- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences

Kodak’s Downfall Wasn’t About Technology
- Scott D. Anthony
What it missed was the business model.
A generation ago, a “Kodak moment” meant something that was worth saving and savoring. Today, the term increasingly serves as a corporate bogeyman that warns executives of the need to stand up and respond when disruptive developments encroach on their market. Unfortunately, as time marches on the subtleties of what actually happened to Eastman Kodak are being forgotten, leading executives to draw the wrong conclusions from its struggles.
- Scott D. Anthony is a clinical professor at Dartmouth College’s Tuck School of Business, a senior partner at Innosight , and the lead author of Eat, Sleep, Innovate (2020) and Dual Transformation (2017). ScottDAnthony
Partner Center
- Data, AI, & Machine Learning
- Managing Technology
- Social Responsibility
- Workplace, Teams, & Culture
- AI & Machine Learning
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Big ideas Research Projects
- Artificial Intelligence and Business Strategy
- Responsible AI
- Future of the Workforce
- Future of Leadership
- All Research Projects
- AI in Action
- Most Popular
- The Truth Behind the Nursing Crisis
- Work/23: The Big Shift
- Coaching for the Future-Forward Leader
- Measuring Culture

The spring 2024 issue’s special report looks at how to take advantage of market opportunities in the digital space, and provides advice on building culture and friendships at work; maximizing the benefits of LLMs, corporate venture capital initiatives, and innovation contests; and scaling automation and digital health platform.
- Past Issues
- Upcoming Events
- Video Archive
- Me, Myself, and AI
- Three Big Points

The Real Lessons From Kodak’s Decline
Eastman Kodak is often mischaracterized as a company whose managers didn’t recognize soon enough that digital technology would decimate its traditional business. However, what really happened at Kodak is much more complicated — and instructive.
- Leading Change
- Business Models
- Developing Strategy
- Technology Innovation Strategy

Eastman Kodak Co. is often cited as an iconic example of a company that failed to grasp the significance of a technological transition that threatened its business. After decades of being an undisputed world leader in film photography, Kodak built the first digital camera back in 1975. But then, the story goes, the company couldn’t see the fundamental shift (in its particular case, from analog to digital technology) that was happening right under its nose.
The big problem with this version of events is that it’s wrong. Moreover, it obscures some important lessons that other companies can learn from. To begin with, senior leaders at Kodak were acutely aware of the approaching storm. I know because I arrived at Kodak from Silicon Valley in mid-1997, just as digital photography was taking off. Management was constantly tracking the rate at which digital media was replacing film. But several factors made it exceedingly difficult for Kodak to shift gears and emerge with a consumer franchise that would be sustainable over the long term. Not only was a major technological change upending our competitive landscape; challenges were also affecting the ecosystem we operated in and our organizational model. Ultimately, refocusing the business with so many forces in motion proved to be impossible.
A Difficult Technology Transition
Kodak’s first challenge had to do with technology. Over the course of more than a century, Kodak and a small number of its competitors had developed and refined manufacturing processes that enabled consumers to capture and preserve images for a lifetime. Color film was an extremely complex product to manufacture. The 60-inch “wide rolls” of plastic base material had to be coated with as many as 24 layers of sophisticated chemicals: photosensitizers, dyes, couplers, and other materials deposited at precise thicknesses while traveling at 300 feet per minute. Wide rolls had to be changed over and spliced continuously in real time; the coated film had to be cut to size and packaged — all in the dark. With film, the entry barriers were high. Only two competitors — Fujifilm and Agfa-Gevaert — had enough expertise and production scale to challenge Kodak seriously.
The transition from analog to digital imaging brought several challenges. First, digital imaging was based on a general-purpose semiconductor technology platform that had nothing to do with film manufacturing — it had its own scale and learning curves.
About the Author
Willy Shih is the Robert and Jane Cizik Professor of Management Practice in Business Administration at Harvard Business School. From 1997 to 2003 he was a senior vice president at Eastman Kodak Co. and served as president of the company’s consumer digital business.
More Like This
Add a comment cancel reply.
You must sign in to post a comment. First time here? Sign up for a free account : Comment on articles and get access to many more articles.
Comments (18)
Craig mcgowan, stephen waybright, giovanbattista testolin, karl schubert, arthur weiss, julian koor, victor yodaiken, john krienke, jeffrey hardy, butch cunnings, charles h. green.

Study at Cambridge
About the university, research at cambridge.
- For Cambridge students
- For our researchers
- Business and enterprise
- Colleges and Departments
- Email and phone search
- Give to Cambridge
- Museums and collections
- Events and open days
- Fees and finance
- Postgraduate courses
- How to apply
- Fees and funding
- Postgraduate events
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
- How the University and Colleges work
- Visiting the University
- Annual reports
- Equality and diversity
- A global university
- Public engagement
The rise and fall of Kodak's moment
- Research home
- About research overview
- Animal research overview
- Overseeing animal research overview
- The Animal Welfare and Ethical Review Body
- Animal welfare and ethics
- Report on the allegations and matters raised in the BUAV report
- What types of animal do we use? overview
- Guinea pigs
- Naked mole-rats
- Non-human primates (marmosets)
- Other birds
- Non-technical summaries
- Animal Welfare Policy
- Alternatives to animal use
- Further information
- Funding Agency Committee Members
- Research integrity
- Horizons magazine
- Strategic Initiatives & Networks
- Nobel Prize
- Interdisciplinary Research Centres
- Open access
- Energy sector partnerships
- Podcasts overview
- S2 ep1: What is the future?
- S2 ep2: What did the future look like in the past?
- S2 ep3: What is the future of wellbeing?
- S2 ep4 What would a more just future look like?
- Research impact

On a shelf in his office in Cambridge Judge Business School, Dr Kamal Munir keeps a Kodak Brownie 127. Manufactured in the 1950s, the small Bakelite camera is a powerful reminder of the rise and fall of a global brand – and of lessons other businesses would do well to learn.
Whenever I ask why a certain company that has fallen on hard times is doing badly, I always start by asking why it was successful in the first place. That is where the answer lies. Kamal Munir.
Earlier this year, Kodak filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection. But when Kamal's camera was made, the company bestrode the world of amateur photography – a world Kodak itself had created.
Established by George Eastman in the 1880s, by the 1950s Kodak had the lion's share of the US amateur film market. “Kodak was a company at the top of its game,” says Kamal, who has studied the Rochester-based business for more than a decade.
“Kodak controlled almost 70% of the highly lucrative US film market. Gross margins on film ran close to 70%, and its success was further underpinned by a massive distribution network and one of the strongest brands in the world. The company completely dominated its industry,” he says. “And then, in 1981, along came digital.”
Thousands of words have been written recently seeking to explain Kodak's failure. The company, all agree, was slow to adapt to digital, its executives suffered from a mentality of “perfect products”, its venture-capital arm never made big enough bets to create breakthroughs, and its leadership lacked vision and consistency.
None of this analysis, however, fully explains why digital – a technology Kodak pioneered – did for the company. Understanding that, Kamal argues, requires a deeper historical and social approach.
“Photography is very much a social activity. You can't really understand how people relate to their pictures – why people take pictures – unless you do a social analysis which is more anthropological or sociological,” he explains.
“Whenever I ask why a certain company that has fallen on hard times is doing badly, I always start by asking why it was successful in the first place. That is where the answer lies.”
For three-quarters of the twentieth century, Kodak's supreme success was not only developing a new technology – the film camera – but creating a completely new mass market.
During the nineteenth century, photography had been the exclusive preserve of a small number of professionals, with their large-format cameras and glass plates. So when Kodak invented the film camera, it needed to teach people how and what to photograph, as well as persuading them why they needed to do so.
“Kodak is the company that made photography a popular pastime around the world. It made a tremendous contribution to how we see things,” Kamal says.
The Kodak moment
Kodak's high-profile advertising campaigns established the need to preserve 'significant' occasions such as family events and holidays. These were labelled 'Kodak moments', a concept that became part of everyday life.
And it was women Kodak cast in the leading role. In its advertisements, women held the cameras, busy preserving moments of domestic bliss for posterity: “Kodak knew how to market to women. If you wanted to be seen as a caring mother and responsible housewife, then you needed to record your family's evolution and growth,” he says.
But women were only part of the story. It was they who took the photographs, but the other half of the Kodak moment required a subject – birthday parties, sporting success and, crucially, family holidays.
“Kodak also played a big role in converting travel to tourism. The idea was that if you hadn't brought back pictures from your vacation you might as well not have gone,” says Kamal. “For them, photography was all about preserving memories for posterity, photography was all about sentiment, and it was women who were doing this.”
By the 1970s, more than 60% of pictures in the US – the world's largest photography market – were being taken by women. And it was partly how men – rather than women – responded to the digital revolution that Kodak couldn't cope with.
Digital disrupted the company's equilibrium in two crucial respects. Firstly, it shifted meaning associated with cameras and secondly, digital devices allowed newcomers such as Sony to bypass one of Kodak's huge strengths – its distribution network.
The knock-on effects of this shift were enormous. Digital cameras came to be viewed as electronic gadgets, rather than pieces of purely photographic equipment. As a result, he explains: “The identification of cameras as gadgets brought about another significant change: women were no longer the main customers, men were.”
The gender shift led to the third source of disruption for the photographic industry in general, and for Kodak in particular. With digital cameras, images could be viewed on cameras, mobile phones or computers without the need for hard prints. And with women giving way to men as primary users of cameras, printing plummeted.
According to Kamal: “The people taking pictures suddenly changed, from 60% women to 70% men. Kodak didn't know how to market to men. But even if they could get them to buy, they didn't want to, because men don't print. Unlike women, they hadn't been socialised in the role of family archivist.”
Faced with such an enormous threat to its business, Kodak did what many companies do in similar circumstances – ignore the problem in the hope it goes away, and when it doesn't, deride the new-comer.
“Some things do go away – not all technology gets diffused,” he says. “When that fails, the second reaction is usually derision – it'll never take off, it's too expensive, it's too difficult, the print quality is too bad, people will never part with hard prints. When I talked to Kodak executives they would always cite the same example – if someone's house catches fire, the first thing they rescue is their photographs.”
From preserving memories to sharing experiences
Having played such a central role in creating meaning for photography, the company failed to believe that meaning had changed, from memories printed on paper to transient images shared by email or on Facebook.
“The change from preserving memories to sharing experiences, and from women to men – these were things Kodak simply couldn't handle,” says Kamal, who saw the writing on the wall when he visited the company's senior management in Rochester a decade ago. “By the end of the day I was convinced the company was not going to be around much longer.”
In 2006, Kamal sent a letter to the Financial Times , pointing out that Kodak's strategy was fundamentally flawed. “Kodak is better off taking a leaf out of Lou Gerstner’s strategy for re-inventing IBM – from a manufacturer to a service-provider,” he wrote.
“Kodak needs to disassociate itself from its traditional strengths and come to terms with the fact that this technology will be commoditised sooner or later. What they need is a new business model for an environment in which people do not ‘preserve memories’ but ‘share experiences’ ... I am afraid Mr Perez's [Kodak CEO] strategy of engulfing the consumer in the Kodak universe has a low likelihood of success."
But rather than a new business model, what Kamal had seen in Rochester was a digital imaging division under pressure from its consumer imaging counterpart, and a company unable to shake-off a corporate mindset that had developed over more than a century.
“Its focus on retail printing, investing in inkjet printing research and development, and selling sensors to mobile manufacturers – altogether, these never added up to a coherent, sustainable business model. And the digital guys were always under pressure because they were seen to be cannibalising sales of much more lucrative products,” says Kamal, who thinks Kodak should have cut the digital business loose and freed it from the Rochester mindset.
Learning from history
In his view, Kodak needed to let a new generation of users and entrepreneurs take charge – people who could embrace uncertainty and were prepared to be driven in unforeseen directions – a far cry from how the company had spent its life.
“It's important for companies to reinvent themselves. Kodak had tremendous market power – one of the things that allowed it to survive thus far. But for this kind of reinvention, where you're faced with a technological discontinuity which has little in common with what you've been doing, you need to radically alter your mindset or world-view and emerge as a completely different company. IBM is a good example of this kind of reinvention, which was a huge cultural shift and took several years. But Kodak wasn't willing to part with their legacy.”
The challenges Kodak faced are not unique, so what can other businesses learn from its failure? Clearly companies that derive a large proportion of their profit from a single product – in Kodak's case film – are more vulnerable. But having a corporate mindset open to new ideas and able to embrace uncertainty is essential.
According to Kamal: “The important things are not to tie the weight of legacy assets onto new ventures; to refrain from prolonging the life of existing product lines, while trying to create false synergies between the old and the new; and, most of all, to base strategy around users, rather than the existing business model.”
As the company approaches its 130 th birthday, what will be its legacy? Those precious family albums, perhaps, and our enduring passion for photography. But its impact could have been even greater, and longer-lasting.
“There was a time when photography was known as 'kodaking',” he concludes. “I don't think Kodak will survive. Someone might buy the brand and its assets, but Kodak is never going to be Kodak again.”

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Licence . If you use this content on your site please link back to this page.
Read this next

Enterprising Minds: Meet the CEO of Nu Quantum

Caring for cancer patients

Policies for People and Planet

Cambridge heads to COP28
Kodak Color Film.
Credit: Dok 1 from Flickr.
Search research
Sign up to receive our weekly research email.
Our selection of the week's biggest Cambridge research news and features sent directly to your inbox. Enter your email address, confirm you're happy to receive our emails and then select 'Subscribe'.
I wish to receive a weekly Cambridge research news summary by email.
The University of Cambridge will use your email address to send you our weekly research news email. We are committed to protecting your personal information and being transparent about what information we hold. Please read our email privacy notice for details.
- digital media
- digital technology
- electronics
- entrepreneurship
- Kamal Munir
- Cambridge Judge Business School
Connect with us

© 2024 University of Cambridge
- Contact the University
- Accessibility statement
- Freedom of information
- Privacy policy and cookies
- Statement on Modern Slavery
- Terms and conditions
- University A-Z
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- Cambridge University Press & Assessment
- Research news
- About research at Cambridge
- Spotlight on...

Why Did Kodak Fail? | Kodak Bankruptcy Case Study

Yash Taneja
Kodak, as we know it today, was founded in the year 1888 by George Eastman as ‘The Eastman Kodak Company’ . It was the most famous name in the world of photography and videography in the 20th century. Kodak brought about a revolution in the photography and videography industries. At the time when only huge companies could access the cameras used for recording movies, Kodak enabled the availability of cameras to every household by producing equipment that was portable and affordable.
Kodak was the most dominant company in its field for almost the entire 20th century, but a series of wrong decisions killed its success. The company declared itself bankrupt in 2012. Why did Kodak, the king of photography and videography, go bankrupt? What was the reason behind Kodak's failure? Why did Kodak fail despite being the biggest name of its time? This case study answers the same.
Why Did Kodak Fail? Biggest Reason Of Kodak's Failure - Fights against Fuji Films Kodak's Bankruptcy Protection Ressurection of Kodak: Kodak in the mobile industry?
Why Did Kodak Fail?

Kodak, for many years, enjoyed unmatched success all over the world. By 1968, it had captured about 80% of the global market share in the field of photography.
Kodak adopted the 'razor and blades' business plan . The idea behind the razor-blade business plan is to first sell the razors with a small margin of profit. After buying the razor, the customers will have to purchase the consumables (the razor blades in this case) again and again; hence, sell the blades at a high-profit margin. Kodak's plan was to sell cameras at affordable prices with only a small margin for profit and then sell the consumables such as films, printing sheets, and other accessories at a high-profit margin .
Using this business model, Kodak was able to generate massive revenues and turned into a money-making machine.
As technology progressed, the use of films and printing sheets gradually came to a halt. This was due to the invention of digital cameras in 1975. However, Kodak dismissed the capabilities of the digital camera and refused to do something about it. Did you know that the inventor of the digital camera, Steven Sasson, was an electrical engineer at Kodak when he developed the technology? When Steven told the bosses at Kodak about his invention, their response was, “That’s cute, but don’t tell anyone about it. That's how you shoot yourself in the foot!"

Kodak ignored digital cameras because the business of films and paper was very profitable at that time and if these items were no longer required for photography, Kodak would be subjected to huge losses and end up closing down the factories which manufactured these items.
The idea was then implemented on a large scale by a Japanese company by the name of ‘Fuji Films’. And soon enough, many other companies started the production and sales of digital cameras, leaving Kodak way behind in the race.
This was Kodak's first mistake. The ignorance of new technology and not adapting to the changing market dynamics initiated Kodak's downfall.
List of Courses Curated By Top Marketing Professionals in the Industry
These are the courses curated by Top Marketing Professionals in the Industry who have spent 100+ Hours reviewing the Courses available in the market. These courses will help you to get a job or upgrade your skills.
Biggest Cause Of Kodak's Failure
After the digital camera became popular, Kodak spent almost 10 years arguing with Fuji Films , its biggest competitor, that the process of viewing an image captured by the digital camera was a typical process and people loved the touch and feel of a printed image. Kodak believed that the citizens of the United States of America would always choose it over Fuji Films, a foreign company.
Fuji Films and many other companies focused on gaining a foothold in the photography & videography segment rather than engaging in a verbal spat with Kodak. And once again, Kodak wasted time promoting the use of film cameras instead of emulating its competitors. It completely ignored the feedback from the media and the market . Kodak tried to convince people that film cameras were better than digital cameras and lost 10 valuable years in the process.
Kodak also lost the external funding it had during that time. People also realized that digital photography was way ahead of traditional film photography. It was cheaper than film photography and the image quality was better.
Around that time, a magazine stated that Kodak was being left behind because it was turning a blind spot to new technology. The marketing team at Kodak tried to convince the managers about the change needed in the company's core principles to achieve success. But Kodak's management committee continued to stick with its outdated idea of relying on film cameras and claimed the reporter who said the statement in the magazine did not have the knowledge to back his proposition.
Kodak failed to realize that its strategy which was effective at one point was now depriving it of success. Rapidly changing technology and market needs negated the strategy. Kodak invested its funds in acquiring many small companies, depleting the money it could have used to promote the sales of digital cameras.
When Kodak finally understood and started the sales and the production of digital cameras, it was too late. Many big companies had already established themselves in the market by then and Kodak couldn't keep pace with the big shots.
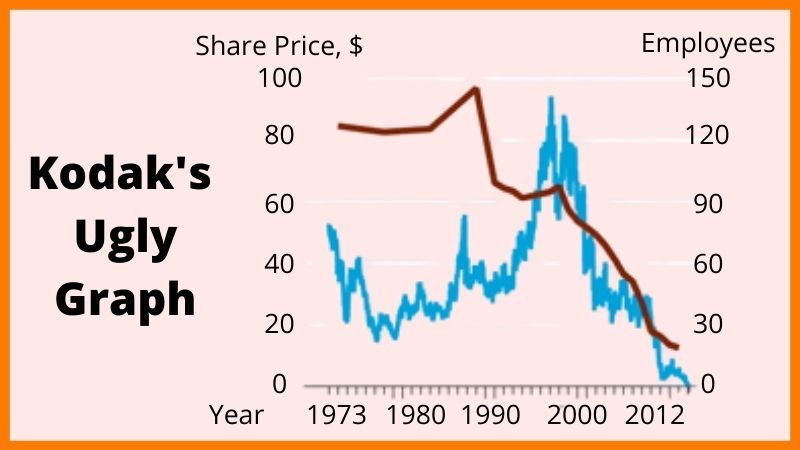
In the year 2004, Kodak finally announced it would stop the sales of traditional film cameras. This decision made around 15,000 employees (about one-fifth of the company’s workforce at that time) redundant. Before the start of the year 2011, Kodak lost its place on the S&P 500 index which lists the 500 largest companies in the United States on the basis of stock performance. In September 2011, the stock prices of Kodak hit an all-time low of $0.54 per share. The shares lost more than 50% of their value throughout that year.
Kodak's Bankruptcy Protection
By January 2012, Kodak had used up all of its resources and cash reserves. On the 19th of January in 2012, Kodak filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection which resulted in the reorganization of the company. Kodak was provided with $950 million on an 18-month credit facility by the CITI group.
The credit enabled Kodak to continue functioning. To generate more revenue, some sections of Kodak were sold to other companies. Along with this, Kodak decided to stop the production and sales of digital cameras and stepped out of the world of digital photography. It shifted to the sale of camera accessories and the printing of photos.
Kodak had to sell many of its patents, including its digital imaging patents, which amounted to more than $500 million in bankruptcy protection. In September 2013, Kodak announced it had emerged from Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection.
Ressurection of Kodak: Kodak in the mobile industry?
Celebrated camera accessory manufacturers of yesteryear, Kodak, is looking to join Chinese smartphone manufacturing giant Oppo for an upcoming flagship smartphone. This new smartphone is rumored to have 50MP dual cameras, where the cameras of the device will be modeled upon the old classic camera designs of the Kodak models.
The all-new flagship model of Oppo is designed to be a tribute to the classic Kodak camera design. The camera of this Oppo model will allegedly use the Sony IMX766 50MP sensor. Furthermore, the phone will also embed a large sensor in its ultrawide camera as well along with a 13MP telephoto lens and a 3MP microscope camera.
No other information on this matter is currently available as of September 13, 2021.
The collaborations between Android OEMs and camera makers are not something new. Yes, numerous other companies have already come together with other camera manufacturing companies like Nokia, which joined hands with German optics company Carl Zeiss earlier in 2007 to bring in the camera phone Nokia N95. This can be concluded as the first of such collaborations that the smartphone industry has seen. Numerous other collaborations happened eventually, which resulted in outstanding results. OnePlus' partnership with Hasselblad, Huawei pairing up with Leica and the recent news of Samsung's associating with Olympus are some of the significant collaborations to be mentioned.
Kodak had earlier made a leap into the smart TV industry and is ushering in success through this new move. Kodak TV India has already commissioned a plant in Hapur, Uttar Pradesh in August 2020, designed to manufacture affordable Android smart TVs for India. Furthermore, the renowned photography company is looking to invest more than Rs 500 crores during the next 3 years for making a fully automated TV manufacturing plant possible in Hapur. The company committed to this plan as part of its ‘Make in India’ initiative and will leverage its Android certification. Kodak's announcement, as it seemed, was further recharged with the Aatmanirbhar Bharat campaign launched by PM Narendra Modi in the wake of the coronavirus pandemic in 2020.
The TV industry of India imports most of its raw materials and exhibits a value addition of only about 10-12%. However, with the investment that Kodak has promised the company has aimed to increase the value-added to around 50-60%. The Hapur R&D facility will foster the manufacturing of technology-driven products and introduce numerous other lines of manufacturing aligned with the "Make in India" belief.
Super Plastronics Pvt Ltd, a Noida-based company has obtained the license from Kodak Smart TVs to produce and sell their products in India in partnership with the New-York based company and has already launched a range of smart TVs already, as of September 2021 including:
- Kodak 40FHDX7XPRO 40-inch Full HD Smart LED TV
- Kodak 43FHDX7XPRO 43-inch Full HD Smart LED TV
- Kodak 42FHDX7XPRO 42-inch Full HD Smart LED TV
- Kodak 32HDXSMART 32-inch HD ready Smart LED TV
and more. Besides, Kodak HD LED TVs were also up for sale at the lowest prices for 2020, in partnership with Flipkart and Amazon for The Big Billion Days Sale and the Great Indian Sale respectively. This sale, which took place between 16th and 21st October 2020, also included the all-new Android 7XPRO series, which starts at Rs 10999 only and is currently dubbed as the most affordable android tv in India.

Want to Work in Top Gobal & Indian Startups or Looking For Remote/Web3 Jobs - Join angel.co
Angel.co is the best Job Searching Platform to find a Job in Your Preferred domain like tech, marketing, HR etc.
What happened to Kodak?
Kodak was ousted from the market of camera and photography due to numerous missteps. Here are some insights into the same:
- The ignorance of new technology and not adapting to changing market needs initiated Kodak's downfall
- Kodak invested its funds in acquiring many small companies, depleting the money it could have used to promote the sales of digital cameras.
- Kodak wasted time promoting the use of film cameras instead of emulating its competitors. It completely ignored the feedback from the media and the market
- When Kodak finally understood and started the sales and the production of digital cameras, it was too late. Many big companies had already established themselves in the market by then and Kodak couldn't keep pace with the big shots
- In September 2011, the stock prices of Kodak hit an all-time low of $0.54 per share
- Kodak declared bankruptcy in 2012
Why did Kodak fail and what can you learn from its demise?
Kodak failed to understand that its strategy of banking on traditional film cameras (which was effective at one point) was now depriving the company of success. Rapidly changing technology and evolving market needs made the strategy obsolete.
Is Kodak still in Business?
Kodak declared itself bankrupt in 2012. Kodak's bankruptcy resulted in the formation of the Kodak Alaris company, a British organization that part-owns the Kodak brand along with the American Eastman Kodak Company.
When did Kodak go out of business?
Kodak faced its demise in 2012.
Is Kodak a good camera?
Kodak's cameras and accessories were of premium quality and the first of the choices professional photographers and others. The company was a winner in the analogue era of photography. However, the company dived down to hit the rock-bottom level.
What does Kodak do now?
Currently, Kodak provides packaging, functional printing, graphic communications, and professional services for businesses around the world. Better known for making cameras, Kodak moved into drug making and has secured a $765m (£592m) loan from the US government in 2020.
Why was Kodak so successful?
Kodak adopted the 'razor and blades' business plan. The idea here was to first sell the razors with a small margin of profit. After buying the razor, the customers will have to purchase the consumables (the razor blades in this case) again and again; hence, sell the blades at a high-profit margin. Kodak's plan was to sell cameras at affordable prices with only a small margin for profit and then sell the consumables such as films, printing sheets, and other accessories at a high-profit margin.

Must have tools for startups - Recommended by StartupTalky
- Convert Visitors into Leads- SeizeLead
- Payment Gateway- Razorpay
- Spy on your Competitors- Adspyder
- Manage your business smoothly- Google Workspace
Shipping and Fulfillment Guide for E-commerce Businesses
This article has been contributed by Ganesh Nair, Director Operations at Mehar. In today's world of e-commerce, the increase in online stores is clearly intensifying the relentless pace of growth. Navigating the complex world of shipping and fulfillment is necessary for one's business success. This comprehensive guide focuses on three
BASIC Home Loan Success Story: Revolutionizing Home Loans in India
Getting a home loan is a big step toward owning a home, providing financial assistance to make your dream a reality. The Indian home loan market, valued at approximately USD 300 billion, is expected to achieve a CAGR of 22.5% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2029. However,
Arpita Katyal of Roperro Shares the Journey of Embracing Indian Craftsmanship in Luxury Bags
In an exclusive interview with StartupTalky, Arpita Katyal, CEO of Roperro, shares insights into the brand's journey. Roperro, an Indian luxury label specializing in luxury bags, emphasizes Indian craftsmanship on a global scale. Katyal discusses Roperro's mission to make luxury accessible, its bootstrapped journey, and maintaining international quality standards while
All Sponsors of Indian Premier League 2024 (IPL 2024)
The Indian Premier League (IPL) is a highly popular and competitive professional Twenty20 (T20) cricket league founded in 2008. The league follows a round-robin group and knockout format, which means that each team plays against the others in a predetermined number of matches, and the top-performing teams advance to the
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- April 2003 (Revised February 2004)
- HBS Case Collection
- Format: Print
- | Pages: 28
About The Author
Rebecca M. Henderson
Related work.
- November 2004 (Revised November 2005)
- Faculty Research
Kodak and The Digital Revolution (A)
- Kodak and The Digital Revolution (A) By: Giovanni M. Gavetti, Rebecca Henderson and Simona Giorgi
- The top legal technology trends of 2023 – ABA Journal
- ODNI Releases the Intelligence Community Data Strategy for 2023–2025 – Office of the Director of National Intelligence
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Drug Development – FDA.gov
- Digital Strategy & Transformation Americas | Healthcare – McKinsey
- Hines Creates Global Digital Strategy Office – Hines

Case Study: Kodak’s Downfall—A Lesson in Failed Digital Transformation and Missed Opportunities
The context: an iconic brand meets digital disruption.
Eastman Kodak, commonly known as Kodak, was once the undisputed leader in the photography industry, boasting a market capitalization of $31 billion at its peak in 1997. However, by 2012, Kodak had filed for bankruptcy, a staggering descent that is often cited as a cautionary tale in the annals of business history. So, what went wrong? How did a company that held 90% of the U.S. film market and 85% of the camera market in 1976 end up in bankruptcy?

The Dilemmas
1. complacency and over-reliance on legacy business models.
Kodak was heavily invested in the film-based photography market. The company’s complacency in sticking to its legacy business model, despite the seismic changes in technology, was its first major mistake. Film processing was a cash cow, and there was a reluctance to explore or transition to emerging technologies for fear of cannibalizing the existing business.
2. Ignoring Technological Innovations
Ironically, Kodak was one of the pioneers in digital photography and invented the first digital camera in 1975. Yet, they did not capitalize on this innovation. This was largely because they perceived digital photography as a threat to their film business. Their failure to adapt to and invest in the new technology would cost them dearly.
3. Misjudging Market Trends and Customer Needs
The management wrongly assumed that the transition from film to digital would be slow. They underestimated how quickly consumers would adopt digital cameras and later, smartphones. Kodak’s inability to read the market and customer needs accurately further exacerbated their downfall.
The Aftermath: The Costs of Inaction
By the time Kodak realized the significance of digital photography, it was too late. Other companies like Canon, Sony, and later tech giants like Apple and Google, had already captured significant market share. In 2012, Kodak filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy and later emerged as a company focusing on digital imaging for businesses, a far cry from its glorious past.
The Data and Statistics
Kodak timeline.
- 1888: George Eastman patents the first roll-film camera and registers the trademark “Kodak.”
- 1900: Eastman introduces the Brownie camera, making photography accessible to the masses.
- 1935: Kodachrome film is launched, becoming the standard for color photography.
- 1962: Kodak introduces the Instamatic camera, popularizing point-and-shoot photography.
- 1975: Kodak engineer Steve Sasson invents the first digital camera prototype.
- 1984: Kodak launches the Photo CD system, allowing digital storage of photos.
- 1990: Kodak’s market share for photographic film peaks at over 80%.
- 1994: Kodak enters the digital camera market, but faces competition from industry newcomers.
- 1997: Kodak’s market capitalization reaches $31 billion.
- 2003: Kodak announces a major restructuring and begins shifting focus to digital technologies.
- 2012: Kodak files for bankruptcy, citing a failure to adapt to the digital age.
- 2013: Kodak emerges from bankruptcy as a restructured company focused on commercial printing.
- 2019: Kodak launches a blockchain cryptocurrency platform for photographers called KODAKCoin.
- Present: Kodak continues to innovate in various imaging and printing technologies, aiming to regain its prominence in the industry.
This timeline captures the major milestones and challenges faced by Kodak throughout its history.
What Could Have Been Done Differently?
- Scenario Planning : Kodak could have considered various future states of technology and the market to identify opportunities and threats better.
- Agile Methodologies : An agile approach to strategy and product development could have made the organization more responsive to change.
- Horizon Planning : A long-term strategy incorporating emerging technologies could have diversified their revenue streams and reduced their dependency on the film business.
- Prioritization : Resource allocation could have been better managed to focus on digital technologies, a future growth area.
Case Study: Dropbox’s Success with the Lean Startup Methodology
The Missed Goldmine: Kodak’s Untapped Digital Patents
One of the most perplexing aspects of Kodak’s downfall is the vast portfolio of digital patents the company held. Kodak was a pioneer in many digital imaging technologies and had over 1,000 patents related to digital cameras, image processing, and various other digital imaging technologies. This arsenal of intellectual property could have been a significant game-changer, positioning Kodak as a dominant player in the digital era. However, Kodak failed to leverage these assets effectively. While some of these patents were eventually sold for $527 million during the bankruptcy proceedings in 2012, the revenue pales in comparison to what could have been earned through strategic application or licensing agreements (Source: Reuters). Kodak’s failure to capitalize on its rich patent portfolio demonstrates a glaring missed opportunity and adds another layer to the tragedy of its downfall. These patents could have been the stepping stones to transition smoothly from a film-based photography company to a digital imaging powerhouse, if only the right strategies and focus were in place.
The Lawler Model for Designing AI Products: A BloombergGPT Case Study
Lessons for Other Organizations: Unpacking the Kodak Tragedy for Modern-Day Strategic Insights
The collapse of Kodak wasn’t just a loss for the company and its employees; it serves as a case study loaded with lessons for other organizations. The corporate world today, more than ever, requires companies to adapt swiftly to emerging technologies and market changes. Here are some key takeaways that could guide other companies in averting a similar fate:
Avoid Complacency
Kodak dominated the film photography industry for years, which likely contributed to an organizational culture of complacency. No matter how successful a business is today, tomorrow’s landscape could be entirely different. Continuous innovation and an ever-curious mindset are vital for long-term sustainability.
Harness Your Intellectual Property
Kodak’s patent portfolio was a goldmine that was not effectively utilized. Intellectual property can provide a competitive edge and open up new avenues for revenue through licensing or forming strategic partnerships. Evaluate your IP assets and think strategically about how to leverage them for future growth.
Case Study: Starbucks’ Success Elevating Customer Experience with Customer Journey Mapping
Prioritize Adaptability
Kodak’s downfall illustrates the importance of adaptability. Employing frameworks like Agile and Horizon Planning can help a company remain flexible and responsive to market needs, ensuring that you’re not only reacting to changes but also anticipating them.
Stakeholder Involvement is Crucial
Kodak’s transition to the digital age was not a smooth one, partly because of resistance from various stakeholders who were invested in the existing film business. Ensure that all stakeholders are aligned with the company’s vision and strategy, and consider using a neutral facilitator to guide strategy meetings effectively.
Keep Your Roadmaps Dynamic
Technology and strategy roadmaps should not be static documents but should evolve with the industry landscape and internal capabilities. Regular updates and revisions keep the roadmap relevant and actionable, allowing for real-time adjustments to market changes.
Financial Prudence
In an era of rapid changes, conserving resources for future investments in innovation and strategic shifts is crucial. Kodak’s lack of financial prudence when the tides were turning led to a situation where they had fewer options when they finally decided to pivot.
How to Create Apps that Customers Want: A Comprehensive Strategy
A Glimmer of Hope: Kodak’s Pivot to Blockchain and Continued Innovation
Even the most harrowing tales of downfall can have a silver lining, and in the case of Kodak, it’s their foray into blockchain technology and ongoing endeavors in imaging and printing technologies. These initiatives not only showcase the brand’s resilience but also provide valuable lessons on how to stage a comeback in the digital age.
KODAKCoin: A Step Towards Decentralization
In 2019, Kodak surprised the tech world by launching KODAKCoin, a blockchain cryptocurrency platform designed for photographers. This innovative move aimed to address issues around image rights and royalties, providing photographers with a secure and transparent platform to manage their intellectual property. With KODAKCoin, Kodak showed its willingness to explore frontier technologies, reflecting a newfound openness to adapt and innovate.
A Commitment to Imaging and Printing Technologies
Kodak has also continued its efforts to innovate in its core areas—imaging and printing technologies. Leveraging its historical strengths, the company is investing in new product lines and partnerships, aiming to re-establish itself as a leader in the industry. While the road to recovery is long, these actions signal a directional shift in Kodak’s strategy, focusing on modernization and value creation.
CDO TIMES Bottom Line Summary
The fall of Kodak serves as a cautionary tale that outlines the importance of adaptability, strategic planning, and stakeholder alignment in today’s volatile business environment. Organizations aiming to avoid a similar fate should consider adopting modern planning frameworks like Agile and Horizon Planning, stay open to revising their technology roadmaps, and leverage intellectual property assets strategically. These lessons are not just theoretical but actionable guidelines that could determine an organization’s survival in the fast-evolving corporate landscape.
Kodak’s pivot towards blockchain with KODAKCoin and its ongoing efforts in imaging and printing technologies show a company striving to reinvent itself. While it’s too early to predict if these steps will fully restore Kodak’s former glory, they do offer a glimmer of hope and a wealth of insights for other companies seeking to pivot or modernize. The lesson here is clear: innovation and adaptability remain at the core of corporate sustainability. For organizations looking to master these qualities, subscribing to CDO TIMES’ unlimited access membership offers an in-depth analysis of successful strategies, emerging technologies, and case studies, arming you with the knowledge you need to stay ahead of the curve.
Love this article? Embrace the full potential and become an esteemed full access member, experiencing the exhilaration of unlimited access to captivating articles, exclusive non-public content, empowering hands-on guides, and transformative training material. Unleash your true potential today!
In this context, the expertise of CDO TIMES becomes indispensable for organizations striving to stay ahead in the digital transformation journey. Here are some compelling reasons to engage their experts:
- Deep Expertise : CDO TIMES has a team of experts with deep expertise in the field of Digital, Data and AI and its integration into business processes. This knowledge ensures that your organization can leverage digital and AI in the most optimal and innovative ways.
- Strategic Insight : Not only can the CDO TIMES team help develop a Digital & AI strategy, but they can also provide insights into how this strategy fits into your overall business model and objectives. They understand that every business is unique, and so should be its Digital & AI strategy.
- Future-Proofing : With CDO TIMES, organizations can ensure they are future-proofed against rapid technological changes. Their experts stay abreast of the latest AI advancements and can guide your organization to adapt and evolve as the technology does.
- Risk Management : Implementing a Digital & AI strategy is not without its risks. The CDO TIMES can help identify potential pitfalls and develop mitigation strategies, helping you avoid costly mistakes and ensuring a smooth transition.
- Competitive Advantage : Finally, by hiring CDO TIMES experts, you are investing in a competitive advantage. Their expertise can help you speed up your innovation processes, bring products to market faster, and stay ahead of your competitors.
By employing the expertise of CDO TIMES, organizations can navigate the complexities of digital innovation with greater confidence and foresight, setting themselves up for success in the rapidly evolving digital economy. The future is digital, and with CDO TIMES, you’ll be well-equipped to lead in this new frontier.
Do you need help with your digital transformation initiatives? We provide fractional CAIO, CDO, CISO and CIO services, do a Tech Navigator Assessment and we will help you drive results and deliver winning digital and AI strategies for you! Schedule your FREE Tech Navigator Call NOW:
Subscribe now for free and never miss out on digital insights delivered right to your inbox!
Type your email…
Share this:
- The Evolution of AI in the Workplace: Optimizing AI + Human Intelligence for Elevated Collaborative Intelligence (ECI)
- The AI Horizon: Top 10 Transformative Predictions for 2025 and Beyond
Carsten Krause
As the CDO of The CDO TIMES I am dedicated delivering actionable insights to our readers, explore current and future trends that are relevant to leaders and organizations undertaking digital transformation efforts. Besides writing about these topics we also help organizations make sense of all of the puzzle pieces and deliver actionable roadmaps and capabilities to stay future proof leveraging technology. Contact us at: [email protected] to get in touch.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Discover more from the cdo times.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Kodak Stunning Journey of Fortune to Misfortune (A Case Study -Financial Analysis

How an organization that had been fortunate over a century with a dominant position in the market, led to briskly misfortune and bankruptcy within short span of time. The entire case study emphasizes the stunning bankruptcy of Kodak. The gloomy journey of market giant, that had a lion's share of imaging world industry and that had positioned the name of photography to its recognition "Kodaking", has been over to ouster from the market. The general purpose of the research is to analyze the financial position of a company by applying financial analysis tools and check the consistency of results. The specific purpose of the research is to conclude the critical issues that have caused organization downfall by evidential support. Data collection has been made in this study on empirical basis and by the use of company annual reports, results & conclusions have been drawn. The prior segment of report shows the financial results and post segment represents the issues regarding failure of Kodak and suggests recommendations to rebuild the company. The research is significantly shown consistent results and reasons. It is widespread useful for business institutions especially for graduate professionals & organizations to envision the vision and insight about financial operations and consequences. It can be helpful to forecast future objectives and drives for sustainability and profitability of an organization.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
Examining+How+Change+Management+Failed

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Kodak's Downfall Wasn't About Technology. A generation ago, a "Kodak moment" meant something that was worth saving and savoring. Today, the term increasingly serves as a corporate bogeyman ...
his Book " The Decision Loop") offe rs three different business desig ns— make-. and-sell, sense-and-respond and a nticipate-and-lead. The right design. depends on the predictability of the ...
A case study of how Kodak is guilty on four counts of serious corporate failure his study undertakes an analysis of five fundamental dichotomies in strategy and applies them to the case of Eastman Kodak in an effort to understand the reasons for the business' continual underperformance and misalignment1 with the operating environment.
I was at Kodak from '83 - '97, most of that time in electronic/digital imaging R&D and product development. With due respect to Dr Shih's perspective having joined in '97, it was the years leading up to that, when Kodak squandered what could have been a dominant position in digital imaging and possibly online social media, due to lack of vision of what was clear to the engineers.
The study significantly emphasizes the reasons of bankruptcy of Kodak Empire. Appropriate financial techniques and tools are applied to investigate the root causes of its failure. The study also suggests the future implications for restructuring and revitalizing the company position. (Schreiner, 2012) , (Http://www.kodak.com)
Kodak's failure to transition from film to digital technology has become a canonical example of a dominant incumbent failing in the face of an industry transition. In this paper, we undertake a systematic study of Kodak's decision-making from its earliest efforts in digital technology in the 1960s through its bankruptcy in 2012.
The case investigates the reasons for he failure of Kodak's digital imaging strategy and offers lessons for other leading companies that face disruptive innovations in their core markets ...
In actuality, Kodak did once proceed with the diversification of its businesses in the 1980s and 1990s, but ultimately it focused on its film business. In the 2000s it invested efforts in digital cameras, but without success. In any case, without being able to transit to a new business, Kodak has been in management crisis for the last few years.
Established by George Eastman in the 1880s, by the 1950s Kodak had the lion's share of the US amateur film market. "Kodak was a company at the top of its game," says Kamal, who has studied the Rochester-based business for more than a decade. "Kodak controlled almost 70% of the highly lucrative US film market.
Lucas and Goh (2009) tried to explain Kodak's failure by extending Chris- ... detailed case study comparison between Kodak and Fujifilm before, during, and shortly after the digital disruption.
This strategic failure was the direct cause of Kodak's decades-long decline as digital photography destroyed its film-based business model. A new book by my Devil's Advocate Group colleague ...
Kodak Failure Case Study. Kodak, as we know it today, was founded in the year 1888 by George Eastman as 'The Eastman Kodak Company'. It was the most famous name in the world of photography and videography in the 20th century. Kodak brought about a revolution in the photography and videography industries.
The main problem was that Kodak was not making money with digital cameras. It was bleeding cash. According to a Harvard case study, it lost $60 for every digital camera it sold by 2001.. This ...
The introduction of digital imaging in the late 1980s had a disruptive effect on Kodak's traditional business model. Examines Kodak's strategic efforts and challenges as the photography industry evolves. After discussing Kodak's history and its past strategic moves in the new landscape, the case questions how CEO Daniel Carp can use digital ...
The fall of Kodak serves as a cautionary tale that outlines the importance of adaptability, strategic planning, and stakeholder alignment in today's volatile business environment. Organizations aiming to avoid a similar fate should consider adopting modern planning frameworks like Agile and Horizon Planning, stay open to revising their technology roadmaps, and leverage intellectual property ...
We propose an extension of Christensen's theory of disruptive technologies and illustrate the extensions with a longitudinal case study of Kodak. Kodak is unique in that it developed and patented many of the components of digital photography, yet this new form of photography has had a serious, negative impact on the firm. The two main ...
I.Abstract Eastman Kodak, 133-year-old firm, has stunned the world, announcing in January 2012 that it has put to its camera business. Kodak was founded by inventor, George Eastman, and its little yellow film packages became one of the world's most popular brands. It, indeed, was an American industrial icon.
Case Studies in US Trade Negotiation Vol. 2 Preview Chapter 3: Snapshot: Kodak v. Fuji. Snapshot: Kodak v. Fuji. On May 18, 1995, the Eastman Kodak Company of Rochester, New York, filed a complaint with the US government under section 301 of the 1974 Trade Act, claiming that its archrival, the Fuji Photo Film Company of Japan, in collusion with ...
A prominent example discussed in scientific literature is the failure of Kodak to digitally innovate their products and, thus, to drive the digital photography revolution (Ho & Chen, 2018 ...
Journalism Expands in Spite of the Crisis: Digital-Native News Media in Spain. Samuel Negredo María-del-Pilar Martínez-Costa J. G. Breiner Ramón Salaverría. Education. 2020. This study received funding from the research project DIGINATIVEMEDIA, funded by the Spanish Ministry of Science, Innovation and Universities (No. RTI2018- 093346-B-C31 ...
reasons why kodak failed_ _ kodak failure case study - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. reasons why kodak failed_ _ kodak failure case study
Kodak is facing fierce competition in the transformation of digital imaging. Kodak's competitors are miles stones ahead then 90% market share. A 131 ancient icon, led to Chapter 11 bankruptcy on January 19th 2012. Kodak management described that they had sufficient cash to support its operations and paid employees throughout the insolvent period.
Examining How Change Management Failed One example of change management failure within a company is the case of Kodak. Kodak, once a giant in the photography industry, failed to adapt to the digital revolution, leading to its decline and bankruptcy filing in 2012. Several factors contributed to this failure: 1. Lack of Visionary Leadership: Kodak's leadership failed to anticipate the shift ...