Long Division
Below is the process written out in full. You will often see other versions, which are generally just a shortened version of the process below . You can also see this done in Long Division Animation .
Let's see how it is done with:
- the number to be divided into is called the dividend
- The number which divides the other number is called the divisor
And here we go:

Long Division
Long Division is a method for dividing large numbers, which breaks the division problem into multiple steps following a sequence. Just like the regular division problems, the dividend is divided by the divisor which gives a result known as the quotient, and sometimes it gives a remainder too. Let us learn how to divide using the long division method , along with long division examples with answers, which include the long division steps in this article.
What is Long Division Method?
Long division is a method for dividing large numbers into steps or parts, breaking the division problem into a sequence of easier steps. It is the most common method used to solve problems based on division . Observe the following long division method to see how to divide step by step and check the divisor, the dividend, the quotient, and the remainder.

The above example also showed us how to do 2 digit by 1 digit division.
Parts of Long Division
While performing long division, we need to know the important parts of long division. The basic parts of long division can be listed as follows:
The following table describes the parts of long division with reference to the example shown above.
How to do Long Division?
Division is one of the four basic mathematical operations, the other three being addition , subtraction , and multiplication . In arithmetic, long division is a standard division algorithm for dividing large numbers, breaking down a division problem into a series of easier steps. Let us learn about the steps that are followed in long division.
Long Division Steps
In order to perform division, we need to understand a few steps. The divisor is separated from the dividend by a right parenthesis 〈)〉 or vertical bar 〈|〉 and the dividend is separated from the quotient by a vinculum (an overbar). Now, let us follow the long division steps given below to understand the process.
- Step 1: Take the first digit of the dividend from the left. Check if this digit is greater than or equal to the divisor.
- Step 2: Then divide it by the divisor and write the answer on top as the quotient.
- Step 3: Subtract the result from the digit and write the difference below.
- Step 4: Bring down the next digit of the dividend (if present).
- Step 5: Repeat the same process.
Let us have a look at the examples given below for a better understanding of the concept. While performing long division, we may come across problems when there is no remainder, while some questions have remainders. So, first, let us learn division in which we get remainders.
Division with Remainders
Case 1: When the first digit of the dividend is equal to or greater than the divisor.
Example: Divide 435 ÷ 4
Solution: The steps of this long division are given below:
- Step 1: Here, the first digit of the dividend is 4 and it is equal to the divisor. So, 4 ÷ 4 = 1. So, 1 is written on top as the first digit of the quotient.
- Step 2: Subtract 4 - 4 = 0. Bring the second digit of the dividend down and place it beside 0.
- Step 3: Now, 3 < 4. Hence, we write 0 as the quotient and bring down the next digit of the dividend and place it beside 3.
- Step 4: So, we have 35 as the new dividend. We can see that 35 > 4 but 35 is not divisible by 4, so we look for the number just less than 35 in the table of 4 . We know that 4 × 8 = 32 which is less than 35 so, we go for it.
- Step 5: Write 8 in the quotient. Subtract: 35 - 32 = 3.
- Step 6: Now, 3 < 4. Thus, 3 is the remainder and 108 is the quotient.
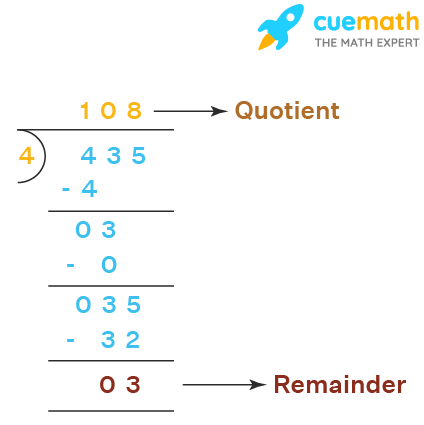
Case 2: When the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor.
Example: Divide 735 ÷ 9
Solution: Let us divide this using the following steps.
- Step 1: Since the first digit of the dividend is less than the divisor, put zero as the quotient and bring down the next digit of the dividend. Now consider the first 2 digits to proceed with the division.
- Step 2: 73 is not divisible by 9 but we know that 9 × 8 = 72 so, we go for it.
- Step 3: Write 8 in the quotient and subtract 73 - 72 = 1.
- Step 4: Bring down 5. The number to be considered now is 15.
- Step 5: Since 15 is not divisible by 9 but we know that 9 × 1 = 9, so, we take 9.
- Step 6: Subtract: 15 - 9 = 6. Write 1 in the quotient.
- Step 7: Now, 6 < 9. Thus, remainder = 6 and quotient = 81.

Case 3: This is a case of long division without a remainder.
Division without Remainder
Example: Divide 900 ÷ 5
Solution: Let us see how to divide step by step.
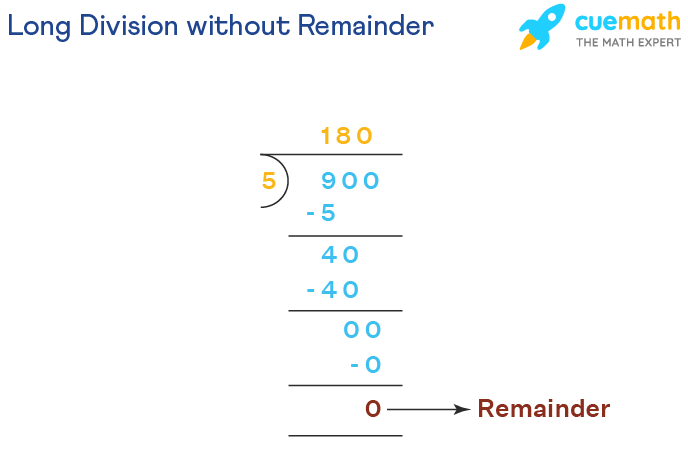
- Step 1: We will consider the first digit of the dividend and divide it by 5. Here it will be 9 ÷ 5.
- Step 2: Now, 9 is not divisible by 5 but 5 × 1 = 5, so, write 1 as the first digit in the quotient.
- Step 3: Write 5 below 9 and subtract 9 - 5 = 4.
- Step 4: Since 4 < 5, we will bring down 0 from the dividend to make it 40.
- Step 5: 40 is divisible by 5 and we know that 5 × 8 = 40, so, write 8 in the quotient.
- Step 6: Write 40 below 40 and subtract 40 - 40 = 0.
- Step 7: Bring down the next 0 from the dividend. Since 5 × 0 = 0, we write 0 as the remaining quotient.
- Step 9: Therefore, the quotient = 180 and there is no remainder left after the division, that is, remainder = 0.
Long division problems also include problems related to long division by a 2 digit number, long division polynomials and long division with decimals. Let us get an an idea about these in the following sections.
Long Division by a 2 Digit Number
Long division by a 2 digit number means dividing a number by a 2-digit number . For long division by a 2 digit number , we consider both the digits of the divisor and check for the divisibility of the first two digits of the dividend.
For example, if we need to divide 7248 by 24, we can do it using the long division steps. Let us see how to divide step by step.
- Step 1: Since it is a long division by a 2 digit number, we will check for the divisibility of the first two digits of the dividend. The first 2 digits of the dividend are 72 and it is greater than the divisor, so, we will proceed with the division.
- Step 2: Using the multiplication table of 24, we know that 24 × 3 = 72. So we write 3 in the quotient and 72 below the dividend to subtract these. Subtract 72 - 72 = 0.
- Step 3: Bring down the next number from the dividend, that is, 4. The number to be considered now is 4.
- Step 4: Since 4 is smaller than 24, we will put 0 as the next quotient, since 24 × 0 = 0 and write 0 below 4 to subtract 4 - 0 = 4
- Step 5: Bring down the next number from the dividend, that is, 8 and place it next to this 4. The number to be considered now is 48.
- Step 6: Using the multiplication table of 24, we know that 24 × 2 = 48. So we write 2 in the quotient and 48 below the dividend to subtract these. Subtract 48 - 48 = 0. Thus, remainder = 0 and quotient = 302. This means, 7248 ÷ 24 = 302.
- Long Division of Polynomials
When there are no common factors between the numerator and the denominator , or if you can't find the factors, you can use the long division process to simplify the expression. For more details about long division polynomials, visit the Dividing Polynomials page.
Long Division with Decimals
Long division with decimals can be easily done just like the normal division. We just need to keep in mind the decimals and keep copying them as they come. For more details about long division with decimals, visit the Dividing Decimals page.
How to Divide Decimals by Whole Numbers?
When we need to divide decimals by whole numbers, we follow the same procedure of long division and place the decimal in the quotient whenever it comes. Let us understand this with the help of an example.
Example: Divide 36.9 ÷ 3
- Step 1: Here, the first digit of the dividend is 3 and it is equal to the divisor. So, 3 ÷ 3 = 1. So, 1 is written on top as the first digit of the quotient and we write the product 3 below the dividend 3.
- Step 2: Subtract 3 - 3 = 0. Bring the second digit of the dividend down and place it beside 0, that is, 6
- Step 3: Using the multiplication table of 3, we know that 3 × 2 = 6. So we write 2 in the quotient and 6 below the dividend to subtract these. Subtract 6 - 6 = 0.
- Step 4 : Now comes the decimal point in the dividend. So, place a decimal in the quotient after 12 and continue with the normal division.
- Step 5: Bring down the next number from the dividend, that is, 9. The number to be considered now is 9.
- Step 6: Using the multiplication table of 3, we know that 3 × 3 = 9. So we write 3 in the quotient and 9 below the dividend to subtract these. Subtract 9 - 9 = 0. Thus, remainder = 0 and quotient = 12.3. This means, 36.9 ÷ 3 = 12.3
Long Division Tips and Tricks:
Given below are a few important tips and tricks that would help you while working with long division:
- The remainder is always smaller than the divisor.
- For division, the divisor cannot be 0.
- The division is repeated subtraction, so we can check our quotient by repeated subtractions as well.
- We can verify the quotient and the remainder of the division using the division formula : Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder.
- If the remainder is 0, then we can check our quotient by multiplying it with the divisor. If the product is equal to the dividend, then the quotient is correct.
☛ Related Articles
- Long Division Formula
- Long Division with Remainders Worksheets
- Long Division Without Remainders Worksheets
- Long Division with 2-digit Divisors Worksheets
- Long Division Calculator
Cuemath is one of the world's leading math learning platforms that offers LIVE 1-to-1 online math classes for grades K-12 . Our mission is to transform the way children learn math, to help them excel in school and competitive exams. Our expert tutors conduct 2 or more live classes per week, at a pace that matches the child's learning needs.
Long Division Examples with Answers
Example 1: Ron planted 75 trees equally in 3 rows. Use long division to find out how many trees did he plant in each row?
The total number of trees planted by Ron = 75. The number of rows = 3. To find the number of trees in each row, we need to divide 75 by 3 because there is an equal number of trees in each of the three rows. Let us also observe how to do 2 digit by 1 digit division here.

Therefore, the number of trees in each row = 25 trees.
Example 2: $4000 needs to be distributed among 25 men for the work completed by them at a construction site. Calculate the amount given to each man.
The total amount is $4000. The number of men at work = 25. We need to calculate the amount given to each man. To do so, we have to divide 4000 by 25 using the long division method. Let us see how to work with long division by a 2 digit number and also see how to do long division step by step.

Each man will be given $160. Therefore, $160 is the amount given to each man.
Example 3: State true or false with respect to long division.
a.) In the case of long division of numbers, the remainder is always smaller than the divisor.
b.) We can verify the quotient and the remainder of the division using the division formula: Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder.
a.) True, in the case of long division of numbers, the remainder is always smaller than the divisor.
b.) True, we can verify the quotient and the remainder of the division using the division formula: Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder.
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on Long Division
go to slide go to slide
FAQs on Long Division
What is long division in math.
Long division is a process to divide large numbers in a convenient way. The number which is divided into smaller groups is known as a dividend, the number by which we divide it is called the divisor, the value received after doing the division is the quotient, and the number left after the division is called the remainder.
The following steps explain the process of long division. This procedure is explained with examples above on this page.
- Write the dividend and the divisor in their respective positions.
- Take the first digit of the dividend from the left.
- If this digit is greater than or equal to the divisor, then divide it by the divisor and write the answer on top as the quotient.
- Write the product below the dividend and subtract the result from the dividend to get the difference. If this difference is less than the divisor, and there are no numbers left in the dividend, then this is considered to be the remainder and the division is done. However, if there are more digits in the dividend to be carried down, we continue with the same process until there are no more digits left in the dividend.
What are the Steps of Long Division?
Given below are the 5 main steps of long division. For example, let us see how we divide 52 by 2.
- Step 1: Consider the first digit of the dividend which is 5 in this example. Here, 5 > 2. We know that 5 is not divisible by 2.
- Step 2: We know that 2 × 2 = 4, so, we write 2 as the quotient.
- Step 3: 5 - 4 = 1 and 1 < 2 (After writing the product 4 below the dividend, we subtract them).
- Step 4: 1 < 2, so we bring down 2 from the dividend and we get 12 as the new dividend now.
- Step 5: Repeat the process till the time you get a remainder less than the divisor. 12 is divisible by 2 as 2 × 6 = 12, so we write 6 in the quotient, and 12 - 12 = 0 (remainder).
Therefore, the quotient is 26 and the remainder is 0.
How to do Long Division with 2 Digits?
For long division with 2 digits, we consider both the digits of the divisor and check for the divisibility of the first two digits of the dividend. If the first 2 digits of the dividend are less than the divisor, then consider the first three digits of the dividend. Proceed with the division in the same way as we divide regular numbers. This procedure is explained with examples above on this page under the heading of 'Long Division by a 2 Digit Number'.
What is the Long Division of Polynomials?
In algebra , the long division of polynomials is an algorithm to divide a polynomial by another polynomial of the same or the lower degree. For example, (4x 2 - 5x - 21) is a polynomial that can be divided by (x - 3) following some defined rules, which will result in 4x + 7 as the quotient.
How to do Long Division with Decimals?
The long division with decimals is performed in the same way as the normal division. This procedure is explained with examples above on this page under the heading of 'How to Divide Decimals by Whole Numbers'? For more details, visit the page about dividing decimals . The basic steps of long division with decimals are given below.
- Write the division in the standard form.
- Start by dividing the whole number part by the divisor.
- Place the decimal point in the quotient above the decimal point of the dividend.
- Bring down the digits on the tenths place, i.e., the digit after the decimal.
- Divide and bring down the other digit in sequence.
- Divide until all the digits of the dividend are over and a number less than the divisor or 0 is obtained in the remainder.
Advertisement
How to Do Long Division: Step-by-Step Instructions
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email
In math, few skills are as practical as knowing how to do long division . It's the art of breaking down complex problems into manageable steps, making it an essential tool for students and adults alike.
This operation has many practical uses in our daily lives. For instance, imagine you have a bag of 2,436 candies and want to share them equally among 4 friends. Long division helps you determine that each friend gets 609 candies, ensuring everyone gets their fair share.
Let's dive into the fundamentals of long division and learn about other everyday situations where we can put it to use.
What Is Long Division?
How to do long division in simple steps, long division method: an apple example, using long division in everyday life, how to divide a decimal point by a whole number, practice problems and answers.
Long division is a handy way to divide big numbers by smaller ones, helping us figure out how many times one number fits into another. It turns a tricky math problem into easier steps.
When we do long division, we work with four main parts:
- the big number we want to divide (called the " dividend ")
- the smaller number we're dividing by (the " divisor ")
- the answer to our division (the " quotient ")
- sometimes a little bit left over (the " remainder ")
Long Division vs. Short Division
Short and long division are both methods to divide numbers, but they differ in complexity. The short-division method is a quick way to find the answer when dividing simple numbers. For example, say you want to divide 36 by 6. You write it as 36 ÷ 6, using a division sign, and quickly get the answer, which is 6.
Long division is used for bigger, more complicated numbers, typically two or more digits. This method involves several steps, like writing out the numbers neatly and carefully.
Let's dive into long division with a clear example. We'll use 845 ÷ 3 to walk through this step-by-step process:
- Set up the problem. Write the dividend (845) under the division bar and the divisor (3) outside the bar.
- Divide. Look at the first digit of the dividend (8). How many times does 3 go into 8? Twice, because 3 x 2 = 6, and that's the closest we can get without going over. Write the 2 above the division bar, over the 8.
- Multiply. Multiply the quotient (2) by the divisor (3). (2 x 3 = 6). Write 6 under the 8.
- Subtract. Subtract 6 from 8 to get 2. Draw a line under the 6, subtract, and write 2 below the line.
- Bring down the next digit. Now, bring down the next digit of the dividend, which is 4, to sit next to the 2, making 24.
- Repeat the steps. 3 goes into 24 eight times (3 x 8 = 24), so write 8 above the bar next to the 2. Subtract 24 from 24 to get 0. Now, follow the same process you used in steps 1 through 5 and bring down the last digit, which is 5, to form 05. The number 3 goes into 5 once (3 x 1 = 3), leaving a remainder of 2. Write the 1 above the bar and the remainder 2 below after subtracting 3 from 5.
- The final answer with a remainder. You've divided 845 by 3 to get a final answer of 281 with a remainder of 2.
- Convert the remainder to decimal form. Depending on how far along you are in learning long division, this may be your final answer. If you've progressed to decimals, you will add .0 to 845 and put a decimal point above the division bar, right after the 1. Bring 0 down to form 20. The number 3 goes into 20 six times (3 x 6 = 18). Write 6 after the decimal point above the division bar. Normally, you would continue adding another 0 after 845. until there is no remainder, but since 20 – 18 = 2, you would be repeating this process infinitely because 3 does not divide evenly into 845. Instead, you will draw a horizontal line over the 6 in 281.6 to indicate that it is a repeating decimal. A calculator would show the answer as 281.666667 to indicate that the repeating decimal rounds up.
Now let's use a practical example to work through the long division process.
Imagine you just went apple picking and came home with a massive haul of delicious fruit. In your kitchen, you have 456 apples, and you want to share them equally among 3 baskets to give to your friends, so you're dividing 3 by 456 (456 ÷ 3).
To figure out how many apples go into each basket, you'd tackle the division problem step by step.
- 3 goes into the first digit (4) once, so you write 1 above the division bar, above the 4 in 456. Then you show the subtraction: 4 – 3 = 1.
- Bring down the next digit (5) to form 15. 3 goes into 15 five times (3 x 5 = 15), so you write 5 above the division bar, above the 5 in 456. Then you show the subtraction: 15 – 15 = 0.
- Bring down the final digit (6) to form 06. 3 goes into 6 twice (3 x 2 = 6), so you write 2 above the division bar, above the 2 in 456. Then you show the subtraction: 6 – 6 = 0.
- Since there is no remainder left to divide, you quotient is now written atop the division bar: 152. You will need to place 152 apples in each of the 3 baskets to evenly distribute the 456 apples.
Long division also pops up in real-life situations . Think about when you need to divide something, like pizza or cake, into equal parts.
Want to cut a large recipe in half or figure out how many days are left till summer vacation? Long division can help with that. It's a great way to help us figure out those splits and manage resources better.
And, of course, practicing long division sharpens our problem-solving skills . It teaches us to tackle big problems step by step, breaking them down into smaller, more manageable pieces. This approach is super helpful in math and figuring out all sorts of challenges we might face.
So, long division is more than just a bunch of steps we follow. It's a key that unlocks a lot of doors in the world of math and beyond, helping us understand and connect different concepts and apply them in all sorts of ways.
Dividing decimals by whole numbers is useful in our everyday lives. For instance, if you're splitting a sum of money equally among a certain number of people, you'll need to divide the total (a decimal) by the number of people (a whole number) to determine how much each person gets.
Dividing a decimal point (decimal number) by a whole number is similar to regular division, but you must be mindful of the placement of the decimal point. Here's how to do it:
Example : Divide 0.5 by 5.
- Set up the problem. Begin by setting up the division, with 0.5 as the dividend (the number you're dividing, which will be under the division bar) and 5 as the divisor (the number you're dividing by, which will be to the left of the division bar).
- Begin dividing. 5 goes into the first digit of the dividend 0 times, so you'll write 0 above the division bar, above the 0 in 0.5, and place a decimal point after the 0 you just wrote. It should be directly above the decimal point in the dividend.
- Bring down the next digit. Bring down the 5 to form 05 (you do not bring the decimal down). 5 goes into 5 once (5 x 1 = 5), so you'll write 1 above the division bar, above the 5 in 0.5.
- Show the final answer. When you show the subtraction (5 – 5 = 0), you'll have no remainder. This means the number above the division bar is your final answer: 0.1.
Let's put our long division skills to the test with some word problems. Tackle these problems one step at a time, and don't rush. If you get stuck, pause and review the steps. Remember, practice makes perfect, and every problem is an opportunity to improve your long-division skills.
1. Emma has 672 pieces of candy to share equally among her 4 friends. How many pieces of candy does each friend get?
Solution : To find out, divide 672 by 4. Start with the first part of 672, which is 6, and see how many times 4 can fit into it. It fits 1 time, leaving us with 2. Bringing down the 7 turns it into 27, which 4 fits into 6 times, leaving us with 3. Finally, bringing down the 2 to join the remaining 3 makes 32, which 4 divides into 8 times. So, each friend gets 168 pieces of candy.
2. A teacher has 945 stickers to distribute equally in 5 of her classes. How many stickers does each class get?
Solution : We'll divide 945 by 5. Looking at 9 first, 5 goes into it 1 time. With 4 leftover, we bring down the 4 from 945 to get 44, which 5 divides into 8 times with another 4 leftover. Lastly, bringing down the 5 to the remaining 4 makes 45, which 5 divides into 9 times. Therefore, each class receives 189 stickers.
3. A library has 2,310 books to be placed equally on 6 shelves. How many books will each shelf contain?
Solution : Divide 2,310 by 6. Starting with 23, 6 goes into it 3 times with 5 leftover. After subtracting, we bring down the 1 to get 51, which 6 divides into 8 times with 3 leftover. Bringing down the 0 to the remaining 3 gives us 30, which 6 divides into 5 times. So, each shelf will have 385 books.
This article was updated in conjunction with AI technology, then fact-checked and edited by a HowStuffWorks editor.
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:

Long Division – Definition, Steps, Method, Examples
Definition of long division, steps to carry out long division, fun facts about long division, solved examples on long division , practice problems on long division, frequently asked questions on long division.
In Math, l ong division is the mathematical method for dividing large numbers into smaller groups or parts. It helps to break down a problem into simple and easy steps . The long divisions have dividends, divisors, quotients , and remainders. In a long division problem, the dividend is the large number that is divided by another number called the divisor . The quotient is the result of the division, and the excess quantity that cannot be divided is called the remainder .

Example of Long Division
Here is an example that will help us understand this concept:

As 75 is not a multiple of 4, it is not divisible by 4 and will leave a remainder at the end.
Related Worksheets

Symbol of Division
To show that two numbers are divided, we can add a division sign ‘÷’ between them. So, for example, if we have to show 36 divided by 6, we can write it as 36 ÷ 6.
We can also show it in a fraction form as 366.
There are five steps to solve every long division problem with ease.
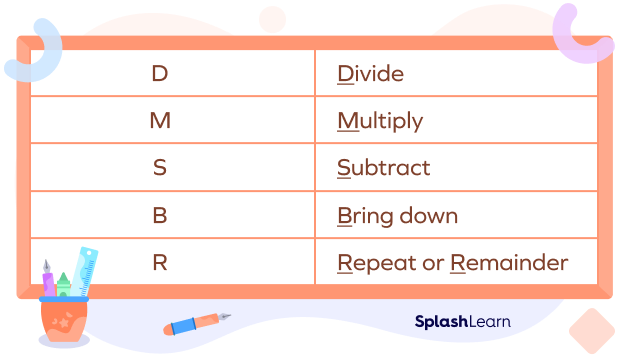
Let’s have a look at the examples given below for a better understanding of the concept.
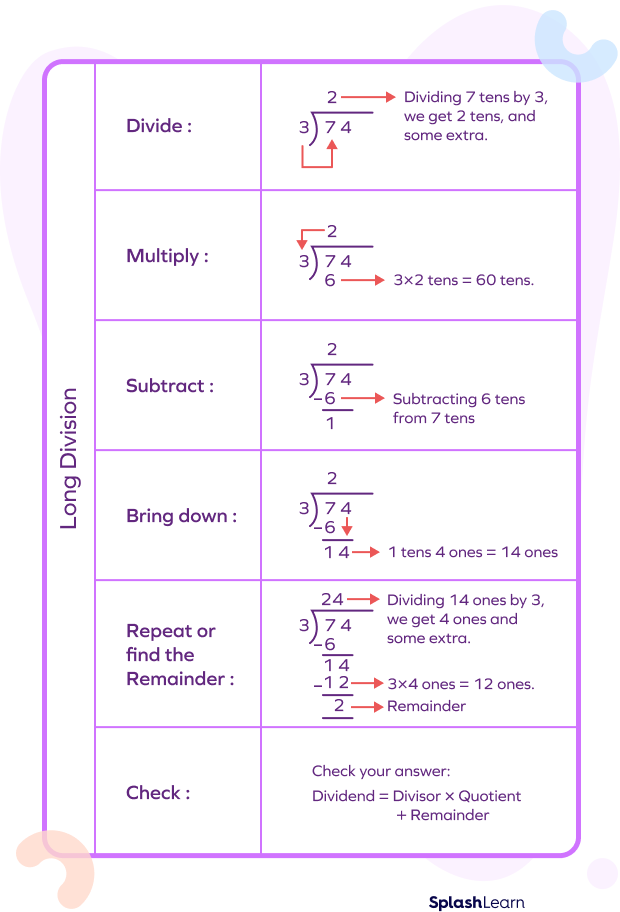
Dividing Decimals Using A Long Division
Long division can also be used to divide decimal numbers into equal groups . It follows the same steps as that of long division, namely, – divide, multiply, subtract , bring down and repeat or find the remainder.
Here’s an example of long division with decimals .
- If the dividend is 0, the quotient will always be zero.
- The remainder is always less than the divisor.
- Multiplying the quotient with the divisor and adding the remainder will give the dividend.
(Divisor x Quotient) + Remainder = Dividend
- When the remainder is 0, the dividend is the product of divisor and quotient.
Divisor x Quotient = Dividend, when remainder = 0
Long Division is an instrument that allows you to divide large numbers into multiple smaller groups or parts. When we divide a dividend with a divisor, the quotient obtained is the number of groups that can be made, and the remainder identifies how many elements or numbers that will be left ungrouped. To understand this concept even better, check out the wide range of interesting exercises available on SplashLearn and become a long division wiz!
Question 1: Divide 726 by 4
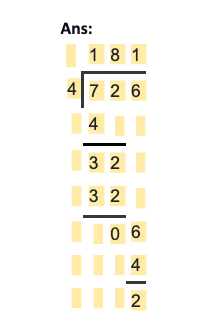
Hence, the quotient of the problem is 181, and the remainder is 2.
Question 2: What is the remainder when we divide 248 by 8?
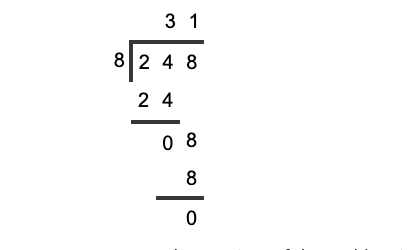
Hence, the quotient of the problem is 31, and the remainder is 0.
Question 3: Laila’s mother collected all family pictures and wanted to place all of them in an album. If each page of an album can contain 9 pictures, how many pages of the album will she need if there are 285 pictures?
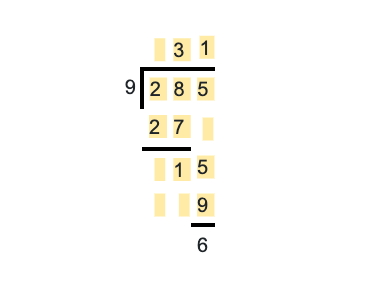
The quotient of the problem is 31, and the remainder is 6. So, she needs 31 + 1 (for the remaining six pictures) or 32 pages.
Long Division
Attend this Quiz & Test your knowledge.
On dividing 426 by 4, we get the remainder as
Find the dividend if the divisor is 8, quotient is 71 and remainder is 4., find the digit that can replace a in the following division problem..
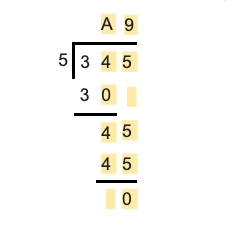
Can the divisor be 0?
No, division by 0 is not defined in Math generally.
What is the Long Division Method?
In Math, long division is the mathematical method for dividing large numbers into multiple smaller groups or parts. The number which we divide into small groups is called the dividend, the number by which we divide is called the divisor. It helps to break down a problem into simple and easy steps.
How can we verify the quotient and remainder of a division problem?
We can verify the quotient and the remainder of the division using the division formula : (Divisor x Quotient) + Remainder = Dividend
What is the difference between long division and short division?
The short division is great for dividing larger numbers by one-digit numbers, whereas the long division is handy for dividing large numbers by numbers with two or more digits.
RELATED POSTS
- Quotient – Definition with Examples
- Commutative Property of Addition – Definition with Examples
- Seconds to Minutes Conversion
- Volume of Cuboid – Definition, Formula, Derivation, Examples, FAQs
- Simple equations and Application – Methods, Examples, Facts, FAQs

Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun., you see real learning outcomes..
Make study-time fun with 14,000+ games & activities, 450+ lesson plans, and more—free forever.
Parents, Try for Free Teachers, Use for Free
- 1st Grade Math
- 2nd Grade Math
- 3rd Grade Math
- 4th Grade Math
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- 7th Grade Math
- 8th Grade Math
- Knowledge Base
- Math for kids
Long Division – Definition, Steps, Method, Examples
Created: December 26, 2023
Last updated: January 13, 2024
Long division is a crucial arithmetic skill that paves the way for understanding more advanced mathematical concepts. At Brighterly , we believe in empowering children with the tools they need to excel in mathematics. In this comprehensive guide, we’ve crafted a step-by-step breakdown of the long division process, enriched with tips, tricks, and insights to simplify learning for children. Welcome to Brighterly’s all-inclusive long division masterclass!
What is Long Division Method?
The long division method is a powerful technique designed to tackle large numbers that are too cumbersome to divide mentally. This systematic approach dissects the problem into smaller, digestible steps, enabling us to conquer complex calculations with ease. By honing this vital skill, children lay a strong foundation for exploring more sophisticated mathematical concepts in the future.
At Brighterly, we understand that mathematics can sometimes feel overwhelming. That’s why we’ve developed our unique approach to long division, transforming it into an engaging and approachable topic for children. Through our carefully designed methods and interactive learning experiences, we aim to spark a love for math that lasts a lifetime. By making long division more accessible and enjoyable, we’re committed to helping children unlock their full potential in mathematics and beyond.
Parts of Long Division
Long division problems involve several key components:
- Dividend: The number being divided
- Divisor: The number by which the dividend is divided
- Quotient: The result of the division
- Remainder: The amount left over after the division
Understanding these parts is crucial to successfully solving long division problems.
How to do Long Division?
Follow these simple steps to solve a long division problem:
- Write the dividend and divisor in the long division format.
- Divide the dividend by the divisor, starting with the leftmost digit.
- Write the result (quotient) above the dividend.
- Multiply the divisor by the quotient and subtract the result from the dividend.
- Bring down the next digit and repeat the process until you reach the end of the dividend or the desired decimal places.
Long Division Steps
Here’s a breakdown of the long division process:
- Divide: Determine how many times the divisor can fit into the dividend.
- Multiply: Multiply the quotient by the divisor.
- Subtract: Subtract the product from the dividend.
- Bring down: Bring down the next digit from the dividend.
- Repeat: Continue the process until you reach the end of the dividend or the desired decimal places.
Long Division Worksheets PDF
Long Division Worksheet PDF
Long Division Worksheet
Division with Remainders
Division with remainders occurs when the divisor does not evenly divide the dividend, leaving a residual amount. Remainders can be expressed as fractions (with the divisor serving as the denominator) or as whole numbers, contingent on the context. Understanding division with remainders is essential for grasping real-world applications of division, as it showcases the intricacies of mathematical problem-solving.
At Brighterly, we’re dedicated to helping children comprehend the complexities of division with remainders, by providing a multitude of practical examples and engaging activities. Our tailored approach encourages children to explore various strategies and techniques for handling remainders, fostering a deeper appreciation for the power of mathematics.
Division without Remainder
Division without remainder signifies that the divisor evenly divides the dividend, resulting in a whole number without any residual amount. In these instances, the division is referred to as exact. Grasping the concept of division without remainders is crucial for building a solid understanding of whole number arithmetic.
Brighterly is committed to making division without remainder an approachable and enjoyable topic for children. Through our wide array of interactive learning experiences, we strive to help students develop a strong foundation in whole number arithmetic, setting them up for future success in more advanced mathematical concepts.
Long Division by a 2-Digit Number
Dividing by a 2-digit number follows the same procedure as dividing by a 1-digit number, with one key distinction: the need to account for the additional digit when comparing the dividend and divisor. Mastering long division by a 2-digit number is essential for tackling more challenging math problems with confidence.
At Brighterly, we prioritize helping children become proficient in long division by 2-digit numbers, by offering a plethora of engaging examples, practice problems, and interactive learning modules. Our innovative approach empowers students to tackle long division with ease, bolstering their mathematical abilities in the process.
Long Division of Polynomials
Long division isn’t limited to numbers; it can also be employed to divide polynomials. When dividing polynomials, you’ll work with variables and coefficients instead of numbers. Although the overall process remains the same, it’s crucial to remain vigilant about the rules of algebra when performing operations.
Brighterly is passionate about guiding children through the exciting world of polynomial long division. Our dynamic resources and captivating explanations simplify the process, enabling children to develop a profound understanding of algebraic concepts and techniques.
Long Division with Decimals
Dividing decimals closely resembles whole number division, with a few minor adjustments. First, convert the divisor into a whole number by shifting the decimal point to the right. Next, move the decimal point in the dividend the same number of places. Finally, proceed with the division as you would with whole numbers.
Brighterly specializes in making long division with decimals accessible and enjoyable for children. Through our comprehensive resources and stimulating activities, we aim to demystify decimal division and help children become proficient in this vital mathematical skill.
How to Divide Decimals by Whole Numbers?
To divide a decimal by a whole number, simply follow the standard whole number division process. The decimal point in the quotient will align directly above the decimal point in the dividend. Brighterly offers a range of engaging resources to help children master this essential skill, ensuring they’re equipped to tackle increasingly complex math problems.
Symbol of Division
The division symbol (÷) is utilized to denote division. In long division, the divisor is positioned outside the division symbol, while the dividend is placed inside. Understanding the proper usage of division symbols is critical for children as they progress in their mathematical journeys. At Brighterly, we are committed to fostering a strong foundation in mathematical notation and symbols.
Dividing Decimals Using Long Division
To divide decimals using long division, follow these steps:
- Adjust the divisor and dividend by moving their decimal points the same number of places to the right, making the divisor a whole number.
- Perform long division as you would with whole numbers.
- Place the decimal point in the quotient directly above the decimal point in the dividend.
Solved Examples on Long Division
Here are a few solved examples to help you understand long division better:
Divide 1275 ÷ 15
- Divide: 1 (leftmost digit) ÷ 15 = 0 (write 0 above the 1)
- Multiply: 0 × 15 = 0
- Subtract: 1 – 0 = 1
- Bring down: Bring down the 2 (12)
- Divide: 12 ÷ 15 = 0 (write 0 above the 2)
- Subtract: 12 – 0 = 12
- Bring down: Bring down the 7 (127)
- Divide: 127 ÷ 15 = 8 (write 8 above the 7)
- Multiply: 8 × 15 = 120
- Subtract: 127 – 120 = 7
- Bring down: Bring down the 5 (75)
- Divide: 75 ÷ 15 = 5 (write 5 above the 5)
- Multiply: 5 × 15 = 75
- Subtract: 75 – 75 = 0 (no remainder)
The result is 85.
Divide 4.32 ÷ 6
- Adjust the divisor and dividend: Move the decimal point 0 places (divisor is already a whole number).
- Divide: 4 ÷ 6 = 0 (write 0 above the 4 and place the decimal point above the dividend’s decimal point)
- Multiply: 0 × 6 = 0
- Subtract: 4 – 0 = 4
- Bring down: Bring down the 3 (43)
- Divide: 43 ÷ 6 = 7 (write 7 above the 3)
- Multiply: 7 × 6 = 42
- Subtract: 43 – 42 = 1
- Divide: 12 ÷ 6 = 2 (write 2 above the 2)
- Multiply: 2 × 6 = 12
- Subtract: 12 – 12 = 0 (no remainder)
The result is 0.72.
Practice Problems on Long Division
Here are some practice problems to help you hone your long division skills:

Long Division Printable Worksheets

Fifth Grade Long Division Worksheets
At Brighterly, we believe that mastering long division is paramount for children to establish a robust foundation in mathematics. This vital skill not only equips them to tackle more advanced math concepts but also cultivates their problem-solving abilities, a valuable asset in all aspects of life. By comprehending the steps involved in long division and engaging in regular practice, children can develop confidence and proficiency in their mathematical skills.
Our mission at Brighterly is to create an immersive learning environment that fosters curiosity, creativity, and a passion for mathematics. Through our comprehensive resources, interactive activities, and expert guidance, we strive to make long division an approachable and enjoyable topic for children. We understand that each child is unique, and our tailored approach caters to individual learning styles, ensuring that every student can reach their full potential.
By investing in the development of strong long division skills, we’re not only empowering children to excel in mathematics but also setting them up for success in their academic and professional endeavors. Together, let’s inspire the next generation of mathematical thinkers, problem solvers, and innovators.
Frequently Asked Questions on Long Division
How can i help my child with long division.
Begin by ensuring they understand the basic concepts of division and the parts of a long division problem. Then, guide them through the steps, providing plenty of practice problems. Encourage them to check their work and learn from their mistakes.
What are some common mistakes made during long division?
Some common mistakes include:
- Misplacing the decimal point
- Incorrectly carrying over remainders
- Forgetting to bring down the next digit
- Not following the steps in the correct order
What are some tips for teaching long division?
Break the process down into smaller steps, use visual aids to illustrate the process, and provide real-life examples to make it more engaging. Encourage patience and persistence, as long division can be challenging at first.
Can long division be used for dividing polynomials and decimals?
Yes, long division can be used to divide both polynomials and decimals. The basic process remains the same, but you’ll need to pay attention to algebra rules when working with polynomials and adjust the divisor and dividend when dividing decimals.
The information in this article is compiled from various reputable sources, including:
- Wikipedia: Long Division
- National Council of Teachers of Mathematics: Teaching Long Division
- Wolfram Alpha: Long Division Examples
I am a seasoned math tutor with over seven years of experience in the field. Holding a Master’s Degree in Education, I take great joy in nurturing young math enthusiasts, regardless of their age, grade, and skill level. Beyond teaching, I am passionate about spending time with my family, reading, and watching movies. My background also includes knowledge in child psychology, which aids in delivering personalized and effective teaching strategies.
Troubles with Division?
- Does your child need extra support with understanding division concepts?
- Start studying with an online tutor.
Kid’s grade
Is your child having trouble mastering division basics? An online tutor could provide the necessary support.

After-School Math Program
Related math.
Welcome to another engaging lesson at Brighterly, where we make mathematics fun and easy to understand for children! Today, we are going to dive into the world of consecutive numbers. Consecutive numbers play a significant role in strengthening a child’s understanding of mathematics and number patterns. By exploring this topic, children will be better equipped […]
The number 49 is written as “forty-nine”. It is one more than forty-eight. For example, if you have forty-nine stamps, you start with forty-eight stamps and then find one more. Tens Ones 4 9 How to Write 49 in Words? The number 49 is expressed in words as ‘Forty-Nine’. It has a ‘4’ in the […]
The number 12600 is written in words as “twelve thousand six hundred”. It’s six hundred more than twelve thousand. For instance, if you have twelve thousand six hundred stamps, you start with twelve thousand stamps and then add six hundred more. Thousands Hundreds Tens Ones 12 6 0 0 How to Write 12600 in Words? […]
We use cookies to help give you the best service possible. If you continue to use the website we will understand that you consent to the Terms and Conditions. These cookies are safe and secure. We will not share your history logs with third parties. Learn More
How To Do Long Division
Turn your big numbers into smaller ones with long division – just master these easy steps.

Author Taylor Hartley

Expert Reviewer Jill Padfield
Published: August 24, 2023

- Key takeaways
- Long division is a process for dividing large numbers – This method breaks dividing large numbers into a sequence of easy steps you can use to find the right answer.
- It’s different from the short division method – Long division is primarily used with dividends of two or more digits. This makes the process less compact, but easier to understand when written out.
- Long division may or may not produce a remainder – Remainders represent leftover values from the division process that can no longer be divided, but represent an extra sum tacked onto the quotient.
Table of contents
What is long division?
What do i need to know before i do long division, how to do long division in 5 easy steps, let’s practice together, practice problems.
Long division might seem a little complicated, but anything’s easier when you divide it into smaller parts.
Let’s explore the process of long division and why it’s so important. First, we’ll explain what long division is and how it relates directly to another important concept—multiplication. If you’ve already mastered the basics of multiplication down, long division won’t be that bad, we promise!
Finally, we’ll run through a few practice examples to make sure you’ve got the hang of things before you go back to the classroom.
Long division is the process of reducing a multi-digit number into smaller groups. It’s also the practice of reversing multiplication: taking a certain value and separating it into the different numbers that were multiplied together to equal that original value.
Division is an important skill if you want to reduce numbers more efficiently, but long division is especially important as those numbers get bigger and bigger.
Long division is a helpful way of breaking a larger number up into two smaller ones. It follows a sequence of steps that, once mastered, makes the process of reducing any large number much easier.
You’ll encounter long division a lot when practicing mathematics, so it’s important that you get the basics down early. You never know when you might need to use it in your everyday life—and trust us, you will!
Follow along as we learn and practice the basics of long division.
How to multiply and divide
One of the most important parts of understanding division is that it’s the opposite of another common mathematical operation—multiplying. The same way you think of multiplication as repeatedly adding a certain value over and over again, division is the practice of subtracting a certain value over and over again, with the number of times you subtract being the quotient.
Think of multiplication as the repeated addition of equal values. And think of division as a way of finding out what those equal values are, and how many times you’re adding them. This way, you’ll be able to see how multiplication and division are inverses, or opposites, of one another.
Division vocabulary
Before we get into the basic steps of how to perform long division, we need to define a few important terms so that we can better understand these steps. There are four main definitions involved in the process of long division:
- Divisor – The number that divides another number
- Dividend – The number that will be divided by another number
- Quotient – The value gotten from the division
- Remainder – Any extra value left over after no more division can be done
Now, let’s take a look at a brief practice problem. This is a good opportunity to rinse and repeat the basic steps of long division, and make sure you’ve got the main points down before we go on to some other practice examples. Take a look below:
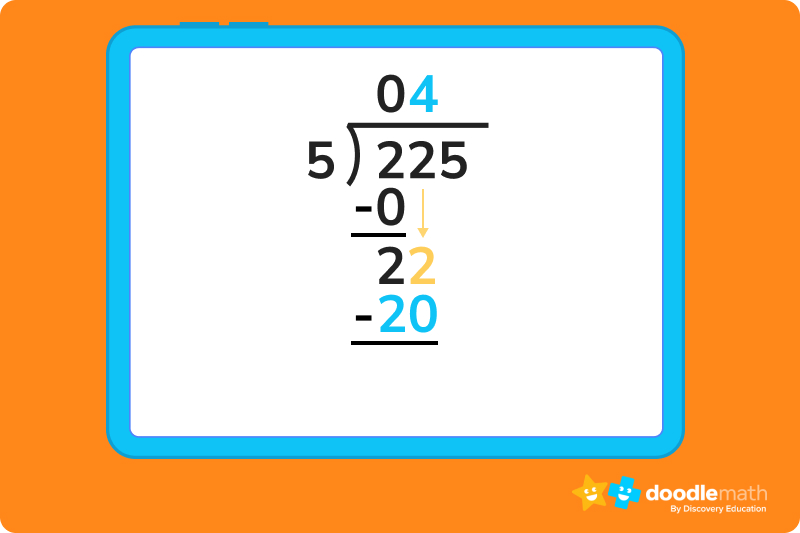
Solve 225÷5
Step 1: separate the divisor from the dividend..
Make sure the divisor is written first, and separate it from the dividend by either a right parentheses [)], or a backslash [/].
Then, draw an overhead bar above the dividend that connects to the parentheses or backslash you just drew. This will help you understand the difference between divisor and dividend.

Now, let’s take a look at the first number from the left in our divisor. Since 2 is less than 5, the dividend, we know we can’t do any division here. So, we write a 0 as our first number in the quotient and multiply it by our 5, giving us a product of 0.

We then need to subtract this 0 from the first digit of the dividend, 2. Now we can drag the 2 in the tens place down and place it next to the difference we calculated in step 2. This gives us a value of 22.
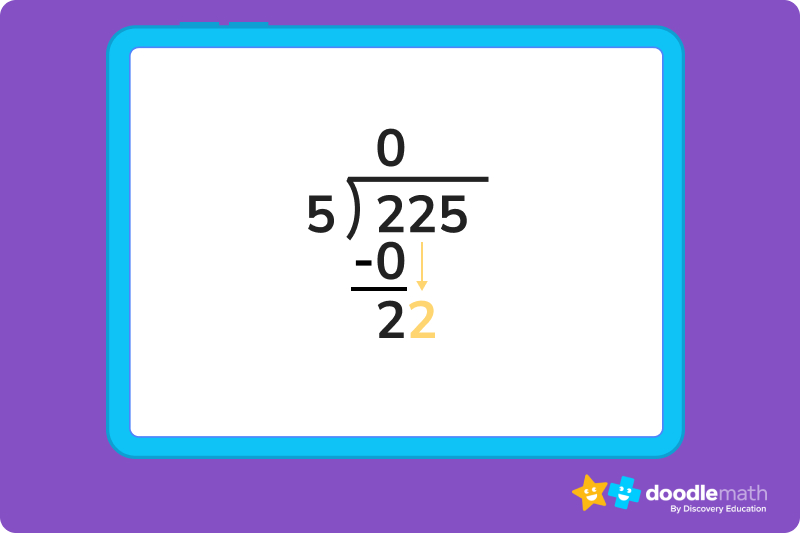
22 isn’t exactly divisible by 5, but we know 5 x 4 = 20, or that 5 fits into 20 four times. That means we can write a four in the quotient to the right of our 0. We then write that 20 below our 22, and subtract.
Our subtraction from step 4 gives us a value of 2. Now we drag the 5 in the ones place of 225 all the way down next to that 2, giving us a value of 25.
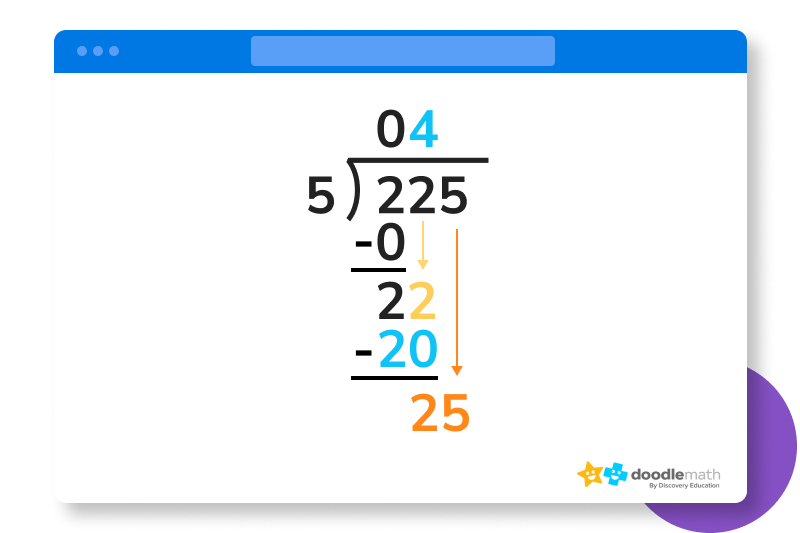
Now, we can divide that final 25 by our original dividend of five. 25 divided by 5 equals 5, which we write in the final place of our quotient.
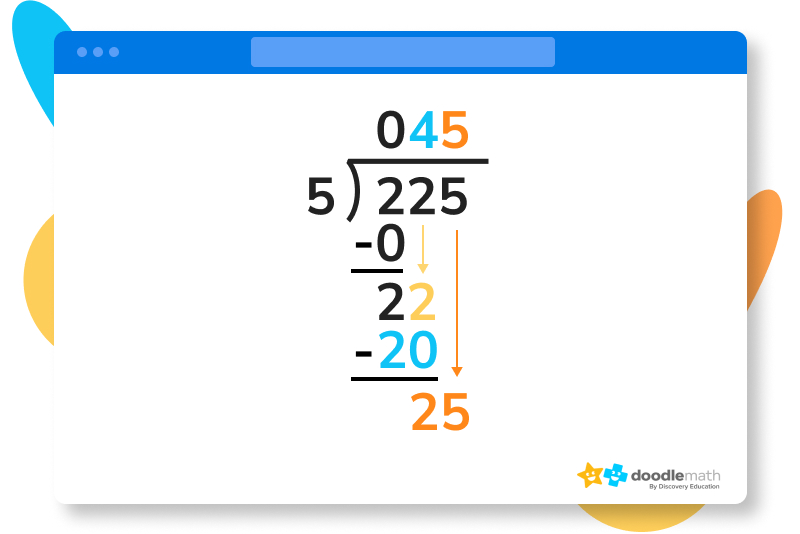
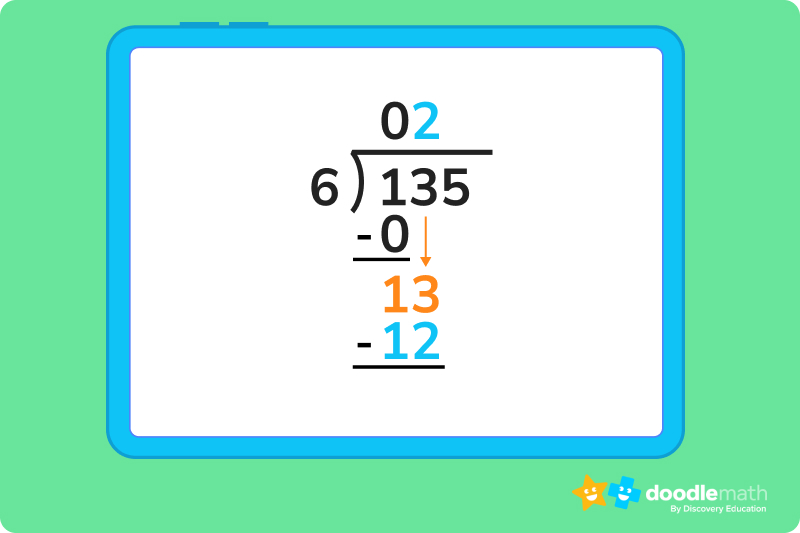
Solve 135 ÷ 6

1. Since we know 1 is less than 6, we can write a 0 as the first number in our quotient, and drag our 1 down.
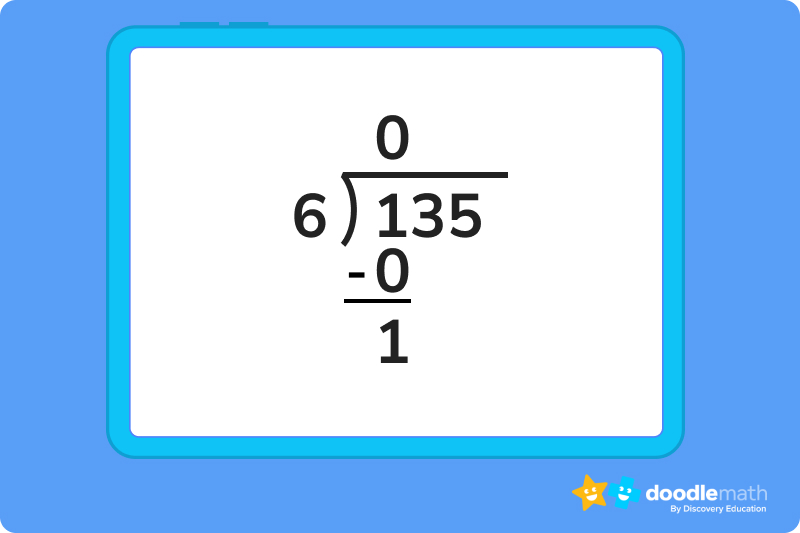
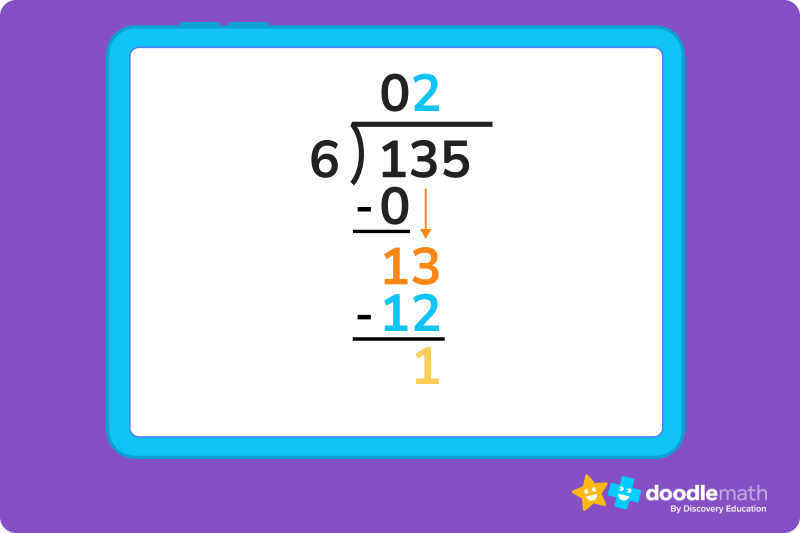
2. We then drag the 3 down next to our 1, giving us a value of 13. Since 6 fits into 13 twice, 6 x 2 = 12, we can write that 2 next to our 0 in the quotient.
3. We then subtract 12 from 13, giving us a 1.
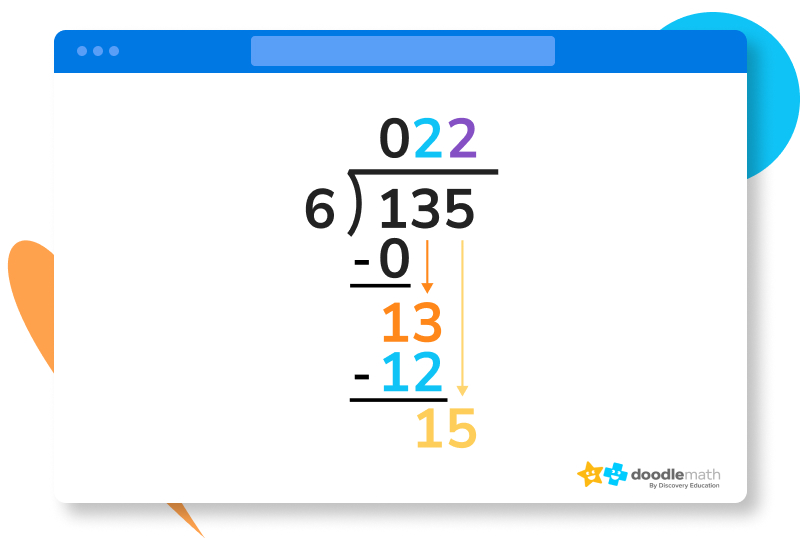
4. Now we can drag our 5 down and place it next to that one, giving us 15. Six fits into 15 twice, meaning we can write another two in our quotient.
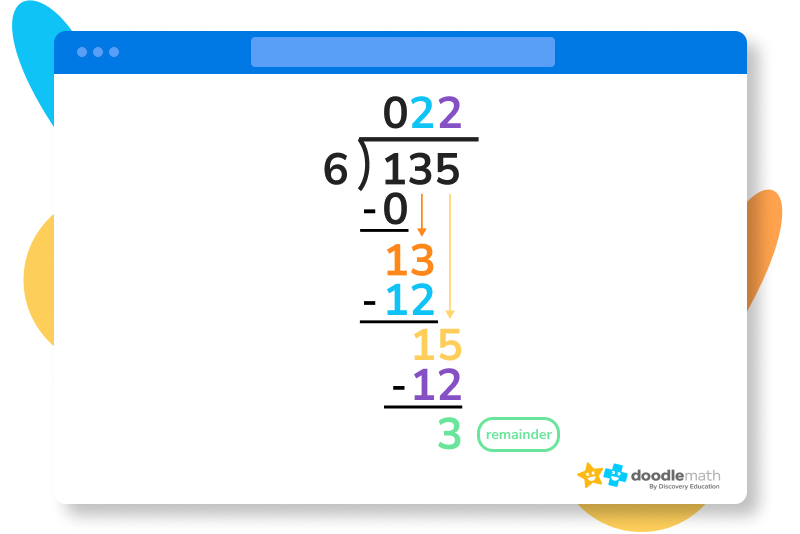
5. However, 15 – 12 = 3, and there are no more numbers to drag down! Here is where we use the term REMAINDER . 3 is the remainder here, since there is no more possible division to perform. Our final answer is 22 with a remainder of 3.
Solve 339 ÷ 3

1. The 3 in the hundreds place of the dividend is divisible by 3, giving us a value of 1 to write first in the quotient.

2. Now, we can write a 3 underneath the 3 in the hundreds place, and subtract. This should give us a value of 0.

3. We can then drag the three in the tens place down next to our 0.

4. Let’s repeat the same process in step 1, since 3 is still divisible by 3. This will give us another 1 in the quotient, and a subtraction equation of 3 – 3 that gives another 0.
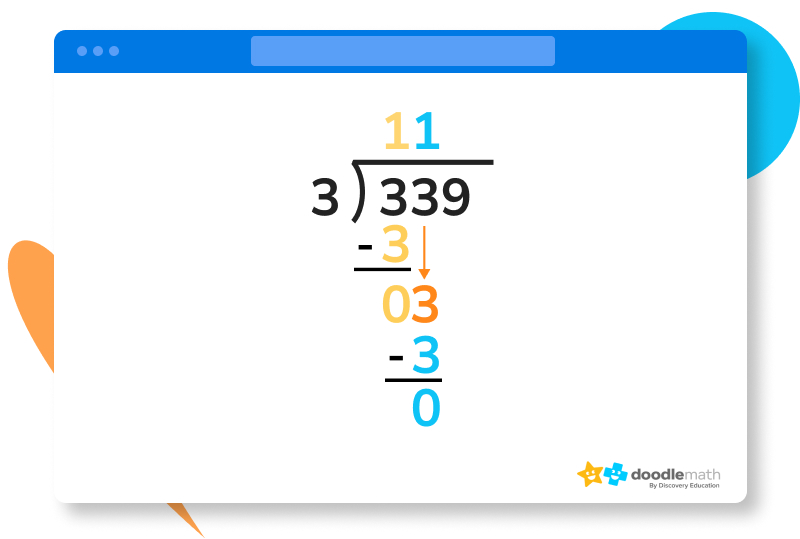
5. Now, let’s drag the 9 down next to our new 0. 9 is also divisible by 3. 93 = 3, meaning we can write a 3 as our last digit in our quotient. 3-3=0, meaning we’ve finished our long division. We should have a value of 113 in our quotient.
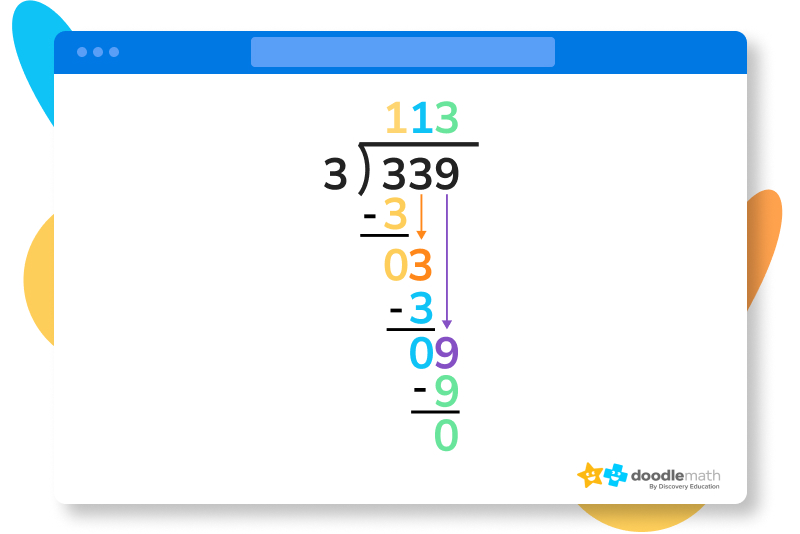
Ready to give it a go?
Now it’s your turn to put your long division skills to the test. Use your knowledge of long division to solve the following problems. Feel free to consult the guide if you get stuck.
Click to reveal the answer.
The answer is 71 with a remainder of 6

The answer is 52 with a remainder of 6

The answer is 54 with a remainder of 2

Parent Guide
The answer is 71 with a remainder of 6
How did we get here?
- 6 is smaller than 9, meaning we write a 0 in the quotient, and subtract that 0 from our 6.
- 6 – 0 = 6, and we can drag our next digit, 4, down to create a value of 64.
- 64 isn’t divisible by 9, but 9 x 7 = 63. That means we can fit seven values of 9 into 64, so we should write a 7 next to our 0 in the quotient.
- 64 – 63 = 1, and we can drag our final digit 5 down next to this 1 to give us 15.
- 9 fits into 15 once, so we write a 1 in the quotient and subtract 9 from 15, giving us 6.
- Since 6 is less than 9, we know we can stop our division, giving us a quotient of 71 with a remainder of 6.
The answer is 52 with a remainder of 6
- 4 is less than 8, so we need to write a 0 in our quotient and subtract this 0 from our 4. 4 – 0 will give us 4.
- Now we can drag our 2 down next to this 4, giving us a value of 42. 8 fits into 42 only 5 times (8 x 5 = 40), so we should write a 5 in our quotient.
- We then subtract 40 from 42, giving us 2. Now we drag the 2 in the ones place of our dividend down, giving us 22.
- 8 fits into 22 twice, meaning we write a two in the quotient and subtract 16 from 22.
- 22 – 16 = 6, so we are left with a quotient of 52 and a remainder of 6.
- 2 is smaller than 4, so we write a 0 in the quotient. We then multiply 2 by 0, and subtract that value from the 2 in the dividend.
- We can then drag the 1 in the tens place down next to this 2 to give us 21.
- 4 fits into 21 five times (4 x 5 = 20), so we write a 5 in the quotient and subtract 20 from 21.
- This gives us a value of one, and then drag our final value of 8 down to give us 18. 4 fits into 18 four times, so we write a 4 in the quotient.
- 18 – 16 = 2, so we are left with a quotient of 54 with a remainder of 2.
Sign up for the DoodleMath app today!
Turn math into an adventure when you sign up for DoodleMath.
Click here to get started for free!
FAQs about math strategies for kids
We understand that diving into new information can sometimes be overwhelming, and questions often arise. That’s why we’ve meticulously crafted these FAQs, based on real questions from students and parents. We’ve got you covered!
Just remember to divide, multiply, subtract, bring that next number down, and keep repeating that process. Long division is all about repeating the same steps over and over again until you can’t do any more division.
The hardest part is remembering to drag that next digit down so you can repeat the process. But if you can master those basic steps, you’ll begin to build some muscle memory that makes the process much easier.
For these problems, we check the first two digits of the dividend and see if they are divisible by our divisor. If the first two digits of the dividend are less than the divisor, we’ll need to consider the first three digits of the dividend instead. Now we can follow the same steps. Figure out how many times we can multiply our divisor into our dividend, and subtract that value.
Long division is often more accurate than shorthand division, because the steps are written out plainly in front of us. This allows us to track our division through a step-by-step process, and continue dividing until we discover an exact remainder. Think of long division as the most convenient and accurate way of dividing larger numbers. As you continue to learn mathematics, it’ll become an essential skill for solving more complicated problems.
This process might seem a bit more complicated, but it relies on the same rules and procedures we’ve been using this whole time. Since we know that the quotient, remainder and divisor are all related to the dividend in some way, there is a mathematical procedure we can use to calculate each. To find the dividend, simply multiply the quotient by the divisor, and add that product to your remainder.

Related Posts
Helpful description
Lesson credits
Taylor Hartley
Taylor Hartley is an author and an English teacher based in Charlotte, North Carolina. When she's not writing, you can find her on the rowing machine or lost in a good novel.

Parents, sign up for a DoodleMath subscription and see your child become a math wizard!
What we offer
Quick links
All rights reserved.

Are you a parent, teacher or student?
Get started for free!
Maths information pack
We ask for your contact info so we can send our info pack directly to your inbox for your convenience, exam prep information pack, case studies information pack.
Book a chat with our team

I’m new to Doodle

My school is already using Doodle

Information pack
We ask for your contact info so that our education consultants can get in touch with you and let you know a bit more about doodle., student login, which programme would you like to use.
DoodleMaths
DoodleTables
DoodleEnglish
DoodleSpell
If you’d like to use Doodle’s browser version, please visit this page on a desktop.
To log in to Doodle on this device, you can do so through our apps. You can find out how to download them here:
- Prodigy Math
- Prodigy English
From our blog
- Is a Premium Membership Worth It?
- Promote a Growth Mindset
- Help Your Child Who's Struggling with Math
- Parent's Guide to Prodigy
- Assessments
- Math Curriculum Coverage
- English Curriculum Coverage
- Game Portal
How to do Long Division: A Simple Step-By-Step Guide with Pictures

Written by Maria Kampen
Help your students master long division
Use Prodigy Math's adaptive algorithm to help your students build their long division skills – all while having fun!
- Teacher Resources
- Teaching Strategies
- A six-step guide to teaching long division
- Two bonus ways to teach division
- 8 activities to make long division engaging for your students
You’ve guided your class through most of the big units: addition, division, subtraction, multiplication. But here’s another tricky one:
How to do long division.
A 2012 study published in Psychological Science found that 5th graders’ understanding of fractions and division could be directly linked with how well they understood algebra in high school and performed in higher-level math classes — even after controlling for various socio-economic factors.No pressure, right? If the thought of teaching long division gives you cold sweats and clammy palms, not to worry — we’ve done all the work for you.
How to do long division in six steps

The first step you should take is a step back.
For a 4th grade student, long division is a complicated mix of different operations. In order to successfully learn how to do long division, they need to review these fundamental concepts.
According to a French study, “the representation and retrieval of mathematical facts from long-term memory” is one of the most important factors in determining a student’s future mathematical success. According to the same study, long division is “a synthesis of all arithmetic knowledge.”
Make sure your students understand that multiplication is the product of repeated addition, and division is simply the opposite — repeated subtraction.
Use base 10 blocks or money to reinforce place value and number sense. Plan activities that ask students to create “fact families” in order to make sure students understand how different functions interact.
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Kirstin Bajkowski (@kirstinbajkowski)
Use multiplication games and other math games to get students excited about learning and to build math confidence before you keep going.
2. Start simple
Let’s begin with a vocabulary lesson.There are lots of different parts in a long division equation. Make sure your students know what they mean and how to identify them.
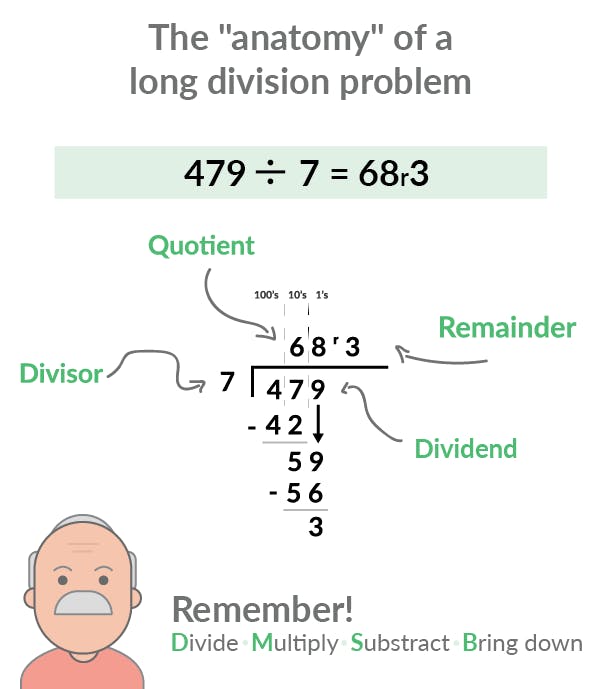
The dividend is the number on the right side of the equation, under the line. It represents the amount being divided.
The divisor is the number on the left -- it’s the one doing the dividing.
The quotient is the number on the top. It represents the answer, or the number of units in each place value once the equation has been completed.
The remainder is the number on the top right. It represents the units left over that can’t be evenly divided into the quotient.First, introduce an equation that doesn’t have any remainders so students can get used to the format and start understanding the new vocabulary they’ve just learned:

Ask students how many times 2 fits into 4. This might be a tricky concept for them, so use the idea of sharing: If you want to share 4 objects between 2 people, how many objects does each person get?
Once they come up with the correct answer, put 2 above 4. Then, repeat the step with the second digit in the dividend.
Use these simple equations to reinforce place value. Teach students that when they’re asking how many times 2 can go into 4, they’re really asking how many times 2 goes into 40.
3. Remainder in the ones
Have your students practise the step above until they’re comfortable with the basic format. Then, it’s time to move on.
Instead of jumping right into an equation with remainders, start with another object lesson . Divide students into groups of three, four or six and give each group 50 cotton balls (or jelly beans, or pompoms, or marshmallows — whatever small object is accessible in your classroom).
Ask students to divide the objects up so each member of the group has an equal number, then watch and wait.
Eventually, they’ll understand they can’t divide it evenly and there will always be some objects left over. That’s where you come in to save the day and explain how to do long division with remainders .
First, show students a problem that has a remainder in the ones:
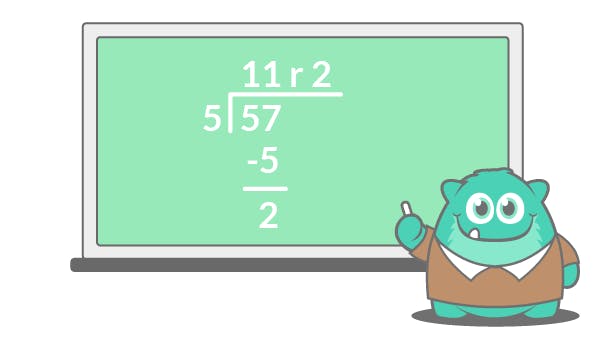
Now, begin with the tens column and work through the problem: 5 goes into 5 exactly once, so there’s nothing left there. But how many times does 5 go into 7, and what do you do with the leftovers?
Show students the new steps:
- Divide the ones column dividend by the divisor
- Multiply the divisor by the quotient in the right place column
- Subtract the product from the ones column
The number they’re left with is the remainder. Make sure to model several problems as a class so students can begin to understand the steps and how to properly write their answers.
This is a good time in the lesson to teach students how to check their answers. Have them multiply the divisor by the quotient and add the remainder — the answer should be the same as the dividend they started with.

4. Remainder in the tens
Now it’s time for students to tackle problems where the divisor doesn’t fit neatly into the tens or ones column. The steps are more or less the same, except for one new addition:
- Divide the tens column dividend by the divisor
- Multiply the divisor by the quotient in the tens place column
- Subtract the product from the divisor
- Bring down the dividend in the ones column and repeat .

Start with one-digit divisors and two-digit dividends to keep things simple. Remember that this is a totally new concept for students, so take the time to model problems on the board. Have a discussion about why the steps work, and help them understand how place value plays an important role in the process.
5. Introduce bigger numbers, gradually
So that’s it. Or is it?
Let students get comfortable with the formula and work on smaller problems. As they develop confidence and begin to understand how to do long division, start presenting them with problems that have a three-digit dividend, and then problems that have a two-digit divisor.
Remind students that the steps stay exactly the same no matter how big the problem is , and encourage them to use scrap paper to “guess-and-check” their multiplication as they go. This is a good spot to make sure that they’re not struggling and that they completely understand the relationship that division has with place value and multiplication.
For a refresher, check out this video from Khan Academy:
6. How to do long division with decimals
If you’ve covered all your content in the first five steps, congrats! Have students keep practicing how to do long division with large and small numbers, and keep reinforcing the relationship between division and other math concepts that they’re learning.But the process isn’t quite done yet — students need to understand how to do long division with decimals.To begin, go back to one of the fundamental concepts of division: place value. However, this time you’ll be going backwards instead of forwards.
Have students solve a problem as they normally would. When they get to the step where they would normally stop with a remainder, have them place a decimal point at the end of the quotient and the divided, and write in several zeros after the dividend.
Have them continue regular division steps for one or two places, bringing down the zeros.
Connect the decimal to fractions . Ask them to convert the quotient, with the decimal, to an improper fraction. This should help them understand the relationship between fractions and place value, and can be a good opportunity to go over fraction basics.
How to do long division (without doing long division)
Congratulations! Your unit is coming to an end, and you’ve successfully taught your students how to do long division.
But did you know that there’s more than one way to divide large numbers? Teaching students other ways of checking their work is an important part of Common Core math standards and can improve student understanding of what long division actually means in a given context.
Area models
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Math Teacher • Middle School (@mathwithmsyi)
Area models are a great way for visual learners to understand and conceptualize division while also enhancing number sense.
This method uses a grid to present the process of division as an area problem: for example, 148÷4 would be divided into a grid that is 4 units high, 148 square units in area, and an unknown number of units wide.
Students break up the grid into more manageable areas: 100 square units, 40 square units and 8 square units. 100÷4 is 25, 40÷4 is 10, and 8÷4 is 2. Those numbers go on the top of the area model and can be added up to reach the answer.
Partial quotients
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Erika | 4th Grade (@learningonleightonlane)
Similar to the area model, partial quotients encourage students to break division questions down into “friendlier” chunks. It helps students understand that division is finding how many times one number can go into another number.
Set up the problem (in this case, 450÷23) like a long division equation. Have student students multiply the divisor by 2 and 5 to use as an easy reference.
Ask how many times 23 goes into 400, but don’t look for the exact closest number: make it an easy number to work with, like 230 (ten times). Subtract 230 from 450 and put the 10 on the right to keep track of it.
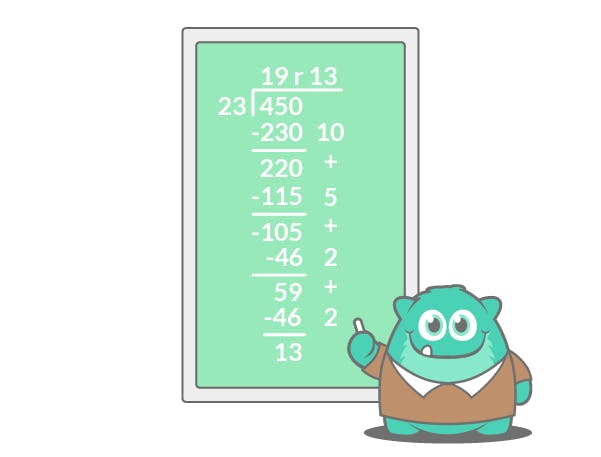
Take the difference and subtract it from the dividend. The answer should be 220.
Ask how many times 23 goes into 220. 5 x 23 is 115, so subtract that from 220 and record the 5.
Keep going, multiplying and subtracting until the final number is too small. When you’ve reached that step, you’ve found your remainder! Add up the numbers in the right-hand column to find your quotient.
Partial quotients have a flexibility that long division doesn’t. Long division needs to be done precisely, but with partial quotients it’s possible to simply subtract the divisor from the dividend repeatedly and still come to the right answer.
Use this method to reinforce place value and the concept of division as repeated subtraction.
Long division activities
The best way for students to learn how to do long division is to practice, practice, practice.
Here’s a list of eight activities that will get your class excited about long division and help them develop solid math skills.
Prodigy is a fun and engaging resource for in-class or at-home long division practice. Students explore a world filled with adventure, where success depends on correctly answering math questions.
Through the teacher dashboard, you can deliver lesson-aligned content based on the grade, skill or student. Then, students answer these questions in-game and provide you with real-time feedback on their learning and comprehension .
Encourage your students to practice all the math skills they’ve been learning in the classroom — including long division. Here's how you can use Prodigy to:
- Reinforce in-class lessons
- Differentiate math content
- Conduct formative assessments

Students play the engaging game-based platform, where they can collect pets, go on quests and battle with friends. And while they’re having fun, you’re helping them develop long division skills. It’s a win for everyone!
2. Life-sized long division
5th graders extended their skills of carrying out #long_division through different activities @DawhaHighSchool @FawziehHn #kinesthetic #online_division_calculator ➗✔ pic.twitter.com/vuNnKGu9Uc — najah shams (@najahshams) December 19, 2018
Bring math to life with a hands-on long division puzzle. Cut out squares of colorful paper with all the numbers that students need to solve a long division problem from start to finish. Use masking tape to make division lines on the floor, and give students the numbered cards.
Starting with a given equation, have students lay out all the cards in the correct order to solve the equation. This activity challenges students to slow down and think about their steps, and it’s especially helpful for a class that’s still looking to master the multiplication steps.
3. Long division bingo
Bingo is a classic for a reason. Each of the numbers on a student’s sheet should match up to a question that you have at the front of the classroom. Write the problem on the board, and then give students scratch paper and a chance to solve it and see if they have it on their card. As always, the first student to fill up a whole row, wins!
Challenge your students, but make sure you take enough time with this activity — some students might have trouble solving problems quickly, and can get frustrated or make mistakes if they’re not able to keep up.
4. Math books
Boost literacy and math learning at the same time with fun books covering tricky math concepts. Use them to explain division and remainders to students in a fun and engaging way, and even to cover more basic concepts before they start learning how to do long division.
Some math books that cover division include:
- A Remainder of One by Elinor J. Pinczes
- Bean Thirteen by Matthew McElligott
- The Doorbell Rang by Pat Hutchins
5. Get creative
Long division has lots of steps, and they have to be done in the right order to get to the correct answer. Students can get confused or frustrated when they don’t remember the steps, which negatively affects their math confidence and performance.
Challenge students to come up with their own unique way to remember how to do long division — divide , multiply , subtract and bring down — to get the creativity flowing in your classroom.
Have them create a poster, song, mnemonic device or even a small skit that they can present to their classmates. If they’re invested in finding a way to remember the steps, they’re more likely to learn quickly.
6. Long division relays
Turn long division practice into a fun classroom game with long division relays . Divide your class up into teams and make cards with long division problems on them.
Line up students in groups. Each group gets a card to start, and the first students complete the first set of steps for the problem they have.
When they’re done, the second student looks for errors and continues the problem. If they finish the problem, they can call for you to come check their work and trade the correct answer for a card with a new problem.
Keep going until every group has answered all their cards, and see which team wins!
7. Treasure chest

This activity is a fun way for your class to celebrate finishing their unit on division. Get a few boxes and fill them with a small treat everyone in the class can enjoy. Include a list of multiplication problems that students must solve in groups to “unlock” the box.
For an added challenge, make it a code: Have every quotient match up to a letter of the alphabet so that students have to correctly decode a key phrase to open the box.
8. Worksheet generator
Worksheets are a tried-and-true staple of math class. Lucky for you, there are lots of websites that will do the work for you and generate a custom worksheet that will give your students the change to practice how to do long division. Here are a few of our favourites:
- Helping with math
- Worksheet genius
Final thoughts on teaching students how to do long division
The most important thing to remember when teaching students how to do long division is to not rush through the material. It’s a big concept that’s different from anything they’ve learned before, and some (if not all) of your students might struggle at first.If you need to, go back to simpler equations and some of the earlier steps that we’ve outlined for you and work through them until your students feel confident. Keep on encouraging and challenging your students, and they’ll be ready to divide and conquer in no time!
Create or log in to your free teacher account on Prodigy – a game-based learning platform for math that’s easy to use for educators and students alike. Aligned with curricula across the English-speaking world, it’s used by millions of teachers and students .

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Multiplication and Division - Long Division
Multiplication and division -, long division, multiplication and division long division.

Multiplication and Division: Long Division
Lesson 5: long division.
/en/multiplicationdivision/introduction-to-division/content/
Long division
When you divide a number, you are splitting it equally . In Introduction to Division , you learned that division can be a way to understand real-life situations. For example, imagine a car dealership has 15 cars. The manager wants the cars parked in three equal rows.
You could write the situation like this and use a times table to solve it:
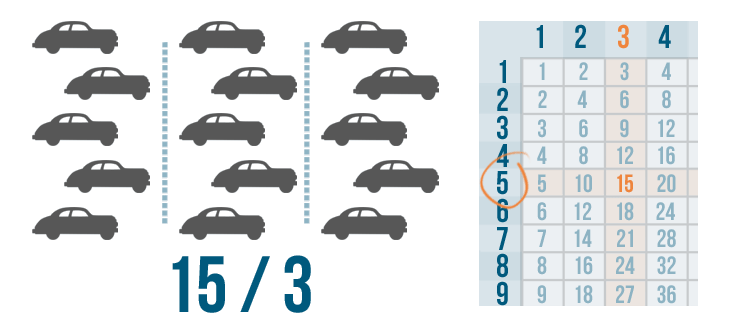
After the cars are divided, counting them shows that each row should have five cars. Now, let's say the car dealership has 42 cars and the manager wants to park them in three rows. The situation would look like this:
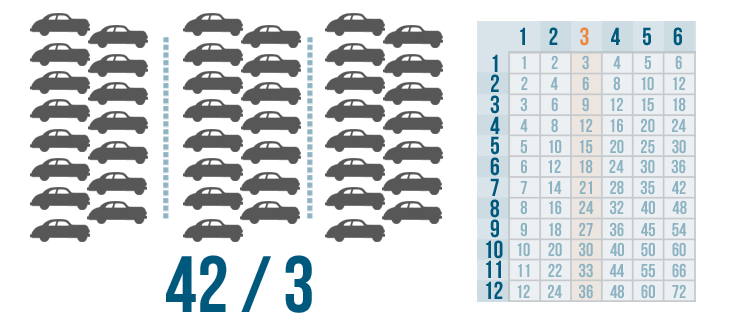
This problem is harder to solve. It would take a lot of time to divide that many cars into three groups. Plus, there's no 42 in the 3's column on the times table. Fortunately, there is a way to set up the problem that makes it easy to solve one step at a time. It's called long division .
Let's learn how to set up these problems. We'll look at the problem we discussed above: 42 / 3 .

In the last lesson, we learned how to write division expressions.
However, dividing a larger number is easier when the expression is written in a different way.

Instead of writing the numbers side by side with a division symbol...
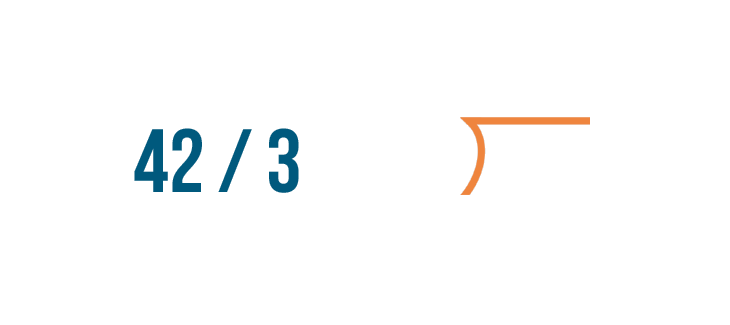
Instead of writing the numbers side by side with a division symbol... we'll use a different symbol called a division bracket .
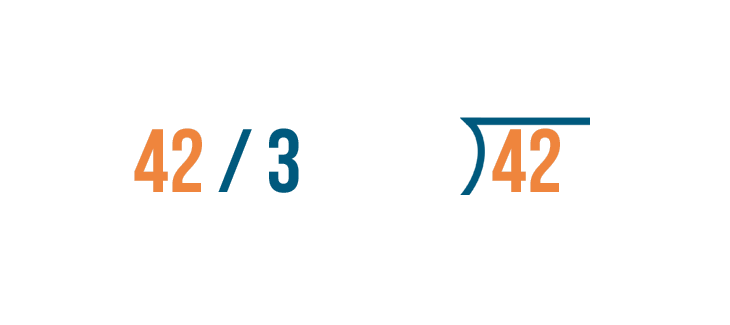
The number you're dividing goes under the division bracket. That's 42 .
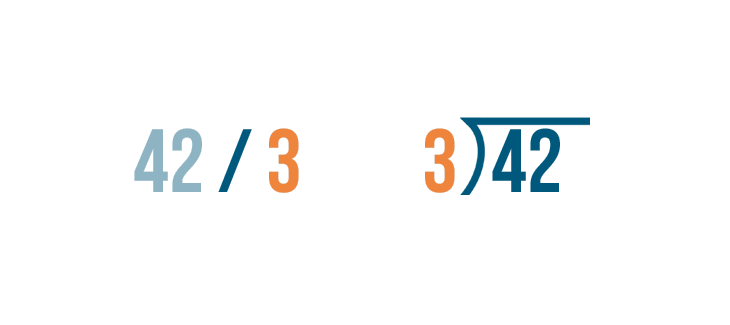
To the left of the division bracket, write the number you're dividing by. In our problem, it's 3 .
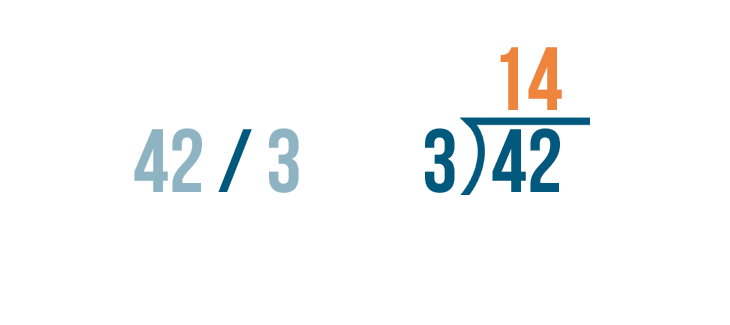
The division bracket is also an equals sign. The quotient , or answer, is written above it.
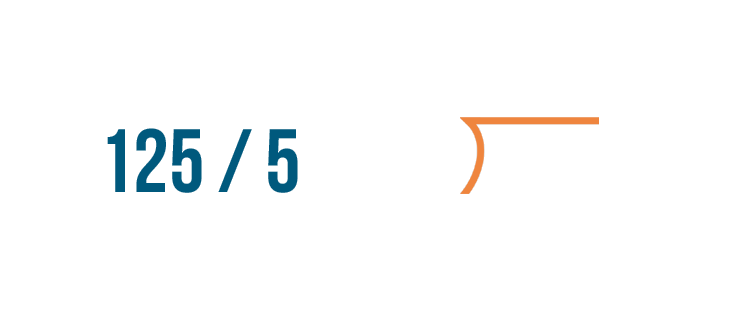
Let's try setting up another expression, 125 / 5 . First, write the division bracket.

Next, write the number being divided, 125 .

Finally, write the number we're dividing by, 5 .

Remember, you should be careful to set up long division problems correctly.

The number you're dividing goes under the division bracket...

The number you're dividing goes under the division bracket... and the number you're dividing by goes to the left of it.

Solving long-division problems
To solve long division problems, you'll use three math skills you've already learned: division , multiplication , and subtraction . It's a good idea to make sure you feel comfortable with all three skills. If you think you might need more practice, take some time to review those lessons first.
When solving a long division problem, the number under the division bracket is split into smaller numbers. This makes division easier. Plus, you can use a familiar tool, like a times table, to help.
Let's see how solving a long division problem works.
Remember the manager of the used car dealership who wanted to divide 42 cars among 3 rows? Let's find out how many cars he should put in each row.
We'll use long division to solve this problem: 42 / 3 .
Long division follows a pattern . You follow the same basic steps again and again until the problem is complete. If this seems confusing, don't worry. We'll go through it step by step.
We'll begin with the left digit under the division bracket. That means we'll start with the 4 ...
We'll begin with the left digit under the division bracket. That means we'll start with the 4 ... and we'll figure out how many times it can be divided by 3 .
Now it's time to solve 4 / 3 .
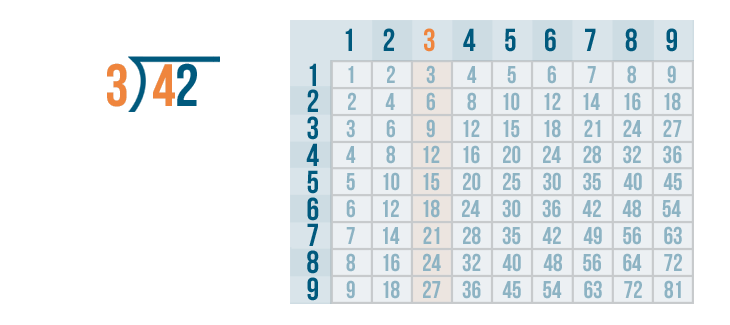
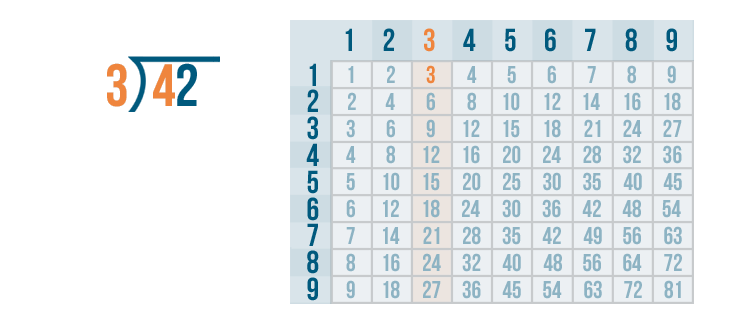
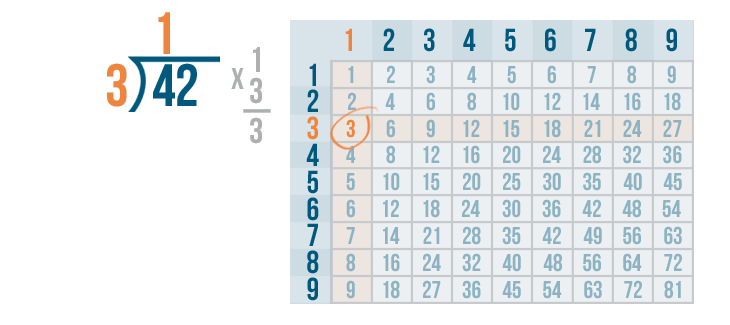
We can use the times table . We'll look at the 3's column.
Since 4 is the number we're dividing, we need to locate the number that is the closest to 4. The number can't be any larger than 4 .
3 is the closest to 4 .
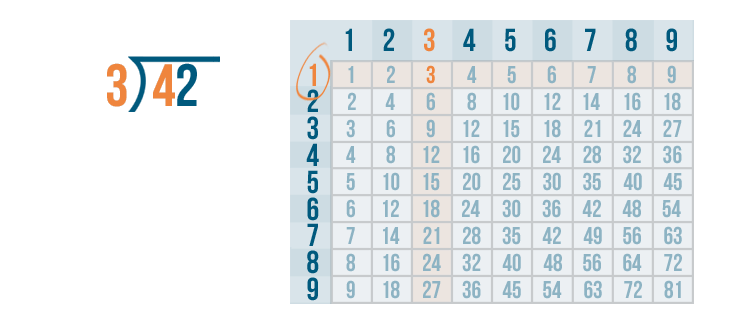
Next, we'll find the row 3 is located in. It's the 1's row.
That means 3 goes into 4 one time.
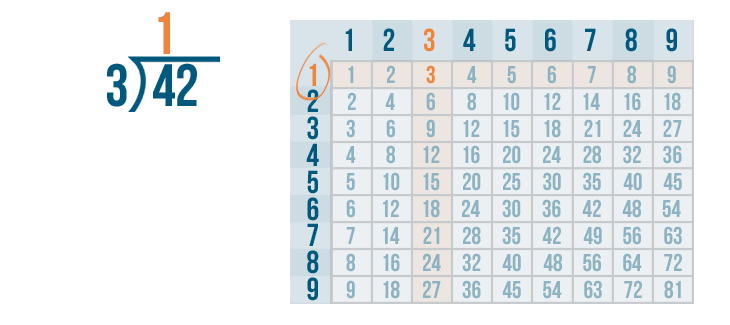
We'll write 1 above the 4 and the division bracket.
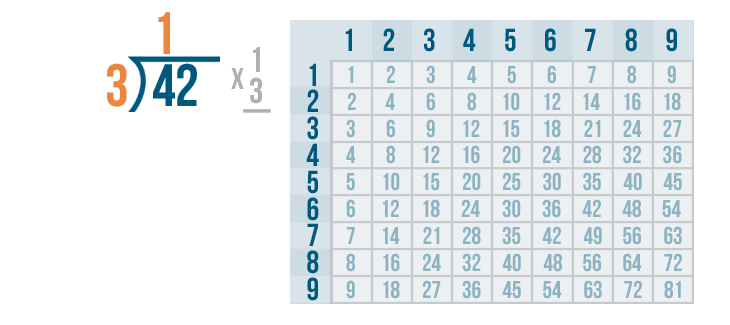
The next step is to multiply the 1 and 3 .
Whenever you multiply a number by 1, that number stays the same. So 1 x 3 is 3 .
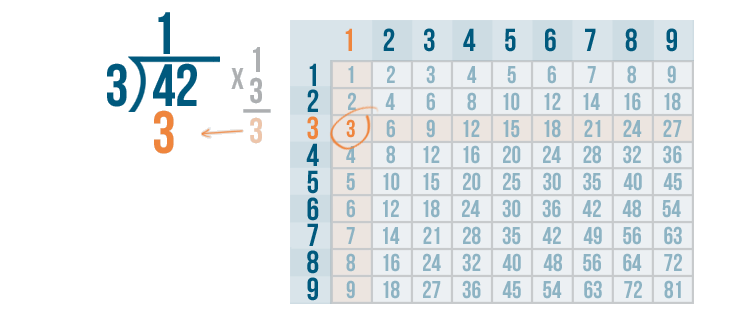
We'll write 3 below the 4 .
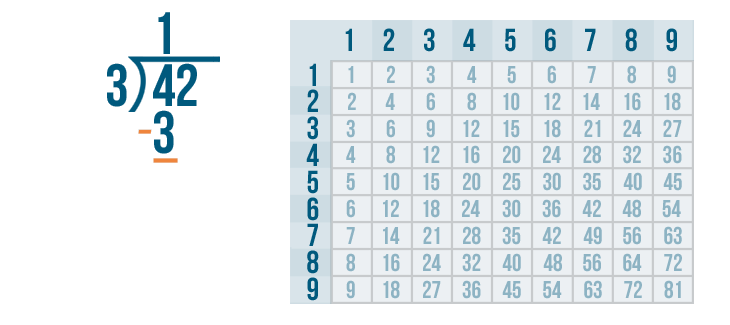
The next step is to subtract .
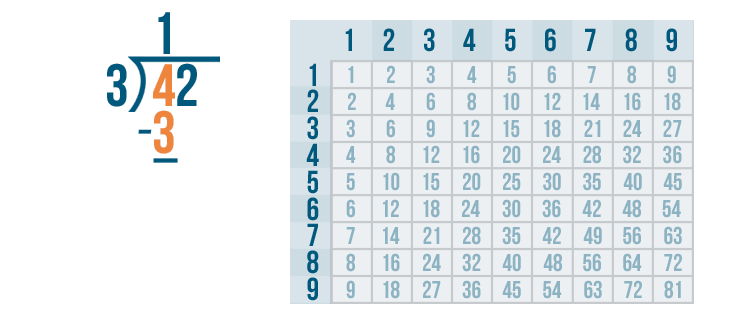
Now we solve 4 - 3 .
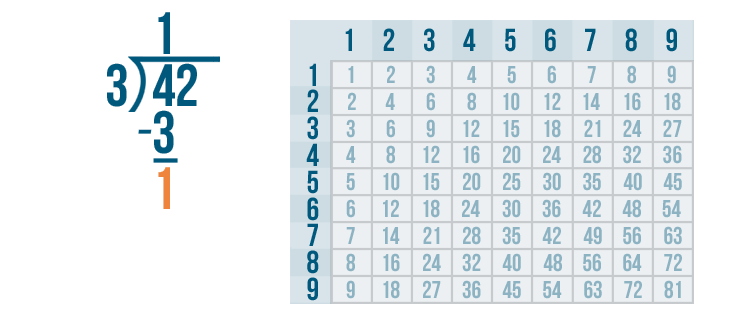
4 - 3 is 1 . We'll write 1 below the 4 and 3 .
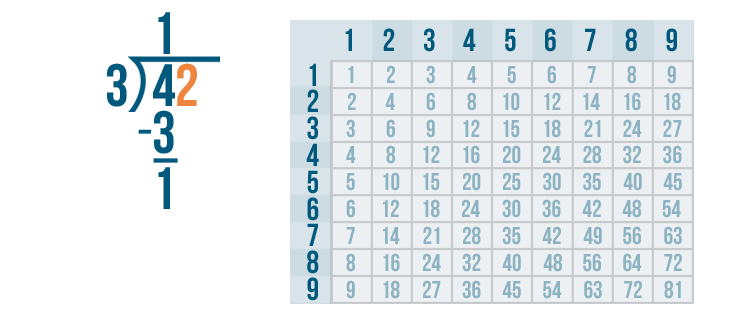
Since our answer is 1 , we're not done yet. We'll know our problem is complete when the answer to our subtraction problem is zero. Plus, there's still another digit under the bracket: 2 .
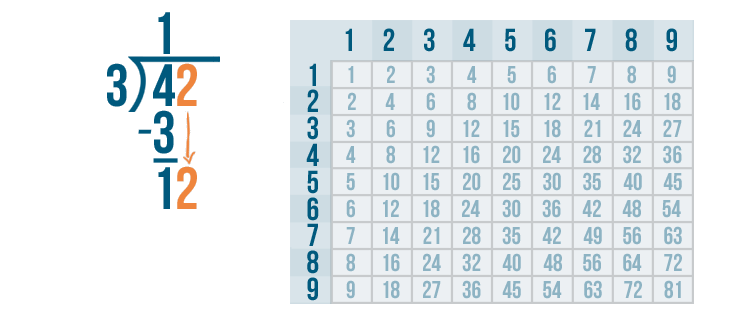
We'll bring the 2 down and rewrite it next to the 1 .
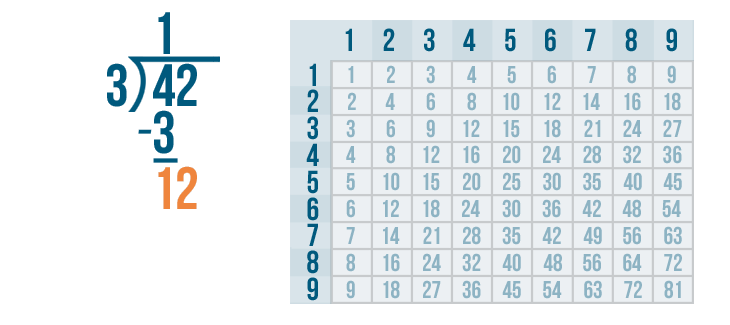
See how the 1 and 2 look like the number 12 ? That's the next number we need to divide.
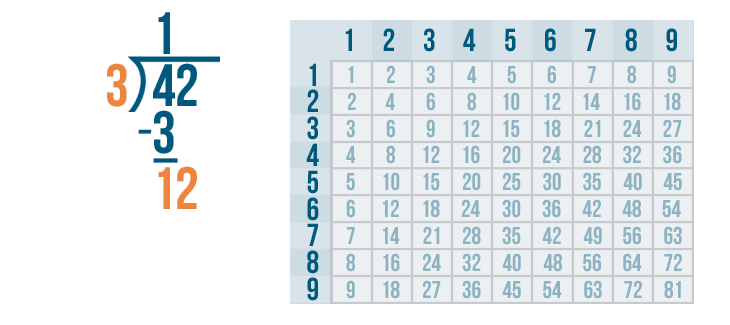
12 is large enough to be divided, so we'll figure out how many times it can be divided by 3 .
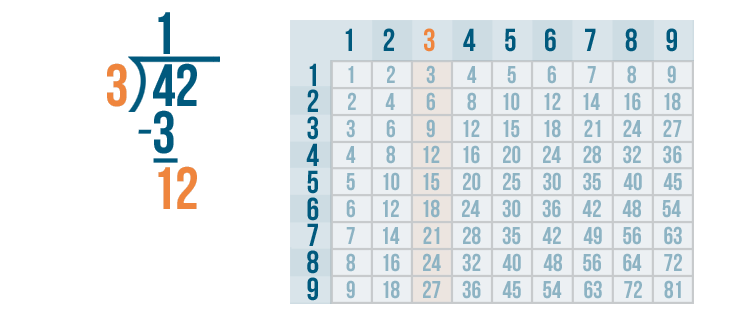
Let's look at the 3's column. Since 12 is the number we're dividing, we'll find the number closest to 12 . Remember, the number can't be any larger than 12 .
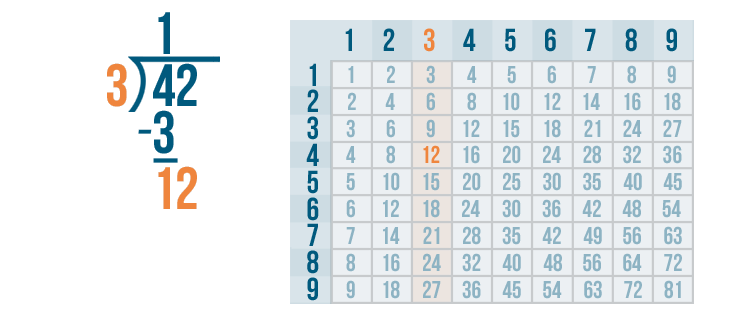
The 3's column has a 12 . It would be impossible to get closer than that!
Now we find the row 12 is located in.
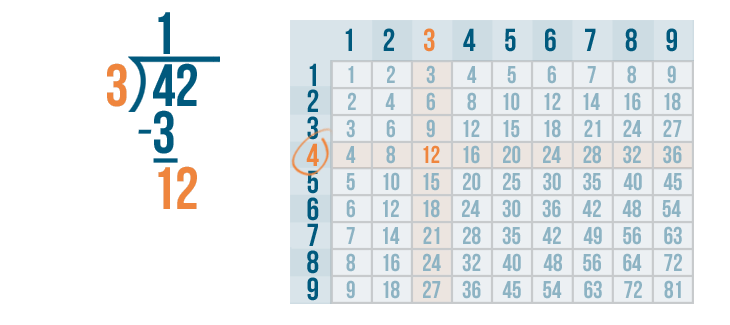
It's the 4's row. 3 goes into 12 four times.
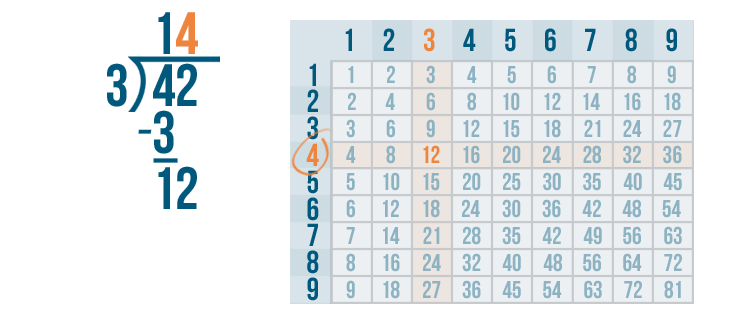
We'll write 4 above the 2 and the division bracket.
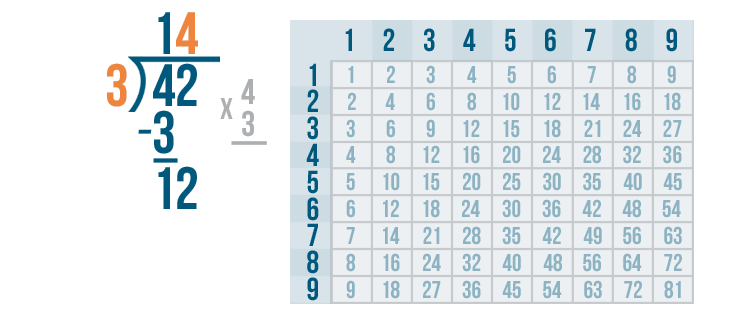
Now it's time to multiply the 4 and 3 .
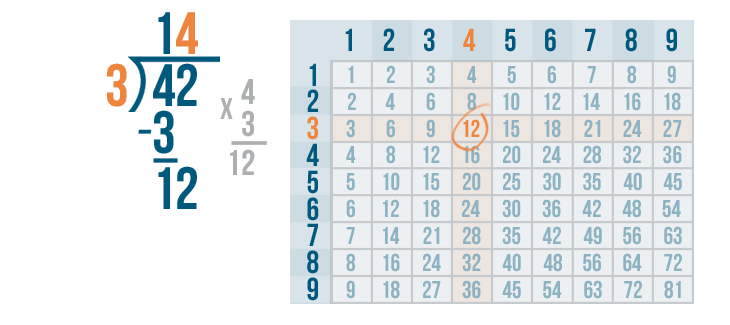
4 x 3 is 12 .
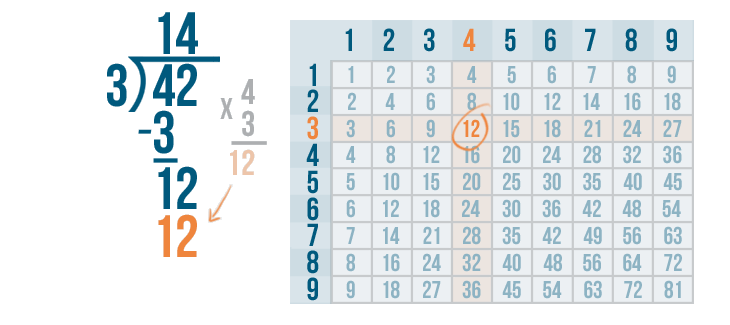
Write the 12 beneath the 12 .
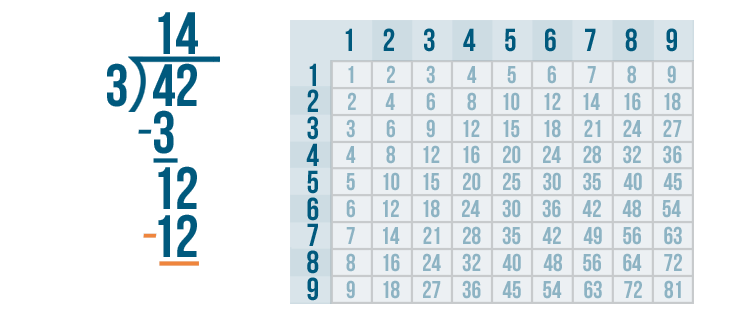
We'll set up our subtraction problem.
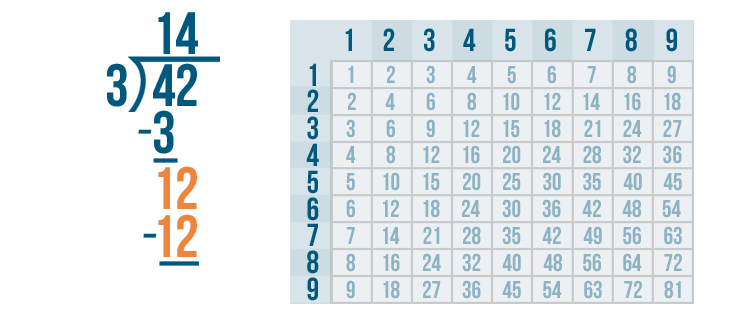
Now it's time to solve 12 - 12 .
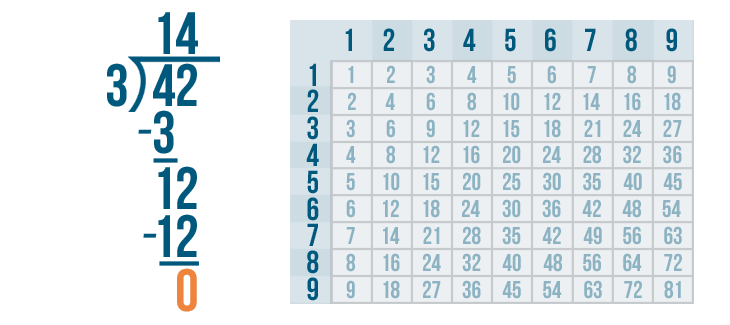
12 - 12 is 0 . Write 0 beneath the line directly below the 2 and 2 .
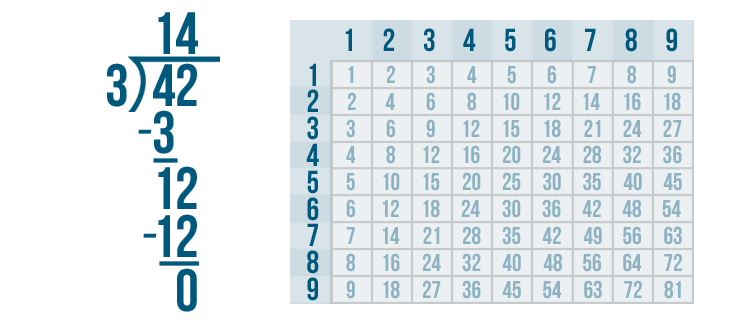
The answer to our subtraction problem is 0 . That means we're done! 42 / 3 = 14 .
Solve these long division problems. Then, check your answer by typing it in the box.
Problems with remainders
In Introduction to Division , you learned that some numbers can't be equally divided. When that happens, there will be an amount left over. This is called a remainder . For instance, let's say you want to share 8 treats equally among your 3 dogs. The answer is that each dog would get two treats with a remainder of two .
The remainder is written as part of the quotient: 8 / 3 = 2 r2 .

Long division problems can have remainders too. Watch the slideshow to see how.
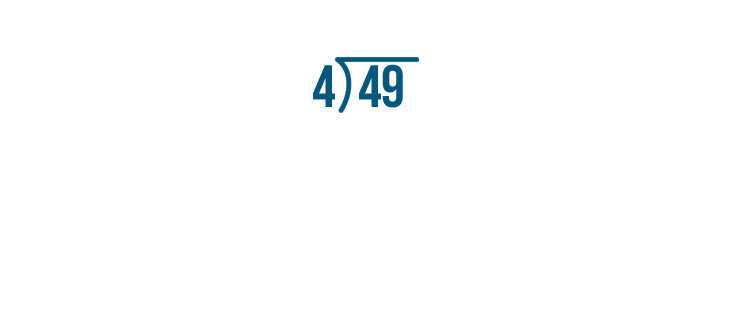
Let's try this problem, 49 / 4 .
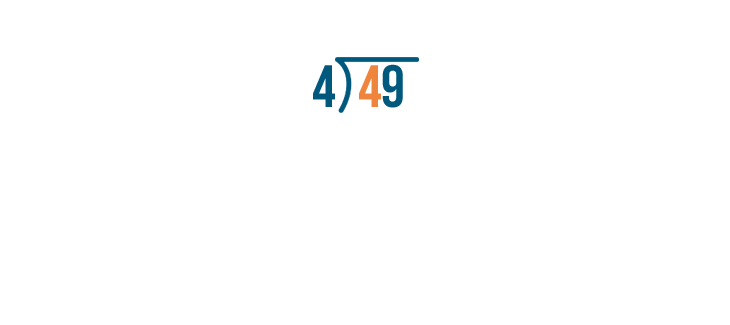
As always, start by dividing the left digit. This means we'll solve for 4 / 4 .
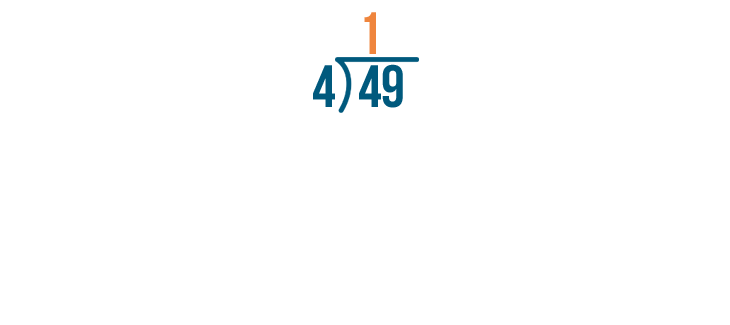
4 / 4 is 1 .
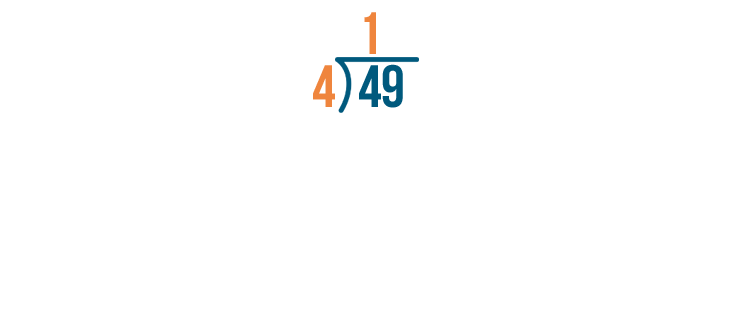
Next, we'll multiply the answer we just got, 1 , by the number we're dividing by, 4 . So 4 x 1 .
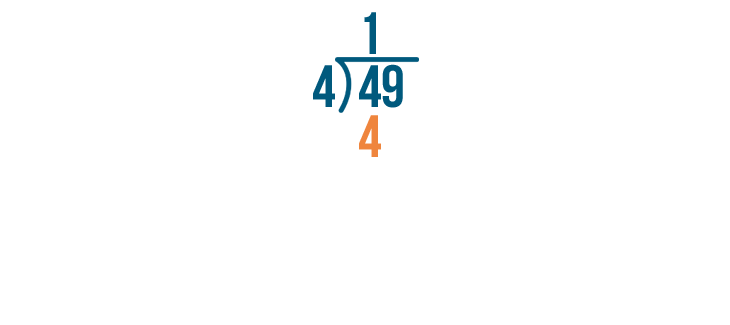
4 x 1 is 4 .
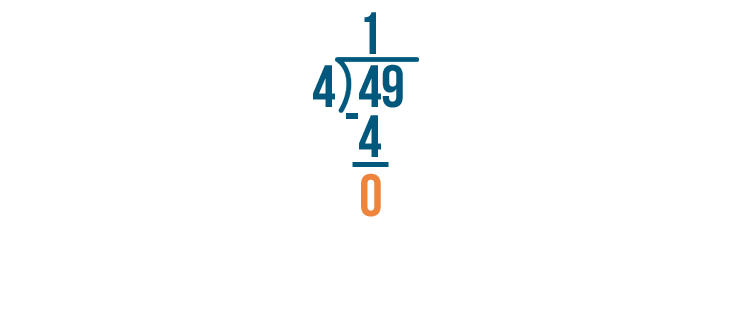
Next, subtract 4 - 4 . Whenever you subtract a number from the same number, the answer is 0 . So 4 - 4 = 0 .
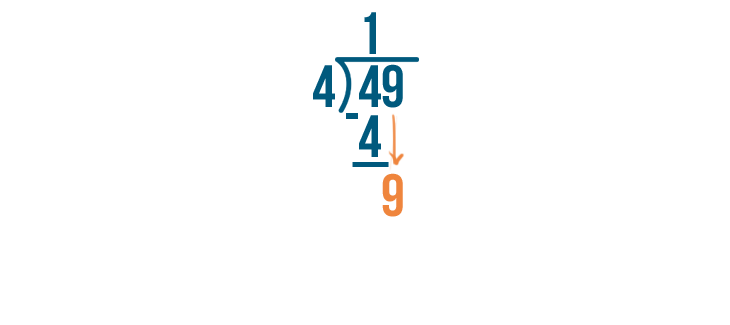
Our problem's not done. The next digit in the number we're dividing is 9 . We'll solve for 9 / 4 .
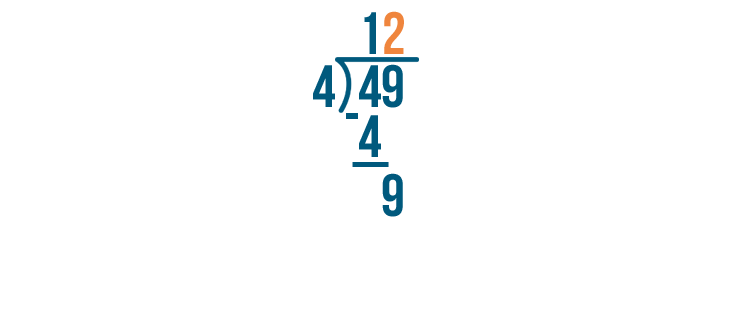
9 / 4 is 2.
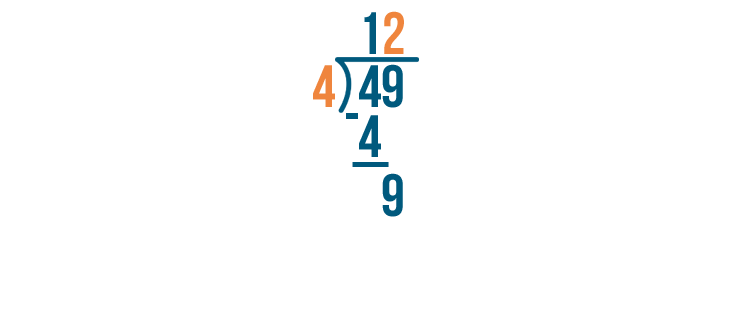
Again, we'll multiply the number we just wrote by the number we're dividing by.
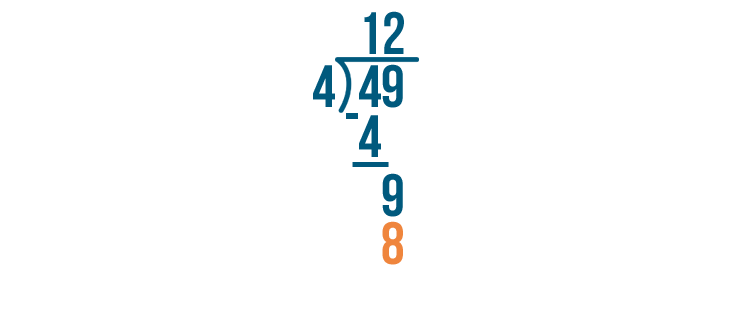
2 x 4 is 8 .
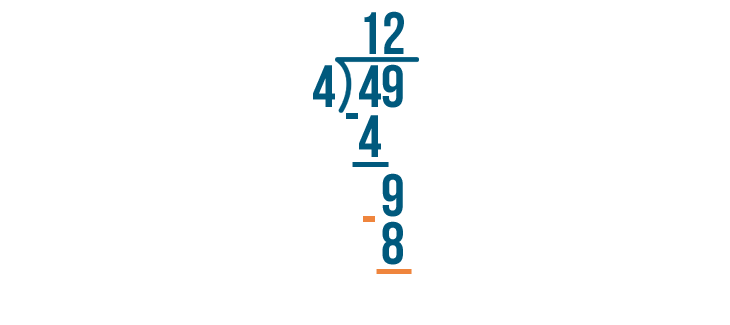
We'll subtract that number, 8 , from the number we were dividing.
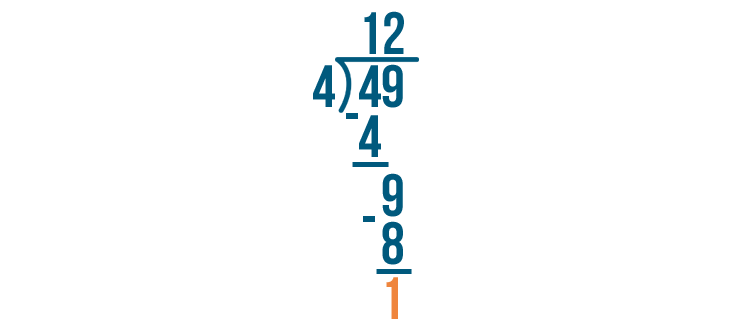
9 - 8 is 1 .
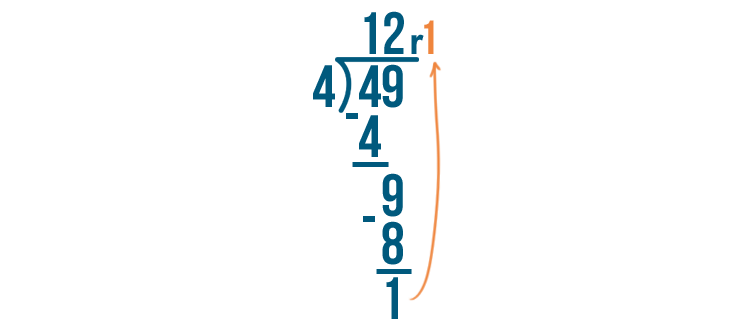
Since 1 is smaller than 4, we can't divide it any further. 1 is our remainder . We'll write it next to the rest of the answer.
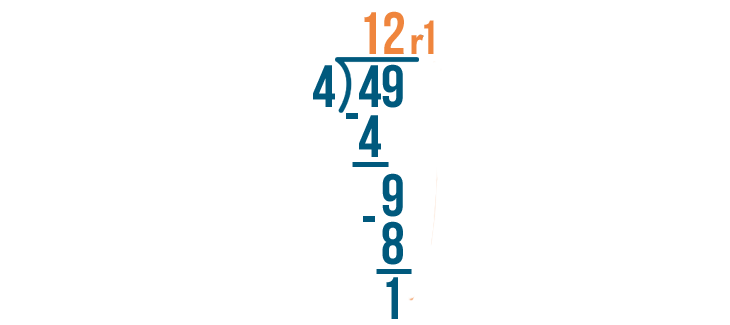
We're done! 49 / 4 = 12 , with a remainder of 1 .
Solve these division problems with remainders. Then, check your answer by typing it into the boxes.
Decimal quotients
On the last page, you learned how to find the remainder for a long division problem that can't be solved evenly. Remainders can be useful if you need to know how much is left over when you divide something, but they might not be very useful in every situation. For example, what if you wanted to divide a 9- foot-long board into 4 equal pieces ? That problem could look like this:
9 / 4 = 2 r1
In other words, when you divide a board that's nine feet long into four pieces , each piece will be two feet long . There will be one foot left over.
What if you don't want to waste any wood? In that case, you can continue to divide until there is no longer a remainder. That way, you'd have four equal pieces of wood, with none left over. That problem would look like this:
9 / 4 = 2.25
The answer, 2.25, is a decimal number. You can tell, because it includes a symbol called a decimal point (.) . The number to the left of the decimal point , 2 , is the whole number. The rest of the answer, .25 , shows the part of the number that didn't divide evenly.
Click through the slideshow below to learn how to find the decimal answer to a division problem.
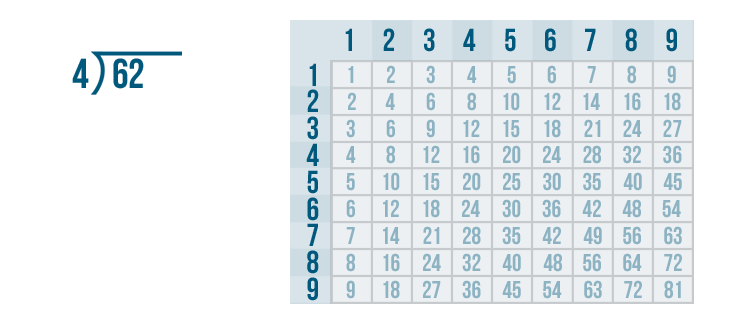
Let's say we have 62 treats to divide equally among 4 dogs. The problem we're solving is 62 / 4 . Let's find out how many treats each dog should get.
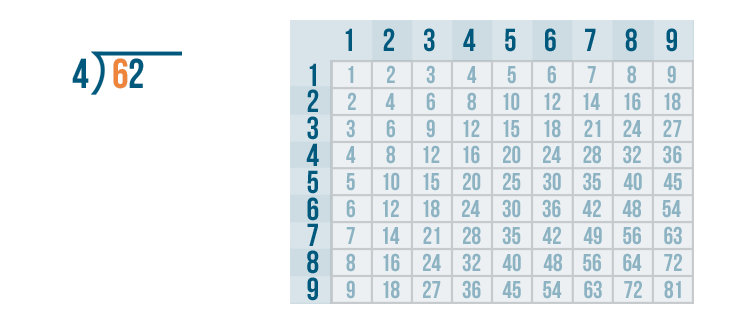
As always, we'll begin with the left digit under the division bracket. That means we'll start with the 6 ...
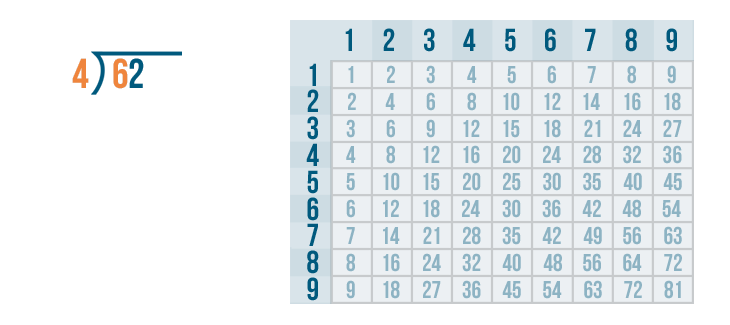
As always, we'll begin with the left digit under the division bracket. That means we'll start with the 6 ... and we'll figure out how many times it can be divided by 4 .
Now it's time to solve 6 / 4 . We'll use the times table.
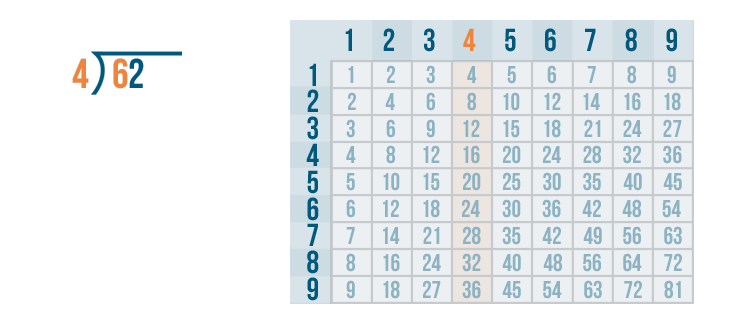
We'll look at the 4's column. Since 6 is the number we are dividing, we need to find the number that is closest to 6 . Remember, it can't be any larger than 6 .
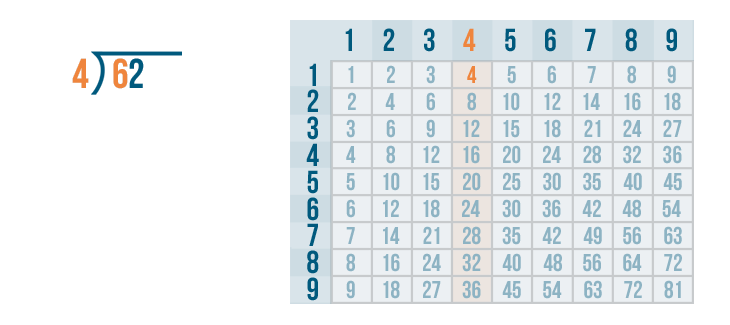
4 is the closest to 6 .
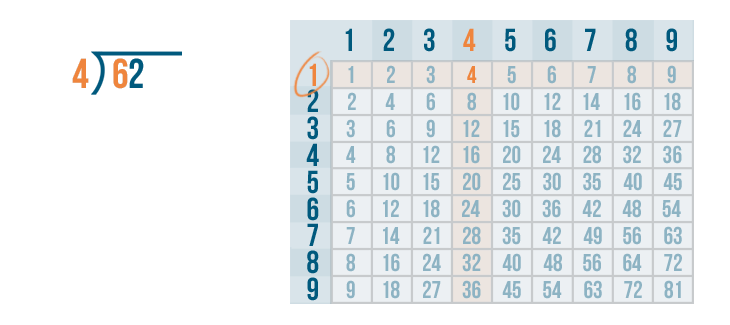
Next, we'll find the row 4 is located in. It's the 1's row.
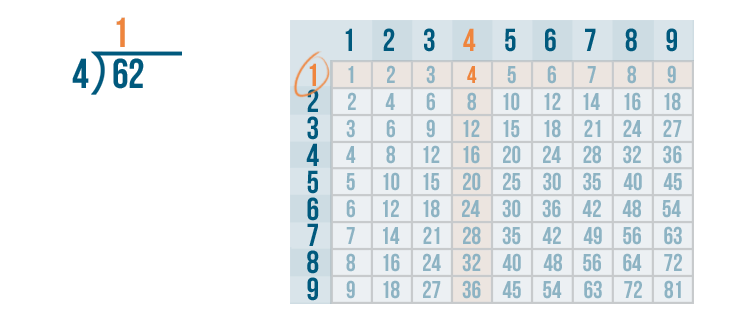
That means 4 goes into 6 one time. We'll write 1 above the 6 .
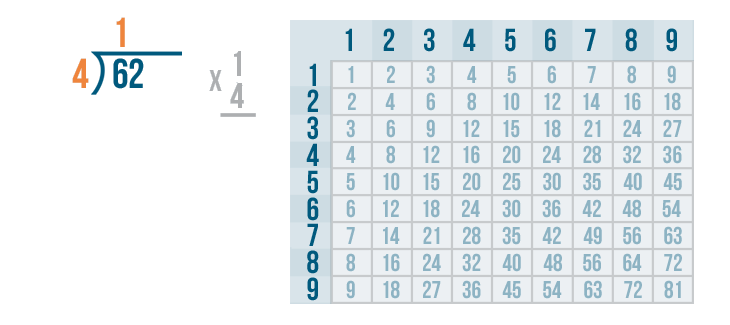
Next, we'll multiply the 1 and 4 .
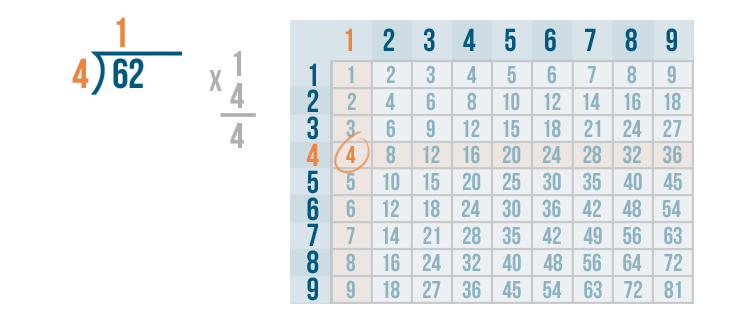
Remember, whenever you multiply a number by 1, that number always stays the same. So 1 x 4 is 4 .
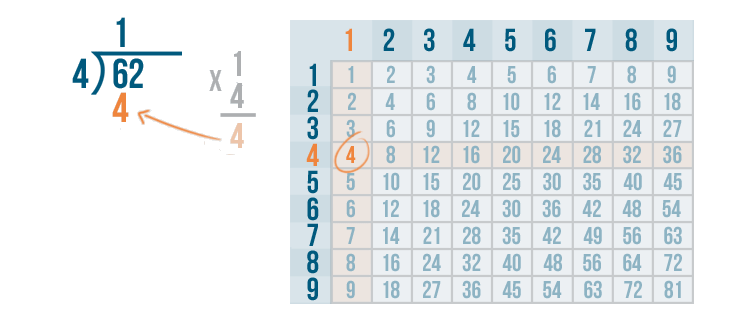
We'll write 4 below the 6 .
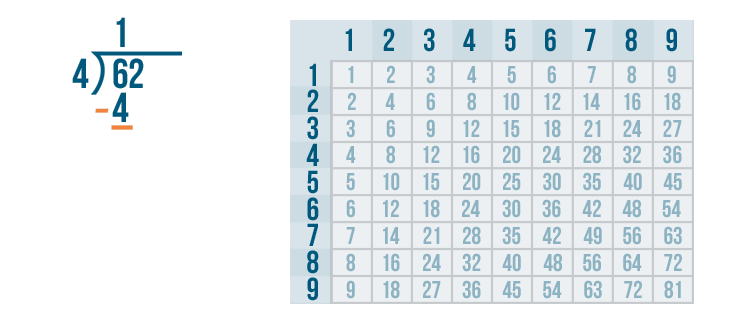
The next step is to subtract.
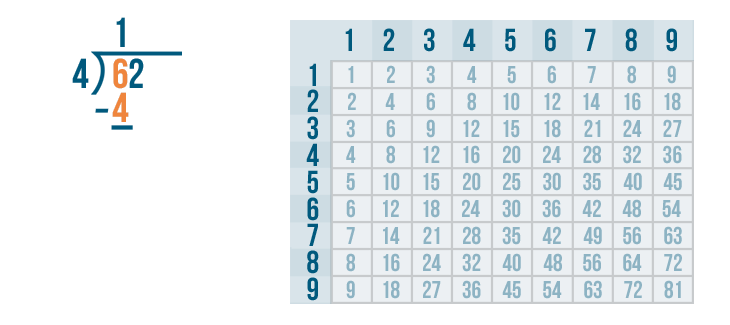
Now we solve 6 - 4 .
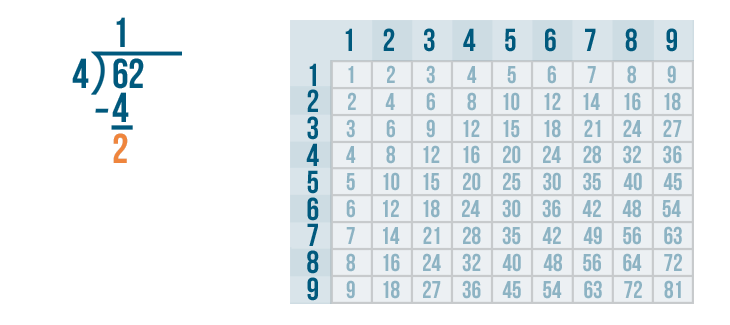
6 - 4 is 2 . We'll write 2 below the line.
Since 2 is more than zero, we know we're not done with our problem.
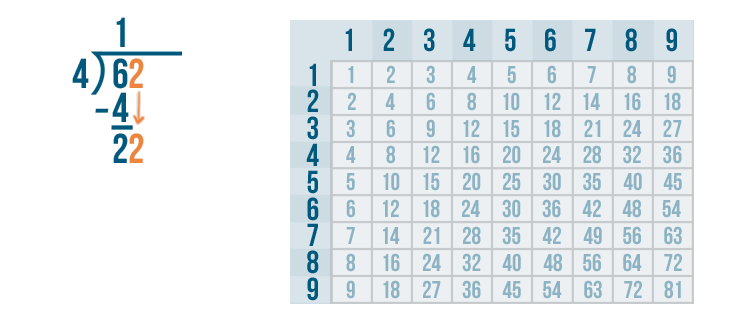
We'll bring the 2 down and rewrite it next to the 2 .
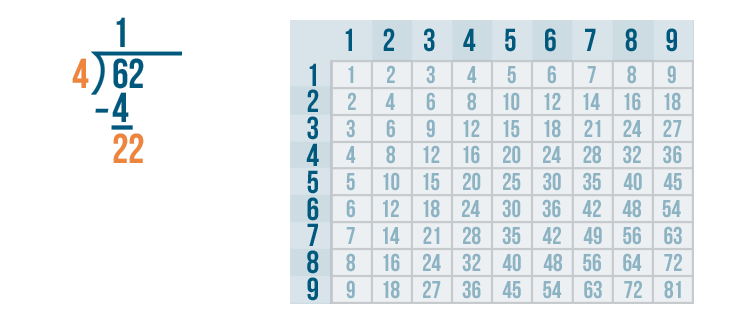
22 is large enough to be divided, so we'll figure out how many times it can be divided by 4 .
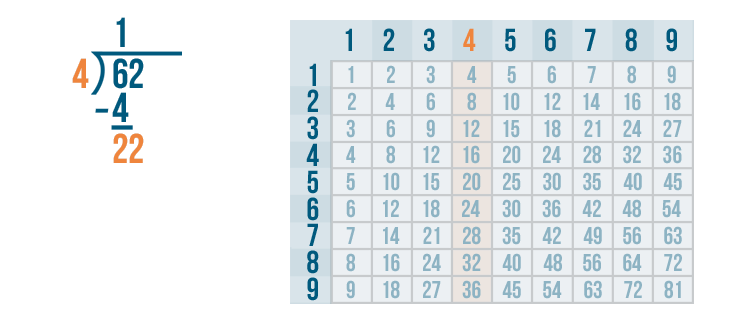
Let's look at the 4's column to locate the number closest to 22 . The number can't be any larger than 22 .
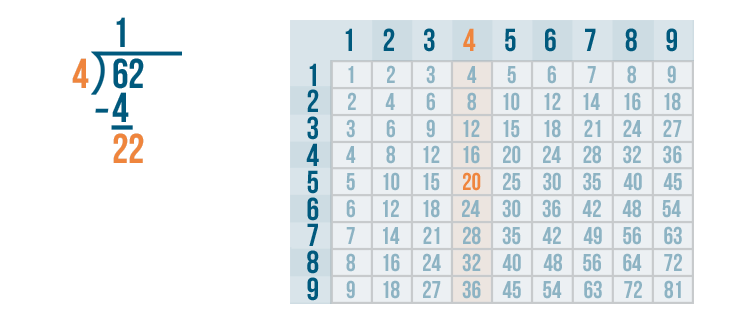
20 is the closest to 22 .
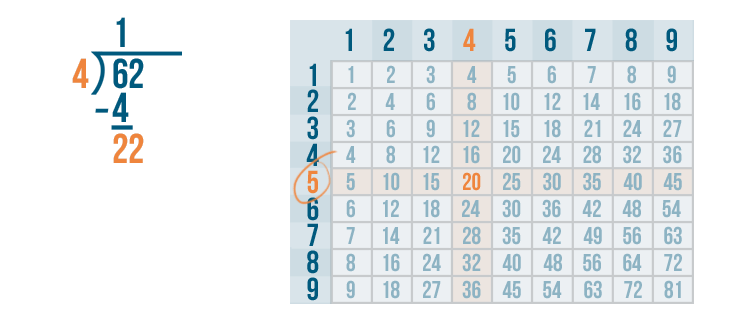
Now we'll find the row 20 is located in. It's the 5's row. So 4 goes into 20 five times.
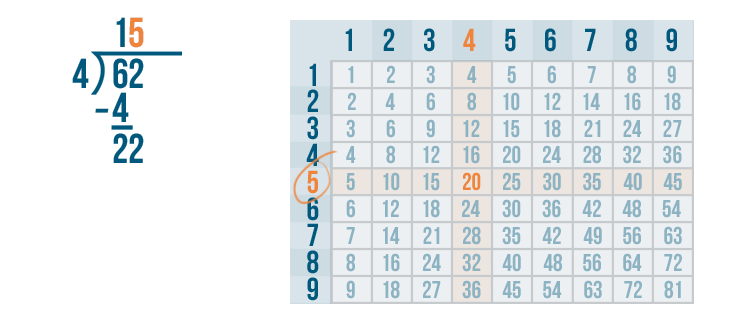
We'll write 5 above the 2 .
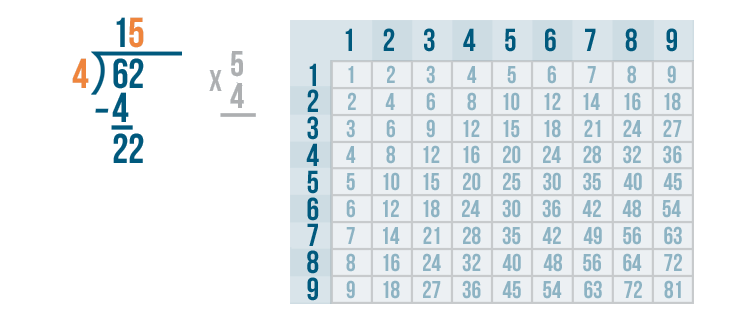
Now we need to multiply the 5 and 4 .
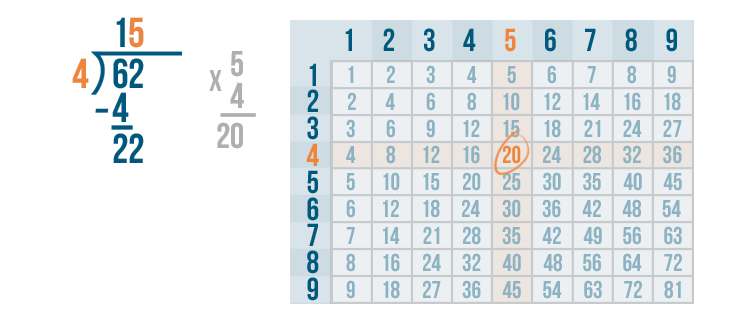
5 x 4 is 20 .
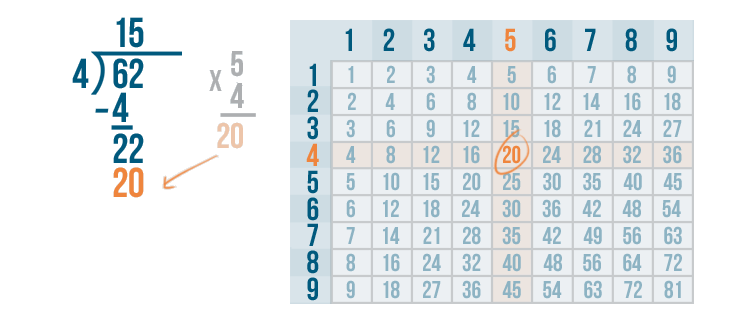
We'll write 20 beneath the 22 .
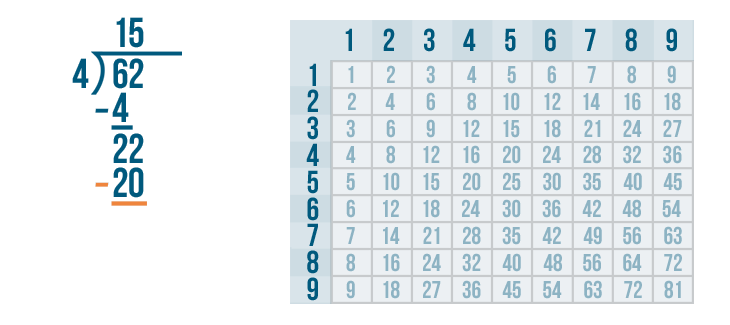
Now it's time to solve 22 - 20 .
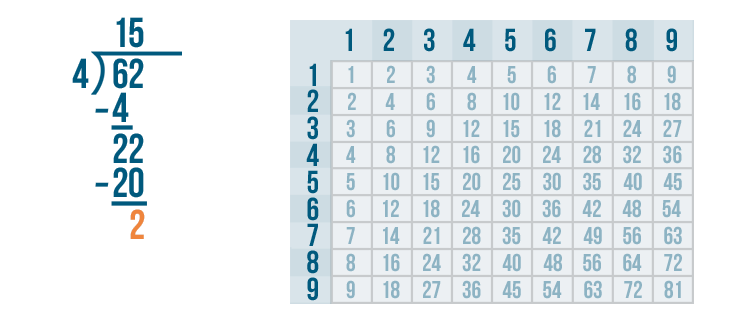
22 - 20 is 2 . We'll write 2 beneath the line directly below the 2 and 0 .
The answer to the last subtraction problem is more than zero, so we'll look under the bracket to see if there is another digit we can bring down.
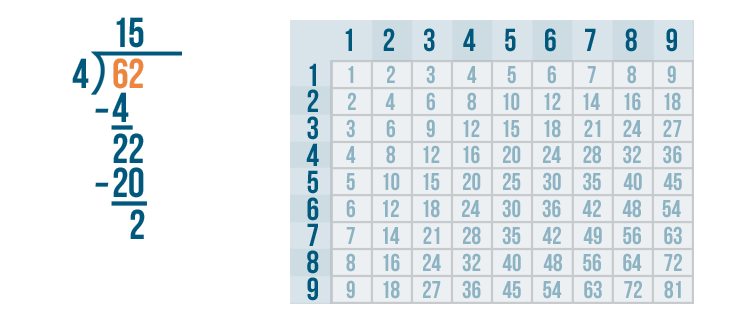
We've divided both of those digits. That means there are no more digits to bring down. But if we write another digit next to 62 , we could bring that digit down.
We don't want to make the 62 any larger. That would change our problem. We only had 62 bones to divide.
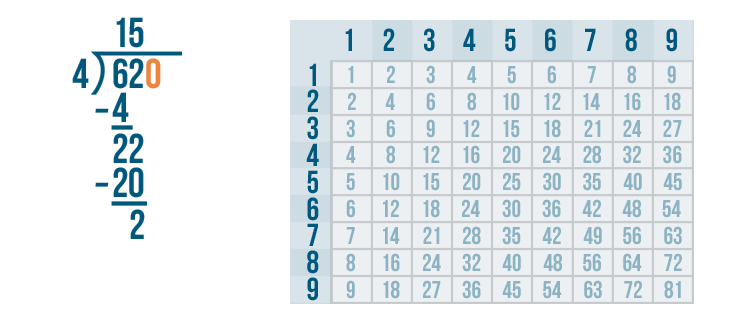
So next to the 62 , we'll write the number that means nothing: 0 .
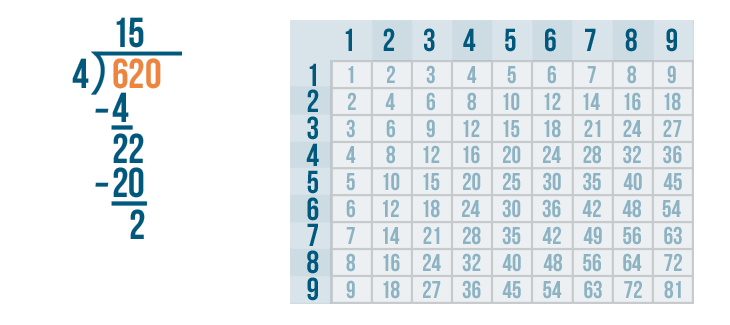
But that changes 62 into a larger number: 620 . That won't work.
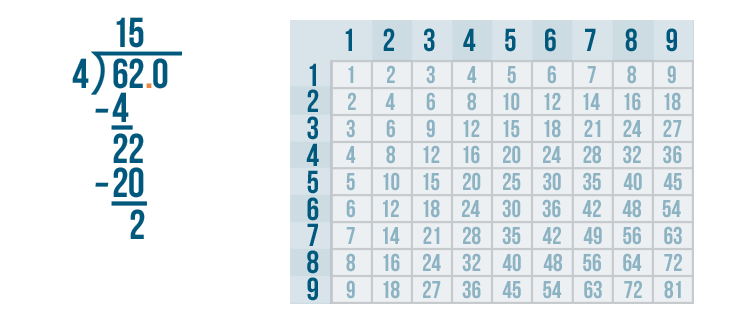
So to keep the value of 62 this same, we'll add a decimal point between the 62 and the 0 .
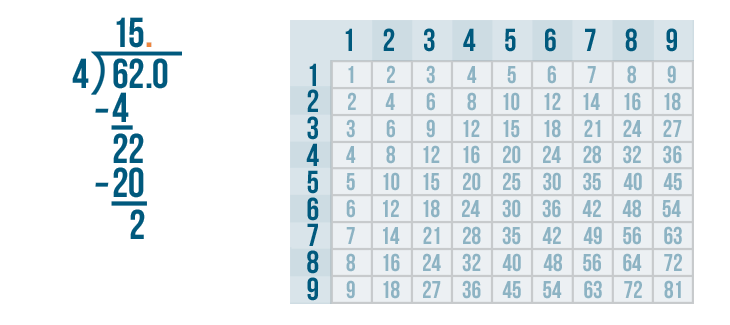
This means our quotient needs a decimal as well. So we'll write a decimal point next to the 15 directly above the other decimal.
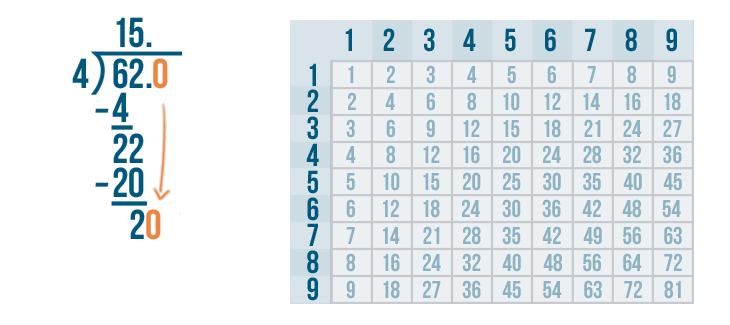
Now we can continue to solve the problem. We'll bring the 0 down and rewrite it next to the 2 .
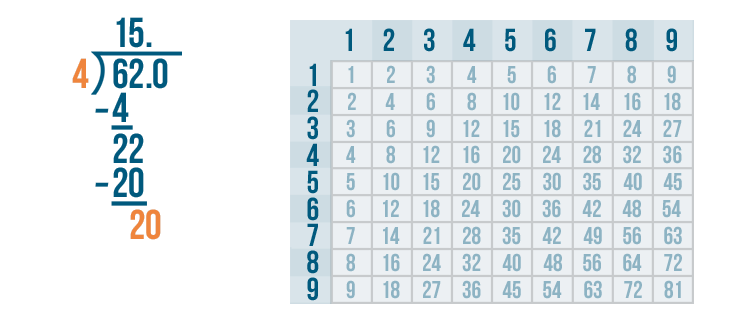
Let's figure out how many times 20 can be divided by 4 .
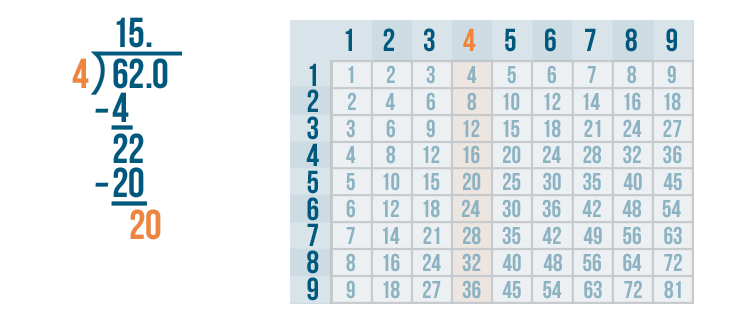
Look at the 4's column. 20 is the number we are dividing, so we'll find the number that is the closest to 20 but not larger than 20 .
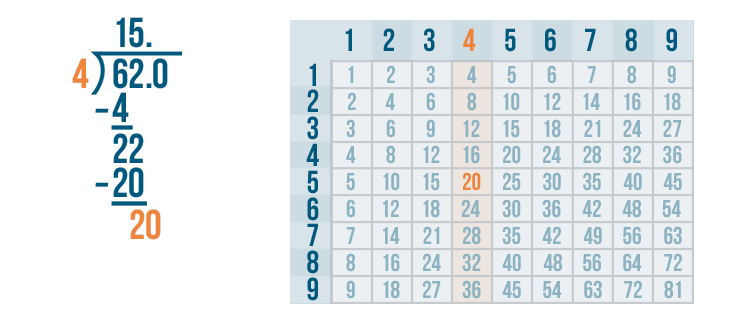
The 4's column has a 20 . That's as close as we can get!
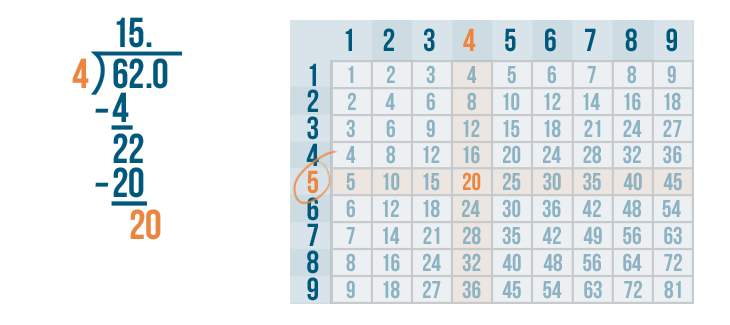
Now we find the row 20 is located in. It's the 5's row. 4 goes into 20 five times.
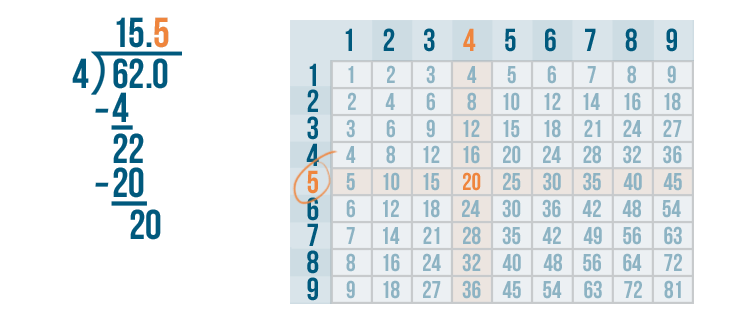
We'll write 5 above the 0 .
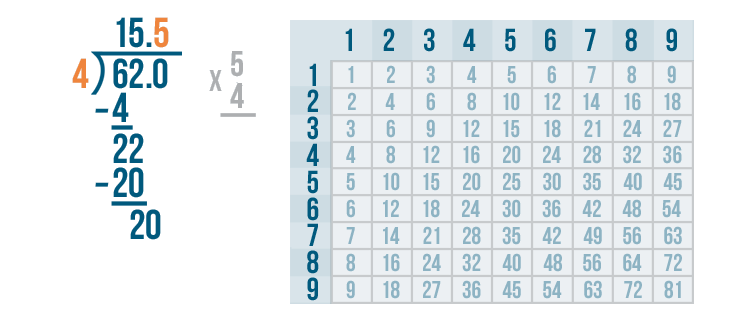
Now it's time to multiply the 5 and 4 .
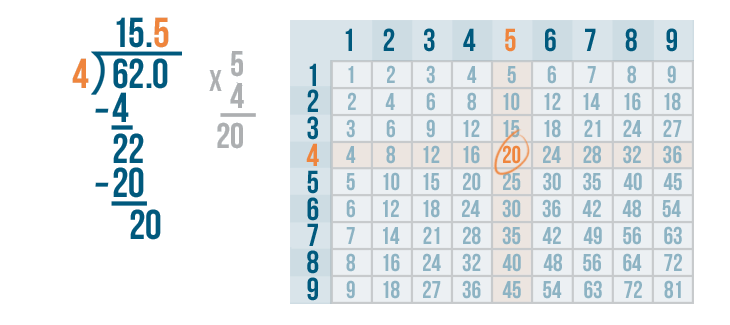
Write 20 beneath the 20 .
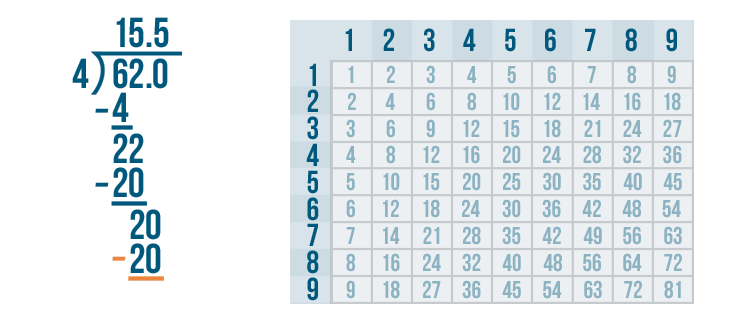
Time to solve 20 - 20 .
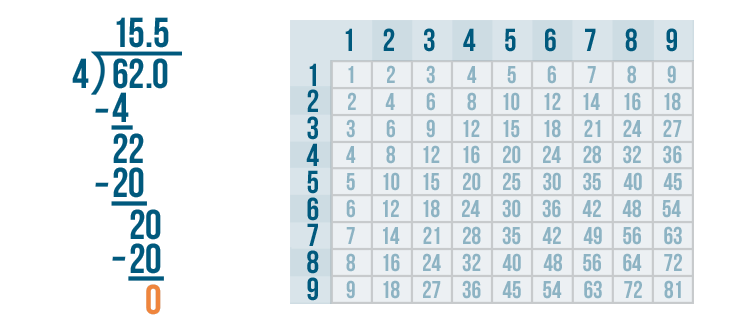
20 - 20 = 0 . Write 0 below the line directly below the 0 and 0 .
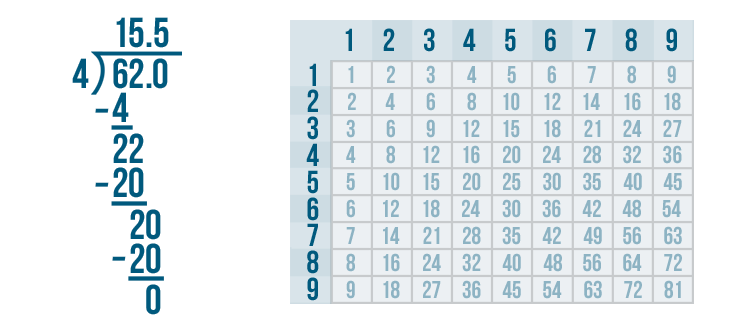
The answer to the subtraction problem is 0 . That means we have completed the problem. So 62 / 4 = 15.5 .
Sometimes, you may notice that a decimal can start to repeat as you continue to add zeros under the division bracket. This is known as a repeating decimal. When this happens, you can place a horizontal line over the digit that repeats.
Look at the image below. A horizontal line has been placed over the repeating digit.
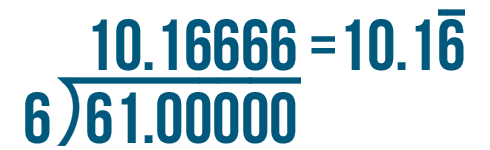
Another way to handle a repeating decimal is to round it. Rounding creates a new number that has a value close to the original number.
When rounding a repeating decimal, you'll reduce the number of digits that come after the decimal point. First, decide which digit you are rounding to. Then look at the digit to the right of it. If the digit is 5 or more, increase the rounded digit by 1. If it is 4 or less, the rounded digit stays the same. The other digits after the rounded digit are not written.
Look at the image below. In this case, each of these repeating decimals has been rounded to the second digit after the decimal point.

Find the decimal quotient for each of the long division problems below.
Checking your work
Checking your work after you divide is a good habit to develop. Checking helps you know that your answer is correct. To check the answer to a division problem, you'll need to use multiplication.

Let's look at this problem: 54 / 6 = 9 .
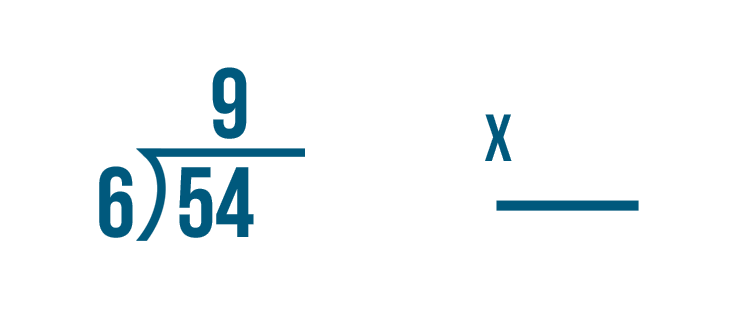
How do we know that 9 is the correct answer? We can check by multiplying.
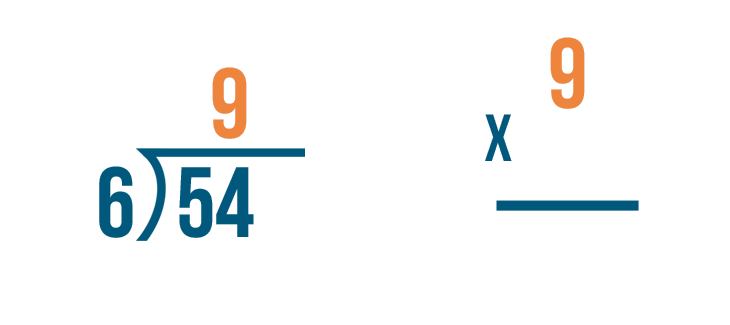
Let's set up our multiplication problem. First, we'll write the quotient. That means we'll write 9 .
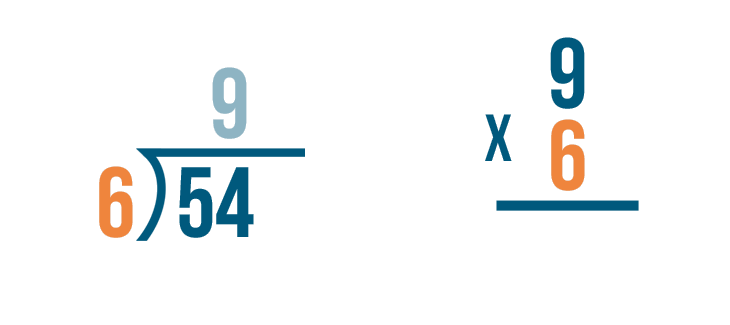
Next, we'll multiply the number that we divided by, 6 .
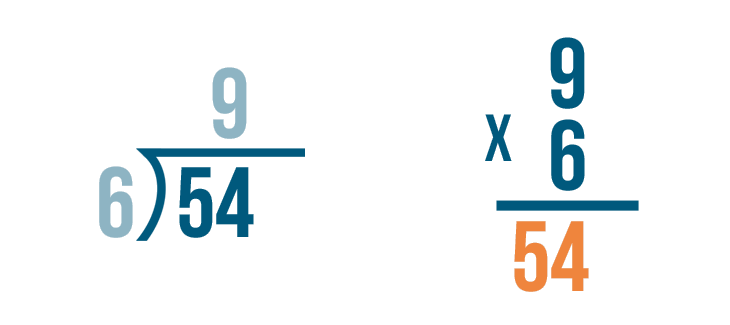
Time to multiply. 9 x 6 = 54 .
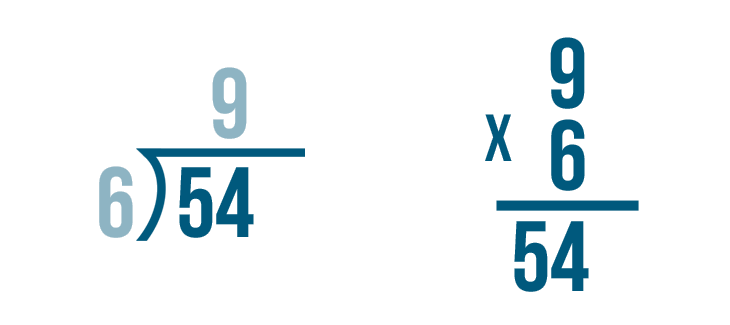
If we divided correctly, the answer will match the larger number in the division problem.
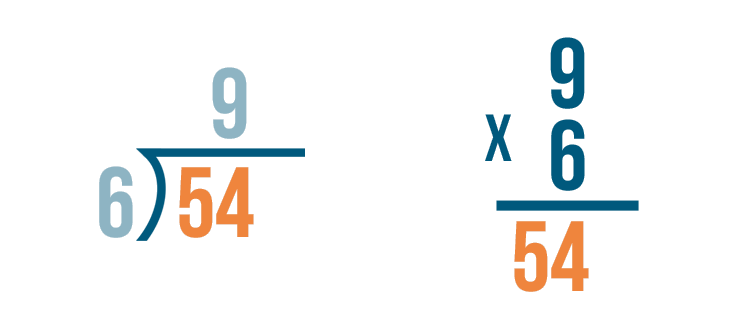
They are both 54 . We checked the problem, and it was correct!
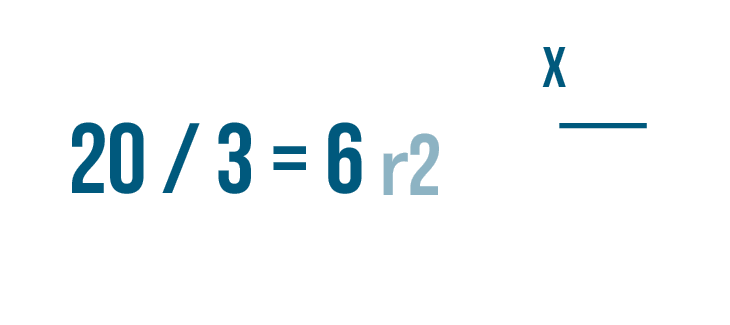
Let's try checking another problem. This time, the quotient has a remainder: 20 / 3 = 6 r2 .
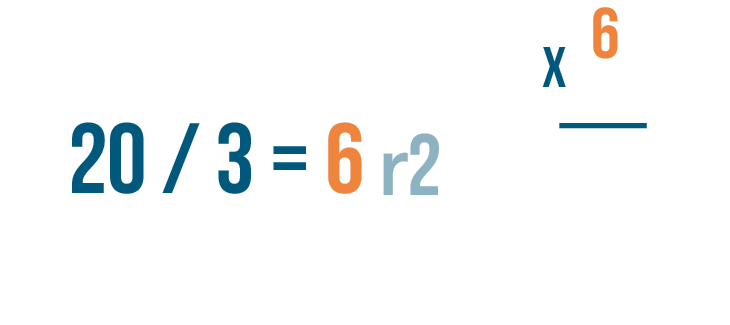
Let's set up our multiplication problem. First write the quotient without the remainder. That's 6 .
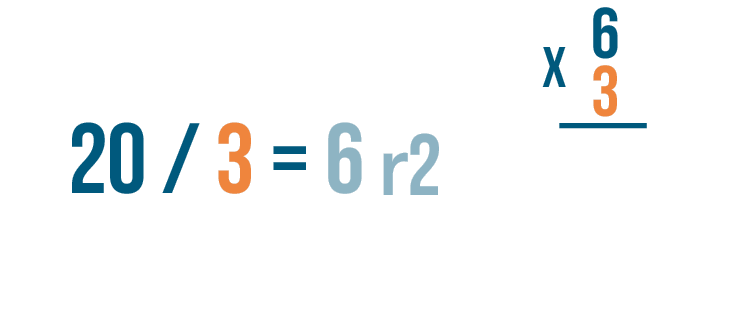
Then multiply the amount that the larger number was divided by, 3 .
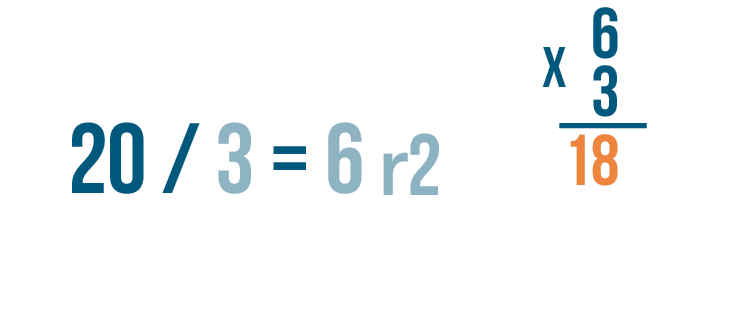
Now it's time to multiply. 6 x 3 = 18 .
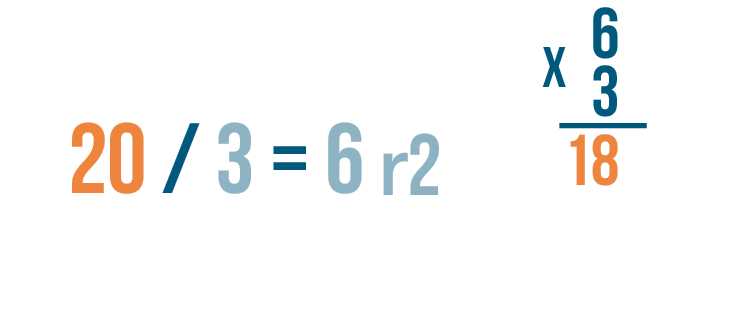
Let's check to see if our answer matches the larger number in the division problem — 18 and 20 . No, they aren't equal.
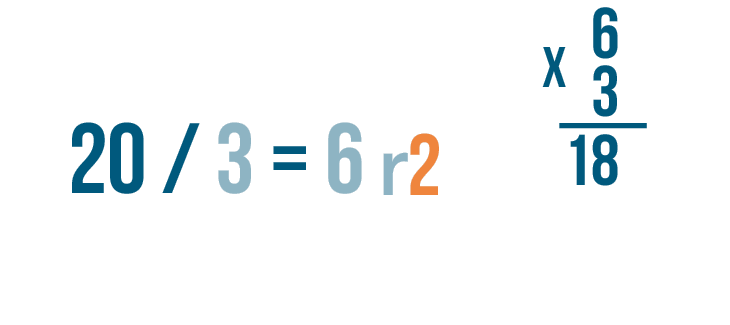
That may be because we haven't included the remainder, 2 .
Since the answer to the division problem has a remainder...
Since the answer to the division problem has a remainder... just multiplying should give you a number less than the original number.
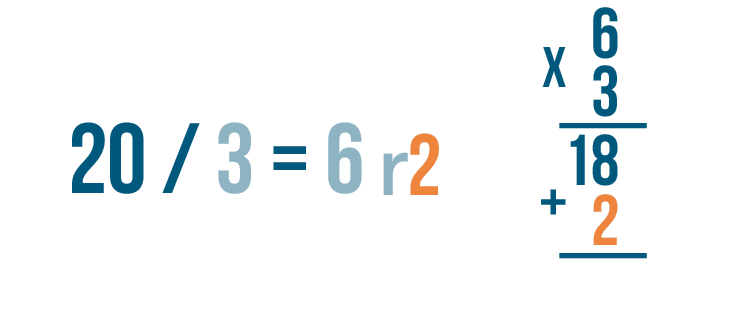
We'll set up an addition problem to add the 2 to 18 .
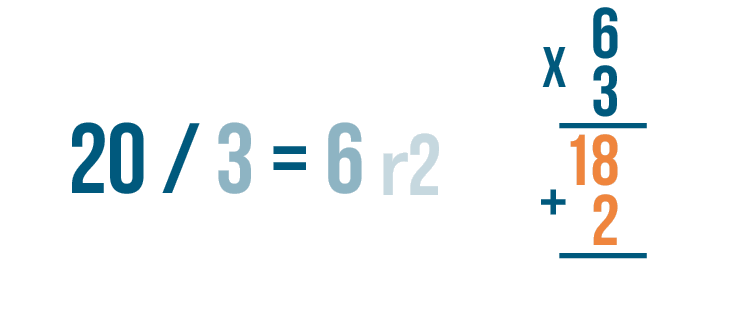
Now add 18 and 2 .
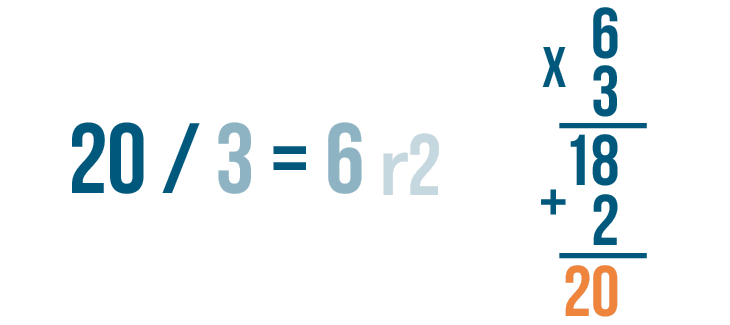
18 + 2 is 20 .
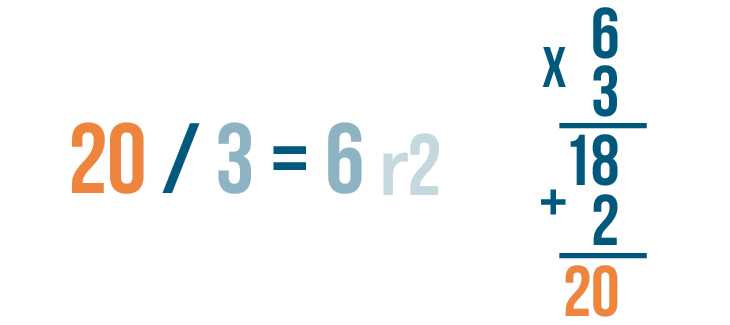
Finally, check to see if 20 matches the larger number in the division problem. It does!
In the slideshow, we used multiplication to check our division. The answer to the multiplication problem should always be the same as the larger number in the division problem. If your two answers don't match, check to see if you added the remainder. If your answers are still different, you might have made a mistake the first time you were dividing. Try solving the problem again.
Long division with decimals
In this lesson, you also learned how to solve division problems that have a decimal in the answer. Checking your work for this type of problem is similar to checking other division problems. You'll follow the same steps.
We'll try checking this problem: 57 / 5 = 11.4 .
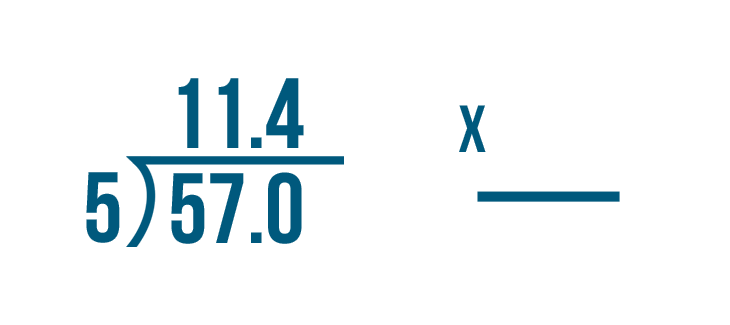
Let's set up our multiplication problem.
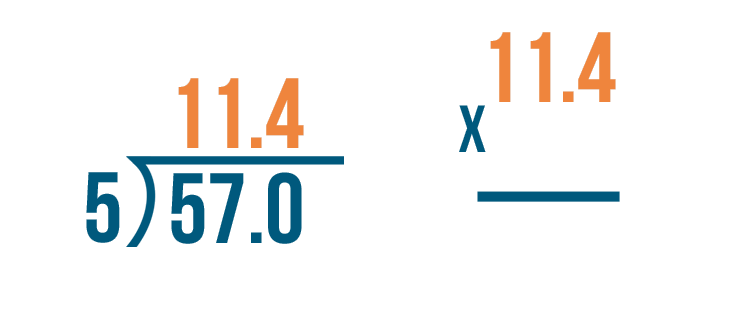
We'll write the decimal quotient, 11.4 .
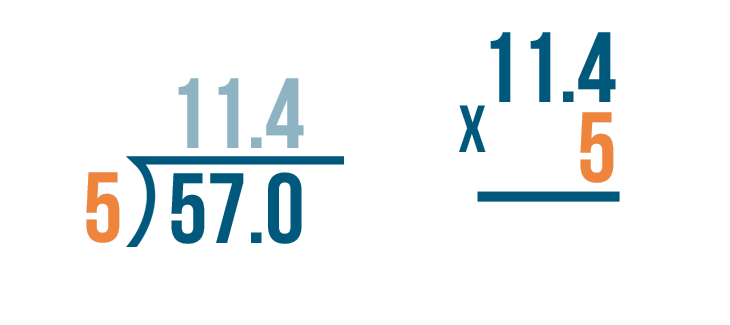
Next, we'll multiply the number that we divided by, 5 .
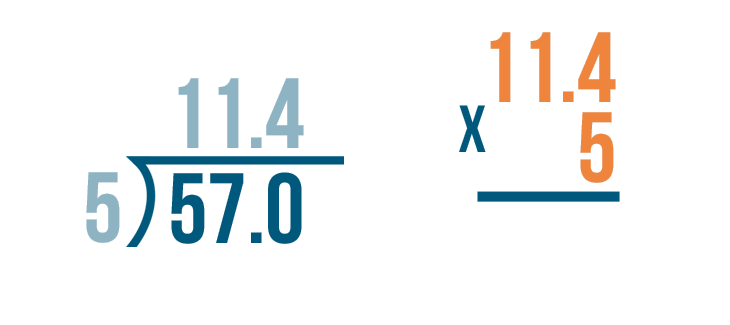
Now it's time to multiply: 11.4 x 5 .
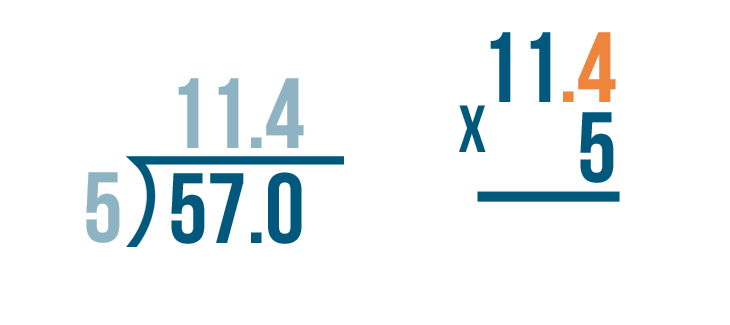
Since the quotient had one digit to the right of the decimal point...
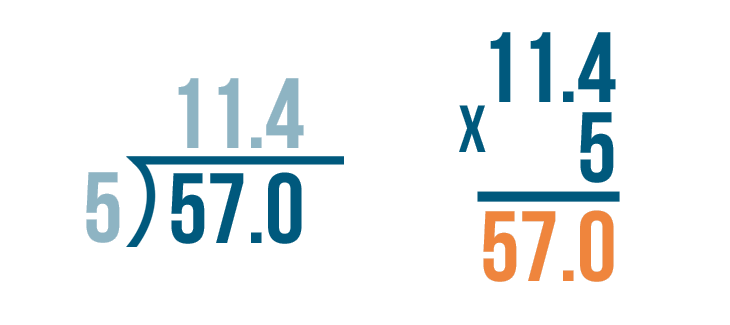
Since the quotient had one digit to the right of the decimal point... we write the answer with one digit to the right of the decimal point. 11.4 x 5 = 57.0 .
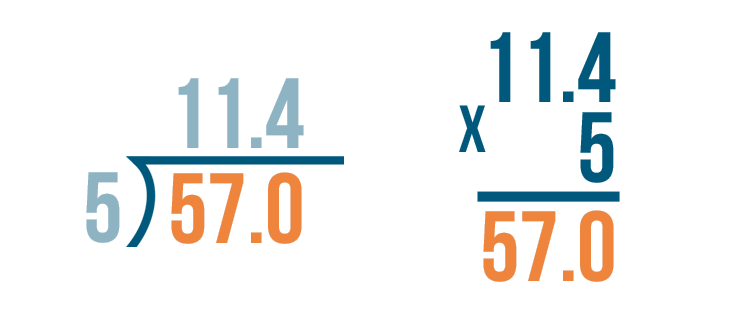
Finally, we'll check to see if 57.0 matches the larger number in our division problem. They are the same. Our answer was correct.
Practice division by solving these problems. There are 3 sets of problems. Each set has 5 problems.
Set 2: Type your answer using remainders.
Set 3: type your answer using decimals..
/en/multiplicationdivision/video-division/content/
- Homework Help
- Article Directory
How to Solve Division Problems and Find the Right Answer
- /
Finding the right answer when you're dividing can be tricky. Keep reading to learn some tips and tricks for getting the correct solution to your division problems!
Getting Division Problems Right
Know how to solve.
The first step in getting division problems right is using the correct process to solve them. When you're working with long division problems, it's important to have the basic division facts memorized. Use flashcards to master all of the division facts within 100.
It also helps to know that division is the inverse of multiplication. This means you can multiply the quotient of a division problem (the answer) by the divisor (number you're dividing by) to get the dividend (number being divided). For instance, in the problem 12 ÷ 3 = 4, 12 is the dividend, 3 is the divisor and 4 is the quotient, so 4 x 3 = 12.
Once you've mastered your basic division facts, the next step is to get a handle on long division. One of the most challenging aspects of dividing larger numbers is estimating each digit of the answer. For instance, when you're dividing 645 by 9, you'll start by estimating how many times 9 goes into 64. Below are several techniques you can use to help you estimate:
Checking Your Answer
Even if you've followed the correct procedure to solve your division problem, it's still possible that you made a small mathematical error somewhere along the line. Fortunately, there's a very effective way to check that your answer is correct. Follow these steps:
Other Articles You May Be Interested In
Division can be confusing, especially when working with larger numbers. Read on to learn how to help your fifth grader remember how to divide many different lengths of numbers.
We Found 7 Tutors You Might Be Interested In
Huntington learning.
- What Huntington Learning offers:
- Online and in-center tutoring
- One on one tutoring
- Every Huntington tutor is certified and trained extensively on the most effective teaching methods
- What K12 offers:
- Online tutoring
- Has a strong and effective partnership with public and private schools
- AdvancED-accredited corporation meeting the highest standards of educational management
Kaplan Kids
- What Kaplan Kids offers:
- Customized learning plans
- Real-Time Progress Reports track your child's progress
- What Kumon offers:
- In-center tutoring
- Individualized programs for your child
- Helps your child develop the skills and study habits needed to improve their academic performance
Sylvan Learning
- What Sylvan Learning offers:
- Sylvan tutors are certified teachers who provide personalized instruction
- Regular assessment and progress reports
Tutor Doctor
- What Tutor Doctor offers:
- In-Home tutoring
- One on one attention by the tutor
- Develops personlized programs by working with your child's existing homework
- What TutorVista offers:
- Student works one-on-one with a professional tutor
- Using the virtual whiteboard workspace to share problems, solutions and explanations
Find the Perfect Tutor
Our commitment to you, free help from teachers, free learning materials, helping disadvantaged youth, learning tools.
- Make learning fun with these online games!
- Looking for ways to bring learning home? Check out our blog.
Want to Help Your Child Learn?
More articles.
- Homework Help for Elementary School Math
- Developmental Domains: Learning and Awareness in Children
- Common Behavioral Problems in Children
- Creating Your Own Math Problems and Worksheets
- Common Problems in Reading Faced by Older Students with Learning Disabilities
- How Practice Problems and Worksheets Can Alleviate Math Anxiety
- Do You Think the Drop Out Age Should Be Raised?
- Doing More with Less: Rural Schools and Student Health
- Elementary Grammar: Learning Nouns, Verbs, Adjectives and Other Parts of Speech
- Transform Your Child's Poor Report Card
- State Regulations Surrounding Homeschooling
- The Effects of Dyslexia on Math Education
- What Good Is Homework Anyway?
- Making the Most of Reading to or with Your Children: Part 2--Preschool
- Middle School Math Help
- Symptoms and Causes of Math Anxiety
- Ways for Students to Manage Stress During High School
- Elementary Reading Help: Helping your 5th and 6th Grader Understand Poetry
- The Importance of Developmental Toys and Games for Babies and Toddlers
- 3rd Grade Math Help
- Third Grade Writing Prompts
- Now Pratice for 8th Grade Crct
- Multiplication Word Problems Third Grade
- Word Problems Involving Fractions
- Are Math Struggles Due to Poor Instruction or Real Learning Disabilities
- Division and Muliplications Problems
- Examples of Division Problems
- Elementary Division Problems
- 5th Grade Long Division Problems
- Division Word Problems
- Free Division Word Problems
- Fifth Grade Division Problems
- Fourth Grade Long Division Problems
- 4th Grade Division Problems
- Division Problems for 10 Year Olds
- Privacy Policy
- Resource Directory
© 2003 - 2024 All other trademarks and copyrights are the property of their respective owners. All rights reserved.
Math teaching support you can trust

resources downloaded

one-on-one tutoring sessions

schools supported
[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities
Engage your students with our ready-to-go packs of no-prep games and activities for a range of abilities across Kindergarten to Grade 5!
8 Long Division Examples And How To Solve Them: Explained For Elementary School
Sophie bartlett.
Long division examples are a great way to introduce and teach long division to 5th grade. Due to the number of steps involved, it can be tricky for students to get their head around the method. In this article, we provide you with long division examples to practice with upper elementary school students, plus expert guidance on how to solve them.
When teaching a new mathematical concept, worked examples are helpful in the same way that a ‘WAGOLL’, or model text, is helpful in writing lessons – children can see what the end result should look like. They can be used as a success criteria for mathematical problem solving- and long division is no exception.
How to solve long division problems
Long division example step by step, 5th grade long division examples, easy long division examples, hard long division examples, top tips for working through long division examples, teaching long division worksheets.
Download this free pack of long division worksheets for grades 3-5.
In any division , the first number (the amount being divided) is called the dividend ; the second number (whatever the dividend is being divided by), is called the divisor ; the answer is called the quotient .
Long division is typically used when dividing larger numbers where the divisor is a two-digit number, although it can also be used with one-digit divisors.
There are five steps that can be used to simplify the long division method. These long division steps are:
- Bring the next digit down
Before beginning long division questions, it is helpful to list 9 multiples of the divisor to reduce the cognitive demand when working through the division method.
Listing multiples can be done through repeated addition or partitioning (partition the tens and ones, list the multiples of each and then add each constituent part).
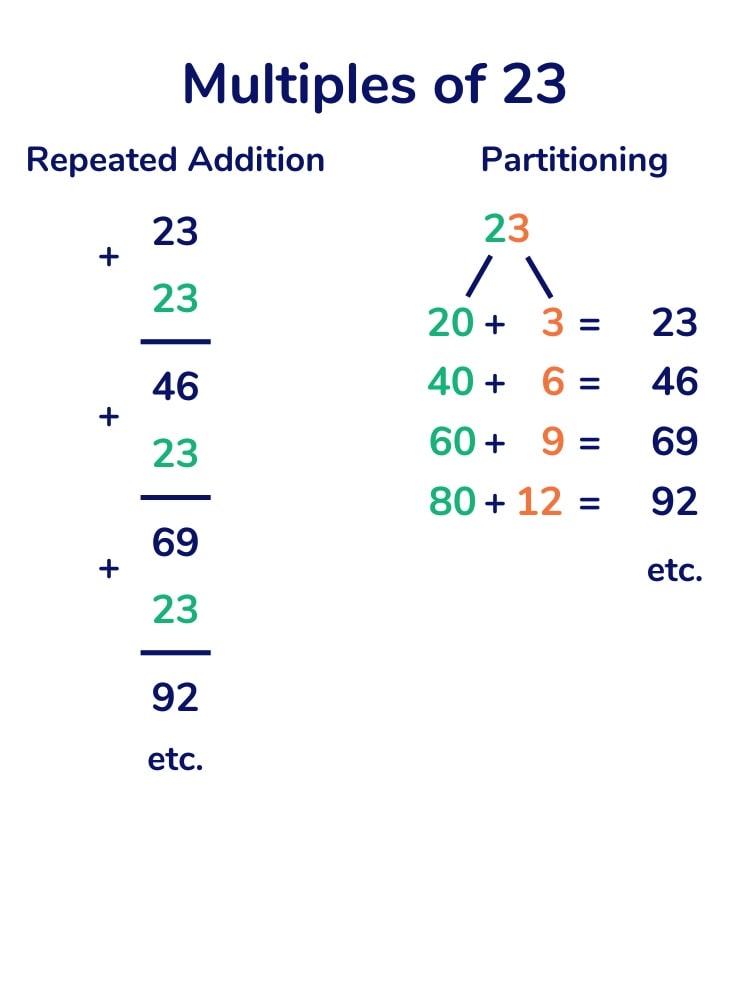
See how the five division steps are then applied using this example below (this layout is also called the bus stop method ):
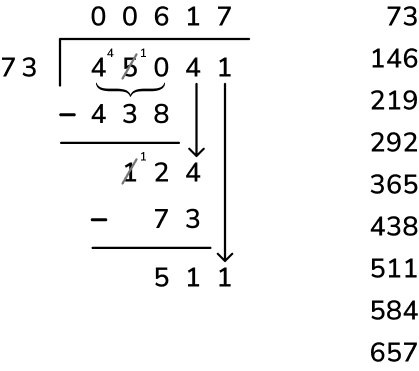
1. Divide : Starting with the first digit of the dividend, divide 4 ten thousands by 73. We cannot do this, so a 0 is placed above the 4 and instead we see the 4 ten thousands as 40 thousands alongside the 5 thousands (the next digit of the dividend).
Now, divide 45 thousands by 73, which also can’t be done, so we place another 0 above the 5 and see the 45 thousands as 450 hundreds. We can finally do 450 hundreds divided by 73, which is 6. This digit is placed above the 0 tens and becomes the first digit of the quotient.

2. Multiply : We need to calculate the remainder for this first step of the division – to do this, first multiply the first digit of the quotient, 6 hundreds, by the divisor, 73, to get 438 hundreds (this is where our list of multiples really helps). Place this underneath the dividend, making sure to align the place values correctly.
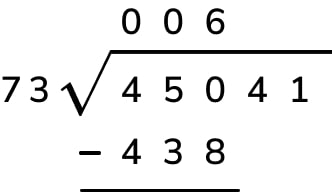
3. Subtract : To finish calculating the remainder for this first step of the division, finally subtract 438 hundreds from 450 hundreds to get 12 hundreds.
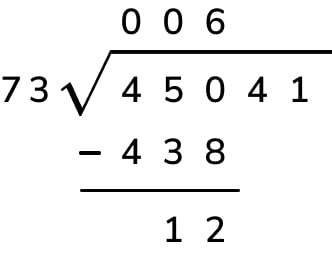
4. Bring the next digit down : In long division, we just bring the next digit of the quotient down – making sure to keep the numbers aligned when the digits above it.
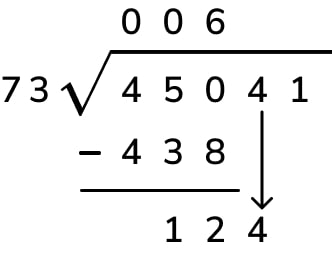
5. Repeat: Now we start the division process again from…
Step 1: divide (divide 124 tens by 73 and place the answer, 1 ten, in the quotient);
Step 2: multiply (multiply the next digit of the quotient, 1 ten, by the divisor, 73, and place the answer, 73 tens, underneath the 124 tens);
Step 3: subtract (finish calculating the remainder to this next step by subtracting 73 tens ones from 124 tens to get 51 tens);
Step 4: bring the next digit down (51 tens plus 1 one becomes 511 ones)
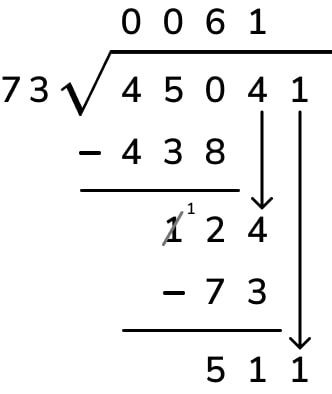
Step 5: repeat (divide 511 ones by 73 to get 7 ones and place this in the quotient as the last digit; multiply 7 ones by 73 to get 511 ones; subtract this from 511 ones to calculate the remainder, which is 0; there is now no next digit to bring down so, as the remainder is now 0, the calculation is complete)
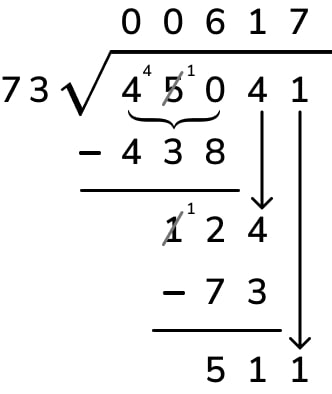
This example has a whole number quotient, but the long division method can be done with remainders .
This example shows how it would be laid out with a decimal remainder (when calculating the remainder, don’t forget to include the decimal point in the quotient as well as in the dividend).
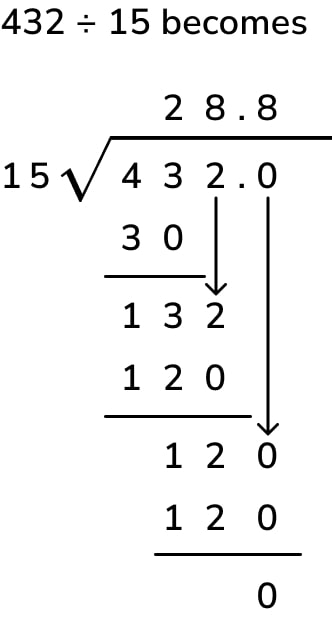
Long division examples
Providing worked examples is helpful when introducing new mathematical concepts to children. Children can use these as success criteria for their own work.
In Third Space Learning’s one-to-one tutoring sessions, tutors model new mathematical methods step by step to support and scaffold children’s learning. We find this is a great way to help students understand and practice the steps involved in long division.
Below, we provide a range of worked long division examples to suit your students’ needs. You can learn more about Third Space Learning and our math interventions for elementary school here.
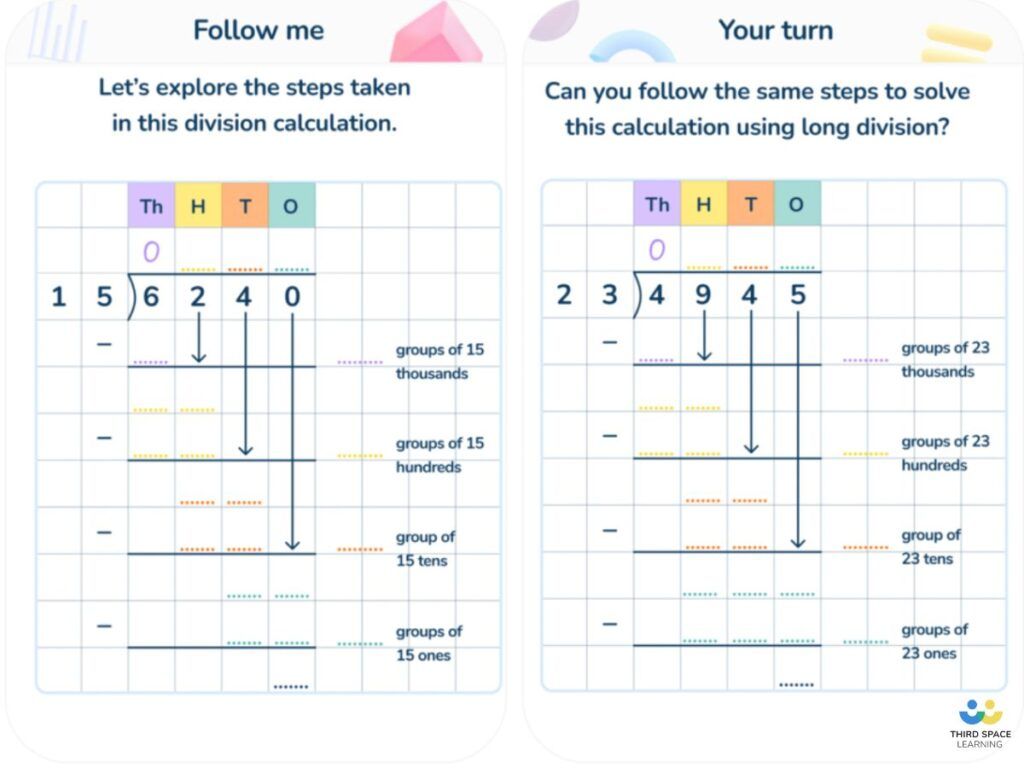
For more support teaching the long division method , read our blog here.
Children aren’t required to do long division until 5th grade. Here are some worked examples of long division problems.
1. 8,051 ÷ 83
Don’t forget to list the first 9 multiples of 83 to help you solve it.
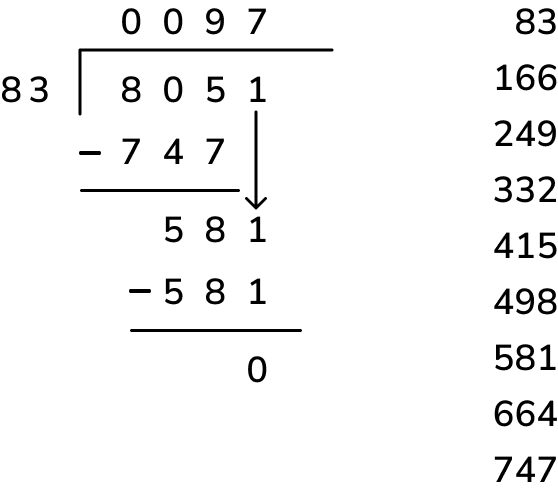
Step by step long division
- We cannot divide 8 thousands by 83
- Write zero in the thousands place of your answer line
- 80 hundreds cannot be divided by 83
- Write zero in the hundreds place of your answer line
- 805 tens divided by 83 is 9 tens
- Write nine in the tens place of your answer line
- Subtract 747 tens (9 x 83) from 805 tens to get 58 tens
- Exchange the 58 tens for ones so now we have 581 ones
- 581 ÷ 83 = 7
- Write 7 in the ones place of your answer line
- Subtract 581 (7 x 83) from 581 to get zero. You have no remainders.
- Check your answer – 83 x 97 = 8051
2. Adam is making booklets. Each booklet must have 34 sheets of paper. He has 2 packets of paper. There are 500 sheets of paper in each packet. How many complete booklets can Adam make from 2 packets of paper?
Final answer is: 2 packets of 500 sheets = 1,000 sheets. 1,000 ÷ 34 = 29 complete booklets
1. Eggs are put in trays of 12. The trays are packed in boxes. Each box contains 180 eggs. How many trays are in each box?
You could use long division for 180 ÷ 12 as we’re dividing by two digits, but in this case it could be just as simple to use multiples of 12 to work it out. We know 12 x 5 = 60, and there are 3 lots of 60 in 180, so there must be 15 lots of 12 in 180. The answer is therefore 15 trays.
2. A lottery donates $504 to 21 different charities. How much does each charity get?
While 504 ÷ 21 may seem tricky at first glance, it’s actually fairly simple as the divisor is an ‘easy’ number to list multiples of – children may be able to complete it without having to list the multiples first and by calculating them mentally instead.
1. A grocer needs to order 1,176 apples. Apples are sold in boxes containing 28 trays, with 14 apples on each tray. How many boxes of apples does the grocer need to order?
28 trays each with 14 apples = 28 x 14 = 392 apples. We could then do 1,176 ÷ 392, but this is a pretty tricky calculation! It would be better to do the long division in two chunks – first dividing by 28, then by 14 (or the other way round – the answer would be the same!) 1176 ÷ 28 = 42, then 42 ÷ 14 = 3, so the grocer would need to order 3 boxes of apples.
2. A factory makes 4,923 teddy bears, and the bears are packed in boxes of 37. How many bears are left over?
4,923 ÷ 37 = 133r2, so there will be 2 bears left over.
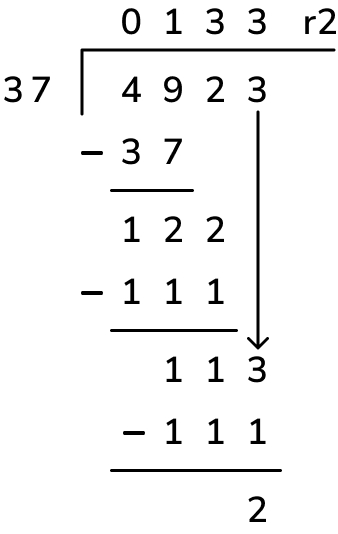
3. 427 children visit a castle. They go in groups of 15. One group has less than 15. Every group of children has one adult with them. How many adults will need to go?
427 ÷ 15 = 28r7, as shown below. This means there are 28 ‘full’ groups (of 15 children) and one more group with only 7 children. There are therefore 29 groups overall, so 29 adults would be required to go. Read more here about how to complete division with remainders .
For more long division questions and long division worksheets to support your teaching, check out our blogs.
- List 9 multiples of the divisor before beginning the division to reduce cognitive load
- Ensure you align the place values correctly (each digit of the quotient going above the appropriate digit of the dividend)
- During the ‘divide’ step, if at any point your divisor will not fit into the dividend, don’t forget to include the 0!
In the example below, we’ve first correctly identified that 52 hundreds divided by 13 is 4 hundreds. This gives us a remainder of 0, but when we bring the next digit down it makes 9 tens.
We can’t divide 9 tens by 13, so here, we’ve incorrectly brought down the next digit as well to make 91 ones. 91 ones ÷ 13 is 7, but this 7 has been placed as the wrong digit in the quotient.
This is what the division should have looked like – after 52 hundreds ÷ 13 = 4 hundreds with 0 remainder, 9 tens divided by 13 = 0, so the 0 has to be placed as the next digit of the quotient (above the 9 in the dividend).
We can then continue with the method – multiply (0 tens x 13 = 0 tens), subtract (9 tens – 0 tens = 9 tens) and bring the next digit down (1 one, to make 91 ones). This takes us to the final step now (91 ones ÷ 13 to get 7 ones) which reaches the correct answer of 407, as opposed to 47 in the misconception above.
During the ‘subtract’ step, if the result of your subtraction (once you’ve brought down the next digit of the dividend) is bigger than 9 multiples of the divisor, something has gone wrong! In the example below, we’ve incorrectly calculated that 42 tens divided by 15 is only 1 ten.
This gave us a remainder of 27 tens + 7 ones, which is 277 ones – we can fit way more than 9 groups of 15 into 277 ones, so we have gone wrong somewhere!

The first digit of the quotient should actually be 2 as 42 tens divided by 15 is 2 tens with 12 tens remaining, as shown below.
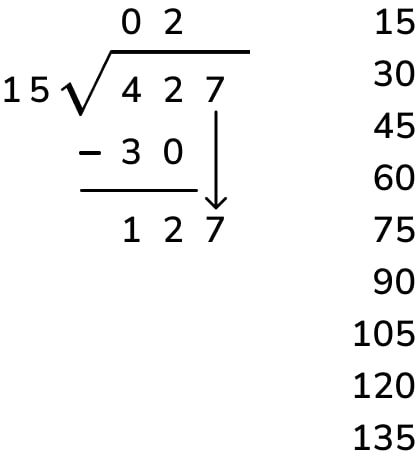
- Use the inverse to check your answer at the end: in a division without a remainder, simply multiply the quotient by the divisor and you should get the dividend (e.g. if you calculate that 1,176 ÷ 28 = 42, then 42 x 28 should = 1,176). In division with a remainder, multiply the quotient by the divisor and then add the remainder – the result should, again, be the dividend (e.g. if you calculate that 427 ÷ 15 = 28r7, then 28 x 15 + 7 should = 427)
Do you have students who need extra support in math? Give your students more opportunities to consolidate learning and practice skills through personalized math tutoring with their own dedicated online math tutor. Each student receives differentiated instruction designed to close their individual learning gaps, and scaffolded learning ensures every student learns at the right pace. Lessons are aligned with your state’s standards and assessments, plus you’ll receive regular reports every step of the way. Personalized one-on-one math tutoring programs are available for: – 2nd grade tutoring – 3rd grade tutoring – 4th grade tutoring – 5th grade tutoring – 6th grade tutoring – 7th grade tutoring – 8th grade tutoring Why not learn more about how it works ?
The content in this article was originally written by primary school teacher Sophie Bartlett and has since been revised and adapted for US schools by elementary math teacher Christi Kulesza.
Math Intervention Pack Operations and Algebraic Thinking [FREE]
Take a sneak peek behind our online tutoring with 6 intervention lessons designed by math experts while supporting your students with Operations and Algebraic Thinking.
As with our full library of lessons, each one includes questions to ask, ways to support students when they are stuck, and answers to the given questions.
Privacy Overview
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Mathematics
- Multiplication and Division
How to Do Division
Last Updated: January 14, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Grace Imson, MA and by wikiHow staff writer, Christopher M. Osborne, PhD . Grace Imson is a math teacher with over 40 years of teaching experience. Grace is currently a math instructor at the City College of San Francisco and was previously in the Math Department at Saint Louis University. She has taught math at the elementary, middle, high school, and college levels. She has an MA in Education, specializing in Administration and Supervision from Saint Louis University. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 498,498 times.
Division is one of the 4 major operations in arithmetic, alongside addition, subtraction, and multiplication. In addition to whole numbers, you can divide decimals, fractions, or exponents. You can do long division or, if one of the numbers is a single digit, short division. Start by mastering long division, though, because it is the key to the entire operation.
Long Division

- Sample problem #1 (beginner): 65 ÷ 5 . Place the 5 outside the division bar, and the 65 inside it. It should look like 5厂65 , but with the 65 underneath the horizontal line.
- Sample problem #2 (intermediate): 136 ÷ 3 . Place the 3 outside the division bar, and the 136 inside it. It should look like 3厂136 , but with the 136 underneath the horizontal line.

- In sample problem #1 ( 5厂65 ), 5 is the divisor and 6 is the first digit of the dividend (65). 5 goes into 6 one time, so place a 1 on the top of the divisor bar, aligned above the 6.
- In sample problem #2 ( 3厂136 ), 3 (the divisor) does not go into 1 (the first digit of the dividend) and result in a whole number. In this case, write a 0 above the division bar, aligned above the 1.

- In sample problem #1 ( 5厂65 ), multiply the number above the bar (1) by the divisor (5), which results in 1 x 5 = 5 , and place the answer (5) just below the 6 in 65.
- In sample problem #2 ( 3厂136 ), there is a zero above the division bar, so when you multiply this by 3 (the divisor), your result is zero. Write a zero on a new line just below the 1 in 136.

- In sample problem #1 ( 5厂65 ), subtract the 5 (the multiplication result in the new row) from the 6 right above it (the first digit of the dividend): 6 - 5 = 1 . Place the result (1) in another new row right below the 5.
- In sample problem #2 ( 3厂136 ), subtract 0 (the multiplication result in the new row) from the 1 right above it (the first digit in the dividend). Place the result (1) in another new row right below the 0.

- In sample problem #1 ( 5厂65 ), drop the 5 from 65 down so that it’s beside the 1 that you got from subtracting 5 from 6. This gives you 15 in this row.
- In sample problem #2 ( 3厂136 ), carry down the 3 from 136 and place it beside the 1, giving you 13.

- To continue 5厂65 , divide 5 (the dividend) into the new number (15), and write the result (3, since 15 ÷ 5 = 3 ) to the right of the 1 above the division bar. Then, multiply this 3 above the bar by 5 (the dividend) and write the result (15, since 3 x 5 = 15 ) below the 15 under the division bar. Finally, subtract 15 from 15 and write 0 in a new bottom row.
- Sample problem #1 is now complete, since there are no more digits in the divisor to carry down. Your answer (13) is above the division bar.

- For 3厂136 : Determine how many times 3 goes into 13, and write the answer (4) to the right of the 0 above the division bar. Then, multiply 4 by 3 and write the answer (12) below the 13. Finally, subtract 12 from 13 and write the answer (1) below the 12.

- For 3厂136 : Continue the process for another round. Drop down the 6 from 136, making 16 in the bottom row. Divide 3 into 16, and write the result (5) above the division line. Multiply 5 by 3, and write the result (15) in a new bottom row. Subtract 15 from 16, and write the result (1) in a new bottom row.
- Because there are no more digits to carry down in the dividend, you’re done with the problem and the 1 on the bottom line is the remainder (the amount left over). Write it above the division bar with an “r.” in front of it, so that your final answer reads “45 r.1”.
Short Division

- In order to do short division , your divisor can't have more than one digit.
- Sample problem: 518 ÷ 4 . In this case, the 4 will be outside the division bar, and the 518 inside it.

- In the sample problem, 4 (the divisor) goes into 5 (the first digit of the dividend) 1 time, with a remainder of 1 ( 5 ÷ 4 = 1 r.1 ). Place the quotient, 1, above the long division bar. Place a small, superscript 1 beside the 5, to remind yourself that you had a remainder of 1.
- The 518 under the bar should now look like this: 5 1 18.

- In the sample problem, the number formed by the remainder and the second number of the dividend is 11. The divisor, 4, goes into 11 twice, leaving a remainder of 3 ( 11 ÷ 4 = 2 r.3 ). Write the 2 above the division line (giving you 12) and the 3 as a superscript number beside the 1 in 518.
- The original dividend, 518, should now look like this: 5 1 1 3 8.

- In the sample problem, the next (and final) dividend number is 38—the remainder 3 from the previous step, and the number 8 as the last term of the dividend. The divisor, 4, goes into 38 nine times with a remainder of 2 ( 38 ÷ 4 = 9 r.2 ), because 4 x 9 = 36 , which is 2 short of 38. Write this final remainder (2) above the division bar to complete your answer.
- Therefore, your final answer above the division bar is 129 r.2.
Dividing Fractions

- Your problem might be, for example, 3/4 ÷ 5/8 . For convenience, use horizontal instead of diagonal lines to separate the numerator (top number) and denominator (bottom number) of each fraction.

- In the sample problem, reverse 5/8 so the 8 is on top and the 5 is on the bottom.

- For example: 3/4 x 8/5 .

- In this case, the numerators are 3 and 8, and 3 x 8 = 24 .

- The denominators are 4 and 5 in the sample problem, and 4 x 5 = 20 .

- In the sample problem, then, 3/4 x 8/5 = 24/20 .

- 24: 1, 2, 3, 4 , 6, 8, 12, 24
- 20: 1, 2, 4 , 5, 10, 20
- 24/20 = 6/5 . Therefore, 3/4 ÷ 5/8 = 6/5

- In the sample problem, 5 goes into 6 one time with a remainder of 1. Therefore, the new whole number is 1, the new numerator is 1, and the denominator remains 5.
- As a result, 6/5 = 1 1/5 .
Dividing Exponents

- As a beginner, start with a sample problem in which both numbers with exponents already have the same base—for instance, 3 8 ÷ 3 5 .

- In the sample problem: 8 - 5 = 3 .

- Therefore: 3 8 ÷ 3 5 = 3 3 .
Dividing Decimals

- For the example 65.5 ÷ 0.5 , 0.5 goes outside the division bar, and 65.5 goes inside it.

- In the sample problem, you only need to move the decimal point over one spot for both the divisor and dividend. So, 0.5 becomes 5, and 65.5 becomes 655.
- If, however, the sample problem used 0.5 and 65.55, you’d need to move the decimal point 2 places in 65.55, making it 6555. As a result, you’d also have to move the decimal point in 0.5 2 places. To do this, you’d add a zero to the end and make it 50.

- In the sample problem, the decimal in 655 would appear after the last 5 (as 655.0). So, write the decimal point above the division line right above where that decimal point in 655 would appear.

- Divide 5 into the hundredths digit, 6. You get 1 with a remainder of 1. Place 1 in the hundredths place on top of the long division bar, and subtract 5 from 6 below the number six.
- Your remainder, 1, is left over. Carry the first five in 655 down to create the number 15. Divide 5 into 15 to get 3. Place the three above the long division bar, next to the 1.
- Carry down the last 5. Divide 5 into 5 to get 1, and place the 1 on top of the long division bar. There is no remainder, since 5 goes into 5 evenly.
- The answer is the number above the long division bar (131), so 655 ÷ 5 = 131 . If you pull out a calculator, you’ll see that this is also the answer to the original division problem, 65.5 ÷ 0.5 .
Practice Problems and Answers

Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/long_division.html
- ↑ https://www.k5learning.com/blog/step-step-guide-long-division
- ↑ https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/znmtsbk/articles/zqpddp3
- ↑ http://www.mathsisfun.com/fractions_division.html
- ↑ https://www.ck12.org/arithmetic/divide-fractions/lesson/Quotients-of-Fractions-MSM6/?referrer=concept_details
- ↑ http://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/variables-exponents-multiply.html
- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/dividing-decimals.html
- ↑ https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/zh7xpv4/articles/zwdc4xs
About This Article

To do simple division, think about how many times one number can go into another number. For example, 6 ÷ 2 is 3, because 3 goes into 6 two times. For larger numbers, it's helpful to spend time reviewing the multiplication tables. To do long division, write the number you want to divide under the division bar, and place the number you want to divide by outside of the bar. For example, if you want to calculate 72 ÷ 3, place 72 under the division bar and 3 outside of it. Then, calculate how many times 3 goes into the first number under the division bar. In this case, you’re calculating how many times 3 goes into 7. The answer is 2, with 1 left over. Write the number 2 above the bar, and the remainder – in this case, 1 – below the 7. Then, if there are any numbers left under the division bar, bring them down to the same row as the remainder. So in this case, you’d write a 2 beside the 1 to get 12. Then, repeat the process: how many times does 3 go into 12? In this example, 3 goes into 12 four times, so you’d write 4 on the line above the problem, beside the other numbers. Therefore, 72 ÷ 3 = 24. If you want to learn how to divide fractions, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Did this article help you?
Cori Landerson
Apr 22, 2017
Sep 12, 2023
Nov 2, 2022

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
Long Division Calculator
Division is one of the basic arithmetic operations, the others being multiplication (the inverse of division), addition, and subtraction. The arithmetic operations are ways that numbers can be combined in order to make new numbers. Division can be thought of as the number of times a given number goes into another number. For example, 2 goes into 8 4 times, so 8 divided by 4 equals 2.
Division can be denoted in a few different ways. Using the example above:
8 ÷ 4 = 2
In order to more effectively discuss division, it is important to understand the different parts of a division problem.
Components of division
Generally, a division problem has three main parts: the dividend, divisor, and quotient. The number being divided is the dividend, the number that divides the dividend is the divisor, and the quotient is the result:
One way to think of the dividend is that it is the total number of objects available. The divisor is the desired number of groups of objects, and the quotient is the number of objects within each group. Thus, assuming that there are 8 people and the intent is to divide them into 4 groups, division indicates that each group would consist of 2 people. In this case, the number of people can be divided evenly between each group, but this is not always the case. There are two ways to divide numbers when the result won't be even. One way is to divide with a remainder, meaning that the division problem is carried out such that the quotient is an integer, and the leftover number is a remainder. For example, 9 cannot be evenly divided by 4. Instead, knowing that 8 ÷ 4 = 2, this can be used to determine that 9 ÷ 4 = 2 R1. In other words, 9 divided by 4 equals 2, with a remainder of 1. Long division can be used either to find a quotient with a remainder, or to find an exact decimal value.
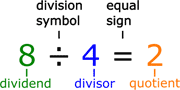
How to perform long division?
To perform long division, first identify the dividend and divisor. To divide 100 by 7, where 100 is the dividend and 7 is the divisor, set up the long division problem by writing the dividend under a radicand, with the divisor to the left (divisorvdividend), then use the steps described below:
This is the stopping point if the goal is to find a quotient with a remainder. In this case, the quotient is 014 or 14, and the remainder is 2. Thus, the solution to the division problem is:
100 ÷ 7 = 14 R2
To continue the long division problem to find an exact value, continue the same process above, adding a decimal point after the quotient, and adding 0s to form new dividends until an exact solution is found, or until the quotient to a desired number of decimal places is determined.
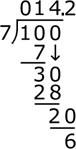
WELCOME! Find what you need

Elementary Math

Elementary Ela-Reading

Teaching Tips

Career Exploration
How to solve long division problems.
Refresh your memory on how to teach long division with success for students and yourself. This step-by-step guide is filled with tips and helpful advice.
So many teachers become frustrated while teaching students how to solve long-division problems. I know that feeling well; I’ve been there. But teaching long division doesn’t have to be as difficult as that – cross my heart!

I’ll walk you through a few steps that make long division easier for you to teach. But first, let’s talk to our students about what long division is and why it exists in the first place.
Introduce the topic to students.
As you’re introducing long division to students, setting the right tone is important. They shouldn’t be told how hard it is or that it’s scary and tough to learn. They need reassurance and confidence that they’ll be successful with your help.
Say something like, “I know you’re excited to learn about long division. We’ll use many skills you’ve learned over the years and put them together to solve division problems.”
Go on to explain that long division is simply a way of splitting a number into smaller, even parts. In real-life terms, it’s a way of dividing a big group of things into many smaller groups.
For example, if we have a bag of candies and a group of children. We want each child to get the same number of candies, so we need to figure out how many candies each child gets. We can find the answer through long division.
Teach the basic terminology.
While instructing students, you should use the correct terminology. Here’s a quick refresher:
- The dividend is the number being divided or split up (the number inside the division symbol).
- The divisor is the number you divide by (the number of groups the dividend is split into).
- The quotient is the name of the answer to the division problem (how many are in each group).
- The remainder is the number that is left over after dividing.
In other words, dividend ÷ divisor = quotient , and the remainder is any extra amount.

You may have to provide several more examples to help students understand why we perform long division.
Long division can be broken down into steps.
Long division is a process that can be broken down into steps. Teaching each step will make it easier for students to become fluent. Long division takes practice, repetition, and feedback, but students will master the skill over time.
As you begin to instruct students on the steps for solving long division, follow these steps:
1. Set up the equation with a dividend and divisor.

2. Divide the first digit in the dividend by the divisor by finding how many times the divisor can go into the first digit of the dividend. Write that number above the first digit of the dividend. That is the first digit of the quotient. In the above example, ask how many groups of 5 are there in 3?
3. If the divisor is larger than the first digit, place a zero above the first digit of the dividend

4. Multiply the digit in the quotient times the divisor. In our example, this is 0.
5. Write the product below the dividend.

6. Write a line under the product.

7. Subtract the product from the dividend. Write the difference (answer) under the line.

8. Bring down the next digit in the dividend.

9. Repeat the process by dividing the new number by your divisor. Write that digit above the dividend as the next digit of the quotient. Continue this process until all the digits in the dividend have been brought down and divided.

10. If the numbers don’t divide evenly, you’ll be left with a remainder. After the quotient, write “R.” and then the number left over. In our example, that remainder is 4.

11. Remember to label your quotient and final answer. If you divide candies between children, you’ll label the final answer “candies.”
Provide several examples and think out loud.
Students learn a lot by hearing how you problem solve.
As you’re explaining the examples, be sure to model your thinking out loud. For example, you might say, “Hmm. How many groups of 7 can be taken out of 30? I know 7 x 4 is 28, and that’s pretty close to 30.”
Be sure to:
- Over-teach by providing plenty of examples.
- Explain your thinking and reasoning for each step of the process.
- Be consistent. Repeat the process the same way every time.
- Provide real-world examples to help students understand how we use division in real-life situations.
- Use visual aids such as anchor charts, reference guides, posters, and diagrams to illustrate the concepts.
- Provide frequent feedback. The more often you provide feedback, the more students can self-correct.
Practice, practice, practice in a group.
Provide a long division problem for students to solve at their seats using whiteboards or paper. Have students practice problems independently or with assistance from a partner. As students are working, circulate around the room to provide frequent feedback. Once most students are finished, invite a student to show their work as they solve the problem in front of the class. Sometimes hearing the steps from a peer helps students understand. Discuss problem areas before moving on to the next problem.
As you’re circulating around the room, if you see students having trouble, ask them questions about their thinking processes. Make corrections on the spot to ensure that students understand the steps.
You can also have students use their whiteboards for questions about what they don’t understand.

More about partner work.
Partner work with whiteboards is a great way for students to learn from each other. Plus, they can check each other’s work while practicing to improve their skills. Teaching others is the highest form of understanding, so students who are comfortable with the process can help classmates who are still struggling. Both students benefit.
Important note – Peer tutoring can be a valuable part of learning for both students. However, don’t overuse it. Advanced students should be challenged so they continue moving forward. Struggling students need direct instruction from trained teachers. Use this approach wisely.
During partner work, you can circulate around the room and catch students’ mistakes immediately. The immediate feedback and reinforcement save students time and frustration.
Be sure to note the students who need more assistance. You can work with those individuals in a small group or individually.
My favorite method for teaching long division.
My absolute favorite method for teaching long division is Shaped Math . It’s fantastic for introducing long division and for students who need support.
Check out the video that explains this visual support for teaching long division.
Grab This FREE Long Division Set:

Grab the FREE Shaped Math Long Division.

Learn more about How to Teach Long Division with Shaped Math.
Additional tools to support students:
For students who need additional support, try out graph paper accommodations.
Standard Algorithm Using Shaped Math.
Conclusion .
Hopefully, you’ve found these tips helpful. If you’re teaching long division, this strategy is a great way for students to learn the skill successfully.

Hi, I’m Jules
Find it fast, browse the blog, visit my teachers pay teachers shop.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Bring down the next digit of the dividend. 175 ÷ 25 = 7 remainder 0. Divide this number by the divisor. The whole number result is placed at the top. Any remainders are ignored at this point. 25 × 7 = 175. The answer from the above operation is multiplied by the divisor . The result is placed under the number divided into.
In long division, you always round down to the nearest whole number, so in this case, our answer would be 4. 4. Enter the first digit of the quotient. Put the number of times the divisor goes into the first digit (or digits) of the dividend above the appropriate digit (s).
Now, let us follow the long division steps given below to understand the process. Step 1: Take the first digit of the dividend from the left. Check if this digit is greater than or equal to the divisor. Step 2: Then divide it by the divisor and write the answer on top as the quotient.
Draw a line under the 6, subtract, and write 2 below the line. Bring down the next digit. Now, bring down the next digit of the dividend, which is 4, to sit next to the 2, making 24. Repeat the steps. 3 goes into 24 eight times (3 x 8 = 24), so write 8 above the bar next to the 2. Subtract 24 from 24 to get 0.
Welcome to Long Division: A Step-By-Step Review with Mr. J! Need a refresher on how to divide by 1-digit numbers and/or how to divide by 2-digit numbers? You...
This long division math youtube video tutorial explains how to divide big numbers the easy way. It explains how to perform long division with 2-digit diviso...
Definition of Long Division. In Math, long division is the mathematical method for dividing large numbers into smaller groups or parts. It helps to break down a problem into simple and easy steps.The long divisions have dividends, divisors, quotients, and remainders.In a long division problem, the dividend is the large number that is divided by another number called the divisor.
Long Division Steps. Here's a breakdown of the long division process: Divide: Determine how many times the divisor can fit into the dividend. Multiply: Multiply the quotient by the divisor. Subtract: Subtract the product from the dividend. Bring down: Bring down the next digit from the dividend.
Solve 339 ÷ 3. 1. The 3 in the hundreds place of the dividend is divisible by 3, giving us a value of 1 to write first in the quotient. 2. Now, we can write a 3 underneath the 3 in the hundreds place, and subtract. This should give us a value of 0. 3. We can then drag the three in the tens place down next to our 0. 4.
Solve 339 ÷ 3. 1. The 3 in the hundreds place of the dividend is divisible by 3, giving us a value of 1 to write first in the quotient. 2. Now, we can write a 3 underneath the 3 in the hundreds place, and subtract. This should give us a value of 0. 3. We can then drag the three in the tens place down next to our 0. 4.
Long division activities. The best way for students to learn how to do long division is to practice, practice, practice. Here's a list of eight activities that will get your class excited about long division and help them develop solid math skills. 1. Prodigy. Prodigy is a fun and engaging resource for in-class or at-home long division ...
Subtract the product from the first digit (s) of the dividend. Write the result below the line. Bring down the next digit of the dividend and write it next to the result from the previous step. This gives you a new number to divide. Repeat steps 2-5 until you have divided all the digits in the dividend.
To check the answer to a division problem, you'll need to use multiplication. Let's look at this problem: 54 / 6 = 9. In the slideshow, we used multiplication to check our division. The answer to the multiplication problem should always be the same as the larger number in the division problem.
In this video, we're going to learn how to do a long division problems with easy step-by-step instructions. We'll use diagrams and examples to make the proce...
Follow these steps: 1. Using a calculator or pencil and paper, multiply the quotient by the divisor. 2. If the answer to the division problem has a remainder, add the remainder to the result of the multiplication. 3. If the answer you get is the same as the dividend, then you've solved the division problem correctly.
5th grade long division examples. Children aren't required to do long division until 5th grade. Here are some worked examples of long division problems. 1. 8,051 ÷ 83. Don't forget to list the first 9 multiples of 83 to help you solve it. Step by step long division. We cannot divide 8 thousands by 83; Write zero in the thousands place of ...
1. Write the problem out with a division bar. Place the divisor, the number you'll be dividing into, outside (and to the left of) the long division bar, and the dividend, the number that you'll be dividing, inside the long division bar. To divide decimals, you'll first convert the decimals into whole numbers.
Thus, the solution to the division problem is: 100 ÷ 7 = 14 R2. To continue the long division problem to find an exact value, continue the same process above, adding a decimal point after the quotient, and adding 0s to form new dividends until an exact solution is found, or until the quotient to a desired number of decimal places is determined ...
Mastering Long Division: Interactive TutorialIn this tutorial, Coach Jon guides learners through several practice problems demonstrating long division. He em...
As you begin to instruct students on the steps for solving long division, follow these steps: 1. Set up the equation with a dividend and divisor. 2. Divide the first digit in the dividend by the divisor by finding how many times the divisor can go into the first digit of the dividend. Write that number above the first digit of the dividend.
These are the remainder. So, the quotient is 2 (2 groups of 4 can be made) and the remainder is 3. To check the work, multiply the quotient, 2, times the divisor, 4. The answer is 8. Then, add the remainder of 3. The answer is 11, which was the original dividend, so the answer is correct. Division can get more and more complicated as the ...
In this video, I give step by step directions for solving long division word problems. I use Dad,Mom,Sister,Brother to help with the steps of long division. ...