
- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
The Five Generations of Computers
Published by Leona Melton Modified over 5 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "The Five Generations of Computers"— Presentation transcript:

Professor: Nabil Elmjati IB100 Introduction to computer Sciences Professor: Nabil Elmjati.

Generations of the Computer

5 Generations of Computers Ms. Ceejay Jader. FIRST GENERATION : Vacuum Tubes a glass tube surrounding a vacuum (an area from which all gases.

HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT By: Pratama Wahyu Purnama ( ) Maulida Yulianti ( )

1 Maninder Kaur

Online Counseling Resource YCMOU ELearning Drive… School of Architecture, Science and Technology Yashwantrao Chavan Maharashtra Open University, Nashik.

I NTRODUCTION TO C OMPUTERS AND P ROGRAMMING Chapter 1 Mr. Mohammed Rahmath.

Chapter Chapter Goals Describe the layers of a computer system Describe the concept of abstraction and its relationship to computing Describe.

Chapter 1 An Overview of Personal Computers

CS 104 Introduction to Computer Science and Graphics Problems History of Computer 09/05/2008 Yang Song (Prepared by Yang Song and Suresh Solaimuthu)

SUBJECT NAME: BASIC COMPUTER SKILLS. What is computer ? A device that computes, especially a programmable electronic machine that performs high-speed.

A Brief History of Computers

Prepared by: Jasper Francisco. The Early Years 1 In the early years, before the computer was invented, there were several inventions of counting machine.

History of computers By Anne Perera.

COMPUTER SYSTEM.

Chapter 01 Nell Dale & John Lewis.

What is a computer? What is its definition? A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic.
SECOND GENERATION COMPUTERS (ERA OF TRANSISTORS)

CS 1410 Intro to Computer Tecnology Computers and History1.

Computer Programming History of Computers
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

computer generation
Related Papers
Mahendra Pratap
magendira mani vinayagam
Carlo Minnaja
fredy kalonzo
chitra devi
Lweendo Mulando
A Computer is machine that performs tasks, such as calculations or electronic communication, under the control of a set of instructions called a program. Programs usually reside within the computer and are retrieved and processed by the computer’s electronics. The program results are stored or routed to output devices, such as video display monitors or printers. Computers perform a wide variety of activities reliably, accurately, and quickly.
tarek mahmud
jovan kabir
Brankica Dimovska
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Inorganic Chemistry
Roger Guilard
IEEE Translation Journal on Magnetics in Japan
Satoshi Hirosawa
Grzegorz Micek
Döndü Çuhadar
Machado Fracalossi
Journal of Clinical Microbiology
Reginaldo Bastos
Pragya Goswamy
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare
Mohamed ElBadry
Gonzalo Oyola Quiroga
Journal of the International Phonetic Association
Martine Grice
IIC - International Review of Intellectual Property and Competition Law
christine Godt
Journal of economics and sustainable development
Dr. Adefemi T A J U D E E N Adeniran
2016 21th IEEE European Test Symposium (ETS)
Wim Dehaene
Acta Physica Polonica A
Piotr Gębara
Rati Ratna Sari
Atomic Energy Society of Japan
Ikuo Kinoshita
Physical Review D
Leszek Motyka
Journal of the American Chemical Society
Mason Haneline
Chemical Physics Letters
Christa Kneip
International Journal of Livestock Production
Skender Muji
Jenaro Guisasola
International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics
snježana škrablin
Sani Ibrahim
EUGENIA Vathakou
The Journal of Infectious Diseases
M. Contrini
See More Documents Like This
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Generation of Computer 1st to 5th with Examples, Features & Tables
In competitive exams, the subject of computer fundamentals is often overlooked as it typically only comprises a small portion of the test. However, the questions that are asked on this subject are relatively simple and can be easily answered with proper preparation.
To assist you in your studies, we have compiled a collection of detailed notes on the generation of computers. By reviewing these notes, you will be able to gain a deeper understanding of the subject and increase your chances of success in your exam. Don’t overlook the importance of computer fundamentals, take the time to review your notes and give yourself an edge in the exam
Table of Contents
Introduction
- In the present era, the term “generation” in computer terminology refers to both hardware and software components of a computer system.
- However, in the past, the term was primarily used to distinguish between different advancements in hardware technology.
- It was used to differentiate between various hardware technologies in the computer industry.
- In the past, when modern computing tools such as graphing calculators, spreadsheets, and computer algebra systems were not yet available, mathematicians and inventors relied on mechanical calculators to ease the computational workload.
- These mechanical calculators were used to perform mathematical operations and were essential tools for performing complex calculations.
▪ 8 Mechanical Calculators Before the Invention of the Modern Computer.
- Abacus (ca. 2700 BC)
- Pascal’s Calculator (1652)
- Stepped Reckoner (1694)
- Arithmometer (1820)
- Comptometer (1887) and Comptograph (1889)
- The Difference Engine (1822)
- Analytical Engine (1834)
- The Millionaire (1893)
- The early computers were not as technologically advanced as the current ones. However, with time, computers have undergone significant improvements in terms of speed, accuracy, size, and cost.
- This long period of evolution is often classified into different stages known as computer generations. These generations reflect the advancements made in computer technology over time.
Generation of Computer 1st to 5th with examples
- There are five computer generations known to date. Each generation has been discussed in detail along with its period and characteristics.
- First Generation Computers (1940-1956)
- Second Generation Computers (1956-1963)
- Third Generation Computers (1964-1971)
- Fourth Generation Computers (1971-Present)
- Fifth Generation Computers (Present and Beyond)
Let’s take a look at the history of computer generation.
First Generation of Computers (1940-1956)
- The first generation of computers was based on vacuum tubes.
- The period of the first-generation Computer is 1940-1956.
Examples of first-generation computers
- UNIVAC-1 (Universal Automatic Computer)

Main features of the First-Generation Computer
- Based on Vacuum tube technology
- Used machine language only
- Very costly
- Produced a lot of heat
- Consumed Huge size
- Need AC for cooling
- Consumes a lot of electricity
- Non-portable (Large size)
- Slow Input / Output process

2nd Generation of Computer (1956-1963)
- Computers of this generation used transistors.
- It supported assembly language as well as high-level programming languages like FORTRAN, and COBOL.
Examples of second-generation computers are
- IBM 1400 series
- IBM 7094 series
- UNIVAC 1107

The main features of the second generation are:
- Transistors-based computer
- It Supported machine and assembly languages.
- Generates less heat as compared to first-generation computers.
- Smaller size as compared to first-generation computers.
- Consumed less electricity as compared to first-generation computers
- Faster than first-generation computers
- Reliable compares to first-generation computers.
- Still very costly
- AC required for cooling

3rd Generation of Computer (1964-1971)
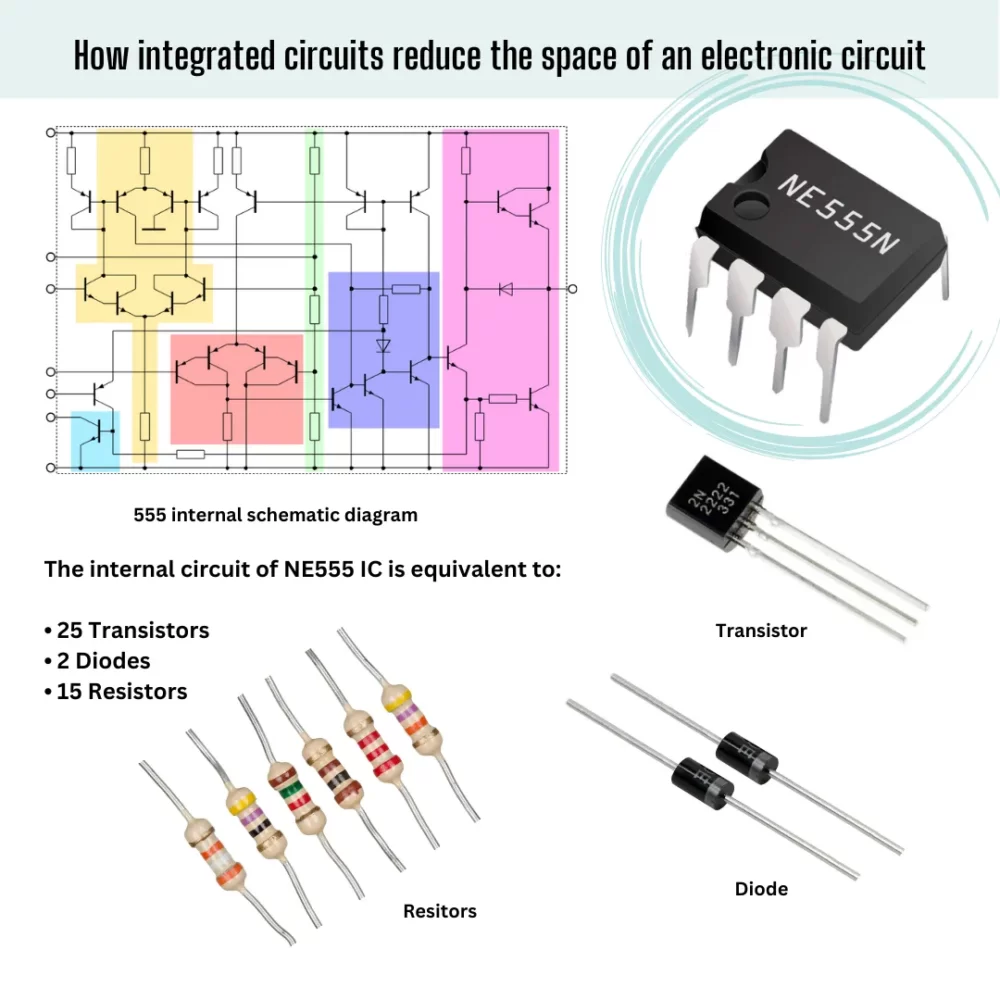
- Third-generation computers are based on Integrated Circuits (ICs).
- It supported remote time-sharing, processing, and multi-programming operating systems.
- Large magnetic core, magnetic tape/disk type memory used in this generation of computers.
- List of High-level languages used in this generation :
– FORTRAN-II – COBOL – PASCAL PL/1 – BASIC – ALGOL-68
Examples of third-generation computer
- UNIVAC 1108
- UNIVAC AC 9000
- IBM-370/168
- IBM-360 series
- Honeywell-6000 series
- PDP (Personal Data Processor)

The main features of the third generation are:
- Based on Integrated Circuits (ICs).
- More reliable than 1st and 2nd generations.
- More Smaller sizes.
- Produced less heat compared to previous generations.
- Faster than vacuum tubes and Transistor-based computers.
- Lesser maintenance
- AC required
- Consumed lesser electricity
- Supported high-level language
4th Generation Computers (1971-1980)
- Fourth-generation computers are based on Very Large Scale Integrated (VLSI) circuits.
- This generation of computers, supported time-sharing, real-time networks, and distributed operating systems were used.
- All the high-level languages like C, C++, DBASE, etc ., were used in this generation.
- Fourth-generation computers were built between 1971 to 1980.
- It uses semiconductor memory such as RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read Only Memory) etc.
Examples of Fourth generation computers
- Apple Macintosh
- CRAY-1 (Super Computer)
- CRAY-X-MP (Super Computer)

The main features of fourth-generation computers
- Based on VLSI technology
- Use of Personal Computers
- Very small size
- Semiconductor memory (ROM, RAM)
- Pipeline processing
- Portable and reliable
- No AC required
- The concept of the internet was introduced.
5th Generation of Computer (1980 to till date)
Fifth-generation computers are based on Ultra Large Scale Integration (ULSI) technology .
- This generation supports Parallel processing hardware and AI (Artificial Intelligence) software .
- All the high-level languages like C and C++, Java, .Net, etc. , are used in this generation.
- Since it supports AI technology, it can understand natural language or human language.
Examples of fifth-generation Computers
The main features and Characteristics of fifth-generation computers
- Based on ULSI ( Ultra Large Scale Integration ) technology
- True artificial intelligence
- Multimedia features
- Development of Natural language processing
- More user-friendly interface
- Advancement in Parallel Processing
- Advancement in Superconductor technology
- Faster Solid State Drive (SSD) memory , It is faster than Hard Disk Drives (HDD).
- Availability of very powerful and compact computers at cheaper rates.
Comparing Computer Generations: A Comprehensive Overview
Frequently asked questions .
Some examples of first-generation computers are ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC
• Notebooks • Desktop PCs of Pentium • Workstations of SUN. • IBM SP/2.
• IBM 1400 series • IBM 1620 • IBM 7094 series • CDC 1604 • CDC 3600 • UNIVAC 1108
• Transistors-based computer • It Supports machine and assembly languages. • Generates less heat as compared to first-generation computers • Smaller size as compared to first-generation computers • Consumed less electricity as compared to first-generation computers • Faster than first-generation computers • Reliable compares to the first generation computers. • Still very costly • AC required for cooling
Discover More Computer Awareness:

Types of Application Software in Computers with Examples

List of Computer Abbreviations with SSC MCQs (Updated List)
6 Types of Network Topologies With Diagram: Computer Awareness
Difference Between Traditional AI and Generative AI

Unveiling DeepSouth: The World’s First Human Brain-Scale Supercomputer

Exploring the First Generation of Computers: Full Details, Examples

Unraveling the Fascinating History of Computer Invention

Computer Storage Devices and Their Storage Capacity: Computer Awareness

High-Level Programming Languages and their Discoverer: Computer GK
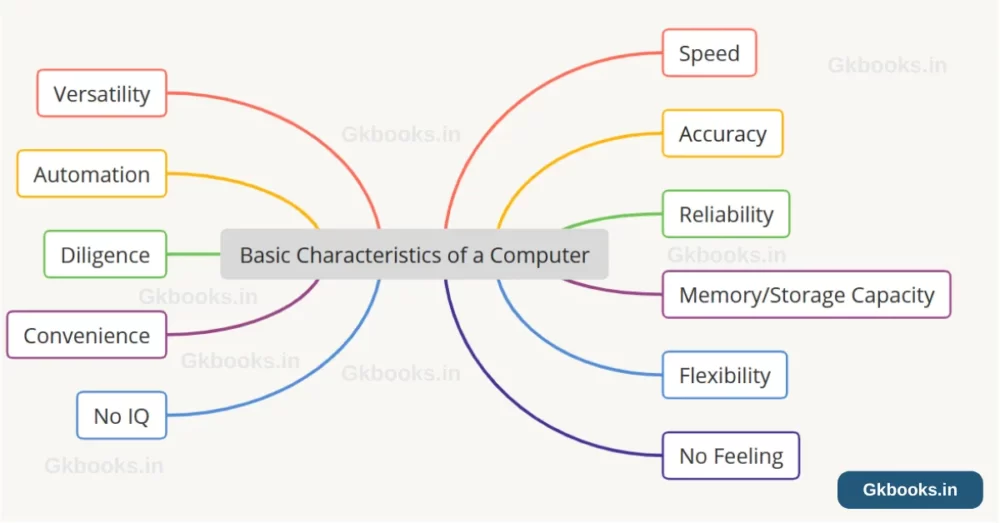
Characteristics of Computer Systems: Computer Awareness

Guided Media in Computer Network: Types, Applications, Advantages, Disadvantages

Web Browser, History, Types, Function, Features, and More
As a professional blogger and passionate educator, I am driven by a deep-seated desire to share knowledge and empower others. With years of experience in the field, I am committed to providing valuable insights and guidance to aspiring learners. My passion lies in helping individuals discover their potential and achieve their goals. I am also a firm believer in the power of motivation and strive to inspire others to pursue their dreams with unwavering determination.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
- Understanding Windows 10 | Class 5
- Write the name of Input and Output Devices and their Features?
- How to Insert Equations in a MS Word Document?
- How to Password Protect a File in MS PowerPoint?
- How to Add a Cover Page in Microsoft Word Document?
- How to Save PowerPoint Presentations as PDF Files using MS PowerPoint?
- How to Double Underline a Text in Microsoft Word?
- How to Add a Watermark in Microsoft Word?
- How to Change Slide Layout in MS PowerPoint ?
- How to Record Screen using Microsoft PowerPoint?
- How to Insert Symbols and Special Characters in Microsoft Word?
- How to Insert SmartArt in Microsoft Word?
- How to set the Background Color of the Textbox in MS Word?
- How to Insert Shapes in MS Word?
- How to Add different Slide Designs in MS PowerPoint?
- 10 Tips for Troubleshooting Your PC
- How to Insert 3D Models in MS PowerPoint?
- How to Use Spell Checker in MS Word?
- How to Print Multiple Slides on One Page in MS PowerPoint?
Generations of Computers – Computer Fundamentals
Generations of Computer : The modern computer took its shape with the arrival of your time. It had been around the 16th century when the evolution of the computer started. The initial computer faced many changes, obviously for the betterment. It continuously improved itself in terms of speed, accuracy, size, and price to urge the form of the fashionable day computer.
Basic Terms Related to Computers
The basic terms related to generations of computers are listed below.
- Vacuum Tube: Vacuum tubes have the functionality of controlling the flow of electronics in a vacuum. Generally, it is used in switches, amplifiers, radios, televisions, etc.
- Transistor: A transistor helps in controlling the flow of electricity in devices, it works as an amplifier or a switch.
- Integrated Circuit (IC): Integrated circuits are silicon chips that contain their circuit elements like transistors, resistors, etc.
- Microprocessors: Microprocessors are the components that contain the CPU and its circuits and are present in the Integrated Circuit.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is called the brain of the computer. CPU performs processing and operations work.
- Magnetic Drum: Magnetic Drum is like a cylinder that stores data and cylinder.
- Magnetic Core: Magnetic cores are used to store information. These are arrays of small rings.
- Machine Language: Machine Language is the language that a computer accepts (in the form of binary digits). It is also called low-level programming language.
- Memory: Memory is used to store data, information, and program in a computer.
- Artificial Intelligence: Artificial Intelligence deals with creating intelligent machines and behaviors.
Phases of Computer Generations
This long period is often conveniently divided into the subsequent phases called computer generations.
- First Generation Computers (1940-1956)
- Second Generation Computers (1956-1963)
- Third Generation Computers (1964-1971)
- Fourth Generation Computers (1971-Present)
- Fifth Generation Computers (Present and Beyond)
Before the generation of computers, we used calculators, spreadsheets, and computer algebra systems, mathematicians and inventors searched for solutions to ease the burden of calculation.
Below are the 8 Mechanical Calculators before modern computers were invented.
- Abacus (ca. 2700 BC)
- Pascal’s Calculator (1652)
- Stepped Reckoner (1694)
- Arithmometer (1820)
- Comptometer (1887) and Comptograph (1889)
- The Difference Engine (1822)
- Analytical Engine (1834)
- The Millionaire (1893)

First Generation Computers
The technology behind the primary generation computers was a fragile glass device, which was called a vacuum tube. These computers were very heavy and really large. These weren’t very reliable and programming on them was a tedious task as they used low-level programming language and used no OS. First-generation computers were used for calculation, storage, and control purpose. They were too bulky and large that they needed a full room and consume a lot of electricity. Punch cards were used for improving the information for external storage. Magnetic card used . Machine and assembly language is developed.
Examples of some main first-generation computers are mentioned below.
- ENIAC: Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer, built by J. Presper Eckert and John V. Mauchly was a general-purpose computer. It had been cumbersome, and large, and contained 18,000 vacuum tubes.
- EDVAC: Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer was designed by von Neumann. It could store data also as instruction and thus the speed was enhanced.
- UNIVAC: Universal Automatic Computer was developed in 1952 by Eckert and Mauchly.
.webp)
Vacuum Tube
Characteristics of First-Generation Computers
Second generation computers.
Second-generation computers used the technology of transistors rather than bulky vacuum tubes. Another feature was the core storage. A transistor may be a device composed of semiconductor material that amplifies a sign or opens or closes a circuit.
Transistors were invented in Bell Labs. The use of transistors made it possible to perform powerfully and with due speed. It reduced the dimensions and price and thankfully the warmth too, which was generated by vacuum tubes. Central Processing Unit (CPU), memory, programming language, and input, and output units also came into the force within the second generation.
The programming language was shifted from high level to programming language and made programming comparatively a simple task for programmers. Languages used for programming during this era were FORTRAN (1956), ALGOL (1958), and COBOL (1959).
.webp)
Characteristics of Second-Generation Computers
Third generation computers.
During the third generation, technology envisaged a shift from huge transistors to integrated circuits, also referred to as IC. Here a variety of transistors were placed on silicon chips, called semiconductors. The most feature of this era’s computer was speed and reliability. IC was made from silicon and also called silicon chips.
The computer programs was designed to make the machine work. Operating system was a program designed to handle a machine completely. Because of the operating system machine could execute multiple jobs simultaneously. Integrated circuits were used to replace many transistors used in the second generation.
A single IC has many transistors, registers, and capacitors built on one thin slice of silicon. The value size was reduced and memory space and dealing efficiency were increased during this generation. Programming was now wiped out Higher level languages like BASIC (Beginners All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code). Minicomputers find their shape during this era.
.webp)
Integrated Circuit
Characteristics of Third-Generation Computers
Fourth generation computers.
In 1971 First microprocessors were used, the large-scale of integration LSI circuits built on one chip called microprocessors. The advantage of this technology is that one microprocessor can contain all the circuits required to perform arithmetic, logic, and control functions on one chip. LSI placed thousands of transistors onto a single chip.
The computers using microchips were called microcomputers. This generation provided even smaller size of computers, with larger capacities. That’s not enough, then Very Large Scale Integrated (VLSI) circuits replaced LSI circuits. The Intel 4004 chip, developed in 1971, located all the components of the pc from the central processing unit and memory to input/ output controls on one chip and allowed the dimensions to reduce drastically. VLSI placed several hundred thousand transistors on a single silicon chip. This silicon chip is known as the micro processor.
Technologies like multiprocessing, multiprogramming, time-sharing, operating speed, and virtual memory made it a more user-friendly and customary device. The concept of private computers and computer networks came into being within the fourth generation.

Microprocessor
Characteristics of Fourth-Generation Computers
Fifth generation computers.
The technology behind the fifth generation of computers is AI. It allows computers to behave like humans. It is often seen in programs like voice recognition, area of medicine, and entertainment. Within the field of game playing also it’s shown remarkable performance where computers are capable of beating human competitors.
The speed is the highest, size is the smallest and area of use has remarkably increased within the fifth generation computers. Though not a hundred percent AI has been achieved to date but keeping in sight the present developments, it is often said that this dream also will become a reality very soon.
To summarize the features of varied generations of computers, it is often said that a big improvement has been seen so far because of the speed and accuracy of functioning care, but if we mention the dimensions, it’s been small over the years. The value is additionally diminishing and reliability is increasing.

AI-Based Computers
Characteristics of Fifth-Generation Computers
Faqs on generations of computer, 1. what are the 5 types of generation of computer.
The five generations of computers are: 1. First Generation (1940s-1950s): Characterized by vacuum tubes and punched cards. Examples: ENIAC, UNIVAC. 2. Second Generation (1950s-1960s): Transistors replaced vacuum tubes, allowing smaller and more efficient computers. Introduction of high-level programming languages. Examples: IBM 1401, IBM 7094. 3. Third Generation (1960s-1970s): Integrated circuits (ICs) replaced transistors, leading to smaller and faster computers. Introduction of operating systems. Examples: IBM System/360, DEC PDP-11. 4. Fourth Generation (1970s-1980s): Microprocessors brought computing power to individual users. Introduction of personal computers. Examples: IBM PC, Apple Macintosh. 5. Fifth Generation (1980s-Present): Focus on parallel processing, artificial intelligence (AI), and natural language processing. Development of supercomputers and expert systems. Ongoing advancements in AI and machine learning. Examples: IBM Watson, Google’s DeepMind.
2. What is Gen Z technology?
Gen Z technology encompasses the digital tools and platforms that define the experiences of individuals born roughly between the mid-1990s and early 2010s. This generation is characterized by its seamless integration of smartphones, social media, online collaboration, and video content into daily life, shaping their communication, learning, and entertainment habits.
3. What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the simulation of human intelligence in machines. It involves programming computers to think, learn, and perform tasks that traditionally require human intelligence, such as problem-solving and decision-making. AI encompasses subfields like machine learning and natural language processing, with applications ranging from virtual assistants to autonomous vehicles.
4. What was the First Computer?
The ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), completed in 1945, is widely regarded as the first electronic general-purpose computer.
5. Who is Known as the Father of Computers?
Charles Babbage is known as the Father of Computers for his pioneering work on the concept of a programmable mechanical computer in the 19th century.
Please Login to comment...
- School Learning
- School Programming
- 10 Best Tools to Convert DOC to DOCX
- How To Summarize PDF Documents Using Google Bard for Free
- Best free Android apps for Meditation and Mindfulness
- TikTok Is Paying Creators To Up Its Search Game
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

Download Generations of Computer PPT, PDF Report
Download Generations of Computer PPT, PDF Report: Initially, the foremost electronic computer was planned and built at the University of Pennsylvania based on vacuum tube technology to perform the logic operations as well as to store the data. Depending on the event causing a change in the technology, the computers have been divided into five types as below:
- First Generation: 1945- 1955
- Second Generation: 1955- 1965
- Third Generation: 1965- 1975
- Fourth Generation: 1975- Present
- Fifth Generation: Present and Beyond
Also See: Optical Coherence Tomography Seminar and PPT with PDF Report
Generations of Computer PPT, PDF Report
First Generation (1945- 1955):
Some of the first generation computers were ENIAC, EDSAC, EDVAC, and UNIVAC. Where
- ENIAC – Electronic Numerical Integrator And Calculator
- EDSAC – Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator
- EDVAC – Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer
- UNIVAC – Universal Automatic Computer IBM 701
In all the above computers, the vacuum tube technology was used and the computational speed was in milliseconds but they were non-portable, not reliable, highly susceptible to hardware failures, very expensive, consume a huge amount of electricity, has to need to assemble every component manually. So, because of all the above reasons, the commercial production was very poor. They also had difficulty to avail as they were machine language dependent.
Second Generation (1955- 1965):
The examples of second generation computers are IBM- 1401, IBM- 7090, IBM- 7030, Digital data corporation’s PDP 1/5/8, Honey well 400.
In this generation vacuum tubes were replaced by the transistors (invented at bell laboratories). These machines were comparatively small in size when compared to the first generation machines. The computational speed was very high i.e. from milliseconds to microseconds and they use to generate fewer amounts but still air conditioning was required. They were portable, reliable and not susceptible to the failures of hardware. They required manual assembling of components to form a functional unit and were assembly language dependent as compilers were developed to change from high-level language to assembly language program.
They were low in cost, magnetic ferrite core memories were used as main memory and magnetic tapes as secondary memory. Improvement of the individual input and output memories helped to operate in parallel with the CPU. They had the wide range of application in many fields like business to the engineering analysis and design.
Third Generation (1965- 1975):
Illustration of the third generation computers was system 360 mainframe from IBM, PDP-8, Mini computers from digital equipment corporation, NCR 395 and B6500.
The computers of the third generation were based on the integrated circuit technology, the central processing unit; input/output processors were equipped by small scale integration and medium scale integration. They were smaller in size, generates less amount of heat, computational speed was very fast (i.e. from microseconds to nanoseconds), low maintenance cost as not prone to hardware failure. In the commencing magnetic core memories were in avail but later semiconductor memories (RAM & ROM) were used in their place.
Only during this generation microprogramming, parallel processing, database management, multi-user application, automatic industrial control and much more were introduced.
Fourth Generation (1975- Present):
During this generation the microprocessors were introduced, the microprocessor is a stamp size chip which has a complete circuit of a computer processor using VLSI. Few integrated circuits with the entire circuitry are Intel’s (8088, 80286, 80386, 80486), Motorola’s (68000, 68030, 68040), Apple II, CRAY I/2/X/MP, Altair 8800 and CRAV-1.
In this semiconductor chips played the role of main memory whereas hard disks are used as secondary memory and floppy disks are used backup memory. They were small in size, have high speed, cheaper in cost, portable, and reliable. These machines don’t generate much heat, have low maintenance cost and low production cost. C language, Graphical user interface, Unix OS were also introduced.
Also See: Grid Computing Seminar and PPT with PDF Report
Fifth Generation (Present and Beyond):
The characteristics found in fifth generation computers are
- Artificial Intelligence
- Parallel Processing
- Multiple Pipelines and Multiple Processors
Artificial Intelligence: Artificial Intelligence refers to the sequence of inter-related technology that generally simulate and reproduce human behavior which includes thinking, speaking and listening.
Parallel Processing: In contrast to serial processing, parallel processing executed several instructions simultaneously at a single operation.
Mega Chips: these generation computers will use super large integrated chips as they require a large amount of storage for storing information as well as instructions.
Ultra Large Scale Integration technology was implemented in the Intel’s Pentium 4 microprocessor. Also, vector processors, SIMD processors, memory chips, hard disks up to 180 GB, object-oriented languages and new operating systems have been developed.
Some of the examples of the fifth generation computers are SUN workstations, Origin 2000, PARAM 10000, IBM SP/2, IBM notebooks, Pentium PCs-Pentium 1/2/3/4/Dual core/Quad core and much more.
Hence, the generations of the computers explain in detail about the past and further development of technology. Coming technologies like quantum mechanism, nanotechnology will change the stage of computers and grid technology is the upcoming technology in the internet application.
Content of the Seminar and pdf report for Generations of Computer
- Introduction
- What is A Computer
- First Generation of Computer
- Features of First Generation
- Second Generation of Computer
- Features of Second Generation
- Third Generation of Computer
- Features of Third Generation
- Fourth Generation of Computer
- Features of Fifth Generation
- Fifth Generation of Computer
Here we are giving you Generations of Computer Seminar and PPT with PDF report. All you need to do is just click on the download link and get it.
Generations of Computer PPT and Seminar Free Download
Generations of Computer pdf Report Free Download
It was all about Generations of Computer Seminar and PPT with pdf report. If you liked it then please share it or if you want to ask anything then please hit comment button.

Related Posts
Chatgpt ppt: presentation seminar free download, 500+ bca project topics: projects ideas for bca students, information and communication technology (ict) ppt, green technology ppt presentation: definition and types, mobile ppt presentation free download: definition and uses, web development ppt: definition, classification and tools, 1 comment already, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Title: sv3d: novel multi-view synthesis and 3d generation from a single image using latent video diffusion.
Abstract: We present Stable Video 3D (SV3D) -- a latent video diffusion model for high-resolution, image-to-multi-view generation of orbital videos around a 3D object. Recent work on 3D generation propose techniques to adapt 2D generative models for novel view synthesis (NVS) and 3D optimization. However, these methods have several disadvantages due to either limited views or inconsistent NVS, thereby affecting the performance of 3D object generation. In this work, we propose SV3D that adapts image-to-video diffusion model for novel multi-view synthesis and 3D generation, thereby leveraging the generalization and multi-view consistency of the video models, while further adding explicit camera control for NVS. We also propose improved 3D optimization techniques to use SV3D and its NVS outputs for image-to-3D generation. Extensive experimental results on multiple datasets with 2D and 3D metrics as well as user study demonstrate SV3D's state-of-the-art performance on NVS as well as 3D reconstruction compared to prior works.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

COMMENTS
Fourth Generation Computers. Fifth Generation Computers (present and beyond) •Fifth generation computing devices, based on artificial intelligence. •Are still in development, though there are some applications, such as voice recognition. •The use of parallel processing and superconductors is helping to make artificial intelligence a reality.
PDF | On Oct 21, 2019, Ishaq Zakari and others published History of computer and its generations. | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
computer, which gets its power by variable programs, with the ability to calculate rapidly, hold lots of information and even learn. We mark computer generations by the logic technology they're built from. We're currently in the fourth generation, called large scale integrated circuit technology. The first generation began
Fifth generation computers are in developmental stage which is based on the artificial intelligence. The goal of the fifth generation is to develop the device which could respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization. Quantum computation and molecular and nanotechnology will be used in this technology.
Computer generations are based on when major technological changes in computers occurred, like the use of vacuum tubes, transistors, and the microprocessor. As of 2018, there are five generations of the computer. Types of Computer Generation and examples 1940 - 1956: First Generation - Vacuum Tubes The first generation of computers used ...
generation computer. Even the later first generation computers could run the first three generations of computer languages (the first high level language, FORTRAN, was released in 1957). There are hundreds of high-level programming languages. Most of these are procedural, emphasizing the algorithmic side of programming (the procedures showing
In comparison to first generation computers, the second generation computer had the following favorable features. 1. Smaller in size as compared to first generation computers 2. More reliable 3. Less heat generated 4. Faster computational speed Disadvantages: Some unfavorable features can also be seen in this generation. 1. Air conditioning ...
Anthony Hyman (1982). Charles Babbage, pioneer of the computer. "In this sense Aiken needed IBM, whose technology included the use of punched cards, the accumulation of numerical data, and the ...
The 5 Generations of Computers - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. All about the 5 generations of computers
First generation computers relied on machine language, the lowest-level programming language understood by computers, to perform operations, and they could only solve one problem at a time. ... (Presentation Software) 6) Adobe Photoshop (Graphics Software) Interaction: Generally, users do not interact with system software as it works in the
Generations of Computer The computer has evolved from a large-sized simple calculating machine to a smaller but much more powerful machine. The evolution of computer to the current state is defined in terms of the generations of computer. Each generation of computer is designed based on a new technological development, resulting in better, cheaper and smaller computers that are more powerful ...
The Computer Generations Ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. The computers of the First Generation were capable to do one job at a time, therefore batch processing was adopted. The Second Generation was oriented towards multiple users i.e. The machine was capable to process multiple tasks concurrently.
A Computer is machine that performs tasks, such as calculations or electronic communication, under the control of a set of instructions called a program. Programs usually reside within the computer and are retrieved and processed by the computer's electronics. The program results are stored or routed to output devices, such as video display ...
CRAY-X-MP (Super Computer) Apple Macintosh, 4th Generation Computer (Photo Credit: Macrumors) The Apple Macintosh was introduced on January 24, 1984 by former Apple CEO Steve Jobs. It was equipped with a 9-inch black and white display, an 8MHz Motorola 68000 processor, 128KB of RAM, a 3.5-inch floppy drive.
Memory. Magnetic core and magnetic tape/disk. Input/output devices. Magnetic tape and punched cards. Power and size. Smaller in size, had low power consumption, and generated less heat (in comparison with the first-generation computers). Examples of the second generation.
PPT on generations of Computer - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This PPT contains information on basic computer history and generations of computer for the beginners in the department of computer science as well as for general stream students.
From the central processing unit and memory to input/output controls—on a single chip. . Fourth generation computers also saw the development of GUIs, the mouse and handheld devices. Fourth generation computers AMD' so. generation compu ers (present and beyond) Fifth generation computing devices, based on artificial intelligence.
In the next two lectures we will focus entirely on Hardware. Computer hardware components can generally be broken down into three categories: Processing - Processing components are responsible for actually carrying out actions in the computer. The main processing component is the Central Processing Unit (CPU).
Depending on the event causing a change in the technology, the computers have been divided into five types as below: First Generation: 1945- 1955. Second Generation: 1955- 1965. Third Generation: 1965- 1975. Fourth Generation: 1975- Present. Fifth Generation: Present and Beyond. Also See: Optical Coherence Tomography Seminar and PPT with PDF ...
Second-Generation Transformer Engine — Fueled by new micro-tensor scaling support and NVIDIA's advanced dynamic range management algorithms integrated into NVIDIA TensorRT™-LLM and NeMo Megatron frameworks, Blackwell will support double the compute and model sizes with new 4-bit floating point AI inference capabilities.
Generation of Computer - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. The five generation of computers
View PDF Abstract: In addition to the advancements in deepfake generation, corresponding detection technologies need to continuously evolve to regulate the potential misuse of deepfakes, such as for privacy invasion and phishing attacks. This survey comprehensively reviews the latest developments in deepfake generation and detection, summarizing and analyzing the current state of the art in ...
Foundation models have exhibited unprecedented capabilities in tackling many domains and tasks. Models such as CLIP are currently widely used to bridge cross-modal representations, and text-to-image diffusion models are arguably the leading models in terms of realistic image generation. Image generative models are trained on massive datasets that provide them with powerful internal spatial ...
We present Stable Video 3D (SV3D) -- a latent video diffusion model for high-resolution, image-to-multi-view generation of orbital videos around a 3D object. Recent work on 3D generation propose techniques to adapt 2D generative models for novel view synthesis (NVS) and 3D optimization. However, these methods have several disadvantages due to either limited views or inconsistent NVS, thereby ...