Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, what is your plagiarism score.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
3 straightforward steps (with examples) + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

38 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very timely.
I appreciate.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Literature Reviews
What is a literature review.
- Literature Review Process
Purpose of a Literature Review
- Choosing a Type of Review
- Developing a Research Question
- Searching the Literature
- Searching Tips
- ChatGPT [beta]
- Documenting your Search
- Using Citation Managers
- Concept Mapping
- Writing the Review
- Further Resources
The Library's Subject Specialists are happy to help with your literature reviews! Find your Subject Specialist here .

If you have questions about this guide, contact Librarian Jamie Niehof ([email protected]).
A literature review is an overview of the available research for a specific scientific topic. Literature reviews summarize existing research to answer a review question, provide context for new research, or identify important gaps in the existing body of literature.
An incredible amount of academic literature is published each year, by estimates over two million articles .
Sorting through and reviewing that literature can be complicated, so this Research Guide provides a structured approach to make the process more manageable.
THIS GUIDE IS AN OVERVIEW OF THE LITERATURE REVIEW PROCESS:
- Getting Started (asking a research question | defining scope)
- Organizing the Literature
- Writing the Literature Review (analyzing | synthesizing)
A literature search is a systematic search of the scholarly sources in a particular discipline. A literature review is the analysis, critical evaluation and synthesis of the results of that search. During this process you will move from a review of the literature to a review for your research. Your synthesis of the literature is your unique contribution to research.
WHO IS THIS RESEARCH GUIDE FOR?
— those new to reviewing the literature
— those that need a refresher or a deeper understanding of writing literature reviews
You may need to do a literature review as a part of a course assignment, a capstone project, a master's thesis, a dissertation, or as part of a journal article. No matter the context, a literature review is an essential part of the research process.

WHAT IS THE PURPOSE OF A LITERATURE REVIEW?
A literature review is typically performed for a specific reason. Even when assigned as an assignment, the goal of the literature review will be one or more of the following:
- To communicate a project's novelty by identifying a research gap
- An overview of research issues , methodologies or results relevant to field
- To explore the volume and types of available studies
- To establish familiarity with current research before carrying out a new project
- To resolve conflicts amongst contradictory previous studies
Reviewing the literature helps you understand a research topic and develop your own perspective.
A LITERATURE REVIEW IS NOT :
- An annotated bibliography – which is a list of annotated citations to books, articles and documents that includes a brief description and evaluation for each entry
- A literary review – which is a critical discussion of the merits and weaknesses of a literary work
- A book review – which is a critical discussion of the merits and weaknesses of a particular book
- Next: Choosing a Type of Review >>
- Last Updated: Feb 29, 2024 10:31 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.umich.edu/litreview
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 2 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.

Literature Reviews
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain what literature reviews are and offer insights into the form and construction of literature reviews in the humanities, social sciences, and sciences.
Introduction
OK. You’ve got to write a literature review. You dust off a novel and a book of poetry, settle down in your chair, and get ready to issue a “thumbs up” or “thumbs down” as you leaf through the pages. “Literature review” done. Right?
Wrong! The “literature” of a literature review refers to any collection of materials on a topic, not necessarily the great literary texts of the world. “Literature” could be anything from a set of government pamphlets on British colonial methods in Africa to scholarly articles on the treatment of a torn ACL. And a review does not necessarily mean that your reader wants you to give your personal opinion on whether or not you liked these sources.
What is a literature review, then?
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period.
A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. It might give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations. Or it might trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates. And depending on the situation, the literature review may evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant.
But how is a literature review different from an academic research paper?
The main focus of an academic research paper is to develop a new argument, and a research paper is likely to contain a literature review as one of its parts. In a research paper, you use the literature as a foundation and as support for a new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
Why do we write literature reviews?
Literature reviews provide you with a handy guide to a particular topic. If you have limited time to conduct research, literature reviews can give you an overview or act as a stepping stone. For professionals, they are useful reports that keep them up to date with what is current in the field. For scholars, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the writer in his or her field. Literature reviews also provide a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. Comprehensive knowledge of the literature of the field is essential to most research papers.
Who writes these things, anyway?
Literature reviews are written occasionally in the humanities, but mostly in the sciences and social sciences; in experiment and lab reports, they constitute a section of the paper. Sometimes a literature review is written as a paper in itself.
Let’s get to it! What should I do before writing the literature review?
If your assignment is not very specific, seek clarification from your instructor:
- Roughly how many sources should you include?
- What types of sources (books, journal articles, websites)?
- Should you summarize, synthesize, or critique your sources by discussing a common theme or issue?
- Should you evaluate your sources?
- Should you provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history?
Find models
Look for other literature reviews in your area of interest or in the discipline and read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or ways to organize your final review. You can simply put the word “review” in your search engine along with your other topic terms to find articles of this type on the Internet or in an electronic database. The bibliography or reference section of sources you’ve already read are also excellent entry points into your own research.
Narrow your topic
There are hundreds or even thousands of articles and books on most areas of study. The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to get a good survey of the material. Your instructor will probably not expect you to read everything that’s out there on the topic, but you’ll make your job easier if you first limit your scope.
Keep in mind that UNC Libraries have research guides and to databases relevant to many fields of study. You can reach out to the subject librarian for a consultation: https://library.unc.edu/support/consultations/ .
And don’t forget to tap into your professor’s (or other professors’) knowledge in the field. Ask your professor questions such as: “If you had to read only one book from the 90’s on topic X, what would it be?” Questions such as this help you to find and determine quickly the most seminal pieces in the field.
Consider whether your sources are current
Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. In the sciences, for instance, treatments for medical problems are constantly changing according to the latest studies. Information even two years old could be obsolete. However, if you are writing a review in the humanities, history, or social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be what is needed, because what is important is how perspectives have changed through the years or within a certain time period. Try sorting through some other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to consider what is currently of interest to scholars in this field and what is not.
Strategies for writing the literature review
Find a focus.
A literature review, like a term paper, is usually organized around ideas, not the sources themselves as an annotated bibliography would be organized. This means that you will not just simply list your sources and go into detail about each one of them, one at a time. No. As you read widely but selectively in your topic area, consider instead what themes or issues connect your sources together. Do they present one or different solutions? Is there an aspect of the field that is missing? How well do they present the material and do they portray it according to an appropriate theory? Do they reveal a trend in the field? A raging debate? Pick one of these themes to focus the organization of your review.
Convey it to your reader
A literature review may not have a traditional thesis statement (one that makes an argument), but you do need to tell readers what to expect. Try writing a simple statement that lets the reader know what is your main organizing principle. Here are a couple of examples:
The current trend in treatment for congestive heart failure combines surgery and medicine. More and more cultural studies scholars are accepting popular media as a subject worthy of academic consideration.
Consider organization
You’ve got a focus, and you’ve stated it clearly and directly. Now what is the most effective way of presenting the information? What are the most important topics, subtopics, etc., that your review needs to include? And in what order should you present them? Develop an organization for your review at both a global and local level:
First, cover the basic categories
Just like most academic papers, literature reviews also must contain at least three basic elements: an introduction or background information section; the body of the review containing the discussion of sources; and, finally, a conclusion and/or recommendations section to end the paper. The following provides a brief description of the content of each:
- Introduction: Gives a quick idea of the topic of the literature review, such as the central theme or organizational pattern.
- Body: Contains your discussion of sources and is organized either chronologically, thematically, or methodologically (see below for more information on each).
- Conclusions/Recommendations: Discuss what you have drawn from reviewing literature so far. Where might the discussion proceed?
Organizing the body
Once you have the basic categories in place, then you must consider how you will present the sources themselves within the body of your paper. Create an organizational method to focus this section even further.
To help you come up with an overall organizational framework for your review, consider the following scenario:
You’ve decided to focus your literature review on materials dealing with sperm whales. This is because you’ve just finished reading Moby Dick, and you wonder if that whale’s portrayal is really real. You start with some articles about the physiology of sperm whales in biology journals written in the 1980’s. But these articles refer to some British biological studies performed on whales in the early 18th century. So you check those out. Then you look up a book written in 1968 with information on how sperm whales have been portrayed in other forms of art, such as in Alaskan poetry, in French painting, or on whale bone, as the whale hunters in the late 19th century used to do. This makes you wonder about American whaling methods during the time portrayed in Moby Dick, so you find some academic articles published in the last five years on how accurately Herman Melville portrayed the whaling scene in his novel.
Now consider some typical ways of organizing the sources into a review:
- Chronological: If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials above according to when they were published. For instance, first you would talk about the British biological studies of the 18th century, then about Moby Dick, published in 1851, then the book on sperm whales in other art (1968), and finally the biology articles (1980s) and the recent articles on American whaling of the 19th century. But there is relatively no continuity among subjects here. And notice that even though the sources on sperm whales in other art and on American whaling are written recently, they are about other subjects/objects that were created much earlier. Thus, the review loses its chronological focus.
- By publication: Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on biological studies of sperm whales if the progression revealed a change in dissection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies.
- By trend: A better way to organize the above sources chronologically is to examine the sources under another trend, such as the history of whaling. Then your review would have subsections according to eras within this period. For instance, the review might examine whaling from pre-1600-1699, 1700-1799, and 1800-1899. Under this method, you would combine the recent studies on American whaling in the 19th century with Moby Dick itself in the 1800-1899 category, even though the authors wrote a century apart.
- Thematic: Thematic reviews of literature are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time. However, progression of time may still be an important factor in a thematic review. For instance, the sperm whale review could focus on the development of the harpoon for whale hunting. While the study focuses on one topic, harpoon technology, it will still be organized chronologically. The only difference here between a “chronological” and a “thematic” approach is what is emphasized the most: the development of the harpoon or the harpoon technology.But more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. For instance, a thematic review of material on sperm whales might examine how they are portrayed as “evil” in cultural documents. The subsections might include how they are personified, how their proportions are exaggerated, and their behaviors misunderstood. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point made.
- Methodological: A methodological approach differs from the two above in that the focusing factor usually does not have to do with the content of the material. Instead, it focuses on the “methods” of the researcher or writer. For the sperm whale project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of whales in American, British, and French art work. Or the review might focus on the economic impact of whaling on a community. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed. Once you’ve decided on the organizational method for the body of the review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out. They should arise out of your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period. A thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue.
Sometimes, though, you might need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. Put in only what is necessary. Here are a few other sections you might want to consider:
- Current Situation: Information necessary to understand the topic or focus of the literature review.
- History: The chronological progression of the field, the literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Methods and/or Standards: The criteria you used to select the sources in your literature review or the way in which you present your information. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed articles and journals.
Questions for Further Research: What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
Begin composing
Once you’ve settled on a general pattern of organization, you’re ready to write each section. There are a few guidelines you should follow during the writing stage as well. Here is a sample paragraph from a literature review about sexism and language to illuminate the following discussion:
However, other studies have shown that even gender-neutral antecedents are more likely to produce masculine images than feminine ones (Gastil, 1990). Hamilton (1988) asked students to complete sentences that required them to fill in pronouns that agreed with gender-neutral antecedents such as “writer,” “pedestrian,” and “persons.” The students were asked to describe any image they had when writing the sentence. Hamilton found that people imagined 3.3 men to each woman in the masculine “generic” condition and 1.5 men per woman in the unbiased condition. Thus, while ambient sexism accounted for some of the masculine bias, sexist language amplified the effect. (Source: Erika Falk and Jordan Mills, “Why Sexist Language Affects Persuasion: The Role of Homophily, Intended Audience, and Offense,” Women and Language19:2).
Use evidence
In the example above, the writers refer to several other sources when making their point. A literature review in this sense is just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence to show that what you are saying is valid.
Be selective
Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the review’s focus, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological.
Use quotes sparingly
Falk and Mills do not use any direct quotes. That is because the survey nature of the literature review does not allow for in-depth discussion or detailed quotes from the text. Some short quotes here and there are okay, though, if you want to emphasize a point, or if what the author said just cannot be rewritten in your own words. Notice that Falk and Mills do quote certain terms that were coined by the author, not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. But if you find yourself wanting to put in more quotes, check with your instructor.
Summarize and synthesize
Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each paragraph as well as throughout the review. The authors here recapitulate important features of Hamilton’s study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study’s significance and relating it to their own work.
Keep your own voice
While the literature review presents others’ ideas, your voice (the writer’s) should remain front and center. Notice that Falk and Mills weave references to other sources into their own text, but they still maintain their own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with their own ideas and their own words. The sources support what Falk and Mills are saying.
Use caution when paraphrasing
When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author’s information or opinions accurately and in your own words. In the preceding example, Falk and Mills either directly refer in the text to the author of their source, such as Hamilton, or they provide ample notation in the text when the ideas they are mentioning are not their own, for example, Gastil’s. For more information, please see our handout on plagiarism .
Revise, revise, revise
Draft in hand? Now you’re ready to revise. Spending a lot of time revising is a wise idea, because your main objective is to present the material, not the argument. So check over your review again to make sure it follows the assignment and/or your outline. Then, just as you would for most other academic forms of writing, rewrite or rework the language of your review so that you’ve presented your information in the most concise manner possible. Be sure to use terminology familiar to your audience; get rid of unnecessary jargon or slang. Finally, double check that you’ve documented your sources and formatted the review appropriately for your discipline. For tips on the revising and editing process, see our handout on revising drafts .
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Jones, Robert, Patrick Bizzaro, and Cynthia Selfe. 1997. The Harcourt Brace Guide to Writing in the Disciplines . New York: Harcourt Brace.
Lamb, Sandra E. 1998. How to Write It: A Complete Guide to Everything You’ll Ever Write . Berkeley: Ten Speed Press.
Rosen, Leonard J., and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
Troyka, Lynn Quittman, and Doug Hesse. 2016. Simon and Schuster Handbook for Writers , 11th ed. London: Pearson.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
- University of Oregon Libraries
- Research Guides
How to Write a Literature Review
Who is my subject librarian.
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it Describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the Question
- 2. Review Discipline Styles
- Searching Article Databases
- Finding Full-Text of an Article
- Citation Chaining
- When to Stop Searching
- 4. Manage Your References
- 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
- 6. Synthesize
- 7. Write a Literature Review
This guide has a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA) License.

This license lets others remix, tweak, and build upon your work non-commercially, as long as they credit you and license their new creations under the identical terms.
- Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) License Deed
This guide is organized around the 7 steps in the graphic to the left to help you understand the process of writing a literature review.
This guide will help you to
- Define a literature review
- Recognize that different fields of study have their own way to perform and write literature reviews
- Prepare to search the literature
- Read critically -- analyze and synthesize
- Prepare to write a literature review
At the end of the tutorial, you will find a quiz that you can submit through Canvas for course credit.
Graphic from Literature Review (2009) by Machi and McEvoy.
Text description of "Literature Review Process" for web accessibility
If you have questions related to a field or discipline, consider reaching out to a Subject Librarian by email, phone, or by scheduling an appointment for a free consultation:
- Subject Librarians
- Next: What's a Literature Review? >>
- Last Updated: Jan 10, 2024 4:46 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.uoregon.edu/litreview
Contact Us Library Accessibility UO Libraries Privacy Notices and Procedures

1501 Kincaid Street Eugene, OR 97403 P: 541-346-3053 F: 541-346-3485
- Visit us on Facebook
- Visit us on Twitter
- Visit us on Youtube
- Visit us on Instagram
- Report a Concern
- Nondiscrimination and Title IX
- Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Find People
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

Africa’s postdoc workforce is on the rise — but at what cost?
Career Feature 02 APR 24

Research assessments are still not fit for purpose — here’s how to change things
World View 02 APR 24

How scientists are making the most of Reddit
Career Feature 01 APR 24
Adopt universal standards for study adaptation to boost health, education and social-science research
Correspondence 02 APR 24
How can we make PhD training fit for the modern world? Broaden its philosophical foundations
Allow researchers with caring responsibilities ‘promotion pauses’ to make research more equitable

The corpse of an exploded star and more — March’s best science images
News 28 MAR 24

How papers with doctored images can affect scientific reviews

Nature is committed to diversifying its journalistic sources
Editorial 27 MAR 24
Head of ClinicalTrials.gov
National Institutes of Health (NIH) National Library of Medicine (NLM) National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Information Engineering...
Washington D.C. (US)
National Library of Medicine, National Center for Biotechnology Information
POSTDOCTORAL FELLOWSHIP IN SYSTEMS BIOLOGY: PRECISION VACCINE PROGRAM (PVP) - BOSTON CHILDREN'
The Data Management and Analysis Core (DMAC) within the Precision Vaccine Program (PVP) at Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School (H...
Boston, Massachusetts
Boston Children's Hospital - Department of Pediatrics
2024 Recruitment notice Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology: Shenzhen, China
The wide-ranging expertise drawing from technical, engineering or science professions...
Shenzhen,China
Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology
Global Talent Recruitment (Scientist Positions)
Global Talent Gathering for Innovation, Changping Laboratory Recruiting Overseas High-Level Talents.
Beijing, China
Changping Laboratory
Senior Scientist, Research
Be part of something altogether life-changing! Working at Cytiva means being at the forefront of providing new solutions to transform human heal...
Vancouver, British Columbia (CA)
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
Literature Reviews
Introduction to literature reviews, websites on literature reviews, books about literature reviews at ubc library, related guides.
- Find Scholarly Articles
- Find Theses and Dissertations
Subject Liaison Librarians
Contact the subject librarian for your discipline or department for assistance with selecting and searching databases, locating specialized materials, and more.
Writing Support at UBC Vancouver
The Centre for Writing and Scholarly Communication offers workshops on a number of academic writing topics for undergrads, graduate students, post-doctoral fellows and faculty members.
Writing Support at UBC Okanagan
The Centre for Scholarly Communication provides one-on-one consultations about all aspects of scholarly communication, including writing support for journal articles, grant proposals, theses, dissertations, and conference presentations, as well as copyright, open access, and author rights.
This comprehensive guide is designed for students preparing an honours thesis, graduating paper, Master's thesis or doctoral dissertation.
What is a literature review?
"Literature review" typically refers to work produced in the context of an article in an academic publication or as part of a Master's thesis or doctoral dissertation.
"A literature review is an evaluative report of information found in the literature related to your selected area of study. The review should describe, summarize, evaluate and clarify this literature. It should give a theoretical base for the research and help you (the author) determine the nature of your research." 1
For information on systematic reviews - a particular type of literature review used primarily in health sciences - please refer to this guide: Knowledge Synthesis: Systematic, Scoping & Other Reviews .
What are the purposes of a literature review?
- situate your work in its discipline/area/subfield
- develop an understanding of how knowledge in your discipline/field/area has changed over time
- develop mastery of what's known in your area, and part of the larger discipline that contains it
- compare different conceptual or sub-disciplinary approaches to your topic
- compare and contrast different theoretical schools or leading researchers in your area
- identify methodologies that you might use in your work
- Types of Literature Reviews
" Traditional Review : adopts a critical approach, which might assess theories or hypotheses by critically examining the methods and results of single primary studies, with an emphasis on background and contextual material.
Conceptual Review : synthesizes areas of conceptual knowledge that contribute to a better understanding of the issues. State of the art: brings readers up to date on the most recent research on the subject. Could be a useful beginning to your research project.
Scoping Review : sets the scene for a future research agenda. This review documents what is already known and then, using a critical analysis of gaps in knowledge, helps to refine the research questions, concepts and theories to point the way to future research." 1
Systematic Review : "attempts to identify, appraise and synthesize all the empirical evidence that meets pre-specified eligibility criteria to answer a given research question [about health care or health policy]. Researchers conducting systematic reviews use explicit methods aimed at minimizing bias, in order to produce more reliable findings that can be used to inform decision making." 2 More info at guide: Knowledge Synthesis: Systematic, Scoping & Other Reviews.
1. Jesson, Jill, Lydia Matheson, and Fiona M. Lacey. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles: SAGE, 2011. Print.
2. About Cochrane Systematic Reviews
- Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review , PLoS
- The Literature Review: A few tips on conducting it , University of Toronto Writing Centre
- The Literature Review , Central Queensland University Library
- What is "the literature"?
- "The literature" relationships diagram
- For Mendeley users: How to do a Literature Review: Citation Tracing, Concept Saturation and Results’ Mind-Mapping by R. Pacheco-Vega
General
- Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper (print)
- Doing your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques (print)
- Evaluating Research Articles from Start to Finish (print)
- The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students (print)
- The Handbook of Scholarly Writing and Publishing (Chapter 11: Writing a Literature Review) (online)
- Telling a research story: writing a literature review (print)
- Writing the Literature Review: A Practical Guide (online)
Science/Social Science
- Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination (print)
- Writing Literature Reviews: A Guide for Students of the Social and Behavioral Sciences (print)
Health Sciences
- Health Sciences Literature Review Made Easy: The Matrix Method . 2017 Ed (online & print)
- Proposal Writing for Nursing Capstones and Clinical Projects (Chapter 4: Into the Literature: Gaining Best Evidence and Relevant Literature. Chapter 5: Synthesizing Best Evidence and Literature Review) (online)
- Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students (online)
Engineering
- So, Your Have to Write a Literature Review: A Guided Workbook for Engineers (online)
- Writing for Science and Engineering: Papers, Presentations and Reports - Chapter 4 (online)
- Systematic and Scoping Reviews Search Methodology
- Resources for Dissertation Writing
- Next: Keep Track >>
- Last Updated: Feb 5, 2024 8:25 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.ubc.ca/litreviews

- General Education Courses
- School of Business
- School of Design
- School of Education
- School of Health Sciences
- School of Justice Studies
- School of Nursing
- School of Technology
- CBE Student Guide
- Online Library
- Ask a Librarian
- Learning Express Library
- Interlibrary Loan Request Form
- Library Staff
- Databases A-to-Z
- Articles by Subject
- Discovery Search
- Publication Finder
- Video Databases
- NoodleTools
- Library Guides
- Course Guides
- Writing Lab
- Rasmussen Technical Support (PSC)
- Copyright Toolkit
- Faculty Toolkit
- Suggest a Purchase
- Refer a Student Tutor
- Live Lecture/Peer Tutor Scheduler
- Faculty Interlibrary Loan Request Form
- Professional Development Databases
- Publishing Guide
- Professional Development Guides (AAOPD)
- Literature Review Guide
The Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- Plan Your Literature Review
- Identify a Research Gap
- Define Your Research Question
- Search the Literature
- Analyze Your Research Results
- Manage Research Results
- Write the Literature Review

What is a Literature Review? What is its purpose?
The purpose of a literature review is to offer a comprehensive review of scholarly literature on a specific topic along with an evaluation of the strengths and weaknesses of authors' arguments . In other words, you are summarizing research available on a certain topic and then drawing conclusions about researchers' findings. To make gathering research easier, be sure to start with a narrow/specific topic and then widen your topic if necessary.
A thorough literature review provides an accurate description of current knowledge on a topic and identifies areas for future research. Are there gaps or areas that require further study and exploration? What opportunities are there for further research? What is missing from my collection of resources? Are more resources needed?
It is important to note that conclusions described in the literature you gather may contradict each other completely or in part. Recognize that knowledge creation is collective and cumulative. Current research is built upon past research findings and discoveries. Research may bring previously accepted conclusions into question. A literature review presents current knowledge on a topic and may point out various academic arguments within the discipline.
What a Literature Review is not
- A literature review is not an annotated bibliography . An annotated bibliography provides a brief summary, analysis, and reflection of resources included in the bibliography. Often it is not a systematic review of existing research on a specific subject. That said, creating an annotated bibliography throughout your research process may be helpful in managing the resources discovered through your research.
- A literature review is not a research paper . A research paper explores a topic and uses resources discovered through the research process to support a position on the topic. In other words, research papers present one side of an issue. A literature review explores all sides of the research topic and evaluates all positions and conclusions achieved through the scientific research process even though some conclusions may conflict partially or completely.
From the Online Library
- SAGE Research Methods This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods is a web-based research methods tool that covers quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods. Researchers can explore methods and concepts to help design research projects, understand a particular method or identify a new method, and write up research. Sage Research Methods focuses on methodology rather than disciplines, and is of potential use to researchers from the social sciences, health sciences and other research areas.
- Sage Research Methods Project Planner - Reviewing the Literature View the resources and videos for a step-by-step guide to performing a literature review.
The Literature Review: Step by Step
Follow this step-by-step process by using the related tabs in this Guide.
- Define your Research question
- Analyze the material you’ve found
- Manage the results of your research
- Write your Review
Getting Started
Consider the following questions as you develop your research topic, conduct your research, and begin evaluating the resources discovered in the research process:
- What is known about the subject?
- Are there any gaps in the knowledge of the subject?
- Have areas of further study been identified by other researchers that you may want to consider?
- Who are the significant research personalities in this area?
- Is there consensus about the topic?
- What aspects have generated significant debate on the topic?
- What methods or problems were identified by others studying in the field and how might they impact your research?
- What is the most productive methodology for your research based on the literature you have reviewed?
- What is the current status of research in this area?
- What sources of information or data were identified that might be useful to you?
- How detailed? Will it be a review of ALL relevant material or will the scope be limited to more recent material, e.g., the last five years.
- Are you focusing on methodological approaches; on theoretical issues; on qualitative or quantitative research?
What is Academic Literature?
What is the difference between popular and scholarly literature?
To better understand the differences between popular and scholarly articles, comparing characteristics and purpose of the publications where these articles appear is helpful.
Popular Article (Magazine)
- Articles are shorter and are written for the general public
- General interest topics or current events are covered
- Language is simple and easy to understand
- Source material is not cited
- Articles often include glossy photographs, graphics, or visuals
- Articles are written by the publication's staff of journalists
- Articles are edited and information is fact checked
Examples of magazines that contain popular articles:

Scholarly Article (Academic Journal)
- Articles are written by scholars and researchers for academics, professionals, and experts in the field
- Articles are longer and report original research findings
- Topics are narrower in focus and provide in-depth analysis
- Technical or scholarly language is used
- Source material is cited
- Charts and graphs illustrating research findings are included
- Many are "peer reviewed" meaning that panels of experts review articles submitted for publication to ensure that proper research methods were used and research findings are contributing something new to the field before selecting for publication.
Examples of academic journals that contain scholarly articles:

Define your research question
Selecting a research topic can be overwhelming. Consider following these steps:
1. Brainstorm research topic ideas
- Free write: Set a timer for five minutes and write down as many ideas as you can in the allotted time
- Mind-Map to explore how ideas are related
2. Prioritize topics based on personal interest and curiosity
3. Pre-research
- Explore encyclopedias and reference books for background information on the topic
- Perform a quick database or Google search on the topic to explore current issues.
4. Focus the topic by evaluating how much information is available on the topic
- Too much information? Consider narrowing the topic by focusing on a specific issue
- Too little information? Consider broadening the topic
5. Determine your purpose by considering whether your research is attempting to:
- further the research on this topic
- fill a gap in the research
- support existing knowledge with new evidence
- take a new approach or direction
- question or challenge existing knowledge
6. Finalize your research question
NOTE: Be aware that your initial research question may change as you conduct research on your topic.
Searching the Literature
Research on your topic should be conducted in the academic literature. The Rasmussen University Online Library contains subject-focused databases that contain the leading academic journals in your programmatic area.
Consult the Using the Online Library video tutorials for information about how to effectively search library databases.
Watch the video below for tips on how to create a search statement that will provide relevant results
Need help starting your research? Make a research appointment with a Rasmussen Librarian .

TIP: Document as you research. Begin building your references list using the citation managers in one of these resources:
- APA Academic Writer
Recommended programmatic databases include:
Data Science
Coverage includes computer engineering, computer theory & systems, research and development, and the social and professional implications of new technologies. Articles come from more than 1,900 academic journals, trade magazines, and professional publications.
Provides access to full-text peer-reviewed journals, transactions, magazines, conference proceedings, and published standards in the areas of electrical engineering, computer science, and electronics. It also provides access to the IEEE Standards Dictionary Online. Full-text available.
Computing, telecommunications, art, science and design databases from ProQuest.
Healthcare Management
Articles from scholarly business journals back as far as 1886 with content from all disciplines of business, including marketing, management, accounting, management information systems, production and operations management, finance, and economics. Contains 55 videos from the Harvard Faculty Seminar Series, on topics such as leadership, sustaining competitive advantage, and globalization. To access the videos, click "More" in the blue bar at the top. Select "Images/ Business Videos." Uncheck "Image Quick View Collection" to indicate you only wish to search for videos. Enter search terms.
Provides a truly comprehensive business research collection. The collection consists of the following databases and more: ABI/INFORM Complete, ProQuest Entrepreneurship, ProQuest Accounting & Tax, International Bibliography of Social Sciences (IBSS), ProQuest Asian Business and Reference, and Banking Information Source.
The definitive research tool for all areas of nursing and allied health literature. Geared towards the needs of nurses and medical professionals. Covers more than 750 journals from 1937 to present.
HPRC provides information on the creation, implementation and study of health care policy and the health care system. Topics covered include health care administration, economics, planning, law, quality control, ethics, and more.
PolicyMap is an online mapping site that provides data on demographics, real estate, health, jobs, and other areas across the U.S. Access and visualize data from Census and third-party records.
Human Resources
Articles from all subject areas gathered from more than 11,000 magazines, journals, books and reports. Subjects include astronomy, multicultural studies, humanities, geography, history, law, pharmaceutical sciences, women's studies, and more. Coverage from 1887 to present. Start your research here.
Cochrane gathers and summarizes the best evidence from research to help you make informed choices about treatments. Whether a doctor or nurse, patient, researcher or student, Cochrane evidence provides a tool to enhance your healthcare knowledge and decision making on topics ranging from allergies, blood disorders, and cancer, to mental health, pregnancy, urology, and wounds.
Health sciences, biology, science, and pharmaceutical information from ProQuest. Includes articles from scholarly, peer-reviewed journals, practical and professional development content from professional journals, and general interest articles from magazines and newspapers.
Joanna Briggs Institute Academic Collection contains evidence-based information from across the globe, including evidence summaries, systematic reviews, best practice guidelines, and more. Subjects include medical, nursing, and healthcare specialties.
Comprehensive source of full-text articles from more than 1,450 scholarly medical journals.
Articles from more than 35 nursing journals in full text, searchable as far back as 1995.
Analyzing Your Research Results
You have completed your research and discovered many, many academic articles on your topic. The next step involves evaluating and organizing the literature found in the research process.
As you review, keep in mind that there are three types of research studies:
- Quantitative
- Qualitative
- Mixed Methods
Consider these questions as you review the articles you have gathered through the research process:
1. Does the study relate to your topic?
2. Were sound research methods used in conducting the study?
3. Does the research design fit the research question? What variables were chosen? Was the sample size adequate?
4. What conclusions were drawn? Do the authors point out areas for further research?
Reading Academic Literature
Academic journals publish the results of research studies performed by experts in an academic discipline. Articles selected for publication go through a rigorous peer-review process. This process includes a thorough evaluation of the research submitted for publication by journal editors and other experts or peers in the field. Editors select articles based on specific criteria including the research methods used, whether the research contributes new findings to the field of study, and how the research fits within the scope of the academic journal. Articles selected often go through a revision process prior to publication.
Most academic journal articles include the following sections:
- Abstract (An executive summary of the study)
- Introduction (Definition of the research question to be studied)
- Literature Review (A summary of past research noting where gaps exist)
- Methods (The research design including variables, sample size, measurements)
- Data (Information gathered through the study often displayed in tables and charts)
- Results (Conclusions reached at the end of the study)
- Conclusion (Discussion of whether the study proved the thesis; may suggest opportunities for further research)
- Bibliography (A list of works cited in the journal article)
TIP: To begin selecting articles for your research, read the highlighted sections to determine whether the academic journal article includes information relevant to your research topic.
Step 1: Skim the article
When sorting through multiple articles discovered in the research process, skimming through these sections of the article will help you determine whether the article will be useful in your research.
1. Article title and subject headings assigned to the article
2. Abstract
3. Introduction
4. Conclusion
If the article fits your information need, go back and read the article thoroughly.
TIP: Create a folder on your computer to save copies of articles you plan to use in your thesis or research project. Use NoodleTools or APA Academic Writer to save APA references.
Step 2: Determine Your Purpose
Think about how you will evaluate the academic articles you find and how you will determine whether to include them in your research project. Ask yourself the following questions to focus your search in the academic literature:
- Are you looking for an overview of a topic? an explanation of a specific concept, idea, or position?
- Are you exploring gaps in the research to identify a new area for academic study?
- Are you looking for research that supports or disagrees with your thesis or research question?
- Are you looking for examples of a research design and/or research methods you are considering for your own research project?
Step 3: Read Critically
Before reading the article, ask yourself the following:
- What is my research question? What position am I trying to support?
- What do I already know about this topic? What do I need to learn?
- How will I evaluate the article? Author's reputation? Research design? Treatment of topic?
- What are my biases about the topic?
As you read the article make note of the following:
- Who is the intended audience for this article?
- What is the author's purpose in writing this article?
- What is the main point?
- How was the main point proven or supported?
- Were scientific methods used in conducting the research?
- Do you agree or disagree with the author? Why?
- How does this article compare or connect with other articles on the topic?
- Does the author recommend areas for further study?
- How does this article help to answer your research question?
Managing your Research
Tip: Create APA references for resources as you discover them in the research process
Use APA Academic Writer or NoodleTools to generate citations and manage your resources. Find information on how to use these resources in the Citation Tools Guide .

Writing the Literature Review
Once research has been completed, it is time to structure the literature review and begin summarizing and synthesizing information. The following steps may help with this process:
- Chronological
- By research method used
- Explore contradictory or conflicting conclusions
- Read each study critically
- Critique methodology, processes, and conclusions
- Consider how the study relates to your topic

- Description of public health nursing nutrition assessment and interventions for home‐visited women. This article provides a nice review of the literature in the article introduction. You can see how the authors have used the existing literature to make a case for their research questions. more... less... Horning, M. L., Olsen, J. M., Lell, S., Thorson, D. R., & Monsen, K. A. (2018). Description of public health nursing nutrition assessment and interventions for home‐visited women. Public Health Nursing, 35(4), 317–326. https://doi.org/10.1111/phn.12410
- Improving Diabetes Self-Efficacy in the Hispanic Population Through Self-Management Education Doctoral papers are a good place to see how literature reviews can be done. You can learn where they searched, what search terms they used, and how they decided which articles were included. Notice how the literature review is organized around the three main themes that came out of the literature search. more... less... Robles, A. N. (2023). Improving diabetes self-efficacy in the hispanic population through self-management education (Order No. 30635901). Available from ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global: The Sciences and Engineering Collection. https://www.proquest.com/dissertations-theses/improving-diabetes-self-efficacy-hispanic/docview/2853708553/se-2
- Exploring mediating effects between nursing leadership and patient safety from a person-centred perspective: A literature review Reading articles that publish the results of a systematic literature review is a great way to see in detail how a literature review is conducted. These articles provide an article matrix, which provides you an example of how you can document information about the articles you find in your own search. To see more examples, include "literature review" or "systematic review" as a search term. more... less... Wang, M., & Dewing, J. (2021). Exploring mediating effects between nursing leadership and patient safety from a person‐centred perspective: A literature review. Journal of Nursing Management, 29(5), 878–889. https://doi.org/10.1111/jonm.13226
Database Search Tips
- Boolean Operators
- Keywords vs. Subjects
- Creating a Search String
- Library databases are collections of resources that are searchable, including full-text articles, books, and encyclopedias.
- Searching library databases is different than searching Google. Best results are achieved when using Keywords linked with Boolean Operators .
- Applying Limiters such as full-text, publication date, resource type, language, geographic location, and subject help to refine search results.
- Utilizing Phrases or Fields , in addition to an awareness of Stop Words , can focus your search and retrieve more useful results.
- Have questions? Ask a Librarian
Boolean Operators connect keywords or concepts logically to retrieve relevant articles, books, and other resources. There are three Boolean Operators:
Using AND
- Narrows search results
- Connects two or more keywords/concepts
- All keywords/concepts connected with "and" must be in an article or resource to appear in the search results list

Venn diagram of the AND connector
Example: The result list will include resources that include both keywords -- "distracted driving" and "texting" -- in the same article or resource, represented in the shaded area where the circles intersect (area shaded in purple).
- Broadens search results ("OR means more!")
- Connects two or more synonyms or related keywords/concepts
- Resources appearing in the results list will include any of the terms connected with the OR connector

Venn diagram of the OR connector
Example: The result list will include resources that include the keyword "texting" OR the keyword "cell phone" (entire area shaded in blue); either is acceptable.
- Excludes keywords or concepts from the search
- Narrows results by removing resources that contain the keyword or term connected with the NOT connector
- Use sparingly

Venn diagram of the NOT connector
Example: The result list will include all resources that include the term "car" (green area) but will exclude any resource that includes the term "motorcycle" (purple area) even though the term car may be present in the resource.
A library database searches for keywords throughout the entire resource record including the full-text of the resource, subject headings, tags, bibliographic information, etc.
- Natural language words or short phrases that describe a concept or idea
- Can retrieve too few or irrelevant results due to full-text searching (What words would an author use to write about this topic?)
- Provide flexibility in a search
- Must consider synonyms or related terms to improve search results
- TIP: Build a Keyword List

Example: The keyword list above was developed to find resources that discuss how texting while driving results in accidents. Notice that there are synonyms (texting and "text messaging"), related terms ("cell phones" and texting), and spelling variations ("cell phone" and cellphone). Using keywords when searching full text requires consideration of various words that express an idea or concept.
- Subject Headings
- Predetermined "controlled vocabulary" database editors apply to resources to describe topical coverage of content
- Can retrieve more precise search results because every article assigned that subject heading will be retrieved.
- Provide less flexibility in a search
- Can be combined with a keyword search to focus search results.
- TIP: Consult database subject heading list or subject headings assigned to relevant resources

Example 1: In EBSCO's Academic Search Complete, clicking on the "Subject Terms" tab provides access to the entire subject heading list used in the database. It also allows a search for specific subject terms.

Example 2: A subject term can be incorporated into a keyword search by clicking on the down arrow next to "Select a Field" and selecting "Subject Terms" from the dropdown list. Also, notice how subject headings are listed below the resource title, providing another strategy for discovering subject headings used in the database.
When a search term is more than one word, enclose the phrase in quotation marks to retrieve more precise and accurate results. Using quotation marks around a term will search it as a "chunk," searching for those particular words together in that order within the text of a resource.
"cell phone"
"distracted driving"
"car accident"
TIP: In some databases, neglecting to enclose phrases in quotation marks will insert the AND Boolean connector between each word resulting in unintended search results.
Truncation provides an option to search for a root of a keyword in order to retrieve resources that include variations of that word. This feature can be used to broaden search results, although some results may not be relevant. To truncate a keyword, type an asterisk (*) following the root of the word.
For example:

Library databases provide a variety of tools to limit and refine search results. Limiters provide the ability to limit search results to resources having specified characteristics including:
- Resource type
- Publication date
- Geographic location
In both the EBSCO and ProQuest databases, the limiting tools are located in the left panel of the results page.
EBSCO ProQuest

The short video below provides a demonstration of how to use limiters to refine a list of search results.
Each resource in a library database is stored in a record. In addition to the full-text of the resources, searchable Fields are attached that typically include:
- Journal title
- Date of Publication
Incorporating Fields into your search can assist in focusing and refining search results by limiting the results to those resources that include specific information in a particular field.
In both EBSCO and ProQuest databases, selecting the Advanced Search option will allow Fields to be included in a search.
For example, in the Advanced Search option in EBSCO's Academic Search Complete database, clicking on the down arrow next to "Select a Field" provides a list of fields that can be searched within that database. Select the field and enter the information in the text box to the left to use this feature.

Stop words are short, commonly used words--articles, prepositions, and pronouns-- that are automatically dropped from a search. Typical stop words include:
In library databases, a stop word will not be searched even if it is included in a phrase enclosed in quotation marks. In some instances, a word will be substituted for the stop word to allow for the other words in the phrase to be searched in proximity to one another within the text of the resource.
For example, if you searched company of America, your result list will include these variatons:
- company in America
- company of America
- company for America
Creating an Search String
This short video demonstrates how to create a search string -- keywords connected with Boolean operators -- to use in a library database search to retrieve relevant resources for any research assignment.
- Database Search Menu Template Use this search menu template to plan a database search.
- Last Updated: Feb 16, 2024 10:01 AM
- URL: https://guides.rasmussen.edu/LitReview

Write a Literature Review
What is a literature review, what is the purpose of a literature review, what are the parts of a literature review, what if i have to write a systematic review.
- Seven Steps to Writing a Literature Review
- Resources for Gathering and Reading the Literature
- Resources for Writing and Revising
- Other Useful Resources
Ask Us: Chat, email, visit or call

More writing resources
- Check out our full list of online writing resources These guides, templates, and videos are designed to help academic writers at various stages of their writing process, including the pre-writing and revising stages.
Get assistance
The library offers a range of helpful services. All of our appointments are free of charge and confidential.
- Book an appointment
A literature review is both a summary and explanation of the complete and current state of knowledge on a narrowed topic as found in academic books and journal articles.
You might be asked to write one of two broad kinds of literature reviews: a stand-alone assignment for a course, often as part of your training in the research of your field, or as a part of an introduction to or preparation for a longer work, usually a thesis or research report. The specific purpose and length of the literature review will vary. One way to understand the differences between these two types is to read published literature reviews or the literature review chapter of theses and dissertations in your own subject area. Analyze the structure of their arguments and note the way they address the issues.
- To summarize, evaluate, and compare articles or studies that are relevant and important to your topic
- To highlight key findings
- To identify inconsistencies, gaps, and contradictions in the literature
- To provide an analysis of the methodologies and approaches of other researchers
- To provide clues as to where future research is heading or recommend areas on which to focus
- To ensure you do not duplicate work that has already been done
Introduction
- To explain the focus and establish the importance of the subject
- provide the framework, selection criteria, or parameters of your literature review
- provide background or history
- outline what kind of work has been done on the topic
- briefly identify any controversies within the field or any recent research that has raised questions about earlier assumptions
- In a stand-alone literature review, this statement will sum up and evaluate the current state of this field of research
- In a review that is an introduction or preparatory to a thesis or research report, it will suggest how the review findings will lead to the research the writer proposes to undertake.
- To summarize and evaluate the current state of knowledge in the field
- To note major themes or topics, the most important trends, and any findings about which researchers agree or disagree
- Often divided by headings/subheadings
- If the review is preliminary to your own thesis or research project, its purpose is to make an argument that will justify your proposed research. Therefore, the literature review will discuss only that research which leads directly to your own project.
- To summarize the evidence presented and show its significance
- Rather than restating your thesis or purpose statement, explain what your review tells you about the current state of the field
- If the review is an introduction to your own research, the conclusion highlights gaps and indicates how previous research leads to your own research project and chosen methodology.
- If the review is a stand-alone assignment for a course, the conclusion should suggest any practical applications of the research as well as the implications and possibilities for future research.
- Find out what style guide you are required to follow (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago)
- Follow the guidelines to format citations and create a reference list or bibliography
- Cite Your Sources
You might be asked to write another type of literature review called a systematic review. Writers of systematic reviews use clearly defined search parameters to gather literature that will help them answer a focused research question.
If you plan to write a systematic review, you can book an appointment with a librarian to develop a search strategy.
- Conduct a Systematic Review
- Next: Seven Steps to Writing a Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Jan 8, 2024 2:25 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uoguelph.ca/LiteratureReview
Suggest an edit to this guide
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

Literature Reviews
- Getting started
What is a literature review?
Why conduct a literature review, stages of a literature review, lit reviews: an overview (video), check out these books.
- Types of reviews
- 1. Define your research question
- 2. Plan your search
- 3. Search the literature
- 4. Organize your results
- 5. Synthesize your findings
- 6. Write the review
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools
- Thompson Writing Studio This link opens in a new window
- Need to write a systematic review? This link opens in a new window

Contact a Librarian
Ask a Librarian
Definition: A literature review is a systematic examination and synthesis of existing scholarly research on a specific topic or subject.
Purpose: It serves to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge within a particular field.
Analysis: Involves critically evaluating and summarizing key findings, methodologies, and debates found in academic literature.
Identifying Gaps: Aims to pinpoint areas where there is a lack of research or unresolved questions, highlighting opportunities for further investigation.
Contextualization: Enables researchers to understand how their work fits into the broader academic conversation and contributes to the existing body of knowledge.

tl;dr A literature review critically examines and synthesizes existing scholarly research and publications on a specific topic to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge in the field.
What is a literature review NOT?
❌ An annotated bibliography
❌ Original research
❌ A summary
❌ Something to be conducted at the end of your research
❌ An opinion piece
❌ A chronological compilation of studies
The reason for conducting a literature review is to:


Literature Reviews: An Overview for Graduate Students
While this 9-minute video from NCSU is geared toward graduate students, it is useful for anyone conducting a literature review.

Writing the literature review: A practical guide
Available 3rd floor of Perkins

Writing literature reviews: A guide for students of the social and behavioral sciences
Available online!

So, you have to write a literature review: A guided workbook for engineers

Telling a research story: Writing a literature review

The literature review: Six steps to success

Systematic approaches to a successful literature review
Request from Duke Medical Center Library

Doing a systematic review: A student's guide
- Next: Types of reviews >>
- Last Updated: Mar 21, 2024 11:32 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/lit-reviews

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries


- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

How to Conduct a Literature Review: A Guide for Graduate Students
- Let's Get Started!
- Traditional or Narrative Reviews
- Systematic Reviews
- Typology of Reviews
- Literature Review Resources
- Developing a Search Strategy
- What Literature to Search
- Where to Search: Indexes and Databases
- Finding articles: Libkey Nomad
- Finding Dissertations and Theses
- Extending Your Searching with Citation Chains
- Forward Citation Chains - Cited Reference Searching
- Keeping up with the Literature
- Managing Your References
- Need More Information?
Bookmark This Guide!
https://instr.iastate.libguides.com/gradlitrev
Where to Get Help
Librarians at ISU are subject experts who can help with your research and course needs. There are experts available for every discipline at ISU who are ready to assist you with your information needs!
What we do:
- Answer questions via phone, chat and in-person
- Consult with student and faculty researchers on request
- Purchase materials for the collection
- Teach instruction session for ISU courses
- Support faculty getting ready for promotion & tenure reviews
- Help with data management plans
Find Your Librarian
“Google can bring you back 100,000 answers. A librarian can bring you back the right one.” - Neil Gaiman
The literature review is an important part of your thesis or dissertation. It is a survey of existing literature that provides context for your research contribution, and demonstrates your subject knowledge. It is also the way to tell the story of how your research extends knowledge in your field.
The first step to writing a successful literature review is knowing how to find and evaluate literature in your field. This guide is designed to introduce you to tools and give you skills you can use to effectively find the resources needed for your literature review.
Before getting started, familiarize yourself with some essential resources provided by the Graduate College:
- Dissertation and Thesis Information
- Center for Communication Excellence
- Graduate College Handbook
Below are some questions that you can discuss with your advisor as you begin your research:
Questions to ask as you think about your literature review:
What is my research question.
Choosing a valid research question is something you will need to discuss with your academic advisor and/or POS committee. Ideas for your topic may come from your coursework, lab rotations, or work as a research assistant. Having a specific research topic allows you to focus your research on a project that is manageable. Beginning work on your literature review can help narrow your topic.
What kind of literature review is appropriate for my research question?
Depending on your area of research, the type of literature review you do for your thesis will vary. Consult with your advisor about the requirements for your discipline. You can view theses and dissertations from your field in the library's Digital Repository can give you ideas about how your literature review should be structured.
What kind of literature should I use?
The kind of literature you use for your thesis will depend on your discipline. The Library has developed a list of Guides by Subject with discipline-specific resources. For a given subject area, look for the guide titles "[Discipline] Research Guide." You may also consult our liaison librarians for information about the literature available your research area.
How will I make sure that I find all the appropriate information that informs my research?
Consulting multiple sources of information is the best way to insure that you have done a comprehensive search of the literature in your area. The What Literature to Search tab has information about the types of resources you may need to search. You may also consult our liaison librarians for assistance with identifying resources..
How will I evaluate the literature to include trustworthy information and eliminate unnecessary or untrustworthy information?
While you are searching for relevant information about your topic you will need to think about the accuracy of the information, whether the information is from a reputable source, whether it is objective and current. Our guides about Evaluating Scholarly Books and Articles and Evaluating Websites will give you criteria to use when evaluating resources.
How should I organize my literature? What citation management program is best for me?
Citation management software can help you organize your references in folders and/or with tags. You can also annotate and highlight the PDFs within the software and usually the notes are searchable. To choose a good citation management software, you need to consider which one can be streamlined with your literature search and writing process. Here is a guide page comparing EndNote, Mendeley & Zotero. The Library also has guides for three of the major citation management tools:
- EndNote & EndNote Web Guide
- Mendeley Guide
- Getting Started with Zotero
What steps should I take to ensure academic integrity?
The best way to ensure academic integrity is to familiarize yourself with different types of intentional and unintentional plagiarism and learn about the University's standards for academic integrity. Start with this guide . The Library also has a guide about your rights and responsibilities regarding copyrighted images and figures that you include in your thesis.
Where can I find writing and editing help?
Writing and editing help is available at the Graduate College's Center for Communication Excellence . The CCE offers individual consultations, peer writing groups, workshops and seminars to help you improve your writing.
Where can I find I find formatting standards? Technical support?
The Graduate College has a Dissertation/ Thesis website with extensive examples and videos about formatting theses and dissertations. The site also has templates and formatting instructions for Word and LaTex .
What citation style should I use?
The Graduate College thesis guidelines require that you "use a consistent, current academic style for your discipline." The Library has a Citation Style Guides resource you can use for guidance on specific citation styles. If you are not sure, please consult your advisor or liaison librarians for help.
Adapted from The Literature Review: For Dissertations, by the University of Michigan Library. Available: https://guides.lib.umich.edu/dissertationlitreview
Center for Communication Excellence/ Library Workshop Slides
Slides from the CCE/ Library Workshop "A Citation Here...A Citation There...Pretty Soon You'll Have a Lit Review" held on February 21, 2024 are below:
- CCE Workshop February 21, 2024
- Next: Types of Literature Reviews >>
The library's collections and services are available to all ISU students, faculty, and staff and Parks Library is open to the public .
- Last Updated: Mar 14, 2024 12:15 PM
- URL: https://instr.iastate.libguides.com/gradlitrev
Academic Writing
- Strategies for Writing
- Punctuation
- Plagiarism & Self-Plagiarism
How to Build a Literature Review
- PRISMA - Systematic reviews & meta-analyses
- Other Resources
- Using Zotero for Bibliographies
- Abstract Writing Tips
- Writing Assistance
- Locating a Journal
- Assessing Potential Journals
- Finding a Publisher
- Types of Peer Review
- Author Rights & Responsibilities
- Copyright Considerations
- What is a Lit Review?
- Why Write a Lit Review?
Structure of a Literature Review
Preliminary steps for literature review.
- Basic Example
- More Examples
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a comprehensive summary and analysis of previously published research on a particular topic. Literature reviews should give the reader an overview of the important theories and themes that have previously been discussed on the topic, as well as any important researchers who have contributed to the discourse. This review should connect the established conclusions to the hypothesis being presented in the rest of the paper.
What a Literature Review Is Not:
- Annotated Bibliography: An annotated bibliography summarizes and assesses each resource individually and separately. A literature review explores the connections between different articles to illustrate important themes/theories/research trends within a larger research area.
- Timeline: While a literature review can be organized chronologically, they are not simple timelines of previous events. They should not be a list of any kind. Individual examples or events should be combined to illustrate larger ideas or concepts.
- Argumentative Paper: Literature reviews are not meant to be making an argument. They are explorations of a concept to give the audience an understanding of what has already been written and researched about an idea. As many perspectives as possible should be included in a literature review in order to give the reader as comprehensive understanding of a topic as possible.
Why Write a Literature Review?
After reading the literature review, the reader should have a basic understanding of the topic. A reader should be able to come into your paper without really knowing anything about an idea, and after reading the literature, feel more confident about the important points.
A literature review should also help the reader understand the focus the rest of the paper will take within the larger topic. If the reader knows what has already been studied, they will be better prepared for the novel argument that is about to be made.
A literature review should help the reader understand the important history, themes, events, and ideas about a particular topic. Connections between ideas/themes should also explored. Part of the importance of a literature review is to prove to experts who do read your paper that you are knowledgeable enough to contribute to the academic discussion. You have to have done your homework.
A literature review should also identify the gaps in research to show the reader what hasn't yet been explored. Your thesis should ideally address one of the gaps identified in the research. Scholarly articles are meant to push academic conversations forward with new ideas and arguments. Before knowing where the gaps are in a topic, you need to have read what others have written.
As mentioned in other tabs, literature reviews should discuss the big ideas that make up a topic. Each literature review should be broken up into different subtopics. Each subtopic should use groups of articles as evidence to support the ideas. There are several different ways of organizing a literature review. It will depend on the patterns one sees in the groups of articles as to which strategy should be used. Here are a few examples of how to organize your review:
Chronological
If there are clear trends that change over time, a chronological approach could be used to organize a literature review. For example, one might argue that in the 1970s, the predominant theories and themes argued something. However, in the 1980s, the theories evolved to something else. Then, in the 1990s, theories evolved further. Each decade is a subtopic, and articles should be used as examples.
Themes/Theories
There may also be clear distinctions between schools of thought within a topic, a theoretical breakdown may be most appropriate. Each theory could be a subtopic, and articles supporting the theme should be included as evidence for each one.
If researchers mainly differ in the way they went about conducting research, literature reviews can be organized by methodology. Each type of method could be a subtopic, and articles using the method should be included as evidence for each one.
- Define your research question
- Compile a list of initial keywords to use for searching based on question
- Search for literature that discusses the topics surrounding your research question
- Assess and organize your literature into logical groups
- Identify gaps in research and conduct secondary searches (if necessary)
- Reassess and reorganize literature again (if necessary)
- Write review
Here is an example of a literature review, taken from the beginning of a research article. You can find other examples within most scholarly research articles. The majority of published scholarship includes a literature review section, and you can use those to become more familiar with these reviews.
Source: Perceptions of the Police by LGBT Communities

There are many books and internet resources about literature reviews though most are long on how to search and gather the literature. How to literally organize the information is another matter.
Some pro tips:
- Be thoughtful in naming the folders, sub-folders, and sub, sub-folders. Doing so really helps your thinking and concepts within your research topic.
- Be disciplined to add keywords under the tabs as this will help you search for ALL the items on your concepts/topics.
- Use the notes tab to add reminders, write bibliography/annotated bibliography
- Your literature review easily flows from your statement of purpose (SoP). Therefore, does your SoP say clearly and exactly the intent of your research? Your research assumption and argument is obvious?
- Begin with a topic outline that traces your argument. pg99: "First establish the line of argumentation you will follow (the thesis), whether it is an assertion, a contention, or a proposition.
- This means that you should have formed judgments about the topic based on the analysis and synthesis of the literature you are reviewing."
- Keep filling it in; flushing it out more deeply with your references
Other Resources/Examples
- ISU Writing Assistance The Julia N. Visor Academic Center provides one-on-one writing assistance for any course or need. By focusing on the writing process instead of merely on grammar and editing, we are committed to making you a better writer.
- University of Toronto: The Literature Review Written by Dena Taylor, Health Sciences Writing Centre
- Purdue OWL - Writing a Lit Review Goes over the basic steps
- UW Madison Writing Center - Review of Literature A description of what each piece of a literature review should entail.
- USC Libraries - Literature Reviews Offers detailed guidance on how to develop, organize, and write a college-level research paper in the social and behavioral sciences.
- Creating the literature review: integrating research questions and arguments Blog post with very helpful overview for how to organize and build/integrate arguments in a literature review
- Understanding, Selecting, and Integrating a Theoretical Framework in Dissertation Research: Creating the Blueprint for Your “House” Article focusing on constructing a literature review for a dissertation. Still very relevant for literature reviews in other types of content.
A note that many of these examples will be far longer and in-depth than what's required for your assignment. However, they will give you an idea of the general structure and components of a literature review. Additionally, most scholarly articles will include a literature review section. Looking over the articles you have been assigned in classes will also help you.
- Understanding, Selecting, and Integrating a Theoretical Framework in Dissertation Research: Creating the Blueprint for Your “House” Excellent article detailing how to construct your literature review.
- Sample Literature Review (Univ. of Florida) This guide will provide research and writing tips to help students complete a literature review assignment.
- Sociology Literature Review (Univ. of Hawaii) Written in ASA citation style - don't follow this format.
- Sample Lit Review - Univ. of Vermont Includes an example with tips in the footnotes.
Attribution
Content on this page was provided by Grace Allbaugh
- << Previous: Writing a Literature Review
- Next: PRISMA - Systematic reviews & meta-analyses >>
- Last Updated: Dec 6, 2023 3:23 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.illinoisstate.edu/academicwriting
Additional Links
- Directions and Parking
- Accessibility Services
- Library Spaces
- Staff Directory
- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Faculty of Arts & Sciences Libraries
Chemistry and Chemical Biology Resources
Literature review.
- Getting Started
- Chemistry journals and databases
- Find Dissertations and Theses
- Find Conference Proceedings
- Find Technical Reports
- Managing Citations
- Research Data Management
- Managing Your Academic Identity
- Helpful Tools
Reviewing the Literature: Why do it?
- Personal: To familiarize yourself with a new area of research, to get an overview of a topic, so you don't want to miss something important, etc.
- Required writing for a journal article, thesis or dissertation, grant application, etc.
Literature reviews vary; there are many ways to write a literature review based on discipline, material type, and other factors.
Background:
- Literature Reviews - UNC Writing Center
- Literature Reviews: An Overview for Graduate Students - What is a literature review? What purpose does it serve in research? What should you expect when writing one? - NCSU Video
Where to get help (there are lots of websites, blogs , articles, and books on this topic) :
- The Center for writing and Communicating Ideas (CWCI)
- (these are non-STEM examples: dissertation guidance , journal guidelines )
- How to prepare a scientific doctoral dissertation based on research articles (2012)
- Writing a graduate thesis or dissertation (2016)
- The good paper : a handbook for writing papers in higher education (2015)
- Proposals that work : a guide for planning dissertations and grant proposals (2014)
- Theses and dissertations : a guide to planning, research, and writing (2008)
- Talk to your professors, advisors, mentors, peers, etc. for advice
READ related material and pay attention to how others write their literature reviews:
- Dissertations
- Journal articles
- Grant proposals
- << Previous: Find Technical Reports
- Next: Managing Citations >>
- Last Updated: Sep 13, 2023 2:15 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/CCB
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Stellar Literature Review (with Help from AI)

Table of contents

Aren’t all of us mini versions of Sherlock Holmes when browsing data and archives for a research piece? As we go through the process, a comprehensive literature review is an essential toolkit to make your research shine.
A literature review consists of scholarly sources that validate the content. Its primary objective is to offer a concise summary of the research and to let you explore relevant theories and methodologies. Through this review, you can identify gaps in the existing research and bridge them with your contribution.
The real challenge is how to write an excellent literature review. Let’s learn.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is an introduction to your research. It helps you put your perspective to the table, along with a summary of the theme.
What does my literature review communicate?
- Explanation of your research: how the information was collected, the research method, the justification of the chosen data sources, and an overview of the data analysis.
- Framework: the journey from where the concept began and how it is presented.
- Connects the previous and current research:
It presents the broader scope of your research by connecting it to the existing data and debates and underlining how your content fits the prevailing studies.
In an era of information overload, a literature review must be well-structured.
Let’s learn all about the structure and style of a literature review that’ll help you strengthen your research.
Literature review– structure and style
Begin with a question and end it with the solution– the key to structuring a literature review. It resembles an essay’s format, with the first paragraph introducing the readers to the topic and the following explaining the research in-depth.
The conclusion reiterates the question and summarizes the overall insights of your research. There’s no word count restriction. —it depends on the type of research. For example, a dissertation demands lengthy work, whereas a short paper needs a few pages.
In a literature review, maintaining high quality is vital, with a focus on academic writing style. Informal language should be avoided in favor of a more formal tone.
The content avoids contractions, clearly differentiating between previous and current research through the use of past and present tense. Wordtune assists in establishing a formal tone, enhancing your work with pertinent suggestions. This AI-powered tool ensures your writing remains genuine, lucid, and engaging.

The option of refining the tonality offers multiple possibilities for rephrasing a single sentence. Thus, pick the best and keep writing.
Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
Your friendly step-by-step guide to writing a literary review (with help from AI)
Do you find it challenging to begin the literature review? Don’t worry! We’re here to get you started with our step-by-step guide.
1. Narrow down the research scope
Simply begin with the question: What am I answering through my research?
Whether it’s cooking or painting, the real challenge is the prep-up for it rather than performing the task. Once you’re done, it smoothly progresses. Similarly, for your literature review, prepare the groundwork by narrowing down the research scope.
Browse and scoop out relevant data inclining well with your research. While you can’t cover every aspect of your research, pick a topic that isn’t too narrow nor too broad to keep your literature review well-balanced.
2. Hunt relevant literature
The next question: Does this data align with the issue I’m trying to address?
As you review sources of information, hunt out the best ones. Determine which findings help in offering a focused insight on your topic. The best way to pick primary sources is to opt for the ones featured in reliable publications. You can also choose secondary sources from other researchers from a reasonable time frame and a relevant background.
For example, if your research focuses on the Historical Architecture of 18th-century Europe, the first-hand accounts and surveys from the past would hold more weight than the new-age publications.
3. Observe the themes and patterns in sources
Next comes: What is the core viewpoint in most of the research? Has it stayed constant over time, or have the authors differed in their points of view?
Ensure to scoop out the essential aspects of what each source represents. Once you have collected all this information, combine it and add your interpretations at the end. This process is known as synthesis.
Synthesize ideas by combining arguments, findings and forming your new version.
4. Generate an outline
The next question: How can I organize my review effectively? When navigating multiple data sources, you must have noticed a structure throughout the research. Develop an outline to make the process easier. An outline is a skeletal format of the review, helping you connect the information more strategically.
Here are the three different ways to organize an outline– Chronologically, Thematically, or by Methodology.You can develop the outline chronologically, starting from the older sources and leading to the latest pieces. Another way of organizing is to thematically divide the sections and discuss each under the designated sub-heading.
You can even organize it per the research methods used by the respective authors. The choice of outline depends on the subject. For example, in the case of a science paper, you can divide the information into sections like introduction, types of equipment, method, procedure, findings, etc. In contrast, it’s best to present it in divisions based on timelines like Ancient, Middle Ages, Industrial revolutions, etc., for a history paper.
If you’re confused about how to structure the data, work with Wordtune.

With the Generate with AI feature, you can mention your research topic and let Wordtune curate a comprehensive outline for your study.

Having a precise prompt is the key to getting the best results.
5. Start filling!
Your next question must be: Am I ready to compose all the parts of the literature review?
Once you’re ready with the basic outline and relevant sources, start filling in the data. Go for an introductory paragraph first to ensure your readers understand the topic and how you will present it. Ensure you clearly explain the section in the first sentence.
However, if beginning from the first paragraph seems intimidating, don’t worry! Add the main body content to the sub-headings, then jump to the introduction.
Add headings wherever possible to make it more straightforward and guide your readers logically through different sources. Lastly, conclude your study by presenting a key takeaway and summarizing your findings. To make your task easier, work with Wordtune. It helps align your content with the desired tone and refine the structure.
6. Give attention to detail and edit
The last question: Am I satisfied with the language and content written in the literature review? Is it easy to understand?
Once you’re done writing the first draft of a literature review, it’s time to refine it. Take time between writing and reading the draft to ensure a fresh perspective. It makes it easier to spot errors when you disconnect from the content for some time. Start by looking at the document from a bird's eye to ensure the formatting and structure are in order.
After reviewing the content format, you must thoroughly check your work for grammar, spelling, and punctuation. One of the best approaches to editing and proofreading is to use Wordtune . It helps simplify complex sentences, enhance the content quality, and gain prowess over the tonality.
The dos and don’ts of writing a literature review
Writing a stellar literature review requires following a few dos and don'ts. Just like Sherlock Holmes would never overlook a hint, you must pay attention to every minute detail while writing a perfect narrative. To help you write, below are some dos and don'ts to remember.

Composing a literature review demands a holistic research summary, each part exhibiting your understanding and approach. As you write the content, make sure to cover the following points:
- Keep a historical background of the field of research. Highlight the relevant relation between the old studies and your new research.
- Discuss the core issue, question, and debate of your topic.
- Theories lay the foundation of research. While you’re writing a literature review, make sure to add relevant concepts and ideas to support your statements.
- Another critical thing to keep in mind is to define complex terminologies. It helps the readers understand the content with better clarity.
Examples of comprehensive literature reviews
Aren’t good examples the best way to understand a subject? Let’s look into a few examples of literature reviews and analyze what makes them well-written.
1. Critical Thinking and Transferability: A Review of the Literature (Gwendolyn Reece)
An overview of scholarly sources is included in the literature review, which explores critical thinking in American education. The introduction stating the subject’s importance makes it a winning literature review. Following the introduction is a well-defined purpose that highlights the importance of research.
As one keeps reading, there is more clarity on the pros and cons of the research. By dividing information into parts with relevant subheadings, the author breaks a lengthy literature review into manageable chunks, defining the overall structure.
Along with other studies and presented perspectives, the author also expresses her opinion. It is presented with minimal usage of ‘I,’ keeping it person-poised yet general. Toward the conclusion, the author again offers an overview of the study. A summary is further strengthened by presenting suggestions for future research as well.
2. The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review
This literature review is thematically organized on how technology affects language acquisition. The study begins with an introduction to the topic with well-cited sources. It presents the views of different studies to help readers get a sense of different perspectives. After giving these perspectives, the author offers a personalized opinion.
One of the critical aspects that makes this a good literature review is a dedicated paragraph for definitions. It helps readers proceed further with a clear understanding of the crucial terminologies. There’s a comparison of the modern and previous studies and approaches to give an overall picture of the research.
Once the main body is composed, the author integrates recommendations for action-based tips. Thus, the literature review isn’t just summarizing the sources but offering actions relevant to the topics. Finally, the concluding paragraph has a brief overview with key takeaways.
Wordtune: your writing buddy!
A literature review demands the right balance of language and clarity. You must refine the content to achieve a formal tone and clear structure. Do you know what will help you the most? Wordtune !.
The real-time grammar checker leaves no scope for errors and lets you retain precision in writing. This writing companion is all you need for stress-free working and comprehensive literature review development.
Let the narrative begin
A literary review isn't just about summarizing sources; it's about seamlessly bringing your perspective to the table. Always remember to set a narrative for added interest and a brilliant composition. With structure and style being the pillars of a stellar literature review, work with Wordtune to ensure zero compromises on the quality.
Share This Article:

The Official Wordtune Guide

An Expert Guide to Writing Effective Compound Sentences (+ Examples)
How I Turned Clutter into Cash: 10 Proven Instagram Copywriting Hacks
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul

Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
- Reserve a study room
- Library Account
- Undergraduate Students
- Graduate Students
- Faculty & Staff
Write a Literature Review
- Developing a Research Question
- Database Searching
- Documenting Your Search and Findings
- Discipline-Specific Literature Reviews
Ask Us! Cabell Library

As a student at VCU, VCU Libraries are here to help you succeed! This guide offers an introduction to conducting a literature review and provides links to the resources and tools we offer. To navigate, simply click the blue tabs to the left based on type of information you're needing.
If ever you are in need of research assistance, don't hesitate to consult a specialist based on your subject area.
Please provide feedback on this guide at any point by emailing Kelsey Cheshire, [email protected] .
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is an essential component of every research project. Literature reviews ask: What do we know, or not know, about this particular issue/ topic/ subject?
How well you answer this question depends upon:
- the effectiveness of your search for information
- the quality & reliability of the sources you choose
- your ability to synthesize the sources you select
Literature reviews require “re-viewing” what credible scholars in the field have said, done, and found in order to help you:
- Identify what is currently known in your area of interest
- Establish an empirical/ theoretical/ foundation for your research
- Identify potential gaps in knowledge that you might fill
- Develop viable research questions and hypotheses
- Decide upon the scope of your research
- Demonstrate the importance of your research to the field
A literature review is not a descriptive summary of what you found. All works included in the review must be read, evaluated, and analyzed, and synthesized, meaning that relationships between the works must also be discussed.
- Next: Developing a Research Question >>
- Last Updated: Oct 16, 2023 1:53 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.vcu.edu/lit-review
Writing a Literature Review: Home

A literature review is a guide to the published information on a topic. While a literature review summarizes each author’s ideas and contributions, it is not just an alphabetical or numbered list. Sources are usually grouped into subtopics or ideas important to the topic. For example, a review of the literature on crop circles might be divided into specific geographic areas or it might represent the skeptic’s viewpoint as well as the believer’s.
Here is an excerpt from The Writing Center at UNC-Chapel Hill:
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period.
A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. It might give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations. Or it might trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates. And depending on the situation, the literature review may evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant.
Literature reviews are very valuable to researchers who need an overview of what’s been written about a topic, but they do not count as scholarly journal articles when you are collecting sources for a term paper.
WRITING A LITERATURE REVIEW: CHOOSING A TOPIC
I f you have to write a literature review, you need to take care that the topic you choose is neither too broad or too narrow. You could spend the rest of your life doing a literature review on war whereas a literature review on women in the Gulf War might be adequately addressed in several pages. Conversely, you might choose a topic and discover that almost nothing has been written about it. Consult with a reference librarian or your professor to be certain you’ve chosen wisely.
WRITING A LITERATURE REVIEW: SELECTION CRITERIA
N ext, decide what types of literature will be included. Will you use books, journal articles, magazine articles, newspaper articles, web sites, and/or something else? How old should the material be? How many items will be included?
WRITING A LITERATURE REVIEW: THESIS STATEMENT
T he thesis statement for a literature review argues neither for or against a particular position but for a particular perspective on the literature. Continuing on with our example of crop circles, a possible thesis statement might be:
The phenomenon known as “crop circles” has become worthy of investigation by the scientific community.
The hallmarks of scientific literature on hoaxes are revealed in the literature on the phenomenon known as “crop circles.”
SAMPLE LITERATURE REVIEWS
- Enrichment for Captive TIgers(Panthera tigris): Current Knowledge and Future Directions
Notice how the literature reviews below address different, specific aspects of oil spills:
- Offshore Oil Spill Response Practices and Emerging Challenges
- Oil Spills and Their Impacts on Sand Beach Invertebrate Communities: A Literature Review
- Oil Spill Detection by Satellite Remote Sensing
A Crop Circle

- What is "The Literature"?
FURTHER ASSISTANCE
T here is a lot more to writing a literature review than can be easily covered in this guide. Get all the details you can from your professor. Find a literature review to use as a model. Consult one of these books or Web sites:
- Preparing Literature Reviews : Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches by M. Ling Pan.
- Writing Literature Reviews : a Guide for Students of the Social and Behavioral Sciences by Jose L. Galvan.
- The UNC Writing Center: Literature Reviews
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It
- Social Work Literature Review Guidelines

- Last Updated: Nov 23, 2020 12:18 PM
- URL: https://libguides.csusb.edu/literaturereview

DNP Nursing Resources: Welcome
- Nursing Databases
- Writing, Citing, and Presenting
Welcome to the DNP Nursing Resources Guide
Welcome to the Nursing Resources guide! Use this guide to learn what resources to use for nursing research, and to get help with technology, writing, citing, and presenting.
Technology Assistance
- Office of Information Services (OIS) Help Desk Includes a link to information about your student email account.
- Blackboard Help
Types of Nursing Literature
Systematic reviews.
Also known as "meta-analysis", a systematic review identifies an intervention for a specific disease or other problem in health care, and determines whether or not this intervention works. To do this authors locate, appraise and synthesize evidence from as many relevant scientific studies as possible. They summarize conclusions about effectiveness, and provide a unique collation of the known evidence on a given topic, so that others can easily review the primary studies for any intervention
Empirical research articles
Usually published in peer-reviewed journals. Although a research article will include a bibliography of other literature reviewed, and may lead you to similar articles, its primary purpose is to present original findings. Look for the following elements
- Introduction
- Research design (participants)
- Discussion of data & methods
Evidence-Based Care Sheets and Evidence-Based Articles
Both evidence-based care sheets and evidence-based articles are similar to review articles (described below). These types of articles focus on summarzing research relating to specific ailments and the efficacy of their treatments, and serve as general overviews.
Review articles
Summarizes and synthesizes the results of many different original studies. Its purpose is to define the state of the literature on a particular topic, and discuss different methodologies for conducting research. Review articles are excellent sources for locating research articles, and contain helpful bibliographies.
Clinical articles
Written for practitioners. Clinical articles might present a particular case study or define a new technique.
(source: Clemens, Rachel, "Library Research Guide for Nursing," Dept. of Nursing, Cal State University)
- Next: Nursing Databases >>
- Last Updated: Apr 1, 2024 3:03 PM
- URL: https://library.elmhurst.edu/c.php?g=1391795
Directions | Directory | For Library Staff | Portal | About
630-617-3160 | Reference: 630-617-3173 190 Prospect Ave., Elmhurst, IL 60126
Advertisement
Supported by
Critic’s Notebook
Like My Book Title? Thanks, I Borrowed It.
Literary allusions are everywhere. What are they good for?
- Share full article

By A.O. Scott
You see it everywhere, even if you don’t always recognize it: the literary allusion. Quick! Which two big novels of the past two years borrowed their titles from “Macbeth”? Nailing the answer — “ Birnam Wood ” and “ Tomorrow, and Tomorrow, and Tomorrow ” — might make you feel a little smug.
Perhaps the frisson of cleverness ( I know where that’s from!), or the flip-side cringe of ignorance ( I should know where that’s from! ), is enough to spur you to buy a book, the way a search-optimized headline compels you to click a link. After all, titles are especially fertile ground for allusion-mongering. The name of a book becomes more memorable when it echoes something you might have heard — or think you should have heard — before.
This kind of appropriation seems to be a relatively modern phenomenon. Before the turn of the 20th century, titles were more descriptive than allusive. The books themselves may have been stuffed with learning, but the words on the covers were largely content to give the prospective reader the who (“Pamela,” “Robinson Crusoe,” “Frankenstein”), where (“Wuthering Heights,” “The Mill on the Floss,” “Treasure Island”) or what (“The Scarlet Letter,” “War and Peace,” “The Way We Live Now”) of the book.
Somehow, by the middle of the 20th century, literature had become an echo chamber. Look homeward, angel! Ask not for whom the sound and the fury slouches toward Bethlehem in dubious battle. When Marcel Proust was first translated into English, he was made to quote Shakespeare, and “In Search of Lost Time” (the literal, plainly descriptive French title) became “Remembrance of Things Past,” a line from Sonnet 30 .
Recent Proust translators have erased the Shakespearean reference in fidelity to the original, but the habit of dressing up new books in secondhand clothing persists, in fiction and nonfiction alike. Last year, in addition to “Birnam Wood,” there were Jonathan Rosen’s “ The Best Minds ,” with its whisper of Allen Ginsberg’s “ Howl ,” Paul Harding’s “ This Other Eden ” (“ Richard II ”), and William Egginton’s “ The Rigor of Angels ” (Borges). The best-seller lists and publishers’ catalogs contain multitudes ( Walt Whitman ). Here comes everybody! (James Joyce).
If you must write prose and poems, the words you use should be your own. I didn’t say that: Morrissey did, in a deepish Smiths cut (“ Cemetry Gates , ” from 1986), which misquotes Shakespeare and name-checks John Keats, William Butler Yeats and Oscar Wilde — possibly the most reliably recycled writers (along with John Milton and the authors of the King James Bible) in the English language.
Not that any of them would have minded. When Keats wrote that “ a thing of beauty is a joy forever ,” he surely hoped that at least that much of “ Endymion ” would outlive him. It’s a beautiful sentiment! And he may have been right. Does anyone read his four-part, 4,000-line elegy for Thomas Chatterton outside a college English class, or even for that matter inside one? Nonetheless, that opening line may ring a bell if you remember it from the movies “ Mary Poppins ,” “Yellow Submarine” or “ White Men Can’t Jump .”
Wilde’s witticism and bons mots have survived even as some of his longer works have languished. If it’s true (as he said) that only superficial people do not judge by appearances, maybe it follows that shallow gleaning is the deepest kind of reading. Or maybe, to paraphrase Yeats, devoted readers of poetry lack all conviction , while reckless quoters are full of passionate intensity .
Like everything else, this is the fault of the internet, which has cannibalized our reading time while offering facile, often spurious, pseudo-erudition to anyone with the wit to conduct a search. As Mark Twain once said to Winston Churchill, if you Google, you don’t have to remember anything.
Seriously though: I come not to bury the practice of allusion, but to praise it. (“ Julius Caesar ”) And also to ask, in all earnestness and with due credit to Edwin Starr , “ Seinfeld” and Leo Tolstoy : What is it good for?
The language centers of our brains are dynamos of originality. A competent speaker of any language is capable of generating intelligible, coherent sentences that nobody has uttered before. That central insight of modern linguistics, advanced by Noam Chomsky in the 1950s and ’60s, is wonderfully democratic. Every one of us is a poet in our daily speech, an inglorious Milton ( Thomas Gray ), a Shakespeare minting new coins of eloquence.
Of course, actual poets are congenital thieves (as T.S. Eliot or someone like him may have said), plucking words and phrases from the pages of their peers and precursors. The rest of us are poets in that sense, too. If our brains are foundries, they are also warehouses, crammed full of clichés, advertising slogans, movie catchphrases, song lyrics, garbled proverbs and jokes we heard on the playground at recess in third grade. Also great works of literature.
There are those who sift through this profusion with the fanatical care of mushroom hunters, collecting only the most palatable and succulent specimens. Others crash through the thickets, words latching onto us like burrs on a sweater. If we tried to remove them, the whole garment — our consciousness, in this unruly metaphor — might come unraveled.
That may also be true collectively. If we were somehow able to purge our language of its hand-me-down elements, we might lose language itself. What happens if nobody reads anymore, or if everyone reads different things? Does the practice of literary quotation depend on a stable set of common references? Or does it function as a kind of substitute for a shared body of knowledge that may never have existed at all?
The old literary canon — that dead white men’s club of star-bellied sneetches ( Dr. Seuss ) — may have lost some of its luster in recent decades, but it has shown impressive staying power as a cornucopia of quotes. Not the only one, by any means (or memes). Television, popular music, advertising and social media all provide abundant fodder, and the way we read now (or don’t) has a way of rendering it all equivalent. The soul selects her own society ( Emily Dickinson ).
When I was young, my parents had a fat anthology of mid-20th-century New Yorker cartoons , a book I pored over with obsessive zeal. One drawing that baffled me enough to stick in my head featured a caption with the following words: “It’s quips and cranks and wanton wiles, nods and becks and wreathed smiles.” What on earth was that? It wasn’t until I was in graduate school, cramming for an oral exam in Renaissance literature, that I found the answer in “ L’Allegro, ” an early poem by Milton, more often quoted as the author of “Paradise Lost.”
Not that having the citation necessarily helps. The cartoon, by George Booth, depicts a woman in her living room, addressing members of a multigenerational, multispecies household. There are cats, codgers, a child with a yo-yo, a bird in a cage and a dog chained to the sofa. Through the front window, the family patriarch can be seen coming up the walk, a fedora on his head and a briefcase in his right hand. His arrival — “Here comes Poppa” — is the occasion for the woman’s Miltonic pep talk.

Who is she? Why is she quoting “L’Allegro”? Part of the charm, I now suspect, lies in the absurdity of those questions. But I also find myself wondering: Were New Yorker readers in the early 1970s, when the cartoon was first published, expected to get the allusion right off the bat? They couldn’t Google it. Or would they have laughed at the incongruous eruption of an old piece of poetry they couldn’t quite place?
Maybe what’s funny is that most people wouldn’t know what that lady was talking about. And maybe the same comic conceit animates an earlier James Thurber drawing reprinted in the same book. In this one, a wild-eyed woman bursts into a room, wearing a floppy hat and wielding a basket of meadow flowers. “I come from haunts of coot and hern!” she exclaims to the baffled company, disturbing their cocktail party.
That’s it. That’s the gag.
Were readers also baffled? It turns out that Thurber’s would-be nature goddess is quoting “ The Brook ,” by Alfred, Lord Tennyson. (I’ve never read it either.) Is it necessary to get the reference to get the joke? If you chuckle in recognition, and complete the stanza without missing a beat — “I make a sudden sally/And sparkle out among the fern,/To bicker down a valley” — is the joke on you?
It’s possible, from the standpoint of the present, to assimilate these old pictures to the familiar story about the decline of a civilization based in part on common cultural knowledge. Sure. Whatever. Things fall apart ( Yeats ). In the cartoons’ own terms, though, spouting snippets of poetry is an unmistakable sign of eccentricity — the pastime of kooky women and the male illustrators who commit them to paper. This is less a civilization than a sodality of weirdos, a visionary company ( Hart Crane ) of misfits. But don’t quote me on that.
A.O. Scott is a critic at large for The Times’s Book Review, writing about literature and ideas. He joined The Times in 2000 and was a film critic until early 2023. More about A.O. Scott
Explore More in Books
Want to know about the best books to read and the latest news start here..
James McBride’s novel sold a million copies, and he isn’t sure how he feels about that, as he considers the critical and commercial success of “The Heaven & Earth Grocery Store.”
How did gender become a scary word? Judith Butler, the theorist who got us talking about the subject , has answers.
You never know what’s going to go wrong in these graphic novels, where Circus tigers, giant spiders, shifting borders and motherhood all threaten to end life as we know it .
When the author Tommy Orange received an impassioned email from a teacher in the Bronx, he dropped everything to visit the students who inspired it.
Do you want to be a better reader? Here’s some helpful advice to show you how to get the most out of your literary endeavor .
Each week, top authors and critics join the Book Review’s podcast to talk about the latest news in the literary world. Listen here .
- Account Settings
- Aston Martin
- Lamborghini
- Mercedes-Benz
- Rolls-Royce
Car Reviews
Car comparisons, auto resources.
- Auto Insurance
- Auto Glass Repair
- Auto Warranty
- Product Roundups
Top stories

- Tire Reviews
Review: BFGoodrich All-Terrain T/A KO2 | Still worth considering?

BFGoodrich’s All-Terrain T/A KO2 has been a dominant force in the all-terrain tire game since its launch. It carries the torch once lit by the original BFG A/T which helped develop the category and made its mark by becoming one of the most popular and easily recognizable choices in the off-road, truck, and SUV tire world. To see if the KO2 is worth the hype, BFG sent us a set to test on our ongoing Lexus GX460 daily-driver-meets-off-roader build .
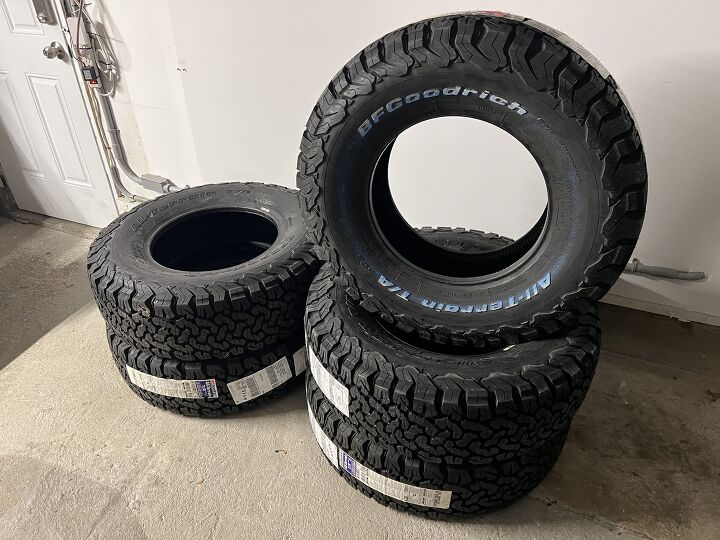

All-terrain tires have come a long way since BFGoodrich launched its KO2 in 2015. New players in the field have tried to unseat BFG from its throne, but the company has sold 5 million KO2s since its debut; we doubt any other brand has sold more of a specialty light truck tire in that time. After nearly 10 years of the KO2 gracing the streets and trails, BFG is on the eve of launching its new All-Terrain T/A KO3, but we wanted to try out the supposed segment leader before the sun sets on the second-gen tire.
Let’s set the stage. For this test, we swapped out our 285/70/17 E Load rating Toyo Open Country A/T IIIs with a set of 34x10.5R17 D Load rating BFGoodrich All-Terrain KO2s . The Toyos measure at a claimed 32.8” tall by 11.5” wide, with the BFGs measuring 33.5” tall by 10.5” wide. On the weight front, the Toyos are 55 pounds to the BFGs at 54 pounds. Every change made to a vehicle undergoing an ongoing "build" must have a goal, and here ours was to gain a little more height from each tire while keeping weight unchanged. Translation: More clearance for improved off-road performance, at no detriment to drive-ability or gas mileage. Tall, skinny “pizza cutter” tires might not have the curb appeal of wider meats, but they tend to have less rolling resistance and perform better in some off-road circumstances. Testing these theories was part of this experiment.

We also swapped wheels at this time, the 17x8.5”, 24.54 pound Motegi Trailites getting changed out for 17x8.0”, 25.31 pound American Racing Baja AR172s. Both wheels have the same offset and backspacing, so the real reason for the swap was for the narrower width which is better for airing down tires off-road, as it allows for a greater contact patch. It also allowed us to change up the looks of the GX at the same time. All-in-all, each wheel/tire combo went from 79.54 lbs/corner to 79.31 lbs/corner, which is a negligible difference. Bear in mind that this isn’t a perfectly scientific test and we're going based on claimed weights, but we want to be transparent in how we review a tire, and part of that entails explaining the parameters from which we are drawing the comparison aspects. It isn’t perfectly apples-to-apples, but it’s as close as we can get when altering up an entire setup.
BFG is certainly playing up its supposed strengths and accomplishments with the KO2. “Baja Champion” is stamped into the rubber, as is the Three-Peak mountain snowflake Severe Snow Rated symbol. BFG includes a 50,000 mile warranty and a 60-day satisfaction guarantee. The tires are offered for wheels ranging from 15” through 22” and it’s available in 92 sizes .
Mounted up, the KO2s look great. We’re a sucker for the old-school vibe, so that meant white letters out when deciding between this and black walls. Though the tires are noticeably narrower than the Toyos, they do stand a bit taller and overall give the GX460 a much more purposeful look.

On the road, it’s immediately apparent that the extra bit of sidewall and lower load rating allow for a softer, cushier ride than did the Toyos. The BFGs ride quite well for an all-terrain tire, and they don’t have any of the vibration or noise low-speed associated with some more aggressive A/Ts. A key feature of the KO2s are the “Interlocking Tread Elements,” which are an evolution of that which was on the original All-Terrain T/A. This design isn’t noticeable around town, but there is slightly more vibration at highway speed from the tires than we noticed with the more traditional tread pattern of the Toyos.
Traction on dry pavement is obviously a non-issue, and the KO2s fared beautifully in heavy rain, too. Some owners have voiced concerns over wet traction with these BFGs and we're glad to report our testing does not corroborate this worry, though the KO2s are perhaps slightly less confident than the Toyo Open Country A/T IIIs over standing water, or would-be hydroplaning situations. We haven’t tested the KO2s in snow yet, though this will (thankfully) have to wait for next winter.
One other tidbit we noticed on tarmac is that the narrower KO2s display a bit less rolling resistance than the wider Toyos. However, the taller size also means the GX460’s gearing is taxed ever-so slightly more, which is noticeable on longer highway climbs. It’s minor, and this note applies more to those specifically looking to go from the very common 285/70/17 size to the 34x10.5R17 “pizza cutters.” Gas mileage seems unaffected, as does fuel range.

Off-road performance is critical with an all-terrain tire, and especially one supposedly as capable as the All-Terrain T/A KO2. Our test included rocks, dirt, mud, sand, hills, water crossings, and so on. Aired down to 17 PSI, the BFGs impressed us in and on every terrain. Traction on the rocks was extremely strong, with the GX’s tires rarely struggling for grip and almost never spinning in trying to gain such. Dirt traction is fantastic, and mud performance was a pleasant surprise with the KO2s clawing well through the muck. Cleaning out once exiting the mud isn’t a strong suit of all-terrain tires and the BFGs’ post-mud pit look is consistent with that notion, though we haven’t pushed the tires to their breaking (i.e., stuck) point in the mud just yet. Overall, the BFGs performed as well or better than the Toyos off-road.
The elephant in the room is the price of this speciality size being tested here. The 34x10.5R17 size carries an MSRP of $452.99 per tire, which is on the higher side for all-terrains and doesn’t compare favorably to $311.62 for the same-size Toyo Open Country A/T III . However, these are the only two mainstream tires available in this size, and you can’t go wrong with either.
All-terrain tires have stiffer competition than ever, and the BFGoodrich All-Terrain A/T KO2 has certainly proven itself as one of the leaders of the pack, even as it hands the baton off to the incoming KO3. Even nearly ten years after its debut, the KO2 is is still a great looking and performing tire that is compliant on road and capable off-road. It only makes us even more excited and hopeful great things from the newest version when it launches properly later this year.

Ross hosts The Off the Road Again Podcast. He has been in the off-road world since he was a kid riding in the back of his dad’s YJ Wrangler. He works in marketing by day and in his free time contributes to Hooniverse, AutoGuide, and ATV.com, and in the past has contributed to UTV Driver, ATV Rider, and Everyday Driver. Ross drives a 2018 Lexus GX460 that is an ongoing build project featured on multiple websites and the podcast.
More by Ross Ballot
Join the conversation
Popular articles.

Car Owners are Driving Past Dealerships to Independent Repair Shops

2024 Alfa Romeo Giulia Veloce Review: A Charmer Let Down by Gremlins

The Plug-in Hybrid With the Longest Range: Top 10 List

Affordable Cars With Surprisingly Higher-End Interiors: Top 10

Toyota Camry LE Vs SE: Which Trim is Right for You?
Latest comparisons.

2024 Porsche Cayenne S and Cayenne Coupe Review

What’s the Difference Between the 2023 and 2024 Subaru Crosstrek?

Volkswagen Atlas SE Vs SEL: Which Trim is Right for You?

Hyundai Palisade Vs Mazda CX-90 Comparison

Toyota Corolla LE Vs Nissan Sentra SR Comparison
Car buying tools.
- How to Buy a Car
- Free dealer Price Quote
You may also be interested in

BFGoodrich All-Terrain T/A KO2 Tire Review

3 Things We Like About the 2023 Grand Wagoneer L and 2 We Don't

2025 Nissan Kicks Debuts with Available AWD, Sharp Looks

Honda Prologue Pricing Announced

5 SUVs the Kia EV9 Will Compete With

IIHS Semi-Autonomous Testing Unveiled: 13 of 14 Automakers Fail

What is Subaru Starlink?

2023 Toyota Corolla Cross Hybrid Review: Quick Take

How the 2024 Ford Ranger Raptor's Trick Fox Shocks Work

2024 Toyota 4Runner TRD Pro Adds Exclusive Color

Milestar Patagonia X/T and M/T-02 Tire Review: American Alternatives

10 Most Expensive Pickup Trucks to Insure for 2024

3 Reasons the Lexus LC is a Modern Classic

What To Keep In Your Car For Winter Driving

Genesis Announces High-Performance Magma Program, Reveals 2 Models

2024 Ford Mustang GT Review: Straddling the Line

2024 Porsche 718 Boxster Style Edition Review: Fashionably Fun

50 Incredible Photos of McLaren's Latest Supercar

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review. Free lecture slides.
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels ...
As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter. Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter.
A literature review is an overview of the available research for a specific scientific topic. Literature reviews summarize existing research to answer a review question, provide context for new research, or identify important gaps in the existing body of literature.. An incredible amount of academic literature is published each year, by estimates over two million articles.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period. ... Literature reviews provide you with a handy guide to a particular topic. If you have limited time to conduct research, literature reviews can give you an overview or act as a ...
Sonja Foss and William Walters* describe an efficient and effective way of writing a literature review. Their system provides an excellent guide for getting through the massive amounts of literature for any purpose: in a dissertation, an M.A. thesis, or preparing a research article for publication in any field of study. Below is a summary of ...
Example: Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398 ; Systematic review: "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139).
This guide will help you to. Define a literature review. Recognize that different fields of study have their own way to perform and write literature reviews. Prepare to search the literature. Read critically -- analyze and synthesize. Prepare to write a literature review. Graphic from Literature Review (2009) by Machi and McEvoy.
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
The review should describe, summarize, evaluate and clarify this literature. It should give a theoretical base for the research and help you (the author) determine the nature of your research." For information on systematic reviews - a particular type of literature review used primarily in health sciences - please refer to this guide: Knowledge ...
A literature review explores all sides of the research topic and evaluates all positions and conclusions achieved through the scientific research process even though some conclusions may conflict partially or completely. From the Online Library. Conducting Your Literature Review by Susanne Hempel. ISBN: 9781433830921.
A literature review is both a summary and explanation of the complete and current state of knowledge on a narrowed topic as found in academic books and journal articles. ... Find out what style guide you are required to follow (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago) Follow the guidelines to format citations and create a reference list or bibliography;
What is a literature review? Definition: A literature review is a systematic examination and synthesis of existing scholarly research on a specific topic or subject. Purpose: It serves to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge within a particular field. Analysis: Involves critically evaluating and summarizing key findings, methodologies, and debates found in ...
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
This guide is designed to introduce you to tools and give you skills you can use to effectively find the resources needed for your literature review. Before getting started, familiarize yourself with some essential resources provided by the Graduate College:
A literature review should help the reader understand the important history, themes, events, and ideas about a particular topic. Connections between ideas/themes should also explored. Part of the importance of a literature review is to prove to experts who do read your paper that you are knowledgeable enough to contribute to the academic ...
Dissertations A Guide to Preparing and Submitting your Dissertation - GSAS The Center for writing and Communicating Ideas (CWCI) Official documentation - find out from publisher websites, journal editors, dissertation advisors, etc. what their expectations are for a lit review (these are non-STEM examples: dissertation guidance, journal guidelines)
Similarly, for your literature review, prepare the groundwork by narrowing down the research scope. Browse and scoop out relevant data inclining well with your research. While you can't cover every aspect of your research, pick a topic that isn't too narrow nor too broad to keep your literature review well-balanced. 2.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
This guide offers an introduction to conducting a literature review and provides links to the resources and tools we offer. To navigate, simply click the blue tabs to the left based on type of information you're needing. ... A literature review is an essential component of every research project. Literature reviews ask: What do we know, or not ...
A literature review is a guide to the published information on a topic. While a literature review summarizes each author's ideas and contributions, it is not just an alphabetical or numbered list. Sources are usually grouped into subtopics or ideas important to the topic. For example, a review of the literature on crop circles might be ...
Review articles. Summarizes and synthesizes the results of many different original studies. Its purpose is to define the state of the literature on a particular topic, and discuss different methodologies for conducting research. Review articles are excellent sources for locating research articles, and contain helpful bibliographies. Clinical ...
A.O. Scott is a critic at large for The Times's Book Review, writing about literature and ideas. He joined The Times in 2000 and was a film critic until early 2023. He joined The Times in 2000 ...
For this test, we swapped out our 285/70/17 E Load rating Toyo Open Country A/T IIIs with a set of 34x10.5R17 D Load rating BFGoodrich All-Terrain KO2s. The Toyos measure at a claimed 32.8" tall ...