No contents are available in this lesson!
No lessons available , lesson contents locked.
Enroll to unlock this lesson.
We will keep fighting for all libraries - stand with us!

Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
Root Cause Analysis And The 8 D Problem Solving Bootcamp
Video item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
3 Favorites
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
In collections.
Uploaded by dukelondon on February 6, 2021
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
An overview of the 8D problem-solving method
The 8D problem-solving method is a powerful tool in product management. It’s designed to help product managers tackle issues systematically and enhance product quality. This method follows eight steps in total, hence the name 8D.
The steps range from identifying problems to implementing long-term solutions. Today you’ll explore how you can effectively apply 8D to your products. You’ll also learn about the benefits of using this approach and analyze some real case studies.
What is 8D?
The 8D problem-solving method is designed to address and resolve problems by identifying, correcting, and eliminating recurring issues.
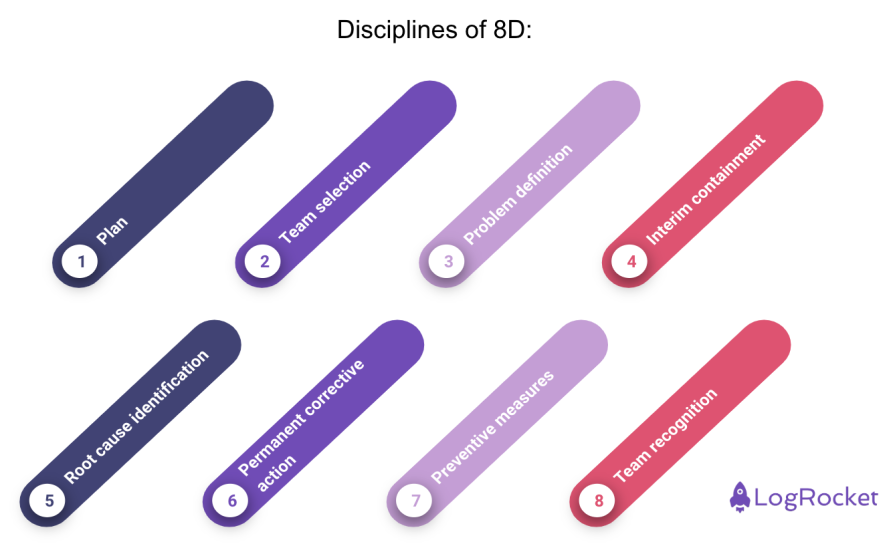
It involves eight different steps:
- Plan — Prepare for the problem-solving process
- Team selection — Assemble a team with the necessary knowledge and skills
- Problem definition — Clearly define the problem and its impact
- Interim containment action — Implement temporary measures to contain the problem
- Root cause identification — Identify the underlying cause(s) of the problem
- Permanent corrective action — Develop and implement a solution to address the root cause
- Preventive measures — Take steps to prevent the recurrence of the problem
- Team recognition — Acknowledge and reward the team’s efforts in resolving the issue
These steps focus on root cause analysis, preventive measures, and long-term solution implementation. The end goal is to improve product quality and operational efficiency.
The eight disciplines of 8D
The eight disciplines of the 8D method represent a comprehensive approach to solve problems within an organization. Each discipline is designed to guide teams through the process at each stage. Here’s a deeper look into each stage:
This initial step involves preparing for the problem-solving process. The goal here is to understand the problem’s magnitude and set up objectives. It’s about getting ready to tackle the issue systematically.
Team selection
In this step, a cross-functional team is formed. The team should consist of individuals with the necessary knowledge, skills, and experience to address the problem effectively. The team works together throughout the 8D process.
Problem definition
Next, the team has to describe the issue in specific terms. The goal here is to understand the impact and scope of the complication. A well-defined problem is easier to solve.
Interim containment
In the process of finding a solution, temporary measures are taken to contain the problem and prevent it from worsening. This reduces further damage or impact to the involved operations.
Root cause identification
In this phase, the team uses various tools and techniques to identify the underlying cause of the problem. An understanding of the root cause is essential for developing an effective, lasting solution.
Permanent corrective action
With the root cause identified, the team moves to develop a permanent corrective action plan to resolve the issue. Now, the team needs to choose the best solution, implement it, and monitor its effectiveness. This analysis will ensure that the problem is truly resolved.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Preventive measures
With such vast processes, there is always a possibility of the problem recurring. To resolve this, the team identifies and implements measures that address the root cause. There might be a need for changes to different aspects of the overall approach.
Team recognition
The final stage focuses on acknowledging and rewarding the team’s efforts. Recognizing the team’s hard work and success in resolving the issue is important for morale. It also promotes a culture of continuous improvement.
By following these eight disciplines, product managers can solve problems more effectively. The other benefit is that it builds a proactive culture that addresses issues before they escalate.
Applying 8D in product management
Applying the 8D problem-solving method in product management involves leveraging its structured approach. This helps you eliminate problems and process improvement initiatives.
Problem identification
The 8D process begins with gathering data and feedback to quickly identify potential issues. After that, a diverse team from various departments works together to uncover issues. And finally, the team solves the problems efficiently.
Once a problem is spotted, quick fixes are applied to limit its impact. Simultaneously, you explore root causes of an issue using methods like the Five Whys . The final step is to implement the solution based on these insights. Occasionally, redesigns or process upgrades are also used to resolve the issue thoroughly.
Elimination
To eliminate recurring problems, it’s crucial to establish preventive measures. Several steps support the main goal of elimination including process adjustments, quality control improvements, and updates to design standards.
The insights gathered from each 8D cycle help with continuous improvement. It also aids in formulating strategies to avert future issues.
Benefits of the 8D method
The main benefit of using the 8D method is its impact on teamwork and continuous improvement. The more obvious benefits focus on root cause analysis and prevention of issues:
- Enhanced quality control
- Efficient problem resolution
- Systematic and thorough approach
- Teamwork and knowledge sharing
- Focus on root cause analysis
- Reduced recurrence of issues
- Cost reduction
- Improved customer satisfaction
The systematic approach to address issues ensures that no effort goes to waste. Eventually, it helps the teams to quickly propose long-term solutions to a range of problem patterns.
Challenges in implementing 8D
The 8D problem-solving method is extremely valuable when used in the right manner. However, there can be challenges at every stage of this process. Because of this, it’s beneficial for you to have an understanding of how to quickly identify these challenges.
These include:
- Resistance to change among team members
- Insufficient teamwork and collaboration
- Lack of training on the 8D methodology
- Difficulties in data collection and analysis
How to solve them?
- Clearly communicate benefits to overcome resistance
- Foster collaboration and teamwork among participants
- Provide targeted training on the 8D process
- Encourage data analysis for effective problem-solving
For a deeper understanding, let’s take a look at two case studies of how the 8D process can enhance the product management workflow.
Real-life examples of 8D
A leading tech company, (similar to Apple) faced public backlash over smartphones overheating and reduced battery life. In this context, the 8D method helped to quickly identify and contain the issues.
The root cause analysis helped it track the problem back to a battery design flaw. Collaborative efforts with the battery supplier led to a redesigned battery and an update to the operating system. This not only resolved the issue but also restored consumer trust. Eventually, the brand’s reputation for quality was restored.
Similarly, a major automaker found a software glitch in its driver-assistance systems. This issue was risking driver safety. Using the 8D method, it pinpointed outdated algorithms as the root cause. The solution was simple, it issued a software update and enhanced its development processes.
Both of these examples are evidence of how the 8D method can be utilized to prevent complications efficiently.
Key takeaways
In wrapping up, it’s clear that this approach is more than just a procedure. Think of it as a strategic framework designed for the product manager. The 8D method equips you with a robust toolkit for addressing and preempting issues, systematically.
On top of that it helps you to:
- Promote teamwork and continuous improvement
- Reduce problem recurrence through root cause analysis
- Overcome implementation challenges with effective communication
Feel free to comment with any questions you may have!
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #agile and scrum
- #project management

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.

Harnessing digital experience analytics for product optimization
Digital experience analytics is a term that covers several different domains of data tracking and understanding from a product context.

Leader Spotlight: The importance of challenging assumptions, with Alex Swain
Alex Swain talks about how the key to avoiding building a product that nobody will purchase is to always challenge assumptions.

How to use the PR/FAQ method to drive product innovation
The PR/FAQ method helps you clarify your vision, communicate your strategy, validate your assumptions, and solicit feedback from others.

Leader Spotlight: The nuances of quality localization, with Drew Wrangles
Drew Wrangles, Head of Product & Design at Taskrabbit, shares his experiences leading product localization.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
8D: Tools and Techniques
- Learn Lean Sigma
- 8D Problem Solving
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way to resolve them once and for all? Look no further than the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology —a comprehensive eight-step approach initially developed in the automotive industry but widely applicable across various sectors.
This systematic method not only aids in diagnosing the root cause of a problem but also offers a roadmap for effective solutions. However, maximizing the potential of the 8D process involves more than just following its steps. It requires the strategic application of specific tools and techniques at each stage. In this educational blog post, we will guide you through the tools and techniques best suited for each of the 8 Disciplines, empowering you to turn challenges into opportunities for improvement. So, let’s delve into this toolkit and make your problem-solving journey as efficient and effective as possible.
Table of Contents
D1: form a team.
The first step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is to form a cross-functional team. A well-assembled team is the backbone of any successful problem-solving initiative. While it may be tempting to rush through this step, investing time and effort here can pay dividends later. Let’s explore some of the key tools that can assist you in forming an effective team.
Suggested Tools:
1. raci matrix.
The RACI Matrix is an invaluable tool for defining roles and responsibilities within the team. The acronym stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed. By using this matrix, you can clearly specify:
- Responsible : Who is doing the task?
- Accountable : Who is ensuring the task gets completed?
- Consulted : Who needs to provide input?
- Informed : Who needs to know the outcome?
Clear delineation of roles prevents overlap, ensures accountability, and minimizes confusion later in the process.
2. Skills Matrix
Selecting team members with the right set of skills is crucial. A Skills Matrix can help you in this aspect by providing a visual representation of each potential team member’s skills and competencies. You can rate skills on a scale (e.g., 1 to 5) and identify gaps that need to be filled. The matrix can include both technical and soft skills like communication, leadership, and domain expertise.
Key Takeaway:
An effective problem-solving team is not just a group of people; it’s a carefully chosen set of individuals with complementary skills and clearly defined roles. Utilizing tools like the RACI Matrix and Skills Matrix can immensely help in this phase, setting the stage for a successful problem-solving endeavor.
By taking the time to carefully form your team and define everyone’s roles and responsibilities, you lay a strong foundation for the rest of the 8D process. Remember, a well-prepared team is more likely to find sustainable solutions and less likely to encounter roadblocks down the line.
D2: Define the Problem
After assembling a competent team, the next critical step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is defining the problem. A well-defined problem serves as a clear roadmap, guiding your team in the right direction from the start. Ambiguity at this stage can lead to misdirection and wasted resources. So what tools can help you clearly and concisely articulate the problem?
1. 5W2H Method
The 5W2H method is a powerful tool for problem definition. It involves asking a series of questions to gain a comprehensive understanding of the issue at hand. These questions include:
- Who is involved or affected?
- What exactly is the problem?
- When did it occur?
- Where did it occur?
- Why is it a problem?
- How did it happen?
- How much is it affecting?
By systematically answering these questions, you define the problem in a manner that is both comprehensive and easily understandable for everyone involved.
2. SMART Criteria
The SMART criteria focus on setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals for the problem-solving effort. This approach helps ensure that the problem is clearly defined and that the team has a focused, achievable objective to aim for.
- Specific : Clearly define what needs to be achieved.
- Measurable : Set criteria for measuring progress and success.
- Achievable : Ensure the goals are realistic given the resources.
- Relevant : Align the goals with broader organizational objectives.
- Time-bound : Establish a timeline for solving the problem.
Defining the problem is not a mere formality; it is a necessity for effective problem-solving. A well-defined problem ensures that everyone is on the same page and focused on the right issues. Tools like the 5W2H method and SMART criteria offer invaluable frameworks for achieving this clarity. They help dissect the problem into manageable parts, setting the stage for focused root cause analysis.
D3: Contain the Problem
Once you have a team in place and a well-defined problem, the next step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is containment. This stage is often overlooked but is crucial for limiting the damage and preventing the problem from exacerbating. Containment actions are essentially short-term solutions aimed at halting the spread of the issue while you work on finding a permanent fix. Let’s delve into some tools that can guide you in this phase.
1. Check Sheet
A Check Sheet is a simple yet effective tool for collecting and organizing data. It’s often a paper-and-pencil tool that allows for quick data collection in real-time. For example, if the problem is a high rate of defects in a manufacturing line, a Check Sheet could be used to tally the number of defects by type or time of occurrence. This provides valuable insights into the scope and pattern of the problem, aiding in containment.
2. SWIFT Checklist
The SWIFT (Short Window Immediate Fix Technique) Checklist is a tool designed for rapid assessment. It outlines immediate actions that should be taken to contain the issue. The checklist could include questions like:
- Are there safety issues that need immediate attention?
- Can the affected products be quarantined?
- Do stakeholders need to be informed?
By quickly going through the SWIFT Checklist, you can prioritize the most critical containment actions and implement them without delay.
Containment is not just about putting a temporary fix; it’s about preventing the problem from causing further harm or affecting other processes. Tools like the Check Sheet and SWIFT Checklist can be instrumental in quickly assessing the situation and implementing immediate containment actions.
Utilizing these tools allows you to create a rapid response mechanism, thereby minimizing the impact and scope of the problem. As you transition to finding a long-term solution, these containment measures ensure that the situation remains under control.
D4: Root Cause Analysis
Reaching the root cause analysis stage in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology signifies a pivotal moment. Here, you transition from understanding and containing the problem to actually solving it. Identifying the root cause(s) is fundamental to ensuring that the issue doesn’t recur. While containment measures provide short-term relief, it’s the root cause analysis that offers a long-term solution. Let’s examine some essential tools that can assist in uncovering the underlying issues.
The “ 5 Whys ” is a powerful questioning technique that helps you drill down into the root cause of a problem by asking “Why?” repeatedly. Often, the apparent issue is just a symptom of a deeper problem. The 5 Whys technique encourages you to move beyond the symptoms and discover the underlying cause.
For instance, if the issue is frequent machine breakdowns, asking “Why?” might reveal:
- Why is the machine breaking down? Because of excessive wear and tear.
- Why is there excessive wear and tear? Because maintenance isn’t performed regularly.
- Why isn’t maintenance regular? Because there’s no schedule.
- Why is there no schedule? Because it was never made a priority.
- Why was it never a priority? Because of a lack of awareness about its importance.
2. Pareto Analysis
Pareto Analysis is based on the Pareto Principle, which states that 80% of problems are often due to 20% of causes. By identifying and focusing on these significant causes, you can resolve the majority of issues with minimum effort. Pareto Analysis typically involves collecting data and creating a Pareto Chart to visualize which factors are most impactful.
3. Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa)
Though also used in problem definition, the Fishbone Diagram is invaluable for root cause analysis as well. It allows you to categorize potential causes and delve deeper into each, often in combination with other tools like the 5 Whys or Pareto Analysis.
Identifying the root cause is not merely a step in the process; it’s the cornerstone for effective corrective action. Tools like the 5 Whys, Pareto Analysis, and Fishbone Diagram provide a structured approach to dig deep into the problem and unearth its roots. Only by understanding the root cause can you implement solutions that are not just quick fixes but long-lasting remedies.
D5: Choose and Verify Corrective Actions
After identifying the root cause of the problem, the next logical step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is to choose and verify corrective actions. It’s crucial to remember that not all solutions are created equal. Some may offer a quick fix but not a long-lasting one, while others could inadvertently introduce new issues. Therefore, this stage involves a delicate balance of selecting an effective solution and ensuring it doesn’t have unintended consequences. Let’s explore some of the tools that can guide you in making informed decisions.
1. FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis)
FMEA is a structured approach for evaluating the potential failure modes of a proposed solution and their impact. By predicting how things could go wrong, you can proactively address these issues before they occur. The FMEA process involves the identification of failure modes, assessment of their effects, and prioritization based on their severity, occurrence, and detectability. This prioritization helps you focus your resources where they’ll be most effective.
2. Pilot Testing
Before implementing a corrective action on a full scale, it’s prudent to test it on a smaller scale to verify its effectiveness. Pilot testing allows you to:
- Evaluate the impact of the solution without large-scale commitment.
- Identify any adjustments or optimizations needed.
- Collect data to validate the solution’s efficacy.
Pilot tests should be carefully designed to mimic the conditions under which the full-scale implementation will occur. This way, the results are indicative of what you can expect in the broader application.
Choosing a corrective action is a significant milestone, but verifying its effectiveness is equally crucial. Tools like FMEA and Pilot Testing enable you to rigorously evaluate your chosen solutions, mitigating risks and ensuring that the corrective actions will address the root cause without creating new problems.
By diligently applying these tools, you not only select the right corrective action but also build a robust verification mechanism. This two-pronged approach ensures that your solution is not just theoretically sound but practically effective as well.
D6: Implement Corrective Actions
Reaching the implementation phase of the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is a big step. You’ve formed a team, defined the problem, contained it, identified its root cause, and chosen and verified corrective actions. Now, it’s time to put those actions into play. However, effective implementation is easier said than done. It requires meticulous planning, execution, and monitoring to ensure the corrective actions yield the desired results. Let’s look at some of the tools that can help you master this crucial stage.
1. Gantt Chart
A Gantt Chart is an excellent tool for project planning and tracking. It provides a visual timeline for the tasks involved in implementing the corrective actions. The chart specifies:
- Start and end dates
- Responsible parties
- Dependencies between tasks
This visual representation makes it easier to manage resources and timelines, ensuring that implementation stays on track.
2. PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act)
The PDCA cycle is a four-step approach for implementing changes in a controlled manner. Each step serves a specific purpose:
- Plan : Establish the objectives, processes, and metrics for the corrective action.
- Do : Execute the plan on a small scale initially.
- Check : Measure the outcomes against the planned objectives and analyze the results.
- Act : Make adjustments based on the analysis and either scale the implementation or revisit the plan.
By cycling through these steps, you can continually refine your implementation approach, ensuring it aligns with your objectives.
Implementation is the stage where your problem-solving efforts come to fruition, but it’s not a one-and-done deal. Effective implementation requires continuous monitoring and adjustment. Tools like the Gantt Chart and PDCA cycle provide you with the means to implement corrective actions in a structured, controlled, and measurable way.
Remember, a well-planned implementation not only solves the current problem but also equips your organization with the knowledge and experience to tackle future challenges more effectively.
D7: Prevent Recurrence
Successfully implementing corrective actions is an accomplishment, but the 8D Problem-Solving journey doesn’t end there. The next crucial step is to ensure that the problem doesn’t recur. This phase focuses on institutionalizing the improvements you’ve made, ensuring they are sustainable over the long term. It involves both documentation of new best practices and ongoing monitoring. Let’s explore the tools that can help solidify these new standards.
1. Standard Work
Standard Work refers to the documentation of the new best practices that led to the resolution of the problem. These could be new procedures, guidelines, or checklists that need to be followed. Standard Work serves multiple purposes:
- It provides a clear and easy-to-follow guide for team members.
- It ensures that the successful corrective actions are repeated, thereby making the improvements sustainable.
- It serves as a training resource for new employees or for refresher training for existing staff.
2. Control Charts
Control Charts are used to monitor process performance over time. These charts can help you:
- Identify any variations in the process.
- Distinguish between normal variations and those that need attention.
- Trigger corrective actions if the process goes out of the defined control limits.
Regularly updating and reviewing the Control Charts ensures that you catch any deviations before they turn into bigger problems.
Prevention is indeed better than cure. The most effective problem-solving initiatives are those that not only solve the immediate issue but also prevent its recurrence. Tools like Standard Work and Control Charts offer a structured way to document and monitor the improvements, making them a part of your organizational culture.
By diligently using these tools, you not only secure the gains made but also create a proactive environment where potential issues are identified and addressed before they escalate.
D8: Congratulate the Team
The final step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is often the most overlooked but is crucial for long-term success: congratulating the team. After navigating through a complex problem-solving journey, taking a moment to acknowledge and celebrate the hard work is vital. It not only boosts morale but also encourages a culture of continuous improvement. Let’s delve into some tools and practices that can help you effectively close out your problem-solving initiative.
1. Recognition and Rewards
Acknowledging the hard work and dedication of the team is essential for maintaining a motivated and engaged workforce. Recognition can take various forms:
- Public acknowledgment in team meetings or company-wide announcements.
- Certificates or plaques to commemorate the achievement.
- Small rewards or bonuses, where appropriate.
This recognition serves as a reminder that efforts are appreciated, which in turn fosters a positive work environment.
2. Lessons Learned Document
Closing out a problem-solving initiative offers a prime opportunity to capture what worked and what didn’t. A Lessons Learned Document serves this purpose:
- It details the challenges faced, how they were overcome, and any roadblocks encountered.
- It captures best practices for future reference.
- It identifies areas for improvement, offering a starting point for future problem-solving endeavors.
Sharing this document organization-wide can serve as a valuable resource for other teams facing similar challenges.
A job well done indeed deserves recognition, but it also lays the groundwork for future improvements. Tools like Recognition and Rewards and the Lessons Learned Document not only celebrate success but also institutionalize the knowledge gained. This twofold approach not only marks the successful completion of one problem-solving initiative but sets the stage for ongoing improvements and future successes.
By taking the time to celebrate and reflect, you not only acknowledge the efforts made but also capture valuable insights that can guide your organization’s continuous improvement journey.
Successfully navigating the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is a commendable achievement, but the journey doesn’t end with implementing a solution. Each step, from forming a team to congratulating them, is a building block in your organization’s culture of continuous improvement.
Employing specific tools like RACI Matrix, 5 Whys, FMEA, and Control Charts at different stages ensures that your problem-solving efforts are not just effective but also sustainable. These tools offer more than just a way to tackle issues; they provide a structured approach to learning from them. Remember, the goal isn’t just to solve a single problem but to refine a system that becomes increasingly resilient and efficient over time. So, take a moment to celebrate your achievements, and then gear up for your next challenge, armed with the knowledge and tools that will make your problem-solving journey even more impactful.
- Sharma, M., Sharma, S. and Sahni, S., 2020. Structured Problem Solving: combined approach using 8D and Six Sigma case study. Engineering Management in Production and Services , 12 (1), pp.57-69.
- Broday, E.E. and Júnior, P.P.A., 2013. Application of a quality management tool (8D) for solving industrial problems. Independent Journal of Management & Production , 4 (2), pp.377-390.
- Engineer, A.T.D., 2016. Managing project using 8D technique. Management , 7 (6), p.67œ76.
Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.
Free Lean Six Sigma Templates
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.
5S Floor Marking Best Practices
In lean manufacturing, the 5S System is a foundational tool, involving the steps: Sort, Set…
How to Measure the ROI of Continuous Improvement Initiatives
When it comes to business, knowing the value you’re getting for your money is crucial,…
8D Problem-Solving: Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective problem-solving is the cornerstone of organizational success. The 8D…
The Evolution of 8D Problem-Solving: From Basics to Excellence
In a world where efficiency and effectiveness are more than just buzzwords, the need for…
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way…
How to Select the Right Lean Six Sigma Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
Going on a Lean Six Sigma journey is an invigorating experience filled with opportunities for…

The 8D of Root Cause Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Addressing Non-Conformances Effectively
- Ossian Muscad
- November 23, 2023
- No Comments

Last Updated on November 23, 2023 by Ossian Muscad
The 8D Root Cause Analysis is a robust, team-oriented problem-solving methodology initially developed by Ford in the late 1980s. It is an invaluable tool for addressing nonconformances within an organization, offering systematic steps to identify, correct, and eliminate recurring problems. This comprehensive guide is designed to provide an in-depth understanding of the method, its application, and its benefits.
Addressing nonconformances efficiently and effectively is critical in today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment. Failing to do so could lead to decreased product quality, increased production costs, and potential reputational damage. The 8D Root Cause Analysis assists in pinpointing the underlying issues, enabling organizations to implement corrective actions that mitigate risks, enhance product quality, and improve overall operational efficiency.
This guide is your roadmap to mastering the 8D Root Cause Analysis. We delve into its nuances, reveal best practices, and highlight common pitfalls to avoid. Whether you’re a novice looking to get started or a seasoned professional seeking to refine your problem-solving skills, this guide offers a comprehensive overview of using the 8D method to resolve nonconformances effectively.

Understanding 8D Root Cause Analysis
The 8D Root Cause Analysis is a step-by-step problem-solving methodology designed to find the root cause of a problem, devise a short-term fix, and implement a long-term solution to prevent recurring issues. The 8D process involves eight disciplines that promote root cause analysis and preventive action.
Ford first introduced the 8D methodology in its 1987 Team-Oriented Problem Solving manual. The idea was to create a systemic approach to problem-solving that was efficient, effective, and adaptable. The 8D tool has since evolved and is now regarded as Ford’s primary problem-solving method, Global 8D.
There are several key principles and components of the 8D process:
- Team Establishment: Assemble a team of people with product/process knowledge, allocate roles, and define the problem.
- Problem Description: Describe the problem accurately and in measurable terms.
- Immediate Containment Actions: Define and implement containment actions to isolate the problem from any customer.
- Root Cause Identification: Identify all potential causes that could explain why the problem occurred. Then, evaluate each potential cause in light of the problem description and available facts.
- Choose and Verify Corrective Actions: Confirm that the selected corrective actions will resolve the problem for the customer and will not cause undesirable side effects.
- Implement and Validate Corrective Actions: Develop and execute optimal corrective measures for effective resolution.
- Prevent Recurrence: To prevent the recurrence of this and similar issues, it is crucial to enhance the management systems, operation systems, practices, and procedures. This will ensure improved efficiency, effectiveness, and problem-solving capabilities.
- Congratulations: Recognize the collective efforts of the team. The organization must extend a formal expression of gratitude to the team for their invaluable contributions.
The Eight Disciplines Explained
The Eight Disciplines of the 8D Root Cause Analysis act as a comprehensive roadmap to navigate problem-solving in a structured and systematic manner. Each discipline is designed to address a specific part of the process, starting from team formation, problem identification, and immediate action and culminating in the full implementation of long-term corrective measures.
This section delves into each of these disciplines, providing a detailed understanding of their function, implementation, and significance in the overall 8D methodology:
D1: Form a Team
The first discipline of the 8D Root Cause Analysis underscores the importance of assembling a competent team. A well-rounded team with diverse skills and comprehensive product/process knowledge is the backbone of successful problem-solving. Team formation should not be taken lightly, as the team’s collective expertise will be the driving force behind identifying the root cause and formulating effective corrective measures.
Roles and responsibilities should be distinctly defined for each team member to ensure smooth collaboration and efficient task management. Each member’s role should align with their expertise, enabling them to contribute effectively to the problem-solving process.
Responsibilities might include leading the team, facilitating communication, managing resources, performing data analysis, or developing corrective measures. By clearly defining roles and responsibilities, organizations can streamline problem-solving, mitigate conflicts, and ensure productive collaboration.
D2: Define the Problem
The second discipline, “Define the Problem,” is a critical step that directs the entire problem-solving process. Firmly rooted in evidence and data, it thoroughly examines the nonconformance to create a clear, concise, and measurable problem statement.
This discipline emphasizes the importance of distinguishing between symptoms and the actual problem. Techniques such as the ‘5 Whys’ and ‘Is/Is Not’ analysis can be used to clarify the problem’s nature and scope.
For instance, consider a scenario in a manufacturing company where a noticeable increase in product defects has been observed. A simple problem statement might be, “Product defect rates have increased by 20% over the last three months.”
However, the team might discover that the issue is more specific through rigorous problem definition techniques like the ‘5 Whys’—”Machine XYZ’s calibration settings are off by 0.05 units, causing a 20% increase in product defects over the last three months.”
Defining the problem accurately is crucial as it paves the way for subsequent steps in the 8D Root Cause Analysis process. It enables teams to focus on addressing the actual problem and not just the symptoms, thereby increasing the effectiveness of the corrective actions implemented.
D3: Containment Actions
The third discipline, “Containment Actions,” centers on implementing quick, temporary solutions to prevent further problem escalation. During this stage, the team should prioritize immediate actions that can effectively isolate the issue, preventing it from affecting customers or other parts of the production process.
While these actions are not meant to address the root cause of the problem, they serve as vital stopgap measures, minimizing negative impacts. At the same time, the team works on identifying the root cause and devising long-term corrective measures. This stage emphasizes the need for swift action, as delays can worsen the problem or branch out into other areas.
Temporary containment actions could include rerouting production, increasing quality checks, or informing customers about potential delays. By swiftly implementing containment actions, teams can minimize the issue’s impact on the overall operation and customer satisfaction until a permanent solution is put in place.
D4: Root Cause Analysis
The fourth discipline, “Root Cause Analysis,” is arguably the heart of the 8D methodology. This stage involves uncovering the problem’s underlying cause, moving beyond the symptoms to identify what is truly driving the issue. A thorough root cause analysis lays the foundation for effective corrective actions that address the problem at its source. Several techniques can be employed to identify root causes accurately:
- 5 Whys: A simple yet powerful tool, the 5 Whys technique involves asking ‘why?’ repeatedly (usually five times) until the root cause is identified. Every answer serves as the foundation for the subsequent question.
- Fishbone Diagram: Also known as Ishikawa or cause-and-effect diagrams, these help teams brainstorm and categorize root causes. The ‘head’ of the fish represents the problem, and the ‘bones’ are potential root causes.
- Fault Tree Analysis: This is a top-down, deductive failure analysis in which an undesired state of a system is analyzed using Boolean logic to combine a series of lower-level events.
- Pareto Analysis: Named after economist Vilfredo Pareto, this method uses the principle that 80% of problems come from 20% of causes. It helps prioritize the potential root causes.
It’s essential to be aware of common pitfalls that can compromise the effectiveness of root cause analysis. This includes:
- Rushing the process: It’s crucial to take the time to identify the root cause accurately and not jump to conclusions too quickly.
- Overlooking systemic issues: Often, problems are not isolated incidents but symptoms of larger, systemic issues. Failing to identify these can lead to recurring problems.
- Lack of team involvement: All team members should actively participate in the root cause analysis to ensure diverse perspectives and insights.
- Focus on blame: The goal is to find the problem’s cause, not assign blame. A blame-oriented approach can stifle open discussion and prevent identifying the true root cause.
The Root Cause Analysis phase of the 8D methodology is vital in preventing the recurrence of the same or similar issues. It demands a systematic approach, active team involvement, and a focus on factual evidence over assumptions. Steering clear of common pitfalls and using proven techniques can greatly enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of this process.
D5: Permanent Corrective Actions
After identifying the root cause of the problem in the previous step, the fifth discipline, “Permanent Corrective Actions,” revolves around developing and implementing long-term solutions that effectively address the identified root cause.
The goal is to enact changes that will prevent the recurrence of the problem in the future, going beyond temporary fixes to create sustainable improvements. To achieve this, teams should follow a strategic approach to implementing permanent corrective actions:
- Develop an Action Plan: Begin by outlining a detailed plan that includes the steps to be taken, the resources needed, and a timeline for implementation. This ensures everyone involved understands their roles and responsibilities.
- Test the Solution: Before full implementation, test the proposed solution under controlled conditions to evaluate its effectiveness. This helps identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments.
- Implement the Solution: Once the solution has proven effective, it’s time to implement it fully. This should be done in accordance with the action plan, with careful monitoring to ensure proper execution.
- Document Everything: Keep detailed records of the actions taken, their effects, and any challenges encountered. This aids in future problem-solving efforts and ensures accountability.
The final part of this stage is “Monitoring Progress,” which is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of the corrective actions over time. Regular monitoring allows teams to determine whether the actions have successfully resolved the problem and to evaluate their impact on overall operations.
If the problem persists or new issues arise, the team may need to revise their approach and consider alternative solutions. This stage reinforces the principle of continuous improvement at the heart of the 8D methodology, encouraging teams to constantly review and refine their practices in pursuit of operational excellence.
D6: Preventive Measures
The sixth discipline, “Preventive Measures,” underscores the proactive approach of the 8D methodology, focusing on taking steps to prevent the recurrence of similar issues in the future. It’s not enough to correct a problem; teams should also implement preventive measures to ensure the same or similar issues do not occur again.
This proactive approach can save time and resources and enhance overall operational efficiency. The following key steps should be taken to establish effective preventative measures:
- System Walk-throughs and Audits: Periodically review processes and systems to identify potential areas of concern before they become a problem.
- FMEA (Failure Mode and Effect Analysis): This is a step-by-step approach for identifying all possible failures in a design, a manufacturing or assembly process, or a product or service.
- Preventive Maintenance: Regular maintenance can catch and address issues before they develop into larger problems.
- Staff Training and Development: Ensure all team members are adequately trained in procedures, protocols, and problem-solving methods.
- Update Documentation: Update procedures and protocols based on lessons learned from the problem-solving process, ensuring they reflect any changes made.
The importance of preventive measures is well illustrated in various industry case studies. For instance, a renowned automobile manufacturer used the 8D methodology to identify a recurring problem in their assembly line, causing significant production delays.
Through a thorough root cause analysis, the team identified the problem and successfully implemented permanent corrective actions. However, the preventive measures, including regular system audits and staff training, ensured the issue did not recur, saving the company significant time and resources in the future.
Another example is a pharmaceutical company that faced a quality assurance issue. The company rectified the problem and took preventive measures, such as updating their documentation and procedures, conducting regular preventive maintenance, and carrying out systematic FMEA.
These steps helped them maintain the high-quality standards of their products and significantly reduce the risk of similar issues in the future.
D7: Verification of Effectiveness
The seventh discipline of the 8D methodology, “Verification of Effectiveness,” confirms the success of the implemented corrective actions. It provides the opportunity to reflect on the changes made and assess their impact on the problem faced. This discipline reinforces the importance of implementing solutions and validating their effectiveness in resolving the problem and improving operations.
This systematic evaluation involves determining whether the corrective actions have met the set objectives, solved the problem, and prevented its recurrence. If the corrective actions have been effective, they should result in noticeable improvements in the processes impacted and overall operations.
It’s essential to remember that verification of effectiveness isn’t an immediate step—it often necessitates a waiting period post-implementation to monitor changes and accurately assess impact. To objectively measure the effectiveness of the corrective actions, it’s crucial to rely on metrics and KPIs. These could include:
- Problem Recurrence Rate: A decrease in the recurrence of the same or similar problems is a strong indicator of effective corrective actions.
- Process Performance Metrics: These include metrics related to quality, efficiency, or productivity, depending on the specific problem addressed.
- Overall Operational Performance: Broader operational metrics like customer satisfaction, cost savings, or reduced waste can also indicate the effectiveness of the corrective actions.
- Employee Feedback: While not a quantitative metric, feedback from team members involved in the process can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of the changes.
Remember, the chosen metrics and KPIs should be clearly defined, measurable, and directly related to the problem at hand and the objectives of the corrective actions. Regular monitoring and reviewing of these indicators will contribute to a more objective and accurate evaluation of the effectiveness of the implemented corrective actions.
D8: Documentation and Closure
The eighth and final discipline highlights the importance of thoroughly documenting the 8D process and its outcomes. Detailed documentation of the problem, the investigation process, the root cause analysis, the implemented corrective actions, and their effectiveness provides valuable insights for future reference. It aids in knowledge transfer within the organization and can be used as a reference to tackle similar problems in the future, enhancing problem-solving efficiency.
Finalizing the 8D process involves:
- Reviewing the entire process.
- Validating the implemented corrective actions.
- Formally recognizing the efforts of everyone involved in the problem-solving process.
This step underscores the importance of team recognition and closure, reinforcing a sense of achievement and encouraging continued commitment to operational excellence. After all, the goal of the 8D methodology is not just to solve individual problems but to foster an environment of continuous learning and improvement.
Documenting the 8D process and achieving closure is not just an administrative task; it’s an integral part of the problem-solving process. It ensures that the lessons learned and best practices adopted remain confined to one problem and institutionalized within the organization, contributing to its long-term success and resilience.
Benefits of Implementing 8D Root Cause Analysis
Implementing the 8D root cause analysis in an organization brings along numerous advantages. These benefits range from enhanced product quality and customer satisfaction to cost savings and efficiency, and they ultimately contribute to fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Let’s delve deeper into these benefits.
Improved Quality and Customer Satisfaction
When organizations use the 8D root cause analysis, they invest in a systematic approach that addresses the root causes of problems rather than just their symptoms. This results in improved product or service quality, as issues are temporarily fixed and eliminated from the process.
Consequently, improvement in quality leads to increased customer satisfaction. Customers are likely to remain loyal to a brand that consistently meets or exceeds their expectations, enhancing the organization’s reputation and market share.
Cost Reduction and Efficiency
The 8D root cause analysis is also instrumental in reducing costs and enhancing efficiency. Addressing problems at their root cause extends beyond immediate cost savings from problem resolution. It also prevents the recurrence of the problem, which could lead to additional costs in the future. Moreover, by streamlining processes and eliminating nonconformances, organizations can significantly improve their efficiency, using their resources better and optimizing productivity.
Building a Culture of Continuous Improvement
One of the most profound advantages of the 8D methodology is its contribution to cultivating a culture of continuous improvement within an organization. The 8D root cause analysis emphasizes learning from mistakes, making necessary changes, and consistently looking for ways to improve.
This approach encourages team members to take ownership of problems, collaborate on solutions, and continually strive to enhance their performance. It fosters a proactive rather than reactive mindset, driving ongoing improvement and innovation.
Challenges and Best Practices
Implementing the 8D root cause analysis in an organization can pose some challenges, particularly for those new to the process. Recognizing potential obstacles in advance can help teams prepare and navigate these hurdles more effectively. Some common challenges include:
- Lack of Training: Without proper training and understanding of the 8D methodology, teams might find it difficult to apply the method correctly.
- Inadequate Resources: Undertaking a thorough root cause analysis and implementing corrective actions often require time, money, and manpower, which can be lacking in some organizations.
- Resistance to Change: Like any new process, the 8D method can meet resistance from team members who are comfortable with existing processes and cautious of change.
- Insufficient Data Collection and Analysis: Gathering and analyzing data is critical to identifying the root cause and evaluating the success of corrective actions but is often overlooked or inadequately done.
- Failure to Follow Through: The final steps of the 8D process—verification of effectiveness and documentation—can sometimes be neglected, undermining the success and sustainability of the corrective actions.
Best Practices for a Successful 8D Process
Organizations should adhere to certain best practices to successfully implement the 8D root cause analysis. These include:
- Training and Education: Provide team members with comprehensive training on the 8D methodology to ensure they understand how to effectively apply it.
- Resource Allocation: Dedicate the necessary resources—time, budget, and personnel—to ensure a thorough and effective problem-solving process.
- Open Communication: Foster a culture of open communication, encouraging team members to voice concerns, share ideas, and collaborate on solutions.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: The 8D process should be guided by accurate and comprehensive data. Invest in data collection and analysis tools and make decisions based on clear, relevant metrics.
- Commitment to Follow-through: It’s crucial to fully commit to each step of the process, especially the often-neglected final steps of verification and documentation. This ensures the sustainability of corrective actions and provides a reference for future problem-solving activities.
Tools and Software for 8D Root Cause Analysis
There are a myriad of tools and software available that can facilitate the 8D root cause analysis process. These tools have been designed to streamline the process, improve accuracy, and increase efficiency, making it easier for teams to identify nonconformities, determine their root cause, and implement effective corrective actions.
Overview of Available Tools
Some of the tools available for 8D root cause analysis stand out due to their comprehensive features and user-friendly interfaces. The options below provide an overview of some of the top tools and software to consider:
- Problem-Solving Software: These are comprehensive programs designed to guide teams through the entire 8D process, from problem identification to resolution and documentation.
- Data Analysis Tools: These tools allow teams to collect, organize, analyze, and visualize data, aiding in identifying root causes.
- Project Management Tools: These platforms help track the progress of corrective actions, assign tasks, and ensure accountability.
- Low-Code Platforms: Low-code platforms provide the means to build custom applications for root cause analysis, allowing organizations to tailor their tools to their specific needs. These platforms are user-friendly and require minimal coding knowledge, making them accessible to all team members.
- Collaboration Tools: Collaboration tools facilitate teamwork and communication, making it easier for team members to work together on a problem-solving project.
Choosing the Right Software for Your Organization
Selecting the right software for 8D root cause analysis is critical to ensure effectiveness and efficiency. Here are some important tips to guide your selection process:
- Understand Your Needs: Consider the unique needs of your organization and the specific problems you’re trying to solve.
- Evaluate Features: Look for software with features that align with your needs. This may include data analysis capabilities, collaboration features, documentation tools, etc.
- Consider User-Friendliness: The software should be intuitive and easy to use. It will be difficult for your team to adopt if it’s overly complicated.
- Check Compatibility: The software should easily integrate with your existing systems.
- Assess Support and Training: Good software providers offer robust support and training to help users make the most of their tools.
- Consider Cost: While cost should not be the only factor, finding a solution that fits within your budget without compromising on essential features is important.
By carefully evaluating available tools and making an informed choice, organizations can ensure they have the right resources to effectively carry out 8D root cause analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: what is the significance of the ‘d’ in the 8d method.
The ‘D’ in the 8D Method stands for ‘Disciplines,’ referring to the eight disciplined steps that the method involves. This systematic approach helps to ensure that no aspect of the problem-solving process is overlooked, improving the likelihood of finding a genuine root cause and effective corrective actions.
Q2: Is the 8D Root Cause Analysis Method applicable to all industries?
Yes, the 8D method is applicable across a wide range of industries. While initially developed within the automotive industry, systematic problem investigation, root cause identification, and corrective action implementation principles are universally relevant. However, the specific application of the method may vary depending on industry regulations, standards, and specific operational contexts.
Q3: What role does the team play in the 8D Root Cause Analysis Method?
The role of a diverse and cross-functional team is vital in the 8D method. Such a team offers a broader perspective, enabling a more extensive understanding of the problem and potential solutions. The collaborative nature of the method allows for a more thorough analysis of the problem, fosters creativity in finding solutions, and ensures shared ownership and accountability in implementing and sustaining corrective actions.
Streamline 8D Root Cause Analysis with DATAMYTE
DATAMYTE is a quality management platform with low-code capabilities. Our Digital Clipboard , in particular, is a low-code workflow automation software that features a workflow, checklist, and smart form builder. This tool lets you create custom applications for 8D root cause analysis, making capturing data, identifying nonconformities, and implementing effective corrective actions easier.
DATAMYTE also lets you conduct layered process audits, a high-frequency evaluation of critical process steps, focusing on areas with the highest failure risk or non-compliance. Conducting LPA with DATAMYTE lets you effectively identify and correct potential defects before they become major quality issues.
With DATAMYTE , you have an all-in-one solution for your 8D root cause analysis, helping you streamline and improve your problem-solving process. Book a demo now to learn more.
The 8D root cause analysis continues to be a reliable and effective method for identifying, resolving, and preventing nonconformities. It leverages a disciplined, team-oriented approach to problem-solving, ensuring a thorough investigation, accurate identification of root causes, and the implementation of effective corrective actions.
Choosing the right software tools can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your 8D process, improving your ability to analyze data, manage projects, and collaborate with your team. As we move forward, the future of root cause analysis lies in integrating advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
These technologies promise to enhance the data analysis capabilities of root cause analysis tools, enabling more precise identification of root causes and prediction of potential nonconformities. Implementing the 8D method can elevate your organization’s problem-solving capabilities, reduce risk, and improve overall productivity.
Don’t hesitate to adopt this proven approach and harness the power of technology to streamline and enhance your 8D process. Invest in your future by investing in the right tools and methodologies today.
Related Articles:
- Decoding BIQS: Essential Insights for Auto Suppliers on GM’s Latest Benchmarking Tool
- A Comprehensive Guide to Torque Testing and its Methodologies

- Implementation
- Case-Studies
- White Papers
- Knowledge Base
Experts in the Connected Factory

- 1-800-455-4359
- (763) 553-0455 ext. 1
- [email protected]
Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Problem Solving Bootcamp
Skills related
People often say.
Good and logic Introduction
High Quality and easy Material
Effective Training Methods
Useful and practical Content
Clear and Concise Explanations
This course covers four Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and problem-solving approaches. Depending upon the complexity of the problem, you may choose one of these approaches. While taking these approaches, there are many tools and techniques which could be applied. The course also includes Descriptive Statistics (means, modes, median, ranges and standard deviation), Graphs and Charts (box and Whisker Plot, individual value plot, bar chart, pie chart, bubble chart, Matrix Plot, and time series), value stream mapping (team roles, team stages, conflict management and negative team behaviour), and tools for D1 (establish the team: team roles, team stages, conflict management and negative team behaviour), and tools for D2 (describe the problem: 5W2H, SIPOC, Gemba walk and stakeholder analysis).
Introduction
Technique #1: Five Whys
Technique #2: Cause and Effect Analysis
AI review summary
Most favorable.
Students appreciate the course for its focus on tools commonly used for quick root cause analysis and reporting. The concepts are explained in a simple way with relevant examples. The instructor's knowledge and high-quality delivery are highly valued. Despite covering difficult topics, the instructor effectively simplifies them for easy understanding. The course also provides clear examples for easy follow-through.
This course includes
SkillMapper rating :
Start date :
Amount of students :
Downloadable resources :
Certificate of completion :
© SkillMapper SAS
Privacy Policy
Terms and use
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Project management |
- What is 8D? A template for efficient pr ...
What is 8D? A template for efficient problem-solving

How you respond when problems arise is one of the most defining qualities of a manager. Luckily, there are tools you can use to master problem-solving. The 8D method of problem-solving combines teamwork and basic statistics to help you reach a logical solution and prevent new issues from arising.
You’ve spent months overseeing the development of your company's newest project. From initiation, planning, and execution, you’re confident this may be your best work yet.
Until the feedback starts rolling in.
There’s no sugar-coating it—things don’t always go as planned. But production or process issues are hardly a signal to throw in the towel. Instead, focus on honing your problem-solving skills to find a solution that keeps it from happening again.
The 8D method of problem solving emphasizes the importance of teamwork to not only solve your process woes but prevent new ones from occurring. In this guide, we’ll break down what 8D is, how to use this methodology, and the benefits it can give to you and your team. Plus, get an 8D template to make solving your issue easier.
What is 8D?
The eight disciplines (8D) method is a problem-solving approach that identifies, corrects, and eliminates recurring problems. By determining the root causes of a problem, managers can use this method to establish a permanent corrective action and prevent recurring issues.
How do you use the 8D method?
The 8D method is a proven strategy for avoiding long-term damage from recurring problems. If you’re noticing issues in your workflow or processes, then it’s a good time to give this problem-solving method a try.
To complete an 8D analysis, follow “the eight disciplines” to construct a statistical analysis of the problem and determine the best solution.
The eight disciplines of problem-solving
8D stands for the eight disciplines you will use to establish an 8D report. As you may notice, this outline starts with zero, which makes nine total disciplines. The “zero stage” was developed later as an initial planning stage.
To illustrate these steps, imagine your organization experienced a decline in team innovation and productivity this past year. Your stakeholders have noticed and want to see changes implemented within the next six months. Below, we’ll use the 8D process to uncover a morale-boosting solution.
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D8 problem solving approach (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/6ab7c188-3258-4d2e-afe6-9a4a084cc09f/inline-productivity-8d-template-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
D0: Prepare and plan
Before starting the problem-solving process, evaluate the problem you want to solve. Understanding the background of the problem will help you identify the root cause in later steps.
Collect information about how the problem has affected a process or product and what the most severe consequences may be. Planning can include:
Gathering data
Determining the prerequisites for solving the problem
Collecting feedback from others involved
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D0 Planning (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/abc3621d-e1ae-47ff-b731-0ee38cff99e9/inline-productivity-8d-template-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
If we look back at our example, you may want to figure out whether this decline in morale is organization-wide or only applies to a few departments. Consider interviewing a few employees from different departments and levels of management to gain some perspective. Next, determine what knowledge and skills you will need to solve this lapse in productivity.
D1: Form your team
Create a cross-functional team made up of people who have knowledge of the various products and workflows involved. These team members should have the skills needed to solve the problem and put corrective actions in place.
Steps in this discipline may include:
Appointing a team leader
Developing and implementing team guidelines
Determining team goals and priorities
Assigning individual roles
Arranging team-building activities
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D1 Team members (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/51986017-5150-4dd4-940c-252cd0eb8ba5/inline-productivity-8d-template-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
From our example, a solid team would consist of people with first-hand experience with the issues—like representatives from all departments and key people close to workshop-level work. You may also want to pull someone in from your HR department to help design and implement a solution. Most importantly, make sure the people you choose want to be involved and contribute to the solution.
D2: Identify the problem
You may have a good understanding of your problem by now, but this phase aims to break it down into clear and quantifiable terms by identifying the five W’s a and two H’s (5W2H):
Who first reported the problem?
What is the problem about?
When did it occur and how often?
Where did it occur (relating to the sector, supplier, machine, or production line involved)?
Why is solving the problem important?
How was the problem first detected?
How many parts/units/customers are affected?
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D2 Problem statement & description (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/9825ecd6-2bd3-4559-a68c-b1ae8aca2e52/inline-productivity-8d-template-4-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Use your team’s insights to answer these questions. From our example, your team may conclude that:
Employees feel overwhelmed with their current workload.
There is no real structure or opportunity to share new ideas.
Managers have had no training for meetings or innovation settings.
Disgruntled employees know they can achieve more—and want to achieve more—even if they seem disengaged.
Once you answer these questions, record an official problem statement to describe the issue. If possible, include photos, videos, and diagrams to ensure all parties have a clear understanding of the problem. It may also help to create a flowchart of the process that includes various steps related to the problem description.
D3: Develop an interim containment plan
Much like we can expect speedy first aid after an accident, your team should take immediate actions to ensure you contain the problem—especially if the problem is related to customer safety.
An interim containment plan will provide a temporary solution to isolate the problem from customers and clients while your team works to develop a permanent corrective action. This band-aid will help keep your customers informed and safe—and your reputation intact.
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D3 Interim containment action (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d6279c36-ccc6-4de3-89d2-f221632a1059/inline-productivity-8d-template-5-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Because your findings revealed workers were overworked and managers lacked training, your team suggests scheduling a few mandatory training sessions for leaders of each department covering time and stress management and combating burnout . You may also want to have a presentation outlining the topics of this training to get key managers and stakeholders interested and primed for positive upcoming changes.
D4: Verify root causes and escape points
Refer back to your findings and consult with your team about how the problem may have occurred. The root cause analysis involves mapping each potential root cause against the problem statement and its related test data. Make sure to test all potential causes—fuzzy brainstorming and sloppy analyses may cause you to overlook vital information.
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D4 Root cause & escape points (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/301717c6-0434-4c88-addf-d500dc23ae87/inline-productivity-8d-template-6-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
In our example, focus on the “why” portion of the 5W2H. You and your team identify six root causes:
Managers have never had any training
There is a lack of trust and psychological safety
Employees don’t understand the objectives and goals
Communication is poor
Time management is poor
Employees lack confidence
In addition to identifying the root causes, try to pinpoint where you first detected the problem in the process, and why it went unnoticed. This is called the escape point, and there may be more than one.
D5: Choose permanent corrective actions
Work with your team to determine the most likely solution to remove the root cause of the problem and address the issues with the escape points. Quantitatively confirm that the selected permanent corrective action(s) (PCA) will resolve the problem for the customer.
Steps to choosing a PCA may include:
Determining if you require further expertise
Ensuring the 5W2Hs are defined correctly
Carrying out a decision analysis and risk assessment
Considering alternative measures
Collecting evidence to prove the PCA will be effective
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D5 Permanent corrective action (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/53509966-18dd-4bb4-88a1-c7ca940fde3f/inline-productivity-8d-template-7-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Your team decides to roll out the training used in the interim plan to all employees, with monthly company-wide workshops on improving well-being. You also plan to implement meetings, innovation sessions, and team-coaching training for managers. Lastly, you suggest adopting software to improve communication and collaboration.
D6: Implement your corrective actions
Once all parties have agreed on a solution, the next step is to create an action plan to remove the root causes and escape points. Once the solution is in effect, you can remove your interim containment actions.
After seeing success with the training in the interim phase, your stakeholders approve all of your team’s proposed PCAs. Your representative from HR also plans to implement periodic employee wellness checks to track employee morale .
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D6 PCA implementation plan (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/ca68af4a-afa7-4be4-93cb-8a8321eb5172/inline-productivity-8d-template-8-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
To ensure your corrective action was a success, monitor the results, customer, or employee feedback over a long period of time and take note of any negative effects. Setting up “controls” like employee wellness checks will help you validate whether your solution is working or more needs to be done.
D7: Take preventive measures
One of the main benefits of using the 8D method is the improved ability to identify necessary systematic changes to prevent future issues from occurring. Look for ways to improve your management systems, operating methods, and procedures to not only eliminate your current problem, but stop similar problems from developing later on.
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] D7 Preventive measure (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/cdd7b133-fb80-4db7-8935-1285a6b62b69/inline-productivity-8d-template-9-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Based on our example, the training your team suggested is now adopted in the new manager onboarding curriculum. Every manager now has a “meeting system” that all meetings must be guided by, and workloads and projects are managed as a team within your new collaboration software . Innovation is improving, and morale is at an all-time high!
D8: Celebrate with your team
The 8D method of problem-solving is impossible to accomplish without dedicated team members and first-class collaboration. Once notes, lessons, research, and test data are documented and saved, congratulate your teammates on a job well done! Make an effort to recognize each individual for their contribution to uncovering a successful solution.
![root cause analysis and the 8d problem solving bootcamp [inline illustration] 8D Team congratulations & reward (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d2055965-bf3d-4bf4-a1ea-a0a7c4bf8a32/inline-productivity-8d-template-10-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
8D report template and example
Check out our 8D report template below to help you record your findings as you navigate through the eight disciplines of problem solving. This is a formal report that can be used as a means of communication within companies, which makes for transparent problem-solving that you can apply to the entire production or process chain.
Benefits of using the 8D method
The 8D method is one of the most popular problem-solving strategies for good reason. Its strength lies in teamwork and fact-based analyses to create a culture of continuous improvement —making it one of the most effective tools for quality managers. The benefits of using the 8D method include:
Improved team-oriented problem-solving skills rather than relying on an individual to provide a solution
Increased familiarity with a problem-solving structure
A better understanding of how to use basic statistical tools for problem-solving
Open and honest communication in problem-solving discussions
Prevent future problems from occurring by identifying system weaknesses and solutions
Improved effectiveness and efficiency at problem-solving
Better collaboration = better problem solving
No matter how good a manager you are, production and process issues are inevitable. It’s how you solve them that separates the good from the great. The 8D method of problem solving allows you to not only solve the problem at hand but improve team collaboration, improve processes, and prevent future issues from arising.
Try Asana’s project management tool to break communication barriers and keep your team on track.
Related resources
Critical path method: How to use CPM for project management

15 project management interview questions, answers, and tips

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to drive product development
Accendo Reliability
Your Reliability Engineering Professional Development Site
by Ray Harkins Leave a Comment
Root Cause Analysis — What is 8D?

The “D” is 8D stands for “disciplines”, and the 8D process is a problem-solving methodology employing eight sequential disciplines or steps that can be applied to a wide range of industries, situations, and disciplines.
The 8D process was developed in the late 1980’s by the Ford Motor Company to give its engineers a standardized method for dealing with design and manufacturing problems. Ford’s predecessor to 8D was called “TOPS”, Team Oriented Problem Solving. This is a fitting name to the methodology since it strongly emphasizes a team-based approach. In fact, the first of the eight D’s is “Assemble the Team”.
The second D is “Describe the Problem”. As former president of General Motors, Charles Kettering tersely said, “A well-stated problem is half solved.” At this step of the process, the failure is analyzed, the data is collected, and the observations are made. This critical fact-finding phase sets the stage for the rest of the process.
The third D is the “Interim Containment Response”. These are the steps to “stop the bleeding”. Recalls, onsite sorting and 100% inspection typically fall under the umbrella of containment. In industries where a very high level of customer satisfaction is paramount, containment is often the most critical step in the process. While containment actions don’t fix problems, they do shield the customer from further effects of the supplier’s shortcoming.
The fourth D is “ Root Cause Analysis ”. This is where tools like capability analysis , the Ishikawa diagram , control charting, 5 Why Analysis, and Measurement System Analysis tie together the inputs of a process to the unintended outputs. By identifying the true root causes, your efforts moving forward to improve the process will yield your intended results.
The fifth D is “Determine the Corrective Action Plan”. This is the step where your understanding of the process, and your knowledge of improvement tools and strategies come together to permanently reduce or even eliminate the defect . It’s not good enough to just have a clear picture of the problem, you must have access to potential solutions as well. This access comes through experience, benchmarking , supplier support, established improvement strategies and a host of other sources.
The sixth D is closely related to the fifth, “Implement Corrective Actions”. Even though the corrective action for a defect is accessible, it may take different types of effort to implement the right solution. This is where project management techniques, soft skills, and networking pay off most in the 8D process. Negotiating, planning, training and communicating often complement the “hard” skills of problem solving to fully implement the solution.
The seventh D is “Implement Preventive and Parallel Actions”. This is where the hard work you investing into the first six D’s is multiplied by applying the same improvement across multiple product lines, machines or departments.
And lastly, the eighth D is “Thank the Team”. Successfully implementing a corrective action is truly a reason to celebrate and to acknowledge the contributions of others. It is common at this step to make a presentation of the improvement project to the executive team. Acknowledging others’ contributions also feeds the culture of continuous improvement and encourages those same people to take on new challenges.
A deeper dive into the 8 D’s, plus dozens of tips and tools like this are available in the online classes “Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Corrective Action Process” .
About Ray Harkins
Ray Harkins is a senior manufacturing professional with over 25 years of experience in manufacturing engineering, quality management, and business analysis.
During his career, he has toured hundreds of manufacturing facilities and worked with leading industry professionals throughout North America and Japan.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses cookies to give you a better experience, analyze site traffic, and gain insight to products or offers that may interest you. By continuing, you consent to the use of cookies. Learn how we use cookies, how they work, and how to set your browser preferences by reading our Cookies Policy .
Workshop Best Practices: 8D
The eight disciplines (8D) methodology is often used to deal with recurring problems, from identification to elimination. It is meant to yield a permanent resolution by drilling down to a problem’s origins and determining its root causes. Usually, the analysis is quantitative and the corrective actions are revealed by statistical analysis – but depending on the domain of application, a qualitative approach is also possible. This blog post gives tips on how to carry out an 8D analysis in a meeting-room workshop using the template included in the free FlatFrog Board whiteboard app.

Running a successful 8D workshop
One key to a successful 8D workshop is pre-planning by the manager/person raising the issue. This is sometimes called the ‘ 0D ’step. The manager does a preliminary identification of the problem and considers the presumptive prerequisites for its solution. These do not have to be 'correct to the last detail’ but are crucial for bootstrapping, which leads to the first step.
Step 1D is the initial selection and establishment of a team with relevant process/product knowledge. The team must initially be somewhat small and highly focused, so it’s important to carefully select appropriate members. The template contains a list of the initial team, whose members receive information about the scope of the problem. To allow time for reflection, it is important to provide a good outline of the problem well in advance of the workshop.
Step 2D is the first step undertaken in the meeting room workshop: defining and describing the problem as a whole team. (Please also refer to the 7 tips for running a successful workshop .) Note that 8D is not a fuzzy brainstorming session . The resulting problem definition and description must ideally be precise and detailed enough to accommodate quantitative causal analysis. It’s crucial to exhaustively state the background, current conditions and goals.
The role of the facilitator or meeting convenor is to identify any fuzziness and push the team to render precise specifications, ideally resulting in quantifiable variables. One way to do this is to have the participants think through “who, what, where, when, why, how and how many” for the problem. This helps with the next step as well. To get a satisfactory problem identification, it may be necessary to call in additional members at this stage.
Step 3D is the intermediate containment option. Provided that the background, current conditions and goals have been comprehensively and precisely specified, it should be possible for the team to identify interim ways of containing the severity and extent of the problem, even before identifying the root causes.
This would be a natural point to take a break in the workshop. This could be a short break or one that requires reconvening the team after the developed intermediate containment solutions have been immediately implemented and verified to provide an adequate stop-gap solution.
Step 4D, undertaken after the break, is the analytical identification and verification of the problem’s root causes. The template provides for the 5 Whys approach. By repeating the ‘Why’ question 5 times, it is possible to drill down to the root causes. It’s also helpful to add the ‘Why Not’ question at the end, namely, why was the problem not noticed earlier? This may help with subsequent steps.
It is also possible to use a root-cause analysis following the 5-Why exercise. Note that a template for Root Cause analysis, aka ‘Fishbone analysis,’ is also available on the free online whiteboard app from FlatFrog . It’s ideal to state the identified causes in operational terms suitable for quantitative verification. Again, additional expertise may be required to get the root cause nailed down at this stage.
Step 5D involves choosing and verifying the permanent corrective measures now that the root cause of the problem has been identified. Ideally, the verification should again be quantitative, with causal modeling used to determine whether the corrective action affects the problem variable in the desired way. The best corrective measures are then recommended for implementation.
In addition, based on the ‘Why Not?’ question, the team can recommend implementations of preventative measures to ensure non-recurrence of the problem. At this stage, there can be another break, possibly of a longer duration while the correctives are implemented. This depends on the nature and extent of the correctives.
Step 6D involves the implementation of the corrective action and real-world verification that it is working. This is undertaken by executive management, on recommendation by the team.
Step 7D also involves management, which is required to put systemic and procedural changes in place and prevent recurrence of the problem. The team can reconvene to evaluate the implementation once it is complete.
Step 8D , coming at the formal conclusion of the workshop, is team recognition for resolving the problem and thanks from the organization and managers.
Additional resources:
How can online whiteboard templates help your meeting? - https://www.flatfrog.com/post/whiteboard-templates-improve-meeting .
Whiteboard for hybrid work - https://www.flatfrog.com/post/hybrid-whiteboard-and-how-it-can-help-your-team .
List of templates- https://www.flatfrog.com/templates .
Workshop use case - https://www.flatfrog.com/use-cases/free-online-workshop-board .
About FlatFrog
FlatFrog is a provider of free online whiteboards ( app.flatfrog.com ).
FlatFrog has also designed patented InGlass™ touch display technology from the ground up, providing the best pen and touch input to mimic the intuitive feeling of a dry-erase board. InGlass™ touch displays are available through our partners, including Dell , Google , Samsung , SMART , Sharp , Ricoh , Avocor , CTOUCH and more ( www.flatfrog.com/partners ).
.png)
- Entrepreneurship
- 3D & Animation
- Deep Learning
- Machine Learning
- Game Development
- Computer Vision
- Data Analysis
- Software Testing
- Spring Framework
- Visual Studio
- Web Development
- Ethical Hacking
- IT Certification
- Network & Security
- Content Marketing
- Digital Marketing
- Social Media Marketing
- Memory & Study Skills
- Photography
- Engineering
Free Educational Tutorials
Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Problem Solving Bootcamp

Description
In this course I will cover four broad strategies or approaches for Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and problem-solving:
1. Five Why’s
2. Cause and Effect Diagram
3. A3 Problem Solving Approach
4. Eight Disciplines or 8D Problem Solving Approach
Depending upon the complexity of the problem you can choose one of these approaches.
While taking these approaches, there are many tools and techniques which could be applied. I will cover many such tools, for example:
1. Seven Basic Quality Tools (Cause and Effect Analysis, Flow Chart, Check Sheet, Pareto Chart, Scatter Plot, Control Charts and Histograms)
2. Descriptive Statistics (Mean, Mode, Median, Range and Standard Deviation)
3. Graphs and Charts (Box and Whisker Plot, Individual Value Plot, Bar Chart, Pie Chart, Bubble Chart, Matrix Plot, and Time Series)
4. Value Stream Mapping
5. Tools for D1 (Establish the Team): Team Roles, Team Stages, Conflict Management and Negative Team Behaviours
6. Tools for D2 (Describe the Problem): 5W2H, SIPOC, Gemba Walk and Stakeholder Analysis
7. Tools for D3 (Interim Containment): Identification and Traceability
8. Tools for D4 (Root Cause Analysis): Brainstorming, Nominal Group Technique and Affinity Diagram
9. Tools for D5 (Develop CA): Poka-yoke, Force Field Analysis, Control Plan and Benefit-Cost Analysis
10. Tools for D6 (Implement CA): Gantt Chart, RACI Matrix, Reports and Dashboard
11. Tools for D7 (Prevent Recurrence): FMEA
Who this course is for:
- Quality Managers
- Quality Engineers
- Continuos Process Improvement team members
- Process Analysts
Requirements
- Some basic understanding of the quality management concepts
Last Updated 1/2021
Download Links
Direct Download
Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Problem Solving Bootcamp.zi p (3.9 GB) | Mirror
Torrent Download
Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Problem Solving Bootcamp.torrent (126 KB) | Mirror
Source: https://www.udemy.com/course/root-cause-analysis-rca-capa-8d-training/
You might also like
Project 2021 and Project Online Desktop Essential Training

Microsoft Excel: Calculate Break-even Points And Analysis

Conducting a SWOT Analysis
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Quality Support Group

Eight Discipline (8D) Root Cause Analysis Problem Solving Workshop
Course Description When some people hear about “eight disciplines” for solving problems, they immediately think that it must be a complex or convoluted methodology. Actually, the 8D Problem Solving process is really not all that complicated. In fact, a number of common problem-solving models are quite similar to this team-based, data-driven approach to solving problems.
8D is a highly structured and effective scientific approach to solving chronic or recurring problems. It uses team synergy and provides excellent guidelines for identifying the root cause of the problem, implementing containment actions, and then developing and implementing lasting corrective and preventive action.
The 8D Problem Solving methodology is deployed to solve critical, major, chronic and recurring problems. It is most effective in addressing complex problems that exceed the ability of one person to resolve them. In this highly interactive workshop, you will learn how to solve future problems by applying a structured methodology that will yield faster and more effective solutions. The program provides opportunities to practice and apply the technique to case studies and participants’ on-job problems.
In this course, participants will learn how to follow the 8D process steps while working in a cross functional team. They will also apply various problem solving tools to identify and verify a root cause and eliminate it through permanent corrective action, followed by additional action to prevent reoccurrence of the root cause(s). Participants can expect team activities and relevant exercises in a workshop format. All activities will include industry-specific examples and terminology.
Who Should Attend This course is designed for managers, engineers, scientists, and other professionals involved in their organizations’ process improvement efforts, as well as anyone interested in improving their problem-solving skills and corrective action processes. This workshop is most beneficial when a team from your organization attends together.
Learning Objectives Upon completion of training, each participant will have the analytical and procedural information needed to understand, describe, and participate in the 8D problem solving process as a team leader, team member, or facilitator.
Course Outline Welcome and Participant Introductions List attendees’ personal concerns and objectives for the training
Introduction to Eight Discipline (8D) Problem Solving What is a problem? Difficulties and pitfalls in solving problems What is an 8D? Getting started on an 8D Problem awareness/triggers for the 8D
An Overview: 8D Steps and Objectives for Each Step Knowing what’s to be accomplished at each step
8D Steps 0 and 1 Problem assessment Preliminary fact gathering Forming the project team Roles and responsibilities: Management 8D champion Team leader Team members Facilitator
8D Step 2: Describe the Problem The key to effective 8D investigations Do Step 2 well and 8D flows smoothly “A problem well-defined is a problem half-solved.” (B. Fuller)
Kepner-Tregoe/IS/IS NOT/Systematic Root Cause Analysis Six steps to Systematic Root Cause Analysis Naming the problem Describing the problem (problem specification) Problem specification dimensions and questions IS/IS NOT problem description Deriving distinctions and changes from the IS/IS NOT Information Break
8D Step 3: Containment Types of containment activities Monitoring and verifying containment effectiveness Containment does not solve the problem!
Step 4: Identify Root Cause(s) “Occurrence, escape and systemic” root causes Tools employed at Step 4 Process flow/process maps Brainstorming Cause-and-effect (CE) analysis CNX (control, noise, experiment) Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Test theories of causes against problem description (Step 2 above)
Workshop to Apply Step 4 Tools
Step 5: Develop and Verify Solution Considerations and objective Developing and selecting solutions Verifying that the solution is effective Error-proofing Step 5 Checklist
Step 6: Implement and Validate Corrective Action Objective and highlights of Step 6 Developing an action plan for implementation Issues to be addressed in plans for implementation and verification Be sure to update FMEA, control plan and other documents to reflect Changes and improvements introduced at Step 6
Examples of 8D Steps 5 and 6 Step 7: Prevent Problem Reoccurrence Considerations: Extend the fix; extend the cause, stair-step the cause Look at the problem and solution systemically “Drill deep” to address systemic root cause(s) Change/update management systems Emphasis shifts to prevention
Step 8: Recognize the Team Recognize and publicize the team’s accomplishments Don’t keep your candle under a bushel! Make sure customers (internal and external) know about the successful application of the 8D methodology.
Prerequisites none
Course Format 16 hours Combination lecture and classroom exercises Available at QSG’s training facilities, on-site at your organization, and virtually
Course instructors: Angelo Scangas – CEO and Chief Customer Officer Bob Deysher – Senior Consultant, Quality Systems/Risk Management/Auditing Laura Halleck – Senior Consultant, Quality Systems Auditing (Automotive, Aerospace) Ed McFayden – Consultant, Quality Systems, Lean Six Sigma, Auditing Kush Shah – Senior Consultant, Lean Six Sigma
8:30am-4:30pm (EST) each day
Follow QSG on LinkedIn ! Become a QSG Member today!
Always Keep Improving!
If you have any questions, would like more information, or would like to speak with a QSG representative, please contact us at any time!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this course I will cover four broad strategies or approaches for Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and problem-solving: 1. Five Why's. 2. Cause and Effect Diagram. 3. A3 Problem Solving Approach. 4. Eight Disciplines or 8D Problem Solving Approach.
2. Cause and Effect Diagram 3. A3 Problem Solving Approach 4. Eight Disciplines or 8D Problem Solving Approach Depending upon the complexity of the problem you can choose one of these approaches. While taking these approaches, there are many tools and techniques which could be applied. I will cover many such tools, for example: 1. Seven Basic ...
Technique #1: Five Whys. Download Section 2 Slides and Templates. 2a Five Whys Intro. 2b Five Whys. 2c Five Whys Demo Preview. Quiz - Five Whys. Technique #2: Cause and Effect Analysis. Technique #3: A3 Problem Solving Approach. Technique #4: 8D Problem Solving Approach.
Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Problem Solving Bootcamp. Skip to main content. We will keep fighting for all libraries - stand with us! ... root-cause-analysis-and-the-8-d-problem-solving-bootcamp Ocr tesseract 4.1.1 Ocr_autonomous true Ocr_detected_lang en Ocr_detected_lang_conf 1.0000 Ocr_detected_script Latin
The 8D problem-solving method is designed to address and resolve problems by identifying, correcting, and eliminating recurring issues. It involves eight different steps: Plan — Prepare for the problem-solving process. Team selection — Assemble a team with the necessary knowledge and skills. Problem definition — Clearly define the problem ...
The 8D problem solving model establishes a permanent corrective action based on statistical analysis of the problem and focuses on the origin of the problem by determining its root causes. Although it originally comprised eight stages, or disciplines, the eight disciplines system was later augmented by an initial planning stage.
D4: Root Cause Analysis. Reaching the root cause analysis stage in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology signifies a pivotal moment. Here, you transition from understanding and containing the problem to actually solving it. Identifying the root cause(s) is fundamental to ensuring that the issue doesn't recur.
The 8D Root Cause Analysis is a step-by-step problem-solving methodology designed to find the root cause of a problem, devise a short-term fix, and implement a long-term solution to prevent recurring issues. The 8D process involves eight disciplines that promote root cause analysis and preventive action. Ford first introduced the 8D methodology ...
This course covers four Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and problem-solving approaches. Depending upon the complexity of the problem, you may choose one of these Root Cause Analysis and the 8D Problem Solving Bootcamp by Sandeep Kumar, Quality Gurus Inc. (Udemy)
The eight disciplines (8D) method is a problem-solving approach that identifies, corrects, and eliminates recurring problems. By determining the root causes of a problem, managers can use this method to establish a permanent corrective action and prevent recurring issues. First introduced by Ford, the 8D method offers a consistent way of ...
Powered by AI and the LinkedIn community. 1. Step 3: Root Cause Analysis. Be the first to add your personal experience. 2. Step 4: Choose and Verify Corrective Actions. Be the first to add your ...
The "D" is 8D stands for "disciplines", and the 8D process is a problem-solving methodology employing eight sequential disciplines or steps that can be applied to a wide range of industries, situations, and disciplines. The 8D process was developed in the late 1980's by the Ford Motor Company to give its engineers a standardized ...
The eight disciplines (8D) methodology is often used to deal with recurring problems, from identification to elimination. It is meant to yield a permanent resolution by drilling down to a problem's origins and determining its root causes. Usually, the analysis is quantitative and the corrective actions are revealed by statistical analysis ...
The 8D (Eight Disciplines) method is a problem-solving methodology designed to find the root cause of a problem, devise a short-term fix, and implement a long-term solution to prevent recurring ...
In this course I will cover four broad strategies or approaches for Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and problem-solving: 1. Five Why's 2. Cause and Effect Diagram 3. A3 Problem Solving Approach 4. Eight Disciplines or 8D Problem Solving Approach Depending upon the complexity of the problem you can choose one of these approaches.
Types of containment activities. Monitoring and verifying containment effectiveness. Containment does not solve the problem! Step 4: Identify Root Cause (s) "Occurrence, escape and systemic" root causes. Tools employed at Step 4. Process flow/process maps. Brainstorming. Cause-and-effect (CE) analysis.
The Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8Ds) is a problem-solving methodology developed by the Ford Motor Company. It is used to approach and resolve problems, typically employed by engineers or other professionals. Its purpose is to identify, correct, and eliminate recurring problems, and is focused on product and process improvement.
The 8D problem-solving process is best known as the 8 Disciplines and used to solve major, critical, chronic, and recurring problems. This short course introduces the 8D approach which provides a better understanding of Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and how to use basic tools required for problem-solving in a health care setting. Need
OUTLINE:00:00:00 Plan00:00:57 Describe the Problem00:01:51 Identify and Verify Root Cause and Escape Point00:02:47 Implement and Validate Permanent Correctiv...