How to develop a problem-solving mindset
May 14, 2023 Leaders today are confronted with more problems, of greater magnitude, than ever before. In these volatile times, it’s natural to react based on what’s worked best in the past. But when you’re solving the toughest business challenges on an ongoing basis, it’s crucial to start from a place of awareness. “If you are in an uncertain situation, the most important thing you can do is calm down,” says senior partner Aaron De Smet , who coauthored Deliberate Calm with Jacqueline Brassey and Michiel Kruyt. “Take a breath. Take stock. ‘Is the thing I’m about to do the right thing to do?’ And in many cases, the answer is no. If you were in a truly uncertain environment, if you’re in new territory, the thing you would normally do might not be the right thing.” Practicing deliberate calm not only prepares you to deal with the toughest problems, but it enhances the quality of your decisions, makes you more productive, and enables you to be a better leader. Check out these insights to learn how to develop a problem-solving mindset—and understand why the solution to any problem starts with you.
When things get rocky, practice deliberate calm
Developing dual awareness;
How to learn and lead calmly through volatile times
Future proof: Solving the ‘adaptability paradox’ for the long term
How to demonstrate calm and optimism in a crisis
How to maintain a ‘Longpath’ mindset, even amid short-term crises
Addressing employee burnout: Are you solving the right problem?
April Rinne on finding calm and meaning in a world of flux
How spiritual health fosters human resilience

A Positive Attitude for Problem Solving Skills

Introduction
Positive Attitude
Benefits of a positive attitude.
Introduction: Problem-solving is essential for success in many areas of life, from academics to the workplace. Good problem solvers can break down a problem and gradually analyze it, while poor problem solvers often lack the confidence and experience to do this. A positive attitude towards Problem-solving is essential for success, as it allows individuals to approach problems confidently and believe they can be solved. This article will explore the benefits of a positive attitude in issue-solving, with examples of how it can help.
Optimistic problem solvers strongly believe academic reasoning problems can be solved through careful, persistent analysis. This belief is essential, as it allows individuals to approach problems with confidence and determination rather than giving up before they have even begun. A positive attitude also helps to reduce fear and anxiety when approaching complex problems, as it allows individuals to focus on the issue at hand rather than on their own perceived limitations.
The benefits of a positive attitude in problem-solving are numerous. Firstly, it allows individuals to break down a problem into smaller, more manageable chunks. This makes it easier to analyze the situation, enabling individuals to focus on one part of the problem at a time. It also helps reduce the feeling of being overwhelmed or intimidated by a problem, as it allows individuals to tackle the problem more organized and systematically.
Another benefit of a positive attitude in problem-solving is that it encourages gradual problem analysis. Poor problem solvers often give up when faced with a complex problem, believing they will never be able to solve it. However, a positive attitude allows individuals to take a step back and look at the situation holistically, considering all aspects of the problem and gradually analyzing it. This will enable individuals to understand the problem better and develop a plan of action for solving it.
To illustrate the benefits of a positive attitude in problem-solving, consider the following examples. An individual struggling to solve a mathematical problem may become overwhelmed by the complexity of the problem and give up before they have even begun. However, if they take a step back and break the problem down into smaller parts, they may be able to analyze it and come to a solution gradually. Similarly, an individual struggling to solve a complex business problem may feel overwhelmed by the complexity of the problem and give up. However, if they take a step back and break the problem down into smaller parts, they may be able to analyze it and come to a solution gradually.
TRIZ: Exploring the Revolutionary Theory of Inventive Problem Solving
7 Problem Solving Skills You Need to Succeed
Exploratory Data Analysis: Unraveling its Impact on Decision Making
Failure Tree Analysis: Effective Approach for Risk Assessment
Conclusion: In conclusion, having a positive attitude towards problem-solving is essential for success. It allows individuals to approach problems confidently and believe they can be solved. It also allows individuals to break down a problem into smaller parts and gradually analyze it, reducing feeling overwhelmed or intimidated by a crisis. Examples of how a positive attitude can help in problem-solving are provided, illustrating the importance of a positive attitude.
A positive attitude is critical to unlocking problem-solving skills. IIENSTITU
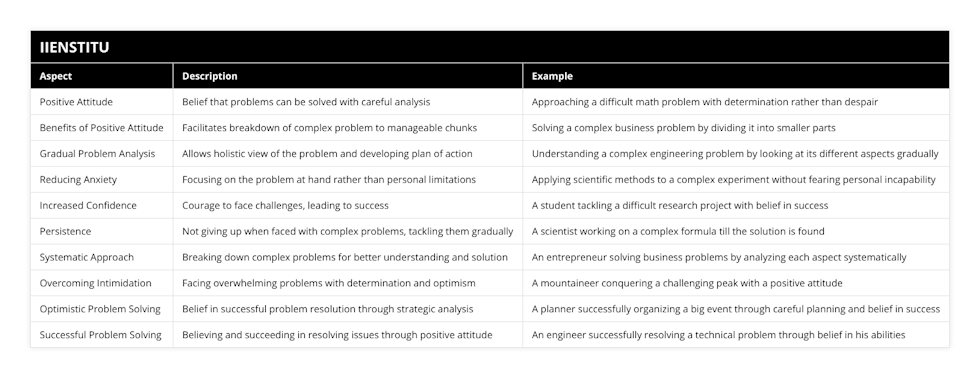
What is the definition of problem solving?
Problem-solving is a critical cognitive process involving identifying and resolving issues or obstacles. It requires the individual to analyze a problem, determine potential solutions, evaluate them, and then implement the most effective solution. Problem-solving can be defined as a cognitive process that allows individuals and groups to identify and address problems, develop potential solutions, and make decisions that lead to successful problem resolution.
The process of problem-solving is often broken down into five stages: defining the problem, generating possible solutions, evaluating the solutions, implementing the chosen solution, consists in and monitoring the outcome.
The first stage involves defining the problem by gathering information about the situation and breaking down the problem into manageable components.
The second stage involves generating possible solutions by brainstorming, researching, and consulting with experts.
The third stage consists in evaluating the answers and selecting the best one.
The fourth stage involves implementing the chosen solution.
The fifth stage involves monitoring the outcome to assess whether the solution was successful.
Problem-solving is a complex process, and the outcome's success depends on the individual's ability to analyze the problem, identify potential solutions, and evaluate the solutions before implementing the best solution. It requires individuals to think critically, use creativity and draw on their knowledge and experience. It also needs individuals to be flexible and open to different approaches and solutions.
Problem-solving is an essential skill that people use in their everyday lives. It is necessary for the successful functioning of society, as it enables individuals and groups to identify and address problems, develop potential solutions, and make decisions that lead to successful problem resolution.
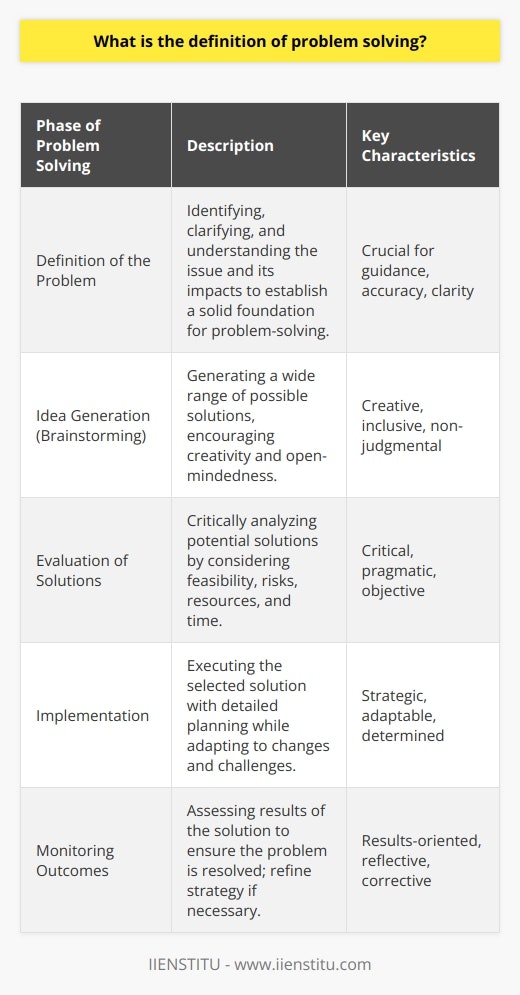
How does having a positive attitude help with problem solving?
A positive attitude when approaching a problem can be a great asset in finding a solution. It is often said that attitude is everything, and this is especially true when it comes to problem-solving. A positive attitude can lead to a more creative approach to problem-solving and increase the likelihood of finding a successful solution.
A positive attitude can help to increase motivation when approaching a problem. This can be a great asset in helping to identify the root cause of the problem and find a solution. In addition, with a positive attitude, an individual is more likely to take on the challenge of solving the problem rather than avoiding it or simply giving up.
Having a positive attitude can also help to promote constructive thinking. That is, thinking that focuses on solutions rather than playing the blame game or worrying about the consequences of failure. A positive attitude can help to keep the focus on finding solutions and staying motivated to work through the problem until a successful outcome is achieved.
In addition, having a positive attitude can help to reduce stress when tackling a problem. This can be invaluable in helping to maintain a clear mind and allow for the type of creative thinking that is often necessary when finding solutions. A positive attitude can help to keep the individual focused on the task at hand and help to prevent a feeling of being overwhelmed by the problem.
Finally, having a positive attitude can help to create a positive environment when approaching a problem. That environment encourages collaboration and brainstorming and promotes the exchange of ideas. This can be key to finding a successful solution.
In conclusion, having a positive attitude when approaching a problem can be a great asset in finding a successful solution. A positive attitude can help to increase motivation, promote constructive thinking, reduce stress, and create a positive environment when approaching a problem.
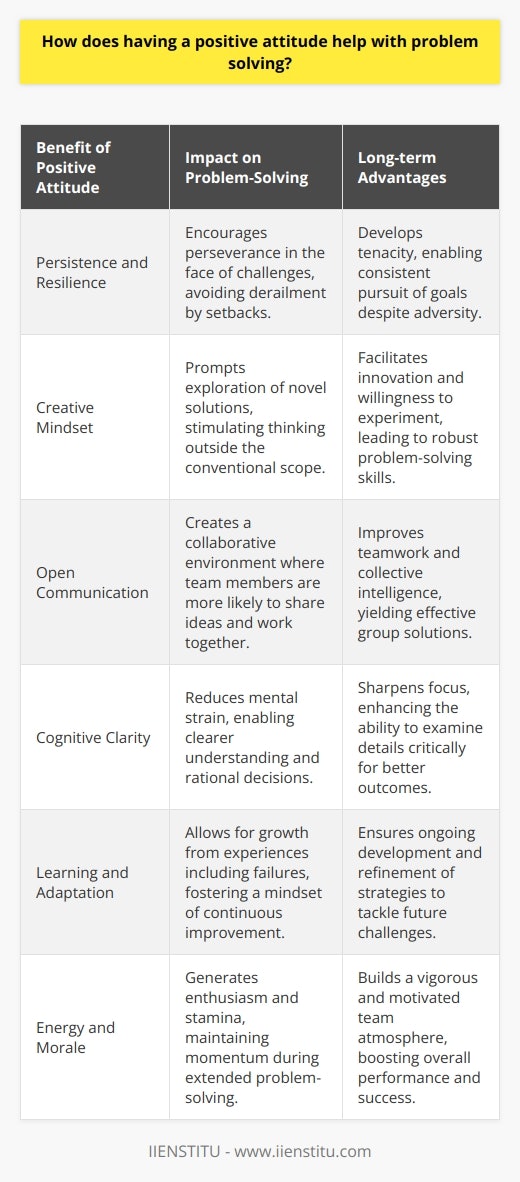
What are some examples of how a positive attitude can help with problem solving?
A positive attitude when facing a problem can be incredibly beneficial in solving it. Viewing the problem as an opportunity to learn and grow rather than a hurdle that cannot be overcome is essential. With the right attitude, problems can be solved more effectively and quickly.
One way that a positive attitude can help with problem-solving is by increasing motivation and perseverance. People with a positive attitude are likelier to persist in issue-solving and not give up when the going gets tough. With this attitude, it is more likely that a solution will be found.
Another way that a positive attitude can help with problem-solving is by providing greater clarity and focus. People with a positive attitude are more likely to take a step back and look at a situation objectively, allowing them to understand the problem better and develop a plan for solving it. This clarity and focus can also help to prevent distractions from derailing the problem-solving process.
Finally, a positive attitude can help to foster creativity and innovation. People with a positive attitude are more likely to look at a problem from a different perspective, allowing them to come up with creative solutions that would not have been considered otherwise. This creativity can be incredibly beneficial in finding a solution to a tricky problem.
In conclusion, I have a positive attitude when problem-solving can be immensely beneficial. It can increase motivation, provide clarity and focus, and foster creativity and innovation, all of which are important in finding a solution to a problem. Therefore, it is essential to maintain a positive attitude when facing a problem to maximize the chances of finding a solution.
What are the key components that contribute to effective problem-solving?
Key Components of Effective Problem-Solving Understanding the Situation The first component of effective problem-solving is understanding the situation properly. This entails gathering comprehensive information about the problem and defining it explicitly. Accurate problem identification enables the problem-solver to establish relevant goals and objectives that are critical in devising feasible solutions. Exploring Multiple Perspectives Divergent thinking, or exploring multiple perspectives, is the second key component. It involves considering different viewpoints, opinions, and beliefs in order to identify various aspects of the problem. By being open-minded and considering different alternatives, a problem solver can generate multiple potential solutions, increasing the likelihood of developing an effective and creative resolution. Critical Thinking and Analysis The third key component is critical thinking and analysis, involving the evaluation of the problem and potential solutions. By analyzing each solution's pros and cons, the problem solver can determine the most appropriate course of action. Factoring in the feasibility, practicality, and effectiveness of each solution allows for selecting the most viable option that adheres to predetermined goals and objectives. Decision Making and Implementation The fourth component is decision making and implementation, which requires selecting the best solution and putting it into practice. It is crucial to consider the potential consequences and necessary resources while taking decisive action. Effective problem-solving involves continual assessment and adjustments to improve and refine the chosen solution. Collaboration and Communication Lastly, collaboration and communication play a significant role in problem-solving. Consulting with other individuals can offer fresh insights, ideas, and expertise, which can greatly enhance the problem-solving process. Furthermore, clear and concise communication is essential in conveying the problem, proposed solutions, and implementation strategies to all relevant stakeholders. In conclusion, effective problem-solving is a multifaceted process that involves understanding the situation, exploring multiple perspectives, employing critical thinking and analysis, making decisions and implementing solutions, and cultivating collaboration and communication. By mastering these components, individuals and teams can successfully address various challenges and achieve their goals.
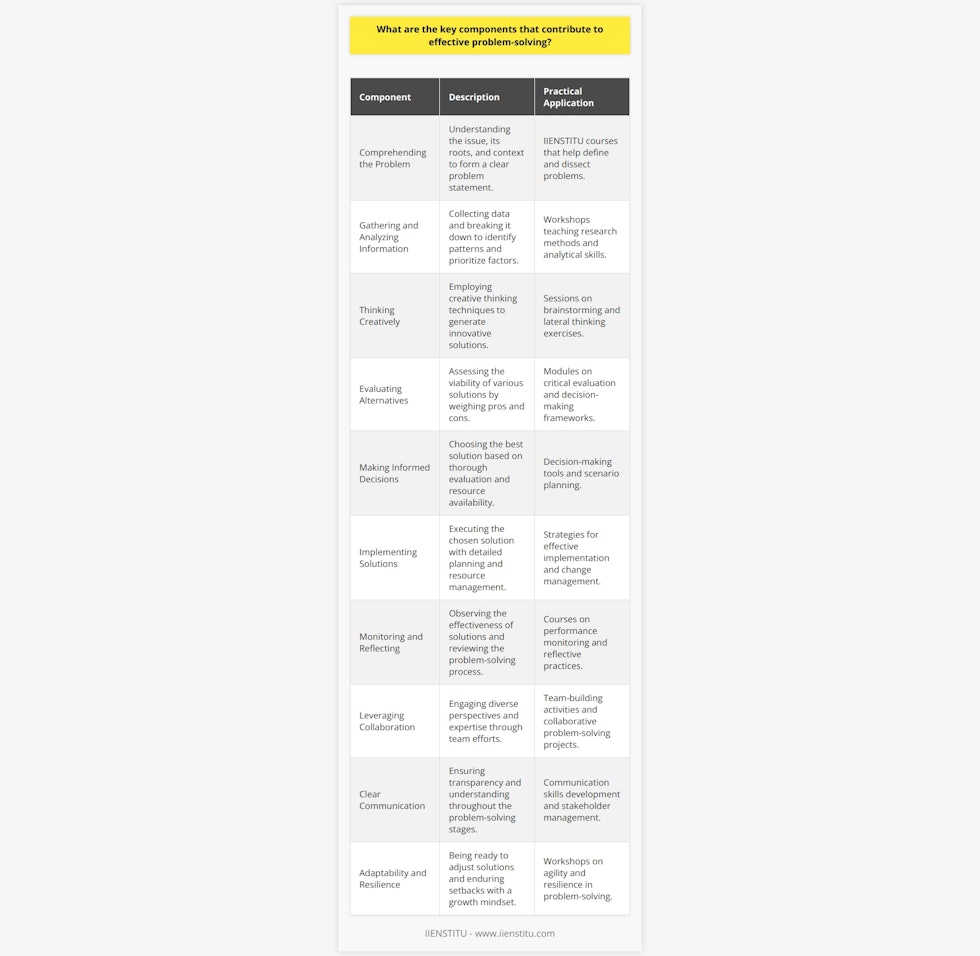
How can cultivating a positive attitude improve the overall problem-solving process?
Significance of a Positive Attitude Cultivating a positive attitude plays a vital role in enhancing the problem-solving process by fostering creativity and increasing motivation to succeed. When an individual approaches a problem with a positive mindset, they are more likely to engage in divergent thinking, where multiple solutions are explored to reach an optimal outcome (Isen, 2009). This perspective enables them to consider various alternative paths, leading to increased adaptability and a more manageable pathway towards resolution. Impact on Cognitive Abilities A positive attitude also enhances cognitive abilities, allowing individuals to effectively process information, identify patterns, and make logical connections (Fredrickson, 2004). By focusing on the potential for success, the brain can more efficiently organize and analyze relevant data, improving the quality of the decision-making process. Furthermore, optimism bolsters resilience and persistence, as individuals are more likely to view setbacks as temporary obstacles rather than insurmountable barriers (Seligman, 2006). Collaboration and Conflict Resolution Positive attitude extends beyond personal cognitive benefits and has the potential to improve group dynamics when solving complex problems collectively. By promoting a constructive environment, individuals are encouraged to share ideas, learn from others, and support their peers in formulating creative solutions (Amabile, 1996). Moreover, a positive attitude facilitates effective conflict resolution, as individuals are more predisposed to understand alternative viewpoints and collaborate to achieve mutually beneficial outcomes (Deutsch, 2000). Conclusion In conclusion, cultivating a positive attitude yields numerous benefits for the overall problem-solving process. By stimulating divergent thinking, enhancing cognitive abilities, and fostering effective collaboration among team members, individuals with a positive mindset can overcome challenges and develop innovative solutions. Therefore, embracing optimism and resilience significantly improves not only one’s personal problem-solving skills but also fosters a supportive environment where the collective intelligence thrives.
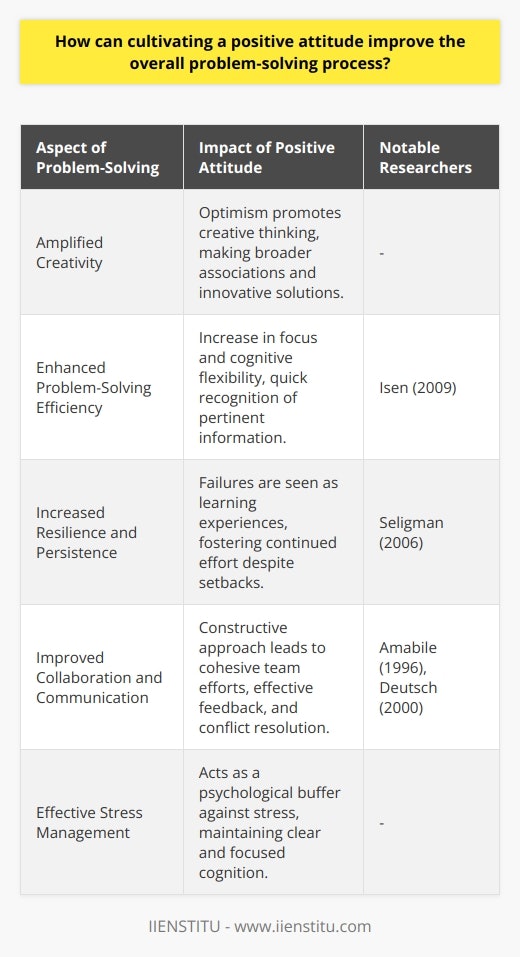
What are some practical strategies that can be employed to maintain a positive attitude while tackling complex problems?
Practical strategies for maintaining a positive attitude Cultivating a growth mindset One practical strategy for maintaining a positive attitude while tackling complex problems is cultivating a growth mindset. This involves embracing challenges, viewing failures as opportunities to learn and persisting in the face of obstacles. Setting smaller, achievable goals Another strategy is setting smaller, achievable goals. Breaking the complex problem down into manageable tasks helps make it less daunting and encourages progress. Completion of each smaller task provides a sense of accomplishment, motivating continued efforts. Adopting effective time management Implementing effective time management not only improves efficiency but also reduces stress. Prioritising tasks, setting realistic deadlines and incorporating breaks into the schedule ensures steady progress and protects against burnout. Emphasising mental and physical well-being Maintaining mental and physical well-being is crucial for sustaining a positive attitude. Prioritising sleep, nutrition, exercise and relaxation promotes a healthy mindset, better focus and increased resilience when faced with difficult problems. Surrounding oneself with positivity Our social environment can significantly impact our attitude. Surrounding oneself with positive, supportive and like-minded individuals helps create an uplifting environment conducive to problem-solving. Practicing self-compassion Recognising that everyone experiences occasional setbacks is essential for maintaining a positive attitude. Instead of being self-critical, practice self-compassion, accepting the present circumstances and focusing on what can be controlled and improved. Using positive affirmations Positive affirmations are statements that promote a positive mindset and stress resilience. Repeating these affirmations throughout the day can help boost self-esteem, motivation and overall attitude. Seeking external resources Lastly, seeking external resources like books, articles, online courses or even consulting with experts can provide valuable insights and tools for solving complex problems. These resources augment understanding and foster a sense of empowerment. In conclusion, incorporating various practical strategies such as cultivating a growth mindset, setting smaller goals, managing time effectively, prioritising well-being, surrounding oneself with positivity, practicing self-compassion, using positive affirmations and seeking external resources can help maintain a positive attitude while tackling complex problems. These approaches not only facilitate problem-solving but also improve overall resilience and well-being.
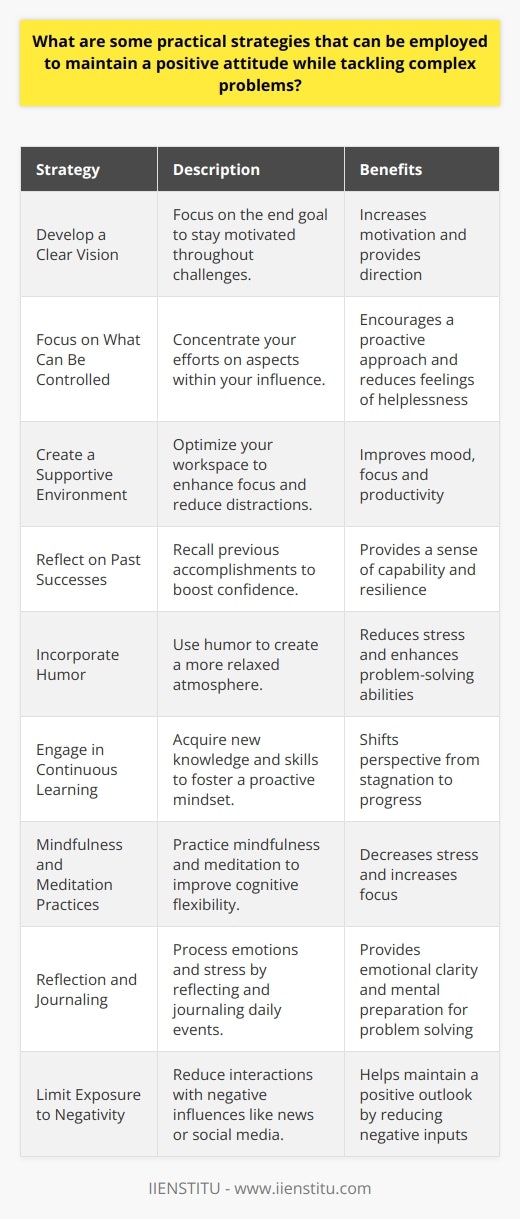
What are the factors that contribute to developing and maintaining a positive attitude during problem-solving?
Factors Influencing Positive Attitude Development Various factors contribute to developing and maintaining a positive attitude during problem-solving, which can enhance an individual's overall performance and success in finding effective solutions. These factors include cognitive, emotional, social, and environmental aspects. Cognitive Factors The cognitive factors involve an individual's inherent beliefs, perceptions, and thought patterns. A growth mindset, which embraces challenges and views effort as a pathway to improvement, is critical for fostering a positive attitude during problem-solving. Additionally, self-efficacy, or the belief in one's ability to achieve a desired outcome, can boost problem-solving efficiency and facilitate a positive attitude. Emotional Factors Positive emotions, like optimism and hope, play a vital role in maintaining a positive attitude during problem-solving. Optimism fosters resilience and encourages an individual to face challenges with a constructive approach. Further, hope promotes goal-directed thinking, adaptive coping strategies, and heightened motivation, which influence one's problem-solving attitude positively. Social Factors The social environment, including the presence of supportive peers, mentors, or supervisors, can contribute to a positive attitude development during problem-solving. Individuals in encouraging social contexts are more likely to feel confident and motivated to tackle challenges. Collaboration and teamwork can also facilitate diverse perspectives and creative solutions, promoting a constructive problem-solving attitude. Environmental Factors Lastly, the physical environment can impact an individual's attitude while addressing problems. A comfortable, organized, and functional workspace can foster focus, productivity, and a positive attitude. Additionally, implementing stress-relief techniques, such as regular breaks and stress-relieving activities, can foster a relaxed state of mind, essential for problem-solving. In conclusion, developing and maintaining a positive attitude during problem-solving involves a holistic approach that takes into account cognitive, emotional, social, and environmental factors. Cultivating a growth mindset, nurturing positive emotions, fostering supportive social connections, and optimizing the physical environment can significantly enhance an individual's problem-solving attitude and performance.
How do positive attitudes in problem-solving influence group dynamics and collaboration?
Impact on Group Dynamics Positive attitudes in problem-solving significantly affect group dynamics by fostering healthy communication channels, active participation, and commitment. With a solution-oriented mindset, group members tend to focus more on finding common ground, thereby minimizing conflicts and misunderstandings. As individuals distinctly acknowledge the potential of diverse perspectives in the resolution of complex tasks, they adopt a proactive approach to engaging with others. Enhancing Collaboration In addition, a positive problem-solving atmosphere promotes a sense of shared responsibility among group members. This feeling of connectedness paves the way for smooth collaboration, allowing individuals to leverage their strengths in achieving a shared objective. When group members support one another in overcoming challenges, they build trust and strengthen their interdependence, which is crucial for promoting a cohesive team culture. Promoting Creativity and Innovation Moreover, positive attitudes in problem-solving stimulate creativity and innovation within groups, as participants feel more comfortable sharing their ideas and thinking outside the box. By fostering an environment that celebrates diverse thinking and encourages open discussions, groups harness a wealth of knowledge that ultimately leads to the generation of novel solutions to complex issues. Encouraging Adaptability Furthermore, groups with a positive problem-solving outlook demonstrate high adaptability and resilience when encountering unexpected obstacles or setbacks. By focusing on solutions rather than dwelling on failure, members develop a sense of empowerment and determination. This, in turn, increases the group's overall capacity to develop and implement effective strategies that address the task at hand. Conclusion In summary, positive attitudes in problem-solving significantly influence group dynamics and collaboration by facilitating effective communication, fostering collective responsibility, stimulating creativity, and promoting adaptability. By cultivating a constructive and solution-oriented environment, groups can enhance their overall effectiveness and maximize their potential in achieving desired outcomes.
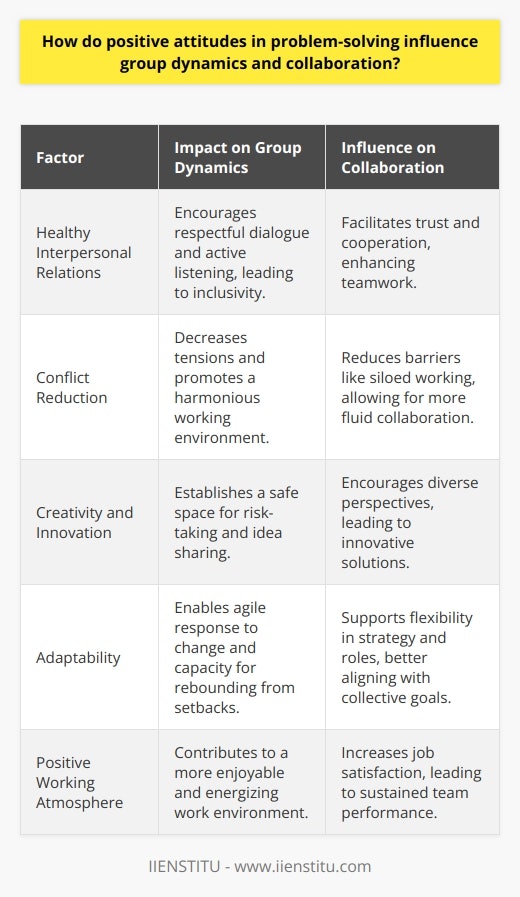
In what ways can fostering a positive attitude in problem-solving enhance creativity and innovation?
The Impact of a Positive Attitude Fostering a positive attitude in problem-solving significantly influences creativity and innovation within individuals and organizations. A positive mindset toward problem-solving allows the individual to explore more possibilities, yielding dynamic approaches for resolving issues. The Role of Cognitive Flexibility One crucial aspect of this influence is cognitive flexibility, which is the ability to think about a problem from multiple perspectives and generate diverse ideas. A positive attitude improves cognitive flexibility by encouraging individuals to focus on the potential benefits of generating innovative solutions, rather than dwelling on the difficulties faced in arriving at those solutions. This shift in focus enhances creative thinking by expanding the range of ideas and perspectives explored. Encouragement of Collaboration Additionally, a positive attitude promotes collaboration and knowledge sharing among team members, fostering a synergistic environment that supports idea generation and innovation. When individuals approach problem-solving with optimism, they are more open to hearing and learning from others' perspectives, facilitating the exchange of valuable insights and ideas. Embracing Risk-taking and Uncertainty Furthermore, a positive mindset empowers individuals to embrace risks and uncertainties associated with innovative problem-solving. By considering setbacks and failures as opportunities for learning and improvement, individuals can develop resilience and adaptability, vital traits for creativity and innovation. A positive attitude toward problem-solving encourages experimentation and learning, cultivating a growth mindset that fuels innovation. Enhanced Motivation and Persistence Finally, a positive attitude bolsters motivation and persistence in the face of challenging problems. When individuals believe in their ability to find solutions and the potential value of their ideas, they become more passionate about the problem-solving process. They are more likely to continue exploring and refining ideas, resulting in an increase in creative output and the development of innovative solutions. In conclusion, fostering a positive attitude in problem-solving can greatly enhance creativity and innovation by supporting cognitive flexibility, encouraging collaboration, embracing risk-taking and uncertainty, and bolstering motivation and persistence. Therefore, individuals and organizations should invest in cultivating a positive outlook for improved problem-solving outcomes, driving overall success.

Yu Payne is an American professional who believes in personal growth. After studying The Art & Science of Transformational from Erickson College, she continuously seeks out new trainings to improve herself. She has been producing content for the IIENSTITU Blog since 2021. Her work has been featured on various platforms, including but not limited to: ThriveGlobal, TinyBuddha, and Addicted2Success. Yu aspires to help others reach their full potential and live their best lives.

What are Problem Solving Skills?

3 Apps To Help Improve Problem Solving Skills

How To Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills

Improve Your Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Skills

Edison's 99%: Problem Solving Skills

How To Become a Great Problem Solver?

Definition of Problem-Solving With Examples

A Problem Solving Method: Brainstorming

6 Steps To Develop A Problem-Solving Mindset That Boosts Productivity
Problem-controlled approach vs. problem-solving approach, benefits of a problem-solving mindset, 6 steps to develop a problem-solving mindset, characteristics of a manager with a problem-solving mindset, problem-solving mindset examples for managers, frequently asked questions.
Other Related Blogs
What is a problem-solving mindset?
- Better decision-making: A problem-solving mindset helps managers analyze problems more effectively and generate various possible solutions. This leads to more informed decision-making , which is critical for effective leadership.
- Improved productivity: By addressing problems proactively, managers can prevent potential obstacles from becoming major issues that impact productivity . A problem-solving mindset can help managers to anticipate and prevent problems before they occur, leading to smoother operations and higher productivity.
- Enhanced teamwork: Encouraging a problem-solving mindset among team members fosters a culture of collaboration and encourages open communication. This can lead to stronger teamwork , as team members are more likely to work together to identify and solve problems.
- Improved morale: When managers take a proactive approach to problem-solving, they demonstrate their commitment to their team’s success. This can improve morale and build trust and respect between managers and team members.
- Better outcomes: Ultimately, a problem solving mindset leads to better outcomes. By effectively identifying and addressing problems, managers can improve processes, reduce costs, and enhance overall performance.
- Acknowledge the issue: Instead of avoiding or dismissing the problem, the first step in adopting a problem-solving mindset is to embrace it. Accept the problem and commit to trying to find a solution.
- Focus on the solutions: Shift your attention from the problem to the solution by concentrating on it. Then, work towards the result by visualizing it.
- Come up with all possible solutions: Create a list of all potential answers, even those that appear unusual or out of the ordinary. Avoid dismissing ideas prematurely and encourage creative thinking.
- Analyze the root cause: After coming up with a list of viable solutions. Finding the fundamental reason enables you to solve the problem and stop it from happening again.
- Take on a new perspective: Sometimes, a new viewpoint might result in game-breakthrough solutions. Consider looking at the problem differently, considering other people’s perspectives, or questioning your presumptions.
- Implement solutions and monitor them: Choose the best course of action, then implement it. Keep an eye on the findings and make changes as needed. Use what you learn from the process to sharpen your problem-solving skills.

- Positive attitude: A problem-solving manager approaches challenges with a positive and proactive mindset, focused on solutions rather than problems.
- Analytical thinking: A problem-solving manager breaks down complex challenges into smaller, more manageable pieces and identifies the underlying causes of difficulties because of their strong analytical skills .
- Creativity: A manager with a problem solving mindset think outside the box to solve difficulties and problems.
- Flexibility: A manager with a problem-solving mindset can change their problem-solving strategy depending on the circumstances. They are receptive to new ideas and other viewpoints.
- Collaboration: A manager who prioritizes problem-solving understands the value of collaboration and teamwork. They value team members’ feedback and are skilled at bringing diverse perspectives together to develop creative solutions.
- Strategic thinking: A problem-solving manager thinks strategically , considering the long-term consequences of their decisions and solutions. They can balance short-term fixes with long-term objectives.
- Continuous improvement: A problem-solving manager is dedicated to continuous improvement, always looking for new ways to learn and improve their problem-solving skills. They use feedback and analysis to improve their approach and achieve better results.
- Creating an inclusive workplace: How to welcome new team members effectively
- 6 Step Process For Ethical Decision Making: A Guide with Examples
- 5 Effective Ways To Always Meeting Deadlines As A Manager
- The Ultimate Guide to Managing a Call Centre: Top Tips Unveiled
- Understanding Referent Power In Leadership With 3 Real-Life Examples
- Assertive Communication for Managers: 5 Hacks to Master the Skill
- The Top 9 Communication Skills Every Manager Needs
- The 7 Best Ways to Effectively Handle Team Tensions As A Manager
- 13 Best Practices For Managing A Call Center: Overcome The Common Challenges
- Satisficer vs Maximizer: 2 types of managers in the workplace
- A manager listens actively to a team member’s concerns and identifies the root cause of a problem before brainstorming potential solutions.
- A manager encourages team members to collaborate and share ideas to solve a challenging problem.
- A manager takes a proactive approach to address potential obstacles, anticipating challenges and taking steps to prevent them from becoming major issues.
- A manager analyzes data and feedback to identify patterns and insights that can inform more effective problem-solving.
- A manager uses various tools and techniques, such as brainstorming , SWOT analysis, or root cause analysis, to identify and address problems.
- To inform about problem-solving, a manager seeks input and feedback from various sources, including team members, stakeholders, and subject matter experts.
- A manager encourages experimentation and risk-taking, fostering a culture of innovation and creativity.
- A manager takes ownership of problems rather than blaming others or deflecting responsibility.
- A manager is willing to admit mistakes and learn from failures rather than become defensive or dismissive.
- A manager focuses on finding solutions rather than dwelling on problems or obstacles.
- A manager can adapt and pivot as needed, being flexible and responsive to changing circumstances or new information.
Suprabha Sharma
Suprabha, a versatile professional who blends expertise in human resources and psychology, bridges the divide between people management and personal growth with her novel perspectives at Risely. Her experience as a human resource professional has empowered her to visualize practical solutions for frequent managerial challenges that form the pivot of her writings.
Are your problem solving skills sharp enough to help you succeed?
Find out now with the help of Risely’s problem-solving assessment for managers and team leaders.
Do I have a problem-solving mindset?
What is a growth mindset for problem-solving , what is problem mindset vs. solution mindset , what is a problem-solving attitude.

Top 15 Tips for Effective Conflict Mediation at Work
Top 10 games for negotiation skills to make you a better leader, manager effectiveness: a complete guide for managers in 2024, 5 proven ways managers can build collaboration in a team.

A Beginner’s Guide for Becoming a Better Problem Solver
How you think about a problem is more important than the problem itself. – Norman Vincent Peale
Three Methods of Thinking
Problem-solving, creative and critical thinking go hand-in-hand helping us to see the world from a number of different vantage points. Each of these ways of thinking strengthens our capacity to think flexibly and intelligently when faced with the unending problems that life throws our way.
This post will specifically focus on the process of problem-solving and how you can use it to break through life’s most difficult challenges. We will specifically explore the attitude, beliefs, habits, and qualities that are indispensable for effective problem-solving. We will also outline a primary problem-solving method that will help you to break down any obstacles that stand in your way. And to finish off we will look at some ongoing problem-solving tactics you can use to keep your mind focused and proactive when dealing with life’s daily challenges.
This article post is part of the Effective Thinking series of IQ Matrix maps that are designed to help you successfully deal with the problems and challenges confronting your reality. Topics within this series include:
• Part 1: Strategic Questions • Part 2: Creative Thinking • Part 3: Problem Solving • Part 4: Critical Thinking • Part 5: Six Thinking Hats
Indispensable Problem Solver Attributes
To become a great problem solver requires a little more than a set of effective problem-solving strategies. In fact, your ability to solve problem starts in your head at a psychological level.
If you do not take the time to fully condition your mind and prepare it for the act of problem-solving, then you will struggle to consistently adopt the daily behaviors and rituals that are required for effective problem-solving.
Within this section, we will identify the indispensable attributes required for problem-solving that you must learn to cultivate on a daily basis. If you fail to incorporate these qualities into your psyche, then you will struggle to apply the relevant problem-solving techniques and strategies discussed in this post.
A Problem Solver’s Attitude
A problem solver’s attitude determines how they consistently tackle problems on a daily basis. This attitude is evident in their thoughts, behaviors, and actions, and it is this attitude that helps build their resolve and shapes their character.
Let’s delve into the mind of an effective problem solver and identify some of the attitudes that are absolutely indispensable to their ongoing success:
“I will make sure to do things carefully.”
An effective problem solver always strives to work through their problems in a patient, meticulous and careful way. They fully understand that the care they give to a problem at the beginning will help them to realize better results in the future.
“This problem can be solved.”
An effective problem solver intuitively understands that any problem can and will be solved, given enough time, patience and meticulous careful attention.
“I must persist until a solution is reached.”
An effective problem solver knows that not all problems will be solved within the time frame they may have expected. However, they also understand that if they are persistent and resolute, that eventually a solution will be found.
“If I don’t solve it now, I will next time.”
An effective problem solver realizes that whatever cannot be solved now, will eventually be solved another time.
They fully understand that due to their current level of skill, knowledge, or simply due to circumstances out of their control, that a solution simply cannot be reached.
An effective problem solver will bide their time to acquire new information and knowledge, to develop and enhance their skill levels, and to gain insights from a variety of perspectives. They completely understand that eventually, the right solution will indeed come their way as long as they never give up.
“I am going to enjoy this process.”
An effective problem solver knows that unless they adopt a playful, curious and inquisitive attitude, that they will struggle to find appropriate solutions. They therefore always strive to find new and unique ways to enjoy the process of working their way through a problem.

A Problem Solver’s Beliefs
An effective problem solver has a set of indispensable beliefs and convictions that direct and propels their thoughts, actions, and daily behaviors. These beliefs are so deeply ingrained in their psyche that it would take the force and willpower of the entire world to shake these feeling of certainty.
Beliefs are opinions that we have about things, ourselves, others and the world around us that are injected with an undeniable sense of certainty.
Let’s now take a look at a handful of beliefs that are critical for effective problem solving:
“There is no failure, only feedback.”
An effective problem solver believes that outcomes bring with them no failure, but rather only feedback. This feedback must be used as a source of knowledge, insight, and inspiration to help enhance the decision-making process.
“There is a way to make this work.”
An effective problem solver believes that there is always a way to make things work. They may not see the solution at this very moment, however with a little persistence they wholeheartedly believe that they will eventually reach a satisfactory outcome.
“Choice is better than no choice.”
An effective problem solver believes that it is better to have more choices than to be limited by the choices that one has. As such, they always strive to expand the possibilities, to expand the opportunities and avenues for answers — allowing for as many choices as possible to further their understanding of the problem.
“Success can be modeled.”
An effective problem solver believes that successful problem solving can be modeled. As such, they consistently seek out other people who have successfully overcome similar problems and they attempt to model their thinking, decisions, and actions in a meticulous way. This helps them to overcome the obstacles and challenges in their own life.
“Curiosity expands opportunities and possibilities.”
An effective problem solver believes that one must be curious at all times if one desires to spot the opportunities and possibilities that lie along one’s path.
Curiosity is an endearing characteristic that helps expand creativity, intelligence and one’s ability to think under pressure.
A Problem Solver’s Habits
An effective problem solver has a set of daily habits and rituals. These habits assist them to think more effectively and proactively about the problems and challenges they are confronted with.
Let’s take a look at three habitual thinking patterns that are indispensable for effective problem solving:
Deep Probing
An effective problem solver cultivates the habit of deep-probing. This involves the process of meticulous thinking, which takes into account all angles and perspectives about a problem — making sure that nothing is left to chance.
They fully realize that through a process of simple deduction that they will be better able to work their way through the problem in a more effective and efficient way.
The habit of deep probing can be compared to the simple act of peeling layers off an onion. Each layer that the problem solver peels allows them to dig deeper into the heart of the problem, and thusly closer to the inevitable solution.
Associating with the Past
An effective problem solver realizes that any new piece of information can effectively be associated with past memories, experiences, and learnings, to further their problem-solving ability.
Recognizing Patterns
An effective problem solver effortlessly recognizes patterns within every problem or circumstance.
Everything within our Universe is built upon patterns and rhythmic dances that create the events and circumstances of our lives. In fact, these same patterns cause and create our life’s problems and circumstances.
By identifying and learning to understand these patterns, effective problem solvers are able to decipher clues that will lead them to reliable solutions and answers.
When attempting to identify patterns look for similarities, differences, rhythms, errors, future scenarios and trends that the problem is bringing to light.
A Problem Solver’s Characteristics
An effective problem solver can easily be distinguished from others by the key personality characteristics that naturally help them to break down boundaries and attain the heights of logical and constructive thought.
The characteristics presented below are the primary traits we must cultivate within our own personalities if we seek to successfully overcome the problems and challenges that are confronting our daily lives.
An effective problem solver understands that many problems will never fully be solved if a risk isn’t involved.
A risk may mean overcoming a fear, thinking outside-the-box, or simply making the tough decisions that at the moment may seem uncertain and unclear.
Problem solvers are risk takers who believe that intelligent risk-taking will enable them to reach effective solutions to the challenges confronting their daily reality.
An effective problem solver is persistent in thought, decision, and action. They clearly understand that there are a means and way around any problem, fully believing that as long as they persist and persevere that they will always find an angle that will help them obtain a desired outcome.
Enthusiastic
An effective problem solver displays passion and enthusiasm at all times. These two qualities provide them with the energy and motivation they need to help them overcome the toughest of challenges.
An effective problem solver is meticulous with every step they take moving towards their desired outcomes.
This thoroughness allows them to work through their problems step-by-step — taking into account all angles and perspectives.
Adaptable and Flexible
An effective problem solver is constantly vigilant and aware of constantly changing circumstances. They clearly understand that problems can shift and change at a moments notice, and as a result, they must adapt their approach accordingly.
It is only through flexibility-of-thought that they are able to work through their problems in an efficient and effective way.
Open Minded
An effective problem solver is always humbly open minded to other people’s opinions and perspectives. They clearly understand that they do have all the answers and that others may indeed have alternative views that will help them to see things from new and unique perspectives. This likewise helps open the doors to new understandings that would not otherwise have been available to them.
Lighthearted
An effective problem solver approaches their daily challenges in a light-hearted and playful manner. They fully realize the overwhelming power that problems can have on their psyche. To counteract this, they approach each problem in a playful and light-hearted way — helping them to find solutions and answers where others only see overwhelm and distress.
An effective problem solver is proactive. They understand, they just have to keep moving forward and continue to take proactive action no matter how uncertain events or circumstances may seem at any specific moment in time.
The opposite of being proactive is being reactive . When we are reactive we become easily overwhelmed by the events and circumstances of our lives because we fail to take control of our emotional responses.
An effective problem solver is a curious thinker .
Curiosity naturally leads to a plethora of questions that need to be answered. Once answered, they can evolve into a myriad of solutions that will help you to attain your desired goals and objectives far more quickly.
Non-Conforming
An effective problem solver does not conform to the standards and norms of mainstream society. Instead, they think out of the box and break the rules in order to attain their desired outcomes.
The Primary Problem Solving Method
There are many problem-solving techniques and strategies that we could present here. However, there is essentially only one primary problem-solving method that will help you to structure and break down a problem step-by-step from the beginning to the very end. To view an advanced version of this problem-solving method, please check out the Visual Thinking Path .
Within this section, we will work our way through a six-step primary problem-solving method.
By consciously learning to apply each of these steps/phases into your problem-solving regime, you will proactively take control of your daily decision-making process.
The Preparation Phase
This phase helps you to identify, define and decipher an overall picture and understanding of the problem that is currently confronting your reality.
As you progress through this phase, it is important to gain as much clarity about your problem as possible from absolutely every angle and perspective. Any assumptions or misunderstandings here could very well sabotage your ability to reach an effective solution. Therefore be very careful to clarify everything clearly and meticulously.
Identify the Problem
Your first step is to always clearly identify the problem that is confronting your reality. Many people fail to do this correctly, and as a result, they discover that what they thought was a problem is, in fact, a mistaken assumption that now requires a dramatically different approach.
Define Problem in Writing
Once you have identified the problem, your next step is to clearly define it on paper. It is only through the process of writing our thoughts down on paper that we attain the clarity we need to effectively deal with the challenges that stand in our way.
Question the Problem
To further clarify and expand your understanding about this problem, it is recommended that you ask yourself a set of open-ended questions that will help you to define the problem from a variety of angles and perspectives.
The questions you should be asking yourself must be focused on the What? When? Where? Why? Who? and How? of the problem under question.
Undertaking this process with meticulous attention will open new insights and understandings that will help you as you move through this problem-solving strategy.
It is important to understand that you are not seeking solutions or answers here but rather gathering insights about the problem from as many different angles and perspectives you can identify.
Here are a few questions to get you started:
What is the actual problem that is impeding my progress? When did this problem occur? Where did this problem first appear? Why is this problem impeding my progress? Who is involved in this problem? How is this problem influencing other areas of my life?
Determine Possible Causes
Once you have clarified the problem, your next step is to identify the possible causes that may have triggered these outcomes.
Again during this stage, you must continue asking What? When? Where? Why? Who? and How? questions.
What could be the potential causes of this problem? When did these causes originate? Where did these causes originate? Why did these causes originate? Who could have triggered this problem? How does all this help me with identifying the causes of this problem?
Reframe the Problem
Once you have identified and defined the causes of the problem, it is important to open your mind to alternative perspectives.
At this stage, you are not yet seeking answers or solutions but rather opening your mind to different perspectives that will help you to understand the problem from a variety of angles.
Here are a few reframing questions to get you started:
How might other people perceive this problem? How would I perceive this problem if I was to look back on it 12 months from this day? What if I was completely detached from this problem and its outcomes. How would I now perceive it? What has to be true for this to be a problem?
Define Desired Outcomes
Finally, you must gain clarity by defining the desired outcomes you would like to attain from successfully working your way through this problem.
These outcomes will help direct your mind towards solutions as you progressively move through the remaining phases.
The strategy you use to achieve this outcome isn’t important at this stage. The only thing that matters is that you clarify on paper the end objective or goal you would like to achieve.

The Generation Phase
This phase allows for free association and exploration of wild and crazy ideas that must not be judged, criticized or condemned for any reason.
The greater flexibility of thought you incorporate into this phase, the more effective the later phases will become.
It is important throughout this phase that you literally overwhelm your brain with as many solutions as possible. The greater the variety of solutions and strategies you come up with, the more insightful and effective the Incubation Phase will become.
Recall Past Learning, Experiences and Mistakes
Recalling your past life experiences will help you to gain a better perspective on your current predicament.
Many people constantly need to deal with the same ongoing problems because they simply fail to learn from their past experience and mistakes.
It is only through a process of self-reflection and understanding that we will gain the necessary insights to move through our current problems efficiently and effectively.
Keep in mind that any past experience — even if not directly related to your current problems — could potentially help you find the solutions you are after.
Explore Strategies and Solutions
Having brought your past learnings and mistakes into the present, you are now ready to brainstorm solutions and strategies that will help you to successfully overcome the challenge confronting your current reality.
While brainstorming it’s important not judge or criticize your solutions. Your thinking must flow effectively and efficiently from one idea to the next like water gently trickling off a leaf. All you are doing is generating possible and potential solutions that will help to expand your thinking and awareness about the problem you are currently experiencing.
You can lightly consider the drawbacks and obstacles that may be attached to each of your solutions, however primarily spend your time on the benefits of each strategy and how it could potentially lead you to the outcome you outlined within the Preparation Phase.
As a final thought, keep in mind that the how isn’t important here. Instead, it is the what that matters.
The Incubation Phase
This could very well be called the Resting Phase .
Your goal here is to simply allow the solutions and ideas you came up with during the Generation Phase to harvest and grow within the recesses of your mind without ridicule or judgment.
The key here is to separate your mind from the problem so completely that it simply becomes irrelevant and insignificant.
Flowers cannot sprout and grow if weeds are dominating your thought process.
Indulge in Brainstorming Naps
Brainstorming naps are short 15 to 30-minute breaks you take throughout your day where you close your eyes and open yourself up to potential solutions.
Before you take these brainstorming naps, it is important that you partake in a good 30 to 45 minutes of intense thought and self-reflection about possible solutions to your problem.
As you lie back in a comfortable position and close your eyes, ask yourself the following questions:
How can I solve this problem in the most effective and efficient way? What must I do to attain my desired outcome?
Once your questions have been asked, simply settle down and observe your thoughts as though you are watching clouds drifting across the sky. Within these visual images, you may very well find the answers you are after.
Sleep on Problem
Simply put your problem to rest and go to sleep.
As you are nodding off, pose yourself insightful questions that will stimulate the thought process and encourage your brain to search for answers.
When you awaken the next morning, immediately reflect on your thoughts and dreams — they may hold the answers you have been searching for.
Change Your Environment to Improve Incubation
Stepping out into nature or simply into an inspiring and energetic environment will separate you from your problem and help you to think more effectively about potential solutions. However, since we are in the Incubation Phase, it is important to simply let go of the process of intense meticulous thinking. Instead, enjoy your surroundings and the answers you are after will eventually reveal themselves to you. And just in case, have a piece of paper and pen ready to write down inspiring solutions as they come your way.
Evolution Phase
Now that your ideas have had a chance to incubate within the recesses of your mind, you are now ready to take your thinking to the next level — becoming your worst and best critic.
Your goal throughout the Evolution Phase is to break down and clarify all your potential solutions progressively and meticulously allowing for deep insights and all round perspectives.
The more thorough you are while undertaking this process, the fewer problems you will face throughout the Implementation Phase that follows.
Prioritize and Evaluate Solutions
Collate all the solutions you brought forward throughout the Generation and Incubation Phases and evaluate them accordingly.
Evaluate the viability of these solutions by looking at them from a variety of different angles and perspectives. Also, take into account the time and energy you have available that will allow you to bring these solutions into the real world.
Once completed, prioritize your solutions to help you better decipher which ones could best assist you in overcoming your problems most effectively.
Speculate Potential Future Outcomes and Negative Consequences
Future-pace each solution and see it clearly helping you overcome your problem.
Identify the possible drawbacks, weaknesses, strengths and potential opportunities that may result.
The greater clarity you gain here, the easier it will be to settle on an ideal and clear-cut solution to your problem.
Settle on Solutions
Having accumulated a thorough and comprehensive list of solutions throughout the Generation and Incubation Phases, and having outlined the possible consequences of each of these outcomes, you are now ready to select one primary desirable solution that will help you overcome your problem in the most effective and efficient manner.
Take everything into consideration and decide which solution will best help you to achieve your desired outcome.
Implementation Phase
Your goal throughout the Implementation Phase is to progressively and meticulously work through the solution to your problem in a step-by-step manner using a process of logical decision making and action. You are basically bringing everything you have thought about and outlined on paper into reality.
Many people will struggle to get through this stage successfully because of the dreaded procrastination bug. Be sure that you don’t fall into this dirty trap. 🙁
Clarify Your Personal Vision of Outcome on Paper
Having settled on your ideal solution to this problem, take some time now to clarify this vision on paper.
Clarify the Personal Resources at Your Disposal
Identify the support, skills, knowledge, and tools you currently have at your disposal that will help you to successfully overcome this problem. These are your resources . If you find that you are lacking in some of these areas, then you may need to regroup and update your skills or knowledge to help you deal with this problem more effectively. Or you may simply need to obtain the help and support of a new group of people who can guide you through this problem in a more proactive and efficient way.
Create Three Alternative Plans of Action
Now that you have the necessary skills, knowledge, support, and tools you need to overcome this problem successfully, your next step is to draw up your plan of action.
As previously discussed, it is important to be flexible with your actions and to take into consideration all the drawbacks and potential pitfalls of these steps.
In order to minimize the possibilities of getting stuck, it is critical that you outline three alternative plans of action. If Plan A works out, then that’s great. However, if it fails miserably, then you still have Plan B and C at your disposal.
Set Clear Defined Deadlines for these Actions
Clear and defined deadlines will motivate you into action while providing you with a time sensitive objective to work towards.
Take Action Committing Yourself to the Result

The Learning Phase
This is an important phase that is very often overlooked. It will help you to clarify your thoughts, including the methods and strategies you used throughout the problem-solving process.
The learnings you gather from self-reflection will provide you with indispensable insights that will put your problem-solving methods in perspectives — improving the effectiveness and efficiency of your approach as you tackle similar challenges in the future.
Monitor Your Outcomes
As you progress along your journey towards implementing your solution, pay attention to the outcomes that result from every thought you make and every decision and action you take. This awareness will help you to better understand your personal traits and tendencies, which will likewise assist you with improving your problem-solving methods in the future.
Reflect on the Problem Solving Process
Once you have successfully overcome your problem, spend some time thinking and reflecting on the problem-solving process.
Here are some questions to get you started:
What did I do well, and what am I proud of about the way I conducted myself throughout this process? What problem solving traits did I cultivate and bring to the forefront throughout this process? What problem solving traits did I neglect? What mistakes did I make as I worked my way through this problem? What have I learned from these experiences? What could I have done better… more effectively and efficiently? How can I use these learnings and experiences to further my problem solving abilities in the future?
For a more advanced look at this problem-solving method, please check out the Visual Thinking Path .
Ongoing Problem Solving Tactics
Becoming an effective problem solver requires an ongoing process of conscious thought and action that opens new doors of opportunity to the solutions and answers you are after.
The solutions and answers you are after will be difficult to attain if you only apply the primary problem-solving method sporadically. Instead, you must consciously instill into your psyche habitual patterns of behavior that are consistent and aligned with a problem solver’s mentality.
Becoming an effective problem solver is not a part-time career, it is rather a full-time process that eventually becomes second nature.
Within this section, we will explore a number of effective ongoing problem-solving tactics you can use consistently throughout your day to keep your mind primed and ready for any challenge that may come your way.
Mindset Oriented Tactics
The following is a list of mindset oriented problem-solving tactics you can use on a consistent basis to keep your mind primed and ready for the challenges that come your way:
Visualize Your Desired Outcomes
It is said that we can only achieve our goals and objectives if we are able to clearly visualize them first in our minds-eye.
That which we are unable to visualize, we will likewise not be able to comprehend and realize within our physical reality.
When we were babies our motor skills developed over time through a process of observation and visualization. Only once we were able to successfully visualize in our minds-eye the process of picking-up physical objects, were we able to bring that same ability successfully into our physical reality. Given this, do you see how important it is to spend time visualizing your outcomes and the possible scenarios and strategies you will use to overcome your problems effectively?
Ask Questions Searching for Solutions
Questions are the keys that will unlock doors of opportunity and answers to even the most pressing of problems.
If you ask the ideal solution focused question , you will receive the right answers to help move you forward through your challenges in the most effective and efficient way.
Always See Opportunities for New Learnings
Problem-solving is essentially built upon the concept of opportunity-spotting.
Effective problem solvers don’t actually see problems as others do. Instead, they see only opportunities for new learnings, insights, and understandings that will help them to keep moving forward towards the attainment of their goals and objectives.
You must train your mind to look at every event or circumstance as an opportunity for you to become and grow to your full potential.
The challenges you face in life are there for a reason to help you attain your highest potential as a human being. See these problems as opportunities and you will move through them more effectively and swiftly than ever before.
Think Critically
By thinking critically about every problem and circumstance in your life, you will break down the walls of the assumption that tend to trap the mind within unhelpful thinking habits.
Think Creatively
Whereas problem-solving is very structured and logical, creativity , on the other hand, is unstructured and imaginative.
These two forms of effective thinking are in many ways tied together and will work in conjunction to help you break through the obstacles standing in your way.
Think is Solitude
In order to think more effectively about the problems in our lives, we must first clear the clutter from our heads.
This process begins when we remove ourselves from the physical distractions that could impede our thinking ability.
Within solitude, you will find peace, harmony and a sense of connection with your body, spirit, and mind. This will help release built-up tension while opening up the channels to intuitive, creative and logical thought — helping you to overcome your problems with far greater ease.
Let Go of Fears
Your fears will rob you of the ability to think effectively and problematically.
Effective problem solvers don’t allow their fears to control their thoughts, decisions, and actions. Instead, they usurp their fears and focus on the pleasures that will bring them the outcomes they desire to experience within their lives.
Let Go of Judgments and Criticisms
Effective problem solving requires us to let go of ill-fated judgments and criticisms.
The ideal solution can only be reached if we take time to harvest and cultivate it within the recesses of our minds for an extended period of time. This process thusly requires us to let go of the Devil’s Advocate role and milk our ideas for all their worth.
It is only towards the end of the problem-solving process that the Devil’s Advocate card should be played.
Let Go of Biases and Assumptions
For the same reason as mentioned above, we must let go of all biases and assumptions that may hold us back from successfully finding a solution to the problem at hand. This is often easier said than done because in many instances our assumptions and biases naturally color our understanding of reality.
If we mistakenly assume something, then we may redirect our thoughts, decisions, and actions down paths that we did not want to tread.
The solution is to ask insightful and carefully structured questions that will help us to break down the biases and assumptions we are holding onto at any one moment in time.
Allow for Fantasizing
Fantasizing can be an effective form of creative problem-solving.
Take time each and every day to remove yourself from physical reality and fantasize about creating a perfect life where everything you imagine becomes your reality.
This process will help to loosen your mind, and may very well open the doors to a set of insightful ideas that will assist you in overcoming your problems more effectively.
Allow for Playfulness
Playfulness is another endearing quality that you must cultivate every single day.
Perceive each and every problem as an intriguing game that you must win at all costs. Play this game, have fun, and enjoy the experience to its fullest.
Allow for Idea Incubation
No idea will fully evolve and grow to its fullest potential if you fail to incubate it within the recesses of your mind for a period of time.
Sometimes brilliant ideas can come to us quite effortlessly. As a result, our excitement takes over and we immediately take action in an attempt to bring the idea into physical reality. However, later we realize that the idea was incomplete or simply didn’t work as expected.
In instances such as these, it is easy to get disheartened. Our idea was great, but for some reason, it just didn’t evolve because little did we realize at the time, that this iceberg-idea was only the tip of a much larger, complete and comprehensive thought-pattern that was never brought to the surface .
In such instances, we must learn from this experience and take time to incubate our ideas as we move forward into the future.
Explore Funny and Foolish Ideas
No idea should ever be ruled out. Every idea is valid and useful no matter how foolish, crazy or funny it might seem on the surface. In fact, some of the most foolish ideas have indeed earned people millions and others billions of dollars. For this very reason, it’s critical that you never discount any idea until you have taken it through the entire problem-solving cycle discussed within this post.

Explore Alternative Perspectives Using Lenses
Lenses are a form of creative problem solving that will help you to expand your understanding and awareness of your circumstances from a variety of unique and interesting perspectives.
Each lens will help you to see the problem from a new point-of-view — assisting you with identifying creative solutions you may not have thought of before.
The following list presents you with just a few lenses you can use to help trigger creative solutions to your problems:
Childhood Lens
Look at your problem from the perspective of an inquisitive and curious child.
See your problem as an innocent circumstance that isn’t tinged with pre-conceived biases or assumptions .
Ask yourself seemingly foolish, funny and creative questions that open new ways of thinking about mundane circumstances and problems.
How would a child approach this problem? What kinds of questions would they ask?
Athlete’s Lens
Look at your problem from the perspective of a motivated and determined athlete.
See your problem as a mountain that you will tame and conquer .
Ask yourself questions that will help you to persist and persevere — effectively expanding the possibilities of your solutions.
How would an athlete approach this problem? What kinds of questions would they ask?
Artist’s Lens
Look at your problem from the perspective of a creative and imaginative thinker.
See your problem as a work of art that progressively takes shape .
Ask yourself questions built around metaphors , stories, visual concepts and ideas that will provide you with a unique perspective on your problem.
How would an artist approach this problem? What kinds of questions would they ask?
Scientist or Inventor’s Lens
Look at your problem from the perspective of an analytical scientist or crazy inventor.
See your problem as an experiment that you must test and perfect .
Ask yourself questions that are built upon logical thought and experimentation.
How would a scientist or crazy inventor approach this problem? What kinds of questions would they ask?
Politician’s Lens
Look at your problem from the perspective of a confident, confronting and ambitious politician.
See your problem as a political campaign that you must win at all costs .
Ask yourself questions that help you poke holes in your problem, thus bringing its weaknesses to the forefront — much like what politicians do to their opponents during television debates.
How would a politician approach this problem? What kinds of questions would they ask?
Action Oriented Tactics
The following is a list of action-oriented problem-solving tactics you can use on a consistent basis to keep your mind primed and ready for the challenges that come your way:
Persistently Write Out Questions
Questions are the keys that will bring forth the answers and solutions to your problems.
Sit down for 30 minutes per day with two sheets of paper and a pen. Now, write out your problem in a question format on top of both sheets. Next, take your 1st sheet of paper and spend 15 minutes writing out as many questions as you can think of that will help expand your understanding and awareness of this problem. Finally, when your 15 minutes is up, take out the 2nd sheet of paper and write out as many solutions as you can think of that will answer the questions you posed on the 1st sheet of paper.
By undertaking this process consistently each and every day, you will develop a problem-solving knack that will help you breakthrough any obstacle standing in your way.
Read Broadly
Sometimes the answers to our problems can come from the most unexpected sources.
Keep your problem in mind as you read a book, magazine or newspaper and observe your brain in overdrive searching for new pieces of information that it can associate with old memories and experiences.
Within every piece of information you read, the pictures you see, and the sounds you listen to, lies the solution to your problem . This awareness will get you halfway to your answer. However, you must be fully committed to lifelong learning.
Update Your Skills and Knowledge
Our problems can only overwhelm us when we feel incapable of dealing with them in an effective and timely manner. The solution for this is to update specific skills and knowledge (pertaining to the problem) that will allow you to better handle and manage these types of challenges in the future.
Use Positive Language
A pessimist will naturally have a very difficult time finding solutions to even the simplest of problems. On the other hand, an optimistic realist who uses positive language will bring forth a great array of solutions that will further expand their thinking and creative potential.
Use Concept Maps and Mind Maps
Mind maps are extraordinary problem-solving tools that will allow you to easily brainstorm effective and creative ideas.
Mind Maps mimic our brain’s natural capacity to think, manage and organize large chunks of information in an efficient way. They will help you to put your problem into perspective while giving birth to new connections and associations that may not have been evident before.
Use Diagrams
Because our brains think in pictures and not words, it just makes sense that diagrams would help us conceptualize our ideas in a much more creative way.
You may be surprised with the insights you will gather from simply drawing up your problem and solutions in a diagrammatic picture format.
Create and Use a Problem Solving System
Finally, it is important to understand that our problems will never evaporate completely. Such is life, that it constantly and continuously tests our resolve in order to help us grow and achieve our most desired goals and objectives.
Those people who don’t seem to experience any problems in life have simply mastered the illusion of hiding their problems from others. They have learned methods that help them manage their problems using a potentially unconscious systematization process.
Every time you successfully work through your problems, it is important to draw up a systematic management plan that will help you to deal with these types of problems in a more effective and efficient way in the future.
Visit Brian Tracy’s website to learn more about his personal development and business courses, books, and programs.
Concluding Thoughts
It has been said that…
It’s not what happens to us that determines our fate, it’s rather what we do with what happens that shapes our destiny.
The problems and challenges that confront our everyday reality are drawn to us for a reason and purpose — teaching us life lessons that help us grow and attain new levels of insight, awareness and understanding.
Without problems we would never grow, we would never mature, we would never fully develop, and we would never experience the joy and satisfaction of attaining our most inspiring goals and objectives .
Yes, problems are indeed blessings in disguise for some, while for others they become steppingstones for misery, stress, mayhem, and dissatisfaction. These people just don’t get it…
Time to Assimilate these Concepts

GET THIS MAP
Did you gain value from this article? Is it important that you know and understand this topic? Would you like to optimize how you think about this topic? Would you like a method for applying these ideas to your life?
If you answered yes to any of these questions, then I’m confident you will gain tremendous value from using the accompanying IQ Matrix for coaching or self-coaching purposes. This mind map provides you with a quick visual overview of the article you just read. The branches, interlinking ideas, and images model how the brain thinks and processes information. It’s kind of like implanting a thought into your brain – an upgrade of sorts that optimizes how you think about these concepts and ideas. 🙂
Recommended IQ Matrix Bundles

If you’re intrigued by the idea of using mind maps for self-improvement then I would like to invite you to become an IQ Matrix Member.
If you’re new to mind mapping or just want to check things out, then register for the Free 12 Month Membership Program . There you will gain access to over 90 mind maps, visual tools, and resources valued at over $500.
If, on the other hand, you want access to an ever-growing library of 100s of visual tools and resources, then check out our Premium Membership Packages . These packages provide you with the ultimate visual reference library for all your personal development needs.

Gain More Knowledge…
Here are some additional links and resources that will help you learn more about this topic:
- The Art of Complex Problem Solving @ iDiagram
- Einstein’s Secret to Amazing Problem Solving @ Litemind
- 16 Practical Tips for Solving Your Problems More Easily @ Positivity Blog
- 10 Timeless Lessons on Better Thinking @ Life Optimizer
- Your Guide to Get Spinning in the Idea Tornado @ Think Simple Now
- How to Find Creative Solutions to Non-Creative Problems @ Scott H Young
- Problem Solving Toolkit – 33 Tricks to Answer Tough Problems @ Scott H Young
- Solve Tough Problems by Using Lenses @ Scott H Young
- Square Watermelon Problem Solving @ Dumb Little Man
- The Best Way to Solve a Problem: Give Up @ Paid to Exist

About The Author
Adam Sicinski
Start typing and press enter to search.

- INTERPERSONAL SKILLS
- Problem Solving and Decision Making
Problem Solving
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Interpersonal Skills:
- A - Z List of Interpersonal Skills
- Interpersonal Skills Self-Assessment
- Communication Skills
- Emotional Intelligence
- Conflict Resolution and Mediation Skills
- Customer Service Skills
- Team-Working, Groups and Meetings
- Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
- Effective Decision Making
- Decision-Making Framework
- Introduction to Problem Solving
- Identifying and Structuring Problems
- Investigating Ideas and Solutions
- Implementing a Solution and Feedback
- Creative Problem-Solving
- Social Problem-Solving
- Negotiation and Persuasion Skills
- Personal and Romantic Relationship Skills
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Everybody can benefit from having good problem solving skills as we all encounter problems on a daily basis. Some of these problems are obviously more severe or complex than others.
It would be wonderful to have the ability to solve all problems efficiently and in a timely fashion without difficulty, unfortunately though there is no one way in which all problems can be solved.
You will discover, as you read through our pages on problem solving, that the subject is complex.
However well prepared we are for problem solving, there is always an element of the unknown. Although planning and structuring will help make the problem solving process more likely to be successful, good judgement and an element of good luck will ultimately determine whether problem solving was a success.
Interpersonal relationships fail and businesses fail because of poor problem solving.
This is often due to either problems not being recognised or being recognised but not being dealt with appropriately.
Problem solving skills are highly sought after by employers as many companies rely on their employees to identify and solve problems.
A lot of the work in problem solving involves understanding what the underlying issues of the problem really are - not the symptoms. Dealing with a customer complaint may be seen as a problem that needs to be solved, and it's almost certainly a good idea to do so. The employee dealing with the complaint should be asking what has caused the customer to complain in the first place, if the cause of the complaint can be eliminated then the problem is solved.
In order to be effective at problem solving you are likely to need some other key skills, which include:
Creativity. Problems are usually solved either intuitively or systematically. Intuition is used when no new knowledge is needed - you know enough to be able to make a quick decision and solve the problem, or you use common sense or experience to solve the problem. More complex problems or problems that you have not experienced before will likely require a more systematic and logical approach to solve, and for these you will need to use creative thinking. See our page on Creative Thinking for more information.
Researching Skills. Defining and solving problems often requires you to do some research: this may be a simple Google search or a more rigorous research project. See our Research Methods section for ideas on how to conduct effective research.
Team Working. Many problems are best defined and solved with the input of other people. Team working may sound like a 'work thing' but it is just as important at home and school as well as in the workplace. See our Team-Working page for more.
Emotional Intelligence. It is worth considering the impact that a problem and/or its solution has on you and other people. Emotional intelligence, the ability to recognise the emotions of yourself and others, will help guide you to an appropriate solution. See our Emotional Intelligence pages for more.
Risk Management. Solving a problem involves a certain amount of risk - this risk needs to be weighed up against not solving the problem. You may find our Risk Management page useful.
Decision Making . Problem solving and decision making are closely related skills, and making a decision is an important part of the problem solving process as you will often be faced with various options and alternatives. See Decision Making for more.
The measure of success is not whether you have a tough problem to deal with, but whether it is the same problem you had last year.
John Foster Dulles, Former US Secretary of State.
What is a Problem?
The Concise Oxford Dictionary (1995) defines a problem as:
“ A doubtful or difficult matter requiring a solution ”
“ Something hard to understand or accomplish or deal with.”
It is worth also considering our own view of what a problem is.
We are constantly exposed to opportunities in life, at work, at school and at home. However many opportunities are missed or not taken full advantage of. Often we are unsure how to take advantage of an opportunity and create barriers - reasons why we can't take advantage. These barriers can turn a potentially positive situation into a negative one, a problem.
Are we missing the 'big problem'? It is human nature to notice and focus on small, easy to solve problems but much harder to work on the big problems that may be causing some of the smaller ones.
It's useful to consider the following questions when faced with a problem.
Is the problem real or perceived?
Is this problem really an opportunity?
Does the problem need solving?
All problems have two features in common: goals and barriers.
Problems involve setting out to achieve some objective or desired state of affairs and can include avoiding a situation or event.
Goals can be anything that you wish to achieve, or where you want to be. If you are hungry then your goal is probably to eat something. If you are the head of an organisation (CEO), then your main goal may be to maximise profits and this main goal may need to be split into numerous sub-goals in order to fulfil the ultimate aim of increasing profits.
If there were no barriers in the way of achieving a goal, then there would be no problem. Problem solving involves overcoming the barriers or obstacles that prevent the immediate achievement of goals.
Following our examples above, if you feel hungry then your goal is to eat. A barrier to this may be that you have no food available - so you take a trip to the supermarket and buy some food, removing the barrier and thus solving the problem. Of course for the CEO wanting to increase profits there may be many more barriers preventing the goal from being reached. The CEO needs to attempt to recognise these barriers and remove them or find other ways to achieve the goals of the organisation.
Our problem solving pages provide a simple and structured approach to problem solving.
The approach referred to is generally designed for problem solving in an organisation or group context, but can also be easily adapted to work at an individual level at home or in education.
Trying to solve a complex problem alone however can be a mistake. The old adage " A problem shared is a problem halved " is sound advice.
Talking to others about problems is not only therapeutic but can help you see things from a different point of view, opening up more potential solutions.
Stages of Problem Solving
Effective problem solving usually involves working through a number of steps or stages, such as those outlined below.
Problem Identification:
This stage involves: detecting and recognising that there is a problem; identifying the nature of the problem; defining the problem.
The first phase of problem solving may sound obvious but often requires more thought and analysis. Identifying a problem can be a difficult task in itself. Is there a problem at all? What is the nature of the problem, are there in fact numerous problems? How can the problem be best defined? By spending some time defining the problem you will not only understand it more clearly yourself but be able to communicate its nature to others, which leads to the second phase.
Structuring the Problem:
This stage involves: a period of observation, careful inspection, fact-finding and developing a clear picture of the problem.
Following on from problem identification, structuring the problem is all about gaining more information about the problem and increasing understanding. This phase is all about fact finding and analysis, building a more comprehensive picture of both the goal(s) and the barrier(s). This stage may not be necessary for very simple problems but is essential for problems of a more complex nature.

Looking for Possible Solutions:
During this stage you will generate a range of possible courses of action, but with little attempt to evaluate them at this stage.
From the information gathered in the first two phases of the problem solving framework it is now time to start thinking about possible solutions to the identified problem. In a group situation this stage is often carried out as a brain-storming session, letting each person in the group express their views on possible solutions (or part solutions). In organisations different people will have different expertise in different areas and it is useful, therefore, to hear the views of each concerned party.
Making a Decision:
This stage involves careful analysis of the different possible courses of action and then selecting the best solution for implementation.
This is perhaps the most complex part of the problem solving process. Following on from the previous step it is now time to look at each potential solution and carefully analyse it. Some solutions may not be possible, due to other problems like time constraints or budgets. It is important at this stage to also consider what might happen if nothing was done to solve the problem - sometimes trying to solve a problem that leads to many more problems requires some very creative thinking and innovative ideas.
Finally, make a decision on which course of action to take - decision making is an important skill in itself and we recommend that you see our pages on decision making .
Implementation:
This stage involves accepting and carrying out the chosen course of action.
Implementation means acting on the chosen solution. During implementation more problems may arise especially if identification or structuring of the original problem was not carried out fully.
Monitoring/Seeking Feedback:
The last stage is about reviewing the outcomes of problem solving over a period of time, including seeking feedback as to the success of the outcomes of the chosen solution.
The final stage of problem solving is concerned with checking that the process was successful. This can be achieved by monitoring and gaining feedback from people affected by any changes that occurred. It is good practice to keep a record of outcomes and any additional problems that occurred.
Continue to: Identifying and Structuring Problems Social Problem Solving
See also: Project Management Risk Management Effective Decision Making

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 7 min read
What Is Problem Solving?
By the Mind Tools Content Team

We all spend a lot of our time solving problems, both at work and in our personal lives.
Some problems are small, and we can quickly sort them out ourselves. But others are complex challenges that take collaboration, creativity, and a considerable amount of effort to solve.
At work, the types of problems we face depend largely on the organizations we're in and the jobs we do. A manager in a cleaning company, for example, might spend their day untangling staffing issues, resolving client complaints, and sorting out problems with equipment and supplies. An aircraft designer, on the other hand, might be grappling with a problem about aerodynamics, or trying to work out why a new safety feature isn't working. Meanwhile, a politician might be exploring solutions to racial injustice or climate change.
But whatever issues we face, there are some common ways to tackle them effectively. And we can all boost our confidence and ability to succeed by building a strong set of problem-solving skills.
Mind Tools offers a large collection of resources to help you do just that!
How Well Do You Solve Problems?
Start by taking an honest look at your existing skills. What's your current approach to solving problems, and how well is it working? Our quiz, How Good Is Your Problem Solving? lets you analyze your abilities, and signposts ways to address any areas of weakness.
Define Every Problem
The first step in solving a problem is understanding what that problem actually is. You need to be sure that you're dealing with the real problem – not its symptoms. For example, if performance in your department is substandard, you might think that the problem lies with the individuals submitting work. However, if you look a bit deeper, the real issue might be a general lack of training, or an unreasonable workload across the team.
Tools like 5 Whys , Appreciation and Root Cause Analysis get you asking the right questions, and help you to work through the layers of a problem to uncover what's really going on.
However, defining a problem doesn't mean deciding how to solve it straightaway. It's important to look at the issue from a variety of perspectives. If you commit yourself too early, you can end up with a short-sighted solution. The CATWOE checklist provides a powerful reminder to look at many elements that may contribute to the problem, keeping you open to a variety of possible solutions.
Understanding Complexity
As you define your problem, you'll often discover just how complicated it is. There are likely several interrelated issues involved. That's why it's important to have ways to visualize, simplify and make sense of this tangled mess!
Affinity Diagrams are great for organizing many different pieces of information into common themes, and for understanding the relationships between them.
Another popular tool is the Cause-and-Effect Diagram . To generate viable solutions, you need a solid understanding of what's causing the problem.
When your problem occurs within a business process, creating a Flow Chart , Swim Lane Diagram or a Systems Diagram will help you to see how various activities and inputs fit together. This may well highlight a missing element or bottleneck that's causing your problem.
Quite often, what seems to be a single problem turns out to be a whole series of problems. The Drill Down technique prompts you to split your problem into smaller, more manageable parts.
General Problem-Solving Tools
When you understand the problem in front of you, you’re ready to start solving it. With your definition to guide you, you can generate several possible solutions, choose the best one, then put it into action. That's the four-step approach at the heart of good problem solving.
There are various problem-solving styles to use. For example:
- Constructive Controversy is a way of widening perspectives and energizing discussions.
- Inductive Reasoning makes the most of people’s experiences and know-how, and can speed up solution finding.
- Means-End Analysis can bring extra clarity to your thinking, and kick-start the process of implementing solutions.
Specific Problem-Solving Systems
Some particularly complicated or important problems call for a more comprehensive process. Again, Mind Tools has a range of approaches to try, including:
- Simplex , which involves an eight-stage process: problem finding, fact finding, defining the problem, idea finding, selecting and evaluating, planning, selling the idea, and acting. These steps build upon the basic, four-step process described above, and they create a cycle of problem finding and solving that will continually improve your organization.
- Appreciative Inquiry , which is a uniquely positive way of solving problems by examining what's working well in the areas surrounding them.
- Soft Systems Methodology , which takes you through four stages to uncover more details about what's creating your problem, and then define actions that will improve the situation.
Further Problem-Solving Strategies
Good problem solving requires a number of other skills – all of which are covered by Mind Tools.
For example, we have a large section of resources to improve your Creativity , so that you come up with a range of possible solutions.
By strengthening your Decision Making , you'll be better at evaluating the options, selecting the best ones, then choosing how to implement them.
And our Project Management collection has valuable advice for strengthening the whole problem-solving process. The resources there will help you to make effective changes – and then keep them working long term.
Problems are an inescapable part of life, both in and out of work. So we can all benefit from having strong problem-solving skills.
It's important to understand your current approach to problem solving, and to know where and how to improve.
Define every problem you encounter – and understand its complexity, rather than trying to solve it too soon.
There's a range of general problem-solving approaches, helping you to generate possible answers, choose the best ones, and then implement your solution.
Some complicated or serious problems require more specific problem-solving systems, especially when they relate to business processes.
By boosting your creativity, decision-making and project-management skills, you’ll become even better at solving all the problems you face.
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Book Insights
The Back of the Napkin: Solving Problems and Selling Ideas With Pictures
Infographic
Creative Problem Solving Infographic
Infographic Transcript
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Team Management
Learn the key aspects of managing a team, from building and developing your team, to working with different types of teams, and troubleshooting common problems.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Connecting Remote and Hybrid Workers to Organizational Mission

Pain Points Podcast - Building Trust
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Toxic leadership test.
Use this exercise to assess if a manager or leader is showing signs of toxic behaviour. No separate facilitator guidance is necessary.
Pain Points Podcast - Receiving Feedback
Accepting What Others Say About You
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Designing future-state customer journeys.
Planning the Ideal Experience for Your Customers
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
The skills and attitudes behind successful problem solving
15 Jan 2018
Executive Director at States of Change.
About Jesper Christiansen
Follow the author:

Jesper is co-founder and Executive Director at States of Change. He is first and foremost a public innovation thinker and practitioner, focused on dealing more effectively with public problems for the common good.
Lead Learning Designer at UNDP's Accelerator Lab Network
About Bas Leurs

Bas is part of the team at UNDP building the Accelerator Lab Network - the world’s largest and fastest learning network around development challenges.
Prior to that, Bas was Head of Learning Experience Design in the Innovation Skills team at Nesta. He helped to design and run the first States of Change learning programme in Victoria, Australia.
Learning Experience Designer
About Kelly Duggan

Kelly is a Learning Experience Designer in the Innovation Skills team.
We worked with leading innovation practitioners from around the world to define the key skills, attitudes and behaviours that public innovators combine in order to successfully solve public problems. Introducing our new competency framework .
Finding the space and time to invest in the future while being responsible for delivering services that people rely on today is a well-known dilemma for governments around the world.
We’ve seen a number of interesting project pilots and inspiring innovation labs but no the larger-scale shift from applying these promising to how governments actually operate. Governments are still struggling to embed innovation in their organisations.
The big question is: how we go beyond individual pilots, projects and labs? How best to apply and spread the approaches, skills and culture that increase the ability of governments to innovate?
Human resources as an enabler of public innovation
We think human resources (HR) has a role to play. There's a relationship between between public workforce skills and innovation. What if we made it easier to hire for the right skills? Governments are increasingly using competency management approaches to set up standards for professional behaviour and performance management, as well as to gain competitive advantage by integrating HR policies with business strategies.
But beyond the broader and more established employee characteristics and behaviours for innovative working - such as motivation, openness to ideas, and change management - less is known about the unique attitudes, skills and competencies needed to support public sector innovation. How do they differ from what people are normally hired on the basis of?
Innovators, but in government
There are already attempts to provide clarity on the core competencies of public sector innovation, from the OECD’s Core Skills for Public Sector Innovation , to Le Nuancier de Formation from La 27e Region .
More clarity on what characterises innovative activity is good. But government is a different beast to most organisations, in scale if nothing else. So what do those innovative skills look like there?
Experimental problem solving
Problem solving is at the heart of how governments operate, and so we need to demystify where innovation approaches can be useful and what the relevant skills and competencies are to actually do the problem solving.
This is core to our work on developing the new competency framework for experimental problem solving . By framing our competencies around experimental problem solving, we try to emphasise how core attitudes and characteristics, in combination with key skills and competencies, enable behaviours that increase the likelihood of successful problem solving activities and better improve capacity. To be reductionist about it:
Skills + attitude (+ circumstance) = Behaviour.
More than brainstorming
Creative thinking techniques and brainstorming are useful for generating ideas, but there are other important competencies needed to systematically create, authorise, test and improve on ideas. The ideas are the easy part.
How we developed the framework
We want the framework to be useful and practical, rather than purely theoretical. We relied on experience to create it:
- The Nesta Innovation Skills team have worked in and with multiple pioneering government innovation labs and teams for a considerable amount of years. This was our starting point.
- Interviewed and workshopped with over 30 leading public sector innovation practitioners from around the world.
- Tested our research with governments and innovation experts to ensure accurate representation, relevance and usefulness.
Taking this forward
Over the coming months, we will co-develop and refine concrete behavioural indicators and assessment criteria . And most importantly, we will be working directly with ambitious governments to test and experiment with how the competency framework can be integrated into their innovation learning journey as part of systematic capacity-building activities.
Content principles for the framework
The framework identifies core skills needed by public servants in order to experiment and adopt a greater range of innovative practices for public problem solving. Some important content principles are:
The broader innovation skillset
The attitudes and skills outlined in the framework are the broader elements that, in combination, drive successful application of experimental problem solving activities. They are crucial for successfully creating impact with established innovation methods, such as human-centred design, behavioural insights, data-science, foresight, etc., which each require a set of more technical skillsets.
Creating and maintaining the mandate for innovation
We’ve found that the effort required to create the space and legitimacy for innovation in government is often significantly underestimated. Good ideas can’t flourish in a hostile environment. So in addition to the skills needed to simply apply innovation methods, our framework focuses on innovation craft. That is, how might we practically and effectively navigate, apply, embed and organise for innovation approaches in government and how to create an enabling environment to make innovation happen and ensure impact.
Team-focused skills framework
Teams are central to successful problem solving and so we start with the team, rather than the individual, as the unit of action. The framework presents a diverse palette of skills and attitudes that are rarely all found in one individual, but need to be present within the wider innovation team. The challenge (and opportunity) is to combine these skills and attitudes in ways that make the team greater than its individual members.
Framework of complex skills
Solving complex problems involves managing the intricate tensions and dynamics between opposing mindsets, skillsets and ways of acting. Such dynamics include: being disruptive and challenging the status quo, while being humble and integrative; making decisions in the face of uncertainty while being able to legitimise these decisions; having a clear plan of action, while adapting to and improvising for unforeseen situations; exploring new possible futures, while focusing on outcomes and committing to real-world effects; keeping the big picture in mind while also considering citizens' needs at an individual level; being reflective and critical while having a strong bias towards action.
All this requires ongoing judgement and the ability to combine multiple different attitudes and skills at the same time. For these reasons, it is important to recognise the elements presented in the framework as “complex skills”.
The framework
With these content principles in mind, we have attempted to describe key attitudes and skills that provide a combined view on what it takes to set up and run explorative innovation processes, while also creating an enabling environment for innovation within an administrative and political context. The framework describes three core categories that - according to our experience and research - are crucial to form the basis of successful experimental problem solving:
- Accelerating learning : Exploring and experimenting to identify knowledge gaps, create new understanding and inform decision-making in new ways
- Working together : Engaging with citizens and multiple stakeholders to ensure co-creation and collaborative ownership of new solutions
- Leading change : Creating space for innovation and driving change processes to mobilise people, inspire action and ensure strategic outcomes
How we plan to use it and next steps
As with many competency frameworks focused on change and innovation, there is a risk of it becoming a static, aspirational artefact rather than a practical tool for shifting practice. In this light, we see our research so far and this synthesis as only a starting point. In its current version, the framework mainly serves the purpose of bringing some clarity to the core elements and as a point of reference to enable further dialogue within the community of practice.Going forwards, we will be focusing on a number of activities to operationalise, test and further develop the framework into concrete activities, tasks, roles and incentive structures that can support real behaviour change. Our aim is to create:
- Tools for setting (un)learning objectives . We will develop context-sensitive and customisable behaviour indicators to support capacity development and assess the impact of innovation learning.
- Team and organisational assessment tools . We will generate tools that can help you assess the readiness and capability of your team, organisation and wider ecosystem.
- Team roles . We will develop a set of innovation team roles to help break down the tasks and functions of an innovation team and support governments in team design and management.
- Learning support and reflection tools . We will develop a set of practical frames for practitioners to use as systematic reflection for professional development and collective sense making.
- Rethinking HR strategy . We will apply the framework to explore how to develop more effective HR strategies focused on behaviour change, enabling better performance and recruitment for successful problem solving.
All of these will be tested and developed further in practice with ambitious government partners.Growing the innovation skillsets and capabilities of the public workforce requires informing hiring practices, career development and training opportunities. It also requires creating the right incentives, processes and structures for public sector innovation. Governments are often aware of all this, and yet struggle with knowing where to start.This framework is meant to be a first step in supporting these efforts and enabling innovation approaches to become strategic drivers of successful experimental problem solving activities. We welcome your feedback . We are especially keen to engage with governments, organisations and people that are doing interesting work in this area and/or want to explore possibilities for transforming their organisations for the better.
Other content you might like
Competency framework for experimental problem solving.
The skills, attitudes and behaviours of innovative teams in the public sector.
Developing an impact framework for cultural change in government
How do we move from measuring outputs to assessing outcomes?
Let's work together
A newsletter about public innovation..
We cover work from labs and governments, resources, insights from the community and anything else we think worth knowing. We also share news from States of Change, like our events, workshops and programs. People tell us it's:
" A constant source of inspiration" and " an incredible wealth of information!"
We hope you agree and you can see our previous newsletters to decide.
We won’t ever share your details, and you can unsubscribe at any time.
States of Change
We use cookie-consent to help us improve this site and your experience. Continue to use the site if you’re happy with this or click to find out more.
How Does Your Attitude Affect Your Ability to Solve Problems?

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Share Podcast

Do You Understand the Problem You’re Trying to Solve?
To solve tough problems at work, first ask these questions.
- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
Problem solving skills are invaluable in any job. But all too often, we jump to find solutions to a problem without taking time to really understand the dilemma we face, according to Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg , an expert in innovation and the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
In this episode, you’ll learn how to reframe tough problems by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that contribute to the situation. You’ll also learn why searching for just one root cause can be misleading.
Key episode topics include: leadership, decision making and problem solving, power and influence, business management.
HBR On Leadership curates the best case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, to help you unlock the best in those around you. New episodes every week.
- Listen to the original HBR IdeaCast episode: The Secret to Better Problem Solving (2016)
- Find more episodes of HBR IdeaCast
- Discover 100 years of Harvard Business Review articles, case studies, podcasts, and more at HBR.org .
HANNAH BATES: Welcome to HBR on Leadership , case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, hand-selected to help you unlock the best in those around you.
Problem solving skills are invaluable in any job. But even the most experienced among us can fall into the trap of solving the wrong problem.
Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg says that all too often, we jump to find solutions to a problem – without taking time to really understand what we’re facing.
He’s an expert in innovation, and he’s the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
In this episode, you’ll learn how to reframe tough problems, by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that contribute to the situation. You’ll also learn why searching for one root cause can be misleading. And you’ll learn how to use experimentation and rapid prototyping as problem-solving tools.
This episode originally aired on HBR IdeaCast in December 2016. Here it is.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Welcome to the HBR IdeaCast from Harvard Business Review. I’m Sarah Green Carmichael.
Problem solving is popular. People put it on their resumes. Managers believe they excel at it. Companies count it as a key proficiency. We solve customers’ problems.
The problem is we often solve the wrong problems. Albert Einstein and Peter Drucker alike have discussed the difficulty of effective diagnosis. There are great frameworks for getting teams to attack true problems, but they’re often hard to do daily and on the fly. That’s where our guest comes in.
Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg is a consultant who helps companies and managers reframe their problems so they can come up with an effective solution faster. He asks the question “Are You Solving The Right Problems?” in the January-February 2017 issue of Harvard Business Review. Thomas, thank you so much for coming on the HBR IdeaCast .
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Thanks for inviting me.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, I thought maybe we could start by talking about the problem of talking about problem reframing. What is that exactly?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Basically, when people face a problem, they tend to jump into solution mode to rapidly, and very often that means that they don’t really understand, necessarily, the problem they’re trying to solve. And so, reframing is really a– at heart, it’s a method that helps you avoid that by taking a second to go in and ask two questions, basically saying, first of all, wait. What is the problem we’re trying to solve? And then crucially asking, is there a different way to think about what the problem actually is?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, I feel like so often when this comes up in meetings, you know, someone says that, and maybe they throw out the Einstein quote about you spend an hour of problem solving, you spend 55 minutes to find the problem. And then everyone else in the room kind of gets irritated. So, maybe just give us an example of maybe how this would work in practice in a way that would not, sort of, set people’s teeth on edge, like oh, here Sarah goes again, reframing the whole problem instead of just solving it.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I mean, you’re bringing up something that’s, I think is crucial, which is to create legitimacy for the method. So, one of the reasons why I put out the article is to give people a tool to say actually, this thing is still important, and we need to do it. But I think the really critical thing in order to make this work in a meeting is actually to learn how to do it fast, because if you have the idea that you need to spend 30 minutes in a meeting delving deeply into the problem, I mean, that’s going to be uphill for most problems. So, the critical thing here is really to try to make it a practice you can implement very, very rapidly.
There’s an example that I would suggest memorizing. This is the example that I use to explain very rapidly what it is. And it’s basically, I call it the slow elevator problem. You imagine that you are the owner of an office building, and that your tenants are complaining that the elevator’s slow.
Now, if you take that problem framing for granted, you’re going to start thinking creatively around how do we make the elevator faster. Do we install a new motor? Do we have to buy a new lift somewhere?
The thing is, though, if you ask people who actually work with facilities management, well, they’re going to have a different solution for you, which is put up a mirror next to the elevator. That’s what happens is, of course, that people go oh, I’m busy. I’m busy. I’m– oh, a mirror. Oh, that’s beautiful.
And then they forget time. What’s interesting about that example is that the idea with a mirror is actually a solution to a different problem than the one you first proposed. And so, the whole idea here is once you get good at using reframing, you can quickly identify other aspects of the problem that might be much better to try to solve than the original one you found. It’s not necessarily that the first one is wrong. It’s just that there might be better problems out there to attack that we can, means we can do things much faster, cheaper, or better.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, in that example, I can understand how A, it’s probably expensive to make the elevator faster, so it’s much cheaper just to put up a mirror. And B, maybe the real problem people are actually feeling, even though they’re not articulating it right, is like, I hate waiting for the elevator. But if you let them sort of fix their hair or check their teeth, they’re suddenly distracted and don’t notice.
But if you have, this is sort of a pedestrian example, but say you have a roommate or a spouse who doesn’t clean up the kitchen. Facing that problem and not having your elegant solution already there to highlight the contrast between the perceived problem and the real problem, how would you take a problem like that and attack it using this method so that you can see what some of the other options might be?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Right. So, I mean, let’s say it’s you who have that problem. I would go in and say, first of all, what would you say the problem is? Like, if you were to describe your view of the problem, what would that be?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: I hate cleaning the kitchen, and I want someone else to clean it up.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: OK. So, my first observation, you know, that somebody else might not necessarily be your spouse. So, already there, there’s an inbuilt assumption in your question around oh, it has to be my husband who does the cleaning. So, it might actually be worth, already there to say, is that really the only problem you have? That you hate cleaning the kitchen, and you want to avoid it? Or might there be something around, as well, getting a better relationship in terms of how you solve problems in general or establishing a better way to handle small problems when dealing with your spouse?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Or maybe, now that I’m thinking that, maybe the problem is that you just can’t find the stuff in the kitchen when you need to find it.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Right, and so that’s an example of a reframing, that actually why is it a problem that the kitchen is not clean? Is it only because you hate the act of cleaning, or does it actually mean that it just takes you a lot longer and gets a lot messier to actually use the kitchen, which is a different problem. The way you describe this problem now, is there anything that’s missing from that description?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: That is a really good question.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Other, basically asking other factors that we are not talking about right now, and I say those because people tend to, when given a problem, they tend to delve deeper into the detail. What often is missing is actually an element outside of the initial description of the problem that might be really relevant to what’s going on. Like, why does the kitchen get messy in the first place? Is it something about the way you use it or your cooking habits? Is it because the neighbor’s kids, kind of, use it all the time?
There might, very often, there might be issues that you’re not really thinking about when you first describe the problem that actually has a big effect on it.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: I think at this point it would be helpful to maybe get another business example, and I’m wondering if you could tell us the story of the dog adoption problem.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Yeah. This is a big problem in the US. If you work in the shelter industry, basically because dogs are so popular, more than 3 million dogs every year enter a shelter, and currently only about half of those actually find a new home and get adopted. And so, this is a problem that has persisted. It’s been, like, a structural problem for decades in this space. In the last three years, where people found new ways to address it.
So a woman called Lori Weise who runs a rescue organization in South LA, and she actually went in and challenged the very idea of what we were trying to do. She said, no, no. The problem we’re trying to solve is not about how to get more people to adopt dogs. It is about keeping the dogs with their first family so they never enter the shelter system in the first place.
In 2013, she started what’s called a Shelter Intervention Program that basically works like this. If a family comes and wants to hand over their dog, these are called owner surrenders. It’s about 30% of all dogs that come into a shelter. All they would do is go up and ask, if you could, would you like to keep your animal? And if they said yes, they would try to fix whatever helped them fix the problem, but that made them turn over this.
And sometimes that might be that they moved into a new building. The landlord required a deposit, and they simply didn’t have the money to put down a deposit. Or the dog might need a $10 rabies shot, but they didn’t know how to get access to a vet.
And so, by instigating that program, just in the first year, she took her, basically the amount of dollars they spent per animal they helped went from something like $85 down to around $60. Just an immediate impact, and her program now is being rolled out, is being supported by the ASPCA, which is one of the big animal welfare stations, and it’s being rolled out to various other places.
And I think what really struck me with that example was this was not dependent on having the internet. This was not, oh, we needed to have everybody mobile before we could come up with this. This, conceivably, we could have done 20 years ago. Only, it only happened when somebody, like in this case Lori, went in and actually rethought what the problem they were trying to solve was in the first place.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, what I also think is so interesting about that example is that when you talk about it, it doesn’t sound like the kind of thing that would have been thought of through other kinds of problem solving methods. There wasn’t necessarily an After Action Review or a 5 Whys exercise or a Six Sigma type intervention. I don’t want to throw those other methods under the bus, but how can you get such powerful results with such a very simple way of thinking about something?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: That was something that struck me as well. This, in a way, reframing and the idea of the problem diagnosis is important is something we’ve known for a long, long time. And we’ve actually have built some tools to help out. If you worked with us professionally, you are familiar with, like, Six Sigma, TRIZ, and so on. You mentioned 5 Whys. A root cause analysis is another one that a lot of people are familiar with.
Those are our good tools, and they’re definitely better than nothing. But what I notice when I work with the companies applying those was those tools tend to make you dig deeper into the first understanding of the problem we have. If it’s the elevator example, people start asking, well, is that the cable strength, or is the capacity of the elevator? That they kind of get caught by the details.
That, in a way, is a bad way to work on problems because it really assumes that there’s like a, you can almost hear it, a root cause. That you have to dig down and find the one true problem, and everything else was just symptoms. That’s a bad way to think about problems because problems tend to be multicausal.
There tend to be lots of causes or levers you can potentially press to address a problem. And if you think there’s only one, if that’s the right problem, that’s actually a dangerous way. And so I think that’s why, that this is a method I’ve worked with over the last five years, trying to basically refine how to make people better at this, and the key tends to be this thing about shifting out and saying, is there a totally different way of thinking about the problem versus getting too caught up in the mechanistic details of what happens.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: What about experimentation? Because that’s another method that’s become really popular with the rise of Lean Startup and lots of other innovation methodologies. Why wouldn’t it have worked to, say, experiment with many different types of fixing the dog adoption problem, and then just pick the one that works the best?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: You could say in the dog space, that’s what’s been going on. I mean, there is, in this industry and a lot of, it’s largely volunteer driven. People have experimented, and they found different ways of trying to cope. And that has definitely made the problem better. So, I wouldn’t say that experimentation is bad, quite the contrary. Rapid prototyping, quickly putting something out into the world and learning from it, that’s a fantastic way to learn more and to move forward.
My point is, though, that I feel we’ve come to rely too much on that. There’s like, if you look at the start up space, the wisdom is now just to put something quickly into the market, and then if it doesn’t work, pivot and just do more stuff. What reframing really is, I think of it as the cognitive counterpoint to prototyping. So, this is really a way of seeing very quickly, like not just working on the solution, but also working on our understanding of the problem and trying to see is there a different way to think about that.
If you only stick with experimentation, again, you tend to sometimes stay too much in the same space trying minute variations of something instead of taking a step back and saying, wait a minute. What is this telling us about what the real issue is?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, to go back to something that we touched on earlier, when we were talking about the completely hypothetical example of a spouse who does not clean the kitchen–
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Completely, completely hypothetical.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Yes. For the record, my husband is a great kitchen cleaner.
You started asking me some questions that I could see immediately were helping me rethink that problem. Is that kind of the key, just having a checklist of questions to ask yourself? How do you really start to put this into practice?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I think there are two steps in that. The first one is just to make yourself better at the method. Yes, you should kind of work with a checklist. In the article, I kind of outlined seven practices that you can use to do this.
But importantly, I would say you have to consider that as, basically, a set of training wheels. I think there’s a big, big danger in getting caught in a checklist. This is something I work with.
My co-author Paddy Miller, it’s one of his insights. That if you start giving people a checklist for things like this, they start following it. And that’s actually a problem, because what you really want them to do is start challenging their thinking.
So the way to handle this is to get some practice using it. Do use the checklist initially, but then try to step away from it and try to see if you can organically make– it’s almost a habit of mind. When you run into a colleague in the hallway and she has a problem and you have five minutes, like, delving in and just starting asking some of those questions and using your intuition to say, wait, how is she talking about this problem? And is there a question or two I can ask her about the problem that can help her rethink it?
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Well, that is also just a very different approach, because I think in that situation, most of us can’t go 30 seconds without jumping in and offering solutions.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Very true. The drive toward solutions is very strong. And to be clear, I mean, there’s nothing wrong with that if the solutions work. So, many problems are just solved by oh, you know, oh, here’s the way to do that. Great.
But this is really a powerful method for those problems where either it’s something we’ve been banging our heads against tons of times without making progress, or when you need to come up with a really creative solution. When you’re facing a competitor with a much bigger budget, and you know, if you solve the same problem later, you’re not going to win. So, that basic idea of taking that approach to problems can often help you move forward in a different way than just like, oh, I have a solution.
I would say there’s also, there’s some interesting psychological stuff going on, right? Where you may have tried this, but if somebody tries to serve up a solution to a problem I have, I’m often resistant towards them. Kind if like, no, no, no, no, no, no. That solution is not going to work in my world. Whereas if you get them to discuss and analyze what the problem really is, you might actually dig something up.
Let’s go back to the kitchen example. One powerful question is just to say, what’s your own part in creating this problem? It’s very often, like, people, they describe problems as if it’s something that’s inflicted upon them from the external world, and they are innocent bystanders in that.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Right, or crazy customers with unreasonable demands.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Exactly, right. I don’t think I’ve ever met an agency or consultancy that didn’t, like, gossip about their customers. Oh, my god, they’re horrible. That, you know, classic thing, why don’t they want to take more risk? Well, risk is bad.
It’s their business that’s on the line, not the consultancy’s, right? So, absolutely, that’s one of the things when you step into a different mindset and kind of, wait. Oh yeah, maybe I actually am part of creating this problem in a sense, as well. That tends to open some new doors for you to move forward, in a way, with stuff that you may have been struggling with for years.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, we’ve surfaced a couple of questions that are useful. I’m curious to know, what are some of the other questions that you find yourself asking in these situations, given that you have made this sort of mental habit that you do? What are the questions that people seem to find really useful?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: One easy one is just to ask if there are any positive exceptions to the problem. So, was there day where your kitchen was actually spotlessly clean? And then asking, what was different about that day? Like, what happened there that didn’t happen the other days? That can very often point people towards a factor that they hadn’t considered previously.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: We got take-out.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: S,o that is your solution. Take-out from [INAUDIBLE]. That might have other problems.
Another good question, and this is a little bit more high level. It’s actually more making an observation about labeling how that person thinks about the problem. And what I mean with that is, we have problem categories in our head. So, if I say, let’s say that you describe a problem to me and say, well, we have a really great product and are, it’s much better than our previous product, but people aren’t buying it. I think we need to put more marketing dollars into this.
Now you can go in and say, that’s interesting. This sounds like you’re thinking of this as a communications problem. Is there a different way of thinking about that? Because you can almost tell how, when the second you say communications, there are some ideas about how do you solve a communications problem. Typically with more communication.
And what you might do is go in and suggest, well, have you considered that it might be, say, an incentive problem? Are there incentives on behalf of the purchasing manager at your clients that are obstructing you? Might there be incentive issues with your own sales force that makes them want to sell the old product instead of the new one?
So literally, just identifying what type of problem does this person think about, and is there different potential way of thinking about it? Might it be an emotional problem, a timing problem, an expectations management problem? Thinking about what label of what type of problem that person is kind of thinking as it of.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: That’s really interesting, too, because I think so many of us get requests for advice that we’re really not qualified to give. So, maybe the next time that happens, instead of muddying my way through, I will just ask some of those questions that we talked about instead.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: That sounds like a good idea.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: So, Thomas, this has really helped me reframe the way I think about a couple of problems in my own life, and I’m just wondering. I know you do this professionally, but is there a problem in your life that thinking this way has helped you solve?
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: I’ve, of course, I’ve been swallowing my own medicine on this, too, and I think I have, well, maybe two different examples, and in one case somebody else did the reframing for me. But in one case, when I was younger, I often kind of struggled a little bit. I mean, this is my teenage years, kind of hanging out with my parents. I thought they were pretty annoying people. That’s not really fair, because they’re quite wonderful, but that’s what life is when you’re a teenager.
And one of the things that struck me, suddenly, and this was kind of the positive exception was, there was actually an evening where we really had a good time, and there wasn’t a conflict. And the core thing was, I wasn’t just seeing them in their old house where I grew up. It was, actually, we were at a restaurant. And it suddenly struck me that so much of the sometimes, kind of, a little bit, you love them but they’re annoying kind of dynamic, is tied to the place, is tied to the setting you are in.
And of course, if– you know, I live abroad now, if I visit my parents and I stay in my old bedroom, you know, my mother comes in and wants to wake me up in the morning. Stuff like that, right? And it just struck me so, so clearly that it’s– when I change this setting, if I go out and have dinner with them at a different place, that the dynamic, just that dynamic disappears.
SARAH GREEN CARMICHAEL: Well, Thomas, this has been really, really helpful. Thank you for talking with me today.
THOMAS WEDELL-WEDELLSBORG: Thank you, Sarah.
HANNAH BATES: That was Thomas Wedell-Wedellsborg in conversation with Sarah Green Carmichael on the HBR IdeaCast. He’s an expert in problem solving and innovation, and he’s the author of the book, What’s Your Problem?: To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve .
We’ll be back next Wednesday with another hand-picked conversation about leadership from the Harvard Business Review. If you found this episode helpful, share it with your friends and colleagues, and follow our show on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts. While you’re there, be sure to leave us a review.
We’re a production of Harvard Business Review. If you want more podcasts, articles, case studies, books, and videos like this, find it all at HBR dot org.
This episode was produced by Anne Saini, and me, Hannah Bates. Ian Fox is our editor. Music by Coma Media. Special thanks to Maureen Hoch, Adi Ignatius, Karen Player, Ramsey Khabbaz, Nicole Smith, Anne Bartholomew, and you – our listener.
See you next week.
- Subscribe On:
Latest in this series
This article is about leadership.
- Decision making and problem solving
- Power and influence
- Business management
Partner Center
Why are problem solving skills in the workplace so important? Subskills, benefits, scenarios
Test your candidates' problem-solving skills with testgorilla.

The importance of problem-solving skills in the workplace can’t be overstated. Every business and job role has its problems. From entry-level hires to senior staffers, every one of your employees will face challenges that don’t can’t be answered by doing a quick Google search – or asking ChatGPT to come up with solutions.
That’s why employers must hire people with excellent problem-solving skills, especially for roles that require dealing with complex business challenges, tight deadlines, and changing variables – for example, when recruiting leaders .
But what are problem-solving skills? What role do they play in the workplace?
And, most importantly, how can you evaluate candidates’ skills before you hire them?
Table of contents
What are problem solving skills, the benefits of problem solving skills: why are problem solving skills important , examples of problems at the workplace – and how problem solving skills can help, how to assess problem solving skills, evaluate problem solving skills and hire candidates who can think for themselves.
To fully understand the importance of problem-solving skills in the workplace, it’s important first to understand the broad skill set that we commonly refer to as “problem solving skills”.
Generally, problem-solving refers to a person’s ability to successfully manage and find solutions for complex and unexpected situations.
Candidates with great problem-solving skills have a combination of analytical and creative thinking. They’re comfortable with making decisions and confident enough to rise to challenges in the workplace.
These candidates possess a combination of analytical, creative, and critical-thinking skills – and a high level of attention to detail . As a result, they will quickly identify problems when they arise and identify the most effective solutions.
They’ll also identify the factors and forces that might have caused the problem and instigate changes to mitigate future challenges.
There are six key problem-solving skills that you should look for when assessing job candidates:

1. Listening skills
Active listeners are generally great problem solvers.
They can listen to those around them to gather the information needed to solve the problem at hand. They also recognize the importance of valuing others’ opinions and experiences to help understand why the problem occurred and define the best course of action to remedy it.
2. Analytical thinking skills
Analytical thinkers can identify the logical reasons why a problem occurred, what the long-term effects of the issue could be, and identify how effective different solutions might be to select the most practical one.
That’s why it’s essential to assess analytical thinking skills during recruitment.
3. Creative thinking skills
Creative thinkers can balance their analytical skills with creative approaches to challenges. Creative thinking skills enable individuals to uncover innovative and progressive solutions to problems.
In this way, they’re able to provide new perspectives and provide imaginative and experimental solutions to all kinds of problems.
4. Communication skills
Problem solvers should also possess great communication skills . The ability to effectively relay complex information thoroughly yet succinctly is a huge benefit for employers working in fast-paced environments.
5. Decision-making skills
Those with problem-solving skills will also possess the ability to make decisions and be confident in them. This is important, because most problem-solving involves making firm decisions to reach a successful outcome.
6. Teamwork
Although problem-solvers need to be independent thinkers, it’s also vital for them to work well as part of a team .
Determining the best solution often requires collaboration, so it’s important that candidates can demonstrate how they can motivate others to come up with the best solutions and work with them to help develop and implement solutions.
Problem-solving skills enable you to find candidates who are cognitively equipped to handle anything their jobs throw at them.
Problem solvers can observe, judge, and act quickly when difficulties arise when they inevitably do. Moreover, they are not afraid of the unknown, which is invaluable to employers who rely on their employees to identify and solve problems.

There are several important benefits of problem-solving skills in the workplace. Below, we’ll go through five of the most significant ones that all problem solvers can bring to their roles and workplaces:
1. Ability to organize their time intelligently
Time management skills can often be underlooked as one of the benefits of problem-solving skills in the workplace.
However, those with problem-solving abilities also typically possess stellar time-management skills. The ability to manage their time wisely and laser-focus on what’s important to the business will lead to better decision-making and business impact.
2. Ability to prioritize, plan, and execute strategies
Problem solvers have no issue with carefully assessing customer and business needs and deciding how to prioritize, plan, and execute strategies to meet them. They can manage all moving parts and strategize to meet multiple unique demands.
3. Ability to think outside the box
Problem solvers can often identify hidden opportunities in problems. Thinking outside of the box is an important problem-solving skill in the workplace, because it can often lead to better outcomes than the originally expected ones.
4. Ability to work under pressure
This is often one of the most important benefits of problem-solving skills in the workplace. Problem solvers often work well under pressure, for example when dealing with short deadlines and changing project requirements.
Depending on your workplace culture, you might prefer someone who can deliver quick solutions or someone who takes their time to identify the next steps. Both are valid and important problem solving qualities.
5. Ability to address risk
Planning is an important problem-solving skill. Problem solvers are not just equipped to deal with the problem at hand but are also able to anticipate problems that will arise in the future based on trends, patterns, experience, and current events.
Let’s now look at some specific examples of problems that could arise at the workplace – at any workplace, really – and how employees’ problem solving skills can help address each issue.
Below, you’ll find five typical scenarios where problem solving skills are essential.
Conflict between team members
Poor team dynamics or lack of a collaborative spirit might result in frequent workplace conflicts – especially within larger teams.
For example, members of cross-functional teams might disagree on the way they should address a particular issue or even on the priority they should give to it.
How problem solving skills can help:
Teamwork is essential when solving conflict – and a cornerstone of effective cross-functional team leadership .
For this, coworkers need to share a common understanding of the team’s goals and also be willing to work towards achieving them, even when they disagree on the specific approaches to each goal. The ability to understand others’ perspectives, analyze information critically, and come up with a few different solutions is key to finding a common ground and making progress on the team’s objectives.
Inefficient processes
Outdated, inefficient processes can reduce productivity and frustrate employees.
Multi-step approval processes are a typical example of this. Having multiple layers of approval for routine decisions can significantly slow down team progress and lead to missed opportunities.
Analytical thinking skills are key in identifying inefficiencies and building better procedures. Employees or team leads can build flowcharts that speed up decision making without having to ask a supervisor’s permission at every step of the process.
Book a free live demo with us and learn how quick and easy it is to create an online skills assessment

Poor communication can lead to misunderstandings and lack of clarity and direction – which, in turn, can be detrimental to team performance.
For example, if you’re a remote-first company, maintaining clear and effective remote communication can be challenging.
The over-reliance on emails and messaging apps might make it feel like teams are communicating effectively and are always connected. However, the lack of non-verbal cues and face-to-face interactions might make it more difficult to build rapport and a positive workplace culture .
Listening skills are essential to solving communication issues – and good listeners are often excellent at solving problems by recognizing, understanding, and acknowledging others’ points of view.
One-on-one meetings enable people to communicate more freely and effectively and solve challenges together, so consider encouraging team members to hop on a call each time they encounter a difficult challenge.
Additionally, you can help employees bond with each other with some remote team building activities to improve team cohesion. Plus, problem solving challenges can be excellent team building exercises.
Technological disruptions
New technologies often disrupt the usual ways of doing things – and sometimes, this can be disruptive for entire teams’ work.
For example, generative AI and automation technologies have revolutionized numerous types of work, including data analysis, marketing, customer service, and even content creation.
Creative thinking and cognitive flexibility are among the top 10 most important skills of the future , according to the World Economic Forum. Both are essential for adopting new technologies successfully – and finding ways to make the most out of each new tool to improve productivity.
Insufficient onboarding resources
Team members may struggle to do their best work if they haven't received proper training or resources.
For example, start-ups that experience rapid growth might hire a few employees at once – or even entire teams.
If they fail to allocate sufficient time and resources to onboarding new hires, this might lead to lost productivity, a lacking sense of belonging, or increased turnover. That’s true not only for junior employees but also for newly hired senior leaders , as the Harvard Business Review points out.
Your leadership team’s analytical and decision-making skills are crucial in enabling them to distribute limited resources in a way that would give their teams the best chances of success.
To build a solid onboarding process , you need leaders who are able to take ownership of it – and who have the right problem-solving skills.
Many organizations use problem-solving interview questions to identify the right candidates for their job openings. However, the most effective way to assess problem-solving skills is with pre-employment skills assessments .
That’s because skills tests provide an objective way to quantify a candidate’s problem-solving skills in a way that isn’t possible during an interview.
How problem solving skills tests work
Tests like TestGorilla’s problem-solving skills test assist organizations in finding candidates who are able to quickly identify the key elements of the problem and work through the problem at speed without making mistakes.
By presenting candidates with a wide range of questions related to typical problem-solving scenarios, hiring teams can rank their candidates based on an intensive assessment of each candidate’s skill level.
The test specifically evaluates whether a candidate can perform problem-solving tasks like:
Creating and adjust schedules
Prioritizing items based on a given set of rules
Interpreting data and applying logic to make decisions
Analyzing textual and numerical information to draw conclusions
As you can see, even the best interviewer would have trouble assessing each of these skill areas while still covering all the other questions that they need to ask.
If you’re convinced of the importance of problem-solving skills in the workplace and want to build a team of employees that can think independently and solve their own problems without constant supervision, assess problem-solving skills during the hiring process.
Problem-solving skills tests like ours are an excellent way to achieve this – especially if you combine them with other skills tests. Check out our extensive test library for other tests you can use in your talent assessment process to hire the best talent.
Sign up for our free plan to start building your first assessment – or schedule a demo with one of our experts to see how to evaluate applicants’ problem solving skills quickly, efficiently, and without bias.
Related posts

The tech skills gap: What it is, why it exists, and how to close it in 2024

7 hiring trends for 2024

Most accurate 16 personalities tests for assessing candidates
Hire the best candidates with TestGorilla
Create pre-employment assessments in minutes to screen candidates, save time, and hire the best talent.

Latest posts

The best advice in pre-employment testing, in your inbox.
No spam. Unsubscribe at any time.
Hire the best. No bias. No stress.
Our screening tests identify the best candidates and make your hiring decisions faster, easier, and bias-free.
Free resources

This checklist covers key features you should look for when choosing a skills testing platform

This resource will help you develop an onboarding checklist for new hires.

How to assess your candidates' attention to detail.

Learn how to get human resources certified through HRCI or SHRM.

Learn how you can improve the level of talent at your company.

Learn how CapitalT reduced hiring bias with online skills assessments.

Learn how to make the resume process more efficient and more effective.

Improve your hiring strategy with these 7 critical recruitment metrics.

Learn how Sukhi decreased time spent reviewing resumes by 83%!

Hire more efficiently with these hacks that 99% of recruiters aren't using.

Make a business case for diversity and inclusion initiatives with this data.
- Open supplemental data
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Brief research report article, the influence of attitudes and beliefs on the problem-solving performance.

- 1 Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Education of Ludwigsburg, Ludwigsburg, Germany
- 2 Hamburg Center for University Teaching and Learning, University of Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany
The problem-solving performance of primary school students depend on their attitudes and beliefs. As it is not easy to change attitudes, we aimed to change the relationship between problem-solving performance and attitudes with a training program. The training was based on the assumption that self-generated external representations support the problem-solving process. Furthermore, we assumed that students who are encouraged to generate representations will be successful, especially when they analyze and reflect on their products. A paper-pencil test of attitudes and beliefs was used to measure the constructs of willingness, perseverance, and self-confidence. We predicted that participation in the training program would attenuate the relationship between attitudes and problem-solving performance and that non-participation would not affect the relationship. The results indicate that students’ attitudes had a positive effect on their problem-solving performance only for students who did not participate in the training.
Introduction
Mathematical problem solving is considered to be one of the most difficult tasks primary students have to deal with ( Verschaffel et al., 1999 ) since it requires them to apply multiple skills ( De Corte et al., 2000 ). It is decisive in this respect that “difficulty should be an intellectual impasse rather than a computational one” ( Schoenfeld, 1985 , p. 74). When solving problems, it is not enough to retrieve procedural knowledge and reproduce a known solution approach. Rather, problem-solving tasks require students to come up with new ways of thinking ( Bransford and Stein, 1993 ). Problem-solvers must activate their existing knowledge network and adapt it to the respective problem situation ( van Dijk and Kintsch, 1983 ). They have to succeed in generating an adequate representation of the problem situation (e.g., Mayer and Hegarty, 1996 ). This requires conceptual knowledge, which novice problem-solvers have to acquire ( Bransford et al., 2000 ). As problem solving is the foundation for learning mathematics, an important goal of primary school mathematics teaching is to strengthen students’ problem-solving performance. One central problem is that problem-solving performance is highly influenced by students’ attitudes towards problem solving ( Reiss et al., 2002 ; Schoenfeld, 1985 ; Verschaffel et al., 2000 ).
Attitudes and beliefs are considered quite stable once they are developed ( Hannula, 2002 ; Goldin, 2003 ). However, students who are novices in a particular content area are still in the process of development, as are their attitudes and beliefs. It can therefore be assumed that their attitudes change over time ( Hannula, 2002 ). However, such a change does not take place quickly ( Higgins, 1997 ; Mason and Scrivani, 2004 ). Nevertheless, in a shorter period of time, it might be possible to reduce the influence of attitudes on problem-solving performance ( Hannula et al., 2019 ). In this paper, we present a training program for primary school students, which aims to do exactly that.
Problem-Solving Performance
Successful problem solving can be observed on two levels: problem-solving success and problem-solving skills. Many studies measure the problem-solving performance of students on the basis of correctly or incorrectly solved problem-solving tasks, that is, the product (e.g., Boonen et al., 2013 ; de Corte et al., 1992 ; Hegarty et al., 1992 ; Verschaffel et al., 1999 ). In this case, only problem-solving success, that is, specifically whether the numerically obtained result is correct or incorrect, is evaluated. This is a strict assessment measure, since the problem-solving process is not taken into account. As a result, the problem-solving performance is only considered from a single, product-oriented perspective. For instance students’ performance is assessed as unsuccessful when they apply an essentially correct procedure or strategy but achieve the wrong result, or it is considered successful when students achieve the right result even though they have misunderstood the problem ( Lester and Kroll, 1990 ). An advantage of this operationalization, however, is that student performance tends to be underestimated rather than overestimated.
A more differentiated view of successful problem solving includes the solver’s problem-solving process ( Lester and Kroll, 1990 ; cf. Adibnia and Putt, 1998 ). In this way, sub-skills such as understanding the problem, adequately representing the situation, applying strategies, or achieving partial solutions are taken into account. These are then incorporated into the evaluation of performance and, thus, of problem-solving skills ( Charles et al., 1987 ; cf. Sturm, 2019 ). The advantage of this operationalization option is that it also takes into account smaller advances by the solver, although they may not yet lead to the correct result. It is therefore less likely to underestimate students’ performance. In order to assess and evaluate the problem-solving skills of students in the best way and, thus, avoid over- and under-estimating their skills, direct observation and questioning should be implemented (e.g., Lester and Kroll, 1990 ). An analysis of written work should not be the only means of assessment ( Lester and Kroll, 1990 ).
Attitudes and Beliefs
Attitudes are dispositions to like or dislike objects, persons, institutions, or events ( Ajzen, 2005 ). They influence behavior (Ajzen, 1991). Therefore, it is not surprising that attitudes–which are sometimes also synonymously referred to as beliefs–are a central construct in psychology ( Ajzen, 2005 ).
Individual attitudes to word problems influence, albeit rather unconsciously, approaches to such problems and willingness to learn mathematics and solve problems ( Grigutsch et al., 1998 ; Awofala, 2014 ). Research on attitudes of primary students to word problems is scarce. Most research focuses on students with well-established attitudes. However, the importance of the attitudes of younger children is undisputed ( Di Martino, 2019 ). Di Martino (2019) conducted a study on kindergarten children as well as on first-, third-, and fifth-graders and found that, with increasing age, students’ perceived competence in problem solving decreases, and negative emotions towards mathematical problems increase. Whether a solver can overcome problem barriers when dealing with word problems depends not only on his or her previous knowledge, abilities, and skills, but also on his or her attitudes and beliefs ( Schoenfeld, 1985 ; Verschaffel et al., 2000 ; Reiss et al., 2002 ). It has been shown many times that attitudes towards problem solving are influencing factors on performance and learning success which should not be underestimated ( Charles et al., 1987 ; Lester et al., 1989 ; Lester & Kroll, 1990 ; De Corte et al., 2002 ; Goldin et al., 2009 ; Awofala, 2014 ). Learners associate a specific feeling with an object, in this case with a word problem, triggering a specific emotional state ( Grigutsch et al., 1998 ). The feelings and states generated are subjective and can therefore vary between individuals ( Goldin et al., 2009 ).
Attitudes towards problem solving can be divided into willingness, perseverance, and self-confidence ( Charles et al., 1987 ; Lester et al., 1989 ). This distinction comes from the Mathematical Problem-Solving Project, in which Webb, Moses, and Kerr (1977) found that willingness to solve problems, perseverance in attempting to find a solution, and self-confidence in the ability to solve problems are the most important influences on problem-solving performance. When students are willing to work on a variety of mathematics tasks and persevere with tasks until they find a solution, they are more task oriented and easier to motivate ( Reyes, 1984 ). Perseverance is defined as the willing pursuit of a goal-oriented behavior even if this involves overcoming obstacles, difficulties, and disappointments ( Peterson and Seligman, 2004 ). Confidence is an individual’s belief in his or her ability to succeed in solving even challenging problems as well as an individual’s belief in his or her own competence with respect to his or her peers ( Lester et al., 1989 ). Students’ lack of confidence in themselves as problem-solvers or their beliefs about mathematics can considerably undermine their ability to solve or even approach problems in a productive way ( Shaughnessy, 1985 ). The division of attitudes into these three sub-categories can also be found in current studies ( Zakaria and Yusoff, 2009 ; Zakaria and Ngah, 2011 ).
Reducing the Influence of Attitudes and Beliefs
As it seems impossible to change attitudes within a short time frame, we developed a training program to reduce the influence of attitudes on problem solving, on the one hand, and to foster the problem-solving performance of primary-school students, on the other hand.
The training program was an integral part of regular math classes and focused on teaching students to generate and use external representations ( Sturm, 2019 ; Sturm et al., 2016 ; Sturm and Rasch, 2015 ; see also Supplementary Appendix A ). Such a program that concentrates on the strengths and weaknesses of novices and on their individually generated external representations can be a benefit for primary-school students in two ways. The class discusses how the structure described in the problem can be adequately represented so that the solution can be found, working out multiple approaches based on different student representations. The students are thus exposed to ideas about how a problem can be solved in different ways. Such a training program fulfils, albeit rather implicitly, another essential component. By respectfully considering their individual thoughts and difficulties, the students are made aware of their strengths and their creativity and of the fact that there is not a single correct approach or solution that everyone has to find ( Lester and Cai, 2016 ; Di Martino, 2019 ). This can counteract fears of failure and lack of self-confidence, and generate positive attitudes ( Lester and Cai, 2016 ; Di Martino, 2019 ). The teacher pays attention to the solution process rather than to the numerical result in order to reduce the influence of attitudes on performance ( Di Martino, 2019 ). In the same way, experiencing success and perceiving increasing flexibility and agility can reduce the influence of attitudes. As a result, we expected attitudes and beliefs to have a smaller effect on problem-solving performance.
Based on previous research, our goal was to reduce the influence of attitudes on the problem-solving performance of students (see Figure 1 ). To this end, the hypothesis was derived that participation in the training program would minimize the effect of attitudes and beliefs on problem-solving success, so that students would succeed at the end of the training despite initial negative attitudes and beliefs.
FIGURE 1 . The moderation model with the single moderator variable training influencing the effect of attitudes and beliefs on problem-solving success.
Participants
In total 335 students from 20 Grade 3 classes from eight different primary schools in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate took part in the intervention study (172 boys and 163 girls). Nineteen students dropped out because of illness during the intervention. The age of the participants ranged between seven and ten years ( M = 8.10, SD = 0.47).
This investigation was part of a large interdisciplinary project 1 . A central focus of the project was to investigate whether representation training has a demonstrable effect on the performance of third-graders (cf. Sturm, 2019 ). For this reason, we implemented a pretest-posttest control group design. The intervention took place between Measurement Points 1 and 2. We measured the problem-solving performance of the students with a word-problem-solving test (WPST) at Measurement Points 1 and 2. All other variables were measured at Measurement Point 1 only (factors to establish comparable experimental conditions: intelligence, text comprehension, and mathematical abilities; co-variates for the mediation model: metacognitive skills, mathematical abilities).
In the intervention, third-grade students worked on challenging word problems for one regular mathematics lesson a week. The intervention was based on six task types with different structures ( Sturm and Rasch, 2015 ): 1) comparison tasks, 2) motion tasks, 3) tasks involving comparisons and balancing items or money, 4) tasks involving combinatorics, 5) tasks in which structure reflects the proportion of spaces and limitations, and 6) tasks with complex information. Two word problems were included for each task type and were presented to all classes in the same random sequence. Each task had to be completed in a maximum of one lesson.
The training was implemented for half of the classes and was conducted by the first author; the other half worked on the tasks with their regular mathematics teacher. They were not informed on the purpose of the intervention and not given any instructions on how to process the tasks. In the lessons for students doing the training, the students were explicitly cognitively stimulated to generate external representations and to use them to develop solutions. They were repeatedly encouraged to persevere and not to give up. The diverse external representations generated by the students were analyzed, discussed, and compared by the class during the training. They jointly identified the characteristics of representations that enabled them to specifically solve the tasks and identified different approaches (for more details about the study, see Sturm and Rasch, 2015 ). With the goal of reducing the influence of attitudes on performance, the class worked directly on the students’ own representations instead of on prefabricated representations. The aim was that students realized that it was worthwhile investing effort into creating representations and that they were able to solve problem tasks independently.
Thus, the study was composed of two experimental conditions: training program ( n = 176; 47% boys) (hereinafter abbreviated to T+) and no training program ( n = 159; 58% boys) (hereinafter abbreviated to T-). In order to control potential interindividual differences, the 20 classes were assigned to the experimental conditions by applying parallelization at class level ( Breaugh and Arnold, 2007 ; Myers and Hansen, 2012 ). The classes were grouped into homogeneous blocks using the R package blockTools Version 0.6-3 and then randomly assigned to the experimental conditions ( Greevy et al., 2004 ; Moore, 2012 ; see also Supplementary Appendix B for more information).
Word-Problem-Solving Test
Before the intervention and immediately after it, the students worked on a WPST, which we created. It consisted in each case of three challenging word problems with an open answer format. Each of the three tasks represented a different type of problem. The word problems from the WPST at Measurement Point 1 and the word problems from the WPST at Measurement Point 2 had the same structure. We implemented two parallel versions; only the context was changed by exchanging single words (see Supplementary Appendix C ). An example of an item from the test is a task with complex information ( Sturm, 2018 ): Classes 3a and 3b go to the computer room. Some students have to work at a computer in pairs. In total there are 25 computers, but 40 students. How many students work alone at a computer? How many students work at a computer in pairs? Direct observation and questioning could not be conducted due to the large number of participants in the project; only the students’ written work was available for analysis. The problem-solving process of the students could therefore only be assessed indirectly. For this reason, the performance of students in the two tests was evaluated based on problem-solving success, ruling out overestimation of performance.
Problem-Solving Success
The success of the solution was measured dichotomously in two forms: 1) correct solution and (0) incorrect solution. Only the correctness of the result achieved was evaluated. This dependent variable acted as a strict criterion that could be quantified with high observer agreement (κ = 0.97; κ min = 0.93, κ max = 1.00). A confirmatory factor analysis using the R package lavaan version 0.6-7 confirmed that the WPST measured the one-dimensional construct problem-solving success. The one-dimensional model exhibited a good model fit ( Nussbeck et al., 2006 ; Hair et al., 2009 ): χ 2 (27) = 36.613, p = 0.103; χ 2 /df = 1.356, CFI = 0.985, TLI = 0.981, SRMR = 0.032, RMSEA = 0.033 ( p = 0.854). The reliability coefficients at Measurement Point 1 were classified as low (Cronbach’s α = 0.39) because the test consisted of only three items ( Eid et al., 2011 ) and a homogeneous sample was required at this measurement point ( Lienert and Raatz, 1998 ). The Cronbach’s alpha for the second measurement point (α = 0.60) was considered to be sufficient ( Hair et al., 2009 ). The test score represented the mean value of all three task scores.
Attitudes and Beliefs About Problem Solving
The attitudes and beliefs of the learners were recorded with the Attitudes Inventory Items ( Webb et al., 1977 ; Charles et al., 1987 ). The original questionnaire comprises 20 items, which are measured dichotomously (“I agree” and “I disagree”). The Attitudes Inventory measures the three categories of attitudes and beliefs related to problem solving: a) willingness (six items), b) perseverance (six items), and c) self-confidence (eight items). An example of an item for willingness is: “I will try to solve almost any problem.” An example of an item for perseverance is: “When I do not get the right answer right away, I give up.” An example of an item for self-confidence is: “I am sure I can solve most problems.”
Because the reported reliabilities were only satisfactory to some extent (α = 0.79, mean = 0.64) ( Webb et al., 1977 ), the Attitudes Inventory was initially tested on a smaller sample ( n = 74; M = 8.6 years old; 59% girls). A satisfactory Cronbach’s α = 0.86 was achieved (mean α = 0.73). The number of items was reduced to 13 (four items for willingness, four items for perseverance, five items for self-confidence), which had only a minor influence on reliability (α = 0.83). For economic reasons, the shortened questionnaire was used in the study. The three-factor structure of the questionnaire was confirmed with a confirmatory factor analysis using the R package lavaan version 0.6–7. As the fit indices show, the three-factor model had a good model fit: χ 2 (62) = 134.856, p < 0.001; χ 2 / df = 2.175, CFI = 0.948, TLI = 0.935, RMSEA = 0.062 ( p = 0.086) ( Hair et al., 2009 ; Brown, 2015 ). The three-factor model had a better fit than the single-factor model ( p = 0.0014): χ 2 (65) = 152.121, p < 0.001; χ 2 / df = 2.340, CFI = 0.938, TLI = 0.926, SRMR = 0.061, RMSEA = 0.066 ( p = 0.028). The students were grouped into three groups ( M –1 SD ; M ; M +1 SD ). The responses were coded in such a way that high scores ( M +1 SD ) indicated positive attitudes and beliefs, and low scores ( M –1 SD ) indicated negative attitudes and beliefs.
Additional Influencing Factors
In order to ensure the internal validity of the investigation, we collected student-related factors that influence the solution of word problems from a theoretical and empirical point of view. It has been shown that the mathematical abilities and metacognitive skills of students significantly influence their performance ( Sturm et al., 2015 ).
Mathematical Abilities
The basic mathematical abilities were determined using a standardized German-language test as a group test (Heidelberger Rechentest HRT 1–4, Haffner et al., 2005 ). The test consists of eleven subtests, from which three scale values were determined: calculation operations, numerical-logical and spatial-visual skills as well as the overall performance for all eleven subtests. The reliability was only satisfactory (Cronbach’s α = 0.74). Total performance was included in the study.
Metacognitive Skills
The metacognitive skills of the students were measured using a paper-pencil version of EPA2000, a test to measure metacognitive skills before and/or after the solving of tasks ( Clercq et al., 2000 ). The prediction skills and evaluation skills of the students were collected for all three word problems of the WPST using a 4-point rating scale: 1) “absolutely sure, it’s wrong,” 2) “sure, it’s wrong,” 3) “sure, it’s right,” and 4) “absolutely sure, it’s right” ( Clercq et al., 2000 ). If the students’ assessments of “absolutely sure” matched their solution, they were awarded 2 points. If they agreed with “sure,” they received 1 point. No match was scored with 0 points ( Desoete et al., 2003 ). The reliabilities were only satisfactory (Cronbach’s α total =0.74, α prediction =0.56, α evaluation = 0.73). A confirmatory factor analysis revealed that prediction skills and evaluation skills represent a single factor (χ 2 (9) = 16.652, p < 0.001; χ 2 / df = 1.850, CFI = 0.952, TLI = 0.919, RMSEA = 0.053 ( p = 0.396)). The aggregated factor was used as a control variable in the moderator analysis.
In addition to the variables considered in this paper, text comprehension and intelligence were also surveyed in the project. However, they are not the focus of this paper; additional information can be found in Sturm et al. (2015) .
Descriptive Statistics and Correlations Between the Measures
The descriptive statistics and correlations of all scales are presented in Table 1 (see Supplementary Appendix D for a separate overview for each of the experimental conditions). The signs for all correlations were as expected. The variable training program is not listed because it is the dichotomous moderator variable (T+ and T−).
TABLE 1 . Descriptive statistics and correlations of all variables for both experimental conditions.
Moderated Regression Analyses
The hypothesis was tested with a moderated regression analysis using product terms from mean-centered predictor variables ( Hayes, 2018 ). This model imposed the constraint that any effect of attitudes and beliefs was independent of all other variables in the model. This was achieved by controlling for mathematical abilities, metacognitive skills, and problem-solving performance at Measurement Point 1. The estimated main effects and interaction terms are presented in Table 2 .
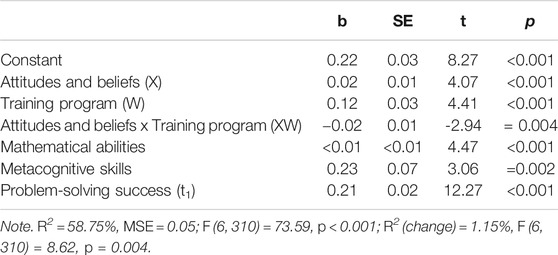
TABLE 2 . Results from the regression analysis examining the moderation of the effect of attitudes and beliefs on problem-solving success (t 2 ) by participation in the training program, controlling for mathematical abilities, metacognitive skills, and problem-solving success from the pretest.
When testing the hypothesis, we found a significant main effect of attitudes and beliefs, a significant main effect of the training program, and a significant moderator effect of the training on attitudes and beliefs as a predictor of problem-solving success. The main effect of the training program indicated that students who participated in the training performed better in the second WPST. The main effect of attitudes and beliefs showed that students with more positive attitudes and beliefs were more successful than students with negative attitudes and beliefs.
To further explore the interaction between attitudes and beliefs and the training program, we analyzed simple slopes at values of 1 SD above and 1SD below the means of attitudes and beliefs ( Hayes, 2018 ). As can be seen from the conditional expectations in Figure 2 , attitudes and beliefs did not affect the problem-solving success of students who participated in the training program. Attitudes and beliefs only had a positive effect on the problem-solving success of students who did not participate in the training.
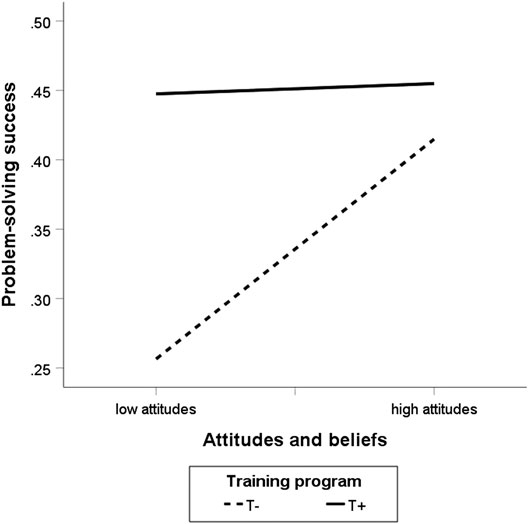
FIGURE 2 . Moderator effect of the training program on problem-solving success at Measurement Point 2.
Our results confirm previous findings that the attitudes and beliefs of students correlate with their problem-solving performance. They indicate that this correlation can be moderated by student participation in a training program. Negative attitudes and beliefs did not affect the performance of students who participated in a problem-solving training program over several weeks. Whether the training program also causes a change in the attitudes and beliefs of the students over time has to be investigated in a follow-up study, which is planned with a longer intervention period with at least two measurements of attitudes and beliefs. A longer intervention period would have the advantage that attitudes develop depending on the individual experiences of a person ( Hannula, 2002 ; Lim and Chapman, 2015 ), for instance, when new experience is gathered or new knowledge is acquired (e.g., Ajzen, 2005 ).
Some limitations need to be considered when interpreting the results of the study. For example, the mitigating processes need to be investigated further. It is also unclear as to which components of the training are ultimately responsible for counteracting the effect of attitudes and beliefs. Although the study did not provide results in this regard, we assume that the following factors might have an effect: generating external representations, reflecting on the representations together as a group, and fostering an appreciative and constructive approach to mistakes. Further studies are needed to show whether and to what extent these factors actually attenuate the effect of attitudes and beliefs.
Furthermore, the measurement instruments for the control variables mathematical abilities and metacognitive skills were rather limited. If researchers are interested in understanding further effects of metacognitive skills, more aspects should be included. Furthermore, according to Lester et al. (1987), investigating attitudes and beliefs using a questionnaire is associated with disadvantages. How accurately students answer the questions depends on how objectively and accurately they can reflect on and assess their own attitudes. Misinterpretations and errors cannot be ruled out. The most serious disadvantage, however, is that data collection using an inventory can easily be assumed to have unjustified validity and reliability. For a deeper insight into the attitudes and beliefs of primary school students, qualitative interviews have to be implemented.
However, for the purpose of this study, it seems sufficient to consider the two control variables mathematical abilities and metacognitive abilities. We were able to ensure that the correlation between attitudes and beliefs and the mathematical performance of students was not influenced by these factors.
Regardless of the limitations, our study has some practical implications. Participation in the training program, independently of the mathematical abilities and text comprehension of students, reduced the influence of attitudes and beliefs on their performance. Thus, for teaching practice, it can be concluded that it is important not only to implement regular problem-solving activities in mathematics lessons, but also to encourage students to externalize and find their own solutions. The aim is to establish a teaching culture that promotes a variety of approaches and procedures, allows mistakes to be made, and makes mistakes a subject for learning. Reflecting on different possible solutions and also on mistakes helps students to progress. Thus, students develop a repertoire of external representations from which they can profit in the long term when solving problems.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/ Supplementary Material , further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Department of Psychology, University of Koblenz and Landau, Germany. Written informed consent to participate in this study was provided by the participants' legal guardian. This study was also carried out in accordance with the guidelines for scientific studies in schools in the German state Rhineland-Palatinate (Wissenschaftliche Untersuchungen an Schulen in Rheinland-Pfalz), Aufsichts- und Dienstleistungsdirektion Trier. The protocol was approved by the Aufsichts- und Dienstleistungsdirektion Trier.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved it for publication.
The project was funded by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, grant number GK1561/1).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feduc.2021.525923/full#supplementary-material
1 This project was part of the first author’s PhD thesis
Adibnia, A., and Putt, I. J. (1998). Teaching problem solving to year 6 students: A new approach. Math. Educ. Res. J. 10 (3), 42–58. doi:10.1007/BF03217057
Ajzen, I. (2005). Attitudes, personality and behavior . Maidenhead, United Kingdom: Open University Press .
Google Scholar
Ajzen, I. (1998). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Proc. 50 (2), 179–211. doi:10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T
Amarel, S. (1966). On the mechanization of creative processes. IEEE Spectr. 3 (4), 112–114. doi:10.1109/MSPEC.1966.5216589
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Awofala, A. O. A. (2014). Examining personalisation of instruction, attitudes toward and achievement in mathematics word problems among nigerian senior secondary school students. Ijemst 2 (4), 273–288. doi:10.18404/ijemst.91464
Boonen, A. J. H., van der Schoot, M., van Wesel, F., de Vries, M. H., and Jolles, J. (2013). What underlies successful word problem solving? A path analysis in sixth grade students. Contemporary Educ. psychol. 38 (3), 271–279. doi:10.1016/j.cedpsych.2013.05.001
Bransford, J. D., Brown, A. L., and Cocking, R. R. (2000). How people learn: brain, mind, experience, and school . Washington, DC: National Academy Press .
Bransford, J. D., and Stein, B. S. (1993). The ideal problem solver: a guide for improving thinking, learning, and creativity . 2nd Edn. New York, NY: W. H. Freeman .
Breaugh, J. A., and Arnold, J. (2007). Controlling nuisance variables by using a matched-groups design. Organ. Res. Methods 10 (3), 523–541. doi:10.1177/1094428106292895
Brown, T. A. (2015). Confirmatory factor analysis for applied research . 2nd Edn. New York, NY: Guilford Press .
Charles, R. I., Lester, F. K., and O’Daffer, P. G. (1987). How to evaluate progress in problem solving . Reston, VA: National Council of Teachers of Mathematics .
Clercq, A. D., Desoete, A., and Roeyers, H. (2000). Epa2000: a multilingual, programmable computer assessment of off-line metacognition in children with mathematical-learning disabilities. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 32 (2), 304–311. doi:10.3758/BF03207799
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Cox, R., and Brna, P. (1995). Supporting the use of external representation in problem solving: the need for flexible learning environments. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 6 (2–3), 239–302. .
Cox, R. (1999). Representation construction, externalised cognition and individual differences. Learn. InStruct. 9 (4), 343–363. doi:10.1016/S0959-4752(98)00051-6
De Corte, E., Op t Eynde, P., and Verschaffel, L. (2002). ““Knowing what to believe”: the relevance of students’ mathematical beliefs for mathematics education,” in Personal epistemology: the psychology of beliefs about knowledge and knowing . Editors B. K. Hofer, and P. R. Pintrich (New Jersey, United States: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers ), 297–320. doi:10.4324/9780203424964
De Corte, E., Verschaffel, L., and Op’t Eynde, P. (2000). “Self-regulation: a characteristic and a goal of mathematics education,” in Handbook of self-regulation . Editors P. R. Pintrich, M. Boekaerts, and M. Zeidner (Cambridge, MA: Academic Press ), 687–726.
de Corte, E., Verschaffel, L., and Pauwels, A. (1992). Solving compare problems: An eye movement test of Lewis and Mayer’s consistency hypothesis. J. Educ. Psychol. 84 (1), 85–94. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.84.1.85
Desoete, A., Roeyers, H., and De Clercq, A. (2003). Can offline metacognition enhance mathematical problem solving?. J. Educ. Psychol. 95 (1), 188–200. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.95.1.188
Di Martino, P. (2019). Pupils’ view of problems: the evolution from kindergarten to the end of primary school. Educ. Stud. Math. 100 (3), 291–307. doi:10.1007/s10649-018-9850-3
Duval, R. (1999). “Representation, vision, and visualization: cognitive functions in mathematical thinking. Basic issues for learning (ED466379),” in Proceedings of the twenty-first annual meeting of the north American chapter of the international group for the psychology of mathematics education XXI , Cuernavaca, Mexico , October 23–26, 1999 . Editors F. Hitt, and M. Santos ( ERIC ), 1, 3–26.
Eid, M., Gollwitzer, M., and Schmitt, M. (2011). Statistik und Forschungsmethoden: lehrbuch . [Statistics and research methods] . 2nd Edn. Weinheim, Germany: Beltz .
Goldin, G. A. (2003). “Affect, meta-affect, and mathematical belief structures,” in Beliefs: a hidden variable in mathematics education? . Editors G. C. Leder, E. Pehkonen, and G. Törner (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers ), 31, 59–72. doi:10.1007/0-306-47958-3_4
Goldin, G. A., Rösken, B., and Törner, G. (2009). “Beliefs—No longer a hidden variable in mathematical teaching and learning processes,” in Beliefs and attitudes in mathematics education . Editors J. Maasz, and W. Schloeglmann (Rotterdam, Netherlands; Sense Publishers ), 1–18.
Greevy, R., Lu, B., Silber, J. H., and Rosenbaum, P. (2004). Optimal multivariate matching before randomization. Biostatistics 5 (2), 263–275. doi:10.1093/biostatistics/5.2.263
Grigutsch, S., Raatz, U., and Törner, G. (1998). Einstellungen gegenüber Mathematik bei Mathematiklehrern. Jmd 19 (1), 3–45. doi:10.1007/BF03338859
Haffner, J., Baro, K., Parzer, P., and Resch, F. (2005). Heidelberger Rechentest (HRT 1-4): erfassung mathematischer Basiskompetenzen im Grundschulalter [Heidelberger Rechentest (HRT 1-4): assessment of basic mathematical skills at primary school age] . Göttingen, Germany: Hogrefe .
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., and Anderson, R. E. (2009). Multivariate data analysis . 7th Edn. London, United Kingdom: Pearson .
Hannula, M. S. (2002). Attitude towards mathematics: emotions, expectations and values. Educ. Stud. Math. 49 (1), 25–46. doi:10.1023/A:1016048823497
Hayes, A. F. (2018). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: a regression-based approach . 2nd Edn. New York, NY: Guilford Press .
Hegarty, M., Mayer, R. E., and Green, C. E. (1992). Comprehension of arithmetic word problems: Evidence from students' eye fixations. J. Educ. Psychol. 84 (1), 76–84. doi:10.1037/0022-0663.84.1.76
Higgins, K. M. (1997). The effect of year-long instruction in mathematical problem solving on middle-school students’ attitudes, beliefs, and abilities. J. Exp. Educ. 66 (1), 5–28. doi:10.1080/00220979709601392
Kirsh, D. (2010). Thinking with external representations. AI Soc. 25 (4), 441–454. doi:10.1007/s00146-010-0272-8
Lester, F. K., and Cai, J. (2016). “Can mathematical problem solving be taught? Preliminary answers from 30 years of research,” in Posing and solving mathematical problems . Editors P. Felmer, E. Pehkonen, and J. Kilpatrick (Washington, DC: Springer ), 117–135. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-28023-3_8
Lester, F. K., Garofalo, J., and Kroll, D. L. (1989). “Self-confidence, interest, beliefs, and metacognition: key influences on problem-solving behavior,” in Affect and mathematical problem solving . Editors D. B. McLeod, and V. M. Adams (Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag ), 75–88. doi:10.1007/978-1-4612-3614-6_6
Lester, F. K., and Kroll, D. L. (1990). “Assessing student growth in mathematical problem solving,” in Assessing higher order thinking in mathematics . Editor G. Kulm (Washington, DC: AAAS Publication ), 53–70.
Lester, F. K. (1985). “Methodological considerations in research on mathematical problem-solving instruction,” in Teaching and learning mathematical problem solving: multiple research perspectives . Editor E. A. Silver (Mahwah NJ: Erlbaum ), 41–69.
Lienert, G. A., and Raatz, U. (1998). Testaufbau und Testanalyse [Test construction and test analysis] . 6th Edn. Weinheim, Germany: Beltz .
Lim, S. Y., and Chapman, E. (2015). Effects of using history as a tool to teach mathematics on students' attitudes, anxiety, motivation and achievement in grade 11 classrooms. Educ. Stud. Math. 90 (2), 189–212. doi:10.1007/s10649-015-9620-4
Mason, L., and Scrivani, L. (2004). Enhancing students' mathematical beliefs: an intervention study. Learn. InStruct. 14 (2), 153–176. doi:10.1016/j.learninstruc.2004.01.002
Mayer, R. E., and Hegarty, M. (1996). “The process of understanding mathematical problems,” in The nature of mathematical thinking . Editors R. J. Sternberg, and T. Ben-Zeev (Mahwah NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum ), 29–54.
Moore, R. T. (2012). Multivariate continuous blocking to improve political science experiments. Polit. Anal. 20 (4), 460–479. doi:10.1093/pan/mps025
M. S. Hannula, G. C. Leder, F. Morselli, M. Vollstedt, and Q. Zhang (Editors) (2019). Affect and mathematics education: fresh perspectives on motivation, engagement, and identity . New York, NY: Springer International Publishing . doi:10.1007/978-3-030-13761-8
Myers, A., and Hansen, C. H. (2012). Experimental psychology . 7th Edn. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth .
Newell, A., and Simon, H. A. (1972). Human problem solving . Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall .
Norman, D. A. (1993). Things that make us smart: defending human attributes in the age of the machine . New York, NY: Perseus Books .
Nussbeck, F. W., Eid, M., and Lischetzke, T. (2006). Analysing multitrait-multimethod data with structural equation models for ordinal variables applying the WLSMV estimator: what sample size is needed for valid results?. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 59 (1), 195–213. doi:10.1348/000711005X67490
Peterson, C., and Seligman, M. E. P. (2004). Character strengths and virtues: a handbook and classification . Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press .
Rasch, R. (2008). 42 Denk- und Sachaufgaben. Wie Kinder mathematische Aufgaben lösen und diskutieren [42 thinking and problem solving tasks. How children solve and discuss mathematical tasks] . 3rd Edn. Seelze-Velber, Germany: Kallmeyer .
Reisberg, D. (1987). “External representations and the advantages of externalizing one’s thought,” in The ninth annual conference of the cognitive science society , Seattle, WA , July 1, 1987 (Hove, United Kingdom: Psychology Press ), 281–293.
Reiss, K., Hellmich, F., and Thomas, J. (2002). “Individuelle und schulische Bedingungsfaktoren für Argumentationen und Beweise im Mathematikunterricht [Individual and educational conditioning factors for argumentation and evidence in mathematics teaching],” in Bildungsqualität von Schule: schulische und außerschulische Bedingungen mathematischer, naturwissenschaftlicher und überfachlicher Kompetenzen . Editors M. Prenzel, and J. Doll ( Weinheim, Germany: Beltz ), 51–64.
Reyes, L. H. (1984). Affective variables and mathematics education. Elem. Sch. J. 84 (5), 558–581. doi:10.1086/461384
Schnotz, W., Baadte, C., Müller, A., and Rasch, R. (2010). “Creative thinking and problem solving with depictive and descriptive representations,” in Use of representations in reasoning and problem solving: analysis and improvement . Editors L. Verschaffel, E. de Corte, T. de Jong, and J. Elen (Abingdon, United Kingdom: Routledge ), 11–35.
Schoenfeld, A. H. (1985). Mathematical problem solving . Cambridge, MA: Academic Press .
Shaughnessy, J. M. (1985). Problem-solving derailers: The influence of misconceptions on problem-solving performance. In E. A. Silver (Hrsg.), Teaching and learning mathematical problem solving: Multiple research perspectives (S. 399 -415). Lawrence Erlbaum.
Stuart, E. A., and Rubin, D. B. (2008). “Best practices in quasi-experimental designs: matching methods for causal inference,” in Best practices in quantitative methods . Editor J. W. Osborne (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE ), 155–176.
Sturm, N. (2018). Problemhaltige Textaufgaben lösen: einfluss eines Repräsentationstrainings auf den Lösungsprozess von Drittklässlern [Solving word problems: influence of representation training on the problem-solving process of third-graders . Berlin, Germany: Springer . | Google Scholar
Sturm, N., and Rasch, R. (2015). “Forms of representation for solving mathematical word problems – development of an intervention study,” in Multidisciplinary research on teaching and learning . Editors W. Schnotz, A. Kauertz, H. Ludwig, A. Müller, and J. Pretsch (London, United Kingdom: Palgrave Macmillan ), 201–223.
Sturm, N., Rasch, R., and Schnotz, W. (2016). Cracking word problems with sketches, tables, calculations and reasoning: do all primary students benefit equally from using them? Pers. Indiv. Differ. 101, 519. doi:10.1016/j.paid.2016.05.317
Sturm, N. (2019). “Self-generated representations as heuristic tools for solving word problems,” in Implementation research on problem solving in school settings. Proceedings of the 2018 joint conference of ProMath and the GDM working group on problem solving . Editors A. Kuzle, I. Gebel, and B. Rott (Münster, Germany: WTM-Verlag ), 173–192.
Sturm, N., Wahle, C. V., Rasch, R., and Schnotz, W. (2015). “Self-generated representations are the key: the importance of external representations in predicting problem-solving success,” in Proceedings of the 39th conference of the international group for the psychology of mathematics education . Editors K. Beswick, T. Muir, and J. Wells ( Basingstoke, United Kingdom: PME ), 4, 209–216.
Sweller, J. (1994). Cognitive load theory, learning difficulty, and instructional design. Learn. InStruct. 4 (4), 295–312. doi:10.1016/0959-4752(94)90003-5
van Dijk, T. A., and Kintsch, W. (1983). Strategies of discourse comprehension . Cambridge, MA: Acadamic Press .
Verschaffel, L., De Corte, E., Lasure, S., Van Vaerenbergh, G., Bogaerts, H., and Ratinckx, E. (1999). Learning to solve mathematical application problems: a design experiment with fifth graders. Math. Think. Learn. 1 (3), 195–229. doi:10.1207/s15327833mtl0103_2
Verschaffel, L., Greer, B., and de Corte, E. (2000). Making sense of word problems . Netherlands: Swets and Zeitlinger .
Webb, N. L., Moses, B. E., and Kerr, D. R. (1977). Mathematical problem solving project technical report IV: developmental acctivities related to summative evaluation (1975–1976) : Mathematics Education Development Center. Bloomington, IN: Indiana University .
Zakaria, E., and Ngah, N. (2011). A preliminary analysis of students’ problem-posing ability and its relationship to attitudes towards problem solving. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 3 (9), 866–870.
Zakaria, E., and Yusoff, N. (2009). Attitudes and problem-solving skills in algebra among malaysian matriculation college students. Eur. J. Soc. Sci. 8 (2), 232–245.
Keywords: attitudes and beliefs, word problem, training program design, problem-solving, problem-solving success, primary school, moderation effect analysis
Citation: Sturm N and Bohndick C (2021) The Influence of Attitudes and Beliefs on the Problem-Solving Performance. Front. Educ. 6:525923. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2021.525923
Received: 21 May 2020; Accepted: 18 January 2021; Published: 17 February 2021.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2021 Sturm and Bohndick. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nina Sturm, [email protected]
This article is part of the Research Topic
Psychology and Mathematics Education
The Intuitive Life
Inspiring conscious changemakers.

Joy Strategist, NLP/Time Line Therapy® Spiritual Mentor, Hypnotherapist

Success or Failure – The Key to Problem Solving is Attitude
What if our problems aren’t the REAL problem? What if the real problem lies in our attitude about the problem? That’s what Norman Vincent Peale, father of positive thinking cautioned when he said “Any fact facing us is not as important as our attitude toward it, for that determines our success or failure.”
Have you noticed that when you’re on edge with a problem that it can become difficult to stay positive and focused? Have you noticed how your mood is affected and your normal resiliency is challenged? Research shows that it’s easier to believe the” bad stuff ” when faced with challenges that make us feel unhappy or nervous—a phenomenon known as negative memory bias. “Our moods shape our ability to recall things about ourselves,” explains University of Toronto Psychotherapist, Zindel Segal, PhD. “Naturally, when you’re feeling down, it’s easier to recall failures or times when you’ve messed up. The mind is mired in a negative view. The same holds true for anxiety: Someone who is timid or frightened might be leery of a new situation, might look for comfort in ways she’s been able to secure it before. It’s staying with the devil you know.”
So to solve our problems, we need to be AWARE and check out our ATTITUDES … a subtle but hugely important step that’s easy to miss because it appears so obvious that we skip it. In the flying industry, a detailed check-list and “walk-around” the aircraft takes place before each flight…. no matter how seasoned a pilot is, this checklist and walk around must be completed each and every time. So too with us, at the start of each day, a check-list and walk-around our attitudes, will keep us safe, prevent problems that could have been avoided, and keep us motivated in personal effectiveness to reach our dreams and goals.
Attitude Checklist
1. Mindfulness Defined as “paying attention in a certain way, on purpose, without judgement,”(Jon Kabbat-Zinn), mindfulness helps keep our awareness (attention) engaged so we’re able to act consciously instead of unconsciously. Developing mindfulness improves our understanding of what’s going on in any situation. It creates a “pattern interrupt ,” so that instead of being distracted or overcome by emotions or messy thinking we determine where our attitude really is – effective, healthy and empowered, or needing an “attitudinal adjustment.” Application: pick an area in life that you’d like to bring more success to. Take a few deep breaths and observe from mindfulness… what do you see or hear from this quiet place?
2. Enthusiasm “Every production of genius must be the production of enthusiasm.” Benjamin Disraeli Enthusiasm re-frames problems and offers new perspectives…. it grows hope, optimism and gratitude, the great elixirs of transformation. Enthusiasm opens pathways to new ways of thinking which brings more choices in how to respond. Application: How can enthusiasm help you work effectively in the challenged areas of your life? Decide and take Action!
3. Action “You must make a decision that you are going to move on. It won’t happen automatically. You will have to rise up and say, “ I don’t care how hard this is, I don’t care how disappointed I am, I’m not going to let this get the best of me. I’m moving on with my life.” (Joel Olsteen). Solutions come through action. Application: Strengthen your commitment to yourself. What action will you take to move through your challenges? Because thought precedes all action, what thoughts do you now need to think? What is that internal communication that needs to take place? Commit to action from these empowered thoughts. This is self-inspired, personal development at its best.
4. Affirm a positive, enthusiastic mindset to fuel consistent action Constant, repeated self talk and images that are positive and rewarding, focus the subconscious from what we don’t want to what we do want (and believe we can create). Be vigilant in catching thoughts and words to “release and replace.” E.g., thinking/saying “I’m always behind, there’s never enough time in the day” is a self-fulfilling prophecy… Application: Affirm a new mindset and actions with “in-process” statements like “I have a new attitude! Each day and in every way, I’m more and more effective in accomplishing my goals!” Here’s one of my favorite daily affirmations based on the Hindu word of “Namaskar”:
“I salute the divinity in myself. I am strong and able. I can do all that I need to do this day. My mind is alert, my body vital and healthy and my way will be strewn with golden opportunities. No matter what this day may bring to me, there is in me that which is great enough to meet it, overcome it, and be blessed by it!” Namaskar

Success or Failure, Mediocrity or Accomplishment, Attitude makes all the difference because it’s a “now” process that activates the happiness, peace and prosperity in the NOW, guaranteeing a future that just keeps getting better and better, no matter what.
If you enjoyed this blog, please ensure you are signed up for both my newsletter and quote of the day. The Intuitive Life is committed to “Inspiring Conscious Changemakers.” I welcome your participation in our growing community! Cheryl Brewster is a certified personal and business intuitive, whose specialty is empowerment through change.
More like this:

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Pave the Way for Self-regulation and Problem-solving With Social-emotional Learning
Posted: April 3, 2024
Problem-solving is a social-emotional learning (SEL) skill children need for lifelong success. Effective problem-solving skills support children's ability to self-regulate, focus on tasks, think flexibly and creatively, work with others, and generate multiple ways to solve problems. When young children develop and build these skills, it positively impacts their interactions with others, grows their capacity to manage challenges, and boosts a sense of competence.

A group of school-age children are stacking plastic blocks with an educator.
The foundation for effective social problem-solving is grounded in self-regulation, or the ability to regulate emotions when interacting with others. It is easier to focus on one's feelings and the feelings and perspectives of others and to work cooperatively toward solutions when a child can self-regulate and calm down. Children develop self-regulation skills over time, with practice and with adult guidance. Equally important is how an adult models emotion regulation and co-regulation.
"Caregivers play a key role in cultivating the development of emotion regulation through co-regulation, or the processes by which they provide external support or scaffolding as children navigate their emotional experiences" (Paley & Hajal, 2022, p. 1).
When adults model calm and self-regulated approaches to problem-solving, it shows children how to approach problems constructively. For example, an educator says, "I'm going to take a breath and calm down so I can think better." This model helps children see and hear a strategy to support self-regulation.
Problem-solving skills help children resolve conflicts and interact with others as partners and collaborators. Developing problem-solving skills helps children learn and grow empathy for others, stand up for themselves, and build resilience and competence to work through challenges in their world.
Eight strategies to support problem-solving
- Teach about emotions and use feeling words throughout the day. When children have more words to express themselves and their feelings, it is easier to address and talk about challenges when they arise.
- Recognize and acknowledge children's feelings throughout the day. For example, when children enter the classroom during circle time, mealtime, and outside time, ask them how they feel. Always acknowledge children's feelings, both comfortable and uncomfortable, to support an understanding that all feelings are OK to experience.
- Differentiate between feelings and behaviors. By differentiating feelings from behaviors, educators contribute to children’s understanding that all feelings are OK, but not all behaviors are OK. For example, an educator says, "It looks like you may be feeling mad because you want the red blocks, and Nila is playing with them. It's OK to feel mad but not OK to knock over your friend’s blocks."
- Support children's efforts to calm down. When children are self-regulated, they can think more clearly. For example, practice taking a breath with children as a self-regulation technique during calm moments. Then, when challenges arise, children have a strategy they have practiced many times and can use to calm down before problem-solving begins.
- Encourage children's efforts to voice the problem and their feelings after they are calm. For example, when a challenge arises, encourage children to use the phrase, "The problem is_______, and I feel______." This process sets the stage to begin problem-solving.
- Acknowledge children's efforts to think about varied ways to solve problems. For example, an educator says, "It looks like you and Nila are trying to work out how to share the blocks. What do you think might work so you can both play with them? Do you have some other ideas about how you could share?"
- Champion children's efforts as they problem-solve. For example, "You and Nila thought about two ways you could share. One way is to divide the red blocks so you can each build, and the other is to build a tower together. Great thinking, friends!"
- Create opportunities for activities and play that offer problem-solving practice. For example, when children play together in the block area, it provides opportunities to negotiate plans for play and role-play, build perspective, talk about feelings, and share. The skills children learn during play, along with adult support, enhance children’s ability to solve more complex and challenging social problems and conflicts when they occur in and out of the early learning setting.
References:
Paley, B., & Hajal, N. J. (2022). Conceptualizing emotion regulation and coregulation as family-level phenomena. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review , 25 (1), 19-43.
Social Media
- X (Twitter)
- Degrees & Programs
- College Directory
Information for
- Faculty & Staff
- Visitors & Public
These 9 Attitudes Will Solve Any Business Problem
One of lingering fallacies about business is believing that Jim Collins is right. As the bestselling researcher-author of Good to Great and now, Great by Choice , Collins is pretty good at retrospectively interpreting what worked in the past for some businesses. But he’s not great at forecasting how they’ll do when the research project is complete and the book is published.
Turns out, if you follow the companies Collins called winners, they are now: not so much. Turns out Collins is a lot like the uncle you’ll soon sit next to at a holiday dinner. The one who tells you how great General Motors was before its CEO Robert McNamara started the Vietnam war.
Okay, that’s harsh. But, it’s the truth. Actually, that’s a good measure when judging whether something important is true. The truth probably hurts, or at least causes you to wince. If someone tells you the so-called truth, and your cheeks are blushing with how wonderful you are? It’s not the truth and it’s not going to help you succeed in this chaotic environment.
What does work in helping you predict the future, and more importantly deliver the greatest odds of succeeding in the nearly incomprehensible rush of problems and opportunities you face?
Your attitude is what really matters.
Not your skill set. Not your network. Not the number of business books you suck back and arm yourself with – or at least buy to fill up your Kindle or iPad.
I had a look back at a course from Dr. Moshe Rubinstein, the father of problem-solving, productivity and leveraging the creative forces that is your brain. Without trying to express how profoundly grateful I am to have found a moving box that included some of my coursework from the then UCLA Graduate School of Management (now Anderson), I will share what Rubinstein knew a long time ago.
The 9 attitudes that solve any business problem
- View a problem as a challenge, an opportunity for new experiences to expand your problem-solving repertoire.
- Focus on the present and future obstacles, and deal with those you can do something about. When obstacles appear to be insurmountable: question the goal, and if necessary, modify it.
- Pay attention to the distinction among facts, opinions and judgments. First get the facts, then interpret them. Don’t judge the facts before you do that analysis.
- Listen to experts, authorities and others you trust as if you will be required to take an exam on what they are saying. Don’t refute or judge what they say when they say it. Ask questions if you don’t understand, but don’t argue.
- Use reason not pride. You will be tempted to distort the facts if you have to manage your ego rather than manage the problem-solving process.
- Don’t solve the problem too soon. Take every minute you can to gather and process information from sources. Don’t take more time than you can afford, but do not begin your evaluation and selection of a solution prematurely.
- Focus your attention on surmountable obstacles that block the way to a solution, any solution. Identify what can’t be overcome, and if a path still exists around those, then pick off the ones that remain.
- Expect that implementation of the solution will be harder than coming to it. You’ll undoubtedly need other people to implement. Educate them about the benefits of a solution, before you tell them what they will need to do.
- Believe you have control, because then you will. Even if you are wrong in fact, the perception that you have control will promote your ability to perform. Ask yourself if you have a choice, and if you answer honestly, you almost always realize that you do. Choice is control.
So no hedgehogs or foxes needed now or in the future, sorry Jim.
What Dr. Rubinstein documented about the power of communication? It is the greatest formula anyone ever devised about how you can get exactly what you want and more: from yourself and others.
Change your attitude; change your life.
Nance Rosen is the author of Speak Up! & Succeed . She speaks to business audiences around the world and is a resource for press, including print, broadcast and online journalists and bloggers covering social media and careers. Read more at NanceRosenBlog . Twitter name: nancerosen

- Main content

Leaders Who Create More Problems Than They Solve
Be on guard against unhealthy, damaging leadership with your team or family..
Posted April 3, 2024 | Reviewed by Davia Sills
- Lack of information or misinformation can nudge people toward poor leadership.
- Emotional deficits exist in all lives and often lead to unhealthy influence.
- Manipulation can trump motivation as people interact with others if they’re not careful.
- Simple wisdom can enable individuals to avoid these five common, but poor leadership habits.
I spoke to the employees at a company that has a glowing reputation. As I explained how problem-solving is the quickest way to earn influence in an organization, it sparked a heated conversation that led to a personal epiphany for me.
Five Problems Leaders Create When Solving Problems
While problem-solving is a fast way to deepen one’s influence on a team, it depends on how one goes about addressing the problem. I have identified five common problems that leaders create when facing challenges in a dysfunctional manner. Do you recognize any?
1. Knee-Jerk Leaders
I’ve done this a few times in my career . It occurs when a leader becomes aware of a problem later than their team knows of it, and they feel left behind, like something’s been going on behind their back. In reaction, they pull the trigger on a decision far too quickly before getting helpful information on the parties involved. They feel they see the big picture more than others can.
While acting on their gut can be helpful, they don’t see the collateral damage they do to the psychological safety of their team members. It’s a tradeoff that may not pay off. A solution? It’s often best to wait a day, gather information, and sleep on the problem before choosing a response.
2. Eggshell Leaders
We all know the term “walking on eggshells.” These leaders find it challenging to make tough decisions because they’re afraid of offending someone; they worry too much about politics , personalities, and the perception others have of them. They can be people pleasers who tiptoe around problems or make decisions that aren’t good long-term solutions. In fact, they prolong problems, creating a culture of distrust and dissatisfaction among teammates.
When leaders tiptoe around problems, it causes staff to tiptoe around, keeping secrets. A solution? You must invite candor from trusted colleagues who’ll hold you accountable for making tough calls.
3. Face-Saving Leaders
This is a term from Dan Rockwell. Face-saving leaders care more about appearances than results and often hide problems from higher-ups; they minimize problems or seize control to cover their reputation. Saving face is very important to them and their status.
These people only succeed long-term in dysfunctional organizations. Over time, people stop trusting them, withholding information from them since face-saving leaders do the same. Soon, productivity slows down as knowledge is impeded within departments.
A solution? You must face problems, own them, and follow through to a successful resolution. This enables you to deepen trust.
4. M.I.A. Leaders
These leaders claim they don’t want to micro-manage, but in reality, they don’t manage at all. They are absent from the process, leaving team members without direction. When they do try to solve problems, they’re often unsure what to do. They procrastinate on taking action for long periods and could be described as “absentee leaders.” People can’t expect them to be in the trenches, fighting battles alongside them; they are missing in action. They put off decisions because they fear making the wrong decision.
A solution? Grow some courage to make a tough call. Form a team to help you face the music and ask for the input you need to make progress.
5. Landmine Leaders
This problem-solving method only adds to the drama that problems already bring with them. It aggravates issues because others don’t know what they’re going to get from this leader. It could be a peaceful exchange or an explosion, like walking around landmines in a field. There is unnecessary drama with this problem-solving approach as this leader keeps bringing up past failures or complaining about mistakes.
A solution? Adopt a “make it better” approach, which is one of our core values. Don’t drudge up the past unless it furnishes positive lessons learned and improves employee attitudes, words, actions, and decisions. Calm is usually better than drama.
The greatest enemies of logic are ego and emotion since they both diminish trust. I love the words of Colin Powell: “ Leadership is solving problems. The day soldiers stop bringing you their problems is the day you have stopped leading them. They have either lost confidence that you can help or concluded you do not care. Either case is a failure of leadership.”

Tim Elmore is the founder and president of Growing Leaders, an international non-profit organization created to develop emerging leaders.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Support Group
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

COMMENTS
Check out these insights to learn how to develop a problem-solving mindset—and understand why the solution to any problem starts with you. When things get rocky, practice deliberate calm. Developing dual awareness; How to learn and lead calmly through volatile times. Future proof: Solving the 'adaptability paradox' for the long term.
Definitions and Examples. Jennifer Herrity. Updated July 31, 2023. When employers talk about problem-solving skills, they are often referring to the ability to handle difficult or unexpected situations in the workplace as well as complex business challenges. Organizations rely on people who can assess both kinds of situations and calmly ...
Problem-Solving Skills Definition. Problem-solving skills are the ability to identify problems, brainstorm and analyze answers, and implement the best solutions. An employee with good problem-solving skills is both a self-starter and a collaborative teammate; they are proactive in understanding the root of a problem and work with others to ...
Introduction. Positive Attitude. Benefits of a Positive Attitude. Examples. Conclusion. Introduction: Problem-solving is essential for success in many areas of life, from academics to the workplace. Good problem solvers can break down a problem and gradually analyze it, while poor problem solvers often lack the confidence and experience to do this.
Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork. 1. Analysis. As a manager, you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first.
A problem-solving attitude is a positive and proactive approach to addressing challenges and obstacles. Those with a problem-solving attitude are willing to take ownership of problems, seek new information and perspectives, and actively work to identify and implement solutions. They also view failures and setbacks as opportunities for growth ...
This article post is part of the Effective Thinking series of IQ Matrix maps that are designed to help you successfully deal with the problems and challenges confronting your reality. Topics within this series include: • Part 1: Strategic Questions. • Part 2: Creative Thinking. • Part 3: Problem Solving. • Part 4: Critical Thinking.
Problem solving is an exceptionally important workplace skill. Being a competent and confident problem solver will create many opportunities for you. By using a well-developed model like Simplexity Thinking for solving problems, you can approach the process systematically, and be comfortable that the decisions you make are solid. ...
Decision Making. Problem solving and decision making are closely related skills, and making a decision is an important part of the problem solving process as you will often be faced with various options and alternatives. See Decision Making for more. The measure of success is not whether you have a tough problem to deal with, but whether it is ...
The first step in solving a problem is understanding what that problem actually is. You need to be sure that you're dealing with the real problem - not its symptoms. For example, if performance in your department is substandard, you might think that the problem lies with the individuals submitting work. However, if you look a bit deeper, the ...
1. Define the problem. Diagnose the situation so that your focus is on the problem, not just its symptoms. Helpful problem-solving techniques include using flowcharts to identify the expected steps of a process and cause-and-effect diagrams to define and analyze root causes.. The sections below help explain key problem-solving steps.
The result shows that the problem solving atti tude is significantly a ssociated to the critical thinking. ability of the students. Students who have high level of problem solving attitude will ...
The broader innovation skillset. The attitudes and skills outlined in the framework are the broader elements that, in combination, drive successful application of experimental problem solving activities. They are crucial for successfully creating impact with established innovation methods, such as human-centred design, behavioural insights ...
Problem solving is the process of achieving a goal by overcoming obstacles, a frequent part of most activities. Problems in need of solutions range from simple personal tasks (e.g. how to turn on an appliance) to complex issues in business and technical fields. The former is an example of simple problem solving (SPS) addressing one issue ...
A problem-solving orientation is a positive attitude toward any given problem; it's your demonstration of a willingness to solve problems and a belief you'll be effective at doing so. To demonstrate this orientation you should view problems as challenges/opportunities; verbalize the solution as reachable and leading to successful outcomes ...
The second step involved in having a good attitude is the decision to be proactive, assume the responsibility, and find a solution, whether it's to make the problem disappear, or to have patience and put yourself in a different mindset so that the problem affects you as little as possible. The third step involves making a plan of action, a road map that will free up as many resources as ...
To Solve Your Toughest Problems, Change the Problems You Solve. In this episode, you'll learn how to reframe tough problems by asking questions that reveal all the factors and assumptions that ...
Thinking outside of the box is an important problem-solving skill in the workplace, because it can often lead to better outcomes than the originally expected ones. 4. Ability to work under pressure. This is often one of the most important benefits of problem-solving skills in the workplace.
1 Encourage curiosity. One of the best ways to promote a positive attitude towards problem-solving is to encourage curiosity among your employees. Curiosity is the drive to explore, discover, and ...
The problem-solving performance of primary school students depend on their attitudes and beliefs. As it is not easy to change attitudes, we aimed to change the relationship between problem-solving performance and attitudes with a training program. The training was based on the assumption that self-generated external representations support the problem-solving process.
Problem solving attitude is one of the most important aspect of the students in handling problems that they encountered. Meanwhile, critical thinking ability is also an important skill of the students in dealing and analyzing the problems and to it appropriately. The study used descriptive correlation design to determine the relationship between problem solving attitude and critical thinking ...
problem-solving skills were not a significant predictor of their scientific attitude. Key words: Problem-solving skills, Scientific attitude, Secondary school students . Introduction . In the 21st century, students have to get an education at a level that can keep up with changes and developments.
Decide and take Action! 3. Action. "You must make a decision that you are going to move on. It won't happen automatically. You will have to rise up and say, " I don't care how hard this is, I don't care how disappointed I am, I'm not going to let this get the best of me. I'm moving on with my life." (Joel Olsteen).
Problem-solving is a social-emotional learning (SEL) skill children need for lifelong success. Effective problem-solving skills support children's ability to self-regulate, focus on tasks, think flexibly and creatively, work with others, and generate multiple ways to solve problems. When young children develop and build these skills, it positively impacts their interactions with others, grows ...
The 9 attitudes that solve any business problem. View a problem as a challenge, an opportunity for new experiences to expand your problem-solving repertoire. Focus on the present and future ...
3. Face-Saving Leaders. This is a term from Dan Rockwell. Face-saving leaders care more about appearances than results and often hide problems from higher-ups; they minimize problems or seize ...
Edited by Lynn Levy. Engineered by Efim Shapiro. Featuring Dennis Overbye. The show "3 Body Problem" premiered on March 21 and quickly became one of Netflix's most-watched titles. It is an ...
The idea that it will change the world has gone from a nerdy obsession to conventional wisdom. What we still don't know is how A.I. will change the world. It could enslave or kill us all. But ...
Tags. HR. Staff. Across Duke, administrative professionals in schools and departments help their units function smoothly. And when things get busy, plans change quickly, or problems arise, these colleagues often find themselves in the middle of the solution. In advance of National Administrative Professionals Day on April 24, we want to hear ...
When it rains in Bangladesh many city areas go underwater and waterlogging in the streets. These cities are situated on the riverside. The project was conducted to solve this problem and to get benefits from the environment. The procedure was Collecting rainwater samples in a flask or large area requires separating pure water vapor in a balloon ...