- Solve equations and inequalities
- Simplify expressions
- Factor polynomials
- Graph equations and inequalities
- Advanced solvers
- All solvers
- Arithmetics
- Determinant
- Percentages
- Scientific Notation
- Inequalities

What can QuickMath do?
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students.
- The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and cancelling common factors within a fraction.
- The equations section lets you solve an equation or system of equations. You can usually find the exact answer or, if necessary, a numerical answer to almost any accuracy you require.
- The inequalities section lets you solve an inequality or a system of inequalities for a single variable. You can also plot inequalities in two variables.
- The calculus section will carry out differentiation as well as definite and indefinite integration.
- The matrices section contains commands for the arithmetic manipulation of matrices.
- The graphs section contains commands for plotting equations and inequalities.
- The numbers section has a percentages command for explaining the most common types of percentage problems and a section for dealing with scientific notation.
Math Topics
More solvers.
- Add Fractions
- Simplify Fractions
Solving Equations
What is an equation.
An equation says that two things are equal. It will have an equals sign "=" like this:
That equations says:
what is on the left (x − 2) equals what is on the right (4)
So an equation is like a statement " this equals that "
What is a Solution?
A Solution is a value we can put in place of a variable (such as x ) that makes the equation true .
Example: x − 2 = 4
When we put 6 in place of x we get:
which is true
So x = 6 is a solution.
How about other values for x ?
- For x=5 we get "5−2=4" which is not true , so x=5 is not a solution .
- For x=9 we get "9−2=4" which is not true , so x=9 is not a solution .
In this case x = 6 is the only solution.
You might like to practice solving some animated equations .
More Than One Solution
There can be more than one solution.
Example: (x−3)(x−2) = 0
When x is 3 we get:
(3−3)(3−2) = 0 × 1 = 0
And when x is 2 we get:
(2−3)(2−2) = (−1) × 0 = 0
which is also true
So the solutions are:
x = 3 , or x = 2
When we gather all solutions together it is called a Solution Set
The above solution set is: {2, 3}
Solutions Everywhere!
Some equations are true for all allowed values and are then called Identities
Example: sin(−θ) = −sin(θ) is one of the Trigonometric Identities
Let's try θ = 30°:
sin(−30°) = −0.5 and
−sin(30°) = −0.5
So it is true for θ = 30°
Let's try θ = 90°:
sin(−90°) = −1 and
−sin(90°) = −1
So it is also true for θ = 90°
Is it true for all values of θ ? Try some values for yourself!
How to Solve an Equation
There is no "one perfect way" to solve all equations.
A Useful Goal
But we often get success when our goal is to end up with:
x = something
In other words, we want to move everything except "x" (or whatever name the variable has) over to the right hand side.
Example: Solve 3x−6 = 9
Now we have x = something ,
and a short calculation reveals that x = 5
Like a Puzzle
In fact, solving an equation is just like solving a puzzle. And like puzzles, there are things we can (and cannot) do.
Here are some things we can do:
- Add or Subtract the same value from both sides
- Clear out any fractions by Multiplying every term by the bottom parts
- Divide every term by the same nonzero value
- Combine Like Terms
- Expanding (the opposite of factoring) may also help
- Recognizing a pattern, such as the difference of squares
- Sometimes we can apply a function to both sides (e.g. square both sides)
Example: Solve √(x/2) = 3
And the more "tricks" and techniques you learn the better you will get.
Special Equations
There are special ways of solving some types of equations. Learn how to ...
- solve Quadratic Equations
- solve Radical Equations
- solve Equations with Sine, Cosine and Tangent
Check Your Solutions
You should always check that your "solution" really is a solution.
How To Check
Take the solution(s) and put them in the original equation to see if they really work.
Example: solve for x:
2x x − 3 + 3 = 6 x − 3 (x≠3)
We have said x≠3 to avoid a division by zero.
Let's multiply through by (x − 3) :
2x + 3(x−3) = 6
Bring the 6 to the left:
2x + 3(x−3) − 6 = 0
Expand and solve:
2x + 3x − 9 − 6 = 0
5x − 15 = 0
5(x − 3) = 0
Which can be solved by having x=3
Let us check x=3 using the original question:
2 × 3 3 − 3 + 3 = 6 3 − 3
Hang On: 3 − 3 = 0 That means dividing by Zero!
And anyway, we said at the top that x≠3 , so ...
x = 3 does not actually work, and so:
There is No Solution!
That was interesting ... we thought we had found a solution, but when we looked back at the question we found it wasn't allowed!
This gives us a moral lesson:
"Solving" only gives us possible solutions, they need to be checked!
- Note down where an expression is not defined (due to a division by zero, the square root of a negative number, or some other reason)
- Show all the steps , so it can be checked later (by you or someone else)
How to Solve Algebra Problems Step-By-Step
- Pre Algebra & Algebra
- Math Tutorials
- Exponential Decay
- Worksheets By Grade
- B.B.A., Finance and Economics, University of Oklahoma
Solving Algebra word problems is useful in helping you to solve earthly problems. While the 5 steps of Algebra problem solving are listed below, the following will help you learn how to first identify the problem.
- Identify the problem.
- Identify what you know.
- Make a plan.
- Carry out the plan.
- Verify that the answer makes sense.
Identify the Problem
Back away from the calculator ; use your brain first. Your mind analyzes, plans, and guides in the labyrinthine quest for the solution. Think of the calculator as merely a tool that makes the journey easier. After all, you wouldn’t want a surgeon to crack your ribs and perform a heart transplant without first identifying the source of your chest pains.
The steps of identifying the problem are:
- Express the problem question or statement.
- Identify the unit of the final answer.
Express the Problem Question or Statement
In Algebra word problems, the problem is expressed as either a question or a statement.
- How many trees will John have to plant?
- How many televisions will Sara have to sell to earn $50,000?
- Find the number of trees John will have to plant.
- Solve for the number of televisions Sara will have to sell to earn $50,000.
Identify the Unit of the Final Answer
What will the answer look like? Now that you understand the word problem’s purpose, determine the answer’s unit. For example, will the answer be in miles, feet, ounces, pesos, dollars, the number of trees, or a number of televisions?
Algebra Word Problem
Javier is making brownies to serve at the family picnic. If the recipe calls for 2 ½ cups of cocoa to serve 4 people, how many cups will he need if 60 people attend the picnic?
- Identify the problem: How many cups will Javier need if 60 people attend the picnic?
- Identify the unit of the final answer: Cups
In the market for computer batteries, the intersection of the supply and demand functions determines the price, p dollars , and the quantity, q , of goods sold. Supply function: 80 q - p = 0 Demand function: 4 q + p = 300 Determine the price and quantity of computer batteries sold when these functions intersect.
- Identify the problem: How much will the batteries cost and how much will be sold when supply and demand functions meet?
- Identify the unit of the final answer: The quantity, or q , will be given in batteries. The price, or p , will be given in dollars.
- Proportions Word Problems Worksheet 1
- Proportions Word Problems Worksheet: Answers and Explanations
- How to Do Algebra Word Problems
- How to Solve Proportions to Adjust a Recipe
- Algebra Age-Related Word Problem Worksheets
- Lesson Plan: Addition and Subtraction with Pictures
- The Quantity Theory of Money
- Stoichiometry Definition in Chemistry
- 2nd Grade Math Word Problems
- Math Glossary: Mathematics Terms and Definitions
- Ideas for Thanksgiving Math Word Problems
- Sixth Grade Word Problems
- Learn to Calculate Percent Change
- Quiz 8th-Graders With These Math Word Problems
- How to Cancel Units - Chemistry Metric Conversions
- Simple Interest Worksheets With Answers

- Mathematicians
- Math Lessons
- Square Roots
- Math Calculators
Simple Algebra Problems – Easy Exercises with Solutions for Beginners
JUMP TO TOPIC
Understanding Algebraic Expressions
Breaking down algebra problems, solving algebraic equations, tackling algebra word problems, types of algebraic equations, algebra for different grades.
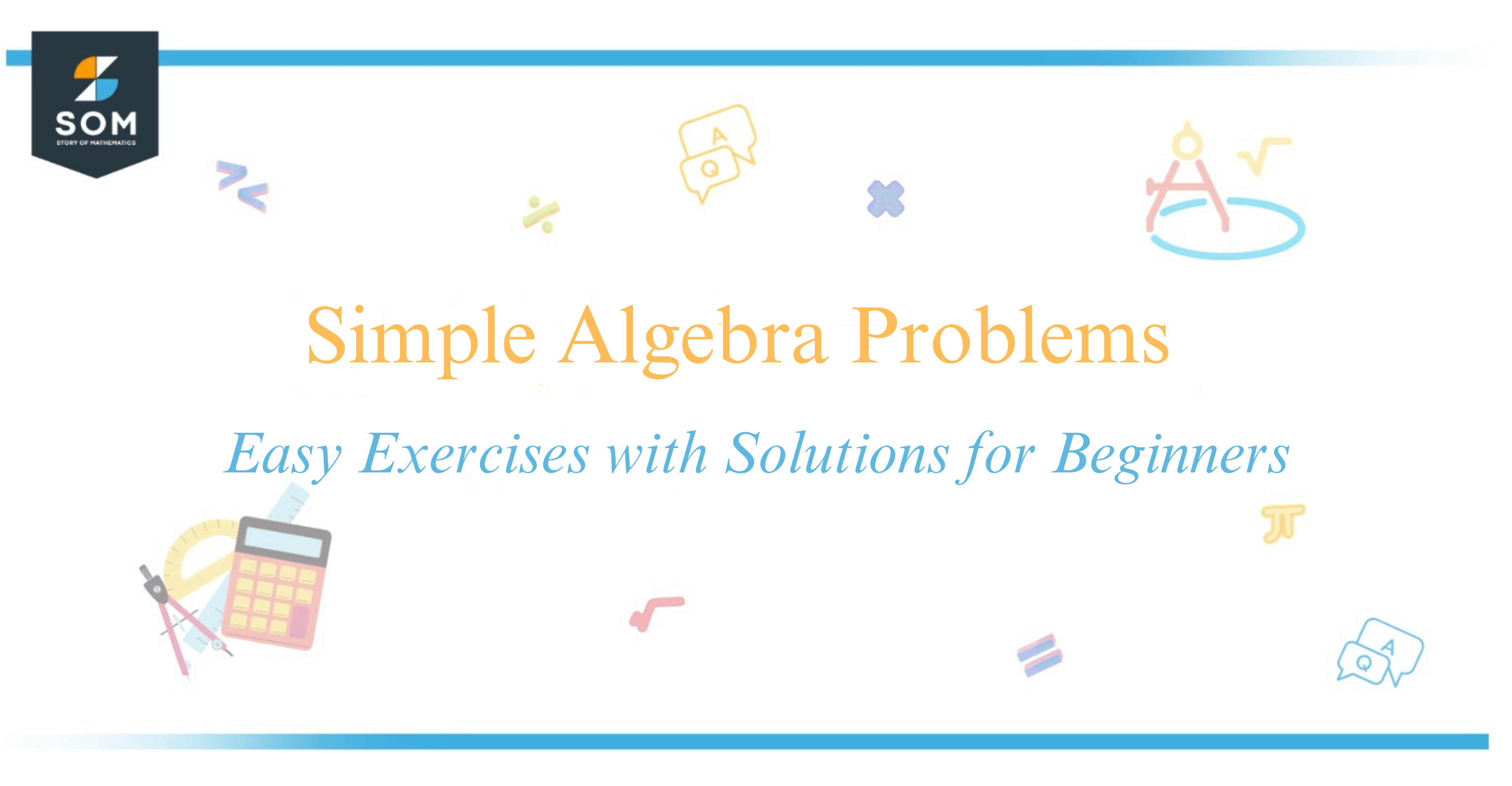
For instance, solving the equation (3x = 7) for (x) helps us understand how to isolate the variable to find its value.

I always find it fascinating how algebra serves as the foundation for more advanced topics in mathematics and science. Starting with basic problems such as ( $(x-1)^2 = [4\sqrt{(x-4)}]^2$ ) allows us to grasp key concepts and build the skills necessary for tackling more complex challenges.
So whether you’re refreshing your algebra skills or just beginning to explore this mathematical language, let’s dive into some examples and solutions to demystify the subject. Trust me, with a bit of practice, you’ll see algebra not just as a series of problems, but as a powerful tool that helps us solve everyday puzzles.
Simple Algebra Problems and Strategies
When I approach simple algebra problems, one of the first things I do is identify the variable.
The variable is like a placeholder for a number that I’m trying to find—a mystery I’m keen to solve. Typically represented by letters like ( x ) or ( y ), variables allow me to translate real-world situations into algebraic expressions and equations.
An algebraic expression is a mathematical phrase that can contain ordinary numbers, variables (like ( x ) or ( y )), and operators (like add, subtract, multiply, and divide). For example, ( 4x + 7 ) is an algebraic expression where ( x ) is the variable and the numbers ( 4 ) and ( 7 ) are terms. It’s important to manipulate these properly to maintain the equation’s balance.
Solving algebra problems often starts with simplifying expressions. Here’s a simple method to follow:
- Combine like terms : Terms that have the same variable can be combined. For instance, ( 3x + 4x = 7x ).
- Isolate the variable : Move the variable to one side of the equation. If the equation is ( 2x + 5 = 13 ), my job is to get ( x ) by itself by subtracting ( 5 ) from both sides, giving me ( 2x = 8 ).
With algebraic equations, the goal is to solve for the variable by performing the same operation on both sides. Here’s a table with an example:
Algebra word problems require translating sentences into equations. If a word problem says “I have six less than twice the number of apples than Bob,” and Bob has ( b ) apples, then I’d write the expression as ( 2b – 6 ).
Understanding these strategies helps me tackle basic algebra problems efficiently. Remember, practice makes perfect, and each problem is an opportunity to improve.
In algebra, we encounter a variety of equation types and each serves a unique role in problem-solving. Here, I’ll brief you about some typical forms.
Linear Equations : These are the simplest form, where the highest power of the variable is one. They take the general form ( ax + b = 0 ), where ( a ) and ( b ) are constants, and ( x ) is the variable. For example, ( 2x + 3 = 0 ) is a linear equation.
Polynomial Equations : Unlike for linear equations, polynomial equations can have variables raised to higher powers. The general form of a polynomial equation is ( $a_nx^n + a_{n-1}x^{n-1} + … + a_2x^2 + a_1x + a_0 = 0$ ). In this equation, ( n ) is the highest power, and ( $a_n$ ), ( $a_{n-1} $), …, ( $a_0$ ) represent the coefficients which can be any real number.
- Binomial Equations : They are a specific type of polynomial where there are exactly two terms. Like ($ x^2 – 4 $), which is also the difference of squares, a common format encountered in factoring.
To understand how equations can be solved by factoring, consider the quadratic equation ( $x^2$ – 5x + 6 = 0 ). I can factor this into ( (x-2)(x-3) = 0 ), which allows me to find the roots of the equation.
Here’s how some equations look when classified by degree:
Remember, identification and proper handling of these equations are essential in algebra as they form the basis for complex problem-solving.
In my experience with algebra, I’ve found that the journey begins as early as the 6th grade, where students get their first taste of this fascinating subject with the introduction of variables representing an unknown quantity.
I’ve created worksheets and activities aimed specifically at making this early transition engaging and educational.
6th Grade :
Moving forward, the complexity of algebraic problems increases:
7th and 8th Grades :
- Mastery of negative numbers: students practice operations like ( -3 – 4 ) or ( -5 $\times$ 2 ).
- Exploring the rules of basic arithmetic operations with negative numbers.
- Worksheets often contain numeric and literal expressions that help solidify their concepts.
Advanced topics like linear algebra are typically reserved for higher education. However, the solid foundation set in these early grades is crucial. I’ve developed materials to encourage students to understand and enjoy algebra’s logic and structure.
Remember, algebra is a tool that helps us quantify and solve problems, both numerical and abstract. My goal is to make learning these concepts, from numbers to numeric operations, as accessible as possible, while always maintaining a friendly approach to education.
I’ve walked through various simple algebra problems to help establish a foundational understanding of algebraic concepts. Through practice, you’ll find that these problems become more intuitive, allowing you to tackle more complex equations with confidence.
Remember, the key steps in solving any algebra problem include:
- Identifying variables and what they represent.
- Setting up the equation that reflects the problem statement.
- Applying algebraic rules such as the distributive property ($a(b + c) = ab + ac$), combining like terms, and inverse operations.
- Checking your solutions by substituting them back into the original equations to ensure they work.
As you continue to engage with algebra, consistently revisiting these steps will deepen your understanding and increase your proficiency. Don’t get discouraged by mistakes; they’re an important part of the learning process.
I hope that the straightforward problems I’ve presented have made algebra feel more manageable and a little less daunting. Happy solving!
- Pre Calculus
- Probability
- Sets & Set Theory
- Trigonometry
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Mathematics
- Exponents and Logarithms
How to Solve Algebraic Problems With Exponents
Last Updated: July 6, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by David Jia . David Jia is an Academic Tutor and the Founder of LA Math Tutoring, a private tutoring company based in Los Angeles, California. With over 10 years of teaching experience, David works with students of all ages and grades in various subjects, as well as college admissions counseling and test preparation for the SAT, ACT, ISEE, and more. After attaining a perfect 800 math score and a 690 English score on the SAT, David was awarded the Dickinson Scholarship from the University of Miami, where he graduated with a Bachelor’s degree in Business Administration. Additionally, David has worked as an instructor for online videos for textbook companies such as Larson Texts, Big Ideas Learning, and Big Ideas Math. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 76,692 times.
In algebra, the operations (adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing) performed on variables work the same as the operations performed on numbers. When performing these operations on exponents, however, the laws are different. By learning these special rules for exponents, you can easily simplify algebraic expressions that include them.
Solving a Problem with Exponents

Understanding the Laws of Exponents

Community Q&A

Things You'll Need
You might also like.

- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/operation-order-pemdas.html
- ↑ https://content.nroc.org/DevelopmentalMath/COURSE_TEXT2_RESOURCE/U11_L1_T2_text_final.html
- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/exponent.html
- ↑ http://www.mathwarehouse.com/algebra/exponents/index.php
- ↑ http://www.mathwarehouse.com/algebra/exponents/laws-of-exponents.php
- ↑ http://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/negative-exponents.html
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Deadra Simmons
Oct 30, 2017
Did this article help you?

Samantha Brizuela
Nov 17, 2018
Sammy Norman
Oct 5, 2016
Sep 11, 2023
Crystal Ellisor-Carrier
Nov 3, 2021


Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life

Get step-by-step solutions to your math problems

Try Math Solver

Get step-by-step explanations
Graph your math problems
Practice, practice, practice

Get math help in your language

Game Central
Related Concepts
The Tech Edvocate
- Advertisement
- Home Page Five (No Sidebar)
- Home Page Four
- Home Page Three
- Home Page Two
- Icons [No Sidebar]
- Left Sidbear Page
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- My Speaking Page
- Newsletter Sign Up Confirmation
- Newsletter Unsubscription
- Page Example
- Privacy Policy
- Protected Content
- Request a Product Review
- Shortcodes Examples
- Terms and Conditions
- The Edvocate
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- Write For Us
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Assistive Technology
- Child Development Tech
- Early Childhood & K-12 EdTech
- EdTech Futures
- EdTech News
- EdTech Policy & Reform
- EdTech Startups & Businesses
- Higher Education EdTech
- Online Learning & eLearning
- Parent & Family Tech
- Personalized Learning
- Product Reviews
- Tech Edvocate Awards
- School Ratings
How to Have a Garage Sale
How to be a modern christian girl, how to cook oha soup: 14 steps, 10 easy ways to keep wasps away from a wood deck, 3 ways to stay young looking after 40, 4 ways to delete add-ons, how to use advair, 4 ways to protect your assets from a lawsuit, discover your type of girl, 10 ways to wear a beige cardigan, how to solve word problems in algebra.
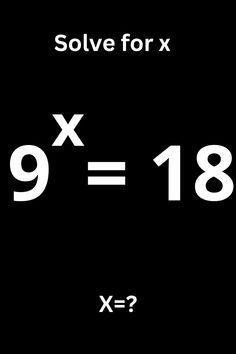
Introduction:
Word problems can be one of the most daunting aspects of algebra for many students. However, by following a few simple steps, you can master the art of solving word problems and improve your algebra skills. In this article, we will discuss the necessary steps to tackle word problems in algebra effectively.
Step 1: Read the problem carefully
The first step in solving any word problem is to read it thoroughly. Be sure to understand the problem’s context and the information provided. Look for clues and keywords that indicate relationships between variables.
Step 2: Identify the variables
Once you have a clear understanding of the problem, identify the unknown quantities or variables. For instance, if the problem involves finding the age of two siblings, you could represent their ages as “a” and “b.”
Step 3: Translate words into algebraic expressions
Convert the problem’s language into algebraic expressions involving variables and operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division. Look for key phrases like “sum,” “difference,” “product,” or “quotient” to guide your translation.
Step 4: Set up an equation (or equations)
Using your translated expressions from step 3, set up an equation that represents the given information. For more complex problems, you may need to write a system of equations that can be solved simultaneously.
Step 5: Solve the equation(s)
Now that you have an equation (or equations) to work with, use your algebra skills to solve for the unknown variable(s). You may need to perform steps like simplification, combining like terms, or using methods specific to linear equations or systems (e.g., substitution or elimination).
Step 6: Check your solution
Before accepting your answer as correct, take a moment to verify whether it makes sense within the context of the original problem. If you find any discrepancies or inconsistencies, revisit your steps to find the error and correct it.
Step 7: Write the final answer in a clear and concise manner
Once you are confident in your solution, present your final answer in a complete and easily understood form. Make sure to include any necessary units or labels to make your answer meaningful.
Conclusion:
By following these seven steps, you can efficiently solve word problems in algebra and boost your confidence in tackling these challenging problems. It takes time and practice but mastering this skill will make you more fluent in algebra and improve your overall mathematical abilities. Happy problem solving!
How to Breed Pit Bulls
How to say horse in spanish: 3 ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

3 Ways to Be Friends with Your Younger Sister

13 Ways to Soothe a Burnt Tongue
Easy Ways to Apply for Survivor

How to Tell Your Dog No: 12 Steps

3 Ways to Do Chicago Style Footnotes
Solver Title
Generating PDF...
- Pre Algebra Order of Operations Factors & Primes Fractions Long Arithmetic Decimals Exponents & Radicals Ratios & Proportions Percent Modulo Number Line Mean, Median & Mode
- Algebra Equations Inequalities System of Equations System of Inequalities Basic Operations Algebraic Properties Partial Fractions Polynomials Rational Expressions Sequences Power Sums Interval Notation Pi (Product) Notation Induction Logical Sets Word Problems
- Pre Calculus Equations Inequalities Scientific Calculator Scientific Notation Arithmetics Complex Numbers Polar/Cartesian Simultaneous Equations System of Inequalities Polynomials Rationales Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Coordinate Geometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Conic Sections Trigonometry
- Calculus Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series Fourier Transform
- Functions Line Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Conic Sections Transformation
- Linear Algebra Matrices Vectors
- Trigonometry Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify
- Statistics Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Average Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability Mid-Range Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal Distribution
- Physics Mechanics
- Chemistry Chemical Reactions Chemical Properties
- Finance Simple Interest Compound Interest Present Value Future Value
- Economics Point of Diminishing Return
- Conversions Roman Numerals Radical to Exponent Exponent to Radical To Fraction To Decimal To Mixed Number To Improper Fraction Radians to Degrees Degrees to Radians Hexadecimal Scientific Notation Distance Weight Time Volume
- Pre Algebra
- One-Step Addition
- One-Step Subtraction
- One-Step Multiplication
- One-Step Division
- One-Step Decimals
- Two-Step Integers
- Two-Step Add/Subtract
- Two-Step Multiply/Divide
- Two-Step Fractions
- Two-Step Decimals
- Multi-Step Integers
- Multi-Step with Parentheses
- Multi-Step Rational
- Multi-Step Fractions
- Multi-Step Decimals
- Solve by Factoring
- Completing the Square
- Quadratic Formula
- Biquadratic
- Logarithmic
- Exponential
- Rational Roots
- Floor/Ceiling
- Equation Given Roots
- Newton Raphson
- Substitution
- Elimination
- Cramer's Rule
- Gaussian Elimination
- System of Inequalities
- Perfect Squares
- Difference of Squares
- Difference of Cubes
- Sum of Cubes
- Polynomials
- Distributive Property
- FOIL method
- Perfect Cubes
- Binomial Expansion
- Negative Rule
- Product Rule
- Quotient Rule
- Expand Power Rule
- Fraction Exponent
- Exponent Rules
- Exponential Form
- Logarithmic Form
- Absolute Value
- Rational Number
- Powers of i
- Partial Fractions
- Is Polynomial
- Leading Coefficient
- Leading Term
- Standard Form
- Complete the Square
- Synthetic Division
- Linear Factors
- Rationalize Denominator
- Rationalize Numerator
- Identify Type
- Convergence
- Interval Notation
- Pi (Product) Notation
- Boolean Algebra
- Truth Table
- Mutual Exclusive
- Cardinality
- Caretesian Product
- Age Problems
- Distance Problems
- Cost Problems
- Investment Problems
- Number Problems
- Percent Problems
- Addition/Subtraction
- Multiplication/Division
- Dice Problems
- Coin Problems
- Card Problems
- Pre Calculus
- Linear Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Conversions

Most Used Actions
Number line.
- -x+3\gt 2x+1
- (x+5)(x-5)\gt 0
- 10^{1-x}=10^4
- \sqrt{3+x}=-2
- 6+11x+6x^2+x^3=0
- factor\:x^{2}-5x+6
- simplify\:\frac{2}{3}-\frac{3}{2}+\frac{1}{4}
- x+2y=2x-5,\:x-y=3
- How do you solve algebraic expressions?
- To solve an algebraic expression, simplify the expression by combining like terms, isolate the variable on one side of the equation by using inverse operations. Then, solve the equation by finding the value of the variable that makes the equation true.
- What are the basics of algebra?
- The basics of algebra are the commutative, associative, and distributive laws.
- What are the 3 rules of algebra?
- The basic rules of algebra are the commutative, associative, and distributive laws.
- What is the golden rule of algebra?
- The golden rule of algebra states Do unto one side of the equation what you do to others. Meaning, whatever operation is being used on one side of equation, the same will be used on the other side too.
- What are the 5 basic laws of algebra?
- The basic laws of algebra are the Commutative Law For Addition, Commutative Law For Multiplication, Associative Law For Addition, Associative Law For Multiplication, and the Distributive Law.
algebra-calculator
- High School Math Solutions – Systems of Equations Calculator, Elimination A system of equations is a collection of two or more equations with the same set of variables. In this blog post,...
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.
Equation Solver
Enter the Equation you want to solve into the editor.
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Share Podcast

Do You Understand the Problem You’re Trying to Solve?
To solve tough problems at work, first ask these questions.
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
Problem solving skills are invaluable in any job. But all too often, we jump to find solutions to a problem without taking time to really understand the dilemma we face, according to Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg , an expert in innovation and the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
In this episode, you’ll learn how to reframe tough problems by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that contribute to the situation. You’ll also learn why searching for just one root cause can be misleading.
Key episode topics include: leadership, decision making and problem solving, power and influence, business management.
HBR On Leadership curates the best case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, to help you unlock the best in those around you. New episodes every week.
- Listen to the original HBR IdeaCast episode: The Secret to Better Problem Solving (2016)
- Find more episodes of HBR IdeaCast
- Discover 100 years of Harvard Business Review articles, case studies, podcasts, and more at HBR.org .
HANNAH BATES: Welcome to HBR on Leadership , case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, hand-selected to help you unlock the best in those around you.
Problem solving skills are invaluable in any job. But even the most experienced among us can fall into the trap of solving the wrong problem.
Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg says that all too often, we jump to find solutions to a problem – without taking time to really understand what we’re facing.
He’s an expert in innovation, and he’s the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
In this episode, you’ll learn how to reframe tough problems, by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that contribute to the situation. You’ll also learn why searching for one root cause can be misleading. And you’ll learn how to use experimentation and rapid prototyping as problem-solving tools.
This episode originally aired on HBR IdeaCast in December 2016. Here it is.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Welcome to the HBR IdeaCast from Harvard Business Review. I’m Sarah Green Carmichael.
Problem solving is popular. People put it on their resumes. Managers believe they excel at it. Companies count it as a key proficiency. We solve customers’ problems.
The problem is we often solve the wrong problems. Albert Einstein and Peter Drucker alike have discussed the difficulty of effective diagnosis. There are great frameworks for getting teams to attack true problems, but they’re often hard to do daily and on the fly. That’s where our guest comes in.
Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg is a consultant who helps companies and managers reframe their problems so they can come up with an effective solution faster. He asks the question “Are You Solving The Right Problems?” in the January-February 2017 issue of Harvard Business Review. Thomas, thank you so much for coming on the HBR IdeaCast .
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Thanks for inviting me.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, I thought maybe we could start by talking about the problem of talking about problem reframing. What is that exactly?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Basically, when people face a problem, they tend to jump into solution mode to rapidly, and very often that means that they don’t really understand, necessarily, the problem they’re trying to solve. And so, reframing is really a– at heart, it’s a method that helps you avoid that by taking a second to go in and ask two questions, basically saying, first of all, wait. What is the problem we’re trying to solve? And then crucially asking, is there a different way to think about what the problem actually is?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, I feel like so often when this comes up in meetings, you know, someone says that, and maybe they throw out the Einstein quote about you spend an hour of problem solving, you spend 55 minutes to find the problem. And then everyone else in the room kind of gets irritated. So, maybe just give us an example of maybe how this would work in practice in a way that would not, sort of, set people’s teeth on edge, like oh, here Sarah goes again, reframing the whole problem instead of just solving it.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I mean, you’re bringing up something that’s, I think is crucial, which is to create legitimacy for the method. So, one of the reasons why I put out the article is to give people a tool to say actually, this thing is still important, and we need to do it. But I think the really critical thing in order to make this work in a meeting is actually to learn how to do it fast, because if you have the idea that you need to spend 30 minutes in a meeting delving deeply into the problem, I mean, that’s going to be uphill for most problems. So, the critical thing here is really to try to make it a practice you can implement very, very rapidly.
There’s an example that I would suggest memorizing. This is the example that I use to explain very rapidly what it is. And it’s basically, I call it the slow elevator problem. You imagine that you are the owner of an office building, and that your tenants are complaining that the elevator’s slow.
Now, if you take that problem framing for granted, you’re going to start thinking creatively around how do we make the elevator faster. Do we install a new motor? Do we have to buy a new lift somewhere?
The thing is, though, if you ask people who actually work with facilities management, well, they’re going to have a different solution for you, which is put up a mirror next to the elevator. That’s what happens is, of course, that people go oh, I’m busy. I’m busy. I’m– oh, a mirror. Oh, that’s beautiful.
And then they forget time. What’s interesting about that example is that the idea with a mirror is actually a solution to a different problem than the one you first proposed. And so, the whole idea here is once you get good at using reframing, you can quickly identify other aspects of the problem that might be much better to try to solve than the original one you found. It’s not necessarily that the first one is wrong. It’s just that there might be better problems out there to attack that we can, means we can do things much faster, cheaper, or better.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, in that example, I can understand how A, it’s probably expensive to make the elevator faster, so it’s much cheaper just to put up a mirror. And B, maybe the real problem people are actually feeling, even though they’re not articulating it right, is like, I hate waiting for the elevator. But if you let them sort of fix their hair or check their teeth, they’re suddenly distracted and don’t notice.
But if you have, this is sort of a pedestrian example, but say you have a roommate or a spouse who doesn’t clean up the kitchen. Facing that problem and not having your elegant solution already there to highlight the contrast between the perceived problem and the real problem, how would you take a problem like that and attack it using this method so that you can see what some of the other options might be?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Right. So, I mean, let’s say it’s you who have that problem. I would go in and say, first of all, what would you say the problem is? Like, if you were to describe your view of the problem, what would that be?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: I hate cleaning the kitchen, and I want someone else to clean it up.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: OK. So, my first observation, you know, that somebody else might not necessarily be your spouse. So, already there, there’s an inbuilt assumption in your question around oh, it has to be my husband who does the cleaning. So, it might actually be worth, already there to say, is that really the only problem you have? That you hate cleaning the kitchen, and you want to avoid it? Or might there be something around, as well, getting a better relationship in terms of how you solve problems in general or establishing a better way to handle small problems when dealing with your spouse?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Or maybe, now that I’m thinking that, maybe the problem is that you just can’t find the stuff in the kitchen when you need to find it.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Right, and so that’s an example of a reframing, that actually why is it a problem that the kitchen is not clean? Is it only because you hate the act of cleaning, or does it actually mean that it just takes you a lot longer and gets a lot messier to actually use the kitchen, which is a different problem. The way you describe this problem now, is there anything that’s missing from that description?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: That is a really good question.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Other, basically asking other factors that we are not talking about right now, and I say those because people tend to, when given a problem, they tend to delve deeper into the detail. What often is missing is actually an element outside of the initial description of the problem that might be really relevant to what’s going on. Like, why does the kitchen get messy in the first place? Is it something about the way you use it or your cooking habits? Is it because the neighbor’s kids, kind of, use it all the time?
There might, very often, there might be issues that you’re not really thinking about when you first describe the problem that actually has a big effect on it.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: I think at this point it would be helpful to maybe get another business example, and I’m wondering if you could tell us the story of the dog adoption problem.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Yeah. This is a big problem in the US. If you work in the shelter industry, basically because dogs are so popular, more than 3 million dogs every year enter a shelter, and currently only about half of those actually find a new home and get adopted. And so, this is a problem that has persisted. It’s been, like, a structural problem for decades in this space. In the last three years, where people found new ways to address it.
So a woman called Lori Weise who runs a rescue organization in South LA, and she actually went in and challenged the very idea of what we were trying to do. She said, no, no. The problem we’re trying to solve is not about how to get more people to adopt dogs. It is about keeping the dogs with their first family so they never enter the shelter system in the first place.
In 2013, she started what’s called a Shelter Intervention Program that basically works like this. If a family comes and wants to hand over their dog, these are called owner surrenders. It’s about 30% of all dogs that come into a shelter. All they would do is go up and ask, if you could, would you like to keep your animal? And if they said yes, they would try to fix whatever helped them fix the problem, but that made them turn over this.
And sometimes that might be that they moved into a new building. The landlord required a deposit, and they simply didn’t have the money to put down a deposit. Or the dog might need a $10 rabies shot, but they didn’t know how to get access to a vet.
And so, by instigating that program, just in the first year, she took her, basically the amount of dollars they spent per animal they helped went from something like $85 down to around $60. Just an immediate impact, and her program now is being rolled out, is being supported by the ASPCA, which is one of the big animal welfare stations, and it’s being rolled out to various other places.
And I think what really struck me with that example was this was not dependent on having the internet. This was not, oh, we needed to have everybody mobile before we could come up with this. This, conceivably, we could have done 20 years ago. Only, it only happened when somebody, like in this case Lori, went in and actually rethought what the problem they were trying to solve was in the first place.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, what I also think is so interesting about that example is that when you talk about it, it doesn’t sound like the kind of thing that would have been thought of through other kinds of problem solving methods. There wasn’t necessarily an After Action Review or a 5 Whys exercise or a Six Sigma type intervention. I don’t want to throw those other methods under the bus, but how can you get such powerful results with such a very simple way of thinking about something?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: That was something that struck me as well. This, in a way, reframing and the idea of the problem diagnosis is important is something we’ve known for a long, long time. And we’ve actually have built some tools to help out. If you worked with us professionally, you are familiar with, like, Six Sigma, TRIZ, and so on. You mentioned 5 Whys. A root cause analysis is another one that a lot of people are familiar with.
Those are our good tools, and they’re definitely better than nothing. But what I notice when I work with the companies applying those was those tools tend to make you dig deeper into the first understanding of the problem we have. If it’s the elevator example, people start asking, well, is that the cable strength, or is the capacity of the elevator? That they kind of get caught by the details.
That, in a way, is a bad way to work on problems because it really assumes that there’s like a, you can almost hear it, a root cause. That you have to dig down and find the one true problem, and everything else was just symptoms. That’s a bad way to think about problems because problems tend to be multicausal.
There tend to be lots of causes or levers you can potentially press to address a problem. And if you think there’s only one, if that’s the right problem, that’s actually a dangerous way. And so I think that’s why, that this is a method I’ve worked with over the last five years, trying to basically refine how to make people better at this, and the key tends to be this thing about shifting out and saying, is there a totally different way of thinking about the problem versus getting too caught up in the mechanistic details of what happens.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: What about experimentation? Because that’s another method that’s become really popular with the rise of Lean Startup and lots of other innovation methodologies. Why wouldn’t it have worked to, say, experiment with many different types of fixing the dog adoption problem, and then just pick the one that works the best?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: You could say in the dog space, that’s what’s been going on. I mean, there is, in this industry and a lot of, it’s largely volunteer driven. People have experimented, and they found different ways of trying to cope. And that has definitely made the problem better. So, I wouldn’t say that experimentation is bad, quite the contrary. Rapid prototyping, quickly putting something out into the world and learning from it, that’s a fantastic way to learn more and to move forward.
My point is, though, that I feel we’ve come to rely too much on that. There’s like, if you look at the start up space, the wisdom is now just to put something quickly into the market, and then if it doesn’t work, pivot and just do more stuff. What reframing really is, I think of it as the cognitive counterpoint to prototyping. So, this is really a way of seeing very quickly, like not just working on the solution, but also working on our understanding of the problem and trying to see is there a different way to think about that.
If you only stick with experimentation, again, you tend to sometimes stay too much in the same space trying minute variations of something instead of taking a step back and saying, wait a minute. What is this telling us about what the real issue is?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, to go back to something that we touched on earlier, when we were talking about the completely hypothetical example of a spouse who does not clean the kitchen–
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Completely, completely hypothetical.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Yes. For the record, my husband is a great kitchen cleaner.
You started asking me some questions that I could see immediately were helping me rethink that problem. Is that kind of the key, just having a checklist of questions to ask yourself? How do you really start to put this into practice?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I think there are two steps in that. The first one is just to make yourself better at the method. Yes, you should kind of work with a checklist. In the article, I kind of outlined seven practices that you can use to do this.
But importantly, I would say you have to consider that as, basically, a set of training wheels. I think there’s a big, big danger in getting caught in a checklist. This is something I work with.
My co-author Paddy Miller, it’s one of his insights. That if you start giving people a checklist for things like this, they start following it. And that’s actually a problem, because what you really want them to do is start challenging their thinking.
So the way to handle this is to get some practice using it. Do use the checklist initially, but then try to step away from it and try to see if you can organically make– it’s almost a habit of mind. When you run into a colleague in the hallway and she has a problem and you have five minutes, like, delving in and just starting asking some of those questions and using your intuition to say, wait, how is she talking about this problem? And is there a question or two I can ask her about the problem that can help her rethink it?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Well, that is also just a very different approach, because I think in that situation, most of us can’t go 30 seconds without jumping in and offering solutions.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Very true. The drive toward solutions is very strong. And to be clear, I mean, there’s nothing wrong with that if the solutions work. So, many problems are just solved by oh, you know, oh, here’s the way to do that. Great.
But this is really a powerful method for those problems where either it’s something we’ve been banging our heads against tons of times without making progress, or when you need to come up with a really creative solution. When you’re facing a competitor with a much bigger budget, and you know, if you solve the same problem later, you’re not going to win. So, that basic idea of taking that approach to problems can often help you move forward in a different way than just like, oh, I have a solution.
I would say there’s also, there’s some interesting psychological stuff going on, right? Where you may have tried this, but if somebody tries to serve up a solution to a problem I have, I’m often resistant towards them. Kind if like, no, no, no, no, no, no. That solution is not going to work in my world. Whereas if you get them to discuss and analyze what the problem really is, you might actually dig something up.
Let’s go back to the kitchen example. One powerful question is just to say, what’s your own part in creating this problem? It’s very often, like, people, they describe problems as if it’s something that’s inflicted upon them from the external world, and they are innocent bystanders in that.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Right, or crazy customers with unreasonable demands.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Exactly, right. I don’t think I’ve ever met an agency or consultancy that didn’t, like, gossip about their customers. Oh, my god, they’re horrible. That, you know, classic thing, why don’t they want to take more risk? Well, risk is bad.
It’s their business that’s on the line, not the consultancy’s, right? So, absolutely, that’s one of the things when you step into a different mindset and kind of, wait. Oh yeah, maybe I actually am part of creating this problem in a sense, as well. That tends to open some new doors for you to move forward, in a way, with stuff that you may have been struggling with for years.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, we’ve surfaced a couple of questions that are useful. I’m curious to know, what are some of the other questions that you find yourself asking in these situations, given that you have made this sort of mental habit that you do? What are the questions that people seem to find really useful?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: One easy one is just to ask if there are any positive exceptions to the problem. So, was there day where your kitchen was actually spotlessly clean? And then asking, what was different about that day? Like, what happened there that didn’t happen the other days? That can very often point people towards a factor that they hadn’t considered previously.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: We got take-out.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: S,o that is your solution. Take-out from [INAUDIBLE]. That might have other problems.
Another good question, and this is a little bit more high level. It’s actually more making an observation about labeling how that person thinks about the problem. And what I mean with that is, we have problem categories in our head. So, if I say, let’s say that you describe a problem to me and say, well, we have a really great product and are, it’s much better than our previous product, but people aren’t buying it. I think we need to put more marketing dollars into this.
Now you can go in and say, that’s interesting. This sounds like you’re thinking of this as a communications problem. Is there a different way of thinking about that? Because you can almost tell how, when the second you say communications, there are some ideas about how do you solve a communications problem. Typically with more communication.
And what you might do is go in and suggest, well, have you considered that it might be, say, an incentive problem? Are there incentives on behalf of the purchasing manager at your clients that are obstructing you? Might there be incentive issues with your own sales force that makes them want to sell the old product instead of the new one?
So literally, just identifying what type of problem does this person think about, and is there different potential way of thinking about it? Might it be an emotional problem, a timing problem, an expectations management problem? Thinking about what label of what type of problem that person is kind of thinking as it of.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: That’s really interesting, too, because I think so many of us get requests for advice that we’re really not qualified to give. So, maybe the next time that happens, instead of muddying my way through, I will just ask some of those questions that we talked about instead.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: That sounds like a good idea.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, Thomas, this has really helped me reframe the way I think about a couple of problems in my own life, and I’m just wondering. I know you do this professionally, but is there a problem in your life that thinking this way has helped you solve?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I’ve, of course, I’ve been swallowing my own medicine on this, too, and I think I have, well, maybe two different examples, and in one case somebody else did the reframing for me. But in one case, when I was younger, I often kind of struggled a little bit. I mean, this is my teenage years, kind of hanging out with my parents. I thought they were pretty annoying people. That’s not really fair, because they’re quite wonderful, but that’s what life is when you’re a teenager.
And one of the things that struck me, suddenly, and this was kind of the positive exception was, there was actually an evening where we really had a good time, and there wasn’t a conflict. And the core thing was, I wasn’t just seeing them in their old house where I grew up. It was, actually, we were at a restaurant. And it suddenly struck me that so much of the sometimes, kind of, a little bit, you love them but they’re annoying kind of dynamic, is tied to the place, is tied to the setting you are in.
And of course, if– you know, I live abroad now, if I visit my parents and I stay in my old bedroom, you know, my mother comes in and wants to wake me up in the morning. Stuff like that, right? And it just struck me so, so clearly that it’s– when I change this setting, if I go out and have dinner with them at a different place, that the dynamic, just that dynamic disappears.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Well, Thomas, this has been really, really helpful. Thank you for talking with me today.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Thank you, Sarah.
HANNAH BATES: That was Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg in conversation with Sarah Green Carmichael on the HBR IdeaCast. He’s an expert in problem solving and innovation, and he’s the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
We’ll be back next Wednesday with another hand-picked conversation about leadership from the Harvard Business Review. If you found this episode helpful, share it with your friends and colleagues, and follow our show on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts. While you’re there, be sure to leave us a review.
We’re a production of Harvard Business Review. If you want more podcasts, articles, case studies, books, and videos like this, find it all at HBR dot org.
This episode was produced by Anne Saini, and me, Hannah Bates. Ian Fox is our editor. Music by Coma Media. Special thanks to Maureen Hoch, Adi Ignatius, Karen Player, Ramsey Khabbaz, Nicole Smith, Anne Bartholomew, and you – our listener.
See you next week.
- Subscribe On:
Latest in this series
This article is about leadership.
- Decision making and problem solving
- Power and influence
- Business management
Partner Center
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 2: Algebraic expressions
About this unit, introduction to variables.
- What is a variable? (Opens a modal)
- Why aren't we using the multiplication sign? (Opens a modal)
- Evaluating an expression with one variable (Opens a modal)
- Evaluating expressions with one variable (Opens a modal)
- Evaluating expressions with one variable Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
Substitution & evaluating expressions
- Evaluating expressions with two variables (Opens a modal)
- Evaluating expressions with multiple variables Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Writing algebraic expressions
- Writing basic expressions with variables (Opens a modal)
- Writing expressions with variables (Opens a modal)
- Writing expressions with variables & parentheses (Opens a modal)
- Writing basic expressions with variables Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
- Writing expressions with variables Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Combining like terms
- Intro to combining like terms (Opens a modal)
- Combining like terms with negative coefficients & distribution (Opens a modal)
- Combining like terms with negative coefficients (Opens a modal)
- Combining like terms with rational coefficients (Opens a modal)
- Combining like terms with negative coefficients Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
- Combining like terms with negative coefficients & distribution Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Combining like terms with rational coefficients Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Distributive property
- Distributive property with variables (Opens a modal)
- Distributive property with variables Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Factor with distributive property (variables) Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Equivalent algebraic expressions
- Equivalent expressions (Opens a modal)
- Equivalent expressions Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
Nested fractions
- Nested fractions (Opens a modal)
- Nested fractions Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. ... While we cover a very wide range of problems, we are currently unable to assist with this specific problem. I spoke with my team and we will make note of this for future training.
QuickMath can solve algebra, equations, calculus, matrices, graphs and more. Enter your problem and get instant solutions with step-by-step explanations.
Algebraic word problems are questions that require translating sentences to equations, then solving those equations. The equations we need to write will only involve. basic arithmetic operations. and a single variable. Usually, the variable represents an unknown quantity in a real-life scenario.
Solve problems from Pre Algebra to Calculus step-by-step . Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Is there a step by step calculator for math? Symbolab is the best step by step calculator for a wide range of math problems, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus and linear algebra. It shows you the solution, graph, detailed steps and explanations ...
Get math help in your language. Works in Spanish, Hindi, German, and more. Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app.
Algebra (all content) 20 units · 412 skills. Unit 1 Introduction to algebra. Unit 2 Solving basic equations & inequalities (one variable, linear) Unit 3 Linear equations, functions, & graphs. Unit 4 Sequences. Unit 5 System of equations. Unit 6 Two-variable inequalities. Unit 7 Functions. Unit 8 Absolute value equations, functions, & inequalities.
Why we do the same thing to both sides: Variable on both sides. Intro to equations with variables on both sides. Equations with variables on both sides: 20-7x=6x-6. Equation with variables on both sides: fractions. Equation with the variable in the denominator.
How to Solve. Algebra is just like a puzzle where we start with something like "x − 2 = 4" and we want to end up with something like "x = 6". But instead of saying "obviously x=6", use this neat step-by-step approach: Work out what to remove to get "x = ..." Remove it by doing the opposite (adding is the opposite of subtracting)
In fact, solving an equation is just like solving a puzzle. And like puzzles, there are things we can (and cannot) do. Here are some things we can do: Add or Subtract the same value from both sides; Clear out any fractions by Multiplying every term by the bottom parts; Divide every term by the same nonzero value; Combine Like Terms; Factoring
Solving Algebra word problems is useful in helping you to solve earthly problems. While the 5 steps of Algebra problem solving are listed below, the following will help you learn how to first identify the problem. Identify the problem. Identify what you know. Make a plan.
First, move everything that isn't under the radical sign to the other side of the equation: √ (2x+9) = 5. Then, square both sides to remove the radical: (√ (2x+9)) 2 = 5 2 =. 2x + 9 = 25. Now, solve the equation as you normally would by combining the constants and isolating the variable: 2x = 25 - 9 =. 2x = 16.
Solving algebra problems often starts with simplifying expressions. Here's a simple method to follow: Combine like terms: Terms that have the same variable can be combined. For instance, ( 3x + 4x = 7x ). Isolate the variable: Move the variable to one side of the equation. If the equation is ( 2x + 5 = 13 ), my job is to get ( x ) by itself ...
Popular Calculators. Fractions Radical Equation Factoring Inverse Quadratic Simplify Slope Domain Antiderivatives Polynomial Equation Log Equation Cross Product Partial Derivative Implicit Derivative Tangent Complex Numbers. Symbolab: equation search and math solver - solves algebra, trigonometry and calculus problems step by step.
The Algebra 1 course, often taught in the 9th grade, covers Linear equations, inequalities, functions, and graphs; Systems of equations and inequalities; Extension of the concept of a function; Exponential models; and Quadratic equations, functions, and graphs. Khan Academy's Algebra 1 course is built to deliver a comprehensive, illuminating, engaging, and Common Core aligned experience!
1. Solve expressions with a positive exponent. An exponent simply tells you how many times you multiply the base (big number) by itself. [4] For example, is the same as . Plugging in a number, you would have. =. =. Expressions to the first degree (expressions with an exponent of 1) always simplify to the base.
This pre-algebra video tutorial explains the process of solving two step equations with fractions and variables on both sides. It also explains how to solve...
Algebra Calculator. Graphing Calculator. Matrix Calculator. Draw, Scan, Solve, and Learn! ... Get step-by-step explanations. See how to solve problems and show your work—plus get definitions for mathematical concepts. Graph your math problems. Instantly graph any equation to visualize your function and understand the relationship between ...
An example with three indeterminates is x³ + 2xyz² − yz + 1. Quadratic equation. The values of x that satisfy the equation are called solutions of the equation, and roots or zeros of the expression on its left-hand side. A quadratic equation has at most two solutions. If there is only one solution, one says that it is a double root.
Intro to equations with variables on both sides. (Opens a modal) Equations with variables on both sides: 20-7x=6x-6. (Opens a modal) Equation with variables on both sides: fractions. (Opens a modal) Equation with the variable in the denominator. (Opens a modal) Figuring out missing algebraic step.
The first step in solving any word problem is to read it thoroughly. Be sure to understand the problem's context and the information provided. Look for clues and keywords that indicate relationships between variables. Step 2: Identify the variables. Once you have a clear understanding of the problem, identify the unknown quantities or variables.
To solve an algebraic expression, simplify the expression by combining like terms, isolate the variable on one side of the equation by using inverse operations. Then, solve the equation by finding the value of the variable that makes the equation true.
Algebra. Equation Solver. Step 1: Enter the Equation you want to solve into the editor. The equation calculator allows you to take a simple or complex equation and solve by best method possible. Step 2: Click the blue arrow to submit and see the result! The equation solver allows you to enter your problem and solve the equation to see the result.
★Algebra is a method to solve for unknown values, using logic, balance, and Arithmetic. so… •Review Arithmetic, (algebra is full of fractions, exponents, signed integers, etc), and… Take advantage of, and learn from Khan Academy's Algebra prep classes. • Pre-Algebra • Get Ready for Algebra 1 Continued in Comments
In this episode, you'll learn how to reframe tough problems by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that contribute to the situation. You'll also learn why searching ...
The core idea in algebra is using letters to represent relationships between numbers without specifying what those numbers are! Let's explore the basics of communicating in algebraic expressions.