
Are Your Problem-Solving Skills Lacking? Try This New Approach
April 22, 2021

Approaches To Problem-Solving
I appreciate a good mechanic. When something goes wrong with my old truck, I take it to Todd. Todd manages to fix impossible problems. Once, he manufactured a part because no new parts were available. I enjoy working with Todd because he is very good at fixing the tough problems I bring to him. Occasionally, I bring a problem to him, and he says, “You don’t want to spend the money to fix that; it’s not worth it!” Many leaders work like Todd; they wait for others to bring them problems, and then they fix the problem.
I also appreciate Golden Retrievers, although I have never owned one. When my brothers and I grew old enough to go pheasant hunting, we only owned one shotgun. It was a 12-gauge single shot, which means that you had one chance to hit your target. Since we did not own a dog, we decided that whoever had the gun was the hunter, and the other two were the dogs. The dogs’ jobs were to flush out the pheasants. I cannot remember ever bringing home a pheasant, but we did have fun. Unlike my brothers, Golden Retrievers can sniff out a pheasant, point to them so the hunter can get ready, and then flush them out. Many leaders are a lot like Golden Retrievers in terms of solving problems. They are constantly looking for what could go wrong. They take time to anticipate problems before they happen.
I wanted to analyze some 360 feedback data to determine who was a more effective leader. Was it the problem solver or the problem anticipator? I identified leaders who had strengths and weaknesses in both traits and used the following criteria to classify each leader.
Characteristics of Problem-Solving Leaders
- Tend to start projects quickly and then resolve problems when they arise.
- Are skilled at spotting problems and fixing them.
- Do a good job every day and fix immediate problems and concerns.
- Tend to react to the present.
- Focus their efforts on work that needs to be done today.
Characteristics of Problem-Anticipating Leaders
- Are effective at anticipating potential problems or things that could go wrong.
- Tend to see trends and patterns in what they and others are doing.
- Prefer to take the long view and focus on the future.
- Like to anticipate the future.
- Are skilled at identifying changes that need to be made.
Using a dataset of 360-degree feedback reports from 110,460 leaders, I classified leaders who were in the top and bottom quartiles on both characteristics. I also identified two outcome variables I was interested in examining. Overall leadership effectiveness (the average of 60 behaviors found to differentiate poor from great leaders) and a confidence rating by direct reports. The confidence rating was an item asked of all direct reports where they indicated the extent to which they agree or disagree with the statement, “I have confidence that this organization will achieve its strategic objectives.” Since not all leaders had direct reports, the number of leaders analyzed on the confidence outcome was 97,851 leaders.
The graph below shows the results comparing groups in the bottom quartile and the top quartile on problem-solving and anticipating. Groups with bottom quartile scores in both dimensions were only rated at the 14 th percentile on their overall leadership effectiveness. Note that problem-solving ability has twice as much impact on overall leadership effectiveness as top-quartile skills at anticipating problems, but the combination of both skills propels leaders into the 87 th percentile.

Check out the latest episodes of The 90th Percentile: An Unconventional Leadership Podcast.
In this second study, I looked at the 97,851 leaders with direct reports. Ratings for anticipation and problem-solving were also only based on data gathered from each leader’s direct reports. The combination of these skills impacted the level of confidence direct reports had in achieving their organizations’ strategic goals.

Problem Solving is an Essential Skill
In another study, over 1.5 million raters were asked to select the top 4 most important competencies based on 19 different competencies. The number two skill rated as most important was solving problems and analyzing issues.
A day of work is often a day of solving one problem after another. Leaders frequently put themselves in the mechanic role—waiting for others to bring them problems rather than getting ahead of the issues by anticipating them before they occur. The leaders who effectively anticipate problems avoid fire drills and stress. If you are a skillful problem solver, take some time to think about and anticipate problems that may occur. The data is compelling that combining these two skills can be a powerful combination to improve your leadership effectiveness and the confidence of your direct reports in the business’s success.
Learn more about problem-solving by registering for this month’s leadership webinar .
-Joe Folkman
Connect with Joe Folkman on LinkedIn , Twitter , or Facebook .
Sign up for our Newsletter for podcast updates and information on our Monthly Leadership Webinar Series .
Other Articles and Podcasts
How Problem Solvers Can Learn To Sell
Episode 29: The Best Problem Solvers Are Solution Sellers
See all articles

The Magic of Asking for Feedback: How Simple Questions Lead to Great Improvements
Articles — March 26, 2024

6 Proven Ways To Increase Empowerment In Your Team
Articles — March 25, 2024

Remote Work Productivity: Does It Need To Be Fixed?
Articles — March 15, 2024

Adaptive Leadership: 6 Ways to Thrive in an Era of Change
Articles — March 08, 2024
Connect with Zenger Folkman
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
STRATEGIC ANALYSIS AND INTUITIVE THINKING

The most comprehensive and authoritative history site on the Internet.
How Erwin Rommel Has Been Lost in Translation
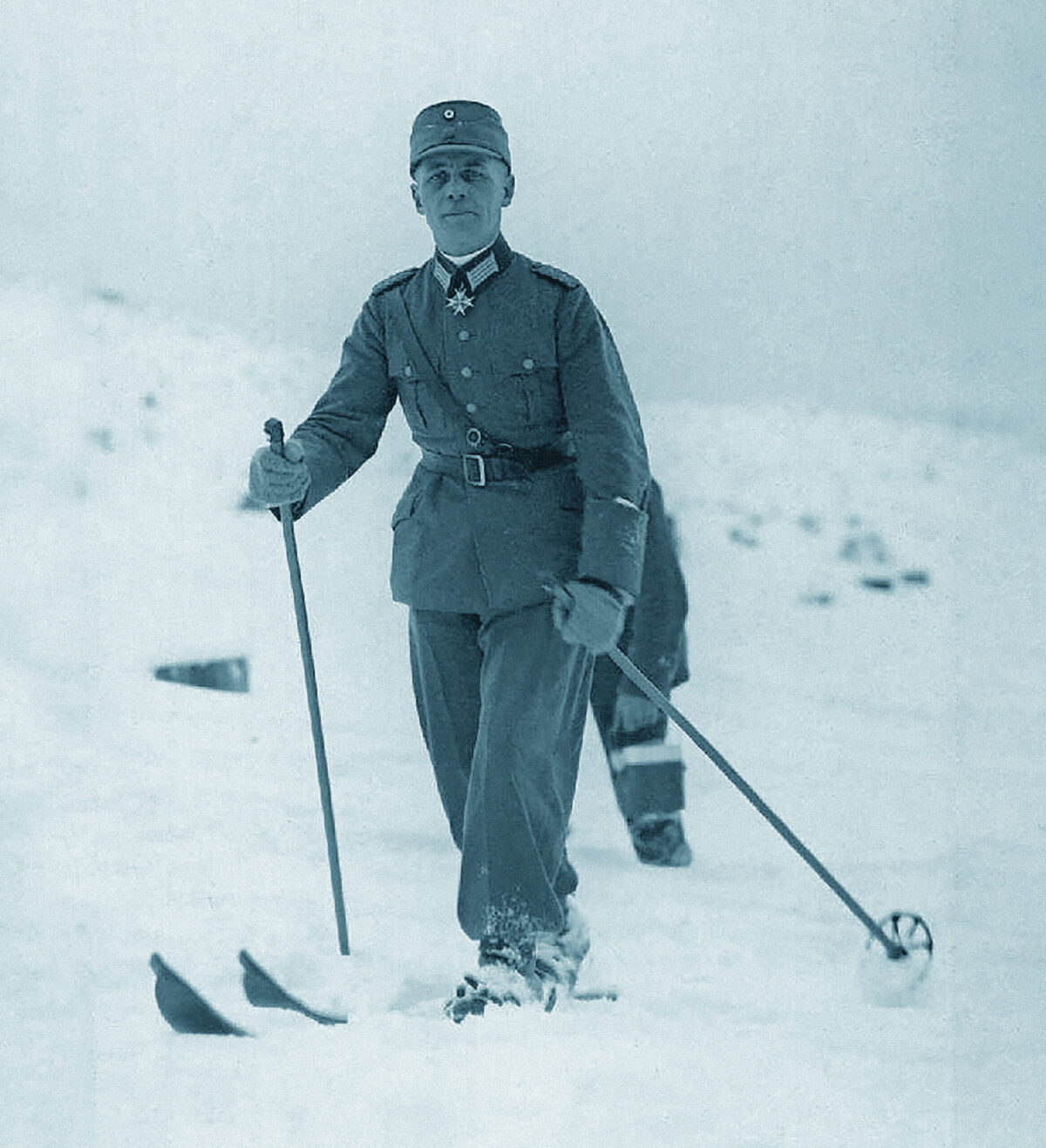

In late October 1917, a detachment of German mountain troopers weary from hard Alpine fighting on the Isonzo front were crossing the river Torre with a group of Italian prisoners. The ordinarily calm waters of the river had swollen into a raging flood after constant heavy rain. Suddenly an Italian prisoner was dragged away by the current. Screaming and flailing, he whirled downstream, sinking under the weight of the large pack he was carrying. An unexpected rescuer came to his aid. The battle-hardened German officer who had defeated the Italian’s comrades and overseen his capture went galloping after him. Driving his horse straight into the torrent, the German risked getting washed away as he drew the helpless prisoner, hanging onto one of his stirrups, to safety.
The German officer was young Oberleutnant Erwin Rommel, and this act of compassion was typical of him. It would be a cornerstone of his career during two world wars in which contempt of one’s enemies and xenophobia were idealized by authorities in power in Germany. Surprisingly, Rommel chose to write about this rescue and other similar anecdotes of humanity in his 1937 World War I memoir, Infantry Attacks! Then a military instructor, Rommel intended to use the book as teaching material for future soldiers training to fight in the Wehrmacht—during a dark era when popular culture in Germany was at its most unmerciful. His original German text offers valuable insights about his outlook and approach to war that censorship and mistranslation had hidden from history.
A Controversial Character
Erwin Rommel is one of the most controversial figures in World War II and German history. Awarded Imperial Germany’s highest decoration for valor, the Pour le Mérite , for his impressive actions as a junior officer during World War I, Rommel reached the pinnacle of his fame during World War II as a brilliant Panzer leader in the 1940 conquest of France and as the daring “Desert Fox” who fought—and ultimately lost to—British and Allied troops in North Africa from 1941 to ’43. Rommel would go on to direct the fortifications of the Normandy coast in preparation for the Allied invasion of France, and command Germany’s Army Group B during the D-Day landings in 1944.
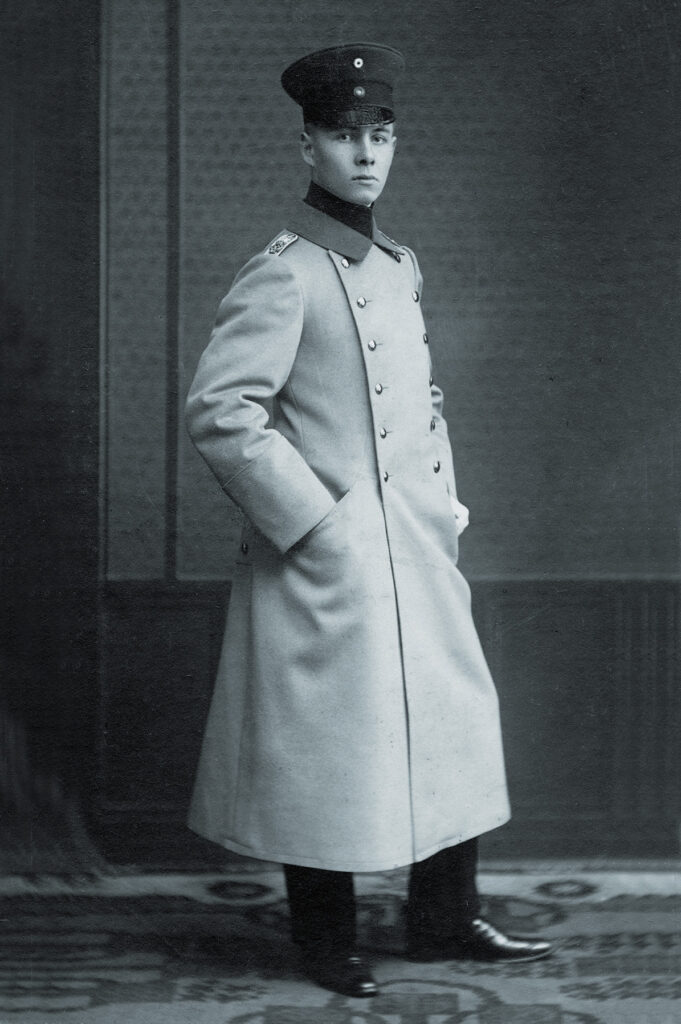

Rommel never joined the Nazi Party nor did he receive any Party decorations, despite the fact that joining would have boosted his career—as it did conversely for Ferdinand Schörner, also a professional soldier, World War I veteran and Pour le Mérite recipient who opted to become a Nazi Party member.
Despite the best efforts of Nazi propaganda to cast Rommel as a hardline ex-SA storm trooper, which he was not, and Allied efforts to depict him as a coldblooded fascist thug, Rommel confounded the expectations of both sides with his unpredictable and humanistic behavior during the war. He disobeyed Adolf Hitler’s infamous Commando Order of 1942 demanding that all Allied “irregular” troops captured were to be delivered to Heinrich Himmler’s security services for immediate execution. Numerous Allied POWs attested to Rommel’s humane treatment of them.
Among them was Capt. Roy Wooldridge of the British Army’s Royal Corps of Engineers, who credited Rommel with saving his life. Wooldridge was captured by a German U-Boat crew while on a secret 1944 mission to scout obstacles around the Normandy coast.
Although Wooldridge was told by interrogators that he would be shot, Rommel unexpectedly summoned Wooldridge, sparing him from a firing squad and sending him off to France after giving him a beer and a pack of cigarettes. “When I got to the prisoner of war camp, a German guard who spoke English said, ‘You’re a very lucky man. If you hadn’t been to see Rommel you would have been shot as a saboteur,’” Wooldridge told the BBC in 2014.
Plotting Against Hitler?
Disillusioned with Hitler’s leadership as early as 1942, Rommel became part of a group of German Army officers conspiring to remove Hitler from power. Contrary to common perceptions, there was not an absence of German Resistance nor did such resistance only come into existence when the war appeared to be closing in around Germany in 1944; pockets of dissent had existed within Germany’s military from much earlier and became more active over time.
Having burned many of his personal papers, particularly from early 1944, to protect himself and others, Rommel’s activities against Hitler—particularly his knowledge or lack thereof regarding Claus von Stauffenberg’s failed July 20 assassination attempt—remain debated.
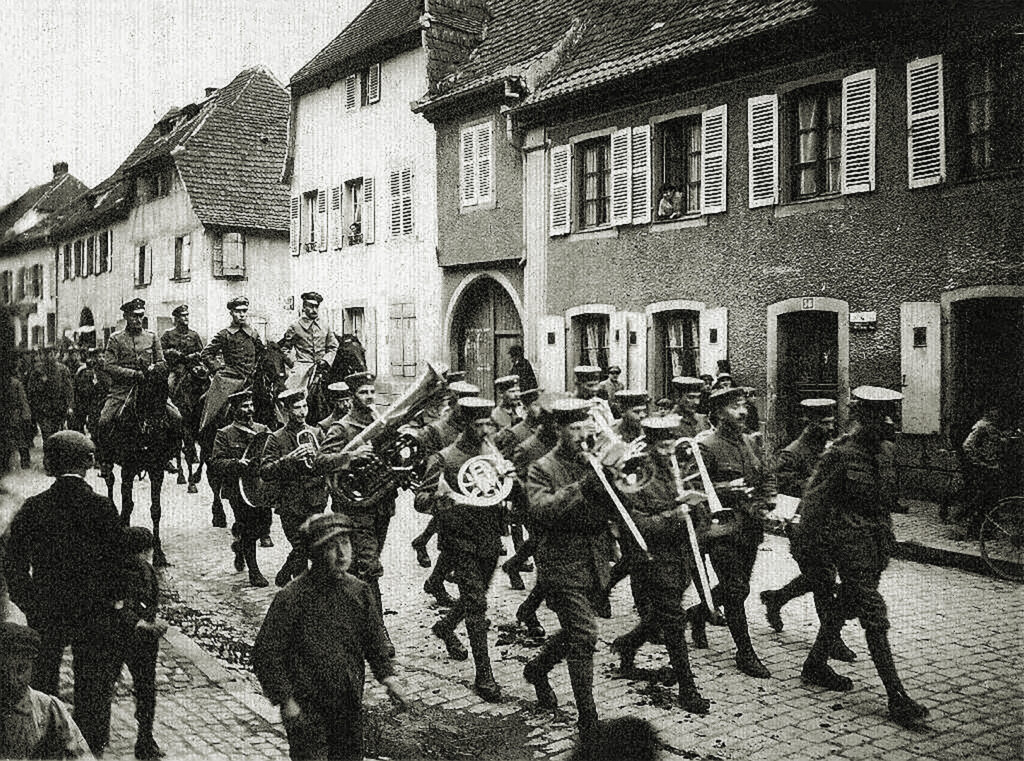

What is indisputable is that Hitler and other leading Nazis perceived Rommel to be a threat and acted quickly to get rid of him. Severely wounded by a plane that strafed his staff car in Normandy on July 17 and left him with a fractured skull, Rommel was executed on Hitler’s orders on Oct. 14, 1944. Representatives of Hitler came to Rommel’s home and threatened to harm his family unless he agreed to commit suicide—immediately. With the house surrounded by Gestapo and SS men, Rommel complied, and took cyanide he was given on an isolated roadside less than 15 minutes from his driveway. Nazi officials concealed the cause of Rommel’s death, initially claiming he had succumbed to wounds from a “car accident” without mentioning a plane strafing.
Doctors who examined Rommel’s body were threatened to falsify his cause of death. Authorities transformed Rommel’s funeral into a propaganda spectacle to rally public support for Hitler. Witnessing Rommel’s executioners use his funeral as political theater was a lifelong source of pain and anger for Rommel’s then 15-year-old son Manfred, aware of the true cause of his father’s death. News of Rommel’s demise was initially celebrated in the Allied press. The darker story emerged after the war was over.
Since then, Rommel has been the focus of endless debate—celebrated, reviled, doubted and admired. Was he a hero? A hopeless fence-sitter? A would-be assassin? A military genius or a blunderer? Although this author is prepared to venture well-researched opinions on these matters, that is not the purpose of this article. Instead, readers of this story are invited to cast an eye back to the start of Rommel’s career and the experiences he recorded in the original German text of his 1937 book, Infantry Attacks! ( Infanterie Greift An ), which provides valuable clues about Rommel’s philosophy and ethos.
Censoring Rommel
The book is inextricably bound up with the story of Rommel’s life and had a propelling effect on his career. It launched him to the heights of military command, unlocked barriers to armored warfare, and paved his road to Africa and Normandy—and, most fatefully, brought him into contact with Hitler, the man who sealed his doom. It was also poorly translated into English. The U.S. Army produced translations of the book in 1943 and 1944, which were heavily redacted and contained errors. Phrases and entire passages were removed. All color and emotion were drained from the original language. This changed not only the content but the tone of the writing.

With Rommel’s personality scrubbed out of the book, readers were left only with a bare skeleton of his work. That bare skeleton has shaped perceptions of Rommel among English readers. It might appear to anyone picking up the U.S. Army’s rendition of Rommel’s writing that he was a bland technocrat who produced one of the most convoluted and tedious war memoirs written by any officer who ever dared to pick up a pen. The contrast between the common 1944 English translation, which is about as exciting as reading an encyclopedia, and the otherwise dashing figure of Rommel is enough to leave a person baffled.
Although Rommel was a meticulous teacher of troops and intended his experiences to be used as a textbook—a blend of memoir with “lessons learned”—the original German book has much more historical value than the tactical teachings it contains, which so far have been the only thing that most English readers have been able to appreciate about it.
Nothing in the material that was censored contained gory, obscene or political language, but ordinary passages for any soldier’s wartime memoir. Many removed passages were ones in which Rommel came across as more relatable or sympathetic on a human level, such as his anecdote of finding a wounded Frenchman by a mountain hut who is subsequently tended by Rommel’s troops, his care for his horse, and friends’ funerals.
Working to produce English translations in the middle of World War II, the U.S. Army also removed passages that they may have worried would intimidate Allied soldiers or civilians, such as some passages describing soldiers’ deaths, violence, or grim scenes. Some praise for German troops was removed, as well as a reference in which Rommel clearly states that he has no fear of Russians. The Russians—allies in World War II, of course—in that sentence were conveniently changed to “Romanians.”
Clues About Rommel From His Writing
Rommel’s use of the German language makes for interesting study. His writing is distinctly straightforward with a colloquial South German twist. Patterns of expression emerge. As an author, Rommel showed a tendency to remove direct references to himself from his own narrative. While this is not unusual in the German language, the lengths that Rommel went through to avoid focus on himself is unique—especially when it comes to describing the hardships of battle or frontline conditions.
Although he didn’t hesitate to describe himself in decision-making, he tended to make difficult or uncomfortable situations into “we” and “us” experiences, or simply speak of the tribulations of war in a more abstract sense. It is clear that Rommel did not wish to complain nor describe his own sense of suffering, but referred to himself as part of a group—and above all, focused on the sacrifices of his comrades. This attitude can often be found in the memoirs and statements of war veterans who wish for others to focus on the deeds of their friends around them rather than on themselves.

A sense of deep affection for his comrades is manifest in Rommel’s writing. He referred to his troops in endearing terms, in many cases as “ mein Häuflein ”—meaning “my little flock,” as if they were a flock of sheep who need to be tended or a small handful of something to be looked after. He stressed his feelings of responsibility towards his men, particularly in situations where they were in danger and he felt compelled to protect them; in one instance, Rommel risked his entire force to save a group of their comrades who were stranded amid enemy forces, taking a “one for all, all for one” type of attitude.
Rommel wrote tributes to fallen comrades, recording their achievements, deaths and funerals. He later revisited former battlefields and photographed his friends’ graves. Additionally, Rommel devoted what sometimes seems like an inordinate amount of energy into building fortifications to protect his men from harm, spending much time analyzing and improving shelters and dugouts. The amount of effort he put into improving structures for defense suggests that Rommel was actually more cautious and circumspect on the front than he is commonly perceived to have been.
‘Homeland’ not ‘Fatherland’
Thought-provoking word choices pop up frequently in Rommel’s writings. While it has been assumed that Rommel had no taste for music or literature, his narrative contains several references to songs and culture, including an ironic reference to a scene from a Richard Wagner opera.
It’s also worth noting that Rommel never used the word “ Vaterland ” (“Fatherland”) to describe Germany, instead preferring to use “ Heimat ”—a folksy term meaning “homeland” which wasn’t quite German nationalists’ cup of tea. While the term “ Vaterland ” was often used by the Nazis to stress the concept of Germany as a strong unified country under Hitler’s rule, “ Heimat ” is an old-fashioned term that can refer to one’s native region and is non-political. Since the book was published within the Third Reich, when Nazism and support for Hitler were encouraged on every level of society, Rommel had no reason not to appeal to mainstream Nazi political sentiments in his book; indeed, it might have made his work more popular. Yet the book contains no mentions of a Führer nor a “new Fatherland”.
Rommel was a native of the Swabian Alps, and after serving as an infantryman on the Western Front early in World War I, was selected to become part of the Württemberg Mountain Battalion, an elite unit of Gebirgsjäger troops—German army mountain rangers. These rangers are highly mobile, extremely resilient and adaptable, and trained to maneuver and fight in all manner of harsh mountain environments. They were and continue to be among the most elite units in German-speaking nations. Entitled to great cultural esteem due to their abilities and affinity with the mountains, they are entitled to wear the symbol of the Edelweiss flower.
Training troops For the Wilderness
The Edelweiss, whose name means “noble white,” is a legendary bloom known for growing in the most austere mountain environments and being difficult to reach. It is a symbol not only of beauty but of hardiness and resilience. Still worn by Gebirgsjäger troops today, the Edelweiss patch was also a hard-earned symbol that Rommel was entitled to wear. It is visible on his cap in several of his World War I photos.
Rommel’s writings reveal his strong sense of identity as a mountain ranger, which arguably has never been properly appreciated by historians. Although he built strong bonds with his men in the trenches of the Argonne, one of the singular events in World War I that truly had a transformative effect on Rommel and his future leadership was his becoming a mountain ranger. Within this close-knit group, Rommel quickly developed a strong sense of pride, along with confidence in harsh training and an attitude of fearlessness. Camaraderie and the tests of combat convinced Rommel that, together, he and his men could accomplish nearly anything.

The Rommel that emerged as a skilled commander of mountain rangers was the same Rommel who would become the “Desert Fox” in North Africa—a man who excelled in the wilderness and at molding soldiers into masters of mobile combat, who could all withstand not only battle but the very elements of nature. An intense spirit of individuality, pride and elite group identity, as well as feelings of a close personal bond with Rommel as their commander, remained with many Afrika Korps veterans for their whole lives. The seeds of this future success are clear to be seen in Rommel’s proud and emotional writings about his love for the mountain troops.
Themes and Slang
Nature forms a major theme in Rommel’s narrative. He had a special flair for describing natural environments such as forests, trees, mountains, and geographic features, as well as elemental forces like thunder, lightning, clouds and different types of storms. Even in the midst of grim battles, Rommel somehow appreciated his natural surroundings and found a way to draw attention to it in writing. His writings on nature are poetic, highly descriptive and sometimes romanticized. In one instance, for example, Rommel compared meadows to the Elysian Fields of Roman mythology.
Despite Rommel’s sense of poetry about nature, his writings abound with slang common to soldiers’ memoirs. Rommel wrote with an understated and ironic sense of humor, and—with a sly attitude similar to the Civil War’s “Gray Ghost,” Col. John Singleton Mosby —clearly enjoyed taking enemies by surprise and chasing fleeing foes. Rommel’s writings on action are far from clinical. Gunfire “rips through” things, men are “gunned down,” and planned actions will be a “piece of cake”—or even “fun”. Rommel’s mix of slang, irony and hard-edged soldierly humor is characteristic of the memoirs of many military professionals.
Humane Treatment of Enemies
Another factor that stands out throughout Rommel’s book is his humane treatment of enemies. The amount of times that Rommel gave his enemies opportunities to surrender rather than shoot them is surprising—in fact, there are several cases when, as Rommel gained opportunities to surprise formidable enemy forces, readers might fairly wonder if opening fire might have been a more practical battlefield measure than yelling at foes to give themselves up.
Rommel however made a constant habit of requesting surrenders even when it seemed clearly inconvenient or downright dangerous to do so. He frequently spoke with prisoners afterwards and gives them cigarettes. In a mirrorlike foreshadowing of events at St. Valery during World War II in 1940, Rommel invited captured officers to have a meal with him. As in 1940, the captured officers were understandably too upset by their situation to appreciate this gesture. But it’s worth noting that this naïve attempt at magnanimity was one that Rommel would repeat in World War II.
Young Rommel also helped enemy wounded, and in one instance intervened to stop his own men from harming POWs. It’s worth mentioning that Rommel, in describing these anecdotes and choosing to include them in his military textbook, risked coming across as “ weich,” or “soft,” in Nazi Germany. His anecdotes of showing kindness to enemies did not correspond to the general sense of bloodthirsty nationalism whipped up by Kaiser Wilhelm II during the First World War nor the iron-hearted cruelty advertised as being “strong” in Hitler’s Germany. Rommel could arguably have gotten farther by describing himself being merciless rather than being empathetic.
If anything, the passages attest not only to Rommel’s inner principles but his independence. As a military instructor during the Third Reich, Rommel must have been aware of the values that the regime wanted to instill in future soldiers, but instead chose to set an example of humanity for his students even if it did not match popular ideology. His behavior also forms a continuum with what Allied POWs witnessed during World War II—that Rommel’s compassionate treatment of POWs was not part of any postwar mythologizing, but was rather a real part of his character that was evident when he was a young man.
World War I had a profound impact on Rommel. Haunted by his experiences, Rommel would return to his former battlegrounds, form a veterans’ group, write about, teach about and dwell on his battlefield experiences for the rest of his life. He also wore his Pour le Mérite medal, earned among his beloved mountain troops, constantly until it chipped and faded. There are many more insights to be gained about Rommel’s early transformation into an effective war leader from his memoir—too many to describe in one article. However, what truly stands out is that, contrary to the commonly read, clinical English translations produced during World War II, Rommel was a gifted writer who expressed more about ethics in war than has been previously realized.
Zita Ballinger Fletcher is Editor of MHQ and the author of Erwin Rommel: First War, A New Look at Infantry Attacks , published in 2023.
this article first appeared in military history quarterly
Related stories

Portfolio: Images of War as Landscape
Whether they produced battlefield images of the dead or daguerreotype portraits of common soldiers, […]

Jerrie Mock: Record-Breaking American Female Pilot
In 1964 an Ohio woman took up the challenge that had led to Amelia Earhart’s disappearance.

The One and Only ‘Booger’ Was Among History’s Best Rodeo Performers
Texan Sam Privett, the colorfully nicknamed proprietor of Booger Red’s Wild West, backed up his boast he could ride anything on four legs.

An SAS Rescue Mission Mission Gone Wrong
When covert operatives went into Italy to retrieve prisoners of war, little went according to plan.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Overview of the Problem-Solving Mental Process
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
- Identify the Problem
- Define the Problem
- Form a Strategy
- Organize Information
- Allocate Resources
- Monitor Progress
- Evaluate the Results
Frequently Asked Questions
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything they can about the issue and then using factual knowledge to come up with a solution. In other instances, creativity and insight are the best options.
It is not necessary to follow problem-solving steps sequentially, It is common to skip steps or even go back through steps multiple times until the desired solution is reached.
In order to correctly solve a problem, it is often important to follow a series of steps. Researchers sometimes refer to this as the problem-solving cycle. While this cycle is portrayed sequentially, people rarely follow a rigid series of steps to find a solution.
The following steps include developing strategies and organizing knowledge.
1. Identifying the Problem
While it may seem like an obvious step, identifying the problem is not always as simple as it sounds. In some cases, people might mistakenly identify the wrong source of a problem, which will make attempts to solve it inefficient or even useless.
Some strategies that you might use to figure out the source of a problem include :
- Asking questions about the problem
- Breaking the problem down into smaller pieces
- Looking at the problem from different perspectives
- Conducting research to figure out what relationships exist between different variables
2. Defining the Problem
After the problem has been identified, it is important to fully define the problem so that it can be solved. You can define a problem by operationally defining each aspect of the problem and setting goals for what aspects of the problem you will address
At this point, you should focus on figuring out which aspects of the problems are facts and which are opinions. State the problem clearly and identify the scope of the solution.
3. Forming a Strategy
After the problem has been identified, it is time to start brainstorming potential solutions. This step usually involves generating as many ideas as possible without judging their quality. Once several possibilities have been generated, they can be evaluated and narrowed down.
The next step is to develop a strategy to solve the problem. The approach used will vary depending upon the situation and the individual's unique preferences. Common problem-solving strategies include heuristics and algorithms.
- Heuristics are mental shortcuts that are often based on solutions that have worked in the past. They can work well if the problem is similar to something you have encountered before and are often the best choice if you need a fast solution.
- Algorithms are step-by-step strategies that are guaranteed to produce a correct result. While this approach is great for accuracy, it can also consume time and resources.
Heuristics are often best used when time is of the essence, while algorithms are a better choice when a decision needs to be as accurate as possible.
4. Organizing Information
Before coming up with a solution, you need to first organize the available information. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? The more information that is available the better prepared you will be to come up with an accurate solution.
When approaching a problem, it is important to make sure that you have all the data you need. Making a decision without adequate information can lead to biased or inaccurate results.
5. Allocating Resources
Of course, we don't always have unlimited money, time, and other resources to solve a problem. Before you begin to solve a problem, you need to determine how high priority it is.
If it is an important problem, it is probably worth allocating more resources to solving it. If, however, it is a fairly unimportant problem, then you do not want to spend too much of your available resources on coming up with a solution.
At this stage, it is important to consider all of the factors that might affect the problem at hand. This includes looking at the available resources, deadlines that need to be met, and any possible risks involved in each solution. After careful evaluation, a decision can be made about which solution to pursue.
6. Monitoring Progress
After selecting a problem-solving strategy, it is time to put the plan into action and see if it works. This step might involve trying out different solutions to see which one is the most effective.
It is also important to monitor the situation after implementing a solution to ensure that the problem has been solved and that no new problems have arisen as a result of the proposed solution.
Effective problem-solvers tend to monitor their progress as they work towards a solution. If they are not making good progress toward reaching their goal, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies .
7. Evaluating the Results
After a solution has been reached, it is important to evaluate the results to determine if it is the best possible solution to the problem. This evaluation might be immediate, such as checking the results of a math problem to ensure the answer is correct, or it can be delayed, such as evaluating the success of a therapy program after several months of treatment.
Once a problem has been solved, it is important to take some time to reflect on the process that was used and evaluate the results. This will help you to improve your problem-solving skills and become more efficient at solving future problems.
A Word From Verywell
It is important to remember that there are many different problem-solving processes with different steps, and this is just one example. Problem-solving in real-world situations requires a great deal of resourcefulness, flexibility, resilience, and continuous interaction with the environment.
Get Advice From The Verywell Mind Podcast
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares how you can stop dwelling in a negative mindset.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
You can become a better problem solving by:
- Practicing brainstorming and coming up with multiple potential solutions to problems
- Being open-minded and considering all possible options before making a decision
- Breaking down problems into smaller, more manageable pieces
- Asking for help when needed
- Researching different problem-solving techniques and trying out new ones
- Learning from mistakes and using them as opportunities to grow
It's important to communicate openly and honestly with your partner about what's going on. Try to see things from their perspective as well as your own. Work together to find a resolution that works for both of you. Be willing to compromise and accept that there may not be a perfect solution.
Take breaks if things are getting too heated, and come back to the problem when you feel calm and collected. Don't try to fix every problem on your own—consider asking a therapist or counselor for help and insight.
If you've tried everything and there doesn't seem to be a way to fix the problem, you may have to learn to accept it. This can be difficult, but try to focus on the positive aspects of your life and remember that every situation is temporary. Don't dwell on what's going wrong—instead, think about what's going right. Find support by talking to friends or family. Seek professional help if you're having trouble coping.
Davidson JE, Sternberg RJ, editors. The Psychology of Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press; 2003. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511615771
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. Published 2018 Jun 26. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

Justin Sullivan/Getty Images
By Dr. Josh Axe Leaders Staff
Dr. Josh Axe
CEO/Founder
Dr. Josh Axe is the co-founder of Ancient Nutrition and the founder and CEO of Leaders.com. He earned his doctorate...
Learn about our editorial policy
Updated May 17, 2023
Reviewed by Colin Baker
Colin Baker
Leadership and Business Writer
Colin Baker is a business writer for Leaders Media. He has a background in as a television journalism, working as...
What Is Problem-Solving? How to Use Problem-Solving Skills to Resolve Issues
What is problem-solving, what is the general process of problem-solving, the best problem-solving strategies and tools, what to do when a problem feels too big to solve.
Great businesses don’t exist to simply grow and make money. Instead, they solve the world’s problems , from tiny issues to giant dilemmas. Problem-solving is essentially the main function of organizations. An effective organization will have systems and processes in place to reach their goals and solve problems. If a company has team members and leaders who have poor problem-solving skills, that means they’re ineffective at one of the core functions of a business.
You need to be good at both external problem-solving (solving problems for others) and internal problem-solving (solving problems before or when they arise within the business). An organization that can solve problems will see its teams come closer together as they bond over providing solutions to serious issues. Companies that solve problems well will also be able to carry out their purpose more efficiently.
Learn the steps you can follow to solve problems both great and small. Additionally, discover some real-world methods and problem-solving skills successful business leaders use to solve problems of their own.
Problem-solving involves the search for solutions that follow an effective process of discovery, identification, ideation, and execution. Problem-solving usually requires overcoming numerous obstacles that stand in the way of reaching your goal. Often, the act of problem-solving includes coming up with solutions to many smaller problems before eventually solving the main issue that prompted the process in the first place.
The key to cultivating excellent problem-solving skills is having a distinct process designed to produce solutions. While it may seem like problem-solving involves a complex strategy, it features several steps that are easy to follow. The following steps represent a general problem-solving process you can use when you need to find a solution.
1. Define the Problem
The first step to take as part of the problem-solving process involves defining what that problem is. While this may seem like a simple idea to follow, the key is to get to the root of the problem . Only once you’re able to identify the root issue you’re tackling through a root cause analysis can you be sure you’re on the right path. Sometimes the surface issue isn’t what you need to address. Just like an earthquake, organizational issues have an epicenter—complete with shockwaves that negatively impact the business. If you don’t resolve the core problem, it can expand , and the damage becomes detrimental. All problem-solving jobs begin with this important first step.
If your organization has a problem with employee retention , you may think you’ll solve it by increasing pay or perks. However, that might not address the root of the issue. If you were to investigate further, you may discover that a manager is creating a toxic work environment, causing good employees to find work elsewhere.
2. Brainstorm Possible Solutions
Once you have a solid idea of what the real problem is, you can proceed to create possible solutions you can pursue. Take the time to brainstorm different solutions. No two problems are the same, and each one will require a creative approach. Make sure you write down the alternative solutions so you can research them in depth. During the course of your brainstorming, you may stumble upon a solution you wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
As you follow this step, you may need to find the best way to inspire your critical thinking skills. Think about when and where you generate ideas and get the creative juices flowing. Then, try to put yourself in that environment as often as possible.
Sara Blakely , the founder of SPANX®, says her most productive creative thinking happens when she’s driving in her car . Even though she doesn’t have a real commute, she gets in the car and makes one up. “I live really close to Spanx,” she said on the “Masters of Scale” podcast, “so I’ve created what my friends call my ‘fake commute,’ and I get up an hour early before I’m supposed to go to Spanx, and I drive around aimlessly in Atlanta with my commute so that I can have my thoughts come to me.” As a result, she sets time aside for developing her best problem-solving strategies every single day.
3. Research Several Options
After you’ve come up with several possible alternative solutions, pick two or three that seem the most promising using your analytical skills. Then you’ll need to buckle down and do some research to see which one to pursue. Conduct your research using primary and secondary resources.
Conduct primary research by:
- Having a discussion with a mentor
- Interviewing a person who’s successfully solved this problem before
- Strategizing with team members closest to the issue
Great secondary sources include:
- Trustworthy online articles and news sources from credible websites
- Leadership books from experts who have written about the problem
- Business podcast interviews on the issue
- YouTube videos featuring established leaders
4. Select a Solution
At the conclusion of your research, you’ll be better equipped to select the right solution. Evaluate the data you have gathered. To ensure you make a good pick, you’ll need to keep several considerations in mind.
Here are some good questions to ask when picking a solution:
- Is this solution in line with the company’s core values?
- Is it a realistic option?
- Could it lead to additional problems?
- Will everyone involved accept the solution?
- Does it truly solve the problem, or does it only delay negative effects?
As you employ your creative thinking skills in answering these questions, you’ll eventually need to settle on a single solution. Adhering to a decision-making process helps you objectively choose the best solution out of many options. Don’t make a quick decision you may later regret. Be deliberate in your analysis, and try to remain as objective as possible.
In order to make the most objective decision:
- Get into a humble mindset and make sure you’re willing to listen and learn.
- Don’t let emotions influence the choice.
- Reverse-engineer the possible outcome of any given solution.
- Weigh the pros and cons of each choice.
- Seek wise counsel from trusted mentors, leaders, and team members.
5. Develop an Action Plan
Once you’ve settled on a solution, you’ll be ready to pursue it. Before moving too quickly, revisit step one and make sure your choice aligns with the main objective . If it doesn’t, although it may be a valid choice, it’s most likely not the best for your team. If this is the case, don’t get discouraged. Creative problem-solving takes time.
When the right choice is made, and the solution is placed into the overall strategy, start developing an action plan . Lay out the “who,” “what,” “when,” “why,” and “how.” Visualize exactly what success looks like with this new plan. When working through the problem-solving process, write all the details down. This helps leaders construct action items and delegate them accordingly. Never leave this part of the process empty-handed. Your team needs a clear picture of expectations so they can properly implement the solution. And if everything works, you can use this problem-solving model in the future.
You will undoubtedly encounter many problems that need to be solved in your life. There are a variety of ways to solve those problems. With all the problem-solving techniques out there, it can be helpful to learn some of them so you can employ the best one at the right moment. The following are just a few examples of what these strategies and problem-solving tools look like in the real world.
One of the best ways to discover the root cause of a problem is by utilizing the 5 Whys method. This strategy was developed by Sakichi Toyoda, founder of Toyota Industries. It’s as simple as it sounds. When a problem occurs, ask why it happened five times. In theory, the last answer should get to the heart of the issue.
Here’s an example of how the 5 Whys work in action:

When business leaders use the 5 Whys method , problems are given more context. Uncovering how, when, and why they happen helps company owners and executives identify the organization’s core issues.
First Principles Thinking
When one engages in first principles thinking , they end up questioning what everyone just assumes to be true. It effectively removes those assumptions , breaking things down into their most basic elements that are probably true. It’s all about getting to that core foundation of truth and building out from there. Problem-solving skills should always include first principles thinking.
Elon Musk most famously pursued this strategy when it comes to space travel. Instead of accepting that building a rocket was too expensive, he got to the fundamental truths of construction, all the way down to pricing each component. Musk once explained that he follows first principles thinking by following three simple steps .
- Identify the assumptions
- Break down the issue into its core, fundamental components
- Innovate by creating new solutions
Other business leaders have engaged in similar strategies, such as Jeff Bezos when he advised the need for finding out key truths for yourself. First principles thinking is an important part of innovating beyond what we assume can’t be changed. It’s a way to use analytical skills to discover potential solutions through constant learning and acquiring new information.
Steve Jobs’ Problem-Solving Method
Steve Jobs gained a reputation for solving problems through Apple. He was always on the lookout for simple solutions to complex problems. He followed his own three-step method that helped him tackle difficult issues.
- Zoom Out: When facing a problem, zoom out to get a larger view of the bigger picture. This is another way to help you define the problem and pinpoint the root cause.
- Focus In: After defining the problem, focus all your attention on solving it. Concentrate your efforts, and don’t stop until the problem is fixed. Give yourself a period of intense focus and dedication as you bring the solution to life.
- Disconnect: If things aren’t proceeding the way you thought they would, it may be time to disconnect. That means walking away and giving yourself a break so you can clear your mind. Sometimes, a break is all you need to approach the problem once more, this time from a fresh angle with your mind fully reenergized.
From increasing sales to engaging in conflict resolution , business leaders have a lot of problems to solve. However, some people may still feel overwhelmed, especially if the problem is large in scope and could even threaten to close the company. Fortunately, there are steps you can take to get in the right mindset as outlined by James Clear, author of Atomic Habits :
- Break the bigger problem down into a lot of smaller problems
- Focus on one small problem and solve it
- Use what you learned from solving that problem to increase your knowledge about the bigger problem
- Repeat these steps until the larger problem is solved
Tackling a problem that feels too big to solve requires a can-do, positive mindset. In order to improve your problem-solving, you’ll need to take remember these steps. Imagine what is possible instead of focusing on what seems impossible. As you do so, you’ll become skilled in solving all sorts of problems while also improving your decision-making.
For more help in growing your skillset, check out the following article:
Growth Mindset: Creating an Environment for Innovation
Leaders Media has established sourcing guidelines and relies on relevant, and credible sources for the data, facts, and expert insights and analysis we reference. You can learn more about our mission, ethics, and how we cite sources in our editorial policy .
- Abadi, Mark. “The CEO of Spanx Wakes up an Hour Early to Drive around ‘Aimlessly’ on a ‘Fake Commute’ Because She Does Her Best Thinking in the Car.” Insider , 15 Nov. 2018, https://www.businessinsider.com/spanx-ceo-sara-blakely-fake-commute-2018-11.
- Oshin, Mayo. “Elon Musks’ ‘3-Step’ First Principles Thinking: How to Think and Solve Difficult Problems Like A….” Mission.Org , 2 Nov. 2020, https://medium.com/the-mission/elon-musks-3-step-first-principles-thinking-how-to-think-and-solve-difficult-problems-like-a-ba1e73a9f6c0.
- Clear, James. “How to Solve Big Problems.” James Clear , 25 July 2014, https://jamesclear.com/narrow-focus.
- Nast, C. (n.d.). WIRED. https://www.wired.com/2012/10/ff-elon-musk-qa/all/
- Just a moment. . . (n.d.). https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/5-whys-example
- inc.com . (n.d.). https://www.inc.com/kelly-main/apple-steve-jobs-problem-solving.html
- How to find your big idea . (2022, October 6). Masters of Scale. https://mastersofscale.com/sara-blakely-how-to-find-your-big-idea/
- EX-99.1 . (n.d.). https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1018724/000119312517120198/d373368dex991.htm
Search Leaders.com
What Are Problem-Solving Skills? (Examples Included)
Mike Simpson 0 Comments

By Mike Simpson
Problem-solving skills are important not just for work. In the words of Karl Popper , “All life is problem-solving.”
What on earth does that mean? Simply that being alive means facing challenges. With problem-solving skills, you can navigate issues with greater ease, making hard times, well, less hard.
But what are problem-solving skills? How do you know if you have them or not? Why do they matter to your job search? And what should you do if you don’t feel yours are up to snuff? Luckily, we’re about to get into all of that.
If you’re curious about the world of problem-solving skills, here’s what you need to know.
What Are Problem-Solving Skills?
Before we dig into any examples, let’s focus first on an important question: what are problem-solving skills.
To answer that question, let’s start with the barebones basics. According to Merriam-Webster , problem-solving is “the process or act of finding a solution to a problem.” Why does that matter? Well, because it gives you insight into what problem-solving skills are.
Any skill that helps you find solutions to problems can qualify. And that means problem-solving skills aren’t just one capability, but a toolbox filled with soft skills and hard skills that come together during your time of need.
The ability to solve problems is relevant to any part of your life. Whether your writing a grocery list or dealing with a car that won’t start, you’re actually problem-solving.
The same is true at work, too. Most tasks actually involve a degree of problem-solving. Really? Really.
Think about it this way; when you’re given an assignment, you’re being asked, “Can you do this thing?” Doing that thing is the problem.
Then, you have to find a path that lets you accomplish what you need to do. That is problem-solving.
Yes, sometimes what you need to handle isn’t “challenging” in the difficulty sense. But that doesn’t mean it doesn’t count.
Besides, some of what you need to do will legitimately be hard. Maybe you’re given a new responsibility, or something goes wrong during a project. When that happens, you’ll have to navigate unfamiliar territory, gather new information, and think outside of the box. That’s problem-solving, too.
That’s why hiring managers favor candidates with problem-solving skills. They make you more effective in your role, increasing the odds that you can find solutions whenever the need arises.
How Are Problem-Solving Skills Relevant to a Job Search?
Alright, you probably have a good idea of what problem-solving skills are. Now, it’s time to talk about why they matter to your job search.
We’ve already touched on one major point: hiring managers prefer candidates with strong problem-solving skills. That alone makes these capabilities a relevant part of the equation. If you don’t show the hiring manager you’ve got what it takes to excel, you may struggle to land a position.
But that isn’t the only reason these skills matter. Problem-solving skills can help you during the entire job search process. After all, what’s a job search but a problem – or a series of problems – that needs an answer.
You need a new job; that’s the core problem you’re solving. But every step is its own unique challenge. Finding an opening that matches your skills, creating a resume that resonates with the hiring manager, nailing the interview, and negotiating a salary … those are all smaller problems that are part of the bigger one.
So, problem-solving skills really are at the core of the job search experience. By having strong capabilities in this area, you may find a new position faster than you’d expect.
Okay, you may be thinking, “If hiring managers prefer candidates with problem-solving skills, which ones are they after? Are certain problem-solving capabilities more important today? Is there something I should be going out of my way to showcase?”
While any related skills are worth highlighting, some may get you further than others. Analysis, research, creativity, collaboration , organization, and decision-making are all biggies. With those skills, you can work through the entire problem-solving process, making them worthwhile additions to your resume.
But that doesn’t mean you have to focus there solely. Don’t shy away from showcasing everything you bring to the table. That way, if a particular hiring manager is looking for a certain capability, you’re more likely to tap on what they’re after.
How to Highlight Problem-Solving Skills for Job Search
At this point, it’s ridiculously clear that problem-solving skills are valuable in the eyes of hiring managers. So, how do you show them that you’ve got all of the capabilities they are after? By using the right approach.
When you’re writing your resume or cover letter , your best bet is to highlight achievements that let you put your problem-solving skills to work. That way, you can “show” the hiring manager you have what it takes.
Showing is always better than telling. Anyone can write down, “I have awesome problem-solving skills.” The thing is, that doesn’t really prove that you do. With a great example, you offer up some context, and that makes a difference.
How do you decide on which skills to highlight on your resume or cover letter? By having a great strategy. With the Tailoring Method , it’s all about relevancy. The technique helps you identify skills that matter to that particular hiring manager, allowing you to speak directly to their needs.
Plus, you can use the Tailoring Method when you answer job interview questions . With that approach, you’re making sure those responses are on-point, too.
But when do you talk about your problem-solving capabilities during an interview? Well, there’s a good chance you’ll get asked problem-solving interview questions during your meeting. Take a look at those to see the kinds of questions that are perfect for mentioning these skills.
However, you don’t have to stop there. If you’re asked about your greatest achievement or your strengths, those could be opportunities, too. Nearly any open-ended question could be the right time to discuss those skills, so keep that in mind as you practice for your interview.
How to Develop Problem-Solving Skills If You Don’t Have Them
Developing problem-solving skills may seem a bit tricky on the surface, especially if you think you don’t have them. The thing is, it doesn’t actually have to be hard. You simply need to use the right strategy.
First, understand that you probably do have problem-solving skills; you simply may not have realized it. After all, life is full of challenges that you have to tackle, so there’s a good chance you’ve developed some abilities along the way.
Now, let’s reframe the question and focus on how to improve your problem-solving skills. Here’s how to go about it.
Understand the Problem-Solving Process
In many cases, problem-solving is all about the process. You:
- Identify the problem
- Analyze the key elements
- Look for potential solutions
- Examine the options for viability and risk
- Decide on an approach
- Review the outcome for lessons
By understanding the core process, you can apply it more effectively. That way, when you encounter an issue, you’ll know how to approach it, increasing the odds you’ll handle the situation effectively.
Try Puzzles and Games
Any activity that lets you take the steps listed above could help you hone your problem-solving skills. For example, brainteasers, puzzles, and logic-based games can be great places to start.
Whether it’s something as straightforward – but nonetheless challenging – as Sudoku or a Rubik’s Cube, or something as complex as Settlers of Catan, it puts your problem-solving skills to work. Plus, if you enjoy the activity, it makes skill-building fun, making it a win-win.
Look for Daily Opportunities
If you’re looking for a practical approach, you’re in luck. You can also look at the various challenges you face during the day and think about how to overcome them.
For example, if you always experience a mid-day energy slump that hurts your productivity, take a deep dive into that problem. Define what’s happening, think about why it occurs, consider various solutions, pick one to try, and analyze the results.
By using the problem-solving approach more often in your life, you’ll develop those skills further and make using these capabilities a habit. Plus, you may find ways to improve your day-to-day living, which is a nice bonus.
Volunteer for “Stretch” Projects
If you’re currently employed, volunteering for projects that push you slightly outside of your comfort zone can help you develop problem-solving skills, too. You’ll encounter the unknown and have to think outside of the box, both of which can boost critical problem-solving-related skills.
Plus, you may gain other capabilities along the way, like experience with new technologies or tools. That makes the project an even bigger career booster, which is pretty awesome.
List of Problem-Solving Skills
Alright, we’ve taken a pretty deep dive into what problem-solving skills are. Now, it’s time for some problem-solving skills examples.
As we mentioned above, there are a ton of capabilities and traits that can support better problem-solving. By understanding what they are, you can showcase the right abilities during your job search.
So, without further ado, here is a quick list of problem-solving skill examples:
- Collaboration
- Organization
- Decision-Making
- Troubleshooting
- Self-Reliance
- Self-Motivation
- Communication
- Attention to Detail
- Brainstorming
- Forecasting
- Active Listening
- Accountability
- Open-Mindedness
- Critical Thinking
- Flexibility
Do you have to showcase all of those skills during your job search individually? No, not necessarily. Instead, you want to highlight a range of capabilities based on what the hiring manager is after. If you’re using the Tailoring Method, you’ll know which ones need to make their way into your resume, cover letter, and interview answers.
Now, are there other skills that support problem-solving? Yes, there certainly can be.
Essentially any skill that helps you go from the problem to the solution can, in its own right, be a problem-solving skill.
All of the skills above can be part of the equation. But, if you have another capability that helps you flourish when you encounter an obstacle, it can count, too.
Reflect on your past experience and consider how you’ve navigated challenges in the past. If a particular skill helped you do that, then it’s worth highlighting during a job search.
If you would like to find out more about skills to put on a resume , we’ve taken a close look at the topic before. Along with problem-solving skills, we dig into a variety of other areas, helping you choose what to highlight so that you can increase your odds of landing your perfect job.
Putting It All Together
Ultimately, problem-solving skills are essential for professionals in any kind of field. By honing your capabilities and showcasing them during your job search, you can become a stronger candidate and employee. In the end, that’s all good stuff, making it easier for you to keep your career on track today, tomorrow, and well into the future.

Co-Founder and CEO of TheInterviewGuys.com. Mike is a job interview and career expert and the head writer at TheInterviewGuys.com.
His advice and insights have been shared and featured by publications such as Forbes , Entrepreneur , CNBC and more as well as educational institutions such as the University of Michigan , Penn State , Northeastern and others.
Learn more about The Interview Guys on our About Us page .
About The Author
Mike simpson.

Co-Founder and CEO of TheInterviewGuys.com. Mike is a job interview and career expert and the head writer at TheInterviewGuys.com. His advice and insights have been shared and featured by publications such as Forbes , Entrepreneur , CNBC and more as well as educational institutions such as the University of Michigan , Penn State , Northeastern and others. Learn more about The Interview Guys on our About Us page .
Copyright © 2024 · TheInterviewguys.com · All Rights Reserved
- Our Products
- Case Studies
- Interview Questions
- Jobs Articles
- Members Login

Snapsolve any problem by taking a picture. Try it in the Numerade app?
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Share Podcast

Do You Understand the Problem You’re Trying to Solve?
To solve tough problems at work, first ask these questions.
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
Problem solving skills are invaluable in any job. But all too often, we jump to find solutions to a problem without taking time to really understand the dilemma we face, according to Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg , an expert in innovation and the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
In this episode, you’ll learn how to reframe tough problems by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that contribute to the situation. You’ll also learn why searching for just one root cause can be misleading.
Key episode topics include: leadership, decision making and problem solving, power and influence, business management.
HBR On Leadership curates the best case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, to help you unlock the best in those around you. New episodes every week.
- Listen to the original HBR IdeaCast episode: The Secret to Better Problem Solving (2016)
- Find more episodes of HBR IdeaCast
- Discover 100 years of Harvard Business Review articles, case studies, podcasts, and more at HBR.org .
HANNAH BATES: Welcome to HBR on Leadership , case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, hand-selected to help you unlock the best in those around you.
Problem solving skills are invaluable in any job. But even the most experienced among us can fall into the trap of solving the wrong problem.
Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg says that all too often, we jump to find solutions to a problem – without taking time to really understand what we’re facing.
He’s an expert in innovation, and he’s the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
In this episode, you’ll learn how to reframe tough problems, by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that contribute to the situation. You’ll also learn why searching for one root cause can be misleading. And you’ll learn how to use experimentation and rapid prototyping as problem-solving tools.
This episode originally aired on HBR IdeaCast in December 2016. Here it is.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Welcome to the HBR IdeaCast from Harvard Business Review. I’m Sarah Green Carmichael.
Problem solving is popular. People put it on their resumes. Managers believe they excel at it. Companies count it as a key proficiency. We solve customers’ problems.
The problem is we often solve the wrong problems. Albert Einstein and Peter Drucker alike have discussed the difficulty of effective diagnosis. There are great frameworks for getting teams to attack true problems, but they’re often hard to do daily and on the fly. That’s where our guest comes in.
Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg is a consultant who helps companies and managers reframe their problems so they can come up with an effective solution faster. He asks the question “Are You Solving The Right Problems?” in the January-February 2017 issue of Harvard Business Review. Thomas, thank you so much for coming on the HBR IdeaCast .
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Thanks for inviting me.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, I thought maybe we could start by talking about the problem of talking about problem reframing. What is that exactly?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Basically, when people face a problem, they tend to jump into solution mode to rapidly, and very often that means that they don’t really understand, necessarily, the problem they’re trying to solve. And so, reframing is really a– at heart, it’s a method that helps you avoid that by taking a second to go in and ask two questions, basically saying, first of all, wait. What is the problem we’re trying to solve? And then crucially asking, is there a different way to think about what the problem actually is?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, I feel like so often when this comes up in meetings, you know, someone says that, and maybe they throw out the Einstein quote about you spend an hour of problem solving, you spend 55 minutes to find the problem. And then everyone else in the room kind of gets irritated. So, maybe just give us an example of maybe how this would work in practice in a way that would not, sort of, set people’s teeth on edge, like oh, here Sarah goes again, reframing the whole problem instead of just solving it.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I mean, you’re bringing up something that’s, I think is crucial, which is to create legitimacy for the method. So, one of the reasons why I put out the article is to give people a tool to say actually, this thing is still important, and we need to do it. But I think the really critical thing in order to make this work in a meeting is actually to learn how to do it fast, because if you have the idea that you need to spend 30 minutes in a meeting delving deeply into the problem, I mean, that’s going to be uphill for most problems. So, the critical thing here is really to try to make it a practice you can implement very, very rapidly.
There’s an example that I would suggest memorizing. This is the example that I use to explain very rapidly what it is. And it’s basically, I call it the slow elevator problem. You imagine that you are the owner of an office building, and that your tenants are complaining that the elevator’s slow.
Now, if you take that problem framing for granted, you’re going to start thinking creatively around how do we make the elevator faster. Do we install a new motor? Do we have to buy a new lift somewhere?
The thing is, though, if you ask people who actually work with facilities management, well, they’re going to have a different solution for you, which is put up a mirror next to the elevator. That’s what happens is, of course, that people go oh, I’m busy. I’m busy. I’m– oh, a mirror. Oh, that’s beautiful.
And then they forget time. What’s interesting about that example is that the idea with a mirror is actually a solution to a different problem than the one you first proposed. And so, the whole idea here is once you get good at using reframing, you can quickly identify other aspects of the problem that might be much better to try to solve than the original one you found. It’s not necessarily that the first one is wrong. It’s just that there might be better problems out there to attack that we can, means we can do things much faster, cheaper, or better.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, in that example, I can understand how A, it’s probably expensive to make the elevator faster, so it’s much cheaper just to put up a mirror. And B, maybe the real problem people are actually feeling, even though they’re not articulating it right, is like, I hate waiting for the elevator. But if you let them sort of fix their hair or check their teeth, they’re suddenly distracted and don’t notice.
But if you have, this is sort of a pedestrian example, but say you have a roommate or a spouse who doesn’t clean up the kitchen. Facing that problem and not having your elegant solution already there to highlight the contrast between the perceived problem and the real problem, how would you take a problem like that and attack it using this method so that you can see what some of the other options might be?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Right. So, I mean, let’s say it’s you who have that problem. I would go in and say, first of all, what would you say the problem is? Like, if you were to describe your view of the problem, what would that be?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: I hate cleaning the kitchen, and I want someone else to clean it up.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: OK. So, my first observation, you know, that somebody else might not necessarily be your spouse. So, already there, there’s an inbuilt assumption in your question around oh, it has to be my husband who does the cleaning. So, it might actually be worth, already there to say, is that really the only problem you have? That you hate cleaning the kitchen, and you want to avoid it? Or might there be something around, as well, getting a better relationship in terms of how you solve problems in general or establishing a better way to handle small problems when dealing with your spouse?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Or maybe, now that I’m thinking that, maybe the problem is that you just can’t find the stuff in the kitchen when you need to find it.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Right, and so that’s an example of a reframing, that actually why is it a problem that the kitchen is not clean? Is it only because you hate the act of cleaning, or does it actually mean that it just takes you a lot longer and gets a lot messier to actually use the kitchen, which is a different problem. The way you describe this problem now, is there anything that’s missing from that description?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: That is a really good question.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Other, basically asking other factors that we are not talking about right now, and I say those because people tend to, when given a problem, they tend to delve deeper into the detail. What often is missing is actually an element outside of the initial description of the problem that might be really relevant to what’s going on. Like, why does the kitchen get messy in the first place? Is it something about the way you use it or your cooking habits? Is it because the neighbor’s kids, kind of, use it all the time?
There might, very often, there might be issues that you’re not really thinking about when you first describe the problem that actually has a big effect on it.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: I think at this point it would be helpful to maybe get another business example, and I’m wondering if you could tell us the story of the dog adoption problem.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Yeah. This is a big problem in the US. If you work in the shelter industry, basically because dogs are so popular, more than 3 million dogs every year enter a shelter, and currently only about half of those actually find a new home and get adopted. And so, this is a problem that has persisted. It’s been, like, a structural problem for decades in this space. In the last three years, where people found new ways to address it.
So a woman called Lori Weise who runs a rescue organization in South LA, and she actually went in and challenged the very idea of what we were trying to do. She said, no, no. The problem we’re trying to solve is not about how to get more people to adopt dogs. It is about keeping the dogs with their first family so they never enter the shelter system in the first place.
In 2013, she started what’s called a Shelter Intervention Program that basically works like this. If a family comes and wants to hand over their dog, these are called owner surrenders. It’s about 30% of all dogs that come into a shelter. All they would do is go up and ask, if you could, would you like to keep your animal? And if they said yes, they would try to fix whatever helped them fix the problem, but that made them turn over this.
And sometimes that might be that they moved into a new building. The landlord required a deposit, and they simply didn’t have the money to put down a deposit. Or the dog might need a $10 rabies shot, but they didn’t know how to get access to a vet.
And so, by instigating that program, just in the first year, she took her, basically the amount of dollars they spent per animal they helped went from something like $85 down to around $60. Just an immediate impact, and her program now is being rolled out, is being supported by the ASPCA, which is one of the big animal welfare stations, and it’s being rolled out to various other places.
And I think what really struck me with that example was this was not dependent on having the internet. This was not, oh, we needed to have everybody mobile before we could come up with this. This, conceivably, we could have done 20 years ago. Only, it only happened when somebody, like in this case Lori, went in and actually rethought what the problem they were trying to solve was in the first place.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, what I also think is so interesting about that example is that when you talk about it, it doesn’t sound like the kind of thing that would have been thought of through other kinds of problem solving methods. There wasn’t necessarily an After Action Review or a 5 Whys exercise or a Six Sigma type intervention. I don’t want to throw those other methods under the bus, but how can you get such powerful results with such a very simple way of thinking about something?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: That was something that struck me as well. This, in a way, reframing and the idea of the problem diagnosis is important is something we’ve known for a long, long time. And we’ve actually have built some tools to help out. If you worked with us professionally, you are familiar with, like, Six Sigma, TRIZ, and so on. You mentioned 5 Whys. A root cause analysis is another one that a lot of people are familiar with.
Those are our good tools, and they’re definitely better than nothing. But what I notice when I work with the companies applying those was those tools tend to make you dig deeper into the first understanding of the problem we have. If it’s the elevator example, people start asking, well, is that the cable strength, or is the capacity of the elevator? That they kind of get caught by the details.
That, in a way, is a bad way to work on problems because it really assumes that there’s like a, you can almost hear it, a root cause. That you have to dig down and find the one true problem, and everything else was just symptoms. That’s a bad way to think about problems because problems tend to be multicausal.
There tend to be lots of causes or levers you can potentially press to address a problem. And if you think there’s only one, if that’s the right problem, that’s actually a dangerous way. And so I think that’s why, that this is a method I’ve worked with over the last five years, trying to basically refine how to make people better at this, and the key tends to be this thing about shifting out and saying, is there a totally different way of thinking about the problem versus getting too caught up in the mechanistic details of what happens.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: What about experimentation? Because that’s another method that’s become really popular with the rise of Lean Startup and lots of other innovation methodologies. Why wouldn’t it have worked to, say, experiment with many different types of fixing the dog adoption problem, and then just pick the one that works the best?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: You could say in the dog space, that’s what’s been going on. I mean, there is, in this industry and a lot of, it’s largely volunteer driven. People have experimented, and they found different ways of trying to cope. And that has definitely made the problem better. So, I wouldn’t say that experimentation is bad, quite the contrary. Rapid prototyping, quickly putting something out into the world and learning from it, that’s a fantastic way to learn more and to move forward.
My point is, though, that I feel we’ve come to rely too much on that. There’s like, if you look at the start up space, the wisdom is now just to put something quickly into the market, and then if it doesn’t work, pivot and just do more stuff. What reframing really is, I think of it as the cognitive counterpoint to prototyping. So, this is really a way of seeing very quickly, like not just working on the solution, but also working on our understanding of the problem and trying to see is there a different way to think about that.
If you only stick with experimentation, again, you tend to sometimes stay too much in the same space trying minute variations of something instead of taking a step back and saying, wait a minute. What is this telling us about what the real issue is?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, to go back to something that we touched on earlier, when we were talking about the completely hypothetical example of a spouse who does not clean the kitchen–
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Completely, completely hypothetical.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Yes. For the record, my husband is a great kitchen cleaner.
You started asking me some questions that I could see immediately were helping me rethink that problem. Is that kind of the key, just having a checklist of questions to ask yourself? How do you really start to put this into practice?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I think there are two steps in that. The first one is just to make yourself better at the method. Yes, you should kind of work with a checklist. In the article, I kind of outlined seven practices that you can use to do this.
But importantly, I would say you have to consider that as, basically, a set of training wheels. I think there’s a big, big danger in getting caught in a checklist. This is something I work with.
My co-author Paddy Miller, it’s one of his insights. That if you start giving people a checklist for things like this, they start following it. And that’s actually a problem, because what you really want them to do is start challenging their thinking.
So the way to handle this is to get some practice using it. Do use the checklist initially, but then try to step away from it and try to see if you can organically make– it’s almost a habit of mind. When you run into a colleague in the hallway and she has a problem and you have five minutes, like, delving in and just starting asking some of those questions and using your intuition to say, wait, how is she talking about this problem? And is there a question or two I can ask her about the problem that can help her rethink it?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Well, that is also just a very different approach, because I think in that situation, most of us can’t go 30 seconds without jumping in and offering solutions.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Very true. The drive toward solutions is very strong. And to be clear, I mean, there’s nothing wrong with that if the solutions work. So, many problems are just solved by oh, you know, oh, here’s the way to do that. Great.
But this is really a powerful method for those problems where either it’s something we’ve been banging our heads against tons of times without making progress, or when you need to come up with a really creative solution. When you’re facing a competitor with a much bigger budget, and you know, if you solve the same problem later, you’re not going to win. So, that basic idea of taking that approach to problems can often help you move forward in a different way than just like, oh, I have a solution.
I would say there’s also, there’s some interesting psychological stuff going on, right? Where you may have tried this, but if somebody tries to serve up a solution to a problem I have, I’m often resistant towards them. Kind if like, no, no, no, no, no, no. That solution is not going to work in my world. Whereas if you get them to discuss and analyze what the problem really is, you might actually dig something up.
Let’s go back to the kitchen example. One powerful question is just to say, what’s your own part in creating this problem? It’s very often, like, people, they describe problems as if it’s something that’s inflicted upon them from the external world, and they are innocent bystanders in that.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Right, or crazy customers with unreasonable demands.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Exactly, right. I don’t think I’ve ever met an agency or consultancy that didn’t, like, gossip about their customers. Oh, my god, they’re horrible. That, you know, classic thing, why don’t they want to take more risk? Well, risk is bad.
It’s their business that’s on the line, not the consultancy’s, right? So, absolutely, that’s one of the things when you step into a different mindset and kind of, wait. Oh yeah, maybe I actually am part of creating this problem in a sense, as well. That tends to open some new doors for you to move forward, in a way, with stuff that you may have been struggling with for years.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, we’ve surfaced a couple of questions that are useful. I’m curious to know, what are some of the other questions that you find yourself asking in these situations, given that you have made this sort of mental habit that you do? What are the questions that people seem to find really useful?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: One easy one is just to ask if there are any positive exceptions to the problem. So, was there day where your kitchen was actually spotlessly clean? And then asking, what was different about that day? Like, what happened there that didn’t happen the other days? That can very often point people towards a factor that they hadn’t considered previously.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: We got take-out.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: S,o that is your solution. Take-out from [INAUDIBLE]. That might have other problems.
Another good question, and this is a little bit more high level. It’s actually more making an observation about labeling how that person thinks about the problem. And what I mean with that is, we have problem categories in our head. So, if I say, let’s say that you describe a problem to me and say, well, we have a really great product and are, it’s much better than our previous product, but people aren’t buying it. I think we need to put more marketing dollars into this.
Now you can go in and say, that’s interesting. This sounds like you’re thinking of this as a communications problem. Is there a different way of thinking about that? Because you can almost tell how, when the second you say communications, there are some ideas about how do you solve a communications problem. Typically with more communication.
And what you might do is go in and suggest, well, have you considered that it might be, say, an incentive problem? Are there incentives on behalf of the purchasing manager at your clients that are obstructing you? Might there be incentive issues with your own sales force that makes them want to sell the old product instead of the new one?
So literally, just identifying what type of problem does this person think about, and is there different potential way of thinking about it? Might it be an emotional problem, a timing problem, an expectations management problem? Thinking about what label of what type of problem that person is kind of thinking as it of.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: That’s really interesting, too, because I think so many of us get requests for advice that we’re really not qualified to give. So, maybe the next time that happens, instead of muddying my way through, I will just ask some of those questions that we talked about instead.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: That sounds like a good idea.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, Thomas, this has really helped me reframe the way I think about a couple of problems in my own life, and I’m just wondering. I know you do this professionally, but is there a problem in your life that thinking this way has helped you solve?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I’ve, of course, I’ve been swallowing my own medicine on this, too, and I think I have, well, maybe two different examples, and in one case somebody else did the reframing for me. But in one case, when I was younger, I often kind of struggled a little bit. I mean, this is my teenage years, kind of hanging out with my parents. I thought they were pretty annoying people. That’s not really fair, because they’re quite wonderful, but that’s what life is when you’re a teenager.
And one of the things that struck me, suddenly, and this was kind of the positive exception was, there was actually an evening where we really had a good time, and there wasn’t a conflict. And the core thing was, I wasn’t just seeing them in their old house where I grew up. It was, actually, we were at a restaurant. And it suddenly struck me that so much of the sometimes, kind of, a little bit, you love them but they’re annoying kind of dynamic, is tied to the place, is tied to the setting you are in.
And of course, if– you know, I live abroad now, if I visit my parents and I stay in my old bedroom, you know, my mother comes in and wants to wake me up in the morning. Stuff like that, right? And it just struck me so, so clearly that it’s– when I change this setting, if I go out and have dinner with them at a different place, that the dynamic, just that dynamic disappears.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Well, Thomas, this has been really, really helpful. Thank you for talking with me today.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Thank you, Sarah.
HANNAH BATES: That was Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg in conversation with Sarah Green Carmichael on the HBR IdeaCast. He’s an expert in problem solving and innovation, and he’s the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
We’ll be back next Wednesday with another hand-picked conversation about leadership from the Harvard Business Review. If you found this episode helpful, share it with your friends and colleagues, and follow our show on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts. While you’re there, be sure to leave us a review.
We’re a production of Harvard Business Review. If you want more podcasts, articles, case studies, books, and videos like this, find it all at HBR dot org.
This episode was produced by Anne Saini, and me, Hannah Bates. Ian Fox is our editor. Music by Coma Media. Special thanks to Maureen Hoch, Adi Ignatius, Karen Player, Ramsey Khabbaz, Nicole Smith, Anne Bartholomew, and you – our listener.
See you next week.
- Subscribe On:
Latest in this series
This article is about leadership.
- Decision making and problem solving
- Power and influence
- Business management

Partner Center

- Senior Fellows
- Research Fellows
- Submission Guidelines
- Media Inquiries
- Commentary & Analysis
Upcoming Events
- Past Events
- October 2021 War Studies Conference
- November 2020 War Studies Conference
- November 2018 War Studies Conference
- March 2018 War Studies Conference
- November 2016 War Studies Conference
- MWI Podcast
- Urban Warfare Project Podcast
- Irregular Warfare Podcast
- Social Science of War
- Urban Warfare Project
- Irregular Warfare Initiative
- Project 6633
- Shield Notes
- Rethinking Civ-Mil
- Competition in Cyberspace Project
- Book Reviews
Select Page
Reading Rommel
Kevin Shinnick | 09.21.22
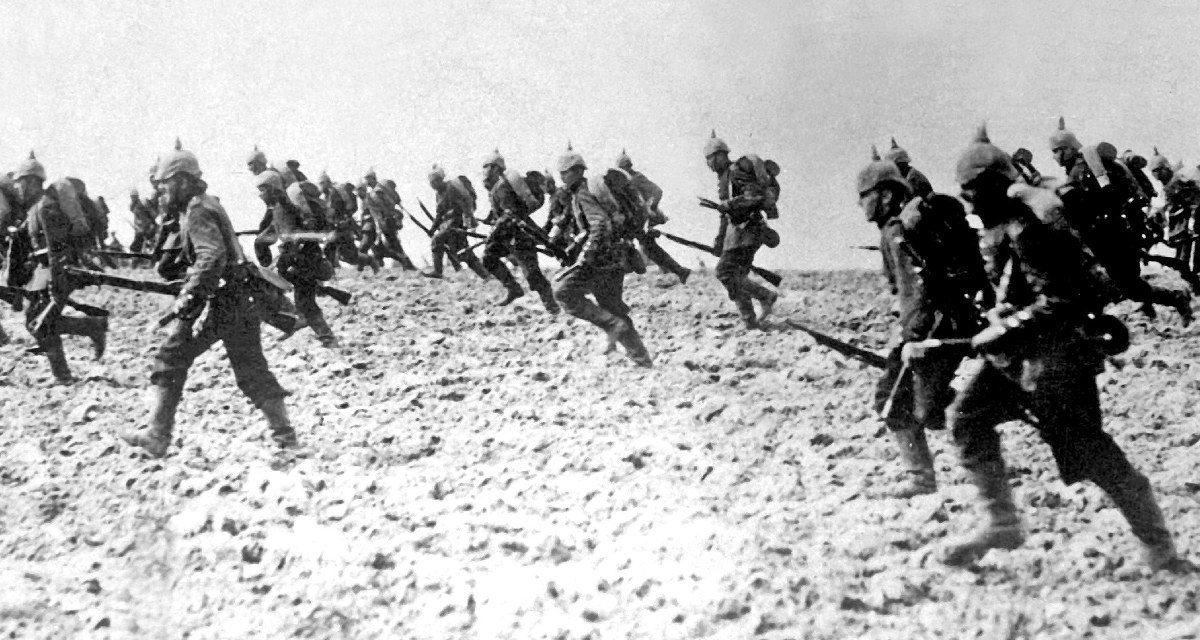

Military professional reading lists encompass a wide variety of subjects and offer varying applicability based on the reader’s occupation, position, and echelon of leadership. The subject of leadership is broad and timeless, whereas roles within the military are distinct and time-sensitive. What is best for a field grade officer will differ from what is best for a junior officer. For the latter, recommended reading lists invariably include a handful of mainstay titles— Once and Eagle , for example, or A Message to Garcia —along with a selection that reflect the strategic environment of the moment and the likely missions on the horizon. One that rarely appears, but is extraordinarily relevant especially for junior officers in the combat arms, is Erwin Rommel’s Infantry Attacks —a must-read prior to assuming platoon leadership.
The book, a reflection of Rommel’s experiences in World War I, is a firsthand account of a leader operating in an era that, despite the intervening century of change, shares much in common with our own—an era in which a combined arms approach was emphasized as the ideal and where tactics and technology spurred each other’s growth at a dizzying rate. In detailing his experiences from platoon leader to company commander, Rommel’s Infantry Attacks offers a timeless perspective on the lasting characteristics of war and provides invaluable insights specific to today’s battlefields.
Lasting Characteristics of War
Infantry Attacks instills meaning behind three characteristics of war that every leader would be wise to familiarize themselves with. Considerations of terrain, weather, and logistics appear in every account of battle and provide the reader with timeless insights on how they shape decision-making and outcomes.
Rommel attributes his tactical successes to careful map analysis and reconnaissance, which allowed him to “tak[e] skillful advantage of the smallest irregularities of the terrain.” The book is replete with examples, such as the capture of Mount Cosna, where Rommel and his noncommissioned officers identified terrain features such as draws, ditches, and small berms to recon and ultimately penetrate developed defenses at little to no cost. These details were novel for their time and reinforce the importance of mastering what are now basic competencies .
Infantry Attacks illustrates indirect utilizations of terrain as well. In one instance, Rommel realizes he does not need to rush an attack because the rocky terrain will significantly delay the enemy’s ability to dig in positions. He even directs artillery onto the cliffs above the enemy forces to rain increased stone and shrapnel ahead of the attack. Similar woodland effects are described when Rommel’s unit takes heavier casualties from splinters erupting from mortar rounds exploding in the treetops. These terrain-based effects, while rarely discussed, are very much applicable to mortars and artillery today.
Weather can be a blessing or a curse, and Infantry Attacks exhibits this duality. Readers may be unsurprised that morale will be lowered when rain weighs down rucksacks on a long march. However, they may be intrigued by how those effects can be used for gain. Rommel knew that if the weather kept his soldiers’ heads down and in their jackets, it affected the enemy the same. He would pray for terrible weather, understanding that rain would muffle the sound of their approach, the clouds would reduce the moonlight, and the fog would obscure them to within meters. Rommel admits his failures to plan for the weather as well. When ambushed in the winter, his machine guns could not return fire due to their crews failing to have thawed them with alcohol. Some doctrinal resources cover weather considerations but non apply such specifically applicable examples as Infantry Attacks .
The effects of subpar and degraded logistics are on full display today in Russia’s stalled invasion of Ukraine. While the United States is well regarded for its logistical capabilities, its leaders on the ground are rarely afforded critical opportunities to train with their systems stressed or collapsed entirely . Rommel’s account of the depleted German offensive intimately portrays the personal and materiel struggles of logistical failures. At the end of nearly every battle, one of his first priorities was to see if the field kitchens had been brought forward to replenish his drained soldiers. They never were; thus, out of necessity, he, like any leader, began accounting for his soldiers’ energy levels in his decision-making processes. He also found himself having to devote increasing amounts of time and attention to his soldiers’ discipline in urban environments as “hunger makes soldiers enterprising.”
Ammunition likewise proved to be a constraint. The success of German assaults depended greatly on the physical and psychological suppression provided by artillery ahead of the infantry advance. Infantry Attacks recounts many instances of last-minute abandonments of plans due to the unavailability of planned resources. In other cases, when abandoning was not an option, plans were adjusted, typically to a less optimal options—such as resorting to sheer surprise and violence. The loss of psychological suppression was worsened by Rommel’s own men being aware that they would be assaulting without indirect fires. Readers will quickly begin to understand the importance of logistics and the finite nature of their commodities. Losing priority of fires ahead of an assault or machine gun ammunition before a counterattack are just a few contingencies found in the book that remain very much a possibility today.
Modern Applicability
Infantry Attacks ’ keen descriptions of century-old battlefields yield specific, relevant insights into modern war. There are many sections where, if not for dated nomenclature, it would be difficult to discern the era in which it was written. Rommel’s details of command post survivability, descriptions of the challenges of mission command and combined arms warfare, and reflections of his noncommissioned officer corps are as relevant today as the day they were written.
Early in the book, Rommel recounts having to call off an attack due to his higher headquarters coming under intense indirect fire. He notes how his battalion and regimental command posts were “situated close together in a highway cut” and that “their location was betrayed to the enemy by the large number of messengers who converged from all directions.” Today, the physical messengers and telephone wires of 1914 have been replaced by equally inconspicuous concentrations of electronic signatures revealing force dispositions. The barrages resulted in more than 250 casualties and forced Rommel to call off the attack from the failures in command and control.
The necessity of continuously improving one’s battle position is constantly mentioned throughout the book. Besides the obvious benefits of physical protection, the emphasis is increasingly relevant today in another way: concealment. Sensors dominate today’s battlefields and require service members to be increasingly adept at camouflaging and concealing their positions. Modern battlefields share the same threats of indirect fire as those of World War I, but also the added risks of armed drones and rockets. Leaders today are not often afforded opportunities to practice physically and electronically concealing their battle positions. Where Rommel was equipped with telescopes and sketches to dial in fires, the modern mapping resources leaders have at their disposal include satellites and Google Earth .
Infantry Attacks provides lessons in executing mission command as well. The reader will derive insights from battles spanning a wide variety of physical environments—mountains, forests, trenches, and urban centers. In these environments, the coordination necessary to conduct even early combined arms warfare proved difficult. The offensive technology of the time was outpacing the means of communication. Complex plans typically hinged on precise timing based on synchronized watches, last bursts of artillery shells, or opening salvos of machine guns, such that mission success greatly depended on disciplined initiative .
Rommel’s book illustrates the importance of knowing the full details of everyone’s role in a plan, to enable safe deviation when necessary. In one case, Rommel’s position came under intense surprise attack, and his platoon was forced to prematurely assault in a new direction that was in an adjacent platoon’s sector of fire. He made the split-second decision on his own, understanding that the cue for his adjacent platoon to open fire had not yet been triggered. Other situations required outright disobedience to achieve victory or survival. One such instance saw Rommel’s platoon being ordered to withdraw immediately; however, his headquarters was unaware of the tactical situation. Regressing immediately would have forced his soldiers into open fields, exposing them to high concentrations of fire; Rommel instead ordered an immediate attack forward to disorient the enemy and gain access to a different path of retreat. The assault led to a successful displacement of his troops with minimal cost.
Lastly, throughout Infantry Attacks , Rommel frequently refers to the high quality of his noncommissioned officers . While readers may associate World War I as a war of attrition fought in trenches, Rommel describes episodes of skillful maneuver warfare with enlisted leaders at the front. Noncommissioned officers were charged with the most complex tasks, such as deep reconnaissance, route clearing, obstacle breaching, and ultimately leading the attack. They were critical in maintaining cohesion and forward momentum in the face of intense fire. Their expertise and reliability, which Rommel takes the time to describe throughout the book, allowed his Sturmtruppen to execute the bold maneuver tactics that resulted in his enemies’ physical and mental defeat. Infantry Attacks is a testament to the importance of leader development within the noncommissioned officer corps. Even the most skilled leader cannot be everywhere at once, nor do they allow plans to rely on their presence.
Same Lessons, New Approaches
As compelling as Rommel’s tactical and organizational insights remain today, his methods are not without fault. His particularly impersonal leadership style and overreliance on his legal authority are incompatible with today’s people-centric US military, especially at the company and platoon levels. He often wrote about how he demanded “superhuman strength” from his soldiers but never elaborates on how he inspired or achieved such effects. In one case where a subordinate lieutenant hesitated to assault, Rommel gave him an ultimatum: “Obey my orders or be shot on the spot.” The book also lacks insight into garrison operations. The author compliments his soldiers’ actions as a product of superior training during their brief respites. He importantly notes that “war makes extremely heavy demands on [your] soldiers’ strength and nerves . . . . For this reason make heavy demands on your men in peace.” But he stops short of offering any details on how he designed such training. Readers will learn much regarding tactics but will need to figure out themselves, alongside their noncommissioned officers, how to train to act on what they’ve learned.
Infantry Attacks is a must-read for junior officers preparing for leadership positions in the combat arms. Many reading lists recommend books to broaden perspectives , and such breadth will be necessary later on in military leaders’ careers. But young officers will benefit immediately and significantly from delving specifically into their craft. The descriptions within are telling that certain characteristics of war remain unchanged and that the challenges leaders faced a century ago are very much a reality for leaders in the twenty-first century. A junior officer who will face countless challenges in situational training exercises, training center rotations, or actual combat will be well served by choosing to encounter them first in Rommel’s Infantry Attacks .
First Lieutenant Kevin Shinnick is an infantry platoon leader currently assigned to 1st Squadron, 2nd Cavalry Regiment with prior enlisted service in the 75th Ranger Regiment. He is a graduate of the United States Military Academy and a native of Milford, Massachusetts.
The views expressed are those of the author and do not reflect the official position of the United States Military Academy, Department of the Army, or Department of Defense.
A very good summary of one of my favourite books that was and is inspiring. I read it while in training as an Infantry Officer and was lucky enough to be able to put some of his educational lessons into practice on exercises and real operations.
I was also very lucky to walk around Rommels Regiments barracks in Weingarten, Germany and looked up his room in the barrracks and walked across the parade square where he formed up as a young Lt before marching off to WW1.
As a companion book to read on Rommel, the following book provides a profound insight into why Rommel was so successful in much of his earlier African operational maneuver during WWII. It talks about the failure in operational security and cyphers by the US (of all compabtants!), which led to Rommel being privy to much of the UK's/combined forces planned operations. In many ways it illustrates that the various branches of both the Army and the Joint Force may have a critical impact on the outcome of operations – in some cases as great or better than the manuever force's own planned tactical schemes:
I highly recommend reading the following:
Author: Gorenberg, Gershom. Title: War of shadows : codebreakers, spies, and the secret struggle to drive the Nazis from the Middle East / Gershom Gorenberg. Call Number: 940.5486 Gorenbe 2021 Edition: First edition. Publisher, Date: New York : PublicAffairs, Hachette Book Group, c2021. Description: xix, 474 pages : map ; 25 cm Summary: "As World War II rages in North afr5ica, General Irwin Rommel marches his troops swiftly through Egypt, aiming to overrun he entire Middle East. An uncanny sense of his enemies' weaknesses and positions informs each move. The Nazis, somehow, have a source for the Allies' greatest secrets. Yet Rommel is not the only one with stolen knowledge. allies cryptographers are breaking the extraordinarily complex Nazi code Enigma. On the brink of disaster, a fevered, high-stakes search for the Nazis' source begins."–Dust jacket flap.
Leave a reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
The articles and other content which appear on the Modern War Institute website are unofficial expressions of opinion. The views expressed are those of the authors, and do not reflect the official position of the United States Military Academy, Department of the Army, or Department of Defense.
The Modern War Institute does not screen articles to fit a particular editorial agenda, nor endorse or advocate material that is published. Rather, the Modern War Institute provides a forum for professionals to share opinions and cultivate ideas. Comments will be moderated before posting to ensure logical, professional, and courteous application to article content.
Most Popular Posts
- The Return of the Tactical Crisis
- The Return of Tactical Antiaircraft Artillery: Optimizing the Army Inventory for the Era of Small Drone Proliferation
- War Books: Manga and Anime
Announcements
- Announcing the Modern War Institute’s 2023–24 Senior and Research Fellows
- Essay Contest Call for Submissions: Solving the Military Recruiting Crisis
- Call for Applications: MWI’s 2023–24 Research Fellows Program
- Join Us This Friday for a Livestream with Ambassador Michael McFaul and Secretary Chuck Hagel
Explore Jobs
- Jobs Near Me
- Remote Jobs
- Full Time Jobs
- Part Time Jobs
- Entry Level Jobs
- Work From Home Jobs
Find Specific Jobs
- $15 Per Hour Jobs
- $20 Per Hour Jobs
- Hiring Immediately Jobs
- High School Jobs
- H1b Visa Jobs
Explore Careers
- Business And Financial
- Architecture And Engineering
- Computer And Mathematical
Explore Professions
- What They Do
- Certifications
- Demographics
Best Companies
- Health Care
- Fortune 500
Explore Companies
- CEO And Executies
- Resume Builder
- Career Advice
- Explore Majors
- Questions And Answers
- Interview Questions
What Are Problem-Solving Skills? (Definition, Examples, And How To List On A Resume)
- What Are Skills Employers Look For?
- What Are Inductive Reasoning?
- What Are Problem Solving Skills?
- What Are Active Listening Skills?
- What Are Management Skills?
- What Are Attention To Detail?
- What Are Detail Oriented Skills?
- What Are Domain Knowledge?
- What Is Professionalism?
- What Are Rhetorical Skills?
- What Is Integrity?
- What Are Persuasion Skills?
- How To Start A Conversation
- How To Write A Conclusion For A Research Paper
- Team Player
- Visual Learner
- High Income Skills
- The Most Important Professional Skills
Find a Job You Really Want In
Summary. Problem-solving skills include analysis, creativity, prioritization, organization, and troubleshooting. To solve a problem, you need to use a variety of skills based on the needs of the situation.
Most jobs essentially boil down to identifying and solving problems consistently and effectively. That’s why employers value problem-solving skills in job candidates for just about every role.
We’ll cover problem-solving methods, ways to improve your problem-solving skills, and examples of showcasing your problem-solving skills during your job search .
Key Takeaways:
If you can show off your problem-solving skills on your resume , in your cover letter , and during a job interview, you’ll be one step closer to landing a job.
Companies rely on employees who can handle unexpected challenges, identify persistent issues, and offer workable solutions in a positive way.
It is important to improve problem solving skill because this is a skill that can be cultivated and nurtured so you can become better at dealing with problems over time.

Types of Problem-Solving Skills
How to improve your problem-solving skills, example answers to problem-solving interview questions, how to show off problem-solving skills on a resume, example resume and cover letter with problem-solving skills, more about problem-solving skills, problem solving skills faqs.
- Sign Up For More Advice and Jobs
Problem-solving skills are skills that help you identify and solve problems effectively and efficiently . Your ability to solve problems is one of the main ways that hiring managers and recruiters assess candidates, as those with excellent problem-solving skills are more likely to autonomously carry out their responsibilities.
A true problem solver can look at a situation, find the cause of the problem (or causes, because there are often many issues at play), and then come up with a reasonable solution that effectively fixes the problem or at least remedies most of it.
The ability to solve problems is considered a soft skill , meaning that it’s more of a personality trait than a skill you’ve learned at school, on the job, or through technical training.
That being said, your proficiency with various hard skills will have a direct bearing on your ability to solve problems. For example, it doesn’t matter if you’re a great problem-solver; if you have no experience with astrophysics, you probably won’t be hired as a space station technician .
Problem-solving is considered a skill on its own, but it’s supported by many other skills that can help you be a better problem solver. These skills fall into a few different categories of problem-solving skills.
Problem recognition and analysis. The first step is to recognize that there is a problem and discover what it is or what the root cause of it is.
You can’t begin to solve a problem unless you’re aware of it. Sometimes you’ll see the problem yourself and other times you’ll be told about the problem. Both methods of discovery are very important, but they can require some different skills. The following can be an important part of the process:
Active listening
Data analysis
Historical analysis
Communication
Create possible solutions. You know what the problem is, and you might even know the why of it, but then what? Your next step is the come up with some solutions.
Most of the time, the first solution you come up with won’t be the right one. Don’t fall victim to knee-jerk reactions; try some of the following methods to give you solution options.
Brainstorming
Forecasting
Decision-making
Topic knowledge/understanding
Process flow
Evaluation of solution options. Now that you have a lot of solution options, it’s time to weed through them and start casting some aside. There might be some ridiculous ones, bad ones, and ones you know could never be implemented. Throw them away and focus on the potentially winning ideas.
This step is probably the one where a true, natural problem solver will shine. They intuitively can put together mental scenarios and try out solutions to see their plusses and minuses. If you’re still working on your skill set — try listing the pros and cons on a sheet of paper.
Prioritizing
Evaluating and weighing
Solution implementation. This is your “take action” step. Once you’ve decided which way to go, it’s time to head down that path and see if you were right. This step takes a lot of people and management skills to make it work for you.
Dependability
Teambuilding
Troubleshooting
Follow-Through
Believability
Trustworthiness
Project management
Evaluation of the solution. Was it a good solution? Did your plan work or did it fail miserably? Sometimes the evaluation step takes a lot of work and review to accurately determine effectiveness. The following skills might be essential for a thorough evaluation.
Customer service
Feedback responses
Flexibility
You now have a ton of skills in front of you. Some of them you have naturally and some — not so much. If you want to solve a problem, and you want to be known for doing that well and consistently, then it’s time to sharpen those skills.
Develop industry knowledge. Whether it’s broad-based industry knowledge, on-the-job training , or very specific knowledge about a small sector — knowing all that you can and feeling very confident in your knowledge goes a long way to learning how to solve problems.
Be a part of a solution. Step up and become involved in the problem-solving process. Don’t lead — but follow. Watch an expert solve the problem and, if you pay attention, you’ll learn how to solve a problem, too. Pay attention to the steps and the skills that a person uses.
Practice solving problems. Do some role-playing with a mentor , a professor , co-workers, other students — just start throwing problems out there and coming up with solutions and then detail how those solutions may play out.
Go a step further, find some real-world problems and create your solutions, then find out what they did to solve the problem in actuality.
Identify your weaknesses. If you could easily point out a few of your weaknesses in the list of skills above, then those are the areas you need to focus on improving. How you do it is incredibly varied, so find a method that works for you.
Solve some problems — for real. If the opportunity arises, step in and use your problem-solving skills. You’ll never really know how good (or bad) you are at it until you fail.
That’s right, failing will teach you so much more than succeeding will. You’ll learn how to go back and readdress the problem, find out where you went wrong, learn more from listening even better. Failure will be your best teacher ; it might not make you feel good, but it’ll make you a better problem-solver in the long run.
Once you’ve impressed a hiring manager with top-notch problem-solving skills on your resume and cover letter , you’ll need to continue selling yourself as a problem-solver in the job interview.
There are three main ways that employers can assess your problem-solving skills during an interview:
By asking questions that relate to your past experiences solving problems
Posing hypothetical problems for you to solve
By administering problem-solving tests and exercises
The third method varies wildly depending on what job you’re applying for, so we won’t attempt to cover all the possible problem-solving tests and exercises that may be a part of your application process.
Luckily, interview questions focused on problem-solving are pretty well-known, and most can be answered using the STAR method . STAR stands for situation, task, action, result, and it’s a great way to organize your answers to behavioral interview questions .
Let’s take a look at how to answer some common interview questions built to assess your problem-solving capabilities:
At my current job as an operations analyst at XYZ Inc., my boss set a quarterly goal to cut contractor spending by 25% while maintaining the same level of production and moving more processes in-house. It turned out that achieving this goal required hiring an additional 6 full-time employees, which got stalled due to the pandemic. I suggested that we widen our net and hire remote employees after our initial applicant pool had no solid candidates. I ran the analysis on overhead costs and found that if even 4 of the 6 employees were remote, we’d save 16% annually compared to the contractors’ rates. In the end, all 6 employees we hired were fully remote, and we cut costs by 26% while production rose by a modest amount.
I try to step back and gather research as my first step. For instance, I had a client who needed a graphic designer to work with Crello, which I had never seen before, let alone used. After getting the project details straight, I began meticulously studying the program the YouTube tutorials, and the quick course Crello provides. I also reached out to coworkers who had worked on projects for this same client in the past. Once I felt comfortable with the software, I started work immediately. It was a slower process because I had to be more methodical in my approach, but by putting in some extra hours, I turned in the project ahead of schedule. The client was thrilled with my work and was shocked to hear me joke afterward that it was my first time using Crello.
As a digital marketer , website traffic and conversion rates are my ultimate metrics. However, I also track less visible metrics that can illuminate the story behind the results. For instance, using Google Analytics, I found that 78% of our referral traffic was coming from one affiliate, but that these referrals were only accounting for 5% of our conversions. Another affiliate, who only accounted for about 10% of our referral traffic, was responsible for upwards of 30% of our conversions. I investigated further and found that the second, more effective affiliate was essentially qualifying our leads for us before sending them our way, which made it easier for us to close. I figured out exactly how they were sending us better customers, and reached out to the first, more prolific but less effective affiliate with my understanding of the results. They were able to change their pages that were referring us traffic, and our conversions from that source tripled in just a month. It showed me the importance of digging below the “big picture” metrics to see the mechanics of how revenue was really being generated through digital marketing.
You can bring up your problem-solving skills in your resume summary statement , in your work experience , and under your education section , if you’re a recent graduate. The key is to include items on your resume that speak direclty to your ability to solve problems and generate results.
If you can, quantify your problem-solving accomplishments on your your resume . Hiring managers and recruiters are always more impressed with results that include numbers because they provide much-needed context.
This sample resume for a Customer Service Representative will give you an idea of how you can work problem solving into your resume.
Michelle Beattle 111 Millennial Parkway Chicago, IL 60007 (555) 987-6543 [email protected] Professional Summary Qualified Customer Services Representative with 3 years in a high-pressure customer service environment. Professional, personable, and a true problem solver. Work History ABC Store — Customer Service Representative 01/2015 — 12/2017 Managed in-person and phone relations with customers coming in to pick up purchases, return purchased products, helped find and order items not on store shelves, and explained details and care of merchandise. Became a key player in the customer service department and was promoted to team lead. XYZ Store — Customer Service Representative/Night Manager 01/2018 — 03/2020, released due to Covid-19 layoffs Worked as the night manager of the customer service department and filled in daytime hours when needed. Streamlined a process of moving customers to the right department through an app to ease the burden on the phone lines and reduce customer wait time by 50%. Was working on additional wait time problems when the Covid-19 pandemic caused our stores to close permanently. Education Chicago Tech 2014-2016 Earned an Associate’s Degree in Principles of Customer Care Skills Strong customer service skills Excellent customer complaint resolution Stock record management Order fulfillment New product information Cash register skills and proficiency Leader in problem solving initiatives
You can see how the resume gives you a chance to point out your problem-solving skills and to show where you used them a few times. Your cover letter is your chance to introduce yourself and list a few things that make you stand out from the crowd.
Michelle Beattle 111 Millennial Parkway Chicago, IL 60007 (555) 987-6543 [email protected] Dear Mary McDonald, I am writing in response to your ad on Zippia for a Customer Service Representative . Thank you for taking the time to consider me for this position. Many people believe that a job in customer service is simply listening to people complain all day. I see the job as much more than that. It’s an opportunity to help people solve problems, make their experience with your company more enjoyable, and turn them into life-long advocates of your brand. Through my years of experience and my educational background at Chicago Tech, where I earned an Associate’s Degree in the Principles of Customer Care, I have learned that the customers are the lifeline of the business and without good customer service representatives, a business will falter. I see it as my mission to make each and every customer I come in contact with a fan. I have more than five years of experience in the Customer Services industry and had advanced my role at my last job to Night Manager. I am eager to again prove myself as a hard worker, a dedicated people person, and a problem solver that can be relied upon. I have built a professional reputation as an employee that respects all other employees and customers, as a manager who gets the job done and finds solutions when necessary, and a worker who dives in to learn all she can about the business. Most of my customers have been very satisfied with my resolution ideas and have returned to do business with us again. I believe my expertise would make me a great match for LMNO Store. I have enclosed my resume for your review, and I would appreciate having the opportunity to meet with you to further discuss my qualifications. Thank you again for your time and consideration. Sincerely, Michelle Beattle
You’ve no doubt noticed that many of the skills listed in the problem-solving process are repeated. This is because having these abilities or talents is so important to the entire course of getting a problem solved.
In fact, they’re worthy of a little more attention. Many of them are similar, so we’ll pull them together and discuss how they’re important and how they work together.
Communication, active listening, and customer service skills. No matter where you are in the process of problem-solving, you need to be able to show that you’re listening and engaged and really hearing what the problem is or what a solution may be.
Obviously, the other part of this is being able to communicate effectively so people understand what you’re saying without confusion. Rolled into this are customer service skills , which really are all about listening and responding appropriately — it’s the ultimate in interpersonal communications.
Analysis (data and historical), research, and topic knowledge/understanding. This is how you intellectually grasp the issue and approach it. This can come from studying the topic and the process or it can come from knowledge you’ve gained after years in the business. But the best solutions come from people who thoroughly understand the problem.
Creativity, brainstorming, troubleshooting, and flexibility. All of you creative thinkers will like this area because it’s when your brain is at its best.
Coming up with ideas, collaborating with others, leaping over hurdles, and then being able to change courses immediately, if need be, are all essential. If you’re not creative by nature, then having a team of diverse thinkers can help you in this area.
Dependability, believability, trustworthiness, and follow-through. Think about it, these are all traits a person needs to have to make change happen and to make you comfortable taking that next step with them. Someone who is shifty and shady and never follows through, well, you’re simply not going to do what they ask, are you?
Leadership, teambuilding, decision-making, and project management. These are the skills that someone who is in charge is brimming with. These are the leaders you enjoy working for because you know they’re doing what they can to keep everything in working order. These skills can be learned but they’re often innate.
Prioritizing, prediction, forecasting, evaluating and weighing, and process flow. If you love flow charts, data analysis, prediction modeling, and all of that part of the equation, then you might have some great problem-solving abilities.
These are all great skills because they can help you weed out bad ideas, see flaws, and save massive amounts of time in trial and error.
What is a good example of problem-solving skills?
Good examples of porblem-solving skills include research, analysis, creativity, communciation, and decision-making. Each of these skills build off one another to contribute to the problem solving process. Research and analysis allow you to identify a problem.
Creativity and analysis help you consider different solutions. Meanwhile, communication and decision-making are key to working with others to solve a problem on a large scale.
What are 3 key attributes of a good problem solver?
3 key attributes of a good problem solver are persistence, intellegince, and empathy. Persistence is crucial to remain motivated to work through challenges. Inellegince is needed to make smart, informed choices. Empathy is crucial to maintain positive relationships with others as well as yourself.
What can I say instead of problem-solving skills?
Instead of saying problem-solving skills, you can say the following:
Critical thinker
Solutions-oriented
Engineering
Using different words is helpful, especially when writing your resume and cover letter.
What is problem-solving in the workplace?
Problem-solving in the workplace is the ability to work through any sort of challenge, conflict, or unexpected situation and still achieve business goals. Though it varies by profession, roblem-solving in the workplace is very important for almost any job, because probelms are inevitable. You need to have the appropriate level of problem-solving skills if you want to succeed in your career, whatever it may be.
Department of Labor – Problem Solving and Critical Thinking
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating / 5. Vote count:
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Kristin Kizer is an award-winning writer, television and documentary producer, and content specialist who has worked on a wide variety of written, broadcast, and electronic publications. A former writer/producer for The Discovery Channel, she is now a freelance writer and delighted to be sharing her talents and time with the wonderful Zippia audience.
Recent Job Searches
- Registered Nurse Jobs Resume Location
- Truck Driver Jobs Resume Location
- Call Center Representative Jobs Resume Location
- Customer Service Representative Jobs Resume
- Delivery Driver Jobs Resume Location
- Warehouse Worker Jobs Resume Location
- Account Executive Jobs Resume Location
- Sales Associate Jobs Resume Location
- Licensed Practical Nurse Jobs Resume Location
- Company Driver Jobs Resume
Related posts

The Most Important Verbal Communication Skills (With Examples)

Creative Thinking Skills (Definitions, Examples, And How To Improve)

Most Common Resume Items of Business Founders and CEOs

50 Jobs That Use Sql The Most
- Career Advice >
- Desired Traits >
- Problem Solving Skills
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Media
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business Ethics
- Business History
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic History
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >

48 Problem Solving
Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences, University of California, Santa Barbara
- Published: 03 June 2013
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Problem solving refers to cognitive processing directed at achieving a goal when the problem solver does not initially know a solution method. A problem exists when someone has a goal but does not know how to achieve it. Problems can be classified as routine or nonroutine, and as well defined or ill defined. The major cognitive processes in problem solving are representing, planning, executing, and monitoring. The major kinds of knowledge required for problem solving are facts, concepts, procedures, strategies, and beliefs. Classic theoretical approaches to the study of problem solving are associationism, Gestalt, and information processing. Current issues and suggested future issues include decision making, intelligence and creativity, teaching of thinking skills, expert problem solving, analogical reasoning, mathematical and scientific thinking, everyday thinking, and the cognitive neuroscience of problem solving. Common themes concern the domain specificity of problem solving and a focus on problem solving in authentic contexts.
The study of problem solving begins with defining problem solving, problem, and problem types. This introduction to problem solving is rounded out with an examination of cognitive processes in problem solving, the role of knowledge in problem solving, and historical approaches to the study of problem solving.
Definition of Problem Solving
Problem solving refers to cognitive processing directed at achieving a goal for which the problem solver does not initially know a solution method. This definition consists of four major elements (Mayer, 1992 ; Mayer & Wittrock, 2006 ):
Cognitive —Problem solving occurs within the problem solver’s cognitive system and can only be inferred indirectly from the problem solver’s behavior (including biological changes, introspections, and actions during problem solving). Process —Problem solving involves mental computations in which some operation is applied to a mental representation, sometimes resulting in the creation of a new mental representation. Directed —Problem solving is aimed at achieving a goal. Personal —Problem solving depends on the existing knowledge of the problem solver so that what is a problem for one problem solver may not be a problem for someone who already knows a solution method.
The definition is broad enough to include a wide array of cognitive activities such as deciding which apartment to rent, figuring out how to use a cell phone interface, playing a game of chess, making a medical diagnosis, finding the answer to an arithmetic word problem, or writing a chapter for a handbook. Problem solving is pervasive in human life and is crucial for human survival. Although this chapter focuses on problem solving in humans, problem solving also occurs in nonhuman animals and in intelligent machines.
How is problem solving related to other forms of high-level cognition processing, such as thinking and reasoning? Thinking refers to cognitive processing in individuals but includes both directed thinking (which corresponds to the definition of problem solving) and undirected thinking such as daydreaming (which does not correspond to the definition of problem solving). Thus, problem solving is a type of thinking (i.e., directed thinking).
Reasoning refers to problem solving within specific classes of problems, such as deductive reasoning or inductive reasoning. In deductive reasoning, the reasoner is given premises and must derive a conclusion by applying the rules of logic. For example, given that “A is greater than B” and “B is greater than C,” a reasoner can conclude that “A is greater than C.” In inductive reasoning, the reasoner is given (or has experienced) a collection of examples or instances and must infer a rule. For example, given that X, C, and V are in the “yes” group and x, c, and v are in the “no” group, the reasoning may conclude that B is in “yes” group because it is in uppercase format. Thus, reasoning is a type of problem solving.
Definition of Problem
A problem occurs when someone has a goal but does not know to achieve it. This definition is consistent with how the Gestalt psychologist Karl Duncker ( 1945 , p. 1) defined a problem in his classic monograph, On Problem Solving : “A problem arises when a living creature has a goal but does not know how this goal is to be reached.” However, today researchers recognize that the definition should be extended to include problem solving by intelligent machines. This definition can be clarified using an information processing approach by noting that a problem occurs when a situation is in the given state, the problem solver wants the situation to be in the goal state, and there is no obvious way to move from the given state to the goal state (Newell & Simon, 1972 ). Accordingly, the three main elements in describing a problem are the given state (i.e., the current state of the situation), the goal state (i.e., the desired state of the situation), and the set of allowable operators (i.e., the actions the problem solver is allowed to take). The definition of “problem” is broad enough to include the situation confronting a physician who wishes to make a diagnosis on the basis of preliminary tests and a patient examination, as well as a beginning physics student trying to solve a complex physics problem.
Types of Problems
It is customary in the problem-solving literature to make a distinction between routine and nonroutine problems. Routine problems are problems that are so familiar to the problem solver that the problem solver knows a solution method. For example, for most adults, “What is 365 divided by 12?” is a routine problem because they already know the procedure for long division. Nonroutine problems are so unfamiliar to the problem solver that the problem solver does not know a solution method. For example, figuring out the best way to set up a funding campaign for a nonprofit charity is a nonroutine problem for most volunteers. Technically, routine problems do not meet the definition of problem because the problem solver has a goal but knows how to achieve it. Much research on problem solving has focused on routine problems, although most interesting problems in life are nonroutine.
Another customary distinction is between well-defined and ill-defined problems. Well-defined problems have a clearly specified given state, goal state, and legal operators. Examples include arithmetic computation problems or games such as checkers or tic-tac-toe. Ill-defined problems have a poorly specified given state, goal state, or legal operators, or a combination of poorly defined features. Examples include solving the problem of global warming or finding a life partner. Although, ill-defined problems are more challenging, much research in problem solving has focused on well-defined problems.
Cognitive Processes in Problem Solving
The process of problem solving can be broken down into two main phases: problem representation , in which the problem solver builds a mental representation of the problem situation, and problem solution , in which the problem solver works to produce a solution. The major subprocess in problem representation is representing , which involves building a situation model —that is, a mental representation of the situation described in the problem. The major subprocesses in problem solution are planning , which involves devising a plan for how to solve the problem; executing , which involves carrying out the plan; and monitoring , which involves evaluating and adjusting one’s problem solving.
For example, given an arithmetic word problem such as “Alice has three marbles. Sarah has two more marbles than Alice. How many marbles does Sarah have?” the process of representing involves building a situation model in which Alice has a set of marbles, there is set of marbles for the difference between the two girls, and Sarah has a set of marbles that consists of Alice’s marbles and the difference set. In the planning process, the problem solver sets a goal of adding 3 and 2. In the executing process, the problem solver carries out the computation, yielding an answer of 5. In the monitoring process, the problem solver looks over what was done and concludes that 5 is a reasonable answer. In most complex problem-solving episodes, the four cognitive processes may not occur in linear order, but rather may interact with one another. Although some research focuses mainly on the execution process, problem solvers may tend to have more difficulty with the processes of representing, planning, and monitoring.
Knowledge for Problem Solving
An important theme in problem-solving research is that problem-solving proficiency on any task depends on the learner’s knowledge (Anderson et al., 2001 ; Mayer, 1992 ). Five kinds of knowledge are as follows:
Facts —factual knowledge about the characteristics of elements in the world, such as “Sacramento is the capital of California” Concepts —conceptual knowledge, including categories, schemas, or models, such as knowing the difference between plants and animals or knowing how a battery works Procedures —procedural knowledge of step-by-step processes, such as how to carry out long-division computations Strategies —strategic knowledge of general methods such as breaking a problem into parts or thinking of a related problem Beliefs —attitudinal knowledge about how one’s cognitive processing works such as thinking, “I’m good at this”
Although some research focuses mainly on the role of facts and procedures in problem solving, complex problem solving also depends on the problem solver’s concepts, strategies, and beliefs (Mayer, 1992 ).
Historical Approaches to Problem Solving
Psychological research on problem solving began in the early 1900s, as an outgrowth of mental philosophy (Humphrey, 1963 ; Mandler & Mandler, 1964 ). Throughout the 20th century four theoretical approaches developed: early conceptions, associationism, Gestalt psychology, and information processing.
Early Conceptions
The start of psychology as a science can be set at 1879—the year Wilhelm Wundt opened the first world’s psychology laboratory in Leipzig, Germany, and sought to train the world’s first cohort of experimental psychologists. Instead of relying solely on philosophical speculations about how the human mind works, Wundt sought to apply the methods of experimental science to issues addressed in mental philosophy. His theoretical approach became structuralism —the analysis of consciousness into its basic elements.
Wundt’s main contribution to the study of problem solving, however, was to call for its banishment. According to Wundt, complex cognitive processing was too complicated to be studied by experimental methods, so “nothing can be discovered in such experiments” (Wundt, 1911/1973 ). Despite his admonishments, however, a group of his former students began studying thinking mainly in Wurzburg, Germany. Using the method of introspection, subjects were asked to describe their thought process as they solved word association problems, such as finding the superordinate of “newspaper” (e.g., an answer is “publication”). Although the Wurzburg group—as they came to be called—did not produce a new theoretical approach, they found empirical evidence that challenged some of the key assumptions of mental philosophy. For example, Aristotle had proclaimed that all thinking involves mental imagery, but the Wurzburg group was able to find empirical evidence for imageless thought .
Associationism
The first major theoretical approach to take hold in the scientific study of problem solving was associationism —the idea that the cognitive representations in the mind consist of ideas and links between them and that cognitive processing in the mind involves following a chain of associations from one idea to the next (Mandler & Mandler, 1964 ; Mayer, 1992 ). For example, in a classic study, E. L. Thorndike ( 1911 ) placed a hungry cat in what he called a puzzle box—a wooden crate in which pulling a loop of string that hung from overhead would open a trap door to allow the cat to escape to a bowl of food outside the crate. Thorndike placed the cat in the puzzle box once a day for several weeks. On the first day, the cat engaged in many extraneous behaviors such as pouncing against the wall, pushing its paws through the slats, and meowing, but on successive days the number of extraneous behaviors tended to decrease. Overall, the time required to get out of the puzzle box decreased over the course of the experiment, indicating the cat was learning how to escape.
Thorndike’s explanation for how the cat learned to solve the puzzle box problem is based on an associationist view: The cat begins with a habit family hierarchy —a set of potential responses (e.g., pouncing, thrusting, meowing, etc.) all associated with the same stimulus (i.e., being hungry and confined) and ordered in terms of strength of association. When placed in the puzzle box, the cat executes its strongest response (e.g., perhaps pouncing against the wall), but when it fails, the strength of the association is weakened, and so on for each unsuccessful action. Eventually, the cat gets down to what was initially a weak response—waving its paw in the air—but when that response leads to accidentally pulling the string and getting out, it is strengthened. Over the course of many trials, the ineffective responses become weak and the successful response becomes strong. Thorndike refers to this process as the law of effect : Responses that lead to dissatisfaction become less associated with the situation and responses that lead to satisfaction become more associated with the situation. According to Thorndike’s associationist view, solving a problem is simply a matter of trial and error and accidental success. A major challenge to assocationist theory concerns the nature of transfer—that is, where does a problem solver find a creative solution that has never been performed before? Associationist conceptions of cognition can be seen in current research, including neural networks, connectionist models, and parallel distributed processing models (Rogers & McClelland, 2004 ).
Gestalt Psychology
The Gestalt approach to problem solving developed in the 1930s and 1940s as a counterbalance to the associationist approach. According to the Gestalt approach, cognitive representations consist of coherent structures (rather than individual associations) and the cognitive process of problem solving involves building a coherent structure (rather than strengthening and weakening of associations). For example, in a classic study, Kohler ( 1925 ) placed a hungry ape in a play yard that contained several empty shipping crates and a banana attached overhead but out of reach. Based on observing the ape in this situation, Kohler noted that the ape did not randomly try responses until one worked—as suggested by Thorndike’s associationist view. Instead, the ape stood under the banana, looked up at it, looked at the crates, and then in a flash of insight stacked the crates under the bananas as a ladder, and walked up the steps in order to reach the banana.
According to Kohler, the ape experienced a sudden visual reorganization in which the elements in the situation fit together in a way to solve the problem; that is, the crates could become a ladder that reduces the distance to the banana. Kohler referred to the underlying mechanism as insight —literally seeing into the structure of the situation. A major challenge of Gestalt theory is its lack of precision; for example, naming a process (i.e., insight) is not the same as explaining how it works. Gestalt conceptions can be seen in modern research on mental models and schemas (Gentner & Stevens, 1983 ).
Information Processing
The information processing approach to problem solving developed in the 1960s and 1970s and was based on the influence of the computer metaphor—the idea that humans are processors of information (Mayer, 2009 ). According to the information processing approach, problem solving involves a series of mental computations—each of which consists of applying a process to a mental representation (such as comparing two elements to determine whether they differ).
In their classic book, Human Problem Solving , Newell and Simon ( 1972 ) proposed that problem solving involved a problem space and search heuristics . A problem space is a mental representation of the initial state of the problem, the goal state of the problem, and all possible intervening states (based on applying allowable operators). Search heuristics are strategies for moving through the problem space from the given to the goal state. Newell and Simon focused on means-ends analysis , in which the problem solver continually sets goals and finds moves to accomplish goals.
Newell and Simon used computer simulation as a research method to test their conception of human problem solving. First, they asked human problem solvers to think aloud as they solved various problems such as logic problems, chess, and cryptarithmetic problems. Then, based on an information processing analysis, Newell and Simon created computer programs that solved these problems. In comparing the solution behavior of humans and computers, they found high similarity, suggesting that the computer programs were solving problems using the same thought processes as humans.
An important advantage of the information processing approach is that problem solving can be described with great clarity—as a computer program. An important limitation of the information processing approach is that it is most useful for describing problem solving for well-defined problems rather than ill-defined problems. The information processing conception of cognition lives on as a keystone of today’s cognitive science (Mayer, 2009 ).
Classic Issues in Problem Solving
Three classic issues in research on problem solving concern the nature of transfer (suggested by the associationist approach), the nature of insight (suggested by the Gestalt approach), and the role of problem-solving heuristics (suggested by the information processing approach).
Transfer refers to the effects of prior learning on new learning (or new problem solving). Positive transfer occurs when learning A helps someone learn B. Negative transfer occurs when learning A hinders someone from learning B. Neutral transfer occurs when learning A has no effect on learning B. Positive transfer is a central goal of education, but research shows that people often do not transfer what they learned to solving problems in new contexts (Mayer, 1992 ; Singley & Anderson, 1989 ).
Three conceptions of the mechanisms underlying transfer are specific transfer , general transfer , and specific transfer of general principles . Specific transfer refers to the idea that learning A will help someone learn B only if A and B have specific elements in common. For example, learning Spanish may help someone learn Latin because some of the vocabulary words are similar and the verb conjugation rules are similar. General transfer refers to the idea that learning A can help someone learn B even they have nothing specifically in common but A helps improve the learner’s mind in general. For example, learning Latin may help people learn “proper habits of mind” so they are better able to learn completely unrelated subjects as well. Specific transfer of general principles is the idea that learning A will help someone learn B if the same general principle or solution method is required for both even if the specific elements are different.
In a classic study, Thorndike and Woodworth ( 1901 ) found that students who learned Latin did not subsequently learn bookkeeping any better than students who had not learned Latin. They interpreted this finding as evidence for specific transfer—learning A did not transfer to learning B because A and B did not have specific elements in common. Modern research on problem-solving transfer continues to show that people often do not demonstrate general transfer (Mayer, 1992 ). However, it is possible to teach people a general strategy for solving a problem, so that when they see a new problem in a different context they are able to apply the strategy to the new problem (Judd, 1908 ; Mayer, 2008 )—so there is also research support for the idea of specific transfer of general principles.
Insight refers to a change in a problem solver’s mind from not knowing how to solve a problem to knowing how to solve it (Mayer, 1995 ; Metcalfe & Wiebe, 1987 ). In short, where does the idea for a creative solution come from? A central goal of problem-solving research is to determine the mechanisms underlying insight.
The search for insight has led to five major (but not mutually exclusive) explanatory mechanisms—insight as completing a schema, insight as suddenly reorganizing visual information, insight as reformulation of a problem, insight as removing mental blocks, and insight as finding a problem analog (Mayer, 1995 ). Completing a schema is exemplified in a study by Selz (Fridja & de Groot, 1982 ), in which people were asked to think aloud as they solved word association problems such as “What is the superordinate for newspaper?” To solve the problem, people sometimes thought of a coordinate, such as “magazine,” and then searched for a superordinate category that subsumed both terms, such as “publication.” According to Selz, finding a solution involved building a schema that consisted of a superordinate and two subordinate categories.
Reorganizing visual information is reflected in Kohler’s ( 1925 ) study described in a previous section in which a hungry ape figured out how to stack boxes as a ladder to reach a banana hanging above. According to Kohler, the ape looked around the yard and found the solution in a flash of insight by mentally seeing how the parts could be rearranged to accomplish the goal.
Reformulating a problem is reflected in a classic study by Duncker ( 1945 ) in which people are asked to think aloud as they solve the tumor problem—how can you destroy a tumor in a patient without destroying surrounding healthy tissue by using rays that at sufficient intensity will destroy any tissue in their path? In analyzing the thinking-aloud protocols—that is, transcripts of what the problem solvers said—Duncker concluded that people reformulated the goal in various ways (e.g., avoid contact with healthy tissue, immunize healthy tissue, have ray be weak in healthy tissue) until they hit upon a productive formulation that led to the solution (i.e., concentrating many weak rays on the tumor).
Removing mental blocks is reflected in classic studies by Duncker ( 1945 ) in which solving a problem involved thinking of a novel use for an object, and by Luchins ( 1942 ) in which solving a problem involved not using a procedure that had worked well on previous problems. Finding a problem analog is reflected in classic research by Wertheimer ( 1959 ) in which learning to find the area of a parallelogram is supported by the insight that one could cut off the triangle on one side and place it on the other side to form a rectangle—so a parallelogram is really a rectangle in disguise. The search for insight along each of these five lines continues in current problem-solving research.
Heuristics are problem-solving strategies, that is, general approaches to how to solve problems. Newell and Simon ( 1972 ) suggested three general problem-solving heuristics for moving from a given state to a goal state: random trial and error , hill climbing , and means-ends analysis . Random trial and error involves randomly selecting a legal move and applying it to create a new problem state, and repeating that process until the goal state is reached. Random trial and error may work for simple problems but is not efficient for complex ones. Hill climbing involves selecting the legal move that moves the problem solver closer to the goal state. Hill climbing will not work for problems in which the problem solver must take a move that temporarily moves away from the goal as is required in many problems.
Means-ends analysis involves creating goals and seeking moves that can accomplish the goal. If a goal cannot be directly accomplished, a subgoal is created to remove one or more obstacles. Newell and Simon ( 1972 ) successfully used means-ends analysis as the search heuristic in a computer program aimed at general problem solving, that is, solving a diverse collection of problems. However, people may also use specific heuristics that are designed to work for specific problem-solving situations (Gigerenzer, Todd, & ABC Research Group, 1999 ; Kahneman & Tversky, 1984 ).
Current and Future Issues in Problem Solving
Eight current issues in problem solving involve decision making, intelligence and creativity, teaching of thinking skills, expert problem solving, analogical reasoning, mathematical and scientific problem solving, everyday thinking, and the cognitive neuroscience of problem solving.
Decision Making
Decision making refers to the cognitive processing involved in choosing between two or more alternatives (Baron, 2000 ; Markman & Medin, 2002 ). For example, a decision-making task may involve choosing between getting $240 for sure or having a 25% change of getting $1000. According to economic theories such as expected value theory, people should chose the second option, which is worth $250 (i.e., .25 x $1000) rather than the first option, which is worth $240 (1.00 x $240), but psychological research shows that most people prefer the first option (Kahneman & Tversky, 1984 ).
Research on decision making has generated three classes of theories (Markman & Medin, 2002 ): descriptive theories, such as prospect theory (Kahneman & Tversky), which are based on the ideas that people prefer to overweight the cost of a loss and tend to overestimate small probabilities; heuristic theories, which are based on the idea that people use a collection of short-cut strategies such as the availability heuristic (Gigerenzer et al., 1999 ; Kahneman & Tversky, 2000 ); and constructive theories, such as mental accounting (Kahneman & Tversky, 2000 ), in which people build a narrative to justify their choices to themselves. Future research is needed to examine decision making in more realistic settings.
Intelligence and Creativity
Although researchers do not have complete consensus on the definition of intelligence (Sternberg, 1990 ), it is reasonable to view intelligence as the ability to learn or adapt to new situations. Fluid intelligence refers to the potential to solve problems without any relevant knowledge, whereas crystallized intelligence refers to the potential to solve problems based on relevant prior knowledge (Sternberg & Gregorenko, 2003 ). As people gain more experience in a field, their problem-solving performance depends more on crystallized intelligence (i.e., domain knowledge) than on fluid intelligence (i.e., general ability) (Sternberg & Gregorenko, 2003 ). The ability to monitor and manage one’s cognitive processing during problem solving—which can be called metacognition —is an important aspect of intelligence (Sternberg, 1990 ). Research is needed to pinpoint the knowledge that is needed to support intelligent performance on problem-solving tasks.
Creativity refers to the ability to generate ideas that are original (i.e., other people do not think of the same idea) and functional (i.e., the idea works; Sternberg, 1999 ). Creativity is often measured using tests of divergent thinking —that is, generating as many solutions as possible for a problem (Guilford, 1967 ). For example, the uses test asks people to list as many uses as they can think of for a brick. Creativity is different from intelligence, and it is at the heart of creative problem solving—generating a novel solution to a problem that the problem solver has never seen before. An important research question concerns whether creative problem solving depends on specific knowledge or creativity ability in general.
Teaching of Thinking Skills
How can people learn to be better problem solvers? Mayer ( 2008 ) proposes four questions concerning teaching of thinking skills:
What to teach —Successful programs attempt to teach small component skills (such as how to generate and evaluate hypotheses) rather than improve the mind as a single monolithic skill (Covington, Crutchfield, Davies, & Olton, 1974 ). How to teach —Successful programs focus on modeling the process of problem solving rather than solely reinforcing the product of problem solving (Bloom & Broder, 1950 ). Where to teach —Successful programs teach problem-solving skills within the specific context they will be used rather than within a general course on how to solve problems (Nickerson, 1999 ). When to teach —Successful programs teaching higher order skills early rather than waiting until lower order skills are completely mastered (Tharp & Gallimore, 1988 ).
Overall, research on teaching of thinking skills points to the domain specificity of problem solving; that is, successful problem solving depends on the problem solver having domain knowledge that is relevant to the problem-solving task.
Expert Problem Solving
Research on expertise is concerned with differences between how experts and novices solve problems (Ericsson, Feltovich, & Hoffman, 2006 ). Expertise can be defined in terms of time (e.g., 10 years of concentrated experience in a field), performance (e.g., earning a perfect score on an assessment), or recognition (e.g., receiving a Nobel Prize or becoming Grand Master in chess). For example, in classic research conducted in the 1940s, de Groot ( 1965 ) found that chess experts did not have better general memory than chess novices, but they did have better domain-specific memory for the arrangement of chess pieces on the board. Chase and Simon ( 1973 ) replicated this result in a better controlled experiment. An explanation is that experts have developed schemas that allow them to chunk collections of pieces into a single configuration.
In another landmark study, Larkin et al. ( 1980 ) compared how experts (e.g., physics professors) and novices (e.g., first-year physics students) solved textbook physics problems about motion. Experts tended to work forward from the given information to the goal, whereas novices tended to work backward from the goal to the givens using a means-ends analysis strategy. Experts tended to store their knowledge in an integrated way, whereas novices tended to store their knowledge in isolated fragments. In another study, Chi, Feltovich, and Glaser ( 1981 ) found that experts tended to focus on the underlying physics concepts (such as conservation of energy), whereas novices tended to focus on the surface features of the problem (such as inclined planes or springs). Overall, research on expertise is useful in pinpointing what experts know that is different from what novices know. An important theme is that experts rely on domain-specific knowledge rather than solely general cognitive ability.
Analogical Reasoning
Analogical reasoning occurs when people solve one problem by using their knowledge about another problem (Holyoak, 2005 ). For example, suppose a problem solver learns how to solve a problem in one context using one solution method and then is given a problem in another context that requires the same solution method. In this case, the problem solver must recognize that the new problem has structural similarity to the old problem (i.e., it may be solved by the same method), even though they do not have surface similarity (i.e., the cover stories are different). Three steps in analogical reasoning are recognizing —seeing that a new problem is similar to a previously solved problem; abstracting —finding the general method used to solve the old problem; and mapping —using that general method to solve the new problem.
Research on analogical reasoning shows that people often do not recognize that a new problem can be solved by the same method as a previously solved problem (Holyoak, 2005 ). However, research also shows that successful analogical transfer to a new problem is more likely when the problem solver has experience with two old problems that have the same underlying structural features (i.e., they are solved by the same principle) but different surface features (i.e., they have different cover stories) (Holyoak, 2005 ). This finding is consistent with the idea of specific transfer of general principles as described in the section on “Transfer.”
Mathematical and Scientific Problem Solving
Research on mathematical problem solving suggests that five kinds of knowledge are needed to solve arithmetic word problems (Mayer, 2008 ):
Factual knowledge —knowledge about the characteristics of problem elements, such as knowing that there are 100 cents in a dollar Schematic knowledge —knowledge of problem types, such as being able to recognize time-rate-distance problems Strategic knowledge —knowledge of general methods, such as how to break a problem into parts Procedural knowledge —knowledge of processes, such as how to carry our arithmetic operations Attitudinal knowledge —beliefs about one’s mathematical problem-solving ability, such as thinking, “I am good at this”
People generally possess adequate procedural knowledge but may have difficulty in solving mathematics problems because they lack factual, schematic, strategic, or attitudinal knowledge (Mayer, 2008 ). Research is needed to pinpoint the role of domain knowledge in mathematical problem solving.
Research on scientific problem solving shows that people harbor misconceptions, such as believing that a force is needed to keep an object in motion (McCloskey, 1983 ). Learning to solve science problems involves conceptual change, in which the problem solver comes to recognize that previous conceptions are wrong (Mayer, 2008 ). Students can be taught to engage in scientific reasoning such as hypothesis testing through direct instruction in how to control for variables (Chen & Klahr, 1999 ). A central theme of research on scientific problem solving concerns the role of domain knowledge.
Everyday Thinking
Everyday thinking refers to problem solving in the context of one’s life outside of school. For example, children who are street vendors tend to use different procedures for solving arithmetic problems when they are working on the streets than when they are in school (Nunes, Schlieman, & Carraher, 1993 ). This line of research highlights the role of situated cognition —the idea that thinking always is shaped by the physical and social context in which it occurs (Robbins & Aydede, 2009 ). Research is needed to determine how people solve problems in authentic contexts.
Cognitive Neuroscience of Problem Solving
The cognitive neuroscience of problem solving is concerned with the brain activity that occurs during problem solving. For example, using fMRI brain imaging methodology, Goel ( 2005 ) found that people used the language areas of the brain to solve logical reasoning problems presented in sentences (e.g., “All dogs are pets…”) and used the spatial areas of the brain to solve logical reasoning problems presented in abstract letters (e.g., “All D are P…”). Cognitive neuroscience holds the potential to make unique contributions to the study of problem solving.
Problem solving has always been a topic at the fringe of cognitive psychology—too complicated to study intensively but too important to completely ignore. Problem solving—especially in realistic environments—is messy in comparison to studying elementary processes in cognition. The field remains fragmented in the sense that topics such as decision making, reasoning, intelligence, expertise, mathematical problem solving, everyday thinking, and the like are considered to be separate topics, each with its own separate literature. Yet some recurring themes are the role of domain-specific knowledge in problem solving and the advantages of studying problem solving in authentic contexts.
Future Directions
Some important issues for future research include the three classic issues examined in this chapter—the nature of problem-solving transfer (i.e., How are people able to use what they know about previous problem solving to help them in new problem solving?), the nature of insight (e.g., What is the mechanism by which a creative solution is constructed?), and heuristics (e.g., What are some teachable strategies for problem solving?). In addition, future research in problem solving should continue to pinpoint the role of domain-specific knowledge in problem solving, the nature of cognitive ability in problem solving, how to help people develop proficiency in solving problems, and how to provide aids for problem solving.
Anderson L. W. , Krathwohl D. R. , Airasian P. W. , Cruikshank K. A. , Mayer R. E. , Pintrich P. R. , Raths, J., & Wittrock M. C. ( 2001 ). A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives. New York : Longman.
Baron J. ( 2000 ). Thinking and deciding (3rd ed.). New York : Cambridge University Press.
Google Scholar
Google Preview
Bloom B. S. , & Broder B. J. ( 1950 ). Problem-solving processes of college students: An exploratory investigation. Chicago : University of Chicago Press.
Chase W. G. , & Simon H. A. ( 1973 ). Perception in chess. Cognitive Psychology, 4, 55–81.
Chen Z. , & Klahr D. ( 1999 ). All other things being equal: Acquisition and transfer of the control of variable strategy . Child Development, 70, 1098–1120.
Chi M. T. H. , Feltovich P. J. , & Glaser R. ( 1981 ). Categorization and representation of physics problems by experts and novices. Cognitive Science, 5, 121–152.
Covington M. V. , Crutchfield R. S. , Davies L. B. , & Olton R. M. ( 1974 ). The productive thinking program. Columbus, OH : Merrill.
de Groot A. D. ( 1965 ). Thought and choice in chess. The Hague, The Netherlands : Mouton.
Duncker K. ( 1945 ). On problem solving. Psychological Monographs, 58 (3) (Whole No. 270).
Ericsson K. A. , Feltovich P. J. , & Hoffman R. R. (Eds.). ( 2006 ). The Cambridge handbook of expertise and expert performance. New York : Cambridge University Press.
Fridja N. H. , & de Groot A. D. ( 1982 ). Otto Selz: His contribution to psychology. The Hague, The Netherlands : Mouton.
Gentner D. , & Stevens A. L. (Eds.). ( 1983 ). Mental models. Hillsdale, NJ : Erlbaum.
Gigerenzer G. , Todd P. M. , & ABC Research Group (Eds.). ( 1999 ). Simple heuristics that make us smart. Oxford, England : Oxford University Press.
Goel V. ( 2005 ). Cognitive neuroscience of deductive reasoning. In K. J. Holyoak & R. G. Morrison (Eds.), The Cambridge handbook of thinking and reasoning (pp. 475–492). New York : Cambridge University Press.
Guilford J. P. ( 1967 ). The nature of human intelligence. New York : McGraw-Hill.
Holyoak K. J. ( 2005 ). Analogy. In K. J. Holyoak & R. G. Morrison (Eds.), The Cambridge handbook of thinking and reasoning (pp. 117–142). New York : Cambridge University Press.
Humphrey G. ( 1963 ). Thinking: An introduction to experimental psychology. New York : Wiley.
Judd C. H. ( 1908 ). The relation of special training and general intelligence. Educational Review, 36, 28–42.
Kahneman D. , & Tversky A. ( 1984 ). Choices, values, and frames. American Psychologist, 39, 341–350.
Kahneman D. , & Tversky A. (Eds.). ( 2000 ). Choices, values, and frames. New York : Cambridge University Press.
Kohler W. ( 1925 ). The mentality of apes. New York : Liveright.
Larkin J. H. , McDermott J. , Simon D. P. , & Simon H. A. ( 1980 ). Expert and novice performance in solving physics problems. Science, 208, 1335–1342.
Luchins A. ( 1942 ). Mechanization in problem solving. Psychological Monographs, 54 (6) (Whole No. 248).
Mandler J. M. , & Mandler G. ( 1964 ). Thinking from associationism to Gestalt. New York : Wiley.
Markman A. B. , & Medin D. L. ( 2002 ). Decision making. In D. Medin (Ed.), Stevens’ handbook of experimental psychology, Vol. 2. Memory and cognitive processes (2nd ed., pp. 413–466). New York : Wiley.
Mayer R. E. ( 1992 ). Thinking, problem solving, cognition (2nd ed). New York : Freeman.
Mayer R. E. ( 1995 ). The search for insight: Grappling with Gestalt psychology’s unanswered questions. In R. J. Sternberg & J. E. Davidson (Eds.), The nature of insight (pp. 3–32). Cambridge, MA : MIT Press.
Mayer R. E. ( 2008 ). Learning and instruction. Upper Saddle River, NJ : Merrill Prentice Hall.
Mayer R. E. ( 2009 ). Information processing. In T. L. Good (Ed.), 21st century education: A reference handbook (pp. 168–174). Thousand Oaks, CA : Sage.
Mayer R. E. , & Wittrock M. C. ( 2006 ). Problem solving. In P. A. Alexander & P. H. Winne (Eds.), Handbook of educational psychology (2nd ed., pp. 287–304). Mahwah, NJ : Erlbaum.
McCloskey M. ( 1983 ). Intuitive physics. Scientific American, 248 (4), 122–130.
Metcalfe J. , & Wiebe D. ( 1987 ). Intuition in insight and non-insight problem solving. Memory and Cognition, 15, 238–246.
Newell A. , & Simon H. A. ( 1972 ). Human problem solving. Englewood Cliffs, NJ : Prentice-Hall.
Nickerson R. S. ( 1999 ). Enhancing creativity. In R. J. Sternberg (Ed.), Handbook of creativity (pp. 392–430). New York : Cambridge University Press.
Nunes T. , Schliemann A. D. , & Carraher D. W , ( 1993 ). Street mathematics and school mathematics. Cambridge, England : Cambridge University Press.
Robbins P. , & Aydede M. (Eds.). ( 2009 ). The Cambridge handbook of situated cognition. New York : Cambridge University Press.
Rogers T. T. , & McClelland J. L. ( 2004 ). Semantic cognition: A parallel distributed processing approach. Cambridge, MA : MIT Press.
Singley M. K. , & Anderson J. R. ( 1989 ). The transfer of cognitive skill. Cambridge, MA : Harvard University Press.
Sternberg R. J. ( 1990 ). Metaphors of mind: Conceptions of the nature of intelligence. New York : Cambridge University Press.
Sternberg R. J. ( 1999 ). Handbook of creativity. New York : Cambridge University Press.
Sternberg R. J. , & Gregorenko E. L. (Eds.). ( 2003 ). The psychology of abilities, competencies, and expertise. New York : Cambridge University Press.
Tharp R. G. , & Gallimore R. ( 1988 ). Rousing minds to life: Teaching, learning, and schooling in social context. New York : Cambridge University Press.
Thorndike E. L. ( 1911 ). Animal intelligence. New York: Hafner.
Thorndike E. L. , & Woodworth R. S. ( 1901 ). The influence of improvement in one mental function upon the efficiency of other functions. Psychological Review, 8, 247–261.
Wertheimer M. ( 1959 ). Productive thinking. New York : Harper and Collins.
Wundt W. ( 1973 ). An introduction to experimental psychology. New York : Arno Press. (Original work published in 1911).
Further Reading
Baron, J. ( 2008 ). Thinking and deciding (4th ed). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Duncker, K. ( 1945 ). On problem solving. Psychological Monographs , 58(3) (Whole No. 270).
Holyoak, K. J. , & Morrison, R. G. ( 2005 ). The Cambridge handbook of thinking and reasoning . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Mayer, R. E. , & Wittrock, M. C. ( 2006 ). Problem solving. In P. A. Alexander & P. H. Winne (Eds.), Handbook of educational psychology (2nd ed., pp. 287–304). Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Sternberg, R. J. , & Ben-Zeev, T. ( 2001 ). Complex cognition: The psychology of human thought . New York: Oxford University Press.
Weisberg, R. W. ( 2006 ). Creativity . New York: Wiley.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Is problem solving a skill? Tips To solve Your Daily Life Problems

Some people can solve problems — whether they’re professional or personal — better than others, which makes one wonder, is problem-solving a skill? Is it inherent? Or do you have to learn how to solve problems?
Even the most successful entrepreneurs can struggle with enormous problems. Sometimes the work itself paves the way for them, other times it’s the circumstances themselves that create a conflict.
Having control over what happens and creating solutions to resolve any issue is the key.
Work problems decrease productivity
Professional problems, or work problems , are all those situations that create conflict, dissatisfaction, or difficulty at work. It can be problems with your boss or teammates, excessive workload, or lack of motivation.
Problems at work not only end up affecting your productivity but can also trigger mood disorders.
Good examples of work problems include:
Work stress.
Too much pressure at work can cause stress, a very common problem that emerges when too many responsibilities weigh heavily on the shoulders of professionals.
Also known as burnout syndrome and very common for in-service professionals who are in permanent contact with other people. Like stress, burnout happens when you take on too many responsibilities and too much work. Prolonged exposure to stress pushes your mind and body to the limit, causing you to feel overwhelmed and defeated.
Relationship problems
Disagreements with your colleagues or with your boss can generate a climate of work tension. Bosses can make life difficult. This happens because of poor management skills. An overly competitive environment generates friction between workers or struggles for leadership among teammates. In the long run, these problems at work often generate frustration and, if not resolved, will generate deep job dissatisfaction.
Workplace harassment
It is psychological violence that is continuously exercised in the person in his workplace. That harassment can come from your superior, your co-workers, or the company itself. Harassment generates an unsustainable work climate as it resorts to tactics that undermine your trust.
Reorientation of the work career
You know what you don’t want, but you don’t know what you want. You think you should change jobs, but you do not know how or what path to follow. During this confusion, you find it difficult to reinvent yourself professionally . This creates a state of uncertainty and anguish that is difficult to sustain for a long time.
How to recognize symptoms of problems at work
If you have any of the following symptoms, ask for help:
- Being harassed by colleagues or your boss.
- You’re always frustrated, and work makes you feel demotivated.
- Your productivity has decreased, and you feel more exhausted than usual.
- Your working climate is tense and every day you find it more unsustainable.
- Work is more stressful than enjoyable.
Causes of problems at work
- Managers with poor leadership skills cause problems among employees.
- The economic crisis in the company, which creates a more tense work environment. This creates a huge amount of pressure to perform more.
- Cultural and personality differences between peers, which leads to conflicts in relationships.
- Power struggles create a very competitive environment because the goals set are so aggressive that everyone wants to reach the top at the expense of others.
- Difficulties in internal communication between employees, which give rise to rumors and lack of information.
- Wrong choice of work. Maybe you studied a career because you “had exits” or you’re working on something you don’t like just to “pay the bills”.
- Lack of harmony between personal and corporate values. Thus, you don’t feel comfortable in the working climate that is breathed in the company.
- A mismatch between personal perspectives and work reality. This is a very common problem in companies forced to restructure. Thanks to this, workers have had to assume tasks and functions that did not correspond to them.
So is problem solving a skill?
You need methods for solving problems quickly and effectively, not just improvisation. For example, if you’re at work and you’re facing a stressful issue, what good does it do if panic gets hold of you? This is where your problem-solving skills come in handy.
If you’re ever been in an interview, you would know this: the interviewer would give you a situation and then ask you how you would deal with it. Or, he would ask you about past problems you faced at work and how you dealt with them. There is a reason interviewers ask these questions: they want to know how you behave under pressure. Are you on your best behavior or can you maintain your cool and find solutions to your problems?
The reason they want to know this is simple:
Problem-solving is considered a soft skill learned through education, training, and hard work, and employers perceive it as a major quality to have.
Is it inherent? No. Anyone can learn how to solve problems.
Take the same scenario I mentioned earlier. Instead of panic, a skilled problem-solver would analyze the causes of an unwanted situation, hatch a plan, write a variety of solutions, evaluate the best ones, and implement his plan.
Sounds easy when it’s put like that, doesn’t it?
It takes years of work and training to master this skill. Practice doesn’t make perfect. It makes progress, and it’s a skill worth learning.
Employers pay attention to it. They want people with a can-do attitude who can stand up in the face of adversity, or in this case: work problems.
Here’s another example: when a student cannot write an organized essay, his teacher gives him ways to break up paragraphs and sentences, shows him how to write a decent introduction, body, and conclusion, and shows him ways to construct simple, clear sentences to avoid writing blocks of texts.
The more the student uses the teacher’s approach, the easier it gets to write essays better and quicker. It all starts with a plan and a willingness to implement it.
The same rule applies in life. We can deal with any obstacle we encounter.
4 Methods for solving problems at work
2. Get comfortable with the uncomfortable before anything, and you’ll be on the right track.
3. The difference between a good problem solver and an amateur problem solver is experience.
4. Here are steps for solving problems you can take.
1- Identify your problems
Know the causes of the problems. You can’t solve a problem without first knowing what caused it.
To do this, you’ll need to analyze data, look up facts, and pinpoint the major obstacles that need addressing.
2- Brainstorm solutions
Knowing what caused the problem will make it easier for you to brainstorm solutions. Make a list of solutions, or better yet, have someone else help with you this.
Working with someone else at this stage will facilitate the brainstorming process. You’ll end up with a long list of solutions to compare, evaluate, and choose from.
3- Evaluate solutions
It is now time to find the right solution for the identified problem. After the first two stages, things will become much clearer.
For a successful solution, evaluating solutions is perfect for predicting potential barriers that may arise in the future.
Thus, you can cut down on losses. When teams have solutions for problems, they bring them up to their superiors, who then evaluate and make the final decision.
4- Make a plan, execute, and assess
Once everything is set in motion, now’s the time to determine if it’s working. Whether it’s a campaign ad, a promotional venture, or else, this is the ideal time to assess. It’s a big part to learn what’s working and what’s not.
4- Bonus tips to develop your problem-solving skills
1- look back on your professional successes and failures.
It’s customary not to look back when we are in the middle of a crisis. We obsess about quickly seeking the solution because we rush to escape the anguish.
We then make the mistake of not thinking about our past, of relating actions in which we were successful and which can help us today.
Crises are great opportunities to grow, have positive changes, and learn lessons. This is how entrepreneurs become successful.
2- Look for strengths in your sports results
Physical activity significantly increases self-confidence as well as provides better mental resilience.
It doesn’t matter if you run 1 kilometer or 10. Getting out there and improving your physical capacity implies incredible progress.
It’s not about being the best in the world. Exercising relaxes the mind and removes stress, keeping you focused and sane.
When you take on new sporting challenges and reach them, you get striking personal satisfaction.
Likewise, taking on problems at work contributes to your personal and professional growth.
3- Remember the emotional challenges you’ve overcome
Comparing a work problem with a personal one makes no sense. But here’s the thing, it makes you put this work problem on the same level as other difficult moments in your life.
If you beat the previous ones, what makes you think you won’t be able to do the same with this one?
They are situations of your own life. There are a few situations in our life that we cannot control; work is surely not one of them.
4- Lean on other people if necessary
Remember the people who have always been there for you: friends, partners, family, and co-workers who helped you achieve your goals.
If you think you can’t solve the situation yourself, fret not!
Look for that trusted person who can help you. Don’t be afraid or feel ashamed. They will be there for you as you will be when that person needs it.
Creating personal and professional bonds is key to making problems easier to deal with.
Having work problems means you have already overcome something really hard. It’s just one more step in the race you’re fighting for. Set new goals without fear.
- The next sometimes asks you, “is problem-solving a skill?”, tell them heck yeah! it’s just as good a skill as time-management or team collaboration. Problem-solving is definitely a skill worth learning.
- Learning fresh approaches to solving problems is essential to face and overcome situations. This is especially important in the workplace.
- Employers will always ask you about your problem-solving skills, and you’ll have a leg up if you’ve already developed this skill.
- A place to resolve your problems at work is necessary to come out on top. Learn how to identify problems, brainstorm solutions, evaluate solutions with your team, execute them, and assess the process for better implementation in the future.
You might also like

Leave a Reply
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Virginie Lemay-Vriesde 1, rue du potager L-2347 Luxembourg LUXEMBOURG
- List of inspiring items
- thank you Write For Us
- Write For Us

Send us to our email the titles you have in mind and our team will get in touch with you as soon as possible to arrange the publication of your text.
Your Titles*
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Nom (obligatoire)
Email (obligatoire)
Name (required)
Email (required)
Your Message
- No category
TNCS PREP W2

Related documents
Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The combination of these skills impacted the level of confidence direct reports had in achieving their organizations' strategic goals. Problem Solving is an Essential Skill. In another study, over 1.5 million raters were asked to select the top 4 most important competencies based on 19 different competencies.
In addition, his problem-solving skills might also be lacking in terms of considering other solutions to the problem, such as placing the jar in a different location, or using a different method to keep the ants away. For more information problem solving skills, click the link below. brainly.ph/question/16734053. #SPJ6
Men tended to act more independently. If you're going to solve a problem quickly, involve those around you and share the glory. 4. They know how to explain the problem and solution effectively. A ...
What is lacking in his problem-solving? ... SALT Mustrated by Rommel P. Mangiduyes Rommel, a five-year-old boy, put a label ... Here is an example: I have an issue with the lack of customers coming in. Q&A. Can you please provide an explanation for all steps taken. Q&A. Please refer to the attachment to answer this question. This question was ...
Rommel, a five-year -old boy, put a label <Salt= into a jar of sugar. Actually, he has been observing it almost every day because many ants are invading the jar. ... There are lacking steps on his problem solving because the way I see it he directly goes for solution without knowing or identifying the problem which should come first. Secondly ...
Rommel, a five-year-old boy, puts a label "salt" into a jar of sugar. ... What is lacking in his problem-solving skill? B. Think of specific events in your life where you had to exercise intuitive thinking and strategic analysis in your decisions. Reflect on the insights you have gained from both experiences.
With the house surrounded by Gestapo and SS men, Rommel complied, and took cyanide he was given on an isolated roadside less than 15 minutes from his driveway. Nazi officials concealed the cause of Rommel's death, initially claiming he had succumbed to wounds from a "car accident" without mentioning a plane strafing.
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
Problem-solving skills defined. Problem-solving skills are skills that allow individuals to efficiently and effectively find solutions to issues. This attribute is a primary skill that employers look for in job candidates and is essential in a variety of careers. This skill is considered to be a soft skill, or an individual strength, as opposed ...
The key to cultivating excellent problem-solving skills is having a distinct process designed to produce solutions. While it may seem like problem-solving involves a complex strategy, it features several steps that are easy to follow. The following steps represent a general problem-solving process you can use when you need to find a solution. 1.
While any related skills are worth highlighting, some may get you further than others. Analysis, research, creativity, collaboration, organization, and decision-making are all biggies. With those skills, you can work through the entire problem-solving process, making them worthwhile additions to your resume.
Problem-solving skills are the ability to identify problems, brainstorm and analyze answers, and implement the best solutions. An employee with good problem-solving skills is both a self-starter and a collaborative teammate; they are proactive in understanding the root of a problem and work with others to consider a wide range of solutions ...
Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork. 1. Analysis. As a manager, you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first.
VIDEO ANSWER: Hello students, the behavior that indicates the development of theory of mind or TOM during mean monkey task is crossing fingers behind their back in hopes the mean monkey won't choose the sticker…
Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below. Step. Characteristics. 1. Define the problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically.
Problem solving skills are invaluable in any job. But even the most experienced among us can fall into the trap of solving the wrong problem. Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg says that all too often, we ...
Rommel's book illustrates the importance of knowing the full details of everyone's role in a plan, to enable safe deviation when necessary. In one case, Rommel's position came under intense surprise attack, and his platoon was forced to prematurely assault in a new direction that was in an adjacent platoon's sector of fire.
Problem-solving skills include analysis, creativity, prioritization, organization, and troubleshooting. To solve a problem, you need to use a variety of skills based on the needs of the situation. Most jobs essentially boil down to identifying and solving problems consistently and effectively. That's why employers value problem-solving skills ...
Problem solving refers to cognitive processing directed at achieving a goal when the problem solver does not initially know a solution method. A problem exists when someone has a goal but does not know how to achieve it. Problems can be classified as routine or nonroutine, and as well defined or ill defined.
Problem-Solution - a method or organization, composed of two main sections: (1) the problem and (2) the solution. Ex: the problem is the question is a solution next one answer is. A difficulty is clearly obviously to solve. Cause-and-Effect - the author discusses the relationship between two or more events or experiences.
4 Methods for solving problems at work. 1. To develop problem-solving skills, you need to invite uncomfortable situations. 2. Get comfortable with the uncomfortable before anything, and you'll be on the right track. 3. The difference between a good problem solver and an amateur problem solver is experience. 4.
know the way to complete a task, the problem occurs. Problem-solving is a process, which. involves systematic observation and critical thinking to find an appropriate solution or way to. reach the ...
TNCS PREP W2. advertisement. Directions: Examine the picture below. Write your reasons and answer to the questions. provided on your notebook. Rommel, a five-year-old boy, puts a label "salt" into a jar of sugar. Actually, he has been. observing it almost everyday because many ants are attacking the jar. •.
Rommel, a five-year-old boy, puts a label "salt" into a jar of sugar. ... What is lacking in his problem-solving skill? B. Think of specific events in your life where you had to exercise intuitive thinking and strategic analysis in your decisions. Reflect on the insights you have gained from both experiences. Write your answers on a ...