- Coaching Skills Training
- Coaching TIPS²™
- Continuous Improvement Coaching
- Courageous Conversations Workshop
- Executive Coaching Program
- Feedback 360
- Safety Coaching
- Sales Coaching Training Program
- Free Consultation
- Applied Strategic Thinking®
- Strategic Leadership Course
- Strategic Teaming
- Strategy Development Processes and Services
- Communication Training for Managers
- Conflict and Collaboration
- Confronting Racism Workshop
- Delegation & Accountability
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Workshop
- Flexible Leadership
- Leading Change
- Leading Groups to Solutions
- Leading Innovation
- Mid-Level Management Training
- Qualities of Leadership
- Bottom Line Leadership
- Customized Leadership Development Programs
- Leadership Development Program Design
- Mini-MBA & Operational Finance
- Problem Solving and Decision Making in the Workplace
- Transition to Leadership
- Virtual Leadership
- High-Performance Teamwork
- Leadership Team Alignment Workshop
- Orienteering
- Corporate Outdoor Training and Team Building
- Retreats for Teams
- Innovation Skills Training
- Personal Impact Workshop
- Supervisor Training Programs
- Customization of CMOE’s Learning Library
- Full Curriculum Development and Design
- Learning & Development Advisory Services
- Bottom Line Leadership Training
- Consulting Services
- Leadership Retreats
- Learning and Development Consulting Services
- Needs Analysis and Organization Assessments
- Transformation & Change Solutions
- Facilitator Training Workshop
- Empathic Leadership
- Supervisor Development Series
- All Courses
- Digital Learning
- Books and Publications
- Assessments and Surveys
- Clients Served
- History and Experience
- Meet the CMOE Team
- Testimonials
- Articles & Tools
- Scenario Templates
- Certified Partners
- Event Resources
- Industry Insights
- Resource Library
- Video Library
- News and Events
- Professional Accreditation and Continuing Education Units
- Surveys & Assessments
- Problem Solving in Business
- 360-Degree Leadership Assessment
- Adaptive Communication
- Adaptive Leadership
- Authentic Leadership Style
- Boundary Spanning Leadership
- Business Change Strategies
- Business-Strategy Principles
- Capacity Building
- Cascading Strategy
- Change Management
- Coaching Framework
- Coaching in the Workplace
- Coaching Leadership Style
- Collaborative Coaching
- Competency Assessment
- Conflict Resolution in the Workplace
- Core Competence
- Corporate Strategic Planning
- Crisis Leadership
- Critical Success Factors
- DEI in the Workplace
- Directive Leader
- Empathetic Leadership Definition
- Horizontal Leadership
- Inclusive Leadership
- Innovation Strategy
- Leadership Competency Framework
- Leadership Model
- Management Succession Planning
- Operational Excellence
- Organizational Alignment
- Participative Leadership Style
- Performance Deficiency Coaching
- Persuasive Leadership Style
- Servant Leadership Style
- Strategic Agility
- Strategic Alignment
- Strategic Audit
- Strategic Framework
- Strategic Management
- Strategic Mindset Competency
- Strategic Thinking
- Strategy Committee
- Strategy Issues
- Strategy Maps
- Supportive Leadership Style: Definition and Qualities
- Team Building Interventions
- Team Environment
- Team Performance Assessment
- Teamwork Atmosphere
- Total Employee Involvement
- Training Needs Analysis (TNA) Definition
- Transformational Leadership
- Visionary Leadership Style
- What Are Strategic Initiatives: Examples and Development

What Is Problem Solving in Business?
Problem-solving in business is defined as implementing processes that reduce or remove obstacles that are preventing you or others from accomplishing operational and strategic business goals.
In business, a problem is a situation that creates a gap between the desired and actual outcomes. In addition, a true problem typically does not have an immediately obvious resolution.
Business problem-solving works best when it is approached through a consistent system in which individuals:
- Identify and define the problem
- Prioritize the problem based on size, potential impact, and urgency
- Complete a root-cause analysis
- Develop a variety of possible solutions
- Evaluate possible solutions and decide which is most effective
- Plan and implement the solution
Why Is Problem-Solving Important in Business?
Understanding the importance of problem-solving skills in the workplace will help you develop as a leader. Problem-solving skills will help you resolve critical issues and conflicts that you come across. Problem-solving is a valued skill in the workplace because it allows you to:
- Apply a standard problem-solving system to all challenges
- Find the root causes of problems
- Quickly deal with short-term business interruptions
- Form plans to deal with long-term problems and improve the organization
- See challenges as opportunities
- Keep your cool during challenges
How Do You Solve Business Problems Effectively?
There are many different problem-solving strategies, but most can be broken into general steps. Here is a six-step method for business problem solving:
1) Identify the Details of the Problem: Gather enough information to accurately define the problem. This can include data on procedures being used, employee actions, relevant workplace rules, and so on. Write down the specific outcome that is needed, but don’t assume what the solution should be.
- Use the Five Whys: When assessing a problem, a common strategy is to ask “why” five times. First, ask why the problem occurred. Then, take the answer and ask “why” again, and so on. The intention is to help you get down to the root cause of the problem so you can directly target that core issue with your solution.
2) Creatively Brainstorm Solutions: State every solution you can think of. Write them down. Seek input from those who possess in-depth knowledge of or experience with the problem you’re trying to solve. These insights will provide you with valuable perspectives you can transform into tangible and impactful solutions.
3) Evaluate Solutions and Make a Decision: Assess the feasibility of each solution. Is the deadline realistic? Are there readily available resources you can leverage to successfully implement the solution? What is the return on investment of each solution? If necessary, come up with alternative solutions or adjust the initial ones you brainstormed in step 2.
4) Make a Decision: Finally, make a firm decision on one solution. This final solution should clearly address the root cause of the problem.
- Perform a SWOT Analysis: You can use a SWOT analysis to help you decide on the best solution. A SWOT analysis involves identifying the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats linked to a specific decision. With this framework, your team can assess a decision from various angles, thereby gaining a holistic view of it.
5) Take Action: Write up a detailed plan. This involves developing a comprehensive roadmap that outlines the steps required to implement your solution. The steps should specify milestones, deadlines, roles, and how to obtain the necessary approvals. To ensure accountability, your entire team should have access to this action plan. Each team member should be able to track and share their progress with the group.
6) Gather and Share Feedback: Problem-solving is not a “set it and forget it” process. It’s a dynamic journey that necessitates ongoing attention, deliberation, and refinement to achieve optimal results. Thus, periodic feedback is critical in validating whether the chosen solution creates the desired impact. It allows key stakeholders to check in and make any necessary changes.
What Are Problem-Solving Skills?
Problem-solving skills are specific procedures that can be used to complete one or more of the six general steps of problem-solving (discussed above). Here are five important examples:
Using Emotional Intelligence: You’ll solve problems more calmly when you learn to recognize your own emotional patterns and to empathize with and guide the emotions of others. Avoid knee-jerk responses and making assumptions.
Researching Problems: An effective solution requires an accurate description of the problem. Define simple problems using quick research methods such as asking, “What? Where? When? and How much?.” Difficult problems require more in-depth research, such as data exploration, surveys, and interviews.
Creative Brainstorming: When brainstorming with a group, encourage idea creation by listening attentively to everyone, and recognizing everyone’s unique contributions.
Logical Reasoning: Develop standard logical steps for analyzing possible solutions to problems. Study and apply ideas about logical fallacies, deductive reasoning, and other areas of analytical thought.
Decisiveness: Use an agreed-upon system for choosing a solution, which can include assigning pros and cons to solutions, identifying mandatory results, getting feedback about solutions, choosing the decision-maker(s), and finishing or repeating the process.
How Can You Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills?
Learning how to solve business problems takes time and effort. Though some people appear to have been born with superior problem-solving skills, great problem-solvers usually have taken the time to refine their abilities. You can develop high-level skills for solving problems too, through the following methods:
Ask and Listen: Don’t expect to solve every problem alone. Ask for advice, and listen to it carefully.
Practice Curiosity: Any time you’re involved in solving a problem, practice researching and defining the problem just a little longer than you would naturally.
Break Down Problems: Whenever possible, break large problems into their smallest units. Then, search for solutions to one unit at a time.
Don’t Label Yourself Negatively: Don’t allow a problem to mean something negative about you personally. Separate yourself from it. Look at it objectively and be part of the solution.
Enhance Your Problem-Solving Skills with CMOE
Problem-solving skills in business are not developed overnight. Developing then takes ongoing practice and the right guidance to get right. We encourage you to leverage CMOE’s Problem-Solving and Decision Making in the Workplace workshop to further develop your skills. We’ll help you identify new ways to solve problems methodically so you can create greater impact.
Clients We’ve Worked With
Contact form.
Need More Information? Please fill out the following form and we will be in contact with you with more information.
" * " indicates required fields
As Featured In:
The Better Business Bureau has determined that CMOE meets accreditation standards. These standards verify that CMOE’s product quality and competence enhance customer trust and confidence.
©2023 Center for Management & Organization Effectiveness. All rights reserved.

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)
- A Step-by-Step Guide to A3 Problem Solving Methodology
- Learn Lean Sigma
- Problem Solving
Problem-solving is an important component of any business or organization. It entails identifying, analyzing, and resolving problems in order to improve processes, drive results, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. A3 Problem solving is one of the most effective problem-solving methodologies.
A3 Problem solving is a structured and systematic approach to problem-solving that originated with the lean manufacturing methodology. It visualizes the problem-solving process using a one-page document known as an A3 report. The A3 report provides an overview of the problem, data analysis, root causes, solutions, and results in a clear and concise manner.
A3 Problem Solving has numerous advantages, including improved communication, better decision-making, increased efficiency, and reduced waste. It is a powerful tool for businesses of all sizes and industries, and it is especially useful for solving complex and multi-faceted problems.
In this blog post, we will walk you through the A3 Problem Solving methodology step by step. Whether you are new to A3 Problem Solving or simply want to improve your skills, this guide will help you understand and apply the process in your workplace.
Table of Contents
What is a3 problem solving.
A3 Problem Solving is a structured and systematic approach to problem-solving that makes use of a one-page document called an A3 report to visually represent the process. The A3 report provides an overview of the problem, data analysis, root causes, solutions, and results in a clear and concise manner. The method was created within the framework of the Lean manufacturing methodology and is based on the principles of continuous improvement and visual management.
Looking for a A3 Problem solving template? Click here
Origin and History of A3 Problem Solving
A3 Problem Solving was developed by Toyota Motor Corporation and was first used in the manufacture of automobiles. The term “A3” refers to the size of the paper used to create the report, which is an ISO standard known as “A3”. The goal of the A3 report is to provide a visual representation of the problem-solving process that all members of the organisation can easily understand and share. A3 Problem Solving has been adopted by organisations in a variety of industries over the years, and it has become a widely used and recognised method for problem-solving.
Key Principles of A3 Problem Solving
The following are the key principles of A3 Problem Solving:
- Define the problem clearly and concisely
- Gather and analyze data to gain a deep understanding of the problem
- Identify the root causes of the problem
- Develop and implement effective solutions
- Evaluate results and continuously improve
These principles serve as the foundation of the A3 Problem Solving methodology and are intended to assist organisations in continuously improving and achieving their objectives. Organizations can effectively solve problems, identify areas for improvement, and drive results by adhering to these principles.
Step 1: Define the Problem
Importance of clearly defining the problem.
The first step in the A3 Problem Solving process is critical because it lays the groundwork for the remaining steps. To define the problem clearly and accurately, you must first understand the problem and identify the underlying root cause. This step is critical because if the problem is not correctly defined, the rest of the process will be based on incorrect information, and the solution developed may not address the issue effectively.
The significance of defining the problem clearly cannot be overstated. It aids in the collection and analysis of relevant data, which is critical for developing effective solutions. When the problem is clearly defined, the data gathered is more relevant and targeted, resulting in a more comprehensive understanding of the issue. This will enable the development of solutions that are more likely to be effective because they are founded on a thorough and accurate understanding of the problem.
However, if the problem is not clearly defined, the data gathered may be irrelevant or incorrect, resulting in incorrect conclusions and ineffective solutions. Furthermore, the process of collecting and analysing data can become time-consuming and inefficient, resulting in resource waste. Furthermore, if the problem is not accurately defined, the solutions developed may fail to address the root cause of the problem, resulting in ongoing issues and a lack of improvement.
Techniques for Defining the Problem
The first step in the A3 Problem Solving process is to clearly and accurately define the problem. This is an important step because a clearly defined problem will help to ensure that the appropriate data is collected and solutions are developed. If the problem is not clearly defined, incorrect data may be collected, solutions that do not address the root cause of the problem, and time and resources may be wasted.
A problem can be defined using a variety of techniques, including brainstorming , root cause analysis , process mapping , and Ishikawa diagrams . Each of these techniques has its own advantages and disadvantages and can be used in a variety of situations depending on the nature of the problem.
Best Practice for Defining the Problem
In addition to brainstorming, root cause analysis, process mapping, and Ishikawa diagram s, best practices should be followed when defining a problem in A3 Problem Solving. Among these best practices are:
- Define the issue in a specific and quantifiable way: It is critical to be specific and concise when defining the problem, as well as to quantify the problem in terms of its impact. This will help to ensure that all stakeholders understand the problem and that data collection is focused on the right areas.
- Focus on the problem’s root cause: The A3 Problem Solving methodology is intended to assist organisations in identifying and addressing the root cause of a problem, rather than just the symptoms. Organizations can ensure that their solutions are effective and long-lasting by focusing on the root cause of the problem.
- Ascertain that all stakeholders agree on the problem’s definition: All stakeholders must agree on the definition of the problem for the A3 Problem Solving process to be effective. This ensures that everyone is working towards the same goal and that the solutions developed are relevant and appropriate.
- Consider the problem’s impact on the organisation and its stakeholders: It is critical to consider the impact of the problem on the organisation and its stakeholders when defining it. This will assist in ensuring that the appropriate data is gathered and that the solutions developed are relevant and appropriate.
Organizations can ensure that their problem is defined in a way that allows for effective data collection, analysis, and solution development by following these best practices. This will aid in the development of appropriate solutions and the effective resolution of the problem, resulting in improvements in the organization’s processes and outcomes.
Step 2: Gather Data
Gathering data in a3 problem solving.
Data collection is an important step in the A3 Problem Solving process because it allows organisations to gain a thorough understanding of the problem they are attempting to solve. This step entails gathering pertinent information about the problem, such as data on its origin, impact, and any related factors. This information is then used to help identify root causes and develop effective solutions.
One of the most important advantages of data collection in A3 Problem Solving is that it allows organisations to identify patterns and trends in data, which can be useful in determining the root cause of the problem. This information can then be used to create effective solutions that address the problem’s root cause rather than just its symptoms.
In A3 Problem Solving, data collection is a collaborative effort involving all stakeholders, including those directly impacted by the problem and those with relevant expertise or experience. Stakeholders can ensure that all relevant information is collected and that the data is accurate and complete by working together.
Overall, data collection is an important step in the A3 Problem Solving process because it serves as the foundation for effective problem-solving. Organizations can gain a deep understanding of the problem they are attempting to solve and develop effective solutions that address its root cause by collecting and analysing relevant data.
Data Collection Methods
In A3 Problem Solving, several data collection methods are available, including:
- Observations
- Process diagrams
The best data collection method will be determined by the problem being solved and the type of data required. To gain a complete understanding of the problem, it is critical to use multiple data collection methods.
Tools for Data Analysis and Visualization
Once the data has been collected, it must be analysed and visualised in order to gain insights into the problem. This process can be aided by the following tools:
- Excel Spreadsheets
- Flow diagrams
- Pareto diagrams
- Scatter Plots
- Control diagrams
These tools can assist in organising data and making it easier to understand. They can also be used to generate visual representations of data, such as graphs and charts, to communicate the findings to others.
Finally, the data collection and analysis step is an important part of the A3 Problem Solving process. Organizations can gain a better understanding of the problem and develop effective solutions by collecting and analysing relevant data.
Step 3: Identify Root Causes
Identifying the root causes of the problem is the third step in the A3 Problem Solving process. This step is critical because it assists organisations in understanding the root causes of a problem rather than just its symptoms. Once the underlying cause of the problem is identified, it can be addressed more effectively, leading to more long-term solutions.
Overview of the Root Cause Analysis Process
The process of determining the underlying causes of a problem is known as root cause analysis. This process can assist organisations in determining why a problem is occurring and what can be done to prevent it from recurring in the future. The goal of root cause analysis is to identify the underlying cause of a problem rather than just its symptoms, allowing it to be addressed more effectively.
To understand Root cause analysis in more detail check out RCA in our Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt Course Root Cause Analysis section
Techniques for Identifying Root Causes
There are several techniques for determining the root causes of a problem, including:
- Brainstorming
- Ishikawa diagrams (also known as fishbone diagrams)
- Root Cause Tree Analysis
These methods can be used to investigate the issue in-depth and identify potential root causes. Organizations can gain a deeper understanding of the problem and identify the underlying causes that must be addressed by using these techniques.
Best Practices for Conducting Root Cause Analysis
It is critical to follow these best practices when conducting root cause analysis in A3 Problem Solving:
- Make certain that all stakeholders participate in the root cause analysis process.
- Concentrate on determining the root cause of the problem rather than just its symptoms.
- Take into account all potential root causes, not just the most obvious ones.
- To identify root causes, use a systematic approach, such as the 5 Whys or root cause tree analysis.
Organizations can ensure that root cause analysis is carried out effectively and that the root cause of the problem is identified by adhering to these best practises. This will aid in the development of appropriate solutions and the effective resolution of the problem.
Step 4: Develop Solutions
Developing solutions is the fourth step in the A3 Problem Solving process. This entails generating ideas and options for dealing with the problem, followed by selecting the best solution. The goal is to develop a solution that addresses the root cause of the problem and prevents it from recurring.
Solution Development in A3 Problem Solving
A3 solution development Problem solving is an iterative process in which options are generated and evaluated. The data gathered in the previous steps, as well as the insights and understanding gained from the root cause analysis, guide this process. The solution should be based on a thorough understanding of the problem and address the underlying cause.
Techniques for Developing Solutions
There are several techniques that can be used to develop solutions in A3 Problem Solving, including:
- Brainwriting
- Solution matrix
- Multi voting
- Force field analysis
These techniques can help to generate a range of options and to select the best solution.
Best Practice for Developing Solutions
It is critical to follow the following best practices when developing solutions in A3 Problem Solving:
- Participate in the solution development process with all stakeholders.
- Make certain that the solution addresses the underlying cause of the problem.
- Make certain that the solution is feasible and achievable.
- Consider the solution’s impact on the organisation and its stakeholders.
Organizations can ensure that the solutions they develop are effective and sustainable by adhering to these best practises. This will help to ensure that the problem is addressed effectively and that it does not reoccur.
Step 5: Implement Solutions
The final and most important step in the A3 Problem Solving methodology is solution implementation. This is the stage at which the identified and developed solutions are put into action to address the problem. This step’s goal is to ensure that the solutions are effective, efficient, and long-lasting.
The implementation Process
The implementation process entails putting the solutions developed in the previous step into action. This could include changes to processes, procedures, and systems, as well as employee training and education. To ensure that the solutions are effective, the implementation process should be well-planned and meticulously executed.
Techniques for Implementing Solutions
A3 Problem Solving solutions can be implemented using a variety of techniques, including:
- Piloting the solution on a small scale before broadening its application
- Participating in the implementation process with all relevant stakeholders
- ensuring that the solution is in line with the goals and objectives of the organisation
- Monitoring the solution to determine its effectiveness and make any necessary changes
Best Practice for Implementing Solutions
It is critical to follow these best practices when implementing solutions in A3 Problem Solving:
Make certain that all relevant stakeholders are involved and supportive of the solution. Have a clear implementation plan that outlines the steps, timeline, and resources required. Continuously monitor and evaluate the solution to determine its efficacy and make any necessary changes. Encourage all stakeholders to communicate and collaborate openly. Organizations can ensure that solutions are effectively implemented and problems are effectively addressed by adhering to these best practices. The ultimate goal is to find a long-term solution to the problem and improve the organization’s overall performance.
In conclusion, A3 Problem Solving is a comprehensive and structured methodology for problem-solving that can be applied in various industries and organisations. The A3 Problem Solving process’s five steps – Define the Problem, Gather Data, Identify Root Causes, Develop Solutions, and Implement Solutions – provide a road map for effectively addressing problems and making long-term improvements.
Organizations can improve their problem-solving skills and achieve better results by following the key principles, techniques, and best practices outlined in this guide. As a result, both the organisation and its stakeholders will benefit from increased efficiency, effectiveness, and satisfaction. So, whether you’re an experienced problem solver or just getting started, consider incorporating the A3 Problem Solving methodology into your work and start reaping the benefits right away.
Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.
Free Lean Six Sigma Templates
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.
5S Floor Marking Best Practices
In lean manufacturing, the 5S System is a foundational tool, involving the steps: Sort, Set…
How to Measure the ROI of Continuous Improvement Initiatives
When it comes to business, knowing the value you’re getting for your money is crucial,…
8D Problem-Solving: Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective problem-solving is the cornerstone of organizational success. The 8D…
The Evolution of 8D Problem-Solving: From Basics to Excellence
In a world where efficiency and effectiveness are more than just buzzwords, the need for…
8D: Tools and Techniques
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way…
How to Select the Right Lean Six Sigma Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
Going on a Lean Six Sigma journey is an invigorating experience filled with opportunities for…

Effective Problem-Solving Techniques in Business

January 20, 2023
Purdue Online
Problem solving is an increasingly important soft skill for those in business. The Future of Jobs Survey by the World Economic Forum drives this point home. According to this report, complex problem solving is identified as one of the top 15 skills that will be sought by employers in 2025, along with other soft skills such as analytical thinking, creativity and leadership.
Dr. Amy David , clinical associate professor of management for supply chain and operations management, spoke about business problem-solving methods and how the Purdue University Online MBA program prepares students to be business decision-makers.
Why Are Problem-Solving Skills Essential in Leadership Roles?
Every business will face challenges at some point. Those that are successful will have people in place who can identify and solve problems before the damage is done.
“The business world is constantly changing, and companies need to be able to adapt well in order to produce good results and meet the needs of their customers,” David says. “They also need to keep in mind the triple bottom line of ‘people, profit and planet.’ And these priorities are constantly evolving.”
To that end, David says people in management or leadership need to be able to handle new situations, something that may be outside the scope of their everyday work.
“The name of the game these days is change—and the speed of change—and that means solving new problems on a daily basis,” she says.
The pace of information and technology has also empowered the customer in a new way that provides challenges—or opportunities—for businesses to respond.
“Our customers have a lot more information and a lot more power,” she says. “If you think about somebody having an unhappy experience and tweeting about it, that’s very different from maybe 15 years ago. Back then, if you had a bad experience with a product, you might grumble about it to one or two people.”
David says that this reality changes how quickly organizations need to react and respond to their customers. And taking prompt and decisive action requires solid problem-solving skills.
What Are Some of the Most Effective Problem-Solving Methods?
David says there are a few things to consider when encountering a challenge in business.
“When faced with a problem, are we talking about something that is broad and affects a lot of people? Or is it something that affects a select few? Depending on the issue and situation, you’ll need to use different types of problem-solving strategies,” she says.
Using Techniques
There are a number of techniques that businesses use to problem solve. These can include:
- Five Whys : This approach is helpful when the problem at hand is clear but the underlying causes are less so. By asking “Why?” five times, the final answer should get at the potential root of the problem and perhaps yield a solution.
- Gap Analysis : Companies use gap analyses to compare current performance with expected or desired performance, which will help a company determine how to use its resources differently or adjust expectations.
- Gemba Walk : The name, which is derived from a Japanese word meaning “the real place,” refers to a commonly used technique that allows managers to see what works (and what doesn’t) from the ground up. This is an opportunity for managers to focus on the fundamental elements of the process, identify where the value stream is and determine areas that could use improvement.
- Porter’s Five Forces : Developed by Harvard Business School professor Michael E. Porter, applying the Five Forces is a way for companies to identify competitors for their business or services, and determine how the organization can adjust to stay ahead of the game.
- Six Thinking Hats : In his book of the same name, Dr. Edward de Bono details this method that encourages parallel thinking and attempting to solve a problem by trying on different “thinking hats.” Each color hat signifies a different approach that can be utilized in the problem-solving process, ranging from logic to feelings to creativity and beyond. This method allows organizations to view problems from different angles and perspectives.
- SWOT Analysis : This common strategic planning and management tool helps businesses identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT).
“We have a lot of these different tools,” David says. “Which one to use when is going to be dependent on the problem itself, the level of the stakeholders, the number of different stakeholder groups and so on.”
Each of the techniques outlined above uses the same core steps of problem solving:
- Identify and define the problem
- Consider possible solutions
- Evaluate options
- Choose the best solution
- Implement the solution
- Evaluate the outcome
Data drives a lot of daily decisions in business and beyond. Analytics have also been deployed to problem solve.
“We have specific classes around storytelling with data and how you convince your audience to understand what the data is,” David says. “Your audience has to trust the data, and only then can you use it for real decision-making.”
Data can be a powerful tool for identifying larger trends and making informed decisions when it’s clearly understood and communicated. It’s also vital for performance monitoring and optimization.
How Is Problem Solving Prioritized in Purdue’s Online MBA?
The courses in the Purdue Online MBA program teach problem-solving methods to students, keeping them up to date with the latest techniques and allowing them to apply their knowledge to business-related scenarios.
“I can give you a model or a tool, but most of the time, a real-world situation is going to be a lot messier and more valuable than what we’ve seen in a textbook,” David says. “Asking students to take what they know and apply it to a case where there’s not one single correct answer is a big part of the learning experience.”
Make Your Own Decision to Further Your Career
An online MBA from Purdue University can help advance your career by teaching you problem-solving skills, decision-making strategies and more. Reach out today to learn more about earning an online MBA with Purdue University .
About the Author
- Communication
- Health Sciences
- Student Advice
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu

What is problem-solving? And why is it important in the workplace?
September 28, 2023 by MindManager Blog
If there’s one thing you can count on as a business professional, it’s that you’ll never run short of new problems to solve. Thankfully, whether it includes handling difficult or unexpected situations in the workplace, or resolving complex organizational challenges, we all have the capacity to develop our business problem-solving skills.
The best way to get better at tackling problems productively is to start at the beginning. After all, the better you understand what problem-solving is – and the significant role it plays in every organization – the easier you’ll find it to improve on problem-solving skills in the workplace.
Let’s dive in!
What is problem-solving?
Problem-solving refers to the act of find solutions to difficult or complex issues.
A good problem-solving definition might be finding solutions to difficult or complex issues . In practice, however, solving problems in the workplace is a little more immersive than that.
In the workplace, problem-solving includes a variety of tools, resources, and techniques to:
- Identify what’s not working.
- Figure out why it’s broken.
- Determine the best course of action to fix it.
Whether you know them as obstacles, glitches, or setbacks, problems are a part of our everyday lives. The good news is that our brains excel at reasoning out intricate scenarios and making calculations in situations we’ve never experienced before. That means every one of us is hard-wired to be an adept problem-solver.
The trick is to learn how to take that innate ability and apply it in a deliberate and practiced way.
However, one thing is certain: successfully resolving business and workplace issues is essential.
Not only does effective problem-solving create value that encourages growth, it goes hand-in-hand with impactful decision making.
What are the benefits of problem-solving in business?
Practically speaking, problem-solving provides a golden opportunity to improve your processes, products, and systems – especially when you work through those challenges with others.
Learning to face difficulties calmly, and deal with them intentionally, can also:
- Ramp up your confidence.
- Increase your resilience.
- Help you develop valuable critical thinking skills.
Applying problem-solving skills in the face of an obstacle that seems insurmountable trains you to shift your perspective and look at potential hurdles in a different way.
It also gets you used to examining multiple options for dealing with a problem, which can help you feel more confident in the direction you take.
Solving problems as a team
Business problem solving as a team offers an even wider range of benefits since active collaboration tends to make good things happen at both the individual and group level.
For example:
- Team-based problem-solving is akin to having a built-in sounding board when you explore new approaches and ideas.
- As each team member’s critical thinking skills evolve, they bring fresh insights to the collective problem-solving process, bearing out the old adage that many heads are better than one.
- Solving problems as a team also reduces the feeling of personal risk and exposure that’s common when one person is tasked with solving a puzzle. When that same problem is shared, the sense of risk gets dispersed, and individual team members are less likely to feel singled out.
Not only is there less chance of arriving at an unreasonable or biased solution when you problem-solve as a group, team members assigned to carry that solution out will feel more invested in its success.
Examples of problem solving skills in the workplace
Improving on your problem-solving skills helps you make the most of your brain’s natural capacity to analyze and reason things out.
There are dozens of problem-solving skills that play out in the average workplace – all of which can contribute to your ability to correct oversights, resolve conflict , and work around unexpected obstructions.
Here are a few common examples of problem-solving skills in the workplace, and tips on how to improve them.
1. Data gathering
Figuring out the cause of a problem hinges on collecting relevant data. Consulting efficiently with colleagues, conducting online research, and brainstorming with your team are all valuable data gathering skills.
2. Active listening
As opposed to listening in a purely supportive or empathetic way, active listening involves concentrating fully on what the other person is saying so you can understand the content, respond accordingly, and remember what was said later.
3. Troubleshooting
The ability to analyze and troubleshoot a situation with the help of any data and human input you’ve gathered is essential for drilling down into the core of a problem, and scrutinizing potential solutions.
4. Brainstorming
Brainstorming has become synonymous with creative thinking, innovative idea generation, and problem-solving. The more productive your brainstorming sessions, the more likely you and your group are to put together a list of quality, workable solutions.
It’s interesting to note that effective decision making is both a contributor to, and a by-product of, effective problem-solving.
For example, honing your analytical abilities and other problem-solving skills will inevitably help you make better decisions. The more efficient your decision-making process becomes, meanwhile, the better you’ll get at uncovering and acting on the most promising solution to any dilemma.
A simple problem-solving scenario
It’s clear that we can all benefit from getting more comfortable with problem-solving in the workplace.
Examples of situations where your problem-solving skills will come in handy aren’t difficult to find, and might include:
- Fixing a technical issue for your customer.
- Improving your student’s test performance.
- Reducing the theft of your in-store merchandise.
- Bumping up your marketing reach.
But, here’s the interesting thing. While it’s evident in each of these situations that there’s a problem to be solved, the exact nature of that problem isn’t so obvious.
In the student’s case, for example, you’d need additional input to help you figure out why they’re performing poorly. Only then would you be able to take steps to find the best-fit solution and achieve the desired learning outcome.
Here’s a simple scenario to help demonstrate that idea:
Bringing new customers onboard in a timely manner is an important part of your client relations strategy. Since hiring Alex a few weeks ago, however, your onboarding process has been taking longer than it should and team members are beginning to complain.
While you can see that the problem in this scenario is the fact that your team isn’t meeting their client onboarding goals, the key is to get clear on exactly what’s causing the hold-up.
You could jump to the conclusion that Alex has time management issues and that it’s time to start looking for a replacement. But, since one of the most common mistakes in business problem-solving is attempting to seize on a solution right away, that might cause you to waste time and resources on a remedy that ultimately proves unnecessary, or that doesn’t provide a viable fix.
Instead, it’s time to put your problem-solving skills to work.
Using data gathering and troubleshooting to pinpoint and clarify the bottleneck in your onboarding process – and active listening to interpret the situation from Alex’s perspective – you soon determine that the real cause of the problem is not what you thought.
In truth, an administrative oversight during the hiring process (yet another problem to be solved!) left Alex unaware of, and without access to, the business process map that’s so vital to efficiently onboarding new customers. Once you provide the necessary resources, it doesn’t take Alex long to get up to speed – and your client onboarding process to revert back to the well-oiled machine that it was.
Even with a team of eager problem-solvers by your side, the truth is that it’s often necessary to have the right problem-solving tools in place to achieve your desired results. That’s where versatile mind mapping software can help.
Not only does MindManager® provide a visual framework that fully supports the problem-solving process, it improves comprehension, inspires more creative solutions, and boosts your ability to make the best possible decisions.
Ready to take the next step?
MindManager helps boost collaboration and productivity among remote and hybrid teams to achieve better results, faster.
Why choose MindManager?
MindManager® helps individuals, teams, and enterprises bring greater clarity and structure to plans, projects, and processes. It provides visual productivity tools and mind mapping software to help take you and your organization to where you want to be.
Explore MindManager
Transition to growth mode
with LivePlan Get 40% off now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
10 Step Process for Effective Business Problem Solving
Posted august 3, 2021 by harriet genever.

When you start a small business or launch a startup, the one thing you can count on is the unexpected. No matter how thoroughly you plan, forecast , and test, problems are bound to arise. This is why as an entrepreneur, you need to know how to solve business problems effectively.
What is problem solving in business?
Problem solving in business relates to establishing processes that mitigate or remove obstacles currently preventing you from reaching strategic goals . These are typically complex issues that create a gap between actual results and your desired outcome. They may be present in a single team, operational process, or throughout your entire organization, typically without an immediate or obvious solution.
To approach problem solving successfully, you need to establish consistent processes that help you evaluate, explore solutions, prioritize execution, and measure success. In many ways, it should be similar to how you review business performance through a monthly plan review . You work through the same documentation, look for gaps, dig deeper to identify the root cause, and hash out options. Without this process, you simply cannot expect to solve problems efficiently or effectively.
Why problem solving is important for your business
While some would say problem-solving comes naturally, it’s actually a skill you can grow and refine over time. Problem solving skills will help you and your team tackle critical issues and conflicts as they arise. It starts from the top. You as the business owner or CEO needing to display the type of level-headed problem solving that you expect to see from your employees.
Doing so will help you and your staff quickly deal with issues, establish and refine a problem solving process, turn challenges into opportunities, and generally keep a level head. Now, the best business leaders didn’t just find a magic solution to solve their problems, they built processes and leveraged tools to find success. And you can do the same.
By following this 10-step process, you can develop your problem-solving skills and approach any issue that arises with confidence.
1. Define the problem
When a problem arises, it can be very easy to jump right into creating a solution. However, if you don’t thoroughly examine what led to the problem in the first place, you may create a strategy that doesn’t actually solve it. You may just be treating the symptoms.
For instance, if you realize that your sales from new customers are dropping, your first inclination might be to rush into putting together a marketing plan to increase exposure. But what if decreasing sales are just a symptom of the real problem?
When you define the problem, you want to be sure you’re not missing the forest for the trees. If you have a large issue on your hands, you’ll want to look at it from several different angles:
Competition
Is a competitor’s promotion or pricing affecting your sales? Are there new entrants in your market? How are they marketing their product or business?
Business model
Is your business model sustainable? Is it realistic for how fast you want to grow? Should you explore different pricing or cost strategies?
Market factors
How are world events and the nation’s economy affecting your customers and your sales?
Are there any issues affecting your team? Do they have the tools and resources they need to succeed?
Goal alignment
Is everyone on your team working toward the same goal ? Have you communicated your short-term and long-term business goals clearly and often?
There are a lot of ways to approach the issue when you’re facing a serious business problem. The key is to make sure you’re getting a full snapshot of what’s going on so you don’t waste money and resources on band-aid solutions.
Going back to our example, by looking at every facet of your business, you may discover that you’re spending more on advertising than your competitors already. And instead, there’s a communication gap within your team that’s leading to the mishandling of new customers and therefore lost sales.
If you jumped into fixing the exposure of your brand, you would have been dumping more money into an area you’re already winning. Potentially leading to greater losses as more and more new customers are dropped due to poor internal communication.
This is why it’s so vital that you explore your blind spots and track the problem to its source.
2. Conduct a SWOT analysis
All good businesses solve some sort of problem for customers. What if your particular business problem is actually an opportunity, or even a strength if considered from a different angle? This is when you’d want to conduct a SWOT analysis to determine if that is in fact the case.
SWOT is a great tool for strategic planning and bringing multiple viewpoints to the table when you’re looking at investing resources to solve a problem. This may even be incorporated in your attempts to identify the source of your problem, as it can quickly outline specific strengths and weaknesses of your business. And then by identifying any potential opportunities or threats, you can utilize your findings to kickstart a solution.
3. Identify multiple solutions with design thinking
As you approach solving your problem, you may want to consider using the design thinking approach . It’s often used by organizations looking to solve big, community-based problems. One of its strengths is that it requires involving a wide range of people in the problem-solving process. Which leads to multiple perspectives and solutions arising.
This approach—applying your company’s skills and expertise to a problem in the market—is the basis for design thinking.
It’s not about finding the most complex problems to solve, but about finding common needs within the organization and in the real world and coming up with solutions that fit those needs. When you’re solving business problems, this applies in the sense that you’re looking for solutions that address underlying issues—you’re looking at the big picture.
4. Conduct market research and customer outreach
Market research and customer outreach aren’t the sorts of things small business owners and startups can do once and then cross off the list. When you’re facing a roadblock, think back to the last time you did some solid market research or took a deep dive into understanding the competitive landscape .
Market research and the insights you get from customer outreach aren’t a silver bullet. Many companies struggle with what they should do with conflicting data points. But it’s worth struggling through and gathering information that can help you better understand your target market . Plus, your customers can be one of the best sources of criticism. It’s actually a gift if you can avoid taking the negatives personally .
The worst thing you can do when you’re facing challenges is isolating yourself from your customers and ignore your competition. So survey your customers. Put together a competitive matrix .
5. Seek input from your team and your mentors
Don’t do your SWOT analysis or design thinking work by yourself. The freedom to express concerns, opinions, and ideas will allow people in an organization to speak up. Their feedback is going to help you move faster and more efficiently. If you have a team in place, bring them into the discussion. You hired them to be experts in their area; use their expertise to navigate and dig deeper into underlying causes of problems and potential solutions.
If you’re running your business solo, at least bring in a trusted mentor. SCORE offers a free business mentorship program if you don’t already have one. It can also be helpful to connect with a strategic business advisor , especially if business financials aren’t your strongest suit.
Quoting Stephen Covey, who said that “strength lies in differences, not in similarities,” speaking to the importance of diversity when it comes to problem-solving in business. The more diverse a team is , the more often innovative solutions to the problems faced by the organization appear.
In fact, it has been found that groups that show greater diversity were better at solving problems than groups made up specifically of highly skilled problem solvers. So whoever you bring in to help you problem-solve, resist the urge to surround yourself with people who already agree with you about everything.
6. Apply lean planning for nimble execution
So you do your SWOT analysis and your design thinking exercise. You come up with a set of strong, data-driven ideas. But implementing them requires you to adjust your budget, or your strategic plan, or even your understanding of your target market.
Are you willing to change course? Can you quickly make adjustments? Well in order to grow, you can’t be afraid to be nimble .
By adopting the lean business planning method —the process of revising your business strategy regularly—you’ll be able to shift your strategies more fluidly. You don’t want to change course every week, and you don’t want to fall victim to shiny object thinking. But you can strike a balance that allows you to reduce your business’s risk while keeping your team heading in the right direction.
Along the way, you’ll make strategic decisions that don’t pan out the way you hoped. The best thing you can do is test your ideas and iterate often so you’re not wasting money and resources on things that don’t work. That’s Lean Planning .
7. Model different financial scenarios
When you’re trying to solve a serious business problem, one of the best things you can do is build a few different financial forecasts so you can model different scenarios. You might find that the idea that seemed the strongest will take longer than you thought to reverse a negative financial trend. At the very least you’ll have better insight into the financial impact of moving in a different direction.
The real benefit here is looking at different tactical approaches to the same problem. Maybe instead of increasing sales right now, you’re better off in the long run if you adopt a strategy to reduce churn and retain your best customers. You won’t know unless you model a few different scenarios. You can do this by using spreadsheets, and a tool like LivePlan can make it easier and quicker.
8. Watch your cash flow
While you’re working to solve a challenging business problem, pay particular attention to your cash flow and your cash flow forecast . Understanding when your company is at risk of running out of cash in the bank can help you be proactive. It’s a lot easier to get a line of credit while your financials still look good and healthy, than when you’re one pay period away from ruin.
If you’re dealing with a serious issue, it’s easy to start to get tunnel vision. You’ll benefit from maintaining a little breathing room for your business as you figure out what to do next.
9. Use a decision-making framework
Once you’ve gathered all the information you need, generated a number of ideas, and done some financial modeling, you might still feel uncertain. It’s natural—you’re not a fortune-teller. You’re trying to make the best decision you can with the information you have.
This article offers a really useful approach to making decisions. It starts with putting your options into a matrix like this one:

Use this sort of framework to put everything you’ve learned out on the table. If you’re working with a bigger team, this sort of exercise can also bring the rest of your team to the table so they feel some ownership over the outcome.
10. Identify key metrics to track
How will you know your problem is solved? And not just the symptom—how will you know when you’ve addressed the underlying issues? Before you dive into enacting the solution, make sure you know what success looks like.
Decide on a few key performance indicators . Take a baseline measurement, and set a goal and a timeframe. You’re essentially translating your solution into a plan, complete with milestones and goals. Without these, you’ve simply made a blind decision with no way to track success. You need those goals and milestones to make your plan real .
Problem solving skills to improve
As you and your team work through this process, it’s worth keeping in mind specific problem solving skills you should continue to develop. Bolstering your ability, as well as your team, to solve problems effectively will only make this process more useful and efficient. Here are a few key skills to work on.
Emotional intelligence
It can be very easy to make quick, emotional responses in a time of crisis or when discussing something you’re passionate about. To avoid making assumptions and letting your emotions get the best of you, you need to focus on empathizing with others. This involves understanding your own emotional state, reactions and listening carefully to the responses of your team. The more you’re able to listen carefully, the better you’ll be at asking for and taking advice that actually leads to effective problem solving.
Jumping right into a solution can immediately kill the possibility of solving your problem. Just like when you start a business , you need to do the research into what the problem you’re solving actually is. Luckily, you can embed research into your problem solving by holding active reviews of financial performance and team processes. Simply asking “What? Where? When? How?” can lead to more in-depth explorations of potential issues.
The best thing you can do to grow your research abilities is to encourage and practice curiosity. Look at every problem as an opportunity. Something that may be trouble now, but is worth exploring and finding the right solution. You’ll pick up best practices, useful tools and fine-tune your own research process the more you’re willing to explore.
Brainstorming
Creatively brainstorming with your team is somewhat of an art form. There needs to be a willingness to throw everything at the wall and act as if nothing is a bad idea at the start. This style of collaboration encourages participation without fear of rejection. It also helps outline potential solutions outside of your current scope, that you can refine and turn into realistic action.
Work on breaking down problems and try to give everyone in the room a voice. The more input you allow, the greater potential you have for finding the best solution.
Decisiveness
One thing that can drag out acting upon a potential solution, is being indecisive. If you aren’t willing to state when the final cutoff for deliberation is, you simply won’t take steps quickly enough. This is when having a process for problem solving comes in handy, as it purposefully outlines when you should start taking action.
Work on choosing decision-makers, identify necessary results and be prepared to analyze and adjust if necessary. You don’t have to get it right every time, but taking action at the right time, even if it fails, is almost more vital than never taking a step.
Stemming off failure, you need to learn to be resilient. Again, no one gets it perfect every single time. There are so many factors in play to consider and sometimes even the most well-thought-out solution doesn’t stick. Instead of being down on yourself or your team, look to separate yourself from the problem and continue to think of it as a puzzle worth solving. Every failure is a learning opportunity and it only helps you further refine and eliminate issues in your strategy.
Problem solving is a process
The key to effective problem-solving in business is the ability to adapt. You can waste a lot of resources on staying the wrong course for too long. So make a plan to reduce your risk now. Think about what you’d do if you were faced with a problem large enough to sink your business. Be as proactive as you can.
Editor’s note: This article was originally published in 2016. It was updated in 2021.
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Harriet Genever
Posted in management, join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Creative Problem-Solving & Why Is It Important?

- 01 Feb 2022
One of the biggest hindrances to innovation is complacency—it can be more comfortable to do what you know than venture into the unknown. Business leaders can overcome this barrier by mobilizing creative team members and providing space to innovate.
There are several tools you can use to encourage creativity in the workplace. Creative problem-solving is one of them, which facilitates the development of innovative solutions to difficult problems.
Here’s an overview of creative problem-solving and why it’s important in business.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Creative Problem-Solving?
Research is necessary when solving a problem. But there are situations where a problem’s specific cause is difficult to pinpoint. This can occur when there’s not enough time to narrow down the problem’s source or there are differing opinions about its root cause.
In such cases, you can use creative problem-solving , which allows you to explore potential solutions regardless of whether a problem has been defined.
Creative problem-solving is less structured than other innovation processes and encourages exploring open-ended solutions. It also focuses on developing new perspectives and fostering creativity in the workplace . Its benefits include:
- Finding creative solutions to complex problems : User research can insufficiently illustrate a situation’s complexity. While other innovation processes rely on this information, creative problem-solving can yield solutions without it.
- Adapting to change : Business is constantly changing, and business leaders need to adapt. Creative problem-solving helps overcome unforeseen challenges and find solutions to unconventional problems.
- Fueling innovation and growth : In addition to solutions, creative problem-solving can spark innovative ideas that drive company growth. These ideas can lead to new product lines, services, or a modified operations structure that improves efficiency.

Creative problem-solving is traditionally based on the following key principles :
1. Balance Divergent and Convergent Thinking
Creative problem-solving uses two primary tools to find solutions: divergence and convergence. Divergence generates ideas in response to a problem, while convergence narrows them down to a shortlist. It balances these two practices and turns ideas into concrete solutions.
2. Reframe Problems as Questions
By framing problems as questions, you shift from focusing on obstacles to solutions. This provides the freedom to brainstorm potential ideas.
3. Defer Judgment of Ideas
When brainstorming, it can be natural to reject or accept ideas right away. Yet, immediate judgments interfere with the idea generation process. Even ideas that seem implausible can turn into outstanding innovations upon further exploration and development.
4. Focus on "Yes, And" Instead of "No, But"
Using negative words like "no" discourages creative thinking. Instead, use positive language to build and maintain an environment that fosters the development of creative and innovative ideas.
Creative Problem-Solving and Design Thinking
Whereas creative problem-solving facilitates developing innovative ideas through a less structured workflow, design thinking takes a far more organized approach.
Design thinking is a human-centered, solutions-based process that fosters the ideation and development of solutions. In the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar leverages a four-phase framework to explain design thinking.
The four stages are:

- Clarify: The clarification stage allows you to empathize with the user and identify problems. Observations and insights are informed by thorough research. Findings are then reframed as problem statements or questions.
- Ideate: Ideation is the process of coming up with innovative ideas. The divergence of ideas involved with creative problem-solving is a major focus.
- Develop: In the development stage, ideas evolve into experiments and tests. Ideas converge and are explored through prototyping and open critique.
- Implement: Implementation involves continuing to test and experiment to refine the solution and encourage its adoption.
Creative problem-solving primarily operates in the ideate phase of design thinking but can be applied to others. This is because design thinking is an iterative process that moves between the stages as ideas are generated and pursued. This is normal and encouraged, as innovation requires exploring multiple ideas.
Creative Problem-Solving Tools
While there are many useful tools in the creative problem-solving process, here are three you should know:
Creating a Problem Story
One way to innovate is by creating a story about a problem to understand how it affects users and what solutions best fit their needs. Here are the steps you need to take to use this tool properly.
1. Identify a UDP
Create a problem story to identify the undesired phenomena (UDP). For example, consider a company that produces printers that overheat. In this case, the UDP is "our printers overheat."
2. Move Forward in Time
To move forward in time, ask: “Why is this a problem?” For example, minor damage could be one result of the machines overheating. In more extreme cases, printers may catch fire. Don't be afraid to create multiple problem stories if you think of more than one UDP.
3. Move Backward in Time
To move backward in time, ask: “What caused this UDP?” If you can't identify the root problem, think about what typically causes the UDP to occur. For the overheating printers, overuse could be a cause.
Following the three-step framework above helps illustrate a clear problem story:
- The printer is overused.
- The printer overheats.
- The printer breaks down.
You can extend the problem story in either direction if you think of additional cause-and-effect relationships.
4. Break the Chains
By this point, you’ll have multiple UDP storylines. Take two that are similar and focus on breaking the chains connecting them. This can be accomplished through inversion or neutralization.
- Inversion: Inversion changes the relationship between two UDPs so the cause is the same but the effect is the opposite. For example, if the UDP is "the more X happens, the more likely Y is to happen," inversion changes the equation to "the more X happens, the less likely Y is to happen." Using the printer example, inversion would consider: "What if the more a printer is used, the less likely it’s going to overheat?" Innovation requires an open mind. Just because a solution initially seems unlikely doesn't mean it can't be pursued further or spark additional ideas.
- Neutralization: Neutralization completely eliminates the cause-and-effect relationship between X and Y. This changes the above equation to "the more or less X happens has no effect on Y." In the case of the printers, neutralization would rephrase the relationship to "the more or less a printer is used has no effect on whether it overheats."
Even if creating a problem story doesn't provide a solution, it can offer useful context to users’ problems and additional ideas to be explored. Given that divergence is one of the fundamental practices of creative problem-solving, it’s a good idea to incorporate it into each tool you use.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a tool that can be highly effective when guided by the iterative qualities of the design thinking process. It involves openly discussing and debating ideas and topics in a group setting. This facilitates idea generation and exploration as different team members consider the same concept from multiple perspectives.
Hosting brainstorming sessions can result in problems, such as groupthink or social loafing. To combat this, leverage a three-step brainstorming method involving divergence and convergence :
- Have each group member come up with as many ideas as possible and write them down to ensure the brainstorming session is productive.
- Continue the divergence of ideas by collectively sharing and exploring each idea as a group. The goal is to create a setting where new ideas are inspired by open discussion.
- Begin the convergence of ideas by narrowing them down to a few explorable options. There’s no "right number of ideas." Don't be afraid to consider exploring all of them, as long as you have the resources to do so.
Alternate Worlds
The alternate worlds tool is an empathetic approach to creative problem-solving. It encourages you to consider how someone in another world would approach your situation.
For example, if you’re concerned that the printers you produce overheat and catch fire, consider how a different industry would approach the problem. How would an automotive expert solve it? How would a firefighter?
Be creative as you consider and research alternate worlds. The purpose is not to nail down a solution right away but to continue the ideation process through diverging and exploring ideas.

Continue Developing Your Skills
Whether you’re an entrepreneur, marketer, or business leader, learning the ropes of design thinking can be an effective way to build your skills and foster creativity and innovation in any setting.
If you're ready to develop your design thinking and creative problem-solving skills, explore Design Thinking and Innovation , one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses. If you aren't sure which course is the right fit, download our free course flowchart to determine which best aligns with your goals.


About the Author
Problem-Solving in Business: PROBLEM-SOLVING DEFINED AND WHY IT IS IMPORTANT
- ABOUT THIS LIBGUIDE
- PROBLEM-SOLVING DEFINED AND WHY IT IS IMPORTANT
- SKILLS AND QUALIFICATIONS NEEDED IN PROBLEM-SOLVING
- PROBLEM-SOLVING STEPS
- CASE STUDIES
- MORE HELPFUL RESOURCES

- << Previous: ABOUT THIS LIBGUIDE
- Next: SKILLS AND QUALIFICATIONS NEEDED IN PROBLEM-SOLVING >>
- Last Updated: Mar 23, 2024 4:47 PM
- URL: https://libguides.nypl.org/problem_solving_in_business
Why problem-solving Is Important in Business
Problem-solving is a critical skill in business.
It involves the ability to identify and solve problems efficiently and effectively to move a company forward.
Whether it’s resolving a technical issue, finding a new solution to an age-old problem, or simply making a difficult decision, strong problem-solving skills are essential for the success of any business.
In this blog post, we’ll explore why problem-solving is so important in the business world and how it can help organizations thrive.
The Importance of Problem-Solving in Business
As mentioned in the introduction, problem-solving is a crucial skill in the business world. It allows organizations to identify and address challenges in a timely and effective manner, which is essential for driving progress and growth.
Without strong problem-solving abilities, businesses may struggle to adapt to change and overcome obstacles, ultimately hindering their success.
But the importance of problem-solving goes beyond just overcoming challenges.
It can also help businesses to identify and seize new opportunities, allowing them to stay ahead of the competition and remain innovative.
Whether it’s finding a new market to tap into or developing a more efficient production process, problem-solving skills are key to driving innovation and staying ahead of the curve.
In short, strong problem-solving skills are essential for businesses of all sizes and industries.
They help organizations to overcome challenges, stay adaptable, and identify and seize new opportunities.
In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into the various ways that problem-solving can benefit businesses and the different techniques and strategies that can be used to tackle problems effectively.
Developing Problem-Solving Skills
Developing strong problem-solving skills is essential for the success of any business, and there are several ways that organizations can help their employees to hone these skills. Some strategies for developing problem-solving skills include:
Providing training and development opportunities
Many organizations offer training programs or workshops specifically designed to help employees develop problem-solving skills. These programs may include simulations, case studies, or hands-on exercises that allow employees to practice and apply their skills.
Encouraging a growth mindset
A growth mindset is a belief that abilities can be developed through effort and learning. By fostering a culture of continuous learning and encouraging employees to embrace challenges and failures as opportunities to grow and improve, businesses can help to develop problem-solving skills.
Encouraging collaboration and open communication
Collaboration and open communication can be key to solving problems effectively. By creating an environment where employees feel comfortable sharing ideas and seeking help, businesses can foster a culture of problem-solving and continuous improvement.
Providing resources and support
Organizations can also support the development of problem-solving skills by providing employees with the resources and support they need to tackle problems. This may include access to data and analytics tools, training materials, or guidance from experienced colleagues.
By implementing these strategies and providing opportunities for employees to practice and develop their problem-solving skills, businesses can build a strong problem-solving culture and equip their teams with the skills they need to drive success.
The Role of Leadership in Problem-Solving
Effective leadership is crucial for driving problem-solving within an organization. Leaders play a key role in setting the tone and culture of a business, and by fostering a culture of problem-solving and continuous improvement, they can help to develop strong problem-solving skills throughout the organization.
Some specific ways that leaders can support problem-solving within their organization include:
Modeling good problem-solving behavior
Leaders can set a good example by demonstrating strong problem-solving skills themselves. This can include taking a proactive approach to identifying and addressing challenges, seeking out new opportunities, and continuously learning and improving.
Encouraging a culture of continuous improvement
Leaders can create an environment that supports problem-solving by encouraging employees to embrace challenges, think creatively, and seek out new opportunities for improvement.
Leaders can also support problem-solving by providing employees with the resources and support they need to tackle problems effectively. This may include access to data and analytics tools, training materials, or guidance from experienced colleagues.
Recognizing and rewarding problem-solving efforts
By recognizing and rewarding employees who demonstrate strong problem-solving skills, leaders can encourage a culture of problem-solving and continuous improvement within the organization.
By taking an active role in fostering a problem-solving culture and providing the resources and support needed to tackle challenges, leaders can help their organizations to thrive and succeed.
The Benefits of Problem-Solving in Business
In addition to helping businesses to overcome challenges and seize opportunities, strong problem-solving skills can bring a range of other benefits to an organization. Some of the key advantages of problem-solving in business include:
Improved decision-making
Problem-solving skills help organizations to make informed and effective decisions. By using structured approaches and analyzing data, businesses can develop a clear understanding of the issues they face and identify the best course of action.
Enhanced adaptability
Problem-solving skills help businesses to stay adaptable and responsive to change. By being able to identify and address challenges quickly and effectively, organizations can better navigate the constantly-evolving business landscape.
Increased productivity
By resolving issues and identifying efficiencies, problem-solving can help businesses to increase productivity and reduce waste. This can lead to cost savings and improved profitability.
Improved customer satisfaction
Strong problem-solving skills can also help businesses to better serve their customers. By being able to identify and address issues promptly and effectively, organizations can improve customer satisfaction and build stronger relationships with their clients.
Enhanced innovation
Problem-solving skills can also drive innovation within an organization. By encouraging employees to think creatively and critically , businesses can identify and seize new opportunities, leading to new products, services, or processes that set them apart from the competition.
Problem-solving is a critical skill in business, with the potential to drive progress, increase productivity, improve customer satisfaction, and drive innovation. By developing strong problem-solving skills and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, organizations can set themselves up for success.
Conclusion: The Vital Role of Problem-Solving in Business
Problem-solving is a vital skill in the business world. It allows organizations to identify and address challenges efficiently and effectively, helping them to overcome obstacles and seize new opportunities.
Strong problem-solving skills also drive innovation and improve decision-making, leading to increased productivity and customer satisfaction.
Developing and fostering a culture of problem-solving is essential for the success of any business.
By providing training and development opportunities, encouraging a growth mindset, and recognizing and rewarding problem-solving efforts, organizations can help their employees to hone their skills and drive progress.
Effective leadership also plays a key role in fostering a culture of problem-solving, providing the resources and support needed to tackle challenges and seize opportunities.
In short, problem-solving is a critical skill for businesses of all sizes and industries. By developing and fostering strong problem-solving abilities, organizations can set themselves up for success and thrive in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Are you good at problem-solving? Find out with our self-assessment!
Disclaimers
All the information on this website - https://melbado.com/ - is published in good faith and for general information purpose only. Melbado does not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. Any action you take upon the information you find on this website (Melbado), is strictly at your own risk. Melbado will not be liable for any losses and/or damages in connection with the use of our website.
From our website, you can visit other websites by following hyperlinks to such external sites. While we strive to provide only quality links to useful and ethical websites, we have no control over the content and nature of these sites. These links to other websites do not imply a recommendation for all the content found on these sites. Site owners and content may change without notice and may occur before we have the opportunity to remove a link which may have gone 'bad'.
Please be also aware that when you leave our website, other sites may have different privacy policies and terms which are beyond our control. Please be sure to check the Privacy Policies of these sites as well as their "Terms of Service" before engaging in any business or uploading any information.
By using our website, you hereby consent to our disclaimer and agree to its terms.
- Become a Partner
- Product Overview Know more about our products
- OKR Management Strategy-execution made easy
- Performance Management Build a high performance team
- Task Management Increase day-to-day productivity
- Employee Engagement Engage, align and inspire your team
- Integrations Integrate easily with all your favorite apps
- Case Study Know why 1000s of brands trust Profit.co
- Why Profit.co? Know what customers like you think about us.
- OKR Certification Iterate Faster with OKRs Coaching & Certification Programs
- OKR University OKR resources for beginners and experts
- eBooks Books sharing our OKR expertise, ideas and insights
- KPI Library Find the Most Effective KPIs for your business
- OKR Examples Collection of OKR examples for your business
- OKR Webinars Discover current trends and expert insights
- Answers (FAQs) Get instant solutions to your queries
- OKR Canvas Kick start your OKR implementation right away
- Help Center Endless support in case you are stuck
- Release Updates Outlined feature updates from our last releases
- Try it Free
- Schedule Demo
How do Great Leaders Solve Problems in Business?

Category: Behavioral Economics .
Companies today are expected to adapt and respond quickly to challenges in a rapidly changing business environment. Notwithstanding sound planning and flawless strategy execution, businesses can still face problems. While they foresee some of those problems, others can pop up unexpectedly. These unforeseeable problems make it essential for businesses to be agile enough to respond to those challenges quickly and have excellent problem-solving skills to navigate them successfully. Problem-solving is an indispensable part of business management.
In this article, we will examine the following in detail
Introduction
- Understanding the Importance of Problem-Solving in Business
- Types of Business Problems
- Challenges in Problem-solving
- Skills Required for Effective Problem-solving in Business
- A Step-by-step Process to Problem-solving in Business
TL;DR Version
Problem-solving is integral to business success, dealing with diverse issues ranging from operational hiccups to strategic challenges. Identifying and understanding these problems is vital, but navigating potential obstacles during problem-solving, such as cognitive biases, resource constraints, and lack of information, is crucial.
Effective problem-solving skills include research and analytical abilities, creativity, decision-making, communication , time management, and leadership. These skills allow business leaders to dissect complex issues, ideate innovative solutions, make informed decisions, communicate effectively, manage time, and lead teams toward resolution.
The problem-solving process involves defining the problem, understanding its root cause, collecting relevant information, brainstorming potential solutions, evaluating these solutions, choosing the best one, developing and implementing an action plan, monitoring progress, evaluating results, and reflecting on the process for continuous improvement. This iterative process ensures that businesses are resolving immediate issues and refining their problem-solving mechanism for future challenges.
Unmanaged and unmitigated problems can cause severe consequences to businesses. They can lead to project delays, missed deadlines, and financial losses. Moreover, they may negatively impact employee morale and customer satisfaction and even damage the reputation of the company. So businesses must have strong problem-solving abilities.
When businesses have strong problem-solving abilities, they can quickly and proactively rise to the occasion and address the problems, minimizing their impact, preventing them from escalating into bigger problems, and capitalizing on opportunities that arise from those challenges. Ultimately, the problem-solving ability of a company can help them gain a competitive advantage.
To solve problems and fix issues, companies require leaders who can handle complex issues with ease and guide and motivate their teams to identify problems and develop creative solutions to overcome them. They can leverage the collective expertise and experience of the employees to make well-informed decisions that align with the business goals and objectives. Leaders also work with employees to foster a culture of problem-solving to help the company build a resilient business that can thrive in today’s dynamic business environment.
What is Problem-Solving in Business?
Problem-solving involves identifying, analyzing, and resolving issues or challenges arising during various business operations to achieve the desired outcomes and business goals. It involves a systematic approach to defining the problem, gathering relevant information, generating possible solutions, evaluating them, and implementing the best course of action.
Take action today and start paving the way for your business towards Problem- solving.
Book a free demo
we Cannot solve our problems with the same thinking we used when we created them. Albert Einstein
Why is Problem-Solving Important?
Problem-solving in business is important because of the following reasons.
1. Efficiency
Problems not only hinder progress but also reduce the efficiency of your operations by bringing everything to a halt/slowing you down, causing downtime, and costing you precious productivity. When left unchecked at the initial stages, these problems may also demand additional resources and budget to solve them, leading to cost overruns, losses, and inefficiency. So addressing the problems on time can help achieve efficiency.
2. Profitability
Profitability is one of the topmost priorities of an organization. So any impact on profitability is seen as a problem that requires immediate attention. Effective problem-solving helps businesses identify and address cost inefficiencies, optimize processes, and capitalize on new opportunities, thus improving the bottom line.
3. Leadership
Great leaders emerge during testing times. They can lead the employees, leverage collective effort and give a sense of direction toward finding solutions and workarounds. Problem-solving helps companies identify the right leaders.
4. Teamwork
Problem-solving requires team effort and participation. It calls for collaboration and communication between various departments, teams, and individuals. When companies manage to weather challenges and solve problems effectively, it brings the employees together to work towards a common cause, build stronger teams and create a habit of continuous improvement.

5. Innovation
Problem-solving requires creativity and innovation to find solutions and workarounds. When a company fosters problem-solving culture, it automatically imbibes creative thinking and innovation. It gets reflected in developing new products, services, processes, and best practices.
6. Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction helps businesses retain and find new customers. Problems with the products/services and customer support can lead to poor customer experience. Effective problem-solving helps businesses resolve customer complaints and issues quickly and satisfactorily, thus increasing customer loyalty and retention.
The Problems that Businesses Face Today and how they Solve Them
There are several different kinds of problems that businesses face, including
1. Strategic problems
Strategic problems are related to the long-term direction of a business. They typically involve decisions about resource allocation, product strategy, choosing the market, pricing strategy, product positioning, etc. Solving strategic problems requires a long-term vision, able leadership, and the ability to forecast market trends.

Business problem examples
Selecting the markets.
Businesses need to decide their focus on specific geographic markets, target customer segments, and product categories. They must make these decisions and select the focus areas by analyzing the data and insights into factors, including market size, competition, and the company’s core competencies.
Product development
Developing new products enables companies to remain relevant and achieve leadership in a highly competitive market scenario. They have to meet the customer requirements and provide a compelling reason for customers to purchase them. Solving the problem of new product development requires creativity and innovation and allocating resources for R&D. New products should be developed based on sound market analyses of customer requirements and pain points.
For instance, the need to learn and upskill anytime without compromising work hours pushed the companies to create e-learning platforms.
Positioning the company
Differentiating your business from the competition involves developing a strong brand identity, focusing on a specific niche or segment of the market, or offering unique value propositions. Setting the company apart by gaining a competitive advantage attracts customers. You can solve the problem of positioning your company by doing a SWOT analysis, finding your strengths and unique qualities that enable you to meet the customers’ requirements and address their pain points. You can base your brand identity, USP, and niche on your stand-out qualities that benefit customers. For instance, Volvo positions itself as the company that makes the safest cars in the world.
2. Operational problems
Operational problems are daily issues that hinder companies from efficiently delivering products or services to customers, affecting their ability to meet deadlines and targets. These problems arise from bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and system flaws. Addressing them involves identifying issues, providing employee training, upgrading technology, ensuring product testing and quality control, and implementing contingency planning, deadline management, and risk mitigation.

Business problem-solving examples
Supply chain disruptions.
Supply chain disruptions happen when businesses face challenges in sourcing raw materials or components, leading to production delays or quality issues. For instance, during the pandemic, companies faced chip shortages, which led to losses and the inability to deliver products to customers on time. It also caused a rise in demand and an increase in prices.
Quality control issues
Quality control issues occur when design flaws or manufacturing issues impact the products. Businesses may need to identify and address quality issues to maintain customer satisfaction and loyalty. For instance, it is not uncommon to recall new automobile models, sometimes the ones from specific batches, to replace faulty components with redesigned parts before they might fail.
Managing staffing levels
Fluctuating staffing needs are part of operational issues. At any given time, if a company is understaffed, it can lead to operational inefficiency; if it is over-staffed, the company will suffer from cost infficiency. So, it requires careful planning. You can address the problem by either recruiting or downsizing and restructuring. For instance, the tech companies that designed software solutions for remote and hybrid work environments hired many employees during the pandemic. After the pandemic, when the need for these software solutions decreased, they had to downsize their workforce in light of the impending recession.
3. Financial problems
Financial problems are issues involving managing cash flow, revenue growth, and expenses. They are related to the financial health of a business. Businesses can fix them by managing costs effectively through process improvement and cost-cutting measures.

Managing cash flow
Businesses must ensure that they have enough financial resources on hand to meet their obligations, such as payroll, vendor payments, logistics, managing retail channels, etc. For instance, many start-ups stall despite successful product development and prototyping, as they fail to secure adequate funding to bring the products to the market.
Identifying new revenue streams:
Businesses that focus on a particular niche are always vulnerable to competition and changing market conditions. They need to diversify their revenue streams to maintain growth and profitability. They may have to focus on research and product development to identify new revenue streams. For instance, some of the most successful and established DSLR camera manufacturers faced a major crisis when mirrorless cameras started eating into their market share. They had to revise the product strategy, downsize their manpower, and invest vast resources into developing competitive mirrorless systems to mitigate the company. On the contrary, DSLR manufacturers with diversified businesses remained more resilient.
Managing costs
Businesses must control expenses to maintain profitability. It may involve identifying areas where costs can be cut or negotiating better deals with vendors. For instance, Google is known to initiate moonshot projects. At the same time, they kill non-profitable projects quickly. It has helped the company retain leadership while managing costs judiciously.
4. Human resource problems
HR problems are issues related to recruiting, retaining, and developing talent. They are issues about the management of employees. Managing these problems requires assessing staffing needs, recruiting, restructuring, identifying training and upskilling needs, and retaining top talent through employee engagement initiatives, welfare measures, and career development opportunities.

Retaining top talent
Retaining top talent can be a determining factor for the success of a company. Businesses must build an environment that attracts top talent by creating opportunities for career advancement and offering competitive compensation packages. For instance, highly specialized jobs with business-critical responsibilities, such as chief aero designers in motor racing teams, are hard to find and recruit. So retaining them is crucial for the success of the company.
Addressing employee morale and motivation issues
Lack of motivation, stagnant career, unfavorable team dynamics, etc., are some factors that cause a dip in employee morale. These factors can affect productivity and quality of work. Businesses must address these issues through employee engagement initiatives, career planning, team building, welfare measures, training, upskilling, etc.
Managing a diverse workforce
In an increasingly globalized work scenario, businesses must ensure that they create a work environment that is inclusive and welcoming to employees from different backgrounds and with diverse skill sets. They should also manage hybrid and remote work to address ambiguities and ensure clarity and synergy among teams and individuals based in various locations. For instance, many companies reserve certain positions for people of different racial/ethnic backgrounds or genders to meet their diversity goals. They also put policies and systems in place to prevent/address discrimination in the workplace.
Marketing problems
Marketing problems are related to promoting and selling a company’s products or services. Problems usually arise in understanding customer behavior and preferences and developing marketing strategies that appeal to those customers. Solving marketing problems requires revisiting the marketing strategy, understanding customer needs and behaviors by analyzing data, positioning the products more appealingly, and branding them better to reflect the strengths of the company and its product offerings.
Understanding customer needs and behavior
Customer needs to dictate the direction of product development and positioning. To design and deliver successful products, businesses must gain a deep understanding of customer needs, preferences, and pain points. For instance, the Japanese car makers capitalized on the high gas prices during the oil crisis and managed to capture the market in the US with their more efficient and reliable cars. The sudden loss in interest in the large, thirsty cars caused a considerable shift in the market, allowing Japanese car manufacturers to position their products in line with the customers’ preferences and succeed.
Developing a strong brand identity
Businesses must create a brand identity that resonates with the customers and sets them apart from competitors. For instance, it is common for companies to change their logo and brand identity in line with the changing trends, customer preferences, and product strategy.
Identifying new marketing channels and tactics
Businesses must be able to identify and adapt to changing customer preferences and identify new channels and tactics for reaching those customers. For instance, many retail businesses have adopted an eCommerce strategy to cater to mobile-savvy customers and to reach new markets.

What Skills do Business Leaders Require for Effective Problem-Solving?
Following are some of the skills required for effective problem-solving in business.
1. Research and analytical skills
Problems have various potential implications. Trying to solve them straight away without doing proper research can cause further problems. Business leaders should study the problem to gain a deeper understanding, assess the solutions thoroughly, and test them before deploying them. They also need good analytical skills to review the performance metrics that indicate the problem areas and analyze information and data to understand the problem. Analytical skills help business leaders break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts, identify their root causes, avoid bounded rationality in decision making , and develop effective solutions and creative workarounds.
2. Creativity
When the problems are complex and multi-dimensional, they may require unique solutions that never existed before. Finding solutions for these problems requires creativity and a culture of innovation in the company. Business leaders must think creatively and tread unconventional paths to create innovative solutions. For instance, during the pandemic, when customers did not want to take the risk of going to retail stores to buy things but were reluctant to pay for the high shipping costs involved in e-commerce, retail businesses offered solutions such as BOPIS that let customers order online and collect their purchases safely from collection booth/kiosk at a convenient time. It helped them meet customer needs by offering the best of both worlds
3. Decision-making
Effective problem-solving in business requires sound decision-making skills. Problem-solving often involves making choices and tough decisions. For instance, the decision to axe a product line that has performed well in the past but has no future potential is a tough one to make. But retaining it will cost resources and yield decreasing returns. Great business leaders evaluate multiple options/solutions and make decisions in the company’s best interest. Being decisive or having decision clarity also means making the right decisions at the right time. Delays in decision-making can cause severe consequences even if you ultimately make the right decision. So business leaders must analyze everything and make the right decision when it matters the most.
4. Communication
Business leaders cannot single-handedly solve problems. Problem-solving requires a team effort. Good business leaders harness the potential of every employee with their communication skills and excellent coordination. They communicate effectively with colleagues, customers, and stakeholders to identify problems and develop solutions. For instance, in a crowded restaurant, the chef needs to coordinate the kitchen staff continuously, check if they are doing their part efficiently, control food quality, and make sure that food is served at the right table as quickly as possible. Lack of communication from the chef can escalate into a full-fledged nightmare, where customers keep waiting for their orders, kitchen staff make mistakes and deliver poor quality food, and the waiters get the flak for not serving food on time. Such situations can ruin the reputation of the restaurant and lead to the loss of customer trust. So good business leaders must communicate and build synergy among the individuals within and among other teams to get work done effectively.
5. Marketing problems

6. Leadership
Problem-solving is about working with many individuals and bringing the best out of them. So business leaders need great leadership qualities to motivate and inspire their teams to work together and solve problems. For example, innovations come from the R&D department; they get incorporated into products by the product development team, and the products are positioned and promoted in the market by the marketing team. Great business leaders lead product development and deployment by coordinating with all these teams, getting their insights, considering their views, and making important decisions regarding product strategy, product positioning, and branding. Situational Leadership is essential to deal with shifting priorities. Leaders motivate the teams and guide them in the right direction. Without good leadership, a company cannot solve problems effectively.
A Step-by-Step Process to Problem-Solving in Business
Problem-solving in business is often an iterative process. So the steps involved may need to be repeated or revised as new information becomes available. Problem-solving usually involves the following steps:
- Define the problem; include any present symptoms or effects.
- Understand the root cause of the problem and find out how it impacts the business.
- Collect all the necessary information related to the problem by analyzing data, conducting interviews, researching, and seeking input from others.
- Brainstorm with the stakeholders and generate potential solutions to the problem. Encourage open communication, collaboration, and participation among team members.
- Weigh the pros and cons, evaluate all the potential solutions, analyze the risks, and consider the feasibility of each.
- Choose the best solution from the evaluated solutions and consider how it will impact the stakeholders, including customers, employees, suppliers, and shareholders.
- Develop an action plan to implement the chosen solution, detailing specific steps, timelines, and responsibilities.
- Implement the solution, monitor progress closely, adjust the plan, make changes as required, and communicate those changes to the stakeholders.
- Evaluate the results, determine if the solution addressed the problem, assess its effectiveness, and identify any areas for improvement.
- Reflect on the problem-solving process, and identify and document the lessons learned.
- Consider how you can improve the process for future problem-solving efforts.

Problem Solving Key Takeaways
Problem-solving is a critical skill for business success. It involves identifying, understanding, and resolving issues in various facets of business operations and strategy. Common obstacles during problem-solving can include cognitive biases, resource constraints, and lack of information. Business leaders must navigate these potential pitfalls to ensure effective resolution of issues.
Essential skills for effective problem-solving include research and analytical abilities, creativity, decision-making, communication, time management, and leadership. These skills enable business leaders to dissect complex issues, devise innovative solutions, make informed decisions, effectively communicate, manage time, and guide teams toward resolution.
Problem-solving is an iterative process that involves multiple stages, from defining the problem and understanding its root cause to brainstorming and evaluating potential solutions, choosing the best one, and developing and implementing an action plan. This process also includes monitoring progress, evaluating results, and reflecting on the process for continuous improvement. An effective problem-solving method is the root cause analysis method. Ultimately, successful problem-solving in business is not just about resolving immediate issues but also about refining and improving the problem-solving process to tackle future challenges more effectively.
Problem Solving in Business FAQs
Answer: The four types of problem-solving strategies typically include:
Trial and Error: Involves trying different solutions until the problem is solved. It’s often used when there are limited possibilities that can be explored quickly.
Algorithm: A step-by-step procedure that, if followed correctly, will always lead to the solution of the problem. It is highly logical and often used in mathematical problems.
Heuristic: A general problem-solving strategy that involves using rules-of-thumb or shortcuts. Heuristics may not always yield the perfect solution but can often lead to a satisfactory one in a reasonable time frame.
Insight: Sometimes also referred to as creative problem-solving. It involves sudden realization, a flash of inspiration, or an ‘Aha!’ moment that provides a solution.
- What is an example of problem-solving in business?
Answer: A common example of problem-solving in business is addressing a sudden drop in sales. The problem-solving process would begin with identifying and defining the problem (drop in sales). The next step would involve researching and analyzing the issue to understand its root cause, such as market conditions, competition, or internal factors. Brainstorming for potential solutions could include improving the product, adjusting pricing, or enhancing marketing efforts. After evaluating and selecting the best solution, an action plan would be developed and implemented. Progress would be monitored, results evaluated, and the process reflected upon for future problem-solving efforts.
- Why is problem-solving important in business?
Answer: Problem-solving is vital in business as it enables organizations to navigate challenges and obstacles that could hamper their growth and success. It allows businesses to identify issues, understand their implications, and devise effective solutions. This process not only resolves the immediate issue at hand but also helps prevent similar problems in the future. Moreover, effective problem-solving can lead to improved business processes, innovation, and a competitive advantage. It also plays a crucial role in customer satisfaction, profitability, and overall sustainability of the business.
- What is the most important problem-solving tool for business?
Answer: There isn’t a one-size-fits-all problem-solving tool for all businesses, as the most effective tool often depends on the specific problem and the business context. However, one universally important tool is effective communication. Clear, open, and honest communication fosters better understanding of problems, facilitates brainstorming of solutions, and aids in the implementation of action plans. Other essential tools include data analysis tools (for understanding and diagnosing problems), brainstorming techniques (for generating solutions), and project management tools (for implementing solutions).
Great leaders possess a unique problem-solving mindset that enables them to navigate complex challenges in the business world. By following this step-by-step guide, you can cultivate these essential skills and unlock your potential for success. Remember, problem-solving is not just about finding solutions but also about fostering a culture of innovation, collaboration, and continuous improvement. Embrace the challenges, seize the opportunities, and lead confidently as you embark on your journey towards becoming an exceptional problem solver and a remarkable leader in the business realm.
Bridge the Strategy Execution Gap with Profit.co
Related articles, the evolving role of natural language processing in communication.
Artificial Intelligence is rapidly becoming a cornerstone of industry practices as companies actively seek innovative ways to integrate it into... Read more
How Can AI Assist and Advance Communication?
Nothing has quite revolutionized communication like technology has. Whether the invention of the telephone in 1876 or the internet in... Read more
How to Conquer Sunday Scaries?
Do you feel anxious, stressed, or depressed every Sunday night? Do you dread the thought of going back to work... Read more
Business Communication for 2024
The bedrock of efficiency is communication perhaps a blanket statement but one with a degree of truth. If you were... Read more

What is Iterative Business Execution?
Get a Personalized Demo
Execute your strategy with the industry’s most preferred and intuitive software
Problem-solving in Business: Unleashing the Power of Solutions

By Team SOLVEDIO │ Updated Jun 13, 2023
Introduction
In business, challenges are inevitable. A problem in business occurs when what you want to happen doesn't match what's happening, and finding a solution can be challenging. Problem-solving in business involves identifying, analyzing, and solving problems to improve productivity, perfect performance, and achieve strategic goals. Business problem-solving involves implementing effective processes to overcome obstacles that stand in the way of achieving your operational and strategic goals. Successful businesses embrace problems as opportunities for growth and improvement instead of seeing them as obstacles.
Common Problems Faced by Businesses
Businesses face many challenges on their path to success. From quality issues and operational inefficiencies to supply chain disruptions and cost control, these common problems can hinder productivity and profitability.
- Supply chain disruptions: Businesses often rely on complex supply chains to source raw materials and components. Any disruption in the supply chain can lead to delays, shortages, and increased costs.
- Quality control issues: Keeping consistent product quality is crucial for businesses. However, manufacturing defects, equipment malfunctions, or human errors can result in defective products, customer dissatisfaction, and potential recalls.
- Operational inefficiencies: Inefficient processes and workflows can hinder productivity and increase costs. Common issues include inadequate production planning, poor inventory management, excessive downtime, or ineffective communication between different departments.
- Workforce management: Managing a diverse workforce and ensuring employee satisfaction can be challenging. Problems can arise from a lack of skilled workers, high turnover rates, poor employee attendance, or team conflicts.
- Regulatory compliance: Businesses must follow various regulations and standards, varying depending on the industry and location. Non-compliance can lead to fines, legal issues, damage to the company's reputation, and even closure.
- Technology integration: Adopting new technologies or upgrading existing systems can be complex and costly. Integration challenges, employee resistance, and the need for specialized ability can pose hurdles to successful technology implementation.

Importance of Problem Statement and Problem-solving in Business
To effectively solve business problems, gaining a deep understanding of their nature and root causes is essential, which requires careful analysis and critical thinking. Problems can manifest in different forms, ranging from minor operational glitches to complex strategic dilemmas. By understanding the intricacies of these problems, businesses can devise targeted solutions that address the core issues and lead to sustainable outcomes.
Problem statement refers to clearly defining a problem, understanding its underlying causes, and setting specific goals and aims to address it. On the other hand, problem-solving involves analyzing the identified problem and devising strategies to overcome it. Effective problem statement lays the foundation for successful problem-solving.
Problem-solving is a vital competency for individuals and organizations alike. It enables businesses to tackle challenges head-on, adapt to changing circumstances, and seize opportunities. Effective problem-solving fosters innovation, enhances decision-making, boosts operational efficiency, and drives business growth. By encouraging a problem-solving culture, companies can nurture a proactive mindset that empowers employees at all levels to contribute to the organization's success.
The Process of Problem-solving
Problem-solving in business involves a structured approach to identifying, analyzing, and solving problems. It's a way to enhance productivity, perfect performance, and achieve strategic goals. Let's break down the necessary steps:
1. Defining the Problem
The first step is to understand the issue clearly, which involves articulating the problem, understanding its impact on the business, and envisioning the desired outcome.
2. Gathering Information
Once the problem is defined, it's important to gather relevant information, including data, feedback, stakeholder insights, market research, and internal resources. This information forms the foundation for further analysis and decision-making.
3. Analyzing the Problem
Thoroughly examining the problem is crucial to uncover its causes and implications. Tools like root cause analysis, SWOT analysis, and fishbone diagrams can help understand the underlying factors comprehensively.
4. Generating Solutions
Generating solutions is the creative phase, where you brainstorm and generate various potential solutions. Encourage diverse perspectives and innovative thinking to explore different ideas and options.
5. Evaluating and Selecting a Solution
Once you have generated a range of solutions, it's time to evaluate them based on predetermined criteria. Consider factors such as feasibility, cost-effectiveness, and alignment with strategic goals. Select the most suitable solution for further implementation.
6. Implementing the Solution
With the chosen solution in hand, it's time to implement it. Develop a clear plan, assign responsibilities, and give necessary resources. Effective communication and collaboration are essential during this phase.
7. Monitoring and Adjusting
After implementing the solution, check its progress and evaluate its effectiveness. Regular monitoring allows for prompt adjustments and fine-tuning, ensuring that the solution continues to address the problem efficiently.
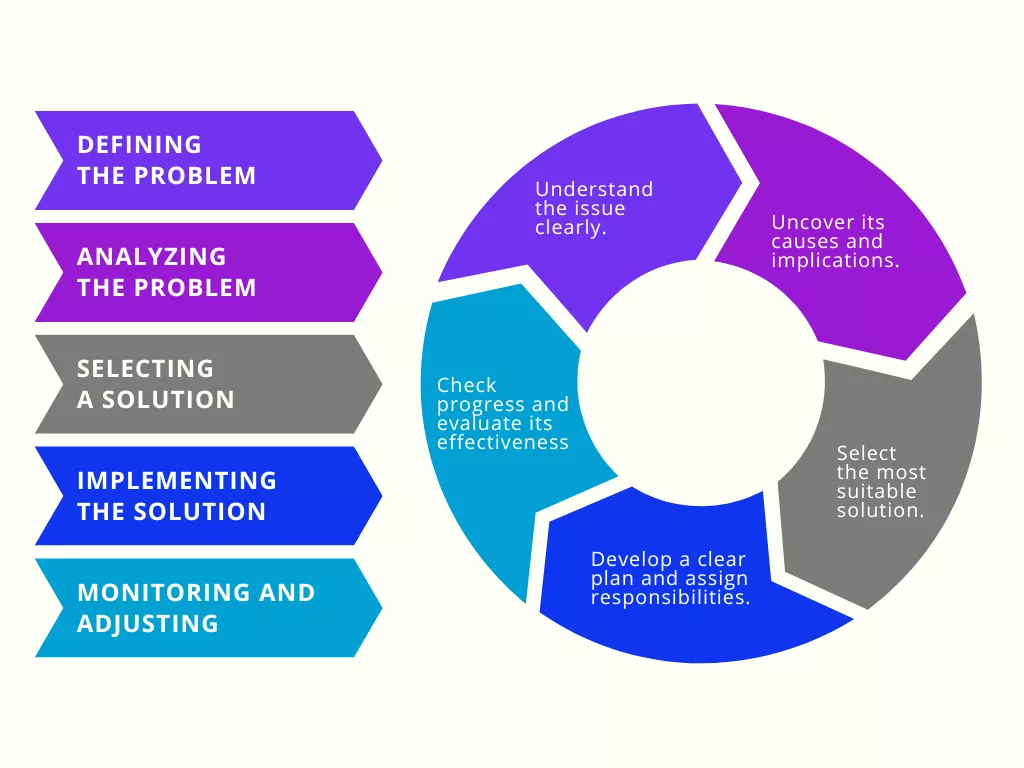
Challenges in Problem-solving
Problem-solving is a complex process that involves various challenges. One of these challenges is lack of data . When businesses have limited access to relevant data and insights, it becomes increasingly difficult to identify and understand the root causes of problems. Another common obstacle in problem-solving is ineffective collaboration . Departments within a business may operate in silos, isolating valuable information and perspectives. Poor communication further compounds the problem, hindering the collective effort to solve issues.
Time constraints also pose a significant challenge in problem-solving. In a rapidly changing business landscape, quick decision-making and problem resolution are vital. However, the need for speed often hampers the thorough analysis and evaluation of potential solutions. Time limitations prevent businesses from conducting a comprehensive examination of all available options, potentially leading to suboptimal or short-term fixes that do not address the root causes.
To overcome these challenges, businesses must prioritize data accessibility, collaboration, and time management in their problem-solving endeavors.
Problem-solving in Business
Digital tools for problem-solving in business.
You can significantly enhance your organizational performance by addressing your business's quality issues, operational inefficiencies, supply chain disruptions, or cost control. One effective approach is to digitize your problem-solving process and use customizable digital tools. These tools use advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, data analytics, and automation to enhance problem-solving capabilities. The benefits of using problem-solving digital tools include:
- Data-driven insights: Problem-solving tools provide businesses with real-time data and analytics, enabling informed decision-making and more accurate problem diagnosis.
- Collaboration and knowledge sharing: These tools facilitate team collaboration by providing a centralized platform for sharing information, ideas, and solutions.
- Process optimization: Problem-solving digital tools streamlines and automates processes, reducing manual effort and enabling faster and more efficient problem resolution.
Solvedio's Problem-solving Solution
Solvedio is a platform that offers digital solutions for problem-solving in manufacturing and business. By leveraging the power of technology, Solvedio provides an intuitive and efficient way to streamline your problem-solving process.
Solvedio's Problem-solving Solution revolutionizes organizations' problem-solving and resolution approach, offering a streamlined and efficient cloud-based tool. It enables quick problem recording with easy attachment and photo integration, eliminating manual spreadsheet entry. The platform provides a comprehensive overview of ongoing issues, offers popular problem-solving methods, and ensures faster and more efficient resolution. Automation escalates problems quickly and suggests suitable solvers, leading to optimal results. Solvedio also enables the creation of lasting solutions, preventing problem recurrence and facilitating uninterrupted workflow for employees.
Irrespective of your company's industry, size, or the specific challenges you encounter, Solvedio provides a fully customizable solution to digitize problem-solving within your business. With Solvedio, you can choose and utilize only the features that align with your unique needs. This tailored approach ensures maximum efficiency and lets you derive the most significant value from the platform. By leveraging Solvedio, you can optimize your problem-solving processes and unlock enhanced organizational productivity.

Benefits of Effective Problem-solving
Adopting effective problem formulation and problem-solving strategies offers numerous benefits for businesses.
✔️ Increased Efficiency and Productivity
By addressing problems proactively, businesses can streamline processes, eliminate bottlenecks, and enhance overall efficiency and productivity, which leads to cost savings and improved operational performance.
✔️Enhanced Decision-Making Capabilities
Effective problem-solving provides businesses with a clear understanding of the issues, enabling informed decision-making, which reduces the likelihood of making hasty or ill-informed decisions that could have adverse consequences.
✔️Improved Customer Satisfaction
Swift problem-solving helps resolve customer issues promptly, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty. Satisfied customers are more likely to become brand advocates and refer others, contributing to business growth.
✔️Competitive Advantage in the Market
Organizations that excel in problem-solving gain a competitive edge in the market. Their ability to address challenges efficiently and innovate solutions sets them apart from competitors and enhances their reputation.
Conclusion: Embrace, Analyze, Solve
In a rapidly changing business landscape, problem-solving is essential for growth and resilience . By adopting a structured approach and utilizing digital tools like Solvedio , businesses can navigate challenges, unlock innovation, and achieve sustainable success. Remember, every problem is an opportunity in disguise. Embrace it, analyze it, and solve it. Your business's future depends on it.
Problem-Solving Solution
What is problem-solving in business.
In business, problem-solving is a systematic approach to identifying, analyzing, and resolving issues or obstacles that impede organizational goals. It involves the application of critical thinking, analytical skills, and decision-making techniques to find optimal solutions.
Why is problem-solving important in business?
Problem-solving is crucial in business as it enables organizations to overcome challenges, make informed decisions, and drive innovation. Effective problem-solving helps improve efficiency, productivity, and profitability while fostering a proactive and adaptable work environment.
What are some problem-solving methodologies in business?
There are several problem-solving methodologies used in business, including the 5 Whys technique, SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats), Fishbone Diagram, Pareto analysis, root cause analysis, brainstorming, Lean management, and agile problem-solving.
How can digital tools like Solvedio help with problem-solving in manufacturing/business?
Digital tools like Solvedio offer intuitive platforms that streamline problem-solving. Solvedio automates and simplifies the entire problem-solving process, offering digitized processes and problem-solving techniques. With one intuitive interface, you have everything you need to efficiently tackle problem formulation and the whole problem-solving process in your company without complex setups, procedures, or documentation.
Transform Your Business Problem-Solving

- All Access Pass
- PLR Articles
- PLR Courses
- PLR Social Media
Grab Our Free eBook to Learn How to Grow Your Wellness Business Exponentially!
What is problem solving (a definition), why problem solving is important.
- Substance use disorder
- Alcohol use disorder
- Low back pain
- Improving mood in children, adults, and elderly adults
- Emotional distress due to cancer and divorce
Problem Solving vs Critical Thinking

Problem Solving Theory (in Psychology)
Video: the psychology of problem-solving.
Problem Solving Skills
Video: figure it out - the art of problem solving.
Problem-Solving Process & Steps
- Attempting to identify a problem when it occurs
- Defining a problem
- Attempting to understand the problem
- Setting goals related to the problem
- Generating alternative solutions
- Evaluating and choosing the best alternatives
- Implementing the chosen alternatives
- Evaluating the efficacy of the effort at problem-solving
Examples of Problem Solving
- Solution #1: Tanya decides to tackle the problem head-on and decides to change the tire by herself. She lets her work know she might be late, reads the owner’s manual, and successfully changes the tire on her own.
- Solution #2: Tanya decides she doesn’t feel comfortable changing a tire on the busy highway. She lets her work know that she will miss the morning meeting and calls her brother to come and help her change the tire.
- Solution #1: Yasmin decides to modify her workout to a 15-minute stretch on the days she is sick. This way she sticks to her commitment and allows her body to rest.
- Solution #2: Yasmin decides she really doesn’t feel well enough to get out of bed. She takes care of her body by drinking plenty of water and resting. She resumes her routine as soon as she feels better and doesn't beat herself up about the lapse in routine.
- Solution #1: Kai was prepared for this situation because he has seen how bad the technology in the classroom is. He hands out printed copies of his presentation to the professor and class.
- Solution #2: Kai decides to do an oral presentation instead of using his digital materials. He uses notes he prepared to do the presentation without the aid of his slides.

Problem Solving Strategies
Video: problem solving through perspective change.
Problem Solving Methods

Problem-Solving Games & Activities
- Crossword puzzles
- Escape rooms
- Rubik’s cube
- 20 dry spaghetti noodles
- Roll of masking tape
- Yard of string
- 1 marshmallow
- Each team will need a set of materials listed above.
- Instruct each team they have ten minutes to construct the tallest spaghetti tower capable of supporting a marshmallow on top using only the materials provided.
- Once complete, stick a single marshmallow on top of the tower.
- The team whose tower is the tallest and can support a marshmallow wins.
Video: How to Teach Kids Better Problem Solving
Articles Related to Problem Solving
- Self-Management: Definition, Skills & Strategies
- Life Skills: Definition, Examples, & Skills to Build
- Overthinking: Definition, Causes, & How to Stop
Books Related to Problem Solving
- Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything
- Critical thinking, Logic & Problem Solving: The Ultimate Guide to Better Thinking, Systematic Problem Solving and Making Impeccable Decisions with Secret Tips to Detect Logical Fallacies
- Solve It!: The Mindset and Tools of Smart Problem Solvers
- Think Like a Programmer: An Introduction to Creative Problem Solving
Final Thoughts on Problem Solving
Don't forget to grab our free ebook to learn how to grow your wellness business exponentially.
- Dostál, J. (2015). Theory of problem-solving . Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 174, 2798–2805.
- D'Zurilla, T. J., & Goldfried, M. R. (1971). Problem-solving and behavior modification . Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 78(1), 107–126.
- Malouff, J., Thorsteinsson, E., & Schutte, N. (2007). The efficacy of problem-solving therapy in reducing mental and physical health problems: A meta-analysis . Clinical Psychology Review, 27(1), 46–57.
- Happiness
- Stress Management
- Self-Confidence
- Manifestation
- All Articles...
- All-Access Pass
- PLR Content Packages
- PLR Courses
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Share Podcast

Do You Understand the Problem You’re Trying to Solve?
To solve tough problems at work, first ask these questions.
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
Problem solving skills are invaluable in any job. But all too often, we jump to find solutions to a problem without taking time to really understand the dilemma we face, according to Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg , an expert in innovation and the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
In this episode, you’ll learn how to reframe tough problems by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that contribute to the situation. You’ll also learn why searching for just one root cause can be misleading.
Key episode topics include: leadership, decision making and problem solving, power and influence, business management.
HBR On Leadership curates the best case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, to help you unlock the best in those around you. New episodes every week.
- Listen to the original HBR IdeaCast episode: The Secret to Better Problem Solving (2016)
- Find more episodes of HBR IdeaCast
- Discover 100 years of Harvard Business Review articles, case studies, podcasts, and more at HBR.org .
HANNAH BATES: Welcome to HBR on Leadership , case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, hand-selected to help you unlock the best in those around you.
Problem solving skills are invaluable in any job. But even the most experienced among us can fall into the trap of solving the wrong problem.
Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg says that all too often, we jump to find solutions to a problem – without taking time to really understand what we’re facing.
He’s an expert in innovation, and he’s the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
In this episode, you’ll learn how to reframe tough problems, by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that contribute to the situation. You’ll also learn why searching for one root cause can be misleading. And you’ll learn how to use experimentation and rapid prototyping as problem-solving tools.
This episode originally aired on HBR IdeaCast in December 2016. Here it is.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Welcome to the HBR IdeaCast from Harvard Business Review. I’m Sarah Green Carmichael.
Problem solving is popular. People put it on their resumes. Managers believe they excel at it. Companies count it as a key proficiency. We solve customers’ problems.
The problem is we often solve the wrong problems. Albert Einstein and Peter Drucker alike have discussed the difficulty of effective diagnosis. There are great frameworks for getting teams to attack true problems, but they’re often hard to do daily and on the fly. That’s where our guest comes in.
Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg is a consultant who helps companies and managers reframe their problems so they can come up with an effective solution faster. He asks the question “Are You Solving The Right Problems?” in the January-February 2017 issue of Harvard Business Review. Thomas, thank you so much for coming on the HBR IdeaCast .
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Thanks for inviting me.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, I thought maybe we could start by talking about the problem of talking about problem reframing. What is that exactly?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Basically, when people face a problem, they tend to jump into solution mode to rapidly, and very often that means that they don’t really understand, necessarily, the problem they’re trying to solve. And so, reframing is really a– at heart, it’s a method that helps you avoid that by taking a second to go in and ask two questions, basically saying, first of all, wait. What is the problem we’re trying to solve? And then crucially asking, is there a different way to think about what the problem actually is?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, I feel like so often when this comes up in meetings, you know, someone says that, and maybe they throw out the Einstein quote about you spend an hour of problem solving, you spend 55 minutes to find the problem. And then everyone else in the room kind of gets irritated. So, maybe just give us an example of maybe how this would work in practice in a way that would not, sort of, set people’s teeth on edge, like oh, here Sarah goes again, reframing the whole problem instead of just solving it.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I mean, you’re bringing up something that’s, I think is crucial, which is to create legitimacy for the method. So, one of the reasons why I put out the article is to give people a tool to say actually, this thing is still important, and we need to do it. But I think the really critical thing in order to make this work in a meeting is actually to learn how to do it fast, because if you have the idea that you need to spend 30 minutes in a meeting delving deeply into the problem, I mean, that’s going to be uphill for most problems. So, the critical thing here is really to try to make it a practice you can implement very, very rapidly.
There’s an example that I would suggest memorizing. This is the example that I use to explain very rapidly what it is. And it’s basically, I call it the slow elevator problem. You imagine that you are the owner of an office building, and that your tenants are complaining that the elevator’s slow.
Now, if you take that problem framing for granted, you’re going to start thinking creatively around how do we make the elevator faster. Do we install a new motor? Do we have to buy a new lift somewhere?
The thing is, though, if you ask people who actually work with facilities management, well, they’re going to have a different solution for you, which is put up a mirror next to the elevator. That’s what happens is, of course, that people go oh, I’m busy. I’m busy. I’m– oh, a mirror. Oh, that’s beautiful.
And then they forget time. What’s interesting about that example is that the idea with a mirror is actually a solution to a different problem than the one you first proposed. And so, the whole idea here is once you get good at using reframing, you can quickly identify other aspects of the problem that might be much better to try to solve than the original one you found. It’s not necessarily that the first one is wrong. It’s just that there might be better problems out there to attack that we can, means we can do things much faster, cheaper, or better.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, in that example, I can understand how A, it’s probably expensive to make the elevator faster, so it’s much cheaper just to put up a mirror. And B, maybe the real problem people are actually feeling, even though they’re not articulating it right, is like, I hate waiting for the elevator. But if you let them sort of fix their hair or check their teeth, they’re suddenly distracted and don’t notice.
But if you have, this is sort of a pedestrian example, but say you have a roommate or a spouse who doesn’t clean up the kitchen. Facing that problem and not having your elegant solution already there to highlight the contrast between the perceived problem and the real problem, how would you take a problem like that and attack it using this method so that you can see what some of the other options might be?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Right. So, I mean, let’s say it’s you who have that problem. I would go in and say, first of all, what would you say the problem is? Like, if you were to describe your view of the problem, what would that be?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: I hate cleaning the kitchen, and I want someone else to clean it up.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: OK. So, my first observation, you know, that somebody else might not necessarily be your spouse. So, already there, there’s an inbuilt assumption in your question around oh, it has to be my husband who does the cleaning. So, it might actually be worth, already there to say, is that really the only problem you have? That you hate cleaning the kitchen, and you want to avoid it? Or might there be something around, as well, getting a better relationship in terms of how you solve problems in general or establishing a better way to handle small problems when dealing with your spouse?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Or maybe, now that I’m thinking that, maybe the problem is that you just can’t find the stuff in the kitchen when you need to find it.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Right, and so that’s an example of a reframing, that actually why is it a problem that the kitchen is not clean? Is it only because you hate the act of cleaning, or does it actually mean that it just takes you a lot longer and gets a lot messier to actually use the kitchen, which is a different problem. The way you describe this problem now, is there anything that’s missing from that description?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: That is a really good question.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Other, basically asking other factors that we are not talking about right now, and I say those because people tend to, when given a problem, they tend to delve deeper into the detail. What often is missing is actually an element outside of the initial description of the problem that might be really relevant to what’s going on. Like, why does the kitchen get messy in the first place? Is it something about the way you use it or your cooking habits? Is it because the neighbor’s kids, kind of, use it all the time?
There might, very often, there might be issues that you’re not really thinking about when you first describe the problem that actually has a big effect on it.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: I think at this point it would be helpful to maybe get another business example, and I’m wondering if you could tell us the story of the dog adoption problem.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Yeah. This is a big problem in the US. If you work in the shelter industry, basically because dogs are so popular, more than 3 million dogs every year enter a shelter, and currently only about half of those actually find a new home and get adopted. And so, this is a problem that has persisted. It’s been, like, a structural problem for decades in this space. In the last three years, where people found new ways to address it.
So a woman called Lori Weise who runs a rescue organization in South LA, and she actually went in and challenged the very idea of what we were trying to do. She said, no, no. The problem we’re trying to solve is not about how to get more people to adopt dogs. It is about keeping the dogs with their first family so they never enter the shelter system in the first place.
In 2013, she started what’s called a Shelter Intervention Program that basically works like this. If a family comes and wants to hand over their dog, these are called owner surrenders. It’s about 30% of all dogs that come into a shelter. All they would do is go up and ask, if you could, would you like to keep your animal? And if they said yes, they would try to fix whatever helped them fix the problem, but that made them turn over this.
And sometimes that might be that they moved into a new building. The landlord required a deposit, and they simply didn’t have the money to put down a deposit. Or the dog might need a $10 rabies shot, but they didn’t know how to get access to a vet.
And so, by instigating that program, just in the first year, she took her, basically the amount of dollars they spent per animal they helped went from something like $85 down to around $60. Just an immediate impact, and her program now is being rolled out, is being supported by the ASPCA, which is one of the big animal welfare stations, and it’s being rolled out to various other places.
And I think what really struck me with that example was this was not dependent on having the internet. This was not, oh, we needed to have everybody mobile before we could come up with this. This, conceivably, we could have done 20 years ago. Only, it only happened when somebody, like in this case Lori, went in and actually rethought what the problem they were trying to solve was in the first place.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, what I also think is so interesting about that example is that when you talk about it, it doesn’t sound like the kind of thing that would have been thought of through other kinds of problem solving methods. There wasn’t necessarily an After Action Review or a 5 Whys exercise or a Six Sigma type intervention. I don’t want to throw those other methods under the bus, but how can you get such powerful results with such a very simple way of thinking about something?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: That was something that struck me as well. This, in a way, reframing and the idea of the problem diagnosis is important is something we’ve known for a long, long time. And we’ve actually have built some tools to help out. If you worked with us professionally, you are familiar with, like, Six Sigma, TRIZ, and so on. You mentioned 5 Whys. A root cause analysis is another one that a lot of people are familiar with.
Those are our good tools, and they’re definitely better than nothing. But what I notice when I work with the companies applying those was those tools tend to make you dig deeper into the first understanding of the problem we have. If it’s the elevator example, people start asking, well, is that the cable strength, or is the capacity of the elevator? That they kind of get caught by the details.
That, in a way, is a bad way to work on problems because it really assumes that there’s like a, you can almost hear it, a root cause. That you have to dig down and find the one true problem, and everything else was just symptoms. That’s a bad way to think about problems because problems tend to be multicausal.
There tend to be lots of causes or levers you can potentially press to address a problem. And if you think there’s only one, if that’s the right problem, that’s actually a dangerous way. And so I think that’s why, that this is a method I’ve worked with over the last five years, trying to basically refine how to make people better at this, and the key tends to be this thing about shifting out and saying, is there a totally different way of thinking about the problem versus getting too caught up in the mechanistic details of what happens.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: What about experimentation? Because that’s another method that’s become really popular with the rise of Lean Startup and lots of other innovation methodologies. Why wouldn’t it have worked to, say, experiment with many different types of fixing the dog adoption problem, and then just pick the one that works the best?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: You could say in the dog space, that’s what’s been going on. I mean, there is, in this industry and a lot of, it’s largely volunteer driven. People have experimented, and they found different ways of trying to cope. And that has definitely made the problem better. So, I wouldn’t say that experimentation is bad, quite the contrary. Rapid prototyping, quickly putting something out into the world and learning from it, that’s a fantastic way to learn more and to move forward.
My point is, though, that I feel we’ve come to rely too much on that. There’s like, if you look at the start up space, the wisdom is now just to put something quickly into the market, and then if it doesn’t work, pivot and just do more stuff. What reframing really is, I think of it as the cognitive counterpoint to prototyping. So, this is really a way of seeing very quickly, like not just working on the solution, but also working on our understanding of the problem and trying to see is there a different way to think about that.
If you only stick with experimentation, again, you tend to sometimes stay too much in the same space trying minute variations of something instead of taking a step back and saying, wait a minute. What is this telling us about what the real issue is?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, to go back to something that we touched on earlier, when we were talking about the completely hypothetical example of a spouse who does not clean the kitchen–
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Completely, completely hypothetical.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Yes. For the record, my husband is a great kitchen cleaner.
You started asking me some questions that I could see immediately were helping me rethink that problem. Is that kind of the key, just having a checklist of questions to ask yourself? How do you really start to put this into practice?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I think there are two steps in that. The first one is just to make yourself better at the method. Yes, you should kind of work with a checklist. In the article, I kind of outlined seven practices that you can use to do this.
But importantly, I would say you have to consider that as, basically, a set of training wheels. I think there’s a big, big danger in getting caught in a checklist. This is something I work with.
My co-author Paddy Miller, it’s one of his insights. That if you start giving people a checklist for things like this, they start following it. And that’s actually a problem, because what you really want them to do is start challenging their thinking.
So the way to handle this is to get some practice using it. Do use the checklist initially, but then try to step away from it and try to see if you can organically make– it’s almost a habit of mind. When you run into a colleague in the hallway and she has a problem and you have five minutes, like, delving in and just starting asking some of those questions and using your intuition to say, wait, how is she talking about this problem? And is there a question or two I can ask her about the problem that can help her rethink it?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Well, that is also just a very different approach, because I think in that situation, most of us can’t go 30 seconds without jumping in and offering solutions.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Very true. The drive toward solutions is very strong. And to be clear, I mean, there’s nothing wrong with that if the solutions work. So, many problems are just solved by oh, you know, oh, here’s the way to do that. Great.
But this is really a powerful method for those problems where either it’s something we’ve been banging our heads against tons of times without making progress, or when you need to come up with a really creative solution. When you’re facing a competitor with a much bigger budget, and you know, if you solve the same problem later, you’re not going to win. So, that basic idea of taking that approach to problems can often help you move forward in a different way than just like, oh, I have a solution.
I would say there’s also, there’s some interesting psychological stuff going on, right? Where you may have tried this, but if somebody tries to serve up a solution to a problem I have, I’m often resistant towards them. Kind if like, no, no, no, no, no, no. That solution is not going to work in my world. Whereas if you get them to discuss and analyze what the problem really is, you might actually dig something up.
Let’s go back to the kitchen example. One powerful question is just to say, what’s your own part in creating this problem? It’s very often, like, people, they describe problems as if it’s something that’s inflicted upon them from the external world, and they are innocent bystanders in that.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Right, or crazy customers with unreasonable demands.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Exactly, right. I don’t think I’ve ever met an agency or consultancy that didn’t, like, gossip about their customers. Oh, my god, they’re horrible. That, you know, classic thing, why don’t they want to take more risk? Well, risk is bad.
It’s their business that’s on the line, not the consultancy’s, right? So, absolutely, that’s one of the things when you step into a different mindset and kind of, wait. Oh yeah, maybe I actually am part of creating this problem in a sense, as well. That tends to open some new doors for you to move forward, in a way, with stuff that you may have been struggling with for years.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, we’ve surfaced a couple of questions that are useful. I’m curious to know, what are some of the other questions that you find yourself asking in these situations, given that you have made this sort of mental habit that you do? What are the questions that people seem to find really useful?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: One easy one is just to ask if there are any positive exceptions to the problem. So, was there day where your kitchen was actually spotlessly clean? And then asking, what was different about that day? Like, what happened there that didn’t happen the other days? That can very often point people towards a factor that they hadn’t considered previously.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: We got take-out.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: S,o that is your solution. Take-out from [INAUDIBLE]. That might have other problems.
Another good question, and this is a little bit more high level. It’s actually more making an observation about labeling how that person thinks about the problem. And what I mean with that is, we have problem categories in our head. So, if I say, let’s say that you describe a problem to me and say, well, we have a really great product and are, it’s much better than our previous product, but people aren’t buying it. I think we need to put more marketing dollars into this.
Now you can go in and say, that’s interesting. This sounds like you’re thinking of this as a communications problem. Is there a different way of thinking about that? Because you can almost tell how, when the second you say communications, there are some ideas about how do you solve a communications problem. Typically with more communication.
And what you might do is go in and suggest, well, have you considered that it might be, say, an incentive problem? Are there incentives on behalf of the purchasing manager at your clients that are obstructing you? Might there be incentive issues with your own sales force that makes them want to sell the old product instead of the new one?
So literally, just identifying what type of problem does this person think about, and is there different potential way of thinking about it? Might it be an emotional problem, a timing problem, an expectations management problem? Thinking about what label of what type of problem that person is kind of thinking as it of.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: That’s really interesting, too, because I think so many of us get requests for advice that we’re really not qualified to give. So, maybe the next time that happens, instead of muddying my way through, I will just ask some of those questions that we talked about instead.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: That sounds like a good idea.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, Thomas, this has really helped me reframe the way I think about a couple of problems in my own life, and I’m just wondering. I know you do this professionally, but is there a problem in your life that thinking this way has helped you solve?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I’ve, of course, I’ve been swallowing my own medicine on this, too, and I think I have, well, maybe two different examples, and in one case somebody else did the reframing for me. But in one case, when I was younger, I often kind of struggled a little bit. I mean, this is my teenage years, kind of hanging out with my parents. I thought they were pretty annoying people. That’s not really fair, because they’re quite wonderful, but that’s what life is when you’re a teenager.
And one of the things that struck me, suddenly, and this was kind of the positive exception was, there was actually an evening where we really had a good time, and there wasn’t a conflict. And the core thing was, I wasn’t just seeing them in their old house where I grew up. It was, actually, we were at a restaurant. And it suddenly struck me that so much of the sometimes, kind of, a little bit, you love them but they’re annoying kind of dynamic, is tied to the place, is tied to the setting you are in.
And of course, if– you know, I live abroad now, if I visit my parents and I stay in my old bedroom, you know, my mother comes in and wants to wake me up in the morning. Stuff like that, right? And it just struck me so, so clearly that it’s– when I change this setting, if I go out and have dinner with them at a different place, that the dynamic, just that dynamic disappears.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Well, Thomas, this has been really, really helpful. Thank you for talking with me today.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Thank you, Sarah.
HANNAH BATES: That was Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg in conversation with Sarah Green Carmichael on the HBR IdeaCast. He’s an expert in problem solving and innovation, and he’s the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
We’ll be back next Wednesday with another hand-picked conversation about leadership from the Harvard Business Review. If you found this episode helpful, share it with your friends and colleagues, and follow our show on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts. While you’re there, be sure to leave us a review.
We’re a production of Harvard Business Review. If you want more podcasts, articles, case studies, books, and videos like this, find it all at HBR dot org.
This episode was produced by Anne Saini, and me, Hannah Bates. Ian Fox is our editor. Music by Coma Media. Special thanks to Maureen Hoch, Adi Ignatius, Karen Player, Ramsey Khabbaz, Nicole Smith, Anne Bartholomew, and you – our listener.
See you next week.
- Subscribe On:
Latest in this series
This article is about leadership.
- Decision making and problem solving
- Power and influence
- Business management
Partner Center
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
problem-solving
Definition of problem-solving
Examples of problem-solving in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'problem-solving.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Dictionary Entries Near problem-solving
Cite this entry.
“Problem-solving.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/problem-solving. Accessed 10 Apr. 2024.
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - apr. 5, 12 bird names that sound like compliments, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 8 uncommon words related to love, games & quizzes.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Problem-solving in business is defined as implementing processes that reduce or remove obstacles that are preventing you or others from accomplishing operational and strategic business goals. In business, a problem is a situation that creates a gap between the desired and actual outcomes. In addition, a true problem typically does not have an ...
Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below. Step. Characteristics. 1. Define the problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically.
4 Problem-Solving Skills All Leaders Need. 1. Problem Framing. One key skill for any leader is framing problems in a way that makes sense for their organization. Problem framing is defined in Design Thinking and Innovation as determining the scope, context, and perspective of the problem you're trying to solve.
Structured problem solving strategies can be used to address almost any complex challenge in business or public policy. ... and I think Hugo's description is perfect. When we do problem definition well in classic problem solving, we are demonstrating the kind of empathy, at the very beginning of our problem, that design thinking asks us to ...
Definition and Importance. Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional ...
Problem-solving is an important component of any business or organization. It entails identifying, analyzing, and resolving problems in order to improve ... All stakeholders must agree on the definition of the problem for the A3 Problem Solving process to be effective. This ensures that everyone is working towards the same goal and that the ...
That's what we've found after decades of problem solving with leaders across business, nonprofit, and policy sectors. These leaders learn to adopt a particularly open and curious mindset, and adhere to a systematic process for cracking even the most inscrutable problems. They're terrific problem solvers under any conditions.
The McKinsey guide to problem solving. Become a better problem solver with insights and advice from leaders around the world on topics including developing a problem-solving mindset, solving problems in uncertain times, problem solving with AI, and much more.
Problem solving is an increasingly important soft skill for those in business. The Future of Jobs Survey by the World Economic Forum drives this point home. According to this report, complex problem solving is identified as one of the top 15 skills that will be sought by employers in 2025, along with other soft skills such as analytical thinking, creativity and leadership.
Teams today aren't just asked to execute tasks: They're called upon to solve problems. You'd think that many brains working together would mean better solutions, but the reality is that too ...
A good problem-solving definition might be finding solutions to difficult or complex issues. In practice, however, solving problems in the workplace is a little more immersive than that. ... But, since one of the most common mistakes in business problem-solving is attempting to seize on a solution right away, that might cause you to waste time ...
And you can do the same. By following this 10-step process, you can develop your problem-solving skills and approach any issue that arises with confidence. 1. Define the problem. When a problem arises, it can be very easy to jump right into creating a solution. However, if you don't thoroughly examine what led to the problem in the first ...
This guide is designed to help you approach your business problem-solving process in a systematic way through information sources that can help you understand your situation more clearly and provide a distinct direction towards the appropriate solution. ... Technically Sound-- meaning that in developing alternatives for achieving the objectives
The Power of Defining the Problem. by. Dwayne Spradlin. September 25, 2012. Well-defined problems lead to breakthrough solutions. When developing new products, processes, or even businesses, most ...
Summary. Reprint: R1209F. The rigor with which a problem is defined is the most important factor in finding a good solution. Many organizations, however, are not proficient at articulating their ...
Its benefits include: Finding creative solutions to complex problems: User research can insufficiently illustrate a situation's complexity. While other innovation processes rely on this information, creative problem-solving can yield solutions without it. Adapting to change: Business is constantly changing, and business leaders need to adapt.
To find books on problem solving in business, type the search terms "business and problem solving" in the search box. Available with a valid New York Public Library card. STUDIES AND ARTICLES _____ EBSCOHost -- Enter the search phrase "problem solving in business" or "problem solving in business" to retrieve articles on the topic.
Problem-solving is a vital skill in the business world. It allows organizations to identify and address challenges efficiently and effectively, helping them to overcome obstacles and seize new opportunities. Strong problem-solving skills also drive innovation and improve decision-making, leading to increased productivity and customer ...
Problem-solving is a critical skill for business success. It involves identifying, understanding, and resolving issues in various facets of business operations and strategy. Common obstacles during problem-solving can include cognitive biases, resource constraints, and lack of information.
By encouraging a problem-solving culture, companies can nurture a proactive mindset that empowers employees at all levels to contribute to the organization's success. The Process of Problem-solving. Problem-solving in business involves a structured approach to identifying, analyzing, and solving problems.
Having a clear vision of the best possible business cycle for your company is always the first step in problem solving. This lets you make the best decisions for long-term and short-term growth ...
Problem-solving is an important skill to develop because life will always throw you curveballs. Being able to respond to these problems with flexibility and calmness will generate much better results than if you respond to the problem with resistance or avoidance. Also, research has shown that increasing problem-solving skills through problem-solving therapy is beneficial for several physical ...
To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve. In this episode, you'll learn how to reframe tough problems by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that ...
The meaning of PROBLEM-SOLVING is the process or act of finding a solution to a problem. How to use problem-solving in a sentence.