E-banking Overview: Concepts, Challenges and Solutions
- Published: 28 November 2020
- Volume 117 , pages 1059–1078, ( 2021 )

Cite this article
- Belbergui Chaimaa 1 ,
- Elkamoun Najib 1 &
- Hilal Rachid 1
4218 Accesses
21 Citations
1 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The expansion of information technology has led to a new form of banking. Traditional banking, based on the physical presence of the customer, is only a part of banking activities. In the last few years, electronic banking has emerged, adopting a new distribution channels like Internet and mobile services. The main goal was to allow businesses to improve the quality of service delivery and reduce transaction cost, and anytime and anywhere service demand for customers. However, it increased the vulnerability to fraudulent activities like spamming, phishing and credit card frauds. Then, the main challenge that opposes electronic banking is ensuring banking security. In this context, this paper aims to provide an overview of the electronic banking service highlighting various aspects, investigating various challenges and risks, and discussing some proposed solutions.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

New Trends in the Banking Sector and the Development of E-Banking

A Study of Digital Banking: Security Issues and Challenges

Study of Online Bank in E-Commerce Environment
Kurnia, S., Peng, F., & Liu, Y. R. (2010). Understanding the adoption of electronic banking in China. In 43rd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences , Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, pp. 1–10.
Vrîncianu, M., & Popa, L. A. (2010). Considerations regarding the security and protection of e-banking services consumers’ interests. The Amfiteatru Economic Journal , 12 (28), 388–403.
Google Scholar
Peotta, L., Holtz, M. D., David, B. M., Deus, F. G., & Timoteo de Sousa, R. (2011). A formal classification of internet banking attacks and vulnerabilities. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology, 3 (1), 186–197.
Article Google Scholar
Drig, I., & Isac, C. (2014). E-banking services – Features, challenges and benefits. 10.
Chavan, J. (2013). Internet banking – Benefits and challenges in an emerging economy. International Journal of Research in Business Management, 1 (1), 19–26.
MathSciNet Google Scholar
Singhal, D., & Padhmanabhan, V. (2009). A study on customer perception towards internet banking: Identifying major contributing factors. Journal of Nepalese Business Studies, 5 (1), 101–111.
Liao, S., Shao, Y. P., Wang, H., & Chen, A. (1999). The adoption of virtual banking: An empirical study. International Journal of Information Management, 19 (1), 63–74.
Bahl, D. S. (2012). E-banking: Challenges and policy implications. International Journal of Computing & Business Research , 229–6166.
Zarei, S. (2011). Risk management of internet banking. In 10th WSEAS International conference on Artificial Intelligence, Knowledge Engineering and Data Bases , Cambridge, UK, pp. 134–139.
Hanaek, P., Malinka, K., & Schafer, J. (2008). E-banking security - comparative study. In 42nd Annual IEEE International Carnahan Conference on Security Technology , Prague, Czech Republic, pp. 326–330.
Omariba, Z. B., & Masese, N. B. (2012). Security and privacy of electronic banking. International Journal of Computer Science Issues (IJCSI), 9 (4), 432–446.
Park, K. C., Shin, J. W., & Lee, B. G. (2014). Analysis of authentication methods for smartphone banking service using ANP. KSII Transactions on Internet & Information Systems, 8 (6).
Brar, T. P. S., Sharma, D., & Khurmi, S. S. (2012). Vulnerabilities in e-banking: A study of various security aspects in e-banking. International Journal of Computing & Business Research .
Yang, Y. J. (1997). The security of electronic. In International Systems Security Conference , pp. 41–52.
Yang, J., Cheng, L., & Luo, X. (2009). A comparative study on e-banking services between China and USA. International Journal of Electronic Finance, 3 (3), 235–252.
Zahid, N., Mujtaba, A., & Riaz, A. (2010). Consumer acceptance of online banking. European Journal of Economics, Finance and Administrative Sciences, 27 (1).
Geetha, K. T., & Malarvizhi, V. (2011). Acceptance of E-banking among customers: An empirical investigation in India. The Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce, 15 (2), 1–17.
Deb, M., & Lomo-David, E. (2014). An empirical examination of customers’ adoption of m-banking in India. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 32 (4), 475–494.
Lee, J. H., Lim, W. G., & Lim, J. I. (2013). A study of the security of Internet banking and financial private information in South Korea. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 58 (1–2), 117–131.
Moga, L., Nor, K., Neculita, M., & Khani, N. (2012). Trust and security in e-banking adoption in Romania. Communications of the IBIMA , 1–10.
Komb, F., Korau, M., Belás, J., & Korauš, A. (2016). Electronic banking security and customer satisfaction in commercial banks. Journal of Security and Sustainability Issues, 5 (3), 411–422.
Ranaweera, H. (2019). Risk of electronic payments of the banking sector in Sri Lanka: Case of Colombo district. 4 (1).
Rajaratnam, A. (2019). The factors influencing on internet banking adoption in Trincomalee District, Sri Lanka, Sri Lanka. International Research Journal of Advanced Engineering and Science, 4 (1), 160–164.
Hasan, A. S., Baten, M. A., Kamil, A. A., & Parveen, S. (2010). Adoption of e-banking in Bangladesh: An exploratory study. African Journal of Business Management, 4 (13), 2718–2727.
Jalal, A., Marzooq, J., & Nabi, H. A. (2011). Evaluating the impacts of online banking factors on motivating the process of e-banking. Journal of Management and Sustainability, 1 (1).
Abukhzam, M., & Lee, A. (2010). Factors affecting bank staff attitude towards E-banking adoption in Libya. The Electronic Journal of Information Systems in Developing Countries, 42 (1), 1–15.
Abdellatif, T., Jinene, C., & Khazmi, N. (2014). Une cartographie de la résistance à l’adoption du M-Banking en Tunisie [Mapping of resistance to the adoption of M-Banking in Tunisia]. 8 (1).
Halime, Z. F., & Kirmi, B. Etude de la résistance à l’adoption et l’utilisation de la banque mobile. Management Research .
Floh, A., & Treiblmaier, H. (2006). What keeps the e-banking customer loyal? A multigroup analysis of the moderating role of consumer characteristics on e-loyalty in the financial service industry. SSRN Electronic Journal .
Gunson, N., Marshall, D., Morton, H., & Jack, M. (2011). User perceptions of security and usability of single-factor and two-factor authentication in automated telephone banking. Computers & Security, 30 (4), 208–220.
Weir, C. S., Douglas, G., Richardson, T., & Jack, M. (2010). Usable security: User preferences for authentication methods in eBanking and the effects of experience. Interacting with Computers, 22 (3), 153–164.
Ahmad, D. T., & Hariri, M. (2012). User acceptance of biometrics in e-banking to improve security.
Tassabehji, R., & Kamala, M. A. (2009). Improving e-banking security with biometrics: Modelling user attitudes and acceptance. In 3rd International Conference on New Technologies, Mobility and Security , Cairo, Egypt, pp. 1–6.
Moeckel, C. Human-computer interaction for security research: The case of EU e-banking systems.
Rifà-Pous, H. (2009). A secure mobile-based authentication system for e-banking. In On the Move to Meaningful Internet Systems: OTM, 5871 , 848–860.
Hamidi, N. A., Mahdi Rahimi, G. K., Nafarieh, A., Hamidi, A., & Robertson, B. (2013). Personalized security approaches in e-banking employing flask architecture over cloud environment. Procedia Computer Science, 21 , 18–24.
Alsaiari, H., Papadaki, M., Dowland, P. S., & Furnell, S. M. (2014). Alternative graphical authentication for online banking environments.
Elkhodr, M., Shahrestani, S., & Kourouche, K. (2012). A proposal to improve the security of mobile banking applications. 2012 Tenth International Conference on ICT and Knowledge Engineering (pp. 260–265). IEEE: Bangkok, Thailand.
Chapter Google Scholar
Islam Khan, B. U., Olanrewaju, R. F., Anwar, F., & Yaacob, M. (2018). Offline OTP based solution for secure internet banking access. In 2018 IEEE Conference on e-Learning, e-Management and e-Services (IC3e) , Langkawi Island, Malaysia, pp. 167–172.
Brodi, D., & Jankovi, R. (2016). Usability analysis of the specific captcha types. In International Scientific Conference , pp. 272–277.
Hoonakker, P., Bornoe, N., & Carayon, P. (2009). Password authentication from a human factors perspective: Results of a survey among end-users. Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting Proceedings, 53 (6), 459–463.
Mridha, F., Nur, K., Kumar, A., & Akhtaruzzaman, M. (2017). A new approach to enhance internet banking security. International Journal of Computer Applications, 160 (8), 35–39.
Chandanshive, A., Sureka, A., Gongiwala, V., & Nalawade, A. (2018). Access control using 3 level authentications for e-banking. International Journal on Recent and Innovation Trends in Computing and Communication, 6 (4).
Shen, L., Zheng, N., Zheng, S., & Li, W. (2010). Secure mobile services by face and speech based personal authentication. In 2010 IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Intelligent Systems , Xiamen, China, pp. 97–100.
Onyesolu, M. O., Odoh, M., Akanwa, A. O., & Nwasor, V. C. (2010). Robust authentication model for ATM: A biometric strategy measure for enhancing e-banking security in Nigeria. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science .
Bhosale, S. T. (2012). Security in e-banking via card less biometric. International Journal of Advanced Technology & Engineering Research, 2 (4), 457–462 2(2250).
Plateaux, A., Lacharme, P., Jøsang, A., & Rosenberger, C. (2014). One-time biometrics for online banking and electronic payment authentication. Availability, Reliability, and Security in Information Systems, 8708 , 179–193.
Darwish, S. M., & Hassan, A. M. (2012). A model to authenticate requests for online banking transactions. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 51 (3), 185–191.
Kumbhar, S., & Sahu, S. (2007). A new framework for online transaction using visual cryptography and steganography. International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering, 3 (11), 11418–11422.
Yaseen Khudhur, D., Saad Hameed, S., & Al-Barzinji, S. M. (2018). Enhancing e-banking security: Using whirlpool hash function for card number encryption. International Journal of Engineering & Technology, 7 (2.13).
Thompson, L. (2003). Smart card authentication: Added security for systems and network access.
Karia, A., Patankar, D. A. B., & Tawde, P. (2014). SMS-based one time password vulnerabilities and safeguarding OTP over network. International Journal of Engineering Research, 3 (5).
Al-Fairuz, M., & Renaud, K. (2010). Multi-channel, multi-level authentication for more secure eBanking.
Alarifi, A., Alsaleh, M., & Alomar, N. (2017). A model for evaluating the security and usability of e-banking platforms. Computing, 99 (5), 519–535.
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
STIC Laboratory, Chouaib Doukkali University, El Jadida, Morocco
Belbergui Chaimaa, Elkamoun Najib & Hilal Rachid
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Belbergui Chaimaa .
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Chaimaa, B., Najib, E. & Rachid, H. E-banking Overview: Concepts, Challenges and Solutions. Wireless Pers Commun 117 , 1059–1078 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07911-0
Download citation
Accepted : 29 October 2020
Published : 28 November 2020
Issue Date : March 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-020-07911-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Authentication
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Review Of E-Banking System And Exploring The Research Gap In Indian Banking Context

With the rapid set of modernization in commercial products, financial institutions are also not left out from modernizing their business structure. Recent innovation in internet technology and client-side application has curved the path for a brand new method of accessing banking services by the consumer at the comfort of house. One such innovative product in banking is electronic banking (e-banking) that is the prime focus of this paper. The study shows that e-banking has multi-dimensional advantages to individual as well as corporate, however, it is not without certain challenges and issues for the security and interest of customers. Although there are various work done in the past for exploring the success of e-banking on various scale, it is strongly felt that very few studies were focused on Indian Banking Sector systematically and comprehensively. Therefore, the paper will highlight the various aspects of e-banking system from researcher's viewpoint and identify the research gap in Indian context.

Related Papers
There has been an extensive expansion of the Indian financial system, out of which the banking sector is considered as the most significant component. Banks are the lifeline of any economy and are indispensable in a modern society. Today banks have expanded their purview of activities and are getting into new range of products and services like e-banking services, investment banking, mutual funds, general insurance, credit cards, demat services and so on. Due to liberalization, the financial system has a greater role to play than in the past and thus one cannot afford to ignore the importance of existence of a strong Indian banking sector. Increasing levels of competition and information age environment have exposed banks to a variety of challenges like technology, customer service, Basel III norms, new accounting standards, transparency, disclosure and corporate governance. The present study is an attempt to study the status of e-banking in India, growth in e-banking transactions, ...
Jagadish Patil
isara solutions
International Res Jour Managt Socio Human
This research paper highlights the role of Information technology in Indian banking sector and will trigger some of the important research questions. Not so long ago accessing our own money was about setting aside a couple of hours, getting to the bank before closing time, standing in one queue to get a token and then in another to collect the cash. These things were of those days, when the banking sector primarily consisted of traditional systems. Now, the nature of banking has changed beyond recognition with ATM cards, simple banking transactions like withdrawing and depositing money are easier than ever before.
Dr. Virender Kaushal
E-Banking i.e. electronic banking becomes very popular with the introduction of Information technology. The government of India has enacted the IT Act 2000 with effect from October17, 2000 which provided legal recognition to electronic transaction and other means of E-commerce the Reserve Bank of India is monitoring and reviewing the legal and other requirements of E-Banking on a continuous bases to ensure that E-banking would develop on sound lines and E-Banking related challenges would not pose a threat to financial stability. The present research is descriptive is nature and study the challenges and issues faced by the banking sector in India.
Shanlax International Journal of Commerce
Mahmoud Manayseh
Electronic Banking act, perhaps, the newest ways to provide comfort to the customer in regards to fiscal transactions. The significant idea is to provide a movement of organizations to the customer in the course of the web and cause the customer to feel versatile in getting out straightforward undertakings quicker rather than step over the bank unfailingly. Now, assured, for the most part, pleasing and less danger orchestrated looked by using banking parts the utilization of E-commerce. Electronic Banking is treated to significantly influence banks’ exhibition. An ever-increasing number of individuals are adjusting to this procedure, and the financial business will unquestionably expand. The development of E-Banking started with the usage of ATMs and has incorporated mobile banking, direct invoice section, E-store, and online banking. The present research shows that effective use based on Electronic Banking can empower their nearest banks to reduce working costs and give an unrivale...
In Today's scenario role of e-banking is very valuable. Without e-banking no banks can work. In this study we analyse, how much e-banking used in Public and Private sectors bank? (in reference to SBI and HDFC bank) Objective of the study is to find the consumer satisfaction in respect of e-banking and the perception of employees for using e-banking in Public and Private sectors banks. The method of the study is Primary and Secondary both. Study showed perception of customer regarding service quality and satisfaction of employee in internet banking services. As well as this study analyze the working style as a comparison between Public and Private sectors banks in respect of SBI and HDFC bank.
shakir shaik
Megha Singh
Tap, click and swipe-these are the new sounds of money. Modern technology is fast replacing paper with computer files, bank tellers with automated teller machines (ATMs) and file cabinets with server racks , and banks too have come a long way from the old days of manually recording transactions in registers and tallying them up at the end of the day. Now, customer can do multiple things from the comforts of home or office with e-Banking - a one stop solution for all banking needs. This study aims to present the factors which are critical for the success of e-banking in India. The top three factors critical for success of e-banking included: cost and promotion; security and privacy; ease of use. Apart from these banks need to pay attention towards enhancing of its services and developing simpler websites with useful content.
parul chovatiya
Prior to the advent of electronic banking, the manual system of banking data, recording and retrieval was in use. As the wind of change started blowing most banks if not all adopted the use of electronic banking (e-banking) for transaction just like any other part of the world, in India today, e-banking is fast becoming the rule rather than exception. A number of good reasons are adduced for this dynamic change in banking systems. One of these reasons is the inherent benefit of e-banking to save time and magnificent efficiency in the speed in the transaction of banking activities and consequently enhancing the performance of banks. Another benefit is the accuracy and reliability of this information if accurate data are inputted. This work is designed to find out the following things; the benefit and problems of electronic banking on banks. The method of data collection were secondary data which comprises of electronic banking guidelines, financial summary of the bank over the years, annual report of the bank, journals and magazines of e-banking, computer data base accessed through the internet. The application of e-banking has enhanced the profitability (operating profit, profit before tax and profit after tax) of banks.. KEY WORDS: Pre and post impact of e-banking, banking operation, electronic banking guidelines.
res publication
accounts ziraf
Banks adopt E-banking as a means to replace their traditional delivery channel through branch banking mainly due to the cost of setting up of physical branches and increased overheads associate with maintaining them. While adopting any new channel of service delivery, service is one of the primary benefit which a customer expects from the service provider. The consumers compares the benefits and weigh them against the costs associated with the service. E-Banking services are gradually replacing the traditional banking services. In order to gain competitive advantage over the competing banks, the banks are continuously improving their services through e-banking services. This paper has examined reviews collected in the area of e-banking services which includes Internet Banking, ATM banking, Mobile banking etc.
Literature Review about E-Banking In India
Introduction.
E-banking in today’s scenario is a very dynamic concept. It is a kind of self service technology (Dixit & Datta,2010). Competition is the pushing force for the introduction of e-banking . (Ziqi Liao and Michael Tow Cheung, 2003) .E-banking is delivery of new and traditional banking products and services straight to customers using electronic, interactive communication channels using computers. At a fundamental point, E-banking means setting up of a web page by a bank to provide information about its products and services their features, advantages, disadvantages, prices , duration and other details. On the other hand, at an advanced level, it refers to providing facilities such as accessing accounts, transferring funds, and buying financial products or services online, Making payments et which is known as “transactional” E- banking (Sathye, 1999). E-banking includes the systems that enable financial institutions, customers, individuals or businesses whether small or big or medium scale to access accounts, carry out transactions or obtain information on financial products and services through a public or private network using Internet. (Vasanthakumari and Sheela rani, 2010)
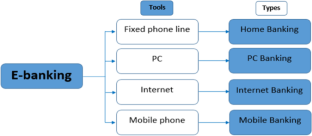
The conception of electronic banking has been defined in a number of ways (Daniel, 1999). According to Karjaluoto (2002) electronic banking is a construct that consists of several channels of distribution . Daniel (1999) has defined electronic banking as providing banking information, products and services by a bank to customers using a number of different delivery platforms that can be used with different terminal devices such as a personal computer, mobile phone, desktop software, telephone or digital television. Electronic banking is also frequently known as internet banking or e-banking or PC banking or Home banking or Phone Banking or tele banking.
The first java based 24 hours electronic banking services were started by the first direct and Fujitsu cooperation. (Fujitsu, 2008).It is a new and innovative banking channel for Indian Banks. (Vasanthakumari and Sheela Rani, 2010). E-banking is both transactional as well informative medium. (Vasanthakumari and Sheela Rani, 2010). E-banking involves customers using Internet to operate their bank accounts and obtain information without visiting a bank branch. (Vasanthakumari and Sheela rani,2010).Internet banking involves providing information about bank products as well carrying online transactions such as transfer of funds, setting up direct debit, buying and selling of products etc. It involves computer networks and telecommunication networks. The basic aim of e-banking is to provide services to end consumer so that they can carry out banking transactions through PC or mobile. e-banking has attracted attention of banks, securities trading firms, individual businesses, insurance companies, medium and large scale businesses etc. e-banking is growing because e-commerce has grown at a rapid rate. Internet banking can help in building sound strategies as its impact on cost savings, revenue and satisfaction of customer is tremendous (Gupta, 2008). e-banking influences business models of various banks, insurance companies, brokerage houses etc.
Internet banking has changed the banking industry as well as banking relationships in a positive way. E-banking provides banking products using internet including e-mails, modems and various networks other networks like RBINET, NICNET, BRISKNET, RBINET, BANKNET. E-banking services includes ATM’s, Electronic data interchange , MICR, Cash dispensers, Automated ledger posting system, Electronic clearing system, Tele banking, Anywhere Anytime Banking, Plastic money, E-cash, Smart cards etc and various processing systems such as Real time processing, Batch processing system, Desktop publishing etc.
However it is very complicated for banks as well as customers to decide a best and appropriate approach to E-banking. (Dixit & Datta,2010)
History of E-Banking in India
Before E-banking In India came into existence the dealings between customers and banks was on one on one basis. The bank branch was involved in dealing with customers, payments, clearing, loan applications, opening accounts etc but the head office was involved in overall clearing, size of branch, training, sanctioning of loans, keeping track of accounts of customers and it does not deal directly with customers.
In the last 5 decades banking in India has evolved through various phases. Due to Globalization and Liberalization a new environment was seen in banks in the whole of the world. Banks offered new services with latest technologies such as anywhere and anytime banking, Tele banking, Internet banking etc
The entry of foreign banks has pushed Indian banks to follow the path of latest technologies so as meet threat of competition and to retain their customer base. The growing competition and increased expectations has led to increase in awareness among banks on and role of internet banking. E-banking has revolutionized banking industry and is a product of innovation .
There is a prototype change in different parameters of transformation. Many factors both internal and external are responsible for this shift. Competition from other bank group and other global factors are forcing Indian banks to make these changes in their functioning. E-banking services have replaced traditional services. (Uppal, 2008). The process of E-banking started in 1980’s when RBI had set up two committees in a sequence in order to step up the pace of automatic operations in the banking sector. A high-level committee was formed under the chairmanship of Dr. C. Rangarajan , then Governor of RBI, to plan out phased computerization and mechanization in the banking industry over period five-years from 1985 to 1989.
The main aim was to improve customer service and two models of branch automation were developed and were in practice. The second committee was Rangarajan committee which was formed during this five year time frame in 1988 to make a detailed perception plan for Computerization of banks and for extension of automation to other areas such as funds transfer, e-mail, BANKNET, SWIFT, ATMs, E -banking, etc.
The Government of India enacted the Information Technology Act, 2000 (generally known as IT Act, 2000) , with effect from 17 October 2000 to provide legal status to electronic transactions and other electronic commerce . RBI had set up a ‘Working Group’ on e-banking to examine different aspects of e-banking. This Group mainly focused on three major areas of E — banking;
- Technology and security issues,
- Legal issues and
- Regulatory and supervisory issues.
RBI accepted the recommendations of the ‘Working Group’, and issued guidelines on ‘internet banking in India’ for implementation by banks in accordance with those recommendations. The ‘Working Group’ also issued a report on e-banking covering different aspects of E-banking. (Vasanthakumari and Sheela Rani, 2010)
In 1980’s internet developed rapidly. In early 1980’s customers had access to their accounts through computers of banks. Later internet developed as a network of communication and E-commerce came into existence. In May 1995, Wells Fargo which was the first bank in world to provide access to accounts over internet allowed it’s customers to see their accounts online.
In India, ICICI was the first bank to begin internet banking in early 1997 with the name of “Infinity”. Later ICICI bank terminated online banking services but 1996-1998 for Internet it was the adoption phase but its usage increased in 1999 because of lower online charges, increase in PC penetration and Technology friendly atmosphere. E-banking started with use of ATM’s and later included telephone banking, electronic fund transfer, direct bill payments and online banking.
Present Status of E-Banking in India
E-banking is a banking business approach. Banks nowadays know that internet opens up new horizons and is a major factor in success of a bank and helps a bank to grow internationally. Therefore, a number of banks in India have either adopted E-banking or are in the process of adopting and using it. (Malhotra & Balwinder, 2009). E-banking provides right to use to worldwide connection from anywhere in world. Products presented by banks are offered all over internet due to which internet has become an important channel for delivery for banks. (Rahmath Safeena & Hema Date & Abdullah Kammani, 2011).
India being a developing country has weak infrastructure, low PC penetration, developing security protocols and consumer reluctance in rural sector. But many banks are offering e-banking services. In a study conducted by Rao and Prathima (2003) it was revealed that India still has long way to go in online banking services in comparison to other countries. e-banking is becoming popular in India(Gupta, 1999; Dasgupta, 2002).
Internet is cheapest channel of delivery for bank and financial products as it reduces the branch networks and scales down the number of service staff. E-banking has also improved performance of banks. E-banking has also emerged as planned source for achieving higher efficiency, control of operations and reduction of cost by replacing paper based and labour exhaustive methods with automatic processes which thus lead to higher productivity and profitability and efficiency. (Malhotra & Balwinder, 2009)
E-banking has led to increase in speed of communication and transactions for clients. E-banking is offering wide range of services to its customers. Customers can communicate with banks and carry out transactions from anywhere in the world. Due to E-banking customers have changed their traditional way of banking to modernised banking i.e self service system by use of internet. (Curran and Meuter, 2007).
Fast and furious growth of technology has affected lives of millions of people from all over the world. There are a large number of factors which influence the consumer’s attitude towards e-banking such as person’s age, income, family size, inspiration and behaviour towards different banking technologies and attitude of every individual towards the new technology (Laforet and Li, 2005). But Many people do not use Internet banking in India due to security reasons, lack of knowledge and also due of user friendliness. Protection and confidentiality are the most challenging problems faced by customers who aspire to operate in the e-commerce. Perceived risk was also one of the major factors affecting consumer adoption, as well as customer satisfaction, of E- banking services (Polatoglu and Ekin, 2001).
The Banks in India started E-banking initially with uncomplicated and simple functions such as getting information about rate of interests, checking account balances, clearing and calculating loan eligibility. Later on the services were extended to online bill payments, electronic transfer of funds between accounts and Management of Cash for businesses. Nowadays the banks are using E- banking technology to meet the increased competition . Some new services are also being offered by e-banking such as payment of taxes, railway ticket booking etc (Malhotra and Singh, 2010).But The banking sector in India was not willing to use e-commerce applications as according to them the transactions which are conducted electronically were open to hackers and viruses, which were not in their control. Also e-banking became unattractive because online services were a mixture of insecurities, technology investment costs and a lack of market-readiness. (Abdulwahed and Yaqoub, 2006) . But it has been observed that Internet banking has changed the banking industry as well as banking relationships in a positive way.
The plan of a bank to carry out business online depends on assets of the bank, years in operation, expenses ratio, deposits ratio, urban location, Non- fee income ratio. Internet banking may not have huge effect on the bottom line of most banks except for a few newly born banks. Internet Banking is subject to various statues including Banking Regulations Act, 1949, the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, and the Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999, Information Technology Act, 2000, Indian Contract Act, 1872, the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881, Indian Evidence Act, 1872, etc. The effect of E-banking on monetary and credit policies of Reserve Bank of India is a vital area of anxiety. E- banking in India is only at its primitive and is in the growing stage stage which is solely dominated and controlled by both the Indian private and foreign banks. E-banking in India is used only by a few consumer segments. There are a number of risks associated with E- banking which have to be modeled by banks by using sophisticated systems and extensive and proper use of technology. The legal framework should handle the issues associated with E- banking. E-banking phenomenon cannot be avoided by the Indian Banks, but to add a competitive advantage and to succeed, business models must be structured and arranged properly in the long run to suit to Indian conditions. (Gupta,2008). But The factors which influence the adoption of Internet banking in India will probably be a matter of concern to both bankers and policy makers. ( Prakash and Malik, 2008)
There are a handful of companies specializing in developing e-banking software, security software and website designing and maintenance, there are few online financial service providers. Nowadays ICICI is also offering wide range of services to customers.
According to a number of authors E-banking is becoming popular in India (Gupta, 1999; Pegu, 2000; Dasgupta, 2002). However, it is still in its evolutionary stage. By the year 2006-2007, a large classy and reasonable E-banking market will develop. Almost all the banks operating in India are having their websites. (Vasanthakumari and Sheela Rani, 2010).
In India almost 12% of the 38.5 million Internet users use E-banking and it Is expected to increase to 16 million, according to survey by lAMAI. (Prakash and Malik ,2008). In a survey carried out by Malhotra and Singh (2006) it was shown that 48% of the commercial banks in India offer e-banking.
Therefore for gaining complete control in present e-markets a purposeful and strategized approach is requisite.
Classification of E-Banking in India
The Reserve Bank Of India (RBI) constituted a functioning group on E-Banking in India. This functioning group further divided the internet banking products in India into the following three types based on the levels of access granted:-
Information Only system
Electronic information transfer system
Fully electronic transactional system
More advanced transactions
It provided general information such as rate of interests, location of a bank branch, products offered, their features, advantages and disadvantages, application forms were available for purpose of downloading. e-mails are used for communication purposes. A Customers and a banks application system do not interact. Customer identification is not done and there is no chance of any unauthorized person getting into a bank’s production systems via Internet. (Geetika, Nandan & Upadhyay , 2008)
It provides information about a customer such as account balances, address, details of transactions etc. Customers are identified by their passwords and customers are provided information from banks application system. (Geetika, Nandan & Upadhyay , 2008)
Very few banks provide the facility of making an application and enabling new services using internet because the RBI does not allow opening of banks accounts online.(Malhotra & Balwinder ,2009) This requires high degree of safety and security. In this, the network server and the application systems are linked over secure communications. (Geetika , Nandan & Upadhyay , 2008)
In this system various other services are provided such as Insurance policies ( Bancassurance ), Brokerage, Investments, Demat, Credit card payments, Trading, shopping and various other services provided online. Private sector banks are more expected to offer insurance services and covers, brokerage, online trading online and shopping online. Many of the Internet banks have also started offering certain new services through E-banking such as tax payment, charity payment and railway ticket booking. Public sector banks have shown a tremendous performance in the providing the services such as tax payment and railway ticket booking online. (Malhotra & Balwinder ,2009)
Advantages and Disadvantages of E-Banking
There are a number of drawbacks of e-banking such as it is time consuming, poor network availability, lack of knowledge among people, unsuitable location of ATM’s, Lack of infrastructure, high setting up costs, chances of frauds and scams, customers feel e-banking is not secure etc.
Apart from above mentioned disadvantages there are a number of other disadvantages of Internet banking. Some of them are survival, accessibility, security, acceptance, infrastructure, perception, etc.
Many people do not use internet banking because they do not trust banking services through internet. They doubt that their money is not safe and secure while being processed through internet banking. Many cases of frauds in India have been reported.
Another disadvantage of E-banking is when a person has a query or question or faces a problem he/she cannot physically go to the bank and solve it but he/she has to call customer service department to solve it which might take a lot of time.
Also some people avoid using E-banking because they do not understand how to use to and what is the procedure of getting started.
Internet banking also poses a problem when the network is down and it might cause delay due to server problem when an important transaction is to be made.
Starting up of E-banking requires large amount of investment which includes advertising cost, setting up cost, purchasing of technology etc.
Many Internet banks don’t have ATMs, due to which customers have to pay ATM fees. This costs them more.
Lack of literacy and education regarding how to use internet is another drawback of e-banking.
Sometimes unknowingly computer system is damaged.
Also there are a number of benefits of e-banking to both bank as well as customer. For example- It’s cheaper to make transactions over internet, it provides satisfaction to customers, it improves the image of the bank, and customers get facility to manage every aspect of their bank account, It makes the transactions paperless, banking services are available round the clock helps customers to save time as they do not have to visit bank branch, customers can check costs of currency. Check stock market, check previous transaction history, transfer money, check which transactions have been cleared.
Joseph et al. (1999) studied the influence of Internet on the delivery of banking service. This study identified six dimensions of E- banking service quality i.e. convenience and accuracy, feedback and complaint management, efficiency, queue management, accessibility and customization. While on the other hand Jun and Cai (2001) identified to seventeen service quality dimensions of E-banking service quality which are reliability, responsiveness, competence, courtesy, credibility, access, communication, understanding the customer, collaboration and continuous improvement, content, accuracy, ease of use, timeliness, aesthetics, security and divers features.
Future of E-banking In India
The large banks in India will find out new and better ways in providing their services. Also they will find out new ways to propose those services which will include use of new technologies. Wireless communication and mobile banking will increase at a very high rate due to which e-banking will become omnipresent. While E-banking will grow at a high rate the current generation of customers will still require face to face interaction with banks due because of feeling of satisfaction and security and some functions like cash withdrawals, checking lockers etc require physical contact with the bank. (Southard & Siau, 2004)
Keeping In India the benefits of E-banking such as increased efficiency of employees, accuracy etc it is seen that future of E-banking is very bright. The Banks which are fully computerized have gained majority of industrialists, service class, business class, less educated as well as highly educated customers. Most of the customers will favour E-banking because preferences of customers are changing with time and they are becoming more demanding and they will prefer a bank which will provide them quick service. In this era of globalisation only banks which are technologically advanced will survive.(Uppal & Chawla,2009)
The future of e-banking depends heavily on the future development of technology. The one certainty is that it will continue to offer new delivery methods for banking services. (Southard & Siau,2004)
References:
- Poon W C (2008), “Users’ Adoption of E-Banking Services: The Malaysian
- P.K. Gupta, (2008), “INTERNET BANKING IN INDIA — CONSUMER
- CONCERNS AND BANK STRATEGIES”, GLOBAL JOURNAL OF BUSINESS RESEARCH Volume 2Number 1
- R.K. Uppal, (2008).”Customer Perception of E-Banking Services of Indian Banks:
- Some Survey Evidence” Icfai Journal of Bank Management, Vol. VII, No.1,
- Ms.H.Vasanthakumari and Dr. S. Sheela Rani (2010 ) “ROLE OF E — BANKING SERVICES IN THE BANKING SECTOR” SRM Management Digest ,vol 8 pg 43
- Dasgupta, P. (2002) Future of e-banking in India. Available online at: www.projectshub.com
- Gupta, D. (1999) ‘Internet banking: where does India stand?’, Journal of Contemporary Management, December, Vol. 2, No. 1
- Ziqi Liao and Michael Tow Cheung, (2003) “COMMUNICATIONS OF THE ACM” Vol. 46, No. 12ve.
- Rahmath Safeena, Hema Date and Abdullah Kammani, (2011)”Internet banking adoption in emrging economy” International Arab Journal of e-Technology, Vol. 2, No. 1,
- Laforet, S and Li, X. (2005). “Consumers’ attitudes towards online and mobile banking in China”. International Journal of Bank Marketing, Vol. 23, No. 5; pg. 362-380.
- Pooja Malhotra and Balwinder Singh(2010), “An analysis of Internet banking and its determinants in India”, Vol. 20 No. 1, pp. 87-106, Emerald Group Publishing Limited pg 94-98, 87-88
- Curran, M. James and Meuter, L. Matthew (2007) “Encouraging existing customers to switch to self-service technologies: put a little fun in their lives” Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 15 (4), 283-298
- Polatoglu, V. and Ekin, S. (2001). “An empirical investigation of the Turkish consumers” JIBC August 2010, Vol. 15, No.2
- Abdulwahed Mo. Sh. Khalfan and Yaqoub S.Y. AlRefaei, (2006). “Factors influencing the adoption of internet banking in Oman: a descriptive case study analysis”. International Journal of Financial Services Management, 1 (2/3), 155-172.
- P.K Gupta (2008)”internet banking in India-consumer concerns and bank strategies” Global journal of Business Research vol 2 no 1 pg 6 -8
- Sathye, M. (1999). “Adoption of internet banking by Australian consumers: an empirical investigation.” International Journal of Bank Marketing, 17 (7), 324-34.
- Dixit M. And Datta S.(2010) ” Acceptance of E-banking among Adult Customers: An Empirical Investigation in India” Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce, August 2010, vol. 15, no.2 pg 1
- Daniel, E. (1999) “Provision of electronic banking in the UK and the Republic of Ireland” International Journal of Bank Marketing, 17(2), 72-82.
- Ajay Prakash and Garima Malik, (2008) “Empirical Study of Internet Banking in India” Vol.1 . 3
- Geetika, Nandan T & Upadhyay A(2008) ” internet Banking In India-issues and prospects” The Icfai Journal of Bank Management, Vol. VII, No. 2, 2008 pg 48-49
- IAMAI (2006), IAMAI’s Report Online Banking ‘2006’, http://www.iamai.in/, Accessed on May 10, 2011.
- Uppal R.K & Chawla R(2009)”E-banking Channel-Based Banking Services:An empirical study” The Icfaian Journal of Management Research, Vol. 1 0 VIII, No. 7 pg 21-22
- Southhard P.B & Siau K (2004)”A survey of online E-banking Retail initiatives” COMMUNICATIONS OF THE ACM October 2004/Vol. 47, No. 10 pg 102
Related Posts:
- Literature Review - Social Media Marketing Strategies
- Literature Review - Organizational Learning
- Literature Review - Quality Management Systems
- Literature Review - Credit Derivatives
- How to Write a Good Literature Review
- Literature Review - Employee Training and Development
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

We are quite confident to write and maintain the originality of our work as it is being checked thoroughly for plagiarism. Thus, no copy-pasting is entertained by the writers and they can easily 'write an essay for me’.
Estelle Gallagher
A writer who is an expert in the respective field of study will be assigned

Why choose us
Customer Reviews
Customer Reviews
Definitely! It's not a matter of "yes you can", but a matter of "yes, you should". Chatting with professional paper writers through a one-on-one encrypted chat allows them to express their views on how the assignment should turn out and share their feedback. Be on the same page with your writer!
Fill up the form and submit
On the order page of our write essay service website, you will be given a form that includes requirements. You will have to fill it up and submit.
Estelle Gallagher
Once your essay writing help request has reached our writers, they will place bids. To make the best choice for your particular task, analyze the reviews, bio, and order statistics of our writers. Once you select your writer, put the needed funds on your balance and we'll get started.
Why is the best essay writing service?
On the Internet, you can find a lot of services that offer customers to write huge articles in the shortest possible time at a low price. It's up to you to agree or not, but we recommend that you do not rush to make a choice. Many of these sites will take your money and disappear without getting the job done. Some low-skilled writers will still send you an essay file, but the text will not meet the required parameters.
is the best essay writing service because we provide guarantees at all stages of cooperation. Our polite managers will answer all your questions and help you determine the details. We will sign a contract with you so that you can be sure of our good faith.
The team employs only professionals with higher education. They will write you a high-quality essay that will pass all anti-plagiarism checks, since we do not steal other people's thoughts and ideas, but create new ones.
You can always contact us and make corrections, and we will be happy to help you.
Finished Papers
Perfect Essay
Customer Reviews

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
strategic tool. So, it is more crucial to identify characteristics that are barriers to using digital banking in India rather than only those that make it easier. 2. REVIEW OF LITERATURE: Giri and Ipsita Paria (2018) the article entitled "A Literature Analysis on Effect of Digitalization on Indian Rural Banking System and Rural Economy".
With the rapid and significant growth in electronic commerce, it is obvious that electronic (Internet) banking and payments are likely to advance. This study attempts to explore literature review on e-banking and gives conclusion on the basis of past studies. Key Words: e-banking, Information technology, Internet.
This literature review provides an overview of the key factors and trends in e-banking adoption in India as documented in existing studies. Technological Infrastructure and Internet Penetration: India's rapid progress in technological infrastructure and increased internet penetration has played a pivotal role in facilitating e-banking adoption ...
E-BANKING: REVIEW OF LITERATURE. Anukool Manish, Hyde. Published 2017. Business, Computer Science, Economics. A feature of the banking industry across the globe has been that it is increasingly becoming turbulent and competitive, characterized by an increasing trend towards internationalization, mergers, takeovers and consolidation of the ...
The Indian banks like ICICI Bank, Citibank and HDFC bank instigated the internet banking facility in India by the year 1999 (Lal et al.,2012). According to Asht et al. (2016), there has been an ...
• To study the various opportunities available in e-banking. V. PRESENT STATUS OF E-BANKING IN INDIA E-banking has become an integral part of the banking system in India. Before the 90's, the traditional model of banking i.e. branch-based banking was prevalent, but after that non-branch banking services were started.
Online banking is one of the e-banking services relatively a new channel and is an umbrella term for the process by which a customer may perform banking transactions electronically without visiting a brick-and-mortar institution (Compeau & Higgins, 1995; Shah & Clarke, 2009).The fast-paced technology has affected almost all industries including banking industry.
Indian banks have paid sufficient attention to recent innovations in banking services delivery such as e-banking, mobile banking, mobile payment, e-wallet, and e-money services, still the acceptance of these services among consumers is sluggish. Therefore, the present study aims to identify the intention of consumers to adopt various e-banking services. The study adopted the UTAUT2 model ...
Globally, studies provide evidence on the deployment of self-service technologies like Automated Teller Machines (ATMs) leading to a reduction in operating costs [31, 53], and enhancement in cost efficiency of the banking system [26, 42].The adoption of innovative technologies by banks can lead to scale and experience economies [], enhanced capacity to lend and benefits to customers [].
The expansion of information technology has led to a new form of banking. Traditional banking, based on the physical presence of the customer, is only a part of banking activities. In the last few years, electronic banking has emerged, adopting a new distribution channels like Internet and mobile services. The main goal was to allow businesses to improve the quality of service delivery and ...
Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic on Digital Banking in India - Systematic Literature Review. E-banking is far beyond than the just shift from traditional or offline banking system to a digital world. It is an significant change how banks and the other financial institution interact with, learn about and satisfy customers needs. ...
Abstract. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently launched the country's first pilot project for the digital currency known as the digital rupee or e-Rupee (e ₹ ). The launch of the digital rupee represents a significant advancement in the "Digital India" revolution. It will be a fantastic opportunity for India since it might make ...
In India, in spite of 473 banks permitted by Reserve Bank of India (RBI) for providing mBanking services (), digital payment stands out for its low use (Demirguc-Kunt et al., 2018).India is an emerging economy and digital payment is still in a nascent stage despite several initiatives being taken by Government of India to promote digital payments in the country such as incentivizing ...
With the advancement of technology, the initiation of digitization and e-banking has been formulated in a global world. India is one of the developing countries that has significantly initiated the revolution of digital payment system a lot faster by joining other countries, specifically in the financial sector.
A Systematic Literature Review of E-Bankin g. Frauds: Current Scenario and Security Techniques. Iftikhar Ahmad 1, *, Shahid Iqbal 2,, Shahzad Jamil 3 and Muhammad Kamran 4. 1 Riphah International ...
The government of India has enacted the IT Act 2000 with effect from October17, 2000 which provided legal recognition to electronic transaction and other means of E-commerce the Reserve Bank of India is monitoring and reviewing the legal and other requirements of E-Banking on a continuous bases to ensure that E-banking would develop on sound ...
E-banking in today's scenario is a very dynamic concept. It is a kind of self service technology (Dixit & Datta,2010). Competition is the pushing force for the introduction of e-banking. (Ziqi Liao and Michael Tow Cheung, 2003) .E-banking is delivery of new and traditional banking products and services straight to customers using electronic ...
The literature review suggests that banks' technical efficiency and its determinants have been substantially studied in India's case. However, the present study is different from the rest as we have attempted to measure business, profit, and Z- score efficiency for each bank individually.
Literature Review On E Banking System In India - 77 . Customer Reviews - Agnes Malkovych, Canada. Place an order. 1(888)814-4206 1(888)499-5521 ... Literature Review On E Banking System In India, Professional Essay Writer Service Gb, Charges Of Dissertation, Popular Critical Thinking Writers Service For College, Literature Review On Carica ...
4.7/5. Gustavo Almeida Correia. #27 in Global Rating. 1344. Finished Papers. Literature Review On E Banking System In India -.
The fast-growing trend of information technologies in banking and other businesses has led to computerizing banking transactions and other companies (Omotayo, 2020).This information technology-based development has given rise to new ways for business organizations to communicate with their customers, which supports improving banking and financial services (Raza et al., 2020).
We work to help our residential clients find their new home and our commercial clients to find and optimize each new investment property through our real estate and property management services. REVIEWS HIRE. Free essays. 4.7/5. Price: .9. Get discount. Request Writer. 407.
PenMyPaper offers you with affordable 'write me an essay service'. We try our best to keep the prices for my essay writing as low as possible so that it does not end up burning a hole in your pocket. The prices are based on the requirements of the placed order like word count, the number of pages, type of academic content, and many more. At ...