Corporate Social Responsibility and Stock Prices After the Financial Crisis: The Role of Strategic CSR Activities
- Original Paper
- Published: 15 September 2021
- Volume 182 , pages 223–242, ( 2023 )

Cite this article
- Aneta Havlinova 1 &
- Jiri Kukacka ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8680-2896 1 , 2
3896 Accesses
10 Citations
Explore all metrics
We analyze the relationship between corporate social responsibility and the stock market performance in the post-global financial crisis period. A new measure of social responsibility by Thomson Reuters, called the ESG Combined Score, is used. As a novel feature of our analysis, socially responsible engagement is divided into the strategic activities closely related to the examined companies’ core business and the remaining secondary activities. The results of the fixed effects regression show a positive and statistically, as well as economically, significant impact of the strategic activities on the corporate stock market performance of companies. This impact is up to 103% higher compared to the secondary activities. The empirical results suggest that if companies aim to increase their share prices via the corporate social responsibility channel, they should strategically select their socially responsible initiatives.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Changes in Corporate Social Responsibility and Stock Performance
Hui-Ju Tsai & Yangru Wu
Corporate social responsibility: How much is enough? A higher dimension perspective of the relationship between financial and social performance
Iordanis Kalaitzoglou, Hui Pan & Jacek Niklewski

Corporate Social Responsibility, Investor Sentiment, and Stock Returns
Data availability.
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the Refinitiv Eikon database (Thomson Reuters, 2021 , accessed 2021-01-28). Restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for this study. Data are available at https://eikon.thomsonreuters.com with the permission of Thomson Reuters.
Please note that due to the logarithmic nature of the dependent variable, the precise interpretation of the estimated coefficient of the non-logaritmized independent variable follows: an increase of the independent variable by 1 (small) unit is associated with a change of the dependent variable by \(\big (exp({\widehat{\beta }})-1\big ) \times 100\) percent. This is often approximated by \({\widehat{\beta }} \times 100\) percent. However, such simplification holds well only for ‘very small’ values of \({\widehat{\beta }}\) .
Abbott, W. F., & Monsen, R. J. (1979). On the measurement of corporate social responsibility: self-reported disclosures as a method of measuring corporate social involvement. Acad. Manag. J., 22 (3), 501–515.
Article Google Scholar
Arellano, M. (1987). PRACTITIONERS’ CORNER: computing robust standard errors for within-groups estimators. Oxford Bull. Econ. Stat., 49 (4), 431–434.
Bansal, P., & Song, H.-C. (2017). Similar but not the same: differentiating corporate sustainability from corporate responsibility. Acad. Manag. Ann., 11 (1), 105–149.
Barnett, M. L., & Salomon, R. M. (2006). Beyond dichotomy: the curvilinear relationship between social responsibility and financial performance. Strategic Manag. J., 27 (11), 1101–1122.
Baron, D. P. (2001). Private politics, corporate social responsibility, and integrated strategy. J. Econ. Manag. Strategy, 10 (1), 7–45.
Barth, M. E., Beaver, W. H., & Landsman, W. R. (1992). The market valuation implications of net periodic pension cost components. J. Account. Econ., 15 (1), 27–62.
Bénabou, R., & Tirole, J. (2010). Individual and corporate social responsibility. Economica, 77 (305), 1–19.
Bowen, H. R. (1953). Social Responsibilities of the Businessman . New York: Harper & Row.
Google Scholar
Bowman, E. H., & Haire, M. (1975). A strategic posture toward corporate social responsibility. CA Manag. Rev., 18 (2), 49–58.
Brammer, S., & Millington, A. (2008). Does it pay to be different? An analysis of the relationship between corporate social and financial performance. Strategic Manag. J., 29 (12), 1325–1343.
Brown, S. J., Lajbcygier, P., & Li, B. (2008). Going negative: what to do with negative book equity stocks. J. Portfolio Manag., 35 (1), 95–102.
Burbano, V. C. (2016). Social responsibility messages and worker wage requirements: field experimental evidence from online labor marketplaces. Org. Sci., 27 (4), 1010–1028.
Carroll, A. B. (1981). Business and Society: Managing Corporate Social Performance . Boston: Little Brown and Company.
Chatterji, A. K., Durand, R., Levine, D. I., & Touboul, S. (2015). Do ratings of firms converge? Implications for managers, investors and strategy researchers. Strategic Manag. J., 37 (8), 1597–1614.
Chatterji, A. K., Levine, D. I., & Toffel, M. W. (2009). How well do social ratings actually measure corporate social responsibility? J. Econ. Manag. Strategy, 18 (1), 125–169.
Cheng, B., Ioannou, I., & Serafeim, G. (2014). Corporate social responsibility and access to finance. Strategic Manag. J., 35 (1), 1–23.
Clark, J. M. (1939). Social Control of Business . New York: McGraw-Hill.
Cochran, P. L., & Wood, R. A. (1984). Corporate social responsibility and financial performance. Acad. Manag. J., 27 (1), 42–56.
De Klerk, M., de Villiers, C., & van Staden, C. (2015). The influence of corporate social responsibility disclosure on share prices: evidence from the United Kingdom. Pac. Account. Rev., 27 (2), 208–228.
DesJardine, M., Bansal, P., & Yang, Y. (2019). Bouncing back: building resilience through social and environmental practices in the context of the 2008 global financial crisis. J. Manag., 45 (4), 1434–1460.
Durand, R., Paugam, L., & Stolowy, H. (2019). Do investors actually value sustainability indices? Replication, development, and new evidence on CSR visibility. Strategic Manag. J., 40 (9), 1471–1490.
Eccles, R. G., Ioannou, I., & Serafeim, G. (2014). The impact of corporate sustainability on organizational processes and performance. Manag. Sci., 60 (11), 2835–2857.
Fama, E. F., & French, K. R. (1993). Common risk factors in the returns on stocks and bonds. J. Financ. Econ., 33 (1), 3–56.
Flammer, C. (2015). Does corporate social responsibility lead to superior financial performance? A regression discontinuity approach. Manag. Sci., 61 (11), 2549–2568.
Flammer, C. (2018). Competing for government procurement contracts: the role of corporate social responsibility. Strategic Manag. J., 39 (5), 1299–1324.
Flammer, C., & Luo, J. (2017). Corporate social responsibility as an employee governance tool: evidence from a quasi-experiment. Strategic Manag. J., 38 (2), 163–183.
Freeman, R. E. (1984). Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach . Boston: Pitman.
Godfrey, P. C. (2005). The relationship between corporate philanthropy and shareholder wealth: a risk management perspective. Acad. Manag. Rev., 30 (4), 777–798.
Gond, J.-P., Palazzo, G., & Basu, K. (2009). Reconsidering instrumental corporate social responsibility through the Mafia metaphor. Business Ethics Q., 19 (1), 57–85.
Gregory, A., Tharyan, R., & Whittaker, J. (2014). Corporate social responsibility and firm value: disaggregating the effects on cash flow, risk and growth. J. Business Ethics, 124 (4), 633–657.
Griffin, J. M., & Lemmon, M. L. (2002). Book-to-market equity, distress risk, and stock returns. J. Finance, 57 (5), 2317–2336.
Hausman, J. A. (1978). Specification tests in econometrics. Econometrica, 46 (6), 1251–1271.
Hausman, J. A., & Taylor, W. E. (1981). Panel data and unobservable individual effects. Econometrica, 49 (6), 1377–1398.
Hawn, O., Chatterji, A. K., & Mitchell, W. (2018). Do investors actually value sustainability? New evidence from investor reactions to the Dow Jones sustainability index (DJSI). Strategic Manag. J., 39 (4), 949–976.
Hillman, A. J., & Keim, G. D. (2001). Shareholder value, stakeholder management, and social issues: what’s the bottom line? Strategic Manag. J., 22 (2), 125–139.
Hull, C. E., & Rothenberg, S. (2008). Firm performance: the interactions of corporate social performance with innovation and industry differentiation. Strategic Manag. J., 29 (7), 781–789.
Inoue, Y., & Lee, S. (2011). Effects of different dimensions of corporate social responsibility on corporate financial performance in tourism-related industries. Tour. Manag., 32 (4), 790–804.
Ioannou, I., & Serafeim, G. (2015). The impact of corporate social responsibility on investment recommendations: analysts’ perceptions and shifting institutional logics. Strategic Manag. J., 36 (7), 1053–1081.
Jan, C.-L., & Ou, J. A. (2012). Negative-book-value firms and their valuation. Account. Horizons, 26 (1), 91–110.
Khan, M., Serafeim, G., & Yoon, A. (2016). Corporate sustainability: first evidence on materiality. Account. Rev., 91 (6), 1697–1724.
KLD Research & Analytics, Inc., KLD database (2019). http://www.whartonwrds.com/datasets/kld/
Koh, P.-S., Reeb, D. M., & Zhao, W. (2018). CEO confidence and unreported R&D. Manag. Sci., 64 (12), 5725–5747.
Kramer, M. R., & Porter, M. (2011). Creating shared value. Harvard Business Rev., 89 (1/2), 62–77.
Kreps, T.J.: Measurement of the social performance of business. In: An Investigation of Concentration of Economic Power for the Temporary National Economic Committee, Monograph No. 7, Washington, DC: American Enterprise Institute for Public Policy Research (1940).
Luo, X., & Bhattacharya, C. (2006). Corporate social responsibility, customer satisfaction, and market value. J. Market., 70 (4), 1–18.
Lydenberg, S., Rogers, J., Wood, D.: From transparency to performance: industry-based sustainability reporting on key issues (2010). https://bit.ly/3ryITrp
Makni, R., Francoeur, C., & Bellavance, F. (2009). Causality between corporate social performance and financial performance: evidence from Canadian firms. J. Business Ethics, 89 (3), 409.
Refinitiv. (2020a) Refinitiv ESG Scores. https://www.refinitiv.com/en/sustainable-finance/esg-scores
Refinitiv. (2020b). Refinitiv ESG Scores (backup for 2020 methodology in .pdf). https://bit.ly/3hY2I8q
Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (2021), SASB Materiality Map. https://www.sasb.org/
Thomson Reuters (2017), Thomson Reuters ESG Scores 2017. https://bit.ly/2HAiBA2
Thomson Reuters (2021), Eikon database. https://eikon.thomsonreuters.com
McGuire, J. B., Sundgren, A., & Schneeweis, T. (1988). Corporate social responsibility and firm financial performance. Acad. Manag. J., 31 (4), 854–872.
McWilliams, A., & Siegel, D. (2000). Corporate social responsibility and financial performance: correlation or misspecification? Strategic Manag. J., 21 (5), 603–609.
Moneva, J. M., Rivera-Lirio, J. M., & Muñoz-Torres, M. J. (2007). The corporate stakeholder commitment and social and financial performance. Ind. Manag. Data Syst., 107 (1), 84–102.
Moskowitz, M. (1972). Choosing socially responsible stocks. Business Soc. Rev., 1 (1), 71–75.
Ohlson, J. A. (1995). Earnings, book values, and dividends in equity valuation. Contemp. Account. Res., 11 (2), 661–687.
Perrini, F., Russo, A., Tencati, A., & Vurro, C. (2011). Deconstructing the relationship between corporate social and financial performance. J. Business Ethics, 102 (1), 59–76.
Porter, M. E., & Kramer, M. R. (2006). The link between competitive advantage and corporate social responsibility. Harvard Business Rev., 84 (12), 78–92.
Qiu, Y., Shaukat, A., & Tharyan, R. (2016). Environmental and social disclosures: link with corporate financial performance. Br. Account. Rev., 48 (1), 102–116.
Revelli, C., & Viviani, J.-L. (2015). Financial performance of socially responsible investing (SRI): what have we learned? A meta-analysis. Business Ethics, 24 (2), 158–185.
Schadewitz, H., & Niskala, M. (2010). Communication via responsibility reporting and its effect on firm value in Finland. Corp. Soc. Resp. Environ. Manag., 17 (2), 96–106.
Scherer, A. G., & Palazzo, G. (2011). The new political role of business in a globalized world: a review of a new perspective on CSR and its implications for the firm, governance, and democracy. J. Manag. Stud., 48 (4), 899–931.
Seele, P., & Lock, I. (2015). Instrumental and/or deliberative? A typology of CSR communication tools. J. Business Ethics, 131 (2), 401–414.
Servaes, H., & Tamayo, A. (2013). The impact of corporate social responsibility on firm value: the role of customer awareness. Manag. Sci., 59 (5), 1045–1061.
Siegel, D. S., & Vitaliano, D. F. (2007). An empirical analysis of the strategic use of corporate social responsibility. J. Econ. Manag. Strategy, 16 (3), 773–792.
Spicer, B. H. (1978). Investors, corporate social performance and information disclosure: an empirical study. Account. Rev., 53 (1), 94–111.
Sturdivant, F. D., & Ginter, J. L. (1977). Corporate social responsiveness: management attitudes and economic performance. CA Manag. Rev., 19 (3), 30–39.
Tirole, J. (2001). Corporate governance. Econometrica, 69 (1), 1–35.
Van der Laan, G., Van Ees, H., & Van Witteloostuijn, A. (2008). Corporate social and financial performance: an extended stakeholder theory, and empirical test with accounting measures. J. Business Ethics, 79 (3), 299–310.
Vance, S. C. (1975). Are socially responsible corporations good investment risks. Manag. Rev., 64 (8), 19–24.
Vassalou, M., & Xing, Y. (2004). Default risk in equity returns. J. Finance, 59 (2), 831–868.
Waddock, S. A., & Graves, S. B. (1997a). The corporate social performance-financial performance link. Strategic Manag. J., 18 (4), 303–319.
Waddock, S. A., & Graves, S. B. (1997b). Quality of management and quality of stakeholder relations: are they synonymous? Business Soc., 36 (3), 250–279.
Zhao, X., & Murrell, A. J. (2016). Revisiting the corporate social performance-financial performance link: a replication of Waddock and Graves. Strategic Manag. J., 37 (11), 2378–2388.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Jiri Kukacka gratefully acknowledges financial support from the Charles University PRIMUS program [project PRIMUS/19/HUM/17] and from the Charles University UNCE program [project UNCE/HUM/035]. We are also indebted to I. Jupa and M. Walter for their professional consultation. Finally, we are very thankful to the two anonymous reviewers for their inspiring comments and detailed suggestions.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Charles University, Faculty of Social Sciences, Institute of Economic Studies, Opletalova 26, 110 00, Prague 1, Czechia
Aneta Havlinova & Jiri Kukacka
Czech Academy of Sciences, Institute of Information Theory and Automation, Pod Vodarenskou vezi 4, 182 00, Prague 8, Czechia
Jiri Kukacka
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jiri Kukacka .

Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A: Multicollinearity Assessment: Correlations
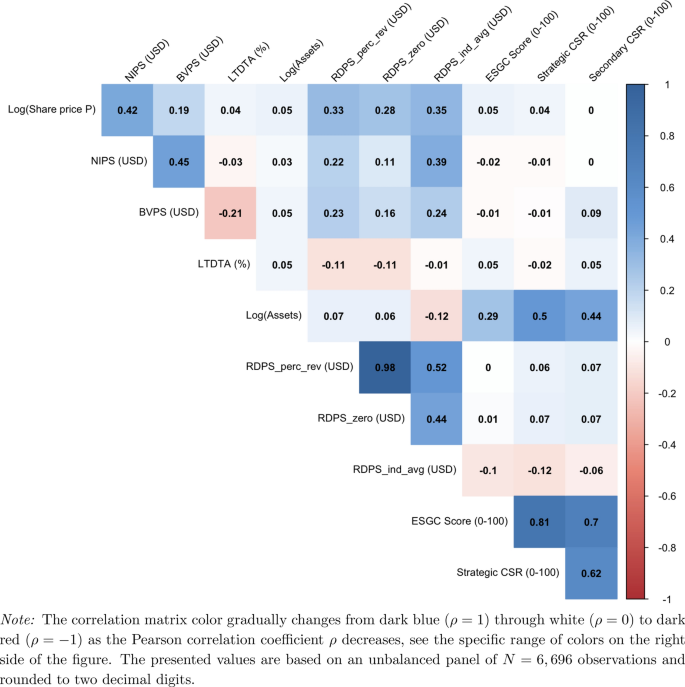
Descriptive statistics of the dataset: Correlations
Appendix B: Regression Results Con’t
Appendix c: regression results for the strategic and secondary csr con’t, rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Havlinova, A., Kukacka, J. Corporate Social Responsibility and Stock Prices After the Financial Crisis: The Role of Strategic CSR Activities. J Bus Ethics 182 , 223–242 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-021-04935-9
Download citation
Received : 20 May 2020
Accepted : 26 August 2021
Published : 15 September 2021
Issue Date : January 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-021-04935-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Corporate social responsibility
- Strategic CSR
- Business ethics
- Corporate financial performance
- Fixed effects
JEL Classifications
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
The Use of Machine Learning to Forecast Financial Performance: A Literature Review
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1 INTRODUCTION. Since Bowen's first work, the relationship between corporate social responsibility (CSR) and financial performance in the business context has become a topic of significant relevance.The idea and perception of CSR change from company to company, between managers, and in different societies (Lau, Hulpke, To and Kelly, 2007).However, a common aspect exists: instead of companies ...
This paper aims to investigate the literature on Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) to provide a comprehensive overview of whether CSR would make a difference to organisational financial ...
2. Corporate social responsibility. CSR has been studied for some time now, but a consensus is still missing concerning its definition and its constituent dimensions, constructs and principles (Crane et al., Citation 2008). In a comprehensive literature review, Dahlsrud (Citation 2008) identified 37 different definitions of CSR.There is great variation in these CSR perceptions and definitions.
This literature review includes 54 meta-analyses on CSR and states that the majority of quantitative CSR research concentrates on the CSR-financial performance-link. In line with the business case for CSR, board independence, board gender diversity and board size as key corporate governance factors have a positive impact on CSR performance.
This study aims to present a literature review of recent studies on the relationship between environmental, social and governance (ESG) performance, corporate social responsibility (CSR) and ...
Substantial number of studies have been conducted to explore the relationship between CSR and financial performance. However, no conclusive results have been reported. This paper attempts to explore present literature review and adopts bibliometric analysis to depict the literature review in quantitatively structured manner.
This study aims to present a literature review of recent studies on the relationship between environmental, social and governance (ESG) performance, corporate social responsibility (CSR) and corporate financial performance (CFP) and to provide a path for future researches. Using content analysis method, a total of 88 papers published in ...
1. Introduction. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is considered a progressively indispensable research area for scholars in management; it has also become an essential part of higher education (Ruiz-Lozano & Nieto, Citation 2016; Wigmore-Alvarez et al., Citation 2020).The existing literature examines CSR's concept in various aspects to found the effect of firms' CSR activities.
Han, Kim, and Yu (2016) examine the relationship between corporate social responsibility and corporate profit by testing the ESG performance score on the financial performance of firms listed in the Korean stock market between 2008 and 2014. The study's findings reveal no statistically significant evidence or a relationship between CSR ...
The mission to establish the impact of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) on a firm's performance in the literature has been the focus of many past research studies (Orlitzky et al., 2003; Waddock & Graves, 1997).Exploring and analyzing the effect of corporations being socially responsible on their performance have been explained using various theoretical and conceptual underpinnings.
2.1. Corporate social responsibility and firms performance. The review of the literature suggests that there are two major theoretical approaches which explain the association between corporate social responsibility (CSR) and financial performance of the firms.
This paper investigates the influence of corporate social responsibility on firm performance by integrating simultaneously the moderating effects of the firm size and its industry profile. To conduct our study, we use annual environmental, social and governance (ESG) data on 407 European firms listed in STOXX Europe 600 Index during the period 2002-2018. Results reveal that the moderating ...
Despite scads research on the relationship between corporate social responsibility and financial performance, literature is still inconclusive. ... Review of literature. ... This school asserts that CSR is an important driver of enhancing financial performance. CSR, according to stakeholders and agency theory, exerts a positive influence on ...
To shed new light on this issue, we mapped this topic via a systematic review and content analysis of 53 articles identified in the confluence between CSR and financial performance from 1984 to 2021. Our study suggests that CSR directly impacts a company's financial performance, and this impact becomes more significant as the company's ...
2.2 Corporate reputation and firm performance. CR is considered to be an intangible asset that differentiates a firm and encourages customers to pay a premium and repurchase (Pradhan, 2016, 2018).FP signifies performance indicators associated with a firm's objectives ().So, FP is determined based on the organizational goals (Vij and Bedi, 2016).For this study, we have considered return on ...
A prominent claim within the literature is that corporate social responsibility-disclosured firms are fundamentally more resilient to financial shocks, relative to firms that take no corporate social responsibility action. To test this, we examine the impact of corporate social responsibility (CSR) information disclosure on financial constraints (FC). Our sample is composed of A-share publicly ...
Due to the volume of empirical research, it is necessary to conduct a systematic review of empirical studies. In doing so, this paper identified three fundamental thematic areas: (i) CSR and corporate financial performance; (ii) CSR and corporate non-financial performance; and (iii) CSR practices and control. Download : Download high-res image ...
the nature, intensity, and direction of the relationship between CSR and financial performance. This study aimed to answer the following research question: What is the relationship between CSR and com-panies' financial performance? To this end, we conducted a system-atic literature review using the Web of Science database, followed
2. Corporate social responsibility CSR has been studied for some time now, but a consensus is still missing concerning its definition and its constituent dimensions, constructs and principles (Crane et al., 2008). In a comprehensive literature review, Dahlsrud (2008) identified 37 different definitions of CSR.
We analyze the relationship between corporate social responsibility and the stock market performance in the post-global financial crisis period. A new measure of social responsibility by Thomson Reuters, called the ESG Combined Score, is used. As a novel feature of our analysis, socially responsible engagement is divided into the strategic activities closely related to the examined companies ...
The purpose of this study is to examine the effect of corporate social responsibility (CSR) on the financial performance of international engineering contracting enterprises (IECEs). The study also explores the mechanisms of CSR influence on financial performance from three perspectives: customer, employee, and corporate, namely the mediating roles of customer satisfaction, employee loyalty ...
This paper delves into the concept of socially responsible marketing and its significance in fostering diversity, equity, and inclusion within organizational environments. It elucidates the connection between marketing and corporate social responsibility (CSR), showcasing methods of integrating social responsibility into marketing activities. Ethical principles inherent in socially responsible ...
This study aims to examine the impact of corporate social responsibility (CSR) on the financial performance of Vietnamese listed companies from 2012 to 2017. The study uses Fixed effects model and System Generalized Method of Moments to estimate models. The study contributes by analyzing the impact of social responsibility under three ...
The paper offers a comprehensive analysis of ten studies covering different facets of the application of artificial intelligence (AI) techniques for identifying financial performance. The financial stability of organizations is a major concern for decision-makers, particularly in the finance field. Diagnosing financial problems in the early stages can prevent further complications. Many of the ...