sources.
11. What are the types of literature review?
• Argumentative review
• Integrative review
• Methodological review
• Systematic review
• Meta-analysis review
• Historical review
• Theoretical review
• Scoping review
• State-of-the-Art review
12. Is a literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research, and provide a background for the rest of your work.
But before you go,
- Six Online Tools for Easy Literature Review
- Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing
Skip to Content
Massey University
- Search OWLL
- Handouts (Printable)
- Pre-reading Service
- StudyUp Recordings
- StudyUp Postgraduate
- Academic writing
- Intro to academic writing
- What is academic writing?
- Writing objectively
- Writing concisely
- 1st vs. 3rd person
- Inclusive language
- Te Reo Māori
- Assignment planning
- Assignment planning calculator
- Interpreting the assignment question
- Command words
- Organising points
- Researching
- Identifying academic sources
- Evaluating source quality
- Editing & proofreading
- Apostrophes
- Other punctuation
- Active voice
- American vs. British spelling
- Conditionals
- Prepositions
- Pronoun Reference
- Sentence fragments
- Sentence Structure
- Subject-verb agreement
- Formatting and layout
- Word limits and assignment length
- Commonly confused words
- How assignments are marked
- Marking guides
- Getting an A
- Levels of assessment
- Using feedback
- Professional emails
- Forum posts
- Forum netiquette guidelines
- Sharing personal information
- Writing about personal experiences
- Assignment types
- What is an essay?
- Essay planning and structure
- Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Body paragraphs
- Essay revision
- Essay writing resources
- What is a report?
- Report structure
- Analysing issues for a report
- Business report
- What is a business report?
- Business report structure
- Inductive vs. deductive reports
- Other kinds of business communication
- Business report format and layout
- What is a lab report?
- Lab report structure
- Science lab report writing resources
- Psychology lab report writing resources
- Lab report body paragraphs
- Literature review
- What is a literature review?
- Writing a literature review
- Literature review structure
- Literature review writing resources
- Research proposal
- Writing a research proposal
- Research proposal structure
- Other types
- Article critique
- Book review
- Annotated bibliography
- Reflective writing
- Oral presentation
- Thesis / dissertation
- Article / conference paper
- Shorter responses
- Computer skills
- Microsoft Word
- Basic formatting
- Images, tables, & figures
- Long documents
- Microsoft Excel
- Basic spreadsheets
- Navigating & printing spreadsheets
- Charts / graphs & formulas
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Basic skills
- Advanced skills
- Distance study
- Getting started
- How to study
- Online study techniques
- Distance support
- Reading & writing
- Reading strategies
- Writing strategies
- Grammar resources
- Listening & speaking
- Listening strategies
- Speaking strategies
- Maths & statistics
- Trigonometry
- Finance formulas
- Postgraduate study
- Intro to postgrad study
- Planning postgrad study
- Postgrad resources
- Postgrad assignment types
- Referencing
- Intro to referencing
- What is referencing?
- Why reference?
- Common knowledge
- Referencing styles
- What type of source is this?
- Reference list vs. bibliography
- Referencing software
- Quoting & paraphrasing
- Paraphrasing & summarising
- Paraphrasing techniques
- APA Interactive
- In-text citation
- Reference list
- Online material
- Other material
- Headings in APA
- Tables and Figures
- Referencing elements
- 5th vs. 6th edition
- 6th vs. 7th edition
- Chicago style
- Chicago Interactive
- About notes system
- Notes referencing elements
- Quoting and paraphrasing
- Author-date system
- MLA Interactive
- Abbreviations
- List of works cited
- Captions for images
- 8th vs 9th edition
- Oxford style
- Other styles
- Harvard style
- Vancouver style
- Legal citations
- Visual material
- Sample assignments
- Sample essay 1
- Sample essay 2
- Sample annotated bibliography
- Sample book review
- Study skills
- Time management
- Intro to time management
- Procrastination & perfectionism
- Goals & motivation
- Time management for internal students
- Time management for distance students
- Memory skills
- Principles of good memory
- Memory strategies
- Note-taking
- Note-taking methods
- Note-taking in lectures
- Note-taking while reading
- Digital note-taking
- Reading styles
- In-depth reading
- Reading comprehension
- Reading academic material
- Reading a journal article
- Reading an academic book
- Critical thinking
- What is critical thinking?
- Constructing an argument
- Critical reading
- Logical fallacies
- Tests & exams
- Exam & test study
- Planning exam study
- Gathering & sorting information
- Reviewing past exams
- Phases of revision
- Last-minute study strategies
- Question types
- Short answer
- Multi-choice
- Problem / computational
- Case-study / scenario
- Open book exam
- Open web exam or test
- Take home test
- In the exam
- Online exam
- Physical exam
Use of verb tenses in APA, Chicago and MLA styles
APA, Chicago and MLA are the three main referencing systems/writing styles used at Massey. Re commendations they make in relation to verb tenses are summarized below. Implementing these recommendations may be especially important if you are planning to publish work in a journal that requires certain style guidelines to be followed. However, for assignments or theses at Massey, it is important to be guided by any advice your lecturer or supervisor may provide in relation to use of tenses.
Referring to the ideas of other researchers (e.g. in a literature review)
Simple past tense
- Brown (2019) argued that… However, Small (2020) suggested that…
Present perfect tense
- Doñoso (1992) has demonstrated that…
Note : A shift of tense may be used to indicate that the research findings are still relevant.
- Molland (2018) discovered that educational outcomes improve when….
Describing a method or procedure
- The participants were interviewed…
- Other researchers have followed a similar procedure.
Reporting results (your own or those of others)
- The results supported the hypothesis
Personal reactions
Simple present tense
- I believe …
- I sensed a need for…
- I have encountered challenges…
Commenting on the implications of results or findings
- The findings indicate that…
Presenting limitations
- The limitations of this case study are …
Conclusions
- We can conclude that…
Suggesting future directions
- This is an area for future research
Chicago and MLA
Both Chicago and MLA recommend the use of the simple present tense (e.g. ‘argues’) or present perfect tense (e.g. ‘has argued’) in the following situations:
No matter how long ago the work was published, the present tense is used, and even a deceased author ‘argues’ or ‘claims’.
- Vasquez and Lopez argue that…
- Bailey has outlined …
Discussing the actions of characters in literature
- In Episode 4 of James Joyce’s Ulysses , Leopold Bloom walks to the butchers and buys a pork kidney
Narrating a fictional work’s plot
- The plot of Ulysses centres on the wanderings and encounters of Leopold Bloom in Dublin, Ireland, over the course of a single day (16 June 1904)
Discussing a literary work, author or theme.
- James Joyce structures Ulysses around 18 episodes that loosely mirror episodes in Homer's Odyssey
- The themes of Ulysses include compassion and remorse
Note : If the context is clearly historical (rather than textual), use of the past tense is acceptable.
- Ulysses was published on 2 February 1922, James Joyce’s 40th birthday.
These pages are provided as a guide to proper referencing. Your course, department, school, or institute may prescribe specific conventions, and their recommendations supersede these instructions. If you have questions not covered here, check in the style guide listed above, ask your course coordinator, or ask at Academic Q+A .
Page authorised by Director - Centre for Learner Success Last updated on 17 November, 2020
- Academic Q+A
Have a study or assignment writing question? Ask an expert at Academic Q+A
Live online workshops
- StudyUp (undergraduate)
- Campus workshops
- Albany (undergraduate)
- Albany (postgraduate)
- Albany (distance)
- Manawatu (undergraduate)
- Manawatu (postgraduate)
Upcoming events
- All upcoming events
- Academic writing and learning support
- 0800 MASSEY | (+64 6 350 5701)
- [email protected]
- Online form

- RRU Writing Centre
- WriteAnswers
Q. According to the APA Style (7th ed.) rules, which verb tense should I use in the different sections of my major research paper?
- 2 Academic Integrity
- 48 Academic writing
- 41 APA Style
- 33 APA Style: Formatting
- 108 APA Style: In-text citations
- 106 APA Style: References
- 18 Legal citations
- 16 Paraphrasing
- 10 Punctuation
- 25 Quotations
- 16 Writing Centre information
- 63 Writing Centre resources
Answered By: Theresa Bell (she/her/hers) Last Updated: Nov 04, 2021 Views: 3526
The 7th edition style manual of the American Psychological Association (APA) provides suggestions on which verb tense is appropriate for various sections of a thesis, major project or journal article:
- Past or present perfect tense: "Literature review (or whenever discussing other researchers' work)" (APA, 2020, p. 118), "method" (APA, 2020, 118), and "description of procedure" (APA, 2020, 118)
- Past tense: "Reporting of results" (APA, 2020, p. 118)
- Present tense: "Discussion of implications of results" (APA, 2020, p. 118) and "presentation of conclusions, limitations, future directions, and so forth" (APA, 2020, p. 118).
As much as possible, try to be consistent with your chosen verb tense within a section "to ensure smooth expression" (APA, 2020, p. 118). If the verb tenses suggested above don't make sense for the purposes of your document, please check with your instructor or academic supervisor to get their recommendation on the best approach for your document.
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 0 No 2
- Generating Ideas
- Drafting and Revision
- Sources and Evidence
- Style and Grammar
- Specific to Creative Arts
- Specific to Humanities
- Specific to Sciences
- Specific to Social Sciences
- CVs, Résumés and Cover Letters
- Graduate School Applications
- Other Resources
- Hiatt Career Center
- University Writing Center
- Classroom Materials
- Course and Assignment Design
- UWP Instructor Resources
- Writing Intensive Requirement
- Criteria and Learning Goals
- Course Application for Instructors
- What to Know about UWS
- Teaching Resources for WI
- FAQ for Instructors
- FAQ for Students
- Journals on Writing Research and Pedagogy
- University Writing Program
- Degree Programs
- Majors and Minors
- Graduate Programs
- The Brandeis Core
- School of Arts and Sciences
- Brandeis Online
- Brandeis International Business School
- Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
- Heller School for Social Policy and Management
- Rabb School of Continuing Studies
- Precollege Programs
- Faculty and Researcher Directory
- Brandeis Library
- Academic Calendar
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Summer School
- Financial Aid
- Research that Matters
- Resources for Researchers
- Brandeis Researchers in the News
- Provost Research Grants
- Recent Awards
- Faculty Research
- Student Research
- Centers and Institutes
- Office of the Vice Provost for Research
- Office of the Provost
- Housing/Community Living
- Campus Calendar
- Student Engagement
- Clubs and Organizations
- Community Service
- Dean of Students Office
- Orientation
- Spiritual Life
- Graduate Student Affairs
- Directory of Campus Contacts
- Division of Creative Arts
- Brandeis Arts Engagement
- Rose Art Museum
- Bernstein Festival of the Creative Arts
- Theater Arts Productions
- Brandeis Concert Series
- Public Sculpture at Brandeis
- Women's Studies Research Center
- Creative Arts Award
- Our Jewish Roots
- The Framework for the Future
- Mission and Diversity Statements
- Distinguished Faculty
- Nobel Prize 2017
- Notable Alumni
- Administration
- Working at Brandeis
- Commencement
- Offices Directory
- Faculty & Staff
- Alumni & Friends
- Parents & Families
- 75th Anniversary
- New Students
- Shuttle Schedules
- Support at Brandeis
Writing Resources
Verb tenses – literature.
This handout is available for download in DOCX format and PDF format .
Use of the correct verb tense allows you to express clearly the time relationships among your ideas. When deciding which verb tense to use, aim for consistency, simplicity, and clarity. Whenever possible, keep verbs in the same tense (consistency), and use either the simple present or the past tense (simplicity). Above all, choose the verb tense that most clearly expresses the idea you want to convey (clarity). In general, use the present tense to describe actions and states of being that are still true in the present; use the past tense to describe actions or states of being that occurred exclusively in the past.
Below are some discipline-specific guidelines for how to use verb tenses effectively in literature and the humanities. For details on tenses in science writing, see handout “Verb Tenses—Science.”
Decribing the Text
Use the present tense to describe fictional events that occur in the text:.
(This use of present tense is referred to as "the historical present.")
- In Milton's Paradise Lost , Satan tempts Eve in the form of a serpent.
- Voltaire's Candide encounters numerous misfortunes throughout his travels.
Use the present perfect tense to describe an event that occurs in the text previous to the principal event you are describing:
- The governess questions the two children because she believes they have seen the ghosts.
- Convinced that Desdemona has been unfaithful to him, Othello strangles her.
Use the past tense when referring to an event occurring before the story begins:
- In the opening scenes of Hamlet , the men are visited by the ghost of Hamlet's father, whom Claudius murdered .
Providing Factual Information
Use the present tense to report your interpretations and the interpretations of other sources:.
- Odysseus represents the archetypal epic hero.
- Flanagan suggests that Satan is the protagonist of Paradise Lost .
Use the past tense to explain historical context or elements of the author's life that occurred exclusively in the past:
- Hemingway drew on his experiences in World War I in constructing the character of Jake Barnes.
Combining Fact and Fiction
When writing about literature, use both present and past tense when combining observations about fictional events from the text (present tense) with factual information (past tense):.
- James Joyce, who grew up in the Catholic faith, draws on church doctrine to illuminate the roots of Stephen Dedalus' guilt.
- In Les Belles Images , Simone de Beauvoir accurately portrays the complexities of a marriage even though she never married in her lifetime.
Credit: Adapted from “Verb Tense,” Hamilton University Writing Center. 16 October 2017, https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/writing/writing-resources/verb-tense .
- Resources for Students
- Writing Intensive Instructor Resources
- Research and Pedagogy

Capstone Form and Style
Grammar and mechanics: verb tenses, most common verb tenses in academic writing.
According to corpus research, in academic writing, the three tenses used the most often are the simple present , the simple past , and the present perfect (Biber et al., 1999; Caplan, 2012). The next most common tense for capstone writers is the future ; the doctoral study/dissertation proposal at Walden is written in this tense for a study that will be conducted in the future. The blog post on What Verb Tenses Do You Need to Master for Academic Writing addresses these ideas as well.
Biber, D., Johansson, S., Leech, G., Conrad, S., & Finegan, E. (1999). Longman grammar of written and spoken English . Pearson. https://doi.org/10.1162/089120101300346831
Caplan, N. A. (2012). Grammar choices for graduate and professional writers . University of Michigan Press.
Simple present: Use the simple present to describe a general truth or a habitual action. This tense indicates that the statement is generally true in the past, present, and future.
- Example: Research methods include qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods.
Simple past : Use the simple past tense to describe a completed action that took place at a specific point in the past (e.g., last year, 1 hour ago, last Sunday). In this example, the specific point of time in the past is 1998.
- Example: Zimbardo (1998) researched many aspects of social psychology.
Present perfect: Use the present perfect to indicate an action that occurred at a nonspecific time in the past. This action has relevance in the present. The present perfect is also sometimes used to introduce background information in a paragraph. After the first sentence, the tense shifts to the simple past.
- Example: Numerous researchers have used this method.
- Example: Many researchers have studied how small business owners can be successful beyond the initial few years in business. They found common themes among small business owners.
Future: Use the future to describe an action that will take place at a particular point in the future (at Walden, this is used especially when writing a proposal for a doctoral capstone study).
- Example: I will conduct semistructured interviews.
Keep in mind that verb tenses should be adjusted after the proposal after the research has been completed. See Verb Tense Considerations: Proposal to Final Study farther down on this page and this blog post about Revising the Proposal for the Final Capstone Document for more information.
APA Style Guidelines on Verb Tense
APA calls for consistency and accuracy in verb tense usage. In other words, avoid unnecessary shifts in verb tense within a paragraph or in adjacent paragraphs to help ensure smooth expression.
- Use the past tense (e.g., researchers presented ) or the present perfect (e.g., researchers have presented ) for the literature review and the description of the procedure if discussing past events.
- Use the past tense to describe the results (e.g., test scores improved significantly ).
- Use the present tense to discuss implications of the results and present conclusions (e.g., the results of the study show …).
Refer to the work of another researcher in the past.
- Patterson (2017) presented, found, stated, discovered…
However, there can be a shift to the present tense if the research findings still hold true:
- King (2016) found that revising a document three times improves the final grade.
- Smith (2018) discovered that the treatment is effective.
Verb Tense Guidelines When Referring to the Document Itself
To preview what is coming in the document or to explain what is happening at that moment in the document, use the present or future tense:
- In this study, I will describe …
- In this study, I describe …
- In the next chapter, I will discuss …
- In the next chapter, I discuss …
To refer back to information already covered, such as summaries of discussions that have already taken place or conclusions to chapters/sections, use the past tense:
- Chapter 1 included my original discussion of the research questions.
- In summary, in this section, I presented information on…
Simple Past Versus the Present Perfect
Rules for the use of the present perfect differ slightly in British and American English. Researchers have also found that among American English writers, sometimes individual preferences dictate whether the simple past or the present perfect is used. In other words, one American English writer may choose the simple past in a place where another American English writer may choose the present perfect.
Keep in mind, however, that the simple past is used for a completed action. It often is used with signal words such as yesterday, last week, 1 year ago, or in 2015 to indicate the specific time in the past when the action took place.
- I collected data in 2017 .
- All prospective participants signed an informed consent form in a 1-week period before data collection began.
The present perfect focuses more on an action that occurred without focusing on the specific time it happened. Note that the specific time is not given, just that the action has occurred.
- I have examined several possible research designs.
The present perfect focuses more on the result of the action.
- The panel of experts has completed the instrument validation.
The present perfect is often used with signal words such as since, already, just, until now, (not) yet, so far, ever, lately , or recently .
- I have already examined several possible research designs.
- The panel of experts has recently completed the instrument validation.
- Researchers have used this method since it was developed.
Also see the blog post on Choosing the Present Perfect Tense in Academic Writing for more information and examples.
Verb Tense Considerations: Proposal to Final Study
Unlike the proposal , where the writer describes a study not yet conducted, the final study is a report of what actually happened in the research or project study process, so the writer must revise the relevant portions of the proposal accordingly when incorporating them into the final capstone document. One essential step is to determine which verbs require a change in tense for logical and accurate reporting of the completed study. Although many sentences will shift from future to past tense, this shift is not appropriate in all cases. These guidelines address specific considerations for deciding where a shift in tense is necessary during this revision process.
Future tense verbs that need to shift to past tense in the final study include those representing actions, decisions, or processes that happened after approval of the proposal, such as in the following examples:
Proposal: In this study, I will employ face-to-face interviews with key participants, reflexive notes, and a review of literature… Final study: In this study, I employed face-to-face interviews with key participants, reflexive notes, and a review of literature…
Proposal: The sample will consist of 10 to 20 graduate students who have completed at least three graduate courses in the past year. Final study: The sample consisted of 12 graduate students who had completed * at least three graduate courses in the past year. * Note the related verb tense shift from present perfect to past perfect in the second example.
Not all verbs require a shift in tense. Here are a few such cases:
- In this chapter, I describe … (or will describe … )
- NOT: In this chapter, I described …
- This study’s findings could lead to positive social change by…
- The results of this study may serve to increase awareness of…
- Researchers have argued that the continued loss of experienced nurses will have negative effects on...
- As technology advances, future researchers will want to focus on…
- This professional development project will address the problem of…
- This systematic review will provide support for evidence-based best practices for…
Strategy for revising verb tense from proposal to final study:
- Use Ctrl+F (or Command+F on a Mac) or click the Find button under the Home tab to search for occurrences of the word will in the document.
- On a case-by-case basis, examine each statement containing will to determine whether revision is needed. Avoid using Replace All in the Find and Replace menu because, as noted above, not all uses of future tense refer to the proposal itself.
- Check the context in which the word will occurs to see if other revisions are warranted nearby.
Keep in mind that, although this strategy can make finding and revising proposal-specific language a bit easier, there is no substitute for careful, systematic proofreading of the document.
Final note and related resources:
Inadequate revision of verb tense and other proposal-specific language is among the Top 10 Reasons for Delays at the F&S Review , so taking the time for this process well before that stage is important.
Capstone writers should consult the Form and Style Checklist for this and other important aspects of revising the final study or project in preparation for the Form and Style Review .
Summary of English Verb Tenses
The 12 main tenses:
- Simple present : She writes every day.
- Present progressive: She is writing right now.
- Simple past : She wrote last night.
- Past progressive: She was writing when he called.
- Simple future : She will write tomorrow.
- Future progressive: She will be writing when you arrive.
- Present perfect : She has written Chapter 1.
- Present perfect progressive: She has been writing for 2 hours.
- Past perfect: She had written Chapter 3 before she started Chapter 4.
- Past perfect progressive: She had been writing for 2 hours before her friends arrived.
- Future perfect: She will have written Chapter 4 before she writes Chapter 5.
- Future perfect progressive: She will have been writing for 2 hours by the time her friends come over.
Conditionals:
Zero conditional (general truths/general habits).
- Example: If I have time, I write every day.
First conditional (possible or likely things in the future).
- Example: If I have time, I will write every day.
Second conditional (impossible things in the present/unlikely in the future).
- Example : If I had time, I would write every day.
Third conditional (things that did not happen in the past and their imaginary results)
- Example : If I had had time, I would have written every day.
Subjunctive : This form is sometimes used in that -clauses that are the object of certain verbs or follow certain adjectives. The form of the subjective is the simple form of the verb. It is the same for all persons and number.
- Example : I recommend that future researchers include other populations in their studies.
- Example: It is important that staff at the study site establish criteria for implementing study findings.
- Previous Page: Relative, Restrictive, and Nonrestrictive Clauses
- Next Page: Subject–Verb Agreement
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Avoiding Common Math Mistakes-Expanding
- Avoiding Common Math Mistakes-Trigonometry
- Avoiding Common Math Mistakes-Simplifiying
- Avoiding Common Math Mistakes-Square Roots
- Avoiding Common Math Mistakes-Working with negatives
- Complex Numbers
- Decimal and Percent
- Dosage Calculations
- Adding and Subtracting Fractions
- BEDMAS with Fractions
- Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
- Long Division
- Long Multiplication
- Order of Operations
- Calculating Slope Examples
- Graphs of Functions
- Least Squares Trendline and Correlation
- Semi-Log and Log-Log Graphs
- Pythagorean Theorem
- Ratio and Proportion
- Rounding and Significant Figures
- Scientific Notation
- Square Root
- Unit Conversion for the Sciences
- Unit Conversion Examples
- Application of Derivatives: Examples
- Chain Rule: Examples
- Higher Order Derivatives: Examples
- Power Rule: Example
- Product Rule: Examples
- Quotient Rule: Examples
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- Net Change Theorem: Example
- Newton's Method
- Completing the Square
- Simplifying Expressions
- Absolute Value Equations
- The Quadratic Formula
- Rational Equations
- Solving Equations: Application
- Solving Linear Equations
- Solving Linear Inequalities
- Solving Linear Systems
- Word Problems
- Domain and Range of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
- Transformation of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
- Solving Exponential and Logarithmic Equations
- Logarithmic Models
- Composition of Functions
- Domain and Range Examples
- Domain and Range Exponential and Logarithmic Fuctions
- Domain and Range of Trigonometric Functions
- Evaluating Functions
- One-to-One and Onto Functions
- Inverse Functions
- Equations of Lines
- Setting Up Linear Models
- Piecewise-Defined Functions
- Transformations of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
- Transformations of Trigonometric Functions
- Bar Graph and Pie Chart
- Linear Regression and Correlation
- Normal Distribution
- Standard Deviation
- Avoiding Common Math Mistakes in Trigonometry
- Solving Trigonometric Equations
- Trigonometry on the Unit Circle
- Introduction to Trigonometric Functions
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- Setting Up Trigonometric Models
- Vector Magnitude, Direction, and Components
- Angle Between Vectors
- Vector Addition, Subtraction, and Scalar Multiplication
- Vector Dot Product and Cross Product
- Matrix Addition, Subtraction, and Multiplication by a Scalar
- Matrix Multiplication
- Special Matrices and Definitions
- How do I use my scientific calculator?
- How do I approach word problems?
- I got the right answer, so why didn't I get full marks?
- Open Educational Resources
- Balancing equations
- Chemical bonding
- Lewis Structures
- Periodic table
- Significant figures
- Stoichiometry
- The Clausius-Clapeyron equation
- Yield calculations
- Assignment Planning Calculator
- Grammar Resources
- Misused Modifiers
- Overview of future times
- Overview of past tenses
- Overview of present tenses
Overview of verb tenses and APA recommendations for tense usage in academic writing
- Parallel Structure
- Pronoun Usage
- Run-on Sentences
- Sentence Fragments
- Sentence Structure: Prepositional Phrases
- Slang and Colloquial Language
- The Important Joining Words
- Word Classes, Prefixes and Suffixes
- Wordiness: Using more words than is necessary
- Words Frequently Misused
- Apostrophe Usage
- Capitalization
- Comma Splice
- How to use a semi-colon
- Pronunciation Resources
- Words that sound similar
- Vocabulary Resources
- Research proposals
- Writing a review of literature
- Accessing Citation Guides at the Ontario Tech University Library
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- What is Turnitin.com?
- About Documenting Your Work
- American Chemical Society (ACS) Citations
- American Institute of Physics (AIP) Citations
- APA 7th Edition: Formatting
- APA 7th Edition: Sample Student Paper
- APA 7th Edition: Paper Checklist
- American Psychological Association (APA) 7th Edition: Tables and Figures
- APA 7th Edition: In-text Citations
- APA 7th Edition: Referencing
- APA 7th Edition: Common Errors in Citation
- The Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS): Notes
- The Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS): Bibliography
- CMOS Quick Reference Guide
- Council of Science Editors
- McGill Guide: Footnotes
- MLA: Quick Reference Guide 8th Edition
- Vancouver Style
- Example IEEE References
- Assignment Comprehension
- Developing a Thesis Statement
- Essay Outline
- Primary Data Collection
- Wikipedia and Google Scholar
- Finding Sources
- How to Find Articles Using Google Scholar
- How to Find Books on the Library Website
- OMNI Searches
- Types of Source
- Body Paragraph Structure
- Introductions and Conclusions
- Patterns of Organization
- When Researching, Keep Track of the Following
- Incorporating Sources into your Writing
- Paraphrasing
- Summarizing
- Integrating Technical Writing
- Helpful Resources
- Why Revise?
- How Do I Revise?
- Switching from Writer to Reader
- Incorrect Prefixes and Suffixes
- Missing Words
- Pronoun Errors
- Subject-Verb Agreement
- Frequently Misused Words
- Proofreading
- What Causes Writer's Block?
- Strategies to Overcome Writer's Block
- Annotated Bibliography
- Article/Journal Reviews
- Business and Professional Communication
- Business Plans
- Case Studies
- Laboratory Reports
- Literature Review
- Presentations
- Primary/Field Research
- Progress Reports
- Project Proposals
- Reflective Progress Notes
- Research Paper
- Scientific Manuscript By Dr. Chris Garside
- Scientific Manuscript By Sylvie Bardin
- Standards of Practice Project
- Thesis and Capstone Projects
- Business Financial Database Tutorial
- Business Terms
- A Short Guide to Annotated Bibliographies
- Quick exam tips
- Exam preparation self-assessment
- Regular review
- Planning tools
- Figuring out what to study
- Staying calm before the test
- Essay questions
- Multiple-choice questions
- Problem-solving and math questions
- Short and long answer questions
- Exam preparation resources
- Calculate your course grade
- How Do We Divide Tasks?
- How to Get Started
- Self-Assessment
- Optimize Your Study Session
- Active Study Strategies
- Recall Techniques
- Problem Solving, Experiential Learning, and Critical Thinking
- Online Learning
- Organizational Tools
- Procrastination, Burnout, and Motivation
- Concept Maps
- Studying for Math
- Evernote Tutorials: Note-taking and Organization tool
- Study Blue Tutorial: Note-taking and Flashcard Tool
We are thankful to be welcome on these lands in friendship. The lands we are situated on are covered by the Williams Treaties and are the traditional territory of the Mississaugas, a branch of the greater Anishinaabeg Nation, including Algonquin, Ojibway, Odawa and Pottawatomi. These lands remain home to many Indigenous nations and peoples.
We acknowledge this land out of respect for the Indigenous nations who have cared for Turtle Island, also called North America, from before the arrival of settler peoples until this day. Most importantly, we acknowledge that the history of these lands has been tainted by poor treatment and a lack of friendship with the First Nations who call them home.
This history is something we are all affected by because we are all treaty people in Canada. We all have a shared history to reflect on, and each of us is affected by this history in different ways. Our past defines our present, but if we move forward as friends and allies, then it does not have to define our future.
Learn more about Indigenous Education and Cultural Services
- English Language Resources
Video Resources
To help you understand active and passive voice use, watch this video below by lund university:.
American Psychological Association. (2010). Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (6th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Azar, B. S.; & Hagen, S. A. (2009). Understanding and Using English Grammar (4th ed.). Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall Regents.
English verbs have:
- Two voices: active and passive.
- Three moods: indicative, subjunctive, imperative.
- Two tenses and one time (in the indicative mood): past and present (tenses), future (time).
- Four aspects (in the indicative mood): simple, progressive, perfect, perfect progressive.
A few examples were created by us at Ontario Tech University.
Active and passive voice
We chose a semi-structured approach (active).
was chosen (passive).
Most of the time we use the active voice in speaking. APA recommends that we use the active voice in academic writing as much as possible.
The passive is most frequently used when it is not important to know exactly who performs an action or when the speaker or writer wants to focus attention “on the recipient of the action rather than on the actor” (p. 77).
Indicative, subjunctive, and imperative mood
to provide guidance for the researcher conducting case studies (indicative).
Be mindful of APA formatting , style and usage issues! (imperative)
be interpreted properly (subjunctive).
Most of the time, in both speaking and writing, we use the indicative mood. For example, to ask questions and make factual statements.
When we want to express commands and requests, however, we use the imperative mood.
) and in the verb to be (which remains ‘be’ in the present for all persons and becomes ‘were’ in the past for all persons).

Past, present, and future in the indicative mood
Evaluation feedback identified a need for a more condensed checklist for readers and reviewers (past).
constitutes a case study varies (present).
A case study will never provide conclusions with statistical significance (future).
Simple, progressive, perfect, and perfect progressive aspects in the indicative mood
methodology for software engineering research (simple).
The acceptance of empirical studies in software engineering and their contributions to increasing knowledge is continuously growing (progressive).
We have found interviews, observations, archival data and metrics being applicable to software engineering case studies (perfect).
For the past few years, researchers have been investigating the effectiveness of the use of case studies in engineering (perfect progressive).
There are twelve combinations of tenses and aspects in the indicative mood:
- The simple present: Researchers investigate the effectiveness of the use of case studies in engineering.
- The simple past: Researchers investigated the effectiveness of the use of case studies in engineering.
- The simple future: Researchers will investigate the effectiveness of the use of case studies in engineering.
- The present progressive: Researchers are investigating the effectiveness of the use of case studies in engineering.
- The past progressive: researchers were investigating the effectiveness of the use of case studies in engineering.
- The present perfect: Researchers have investigated the effectiveness of the use of case studies in engineering.
- The past perfect: Researchers had investigated the effectiveness of the use of case studies in engineering.
- The future perfect: Researchers will have investigated the effectiveness of the use of case studies in engineering.
- The present perfect progressive: Researchers have been investigating the effectiveness of the use of case studies in engineering.
- The past perfect progressive: Researchers had been investigating the effectiveness of the use of case studies in engineering.
- The future perfect progressive: Researchers will have been investigating the effectiveness of the use of case studies in engineering.
The most commonly used verb tenses in academic writing, however, are the simple present, simple past, present perfect, and simple future tenses .
APA (2010) says that, in an academic paper:
- The simple past tense is appropriate to describe the results (p. 66).
- The simple present tense is appropriate to discuss implications of the results and to present the conclusions (p. 66).
Note: For more information on verb tenses, see the overview of past tenses , present tenses , and future times pages.

Mastering the Use of Tenses in Your Research Paper

Many students and early career researchers find themselves grappling with various aspects of academic writing. One critical aspect is ensuring correct grammar, most importantly the appropriate use of tenses in your research paper. In this article, we explain the basics of using tenses in scientific writing and list best practices for different sections of your academic manuscript. By understanding the role of tenses in your research paper and applying them accurately, you can enhance the clarity and credibility of our research work.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the basics: Using tenses in research papers
- The simple past tense: Literature review, methods
- The past perfect tense: Methods, conclusion
- The simple present tense: Introduction, results, tables and figures
- The present perfect tense: Introduction, literature review
- The future tense: Discussion, conclusions
- How Paperpal can help you ensure correct usage of verb tenses in academic writing?
Understanding the basics: Using tenses in research papers
Tenses in scientific writing serve as valuable tools to indicate the time frame in which certain actions or ideas take place. The simple past tense and simple present tense are the most used tenses in research papers. They are supplemented by the present perfect, past perfect, and occasionally the future tense. Consistency and precision are crucial in academic writing, so let’s into the basics of tenses in your research paper and discuss the recommended tenses for each section.
Fix language and grammar, including tense errors, in minutes with Paperpal. Try it for free!
The simple past tense: Literature review, methods
Use this tense in your research paper when talking of or describing specific actions or events that occurred in the past; they should not be linked to the present in the same sentence. The simple past tense is used predominantly in the literature review to talk about existing research on the topic, for example, “Watson and Crick published their landmark paper on the structure of DNA in 1953.” It is also typically used in the methods section to describe the methods used in previous studies; what you did and how you did it. For example, “We selected five samples at random.” This tense in scientific writing can also be used to state facts that were once believed to be true but have since been invalidated, for example, “Bats were thought to be blind.”
The past perfect tense: Methods, conclusion
Best used to describe two related events that occurred at different times in the past, this tense is typically used in the methods section, especially when describing earlier stages of the experimental procedure. For example, “By the time the temperature and humidity reached optimal levels, the plants had already begun to revive,” or “Respondents who had been grouped into different control groups were given a placebo instead of the new formulation.” Use the past perfect tense in your research paper to describe research or experiments that may have already been completed at the time of writing the manuscript and in the conclusion to summarize the research findings.
The simple present tense: Introduction, results, tables and figures
A researcher or academic writer can use simple present tense in the introduction when stating the objectives of the study, to interpret the results, discuss the significance of the findings or to present conclusions. Use the simple present tense in your research papers when referring to results presented in tables and figures in your writing. For example, “Fig.3 shows that…”. The present tense an also be used to talk about the research paper as a whole, for example, “Section 4.1 discusses…”.
This tense in scientific writing is also used to state what is generally true and what is unlikely to change. For example, “The Earth revolves around the sun” or “Human babies generally start speaking when they are 2 years old.” This tense works well in the results section , which indicates what one believes to be true and relevant to the present research. For example, “Robinson maintains that soaking seeds in strong acid helps in breaking seed dormancy.”
Avoid inconsistent verb tenses in academic writing. Check your writing with Paperpal now!
The present perfect tense: Introduction, literature review
The present perfect tense in scientific writing is used to talk about a past event that is linked to the present or to talk about trends or events that have occurred recently. One may need to use this tense in the introduction while providing a background to the study. For example, “The demand for more sophisticated 5G devices has increased significantly over the past few years.” Additionally, the present perfect tense is also used frequently in the literature review sections while referring to previous research that is fairly recent. For example, “Recent experiments on the samples collected have revealed high levels of saline.”
The future tense: Discussion, conclusions
Use the future tense in your research paper when describing events that are expected to occur in the future; this is not very common in academic writing. Typically, its use is limited to the discussion section toward the end, when one needs to make recommendations or indicate a future course of action based on the research results. It is usually recommended that parts of the conclusion section be written in the future tense. For example, “These research findings will open up new possibilities for the effective use of Epsom salt in agriculture.”
Remember that the grammar and tense guidelines provided above are not hard and fast rules, which can make it more confusing, especially for those who do not have English as their first language. Ask peers to proofread your work carefully for incorrect or mixed tenses in a single sentence or paragraph or turn to trusted AI academic writing tools like Paperpal.
How Paperpal can help you ensure correct usage of verb tenses in academic writing?
Academic writing demands high-quality standards; it’s essential to adhere to grammar and style conventions. This ensures conformity with institutional and field-specific standards, and clarity in communicating what was studied, when it happened, and from which perspective the research is discussed. To determine the flow and coherency of your paper, using the right verb tenses is essential.
Here’s how Paperpal, an AI academic writing assistant, can help you maintain consistency in verb tenses so that readers can easily follow the progress of your ideas and arguments:
- Sign Up or Log In: Start by creating an account or logging into Paperpal .
- Paste your content: Once logged in, paste your research paper’s content onto the writing document.
- Get language and grammar suggestions: Click on the Edit icon on the right pane. Paperpal analyzes your text to identify errors, including verb form, tense usage, spellings, punctuations, word choice, and grammar.
- Fix errors and review: You can accept the relevant suggestions, and reject the irrelevant ones, and correct all the errors in a go.
Researchers need to familiarize themselves with the correct use of tenses in research papers, but with Paperpal, it gets easier. Paperpal is not just a grammar and language checker. It also provides rewriting, word reduction, and academic tone checks to align your writing with academic conventions. You can even build your writing skills and learn how to avoid such errors in the future with Paperpal’s detailed writing “tips” with simple explanations for editing suggestions.
Understanding and implementing the appropriate use of tenses in different sections of your research paper is essential for effective communication of your ideas. By mastering the use of tenses in your research paper, you can ensure clarity, consistency, and accuracy and elevate the quality of your academic writing.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Differences Between Editing and Proofreading
- Raise vs. Rise: The Right Usage
- Is there a Difference Between ‘Among’ and ‘Between’?
How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
Getting it right: inquire vs. enquire in research writing, academic translation and more: 4 ways paperpal meets real-world researcher needs , you may also like, 4 types of transition words for research papers , paraphrasing in academic writing: answering top author queries, sentence length: how to improve your research paper..., navigating language precision: complementary vs. complimentary, climatic vs. climactic: difference and examples, language and grammar rules for academic writing, transitive and intransitive verbs in the world of..., led vs. lead: how to differentiate between the..., academic writing for esl students: 7 tips and strategies....
Introduction
- Welcome to Writing in the Social Sciences!
- Author Biographies
- Acknowledgments
- UNIT 1. WRITING TOOLS
- 1. Writing in the Social Sciences
- 2. Writing Tools
- 3. Writing Processes
- 4. Grammar & Mechanics
- UNIT 2. ACADEMIC AUDIENCES
- 7. Writing for Academic Audiences
- 8. Finding & Evaluating Sources
- 9. Discussing & Citing Sources
- 10. Defining Literature Reviews
- 11. Planning Literature Reviews
- 12. Writing Literature Reviews
- 13. Crafting Proposals
- UNIT 3. GENERAL AUDIENCES
- 14. Writing for General Audiences
- 15. Applying for Jobs & Graduate Schools
- 16. Creating Public Texts
- 17. Presenting
- Translations
Writing Literature Reviews
Choose a sign-in option.
Tools and Settings
Questions and Tasks
Citation and Embed Code

Learning Outcomes
- writing an introduction, body paragraphs, a discussion/conclusion, abstract, and other elements
- drafting and getting feedback
- revising your literature review
Note: Because this chapter involves the steps for writing your Literature Review, the discussion questions in each section will be more involved than in other chapters, so give yourself extra time. But never fear! They will all lead to writing a better paper.
12.1 Draft and Synthesize
First, I want you to watch this 10-minute video because it both reviews what we talked about in the last chapter and provides great ways to get started on the actual writing of your paper. Here are some highlights to pay attention to:
questions to ask as you take or review your notes that will guide your writing
suggestions for how to organize your notes. (Or actually, I should spell it "organise" with an "s" since the video comes from Australia.)
ways to add interpretation to what you say about your sources
language to use to comment on the studies you're summarizing and synthesizing
examples of literature review synthesis

Video Review
What three strategies or elements from the video do you plan to incorporate into your own Literature Review?
Start Drafting
Now it's time to start drafting your paper. Follow the structure from your outline and start filling in the missing parts. Get out your notes and remind yourself of the sources you plan to talk about. You don't have to write your paper from beginning to end in order—you can go to the parts that feel the easiest and start there. Here are some places you can start:
Bullet-Point Draft

Writing your Bullet Points should be as fast as this Bullet Train. Photo by Fikri Rasyid on Unsplash
I often have my students start with a Bullet-Point draft that takes the ideas they've been outlining and fills them in with more details but only in bullet-point form. The beauty of bullet points is that they keep you from getting caught up in the language and style and allow you to focus simply on your main points. You can smooth out the sentences and transitions later, but for now, just get your ideas on the page.
Write the Introduction
Another way to get started is to just write the Introduction. You already have a thesis statement that can go at the end, so now you can start introducing your topic and its importance, setting up your Literature Review. See below for more specific help with Introductions.
Write a Body Paragraph
Or a third place to start is to jump into writing a body paragraph that synthesizes your sources—the way you did in that synthesis activity earlier. Take your notes and choose one set to talk about in paragraph form.
Don't think too hard about getting things perfect when you're drafting—that's what revision is for. Just focus on getting started and filling in some of the missing pieces. If you get stuck, do some brainstorming activities to get your creative juices flowing. Once you have something written, I suggest seeking feedback to make sure you're going in the right direction. In fact, I recommend getting as much feedback as possible along the way.
Start Writing
Now it's your turn to choose somewhere to start writing—choose either a bullet-point draft, the introduction, a body paragraph or something else. Then write the equivalent of at least one paragraph.
How to Write Each Section
Once you know what your main points will be, you're ready to introduce your ideas. As in any paper, you can't just jump right into your thesis statement and points; you need to set the stage first. Here are the elements of a good introduction to a literature review:
A good introduction
- introduces the topic and indicates its importance (impact on individuals)
- gives a context for the research question
- defines key terms, concepts, and/or theories
- explains what search methods were used and how many and what types of sources were reviewed (this is sometimes optional)
- suggests the organization of the rest of the paper
Remember in some style guides like the APA Manual , you don't need to title your Introduction "Introduction"—you simply center the title of your paper at the top of your page (bolded and in title capitalization format) and then jump right into your first paragraph.
Tip: You don't always know where you're going when you start a paper, so just get a good draft of an introduction down. Then when you finish writing a first draft of your paper, read your conclusion and consider using some of it in your introduction instead. I often tell my students that conclusions make good introductions because you finally know exactly where you went in your paper. Either way, you'll want to revisit your introduction once your paper's done so you can adjust it to better match where your paper went.
Get a start on your introduction by writing an opening sentence that introduces your topic and/or indicates its importance. Then you can use that to jump start the rest of your introduction.
The body of your paper is where you can develop your points and use your newfound synthesis skills. Remember the synthesis activity with the videos you did in the last chapter? As you create a draft, you can start composing paragraphs using your awesome notes just like you practiced with those videos. Try to incorporate several sources into each paragraph to be sure that you're synthesizing and not just summarizing or listing without making connections. Your color-coded notes can help you be sure that each paragraph contains multiple sources.
In the body of your paper, you should
synthesize previous studies to inform the reader of the state of research
“identify relations, contradictions, gaps, and inconsistencies in the literature” ( APA Manual , p. 8)
group your points into major headings and subheadings (You choose the arrangement based on what you’ve found: similar concepts or theories, similar methods, chronological development, controversies, etc.)
support all points with sound reasoning or evidence drawn from sources and in which all borrowed information is documented
summarize sources most of the time, paraphrase sometimes, and use quotations very sparingly—only when specific wording is poignant or can’t be said in any other way.
One way to talk about your sources is known as the CEC Method: Claim-Evidence-Commentary.
Claim + Evidence + Commentary
Just like any paragraph, you should start with a Topic sentence that acts as a mini-Thesis statement or a general claim about your topic. Then you need to give evidence to support that claim. In a literature review, your evidence comes in the form of studies that have been done—all those brilliant notes you've been taking. This is where you can synthesize your sources and show that they are related under the umbrella of a topic. However, just listing or summarizing sources does not make the connection between them and your topic sentence clear. This is where commentary comes in. Your job is also to comment on and interpret the significance of your "evidence" so your audience can understand the connections between them. In synthesis, your language is the key.
In the next chapter, we'll talk more about how to do this, especially how to incorporate metacommentary into your paragraphs.
Add Metacommentary
Metacommentary is the key to synthesis. metacommentary (aka metadiscourse) is a type of commentary that guides your reader and helps them interpret the sources and evidence you're presenting. Think of it as really powerful transitions. First, let's remind ourselves what transitions are. Transition words act like signposts—they guide your reader through your points. They can also glue your ideas together so they feel more cohesive. Beware that transitions can definitely be overdone, but I'd say most students in general could use more transitions in their papers rather than fewer.

Here's an awesome list of transition words (also linked in the frame below) that are grouped by category from the famous Purdue OWL (Online Writing Lab—scroll down to see the list). You can also download a great handout from the University of Maryland here .
I always suggest that my students keep a categorized transition list like this handy as they write so that when they know they want to connect ideas in a certain way (e.g. to show contrast), you can easily find a good list of options (e.g. in contrast, conversely, etc.). Not only will transitions help your ideas feel more connected, they will also smooth out your writing style like butter.
You might think you can just stop at transition words, but metacommentary is much more than just sprinkling some "therefores" and "howevers" throughout your paper—metacommentary actually takes your synthesis to the next level. Remember the Claim-Evidence-Commentary pattern I've mentioned? The commentary part of that sandwich is where you should focus right now. What do you comment on? You can either highlight why a source is important or connect it with other sources. This is your chance to point out the answers to the four questions you looked for in your note-taking:
What do researchers agree and disagree about?
How are researchers narrowing or changing their focus to create new information?
What are each study’s limitations and strengths?
What’s the next step in research—what should be studied in the future? (The research gap)
You can think of metacommentary as a sandwich with your name on it. If my student's name were Alisa, here's what an "Alisa sandwich" would look like:
ALISA—SOURCE—ALISA
First, Alisa starts with a claim about what's happening in the field or about a particular subsection or focus of the field. This could serve as a topic sentence for a paragraph, for example.
Second, she sets up the source with guiding language like transitions and references to her past points or sources.
Third, she talks about the source itself and summarizes pertinent information.
Lastly, Alisa comments on the source and/or connects it to her main point or to next source.
This metacommentary is a lot like the interpretation mentioned in the video at the beginning of this chapter. This type of "sandwich" can occur several times in a paragraph as you synthesize your sources. Here's a sample paragraph from Chris, a Public Health student, (check this) who wrote a paper called "The Causes of a Behavioral Pandemic: Screen-time Addiction and Consequent Depression Among Adolescents." I've bolded the metacommentary Chris had added to guide his readers and to connect his points together.
Even though there have been far fewer studies on adolescents than adults , adolescent studies have consistently shown that those who are more physically active experience less depressive and associated symptoms, as well as a greater overall state of well-being (Kremer 2014). These studies have also shown that low levels of vigorous exercise in youth can independently cause depressive symptoms. One longitudinal study revealed that over 30% of children who participate in high levels of screen-time use experience moderate to high levels of depressive symptoms (Kremer 2014). Additionally, another study of children in the United States demonstrated that those who participated on a sports team were less likely to exceed recommended screen-time limits established by the US Department of Health. This study also demonstrated that as the number of total physical activity sessions increased among youth, both during free time and at organized events, children were less likely to exceed recommended screen-time limits (Carlson 2010). In this study, children who were more physically active consistently showed lower rates of depression and other emotional disorders. Therefore, evidence across multiple studies suggests that participating in screen-time activity may not be the direct cause of depressive symptoms, but rather the sedentary lifestyle and lack physical activity it causes among youth. With this recent evidence, experts are beginning to search for ways to replace screen-time participation of adolescents with physical activities.
If You Get Stuck
Literature reviews can be hard. If you get stuck, I have a little trick I tell my students. For your first draft, try starting every sentence with "Researchers . . ." I know this seems formulaic, but if you can keep your focus on what particular researchers did or what they agree or disagree on, you'll avoid the most common pitfalls of literature reviews: sounding like a typical argumentative research paper. If your focus is always on what researchers are doing or what they've found, then at the very least you'll stay in the realm of the literature review genre. Later you can go back through and change up your sentence structure, but I've found that this is an easy way for students to get through a first draft.
A Quick Word on Verb Tense
Verb Tenses to Use in Literature Reviews
Discussion/Conclusion
Your last section will either be called discussion or conclusion (or will possibly not have a heading depending on your teacher's preferences or the style guide you're following). In an effective Discussion (aka Conclusion) section you should
do more than sum up what you have said (though you should do that as well)
explain where there are gaps and limitations in the previous research done
indicate recommendations for future research based on those gaps
At the end of this section,
restate your position (thesis statement)
show the implications of your findings
You must also include a list of your References (also known as a Bibliography or Works Cited page depending on the documentation style) showing all the sources you referred to in your paper. Your references page must be in alphabetical order and formatted according to your chosen style guide (see Chapter 9: Talking About Sources ).
Other Elements
Your teacher might require you to include these other elements in your Literature Review paper. Be sure to follow the format from your style guide .
I've waited until now to talk about titles because it's wise to wait until you have a good draft before you choose a title. Why? Because you often don't know exactly where your paper will go until you've written it out. Your title is your readers' first entry into your paper, so you want it to be interesting and also reflect what's inside. Your title should also include as much information as possible while remaining appropriately short and sweet. For example, the APA Manual recommends not using extraneous words but sticking to the main point of your paper. My student Justin's title follows this model:
Implications of Chinese Involvement on Africa's Economy
He basically summarizes his main point in one succinct statement—the ultimate summary. APA would be proud.

However, depending on your sub-field in the Social Sciences, many scholars like to do what I call a "reverse mullet." As you might know, the rad '80s mullet haircut that's short on top and long in the back has been described as
The Mullet: Business in the front, party in the back
A mullet starts with the serious and ends with the fun. But academic titles often do the reverse: they have an interesting introductory phrase, then a colon, and then the standard, more serious title. That's why I call them the

The Reverse Mullet: Party in the front, Business in back
A reverse mullet title gets the reader's attention before adding the serious explanation. For example, one of my students named Katelyn wrote her Literature Review on how much high school students' perception of their teachers was influenced by their teachers' apparel. Her title included a Reverse Mullet structure:
Keeping it Class-y: How Formality of Teacher Apparel Affects Student Perceptions of the Teacher in the Classroom
- Your Name (centered)
- Your Teacher's Name (centered on the next line)
- A Page Number (in the top right corner that's continued throughout the paper)
- Optional: the Name of the School or Department
- Optional: the Name/Number of Your Course (e.g., English 315)
- Optional: the Date
You should save writing your abstract until after you've completed your paper because it's a summary of the main points of your paper. You can try writing a preliminary abstract now as a type of outline, but you run the risk of finding out that once you're done with your paper, you actually went in some different directions. My advice is to hold off and wait to write the abstract until the end. You can create a page after the title page where your abstract will go, but to emphasize that you should write this last, we'll wait to cover the details of writing an an abstract until the next section.
If you have tables or figures ( or formulas or other data) that are too big to be added inside the text of your paper, you can put them at the end. If you only have one Appendix , you can call it just that. But if you have more than one, call them Appendix A, Appendix B, etc. and refer to them as such in the text of your paper.
Tables and Figures
One more element that could be helpful to your paper is to include tables and/or figures. You're probably familiar with Tables (you know, the boxes with lots of horizontal and vertical cells). A Figure is any type of image, graph, or chart besides a table. You can use tables or figures from your sources as long as you cite them properly. You can also create your own table or figure either from existing data or to explain a concept. See Chapter 6: Design for the details of how to create, use, or format tables and figures. Just remember to check your style guide; for example, in APA Format, you need to title and number your tables and figures separately.
I hope you feel like you have a better sense of the structure for your own Literature Review paper. In the next chapter, we'll talk about how to draft and revise your paper.
12.2 Write an Abstract

Not that kind of abstract! As great as abstract art is, what you need now is the abstract of your paper. (Note: some teacher's won't require an abstract, so you can skip this section in that case.) Why do you think we've saved the abstract for last even though it's the first thing your audience will read (after your title)? You guessed it: it's because the abstract is a summary of everything you've talked about in your paper, so if you haven't written your paper yet, it's pretty hard to summarize it.
A lot of students think that the abstract is a preview of your paper that simply invites the reader to learn more. But that's not the purpose of the abstract, that's the purpose of the Introduction . If your paper were a movie, your abstract would not be the movie trailer. A movie trailer is an invitation to see more without giving away too much; that's the point of your Introduction . Instead, your abstract would be the movie plot synopsis. It would have a big SPOILER ALERT sign in front of it because in it you want to give away all the punchlines from your paper. In fact, the more you include your most important points or findings, the better. Because readers might only ever read your abstract, you want the most important information there. Then just like you did in your own database searching, they will decide based on the abstract whether they should open your paper and read more details. Your job is to make sure they have the best information to do that.
An abstract has a few main parts that mirror the parts of your paper but in miniature. First, in 1-2 sentences, you should introduce the topic, its importance, and the problem or question you tried to answer. Then you should succinctly explain your methods (database searching) and the scope of your project. The last and largest part should consist of your main findings such as the main areas of inquiry where researchers are congregating. You should include the major strengths and limitations (gaps) you found in your review. Finally, you should explain any implications of your study and suggest where future research should go. See? A miniature paper. It should be so miniature, that the APA Manual says an abstract should not exceed 250 words. At the end, you can also list a few Keywords to make it easy to search for your paper on databases.
To solidify your understanding of how to write an abstract, watch this 3-minute video from the University of Melbourne that takes you through a good example. Try not to get distracted by their awesome Australian accents.

Now if you would like more details, you can refer to this explanation.
12.3 The Real Last Step: Revise (and Revise and Revise)

The best writers revise (and revise and revise). Think back to Chapter 3: Writing Processes and the section on Revision. You need to think like your audience, which means you have to get out of your own head and think mindfully. One way to do this is to revise with purpose or in other words, with specific goals in mind.
You can't revise without a decent draft, so don't blow off the first draft deadline. The better your first draft, the better your paper will be in the end because you'll have enough time to really look at your paper. Actually re-look at your paper, or in other words, re-vise. Get it? Re-vision?
So how can you get out of your own head? Two ways: people and levels. The first way to get a fresh perspective is audience-oriented revision: peer review, teacher conferences, writing center appointments, and other outside feedback from real, live people.
Get Feedback!

When you find out how other people react to your paper, it will give you invaluable perspective into what's working and what's not. This is feedback and is extremely valuable. Your teacher should help you do these kinds of peer reviews and revisions in class.
Feedback can also come from anyone—friends, teachers, relatives, Writing Center tutors, roommates—just be sure to choose someone you trust who also knows about good writing and won't hesitate to tell you where you can improve. I don't know your grandma, but if she's the type of grandma who will tell you your paper is great no matter what's in it because you're just so nice, then run away! Okay, don't really run away from your grandma—she's probably very loving and supportive. Give her a hug instead. However, don't give your paper to your grandma to critique in that case. My grandma is actually a fantastic writer and wouldn't be afraid to tell me where I can improve. Do give your paper to someone like my grandma.
Here's a tip: Most universities have a Writing Center where you can take your paper to a Writing Tutor for help and feedback for free. Do it! It's free! And they can even meet with you online.
We're lucky at BYU that we even have our very own Social Science-specific Writing Center: the FHSS Writing Lab . They know Literature Reviews well and can help you with any stage of the writing process from selecting a topic to citing sources to synthesis. If you have more general writing questions (or if you need an appointment after 5pm), you can also go to the main BYU Research & Writing Center . They also offer online appointments. If you're not on our campus, look up your school's writing center.
As an undergrad, my husband didn't start out with the best writing skills, so he used to take his papers to the BYU Writing Center over and over and over. I think they made the rule that you can only go once a day because of him. And guess what? It helped! His grades went up! That was his secret to success that I'm passing on to you. Your teacher doesn't have time to personally meet with each student over and over and over, but the Writing Tutors are literally paid to do just that. Well, maybe keep your visits to only one per day, but you get what I mean. Take advantage! Make an appointment right now! Did I mention that it's free?
If you need more motivation to just do it, watch this "motivational" video by Shia Le Boeuf.
Revise by Levels
The second way to improve your paper is to go through a layered revision process focusing on global and then local issues. As you re-see your paper, take my advice and tackle Global Revision before you focus on Local Revision . What do I mean by that? Let me tell you a quick story.
A Revision Story Involving Cats
When my family and I were moving to our town, we looked at a lot of houses online. We fell in love with a beautiful old house that had been totally renovated but was selling at a shockingly low price. When we finally visited the house with our realtor, we discovered why it had been on the market for so long: it smelled like cat pee. Like really, really smelled. It turns out the house had been occupied by what many people would call a "crazy cat lady"—an older woman who lived with at least 50 cats. Then tragically, a fire completely destroyed the house (I'm pretty sure the woman and her cats survived).

The home owner used $400,000 of insurance money to beautifully restore the house. They rebuilt the intricate wooden staircase, restored the stately crown molding, installed lush carpet, and added upgrades to a gorgeous kitchen. The only problem was that they did their restoration in the wrong order—they took care of the local issues of paint color and carpet thickness while ignoring the more global issue of the smell. Eventually, they had to rip up all their work in the basement in order to treat the floor with a special enzyme that combated cat urine. If they'd just treated the cat smell first, then they could have saved themselves thousands of dollars, hours of work, and could have sold their house for a much higher price.
The Moral of the Story

What does all this have to do with revision? You've got it—treat the g lobal issues first! Get rid of the cat pee! Don't worry about local issues like flowery language or sentences that connect perfectly to each other if you're just going to have to completely renovate that section later. Work on the global issues like ideas, logical order, and evidence first and wait until those are intact before focusing on the details. Put another way, whole-paper and paragraph-level revisions should come before sentence-level and word-level changes.
As a final gift, fantastic BYU Family Science professor Julie Haupt offers the following path for doing four purposeful revisions—two global revisions and two local revisions. If you really want to improve your literature review, follow these steps.
GLOBAL REVISION—The Forest

Level 1: Structural Review (Global)
Purpose: The structural review examines the document as a whole to see if all requirements are met and the document’s organization is sound.
Meet Assignment Requirements. Ask yourself if your paper meets all the requirements of the assignment? Look at your structure and make sure you have all necessary sections such as the following:
Introduction (with Thesis Statement and/or Organizing Statement)
Body with Headings
Conclusion/Discussion
Include a Thesis and an Organizing Statement. Does the current version of the thesis statement match the tone, scope, and organization of the body text? Does an organizing statement after the thesis introduce the major topics and the order they will appear in the body (e.g., “In this review, I will first discuss . . . then . . . and finally . . .)
Use Headings. Is the body text subdivided in a logical way with evidence-based information located in appropriate sections? Are the major sections roughly symmetrical (in terms of length)? Are the headings brief, yet descriptive? If subheadings are used, does the major section contain at least two? Are all levels of headings separated by text?
Level 2 (Global): Paragraph/Logic Review
Purpose: The Paragraph/Logic Review is designed to review each paragraph for cohesion and compliance to the CEC (Claim-Evidence-Commentary) format.
Sequence Paragraphs Effectively. When reading only the first sentence of each paragraph, does the logical pattern of the paper emerge? Do the claims made in these topic sentences coordinate well with the thesis of the paper?
LOCAL REVISION—The Tree

Level 3 (Local): APA Formatting Review
Purpose: The APA Formatting Review is designed to make sure all APA conventions are explicitly followed to help the paper reflect a high level of professionalism.
Check Document Formatting. Do the title page, abstract, body text, and reference page appear in the correct page formatting as required? (Use the APA Manual if you have questions.)
Examine the Reference List Closely. Are all references in the reference list ordered alphabetically? Is the reference list double spaced entirely (with no extra gaps between paragraphs)? Are all references (e.g., journal articles, internet resources, or books) listed in the correct format? Is every reference on the reference list cited at least once in the body and does each in-text citation have a corresponding reference in the reference list?
Make a Final Check of the In-Text Citations. Is all information properly cited with an in-text citation when needed? Do all in-text citations include the year next to the author(s)? When more than one citation is listed within parentheses are they separated by semi-colons and ordered alphabetically by first author’s last name? If included in parentheses, do studies with multiple authors use ampersands ("&" rather than the word "and") before listing the last author?
Use “et al.” Correctly. If a study has three or more authors, do you include only the first author’s last name + et al. + publication year in in-text citations? Do you include all authors up to 20 in the References page? For any publications with 21 or more authors, do you include the first 19 authors' name, then insert an ellipsis ( . . . ), and then the last author's name?
Level 4 (Local): Finishing Review
Purpose: The Finishing Review is an opportunity to look closely at sentence construction, language, hedging (qualifying statements), and grammar/punctuation.
Review Phrasing with a Read-Aloud Session. Read your paper aloud. Since having to read a sentence twice to get its meaning or “tripping over” phrasing can be an indication of awkward construction, are all sentences easily read aloud? Are any sentences so long that they have become difficult to comprehend, but could be split without changing the meaning?
Use Non-Biased, Non-Absolute Language. Do all references to people comply with the “people first” designation and avoid inappropriate uses of terms for various groups? Are the findings and summary statements in the review properly “ hedged ”?
Check Punctuation and Grammar. Are all commas, semicolons, colons, hyphens, and other punctuation used correctly throughout the document (including the reference page)? Are common grammar mistakes, such as parallelism, subject-verb agreement, incorrect misuse of pronouns, and other grammatical issues corrected?
I know Literature Reviews can be daunting, but I hope that after reading this chapter you feel better prepared to tackle this bodacious writing assignment. As you practice writing, you'll find that it'll get easier and easier until it's as intuitive as riding a hoverboard.

*Bonus Video
If you're still confused or would like more guidance on writing a literature review, here is an optional 25-minute video that thoroughly goes through the entire process of writing a literature review. As an extra bonus, it's made by Michael Paye from the University of Dublin who has an awesome Irish accent. Enjoy!

Brigham Young University
Cristie Cowles Charles teaches writing and literature courses at Brigham Young University in Provo, Utah. She enjoys sparking a love for writing in her students--or at least a love for having had written (it's always worth it in the end, right?). She thinks pumpkin pie counts as a vegetable, is married to a super hot mechanical engineering and neuroscience professor (yes, they exist), and adores her five magnificent children.
This content is provided to you freely by EdTech Books.
Access it online or download it at https://edtechbooks.org/writing/literature_review_2 .
Dissertations & projects: Tenses
- Research questions
- The process of reviewing
- Project management
- Literature-based projects
On this page:
“You will use a range of tenses depending on what you are writing about . ” Elizabeth M Fisher, Richard C Thompson, and Daniel Holtom, Enjoy Writing Your Science Thesis Or Dissertation!
Tenses can be tricky to master. Even well respected journals differ in the guidance they give their authors for their use. However, their are some general conventions about what tenses are used in different parts of the report/dissertation. This page gives some advice on standard practice.
What tenses will you use?

There are exceptions however, most notably in the literature review where you will use a mixture of past , present and present perfect tenses (don't worry, that is explained below), when discussing the implications of your findings when the present tense is appropriate and in the recommendations where you are likely to use the future tense.
The tenses used as standard practice in each of these sections of your report are given and explained below.
In your abstract
You have some leeway with tense use in your abstract and guidance does vary which can sometimes be confusing. We recommend the following:
Describing the current situation and reason for your study
Mostly use the present tense, i.e. "This is the current state of affairs and this is why this study is needed."
Occasionally, you may find the need to use something called the present perfect tense when you are describing things that happened in the past but are still relevant. The present perfect tense uses have/has and then the past participle of the verb i.e. Previous research on this topic has focused on...
Describing the aims of your study
Here you have a choice. It is perfectly acceptable to use either the present or past tense, i.e. "This study aims to..." or "This study aimed to..."
Describing your methodology
Use the past tense to describe what you did, i.e. "A qualitative approach was used." "A survey was undertaken to ...". "The blood sample was analysed by..."
Describing your findings
Use the past tense to describe what you found as it is specific to your study, i.e. "The results showed that...", "The analysis indicated that..."
Suggesting the implications of your study
Use the present tense as even though your study took place in the past, your implications remain relevant in the present, i.e. Results revealed x which indicates that..."
Example abstract
An example abstract with reasoning for the tenses chosen can be found at the bottom of this excellent blog post:
Using the Present Tense and Past Tense When Writing an Abstract
In your methodology
The methodology is one of the easiest sections when it comes to tenses as you are explaining to your reader what you did. This is therefore almost exclusively written in the past tense.
Blood specimens were frozen at -80 o C.
A survey was designed using the Jisc Surveys tool.
Participants were purposefully selected.
The following search strategy was used to search the literature:
Very occasionally you may use the present tense if you are justifying a decision you have taken (as the justification is still valid, not just at the time you made the decision). For example:
Purposeful sampling was used to ensure that a range of views were included. This sampling method maximises efficiency and validity as it identifies information-rich cases and ... (Morse & Niehaus, 2009).
In your discussion/conclusion
This will primarily be written in the present tense as you are generally discussing or making conclusions about the relevance of your findings at the present time. So you may write:
The findings of this research suggest that.../are potentially important because.../could open a new avenue for further research...
There will also be times when you use the past tense , especially when referring to part of your own research or previous published research research - but this is usually followed by something in the present tense to indicate the current relevance or the future tense to indicate possible future directions:
Analysis of the survey results found most respondents were not concerned with the processes, just the outcome. This suggests that managers should focus on...
These findings mirrored those of Cheung (2020), who also found that ESL pupils failed to understand some basic yet fundamental instructions. Addressing this will help ensure...
In your introduction
The introduction generally introduces what is in the rest of your document as is therefore describing the present situation and so uses the present tense :
Chapter 3 describes the research methodology.
Depending on your discipline, your introduction may also review the literature so please also see that section below.
In your literature review
The findings of some literature may only be applicable in the specific circumstances that the research was undertaken and so need grounding to that study. Conversely, the findings of other literature may now be accepted as established knowledge. Also, you may consider the findings of older literature to be still relevant and relatively recent literature be already superseded. The tenses you write in will help to indicate a lot of this to the reader. In other words, you will use a mix of tenses in your review depending on what you are implying.
Findings only applicable in the specific circumstances
Use the past tense . For example:
In an early study, Sharkey et al. (1991) found that isoprene emissions were doubled in leaves on sunnier sides of oak and aspen trees.
Using the past tense indicates that you are not implying that isoprene emissions are always doubled on the sunnier side of the trees, just that is what was found in the Sharkey et al. study.
Findings that are still relevant or now established knowledge
Mostly use the present tense , unless the study is not recent and the authors are the subject of the sentence (which you should use very sparingly in a literature review) when you may need to use a mixture of the past and present. For example:
A narrowing of what 'graduateness' represents damages students’ abilities to thrive as they move through what will almost certainly be complex career pathways (Holmes, 2001).
Holmes (2001) argued strongly that a narrowing of what 'graduateness' represents damages students’ abilities to thrive as they move through what will almost certainly be complex career pathways
Both of these imply that you think this is still the case (although it is perhaps more strongly implied in the first example). You may also want to use some academic caution too - such as writing 'may damage' rather than the more definite 'damages'.
Presenting your results
As with your methodology, your results section should be written in the past tense . This indicates that you are accepting that the results are specific to your research. Whilst they may have current implications, that part will not be considered until your discussion/conclusions section(s).
Four main themes were identified from the interview data.
There was a significant change in oxygen levels.
Like with the methodology, you will occasionally switch to present tense to write things like "Table 3.4 shows that ..." but generally, stick to the past tense.
In your recommendations
Not everyone will need to include recommendations and some may have them as part of the conclusions chapter. Recommendations are written in a mixture of the present tense and future tense :
It is recommended that ward layout is adapted, where possible, to provide low-sensory bays for patients with autism. These will still be useable by all patients but...
Useful links
- Verb tenses in scientific manuscripts From International Science Editing
- Which Verb Tenses Should I Use in a Research Paper? Blog from WordVice
- << Previous: Writing style
- Next: Voice >>
- Last Updated: Feb 28, 2024 10:39 AM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/dissertations
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem
Loading metrics
Open Access
Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliations Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France, Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
- Marco Pautasso

Published: July 18, 2013
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149
- Reader Comments
Citation: Pautasso M (2013) Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review. PLoS Comput Biol 9(7): e1003149. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149
Editor: Philip E. Bourne, University of California San Diego, United States of America
Copyright: © 2013 Marco Pautasso. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Funding: This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
Competing interests: The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149.g001
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
- 1. Rapple C (2011) The role of the critical review article in alleviating information overload. Annual Reviews White Paper. Available: http://www.annualreviews.org/userimages/ContentEditor/1300384004941/Annual_Reviews_WhitePaper_Web_2011.pdf . Accessed May 2013.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- 7. Budgen D, Brereton P (2006) Performing systematic literature reviews in software engineering. Proc 28th Int Conf Software Engineering, ACM New York, NY, USA, pp. 1051–1052. doi: https://doi.org/10.1145/1134285.1134500 .
- 16. Eco U (1977) Come si fa una tesi di laurea. Milan: Bompiani.
- 17. Hart C (1998) Doing a literature review: releasing the social science research imagination. London: SAGE.
- 21. Ridley D (2008) The literature review: a step-by-step guide for students. London: SAGE.

Academic Writing - Education & CCSC students: Tense
- Publication Style
- Assignment Question
- Assignment Genre
- Literature Searches
- Referencing
- Anthropomorphism
Use past tense when reporting research (e.g. writing a literature review). One way to think about this is that the research reports about which you are writing have been written in the past: the research is finished and reported. If you are writing a research proposal, the tense you use will help distinguish between your proposed study and the research literature you draw upon. The APA Manual advises that "the past tense is appropriate when expressing an action or a condition that occurred at a specific, definite time in the past, such as when discussing another researcher's work" (APA, 2020, pp. 117-118).
Examples of verb tense: https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/grammar/verb-tense
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.).
American Psychological Association. (2020). Verb tense. Retrieved 26 May, 2020, from https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/grammar/verb-tense
- << Previous: Verbs
- Next: Workflow >>
- Last Updated: Sep 5, 2023 11:44 AM
- URL: https://morlingcollege.libguides.com/academic-writing
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Writing Studio
How (and why) do i write in literary present tense.
In an effort to make our handouts more accessible, we have begun converting our PDF handouts to web pages. Download this page as a PDF: How (and why) do I write in literary present tense? Return to Writing Studio Handouts
Literary works, paintings, films, and other artistic creations are assumed to exist in an eternal present. Therefore, when you write about writers or artists as they express themselves in their work, use the present tense.
Past or Present Tense? A Basic Guideline
You should use the past tense when discussing historical events, and you should use the literary present when discussing fictional events.
Context matters , though, so take a look through the more granular guidelines below and keep in mind that expectations and conventions around the tense we use to write about textual sources we are engaging or analyzing may differ between disciplines (for instance, in a history class you might be told to write about texts using past tense that you would be expected to discuss in the ‘literary present’ in an English class.).
Taking a Closer Look: Context-Based Guidelines
1. when commenting on what a writer says, use the present tense..
- Example: “Dunn begins his work with a view into the lives and motivations of the very first settlers.”
- Example: “Through this anecdote, Richter illustrates common misconceptions about native religion and shows why missionary attempts were less than successful.”
2. When describing an author’s work, however, use the past tense.
- Example: “In 1966, Driss Chraïbi published La Civilisation, ma Mère! “
3. When you are writing about a certain historical event (even the creation of a literary or artistic work), use the past tense.
- Example: “Henry Fielding wrote in the eighteenth century.”
- Example: “Picasso produced a series of sculptures.”
4. When discussing events in a literary work (novel, story, play, or poem) always use the present tense, unless there is a shift in the time frame within the world of the text.
- Example: “Evelyn then rips into the carefully wrapped package and finds the greatest gift she has ever received. Her eyes fill with tears as she gazes at the jewel, but Philip does not know that these tears are the results of more than surprised joy. Evelyn is suffering from guilt as she compares this present to the shoddy gift that she bought* for her beau.”
*“ Bought ” is in past tense because the buying of the present occurred before the described set of events.
- Example: “In Michelangelo’s painting, Christ judges the world.”
- Example: “Johnson’s characters journey to Cairo.”
- Example: “Plato argues without much conviction.”
- Example: “Paul writes about the hardships he has endured.”
5. Sometimes a sentence must employ both present and past tense.
- Example: “The first part of the poem, which she completed in 1804, describes the effects of isolation from society.”
- Example: “Aeschylus’ drama is concerned with what happens to Orestes after he has killed his mother.”
Final Tips and Reminders
Remember: it is important to stay consistent..
Moving between verb tenses can be confusing for your reader. Examine your changes of tense very carefully and make sure there is a logical reason for them.
Style Tip: Keeping Sentence-Level Tense Shifts Manageable
If you need to shift tense more than three times in a single sentence, consider breaking up the sentence into a couple of shorter sentences to maintain reading ease.
Last revised: 8/10/2007 | Adapted for web delivery: 07/2021
In order to access certain content on this page, you may need to download Adobe Acrobat Reader or an equivalent PDF viewer software.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Mastering Verb Tenses in Literature Reviews. Suzanne Hall Johnson, MN, RN,C, CNS. Deciding on which verb tense to use when writing the literature review sec tion ofa manuscript is challenging. Edi tors find that verb tense problems are common in literature report sections of manuscripts. Authors, reviewers, and ed itors need to be able to spot ...
Typically, for the former, using the simple past tense is common, e.g., "Jones (2013) found that...." But it is possible to use more than one tense in a literature review. Here are a few tips to consider when presenting a review of previously published work: Past tense: If your focus is on the study itself or the people who studied it, then it ...
Recommended tense. Example. Literature review (or whenever discussing other researchers' work) Past. Martin (2020) addressed. Present perfect. Researchers have studied. Method. Description of procedure. Past. Participants took a survey. Present perfect. Others have used similar approaches. Reporting of your own or other researchers' results ...
In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense. Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical.
Aug 14, 2023 at 22:45. Add a comment. 8. Generally speaking any are acceptable. If you focus on the authors then "did show" or "have shown" feels about right. But if you take the citation to mean the paper itself, then the present tense is fine since the paper still exists and does still show...
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present ...
Referring to the ideas of other researchers (e.g. in a literature review) Simple past tense. Brown (2019) argued that… However, Small (2020) suggested that… Present perfect tense. Doñoso (1992) has demonstrated that… Note: A shift of tense may be used to indicate that the research findings are still relevant.
As much as possible, try to be consistent with your chosen verb tense within a section "to ensure smooth expression" (APA, 2020, p. 118). If the verb tenses suggested above don't make sense for the purposes of your document, please check with your instructor or academic supervisor to get their recommendation on the best approach for your document.
Use the past tense (e.g., researchers presented) or the present perfect (e.g., researchers have presented) for the literature review and the description of the procedure if discussing past events. Use the past tense to describe the results (e.g., test scores improved significantly). Use the present tense to discuss implications of the results ...
In general, use the present tense to describe actions and states of being that are still true in the present; use the past tense to describe actions or states of being that occurred exclusively in the past. Below are some discipline-specific guidelines for how to use verb tenses effectively in literature and the humanities.
In other words, avoid unnecessary shifts in verb tense within a paragraph or in adjacent paragraphs to help ensure smooth expression. Use the past tense (e.g., researchers presented) or the present perfect (e.g., researchers have presented) for the literature review and the description of the procedure if discussing past events.
The most commonly used verb tenses in academic writing, however, are the simple present, simple past, present perfect, and simple future tenses. APA (2010) says that, in an academic paper: The simple past tense or present perfect tense is appropriate for the literature review and the description of the procedure if the discussion is of past ...
The simple past tense: Literature review, methods. Use this tense in your research paper when talking of or describing specific actions or events that occurred in the past; they should not be linked to the present in the same sentence. ... The present perfect tense: Introduction, literature review.
Tense. Reference. Example. Past Tense. A Single Study or Event. McFly (1989) investigated the usefulness of hoverboards in a chase. Present Tense. Generally Accepted Knowledge of the Field. One of the most promising areas of hoverboard technology is the use of electromagnets (Allain, 2015). Present Perfect Tense. An Area of Inquiry
A recent flurry of tweets, seemingly initiated by @thesiswhisperer, discussed the use of tense in literature review.There doesn't seem to be a definitive rule to using either present or past tense (i.e. Smith (1989) argues… vs. Smith (1989) argued… etc.), though switching from one to the other can be problematic and should only be done within grammatical conventions.
The methodology is one of the easiest sections when it comes to tenses as you are explaining to your reader what you did. This is therefore almost exclusively written in the past tense.. Blood specimens were frozen at -80 o C.. A survey was designed using the Jisc Surveys tool.. Participants were purposefully selected.. The following search strategy was used to search the literature:
In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense. Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical.
Use past tense when reporting research (e.g. writing a literature review). One way to think about this is that the research reports about which you are writing have been written in the past: the research is finished and reported. ... The APA Manual advises that "the past tense is appropriate when expressing an action or a condition that ...
Ideally, Chapter 1 (introduction) should be past tense, chapter 2 (literature) can be present or past depending on how you quote, chapter 3( methodology) definitely past tense, chapter 4( results ...
1 Answer. Sorted by: 2. Either past or present tense is reasonable for a literature survey. You could argue for the past tense since the work was already completed, or use the present tense because the papers currently exist and describe something that can be found now. The main issue is to be consistent in your usage throughout the review. Share.
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels ...
3. When you are writing about a certain historical event (even the creation of a literary or artistic work), use the past tense. Example: "Henry Fielding wrote in the eighteenth century.". Example: "Picasso produced a series of sculptures.". 4. When discussing events in a literary work (novel, story, play, or poem) always use the ...