Please enable JavaScript in your browser to enjoy a better experience.

15 Common PC Problems and How to Troubleshoot Them
There’s no need to rush off to the tech repair store for every problem your PC might have. A lot of usual computer issues can be solved quite easily on your own , allowing you to handle them with a few straightforward steps .
This guide is here to help you fix common PC issues by yourself. Below, you’ll find a rundown of the top 15 hardware problems that PC users encounter and how you can deal with them without outside help.
How to Fix Corrupted Windows System with System File Checker
There comes a time in every Windows user's life when their precious machine gets corrupted for whatever reason.... Read more
1. PC Overheating
A heating PC slows down the entire system and can lead to frequent crashes. Moreover, PC components might permanently damage due to continuous exposure to heat.
There are two primary reasons your PC might overheat: either the cooling system isn’t functioning correctly, or the PC is generating more heat than the cooling system can manage. For both scenarios, I’ve detailed a comprehensive guide on various methods to manage an overheating PC. Make sure to check it out.
2. Dysfunctional USB Port
If your USB port stops working, it might not necessarily be broken. Here are some solutions that can help resolve this issue:
Method 1: Restart the PC
Restarting your PC can solve many issues, including problems with the USB port.
Method 2: Uninstall USB Port Driver
Uninstalling the driver of the USB port will prompt Windows to reinstall it upon restarting your PC, potentially fixing the issue. Here’s how to do it:
- Press Windows + R keys and enter devmgmt.msc in the Run dialog to open the Device Manager .
- Expand the Universal Serial Bus controllers option.
- Right-click the entry USB Host Controller and then click on Uninstall .
- Repeat this for all entries with USB Host Controller to uninstall drivers for all the USB ports.
- Once deleted, restart your PC, and Windows will automatically reinstall the drivers , fixing any driver-related issues.
Method 3: Disable USB Selective Suspend
The USB Selective Suspend feature in Windows saves power by suspending idle USB ports, but sometimes it might prevent a USB port from working. Here’s how to disable it:
- Press Windows + R keys and type powercfg.cpl in the Run dialog to open Windows Power Options.
- Click on Change plan settings next to your current plan, then click on Change advanced power settings .
- Expand USB settings and disable USB selective suspend setting .
- Restart your PC to see if the issue with the USB port is resolved.
Note: Keep this option enabled to save battery power. If disabling it doesn’t resolve the USB port issue, consider enabling it again.
3. PC Keeps Disconnecting from WiFi
If your Wi-Fi is functioning properly but your PC keeps disconnecting from it, the issue may be due to your PC’s network card not receiving full power. Windows features a built-in power saver option that reduces power to the network card. You’ll need to disable this feature by following these steps:
- Navigate to Advanced settings in the Power Options .
- Expand Wireless Adapter Settings and then Power Saving Mode .
- Adjust this to Maximum Performance .
Alternatively, if your PC continues to disconnect from Wi-Fi and the issue persists, the problem might be a faulty wireless adapter driver. Consider using Auslogics’ Driver Updater to detect and resolve issues with device drivers by fetching and installing the latest official driver software.
4. PC Beeps
The motherboard of your PC is equipped to detect issues and uses beeps of varying rhythms to communicate problems. For an in-depth understanding of what different beep patterns mean, check out this detailed article on interpreting these signals.
If your PC fails to start after emitting these beeps, solving the problem can be challenging. Nonetheless, I’ll discuss two common issues that cause beeps and how you can resolve them yourself.
Problem 1: RAM Displacement
One common issue I encountered is the RAM becoming loose or displaced, leading to 2-3 beeps from the PC without it booting up. The solution is straightforward: open up the PC (though laptop users might prefer professional help) and reseat the RAM. Here’s how:
- Clean any dirt from the RAM slot using a cotton bud after removing the RAM completely.
- Reinsert the RAM, applying sufficient pressure on both ends to ensure it is fully seated.
- Secure the clips, ensuring they’re properly locked, as even slightly loose RAM can prevent your PC from working.
Refer to this video for guidance on installing the RAM properly:
Problem 2: Issues with Newly Added Hardware
Beeps can also result from damaged or incorrectly installed hardware components. Remove any hardware you’ve recently added to see if it addresses the issue. If your PC functions correctly afterward, ensure the component is installed correctly or consider repairing or replacing it.
5. PC Fans Not Working
If you discover that one or more fans within your PC are not functioning, it might be due to accumulated dirt. You’ll need to open your PC and clean the fans and other components using a can of compressed air or a leaf blower.
For guidance on the cleaning process, watch this helpful video:
If cleaning doesn’t solve the issue, consider using the SpeedFan app to diagnose and possibly fix the problem. This app allows you to control your PC’s fans, though your motherboard must support fan control to utilize this feature.
6. PC Not Using Full RAM Capacity
There are times when your PC might not utilize all the RAM installed. For instance, you could have 4GB of RAM, but the Task Manager only shows 2GB in use. Often, this is due to a specific Windows setting.
Note: If a small amount of RAM (200-400MB) is not being utilized, it’s likely reserved for hardware use, and there’s not much that can be done about it.
The solution is straightforward – Windows may have been set to use only a part of the available RAM. Here’s how you can adjust it:
- Press Windows + R keys and type msconfig in the Run dialog to open System Configurations .
- Navigate to the Boot tab and click on Advanced options .
- Check the box next to Maximum memory and enter the total amount of RAM installed (in MBs).
- Click OK and restart your PC to apply the changes.
Good to know: While adjusting these settings, also consider checking the Number of processors option to ensure your PC is using all available CPU cores. Set it to the maximum number to utilize full CPU power.
If the issue persists, it’s possible that one of the RAM modules may not be properly installed. Attempt reinstallation to see if it resolves the issue.
7. Overworking Fan
Your PC’s fan speeds up based on your PC’s temperature—the higher the temperature, the faster the fan runs. If your PC’s temperature is normal (you can check it using HWMonitor), but the fan is still running at full speed, you might need to manually adjust the fan speed.
The SpeedFan app can help you monitor and adjust the speed of your PC’s fans. This issue of fans overworking typically occurs only with motherboards that have fan control capabilities, so compatibility with the app shouldn’t be a concern.
8. PC Crashes Before Loading the OS
If your PC crashes immediately after showing the manufacturer logo and before loading the operating system, the issue likely lies with the RAM or the hard disk. This means the operating system can’t load because the RAM is corrupted or the hard disk is damaged.
For those with multiple RAM slots, removing each RAM module one at a time and starting the PC can help identify the faulty component. Ultimately, you’ll need to replace the corrupted RAM or hard disk.
9. PC Isn’t Powering On
If your PC isn’t powering on at all, with no lights turning on, the problem could be with the power source.
Desktop users: Ensure that the extension cord, power outlet, and all connections are functioning correctly. If they are, try swapping the power cable with another one, such as the monitor’s, to see if the PC turns on. If this resolves the issue, you’ll need a new power cable.
Laptop users: Try removing the battery and then reinserting it before starting the laptop. If that doesn’t work, remove the battery again and connect the laptop to the charger to try powering it on without the battery. If the laptop powers on, the battery may need to be replaced.
Note: It’s also wise to disconnect any external devices from your PC when attempting these solutions, as a malfunctioning device could be the cause of the power issue.
10. Noisy PC
A noisy PC often signals the need for a thorough cleaning. You can clean it yourself using a can of compressed air or a leaf blower. Overclocking your PC’s GPU and CPU might also contribute to the noise.
Here’s a video demonstrating simple methods to clean your PC:
Sometimes, the noise could be coming from a disc in the DVD ROM. For more details on PC components that can cause noise, check out this informative article.
11. Noisy Hard Drive
Clicking or grinding noises from your hard drive are warning signs that it may be failing. Hard drives have a finite lifespan, and these sounds often indicate imminent failure. The CrystalDiskInfo hard drive monitoring tool can help assess the health of your hard drive, displaying conditions like “Good,” “Caution,” or “Bad.”
It’s crucial to back up your data immediately and consider acquiring a replacement hard drive before the current one fails.
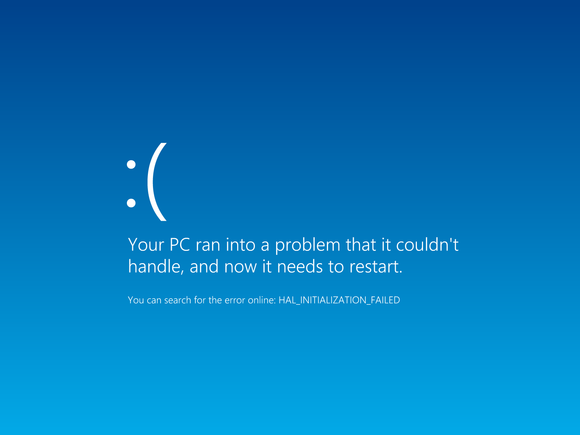
12. Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)
The feared Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) can be triggered by both software and hardware issues, though it often points to hardware problems. It’s crucial to address BSOD promptly as it indicates significant trouble.
BlueScreenView, a helpful Nirsoft utility, provides valuable information following a BSOD event, aiding in the identification and resolution of the issue. Here are some common BSOD triggers and their fixes.
How to Fix “Apps Not Responding” in Windows 10
In my years of experience with Windows, I have faced the app not responding error as one of... Read more
Corrupted Drivers
Corrupted drivers can lead to BSOD. To diagnose and address this issue, follow these steps:
- Access Device Manager by typing devmgmt.msc in the Run dialog.
- Expand each category and look for any drivers marked with a yellow triangle icon.
- If any are found, right-click on the driver and select Update Driver Software to update it.
Alternatively, third-party apps like IObit Driver Booster can automate the process of identifying and resolving driver issues.
Excessive Load on RAM
Opening more programs than the RAM can handle might freeze the system and trigger BSOD. Limit the number of concurrent programs or consider upgrading your RAM to avoid this issue.
Faulty Hard Disk
A BSOD can also signal a failing hard disk. Refer to the guidelines in problem #11 to detect hard disk issues.
Overheating PC
An overheating PC may lead to BSOD if excessive stress is placed on the components. Follow the instructions provided in problem #1 to address this.
13. Blank Monitor
If your monitor displays nothing, it could indicate an issue with the monitor itself or the graphics card. Test the monitor with another PC to determine the source of the problem.
If the monitor doesn’t power on at all, try replacing the power cable with one that’s known to work. For more troubleshooting tips, here’s a useful article on fixing a monitor that shows nothing.
14. Monitor Goes Black After a Few Seconds
If your monitor goes black after displaying for a few seconds, it may be related to color quality or screen adjustment settings. Try pressing the auto-adjust button on your monitor. If that doesn’t resolve the issue, consider changing the display color from 32-bit to 16-bit.
Connecting your PC to a different monitor to adjust the graphics card settings could also be helpful. Using the auto-adjust feature might briefly restore the display, allowing you to tweak the color settings in that short window.
15. Keyboard Issues
If your keyboard is noisy or fails to type repeated words correctly, it’s likely not a hardware issue. Windows settings such as toggle keys and filter keys might be activated, leading to these symptoms. To disable them, follow these steps:
- Access the Control Panel and select Ease of Access .
- Click on Change how your keyboard works .
- Uncheck the boxes next to Toggle keys and Filter Keys to resolve the issue.
How to Fix Mouse Left-click Malfunction in Windows
Some of the most accepted solutions to fix left-click not working issue on your Windows. Read more
Wrapping Up
While many hardware issues can be resolved by adjusting settings or using specific software, some problems may necessitate a trip to the computer repair shop. Knowing what’s wrong with your PC enables you to take appropriate action. We’d love to hear about any PC hardware problems you’ve encountered and how you solved them, so please share your experiences in the comments.
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Online Guide to Writing and Research
Thinking strategies and writing patterns, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
Patterns for Presenting Information
Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
According to conventional wisdom, you can summarize every story ever told in the following way: someone falls into a hole and must climb out. In other words, every story is about solving a problem. There are probably many exceptions to this observation; however, connecting the need to solve a real-life problem to your subject can draw your readers’ attention. The problem-cause-solution pattern can help you do this.

In a sense, this pattern is a variety of the specific-to-general pattern, as it often begins with specific details and moves to a somewhat generalized solution. However, rather than evoking a sense of mystery and suspense, the problem-cause-solution pattern focuses on concrete difficulties; and though a solution may appeal to abstract principles, the solution should have a practical application, enough to solve the real-life problem.
When to Use this Pattern
You may find the problem-cause-solution pattern useful in writing case studies, critiques, introductions, reports of scientific investigations, literary reviews, political and social discourse, white papers, proposals, many kinds of reports, and essay examinations.
How to Create this Pattern
The name of the problem-cause-solution pattern also describes the sequence in which to present your information.
Begin by describing the problem.
Proceed through diagnosing and analyzing the problem.
Then propose a solution.
The forms of analysis used to diagnose the problem may vary. You might, for example, use comparative analysis to evaluate for flaws in a process that may have led to the problem. You might use a combination of synthesis and cause and effect analysis to locate systemic conditions which caused the problem. However, in each instance—whether analyzing an entire process or analyzing a specific cause—the goal is to locate a cause or causes.
Example of this Pattern
There are two main kinds of ice that shape sea levels. The first is sea ice, which comes from ocean water that freezes solid. It makes up most of the ice at the North Pole. As it forms, it changes the saltiness of seawater and helps shape powerful ocean currents.
Melting sea ice doesn’t change the overall amount of water in the ocean, just as melting ice cubes don’t change the water level in a glass of water. But sea ice tends to reflect sunlight, while the darker ocean tends to soak up its heat. That speeds up warming and drives more ice melt in a worrying feedback loop. The warmer temperatures also contribute to the thermal expansion of water, which in turn can raise sea levels.
The second kind of ice is land ice, which builds up in sheets over thousands of years from compacted snow. In Antarctica, the ice sheet is 1.5 miles thick (2.4 km) on average, reaching up to 3 miles (5 km) in some areas. Greenland’s ice sheet averages a mile in thickness. When land ice starts to jut out over the ocean, it creates a floating ice shelf (Irfan, 2022, paras. 9-11).
Example Explained
Notice how the passage above begins with an implied problem: ice causing changes to sea levels. The passage proceeds to explain the causes of changing sea levels. These are the first two parts of our pattern. A few paragraphs later, the author shifts to discussing the beginnings of a solution.
Key Takeaways
- The problem-cause-solution approach will first describe the problem, then analyze the cause or responses to the problem, and then will lead to a solution.
- We practice this approach daily in our interactions with others, whether at work or home.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10.2 Using Common Organizing Patterns
Learning objectives.
- Differentiate among the common speech organizational patterns: categorical/topical, comparison/contrast, spatial, chronological, biographical, causal, problem-cause-solution, and psychological.
- Understand how to choose the best organizational pattern, or combination of patterns, for a specific speech.

Twentyfour Students – Organization makes you flow – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Previously in this chapter we discussed how to make your main points flow logically. This section is going to provide you with a number of organization patterns to help you create a logically organized speech. The first organization pattern we’ll discuss is categorical/topical.
Categorical/Topical
By far the most common pattern for organizing a speech is by categories or topics. The categories function as a way to help the speaker organize the message in a consistent fashion. The goal of a categorical/topical speech pattern is to create categories (or chunks) of information that go together to help support your original specific purpose. Let’s look at an example.
In this case, we have a speaker trying to persuade a group of high school juniors to apply to attend Generic University. To persuade this group, the speaker has divided the information into three basic categories: what it’s like to live in the dorms, what classes are like, and what life is like on campus. Almost anyone could take this basic speech and specifically tailor the speech to fit her or his own university or college. The main points in this example could be rearranged and the organizational pattern would still be effective because there is no inherent logic to the sequence of points. Let’s look at a second example.
In this speech, the speaker is talking about how to find others online and date them. Specifically, the speaker starts by explaining what Internet dating is; then the speaker talks about how to make Internet dating better for her or his audience members; and finally, the speaker ends by discussing some negative aspects of Internet dating. Again, notice that the information is chunked into three categories or topics and that the second and third could be reversed and still provide a logical structure for your speech
Comparison/Contrast
Another method for organizing main points is the comparison/contrast speech pattern . While this pattern clearly lends itself easily to two main points, you can also create a third point by giving basic information about what is being compared and what is being contrasted. Let’s look at two examples; the first one will be a two-point example and the second a three-point example.
If you were using the comparison/contrast pattern for persuasive purposes, in the preceding examples, you’d want to make sure that when you show how Drug X and Drug Y differ, you clearly state why Drug X is clearly the better choice for physicians to adopt. In essence, you’d want to make sure that when you compare the two drugs, you show that Drug X has all the benefits of Drug Y, but when you contrast the two drugs, you show how Drug X is superior to Drug Y in some way.
The spatial speech pattern organizes information according to how things fit together in physical space. This pattern is best used when your main points are oriented to different locations that can exist independently. The basic reason to choose this format is to show that the main points have clear locations. We’ll look at two examples here, one involving physical geography and one involving a different spatial order.
If you look at a basic map of the United States, you’ll notice that these groupings of states were created because of their geographic location to one another. In essence, the states create three spatial territories to explain.
Now let’s look at a spatial speech unrelated to geography.
In this example, we still have three basic spatial areas. If you look at a model of the urinary system, the first step is the kidney, which then takes waste through the ureters to the bladder, which then relies on the sphincter muscle to excrete waste through the urethra. All we’ve done in this example is create a spatial speech order for discussing how waste is removed from the human body through the urinary system. It is spatial because the organization pattern is determined by the physical location of each body part in relation to the others discussed.
Chronological
The chronological speech pattern places the main idea in the time order in which items appear—whether backward or forward. Here’s a simple example.
In this example, we’re looking at the writings of Winston Churchill in relation to World War II (before, during, and after). By placing his writings into these three categories, we develop a system for understanding this material based on Churchill’s own life. Note that you could also use reverse chronological order and start with Churchill’s writings after World War II, progressing backward to his earliest writings.
Biographical
As you might guess, the biographical speech pattern is generally used when a speaker wants to describe a person’s life—either a speaker’s own life, the life of someone they know personally, or the life of a famous person. By the nature of this speech organizational pattern, these speeches tend to be informative or entertaining; they are usually not persuasive. Let’s look at an example.
In this example, we see how Brian Warner, through three major periods of his life, ultimately became the musician known as Marilyn Manson.
In this example, these three stages are presented in chronological order, but the biographical pattern does not have to be chronological. For example, it could compare and contrast different periods of the subject’s life, or it could focus topically on the subject’s different accomplishments.
The causal speech pattern is used to explain cause-and-effect relationships. When you use a causal speech pattern, your speech will have two basic main points: cause and effect. In the first main point, typically you will talk about the causes of a phenomenon, and in the second main point you will then show how the causes lead to either a specific effect or a small set of effects. Let’s look at an example.
In this case, the first main point is about the history and prevalence of drinking alcohol among Native Americans (the cause). The second point then examines the effects of Native American alcohol consumption and how it differs from other population groups.
However, a causal organizational pattern can also begin with an effect and then explore one or more causes. In the following example, the effect is the number of arrests for domestic violence.
In this example, the possible causes for the difference might include stricter law enforcement, greater likelihood of neighbors reporting an incident, and police training that emphasizes arrests as opposed to other outcomes. Examining these possible causes may suggest that despite the arrest statistic, the actual number of domestic violence incidents in your city may not be greater than in other cities of similar size.
Problem-Cause-Solution
Another format for organizing distinct main points in a clear manner is the problem-cause-solution speech pattern . In this format you describe a problem, identify what you believe is causing the problem, and then recommend a solution to correct the problem.
In this speech, the speaker wants to persuade people to pass a new curfew for people under eighteen. To help persuade the civic group members, the speaker first shows that vandalism and violence are problems in the community. Once the speaker has shown the problem, the speaker then explains to the audience that the cause of this problem is youth outside after 10:00 p.m. Lastly, the speaker provides the mandatory 10:00 p.m. curfew as a solution to the vandalism and violence problem within the community. The problem-cause-solution format for speeches generally lends itself to persuasive topics because the speaker is asking an audience to believe in and adopt a specific solution.
Psychological
A further way to organize your main ideas within a speech is through a psychological speech pattern in which “a” leads to “b” and “b” leads to “c.” This speech format is designed to follow a logical argument, so this format lends itself to persuasive speeches very easily. Let’s look at an example.
In this speech, the speaker starts by discussing how humor affects the body. If a patient is exposed to humor (a), then the patient’s body actually physiologically responds in ways that help healing (b—e.g., reduces stress, decreases blood pressure, bolsters one’s immune system, etc.). Because of these benefits, nurses should engage in humor use that helps with healing (c).
Selecting an Organizational Pattern
Each of the preceding organizational patterns is potentially useful for organizing the main points of your speech. However, not all organizational patterns work for all speeches. For example, as we mentioned earlier, the biographical pattern is useful when you are telling the story of someone’s life. Some other patterns, particularly comparison/contrast, problem-cause-solution, and psychological, are well suited for persuasive speaking. Your challenge is to choose the best pattern for the particular speech you are giving.
You will want to be aware that it is also possible to combine two or more organizational patterns to meet the goals of a specific speech. For example, you might wish to discuss a problem and then compare/contrast several different possible solutions for the audience. Such a speech would thus be combining elements of the comparison/contrast and problem-cause-solution patterns. When considering which organizational pattern to use, you need to keep in mind your specific purpose as well as your audience and the actual speech material itself to decide which pattern you think will work best.
Key Takeaway
- Speakers can use a variety of different organizational patterns, including categorical/topical, comparison/contrast, spatial, chronological, biographical, causal, problem-cause-solution, and psychological. Ultimately, speakers must really think about which organizational pattern best suits a specific speech topic.
- Imagine that you are giving an informative speech about your favorite book. Which organizational pattern do you think would be most useful? Why? Would your answer be different if your speech goal were persuasive? Why or why not?
- Working on your own or with a partner, develop three main points for a speech designed to persuade college students to attend your university. Work through the preceding organizational patterns and see which ones would be possible choices for your speech. Which organizational pattern seems to be the best choice? Why?
- Use one of the common organizational patterns to create three main points for your next speech.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Industrial Engineering Internship: Optimizing Problem-Cause-Solution diagnostics
Interns and Trainees
Veldhoven, Netherlands
Educational background
Data Science, Other technical backgrounds
Workplace type
Fulltime/parttime
Work Experience:
Workplace Types:
Job Description:
Introduction
Are a Bachelor or Master student in Industrial Engineering, Data Science, ICT? Do you have experience with process optimization and data analysis? Are you enthusiastic about the technology and have a passion for process optimization? Then this internship might be interesting to you!
Background Information
Within EUV Source Laser, our vision is to accelerate the EUV wafer ramp with high productivity Source Laser Solutions. We have a strong roadmap in place to achieve this vision, focusing both on development and industrialization. Diagnostics is a major part of the future roadmap for EUV Source Laser. We have different ways to diagnose our systems. One way is via PCS-es, (PCS-Problem Cause Solution).
Your Assignment
ASML invites interns to contribute to the improvement of the diagnostic data base (PCS-Problem Cause Solution), focusing on optimizing the Way of Working. This internship provides a unique opportunity to collaborate with experts in the field of semiconductor manufacturing and gain valuable insights into ASML's cutting edge technology.
The Problem Cause Solution database (PCS) is the primary diagnostic knowledge / experience database for Service and Manufacturing Engineers to consult in the case of equipment and performance issues, both at the customer site, at the local office and in Veldhoven. It displays relevant information (i.e. problem, symptom, cause and solution information) about possible future technical issues (referred to as “pro-active” PCS’s) and technical issues in the past (referred to as “re-active” PCS’s) and allows the Service Engineer to quickly benefit from the diagnostic experience of others.
The engineers at ASML encounter obstacles when dealing with the new programs due to the inefficient workflow of PCS’s
Objective: Enhance the efficiency and functionality of the diagnostic data base (PCS-Problem Cause Solution) workflow and improve overall productivity.
Key Responsibilities: • Conduct a comprehensive analysis of the current Way of Working for the PCS’s; • Evaluate and compare with the other existing diagnostic processes; • Identify the bottlenecks and inefficiencies in maintaining the PCS’s; • Collaborate with cross-functional teams to identify the areas for improvement; • Conduct assessments to measure the impact of changes; • Collaborate with team members to brainstorm innovative solutions for improvement; • Develop a plan to implement changes, considering feasibility and impact; • Work closely with relevant stakeholders, software developers and end-users to ensure seamless integration of new methods;
Expected outcome: A more efficient and user-friendly diagnostic data base that enhances productivity and improves the overall working experience.
Your Profile
To be a perfect match with this internship, you:
- Are a Bachelor or Master student in Industrial Engineering, Data Science, ICT or similar;
- Have knowledge of data analysis and process optimization;
- Have strong analytical and problem-solving skills;
- Have excellent communication skills to effectively collaborate with diverse teams;
- Are enthusiastic about the technology and a passion for process optimization;
- Have experience with Lean Six Sigma and with diagnostics is pro;
- Thrive in a dynamic work environment, adapting to changes and challenges
- Have good communication skills in English (verbal and written).
This is a Bachelor apprentice/graduation or Master apprentice internship.
Availability for 4-5 days per week, for minimum 5 months.
Please note that we can only consider students who are enrolled at a school for the entire duration of the internship.
Diversity and inclusion
ASML is an Equal Opportunity Employer that values and respects the importance of a diverse and inclusive workforce. It is the policy of the company to recruit, hire, train, and promote persons in all job titles without regard to race, color, religion, sex, age, national origin, veteran status, disability, sexual orientation, or gender identity. We recognize that diversity and inclusion is a driving force in the success of our company.
Other information
Change the world – one nanometer at a time Become an intern at a Dutch company that’s a global industry leader. You’ll gain valuable experience in a highly innovative environment – one that sparks your imagination and creativity. In addition to a monthly internship allowance of maximum €600 (plus a housing and free public transport), you’ll get practical guidance from experts in the field and the chance to work in and experience a dynamic team environment. ASML: be part of progress ASML is a high-tech company headquartered in the Netherlands. We manufacture the complex lithography machines that chipmakers use to produce integrated circuits, or computer chips. What we do is at the heart of all the electronic devices that keep us informed, entertained, and connected. Every day, you use electronics that simply wouldn’t exist without our machines. Behind ASML’s innovations are engineers who think ahead. The people who work at our company include some of the most creative minds in physics, electrical engineering, mathematics, chemistry, mechatronics, optics, mechanical engineering, and computer science and software engineering. We believe we can always do better. We believe the winning idea can come from anyone. We love what we do – not because it’s easy, but because it’s hard. Students: getting ready for real-world R&D We’re a global team of about 39,000 people of 140 different nationalities and counting. Headquartered in Europe’s top tech hub, the Brainport Eindhoven region in the Netherlands, our operations are spread across Europe, Asia and the US. In such an environment, your colleagues may be sitting next door, or they could be thousands of kilometers away in a different country – or even working for a different company. An internship at ASML is the opportunity to get to know not only the world of industrial-strength R&D, but yourself – you’ll discover just what excites you most. Will you design a part of the machine, or make sure it gets built to the tightest possible specifications? Will you write software that drives the system to its best performance, or work side-by-side with the engineers of our customers in a fab, optimizing a system to the requirements of the customer?
How will you be part of progress?
- ASML at a glance
- Working at ASML
- Accessories
- Entertainment
- PCs & Components
- Wi-Fi & Networks
- Newsletters
- Digital Magazine – Subscribe
- Digital Magazine – Log in
- Smart Answers
- Best laptops
- Best antivirus
- Best monitors
- Laptop deals
- Desktop PC deals
When you purchase through links in our articles, we may earn a small commission. This doesn't affect our editorial independence .
Anatomy of a PC crash: 7 scenarios, and how to avoid them
First there’s a little stutter. Next a program hangs, and a funny noise creeps from your machine. Then that familiar blue screen slaps you in the face. Your computer just crashed, and all you can do is sit in the awkward silence of a restart, and hope it wasn’t fatal.
There are many possible causes for these hellish episodes, and it’s important to be educated on the whys and hows of PC crashes to prevent them in the future. After all, the next crash could be your PC’s last. Following is a rundown of seven common causes and solutions.
Hardware conflicts
Many blue screens are a result of hardware and installation conflicts. All of your system’s components consume IRQs (interrupt request channels) when installed, and every device requires its own channel to function properly. When two devices share the same channel and are used simultaneously, a crash can occur.
Thumb through your Device Manager, and look for any devices marked with a yellow exclamation point. These are the ones with issues, and can usually be fixed with a driver update. Just search your device manufacturer’s website for the latest driver software, or, in a pinch, reinstall the offending hardware itself.

Bad memory is to blame for many blue screens and failed boots. Fortunately, however, your RAM modules are some of the easiest components to check and replace.
First, use the software utility Memtest86+ to ensure your RAM is the problem. If errors arise, you next need to determine exactly which memory stick is to blame. To do this, remove all the sticks from your system—save one inserted in the primary memory slot. If the system boots fine, and no errors are detected in Memtest86+, continue testing in the same fashion—one stick at a time, inserted in the primary slot—until the system fails to boot, or Memtest86+ indicates problems.
Eventually, you’ll nail down exactly which memory module is causing trouble, and then you can replace it with a fresh, clean stick (just make it’s fully compatible with your motherboard and other sticks of RAM).

Heat is thy enemy
Computers get hot. We know this from the loud fans bolted inside our desktops, and the alarming burning sensation we feel on our legs after using a laptop for too long. Everything inside a PC generates heat, and heat can cause components to become unstable and crash your PC. Indeed, computers are designed to crash as a last-ditch effort to protect their own internal components from permanent heat damage.
If you suspect your PC isn’t effectively dispersing enough heat, first check to make sure all your fans are spinning properly. If one isn’t moving, or appears to be spinning abnormally slow, check its connections to make sure it’s properly powered. If all appears fine, but the fan still isn’t doing its job, it’s best to replace it.
Next, make sure that all of your PC’s vents, grates, and filters are unhindered by dust, pet hair, and other gross materials that prevent proper airflow. These areas are hotbeds (pun intended) for heat buildup. If you find any problem areas (see the disgusting example below), use a can of compressed air to clear the airways.
For laptops, make sure that the machine is on a hard, flat surface that won’t “smother” the chassis around its vents, thus restricting airflow.

You can monitor the temperature of your CPU with my favorite free monitoring tool, PC Wizard . In addition to other helpful uses, it will show you the real-time temperature of all your system components.
If everything looks good with your airflow but the temperatures continue to rise, check your BIOS settings. If you’ve messed around with voltage settings during some kind of overclocking escapade, reset the values to their defaults. The more voltage a component receives, the hotter it becomes.

If you have recently installed a new CPU, the crashing could stem from a poor application of thermal paste. So remove your heatsink, clean your surfaces with a cotton ball and a little rubbing alcohol, and try again.
There are competing theories on how to apply thermal paste, but your goal is always the same. The thermal compound fills the microscopic valleys on the surfaces of the CPU and heatsink to provide the most even and full contact between the two components. The paste is ineffective when too little—or too much—is applied. So I use the pea-drop method: I place a small, pea-size drop in the middle of the CPU, and then place the heatsink directly on top, letting the natural pressure of the heatsink spread the paste evenly.
Not enough power
It’s always fun to cram more powerful components inside your PC, and of course overclocking your CPU will yield performance dividends. But you can only upgrade so far before you begin running low on juice. Your PC will become unstable and unexpectedly restart if you put too much strain on your power supply.
There’s no easy way to determine which components are drawing the most power, but your component manufacturers’ websites might list power consumption specs online. From there, you can calculate your approximate total power consumption, and compare it to the output of your power supply.

If you determine your PSU can’t handle the load of all your components, you have to make some difficult decisions. If you overclocked your CPU, you can return the processor to its original state. Otherwise, you can replace your power-hungry components for less needy ones, or follow the most sensible path and simply upgrade your power supply. A 500- to 650-watt power supply should be able to properly power an average performance PC .
Fragmented hard drive
Your hard drive can become a bit more fragmented—and unstable—every time you save a file, install a program, or delete something. Not only does this slow down the hard drive, it can also give your OS trouble when trying to find necessary files to function. So your system will eventually give up and try again—with a crash.

Run the Disk Defragmenter in your System Tools every week or so to keep your files straightened out. The process is a pain in the butt while using the PC (you can’t save data to the disk while it defragments), and it can take upwards of an entire day to complete. So set it and forget it before going to bed or work.
One very important note, however: Defragmenting isn’t necessary for solid-state drives. SSDs already store data in a sequential order (as opposed to random order) and can be susceptible to damage if defragmented.
A cluttered Registry
Your PC’s Registry is a vast library of system settings—settings that can sometimes lead to blue screens and other instabilities. Indeed, even when programs are uninstalled, their Registry settings can stay behind. The settings are useless to the daily operation of your PC, but can nonetheless lead to system bloat, conflict and errors. Your computer continues to scan these error-ridden Registry entries, slowing everything down. Too much of this, and you can kiss stability goodbye.

A good Registry cleaner, such as Free Wise , is the perfect tool for clearing away the clutter. Free Wise will scan your Registry, find the problems, and exterminate them, leaving your Registry obstruction free.
The dreaded virus
Yes, malware is a significant cause of blue screens. But, luckily, the solution is simple. Start up your trusted antivirus program , make sure it’s up-to-date, and give your system the most robust scan available.

If the virus has disabled your ability to start up your antivirus software, mutter angrily to yourself while you restart in safe mode by pressing F8 before the Windows logo appears. Safe mode will disable any extraneous programs and drivers from launching, and allows just the core operating system to load. Once in safe mode, you should be able to run your antivirus program, and complete a thorough scan from there.
Gather clues to fix the problem
Any information you can pull off a BSOD can provide a problem-solving clue. So when you get a blue screen like the one below, write down as much as you can, and search online for information on the error it’s throwing at you. Diagnose the problem and get it solved, because ignoring the problem will make everything worse in the long run.
That’s right: Every time the computer crashes and you don’t fix it, you make Windows sad.
Request for Proposal Template
22 common pc hardware problems-solved.
Dealing with PC hardware problems can be frustrating, significantly when they hinder our productivity and cause inconvenience. From blank monitors to keyboard malfunctions, and display image distortions, these issues can disrupt our workflow. However, fear not, as we’ve got you covered! In this article, we’ll explore eight common PC hardware problems and provide practical solutions to get your system back on track.
We all know that hardware failure is very common. So after polling nearly two hundred clients, it’s not surprising that 99% per cent of them had experienced a hardware failure. But the problem is that during this collapse, they lose data.

Source: Arcserve
Blank Monitors
One of the most unsettling issues is encountering a blank computer monitor when you power on your PC. Before panicking, check the monitor’s power supply and connection to the computer. If the issue persists, try connecting the monitor to another computer to identify whether the problem lies with the monitor or the PC. Faulty cables or outdated graphics drivers could be potential culprits.
Keys Not Working on the Keyboard
Are some of your keyboard keys unresponsive? This problem could occur due to debris accumulation beneath the keys or a malfunctioning keyboard driver. Try cleaning the keyboard gently using compressed air and update the keyboard driver. If the issue persists, consider replacing the keyboard with a new one.
Mouse Problems
A malfunctioning mouse can significantly hinder your computing experience. If your mouse cursor is freezing or moving erratically, check the mouse’s physical condition and its connection to the PC. You may also want to update the mouse driver or try using a different USB port to see if the issue resolves.
Uninstall the USB Port Driver
When multiple USB devices stop working, it might be due to a corrupted USB port driver. Uninstalling the driver and restarting your PC will prompt Microsoft Windows to reinstall the appropriate driver automatically. This simple step can often fix USB-related problems.

Laptop Touchpad Causing the Cursor to Jump Randomly
For laptop and computer users experiencing cursor jumps or erratic movements, disabling the touchpad while typing can be an effective solution. Navigate to your touchpad settings and enable the option to disable the touchpad temporarily when typing.
Disable USB Selective Suspend
If your PC encounters issues with USB devices, such as external hard drives disconnecting unexpectedly, the USB Selective Suspend feature might be to blame. Disabling this feature in the Power Options can resolve such complex computer issues.

Display Screen Image Distortion
Distorted images or strange artefacts on the screen can be disconcerting. Check the graphics card connections and ensure that the drivers are up to date. If the problem persists, consider testing the monitor on another personal computer or using a different monitor to isolate the issue.
Keyboard Problems
If your keyboard is typing multiple characters with a single keystroke or repeating keys, adjusting the keyboard repeat rate and delay system hardware settings in Windows can often resolve the problem. Additionally, cleaning the keyboard and ensuring there is no physical damage may help.
Motherboard Problems
The motherboard is the heart of your PC, and when it encounters issues, the entire system can suffer. If you experience frequent crashes before the operating system loads or notice random reboots, it could indicate a problem with the motherboard. Consult a professional technician for a thorough diagnosis and possible repair.
Laptop Speaker Making Static Noises
If your laptop’s speakers produce annoying static or crackling sounds, try updating the audio drivers first. If the issue persists, the speakers may be faulty, and a technician can help with necessary repairs or replacements.

Signs You Need to Call a Professional
Certain hardware issues might require the expertise of a professional. For instance, persistent fan noises, signs of virus infection, or a failing hard disk demand immediate attention from an experienced technician. Don’t hesitate to seek professional help to prevent further damage.
Noisy fans can be annoying and disruptive. Regularly clean the fans and ensure proper airflow to minimize fan noises. If the noise continues, you may need to replace the fan or consider upgrading to a quieter cooling solution.
PC Fans Not Working Properly
Overheating is a serious concern for PCs, and malfunctioning fans can worsen the problem. Regularly check your PC’s fans for proper functioning, and consider cleaning them to ensure an optimal cooling system.

Signs of Virus Infection
Virus infections can wreak havoc on your PC, causing performance issues, unexpected crashes, and data breaches. Keep your system updated with reliable antivirus software and perform regular scans to detect and remove potential threats.
Apple Macbook Dimmed Screen as a Sign of Motherboard Failure
For MacBook users, a dimmed or blacked-out screen might indicate a problem with the motherboard. Seek assistance from an authorized service centre or an Apple-certified technician to diagnose and resolve the issue.
Too Much Pressure on the RAM
Physical pressure on the RAM modules can lead to connection issues, causing your PC to crash or freeze. Make sure the RAM is properly seated and not subject to unnecessary pressure or force.

Keyboard Issues
Keyboard malfunctions, such as keys not registering or sticking, can be caused by dirt or debris between the keys. Carefully clean your keyboard or consider replacing it if the problem persists.

Unusual grinding or whirring sounds coming from your PC could be a sign of hardware issues. Check your hard drive and fans to identify the source of the noise, and seek professional help if needed.
Fix the Blue Screen of Death
Encountering the dreaded Blue Screen of Death can be alarming. BSoD errors often indicate hardware or driver problems. Troubleshoot the issue by updating drivers or performing a system restore.

We are a leading hardware development company that provides A-class services globally. Read more about us
Noisy Hard Drive
If your hard drive starts making strange noises, it might be failing. Back up your data immediately and consider replacing the hard drive to avoid data loss.
Faulty Hard Disk
A faulty hard disk can lead to data loss and system crashes. If your PC shows signs of a failing hard disk, such as slow performance or frequent error messages, back up your important data immediately. Replacing the faulty hard disk with a new one and restoring your data can prevent further complications.
Blank Monitor
Encountering a blank monitor upon starting your PC can be alarming. Before panicking, ensure that all connections between the monitor and PC are secure. If the issue persists, it may indicate a problem with the graphics card or the monitor itself. Testing the monitor on another PC or trying a different monitor will help identify the source of the problem.
When The Monitor Goes Black After a Few Seconds
If your monitor loses signal and goes black after a few seconds, the issue could be related to the graphics card, monitor settings, or cable connections. Double-check all connections and ensure the monitor settings are correct. If the problem persists, consult a professional technician for further assessment.
How to Fix Mouse Left-click Malfunction in Windows
Mouse left-click malfunctions can hinder your productivity and cause frustration. To fix this issue in Windows, follow these steps:
- Check Mouse Hardware: Ensure that there are no physical issues with the mouse, such as damaged buttons or loose connections.
- Update Mouse Driver: Go to Device Manager, locate the mouse under “Mice and other pointing devices,” right-click, and select “Update driver.” Choose the option to search automatically for updated driver software.
- Roll Back Driver: If the issue started after a driver update, you can roll back to the previous driver version. In Device Manager, right-click the mouse and choose “Properties.” Under the “Driver” tab, select “Roll Back Driver” if the option is available.
- Check Mouse Settings: Access Mouse Settings in the Control Panel or Settings app and adjust the mouse click settings. Ensure that the left-click function is set to the correct action.
- Scan for Malware: Malware can cause unexpected behaviour, including mouse issues. Run a full system scan using your antivirus software.
- Try Another Mouse: If the problem persists, try using a different mouse to determine if the issue is with the hardware or software.
Three Things That Help You To Avoid Common Hardware Problems in Computer
Keep inside clean and clear for effective cooling.
Overheating is a common problem that can lead to hardware failures. Dust and debris can accumulate inside your PC, obstructing airflow and causing components to overheat. Regularly clean the interior of your PC and ensure that all fans are functioning correctly to maintain effective cooling.
Run Diagnostics
When faced with mysterious PC issues, running diagnostics is often the first step towards identifying the root cause. Most PCs have built-in diagnostic tools that can perform comprehensive tests on hardware components. By analyzing the results, you can pinpoint potential problems and take appropriate action.
Getting a Professional Repair
While some hardware issues are easily resolved, others require the expertise of a professional technician. Don’t hesitate to seek professional help when needed, especially for complex problems like motherboard failures or hard disk issues. A trained specialist can diagnose the problem accurately and provide reliable solutions.
What about a professional repair of your hardware problems? INTechHouse can find any level solution for reasonable rates!
INTechHouse Advice: How to Avoid Computer Hardware Problems
As technology continues to advance, our dependence on personal computers has grown exponentially. Whether for work, entertainment, or communication, PCs play a vital role in our daily lives. However, encountering hardware problems can disrupt our productivity and cause frustration. In this article, we will provide you with expert advice from INTechHouse on how to avoid common PC hardware problems and keep your computer running smoothly.
- Invest in Quality Components:
When building or buying a PC, opt for quality components from reputable manufacturers. Quality components are more reliable, tend to have longer lifespans, and are less likely to encounter hardware failures. While they may come at a slightly higher cost, the peace of mind and reduced risk of issues are well worth it.
- Properly Install Hardware:
Whether you’re upgrading components or assembling a new PC, proper installation is crucial. Follow manufacturer guidelines, use the right tools, and avoid applying excessive force when connecting components. Incorrect installations can lead to physical damage or compatibility issues, causing potential hardware failures.
- Keep Your PC Clean:
Dust and debris accumulation inside your PC can hinder airflow and cause overheating. Regularly clean the interior of your PC, especially around fans and heat sinks, to prevent hardware components from overheating and potentially failing. Use compressed air to blow away dust gently, and consider investing in dust filters for improved long-term maintenance.
- Use a Surge Protector:
Power surges and electrical spikes can damage your PC’s components, leading to hardware failures. Invest in a good-quality surge protector to safeguard your PC from voltage fluctuations. Surge protectors act as a buffer and can save your PC from potential damage caused by sudden power surges.
- Keep Your PC Cool:
Overheating is a significant cause of hardware problems. Ensure your PC has proper ventilation and is placed in a well-ventilated area. Consider adding additional cooling solutions, such as case fans or liquid cooling systems, if you engage in resource-intensive tasks like gaming or video editing.
- Install Reliable Antivirus Software:
Virus infections can wreak havoc on your PC, leading to data loss and system instability. Install reliable antivirus software and keep it up to date to detect and prevent potential threats. Regularly perform full system scans to ensure your PC remains virus-free.
- Keep Software Updated:
Outdated software, including operating systems and drivers, can cause compatibility issues and impact hardware performance. Regularly update your operating system and hardware drivers to access bug fixes, security updates, and improved compatibility with the latest applications.
- Properly Shut Down Your PC:
Avoid abrupt power-offs and improper shutdowns, as they can lead to file corruption and hardware damage. Always shut down your PC through the appropriate software options or use the “Shutdown” button in your operating system.
By following INTechHouse’s expert advice on how to avoid common PC hardware problems, you can ensure that your computer remains reliable and efficient. Investing in quality components, proper installation, regular cleaning, and keeping your PC cool are essential steps to prevent hardware failures. Moreover, protecting your PC from power surges, using reliable antivirus software, and keeping your software up to date will enhance your overall computing experience. With these proactive measures, you can enjoy trouble-free PC usage, allowing you to focus on what matters most – your tasks, projects, and digital endeavoursINTechHouse Advice: How to Avoid Common PC Hardware Problems
Ready to embark on your hardware project journey?
Ready to tackle common PC hardware problems and keep your computer running smoothly? Discover expert solutions and tips in our comprehensive guide! If you have problems without solutions, just ask
Table of contents

Welcome to INTechHouse
We restore the natural balance and improve the quality of life for future generations!
Latest posts
How to write an rfp for embedded software development project, data mesh implementation: step-by-step process, ensuring device reliability: pcb design and embedded software consultant company.
Train With CTG
Troubleshooting Step 2: Establish Theory of Probable Cause
Once you have gathered sufficient information to identify the problem, the next step in the CompTIA troubleshooting methodology is to “Establish a Theory of Probable Cause”. Here, you use your experience and knowledge to determine what you believe to be the underlying issue. Ask yourself, “What do I think caused the problem?”. Sometimes the first answer that comes to mind is indeed the cause. Other times that answer is not forthcoming. You may need to work through a series of tests to help you arrive at that theory.

Question The Obvious
Have you heard of Occam’s razor? Many folks have. Occam’s razor is a problem solving principle asserting that simpler solutions are more likely correct than complex solutions. We work in the IT industry. It is a complex world. Most of us know a lot about networks, protocols, PCs, servers, Wi-Fi, and a bunch of other stuff. The tendency you should watch out for is believing that the cause of a problem is something complicated or obscure.
So, ask yourself this question: What could be the simplest cause for this problem?”. Could it be something simple like a power issue or an unplugged cable? I once solved an executive’s “broken computer” by connecting and securing a loose monitor cable. This approach works a surprisingly often. It’s worth a try!
Scenario: Since you previously observed Jasper restart his computer and attempt to connect to the department server his cable is connected and the computer has power.
Consider Multiple Approaches
You should approach developing your theory of probable cause by systematically eliminating categories of causes and common issues. You want to narrow down the list of possibilities. The Network+ objectives speak of a top-to-bottom or bottom-to-top approach. I have found the OSI model to be a useful guide to eliminating common issues and categories of causes. Use your troubleshooting tools and follow the OSI model starting at layer 1. You will often find the cause within the first 3 layers. Here is my recommended approach to help determine where the problem cause may lie:
- Layer 1: verify the workstation cable is connected to the correct port and not damaged. You can verify the continuity of the cable by observing that the link lights on both the NIC card and switch are lit.
- Layer 2: Use the netstat -e command to verify that the NIC card is sending and receiving frames without errors.
- Layer 3: Use the ipconfig /all command and document the current IP configuration of the workstation. Hint: if the IP address is an APIPA address, the workstation is not communicating with the DHCP server. Use the ping command to verify IP communications in a step-wise manner, starting from the workstation. First, ping 127.0.0.1 to ensure the protocol stack is not malfunctioning. Then ping the default gateway you earlier documented to verify communications through the switch to the router interface. Finally, ping the desired server (or a known working resource) to check communications past the router. If this step fails, the traceroute command can help pinpoint where communications fail.
Scenario: You have verified that Jasper’s workstation cable is connected and is not damaged. The netstat -e command shows Ethernet frames being sent and received with zero errors. You used the ipconfig command to establish that the computer has a valid IP address. You can ping the configured default gateway, but you are unable to ping the department server and printer. Finally, you can access the public Internet using Jasper’s computer.
After working your preferred troubleshooting approach and gathering more information, you are ready to establish your theory of probable cause. Given what you know now, what is the most likely cause of the problem?
Scenario: Your theory of probable cause for the issues experienced by Jasper is that his workstation was mistakenly connected to the wrong port on the switch during the maintenance performed the day before. If Jasper’s computer was plugged into the wrong switch port it would be in a different VLAN. That would explain the valid IP address, ability to access the public Internet, and the inability to access department resources.
Now that you have established your theory of probable cause you can proceed to the third step of the CompTIA troubleshooting methodology: “Test the Theory to Determine Cause”. That is the topic of the next blog post in this series, so keep an eye on our website for that post. The best way to know when a new post is made is to follow us on social media.
If you missed the first post in this series, you can find it here . The remaining posts of this series are scheduled to be made on a weekly basis.
Thanks for reading, and I hope you are learning from this series. After all, that is why I am writing them. Feel free to share your own troubleshooting adventures in the comments. If you have colleagues or friends who could benefit from this information, please share the posts.
Why Did Windows Crash? A Troubleshooting Guide
When Windows crashes, keep calm and reboot. In most cases, it's a singular event. If your computer crashes again, however, consult this step-by-step troubleshooting guide. Bookmark for future use.
You were minding your business -- going through expense reports or browsing the internet -- when the worst struck . Your PC crashed, and you don't know what to do. Confusion is typical when your otherwise normal day gets interrupted. Yet, there's no reason to worry.
With this simple guide, you'll be able to diagnose the case of a PC crash in minutes.
In this article: What Is a PC Crash? | Software Failure | Hardware Failure | Crash Indicators | Most Common Causes for a PC Crash | First Crash | Problem Persists | Analyzing Hardware Issues | Analyzing Software Issues | Asking for Help | Preparing Precise Logs | Tech Support Forums
1. PC Crashes and You
This article will focus on what an unexpected computer crash is and how to identify the issue. Computer crashes occur for a variety of reasons. To the average PC user , PC crashes are often taken as signs that a PC is broken or damaged. In reality, PC shutdowns are rarely something to worry about. As long as no immediate harm has come to the PC in the form of physical damage, voltage spikes, or product defect, your PC should not be in any lethal danger.
1.1 What Is a PC Crash?
The simplest way to explain a PC crash is through the metaphor of a chain. There are two types of chains in a PC: a hardware chain and a software chain. When you first boot up your PC, the hardware chain activates. The BIOS checks to see which hardware components are connected to the motherboard and powered by the PSU (Power Supply Unit). If a hardware component, such as a hard drive, is not properly connected to the motherboard, you will be informed of the issue through an error message .
Once the hardware chain finishes, the software chain initiates. The first link on the chain is the OS (Operating System). If OS files are damaged in any way, you will receive an error on your display. Afterward, drivers and startup items load. Finally, typical programs become available for use and the chain ends.
A PC crash is caused by a break in this logical chain. Of course this can also happen while the PC is already running. If any links are broken, damaged, or missing, your PC will crash.
1.1.1 Software Failure
The three main reasons for software failure are: OS corruption, program crash, and driver failure . Out of the three, a driver failure is the most common. Different drivers connect with, and control, different hardware components.
OS Corruption -- An OS error occurs in your operating system. This type of error indicates that your system files are corrupted, damaged, or missing. OS files can become corrupt for two main reasons: faulty disk drive sectors or deleted system files. Faulty hardware sectors occur when the physical disk of your hard drive becomes damaged or worn. A damaged hard disk cannot read files properly, which your PC considers a corruption. On the other hand, the issue may stem from system files simply missing. Certain viruses aim to delete system files, which are the most crucial files of a PC. If system files end up missing, the OS cannot perform and your PC will crash.
Program Crashes -- Program crashes are often associated with hardware failure. Programs rarely crash a PC in themselves. If a program fails, the program itself will crash, rather than the PC as a whole. Instead, program crashes are a method of troubleshooting deeper problems. For example, if your PC crashes every time you are using your Chrome web browsers, it may be a result of RAM failure. If your PC crashes every time you begin playing a PC game, your GPU may become easily over-stressed and shut down your PC.
Driver Failure -- The majority of PC crashes do not occur due to software or hardware failure. Drivers allow for the use of hardware components. Driver failures are a type of software bug, wherein the connection between your hardware and software fails. Drivers may be faulty when installed, or may corrupt over time. Outdated drivers may lead to PC crashes, as can the latest drivers.
Driver hotfixes are often released by software developers when a driver works improperly or is released unstable.
1.1.2 Hardware Failure
Unlike software failure, hardware failure cannot be fixed through tweaks or downloads. If a component is defective, the component will not work. Although under-clocking -- a method to reduce the speed of a component -- may prolong the component's use, it will not fix the component. The odds that a hardware component has failed in your PC are fairly low.
Motherboard -- The motherboard allows for communication between the different hardware components. Everything from your flash drives to your hard or solid state drive is connected via the motherboard. A damaged (faulty capacitor, faulty inputs, short-circuited board, etc.) motherboard will lead to frequent crashes and shutdowns. Power surges may burn the motherboard. Faulty slots, such as PCI or RAM slots, may lead to issues as well. Motherboard issues are tricky, but are rarely the cause of frequent PC crashes.
CPU (Central Processing Unit) / GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) -- Most PC crashes caused by hardware problems will involve the CPU or GPU in some capacity. Any issues on behalf of these two hardware components will lead to frequent shutdowns. The CPU handles most processing tasks such as multi-tasking or video rendering. The GPU handles computer graphics. Overheating is the main issue with these two components. CPUs or GPUs automatically shut down when they reach a certain temperature threshold for protection.
PSU (Power Supply Unit) -- PSU provide the electrical power necessary to run your components. A low-quality PSU can ruin a PC with frequent voltage spikes. Improper voltage, voltage spikes, power surges, and the like can do serious damage to all PC components. Most pre-built and factory-made PCs come with cheap power supply units , and are also poorly ventilated. All of these factors may lead to crashes.
1.2 Crash Indicators
Crash indicators are vital for troubleshooting and an attentive observer will spot them immediately. These indicators act as information you can use to troubleshoot your crashing issues. Crash indicators do not imply specific problems in themselves. They do, however, help with gauging the severity of your issue.
Sound Stutter -- Sound stutter is a sure indication that your PC will inevitably crash or become unresponsive. This may sound like a buzzing or a considerable slowing down of audio. Sound stutter may be an audio problem, or may be coupled with another problematic component part.
BSOD -- The BSOD (Blue Screen of Death) is a notable indication of a PC crash. Comparatively speaking, a BSOD is the most helpful of the available PC crashes you could have. BSODs will often provide users with an error code, or error message, which will direct you towards a possible solution. The PC is then restarted.
Screen Shuts Off -- Sometimes a PC will not shut down completely during a crash. Instead, the PC will continue running while the screen shuts off. A screen shutting off is very usually an error with the GPU. This does not mean that the GPU is broken or defective, but that the GPU cannot maintain its connection with the motherboard. It may mean that the GPU's drivers are installed incorrectly, corrupted, or require a rollback . This assumes, of course, that your screen is properly connected and your connecting cables are in working order.
Unresponsive PC -- An unresponsive PC is often the first indications of a PC crash. There are several versions, however, of an unresponsive PC. Some may consider a still mouse unresponsive, while others may be experiencing a complete lack of response -- both audio and visual -- from their PC. In any case, unresponsive PCs are definite indicators that a crash has occurred.
1.3 Most Common Causes for a PC Crash
PCs crash for many common reasons and with the right amount of patience and know-how these types of crashes are easy to fix.
Overheating -- Overheating is possibly the most common issue. Overheating occurs when: PC components are under heavy load, there is poor air circulation in your PC case, PC fans are not working, and too much dust has collected in the PC. Cooling down a PC is a simple process, but does require that the case be opened and components cleaned.
OS Failure -- OS files, for one reason or another, have a way of becoming damaged or missing. This may be due to a virus, malware, spyware, and so on. It may also be due to a simple mishandling of important files on behalf of the user.
Driver Failure -- Driver failure occurs when a driver does not perform well with your PC's hardware or with other installed drivers. This occurs for several reasons: the driver is defective and requires a hot-fix, was installed incorrectly, is not compatible with your version of Windows, etc. Rolling back drivers is a common exercise by PC technicians, and Windows even includes this function in the OS itself.
2. The Nitty-Gritty Troubleshooting
The act of troubleshooting is best conducted through levels of urgency, rather than specific issues. Some crashes are easily fixable, while others will require hours of troubleshooting. Likewise, some may occur monthly, while others occur daily.
Follow each section to ensure that you are acting in accordance with the severity of the issue. This is a general troubleshooting procedure. If one step does not work, continue on to the next.
2.1 First Crash
Restart Your PC -- Seriously, restart your PC . If a crash has occurred and your PC is not restarting automatically, press and hold your PC's power button to turn off the PC. Then, turn the PC back on. One of two events will occur; either the PC acts normally and the crash was a simple hiccup in the logical chain of command, or the PC crashes again.
Check Power Connections -- If a PC component is not receiving power, or not receiving enough power, it will shut down. Before troubleshooting components, ensure that your components are correctly plugged to the power supply. Power connections are listed separately from others because it is easy to forget that components require both a connection to the motherboard and a connection to the PSU as well.
Check Input Cables / Internal Connections -- Ensure that your input cables are in working order. This includes all connections outside the case, such as VGA and HDMI cables, as well as internal cables like SATA cables. Also, ensure that PC components are installed correctly. This includes the GPU (PCI slot) and RAM (RAM slot).
2.2 Problem Persists
WhoCrashed -- Download WhoCrashed , a valuable tool for diagnosing Windows crashes. The program works by looking at your minidump folder. A minidump is a small file which holds information created by a BSOD. WhoCrashed reviews minidump files and provides a reason for why the crash occurred. Once open, click the Analyze button and read the results. WhoCrashed will not work for all crashes.
Anti-Virus, Anti-Malware, Anti-Spyware -- Running a single anti-virus software will not do. I would recommend using three individual programs to ensure that your frequent crashes aren't malware-based. Download and run these three programs in order:
- Malwarebytes
- Windows Defender
Run full scans with each one (RKill does not have a scan settings). Then, download and run CCleaner . Continue doing so until all results come back clean. Ensuring that you have a clean PC is the first step in limiting extraneous variables.
Disable Non-Essential Startup Programs -- To continue minimizing extraneous variables, disable all non-essential startup items. Windows Task Manager provides a simple and easy to use interface for controlling startup items. To access the startup menu, right-click on your task-bar and select Task Manager . Click on the Startup tab and begin disabling items by double-clicking them. The startup tab will not show essential startup items, so feel free to disable them all. Programs like CCleaner also have a startup function to configure startup programs. For in-depth startup program analysis, the official Microsoft Autoruns tool allows users more access to the running applications on a PC .
2.3 Troubleshooting
Thus far, we've been dealing with general PC crash issues, associated with common issues and mistakes. If problems persist, it is no longer due to general PC issues.
2.3.1 Analyzing Hardware Issues
Overheating Troubleshoot -- Overheating is simple to diagnose. If your PC is overheating, take measures to cool it down immediately.
HWMonitor is an impressive, accurate software, which tracks the voltage and temperature readings of your computer components. If any of the components within your PC are above 80--90C on idle -- not under heavy use -- take measures to cool it down. The main cause of overheating is dust buildup, which can also render fans unusable and lead to even more crashes.
GPU Stress Test -- The best way to see whether your GPU is causing a PC crash is to stress test it . Stress testing will put heavy stress on your GPU, causing it to work harder than usual. If your PC shuts down during gaming, it's a good idea to check the stability of the GPU.
Furmark or Unigine: Valley are great stress-testing programs. During the test, ensure that your PC is not overheating. If your PC shuts down due to these tests, and your GPU is not overclocked, the GPU may be the problem. If that is the case, either under-clock your GPU or update/roll back your drivers.
CPU Stress Test -- CPU stress tests are like GPU stress-tests. CPU stress-tests test multi-tasking (among other things) rather than graphics ability. If shutdowns occur when you are using several programs or are rendering files, your CPU may be the issue.
Prime95 or RealBench will stress-test your CPU extensively. CPU stress-tests are different from GPU stress-tests in that CPU tests often take longer to complete. A thorough CPU stress-test will take several hours to complete.
RAM Stress Test -- RAM stress-tests test memory errors. RAM errors will lead to frequent shut downs unless the whole RAM stick is replaced. Windows Memory Diagnostic (WMD) is a windows program which checks for errors associated with your RAM.
Open your Start Menu, type in windows memory diag , and click on the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool to run WMD. WMD will check for memory errors itself, and only requires a restart to run. Memtest is a better memory test than WMD, but requires an external USB drive to download. You must also change your BIOS boot order to run Memtest.
Disk Drive Error Checking -- Hard disks, which is where your OS and programs are stored, wear down over time. They may also be defective. Disk drive errors may lead to frequent shutdowns, especially if shutdowns occur for no particular reason.
To scan a disk drive for errors, locate your disk drive (annotated as the C: drive or similar). Right-click the drive, select Properties , click the Tools tab, and click on Check under the Error checking category. Your PC will then restart. If this scan comes up with any errors, your crashes may be caused by your hard drive.
2.3.2 Analyzing Software Issues
OS Troubleshoot -- If your PC ceases to start up, or crashes despite being idle, there may be something wrong with your OS itself. To prevent or recover corrupted OS files , Windows comes equipped with a system file checker. The System File Checker command will make Windows check, repair, and replace damaged system files. Open the start menu and type in cmd . Right-click on the cmd.exe program as select Run as administrator . From the elevated command prompt window, type sfc /scannow and let the program run. It will scan and repair all damaged system files.
If your PC is not booting at all, create a system repair disc or USB to re-install Windows. Luckily, Windows installations will often create a backup version of Windows named Windows.old . This backup version will save the documents and programs on your previous copy of Windows.
Driver Troubleshoot -- Before rolling back drivers, check WhoCrashed to see if your minidump scan hails any results. You can check individual drivers by opening the Start Menu and typing device manager . Select the Device Manager . This is where you can find all drivers installed on your computer. Double-click on a category and right-click the device. Select Properties and then Drivers to check which driver is installed for which device. In the same window, there are two particular choices to note: Update Driver and Roll Back Driver . Update Driver will scan your PC and the internet for driver updates, although this feature is rarely effective. Instead, type in the name of the product with the added drivers tag to search for new drivers. If your drivers are up to date, try installing an older version of the driver. This option should be present in the driver website.
2.4 Asking for Help
It's virtually impossible to solve all PC crashes with one resource. The specific configuration of every PC is different. Even if the internal components of a PC, in the case of pre-built PCs, are the same, the possible combinations of software drivers and programs are immeasurable. That's why you should always consider asking for help when dealing with PC issues.
For the best results, you should follow a certain protocol you should follow when asking for advice on a tech support forum. This protocol will allow even the most casual PC user to answer troubleshooting questions quickly and efficiently.
Use Your Five Senses -- The process of troubleshooting a PC is fairly technical, and is often comprised of jargon concerning PC parts, drivers, network configurations, and so on. The most basic form of troubleshooting, however, doesn't require any tech-speak . Simply describing what is occurring when a PC shuts down provides important information for an error troubleshoot.
For example, does the PC make any sudden noises before shutting down. Is there any particular item, program, or behavior, i.e. a trigger that causes the crash? Does the screen freeze before going blank? Are the fans in the PC whirring? These basic processes can narrow a PC technician's troubleshooting to a defined list of possibilities. When asking for help, be as specific as possible and use your five senses to gain an exact reading of the situation before asking for help.
2.4.1 Preparing Precise Logs
Sometimes, precise logs are necessary to detail exactly what is going on with your hardware and software. System logs are technical accounts of your PC's software and hardware state. PC technicians use these logs to parse out errors and issues in a system.
System Information Log -- In your Start Menu, type system information and click the System Information program. This program allows users to check system information concerning hidden facets like BIOS version and Serial Ports and copy the information as well. Click on a subcategory, then Edit , then Select All , back to Edit and finally Copy . This will copy all the content in the page you are viewing. When starting a forum inquiry, copy and paste the first page of the System Information window, to offer others an idea as to the type of PC you're using.
DirectX Diagnostic Tool -- The DirectX Diagnostic Tool also provides a log with system information, and is more so directed towards sound and graphics card information. To check this information, open the Start Menu and type in dxdiag . Select dxdiag.exe and you should see your DirectX Diagnostic Tool (DDT). Click on Save All Information to save a copy of the DDT analysis to your desktop. This log contains a comprehensive list of most drivers, peripherals, controllers, decoders, and more present on your computer.
HWMonitor Log -- HWMonitor provides an excellent log which records voltage and temperature readings, along with many other readings and system information. You can access this log by opening HWMonitor, clicking File , and then Save monitoring data .
2.4.2 Tech Support Forums
Outlets for Questioning -- You can ask for help with troubleshooting in various online tech support forums . Some more notable examples are as follows: TomsHardware , HowToGeek , SuperUser , SevenForums (focusing on Windows 7), and TenForums (focusing on Windows 10). Less popular forums, which are no less effective, are Reddit's /r/techsupport subreddit and Microsoft's own Community forum.
These resources are effective because they are easy to use and assistance is often only a few days (if not hours) away. They also have an extensive library of questions which, more often than not, are similar to your own. If a question has been answered, it will most likely be labeled or tagged as Solved . This is commonplace for PC troubleshooting, so searching for the solution to a problem with the added solved tag will lead to better results.
We Wish You a Safe Flight with Windows
PC crashed are rarely total failures; PCs are made of components, and one failing or malfunctioning part does not mean you're at a complete loss. One might assume everything from hackers to viruses. Luckily, most PC crashes are simply the result of out of whack drivers. Rarely do they warrant actual part replacements.
Nevertheless, experiencing frequent shutdowns can be scary. One might think their personal, or professional, work may be put at risk. Worse yet, frequent shutdowns may end up putting a valuable PC resource out of commission. Fear no more! With these resources, you'll be able to troubleshoot, solve, and ask questions concerning PC shutdowns with the best of them.
Do you suffer from frequent shutdowns? Did this article help? If not, what's the issue? Let us know in the comments below?
Windows Errors: Causes and Solutions
Read how to find out why a computer freezes, restarts on its own or flashes a BSOD error , and how to get more detailed information on such errors. Almost every user has to face various difficulties related to the work of a personal computer. Messages about system errors can appear on the screen.

Overview of the Problem
The nature of appearing errors, type one errors: system messages, type two errors: stop errors, questions and answers.
When working with Windows and other OS, such things do not happen often. Still, they do happen. There is no need to panic when you see a failure in the work of a device. In the first place, every user should find the cause of what is happening or at least try doing it. It will determine further actions and their effectiveness. System errors can be very different . It is important to react to all Windows signals in time.

How to Check Your Hard Disk for Errors and Fix Them in Windows 10 🔎🛠️🗄️
Windows errors can be frequent. Some users see them quite seldom. Their appearance is preceded by many various factors. Still, the most important thing for a user is to determine the error type by the system message appearing on the screen.
By no means all errors are critical. That is why many of them can be corrected on your own. However, there are certain groups of errors where you can’t do much without an expert. Let us study typical examples of system errors.

SSD Diagnostics: Programs to Find and Fix SSD Errors 🛠️🔎👨💻
Every operating system is unique in its own way. Windows is used more often than others, but this platform remains to be among the whimsiest. Failures and various errors happen not so seldom. For users, it is very important to understand every system message. It will enable them to quickly respond to problems and solve them in a proper way.
It is important to determine how critical an error is. There are errors to be dealt with immediately. Otherwise, the problem can cause your computer to break down. So you need the skill to evaluate the problem.
Many users are mistaken when they think that finding the cause of the error is more important. Yet, one and the same problem can actualy appear after all kinds of failures. These can include software failures or hardware breakdown .
Classification of errors is a vast field of activity. It is very difficult to distinguish them correctly. To be able to do it, you need to know all small details of how a computer is organized and how the operating system works.
If we look at all errors in a wider aspect, they can be divided into some subgroups:
The first group is appearance of system messages. Most of the time, such errors are harmless.
More dangerous are the errors expressing themselves in the so-called «blue screen of death» (BSoD).

Why Computer Runs into Blue Screen Errors and How to Fix BSOD 💻🛠️🤔
They are followed by another variant – errors at the bootloader level. This error can be recognized only by the users who possess certain knowledge in this field.
A user has to know the explanation of the error code to identify it when it flashes on the screen. This way, a method to eliminate the problem can be selected. If there is a chance to eliminate it on your own, be sure to take it.
Thanks to possessing knowledge and necessary tools, you can try to avoid reinstalling the system, because this is a most critical method often resulting in loss of important data. You should try to ensure the system operability in any case.
For this purpose, a user needs to have a certain set of tools. In the first place, it means having system recovery discs as well as system recovery images and even data recovery software. This is the basic set of tools to recover the operating system or user data which was lost or damaged.

Windows Event Viewer: How to View Information about Errors in Windows 7, 8, 10 💥📜💻
We should review this type of errors first. System messages are among the most frequent. This form of errors is known to almost every user who chose to work with a Windows operating system.
Various system messages appearing on the screen indicate minor problems in the work of a device. A typical error is inability to read from memory or write. The problem can be identified by a window that appears: it usually has a red cross or a yelow question mark in its left side.
Such error is quite frequent. When it appears, you can determine incorrect work of the application the name of which is shown in such window. This program doesn’t work properly. It affects general system performance.
There can be various causes for such errors. These can be viruses; eventually they begin infecting all programs, settings and other system locations, and even cause RAM blocks to break down.
If a user installed drivers which begin to conflict in the end, some system components cease to work properly. The user will learn about it from a corresponding message on his screen.
Another cause of system messages to appear can be a failure or a breakdown of the feed circuit system that gives power to computer components. As there are several possible causes, we need to find out which one exactly caused the problem. You will have to apply every suggested variant and then leave out all defects that certainly do not match your case.
It is also important to determine the moment when this application ceased to work in its normal mode. If trouble began right after installation of this utility, there is almost certainly a problem with this software. In this case, you will have to give up using it. The selected version may be unable to work in a normal mode, so you will have to choose an older or a newer version. Sometimes, the best variant is to choose another program with similar functionality.
More trouble comes with the problem that doesn’t allow Windows to start. It is often called a screen of death. In some cases, you can ignore the system message, and the problem will disappear.
However, most often users have to take certain measures that will really help to get rid of the problem. With the help of special applications you can try and deal with the problem. Still, even this method is not always possible, because your system can refuse to boot at all.
When this problem emerges, don’t think it is so fatally critical. It doesn’t necessarily make your system break down. Anyway, if the OS doesn’t boot and some strange text appears on the screen, you should find out what’s going on. This is the method to help you eliminate the error.

The System Won’t Boot. Recover Windows Bootloader with bootrec, fixmbr, fixboot commands 👨💻⚕️💻
First, you must find the error code. It can help to find the cause of the error and the way to eliminate it. This information can also be found in our website ( https://hetmanrecovery.com/recovery_news/bsod-errors ).
You should also pay attention to the name of the system module, because this object is the root of the problem. The text on the screen also indicates the type of failure. All you need is to understand this information properly. After that, we can try to solve the problem by our own efforts.
First of all, try to restart the system. If it helps, then your problem was a system failure. Yet such play of chance is rare. Instable work of drivers and other components can provoke failures that appear regularly.
The easiest method is to reset the system to its normal working mode. For this purpose, driver roll-back is used. Installing the latest versions of all components that ensure correct work of the operating system can also help.
File system failures can cause errors of this type every time that a user starts the computer. In this case, all errors have to be found. For this purpose, use a boot disk with Windows PE. Then, you will have tostart the command prompt anbd enter «chkdsk C: /f» .
This will start the scanner. All errors will be found and corrected immediately in an automatic mode. This method is rarely used but it is very effective. It would be a good idea to run such check from time to time.

Author: Vladimir Artiukh , Technical Writer
Vladimir Artiukh is a technical writer for Hetman Software, as well as the voice and face of their English-speaking YouTube channel, Hetman Software: Data Recovery for Windows. He handles tutorials, how-tos, and detailed reviews on how the company’s tools work with all kinds of data storage devices.

Editor: Oleg Afonin , Technical Writer
Oleg Afonin is an expert in mobile forensics, data recovery and computer systems. He often attends large data security conferences, and writes several blogs for such resources as xaker.ru, Elcomsoft and Habr. In addition to his online activities, Oleg’s articles are also published in professional magazines. Also, Oleg Afonin is the co-author of a well-known book, Mobile Forensics - Advanced Investigative Strategies.
- 2.02.2024 16:56
- Evaluations:
- Corrupted or missing system files
- Outdated or corrupted drivers
- Malware or viruses
- Registry errors
- Incompatible software
- Insufficient memory
- Conflict between programs
- Overheating of the system
- Incompatible hardware
System files can become corrupted due to a variety of reasons, such as viruses, hardware failure, or software conflicts. When system files become corrupted, it can lead to errors in Windows, such as the Blue Screen of Death, freezing or crashing, and other system errors.
Outdated hardware can play a major role in causing Windows errors. It is important to keep hardware up to date to ensure that the system is running optimally. Outdated hardware can cause compatibility issues with newer software, drivers, and operating systems, leading to system instability, crashes, and errors. It can also cause hardware to become obsolete, resulting in decreased performance and reliability.
- Corrupt or missing system files
- Outdated device drivers
- Malware or virus infection
- Hardware incompatibility
- Overheating or power surges
- Incompatible or faulty applications
- Improperly configured system settings
- Unstable RAM or memory issues
Malware and viruses can contribute to Windows errors in a variety of ways. Malware can corrupt system files, alter system settings, and cause system instability, all of which can lead to errors. Viruses can also delete or corrupt system files, which can lead to errors. Additionally, malicious software can interfere with the normal functioning of Windows, resulting in errors.
Comments (11)
- Restart your computer: This is the most basic and often the most effective solution.
- Update your drivers: Outdated drivers can cause errors and crashes.
- Scan for viruses and malware: Malware can cause errors and crashes.
- Check for hardware issues: Faulty hardware can cause errors and crashes.
- Run System File Checker: This scans for corrupt system files and replaces them with healthy versions.
- Uninstall recently installed software: Newly installed software can cause errors and crashes.
- Perform a clean boot: This eliminates software conflicts that can cause errors and crashes.
- Use System Restore: This restores Windows to an earlier point in time when it was working properly.
- Error code 0x80070057: This error code usually means that a parameter is incorrect or missing when trying to perform a task.
- Error code 0x80070422: This error code usually means that a service is not running or has been disabled.
- Error code 0x80070005: This error code usually means that access to a certain resource has been denied.
- Error code 0x80004005: This error code usually means that an operation has failed due to an unspecified error.
- Error code 0x80070003: This error code usually means that a file cannot be found.
- Event Viewer: Event Viewer is a tool built into Windows that allows you to view detailed information about system and application errors, warnings, and other events that are recorded in the event log.
- System Restore: System Restore allows you to roll back your system to a previous state in order to undo any recent system changes that may be causing errors.
- Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool: The Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool is a built-in utility that can help you diagnose and repair memory-related problems.
- Disk Check Utility: The Disk Check utility can help you diagnose and repair hard drive errors.
- Microsoft Safety Scanner: The Microsoft Safety Scanner is a free tool that can help you detect and remove viruses, spyware, and other malicious software from your computer.
- SFC (System File Checker): SFC is a built-in utility that can help you scan and repair corrupted system files.
- Device Manager: Device Manager is a tool that can help you diagnose and fix hardware-related problems.
- Keep your Windows operating system up to date by regularly installing the latest updates.
- Scan your computer regularly with a reliable antivirus software to detect and remove any malicious software.
- Use a reliable registry cleaner to scan and repair any errors in the Windows registry.
- Run disk cleanup regularly to delete unnecessary files and free up disk space.
- Uninstall any programs that you no longer use to prevent conflicts and errors.
- Make sure your hardware drivers are up to date by downloading the latest versions from the manufacturer’s website.
- Avoid downloading and installing pirated software as it can contain malicious code that can cause errors.
- Disable any unnecessary startup programs as they can slow down your computer and cause errors.
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recommended For You
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Perspect Health Inf Manag
- v.10(Summer); Summer 2013
From Novice to Expert: Problem Solving in ICD-10-PCS Procedural Coding
Justin thomas rousse.
Justin Thomas Rousse, MFA, RHIA, is head of the Health Information Systems Department at the Prince Sultan Military College of Health Sciences in Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, a Visiting Professor in the College of Health Sciences for DeVry University Online, and a doctoral student in the Doctor of Health Sciences program at A.T. Still University in Mesa, AZ
The benefits of converting to ICD-10-CM/PCS have been well documented in recent years. One of the greatest challenges in the conversion, however, is how to train the workforce in the code sets. The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS) has been described as a language requiring higher-level reasoning skills because of the system's increased granularity. Training and problem-solving strategies required for correct procedural coding are unclear. The objective of this article is to propose that the acquisition of rule-based logic will need to be augmented with self-evaluative and critical thinking. Awareness of how this process works is helpful for established coders as well as for a new generation of coders who will master the complexities of the system.
Introduction
On August 24, 2012, the Department of Health and Human Services announced a new date for implementation of the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) and the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS). The former compliance date of October 1, 2013, was changed to October 1, 2014. The announcement appeared in the Federal Register on September 5, 2012, as a final rule of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS). 1 Consequently, the US healthcare industry has gained additional preparation time in which to address the financial, technological, and manpower issues that accompany migration to the new code sets.
Discussion over the past five years has centered on the potential benefits of ICD-10-CM/PCS. These benefits include improvements in measurement and delivery of healthcare services. Improvements in public health surveillance and international comparison of morbidity data are also foreseen, along with advancement in research due to a reduction in coding errors. Enhanced quality of care through the code sets’ increased specificity is another potential benefit. Furthermore, a reduction of healthcare costs is projected for the long term. 2 , 3
One key challenge of implementing ICD-10-CM/PCS is how to train the workforce. General articles on the structure and organization of ICD-10-CM/PCS have appeared in the Journal of AHIMA. Coding experts have delineated root operation guidelines for ICD-10-PCS. Chapter-specific guidelines have provided ICD-10-PCS coding instructions for fractures, spinal surgeries, injuries, and external causes of morbidity, as well as coding directives for the respiratory, nervous, and circulatory systems.
The problem-solving mechanisms inherent in complex ICD-10-PCS procedural coding have not been established despite robust coverage in the literature. In the present article, a psychological framework is used to differentiate novices from experts. Obstacles that might prevent a beginner from transitioning to an expert level of code construction are identified. A problem-solving model is presented, along with the steps that a coder might use in constructing ICD-10-PCS codes. Psychological theories and research support the concept that an individual must move away from rule-governed, entrenched thinking to become an expert. It is hypothesized that being an expert coder will involve critically evaluating one's choices as one moves through the code-building process.
Understanding thinking and problem-solving steps required to build procedural codes from clinical documentation may be helpful to established coders who must upgrade skills and to novices in the process of acquiring skills. ICD-10-PCS coding takes on added significance when seen in the light of psychological theories of cognition, which attempt to explain problem solving. Research studies have explored strategies that differentiate the novice from the expert. 4 , 5 , 6 Many studies suggest ways in which instructional methods may be designed to facilitate acquisition of new knowledge. 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 In the following literature review, the prevailing theories that illuminate learning and problem-solving activities are presented.
Thinking leads to many reference points in consciousness, including what we believe. Modern psychology, however, has focused on identifying the role that thinking plays in solving practical problems. 11
Furthermore, the type of thinking that applies to ICD-10-PCS procedural code construction may be linked to both vertical and convergent thinking. Vertical thinking proceeds in a linear, purposeful fashion from beginning to end, and is limited to a particular problem at hand. 12 The analogue of vertical thinking is convergent thinking, the type of analytic reasoning that facilitates the single best solution to a problem. 13
Reasoning aims at producing new behavior strategies based on former learning experiences. Problem solving involves a “systematic search through a range of possible actions in order to reach a predefined goal.” 14
ICD-10-PCS procedural coding meets the criteria for well-structured problems because of the logical nature of the code set. The coder has a clear solution path, that is, the coder is capable of readily identifying the steps required to reach a solution. Executing each step, however, is where the challenge lies.
The Transition
Transitioning to the ICD-10-PCS procedural code set will undoubtedly present challenges for all learners, regardless of what level of professional expertise they may have. Sternberg and Ben-Zeev identify four characteristics that distinguish the novice problem-solver from the expert problem-solver. 15 These characteristics are listed in Table Table1 1 .
Characteristics of Expert Problem-Solvers
Source: Sternberg, Robert J., and Talia Ben-Zeev. Complex Cognition: The Psychology of Human Thought. New York: Oxford University Press, 2001.
Sternberg, Robert J., and Talia Ben-Zeev. Complex Cognition, p. 156.
Daley has observed that novices rely on rules they have learned in their education because they have had little practical, real-world experience. 16 In addition, Daley identifies five stages of career development that most professionals pass through: from “novice” to “advanced beginner,” “competent,” “proficient,” and finally “expert.” 17
Researchers in nursing have conducted studies that compare the learning strategies of novices to experts. A common theme in two studies is the important role that critical thinking plays in attaining a state of professional expertise. 18 , 19
Daley used interviews and clinical narratives to compare the learning strategies of novice nurses to expert nurses. 20 The nurses were grouped by the number of years of professional experience they had achieved. Findings indicated that novices tended to describe their learning as a process of acquiring new information and then linking it to something they had previously seen, which is termed a “best-fit approach.” 21 They required outside validation and were basically other-directed. Conversely, the experts tended to rely on critical thinking and active assimilation of new knowledge that was essentially self-directed.
Similarly, Forneris and Peden-McAlpine found that critical thinking is more than simple mastery of domain knowledge—it involves broadening of perspectives. 22 Critical thinking can emerge as a result of using what Forneris and Peden-McAlpine term “contextual learning intervention,” which is described as an “intentional thinking process of understanding within context” of caregiving practices. 23 These authors advocate that reflective educational intervention be used as part of nursing education and professional development programs.
Problem-Solving Strategies
In Complex Cognition, Sternberg and Ben-Zeev place the issue of problem solving firmly within the context of daily life. 24 They illustrate various problem-solving strategies that individuals use. These strategies include searches through what the authors define as “problem space,” which comprises “symbolic structures” and “operators”—actions that begin with an input and produce an output—as well as the problem itself. 25 The problem is defined through a set of “initial states, a set of goal states, and a set of path constraints.” 26
Problem-solving strategies include the use of algorithms that lead to a correct response, although algorithms are exhaustive searches and often inefficient. Heuristics, which are prescribed aids to learning, are more commonly used approaches based on trial and error. Examples include the working-forward approach, in which a problem solver attempts to solve a problem from beginning to end, or the working-backward approach, which involves tackling the problem at the end and working back to the beginning. It has been noted that experts tend to favor the working-forward strategy, whereas novices usually select the working-backward approach when solving problems. 27
Means-end analysis is another example of a heuristic that attempts to reduce the distance between the conditions presented by the current problem and the desired end goal by selecting an action (operator). 28 When an obstacle surfaces before the goal is reached, the problem solver begins to tackle the obstacle, which becomes a subgoal. The subgoal temporarily becomes the new end goal. This procedure repeats itself. The end goal is not reached until all the subgoals have been attained. Sternberg and Ben-Zeev point out that individuals often use subgoaling in problem solving. However, because of its diversionary nature, subgoaling frequently delays attainment of the primary end goal. 29
Cognitive Load
White explained that cognitive load theory accounts for the limits of working memory. 30 Cognitive load involves transfer of new information in one's short-term memory to long-term memory. Management of cognitive load has important implications for both clinical instructors and students in clinical settings. Learning occurs whenever new information is linked to existing knowledge in long-term memory. A bottleneck develops, however, when the flow from short-term memory to long-term memory is disrupted. Extraneous cognitive load is caused by anything that diverts the learner's mental focus away from current problem solving. Poorly designed instructional materials and stress induced through the learning environment itself are two examples.
In the world of clinical coding, involvement of coding supervisors or of trainers approved by the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA) in providing a supportive, safe learning environment, especially for novice coders, is crucial. Setting realistic time frames for mastery of procedural coding is also important. Ideally, an AHIMA-approved trainer, that is, a proven expert in coding who has reached a level of greater autonomy, could be instrumental in reducing the cognitive load of novices. For example, White indicated that clinical instructors can support novice learners by explaining how the skill fits into the overall delivery of care, creating an image of a successful outcome, describing the process in detail, performing the skill simultaneously with the learner, and then allowing the learner to perform the skill on his or her own, providing coaching and feedback when appropriate. 31
Boekhout et al. concluded that less cognitive load is imposed on those who have prior knowledge of a task. Through studies with example-based learning in medical education, these authors discovered that second-year medical students required less time to study examples and did not have to invest as much mental effort as novices. 32 This finding raises a question in training ICD-10-PCS coders. Will coders with experience in ICD-9-CM coding make a smoother transition to the new code set?
From these studies, one may reasonably conclude that problem-solving activities occur on a continuous basis in daily life. Learning is circumscribed by conditions that either foster learning or impede it. Moreover, the theory of cognitive load plays a key role in defining how individuals are able to connect new learning with established knowledge structures. In addition, the learning strategies of novices versus experts can be differentiated, especially in clinical practice, where a well-developed awareness of problem solving and critical thinking is crucial.
Knowledge Acquisition
Identifying the knowledge domains that must be mastered in order to produce accurate procedural codes is important. ICD-10-PCS procedural coding may be viewed as “knowledge-rich,” a term used by psychologists to mean that a vast amount of specialized knowledge is necessary for good problem solving in an area. 33 Knowledge must be acquired in three domains:
- Domain 1: Foundational knowledge. An extensive medical vocabulary must be acquired in addition to in-depth understanding of the detailed body system subdivisions in ICD-10-PCS. Specific physiological effects will be relevant to certain procedures. General Equivalence Mappings (GEMs) may be used initially to select appropriate tables that match operations performed. 34 Examples of foundation courses include medical terminology, anatomy and physiology, pathophysiology, and mapping in GEMs.
- Domain 2: Conceptual knowledge. A solid grasp of the CMS coding guidelines will be essential for making root operation, body part, approach, device, and qualifier assignments. The coder will need to correlate the intent of the procedure with the root operation definitions. In time, familiarity with the tables will lead to bypassing the alphabetic index and going directly to the tables. A grasp of the body part key and device key will facilitate the selection of codes for body parts and devices, especially as new medical devices approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) appear on the market.
- Domain 3: Interpretative knowledge. The ability to translate clinical documentation into appropriate root operations will demand careful, detailed reading of operative reports. Furthermore, the coder will need to establish reasons for code construction choices as the reliance on reasoning and logic strengthens. The ability to evaluate and reflect on code construction choices will refine the coder's self-evaluation as the coder gains intensive practice in problem-solving methods. Lastly, critical thinking will develop in the coder's discernment, based on clinical documentation, of what was done and not done in the procedure. The coder will become capable of identifying documentation deficiencies and gaps, leading to communication with the provider through appropriate queries.
Computer-Assisted Coding
Computer-assisted coding (CAC) has been identified as a potential solution for healthcare organizations to minimize productivity losses and to augment the shortage of trained coders once ICD-10-CM/PCS is implemented in 2014. The sheer increase in the number of codes in ICD-10-PCS will demand that the coder devote more time to the selection process, thereby reducing productivity. Whereas ICD-9-CM contains only 4,000 procedural codes to consider, ICD-10-PCS has more than 72,000 procedural codes. 35
As natural language processing (NLP) used in CAC evolves and becomes more sophisticated, healthcare organizations may begin to view CAC as integral to the enterprise. The coder's future role has been identified as a high-level auditor of CAC-generated codes, eliminating the need for the coder to perform routine coding and instead requiring the coder to address more challenging operative scenarios. 36 , 37 Meanwhile, the cost of CAC software and the probability of contextual coding errors still remain relatively high. Manual coding will therefore continue to be the instructional norm in the early stages of ICD-10-PCS implementation and will involve prescribed aids to learning rather than exhaustive algorithmic searches as part of the code selection process.
Working through Problem Space
In the “problem space,” as described above, problem-solving actions are defined as “operators” that transform an input to an output. Solving the problem requires not just the operators themselves but an evaluation of the effectiveness of the operators. 38 For the coder, this process means evaluating all available options. An expert is one who can generate explanations for the steps taken while at the same time evaluating the actions that support these explanations. 39 This process is analogous to the type of deductive reasoning one might use in writing a geometric proof. Postulates and theorems would be used to support each step leading to the conclusion.
In means-end analysis, the individual envisions the goal and then works out the best method for reaching the end goal while minimizing the amount of time required to reach it. 40 In accomplishing this process, the coder is likely to encounter obstacles in working out each character of the ICD-10-PCS code.
For example, in defining the initial root operation, the subgoal becomes the act of differentiating the 31 definitions provided in the code set for the Medical/Surgical section. Once the initial step is resolved, determining the remaining four characters involves additional subgoals that must be attained. The remaining subgoals are identification of the correct characters for the body part, the approach, the device, and the qualifier.
Obstacles to Effective Coding
Several obstacles may be identified that could interfere with learning ICD-10-PCS procedural coding, among them entrenchment, extraneous cognitive load, the lack of well-designed instructional materials, and the prevalence of worked-out instructional examples. 41
Entrenchment
A coder experienced in ICD-9-CM coding may be immersed in habitual patterns of thinking not applicable to ICD-10-PCS. For example, Butler observed that many coders in ICD-9-CM use the procedures that appear in the operative report title as “authoritative” and do not delve into the body of the operative report itself. 42 In ICD-10-PCS, however, this entrenched way of approaching an operation will be untenable. Close reading of the operative details will be necessary to yield accurate surgical codes based on the standardized terminology of the root operations.
Extraneous Cognitive Load
In ICD-10-PCS procedural coding, the cognitive load may increase when the novice learner becomes enmeshed in a set of guidelines and has to decide which resources to devote to solving a given procedural problem or which guideline may be appropriately applied to a coding problem. In the case of a novice coder, a high productivity quota in the department or an organizational expectation that the coder will develop coding expertise within a short period of time (e.g., 50 days) could create undue stress and anxiety, leading to extraneous cognitive load.
Use of Instructional Materials and Learning Styles
The use of visual illustrations and narration as adjuncts to instructional media sometimes enhances learning; this enhancement is referred to as the “modality effect.” 43 The practice of using both visual aids and auditory materials may possibly deepen the amount of information stored in the working memory, which then results in improved learning outcomes. Although not all forms of multimedia instruction are effective, Doube, Tuovinen, and Shaffer state that learning interactivity is a “major advantage of multimedia learning materials for domains requiring procedural knowledge.” 44 Instructional materials in coding currently place more emphasis on narrative descriptions and analysis of coding scenarios without integration of multimedia.
Despite more than 30 years of research, no indisputable, empirical evidence exists that matching learner styles—visual, auditory, and kinesthetic—to instructional methods improves learning and attention. Moreover, even when taking into account individual differences, psychological research indicates that people do not learn differently. 45
Worked-out Examples
An algorithm may be helpful when illustrating a worked-out example for a given problem. 46 However, what happens when a novice tries to use a worked-out example to solve a similar but different problem, even though instructions may guide the coder through a different problem-solving pathway? When given a choice, most novices will opt to follow an example rather than read instructions, resulting in overgeneralization. Learning might be enhanced if negative examples are provided that demonstrate how an algorithm is no longer applicable.
Worked-out examples are equivalent to a “ready-made recipe people can follow without attention to underlying deep structure.” 47 An expert, on the other hand, relies on deep structural analysis of the problem.
Other studies have demonstrated that instructional materials that use worked-out examples are most effective when presenting an example immediately followed by a practice problem. This format should be followed throughout the material rather than placing a set of examples followed by practice problems at the end of the instructional unit. 48
Stages in Problem Solving
Problem solving is regarded as a cyclical rather than a linear process because solving one problem often segues into the next. Sternberg has identified seven stages in the problem-solving process: “Problem identification,” “Problem definition,” “Problem allocation,” “Problem representation,” “Strategy construction,” “Monitoring,” and “Evaluation.” 49 These stages are applicable when a coder attempts to construct an ICD-10-PCS code.
To illustrate, the following section demonstrates a step-by-step problem-solving application that uses subgoaling to construct ICD-10-PCS codes for the coding scenario shown in Table Table2. 2 . Although oversimplified, the seven steps illustrate how the novice coder may become more aware of the problem-solving process itself.
Coding Scenario: Operative Procedure
An established coder may have abstracted detailed concepts into higher-level schemas so that the process does not take the form of recognizable steps. The expert can then focus on the more challenging aspects of solving a problem because of the minimal cognitive load. 50
Problem-Solving Steps Applied to Coding Scenario
Problem identification.
The coder recognizes that an operative procedure must be assigned an ICD-10-PCS code or codes and prepares to read and analyze the operative report and inspect other relevant clinical documentation in the record.
Problem Definition
The coder determines the nature of the operation and defines the operative report as a description of a procedure performed on the female reproductive system.
Resource Allocation
The coder then recalls the nature and extent of resources available in assigning a root operation. The definitions of root operations are highly visible. The coder may decide how much time to devote to using other available resources, including CMS guidelines, to assign the procedure to a root operation. The coder may decide to draw on the expertise of a more experienced coder in the department or ask questions of the supervisor. Time allocation includes careful reading of the operative report, which in this case results in a root operation assignment of excision, which is defined as “cutting out or off, without replacement, a portion of a body part.” 51
Problem Representation
The coder forms a mental framework in the attempt to organize the domain knowledge needed to construct the remainder of the code. After deciding on the root operation, the coder then looks to the appropriate table. The coder recognizes the body part as the vulva and then looks up “excision of vulva” in the index, finding the first four characters: 0UBM.
Strategy Construction
The coder then must decide how to prioritize the resources available and will refer back to the coding guidelines and review the definitions of approach, device, and qualifier. In rereading the operative report, the coder must decide if the approach was open or external because these are the two fifth-character options in the table as the coder follows information across the row. The coder may recall coding guideline B5.3a. 52 According to this coding guideline, since the incision was made on the outside of an orifice that was visible without the use of instrumentation, the coder selects external as the approach. The code now becomes 0UBMX. The next character to be selected is the device. Since no device was left inside the patient and the only option is Z, the code becomes 0UBMXZ.
The coder next assesses whether the code construction is proceeding according to logic. The coder may be aware that there has to be a diagnostic qualifier other than Z since a biopsy of vulvar tissue was taken and sent to the pathology department. The coder selects X, diagnostic, as the seventh-character qualifier. This step completes the reasoning process that underpins the construction of the first code. The coder then goes back to the operative report and notes that another intent of the procedure was to drain the bladder through insertion of a Foley catheter. The coder selects the root operation of drainage, which is defined as “taking or letting out fluids and/or gases from a body part.” 53 The coder represents the problem by choosing 0T9. In the table, the coder selects B, the character for bladder, reasoning that the approach is 7 (via natural or artificial opening). The character 0 represents the drainage device that was left intact at the end of the procedure, and there is no qualifier. The completed code is thus 0T9B70Z.
The coder then evaluates whether the completed code constructions, 0UBMXZX and 0T9B70Z, are correct. The coder may use computer-assisted instruction, an algorithm, or a coding supervisor's feedback to verify the correctness of the codes. If feedback is delayed in this scenario or in more complex scenarios, the coder may have more time in which to reflect on the process and detect possible errors made in constructing the codes, thus enhancing evaluative and self-regulating skills. If feedback is delayed too long, however, it is possible that frustration will result, especially in the case of novice learners. 54
As the momentum toward ICD-10-CM/PCS compliance strengthens, healthcare organizations need to continue training coding professionals already in the workforce as well as those who have no previous coding experience. Because of its unique structure, ICD-10-PCS levels the playing field for all coding professionals, who must gain additional knowledge and experience before cresting the ICD-10-PCS learning curve.
Mapping and implementing educational strategies appropriate to the transitional phases of learning may be necessary. Choosing realistic training time frames that do not place the novice coder under stressful conditions will help reduce cognitive load and ensure that knowledge acquisition is sound. For example, novice coders may require weeks or months of training to master foundational knowledge before moving on to conceptual knowledge, that is, familiarity with the CMS coding guidelines. Immersion in root operations and clinical documentation may require additional time when rudimentary coding problems are introduced.
Moreover, a supervisor or AHIMA-approved trainer may be capable of reducing cognitive load through close guidance of group processes, along with support and encouragement. Carefully chosen examples from the Medical/Surgical division of ICD-10-PCS may be offered through multimedia instruction. Emphasis must be placed on reading all operative report details rather than relying on operative report titles. The trainer could model code construction to illustrate how specific worked-out examples do not apply to all cases. Complex code constructions might then be broken down into their component parts to clarify subgoaling in code selection.
As the novice coder becomes an advanced beginner, more complex coding problems may be introduced, with emphasis on rich resource allocation, such as the availability of the coding guidelines in various formats, including print, online, and interactive, and the supportive intervention of an AHIMA-approved trainer. The progress of the novice will need to be monitored closely until a rudimentary level of competency has been reached. Data gathered throughout the monitoring process may give rise to future research questions and hypotheses.
Once the novice has phased into a proficient stage and learning structures (schemas) have been firmly established through practice, less monitoring and instructor guidance will be required as the learner refines the problem-solving process. Critical thinking will evolve gradually as the coder gains expertise in navigating the ICD-10-PCS tables and in reasoning through the available code options. Subsequently, the expert coder will require less feedback as part of the evaluative stage of problem solving, in which critical thinking slowly emerges and the coder becomes self-directed. Becoming an expert coder in ICD-10-PCS will therefore entail not only a vast amount of foundational, conceptual, and interpretative knowledge but also a willingness to monitor one's reasoning as one proceeds through the problem-solving process itself.
After the implementation of ICD-10-PCS in 2014, research will be required to determine how novices and experts in ICD-10-PCS coding describe their own unique learning experiences. Findings from this research may serve as a new paradigm for clinical practice in the health information management profession.
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
Problem-Solution Speech [Topics, Outline, Examples]

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.

In this article:
Problem-Solution Outline
Problem-solution examples, criminal justice, environment, relationships, teen issues.
What to include in your problem-solution speech or essay?
Problem-solution papers employ a nonfiction text structure, and typically contain the following elements:
Introduction: Introduce the problem and explain why the audience should be concerned about it.
Cause/Effect : Inform the audience on what causes the problem. In some cases, you may also need to take time to dispel common misconceptions people have about the real cause.
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
Thesis Statement: The thesis typically lays out the problem and solution in the form of a question and answer. See examples below.
Solution : Explain the solution clearly and in detail, your problem-solving strategy, and reasons why your solution will work. In this section, be sure to answer common objections, such as “there is a better solution,” “your solution is too costly,” and “there are more important problems to solve.”
Call to Action: Summarize the problem and solution, and paint a picture of what will happen if your final solution is adopted. Also, let the reader know what steps they should take to help solve the problem.
These are the most used methods of developing and arranging:
Problem Solution Method Recommended if you have to argue that there is a social and current issue at stake and you have convince the listeners that you have the best solution. Introduce and provide background information to show what is wrong now.
List the best and ideal conditions and situations. Show the options. Analyze the proper criteria. And present your plan to solve the not wanted situation.
Problem Cause Solution Method Use this pattern for developing and identifying the source and its causes.
Analyze the causes and propose elucidations to the causes.
Problem Cause-Effect Method Use this method to outline the effects of the quandary and what causes it all. Prove the connection between financial, political, social causes and their effects.
Comparative Advantage Method Use this organizational public speaking pattern as recommendation in case everyone knows of the impasse and the different fixes and agrees that something has to be done.
Here are some examples of problems you could write about, with a couple of potential solutions for each one:
Marriage Problem: How do we reduce the divorce rate?
Solution 1: Change the laws to make it more difficult for couples to divorce.
Solution 2: Impose a mandatory waiting period on couples before they can get married.
Environmental Problem: What should we do to reduce the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
Solution 1: Use renewable energy to fuel your home and vehicles.
Solution 2: Make recycling within local communities mandatory.
Technical Problem: How do we reduce Windows error reporting issues on PCs?
Solution 1: Learn to use dialogue boxes and other command prompt functions to keep your computer system clean.
Solution 2: Disable error reporting by making changes to the registry.
Some of the best problems to write about are those you have personal experience with. Think about your own world; the town you live in, schools you’ve attended, sports you’ve played, places you’ve worked, etc. You may find that you love problem-solution papers if you write them on a topic you identify with. To get your creativity flowing, feel free to browse our comprehensive list of problem-solution essay and paper topics and see if you can find one that interests you.
Problem-Solution Topics for Essays and Papers
- How do we reduce murder rates in the inner cities?
- How do we stop police brutality?
- How do we prevent those who are innocent from receiving the death penalty?
- How do we deal with the problem of gun violence?
- How do we stop people from driving while intoxicated?
- How do we prevent people from texting while driving?
- How do we stop the growing child trafficking problem?
- What is the best way to deal with domestic violence?
- What is the best way to rehabilitate ex-cons?
- How do we deal with the problem of overcrowded prisons?
- How do we reduce binge drinking on college campuses?
- How do we prevent sexual assaults on college campuses?
- How do we make college tuition affordable?
- What can students do to get better grades in college?
- What is the best way for students to effectively balance their classes, studies, work, and social life?
- What is the best way for college students to deal with a problem roommate?
- How can college students overcome the problem of being homesick?
- How can college students manage their finances more effectively?
- What is the best way for college students to decide on a major?
- What should be done about the problem of massive student loan debts?
- How do we solve the global debt crisis?
- How do we keep countries from employing child labor?
- How do we reduce long-term unemployment?
- How do we stop businesses from exploiting consumers?
- How do we reduce inflation and bring down the cost of living?
- How do we reduce the home foreclosure rate?
- What should we do to discourage consumer debt?
- What is the best way to stimulate economic growth?
- How do we lower the prime cost of manufacturing raw materials?
- How can book retailers deal with rising bookseller inventory costs and stay competitive with online sellers?
- How do we prevent kids from cheating on exams?
- How do we reduce the illiteracy rate?
- How do we successfully integrate English as a Second Language (ESL) students into public schools?
- How do we put an end to the problem of bullying in schools?
- How do we effectively teach students life management skills?
- How do we give everyone access to a quality education?
- How do we develop a system to increase pay for good teachers and get rid of bad ones?
- How do we teach kids to problem solve?
- How should schools deal with the problem of disruptive students?
- What can schools do to improve reading comprehension on standardized test scores?
- What is the best way to teach sex education in public schools?
- How do we teach students to recognize a noun clause?
- How do we teach students the difference between average speed and average velocity?
- How do we teach math students to use sign charts?
- How can we make public education more like the Webspiration Classroom?
- How do we stop pollution in major population centers?
- How do we reduce the negative effects of climate change?
- How do we encourage homeowners to lower their room temperature in the winter to reduce energy consumption?
- What is the best way to preserve our precious natural resources?
- How do we reduce our dependence on fossil fuels?
- What is the best way to preserve the endangered wildlife?
- What is the best way to ensure environmental justice?
- How can we reduce the use of plastic?
- How do we make alternative energy affordable?
- How do we develop a sustainable transportation system?
- How can we provide quality health care to all our citizens?
- How do we incentivize people to stop smoking?
- How do we address the growing doctor shortage?
- How do we curb the growing obesity epidemic?
- How do we reduce dependence on prescription drugs?
- How do we reduce consumption of harmful substances like phosphoric acid and acetic acid?
- How can we reduce the number of fatal hospital errors?
- How do we handle the health costs of people living longer?
- How can we encourage people to live healthier lifestyles?
- How do we educate consumers on the risk of laxatives like magnesium hydroxide?
- How do we end political corruption?
- How do we address the problem of election fraud?
- What is the best way to deal with rogue nations that threaten our survival?
- What can our leaders do to bring about world peace?
- How do we encourage students to become more active in the political process?
- What can be done to encourage bipartisanship?
- How can we prevent terrorism?
- How do we protect individual privacy while keeping the country safe?
- How can we encourage better candidates to run for office?
- How do we force politicians to live by the rules they impose on everyone else?
- What is the best way to get out of a bad relationship?
- How do we prevent cyberbullying?
- What is the best solution for depression?
- How do you find out where you stand in a relationship?
- What is the best way to help people who make bad life choices?
- How can we learn to relate to people of different races and cultures?
- How do we discourage humans from using robots as a substitute for relationships?
- What is the best way to deal with a long-distance relationship?
- How do we eliminate stereotypical thinking in relationships?
- How do you successfully navigate the situation of dating a co-worker?
- How do we deal with America’s growing drug problem?
- How do we reduce food waste in restaurants?
- How do we stop race and gender discrimination?
- How do we stop animal cruelty?
- How do we ensure that all citizens earn a livable wage?
- How do we end sexual harassment in the workplace?
- How do we deal with the water scarcity problem?
- How do we effectively control the world’s population?
- How can we put an end to homelessness?
- How do we solve the world hunger crisis?
- How do we address the shortage of parking spaces in downtown areas?
- How can our cities be made more bike- and pedestrian-friendly?
- How do we balance the right of free speech and the right not to be abused?
- How can we encourage people to use public transportation?
- How do we bring neighborhoods closer together?
- How can we eliminate steroid use in sports?
- How do we protect players from serious injuries?
- What is the best way to motivate young athletes?
- What can be done to drive interest in local sports?
- How do players successfully prepare for a big game or match?
- How should the revenue from professional sports be divided between owners and players?
- What can be done to improve local sports venues?
- What can be done to ensure parents and coaches are not pushing kids too hard in sports?
- How can student athletes maintain high academic standards while playing sports?
- What can athletes do to stay in shape during the off-season?
- How do we reduce teen pregnancy?
- How do we deal with the problem of teen suicide?
- How do we keep teens from dropping out of high school?
- How do we train teens to be safer drivers?
- How do we prevent teens from accessing pornography on the Internet?
- What is the best way to help teens with divorced parents?
- How do we discourage teens from playing violent video games?
- How should parents handle their teens’ cell phone and social media use?
- How do we prepare teens to be better workers?
- How do we provide a rational decision-making model for teens?
- How do we keep companies from mining our private data online and selling it for profit?
- How do we prevent artificial intelligence robots from taking over society?
- How do we make high-speed internet accessible in rural areas?
- How do we stop hackers from breaking into our systems and networks?
- How do we make digital payments more secure?
- How do we make self-driving vehicles safer?
- What is the best way to improve the battery life of mobile devices?
- How can we store energy gleaned from solar and wind power?
- What is the best way to deal with information overload?
- How do we stop computer makers from pre-installing Internet Explorer?
Compare and Contrast Speech [Topics and Examples]
Proposal Speech [Tips + 10 Examples]
1 thought on “Problem-Solution Speech [Topics, Outline, Examples]”
This is very greatfull Thank u I can start doing my essay
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class
Rethinking Industrial PCs for Industry 4.0

Artificial intelligence (AI) and analytics are transforming manufacturing, ushering in Industry 4.0. Already valued at $1.1 billion, the industrial AI market is expected to reach $16.7 billion by 2026 , according to research firm Markets and Markets.
While there’s enormous potential for the technology, there’s also a challenge. Current industrial infrastructure wasn’t built to provide the flexibility necessary to unlock Industry 4.0’s potential. Workloads are traditionally run on siloed devices that can’t store and analyze data.
“Every big innovation or transformation that’s happened in the past couple of hundred years has had a foundational device that enabled it to occur,” says Adam Berniger, Senior Segment Manager for Industrial PCs (lPCs) for the Intel ® IoT Group. “For example, it’s been the steam engine, the personal computer, or the smartphone. The pathway technology that’s driving Industry 4.0 is the industrial PC.”
The modern industrial PC brings together IT and operational technology (OT) to analyze volumes of edge data that can be collected from factory machines and turned into business intelligence. To facilitate the digital transformation, manufacturers are turning to systems integrators (SIs) to be the experts who help them tap into the valuable information on the factory floor.
Industrial PCs: The Vital Connectors
This represents a major opportunity for SIs. “The edge is growing in strength and value,” says Berniger. “There are three emerging themes that center around the edge: intelligence at the edge, convergence of the edge, and connection to the edge.”
Intelligence at the edge includes analytics, insights, and AI. “It can drive smartness closer to where things are done in a factory,” says Berniger. “Use cases can include predictive maintenance and analysis, improving operational effectiveness, and boosting productivity.”
How can SIs succeed in Industry 4.0? For @axiomtek, Industrial PCs are the key. via @insightdottech
Convergence of the edge encompasses OT and IT best practices, processes, devices, functions, and applications. Connection to the edge means connecting unconnected devices both to one another and to the cloud.
Berniger likens the potential of the industrial PC to the smartphone. “Five or 10 years ago, if we were going on a trip, we had a ‘dumb’ phone for making calls or sending text messages,” he explains. “We had a camera to take pictures, and we had to print off a map to know where we were going. We had multiple devices for separate functions, but today all of those things are converged onto a phone. The industrial PC is going to be like the smartphone, and you’ll have an app store where you can download hardware and software for many different functions.”
SIs Can Lead Factories to Industry 4.0
SIs have an opportunity to be at the forefront of the transformation, and to bring the industry into the future by providing integrated systems using industrial PCs from Intel ® partners, such as Axiomtek .
A good place for SIs to start is by providing solutions that maximize the investment, such as reducing waste, enhancing product quality, or improving factory equipment uptime. “SIs have to make sure that there’s a clear ROI, a path to make the solution cost-effective. They also need to focus on operational metrics, and verify cybersecurity so companies know they’re not opening themselves up to risk,” says Berniger. “Critical projects often involve optimizing production by improving maintenance or quality assurance.”
For example, while Industry 3.0 dictated a set maintenance schedule, such as replacing parts A, B, and C after a set amount of time, Industry 4.0 uses predictive maintenance. By connecting machine parts to edge technology for real-time intelligence, factories can avoid potential production shutdowns.
The latest generation of industrial PCs enables this approach by supporting new levels of intelligence and connectivity. For example, the IPC964-512-FL can be outfitted with an AI card to supplement the on-board Intel ® Core ™ processor ( Figure 1 ).
Another smart solution SIs can provide for industrial PCs is better quality control, enabled by connecting cameras that can replace human eyes for visual inspections. A well-known tire manufacturer, for example, was experiencing an increase in customer complaints from defective tires. Not only was the company’s reputation suffering; it was incurring rising labor and transportation costs from the return of defective tires, cutting into the bottom line.
The company deployed a solution using computer vision and AI, optimized by the Intel ® Distribution of OpenVINO ™ toolkit and running on an IPC based on Intel technology. In just six months, tire returns dropped from 6,000 to a few dozen. Since the solution is highly scalable, the manufacturer has deployed it to additional production lines for inspection tasks.
“Human eyes are not made to look at the same object for eight hours a day, five days a week,” says Berniger. “But a camera connected to an IPC is very good at that ( Video 1 ). When it’s deployed, we see detection rates going from 80 percent to 99.9 percent, with very few false positives. And the speed increases, in some cases cutting inspection time from a minute down to one to five seconds, depending on the job. Machine vision can detect defects and improve quality assurance for everything a factory makes or ships, helping it save money. Waste is very costly.”
IPCs Bring SIs into the Future, Too
Industrial PCs not only bring manufacturing into the future, they also keep SIs relevant. Gone are the days when SIs could simply bank on having a specific set of capabilities, says Berniger.
“You need to differentiate yourself and add value,” he says. “My boss likens it to two body shops. They may have different levels of craftsmanship, but at the end of the day they both fix the scratch on your car. But if one body shop starts offering value-added activities and solutions, they’re no longer just a body shop; they’re an automobile expert.”
SIs who embrace the capabilities of industrial PCs become the experts that manufacturers need, meeting customers where they are, expanding their capabilities, and becoming their expert guides to Industry 4.0.
What to know about the crisis of violence, politics and hunger engulfing Haiti

A long-simmering crisis over Haiti’s ability to govern itself, particularly after a series of natural disasters and an increasingly dire humanitarian emergency, has come to a head in the Caribbean nation, as its de facto president remains stranded in Puerto Rico and its people starve and live in fear of rampant violence.
The chaos engulfing the country has been bubbling for more than a year, only for it to spill over on the global stage on Monday night, as Haiti’s unpopular prime minister, Ariel Henry, agreed to resign once a transitional government is brokered by other Caribbean nations and parties, including the U.S.
But the very idea of a transitional government brokered not by Haitians but by outsiders is one of the main reasons Haiti, a nation of 11 million, is on the brink, according to humanitarian workers and residents who have called for Haitian-led solutions.
“What we’re seeing in Haiti has been building since the 2010 earthquake,” said Greg Beckett, an associate professor of anthropology at Western University in Canada.

What is happening in Haiti and why?
In the power vacuum that followed the assassination of democratically elected President Jovenel Moïse in 2021, Henry, who was prime minister under Moïse, assumed power, with the support of several nations, including the U.S.
When Haiti failed to hold elections multiple times — Henry said it was due to logistical problems or violence — protests rang out against him. By the time Henry announced last year that elections would be postponed again, to 2025, armed groups that were already active in Port-au-Prince, the capital, dialed up the violence.
Even before Moïse’s assassination, these militias and armed groups existed alongside politicians who used them to do their bidding, including everything from intimidating the opposition to collecting votes . With the dwindling of the country’s elected officials, though, many of these rebel forces have engaged in excessively violent acts, and have taken control of at least 80% of the capital, according to a United Nations estimate.
Those groups, which include paramilitary and former police officers who pose as community leaders, have been responsible for the increase in killings, kidnappings and rapes since Moïse’s death, according to the Uppsala Conflict Data Program at Uppsala University in Sweden. According to a report from the U.N . released in January, more than 8,400 people were killed, injured or kidnapped in 2023, an increase of 122% increase from 2022.
“January and February have been the most violent months in the recent crisis, with thousands of people killed, or injured, or raped,” Beckett said.

Armed groups who had been calling for Henry’s resignation have already attacked airports, police stations, sea ports, the Central Bank and the country’s national soccer stadium. The situation reached critical mass earlier this month when the country’s two main prisons were raided , leading to the escape of about 4,000 prisoners. The beleaguered government called a 72-hour state of emergency, including a night-time curfew — but its authority had evaporated by then.
Aside from human-made catastrophes, Haiti still has not fully recovered from the devastating earthquake in 2010 that killed about 220,000 people and left 1.5 million homeless, many of them living in poorly built and exposed housing. More earthquakes, hurricanes and floods have followed, exacerbating efforts to rebuild infrastructure and a sense of national unity.
Since the earthquake, “there have been groups in Haiti trying to control that reconstruction process and the funding, the billions of dollars coming into the country to rebuild it,” said Beckett, who specializes in the Caribbean, particularly Haiti.
Beckett said that control initially came from politicians and subsequently from armed groups supported by those politicians. Political “parties that controlled the government used the government for corruption to steal that money. We’re seeing the fallout from that.”

Many armed groups have formed in recent years claiming to be community groups carrying out essential work in underprivileged neighborhoods, but they have instead been accused of violence, even murder . One of the two main groups, G-9, is led by a former elite police officer, Jimmy Chérizier — also known as “Barbecue” — who has become the public face of the unrest and claimed credit for various attacks on public institutions. He has openly called for Henry to step down and called his campaign an “armed revolution.”
But caught in the crossfire are the residents of Haiti. In just one week, 15,000 people have been displaced from Port-au-Prince, according to a U.N. estimate. But people have been trying to flee the capital for well over a year, with one woman telling NBC News that she is currently hiding in a church with her three children and another family with eight children. The U.N. said about 160,000 people have left Port-au-Prince because of the swell of violence in the last several months.
Deep poverty and famine are also a serious danger. Gangs have cut off access to the country’s largest port, Autorité Portuaire Nationale, and food could soon become scarce.
Haiti's uncertain future
A new transitional government may dismay the Haitians and their supporters who call for Haitian-led solutions to the crisis.
But the creation of such a government would come after years of democratic disruption and the crumbling of Haiti’s political leadership. The country hasn’t held an election in eight years.
Haitian advocates and scholars like Jemima Pierre, a professor at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, say foreign intervention, including from the U.S., is partially to blame for Haiti’s turmoil. The U.S. has routinely sent thousands of troops to Haiti , intervened in its government and supported unpopular leaders like Henry.
“What you have over the last 20 years is the consistent dismantling of the Haitian state,” Pierre said. “What intervention means for Haiti, what it has always meant, is death and destruction.”

In fact, the country’s situation was so dire that Henry was forced to travel abroad in the hope of securing a U.N. peacekeeping deal. He went to Kenya, which agreed to send 1,000 troops to coordinate an East African and U.N.-backed alliance to help restore order in Haiti, but the plan is now on hold . Kenya agreed last October to send a U.N.-sanctioned security force to Haiti, but Kenya’s courts decided it was unconstitutional. The result has been Haiti fending for itself.
“A force like Kenya, they don’t speak Kreyòl, they don’t speak French,” Pierre said. “The Kenyan police are known for human rights abuses . So what does it tell us as Haitians that the only thing that you see that we deserve are not schools, not reparations for the cholera the U.N. brought , but more military with the mandate to use all kinds of force on our population? That is unacceptable.”
Henry was forced to announce his planned resignation from Puerto Rico, as threats of violence — and armed groups taking over the airports — have prevented him from returning to his country.

Now that Henry is to stand down, it is far from clear what the armed groups will do or demand next, aside from the right to govern.
“It’s the Haitian people who know what they’re going through. It’s the Haitian people who are going to take destiny into their own hands. Haitian people will choose who will govern them,” Chérizier said recently, according to The Associated Press .
Haitians and their supporters have put forth their own solutions over the years, holding that foreign intervention routinely ignores the voices and desires of Haitians.
In 2021, both Haitian and non-Haitian church leaders, women’s rights groups, lawyers, humanitarian workers, the Voodoo Sector and more created the Commission to Search for a Haitian Solution to the Crisis . The commission has proposed the “ Montana Accord ,” outlining a two-year interim government with oversight committees tasked with restoring order, eradicating corruption and establishing fair elections.
For more from NBC BLK, sign up for our weekly newsletter .
CORRECTION (March 15, 2024, 9:58 a.m. ET): An earlier version of this article misstated which university Jemima Pierre is affiliated with. She is a professor at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, not the University of California, Los Angeles, (or Columbia University, as an earlier correction misstated).
Patrick Smith is a London-based editor and reporter for NBC News Digital.
Char Adams is a reporter for NBC BLK who writes about race.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This PCS (Problem, Consequence, Solution) roadmap will help you improve patient communication and increase case acceptance. ... but the goal is to identify the underlying cause so we can prevent it from happening again. We've found utilizing a consult to review this information is much more effective than trying to review during a recall exam ...
The problem-cause-solution proposal is a three-pronged speech pattern. The speaker starts by explaining the problem the speaker sees. The speaker then explains what he or she sees as the underlying causes of the problem. Lastly, the speaker proposes a solution to the problem that corrects the underlying causes.
Method 2: Uninstall USB Port Driver. Uninstalling the driver of the USB port will prompt Windows to reinstall it upon restarting your PC, potentially fixing the issue. Here's how to do it: Press Windows + R keys and enter devmgmt.msc in the Run dialog to open the Device Manager.
Soldiers and Families can download free apps to assist with the PCS process: Digital Garrison, Army PCS Move, and PCS My POV. A hotline was established to provide further assistance: 833-MIL-MOVE ...
The problem-cause-solution approach will first describe the problem, then analyze the cause or responses to the problem, and then will lead to a solution. We practice this approach daily in our interactions with others, whether at work or home. Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783. This work is licensed under a ...
Problem, Cause, Solution (PCS) is a logical problem solving technique that does solve problems to root cause. The tool is so effective it will define multiple root causes where they exist - common for complex, recurring problems. Our process enables a common problem solving language to be used throughout your business which aids communication ...
5 Steps. •. • Need: demonstrate the problem and a need for change. • Satisfaction: provide a solution. •. for complex problems described by topic. Visualization: use vivid imagery to show the benefits of the solution. • Action: tell the audience to take action. Attention: gain attention of your audience.
Learning Objectives. Differentiate among the common speech organizational patterns: categorical/topical, comparison/contrast, spatial, chronological, biographical, causal, problem-cause-solution, and psychological. Understand how to choose the best organizational pattern, or combination of patterns, for a specific speech.
The Problem Cause Solution database (PCS) is the primary diagnostic knowledge / experience database for Service and Manufacturing Engineers to consult in the case of equipment and performance issues, both at the customer site, at the local office and in Veldhoven. It displays relevant information (i.e. problem, symptom, cause and solution ...
This will cause overall lagging. CPU-dependent software can lead to bottlenecking too. That means the demands of the game far outpace the capabilities of the processor unit. Other types of demanding software, like 3D modeling and video editing programs, could cause bottlenecking too. Fixing CPU bottlenecking is easy.
Free Wise will scan your Registry, find the problems, and exterminate them, leaving your Registry obstruction free. The dreaded virus. Yes, malware is a significant cause of blue screens. But ...
3. Peripherals Not Working. 4. Audio Issues. 5. Blue Screens. Whether you are designing rockets or grooming poodles, you will most likely work with a PC daily. Like any piece of technology, there are going to be issues eventually. Recognizing and addressing these problems as quickly as possible is the key to maximizing efficiency and reducing ...
Overheating is a significant cause of hardware problems. Ensure your PC has proper ventilation and is placed in a well-ventilated area. Consider adding additional cooling solutions, such as case fans or liquid cooling systems, if you engage in resource-intensive tasks like gaming or video editing. Install Reliable Antivirus Software:
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Set Up MP 1: The problem is gun-free zones do not offer more protection that non-gun free zones MP 2: MP 3:, In the P-C-S organizational pattern, main point two and main point three must be clear, succinct and allow for expounding., Set Up MP 3: The solution is to use hw in public K-12 schools by implementing and effective hw ...
If you have colleagues or friends who could benefit from this information, please share the posts. « Troubleshooting Step 1: Identify The Problem. Troubleshooting Step 3 - Test Theory to Determine Cause ». The second step of network troubleshooting is establishing a theory of probable cause. Read about using your tools for this step.
1.3 Most Common Causes for a PC Crash PCs crash for many common reasons and with the right amount of patience and know-how these types of crashes are easy to fix. ... This is commonplace for PC troubleshooting, so searching for the solution to a problem with the added solved tag will lead to better results. We Wish You a Safe Flight with Windows
There can be various causes for such errors. These can be viruses; eventually they begin infecting all programs, settings and other system locations, and even cause RAM blocks to break down. If a user installed drivers which begin to conflict in the end, some system components cease to work properly.
The International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-PCS) has been described as a language requiring higher-level reasoning skills because of the system's increased granularity. Training and problem-solving strategies required for correct procedural coding are unclear.
The eight disciplines (8D) model is a problem solving approach typically employed by quality engineers or other professionals, and is most commonly used by the automotive industry but has also been successfully applied in healthcare, retail, finance, government, and manufacturing. The purpose of the 8D methodology is to identify, correct, and ...
resolve the problem and implement the solution. Sometimes quick procedures can determine the exact cause of the problem or even correct the problem. If a quick procedure does not correct the problem, further research is needed to establish the exact cause. Divide larger problems into smaller problems that can be analyzed and solved individually.
Thesis Statement: The thesis typically lays out the problem and solution in the form of a question and answer. See examples below. Solution: Explain the solution clearly and in detail, your problem-solving strategy, and reasons why your solution will work.In this section, be sure to answer common objections, such as "there is a better solution," "your solution is too costly," and ...
Figure 1. A robotic arm is connected to edge technology that detects deviations and predicts the need for repairs before problems cause downtime. (Source: Axiomtek) Another smart solution SIs can provide for industrial PCs is better quality control, enabled by connecting cameras that can replace human eyes for visual inspections.
CMST 220. Step 1: Read the following statements. MP 1: The problem is members of Congress continue to vote against allowing women to register for selective service. MP 2: There are two main reasons why members of Congress vote against allowing women to register for selective service. MP 3: The solution, which is to change the law to allow women ...
Chaos has gutted Port-au-Prince and Haiti's government, a crisis brought on by decades of political disruption, a series of natural disasters and a power vacuum left by the president's assassination.