- Directories
- What are citations and why should I use them?
- When should I use a citation?
- Why are there so many citation styles?
- Which citation style should I use?
- Chicago Notes Style
- Chicago Author-Date Style
- AMA Style (medicine)
- Bluebook (law)
- Additional Citation Styles
- Built-in Citation Tools
- Quick Citation Generators
- Citation Management Software
- Start Your Research
- Research Guides
- University of Washington Libraries
- Library Guides
- UW Libraries
- Citing Sources

Citing Sources: What are citations and why should I use them?
What is a citation.
Citations are a way of giving credit when certain material in your work came from another source. It also gives your readers the information necessary to find that source again-- it provides an important roadmap to your research process. Whenever you use sources such as books, journals or websites in your research, you must give credit to the original author by citing the source.
Why do researchers cite?
Scholarship is a conversation and scholars use citations not only to give credit to original creators and thinkers, but also to add strength and authority to their own work. By citing their sources, scholars are placing their work in a specific context to show where they “fit” within the larger conversation. Citations are also a great way to leave a trail intended to help others who may want to explore the conversation or use the sources in their own work.
In short, citations
(1) give credit
(2) add strength and authority to your work
(3) place your work in a specific context
(4) leave a trail for other scholars
"Good citations should reveal your sources, not conceal them. They should honeslty reflect the research you conducted." (Lipson 4)
Lipson, Charles. "Why Cite?" Cite Right: A Quick Guide to Citation Styles--MLA, APA, Chicago, the Sciences, Professions, and More . Chicago: U of Chicago, 2006. Print.
What does a citation look like?
Different subject disciplines call for citation information to be written in very specific order, capitalization, and punctuation. There are therefore many different style formats. Three popular citation formats are MLA Style (for humanities articles) and APA or Chicago (for social sciences articles).
MLA style (print journal article):
Whisenant, Warren A. "How Women Have Fared as Interscholastic Athletic Administrators Since the Passage of Title IX." Sex Roles Vol. 49.3 (2003): 179-182.
APA style (print journal article):
Whisenant, W. A. (2003) How Women Have Fared as Interscholastic Athletic Administrators Since the Passage of Title IX. Sex Roles , 49 (3), 179-182.
Chicago style (print journal article):
Whisenant, Warren A. "How Women Have Fared as Interscholastic Athletic Administrators Since the Passage of Title IX." Sex Roles 49, no. 3 (2003): 179-182.
No matter which style you use, all citations require the same basic information:
- Author or Creator
- Container (e.g., Journal or magazine, website, edited book)
- Date of creation or publication
- Publisher
You are most likely to have easy access to all of your citation information when you find it in the first place. Take note of this information up front, and it will be much easier to cite it effectively later.
- << Previous: Basics of Citing
- Next: When should I use a citation? >>
- Last Updated: Oct 24, 2023 3:46 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uw.edu/research/citations
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Cite an Article
Last Updated: February 14, 2024 References
This article was co-authored by Noah Taxis and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Noah Taxis is an English Teacher based in San Francisco, California. He has taught as a credentialed teacher for over four years: first at Mountain View High School as a 9th- and 11th-grade English Teacher, then at UISA (Ukiah Independent Study Academy) as a Middle School Independent Study Teacher. He is now a high school English teacher at St. Ignatius College Preparatory School in San Francisco. He received an MA in Secondary Education and Teaching from Stanford University’s Graduate School of Education. He also received an MA in Comparative and World Literature from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and a BA in International Literary & Visual Studies and English from Tufts University. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 95,048 times.
Articles in scholarly journals and magazines, both in print and online, are common sources for research papers. Provide an in-text citation every time you paraphrase or quote from the article, and include a full citation in a bibliography at the end of your paper. While the basic information in your citation will be the same, the format varies depending on whether you're using the Modern Language Association (MLA), American Psychological Association (APA), or Chicago style of citation.
Sample Citations

- Example: Buchman, Dana.
- If there are 2 authors, separate their names with a comma, typing the word "and" before the last author's name. Only invert the first author's name. For example: Martin, Johnathan A., and Christopher Jackson.
- For 3 or more authors, list the first author's name, followed by a comma and the abbreviation "et. al." For example: Fontela, Pablo, et. al.

- Example: Buchman, Dana. "A Special Education."
- If the article has a subtitle, type a colon and a space after the title, then type the subtitle in title case. Place a period at the end of the subtitle, inside the closing quotation marks.

- Example: Buchman, Dana. "A Special Education." Good Housekeeping , Mar. 2006,
- For scholarly journals, include the volume and issue numbers after the name of the publication. Separate these elements with commas. For example: Bagchi, Alaknanda. "Conflicting Nationalisms": The Voice of the Subaltern in Mahasweta Devi's Bashai Tudu ." Tulsa Studies in Women's Literature , vol. 15, no. 1, 1996,
- If the article appears in a smaller regional or local publication, type the location in brackets after the title of the publication. For example: Trembacki, Paul. "Brees Hopes to Win Heisman for Team." Purdue Exponent [West Lafayette, IN], 5 Dec. 2000,

- Print example: Buchman, Dana. "A Special Education." Good Housekeeping , Mar. 2006, pp. 143-148.
- Online example: Trembacki, Paul. "Brees Hopes to Win Heisman for Team." Purdue Exponent [West Lafayette, IN], 5 Dec. 2000, www.purdueexponent.org/sports/article_b6f722b8-9595-58b8-849b-5a8447bbf793.html.
MLA Works Cited Format
Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article in Title Case." Title of Publication , Day Month Year, pp. ##-##. URL or DOI.

- For example, you might write: "For a woman who had encountered few obstacles on the road to success, having a daughter with learning disabilities presented challenges and an opportunity to grow as a person (Buchman 147)."
- If the source was not paginated, only the author's name is needed. If you incorporated the author's name in the body of your paper and the source is not paginated, you don't need a parenthetical citation.

- Example: Will, G. F. (2004, July 5).
- If there are multiple authors, separate their names with commas. Use an ampersand (&) before the last author's name.

- Example: Will, G. F. (2004, July 5). Waging war on Wal-Mart.

- Print example: Will, G. F. (2004, July 5). Waging war on Wal-Mart. Newsweek, 144 ,
- For online-only sources, include the domain extension (such as ".com" or ".org) in the publication title. If the source also exists in print, leave the domain extension out of the publication title. For example: Romm, J. (2008, February 27). The cold truth about climate change. Salon.com .

- Print example: Will, G. F. (2004, July 5). Waging war on Wal-Mart. Newsweek, 144 , 64.
- Online example: Romm, J. (2008, February 27). The cold truth about climate change. Salon.com . http://www.salon.com/2008/02/27/global_warming_deniers/
APA Reference List Format
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Year, Month Day). Title of article in sentence case. Title of Publication , Page#. Retrieved from URL.

- For example, you might write: "Romm (2008) concluded that international reports actually underestimated the threat of climate change."
- If you don't include the author's name in the body of your paper, use a standard parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence, inside the closing punctuation. For example, you might write: "Many climate change deniers misinterpret scientific consensus as groupthink (Romm, 2008)."

- Example: Goldman, Jason G.

- Example: Goldman, Jason G. "Lizards Learn a Silly Walk after Losing Their Tail."
- If the article has a subtitle, type a colon and a space after the title, then type the subtitle in title case. Place a period at the end of the subtitle.

- Example: Goldman, Jason G. "Lizards Learn a Silly Walk after Losing Their Tail." Scientific American , December 1, 2017.
- For articles in scholarly journals include the volume and issue numbers, then place the date of publication in parentheses. Place a colon after the date of publication. For example: Bunce, Valerie. "Rethinking Recent Democratization: Lessons from the Postcommunist Experience." World Politics 55, no. 2 (2003):

- Print example: Bunce, Valerie. "Rethinking Recent Democratization: Lessons from the Postcommunist Experience." World Politics 55, no. 2 (2003): 167-192.
- Online example: Goldman, Jason G. "Lizards Learn a Silly Walk after Losing Their Tail." Scientific American , December 1, 2017. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/lizards-learn-a-silly-walk-after-losing-their-tail/.
Chicago Bibliography Format
Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article in Title Case." Title of Publication , Month Day, Year. URL.

- Print example: Valerie Bunce, "Rethinking Recent Democratization: Lessons from the Postcommunist Experience," World Politics 55, no. 2 (2003): 167-192.
- Online example: Jason G. Goldman, "Lizards Learn a Silly Walk after Losing Their Tail," Scientific American , December 1, 2017, https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/lizards-learn-a-silly-walk-after-losing-their-tail/.
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about academic writing, check out our in-depth interview with Noah Taxis .
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_electronic_sources.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ http://guides.libraries.psu.edu/apaquickguide/articles
- ↑ https://libraryguides.vu.edu.au/apa-referencing/7JournalArticles
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://libguides.heidelberg.edu/chicago/article
About This Article

To cite an article in MLA, start with the authors last name, followed by a comma, their first name, and a period. Then, add the title of the article in quotation marks with a period at the end of the title inside the quotes. Next, include the title of the periodical in italics, followed by a comma and the date of publication written in a day-month-year format. Finally, put a comma after the year, followed by the page number or URL where the article can be found and a period. To learn how to cite an article using Chicago or APA style, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Did this article help you?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Penn State University Libraries
Apa quick citation guide.
- In-text Citation
- Citing Generative AI
- Citing Web Pages and Social Media
- Citing Articles
- Citing Books
- Citing Business Reports
- Other Formats
- APA Style Quiz
Note: Citations with more than one line of text should have a hanging indent of 1/2 inch or 5 spaces.
Important Elements:
- Author (last name, initials only for first & middle names)
- Date of publication of article (year and month for monthly publications; year, month and day for daily or weekly publications)
- Title of article (capitalize only the first word of title and subtitle, and proper nouns)
- Title of publication in italics (i.e., Journal of Abnormal Psychology, Newsweek, New York Times )
- Volume number in italics and issue number, if given
- Page numbers of article, if given
- For articles retrieved online, include DOI, if available. Includes URLs only if they will work for readers. For articles retrieved through a database, do not include the database information or URL in the reference. For more information, see the APA Style and Grammar Guidelines pages on databases and DOIs and URLs.
For more examples, see the APA Style and Grammar Guidelines entries for magazine , newspaper, and scholarly journal articles.
Magazine article:
Swedin, E. G. (2006, May/June). Designing babies: A eugenics race with China? The Futurist , 40, 18-21.
Will, G. F. (2004, July 5). Waging war on Wal-Mart. Newsweek , 144 , 64.
Duhigg, C. (2019, October 10). Is Amazon unstoppable? The New Yorker. https://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2019/10/21/is-amazon-unstoppable
Newspaper article:
Dougherty, R. (2006, January 11). Jury convicts man in drunk driving death. Centre Daily Times , p. 1A.
Laber-Warren, E. (2019, October 17). You're only as old as you feel. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2019/10/17/well/mind/age-subjective-feeling-old.html
Scholarly journal article:
Blattner, J., & Bacigalupo, A. (2007). Using emotional intelligence to develop executive leadership and team and organizational development. Consulting Psychology Journal: Practice and Research, 59 (3), 209-219. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/1065-9293.59.3.209
Book Review:
Rifkind, D. (2005, April 10). Breaking their vows. [Review of the book The mermaid chair, by S.M. Kidd]. Washington Post , p. T6.
- << Previous: Citing Web Pages and Social Media
- Next: Citing Books >>
- Last Updated: Jul 19, 2023 2:50 PM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/apaquickguide
Citing sources: Overview
- Citation style guides
Manage your references
Use these tools to help you organize and cite your references:
- Citation Management and Writing Tools
If you have questions after consulting this guide about how to cite, please contact your advisor/professor or the writing and communication center .
Why citing is important
It's important to cite sources you used in your research for several reasons:
- To show your reader you've done proper research by listing sources you used to get your information
- To be a responsible scholar by giving credit to other researchers and acknowledging their ideas
- To avoid plagiarism by quoting words and ideas used by other authors
- To allow your reader to track down the sources you used by citing them accurately in your paper by way of footnotes, a bibliography or reference list
About citations
Citing a source means that you show, within the body of your text, that you took words, ideas, figures, images, etc. from another place.
Citations are a short way to uniquely identify a published work (e.g. book, article, chapter, web site). They are found in bibliographies and reference lists and are also collected in article and book databases.
Citations consist of standard elements, and contain all the information necessary to identify and track down publications, including:
- author name(s)
- titles of books, articles, and journals
- date of publication
- page numbers
- volume and issue numbers (for articles)
Citations may look different, depending on what is being cited and which style was used to create them. Choose an appropriate style guide for your needs. Here is an example of an article citation using four different citation styles. Notice the common elements as mentioned above:
Author - R. Langer
Article Title - New Methods of Drug Delivery
Source Title - Science
Volume and issue - Vol 249, issue 4976
Publication Date - 1990
Page numbers - 1527-1533
American Chemical Society (ACS) style:
Langer, R. New Methods of Drug Delivery. Science 1990 , 249 , 1527-1533.
IEEE Style:
R. Langer, " New Methods of Drug Delivery," Science , vol. 249 , pp. 1527-1533 , SEP 28, 1990 .
American Psychological Association (APA) style:
Langer, R. (1990) . New methods of drug delivery. Science , 249 (4976), 1527-1533.
Modern Language Association (MLA) style:
Langer, R. " New Methods of Drug Delivery." Science 249.4976 (1990) : 1527-33.
What to cite
You must cite:
- Facts, figures, ideas, or other information that is not common knowledge
Publications that must be cited include: books, book chapters, articles, web pages, theses, etc.
Another person's exact words should be quoted and cited to show proper credit
When in doubt, be safe and cite your source!
Avoiding plagiarism
Plagiarism occurs when you borrow another's words (or ideas) and do not acknowledge that you have done so. In this culture, we consider our words and ideas intellectual property; like a car or any other possession, we believe our words belong to us and cannot be used without our permission.
Plagiarism is a very serious offense. If it is found that you have plagiarized -- deliberately or inadvertently -- you may face serious consequences. In some instances, plagiarism has meant that students have had to leave the institutions where they were studying.
The best way to avoid plagiarism is to cite your sources - both within the body of your paper and in a bibliography of sources you used at the end of your paper.
Some useful links about plagiarism:
- MIT Academic Integrity Overview on citing sources and avoiding plagiarism at MIT.
- Avoiding Plagiarism From the MIT Writing and Communication Center.
- Plagiarism: What It is and How to Recognize and Avoid It From Indiana University's Writing Tutorial Services.
- Plagiarism- Overview A resource from Purdue University.
- Next: Citation style guides >>
- Last Updated: Jan 16, 2024 7:02 AM
- URL: https://libguides.mit.edu/citing
- Essay Check
- Chicago Style
APA Citation Examples
- MLA Citation Examples
- Chicago Style Citation Examples
- Writing Tips
- Plagiarism Guide
- Grammar Rules
- Student Life
- Create Account
- powered by Chegg
Cite in apa automatically with bibme, create apa citations for free.
Website Book Journal Other
←Back to All Citation Guides
APA (American Psychological Association) style is most frequently used within the social sciences, in order to cite various sources. This APA Citation Guide provides the general format for in-text citations and the reference page. For more information, please consult the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 7th ed.
In APA style, two citations are used to cite a source:
- A short citation used in the text (called the in-text citation ).
- A full citation (called the reference ) in the reference list at the end of a paper.
The in-text citation is a short citation that is placed next to the text being cited. The in-text citation lets the reader know that the information came from the cited source. The reference list entry provides complete details of a source and is shown at the end of a document.
In order to properly cite a source in APA style, you must have both citation types in your paper. Every in-text citation has a reference list entry. Every reference list entry has at least one (maybe more) corresponding in-text citation.
In-text citations
The basic elements needed for an in-text citation are the author’s surname and the publication year . Sometimes, page numbers are also included, especially when quotes are mentioned in the text. In-text citations are mentioned in the text in two ways: as a narrative citation or a parenthetical citation.
Narrative citations are incorporated into the text and act as a part of the sentence. Usually, narrative citations use the author’s name in the text and the publication year is enclosed in parenthesis after the name. An example of a narrative citation for one author is given below:
Barbarin (2013) examined socioemotional learning in African boys.
Parenthetical
Parenthetical citations add the author’s name and the publication year at the end of the sentence in parenthesis. An example of a parenthetical citation is given below:
Inhibition and working memory in young children were studied extensively (Aase, 2014).
When are page numbers are included?
Page numbers are referred to within in-text citations when quotes are used. Examples of both narrative citations and parenthetical citations are given below.
Ahmed (2004, p. 44)
Ahmed (2004, pp. 53–56)
Parenthetical:
(Ahmed, 2004, p. 44)
(Ahmed, 2004, pp. 53–56)
Examples of in-text citations
Here are a few examples of in-text citations for a different number of authors:
Use the surname of the author in in-text citations. Use a comma before the publication year in parenthetical citations.
Narrative:
Bucher (2018)
Parenthetical:
(Bucher, 2018)
Two authors
Separate the author surnames with an “and” in narrative citations. Use an ampersand symbol (&) in parenthetical citations.
Popescu and Pennacchiotti (2010)
(Popescu & Pennacchiotti, 2010)
Three or more authors
Use the first author surname name followed by et al.
van Dijck et al. (2018)
(van Dijck et al., 2018)
Group author
Treat the group author similar to how you would treat author names.
Auger Collaboration (2003)
(Auger Collaboration, 2018)
If there is no author for the source, use the source title in place of the author’s name. In general, sources with no author appear as parenthetical citations.
When you add such in-text citations, you will either italicize the text or place it in quotations. If the source title is italicized in the reference list entry, italicize the title in the in-text citation. If the title is not italicized, place it in quotation marks.
Parenthetical, book:
( Nothing here , 1997)
Parenthetical, journal article:
(“Examination of parrotfish impact on coral reefs,” 2018)
Reference list entries
Reference list entries are also called full citations. There are four main details that most reference list entries have:
- The author field.
- The publication year.
- The title of the work ( italicized or in “quotation marks”).
- The source from where the reference can be obtained (e.g., URL, DOI, etc.).
Depending on the source type, you will also need additional details like volume number, publication title, contributors, medium, etc.
Examples of reference list entries
Below are a few examples of different types of reference entries along with their templates. The examples given are for one author. Note that “F” and “M” in the templates denote the first and the middle initials of an author’s name.
The title of the book is set in italics and sentence case.
Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Title of the book . Publisher.
Ahmed, S. (2014). The cultural politics of emotion . Edinburgh University Press.
Journal article
The title of the article is in sentence case. The first word of a subtitle is capitalized. The journal title and the volume number are set in italics. If an article has a DOI it should always be included. Use “https://doi.org/” before the DOI. If there is no DOI for an online journal, include the URL instead. Do not use a period after the DOI or URL.
Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Article title: Subtitle. Journal Title, Volume (issue), page range. URL or DOI
Collins, R. (2004). Rituals of solidarity and security in the wake of terrorist attack. Sociological Theory, 22 (1), 53–87. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9558.2004.00204.x
Newspaper or magazine article
Newspaper and magazine articles take the same style. The title of the article is in plain text and sentence case; the title of the newspaper or the magazine is set in italics. Follow the format given in the template and example for setting the date, month, and year.
Surname, F. M. (Date of publication). Title of the article. Title of the Newspaper or Magazine . URL
TNN. (2021, July 18). Parents have a habit of comparing kids to others but you don’t need to. The Times of India . https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com//home/sunday-times/parents-have-a-habit-of-comparing-kids-to-others-but-you-dont-need-to/articleshow/84507857.cms
The webpage title is in plain text, while the Website name is set in italics. Follow the format given in the template and example for setting the date, month, year, and URL.
Author or Organization Name. (Year, Month Day of Publication ). Webpage title. Title of the Website. URL
Lamberth, H. (2021, August 12). Binge drinking is problem drinking: How to get back in control. PSYCOM . https://www.psycom.net/binge-drinking-problem-drinking
YouTube video
The video title is set in sentence case and italicized. The first word after a colon is capitalized. The word “Video” is enclosed in brackets after the video title. This is followed followed by the word “YouTube.” Finally, the link is given. Note that a period is not given after the URL.
Uploader’s name, F. (Year, Month Day Published). Video title [Video]. YouTube. URL
Ananta, P. (2021, February 21). APJ Abdul Kalam inspirational quotes [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pjfL51RFL2k
Reference entries for different number of authors
The number of authors in the source decides how the author name(s) will be set in the references list. Here, you will see many journal references with different numbers of authors.
List the author name followed by the publication year.
Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Article title: Subtitle. Journal Title, Volume (issue), page range.
Spitka, T. (2017). Mediating among mediators: Building a consensus in multilateral interventions. International Negotiation, 23 , 1–30.
Separate the author names by an ampersand. Use a comma between the first author’s initial and the ampersand symbol.
Author Surname, F. M., & Author Surname, F. (Publication Year). Article title: Subtitle. Journal Title, Volume (issue), page range. DOI or URL
Bernstein, B., & Solomon, J. (1999). Pedagogy, identity and the construction of a theory of symbolic control: Basil Bernstein questioned by Joseph Solomon. British Journal of Sociology of Education, 20 (2), 265–279. https://doi:10.1080/01425699995443
When you add two organizations in the author field, do not use a comma before the ampersand.
Organization 1 & Organization 2. (Publication Year). Article title: Subtitle. Journal Title, Volume (issue), page range. DOI or URL
American Psychological Association & American Psychological Society. (2020). Psychology of children. Journal of Child Psychology, 34 (23), 1–12.
3–20 authors
List all author names. Do not forget to insert an “ampersand” before the last author. The example given below is for three authors.
Author Surname, F. M., Author Surname, F. M., & Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Article title: Subtitle. Journal Title, Volume (issue), page range. DOI or URL
Pyysiäinen, J., Halpin, D., & Guilfoyle, A. (2017). Neoliberal governance and ‘responsibilization’ of agents: Reassessing the mechanisms of responsibility-shift in neoliberal discursive environments. Distinktion: Journal of Social Theory, 18 (2), 215–235. https://doi:10.1080/1600910X.2017.1331858
More than 20 authors
List the names of the first 19 authors followed by an ellipsis. Add the final author name after the ellipsis but without the ampersand symbol before the last author name.
Author Surname1, F. M., Author Surname2, F. M., Author Surname3, F. M., Author Surname4, F. M., Author Surname5, F. M., Author Surname6, F. M., Author Surname7, F. M., Author Surname8, F. M., Author Surname9, F. M., Author Surname10, F. M., Author Surname11, F. M., Author Surname12, F. M., Author Surname13, F. M., Author Surname14, F. M., Author Surname15, F. M., Author Surname16, F. M., Author Surname17, F. M., Author Surname18, F. M., Author Surname19, F. M,¼ Last Author name, F. M. (Publication Year). Article title: Subtitle. Journal Title, Volume (issue), page range. DOI or URL
Fox, J., Harper, D., Bird, A., Kindler, F. A., Feng, H.-G., Seng, A. L., Sevel, K., Ed, E., Nell, A., Ten, T., Elin, K. J., Thomas, A., Thendy, S., Fall, W., Fint, E., Gurdy, A. K., Dondy, D., Egert, E., Nanda, A. L., ¼ Long, G. (2015). Pedagogising knowledge: Bernstein’s theory of the pedagogic device. British Journal of Sociology of Education, 23 (4), 571–582.
For additional information on APA format, select from one of the source types below. For help creating APA citations, check out the BibMe APA citation generator.
Source Types:
- How to cite a Book in APA
- How to cite a Magazine in APA
- How to cite a Newspaper in APA
- How to cite a Website in APA
- How to cite a Journal Article in APA
- How to cite a Film in APA
- How to cite an Interview in APA
- How to cite a Lecture in APA
- How to cite a TV Show / Radio Broadcast in APA
- How to cite an Encyclopedia in APA
- How to cite a Photograph in APA
- APA 7 Updates
APA Format:
- In-Text Citation Basics
- Reference Page
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
As per Section 8.17 from the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , for any work that has three or more authors, the name of the first author and “et al.” should be used as in-text citation. The Latin phrase “et al” means “and others” and is used to reduce the citation length.
Example In-Text Citation Entry:
No stretch of reason can categorize cultural appropriation as imaginary (Rahim et al., 2020).
Sometimes, the same set of initial authors and the same publication year appear in a paper. In such rare circumstances, as per Section 8.18 of the APA manual, write out as many names as needed to differentiate between these similar references.
Example In-Text Citation Entries:
Miller, John, Reighstag et al. (2018)
Miller, John, Amudsen, et al. (2018)
As per Section 8.21 and Table 8.1 of the APA Publication Manual , a citation for a group author may be abbreviated in in-text citations. It is not compulsory to do so; however, if the group author is well known or if it appears at least thrice in the paper, then the name of the group may be abbreviated.
Parenthetical in-text citation template and example:
(Full Name of the Group [Abbreviation], year)
(National Institute of Mental Health [NIMH], 2018)
Whether it is a narrative or parenthetical in-text citation, the full name of the group should be mentioned in the first instance, along with the abbreviation.
Narrative in-text citation examples:
The American Psychological Association (APA, 2017) argues that… (first instance)
As per the APA (2017), it is standard practice that… (subsequent instances)

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
How to Cite an Article
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
With Components & Examples

Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Definition: How to Cite an Article
- 3 Components of Full Citations
- 4 Different Citation Systems
- 5 To Cite an Article in APA Style
- 6 In a Nutshell
Definition: How to Cite an Article
You are probably just about to finish your paper and are now looking for a quick way to find out how to cite an article. For your paper to appear professional, it is necessary to cite every source you have used correctly. Citing an article differs from citing other references, such as books or websites. This article will show you how to cite an article.
What exactly is an article in an academic context?
Journal article
An article is a dependent work (unlike a monograph), because articles are published in journals that are often online publications. Scientific journals are published at regular intervals.
Consequently, a full citation of journal articles requires the volume number and, if possible, also the issue number (cf. Lück & Henke 2009: 83).
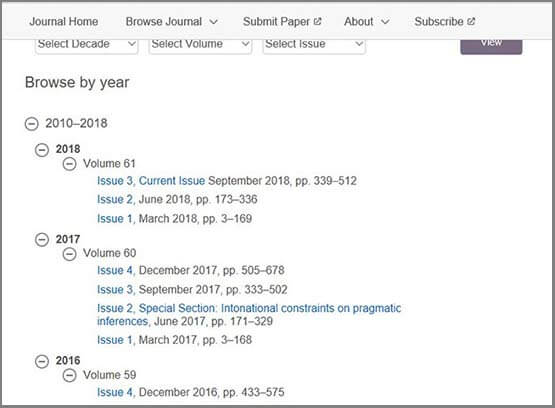
Example: Journal Language and Speech : Browsing the volumes of this journal shows that it is published quarterly (four issues); clicking on the individual issue number lead to the articles.
What is a citation?
A citation is a way of referencing to a published or unpublished source of information that was used in the writing of a journal or research paper . Citations give your readers specific information on sources of the information contained in the text. These citations are written at the end of the report, usually in alphabetical order. This greatly helps the writer avoid plagiarism when writing especially long texts.
How do I cite an article?
Every source used in academic writing must always be cited. Citations for online articles are written as follows: write the author(s) name(s), name of the article in quotation marks, title of the publication in italics, volume and issue numbers of the source, and the year of publication. Be sure that you change the formatting of the citation to suit the referencing style you’re using.
How do I cite an online article?
This type of citation pertains to work obtained from electronic sources on the internet. This is especially complicated and different from the norm because online information can be easily changed, edited, deleted or they just disappear for numerous reasons. It is therefore advised that you store these sources personally by making copies of all the files you used. The exact formatting of an online article citation depends on the referencing style that you’re using. Scroll down for further information about specific citations with each referencing method.
Tip: If you’re not confident with your referencing skills, run your academic work through a plagiarism checker before you hand it in.
How important is citing an article when writing?
Citing an article used when writing has numerous important purposes. One of which is because it helps the writer avoid plagiarizing other writers’ works that were utilized for the academic writing process. It also provides the readers with details about where to find more information about sources mentioned in the text. Plus, it helps the writer to keep track of all the sources they’ve referenced whilst writing.
What are the different citation styles?
There are three (3) major styles of citing across the board (article, book, etc). They are as follows:
a. The APA Style (American Psychological Association): This is an author-year system of citation that ensures that the sources you are referencing can be tracked easily. This style is mostly used for Education, Psychology, and Science writings.
b. The MLA Style (Modern Language Association): This style uses the author-page system of in-text citation. It is popularly referred to as the college writing citation style. It is used for writing in the Humanities field.
c. The Chicago Style: This is an extremely flexible style of citation that unites two referencing styles (footnotes or author-year system) in one manual of style. It is used for Business, History, and Fine Arts writings.
They ultimately defer in the order in which the properties are cited. However, their contents are similar in all three cases.
Components of Full Citations
The following table (cf. APA manual 2010; Oertner, St. John, & Thelen 2014: 48-49) lists all elements that are part of a full citation of a journal article, including examples for each component. The author of the article is a crucial element of the full citation. Each entry in the reference list starts with the author’s surname.
Crucial Elements for Citing an Article
Author: When it comes to journal articles, the author of the article is named first (not the editor of the journal). The surname is followed by the first name. If there is more than one first name, only the first is written in full and the middle name is abbreviated, e.g. Schmitt, Peter A. However, if you are using APA citations , all first names are abbreviated and only the surname is written in full, e.g. Schmitt, P.A.
Journal title: Another vital element is the title of the journal. Depending on the citation system you choose to follow, the title is put in quotation marks. The title of the journal is also part of a full citation and must be italicized to contrast it with the title of the article. Thus, it is possible to distinguish article and journal title at a glance.
Volume Number: Moreover, you have to include the volume number to make sure that the article can be easily found and identified. In addition, the page numbers must be given as this also helps the reader trace your source.
Different Citation Systems
The above table has all the necessary information components that you must include when citing an article. However, the order of the information presented above differs depending on the citation system you are using.
You have to make sure that you consistently follow the same citation style when citing an article or other sources in general, e.g. APA style or Chicago Manual. The latter systems are so-called author/year (or date) systems which means parenthetical references are used in the text (author, year, page number). Short references in the text are directly linked to the full reference in the reference list.
Recommended: How to cite a book
The APA style is frequently used, and there are many reference lists of published works which follow this system. Maybe you came across the term “Harvard Style”. However, this is not a Manual of Style like the APA Style and the Chicago Manual. Bear in mind that Harvard Referencing is just “another name for the author/date citation system, the custom of using author and date in parentheses, e.g. (Robbins 1987), to refer readers to the full bibliographic citations” (cf. Harvard Library 2018, Chernin 1988).
To Cite an Article in APA Style
If you want to cite an article in APA style , you have to start with the author of the article. The surname is mentioned first. This is followed by the year of publication in brackets, the title of the article (no quotation marks), and the title of the journal in italics. The volume and issue number come right after the journal title, and then page numbers. The reference list is ordered alphabetically based on the first letters of the surnames of the authors who are cited.
Examples of Citing Articles in APA Style
The table below shows the general reference form for citing articles in APA style and three examples (cf. APA manual 2010: 198-199 & Szuchman 2005: 103.).
Citing an Article: Short References in the Text
First citation in the text (three authors): (Rogers, McDonald, & Kermit, 2002); subsequent citations in the text:
- (Rogers et al., 2002)
- (Herbst-Damm & Kulik, 2005)
- (Silick & Schutte, 2006)

Journal article as accessed and downloaded. See top of the page on the right-hand side: information regarding volume, issue number, year of publication, and name of journal.

In a Nutshell
- An article is a dependent work , as it is published in a journal (among other articles). A journal is published at regular intervals, e.g. three or four times a year.
- A full citation of an article includes: the name of the author of the article, the title of the article, the title of the journal, the volume number, the issue number, the year of publication, and the page numbers (for APA citation also DOI).
- Different citations systems have different rules on how to order the elements in an entry in the reference list, but they all draw on the same kind of information.
- Author/year systems such as APA style and Chicago Manual (as well as Harvard Style, which is just another term for author/year system) require short references in the text which directly refer to full citations in the reference list.
APA manual (2010). Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Chernin. 1988 . The “Harvard System”: a mystery dispelled. British Medical Journal 297 : 1062-1063.
Harvard Library. Oct 24, 2018 . Citation and Research Management Tools at Harvard – Harvard Style . Retrieved Oct 25, 2018 from the World Wide Web: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/cite/guides .
Lück, Wolfgang, Michael Henke. 2009. Technik des wissenschaftlichen Arbeitens – Seminararbeit, Diplomarbeit, Dissertation. 10th ed. Oldenbourg Verlag: München.
Oertner, Monika, Illona St. John & Gabriele Thelen. 2014 . Wissenschaftlich Schreiben – Ein Praxisbuch für Schreibtrainer und Studierende . Paderborn: Wilhelm Fink.
Szuchman, Leonore T. 2005. Writing With Style – APA Style Made Easy . 3 rd edition. Canada: Thomson Wadsworth.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
APA Formatting and Style Guide (7th Edition)

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
In-Text Citations
Resources on using in-text citations in APA style
Reference List
Resources on writing an APA style reference list, including citation formats
Other APA Resources

What is a Citation in Writing? Definition, Examples
- Posted on June 7, 2023
Writing is not only about expressing your own thoughts but also about using information from other sources to support them. But how do you show your readers where you got that information from?
That’s where citations come in. Citations are a way of giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism. They also help your readers to find the original sources if they want to learn more.
A proper citation includes:
- The author’s name.
- The title of the source.
- The publication date.
- The page number.
- The references page is where all the sources are listed.
You can use different citation styles depending on your writing purpose and audience.
You can also visit a writing lab to get help with citations and other aspects of writing. Citations can make your writing more credible and authoritative because they show that you have done the research and used reliable sources. They can also help search engines to rank your writing higher in the search results.
By the end of this article, you will have gained valuable insights into crafting accurate citations that adhere to formatting guidelines while effectively avoiding plagiarism throughout your writing process.
What is a Citation?
A citation is a way of giving credit to the source of information that you use in your writing. It shows your readers where you got the information from and how they can find it. It also helps you avoid plagiarism, which is copying someone else’s work without permission. A citation usually includes the following information:
- Original author information : This tells your readers who wrote the original source that you are using. For example, if you are citing a journal article, you would include the author’s name and affiliation.
- Date of publication of your copy : This tells your readers when you accessed the source that you are using. For example, if you are citing a web page, you would include the date that you visited the page.
- Year of publication of original copy : This tells your readers when the original source that you are using was published. For example, if you are citing a book, you would include the year that the book was printed.
- Page numbers you are using : This tells your readers which part of the source that you are using. For example, if you are citing a chapter in a book, you would include the page numbers that you are quoting or paraphrasing.
- The material you are using in the citation : This tells your readers what kind of information you are using from the source. For example, if you are citing a quote , a paraphrase, or a summary.
You should include citations in the text of your paper and on a separate references page at the end of your paper.
Why is it Important to Cite Original Sources?
Citing original sources is important for several reasons. First, it shows respect and honesty to the original authors and sources you use, and it acknowledges their contribution and gives them credit for their work.
Second, it helps you avoid plagiarism , which is using someone else’s work as your own without permission. Plagiarism is a serious academic offense that can negatively affect your reputation and career.
Third, it shows the credibility and quality of your own work. It demonstrates that you have researched and used reliable and relevant sources to support your arguments. It also indicates that you have followed the writing style and format of your discipline and source type.
Finally, it helps your readers to find and evaluate your sources. It provides them with a reference list where they can access the original sources if they want to learn more or check your information.
When Do You Need to Cite?
You must cite whenever you borrow ideas, words, or images from another source. Some examples of when you need to cite are:
- When you borrow an idea that someone else has already presented in their work
- When you use a direct quote from a source, using the same words as the author
- When you restate the author’s words in your own words
- When you mention a specific detail from the work of another, such as the title, date, or page number
- When you rely on the research and work of another to create your own ideas or arguments
You can cite your sources in different ways, such as using parentheses with the author’s last name and the year of publication or using footnotes or endnotes. You can also use Libguides to help you with citing your sources correctly for your research paper.
The Most Common Citation Style Guides
In today’s academic and professional world, various citation styles are used to appropriately credit the original authors of the sources referenced in a piece of writing. These citation style guides provide standardized formats for referencing sources, ensuring consistency and clarity across different disciplines.
MLA (Modern Language Association) Style
The MLA citations are popular among humanities scholars like literature and language researchers and use parenthetical citations within text along with an alphabetically arranged Works Cited page at the end.
APA (American Psychological Association) Style
APA citations are commonly used in social sciences such as psychology, education, and sociology. It emphasizes the author-date system for in-text citations and includes a detailed reference list at the end of the document.
In-Text Citation
In-text citations are references in your work that show the source of other authors’ ideas and words. They help readers find more information and avoid plagiarism. There are different in-text citation formats, such as parenthetical and narrative. They usually include the author’s name and publication year, and sometimes page numbers. They should match your reference list, which has all the sources you used.
Chicago Manual of Style
Chicago-style citations are a way of referencing sources in writing, especially in the humanities. They are based on the guidelines of The Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS), a style guide for American English. There are two types of Chicago-style citations: notes and bibliography and author-date. Notes and bibliography use footnotes or endnotes and a bibliography to cite sources, while author-date use parenthetical references and a reference list. Chicago-style citations help writers avoid plagiarism and show respect to the original authors and sources.
Turabian Style
Chicago/Turabian style, favored by historians and other fields that use extensive primary source material, offers two options: notes-bibliography system or author-date system, depending on discipline-specific preferences.
In conclusion, a citation is an essential aspect of writing that helps to acknowledge the original sources used in creating content. It ensures that credit is given where it’s due and prevents plagiarism. Knowing when to cite and which citation style guide to use can be crucial for businesses and marketing teams looking to create high-quality content.
Citing sources can be challenging, but you don’t have to do it alone. Quetext is a trusted tool and partner that can help you avoid plagiarism and generate quality citations. Quetext has a citation generator that can create citations in various styles, such as APA, MLA, Chicago, and more. You can also use Quetext to check your work for plagiarism and improve your writing skills.
Try Quetext today!
Sign Up for Quetext Today!
Click below to find a pricing plan that fits your needs.
You May Also Like

Mastering the Basics: Understanding the 4 Types of Sentences
- Posted on April 5, 2024

Can You Go to Jail for Plagiarism?
- Posted on March 22, 2024 March 22, 2024

Empowering Educators: How AI Detection Enhances Teachers’ Workload
- Posted on March 14, 2024

The Ethical Dimension | Navigating the Challenges of AI Detection in Education
- Posted on March 8, 2024

How to Write a Thesis Statement & Essay Outline
- Posted on February 29, 2024 February 29, 2024

The Crucial Role of Grammar and Spell Check in Student Assignments
- Posted on February 23, 2024 February 23, 2024


Revolutionizing Education: The Role of AI Detection in Academic Integrity
- Posted on February 15, 2024

How Reliable are AI Content Detectors? Which is Most Reliable?
- Posted on February 8, 2024 February 8, 2024
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / MLA Journal Article Citation
How to Cite a Journal Article in MLA
This page is a how-to guide for using scholarly journals as sources and citing them correctly in your papers. Academic journals publish scholarly, peer-reviewed articles written by experts in a specific field. This guide will help you understand what journals are and why they are valuable for your research.
Quickly cite a journal article by using our online form here .
Citing a journal article in mla:, the importance of peer-reviewed academic journals, how journals are organized, where to find journal articles.
- In-text citations
- Works cited references
- Citation with one author
- Citation with two authors
- Citation with three or more authors
- Citation with no known author
- Citation Structures and Examples: Web
- Citation Structures and Examples: Print
Our guide will show you how to cite the journal article both in the text and in the Works Cited page following the guidelines of the Modern Language Association Handbook, 9th Edition.
What is an Academic Journal?
Academic or scholarly journals are periodicals published by universities and other research organizations to present the findings of original research conducted in a particular field. These journals contain highly specific knowledge and are written by experts in that field.
Journals are different from other periodicals such as newspapers or magazines, which cover a broad range of topics and are written in easy to read prose.
Because journals are written by experts for other experts, they can be difficult to read. The writers often use jargon and other complex language that students may not understand. But that doesn’t mean you should not use journals in your research. Journals are where the most recent research is published and provide in-depth information on a topic.
Tip : Reading the abstract and the conclusion first may help you to understand the article as you read.
Journals are good sources for academic research not only because they are written by experts, but because most (but not all) are also reviewed by other experts before the article is published.
Journals that are peer-reviewed have a board of experts in the field that review articles submitted to the journal. The peer reviewers scrutinize every article closely to validate its findings and ensure that the research was done properly. The process of peer review gives credibility to the journal because it means that every article published has been approved by other experts in the field.
Academic journals are organized in volumes and issues.
- Volume: The volume is all of the editions of the journal published in a calendar year.
- Issue(s): The issues are all the specific editions of the journal published in that year.
Tip : Journals frequently publish issues around a certain theme, so all of the articles in that issue will relate to a certain topic. This means that there may be other articles in a particular issue that you can use for your research. It pays to check the table of contents for the issue when you find an article that fits your needs.
You will need to include the volume and the issue numbers, and the page numbers in your citations so make sure to write those down when you take notes from a journal.
When you are doing scholarly research, you can’t use popular search engines like Google, Bing, or Yahoo. These will lead you to popular sources that may not work for a school paper. You need to search for information using an academic database which will lead you to scholarly articles.
Databases are organized computer-based collections of data that allow researchers to find a large number of articles quickly and easily.
Examples of popular general academic databases include:
- Academic Search Premier
- Google Scholar
Examples of popular academic databases focused on specific subjects:
- MEDLINE, PubMed Central — focus on biomedical and life sciences
- Lexis Web — focus on legal information
- Education Resources Information Center (ERIC) — focus on education
Many of these databases charge fees for use. The good news? Many can be accessed through a school or university library. Check your library’s website to see what databases it subscribes to and how you can access them.
Using a Journal Article in a Paper
You can use information from your research in three ways:
- Paraphrase: Take the information from a specific paragraph or section of the article and rewrite it in your own words.
- Summarize: Write a broad overview of the section or the article in your own words.
- Quote: Repeat the exact words used by the author using quotation marks.
Whenever you quote, paraphrase, or summarize information in your paper, you need to follow that information with an in-text citation and create a corresponding reference for the source (in the Works Cited).
Journal Article In-text Citations
Citations within your text are important. Each in-text citation:
- Alerts your reader that you are using information from an outside source.
- Usually appears in parentheses at the end of a sentence.
- Is short and only has enough information to help the reader find the complete reference listed in the Works Cited page at the end of the paper.
A MLA style in-text citation has two parts (MLA Handbook 227-228):
- If there is no author listed, include a shortened version of the title
- While many online sources do not have a page number, academic journals almost always do, even when they are available online.
In most cases, the in-text citation is at the end of the sentence in parentheses. If you use the author’s name in the text, you don’t have to repeat it in the parenthesis at the end. Do not separate the author’s name and the page number with a comma. See below for examples.
Works Cited References for Journal Articles
A Works Cited page is included at the end of your paper. It lists full references/citations for all of the sources mentioned in your paper via your in-text citations.
MLA Containers
In the 9th edition of the official Handbook, MLA includes a new term for citing references, which was first introduced in the 8th edition — containers (134). Periodicals like journals are considered “containers” because they contain the articles that are part of a larger whole.
The container holds the source article and is crucial in identifying the source. The title of the first container, the journal name, is printed in italics and follows the article name. When accessing journals through a database, the database is considered the second container. This title is also printed in italics.
Digital Object Identifier (DOI)
Another feature in citing sources is the DOI (Handbook 188) . DOI stands for Digital Object Identifier, which is used to permanently identify an article or document and link to it on the web.
Although a website or database may change names, the DOI will not change and will help your readers locate the document from your citation. Whenever possible, list the DOI in place of the URL. When you have a DOI, you do not need to give the URL of the website. Indicate that a reference is a DOI by adding “https://doi.org/” before the DOI number of your source.
Another way to identify an online location is with a permalink. Permalinks are URLs that are identified as a stable link that the publisher promises not to change.
For journal references, the following elements need to be included in your Work(s) Cited entries:
- The name of the author or authors. Since journal articles often have more than one author, it is helpful to know when to use et al. in MLA .
- Title of article
- Title of journal (the container)
- Volume and issue number
- Date of publication
- Page numbers
- Database (the 2nd container)
- DOI, permalink, or URL
- Date of access (supplemental, but should be included if the information has no publication date listed)
Citing a Journal Article in MLA (found in databases)
The following are examples of how to cite a journal in MLA 9, both in text and as a full reference in the Works Cited. These were all found via a database.
Note that “Date Accessed” is the day that the journal article was found and read. This information is supplemental and does not always need to be included.
Journal Article Citation With One Author
Cite your source
Journal Article Citation With Two Authors
*Note: When a source has multiple authors, you should always list them in your citation in the same order they are listed in the source.
Journal Article Citation With Three or More Authors
Journal article citation with no known author, citing a journal article in mla (print).
Citing a journal from a print source requires less information than an online source. For a print source, you need the following information:
- The name of the author or authors for articles with one or two authors. For articles with three or more authors, only the first author’s name is used followed by et al.
- The name of the article in quotation marks
- The name of the journal in italics
- The volume and issue numbers of the journal
- The year of publication
- The page number(s)
View Screenshot | Cite your source
Citing an Online Journal Article (not found using a database)
Some journal articles are accessible online without the use of a database. Citing an online journal article not found in a database requires that you cite the website that you used to access the article as the second container. Do not include the https:// in the web address.
*Note : Since journals are usually stable and credible sources, including an access date is supplemental and not required (“When Should I Include an Access Date for an Online Work”).
- Works Cited
MLA Handbook . 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
“When should I include an access date for an online work?” MLA Style Center , Modern Language Association, 29 Dec. 2016, style.mla.org/access-dates/.
Published October 31, 2011. Updated June 6, 2021.
Written by Catherine Sigler. Catherine has a Ph.D. in English Education and has taught college-level writing for 15 years.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples

How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
It’s 100% free to create MLA citations. The EasyBib Citation Generator also supports 7,000+ other citation styles. These other styles—including APA, Chicago, and Harvard—are accessible for anyone with an EasyBib Plus subscription.
No matter what citation style you’re using (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) the EasyBib Citation Generator can help you create the right bibliography quickly.
Yes, there’s an option to download source citations as a Word Doc or a Google Doc. You may also copy citations from the EasyBib Citation Generator and paste them into your paper.
Creating an account is not a requirement for generating MLA citations. However, registering for an EasyBib account is free and an account is how you can save all the citation you create. This can help make it easier to manage your citations and bibliographies.
Yes! Whether you’d like to learn how to construct citations on your own, our Autocite tool isn’t able to gather the metadata you need, or anything in between, manual citations are always an option. Click here for directions on using creating manual citations.
If any important information is missing (e.g., author’s name, title, publishing date, URL, etc.), first see if you can find it in the source yourself. If you cannot, leave the information blank and continue creating your citation.
It supports MLA, APA, Chicago, Harvard, and over 7,000 total citation styles.
To cite a magazine with multiple authors and no page numbers in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the authors, the article’s title, the magazine’s title, the publication date, and the DOI, permalink, or URL. The templates and examples for in-text citations and a works-cited-list entry of a book written by multiple authors are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues” for sources with three or more authors. In subsequent citations, use only the surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues.” In parenthetical citations, always use only the surname of the first author followed by “et al.”
Citation in prose:
First mention: Han Ong and colleagues…. or Han Ong and others ….
Subsequent occurrences: Ong and colleagues…. or Ong and others ….
Parenthetical:
….( Ong et al.).
Works-cited-list entry template and example:
The title of the article is in plain text and title case; it is placed inside double quotation marks. The title of the magazine is set in italics and title case. Follow the format given in the template and example for setting the day, month, and year.
Surname, First., et al. “Title of the Article.” Title of the Magazine , Publication Date, DOI/permalink/URL.
Ong, Han, et al. “The Monkey Who Speaks.” The New Yorker , 13 Sept. 2021, www.newyorker.com/magazine/2021/09/13/the-monkey-who-speaks.
Use only the first author’s name in surname–first name order in the entry followed by “et al.”
To cite an online journal or magazine article in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the author, the article’s title, the journal or magazine’s title, the publication date, and the DOI, permalink, or URL. If available, also include a volume and an issue number of the journal or magazine. The templates for in-text citations and a works-cited-list entry of an online journal article and examples are given below for a source with one author:
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the author on the first occurrence. In subsequent citations, use only the surname. In parenthetical citations, always use only the surname of the author.
First mention: Elizabeth Garber ….
Subsequent occurrences: Garber ….
….(Garber).
The title of the journal or magazine article is set in plain roman text and title case; it is placed inside double quotation marks. The title of the journal or magazine is set in italics and title case. Follow the format given in the template and example for writing the publication month or season and year.
Surname, First. “Title of the Article.” Journal or Magazine Title , Volume, Issue, Publication Date, DOI/permalink/URL.
Garber, Elizabeth. “Craft as Activism.” The Journal of Social Theory in Art Education , vol. 33, no.1, spring 2013, www.scholarscompass.vcu.edu/jstae/vol33/iss1/6/ .
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
What Is Citation?
A "citation" is the way you tell your readers that certain material in your work came from another source. It also gives your readers the information necessary to find that source again, including:
- information about the author
- the title of the work
- the name and location of the company that published your copy of the source
- the date your copy was published
- the page numbers of the material you are borrowing
Why should I cite sources?
Giving credit to the original author by citing sources is the only way to use other people's work without plagiarizing. But there are a number of other reasons to cite sources:
- citations are extremely helpful to anyone who wants to find out more about your ideas and where they came from
- not all sources are good or right -- your own ideas may often be more accurate or interesting than those of your sources. Proper citation will keep you from taking the rap for someone else's bad ideas
- citing sources shows the amount of research you've done
- citing sources strengthens your work by lending outside support to your ideas
Doesn't citing make my work seem less original?
Not at all. On the contrary, citing sources actually helps your reader distinguish your ideas from those of your sources. This will actually emphasize the originality of your own work.
When do I need to cite?
Whenever you borrow words or ideas, you need to acknowledge their source. The following situations almost always require citation:
- whenever you use quotes
- whenever you paraphrase
- whenever you use an idea that someone else has already expressed
- whenever you make specific reference to the work of another
- whenever someone else's work has been critical in developing your own ideas.
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
Cite a Journal
Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper, citing journal articles in apa.
A journal is a scholarly periodical that presents research from experts in a certain field. Typically, but not always, these journals are peer-reviewed in order to ensure that published articles are of the highest quality. That is one reason why journals are a highly credible source of information.
Journal articles in print:
Author Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year Published). Title of article. Title of Periodical, Volume (Issue), page range.
Gleditsch, N. P., Pinker, S., Thayer, B. A., Levy, J. S., & Thompson, W. R. (2013). The forum: The decline of war. International Studies Review, 15 (3), 396-419.
Journal articles online:
- If your source is found online, but there is no DOI provided, you can include the URL instead.
- A DOI (digital object identifier) is basically a number that links a source to its location on the Internet. This number isn’t always provided, but if it is, you should include it in your citation rather than including a URL.
- Unlike previous editions, the current edition does not require including a retrieval date or date accessed for online sources. A retrieval date is only necessary if the source is likely to change (ex. Wikipedia, encyclopedia entry, Facebook homepage, etc.).
Author Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year Published). Title of article. Title of Periodical, Volume (Issue), page range. https://doi.org/xxxx or URL
Burnell, K. J., Coleman, P. G., & Hunt, N. (2010). Coping with traumatic memories: Second World War veterans’ experiences of social support in relation to the narrative coherence of war memories. Ageing and Society, 30 (1), 57-78. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0144686X0999016X
If you need additional help, the Citation Machine APA reference generator will cite your sources automatically for you.
Featured links:
APA Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interview | PDF
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO

How does Citation Statement Search work?

How to interpret search results?
Why search citation statements, i am a student and i am not sure what i should be citing in my research paper.

I am a researcher and I want to understand how a particular dataset is used

I am a pharmaceuticals researcher and I want to know how a particular research asset, reagent, or drug is being discussed in the literature

How is this different from full-text search?
Exact matches, boolean search, grouping, and more, where can i learn more.
Updated on: 10/22/2021
Was this article helpful?
Share your feedback
- Generative AI
- Office Suites
- Collaboration Software
- Productivity Software
- Augmented Reality
- Emerging Technology
- Remote Work
- Artificial Intelligence
- Operating Systems
- IT Leadership
- IT Management
- IT Operations
- Cloud Computing
- Computers and Peripherals
- Data Center
- Enterprise Applications
- Vendors and Providers
- United States
- Netherlands
- United Kingdom
- New Zealand
- Newsletters
- Foundry Careers
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Copyright Notice
- Member Preferences
- About AdChoices
- E-commerce Affiliate Relationships
- Your California Privacy Rights
Our Network
- Network World

How (and why) to use conditional formatting in Excel
Conditional formatting highlights key information in a spreadsheet so it’s easy to see at a glance. This beginner’s guide gets you started.

Spreadsheets usually hold a wealth of information, but it can be difficult to see what’s important in them, such as key data points and trends. There are several ways to make data stand out visually in an Excel spreadsheet, but one of the simplest and most effective is to apply conditional formatting.
What is conditional formatting in Excel?
Conditional formatting is a feature used to make unique, important, or duplicate values stand out or to emphasize trends in a data set. As the name suggests, the feature allows you to format the cells and their data based on conditions you specify, which makes important information easy to see at a glance.
Some common examples:
- Formatting cells that meet specific criteria with a highlight color and/or font
- Applying different colors to different cells based on their values
- Applying color scales or gradients to visually represent cells’ values
Crucially, conditional formatting is dynamic , so it keeps up when your data set changes. For instance, if you create a conditional formatting rule that highlights cells with values over 100, and one of the cells in your set changes from 95 to 102, that cell will become highlighted.
In this article we’ll show you different ways to apply conditional formatting to your data sets. When using conditional formatting, the first option you have is to use preset conditions — formatting options that are built into Excel. We’ll go over some of the best preset conditions for formatting, and then cover how to create your own custom formatting rules.
Excel offers several built-in conditional formatting rules you can apply to your data. (Click image to enlarge it.)
We’ll demonstrate using Excel for Windows under a Microsoft 365 subscription. If you’re using a different version of Excel, you might not have the same interface and options, but the features should work more or less the same way.
Before we begin: How to clear conditional formatting
Throughout this story, we’ll use the same example data set, applying one type of formatting, then clearing it away before applying the next type of formatting. So before we begin, we’ll quickly go over how to clear conditional formatting from a data set.
Simply navigate to the Excel Ribbon’s Home tab. Click the Conditional Formatting button and then select Clear Rules . There you can opt to clear conditional formatting from the selected cells, the entire worksheet, the current table, or the current PivotTable.
It’s easy to remove conditional formatting rules.
How to use highlight cells rules
With that out of the way, we’re going to begin with highlight cells rules. These can be found on the Home tab under Conditional Formatting > Highlight Cells Rules .
The highlight cells rules options.
Here you can see multiple options for highlighting cells based on their values, including greater or less than a certain value, equal to a certain value, between certain values, containing certain text, with a certain date, with duplicate values, and more.
We’ll use the Greater Than option as an example. This will highlight any cells that are greater than a specified number within the data set. For example, you can choose to highlight all cells that are greater than the number 200.
Simply select the set of cells you want to format, then click on Home > Conditional Formatting > Highlight Cells Rules > Greater Than to open the following dialog box.
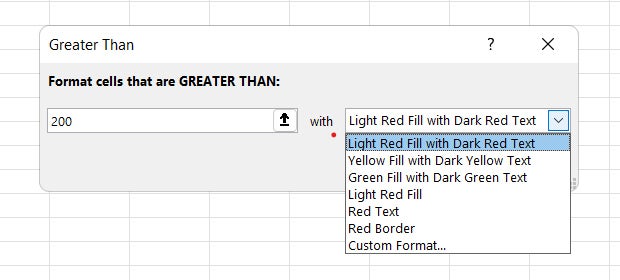
Filling out the conditions for a Greater Than formatting rule.
On the left, select the number to filter by. In this case we are going to highlight any number that is greater than 200. On the right, select the type of highlighting to apply or create a custom format.
As you can see from the screenshot below, the formatting is done in real time, so you can see the effects of your choice before you commit. To finalize your choice, click OK .
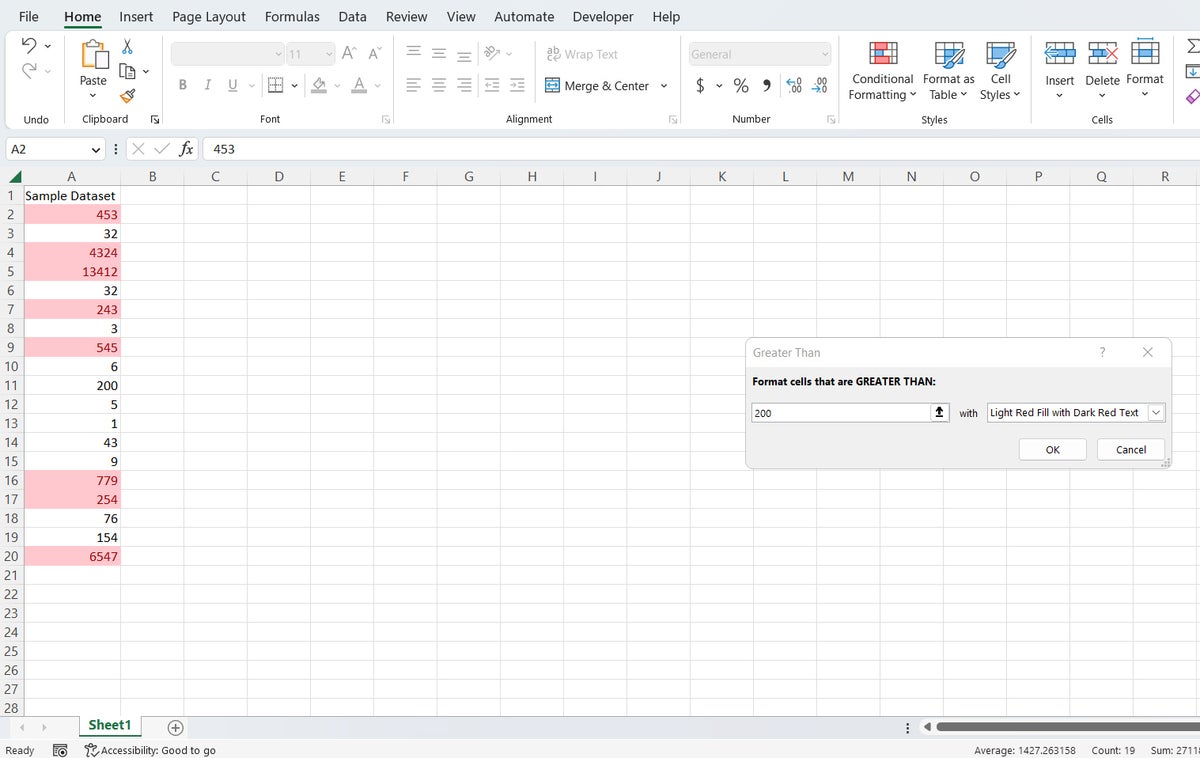
When you make a selection, the formatting is instantly applied to your data. (Click image to enlarge it.)
How to use top/bottom rules
Highlight cells rules are good when you have a specific value in mind, such as numbers greater than 100, cells containing specific words, and so on. But what happens if you need a relative measure — for example, you want to know the highest 10% of values in a data set? In that case, it’s best to use the Top/Bottom Rules option.
This option includes presets for the top or bottom 10 items in the data set, items in the top or bottom 10%, items above or below the average of the data set, and more. The top/bottom presets can be adjusted to show a different percentage or number of items.
Let’s see how these rules work using the Top 10% option. Once you have cleared the highlight cells rules from the data set, select the cells you want to apply the rule to, go to Home > Conditional Formatting > Top/Bottom Rules and select Top 10% .
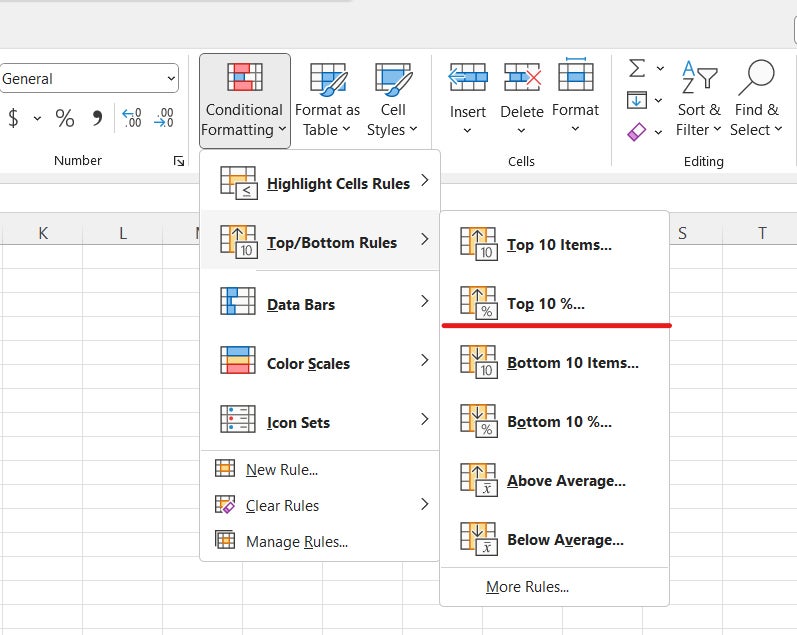
Choosing a top/bottom rules preset.
Once you select that option, you will get a dialog box where you can adjust the exact top percentage you want to highlight and choose the style of the formatting.
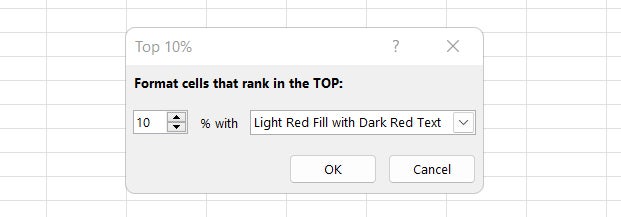
Adjusting Top 10% conditions.
Once you have made your selections, hit OK to confirm the formatting.
Note that you can apply more than one set of conditional formatting rules to a data set — so you could, for instance, highlight the top 5 values in red and the bottom 5 values in yellow.
Our data set with the top 5 and bottom 5 values highlighted in different colors. (Click image to enlarge it.)
How to use data bars
Data bars show a visual representation of how a specific data point relates to the maximum value of the data set. For example, if the largest value in the dataset is 1,000, then a cell with a value of 500 would have a bar that is exactly 50% of the full width of the cell. This allows you to tell at a glance how large a value is compared to the maximum value.
Applying data bars formatting to a data set. (Click image to enlarge it.)
To set up data bars formatting, select the cells you want to apply the rule to, go to Home > Conditional Formatting > Data Bars , and choose one of the styles under Gradient Fill or Solid Fill.
How to use color scales
The color scales option highlights cells with different shades of color depending on how close they are to the data set’s maximum or minimum value. With the target cells selected, choose Home > Conditional Formatting > Color Scales .
Applying color scales formatting to a data set. (Click image to enlarge it.)
You can select any of the preset color scales provided, or you can select More Rules in order to change colors or add more colors for more customized data analysis. For example, if you choose a three-color scale, you can select any percentile you want to be represented by the third value. In the example shown here, I selected the 50 th percentile.
Creating a custom color scale.
The final result is shown below.
Our custom color scale in action. (Click image to enlarge it.)
How to use icon sets
Finally, there are icon sets, which allow you to add icons such as arrows, shapes, flags, or stars to the cells that meet a predefined criterion. You can access this option via Home > Conditional Formatting > Icon Sets .
Select any of the icon sets shown, and it will rank each of the cells based on how close it is to the minimum and maximum number in the data set. For the example below, I selected the star icon set. The top value gets a yellow star and the midpoint a half-yellow star. Because all the other cells are in the bottom third by value, they get white stars.
Applying an icon set to the selected cells. (Click image to enlarge it.)
You can also use the More Rules option at the very bottom of the icon sets menu to customize the formatting to your liking.
Adjusting the value ranges for each icon.
How to create custom formatting rules
If none of these rules work for you, you may want to create fully custom rules from scratch. To do so, select the target cells, go to Home > Conditional Formatting > New Rule , and then select the appropriate rule type. In this case we will choose the second-to-last option, Format only unique or duplicate values , and then under “Format all:” in the “Edit the Rule Description” area, select duplicate .
When creating a custom formatting rule, first select the rule type, then edit its description below. (Click image to enlarge it.)
Once that is done, click the Format button. On the pane that appears, you can choose how you want to format the cells, including changing number layout, changing the font, changing the border, or filling the cell with a certain color. In this case we will select the Fill tab and choose the red fill color.
Choosing the styling for a custom formatting rule. (Click image to enlarge it.)
With the style selection made, click OK , and this style appears in the Preview area of the New Formatting Rule pane. Once you click OK or hit Enter, the cells with duplicate values are highlighted.
Only the cells with duplicate values are colored red.
Managing your conditional formatting rules
As mentioned previously, you can apply more than one conditional formatting rule to the same set of cells, and you can also have different formatting rules for different sets of cells in the same worksheet. To manage all these rules, go to Home > Conditional Formatting > Manage Rules . You’ll see a dialog box with your rules listed.
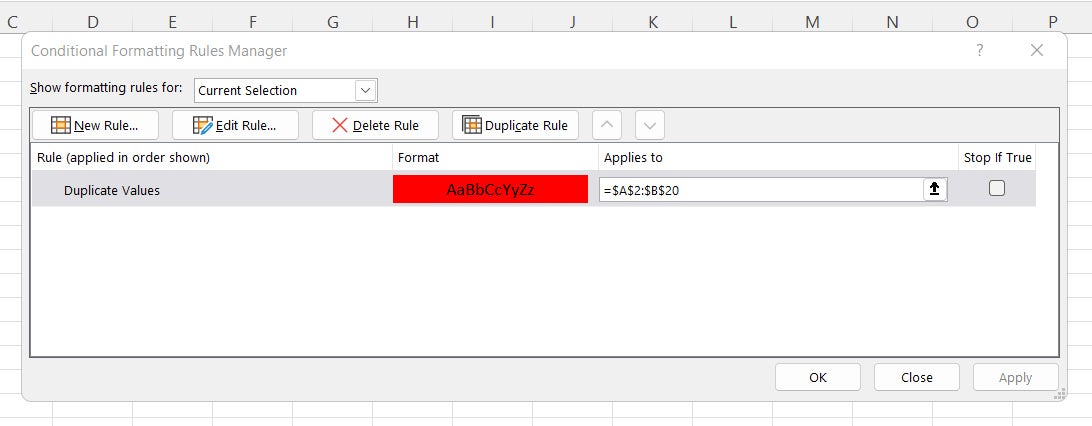
You can manage your rules in the Conditional Formatting Rules Manager. (Click image to enlarge it.)
To delete a rule, simply select it and click the Delete Rule button.
You can also create a new rule from this interface. Click the New Rule button, and you’ll be taken to the same New Formatting Rule dialog box covered in the previous section of the story.
To edit an existing rule, select it in the list and click the Edit Rule button. You’ll see the Edit Formatting Rule dialog box, where you can edit the formatting specifics of the currently selected rule. You can also change the cells the rule applies to by clicking the up arrow icon to the right of its “Applies to” box.
Before you edit a rule, it’s not a bad idea to create a copy of it. That way you’ll have a backup of the original rule that you can revert to if needed. To make a copy, select the rule and click Duplicate Rule .
A duplicate also comes in handy if you want to apply a rule to a different set of cells. You can duplicate the rule, then change the “Applies to” selection for the duplicate.
Related content
How many jobs are available in technology in the us, apple's find my system is coming to android, how to use a smartphone as a mobile hotspot, android 14 upgrade report card: predictable unpredictability, from our editors straight to your inbox.

Shimon Brathwaite is a cybersecurity professional, consultant, and writer at SecurityMadeSimple . He is a graduate of Ryerson University in Toronto, Canada and has worked in several businesses in security-focused roles. His professional certifications include GCIH, Security+, CEH, and AWS Security Specialist. Contact him for writing engagements, consulting, or to ask questions!
More from this author
How to use excel formulas and functions, microsoft forms cheat sheet: how to get started, microsoft visio cheat sheet: how to get started, most popular authors.

- Howard Wen Contributing Writer
Show me more
A phish by any other name should still not be clicked.

India is about to become Apple's third-biggest market

Windows 11 Insider Previews: What’s in the latest build?

The link between smartphones and social media addiction

Sam Bankman-Fried gets 25 years in prison

How to combat social media addiction

Green Chemistry
Sustainable biodegradable coatings for food packaging: challenges and opportunities.

* Corresponding authors
a School of Engineering, Thornbrough Building, University of Guelph, Guelph, Ontario, Canada E-mail: [email protected]
b Bioproducts Discovery and Development Centre, Department of Plant Agriculture, Crop Science Building, University of Guelph, Guelph, Ontario, Canada
This review article provides a thorough overview of barrier coating materials that have been used in food packaging with a focus on biodegradable (bio-based or petroleum-based) materials, such as lipids, proteins, polysaccharides, agriculture waste and polyesters. The goal is to provide an opportunity to acknowledge progress made in this field, focusing on modifications made to coatings. These modifications aim to address the shortcomings of biodegradable substrates (either plastic or paper) and improve their performance, enabling them to compete with traditional petroleum-based food packaging materials. This includes their barrier against water vapor and oxygen, mechanical and surface characteristics (sealability and adhesion), as well as antimicrobial properties. The barrier of most biodegradable polymers underperforms in comparison with petroleum-based non-biodegradable polymers, which possess either high water vapor barrier or high oxygen barrier. Coating technology is a promising solution particularly in barrier improvement of biodegradable polymers. Currently, there are only metallized, or inorganic nanosheet coatings available for biodegradable films that meet food packaging requirements. There are some challenges in this field, for example, being able to retain the coating's biodegradability despite applied modifications to improve it's performance, the large-scale fabrication of biodegradable coatings, the coating's delamination and heat-sealability during service time, and the migration of the coating into the packaged food. Moreover, green chemistry and its sustainability needs in biodegradable polymeric coatings are also discussed regarding new ideas and possible directions for widespread application of coatings in food packaging. This is the first review that specifically summarizes biodegradable coatings on plastic and paper substrates with a focus on coating modifications to improve the performance of the base substrate to meet the required properties for food packaging applications.
Article information
Download Citation
Permissions.
F. Jahangiri, A. K. Mohanty and M. Misra, Green Chem. , 2024, Advance Article , DOI: 10.1039/D3GC02647G
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported Licence . You can use material from this article in other publications, without requesting further permission from the RSC, provided that the correct acknowledgement is given and it is not used for commercial purposes.
To request permission to reproduce material from this article in a commercial publication , please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party commercial publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page .
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Citing sources
- How to Cite a Website | MLA, APA & Chicago Examples
How to Cite a Website | MLA, APA & Chicago Examples
Published on March 5, 2021 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on January 17, 2024.
To cite a page from a website, you need a short in-text citation and a corresponding reference stating the author’s name, the date of publication, the title of the page, the website name, and the URL.
This information is presented differently in different citation styles. APA , MLA , and Chicago are the most commonly used styles.
Use the interactive example generator below to explore APA and MLA website citations.
Note that the format is slightly different for citing YouTube and other online video platforms, or for citing an image .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Citing a website in mla style, citing a website in apa style, citing a website in chicago style, frequently asked questions about citations.
An MLA Works Cited entry for a webpage lists the author’s name , the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the site (in italics), the date of publication, and the URL.
The in-text citation usually just lists the author’s name. For a long page, you may specify a (shortened) section heading to locate the specific passage. Don’t use paragraph numbers unless they’re specifically numbered on the page.
The same format is used for blog posts and online articles from newspapers and magazines.
You can also use our free MLA Citation Generator to generate your website citations.
Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
Citing a whole website.
When you cite an entire website rather than a specific page, include the author if one can be identified for the whole site (e.g. for a single-authored blog). Otherwise, just start with the site name.
List the copyright date displayed on the site; if there isn’t one, provide an access date after the URL.
Webpages with no author or date
When no author is listed, cite the organization as author only if it differs from the website name.
If the organization name is also the website name, start the Works Cited entry with the title instead, and use a shortened version of the title in the in-text citation.
When no publication date is listed, leave it out and include an access date at the end instead.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
An APA reference for a webpage lists the author’s last name and initials, the full date of publication, the title of the page (in italics), the website name (in plain text), and the URL.
The in-text citation lists the author’s last name and the year. If it’s a long page, you may include a locator to identify the quote or paraphrase (e.g. a paragraph number and/or section title).
Note that a general reference to an entire website doesn’t require a citation in APA Style; just include the URL in parentheses after you mention the site.
You can also use our free APA Citation Generator to create your webpage citations. Search for a URL to retrieve the details.
Generate accurate APA citations with Scribbr
Blog posts and online articles.
Blog posts follow a slightly different format: the title of the post is not italicized, and the name of the blog is.
The same format is used for online newspaper and magazine articles—but not for articles from news sites like Reuters and BBC News (see the previous example).
When a page has no author specified, list the name of the organization that created it instead (and omit it later if it’s the same as the website name).
When it doesn’t list a date of publication, use “n.d.” in place of the date. You can also include an access date if the page seems likely to change over time.
In Chicago notes and bibliography style, footnotes are used to cite sources. They refer to a bibliography at the end that lists all your sources in full.
A Chicago bibliography entry for a website lists the author’s name, the page title (in quotation marks), the website name, the publication date, and the URL.
Chicago also has an alternative author-date citation style . Examples of website citations in this style can be found here .
For blog posts and online articles from newspapers, the name of the publication is italicized. For a blog post, you should also add the word “blog” in parentheses, unless it’s already part of the blog’s name.
When a web source doesn’t list an author , you can usually begin your bibliography entry and short note with the name of the organization responsible. Don’t repeat it later if it’s also the name of the website. A full note should begin with the title instead.
When no publication or revision date is shown, include an access date instead in your bibliography entry.
The main elements included in website citations across APA , MLA , and Chicago style are the author, the date of publication, the page title, the website name, and the URL. The information is presented differently in each style.
In APA , MLA , and Chicago style citations for sources that don’t list a specific author (e.g. many websites ), you can usually list the organization responsible for the source as the author.
If the organization is the same as the website or publisher, you shouldn’t repeat it twice in your reference:
- In APA and Chicago, omit the website or publisher name later in the reference.
- In MLA, omit the author element at the start of the reference, and cite the source title instead.
If there’s no appropriate organization to list as author, you will usually have to begin the citation and reference entry with the title of the source instead.
When you want to cite a specific passage in a source without page numbers (e.g. an e-book or website ), all the main citation styles recommend using an alternate locator in your in-text citation . You might use a heading or chapter number, e.g. (Smith, 2016, ch. 1)
In APA Style , you can count the paragraph numbers in a text to identify a location by paragraph number. MLA and Chicago recommend that you only use paragraph numbers if they’re explicitly marked in the text.
For audiovisual sources (e.g. videos ), all styles recommend using a timestamp to show a specific point in the video when relevant.
Check if your university or course guidelines specify which citation style to use. If the choice is left up to you, consider which style is most commonly used in your field.
- APA Style is the most popular citation style, widely used in the social and behavioral sciences.
- MLA style is the second most popular, used mainly in the humanities.
- Chicago notes and bibliography style is also popular in the humanities, especially history.
- Chicago author-date style tends to be used in the sciences.
Other more specialized styles exist for certain fields, such as Bluebook and OSCOLA for law.
The most important thing is to choose one style and use it consistently throughout your text.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2024, January 17). How to Cite a Website | MLA, APA & Chicago Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/citing-sources/cite-a-website/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to cite an image | photographs, figures, diagrams, how to cite a lecture | apa, mla & chicago examples, how to cite a youtube video | mla, apa & chicago, what is your plagiarism score.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A bibliography entry for a journal article lists the title of the article in quotation marks and the journal name in italics—both in title case. List up to 10 authors in full; use "et al." for 11 or more. In the footnote, use "et al." for four or more authors. Chicago format. Author last name, First name.
Different subject disciplines call for citation information to be written in very specific order, capitalization, and punctuation. There are therefore many different style formats. Three popular citation formats are MLA Style (for humanities articles) and APA or Chicago (for social sciences articles). MLA style (print journal article):
To cite an article in MLA, start with the authors last name, followed by a comma, their first name, and a period. Then, add the title of the article in quotation marks with a period at the end of the title inside the quotes. Next, include the title of the periodical in italics, followed by a comma and the date of publication written in a day ...
Articles. Note: Citations with more than one line of text should have a hanging indent of 1/2 inch or 5 spaces. Important Elements: Author (last name, initials only for first & middle names) Date of publication of article (year and month for monthly publications; year, month and day for daily or weekly publications) Title of article (capitalize ...
titles of books, articles, and journals; date of publication; page numbers; volume and issue numbers (for articles) Citations may look different, depending on what is being cited and which style was used to create them. Choose an appropriate style guide for your needs. Here is an example of an article citation using four different citation styles.
7th Edition Reference Guide for Journal Articles, Books, and Edited Book Chapters. Journal Article. Author, A. A., & Author, B. B. (Year). Title of the article.
APA Citation Basics. When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
When you cite a work that appears inside a larger source (for instance, an article in a periodical or an essay in a collection), cite the author of the internal source (i.e., the article or essay). For example, to cite Albert Einstein's article "A Brief Outline of the Theory of Relativity," which was published in Nature in 1921, you might write ...
The title of the article is in plain text and sentence case; the title of the newspaper or the magazine is set in italics. Follow the format given in the template and example for setting the date, month, and year. Template: Surname, F. M. (Date of publication). Title of the article. Title of the Newspaper or Magazine.
The name of the author in a newspaper article is referred to as a byline. Below are examples for citing an article both with and without a byline. Reference list (print) structure: Last name, F. (Year published). 'Article title', Newspaper name, Day Month, Page (s). Example: Hamilton, J. (2018).
Journal article. An article is a dependent work (unlike a monograph), because articles are published in journals that are often online publications. Scientific journals are published at regular intervals. Consequently, a full citation of journal articles requires the volume number and, if possible, also the issue number (cf. Lück & Henke 2009: 83).
Basic guidelines for formatting the reference list at the end of a standard APA research paper Author/Authors Rules for handling works by a single author or multiple authors that apply to all APA-style references in your reference list, regardless of the type of work (book, article, electronic resource, etc.) ...
Narrative citation: Grady et al. (2019) If a journal article has a DOI, include the DOI in the reference. Always include the issue number for a journal article. If the journal article does not have a DOI and is from an academic research database, end the reference after the page range (for an explanation of why, see the database information ...
APA citations are commonly used in social sciences such as psychology, education, and sociology. It emphasizes the author-date system for in-text citations and includes a detailed reference list at the end of the document. In-Text Citation. In-text citations are references in your work that show the source of other authors' ideas and words.
For a print source, you need the following information: The name of the author or authors for articles with one or two authors. For articles with three or more authors, only the first author's name is used followed by et al. The name of the article in quotation marks. The name of the journal in italics.
A "citation" is the way you tell your readers that certain material in your work came from another source. It also gives your readers the information necessary to find that source again, including: information about the author. the title of the work. the name and location of the company that published your copy of the source.
Citing journal articles in APA. A journal is a scholarly periodical that presents research from experts in a certain field. Typically, but not always, these journals are peer-reviewed in order to ensure that published articles are of the highest quality. That is one reason why journals are a highly credible source of information.
The search results are citation statements that were matched to the keywords you searched in order of relevance. The black bold text is the metadata of the citing publication. The blue text is the citation to the cited publication. Other citations are underlined and are the co-citations. All references and citations can be explored by hovering ...
Abstract. The benefit of beta-blockers after myocardial infarction was established before the advent of reperfusion and percutaneous coronary intervention and the availability of effective ...
To do so, select the target cells, go to Home > Conditional Formatting > New Rule, and then select the appropriate rule type. In this case we will choose the second-to-last option, Format only ...
Cite article; Share options; Information, rights and permissions; Metrics and citations; Abstract. We consider the information design problem of a demand-maximizing firm launching a product of unknown quality to a market consisting of customers who have heterogeneous prior beliefs about quality. The firm publicly discloses information about ...
This review article provides a thorough overview of barrier coating materials that have been used in food packaging with a focus on biodegradable (bio-based or petroleum-based) materials, such as lipids, proteins, polysaccharides, agriculture waste and polyesters. The goal is to provide an opportunity to acknowledg
Citing a website in MLA Style. An MLA Works Cited entry for a webpage lists the author's name, the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the site (in italics), the date of publication, and the URL. The in-text citation usually just lists the author's name. For a long page, you may specify a (shortened) section heading to ...