Browse Course Material
Course info, instructors.
- Prof. Charles H. Fine
- Prof. Tauhid Zaman

Departments
- Sloan School of Management
As Taught In
- Mathematics
- Social Science
Introduction to Operations Management
Cases and readings.
The required readings for this course include:
- Cases listed in the Cases/Readings column below
- Goldratt, Eliyah M., and Jeff Cox. The Goal: A Process of Ongoing Improvement . 2nd revised ed. North River Press, 1992. ISBN: 9780884270614.
- [MSD] = Cachon, Gerard, and Christian Terwiesch. Matching Supply with Demand: An Introduction to Operations Management . 3rd ed. McGraw-Hill, 2012. ISBN: 9780073525204.

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare
Smart. Open. Grounded. Inventive. Read our Ideas Made to Matter.
Which program is right for you?

Through intellectual rigor and experiential learning, this full-time, two-year MBA program develops leaders who make a difference in the world.
A rigorous, hands-on program that prepares adaptive problem solvers for premier finance careers.
A 12-month program focused on applying the tools of modern data science, optimization and machine learning to solve real-world business problems.
Earn your MBA and SM in engineering with this transformative two-year program.
Combine an international MBA with a deep dive into management science. A special opportunity for partner and affiliate schools only.
A doctoral program that produces outstanding scholars who are leading in their fields of research.
Bring a business perspective to your technical and quantitative expertise with a bachelor’s degree in management, business analytics, or finance.
A joint program for mid-career professionals that integrates engineering and systems thinking. Earn your master’s degree in engineering and management.
An interdisciplinary program that combines engineering, management, and design, leading to a master’s degree in engineering and management.
Executive Programs
A full-time MBA program for mid-career leaders eager to dedicate one year of discovery for a lifetime of impact.
This 20-month MBA program equips experienced executives to enhance their impact on their organizations and the world.
Non-degree programs for senior executives and high-potential managers.
A non-degree, customizable program for mid-career professionals.
Teaching Resources Library
Operations Management Case Studies

Operations Management
Browse operations management learning materials including case studies, simulations, and online courses. Introduce core concepts and real-world challenges to create memorable learning experiences for your students.
Browse by Topic
- Capacity Planning
- Demand Planning
- Inventory Management
- Process Analysis
- Process Improvement
- Production Planning
- Project Management
- Quality Management
New! Quick Cases in Operations Management
Quickly immerse students in focused and engaging business dilemmas. No student prep time required.

Fundamentals of Case Teaching
Our new, self-paced, online course guides you through the fundamentals for leading successful case discussions at any course level.
New in Operations Management
Explore the latest operations management learning materials
2320 word count
1841 word count
3547 word count
1648 word count
1840 word count
1116 word count
1025 word count
Looking for something specific?
Explore materials that align with your operations management learning objectives
Operations Management Simulations
Give your students hands-on experience making decisions.
Operations Management Cases with Female Protagonists
Explore a collection of operations management cases featuring female protagonists curated by the HBS Gender Initiative.
Operations Management Cases with Protagonists of Color
Discover operations management cases featuring protagonists of color that have been recommended by Harvard Business School faculty.
Foundational Operations Management Readings
Discover readings that cover the fundamental concepts and frameworks that business students must learn about operations management.
Bestsellers in Operations Management
Explore what other educators are using in their operations management courses

Start building your courses today
Register for a free Educator Account and get exclusive access to our entire catalog of learning materials, teaching resources, and online course planning tools.
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .

- About / Contact
- Privacy Policy
- Alphabetical List of Companies
- Business Analysis Topics
BMW’s Operations Management (10 Critical Decisions) & Productivity

Operations management at BMW (Bayerische Motoren Werke/Bavarian Motor Works) involves critical decisions in vehicle manufacturing, distribution, and sales. External factors affecting the automotive and motorcycle industries influence critical decisions in the company’s operations management. For example, the trends discussed in the PESTEL/PESTLE analysis of BMW come with opportunities and threats that affect operations management effectiveness and business productivity. The automaker’s organizational characteristics, strategies, and goals determine business responses to these external influences. Operations management effectiveness influences BMW’s productivity and profitability in manufacturing, distribution, sales, and other areas of the automotive and motorcycle business.
Best practices in operations management optimize the business for high productivity and efficiency that mitigate the effects of the competitive pressure detailed in the Five Forces analysis of BMW . This pressure involves multinational competitors, such as General Motors , Tesla , Ford , Toyota , and other automakers, as well as motorcycle manufacturers, like Harley-Davidson . These competitors’ operations management practices are also aligned toward achieving industry leadership and business growth in vehicle markets where BMW operates.
BMW’s Operations Management: 10 Critical Decisions
1. Goods and Services. BMW’s operations management objective for its products is to maintain consistent production costs and output quality. Consistent costs ensure profit margins, while consistent vehicle quality supports customer satisfaction and competitiveness in the market. Product design revolves around goals based on BMW’s mission statement and vision statement , which focus on premium solutions for transportation and mobility. Thus, the company’s operations management decisions and productivity targets in this area are focused on enhancing business processes for excellent automobiles and motorcycles.
2. Quality Management. BMW’s quality standards and related operating targets align with the company’s premium branding. The company’s operations management ensures that quality satisfies the expectations of customers, including car buyers and drivers. Premium quality measures and standards in operations management contribute to competitiveness and growth that satisfy BMW’s competitive strategy and growth strategies . For example, managers implement quality standards alongside productivity goals to grow the automotive business based on economies of scale and the strategy of product differentiation.
3. Process and Capacity Design. BMW’s strategic objective for this area of operations management is to optimize its business through streamlined manufacturing processes that maximize the utility of organizational capabilities and technological resources. For example, the company uses automation and information technology integrated into the design of car production processes. This critical decision area of operations management utilizes economies of scale and the other business strengths enumerated in the SWOT analysis of BMW . These competitive advantages maximize productivity and output while keeping business profitability and the premium status of BMW’s brands.
4. Location. Operations management at BMW accounts for the proximity of manufacturing operations to suppliers and target markets. The locations of the company’s facilities around the world are based on economic opportunities, market size, ease of doing business, and other variables. For example, the company has many facilities in Europe to support production that matches market demand for BMW cars and motorcycles in the region. This location strategy optimizes the automaker’s productivity in manufacturing processes and ability to satisfy market demand. This strategic decision area of operations management accounts for BMW’s marketing mix (4Ps) , particularly the places or locations involved in the company’s distribution strategy.
5. Layout Design and Strategy. BMW approaches this critical decision of operations management by integrating technology into conventional manufacturing operations, resulting in a hybrid layout strategy that accommodates technology to support efficiency. In this area, the company’s objective is to maximize productivity through the efficient movement of resources and information in facilities, such as manufacturing plants and offices. The departments, divisions, groups, and teams in BMW’s organizational structure (business structure) set some of the requirements for the layouts in this area of operations management.
6. Human Resources and Job Design. BMW’s human resource management aims for continuous development that supports the requirements for innovation, design, competitiveness, and profitability. The automotive company needs to ensure the innovative excellence and productivity of its workforce to satisfy business goals through this critical decision of operations management. The traits of BMW’s organizational culture (business culture) are included in decisions and programs for human resource management. This area of operations management includes cultural considerations in job design to support cohesion in BMW’s business organization.
7. Supply Chain Management. BMW’s supply chain involves suppliers of materials and components used in cars and motorcycles. In this area, the automaker’s operations management focuses on streamlining the supply chain to support manufacturing processes despite fluctuations in productivity targets based on market demand. This critical decision of operations management accounts for technological changes, economic trends, and other external factors affecting BMW’s operations and business performance. For example, smart technology is increasingly a factor in the design of BMW automobiles and, consequently, in procurement decisions in the company’s supply chain management.
8. Inventory. Inventory management depends on markets where BMW facilities are located. For example, the automaker’s operations management objectives and measures for inventory control in the European market are different from those in the North American market. BMW accounts for market-specific supply and demand trends and their effects on productivity, efficiency, and inventory sufficiency.
9. Scheduling. BMW matches production schedules and human resource schedules to market demand and sales. Forecasts are used to inform this critical decision of operations management to maintain schedules that keep operations productive. For example, supply shortage forecasts inform BMW’s operations management when to schedule procurement to prevent disruptions in manufacturing processes.
10. Maintenance. BMW’s operations management objective in this critical decision area is to maintain reliable and consistent resources and processes, including manufacturing and distribution processes. Maintenance determines the automaker’s stability and reliability in satisfying market demand. Effective and timely maintenance supports BMW’s sustainability and other CSR and ESG goals and objectives by ensuring productivity and optimal efficiency that minimizes waste. The company’s managers also provide business maintenance guidelines for operations management at dealerships and other business partners.
Productivity Metrics at BMW
Focus on premium mobility and transportation solutions makes BMW’s operations management apply productivity metrics specific to material procurement and vehicle manufacturing and distribution. The following productivity metrics apply to BMW’s operations:
- Cars assembled per quarter (manufacturing productivity)
- Concept designs completed per year (vehicle design productivity)
- Cars sold per quarter (dealership productivity)
- Motorcycles sold per quarter (dealership productivity)
- BMW Group – Industry 4.0 – Digitalisation in Production .
- BMW Group Design .
- BMW Group Locations Worldwide .
- BMW Group Strategy .
- BMW Group Technology Radar .
- Chan, F. T., & Ding, K. (2023). Industrial intelligence-driven production and operations management. International Journal of Production Research, 61 (13), 4215-4219.
- Chen, L. (2023). The application of fluid mechanics in the research of classic car design in BMW. Highlights in Science, Engineering and Technology, 71 , 53-60.
- Plantec, Q., Deval, M. A., Hooge, S., & Weil, B. (2023). Big data as an exploration trigger or problem-solving patch: Design and integration of AI-embedded systems in the automotive industry. Technovation, 124 , 102763.
- Tsarouhas, P. (2023). New trends in production and operations management. Applied Sciences, 13 (16), 9071.
- Copyright by Panmore Institute - All rights reserved.
- This article may not be reproduced, distributed, or mirrored without written permission from Panmore Institute and its author/s.
- Educators, Researchers, and Students: You are permitted to quote or paraphrase parts of this article (not the entire article) for educational or research purposes, as long as the article is properly cited and referenced together with its URL/link.
Case Related Links
Case studies collection.
Business Strategy Marketing Finance Human Resource Management IT and Systems Operations Economics Leadership and Entrepreneurship Project Management Business Ethics Corporate Governance Women Empowerment CSR and Sustainability Law Business Environment Enterprise Risk Management Insurance Innovation Miscellaneous Business Reports Multimedia Case Studies Cases in Other Languages Simplified Case Studies
Short Case Studies
Business Ethics Business Environment Business Strategy Consumer Behavior Human Resource Management Industrial Marketing International Marketing IT and Systems Marketing Communications Marketing Management Miscellaneous Operations Sales and Distribution Management Services Marketing More Short Case Studies >
Loading Results
No Match Found
Operations strategy case studies
Customer operations.
A leading US non-profit health insurer focused on service as a key differentiator. It wanted to gain insight into current operational performance, and develop customer-centric capabilities like self-service and digital competency. PwC's Strategy& was engaged to evaluate and address gaps in customer and member engagement.
Leveraging our health insurance expertise, proprietary market research databases, and best practices to help the client develop its differentiated customer-centric capabilities, we identified quick wins included outsourcing of manual activities, automation of macros/scripting, and standardization of call center work-from-home policies. We delivered a plan to enhance workforce management, consolidate provider data claim, and move to pre-pay policy. Additional recommendations addressed network rationalization, timely issuance of ID cards, and reducing SG&A expenses.
The project identified $25M investment in provider engagement, flexible network design, personalized member service, and real-time enrollment to achieve the desired differentiating capabilities.
Innovation and product development
A global chemicals specialty company with multiple business units and several existing embedded R&D teams was challenged by stagnating growth in difficult market conditions and the client was seeking to reinvigorate the portfolio. The client sought to consolidate R&D capabilities and establish a corporate innovation function to coordinate and drive its long-term R&D agenda and drive growth.
Strategy& was asked to design the innovation operating model, define the collaboration with business units, and develop a concept for R&D partnerships and venturing to drive growth.
We established a target operating model, refocused product innovation into clusters and developed a venturing approach. The client experienced a significant upswing in R&D productivity, new record numbers of patents filed, and breakthroughs innovations in a number of focus areas. Overall, improved R&D coherence led to 13% direct top line growth and 15% EBITDA improvement.
Strategic supply management
A global lighting company with over $5B sales revenue across more than 130 countries was faced with tremendous market disruptions resulting from the transition from traditional lighting to LED. To successfully play in this significantly different market, the company sold off its traditional business and refocused on the technically driven, fast-cycled LED business. To enable this, the client had to adopt new business models. Within this context, the procurement function had to undergo a major transition towards strategic supply management to effectively support the businesses going forward.
Strategy& supported the client in identifying the new requirements resulting from the changed business models, developing the procurement transformation program based on prioritized 4-6 focus areas (e.g. SRM, Supplier and Innovation Scouting), including appropriate KPIs, and designing a comprehensive change management concept and roadmap to ensure engagement and buy-in from the client team.
The transformation delivered significantly improved service levels for the BUs based on nine key strategic supply management capabilities and an adapted operating model with an improved split of roles and responsibilities between corporate headquarters and business units.

Competitive manufacturing
A global product company with $10B sales revenue across more than 130 countries was suffering from a highly complex manufacturing footprint which was not aligned with the client’s main markets. The client was losing sales and profitability due to high order fulfillment cycle times, high manufacturing costs, and low productivity performance in its key operations.
Strategy& designed the global manufacturing footprint strategy based on clearly defined customer and market requirements. As a consequence, the team agreed to realign the operations footprint from 23 to 15 operations by implementing a more balanced global footprint closer to key customers and/or distribution centers.
The transformation delivered shorter order fulfillment cycle times while simultaneously reducing manufacturing costs by up to 10% and improving overall productivity and flexibility. These results led to a gross margin improvement by 5%.
Capital assets
A leading oil field services and equipment company’s financial performance was lagging its peers, and the company had committed to a 3% improvement in North American net margin. Management believed there was an opportunity to improve the effectiveness of their >$1B equipment maintenance spend, but was unclear on where and how to achieve savings.
Strategy& helped the client pinpoint inefficiencies in their maintenance operating model, shifting from a highly reactive and siloed operation to an integrated team using advanced techniques to deliver maintenance when and where needed based on data. The changes were substantial as the client reorganized to break down functional barriers and create a maintenance process focused on customer performance.
Results were impressive — the maintenance transformation program was implemented at the top 80% of locations by revenue, resulting in a ~2% boost to net margins. It also drove a 20% reduction in maintenance cost, 50% reduction in maintenance related downtime, and improved customer service.
General and administrative (G&A) operations
The securities servicing division of a global banking group sought to address business challenges like reduced productivity, sub-optimal operating model for its Center of Excellence (CoE), lack of process standardization, cost escalation, process fragmentation, and duplication. Strategy& was asked to help in accelerating execution and benefits delivery through process optimization, offshoring and redesign of operating model.
Strategy& developed initial hypothesis through a detailed current state analysis, using both quantitative and qualitative tools, and conducted workshops to identify quick win opportunities. We proposed a redesigned operating model for the CoEs, and suggested in-depth implementation plan to drive the changes.
The project identified potential cost saving of $10M per annum and recommended lean FTE allocation across locations. The project also identified opportunities to achieve process efficiency and provided detailed target state structure of the CoE, including team size, shift patterns, and processes performed.
Enterprise-wide operational excellence
A leading tier-1 automotive supplier for the production and processing of rubber, plastics and metal with $680MM. sales revenue faced significant growth rates, but structures, process efficiency and financial performance did not follow accordingly and significant refinancing/cash flow complications evolved.
Strategy& was tasked with reshaping the company starting from product-market-strategy, developing the organizational structure and optimizing the entire process and operations landscape. An overall restructuring concept based on two pillars was developed: 1) Urgent short-term actions focusing on firefighting to ensure customer satisfaction and 2) sustainable long-term measures facilitating the optimization of the company’s footprint, product creation process, sales initiatives as well as lean production initiatives and the definition of an overall production system.
Continued success of these measures was ensured through the implementation of a common reporting structure and escalation process to track progress and define counter measures in case of deviations. The highly successful project identified cost saving initiatives worth more than $135MM. and had the client achieving EBIT margins of 6-8% during the project.
Strategy&'s global footprint
View the complete list of Strategy& worldwide offices
Partner, Strategy& Germany

Harald Dutzler
Partner, Strategy& Austria

Principal, Strategy& US

Haroon Sheikh
Senior Executive Advisor, Strategy& Middle East

Ben Gilbertson
Partner, Strategy& Australia
© 2019 - 2024 PwC. All rights reserved. PwC refers to the PwC network and/or one or more of its member firms, each of which is a separate legal entity. Please see www.pwc.com/structure for further details.
- Privacy statement
- Terms of use
- Cookies info
- About site provider
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more .
- Compare Products
- Case Collection
- Operations Management
Items 1 - 10 of 14
- You're currently reading page 1

The case is centered around the timeline of the Telangana graduates’ MLC elections 2021, which were held against the backdrop of a known unknown: the COVID-19 pandemic. The electoral officials had to be mindful of the numerous security protocols and complexities involved in implementing the election process in such uncertain times. They had to incorporate additional steps and plan for contingencies to mitigate risks while executing the election process. Halfway through the election planning process, it became clear that the number of voters and candidates was unprecedentedly large. This unexpected development necessitated a revision of the prior plan for conducting the elections. Shashank Goel, Chief Electoral Officer (CEO), and M. Satyavani, Deputy CEO, were architecting the plan for conducting the elections with an unexpectedly large number of voters and candidates under pandemic-induced disruptions. Goel was also reflecting on how to develop contingency plans for these elections, given the uncertainty produced by unforeseen external factors and the associated risks. Although he had the mandate to conduct free and fair elections within the stipulated timelines and was assured that the required resources would be provided, several factors had to be considered. According to the constitutional guidelines for the graduates' MLC elections, qualified and registered graduate voters could cast their vote by ranking candidates preferentially. Paper ballots had to be used because electronic voting machines (EVMs) could not handle preferential voting. The scale and magnitude of the elections necessitated jumbo ballot boxes. To manage the process, the number of polling stations had to be increased, and manpower had to be trained. Further, the presence of healthcare workers to ensure the safety of voters and the deployed staff was imperative. The Telangana CEO’s office had to meet the increased logistical and technical requirements and ensure high voting turnouts while executing the election process.
Postponing the election was not an option for the ECI from the standpoint of the legal code of conduct. The Telangana CEO's office prepared a revised election plan. The project plan was amended to incorporate the need for additional resources and logistical support to execute the election process. As the efforts of the staff were maximized effectively, the elections could be conducted smoothly and transparently although a large number of candidates were in the fray.
Teaching and Learning Objectives:
The key case objectives are to enable students to:
- Appreciate the importance of effective project management, planning, and execution in public administration against the backdrop of uncertainties and complexities.
- Understand the importance of risk identification, risk planning, and prioritization.
- Learn strategies to manage various project risks in a real-life situation.
- Identify the characteristics of effective leadership in times of crisis and the key takeaways from such scenarios

The case is designed to be used in courses on Nonprofit Operations Management, Data Analytics, Six Sigma, and Business Process Excellence/Improvement in MBA or Executive MBA programs. It is suitable for teaching students about the common problem of lower rates of volunteerism in nonprofit organizations. Further, the case study helps present the importance and application of inferential statistics (data analytics) to identify the impact of various factors on the problem (effect). The case is set in early 2021 when Shefali Sharma, the Strategy and Learning Manager with Teach For India (TFI), faced a few challenging questions from a professor at the Indian School of Business (ISB) during her presentation at an industry gathering in Hyderabad, India. Sharma was concerned about the low matriculation rate of TFI fellows, despite the rigorous recruitment, selection, and matriculation (RSM) process. A mere 50-60% matriculation rate was not a commensurate return for an investment of INR 6.5 million and the massive effort put into the RSM process. In 2017, Sharma organized focused informative and experiential events to motivate candidates to join the fellowship, but it was not very clear if these events impacted the TFI matriculation rate. After the industry gathering at ISB, Sharma followed up with the professor to seek his guidance in performing data analytics on the matriculation data. Sharma wondered if inferential data analysis could help her understand which demographic factors and events impact the matriculation rate.
Learning Objective
- Illustrate the importance of inferential statistics as a decision support system in resolving business problems
- Formulating and solving a hypothesis testing problem for attribute (discrete) data
- Visually depicting the flow of work across different stages of a process

In response to the uncontrollable second wave of COVID-19 in the south Indian state of Telangana in April 2021, a few like-minded social activists in the capital city of Hyderabad came together to establish a 100-bed medical care center to treat COVID-19 patients. The project was named Ashray. Dr. Chinnababu Sunkavalli (popularly known as Chinna) was the project manager of Project Ashray. In addition to the inherent inadequacy of hospital beds to accommodate the growing number of COVID- 19 patients till March 2021, the city faced a sudden spike of infections in April that worsened the situation. Consequently, the occupancy in government and private hospitals in Hyderabad increased by 485% and 311%, respectively, from March to April. According to a prediction model, Chinna knew that hospital beds would be exhausted in several parts of the city in the next few days. The Project Ashray team was concerned about the situation. The team met on April 26, 2021, to schedule the project to establish the medical care center within the next 10 days. The case is suitable for teaching students how to approach the scheduling problem of a time- constrained project systematically. It helps as a pedagogical aid in teaching management concepts such as project visualization, estimating project duration, float, and project laddering or activity splitting, and tools such as network diagrams, critical path method, and crashing. The case exposes students to a real-time problem-solving approach under uncertainty and crises and the critical role of NGOs in supporting the governments. Alongside the Project Management and Operations Management courses, other courses like Managerial decision-making in nonprofit organizations, Health care delivery, and healthcare operations could also find support from this case.
Learning Objectives:
To learn: Time-constrained projects and associated scheduling problems Project visualization using network diagrams Activity sequencing and converting sequential activities to parallel activities Critical path method (early start, early finish, late start, late finish, forward pass, backward pass, and float) to estimate a project's overall duration Project laddering to reduce the project duration wherever possible Project crashing using linear programming

The case goes on to describe the enormous challenges involved in building the 4.94 km long Bogibeel Bridge in the North Eastern Region (NER) of India. When it was finally commissioned in 2018, it was hailed as a marvel of engineering. With two rail lines and a two-lane road over it, the bridge spanned the mighty Brahmaputra river. The Bogibeel Bridge was India's longest and Asia's second-longest road and rail bridge with fully-welded bridge technology that met European codes and welding standards. The interstate connectivity provided by the bridge enabled important socio-economic developments in the NER that included improved logistics and transportation, the growth of medical and educational facilities, higher employment, and the rise of international trade and tourism. While the outcomes of the project were significant, the efforts that went into constructing the Bogibeel Bridge were equally so. This case study is designed to teach the importance of effective risk planning in project management. Further, the case introduces students to earned value analysis and project oversight in managing large projects. The case centers on Indian Railways' need to quickly discover why the Bogibeel project was not going according to plan. The case also serves as a resource to teach public operations management where the focus is on projects and operations that result in socio-economic outcomes.
- Appreciate the importance of risk planning and risk prioritization and learn strategies to manage various project risks
- Understand earned value management (EVM) and the associated metrics and calculations for project evaluation on time and cost schedules.
- Identify social impact outcomes in public/infrastructure projects.

Access to clean water is so critical for development and survival that the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal number 6 (SDG-6) was to ensure availability and sustained management of water and sanitation. The World Health Organization (WHO) in 2006 estimated that 97 million Indians lacked clean and safe water. Fluoride and total dissolvable solids (TDS) in drinking water were dangerously high at many parts of rural India, with adverse impacts. On the other hand, buying clean drinking water from commercial vendors at market rates was not a realistic alternative, a costly recurring expense that much of India's rural population could not afford. The case tracks the efforts of Huggahalli, head of the technology group of Sri Sathya Sai Seva Organisations (SSSO), to devise a sustainable solution to the drinking water problem in rural India that is low on cost, high on impact. They eventually develop a model that satisfies all these criteria and becomes the basis for a project called Premamrutha Dhaara. Funded by Sri Sathya Sai Central Trust, the project aims to install water purification plants in more than 100 villages spanning six states in India, with the ultimate goal of turning over plant operations to the beneficiary villages and setting up a welfare fund in each village from the revenue generated. Social service projects, particularly in developing countries, have their unique challenges. The case highlights the importance of performing feasibility analysis as part of the project planning in social projects. The case also describes how the financial and operational dimensions of sustainability could lead to a self-sustainable system. The social innovation framework used to deploy the water purification project to achieve broader rural welfare has wider implications for project management, social innovation and change, sustainable operations management, strategic non-profit management, and public policy.
The case offers four possibilities for central objectives:
- To perform feasibility analysis in a Project Management course
- To design a social innovation framework in a Social Innovation and Change course
- To understand the dimensions of self-sustainability in a Sustainable Operations Management course
- To measure social impact in Strategic Non-profit Management and Public Policy courses

During the Indian general election of 2019, the Nizamabad constituency in Telangana state found itself in an unprecedented situation with a record 185 candidates competing for one seat. Most of these candidates were local farmers who saw the election as a platform for raising awareness about local issues, particularly the perceived lack of government support for guaranteeing minimum support prices for their crops. More than 185 candidates had in fact contested elections from a single constituency in a handful of elections in the past. The Election Commission of India (ECI) had declared them to be "special elections" where it made exceptions to the original election schedule to accommodate the large number of candidates. However, in the 2019 general election, the ECI made no such exceptions, announcing instead that polling in Nizamabad would be conducted as per the original schedule and results would be declared at the same time as the rest of the country. This presented a unique and unexpected challenge for Rajat Kumar, the Telangana Chief Electoral Officer (CEO) and his team. How were they to conduct free and fair and elections within the mandated timeframe with the largest number of electronic voting machines (EVMs) ever deployed to address the will of 185 candidates in a constituency with 1.55 million voters from rural and semi-urban areas? Case A describes the electoral process followed by the world's largest democracy to guarantee free and fair elections. It concludes by posing several situational questions, the answers to which will determine whether the polls in Nizamabad are conducted successfully or not. Case B, which should be revealed after students have had a chance to deliberate on the challenges posed in Case A, describes the decisions and actions taken by Kumar and his team in preparation for the Nizamabad polls and the events that took place on election day and afterward.
To demonstrate how a quantitative approach to decision making can be used in the public policy domain to achieve end goals. To learn how resource allocation decisions can be made by understanding the scale of the problem, the various resource constraints, and the end goals. To discover operational innovations in the face of regulatory and technical constraints and complete the required steps. To understand the multiple steps involved in conducting elections in the Indian context.

Set in April 2017, this case centers around the digital technology dilemma facing the protagonist Dr. Vimohan, the chief intensivist of Prashant Hospital. The case describes the critical challenges afflicting the intensive care unit (ICU) of the hospital. It then follows Dr. Vimohan as he visits the Bengaluru headquarters of Cloudphysician Healthcare, a Tele-ICU provider. The visit leaves Dr. Vimohan wondering whether he can leverage the Tele-ICU solution to overcome the challenges at Prashant Hospital. He instinctively knew that he would need to use a combination of qualitative and quantitative analysis to resolve this dilemma.
The case study enables critical thinking and decision-making to address the business situation. Assessing the pros and cons of a potential technology solution, examining the readiness of an organization and devising a framework for effective stakeholder and change management are some of the key concepts. Associated tools include cost-benefit analysis, net present value (NPV) analysis, force-field analysis, and change-readiness assessment, in addition to a brief discussion on SWOT analysis.

Set in 2016 in Hyderabad, India, the case follows Puvvala Yugandhar, Senior Vice President at Dr. Reddy's Laboratories (DRL), as he decides what to do about an underperforming production policy at their plants. Adopted a decade earlier, the policy, called Replenish to Consumption -Pooled (RTC-P), had not delivered the expected results. Specifically, the plants had been seeing an increase in production switchovers and creeping buffer levels for certain products, which had led to higher holding costs and lost sales for certain products. A senior consultant had suggested that DRL switch to a demand estimation-based policy called Replenish to Anticipation (RTA), which attempted to address the above concerns by segregating production capacity and updating buffer levels using demand estimates. However, Yugandhar, well aware of the challenges of changing production policies, wanted to explore a variant of RTC-P called Replenish to Consumption -Dedicated (RTC-D), which followed the same buffer update rules as RTC-P but maintained dedicated capacities for a subset of products.
By studying and solving the decision problem in the case, students should be able to better appreciate the challenges involved in making long-term operational changes. It gives them an opportunity to: (1) understand how each input might impact the final decision, and (2) how to weigh each of these inputs in arriving at the final decision.

We crafted the case study "Software Acquisition for Employee Engagement at Pilot Mountain Research " for use in Business Marketing, Buyer Behavior, or Operations Management courses in undergraduate, MBA, or Executive Education programs. The Pilot Mountain Market Research (PMMR) case study provides students with the opportunity to examine how buying decisions can be made utilizing online digital tools that are increasingly available to business-to-business (B2B) purchasing managers. To do so, we created fictitious research studies and data to realistically portray the kinds of information that are publicly available to B2B purchasing managers on the Internet today. In this case study, we introduce students to fit analysis, coding quality technical assessment, sentiment analysis, and ratings & reviews analyses. Students are challenged to integrate findings from these diverse analytical tools, combining both qualitative and quantitative data into concrete employee engagement software (EES) purchasing recommendations.
1. Evolving criteria for selecting a software package for organization-wide procurement in a B2B purchase decision context 2. Appreciate increasing digitalization of businesses 3. Understand importance of employee engagement in organizations and what an organization could do to enhance employee engagement among its workforce 4. Understand decision making processes in the context of digitalisation of businesses
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
Cl96abBusiness Analysis Group Project plus 1 page
Early detection of rare and elusive endangered species using environmental DNA: a case study for the Eurasian otter and the white-clawed crayfish in northwestern Italy
- Open access
- Published: 02 April 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Lorenzo Ballini ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0009-5400-2128 1 ,
- Dario Ottonello 2 ,
- Valentina Repetto 2 ,
- Chiara Natali ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0293-171X 1 ,
- Giacomo Chini 1 ,
- Livia Tolve ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0002-2626-0129 1 ,
- Claudio Ciofi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8537-8659 1 ,
- Sara Fratini ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5754-8830 1 &
- Alessio Iannucci ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7729-4412 1
Monitoring, management and conservation of rare and elusive species often requires early detection of individuals, especially for re-introduced and endangered taxa. Environmental DNA (eDNA) approaches can enhance the detection power of traditional biomonitoring methods for low-density, newly-established populations. In this study, we used species-specific Real Time PCR TaqMan assays to assess the presence of two endangered freshwater species, the white-clawed crayfish Austropotamobius pallipes and the Eurasian otter Lutra lutra at eight sites in four river catchments in Liguria (northwestern Italy). The Eurasian otter was considered extinct in the study area since the 1980s. However, recent, although scattered sightings indicated a recolonisation by a few individuals. The white-clawed crayfish populations declined drastically and became increasingly dispersed in the western part of Liguria. Our eDNA analysis confirmed the presence of both species in some of the selected rivers and detected Eurasian otter DNA where the species was not recorded through traditional monitoring methods. This study confirms eDNA-based monitoring approaches as valuable tools to assess the presence of rare and elusive species and help implement protection plans at a local scale.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Biodiversity monitoring is an essential tool to understand species distribution and inform wildlife conservation strategies. The effective management of rare and elusive species often requires early detection of populations, especially for reintroduced and endangered taxa (Maxwell and Jennings 2005 ; Jerde et al. 2011 ; Deiner et al. 2021 ; Peralta et al. 2023 ). The analysis of environmental DNA (eDNA) can complement traditional biomonitoring methods resulting in a more detailed description of community composition, especially in aquatic environments (Tsuji et al. 2019 ).
Monitoring methods based on eDNA allow for early detection of populations in which individuals are either at low densities, early ontogenetic or cryptic stages. eDNA-based techniques can help identify different species from a single sample (metabarcoding eDNA) or record the presence of a species of interest (targeted eDNA). In particular, probe-based Real Time PCR is now widely used to detect presence of a target species in an eDNA sample (Taberlet et al. 2018 ; Xia et al. 2018 ; Pawlowski et al. 2020 ).
Inland waters and freshwater ecosystems are among the most threatened environments and are experiencing high rates of biodiversity decline (Dudgeon 2019 ). The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List reports that almost 22% of the known freshwater species are threatened (IUCN 2023 ; William-Subiza and Epele 2021 ). Two iconic endangered Italian native freshwater species are the Eurasian otter ( Lutra lutra Linnaeus, 1758) and the white-clawed crayfish ( Austropotamobius pallipes species complex Lereboullet, 1858).
Despite being found in a wide variety of aquatic environments in Asia, Europe and North Africa, the Eurasian otter is listed as Near-Threatened in the IUCN Red List. This species is listed as Endangered in Italy (Loy et al. 2020 ), where populations have been steadily declining since the last century due to habitat reduction and degradation (Loy 2018 ). Thanks to a number of conservation actions, otter populations are now recovering in some European countries, including southern and central Italy (Elmeros et al. 2006 ; Prigioni et al. 2007 ; Loy 2018 ; Bolinesi et al. 2019 ; Buglione et al. 2020a , b ; Gaudiano et al. 2023 ). Recently, the presence of L. lutra has also been reported in northern Italian regions (Friuli Venezia Giulia, Veneto, Trentino Alto Adige and Liguria), probably as a result of recolonisation from neighbouring countries (Righetti 2011 ; Pavanello et al. 2015 ; Malthieux 2020 ; Nadai et al. 2022 ).
The white-clawed crayfish is threatened by habitat modification, pollution, competition with invasive alien species and the onset of lethal diseases (Holdich 2003 ). Many countries, including Italy, have experienced a massive population decline over the last few decades, so that this species has been listed as Endangered in the IUCN Red List since 2010 (Füreder et al. 2010 ). Italian populations of the white-clawed crayfish belong to two distinct species: A. pallipes , which occurs in the western part of Liguria, and A. italicus (including four subspecies, see Fratini et al. 2005 ), which is present in the rest of the Italian peninsula.
In this study, we used a Real Time PCR Taqman assay to assess the presence of the white-clawed crayfish and the Eurasian otter in four river catchments in Liguria (northwestern Italy). The Eurasian otter has been considered extinct in this region since the 1980s (see Prigioni et al. 2007 ). However, an isolated population was recently recorded in adjacent areas (Malthieux 2020 ). The white-clawed crayfish populations have declined drastically in numbers and have become increasingly dispersed in western Liguria. In this context, an eDNA-based monitoring approach is an ideal, non-invasive tool to detect the presence of both species which presumably occur in the area at low-densities. Our study aims at defining the current distribution range of L. lutra and A. pallipes in western Liguria and informing future management and conservation plans.
Materials and methods
Study area and sampling.
The study area included four river catchments in western Liguria (Italy): Roia-Bevera, Argentina, Nervia and Tanaro (Fig. 1 ). The Tanaro basin is located at the border of the Padano-Venetian ichthyogeographic district, while the other three catchments belong to the Tuscano-Latium ichthyogeographic zone. The Roia-Bevera basin is partially in French territory (Bianco 1990 , 1995 ). Sampling was conducted in October 2022 in eight sites, two along the Roia river (ROI1 and ROI2), two in the Bevera river (BEV1 and BEV2), and one along the Argentina (ARG2), Tanaro (TAN), Carpasina (CAR) and Nervia (NER2) rivers (Fig. 1 ). Rivers and sampling sites were selected based on occurrence of L. lutra and A. pallipes recorded during previous monitoring campaigns (see Salvidio et al. 2002 ; Bologna and Cristiani 2012 ; Capurro et al. 2015 ; Malthieux 2020 ; Ottonello pers. obs.). Moreover, the study area represents the most direct route for recolonisation by otter populations from France (Malthieux 2020 ).
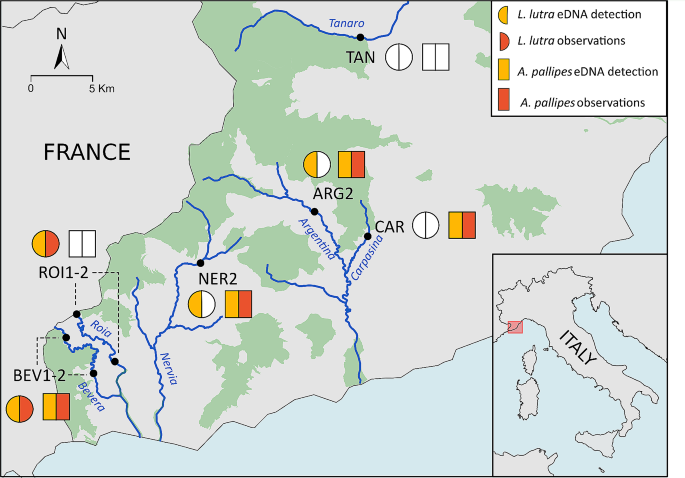
Map of the study area. Environmental DNA detection results and recent observation data are shown for each river. Bullets show locations of sampling sites. White semicircles and rectangles indicate lack of detection or observations. Dark green shading shows Natura 2000 Network areas
Water samples were collected at each site in six spatial replicates randomly selected on the two banks and in the middle of the river along a 150 m long transect. Each replicate consisted of one litre of water collected using plastic jars previously sterilised with sodium hypochlorite. Water samples were filtered on-site using a portable hand vacuum-pump connected to a polypropylene flask (Thermo Fisher Scientific). We used sterile disposable filter units with nitrocellulose membrane and a pore size of 0.2 μm (Thermo Fisher Scientific). All filters were immediately preserved in absolute ethanol upon water collection and stored at -20 °C prior to DNA extraction. A jar containing one litre of DNA-free deionized sterile water was left opened at each site for two minutes. The water was then filtered on-site and used as negative field control.
DNA extraction
Environmental DNA purification was carried out in a laminar flow cabinet using sterile equipment to avoid exogeneous DNA contamination. eDNA was extracted from nitrocellulose membrane filters using the ZymoBIOMICS DNA Miniprep Kit (Zymo Research) according to the manufacturer’s guidelines, eluted in a final volume of 50 µL of sterilised water and preserved at -20 °C.
To verify that DNA extraction from water samples provided sufficient metazoan genetic material, we measured DNA concentrations using the Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit (Invitrogen) and amplified two universal mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) metabarcode markers using PCR primers Tele02 and Vert01 (Riaz et al. 2011 ; Taberlet et al. 2018 ). Amplification reactions were performed using 1X Invitrogen Taq DNA Polymerase PCR Buffer, 1 U of Taq DNA Polymerase (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 2 mM MgCl 2 , 0.3 mM dNTPs, 0.5 µM of each primer and 1 µL of sample DNA in 25 µL total volume. The following amplification conditions were used: 5 min at 94 °C, 35 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 54 °C (Tele02) or 49 °C (Vert01) for 30 s, 72 °C for 1 min and a final extension step at 72 °C for 10 min. PCR products were resolved on a 1.2% agarose gel stained with GelRed Nucleic Acid Gel Stain (Biotum). DNA-free ddH 2 O and L. lutra DNA extracted from fresh biological material were included in each PCR reaction as negative and positive controls, respectively.
Real time PCR assay
Presence of target species in the eDNA samples was detected using species-specific probe-based TaqMan assays. For L. lutra , we used the assay reported by Thomsen et al. ( 2012 ) which amplifies a 80 bp long fragment of the mtDNA cytochrome b gene. For A. pallipes , we used the assay reported by Troth et al. ( 2020 ) which amplifies a 109 bp fragment of the mtDNA cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene. Each assay included two PCR primers and a target-specific dual labelled probe with fluorescent reporter and non-fluorescent quencher. A ROX fluorescent dye included in the Master Mix was used as an internal passive reference to normalize PCR fluorescent dye signals.
Positive controls consisted of L. lutra and A. pallipes DNA extracted from ethanol-preserved samples from the Natural History Museum of the University of Florence, Italy. For the white-clawed crayfish, we included positive controls of A. pallipes and three subspecies of A. italicu s ( A. i. carinthiacus, A. i. italicus and A. i. meridionalis ). DNA extractions were performed from muscle tissues using the PureLink Genomic DNA Mini Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) following the manufacturer’s protocol.
Real Time PCR assays were performed on a QuantStudio 7 Flex Real-Time PCR System (Life Technologies). Ten-fold serial dilutions of positive control DNA were tested in ten replicates to assess Real Time PCR amplification efficiency and define the limit of detection (LOD, expressed as threshold cycle Ct) as reported in Bustin et al. ( 2009 ); Klymus et al. ( 2020a , b ). Amplification conditions were as follows: a Pre-Read Stage at 60 °C for 30 s, hold at 95 °C for 20 s, 55 cycles at 95 °C for 1 s and 52 °C for 20 s followed by a Post-Read Stage at 60 °C for 30 s. Amplification reactions were conducted in a total volume of 20 µL containing 1X TaqMan Fast Advanced Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 0.5 µM of each primer, 0.25 µM TaqMan probe and 5 µL template DNA.
For each sampling site, eDNA samples, positive and negative controls were amplified in technical triplicate in the same PCR run. Negative field controls were processed as eDNA samples. A Real Time PCR replicate was recorded as positive if Ct was lower than the LOD, it had a uniform curve morphology and no amplification occurred in the negative template and field controls (Bustin et al. 2009 ; Ficetola et al. 2015 ; Klymus et al. 2020a , b ). Following the criteria proposed by Taberlet et al. ( 1996 ), Ficetola et al. ( 2015 ), Buxton et al. ( 2021 ) and Sanz et al. ( 2023 ) to avoid false positive and negative results, the presence of a species was considered as ascertained in the case of two positive amplifications out of the total of technical and spatial replicates.
Results and discussion
Environmental DNA concentrations ranged from 0.075 to 36.6 ng µL − 1 . The Tele02 and Vert01 PCR assays confirmed successful extraction of metazoan DNA from the eDNA samples for we obtained a visible band for each sample when loaded on an agarose gel. Negative PCR controls excluded the possibility of false-positive amplification due to human DNA contamination.
For both detection assays, the amplification efficiency of Real Time PCR estimated by means of calibration curves determined using serial dilutions of the positive controls was about 90% ( L. lutra : y = -3.63x + 24.05, r 2 = 0.99; A. pallipes : y = -3.5x + 25.68, r 2 = 0.97). The LOD corresponded to a Ct value of 43.7 ± 0.1 for the Eurasian otter assay and a Ct value of 43.3 ± 0.3 for the white-clawed crayfish assay. Ct values of positive Real Time PCR amplifications ranged from 37.7 to 43.5 for the otter assay and from 36.7 to 40.2 for the crayfish assay (Table 1 ).
Negative field and PCR controls produced no amplification, while PCR products of positive controls confirmed the reliability of the selected assays. For the white-clawed crayfish, we obtained a positive amplification for A. pallipes and the three tested subspecies of A. italicus . This result indicated that the sensitivity of the assay did not allow for the distinction between species and subspecies belonging to the A. pallipes species complex.
We recorded the presence of the Eurasian otter in four out of the six investigated rivers (Roia, Bevera, Argentina and Nervia). No presence of L. lutra was recorded in the Tanaro and Carpasina rivers. We detected the presence of the white-clawed crayfish in all river streams but the Tanaro and Roia rivers (Fig. 1 ; Table 1 ).
Historical sightings of the Eurasian otter in the western part of Liguria suggested the presence of few individuals in the high valley of the Tanaro, Argentina, Nervia, Roia and Bevera rivers (Balletto 1977 ; Vigna Taglianti and Bologna 1982 ). The species was considered extinct in the area ever since (Prigioni et al. 2007 ; Bologna and Cristiani 2012 ). Traces of L. lutra have been recently recorded upstream of BEV1-2 and ROI1-2 sampling sites in the Roia and Bevera rivers, indicating the presence of a relict population (Malthieux 2020 ). Our eDNA analysis confirmed the presence of the Eurasian otter on the Italian side of these rivers and detected the presence of L. lutra in adjacent basins where it was not previously observed (i.e., the Argentina and Nervia rivers).
The presence of the white-clawed crayfish was reported in five out of the six rivers included in this study, that is the Bevera, Nervia, Argentina, Carpasina (Capurro et al. 2015 ) and Tanaro (Salvidio et al. 2002 ). Recent observations, however, confirmed the presence of A. pallipes in all the above rivers but the Tanaro. Our eDNA approach confirmed recent surveys as we recorded the occurrence of the white-clawed crayfish only in BEV1, NER2, CAR and ARG2.
The majority of sites where we detected the presence of our target species are in close proximity to (NER2, ARG2, CAR) or mark the boundaries (BEV1-2) of Natura 2000 sites (Fig. 1 ). None of these Natura 2000 sites report L. lutra in their Standard Data Forms (SDF), while A. pallipes is only listed in the SDF of the protected areas established in the upper parts of the Carpasina and Argentina rivers.
This study confirms that eDNA-based monitoring approaches enhance the detection power of traditional biomonitoring surveys and are valuable tools to inform efficient management and protection schemes for threatened species (Pascher et al. 2022 ). Further investigations are needed to define in detail the distribution range of the target species in western Italy and reconstruct the recolonization routes of L. lutra of the Italian watersheds. Moreover, additional studies are needed to understand whether the presence of the Eurasian otter in western Italy is occasional or the species is reestablishing well-structured and viable populations.
Data availability
The data generated and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Balletto E (1977) Analisi faunistico-venatoria ed ecologica della Regione Liguria. Tipografia Don Bosco, Genova
Google Scholar
Bianco PG (1990) Potential role of the palaeohistory of the Mediterranean and paratethys basins on the early dispersal of Euro-Mediterranean freshwater fishes. Ichthyol Explor Freshw 1:167–184
Bianco PG (1995) Mediterranean endemic freshwater fishes of Italy. Biol Conserv 72(2):159–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3207(94)00078-5
Article Google Scholar
Bolinesi F, Viglietti S, Maio N, Guarino FM (2019) Presence of the eurasian otter Lutra lutra (Linnaeus, 1758) (Mammalia Mustelidae) in the Foce Sele-Tanagro Nature Reserve (Campania, Southern Italy). Biodivers J 10(2):121–126. https://doi.org/10.31396/Biodiv.Jour.2019.10.2.121.126
Bologna MA, Cristiani G (2012) Contributo alla teriofauna dell’atra Val Tanaro, Alpi Liguri (CN-IM). Riv Piemont Stor Nat 33:295–319
Buglione M, Petrelli S, Troiano C, Notomista T, Petrella A, De Riso L, Poerio L, Cascini V, Bartolomei R, Fulgione D (2020a) Spatial genetic structure in the eurasian otter (L utra lutra ) meta-population from its core range in Italy. Contrib Zool 90(1):70–92. https://doi.org/10.1163/18759866-BJA10012
Buglione M, Petrelli S, Troiano C, Notomista T, Rivieccio E, Fulgione D (2020b) The diet of otters ( Lutra lutra ) on the Agri river system, one of the most important presence sites in Italy: a molecular approach. PeerJ 8:e9606. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.9606
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55(4):611–622. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Buxton A, Matechou E, Griffin J, Diana A, Griffiths RA (2021) Optimising sampling and analysis protocols in environmental DNA studies. Sci Rep 11(1):11637. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-91166-7
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Capurro M, Oneto F, Ottonello D, Pericci R, Mignone W, Riina MV, Acuti PL (2015) Nota sulla presenza di esemplari xantocroici di gambero di fiume Austropotamobius pallipes specie complex (Lerebouillet, 1858) in Liguria (Italia nord-occidentale). Ann Mus Civ Stor Nat G Doria VIII:1–12
Deiner K, Yamanaka H, Bernatchez L (2021) The future of biodiversity monitoring and conservation utilizing environmental DNA. Environ DNA 3:3–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/edn3.178
Article CAS Google Scholar
Dudgeon D (2019) Multiple threats imperil freshwater biodiversity in the Anthropocene. Curr Biol 29(19):R960–R967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2019.08.002
Elmeros M, Hammershoj M, Madsen A, Sogaard B (2006) Recovery of the otter Lutra lutra in Denmark monitored by field surveys and collection of carcasses. Hystrix 17(1):17–28. https://doi.org/10.4404/hystrix-17.1-4361
Ficetola GF, Pansu J, Bonin A, Coissac E, Giguet-Covex C, De Barba M, Gielly L, Lopes CM, Boyer F, Pompanon F, Rayé G, Taberlet P (2015) Replication levels, false presences and the estimation of the presence/absence from eDNA metabarcoding data. Mol Ecol Resour 15(3):543–556. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12338
Fratini S, Zaccara S, Barbaresi S, Grandjean F (2005) Phylogeography of the threatened crayfish (genus Austropotamobius ) in Italy: implications for its taxonomy and conservation. Heredity 94(1):108–118. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.hdy.6800581
Füreder L, Gherardi F, Holdich D, Reynolds J, Sibley P, Souty-Grosset C (2010) In: IUCN 2010. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2010.3: e.T2430A9438817
Gaudiano L, Cascella A, L’Erario P, Corriero G (2023) First data on the presence of Lutra lutra in Bosco Incoronata Natural Regional Park (Apulia, South Italy). BORNH Bull Reg Nat Hist 3(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.6093/2724-4393/9985
Holdich D (2003) Ecology of the White-clawed Crayfish. Conserving Natura 2000 Rivers Ecology Series No. 1. English Nature, Peterborough
IUCN (2023) The IUCN Red list of threatened species. Version 2022-2. https://www.iucnredlist.org
Jerde CL, Mahon AR, Chadderton WL, Lodge DM (2011) Sight-unseen detection of rare aquatic species using environmental DNA: eDNA surveillance of rare aquatic species. Conserv Lett 4(2):150–157. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-263X.2010.00158.x
Klymus KE, Merkes CM, Allison MJ, Goldberg CS, Helbing CC, Hunter ME, Jackson CA, Lance RF, Mangan AM, Monroe EM, Piaggio AJ, Stokdyk JP, Wilson CC, Rithcer CA (2020a) Reporting the limits of detection and quantification for environmental DNA assays. Environ DNA 2:271–282. https://doi.org/10.1002/edn3.29
Klymus KE, Ruiz Ramos DV, Thompson NL, Richter CA (2020b) Development and testing of species-specific quantitative PCR assays for environmental DNA applications. J Vis Exp 165:e61825. https://doi.org/10.3791/61825
Loy A (2018) Eurasian otter. Duplaix N. Savage M. The global Otter Conservation Strategy. IUCN/SSC Otter Specialist Group, Salem, Oregon, pp 46–56
Loy A, Kranz A, Oleynikov A, Roos A, Savage M, Duplaix N (2020) Lutra lutra . In IUCN 2020. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2022: e.T12419A218069689
Malthieux L (2020) La Loutre d’Europe Lutra lutra (Linnaeus, 1758) en Roya- Bévéra: relique ou retour ? Prospections, état des lieux et implications. Faune-PACA Publication 98:22
Maxwell D, Jennings S (2005) Power of monitoring programmes to detect decline and recovery of rare and vulnerable fish. J Appl Ecol 42(1):25–37. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2664.2005.01000.x
Nadai GD, Cassol M, Lapini L (2022) First data on the natural recovery of the Eurasian otter ( Lutra lutra Linnaeus, 1758) in Veneto Region (north-eastern Italy). Habitat Online. https://www.habitatonline.eu/2022/11/first-data-on-the-natural-recovery-of-the-eurasian-otter-lutra-l-lutra-linnaeus-1758-in-veneto-region-north-eastern-italy/
Pascher K, Švara V, Jungmeier M (2022) Environmental DNA-based methods in biodiversity monitoring of protected areas: application range, limitations, and needs. Diversity 14(6):463. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14060463
Pavanello M, Lapini L, Kranz A, Iordan F (2015) Rediscovering the eurasian otter ( Lutra lutra L.) in Friuli Venezia Giulia and notes on its possible expansion in northern Italy. IUCN Otter Specialist Group Bull 32(1):12–20
Pawlowski J, Apothéloz-Perret-Gentil L, Mächler E, Altermatt F (2020) Environmental DNA applications for biomonitoring and bioassessment in aquatic ecosystems. Guidelines. Bern, Switzerland, Federal Office for the Environment. https://doi.org/10.5167/UZH-187800
Peralta D, Vaz-Freire T, Ferreira C, Mendes T, Mira A, Santos S, Alves PC, Lambin X, Beja P, Paupério J, Pita R (2023) From species detection to population size indexing: the use of sign surveys for monitoring a rare and otherwise elusive small mammal. Eur J Wildl Res 69:9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-022-01634-2
Prigioni C, Balestrieri A, Remonti L (2007) Decline and recovery in otter Lutra lutra populations in Italy. Mammal Rev 37(1):71–79. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2907.2007.00105.x
Riaz T, Shehzad W, Viari A, Pompanon F, Taberlet P, Coissac E (2011) ecoPrimers: inference of new DNA barcode markers from whole genome sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 39(21):e145. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr732
Righetti D (2011) Return of the otter in South Tyrol (NE Italy). In: Prigioni C, Loy A, Balestrieri A, Remonti L (eds) Proceedings of the IUCN XI International Otter Colloquium. Hystrix It J Mamm Supp. https://doi.org/10.4404/hystrix-22.0-4744
Salvidio S, Mori M, Lattes A, Galli L, Arillo A (2002) The freshwater crayfish Austropotamobius pallipes (Lereboullet, 1858) in Liguria, NW Italy: implications for management at the regional level. Bull Fr Pêche Piscic 367:663–670. https://doi.org/10.1051/kmae:2002057
Sanz N, Franch N, Araguas RM, Viñas J, Vidal O (2023) Environmental DNA assay for the detection of the American Bullfrog ( Lithobates catesbeianus ) in the early stages of the Invasion in the Ebre Delta. Animals 13(4):683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040683
Taberlet P, Griffin S, Goossens B, Questiau S, Manceau V, Escaravage N, Waits LP, Bouvet J (1996) Reliable genotyping of samples with very low DNA quantities using PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 24(16):3189–3194. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/24.16.3189
Taberlet P, Bonin A, Zinger L, Coissac E (2018) Environmental DNA: for Biodiversity Research and Monitoring. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Book Google Scholar
Thomsen PF, Kielgast J, Iversen LL, Wiuf c, Rasmussen M, Gilbert MT, Orlando L, Willerslev E (2012) Monitoring endangered freshwater biodiversity using environmental DNA: species monitoring by environmental DNA. Mol Ecol 21(11):2565–2573. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2011.05418.x
Troth CR, Burian A, Mauvisseau Q, Bulling M, Nigthingale J, Mauvisseau C, Sweet MJ (2020) Development and application of eDNA-based tools for the conservation of white-clawed crayfish. Sci Total Environ 748:141394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141394
Tsuji S, Takahara T, Doi H, Shibata N, Yamanaka H (2019) The detection of aquatic macroorganisms using environmental DNA analysis - A review of methods for collection, extraction, and detection. Environ DNA 1:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1002/edn3.21
Vigna Taglianti A, Bologna MA (1982) La fauna. AA.VV. Piano per Il Parco Naturale Regionale Delle Alpi Liguri. Sistemi I, II, III, Regione Liguria
Williams-Subiza EA, Epele LB (2021) Drivers of biodiversity loss in freshwater environments: a bibliometric analysis of the recent literature. Aquat Conserv: Mar Freshw Ecosyst 31(9):2469–2480. https://doi.org/10.1002/aqc.3627
Xia Z, Johansson ML, Gao Y, Zhan L, Haffner GD, MacIsaac, Zhan A (2018) Conventional versus real-time quantitative PCR for rare species detection. Ecol Evol 8(23):11799–11807. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.4636
Download references
This work was supported by the Liguria Regional Authority (Italy) through grant number G55J19000450007 of the Biodiv’Connect programme of the European Interreg Biodiv’ALP France-Italy ALCOTRA 2014–2020 project. The authors acknowledge the support by the Italian Ministry of University and Research through the National Biodiversity Future Center (NBFC), part of the National Recovery and Resilience Plan, Mission 4, Component 2, Investment 1.4, Project CN00000033. The authors are also grateful to Stefano Cannicci for his useful comments to the manuscript.
Open access funding provided by Università degli Studi di Firenze within the CRUI-CARE Agreement.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Biology, University of Florence, Via Madonna del Piano 6, Sesto Fiorentino (FI), 50019, Italy
Lorenzo Ballini, Chiara Natali, Giacomo Chini, Livia Tolve, Claudio Ciofi, Sara Fratini & Alessio Iannucci
ARPAL, Regional Agency for the Protection of the Ligurian Environment, Via Bombrini 8, Genoa, 16149, Italy
Dario Ottonello & Valentina Repetto
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
L.B., S.F. and A.I. wrote the manuscript. S.F, C.C., D.O., V.R., and A.I. conceptualized and designed the study. L.B., L.T. and G.C. collected the samples. L.B., C.N., A.I and S.F. performed lab work and provided lab support. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sara Fratini .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ballini, L., Ottonello, D., Repetto, V. et al. Early detection of rare and elusive endangered species using environmental DNA: a case study for the Eurasian otter and the white-clawed crayfish in northwestern Italy. Conserv Genet (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-024-01619-5
Download citation
Received : 22 June 2023
Accepted : 07 March 2024
Published : 02 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10592-024-01619-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Lutra lutra
- Austropotamobius pallipes
- Real time PCR
- Biodiversity monitoring
- Conservation
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This article reviews the case study research in the operations management field. In this regard, the paper's key objective is to represent a general framework to design, develop, and conduct case study research for a future operations management research by critically reviewing relevant literature and offering insights into the use of case method in particular settings.
This article reviews the case study research in the operations management field. In this regard, the paper's key objective is to. represent a general framework to design, develop, and conduct ...
Simply, a 'case' is an instance of something, particularly of the phenomenon under study. In operations management that could include a case of implementing a technology, or a case of changing the design of operations in a facility or a case of changing the way operations are managed. A case could also include a case of failure or of some ...
Operations Management Cases William V. Gehrlein,2005 William V. Gehrlein's Operations Management Cases provides a new collection of cases suited for introductory OM students. These OM cases have all been classroom tested with undergraduates and MBA's and are unique in providing plenty of teachable and tested analysis opportunities for students.
The five journals listed were selected on the basis of quality and impact (e.g., Journal of Operations Management, Management Science, etc.). Considerations were also given to geographic coverage (i.e., we wanted to include a leading European journal) and their stated acceptance of qualitative case studies. Analysis, results and implications
Abstract Our study examines the state of qualitative case studies in operations management. Five main operations management journals are included for their impact on the field. ... and data analysis were missing. For instance, there are studies that do not offer sampling logic or a description of the analysis through which research out-comes ...
In areas related to operations management, such as com-puter science, the term 'case study' is often used to refer to the performance of a system 'under' certain conditions. This can be the understanding in the context of simulation or optimisation, 2016 informa uK limited, trading as taylor & Francis group.
The answer seems to lie in the aim of the research. The widely-used paper by Voss et al. (2002) looks at case research and identifies four broad categories of research purpose - exploration, theory-building, theory-testing and theory extension/refinement. One of the interesting aspects of working with industry is that it is sometimes possible ...
The need for the operations management (OM) field to pur-sue more empirical methods, especially the case study method, has been noted in many research types. Recently there have been several ...
Moreover, the case study method is viewed with scepticism by those who consider it to be a weak form of research, one that lacks rigor and objectivity. Here, we offer an introduction to the case study method for OM researchers who may have little background in field based research. We provide an outline of the procedure and cite some excellent ...
Netessine S., and R. Shumsky. "Introduction to the Theory and Practice of Yield Management." INFORMS Transactions on Education 3, no. 1 (2002): 34-44. [MSD] Chapter 16. 21 Revenue management II + Break.com case Case. Roels, Guillaume, and Tyler Skowrup. "Break.com." (PDF) UCLA Anderson School of Management Case. UCLA. October 2008. 22
Abstract. Recently, there have been numerous calls for more empirical field-based research to be conducted in operations management (OM). Knowledge of how operations systems work can be enhanced significantly through contact with the "real-world" conditions that OM models seek to describe. Case study research is a primary means of exploring ...
Accordingly, Operations Management (OM) activities should for the most part engage with firms that are part of the manufacturing sector. Operations Management identifies all the activities necessary to plan, develop and improve the business processes involved in the manufacturing of a product or in the provision of a service .
A cross-case analysis is an act of comparing and contrasting the patterns emerging from the detailed case write-ups (Benbasat et al., 1987; Eisenhardt, ... it was clear that a significant portion of case studies in operations management are concentrated in a specific geographical area, which includes the United States (n = 12). While in other ...
PDF | On Jan 1, 2019, Jingwen Yang published Analysis of Business Operation Management under the Harvard Analytical Framework: A Case Study of the Walt Disney Company | Find, read and cite all the ...
Master of Science in Management Studies. Combine an international MBA with a deep dive into management science. A special opportunity for partner and affiliate schools only. ... Operations Management Case Studies. Teaching Resources Library A Background Note on "Unskilled" Jobs in the United States - Past, Present, and Future.
Operations Management. Browse operations management learning materials including case studies, simulations, and online courses. Introduce core concepts and real-world challenges to create memorable learning experiences for your students.
Best practices in operations management optimize the business for high productivity and efficiency that mitigate the effects of the competitive pressure detailed in the Five Forces analysis of BMW.This pressure involves multinational competitors, such as General Motors, Tesla, Ford, Toyota, and other automakers, as well as motorcycle manufacturers, like Harley-Davidson.
Representing a broad range of management subjects, the ICMR Case Collection provides teachers, corporate trainers, and management professionals with a variety of teaching and reference material. The collection consists of Operations case studies and research reports on a wide range of companies and industries - both Indian and international, cases won awards in varies competitions, EFMD Case ...
Strategy& was tasked with reshaping the company starting from product-market-strategy, developing the organizational structure and optimizing the entire process and operations landscape. An overall restructuring concept based on two pillars was developed: 1) Urgent short-term actions focusing on firefighting to ensure customer satisfaction and ...
Multiple case studies can help researchers to understand the studied phenomenon (Stake Citation 2005) and also develop new approaches to operations management. The combination of case study and other research methods offers a wide range of data acquisition and analysis.
The case is designed to be used in courses on Nonprofit Operations Management, Data Analytics, Six Sigma, and Business Process Excellence/Improvement in MBA or Executive MBA programs. It is suitable for teaching students about the common problem of lower rates of volunteerism in nonprofit organizations. Further, the case study helps present the ...
Author: Diana Nagy, MBA FT 11, Grenoble Graduate School of Business. Course: Operation Management. Prof.: Alexander Fidanza. Assignment: Custom Molds Inc. - case study analysis. Submitted: November 2010. Custom Molds Inc. - Case Study Analysis 1. What are the major issues Tom and Mason Miller are facing?
Management document from Algoma University, 4 pages, Name: Nikhil Student Id: A00177149 Course: Business Case Analysis To: Atashi Bedi 1. How did the company (the one you have chosen) apply Scenario Analysis (Techniques used)? Scenario analysis is a method for planning a strategy that involves creating and
Analysis of Wells Fargo Case Study Importance of Ethics in Managing Business: Ethics play a crucial role in managing business, as demonstrated by the Wells Fargo scandal. CEO John Stumpf's emphasis on cross-selling and achieving high sales targets led to a toxic culture within the organization. Instead of fostering values of integrity and customer- centricity, Stumpf prioritized short-term ...
The management of surface water in basins has become of the utmost importance, especially given the expected changes in climate and land use. Therefore, the current work aimed to aid the management of the Khazir River basin by estimating sediment yield and surface runoff using the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) at the hydrological response unit (HRU) spatial level. The SWAT model was ...
Management document from Moi University, 8 pages, Nestlé Corporate Social Responsibility Nestle has shown commitment to social responsibility and sustainability in its operations. The company aims at making positive impacts on individuals and families and also on surrounding communities and the world thr ... The study was to assess the feeding ...
Monitoring, management and conservation of rare and elusive species often requires early detection of individuals, especially for re-introduced and endangered taxa. Environmental DNA (eDNA) approaches can enhance the detection power of traditional biomonitoring methods for low-density, newly-established populations. In this study, we used species-specific Real Time PCR TaqMan assays to assess ...