- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →

Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Why Problem-Solving Skills Are Essential for Leaders in Any Industry

- 17 Jan 2023
Any organization offering a product or service is in the business of solving problems.
Whether providing medical care to address health issues or quick convenience to those hungry for dinner, a business’s purpose is to satisfy customer needs .
In addition to solving customers’ problems, you’ll undoubtedly encounter challenges within your organization as it evolves to meet customer needs. You’re likely to experience growing pains in the form of missed targets, unattained goals, and team disagreements.
Yet, the ubiquity of problems doesn’t have to be discouraging; with the right frameworks and tools, you can build the skills to solve consumers' and your organization’s most challenging issues.
Here’s a primer on problem-solving in business, why it’s important, the skills you need, and how to build them.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Problem-Solving in Business?
Problem-solving is the process of systematically removing barriers that prevent you or others from reaching goals.
Your business removes obstacles in customers’ lives through its products or services, just as you can remove obstacles that keep your team from achieving business goals.
Design Thinking
Design thinking , as described by Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar in the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , is a human-centered , solutions-based approach to problem-solving and innovation. Originally created for product design, design thinking’s use case has evolved . It’s now used to solve internal business problems, too.
The design thinking process has four stages :

- Clarify: Clarify a problem through research and feedback from those impacted.
- Ideate: Armed with new insights, generate as many solutions as possible.
- Develop: Combine and cull your ideas into a short list of viable, feasible, and desirable options before building prototypes (if making physical products) and creating a plan of action (if solving an intangible problem).
- Implement: Execute the strongest idea, ensuring clear communication with all stakeholders about its potential value and deliberate reasoning.
Using this framework, you can generate innovative ideas that wouldn’t have surfaced otherwise.
Creative Problem-Solving
Another, less structured approach to challenges is creative problem-solving , which employs a series of exercises to explore open-ended solutions and develop new perspectives. This is especially useful when a problem’s root cause has yet to be defined.
You can use creative problem-solving tools in design thinking’s “ideate” stage, which include:
- Brainstorming: Instruct everyone to develop as many ideas as possible in an allotted time frame without passing judgment.
- Divergent thinking exercises: Rather than arriving at the same conclusion (convergent thinking), instruct everyone to come up with a unique idea for a given prompt (divergent thinking). This type of exercise helps avoid the tendency to agree with others’ ideas without considering alternatives.
- Alternate worlds: Ask your team to consider how various personas would manage the problem. For instance, how would a pilot approach it? What about a young child? What about a seasoned engineer?
It can be tempting to fall back on how problems have been solved before, especially if they worked well. However, if you’re striving for innovation, relying on existing systems can stunt your company’s growth.
Related: How to Be a More Creative Problem-Solver at Work: 8 Tips
Why Is Problem-Solving Important for Leaders?
While obstacles’ specifics vary between industries, strong problem-solving skills are crucial for leaders in any field.
Whether building a new product or dealing with internal issues, you’re bound to come up against challenges. Having frameworks and tools at your disposal when they arise can turn issues into opportunities.
As a leader, it’s rarely your responsibility to solve a problem single-handedly, so it’s crucial to know how to empower employees to work together to find the best solution.
Your job is to guide them through each step of the framework and set the parameters and prompts within which they can be creative. Then, you can develop a list of ideas together, test the best ones, and implement the chosen solution.
Related: 5 Design Thinking Skills for Business Professionals
4 Problem-Solving Skills All Leaders Need
1. problem framing.
One key skill for any leader is framing problems in a way that makes sense for their organization. Problem framing is defined in Design Thinking and Innovation as determining the scope, context, and perspective of the problem you’re trying to solve.
“Before you begin to generate solutions for your problem, you must always think hard about how you’re going to frame that problem,” Datar says in the course.
For instance, imagine you work for a company that sells children’s sneakers, and sales have plummeted. When framing the problem, consider:
- What is the children’s sneaker market like right now?
- Should we improve the quality of our sneakers?
- Should we assess all children’s footwear?
- Is this a marketing issue for children’s sneakers specifically?
- Is this a bigger issue that impacts how we should market or produce all footwear?
While there’s no one right way to frame a problem, how you do can impact the solutions you generate. It’s imperative to accurately frame problems to align with organizational priorities and ensure your team generates useful ideas for your firm.
To solve a problem, you need to empathize with those impacted by it. Empathy is the ability to understand others’ emotions and experiences. While many believe empathy is a fixed trait, it’s a skill you can strengthen through practice.
When confronted with a problem, consider whom it impacts. Returning to the children’s sneaker example, think of who’s affected:
- Your organization’s employees, because sales are down
- The customers who typically buy your sneakers
- The children who typically wear your sneakers
Empathy is required to get to the problem’s root and consider each group’s perspective. Assuming someone’s perspective often isn’t accurate, so the best way to get that information is by collecting user feedback.
For instance, if you asked customers who typically buy your children’s sneakers why they’ve stopped, they could say, “A new brand of children’s sneakers came onto the market that have soles with more traction. I want my child to be as safe as possible, so I bought those instead.”
When someone shares their feelings and experiences, you have an opportunity to empathize with them. This can yield solutions to their problem that directly address its root and shows you care. In this case, you may design a new line of children’s sneakers with extremely grippy soles for added safety, knowing that’s what your customers care most about.
Related: 3 Effective Methods for Assessing Customer Needs
3. Breaking Cognitive Fixedness
Cognitive fixedness is a state of mind in which you examine situations through the lens of past experiences. This locks you into one mindset rather than allowing you to consider alternative possibilities.
For instance, your cognitive fixedness may make you think rubber is the only material for sneaker treads. What else could you use? Is there a grippier alternative you haven’t considered?
Problem-solving is all about overcoming cognitive fixedness. You not only need to foster this skill in yourself but among your team.
4. Creating a Psychologically Safe Environment
As a leader, it’s your job to create an environment conducive to problem-solving. In a psychologically safe environment, all team members feel comfortable bringing ideas to the table, which are likely influenced by their personal opinions and experiences.
If employees are penalized for “bad” ideas or chastised for questioning long-held procedures and systems, innovation has no place to take root.
By employing the design thinking framework and creative problem-solving exercises, you can foster a setting in which your team feels comfortable sharing ideas and new, innovative solutions can grow.

How to Build Problem-Solving Skills
The most obvious answer to how to build your problem-solving skills is perhaps the most intimidating: You must practice.
Again and again, you’ll encounter challenges, use creative problem-solving tools and design thinking frameworks, and assess results to learn what to do differently next time.
While most of your practice will occur within your organization, you can learn in a lower-stakes setting by taking an online course, such as Design Thinking and Innovation . Datar guides you through each tool and framework, presenting real-world business examples to help you envision how you would approach the same types of problems in your organization.
Are you interested in uncovering innovative solutions for your organization’s business problems? Explore Design Thinking and Innovation —one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses —to learn how to leverage proven frameworks and tools to solve challenges. Not sure which course is right for you? Download our free flowchart .

About the Author
39 Best Problem-Solving Examples

Problem-solving is a process where you’re tasked with identifying an issue and coming up with the most practical and effective solution.
This indispensable skill is necessary in several aspects of life, from personal relationships to education to business decisions.
Problem-solving aptitude boosts rational thinking, creativity, and the ability to cooperate with others. It’s also considered essential in 21st Century workplaces.
If explaining your problem-solving skills in an interview, remember that the employer is trying to determine your ability to handle difficulties. Focus on explaining exactly how you solve problems, including by introducing your thoughts on some of the following frameworks and how you’ve applied them in the past.
Problem-Solving Examples
1. divergent thinking.
Divergent thinking refers to the process of coming up with multiple different answers to a single problem. It’s the opposite of convergent thinking, which would involve coming up with a singular answer .
The benefit of a divergent thinking approach is that it can help us achieve blue skies thinking – it lets us generate several possible solutions that we can then critique and analyze .
In the realm of problem-solving, divergent thinking acts as the initial spark. You’re working to create an array of potential solutions, even those that seem outwardly unrelated or unconventional, to get your brain turning and unlock out-of-the-box ideas.
This process paves the way for the decision-making stage, where the most promising ideas are selected and refined.
Go Deeper: Divervent Thinking Examples
2. Convergent Thinking
Next comes convergent thinking, the process of narrowing down multiple possibilities to arrive at a single solution.
This involves using your analytical skills to identify the best, most practical, or most economical solution from the pool of ideas that you generated in the divergent thinking stage.
In a way, convergent thinking shapes the “roadmap” to solve a problem after divergent thinking has supplied the “destinations.”
Have a think about which of these problem-solving skills you’re more adept at: divergent or convergent thinking?
Go Deeper: Convergent Thinking Examples
3. Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a group activity designed to generate a multitude of ideas regarding a specific problem. It’s divergent thinking as a group , which helps unlock even more possibilities.
A typical brainstorming session involves uninhibited and spontaneous ideation, encouraging participants to voice any possible solutions, no matter how unconventional they might appear.
It’s important in a brainstorming session to suspend judgment and be as inclusive as possible, allowing all participants to get involved.
By widening the scope of potential solutions, brainstorming allows better problem definition, more creative solutions, and helps to avoid thinking “traps” that might limit your perspective.
Go Deeper: Brainstorming Examples
4. Thinking Outside the Box
The concept of “thinking outside the box” encourages a shift in perspective, urging you to approach problems from an entirely new angle.
Rather than sticking to traditional methods and processes, it involves breaking away from conventional norms to cultivate unique solutions.
In problem-solving, this mindset can bypass established hurdles and bring you to fresh ideas that might otherwise remain undiscovered.
Think of it as going off the beaten track when regular routes present roadblocks to effective resolution.
5. Case Study Analysis
Analyzing case studies involves a detailed examination of real-life situations that bear relevance to the current problem at hand.
For example, if you’re facing a problem, you could go to another environment that has faced a similar problem and examine how they solved it. You’d then bring the insights from that case study back to your own problem.
This approach provides a practical backdrop against which theories and assumptions can be tested, offering valuable insights into how similar problems have been approached and resolved in the past.
See a Broader Range of Analysis Examples Here
6. Action Research
Action research involves a repetitive process of identifying a problem, formulating a plan to address it, implementing the plan, and then analyzing the results. It’s common in educational research contexts.
The objective is to promote continuous learning and improvement through reflection and action. You conduct research into your problem, attempt to apply a solution, then assess how well the solution worked. This becomes an iterative process of continual improvement over time.
For problem-solving, this method offers a way to test solutions in real-time and allows for changes and refinements along the way, based on feedback or observed outcomes. It’s a form of active problem-solving that integrates lessons learned into the next cycle of action.
Go Deeper: Action Research Examples
7. Information Gathering
Fundamental to solving any problem is the process of information gathering.
This involves collecting relevant data , facts, and details about the issue at hand, significantly aiding in the understanding and conceptualization of the problem.
In problem-solving, information gathering underpins every decision you make.
This process ensures your actions are based on concrete information and evidence, allowing for an informed approach to tackle the problem effectively.
8. Seeking Advice
Seeking advice implies turning to knowledgeable and experienced individuals or entities to gain insights on problem-solving.
It could include mentors, industry experts, peers, or even specialized literature.
The value in this process lies in leveraging different perspectives and proven strategies when dealing with a problem. Moreover, it aids you in avoiding pitfalls, saving time, and learning from others’ experiences.
9. Creative Thinking
Creative thinking refers to the ability to perceive a problem in a new way, identify unconventional patterns, or produce original solutions.
It encourages innovation and uniqueness, often leading to the most effective results.
When applied to problem-solving, creative thinking can help you break free from traditional constraints, ideal for potentially complex or unusual problems.
Go Deeper: Creative Thinking Examples
10. Conflict Resolution
Conflict resolution is a strategy developed to resolve disagreements and arguments, often involving communication, negotiation, and compromise.
When employed as a problem-solving technique, it can diffuse tension, clear bottlenecks, and create a collaborative environment.
Effective conflict resolution ensures that differing views or disagreements do not become roadblocks in the process of problem-solving.
Go Deeper: Conflict Resolution Examples
11. Addressing Bottlenecks
Bottlenecks refer to obstacles or hindrances that slow down or even halt a process.
In problem-solving, addressing bottlenecks involves identifying these impediments and finding ways to eliminate them.
This effort not only smooths the path to resolution but also enhances the overall efficiency of the problem-solving process.
For example, if your workflow is not working well, you’d go to the bottleneck – that one point that is most time consuming – and focus on that. Once you ‘break’ this bottleneck, the entire process will run more smoothly.
12. Market Research
Market research involves gathering and analyzing information about target markets, consumers, and competitors.
In sales and marketing, this is one of the most effective problem-solving methods. The research collected from your market (e.g. from consumer surveys) generates data that can help identify market trends, customer preferences, and competitor strategies.
In this sense, it allows a company to make informed decisions, solve existing problems, and even predict and prevent future ones.
13. Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis is a method used to identify the origin or the fundamental reason for a problem.
Once the root cause is determined, you can implement corrective actions to prevent the problem from recurring.
As a problem-solving procedure, root cause analysis helps you to tackle the problem at its source, rather than dealing with its surface symptoms.
Go Deeper: Root Cause Analysis Examples
14. Mind Mapping
Mind mapping is a visual tool used to structure information, helping you better analyze, comprehend and generate new ideas.
By laying out your thoughts visually, it can lead you to solutions that might not have been apparent with linear thinking.
In problem-solving, mind mapping helps in organizing ideas and identifying connections between them, providing a holistic view of the situation and potential solutions.
15. Trial and Error
The trial and error method involves attempting various solutions until you find one that resolves the problem.
It’s an empirical technique that relies on practical actions instead of theories or rules.
In the context of problem-solving, trial and error allows you the flexibility to test different strategies in real situations, gaining insights about what works and what doesn’t.
16. SWOT Analysis
SWOT is an acronym standing for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
It’s an analytic framework used to evaluate these aspects in relation to a particular objective or problem.
In problem-solving, SWOT Analysis helps you to identify favorable and unfavorable internal and external factors. It helps to craft strategies that make best use of your strengths and opportunities, whilst addressing weaknesses and threats.
Go Deeper: SWOT Analysis Examples
17. Scenario Planning
Scenario planning is a strategic planning method used to make flexible long-term plans.
It involves imagining, and then planning for, multiple likely future scenarios.
By forecasting various directions a problem could take, scenario planning helps manage uncertainty and is an effective tool for problem-solving in volatile conditions.
18. Six Thinking Hats
The Six Thinking Hats is a concept devised by Edward de Bono that proposes six different directions or modes of thinking, symbolized by six different hat colors.
Each hat signifies a different perspective, encouraging you to switch ‘thinking modes’ as you switch hats. This method can help remove bias and broaden perspectives when dealing with a problem.
19. Decision Matrix Analysis
Decision Matrix Analysis is a technique that allows you to weigh different factors when faced with several possible solutions.
After listing down the options and determining the factors of importance, each option is scored based on each factor.
Revealing a clear winner that both serves your objectives and reflects your values, Decision Matrix Analysis grounds your problem-solving process in objectivity and comprehensiveness.
20. Pareto Analysis
Also known as the 80/20 rule, Pareto Analysis is a decision-making technique.
It’s based on the principle that 80% of problems are typically caused by 20% of the causes, making it a handy tool for identifying the most significant issues in a situation.
Using this analysis, you’re likely to direct your problem-solving efforts more effectively, tackling the root causes producing most of the problem’s impact.
21. Critical Thinking
Critical thinking refers to the ability to analyze facts to form a judgment objectively.
It involves logical, disciplined thinking that is clear, rational, open-minded, and informed by evidence.
For problem-solving, critical thinking helps evaluate options and decide the most effective solution. It ensures your decisions are grounded in reason and facts, and not biased or irrational assumptions.
Go Deeper: Critical Thinking Examples
22. Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing usually involves formulating a claim, testing it against actual data, and deciding whether to accept or reject the claim based on the results.
In problem-solving, hypotheses often represent potential solutions. Hypothesis testing provides verification, giving a statistical basis for decision-making and problem resolution.
Usually, this will require research methods and a scientific approach to see whether the hypothesis stands up or not.
Go Deeper: Types of Hypothesis Testing
23. Cost-Benefit Analysis
A cost-benefit analysis (CBA) is a systematic process of weighing the pros and cons of different solutions in terms of their potential costs and benefits.
It allows you to measure the positive effects against the negatives and informs your problem-solving strategy.
By using CBA, you can identify which solution offers the greatest benefit for the least cost, significantly improving efficacy and efficiency in your problem-solving process.
Go Deeper: Cost-Benefit Analysis Examples
24. Simulation and Modeling
Simulations and models allow you to create a simplified replica of real-world systems to test outcomes under controlled conditions.
In problem-solving, you can broadly understand potential repercussions of different solutions before implementation.
It offers a cost-effective way to predict the impacts of your decisions, minimizing potential risks associated with various solutions.
25. Delphi Method
The Delphi Method is a structured communication technique used to gather expert opinions.
The method involves a group of experts who respond to questionnaires about a problem. The responses are aggregated and shared with the group, and the process repeats until a consensus is reached.
This method of problem solving can provide a diverse range of insights and solutions, shaped by the wisdom of a collective expert group.
26. Cross-functional Team Collaboration
Cross-functional team collaboration involves individuals from different departments or areas of expertise coming together to solve a common problem or achieve a shared goal.
When you bring diverse skills, knowledge, and perspectives to a problem, it can lead to a more comprehensive and innovative solution.
In problem-solving, this promotes communal thinking and ensures that solutions are inclusive and holistic, with various aspects of the problem being addressed.
27. Benchmarking
Benchmarking involves comparing one’s business processes and performance metrics to the best practices from other companies or industries.
In problem-solving, it allows you to identify gaps in your own processes, determine how others have solved similar problems, and apply those solutions that have proven to be successful.
It also allows you to compare yourself to the best (the benchmark) and assess where you’re not as good.
28. Pros-Cons Lists
A pro-con analysis aids in problem-solving by weighing the advantages (pros) and disadvantages (cons) of various possible solutions.
This simple but powerful tool helps in making a balanced, informed decision.
When confronted with a problem, a pro-con analysis can guide you through the decision-making process, ensuring all possible outcomes and implications are scrutinized before arriving at the optimal solution. Thus, it helps to make the problem-solving process both methodical and comprehensive.
29. 5 Whys Analysis
The 5 Whys Analysis involves repeatedly asking the question ‘why’ (around five times) to peel away the layers of an issue and discover the root cause of a problem.
As a problem-solving technique, it enables you to delve into details that you might otherwise overlook and offers a simple, yet powerful, approach to uncover the origin of a problem.
For example, if your task is to find out why a product isn’t selling your first answer might be: “because customers don’t want it”, then you ask why again – “they don’t want it because it doesn’t solve their problem”, then why again – “because the product is missing a certain feature” … and so on, until you get to the root “why”.
30. Gap Analysis
Gap analysis entails comparing current performance with potential or desired performance.
You’re identifying the ‘gaps’, or the differences, between where you are and where you want to be.
In terms of problem-solving, a Gap Analysis can help identify key areas for improvement and design a roadmap of how to get from the current state to the desired one.
31. Design Thinking
Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that involves empathy, experimentation, and iteration.
The process focuses on understanding user needs, challenging assumptions , and redefining problems from a user-centric perspective.
In problem-solving, design thinking uncovers innovative solutions that may not have been initially apparent and ensures the solution is tailored to the needs of those affected by the issue.
32. Analogical Thinking
Analogical thinking involves the transfer of information from a particular subject (the analogue or source) to another particular subject (the target).
In problem-solving, you’re drawing parallels between similar situations and applying the problem-solving techniques used in one situation to the other.
Thus, it allows you to apply proven strategies to new, but related problems.
33. Lateral Thinking
Lateral thinking requires looking at a situation or problem from a unique, sometimes abstract, often non-sequential viewpoint.
Unlike traditional logical thinking methods, lateral thinking encourages you to employ creative and out-of-the-box techniques.
In solving problems, this type of thinking boosts ingenuity and drives innovation, often leading to novel and effective solutions.
Go Deeper: Lateral Thinking Examples
34. Flowcharting
Flowcharting is the process of visually mapping a process or procedure.
This form of diagram can show every step of a system, process, or workflow, enabling an easy tracking of the progress.
As a problem-solving tool, flowcharts help identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies in a process, guiding improved strategies and providing clarity on task ownership and process outcomes.
35. Multivoting
Multivoting, or N/3 voting, is a method where participants reduce a large list of ideas to a prioritized shortlist by casting multiple votes.
This voting system elevates the most preferred options for further consideration and decision-making.
As a problem-solving technique, multivoting allows a group to narrow options and focus on the most promising solutions, ensuring more effective and democratic decision-making.
36. Force Field Analysis
Force Field Analysis is a decision-making technique that identifies the forces for and against change when contemplating a decision.
The ‘forces’ represent the differing factors that can drive or hinder change.
In problem-solving, Force Field Analysis allows you to understand the entirety of the context, favoring a balanced view over a one-sided perspective. A comprehensive view of all the forces at play can lead to better-informed problem-solving decisions.
TRIZ, which stands for “The Theory of Inventive Problem Solving,” is a problem-solving, analysis, and forecasting methodology.
It focuses on finding contradictions inherent in a scenario. Then, you work toward eliminating the contraditions through finding innovative solutions.
So, when you’re tackling a problem, TRIZ provides a disciplined, systematic approach that aims for ideal solutions and not just acceptable ones. Using TRIZ, you can leverage patterns of problem-solving that have proven effective in different cases, pivoting them to solve the problem at hand.
38. A3 Problem Solving
A3 Problem Solving, derived from Lean Management, is a structured method that uses a single sheet of A3-sized paper to document knowledge from a problem-solving process.
Named after the international paper size standard of A3 (or 11-inch by 17-inch paper), it succinctly records all key details of the problem-solving process from problem description to the root cause and corrective actions.
Used in problem-solving, this provides a straightforward and logical structure for addressing the problem, facilitating communication between team members, ensuring all critical details are included, and providing a record of decisions made.
39. Scenario Analysis
Scenario Analysis is all about predicting different possible future events depending upon your decision.
To do this, you look at each course of action and try to identify the most likely outcomes or scenarios down the track if you take that course of action.
This technique helps forecast the impacts of various strategies, playing each out to their (logical or potential) end. It’s a good strategy for project managers who need to keep a firm eye on the horizon at all times.
When solving problems, Scenario Analysis assists in preparing for uncertainties, making sure your solution remains viable, regardless of changes in circumstances.
How to Answer “Demonstrate Problem-Solving Skills” in an Interview
When asked to demonstrate your problem-solving skills in an interview, the STAR method often proves useful. STAR stands for Situation, Task, Action, and Result.
Situation: Begin by describing a specific circumstance or challenge you encountered. Make sure to provide enough detail to allow the interviewer a clear understanding. You should select an event that adequately showcases your problem-solving abilities.
For instance, “In my previous role as a project manager, we faced a significant issue when our key supplier abruptly went out of business.”
Task: Explain what your responsibilities were in that situation. This serves to provide context, allowing the interviewer to understand your role and the expectations placed upon you.
For instance, “It was my task to ensure the project remained on track despite this setback. Alternative suppliers needed to be found without sacrificing quality or significantly increasing costs.”
Action: Describe the steps you took to manage the problem. Highlight your problem-solving process. Mention any creative approaches or techniques that you used.
For instance, “I conducted thorough research to identify potential new suppliers. After creating a shortlist, I initiated contact, negotiated terms, assessed samples for quality and made a selection. I also worked closely with the team to re-adjust the project timeline.”
Result: Share the outcomes of your actions. How did the situation end? Did your actions lead to success? It’s particularly effective if you can quantify these results.
For instance, “As a result of my active problem solving, we were able to secure a new supplier whose costs were actually 10% cheaper and whose quality was comparable. We adjusted the project plan and managed to complete the project just two weeks later than originally planned, despite the major vendor setback.”
Remember, when you’re explaining your problem-solving skills to an interviewer, what they’re really interested in is your approach to handling difficulties, your creativity and persistence in seeking a resolution, and your ability to carry your solution through to fruition. Tailoring your story to highlight these aspects will help exemplify your problem-solving prowess.
Go Deeper: STAR Interview Method Examples
Benefits of Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is beneficial for the following reasons (among others):
- It can help you to overcome challenges, roadblocks, and bottlenecks in your life.
- It can save a company money.
- It can help you to achieve clarity in your thinking.
- It can make procedures more efficient and save time.
- It can strengthen your decision-making capacities.
- It can lead to better risk management.
Whether for a job interview or school, problem-solving helps you to become a better thinking, solve your problems more effectively, and achieve your goals. Build up your problem-solving frameworks (I presented over 40 in this piece for you!) and work on applying them in real-life situations.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process
In this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , Simon London speaks with Charles Conn, CEO of venture-capital firm Oxford Sciences Innovation, and McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin about the complexities of different problem-solving strategies.
Podcast transcript
Simon London: Hello, and welcome to this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , with me, Simon London. What’s the number-one skill you need to succeed professionally? Salesmanship, perhaps? Or a facility with statistics? Or maybe the ability to communicate crisply and clearly? Many would argue that at the very top of the list comes problem solving: that is, the ability to think through and come up with an optimal course of action to address any complex challenge—in business, in public policy, or indeed in life.
Looked at this way, it’s no surprise that McKinsey takes problem solving very seriously, testing for it during the recruiting process and then honing it, in McKinsey consultants, through immersion in a structured seven-step method. To discuss the art of problem solving, I sat down in California with McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin and also with Charles Conn. Charles is a former McKinsey partner, entrepreneur, executive, and coauthor of the book Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything [John Wiley & Sons, 2018].
Charles and Hugo, welcome to the podcast. Thank you for being here.
Hugo Sarrazin: Our pleasure.
Charles Conn: It’s terrific to be here.
Simon London: Problem solving is a really interesting piece of terminology. It could mean so many different things. I have a son who’s a teenage climber. They talk about solving problems. Climbing is problem solving. Charles, when you talk about problem solving, what are you talking about?
Charles Conn: For me, problem solving is the answer to the question “What should I do?” It’s interesting when there’s uncertainty and complexity, and when it’s meaningful because there are consequences. Your son’s climbing is a perfect example. There are consequences, and it’s complicated, and there’s uncertainty—can he make that grab? I think we can apply that same frame almost at any level. You can think about questions like “What town would I like to live in?” or “Should I put solar panels on my roof?”
You might think that’s a funny thing to apply problem solving to, but in my mind it’s not fundamentally different from business problem solving, which answers the question “What should my strategy be?” Or problem solving at the policy level: “How do we combat climate change?” “Should I support the local school bond?” I think these are all part and parcel of the same type of question, “What should I do?”
I’m a big fan of structured problem solving. By following steps, we can more clearly understand what problem it is we’re solving, what are the components of the problem that we’re solving, which components are the most important ones for us to pay attention to, which analytic techniques we should apply to those, and how we can synthesize what we’ve learned back into a compelling story. That’s all it is, at its heart.
I think sometimes when people think about seven steps, they assume that there’s a rigidity to this. That’s not it at all. It’s actually to give you the scope for creativity, which often doesn’t exist when your problem solving is muddled.
Simon London: You were just talking about the seven-step process. That’s what’s written down in the book, but it’s a very McKinsey process as well. Without getting too deep into the weeds, let’s go through the steps, one by one. You were just talking about problem definition as being a particularly important thing to get right first. That’s the first step. Hugo, tell us about that.
Hugo Sarrazin: It is surprising how often people jump past this step and make a bunch of assumptions. The most powerful thing is to step back and ask the basic questions—“What are we trying to solve? What are the constraints that exist? What are the dependencies?” Let’s make those explicit and really push the thinking and defining. At McKinsey, we spend an enormous amount of time in writing that little statement, and the statement, if you’re a logic purist, is great. You debate. “Is it an ‘or’? Is it an ‘and’? What’s the action verb?” Because all these specific words help you get to the heart of what matters.
Want to subscribe to The McKinsey Podcast ?
Simon London: So this is a concise problem statement.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah. It’s not like “Can we grow in Japan?” That’s interesting, but it is “What, specifically, are we trying to uncover in the growth of a product in Japan? Or a segment in Japan? Or a channel in Japan?” When you spend an enormous amount of time, in the first meeting of the different stakeholders, debating this and having different people put forward what they think the problem definition is, you realize that people have completely different views of why they’re here. That, to me, is the most important step.
Charles Conn: I would agree with that. For me, the problem context is critical. When we understand “What are the forces acting upon your decision maker? How quickly is the answer needed? With what precision is the answer needed? Are there areas that are off limits or areas where we would particularly like to find our solution? Is the decision maker open to exploring other areas?” then you not only become more efficient, and move toward what we call the critical path in problem solving, but you also make it so much more likely that you’re not going to waste your time or your decision maker’s time.
How often do especially bright young people run off with half of the idea about what the problem is and start collecting data and start building models—only to discover that they’ve really gone off half-cocked.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah.
Charles Conn: And in the wrong direction.
Simon London: OK. So step one—and there is a real art and a structure to it—is define the problem. Step two, Charles?
Charles Conn: My favorite step is step two, which is to use logic trees to disaggregate the problem. Every problem we’re solving has some complexity and some uncertainty in it. The only way that we can really get our team working on the problem is to take the problem apart into logical pieces.
What we find, of course, is that the way to disaggregate the problem often gives you an insight into the answer to the problem quite quickly. I love to do two or three different cuts at it, each one giving a bit of a different insight into what might be going wrong. By doing sensible disaggregations, using logic trees, we can figure out which parts of the problem we should be looking at, and we can assign those different parts to team members.
Simon London: What’s a good example of a logic tree on a sort of ratable problem?
Charles Conn: Maybe the easiest one is the classic profit tree. Almost in every business that I would take a look at, I would start with a profit or return-on-assets tree. In its simplest form, you have the components of revenue, which are price and quantity, and the components of cost, which are cost and quantity. Each of those can be broken out. Cost can be broken into variable cost and fixed cost. The components of price can be broken into what your pricing scheme is. That simple tree often provides insight into what’s going on in a business or what the difference is between that business and the competitors.
If we add the leg, which is “What’s the asset base or investment element?”—so profit divided by assets—then we can ask the question “Is the business using its investments sensibly?” whether that’s in stores or in manufacturing or in transportation assets. I hope we can see just how simple this is, even though we’re describing it in words.
When I went to work with Gordon Moore at the Moore Foundation, the problem that he asked us to look at was “How can we save Pacific salmon?” Now, that sounds like an impossible question, but it was amenable to precisely the same type of disaggregation and allowed us to organize what became a 15-year effort to improve the likelihood of good outcomes for Pacific salmon.
Simon London: Now, is there a danger that your logic tree can be impossibly large? This, I think, brings us onto the third step in the process, which is that you have to prioritize.
Charles Conn: Absolutely. The third step, which we also emphasize, along with good problem definition, is rigorous prioritization—we ask the questions “How important is this lever or this branch of the tree in the overall outcome that we seek to achieve? How much can I move that lever?” Obviously, we try and focus our efforts on ones that have a big impact on the problem and the ones that we have the ability to change. With salmon, ocean conditions turned out to be a big lever, but not one that we could adjust. We focused our attention on fish habitats and fish-harvesting practices, which were big levers that we could affect.
People spend a lot of time arguing about branches that are either not important or that none of us can change. We see it in the public square. When we deal with questions at the policy level—“Should you support the death penalty?” “How do we affect climate change?” “How can we uncover the causes and address homelessness?”—it’s even more important that we’re focusing on levers that are big and movable.
Would you like to learn more about our Strategy & Corporate Finance Practice ?
Simon London: Let’s move swiftly on to step four. You’ve defined your problem, you disaggregate it, you prioritize where you want to analyze—what you want to really look at hard. Then you got to the work plan. Now, what does that mean in practice?
Hugo Sarrazin: Depending on what you’ve prioritized, there are many things you could do. It could be breaking the work among the team members so that people have a clear piece of the work to do. It could be defining the specific analyses that need to get done and executed, and being clear on time lines. There’s always a level-one answer, there’s a level-two answer, there’s a level-three answer. Without being too flippant, I can solve any problem during a good dinner with wine. It won’t have a whole lot of backing.
Simon London: Not going to have a lot of depth to it.
Hugo Sarrazin: No, but it may be useful as a starting point. If the stakes are not that high, that could be OK. If it’s really high stakes, you may need level three and have the whole model validated in three different ways. You need to find a work plan that reflects the level of precision, the time frame you have, and the stakeholders you need to bring along in the exercise.
Charles Conn: I love the way you’ve described that, because, again, some people think of problem solving as a linear thing, but of course what’s critical is that it’s iterative. As you say, you can solve the problem in one day or even one hour.
Charles Conn: We encourage our teams everywhere to do that. We call it the one-day answer or the one-hour answer. In work planning, we’re always iterating. Every time you see a 50-page work plan that stretches out to three months, you know it’s wrong. It will be outmoded very quickly by that learning process that you described. Iterative problem solving is a critical part of this. Sometimes, people think work planning sounds dull, but it isn’t. It’s how we know what’s expected of us and when we need to deliver it and how we’re progressing toward the answer. It’s also the place where we can deal with biases. Bias is a feature of every human decision-making process. If we design our team interactions intelligently, we can avoid the worst sort of biases.
Simon London: Here we’re talking about cognitive biases primarily, right? It’s not that I’m biased against you because of your accent or something. These are the cognitive biases that behavioral sciences have shown we all carry around, things like anchoring, overoptimism—these kinds of things.
Both: Yeah.
Charles Conn: Availability bias is the one that I’m always alert to. You think you’ve seen the problem before, and therefore what’s available is your previous conception of it—and we have to be most careful about that. In any human setting, we also have to be careful about biases that are based on hierarchies, sometimes called sunflower bias. I’m sure, Hugo, with your teams, you make sure that the youngest team members speak first. Not the oldest team members, because it’s easy for people to look at who’s senior and alter their own creative approaches.
Hugo Sarrazin: It’s helpful, at that moment—if someone is asserting a point of view—to ask the question “This was true in what context?” You’re trying to apply something that worked in one context to a different one. That can be deadly if the context has changed, and that’s why organizations struggle to change. You promote all these people because they did something that worked well in the past, and then there’s a disruption in the industry, and they keep doing what got them promoted even though the context has changed.
Simon London: Right. Right.
Hugo Sarrazin: So it’s the same thing in problem solving.
Charles Conn: And it’s why diversity in our teams is so important. It’s one of the best things about the world that we’re in now. We’re likely to have people from different socioeconomic, ethnic, and national backgrounds, each of whom sees problems from a slightly different perspective. It is therefore much more likely that the team will uncover a truly creative and clever approach to problem solving.
Simon London: Let’s move on to step five. You’ve done your work plan. Now you’ve actually got to do the analysis. The thing that strikes me here is that the range of tools that we have at our disposal now, of course, is just huge, particularly with advances in computation, advanced analytics. There’s so many things that you can apply here. Just talk about the analysis stage. How do you pick the right tools?
Charles Conn: For me, the most important thing is that we start with simple heuristics and explanatory statistics before we go off and use the big-gun tools. We need to understand the shape and scope of our problem before we start applying these massive and complex analytical approaches.
Simon London: Would you agree with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: I agree. I think there are so many wonderful heuristics. You need to start there before you go deep into the modeling exercise. There’s an interesting dynamic that’s happening, though. In some cases, for some types of problems, it is even better to set yourself up to maximize your learning. Your problem-solving methodology is test and learn, test and learn, test and learn, and iterate. That is a heuristic in itself, the A/B testing that is used in many parts of the world. So that’s a problem-solving methodology. It’s nothing different. It just uses technology and feedback loops in a fast way. The other one is exploratory data analysis. When you’re dealing with a large-scale problem, and there’s so much data, I can get to the heuristics that Charles was talking about through very clever visualization of data.
You test with your data. You need to set up an environment to do so, but don’t get caught up in neural-network modeling immediately. You’re testing, you’re checking—“Is the data right? Is it sound? Does it make sense?”—before you launch too far.
Simon London: You do hear these ideas—that if you have a big enough data set and enough algorithms, they’re going to find things that you just wouldn’t have spotted, find solutions that maybe you wouldn’t have thought of. Does machine learning sort of revolutionize the problem-solving process? Or are these actually just other tools in the toolbox for structured problem solving?
Charles Conn: It can be revolutionary. There are some areas in which the pattern recognition of large data sets and good algorithms can help us see things that we otherwise couldn’t see. But I do think it’s terribly important we don’t think that this particular technique is a substitute for superb problem solving, starting with good problem definition. Many people use machine learning without understanding algorithms that themselves can have biases built into them. Just as 20 years ago, when we were doing statistical analysis, we knew that we needed good model definition, we still need a good understanding of our algorithms and really good problem definition before we launch off into big data sets and unknown algorithms.
Simon London: Step six. You’ve done your analysis.
Charles Conn: I take six and seven together, and this is the place where young problem solvers often make a mistake. They’ve got their analysis, and they assume that’s the answer, and of course it isn’t the answer. The ability to synthesize the pieces that came out of the analysis and begin to weave those into a story that helps people answer the question “What should I do?” This is back to where we started. If we can’t synthesize, and we can’t tell a story, then our decision maker can’t find the answer to “What should I do?”
Simon London: But, again, these final steps are about motivating people to action, right?
Charles Conn: Yeah.
Simon London: I am slightly torn about the nomenclature of problem solving because it’s on paper, right? Until you motivate people to action, you actually haven’t solved anything.
Charles Conn: I love this question because I think decision-making theory, without a bias to action, is a waste of time. Everything in how I approach this is to help people take action that makes the world better.
Simon London: Hence, these are absolutely critical steps. If you don’t do this well, you’ve just got a bunch of analysis.
Charles Conn: We end up in exactly the same place where we started, which is people speaking across each other, past each other in the public square, rather than actually working together, shoulder to shoulder, to crack these important problems.
Simon London: In the real world, we have a lot of uncertainty—arguably, increasing uncertainty. How do good problem solvers deal with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: At every step of the process. In the problem definition, when you’re defining the context, you need to understand those sources of uncertainty and whether they’re important or not important. It becomes important in the definition of the tree.
You need to think carefully about the branches of the tree that are more certain and less certain as you define them. They don’t have equal weight just because they’ve got equal space on the page. Then, when you’re prioritizing, your prioritization approach may put more emphasis on things that have low probability but huge impact—or, vice versa, may put a lot of priority on things that are very likely and, hopefully, have a reasonable impact. You can introduce that along the way. When you come back to the synthesis, you just need to be nuanced about what you’re understanding, the likelihood.
Often, people lack humility in the way they make their recommendations: “This is the answer.” They’re very precise, and I think we would all be well-served to say, “This is a likely answer under the following sets of conditions” and then make the level of uncertainty clearer, if that is appropriate. It doesn’t mean you’re always in the gray zone; it doesn’t mean you don’t have a point of view. It just means that you can be explicit about the certainty of your answer when you make that recommendation.
Simon London: So it sounds like there is an underlying principle: “Acknowledge and embrace the uncertainty. Don’t pretend that it isn’t there. Be very clear about what the uncertainties are up front, and then build that into every step of the process.”
Hugo Sarrazin: Every step of the process.
Simon London: Yeah. We have just walked through a particular structured methodology for problem solving. But, of course, this is not the only structured methodology for problem solving. One that is also very well-known is design thinking, which comes at things very differently. So, Hugo, I know you have worked with a lot of designers. Just give us a very quick summary. Design thinking—what is it, and how does it relate?
Hugo Sarrazin: It starts with an incredible amount of empathy for the user and uses that to define the problem. It does pause and go out in the wild and spend an enormous amount of time seeing how people interact with objects, seeing the experience they’re getting, seeing the pain points or joy—and uses that to infer and define the problem.
Simon London: Problem definition, but out in the world.
Hugo Sarrazin: With an enormous amount of empathy. There’s a huge emphasis on empathy. Traditional, more classic problem solving is you define the problem based on an understanding of the situation. This one almost presupposes that we don’t know the problem until we go see it. The second thing is you need to come up with multiple scenarios or answers or ideas or concepts, and there’s a lot of divergent thinking initially. That’s slightly different, versus the prioritization, but not for long. Eventually, you need to kind of say, “OK, I’m going to converge again.” Then you go and you bring things back to the customer and get feedback and iterate. Then you rinse and repeat, rinse and repeat. There’s a lot of tactile building, along the way, of prototypes and things like that. It’s very iterative.
Simon London: So, Charles, are these complements or are these alternatives?
Charles Conn: I think they’re entirely complementary, and I think Hugo’s description is perfect. When we do problem definition well in classic problem solving, we are demonstrating the kind of empathy, at the very beginning of our problem, that design thinking asks us to approach. When we ideate—and that’s very similar to the disaggregation, prioritization, and work-planning steps—we do precisely the same thing, and often we use contrasting teams, so that we do have divergent thinking. The best teams allow divergent thinking to bump them off whatever their initial biases in problem solving are. For me, design thinking gives us a constant reminder of creativity, empathy, and the tactile nature of problem solving, but it’s absolutely complementary, not alternative.
Simon London: I think, in a world of cross-functional teams, an interesting question is do people with design-thinking backgrounds really work well together with classical problem solvers? How do you make that chemistry happen?
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah, it is not easy when people have spent an enormous amount of time seeped in design thinking or user-centric design, whichever word you want to use. If the person who’s applying classic problem-solving methodology is very rigid and mechanical in the way they’re doing it, there could be an enormous amount of tension. If there’s not clarity in the role and not clarity in the process, I think having the two together can be, sometimes, problematic.
The second thing that happens often is that the artifacts the two methodologies try to gravitate toward can be different. Classic problem solving often gravitates toward a model; design thinking migrates toward a prototype. Rather than writing a big deck with all my supporting evidence, they’ll bring an example, a thing, and that feels different. Then you spend your time differently to achieve those two end products, so that’s another source of friction.
Now, I still think it can be an incredibly powerful thing to have the two—if there are the right people with the right mind-set, if there is a team that is explicit about the roles, if we’re clear about the kind of outcomes we are attempting to bring forward. There’s an enormous amount of collaborativeness and respect.
Simon London: But they have to respect each other’s methodology and be prepared to flex, maybe, a little bit, in how this process is going to work.
Hugo Sarrazin: Absolutely.
Simon London: The other area where, it strikes me, there could be a little bit of a different sort of friction is this whole concept of the day-one answer, which is what we were just talking about in classical problem solving. Now, you know that this is probably not going to be your final answer, but that’s how you begin to structure the problem. Whereas I would imagine your design thinkers—no, they’re going off to do their ethnographic research and get out into the field, potentially for a long time, before they come back with at least an initial hypothesis.

Want better strategies? Become a bulletproof problem solver
Hugo Sarrazin: That is a great callout, and that’s another difference. Designers typically will like to soak into the situation and avoid converging too quickly. There’s optionality and exploring different options. There’s a strong belief that keeps the solution space wide enough that you can come up with more radical ideas. If there’s a large design team or many designers on the team, and you come on Friday and say, “What’s our week-one answer?” they’re going to struggle. They’re not going to be comfortable, naturally, to give that answer. It doesn’t mean they don’t have an answer; it’s just not where they are in their thinking process.
Simon London: I think we are, sadly, out of time for today. But Charles and Hugo, thank you so much.
Charles Conn: It was a pleasure to be here, Simon.
Hugo Sarrazin: It was a pleasure. Thank you.
Simon London: And thanks, as always, to you, our listeners, for tuning into this episode of the McKinsey Podcast . If you want to learn more about problem solving, you can find the book, Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything , online or order it through your local bookstore. To learn more about McKinsey, you can of course find us at McKinsey.com.
Charles Conn is CEO of Oxford Sciences Innovation and an alumnus of McKinsey’s Sydney office. Hugo Sarrazin is a senior partner in the Silicon Valley office, where Simon London, a member of McKinsey Publishing, is also based.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Strategy to beat the odds

Five routes to more innovative problem solving
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
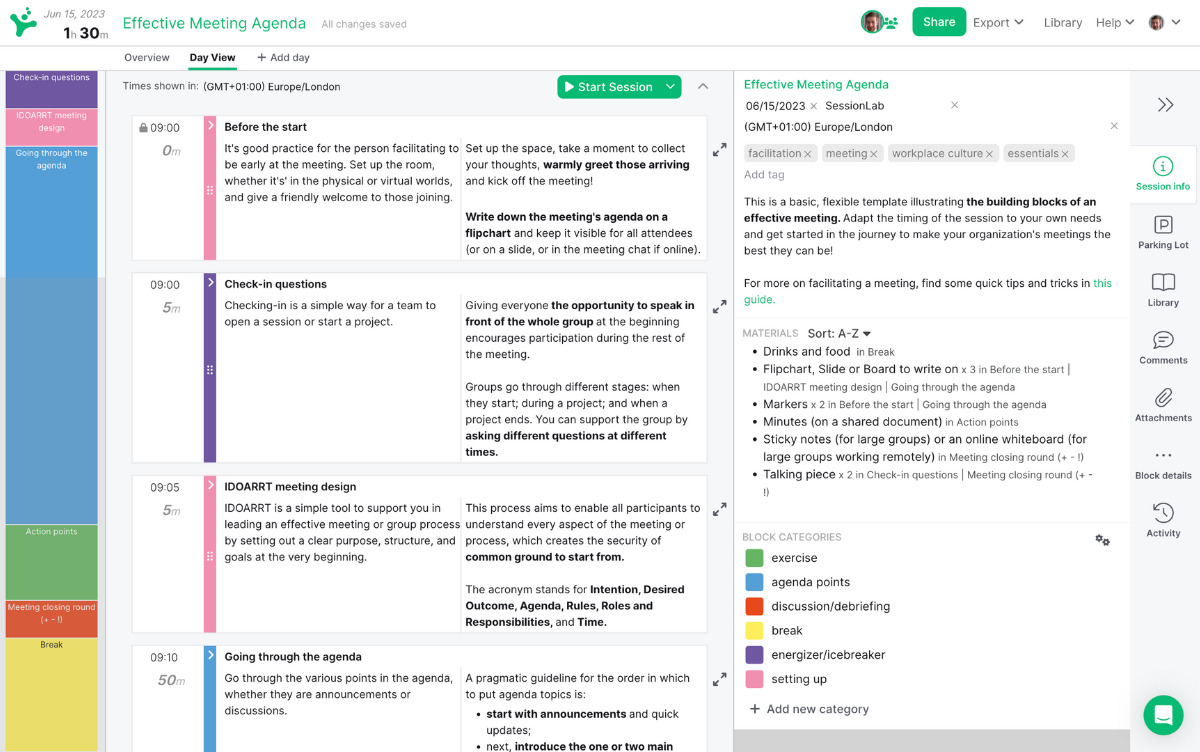
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
Plan Smarter, Grow Faster:
25% Off Annual Plans! Save Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
10 Step Process for Effective Business Problem Solving
Posted august 3, 2021 by harriet genever.

When you start a small business or launch a startup, the one thing you can count on is the unexpected. No matter how thoroughly you plan, forecast , and test, problems are bound to arise. This is why as an entrepreneur, you need to know how to solve business problems effectively.
What is problem solving in business?
Problem solving in business relates to establishing processes that mitigate or remove obstacles currently preventing you from reaching strategic goals . These are typically complex issues that create a gap between actual results and your desired outcome. They may be present in a single team, operational process, or throughout your entire organization, typically without an immediate or obvious solution.
To approach problem solving successfully, you need to establish consistent processes that help you evaluate, explore solutions, prioritize execution, and measure success. In many ways, it should be similar to how you review business performance through a monthly plan review . You work through the same documentation, look for gaps, dig deeper to identify the root cause, and hash out options. Without this process, you simply cannot expect to solve problems efficiently or effectively.
Why problem solving is important for your business
While some would say problem-solving comes naturally, it’s actually a skill you can grow and refine over time. Problem solving skills will help you and your team tackle critical issues and conflicts as they arise. It starts from the top. You as the business owner or CEO needing to display the type of level-headed problem solving that you expect to see from your employees.
Doing so will help you and your staff quickly deal with issues, establish and refine a problem solving process, turn challenges into opportunities, and generally keep a level head. Now, the best business leaders didn’t just find a magic solution to solve their problems, they built processes and leveraged tools to find success. And you can do the same.
By following this 10-step process, you can develop your problem-solving skills and approach any issue that arises with confidence.
1. Define the problem
When a problem arises, it can be very easy to jump right into creating a solution. However, if you don’t thoroughly examine what led to the problem in the first place, you may create a strategy that doesn’t actually solve it. You may just be treating the symptoms.
For instance, if you realize that your sales from new customers are dropping, your first inclination might be to rush into putting together a marketing plan to increase exposure. But what if decreasing sales are just a symptom of the real problem?
When you define the problem, you want to be sure you’re not missing the forest for the trees. If you have a large issue on your hands, you’ll want to look at it from several different angles:
Competition
Is a competitor’s promotion or pricing affecting your sales? Are there new entrants in your market? How are they marketing their product or business?
Business model
Is your business model sustainable? Is it realistic for how fast you want to grow? Should you explore different pricing or cost strategies?
Market factors
How are world events and the nation’s economy affecting your customers and your sales?
Are there any issues affecting your team? Do they have the tools and resources they need to succeed?
Goal alignment
Is everyone on your team working toward the same goal ? Have you communicated your short-term and long-term business goals clearly and often?
There are a lot of ways to approach the issue when you’re facing a serious business problem. The key is to make sure you’re getting a full snapshot of what’s going on so you don’t waste money and resources on band-aid solutions.
Going back to our example, by looking at every facet of your business, you may discover that you’re spending more on advertising than your competitors already. And instead, there’s a communication gap within your team that’s leading to the mishandling of new customers and therefore lost sales.
If you jumped into fixing the exposure of your brand, you would have been dumping more money into an area you’re already winning. Potentially leading to greater losses as more and more new customers are dropped due to poor internal communication.
This is why it’s so vital that you explore your blind spots and track the problem to its source.
2. Conduct a SWOT analysis
All good businesses solve some sort of problem for customers. What if your particular business problem is actually an opportunity, or even a strength if considered from a different angle? This is when you’d want to conduct a SWOT analysis to determine if that is in fact the case.
SWOT is a great tool for strategic planning and bringing multiple viewpoints to the table when you’re looking at investing resources to solve a problem. This may even be incorporated in your attempts to identify the source of your problem, as it can quickly outline specific strengths and weaknesses of your business. And then by identifying any potential opportunities or threats, you can utilize your findings to kickstart a solution.
3. Identify multiple solutions with design thinking
As you approach solving your problem, you may want to consider using the design thinking approach . It’s often used by organizations looking to solve big, community-based problems. One of its strengths is that it requires involving a wide range of people in the problem-solving process. Which leads to multiple perspectives and solutions arising.
This approach—applying your company’s skills and expertise to a problem in the market—is the basis for design thinking.
It’s not about finding the most complex problems to solve, but about finding common needs within the organization and in the real world and coming up with solutions that fit those needs. When you’re solving business problems, this applies in the sense that you’re looking for solutions that address underlying issues—you’re looking at the big picture.
4. Conduct market research and customer outreach
Market research and customer outreach aren’t the sorts of things small business owners and startups can do once and then cross off the list. When you’re facing a roadblock, think back to the last time you did some solid market research or took a deep dive into understanding the competitive landscape .
Market research and the insights you get from customer outreach aren’t a silver bullet. Many companies struggle with what they should do with conflicting data points. But it’s worth struggling through and gathering information that can help you better understand your target market . Plus, your customers can be one of the best sources of criticism. It’s actually a gift if you can avoid taking the negatives personally .
The worst thing you can do when you’re facing challenges is isolating yourself from your customers and ignore your competition. So survey your customers. Put together a competitive matrix .

5. Seek input from your team and your mentors
Don’t do your SWOT analysis or design thinking work by yourself. The freedom to express concerns, opinions, and ideas will allow people in an organization to speak up. Their feedback is going to help you move faster and more efficiently. If you have a team in place, bring them into the discussion. You hired them to be experts in their area; use their expertise to navigate and dig deeper into underlying causes of problems and potential solutions.
If you’re running your business solo, at least bring in a trusted mentor. SCORE offers a free business mentorship program if you don’t already have one. It can also be helpful to connect with a strategic business advisor , especially if business financials aren’t your strongest suit.
Quoting Stephen Covey, who said that “strength lies in differences, not in similarities,” speaking to the importance of diversity when it comes to problem-solving in business. The more diverse a team is , the more often innovative solutions to the problems faced by the organization appear.
In fact, it has been found that groups that show greater diversity were better at solving problems than groups made up specifically of highly skilled problem solvers. So whoever you bring in to help you problem-solve, resist the urge to surround yourself with people who already agree with you about everything.
6. Apply lean planning for nimble execution
So you do your SWOT analysis and your design thinking exercise. You come up with a set of strong, data-driven ideas. But implementing them requires you to adjust your budget, or your strategic plan, or even your understanding of your target market.
Are you willing to change course? Can you quickly make adjustments? Well in order to grow, you can’t be afraid to be nimble .
By adopting the lean business planning method —the process of revising your business strategy regularly—you’ll be able to shift your strategies more fluidly. You don’t want to change course every week, and you don’t want to fall victim to shiny object thinking. But you can strike a balance that allows you to reduce your business’s risk while keeping your team heading in the right direction.
Along the way, you’ll make strategic decisions that don’t pan out the way you hoped. The best thing you can do is test your ideas and iterate often so you’re not wasting money and resources on things that don’t work. That’s Lean Planning .
7. Model different financial scenarios
When you’re trying to solve a serious business problem, one of the best things you can do is build a few different financial forecasts so you can model different scenarios. You might find that the idea that seemed the strongest will take longer than you thought to reverse a negative financial trend. At the very least you’ll have better insight into the financial impact of moving in a different direction.
The real benefit here is looking at different tactical approaches to the same problem. Maybe instead of increasing sales right now, you’re better off in the long run if you adopt a strategy to reduce churn and retain your best customers. You won’t know unless you model a few different scenarios. You can do this by using spreadsheets, and a tool like LivePlan can make it easier and quicker.
8. Watch your cash flow
While you’re working to solve a challenging business problem, pay particular attention to your cash flow and your cash flow forecast . Understanding when your company is at risk of running out of cash in the bank can help you be proactive. It’s a lot easier to get a line of credit while your financials still look good and healthy, than when you’re one pay period away from ruin.
If you’re dealing with a serious issue, it’s easy to start to get tunnel vision. You’ll benefit from maintaining a little breathing room for your business as you figure out what to do next.
9. Use a decision-making framework
Once you’ve gathered all the information you need, generated a number of ideas, and done some financial modeling, you might still feel uncertain. It’s natural—you’re not a fortune-teller. You’re trying to make the best decision you can with the information you have.
This article offers a really useful approach to making decisions. It starts with putting your options into a matrix like this one:

Use this sort of framework to put everything you’ve learned out on the table. If you’re working with a bigger team, this sort of exercise can also bring the rest of your team to the table so they feel some ownership over the outcome.
10. Identify key metrics to track
How will you know your problem is solved? And not just the symptom—how will you know when you’ve addressed the underlying issues? Before you dive into enacting the solution, make sure you know what success looks like.
Decide on a few key performance indicators . Take a baseline measurement, and set a goal and a timeframe. You’re essentially translating your solution into a plan, complete with milestones and goals. Without these, you’ve simply made a blind decision with no way to track success. You need those goals and milestones to make your plan real .
Problem solving skills to improve
As you and your team work through this process, it’s worth keeping in mind specific problem solving skills you should continue to develop. Bolstering your ability, as well as your team, to solve problems effectively will only make this process more useful and efficient. Here are a few key skills to work on.
Emotional intelligence
It can be very easy to make quick, emotional responses in a time of crisis or when discussing something you’re passionate about. To avoid making assumptions and letting your emotions get the best of you, you need to focus on empathizing with others. This involves understanding your own emotional state, reactions and listening carefully to the responses of your team. The more you’re able to listen carefully, the better you’ll be at asking for and taking advice that actually leads to effective problem solving.
Jumping right into a solution can immediately kill the possibility of solving your problem. Just like when you start a business , you need to do the research into what the problem you’re solving actually is. Luckily, you can embed research into your problem solving by holding active reviews of financial performance and team processes. Simply asking “What? Where? When? How?” can lead to more in-depth explorations of potential issues.
The best thing you can do to grow your research abilities is to encourage and practice curiosity. Look at every problem as an opportunity. Something that may be trouble now, but is worth exploring and finding the right solution. You’ll pick up best practices, useful tools and fine-tune your own research process the more you’re willing to explore.
Brainstorming
Creatively brainstorming with your team is somewhat of an art form. There needs to be a willingness to throw everything at the wall and act as if nothing is a bad idea at the start. This style of collaboration encourages participation without fear of rejection. It also helps outline potential solutions outside of your current scope, that you can refine and turn into realistic action.
Work on breaking down problems and try to give everyone in the room a voice. The more input you allow, the greater potential you have for finding the best solution.
Decisiveness
One thing that can drag out acting upon a potential solution, is being indecisive. If you aren’t willing to state when the final cutoff for deliberation is, you simply won’t take steps quickly enough. This is when having a process for problem solving comes in handy, as it purposefully outlines when you should start taking action.
Work on choosing decision-makers, identify necessary results and be prepared to analyze and adjust if necessary. You don’t have to get it right every time, but taking action at the right time, even if it fails, is almost more vital than never taking a step.
Stemming off failure, you need to learn to be resilient. Again, no one gets it perfect every single time. There are so many factors in play to consider and sometimes even the most well-thought-out solution doesn’t stick. Instead of being down on yourself or your team, look to separate yourself from the problem and continue to think of it as a puzzle worth solving. Every failure is a learning opportunity and it only helps you further refine and eliminate issues in your strategy.
Problem solving is a process
The key to effective problem-solving in business is the ability to adapt. You can waste a lot of resources on staying the wrong course for too long. So make a plan to reduce your risk now. Think about what you’d do if you were faced with a problem large enough to sink your business. Be as proactive as you can.
Editor’s note: This article was originally published in 2016. It was updated in 2021.
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Harriet Genever
Posted in management, join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Solve Problems
- Laura Amico

To bring the best ideas forward, teams must build psychological safety.
Teams today aren’t just asked to execute tasks: They’re called upon to solve problems. You’d think that many brains working together would mean better solutions, but the reality is that too often problem-solving teams fall victim to inefficiency, conflict, and cautious conclusions. The two charts below will help your team think about how to collaborate better and come up with the best solutions for the thorniest challenges.
- Laura Amico is a former senior editor at Harvard Business Review.
Partner Center
- Become a Partner
- Product Overview Know more about our products
- OKR Management Strategy-execution made easy
- Performance Management Build a high performance team
- Task Management Increase day-to-day productivity
- Employee Engagement Engage, align and inspire your team
- Integrations Integrate easily with all your favorite apps
- Case Study Know why 1000s of brands trust Profit.co
- Why Profit.co? Know what customers like you think about us.
- OKR Certification Iterate Faster with OKRs Coaching & Certification Programs
- OKR University OKR resources for beginners and experts
- eBooks Books sharing our OKR expertise, ideas and insights
- KPI Library Find the Most Effective KPIs for your business
- OKR Examples Collection of OKR examples for your business
- OKR Webinars Discover current trends and expert insights
- Answers (FAQs) Get instant solutions to your queries
- OKR Canvas Kick start your OKR implementation right away
- Help Center Endless support in case you are stuck
- Release Updates Outlined feature updates from our last releases
- Try it Free
- Schedule Demo
How do Great Leaders Solve Problems in Business?

Category: Behavioral Economics .
Companies today are expected to adapt and respond quickly to challenges in a rapidly changing business environment. Notwithstanding sound planning and flawless strategy execution, businesses can still face problems. While they foresee some of those problems, others can pop up unexpectedly. These unforeseeable problems make it essential for businesses to be agile enough to respond to those challenges quickly and have excellent problem-solving skills to navigate them successfully. Problem-solving is an indispensable part of business management.
In this article, we will examine the following in detail
Introduction
- Understanding the Importance of Problem-Solving in Business
- Types of Business Problems
- Challenges in Problem-solving
- Skills Required for Effective Problem-solving in Business
- A Step-by-step Process to Problem-solving in Business
TL;DR Version
Problem-solving is integral to business success, dealing with diverse issues ranging from operational hiccups to strategic challenges. Identifying and understanding these problems is vital, but navigating potential obstacles during problem-solving, such as cognitive biases, resource constraints, and lack of information, is crucial.
Effective problem-solving skills include research and analytical abilities, creativity, decision-making, communication , time management, and leadership. These skills allow business leaders to dissect complex issues, ideate innovative solutions, make informed decisions, communicate effectively, manage time, and lead teams toward resolution.
The problem-solving process involves defining the problem, understanding its root cause, collecting relevant information, brainstorming potential solutions, evaluating these solutions, choosing the best one, developing and implementing an action plan, monitoring progress, evaluating results, and reflecting on the process for continuous improvement. This iterative process ensures that businesses are resolving immediate issues and refining their problem-solving mechanism for future challenges.
Unmanaged and unmitigated problems can cause severe consequences to businesses. They can lead to project delays, missed deadlines, and financial losses. Moreover, they may negatively impact employee morale and customer satisfaction and even damage the reputation of the company. So businesses must have strong problem-solving abilities.
When businesses have strong problem-solving abilities, they can quickly and proactively rise to the occasion and address the problems, minimizing their impact, preventing them from escalating into bigger problems, and capitalizing on opportunities that arise from those challenges. Ultimately, the problem-solving ability of a company can help them gain a competitive advantage.
To solve problems and fix issues, companies require leaders who can handle complex issues with ease and guide and motivate their teams to identify problems and develop creative solutions to overcome them. They can leverage the collective expertise and experience of the employees to make well-informed decisions that align with the business goals and objectives. Leaders also work with employees to foster a culture of problem-solving to help the company build a resilient business that can thrive in today’s dynamic business environment.
What is Problem-Solving in Business?
Problem-solving involves identifying, analyzing, and resolving issues or challenges arising during various business operations to achieve the desired outcomes and business goals. It involves a systematic approach to defining the problem, gathering relevant information, generating possible solutions, evaluating them, and implementing the best course of action.
Take action today and start paving the way for your business towards Problem- solving.
Book a free demo
we Cannot solve our problems with the same thinking we used when we created them. Albert Einstein
Why is Problem-Solving Important?
Problem-solving in business is important because of the following reasons.
1. Efficiency
Problems not only hinder progress but also reduce the efficiency of your operations by bringing everything to a halt/slowing you down, causing downtime, and costing you precious productivity. When left unchecked at the initial stages, these problems may also demand additional resources and budget to solve them, leading to cost overruns, losses, and inefficiency. So addressing the problems on time can help achieve efficiency.
2. Profitability
Profitability is one of the topmost priorities of an organization. So any impact on profitability is seen as a problem that requires immediate attention. Effective problem-solving helps businesses identify and address cost inefficiencies, optimize processes, and capitalize on new opportunities, thus improving the bottom line.
3. Leadership
Great leaders emerge during testing times. They can lead the employees, leverage collective effort and give a sense of direction toward finding solutions and workarounds. Problem-solving helps companies identify the right leaders.
4. Teamwork
Problem-solving requires team effort and participation. It calls for collaboration and communication between various departments, teams, and individuals. When companies manage to weather challenges and solve problems effectively, it brings the employees together to work towards a common cause, build stronger teams and create a habit of continuous improvement.

5. Innovation
Problem-solving requires creativity and innovation to find solutions and workarounds. When a company fosters problem-solving culture, it automatically imbibes creative thinking and innovation. It gets reflected in developing new products, services, processes, and best practices.
6. Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction helps businesses retain and find new customers. Problems with the products/services and customer support can lead to poor customer experience. Effective problem-solving helps businesses resolve customer complaints and issues quickly and satisfactorily, thus increasing customer loyalty and retention.
The Problems that Businesses Face Today and how they Solve Them
There are several different kinds of problems that businesses face, including
1. Strategic problems
Strategic problems are related to the long-term direction of a business. They typically involve decisions about resource allocation, product strategy, choosing the market, pricing strategy, product positioning, etc. Solving strategic problems requires a long-term vision, able leadership, and the ability to forecast market trends.

Business problem examples
Selecting the markets.
Businesses need to decide their focus on specific geographic markets, target customer segments, and product categories. They must make these decisions and select the focus areas by analyzing the data and insights into factors, including market size, competition, and the company’s core competencies.
Product development
Developing new products enables companies to remain relevant and achieve leadership in a highly competitive market scenario. They have to meet the customer requirements and provide a compelling reason for customers to purchase them. Solving the problem of new product development requires creativity and innovation and allocating resources for R&D. New products should be developed based on sound market analyses of customer requirements and pain points.
For instance, the need to learn and upskill anytime without compromising work hours pushed the companies to create e-learning platforms.
Positioning the company
Differentiating your business from the competition involves developing a strong brand identity, focusing on a specific niche or segment of the market, or offering unique value propositions. Setting the company apart by gaining a competitive advantage attracts customers. You can solve the problem of positioning your company by doing a SWOT analysis, finding your strengths and unique qualities that enable you to meet the customers’ requirements and address their pain points. You can base your brand identity, USP, and niche on your stand-out qualities that benefit customers. For instance, Volvo positions itself as the company that makes the safest cars in the world.
2. Operational problems
Operational problems are daily issues that hinder companies from efficiently delivering products or services to customers, affecting their ability to meet deadlines and targets. These problems arise from bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and system flaws. Addressing them involves identifying issues, providing employee training, upgrading technology, ensuring product testing and quality control, and implementing contingency planning, deadline management, and risk mitigation.

Business problem-solving examples
Supply chain disruptions.
Supply chain disruptions happen when businesses face challenges in sourcing raw materials or components, leading to production delays or quality issues. For instance, during the pandemic, companies faced chip shortages, which led to losses and the inability to deliver products to customers on time. It also caused a rise in demand and an increase in prices.
Quality control issues
Quality control issues occur when design flaws or manufacturing issues impact the products. Businesses may need to identify and address quality issues to maintain customer satisfaction and loyalty. For instance, it is not uncommon to recall new automobile models, sometimes the ones from specific batches, to replace faulty components with redesigned parts before they might fail.
Managing staffing levels
Fluctuating staffing needs are part of operational issues. At any given time, if a company is understaffed, it can lead to operational inefficiency; if it is over-staffed, the company will suffer from cost infficiency. So, it requires careful planning. You can address the problem by either recruiting or downsizing and restructuring. For instance, the tech companies that designed software solutions for remote and hybrid work environments hired many employees during the pandemic. After the pandemic, when the need for these software solutions decreased, they had to downsize their workforce in light of the impending recession.
3. Financial problems
Financial problems are issues involving managing cash flow, revenue growth, and expenses. They are related to the financial health of a business. Businesses can fix them by managing costs effectively through process improvement and cost-cutting measures.

Managing cash flow
Businesses must ensure that they have enough financial resources on hand to meet their obligations, such as payroll, vendor payments, logistics, managing retail channels, etc. For instance, many start-ups stall despite successful product development and prototyping, as they fail to secure adequate funding to bring the products to the market.
Identifying new revenue streams:
Businesses that focus on a particular niche are always vulnerable to competition and changing market conditions. They need to diversify their revenue streams to maintain growth and profitability. They may have to focus on research and product development to identify new revenue streams. For instance, some of the most successful and established DSLR camera manufacturers faced a major crisis when mirrorless cameras started eating into their market share. They had to revise the product strategy, downsize their manpower, and invest vast resources into developing competitive mirrorless systems to mitigate the company. On the contrary, DSLR manufacturers with diversified businesses remained more resilient.
Managing costs
Businesses must control expenses to maintain profitability. It may involve identifying areas where costs can be cut or negotiating better deals with vendors. For instance, Google is known to initiate moonshot projects. At the same time, they kill non-profitable projects quickly. It has helped the company retain leadership while managing costs judiciously.
4. Human resource problems
HR problems are issues related to recruiting, retaining, and developing talent. They are issues about the management of employees. Managing these problems requires assessing staffing needs, recruiting, restructuring, identifying training and upskilling needs, and retaining top talent through employee engagement initiatives, welfare measures, and career development opportunities.

Retaining top talent
Retaining top talent can be a determining factor for the success of a company. Businesses must build an environment that attracts top talent by creating opportunities for career advancement and offering competitive compensation packages. For instance, highly specialized jobs with business-critical responsibilities, such as chief aero designers in motor racing teams, are hard to find and recruit. So retaining them is crucial for the success of the company.
Addressing employee morale and motivation issues
Lack of motivation, stagnant career, unfavorable team dynamics, etc., are some factors that cause a dip in employee morale. These factors can affect productivity and quality of work. Businesses must address these issues through employee engagement initiatives, career planning, team building, welfare measures, training, upskilling, etc.
Managing a diverse workforce
In an increasingly globalized work scenario, businesses must ensure that they create a work environment that is inclusive and welcoming to employees from different backgrounds and with diverse skill sets. They should also manage hybrid and remote work to address ambiguities and ensure clarity and synergy among teams and individuals based in various locations. For instance, many companies reserve certain positions for people of different racial/ethnic backgrounds or genders to meet their diversity goals. They also put policies and systems in place to prevent/address discrimination in the workplace.
Marketing problems
Marketing problems are related to promoting and selling a company’s products or services. Problems usually arise in understanding customer behavior and preferences and developing marketing strategies that appeal to those customers. Solving marketing problems requires revisiting the marketing strategy, understanding customer needs and behaviors by analyzing data, positioning the products more appealingly, and branding them better to reflect the strengths of the company and its product offerings.
Understanding customer needs and behavior
Customer needs to dictate the direction of product development and positioning. To design and deliver successful products, businesses must gain a deep understanding of customer needs, preferences, and pain points. For instance, the Japanese car makers capitalized on the high gas prices during the oil crisis and managed to capture the market in the US with their more efficient and reliable cars. The sudden loss in interest in the large, thirsty cars caused a considerable shift in the market, allowing Japanese car manufacturers to position their products in line with the customers’ preferences and succeed.
Developing a strong brand identity
Businesses must create a brand identity that resonates with the customers and sets them apart from competitors. For instance, it is common for companies to change their logo and brand identity in line with the changing trends, customer preferences, and product strategy.
Identifying new marketing channels and tactics
Businesses must be able to identify and adapt to changing customer preferences and identify new channels and tactics for reaching those customers. For instance, many retail businesses have adopted an eCommerce strategy to cater to mobile-savvy customers and to reach new markets.

What Skills do Business Leaders Require for Effective Problem-Solving?
Following are some of the skills required for effective problem-solving in business.
1. Research and analytical skills
Problems have various potential implications. Trying to solve them straight away without doing proper research can cause further problems. Business leaders should study the problem to gain a deeper understanding, assess the solutions thoroughly, and test them before deploying them. They also need good analytical skills to review the performance metrics that indicate the problem areas and analyze information and data to understand the problem. Analytical skills help business leaders break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts, identify their root causes, avoid bounded rationality in decision making , and develop effective solutions and creative workarounds.
2. Creativity
When the problems are complex and multi-dimensional, they may require unique solutions that never existed before. Finding solutions for these problems requires creativity and a culture of innovation in the company. Business leaders must think creatively and tread unconventional paths to create innovative solutions. For instance, during the pandemic, when customers did not want to take the risk of going to retail stores to buy things but were reluctant to pay for the high shipping costs involved in e-commerce, retail businesses offered solutions such as BOPIS that let customers order online and collect their purchases safely from collection booth/kiosk at a convenient time. It helped them meet customer needs by offering the best of both worlds
3. Decision-making
Effective problem-solving in business requires sound decision-making skills. Problem-solving often involves making choices and tough decisions. For instance, the decision to axe a product line that has performed well in the past but has no future potential is a tough one to make. But retaining it will cost resources and yield decreasing returns. Great business leaders evaluate multiple options/solutions and make decisions in the company’s best interest. Being decisive or having decision clarity also means making the right decisions at the right time. Delays in decision-making can cause severe consequences even if you ultimately make the right decision. So business leaders must analyze everything and make the right decision when it matters the most.
4. Communication
Business leaders cannot single-handedly solve problems. Problem-solving requires a team effort. Good business leaders harness the potential of every employee with their communication skills and excellent coordination. They communicate effectively with colleagues, customers, and stakeholders to identify problems and develop solutions. For instance, in a crowded restaurant, the chef needs to coordinate the kitchen staff continuously, check if they are doing their part efficiently, control food quality, and make sure that food is served at the right table as quickly as possible. Lack of communication from the chef can escalate into a full-fledged nightmare, where customers keep waiting for their orders, kitchen staff make mistakes and deliver poor quality food, and the waiters get the flak for not serving food on time. Such situations can ruin the reputation of the restaurant and lead to the loss of customer trust. So good business leaders must communicate and build synergy among the individuals within and among other teams to get work done effectively.
5. Marketing problems

6. Leadership
Problem-solving is about working with many individuals and bringing the best out of them. So business leaders need great leadership qualities to motivate and inspire their teams to work together and solve problems. For example, innovations come from the R&D department; they get incorporated into products by the product development team, and the products are positioned and promoted in the market by the marketing team. Great business leaders lead product development and deployment by coordinating with all these teams, getting their insights, considering their views, and making important decisions regarding product strategy, product positioning, and branding. Situational Leadership is essential to deal with shifting priorities. Leaders motivate the teams and guide them in the right direction. Without good leadership, a company cannot solve problems effectively.
A Step-by-Step Process to Problem-Solving in Business
Problem-solving in business is often an iterative process. So the steps involved may need to be repeated or revised as new information becomes available. Problem-solving usually involves the following steps:
- Define the problem; include any present symptoms or effects.
- Understand the root cause of the problem and find out how it impacts the business.
- Collect all the necessary information related to the problem by analyzing data, conducting interviews, researching, and seeking input from others.
- Brainstorm with the stakeholders and generate potential solutions to the problem. Encourage open communication, collaboration, and participation among team members.
- Weigh the pros and cons, evaluate all the potential solutions, analyze the risks, and consider the feasibility of each.
- Choose the best solution from the evaluated solutions and consider how it will impact the stakeholders, including customers, employees, suppliers, and shareholders.
- Develop an action plan to implement the chosen solution, detailing specific steps, timelines, and responsibilities.
- Implement the solution, monitor progress closely, adjust the plan, make changes as required, and communicate those changes to the stakeholders.
- Evaluate the results, determine if the solution addressed the problem, assess its effectiveness, and identify any areas for improvement.
- Reflect on the problem-solving process, and identify and document the lessons learned.
- Consider how you can improve the process for future problem-solving efforts.

Problem Solving Key Takeaways
Problem-solving is a critical skill for business success. It involves identifying, understanding, and resolving issues in various facets of business operations and strategy. Common obstacles during problem-solving can include cognitive biases, resource constraints, and lack of information. Business leaders must navigate these potential pitfalls to ensure effective resolution of issues.
Essential skills for effective problem-solving include research and analytical abilities, creativity, decision-making, communication, time management, and leadership. These skills enable business leaders to dissect complex issues, devise innovative solutions, make informed decisions, effectively communicate, manage time, and guide teams toward resolution.
Problem-solving is an iterative process that involves multiple stages, from defining the problem and understanding its root cause to brainstorming and evaluating potential solutions, choosing the best one, and developing and implementing an action plan. This process also includes monitoring progress, evaluating results, and reflecting on the process for continuous improvement. An effective problem-solving method is the root cause analysis method. Ultimately, successful problem-solving in business is not just about resolving immediate issues but also about refining and improving the problem-solving process to tackle future challenges more effectively.
Problem Solving in Business FAQs
Answer: The four types of problem-solving strategies typically include:
Trial and Error: Involves trying different solutions until the problem is solved. It’s often used when there are limited possibilities that can be explored quickly.
Algorithm: A step-by-step procedure that, if followed correctly, will always lead to the solution of the problem. It is highly logical and often used in mathematical problems.
Heuristic: A general problem-solving strategy that involves using rules-of-thumb or shortcuts. Heuristics may not always yield the perfect solution but can often lead to a satisfactory one in a reasonable time frame.
Insight: Sometimes also referred to as creative problem-solving. It involves sudden realization, a flash of inspiration, or an ‘Aha!’ moment that provides a solution.
- What is an example of problem-solving in business?
Answer: A common example of problem-solving in business is addressing a sudden drop in sales. The problem-solving process would begin with identifying and defining the problem (drop in sales). The next step would involve researching and analyzing the issue to understand its root cause, such as market conditions, competition, or internal factors. Brainstorming for potential solutions could include improving the product, adjusting pricing, or enhancing marketing efforts. After evaluating and selecting the best solution, an action plan would be developed and implemented. Progress would be monitored, results evaluated, and the process reflected upon for future problem-solving efforts.
- Why is problem-solving important in business?
Answer: Problem-solving is vital in business as it enables organizations to navigate challenges and obstacles that could hamper their growth and success. It allows businesses to identify issues, understand their implications, and devise effective solutions. This process not only resolves the immediate issue at hand but also helps prevent similar problems in the future. Moreover, effective problem-solving can lead to improved business processes, innovation, and a competitive advantage. It also plays a crucial role in customer satisfaction, profitability, and overall sustainability of the business.
- What is the most important problem-solving tool for business?
Answer: There isn’t a one-size-fits-all problem-solving tool for all businesses, as the most effective tool often depends on the specific problem and the business context. However, one universally important tool is effective communication. Clear, open, and honest communication fosters better understanding of problems, facilitates brainstorming of solutions, and aids in the implementation of action plans. Other essential tools include data analysis tools (for understanding and diagnosing problems), brainstorming techniques (for generating solutions), and project management tools (for implementing solutions).
Great leaders possess a unique problem-solving mindset that enables them to navigate complex challenges in the business world. By following this step-by-step guide, you can cultivate these essential skills and unlock your potential for success. Remember, problem-solving is not just about finding solutions but also about fostering a culture of innovation, collaboration, and continuous improvement. Embrace the challenges, seize the opportunities, and lead confidently as you embark on your journey towards becoming an exceptional problem solver and a remarkable leader in the business realm.
Bridge the Strategy Execution Gap with Profit.co
Related articles, the evolving role of natural language processing in communication.
Artificial Intelligence is rapidly becoming a cornerstone of industry practices as companies actively seek innovative ways to integrate it into... Read more
How Can AI Assist and Advance Communication?
Nothing has quite revolutionized communication like technology has. Whether the invention of the telephone in 1876 or the internet in... Read more
How to Conquer Sunday Scaries?
Do you feel anxious, stressed, or depressed every Sunday night? Do you dread the thought of going back to work... Read more
Business Communication for 2024
The bedrock of efficiency is communication perhaps a blanket statement but one with a degree of truth. If you were... Read more

What is Iterative Business Execution?
Get a Personalized Demo
Execute your strategy with the industry’s most preferred and intuitive software

- Privacy Policy
Practical Guide: Solving Problems Examples in Real-World Scenarios
In today’s fast-paced world, problem-solving is an essential skill that can help individuals navigate various challenges. However, merely possessing this skill is not enough. It is crucial to have practical examples of problem-solving techniques and strategies that can be applied to real-life scenarios.
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of problem-solving skills and techniques that can be implemented in different contexts. It explores various problem-solving strategies, including brainstorming, root cause analysis, decision-making frameworks, and creative problem-solving methods.
Furthermore, this guide showcases practical examples of problem-solving in business and personal settings. It features in-depth case studies of real-life scenarios, highlighting the challenges faced, the strategies employed, and the outcomes achieved.

By the end of this guide, readers will have a deeper understanding of problem-solving techniques and strategies. They will also have the knowledge and tools to apply these skills effectively in different scenarios, both in personal and professional life.
Understanding Different Problem-Solving Techniques
The ability to solve problems is a critical skill in both personal and professional life. It involves identifying and analyzing an issue, generating possible solutions, and selecting the best course of action. There are several problem-solving techniques that can be applied to different situations, including:

Brainstorming
Brainstorming involves generating ideas in a group setting without criticism or judgment. This technique encourages creativity and diversity of thought, allowing individuals to approach a problem from different angles.
Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis involves identifying the underlying cause of a problem. This technique involves asking “why” multiple times to determine the primary reason for the issue. By addressing the root cause, individuals can develop more effective solutions.

Decision-Making Frameworks
Decision-making frameworks involve using a set of criteria to evaluate different options and make an informed decision. These frameworks can be simple or complex and involve weighing the pros and cons of each alternative.
Creative Problem-Solving Methods
Creative problem-solving methods involve using non-traditional approaches to generate innovative solutions. These techniques can include mind mapping, lateral thinking, or the use of analogies.

By understanding and using different problem-solving techniques, individuals can approach challenges with a more comprehensive and effective approach. These techniques can be applied in both personal and professional settings, enhancing critical thinking and decision-making skills.
Problem-Solving Examples in Business Settings
In today’s competitive business environment, companies face numerous challenges that require effective problem-solving skills. Successful businesses employ problem-solving strategies that help them overcome obstacles and achieve their goals. Here are some real-life examples of companies that used problem-solving to overcome challenges:

Example 1: Improving Customer Service
A telecommunications company noticed a decline in customer satisfaction ratings. Through surveys and customer feedback, they discovered that customers were frustrated with the company’s long wait times and unresponsive customer service representatives. The company implemented a new customer service training program for their representatives, which included active listening, problem-solving, and conflict resolution skills. As a result, the company’s customer satisfaction ratings improved, and they gained a competitive advantage in the industry.
Example 2: Reducing Production Costs
A manufacturing company was struggling with high production costs due to inefficient processes and materials. The company conducted a thorough analysis of their production line and identified areas where they could cut costs. They implemented new production methods and materials that were more efficient and cost-effective. As a result, the company was able to reduce their production costs, increase their profit margins, and remain competitive in the market.

These examples demonstrate the importance of problem-solving skills in the business world. By identifying challenges, analyzing the root causes, and implementing effective solutions, companies can achieve their goals and remain competitive in their respective industries.
Problem-Solving Strategies in Personal Life
Effective problem-solving skills aren’t just essential in professional settings. They’re equally crucial in personal life too. Whether it’s making a tough decision, dealing with unexpected challenges, or resolving conflicts, problem-solving is critical to achieving desired outcomes. Here are some practical problem-solving strategies to apply in personal situations:

1. Breakdown the problem:
When you encounter a problem, start by breaking it down into smaller parts. This approach will help you identify the root cause and develop a step-by-step plan to address the issue.
2. Evaluate your options:
Once you have a clear understanding of the problem, evaluate your options objectively. Consider the pros and cons of each alternative and analyze their potential outcomes.

3. Seek advice:
Don’t hesitate to ask for advice from those you trust and respect. Getting an outside perspective can help you gain a new insight into the problem at hand.
4. Use creative problem-solving techniques:
Applying creative problem-solving techniques like brainstorming, mind-mapping, and reverse-thinking can help you explore innovative solutions to complex problems. It’s essential to think outside the box.

5. Learn from failures:
Failure is a part of life, and it’s okay to make mistakes. The key is to learn from these experiences and use them as an opportunity to grow and develop your problem-solving skills further.
By applying these practical problem-solving strategies in your everyday life, you’ll develop a strong problem-solving mindset that enables you to tackle any challenge with confidence and ease.

Case Studies: Real-Life Problem-Solving Examples
In this section, we will explore real-life examples of problem-solving in different industries. These case studies showcase effective problem-solving strategies and provide insights into how challenges can be overcome using a structured approach.
Airbnb: Breaking Through Regulatory Barriers
When Airbnb was expanding into cities around the world, it faced regulatory barriers that threatened to derail its growth. In New York City, for example, hosts were required to register with the city and rent their apartments for a minimum of 30 days at a time.

To overcome these barriers, Airbnb worked with city officials to develop a new regulatory framework that allowed hosts to rent their homes for shorter periods of time. The company also implemented a host education program to ensure compliance with local laws.
Through this problem-solving approach, Airbnb was able to break through regulatory barriers and continue its expansion into new markets.

Toyota: Improving Quality Control
Toyota faced a massive recall of millions of vehicles due to safety concerns related to its accelerator pedals. In response, the company implemented a problem-solving strategy known as “5 Whys,” which involves asking why a problem occurred five times to identify the root cause.
Through this process, Toyota discovered that a faulty design led to the accelerator pedal becoming stuck, which led to the recall. The company then implemented a new quality control process to prevent similar issues from occurring in the future.

By using a structured problem-solving methodology, Toyota was able to identify the root cause of the issue and implement an effective solution to prevent future recalls.
Microsoft: Adapting to Changing Markets
Microsoft faced significant challenges in the early 2010s as the market shifted towards mobile devices and away from personal computers. The company responded by shifting its focus to cloud-based services and mobile devices.

To do this, Microsoft implemented a problem-solving strategy known as “design thinking,” which involves empathizing with users and designing products that meet their needs. By focusing on the needs of its customers, Microsoft was able to adapt to the changing market and remain a leading player in the tech industry.
These case studies demonstrate the power of effective problem-solving strategies in real-world scenarios. By utilizing structured problem-solving methodologies and focusing on the needs of their customers, these companies were able to overcome challenges and achieve success.

Developing Problem-Solving Skills through Exercises
Problem-solving is a skill that can be developed and honed through practice. By engaging in specific exercises and activities, individuals can enhance their problem-solving abilities and become more effective in real-life scenarios.
Here are a few exercises and activities that can help individuals develop their problem-solving skills:

One of the most popular problem-solving techniques is brainstorming. This exercise involves generating multiple ideas in a short amount of time, without evaluating the quality of each idea. It can be used to solve both personal and professional problems. To conduct a brainstorming session, gather a group of individuals and pose a problem or challenge. Encourage everyone to share as many ideas as possible towards a potential solution.
Mock Scenarios
Mock scenarios are another effective way to practice problem-solving. This exercise involves creating a hypothetical scenario and asking individuals to solve it. The scenario can be related to personal or professional challenges and should require critical thinking and decision-making skills. By practicing in a risk-free environment, individuals can experiment with different problem-solving techniques and strategies, and evaluate the effectiveness of each approach.

Gamification
Gamification involves using game-like elements to engage individuals and motivate problem-solving efforts. This exercise can be particularly effective for younger individuals or those who prefer a more interactive approach. Gamification can involve using puzzles, quizzes, or other game formats to solve problems. These activities offer a fun and engaging way to develop problem-solving skills.
Remember that while exercises can be helpful, problem-solving is ultimately a skill that is developed through practice and experience in real-life scenarios. Continually seeking opportunities to engage in problem-solving can improve abilities and build confidence in making informed decisions.

Implementing Problem-Solving Methods in Real-Time
Problem-solving is not a one-time event but an ongoing process. It requires adaptability, critical thinking, and decision-making abilities to achieve desired outcomes. Here are some practical methods for implementing problem-solving in real-time situations:
Stay Focused on the Problem
When faced with a problem, it’s essential to stay focused on the issue at hand. Avoid getting sidetracked by unrelated details, emotions, or distractions. Keep a clear understanding of the problem and the desired outcome.

Brainstorm Possible Solutions
Engage in brainstorming sessions to generate possible solutions to the problem. Encourage everyone’s participation and have an open mind to new ideas. Use a whiteboard or sticky notes to collect and organize ideas for evaluation.
Prioritize Possible Solutions
After generating possible solutions, evaluate and prioritize them based on their potential impact, feasibility, and cost. Choose the most appropriate solution based on these factors, and consider the potential risks and drawbacks associated with it.

Monitor and Adjust the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Check if it’s being executed as planned and if it’s achieving the desired outcomes. Be open to making adjustments to the solution if necessary and continue to monitor its progress.
Document the Problem-Solving Process
Keep a record of the problem-solving process, including the problem, the chosen solution, the implementation process, and the results achieved. Use this information to evaluate the success of the problem-solving process, identify areas for improvement, and apply what you’ve learned to future challenges.

Implementing problem-solving methods in real-time requires focus, creativity, and persistence. With the right approach and mindset, you can successfully overcome challenges and achieve your desired outcomes.
Strategies for Overcoming Common Problem-Solving Challenges
Problem-solving can be a challenging and complex process, and it’s not uncommon to encounter roadblocks along the way. Here are some strategies for overcoming common problem-solving challenges:

Managing ambiguity
Often, problems can be vague and ill-defined, making it difficult to know exactly what to do. To overcome this challenge, it can be helpful to break down the problem into smaller, more manageable pieces. Identifying the root cause of the issue and defining clear objectives can also help reduce ambiguity and provide direction.
Dealing with complexity
Complex problems can be overwhelming, and it’s easy to get bogged down in the details. To tackle complexity, it’s important to step back and take a broader view of the situation. Looking at all the relevant factors and considering different perspectives can help identify potential solutions.

Approaching problems from different perspectives
It can be easy to get stuck in a rut and approach problems in the same way every time. To overcome this challenge, try approaching problems from different angles. Considering multiple perspectives can help uncover new solutions and shed light on potential blind spots.
Building resilience
Problem-solving can be a tough and sometimes frustrating process. It’s important to develop resilience and the ability to persist in the face of obstacles. Practicing mindfulness techniques, maintaining a positive attitude, and taking breaks when needed can all help build resilience.

Maintaining a positive problem-solving mindset
It can be easy to get discouraged when things don’t go as planned. To maintain a positive problem-solving mindset, focus on the progress made, rather than the setbacks encountered. Celebrating small wins along the way can help keep momentum going and boost motivation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Problem-Solving
In this section, we address some of the commonly asked questions related to problem-solving. These FAQ’s aim to provide guidance and clarify doubts on various aspects of problem-solving methods and techniques.

What are the different problem-solving techniques?
There are several problem-solving techniques that individuals and businesses can apply to resolve any challenges they face. Popular strategies include brainstorming, root cause analysis, decision-making frameworks, and creative problem-solving methods.
How can problem-solving skills be developed?
Problem-solving skills can be honed by practicing exercises and activities designed to enhance critical thinking and decision-making processes. Continuous learning and development are also crucial for building effective problem-solving skills.

What are the essential qualities for effective problem-solving?
Effective problem-solving requires critical thinking, adaptability, decision-making skills, a positive mindset, and the ability to manage ambiguity and complexity. Communication and collaboration skills are also important, as problem-solving often involves working with others.
What are some common challenges encountered during problem-solving processes, and how can they be addressed?
Common challenges during problem-solving include managing ambiguity, dealing with complexity, and approaching problems from different perspectives. To overcome these challenges, it is essential to remain flexible, stay focused on the end goal, and break problems down into smaller, more manageable parts. Taking breaks and seeking feedback from others can also be beneficial.

How can problem-solving methods be effectively applied in real-time situations?
Effective problem-solving in real-time situations requires critical thinking, analytical skills, and decision-making abilities. It is important to remain adaptable and flexible, consider multiple options, and prioritize actions based on their potential impact. Communication and collaboration with others can also aid in effective problem-solving.
What are some additional resources for learning about problem-solving?
There are several additional resources available for further learning about problem-solving. Books, online courses, and workshops can provide valuable insights and practical guidance for developing problem-solving skills. Networking with others in similar fields and seeking mentorship can also be beneficial for problem-solving growth and development.

Share this:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.

Unbiased Skillshare Reviews: Expert Insights & Analysis

Mastering the Follow Up Email to Interview: Professional Guide

Expert Guide: Impressive Resume Example Summary for Job Seekers

Crafting an Effective Thank You Letter for the Interviewer

Crafting Effective Interview Thank You Letters: A Guide

Unveiling the Best Time of Year to Apply for Jobs
Problem-Solving in Business: PROBLEM-SOLVING DEFINED AND WHY IT IS IMPORTANT
- ABOUT THIS LIBGUIDE
- PROBLEM-SOLVING DEFINED AND WHY IT IS IMPORTANT
- SKILLS AND QUALIFICATIONS NEEDED IN PROBLEM-SOLVING
- PROBLEM-SOLVING STEPS
- CASE STUDIES
- MORE HELPFUL RESOURCES

- << Previous: ABOUT THIS LIBGUIDE
- Next: SKILLS AND QUALIFICATIONS NEEDED IN PROBLEM-SOLVING >>
- Last Updated: Mar 23, 2024 4:47 PM
- URL: https://libguides.nypl.org/problem_solving_in_business
How to Create a Convincing Problem and Solution Statement

Makenna Crocker
10 min. read
Updated November 3, 2023
“Every sale a business makes is related to a problem. In every case, there is a story.” – Tim Berry
A powerful problem and solution statement should tell a story about your customers and the solution you provide. It’s how you position your business within your business plan .
But crafting a short and compelling description of your problem and solution is easier said than done. This guide will walk you through the process.
Why you need to describe the problem you’re solving
So you’ve got a solid business idea . That’s a great starting point, but it’s just that—a starting point.
The key to moving forward is identifying a real-world problem your product or service aims to solve. This isn’t just a box to tick off; it has serious implications for your business.
Here’s why:
1. Validate real-world demand
First, you need to show actual demand for your offering. This goes beyond mere speculation or gut feelings; you need tangible evidence that proves you have a viable solution.
Example: If you’re planning on opening a gluten-free bakery, for instance, it’s not enough to say there’s a need for one—you should back it up with data.
2. Zero in on your ideal customer
Once you’ve established that a need exists, it’s time to get specific about who you’re targeting . Understanding who will benefit the most from your solution helps you fine-tune nearly every aspect of your business.
Example: In the case of a gluten-free bakery, you’re not targeting just anyone who likes baked goods; you’re focusing on those with specific dietary needs or preferences.
3. Carve out your niche
Knowing the problem you’re solving gives you a leg up when positioning yourself in the market. This is where you find the gaps that competitors are missing and jump right in.
Example: Maybe there are plenty of bakeries, but none have a robust gluten-free selection. That’s your territory; that’s how you stand out.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
4. Keep the team on the same page
A clearly defined problem serves as a guidepost for you and your team . It ensures that everyone knows what the goal is and stays aligned. Whenever there’s a question about what the business should focus on, you can always circle back to that original problem statement.
5. Make stakeholders take notice
A well-defined problem and solution make it easier for stakeholders like potential investors or partners to understand why your business is worth paying attention to. It’s one thing to offer up data; it’s another to weave that into a compelling narrative about why your business matters.
“Stories are the oldest and arguably best way to communicate ideas, truth, beliefs, and even numbers,” says Palo Alto Software founder and business planning expert Tim Berry.
“Stories are powerful… They resonate. We recognize their truths.”
Example: You’re inspired to start a gluten-free bakery because of your niece, who has Celiac disease. Her limited dietary options make social events like birthday parties isolating for her. While some bakeries offer gluten-free items, they are often uninspired and don’t allow her to fully enjoy celebrations with her friends.
Your bakery aims to solve this by providing delicious, gluten-free sweet treats that kids and adults with gluten allergies can freely enjoy.
A well-articulated problem statement is crucial for attracting investors and business partners. Not only does it make them care about the problem you’re solving, but it also simplifies the process of writing your executive summary —the first thing lenders or investors are likely to read in your business plan.
- How to develop your problem and solution statement
Developing your problem and solution statement is an ongoing process, not a one-off task. And it’s not just a random explanation, but something that speaks to the core of why you started your business .
So it’s important to arrive at a clear, succinct, and informative statement. To help develop a strong problem and solution statement, take the following steps:
Identify the problem
When it comes to identifying the problem your business solves, it’s crucial to understand the market you are targeting. You’ll do this by conducting market research . This is the process of gathering information about potential customers.
It helps you find answers to questions like:
- Who are your customers?
- What is the size of your potential customer base?
- What are their shopping habits?
You’ll eventually get into deeper questions like:
- What struggles do these people face?
- What do they desire?
- What currently exists to help fix their problem?
- What would they be willing to pay?
- Are there other, more pressing problems?
After you’ve done the research necessary to reference your target market in your statement—you need to identify the problem . Consider things like:
- How much time, money, or mental anguish does this problem cause?
- Why is no one else solving it?
- How do people cope currently?
Example: With the gluten-free bakery, the problem is there are not enough local options for allergy-friendly fresh baked goods. Ask yourself questions like:
- Why hasn’t anyone started a gluten-free bakery already?
- What are people with gluten allergies doing to satisfy their sweet tooth?
Answering questions like these will help you explore all potential problems and narrow it down to the key elements of the real problem you’re solving.
Define your solution
By now, you should have a clear understanding of who your customers are, what problems they’re experiencing, and how others in the market are trying to solve those problems.
Now it’s time for your proposed solution. Earlier, we mentioned the importance of being able to define the unique value of your business. When you align that value with your customer’s problems, you have a unique value proposition – the thing that sets your solution apart in the eyes of your customers.
As you think about your solution, ask yourself:
- How does your product or service differ from others in the market?
- What makes it valuable?
- Why is it better than other solutions?
Answering these questions will help ensure that you can communicate the value of your business to your target market. After all, if you can’t communicate your value to your customers, they probably won’t see it, either.
- How to write your problem statement
After using your research to identify your problem, it’s time to turn that work into a well-crafted problem statement.
Start by boiling down the core issues you found in your research to pinpoint the most significant problem your business aims to solve.
This is where it can be really important to gather additional feedback beyond your own research. It could include getting feedback from potential customers , creating surveys, or even convening focus groups. These conversations will help ensure that you focus on a genuine problem people are experiencing.
When writing the problem statement, be sure to:
- Clearly and succinctly define the problem. Avoid jargon and complex language.
- Be precise in describing who the problem affects and what the implications are for them
Example: Circling back to our gluten-free bakery—a problem statement might look like this:
“There are no local gluten-free bakeries to serve the growing community of individuals with gluten intolerance. Instead, they’re forced to rely on major grocery store chains with limited selections of poor quality, highly processed baked goods.”
As you can see, the statement starts by generally reciting the problem. Within your business plan, supporting statistics from your market research will follow. For now, we’re sticking to the mechanics of writing the statement.
Make sure your problem statement directly aligns with the solution your business offers. It’s also important to highlight how addressing this problem sets your business apart from competitors.
Be sure to also seek feedback on your problem statement from stakeholders, potential customers, or a mentor to ensure it accurately represents the issue.
- Sell your solution
“The problem is half the story; the solution is the other half. It’s the shoe waiting to drop.” – Tim Berry
You need your solution to hold as much weight as the problem.
So what does it mean to sell your solution? Think about your elevator pitch – you have just a moment to explain how your solution solves a problem in the market. It can’t be convoluted or complex, even if the actual solution is to some degree.
Your solution statement should address how your product or service addresses the core issue or issues raised by the problem statement. It also needs to be grounded in reality – don’t promise a grand solution that you can’t actually deliver on.
Just like with the problem statement, keep the solution statement clear and simple. Using the gluten-free bakery example, you could say: “Our bakery provides a wide range of fresh, locally made gluten-free products to satisfy the cravings and meet the dietary needs of customers with gluten intolerance.”
Let’s look at a real-life example. When the video streaming giant Netflix launched in the late 1990s, it explained its problem and solution statement this way :
Problem: “Going to the video store requires fighting traffic, wandering the aisles, and waiting in long lines just to get a single movie.”
Solution: “Netflix allows anyone to enjoy thousands of titles… delivered to their mailbox.”
Now let’s apply the idea to our bakery example:
Problem: “The area does not have a local spot that offers a wide variety of quality and appealing gluten-free baked goods for those with allergies and intolerances.”
Solution: “Our bakery specializes in beautifully decorated and tasty gluten-free baked goods, so no one misses out on the chance to indulge.”
You’ve already illustrated the target demographic’s pain points in your problem, and your solution clearly explains exactly how you are helping them.
Craft and refine
Now it’s time to edit and perfect your problem and solution statement. Be critical of your own work. Here are some questions to ask yourself:
- If you show the problem and solution statement to your friends or family, can they understand what your business does and get the problem?
- Can you easily remember and recite the statement?
- Is your statement as short as can be? (Tip: focus on making it 3 sentences or less.)
- Would this statement work in ads or on your business website ?
- Problem and solution statement examples
Sometimes, you don’t know what works for you until you are given some samples. Below are some product and solution statement examples to help visualize your final statement. Feel free to copy and rework them for your own business!
Mobile dog groomer example:
Problem: Many dog owners cannot take their dogs to a groomer due to mobility issues, busy schedules, or location.
Solution: Our mobile dog groomer service goes directly to the client, allowing them to stay home while their dog is groomed right outside.
Fertility clinic app example:
Problem: Individuals and couples seeking fertility care struggle to find information on nearby clinics offering the treatment they seek.
Solution: Our fertility clinic app allows users to enter their location and the treatment they are looking for and generates an interactive map that details clinics in and around their area that specialize in their needs.
Home loan company example:
Problem: Recent hikes in interest rates have led to a decline in home purchases, adversely affecting both mortgage companies and potential home buyers.
Solution: Our home loan company introduces a tailored refinancing program that provides existing homeowners with more manageable repayment terms while also assisting prospective buyers in securing mortgage loans with favorable rates to make it easier for individuals looking to sell their current home to purchase a new one.
- Start your business plan
Crafting a compelling problem and solution statement is not just a task – it speaks to why you decided to get into business and is one of the most important sections of your business plan.
If you are ready to get started on your business plan, you have access to over 550 free business plan examples from the Bplans library.
Download your free business plan template today to get started!
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Makenna Crocker is the Marketing Specialist at Richardson Sports. Her work focuses on market and social trends, crafting gripping and authentic content, and enhancing marketing strategy to foster stronger B2B and B2C relationships. With a master’s degree in Advertising and Brand Responsibility from the University of Oregon, she specializes in generating a strong and responsible brand presence through content that positively influences and inspires others.
.png)
Table of Contents
- Why you need to describe the problem you’re solving
Related Articles

10 Min. Read
How to Write a Competitive Analysis for Your Business Plan

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

6 Min. Read
How to Get and Show Initial Traction for Your Business
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of Problem Solving Scenarios in the Workplace. Correcting a mistake at work, whether it was made by you or someone else. Overcoming a delay at work through problem solving and communication. Resolving an issue with a difficult or upset customer. Overcoming issues related to a limited budget, and still delivering good work through the ...
Problem-solving in the workplace is a complex and multifaceted skill that requires a combination of analytical thinking, creativity, and effective communication. It goes beyond simply identifying problems and extends to finding innovative solutions that address the root causes. Essential Problem-Solving Skills for the Workplace
4 Problem-Solving Skills All Leaders Need. 1. Problem Framing. One key skill for any leader is framing problems in a way that makes sense for their organization. Problem framing is defined in Design Thinking and Innovation as determining the scope, context, and perspective of the problem you're trying to solve.
All episodes. Details. Transcript. December 04, 2018. Corey Phelps, a strategy professor at McGill University, says great problem solvers are hard to find. Even seasoned professionals at the ...
That's what we've found after decades of problem solving with leaders across business, nonprofit, and policy sectors. These leaders learn to adopt a particularly open and curious mindset, and adhere to a systematic process for cracking even the most inscrutable problems. They're terrific problem solvers under any conditions.
Problem-Solving Examples 1. Divergent Thinking. ... Benchmarking involves comparing one's business processes and performance metrics to the best practices from other companies or industries. In problem-solving, it allows you to identify gaps in your own processes, determine how others have solved similar problems, and apply those solutions ...
When we do problem definition well in classic problem solving, we are demonstrating the kind of empathy, at the very beginning of our problem, that design thinking asks us to approach. When we ideate—and that's very similar to the disaggregation, prioritization, and work-planning steps—we do precisely the same thing, and often we use ...
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues.You may face challenges around growth, design, user engagement, and even team culture and happiness.In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team's skillset.
And you can do the same. By following this 10-step process, you can develop your problem-solving skills and approach any issue that arises with confidence. 1. Define the problem. When a problem arises, it can be very easy to jump right into creating a solution. However, if you don't thoroughly examine what led to the problem in the first ...
How to Solve Problems. To bring the best ideas forward, teams must build psychological safety. by. Laura Amico. October 29, 2021. HBR Staff/EschCollection/Getty Images. Teams today aren't just ...
Here are 11 common business problems with potential solutions to help you develop plans and strategies for your own organization: 1. Uncertain purpose. Some companies experience a loss of purpose or uncertainty. This can happen if an organization participates in multiple different industries or frequently changes its mission statement.
Problem-solving in business is defined as implementing processes that reduce or remove obstacles that are preventing you or others from accomplishing operational and strategic business goals. In business, a problem is a situation that creates a gap between the desired and actual outcomes. In addition, a true problem typically does not have an ...
Business problem-solving examples Retaining top talent. Retaining top talent can be a determining factor for the success of a company. Businesses must build an environment that attracts top talent by creating opportunities for career advancement and offering competitive compensation packages. For instance, highly specialized jobs with business ...
Here are some examples of problem-solving scenarios: - A manufacturing company is experiencing a high rate of defects in its products. The company needs to identify the root cause of the problem and implement a solution to improve quality control. ... Here is an example of a problem-solving: A small business owner is experiencing a decline in ...
Problem-Solving Examples in Business Settings. In today's competitive business environment, companies face numerous challenges that require effective problem-solving skills. Successful businesses employ problem-solving strategies that help them overcome obstacles and achieve their goals. Here are some real-life examples of companies that used ...
WHAT IS PROBLEM-SOLVING IN BUSINESS? ... EXAMPLES OF COMMON BUSINESS PROBLEMS: Problem-solving is important both to individuals and organizations because it enables them to exert control over their environment. * Fixing things that are broken: Some things wear out and break over time, others are flawed from day-1. Personal and business ...
Problem solving is the process of overcoming issues, mistakes, errors, failures and risks to move forward. This includes approaches such as troubleshooting, analysis, experimenting, rational thought, intuition and creativity designed to find solutions. The following are examples of problem solving followed by a list of problem solving techniques.
Problem Solving Resources. You can also search articles, case studies, and publications for problem solving resources. Books. Innovative Business Management Using TRIZ. Introduction To 8D Problem Solving: Including Practical Applications and Examples. The Quality Toolbox. Root Cause Analysis: The Core of Problem Solving and Corrective Action ...
4. Keep the team on the same page. A clearly defined problem serves as a guidepost for you and your team. It ensures that everyone knows what the goal is and stays aligned. Whenever there's a question about what the business should focus on, you can always circle back to that original problem statement. 5.
Problem solving. The business analysis process can be viewed as an exercise in solving a series of problems to produce beneficial outcomes for an organisation. Those problems may be related to: issues occurring in the business (see 'Example business problems' below) project methodology and personal skills.
For example, a client may request an addition of a step to the process. Diving more and trying to figure out the actual need behind this request may reveal that there is another way of treating the actual need. The following stages are commonly used by Business Analysts when problem solving is required. 1) Problem Definition.
1. A business problem solving proposal can help you focus and give priority on the identification of the solutions that will best work for your business when it comes to dealing with the identified problem. It is important for you to consider the ability of the business to execute your plans as well as the resources that will be used for the ...
The following are illustrative examples of business problems. Adverse geopolitical events. Anti-competitive practices of a large competitor. Brand identity crisis. Budget overruns. Business model disrupted by change. Cash flow issues. Changing customer needs. Competitive pressures.