

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
CBSE Board Exam is on the way, so you must practice some good Case Studies and Passage Based Questions of Class 10 Science to boost your preparation to score 95+% on Boards. In this post, you will get Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Board Exams.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Control and Coordination Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: Control and coordination are vital processes in living organisms that enable them to respond to their environment and maintain internal balance. In humans, the nervous system and the endocrine system work together to carry out these functions. The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, and it transmits signals through electrical impulses. The endocrine system, on the other hand, consists of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream, which regulate various bodily functions. The coordination between the nervous system and the endocrine system ensures the proper functioning of different organs and systems in the body. The nervous system allows for rapid responses, while the endocrine system enables long-term regulation. Understanding control and coordination helps us comprehend the mechanisms behind reflex actions, voluntary actions, and the response to external stimuli.
What are control and coordination processes responsible for? a) Maintaining internal balance in living organisms b) Regulating bodily functions c) Transmitting signals through electrical impulses d) All of the above Answer: d) All of the above
Which systems work together to carry out control and coordination in humans? a) Nervous system and immune system b) Nervous system and respiratory system c) Nervous system and endocrine system d) Nervous system and digestive system Answer: c) Nervous system and endocrine system
What is the role of the nervous system in control and coordination? a) Secreting hormones into the bloodstream b) Transmitting signals through electrical impulses c) Regulating various bodily functions d) Maintaining internal balance Answer: b) Transmitting signals through electrical impulses
What is the role of the endocrine system in control and coordination? a) Transmitting signals through electrical impulses b) Regulating various bodily functions c) Maintaining internal balance d) Carrying out rapid responses Answer: b) Regulating various bodily functions
What is the advantage of the coordination between the nervous system and the endocrine system? a) Rapid responses b) Long-term regulation c) Reflex actions d) Voluntary actions Answer: b) Long-term regulation
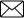
Case Study 2: To carry out a simple function such as eating food there has to be coordination of the eyes, hands, and mouth. The eyes have to focus on the food, the hands have to pick it up and take it to the mouth where it will be chewed. All these actions have to be coordinated in such a manner that they follow a particular sequence and the action is completed. A similar mechanism is also needed for internal functions of the body. This function is carried out by the nervous system. It is composed of (a) Specialised cells which can detect, receive and transmit different kinds of stimuli. These are called neurons. (b) Nerve fibres which are certain bundles of extended processes of nerve cells.
The individuals also have to adjust to the changing conditions around them and vary their responses. At the same time, the internal conditions of the body should be maintained constant. This is called homeostasis. The internal conditions of the body are maintained at a constant by controlling the physiology of the organisms.
(i) What will the correct sequence in which conduction of information through nerves take place? (ii) How homeostasis is said to maintain the equilibrium of the body? (iii) What function does the central nervous system perform? (iv) What happens when the dendrite tip of a nerve cell receives a signal?
Answer: (i) Dendrites → Cell body → Axon → Nerve endings at the tip of axon → Synapse → Dendrite of next neuron (ii) Homeostasis helps in keeping the constant internal environment within a cell or a body and hence maintains the equilibrium of the body. (iii) The central nervous system is comprised of the brain and the spinal cord which process the information received from the receptors on/in the body. (iv) Upon receiving a signal, the dendrite tip of a nerve cell sets off a chemical reaction which creates an electrical impulse in the them.
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 10 Science Control and Coordination Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Extra questions of class 10 science chapter 3 metals and non-metals pdf download.

CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 11 – Constructions MCQ Quiz
Mcq class 10 english how to tell wild animals questions with answers english poem 4, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Control and Coordination
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 7 control and coordination.

control and coordination case study questions answer from class 10 science biology
CBSE Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Control and Coordination. Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Control and Coordination.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Based Questions Class 10 Science Biology Chapter 7
Case study : 1.
If the body design in the squirrel relied only on electrical impulses via nerve cells, the range of tissues instructed to prepare for the coming activity would be limited. On the other hand, if a chemical signal were to be sent as well, it would reach all cells of the body and provide the wideranging changes needed. This is done in many animals, including human beings, using a hormone called adrenaline that is secreted from the adrenal glands.
i) which is the target organ for the adrenaline hormone?
Ans: Heart is the target organ for the adrenaline hormone which increases the heartbeat rate.
ii) Which hormone is released by thyroid gland?
Ans: Thyroxine is released by thyroid gland.
iii) What is the function of thyroxine hormone?
Ans: It regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body and promote the best balance for growth.
iv) Name the hormone released by ovary?
Ans: Estrogen and progesterone
V) Name the three hormonal glands located in the brain?
Ans: Pineal, pituitary and hypothalamus
CASE STUDY : 2
Some plants like the pea plant climb up other plants or fences by means of tendrils. These tendrils are sensitive to touch. When they come in contact with any support, the part of the tendril in contact with the object does not grow as rapidly as the part of the tendril away from the object. This causes the tendril to circle around the object and thus cling to it. More commonly, plants respond to stimuli slowly by growing in a particular direction. Because this growth is directional, it appears as if the plant is moving.
i) How many type of tropism are shown by plants? Name them.
Ans: Generally there are 6 type of tropism namely phototropism, gravitropism, chemotropism, thigmotropism, thermotropism and hydrotropism.
ii) The touch me not plant is an example of which tropism?
Ans: it is an example of thigmotropism.
iii) give one example of chemotropism?
Ans: growth of pollen tubes to wheels is one example of chemotropism.
iv) Name the plants hormone which promotes cell division?
Ans: Cytokinins promotes cell division in plants.
v) Name the plant hormone which inhibits growth?
Ans: Abscisic acid
CASE STUDY : 3
We also think about our actions. Writing, talking, moving a chair, clapping at the end of a programme are examples of voluntary actions which are based on deciding what to do next. So, the brain also has to send messages to muscles. This is the second way in which the nervous system communicates with the muscles. The communication between the central nervous system and the other parts of the body is facilitated by the peripheral nervous system consisting of cranial nerves arising from the brain and spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord. The brain thus allows us to think and take actions based on that thinking.
i) what are the three major parts of the brain?
Ans: Forebrain, Midbrain and hindbrain.
ii) what are the function of medulla?
Ans: It controls all the involuntary action such as blood pressure, salivation, vomiting, etc.
iii) Which fluid is present in our brain?
Ans: Cerebrospinal fluid.
iv) What is the function of hypothalamus?
Ans: It regulates homeostasis, releases hormones.
v) What is the function of mid brain?
Ans: The mid brain connects the forebrain and hindbrain.
CASE STUDY : 4
Body consists of dense networks of intricately arranged neurons. It sits in the forward end of the skull, and receives signals from all over the body which it thinks about before responding to them. Obviously, in order to receive these signals, this thinking part of the brain in the skull must be connected to nerves coming from various parts of the body.
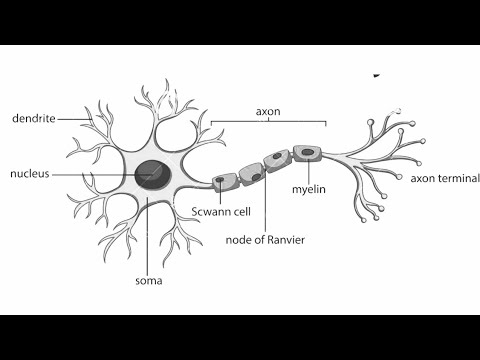
i) What is reflex?
Ans: It is the sudden action done in response to something in the environment.
ii) How does the nervous tissue cause action?
Ans: When a nerve impulse reaches the muscles, the muscles fibres move by changing their shape and their arrangements in the cell.
iii) What is the function of the motor neuron?
Ans: It transmits the impulses from spinal cord to skeletal muscles.
iv) What is reflex arc?
Ans: It is the neural pathway that controls reflex starting from a sensory neuron and end at effector.
v) What is the role of sensory neuron?
Ans: It carry signals from outer part of body to central nervous system.
CASE STUDY : 5
In animals, such control and coordination are provided by nervous and muscular tissues. Touching a hot object is an urgent and dangerous situation for us. We need to detect it, and respond to it. How do we detect that we are touching a hot object? All information from our environment is detected by the specialised tips of some nerve cells. These receptors are usually located in our sense organs, such as the inner ear, the nose, the tongue, and so on. So gustatory receptors will detect taste while olfactory receptors will detect smell.
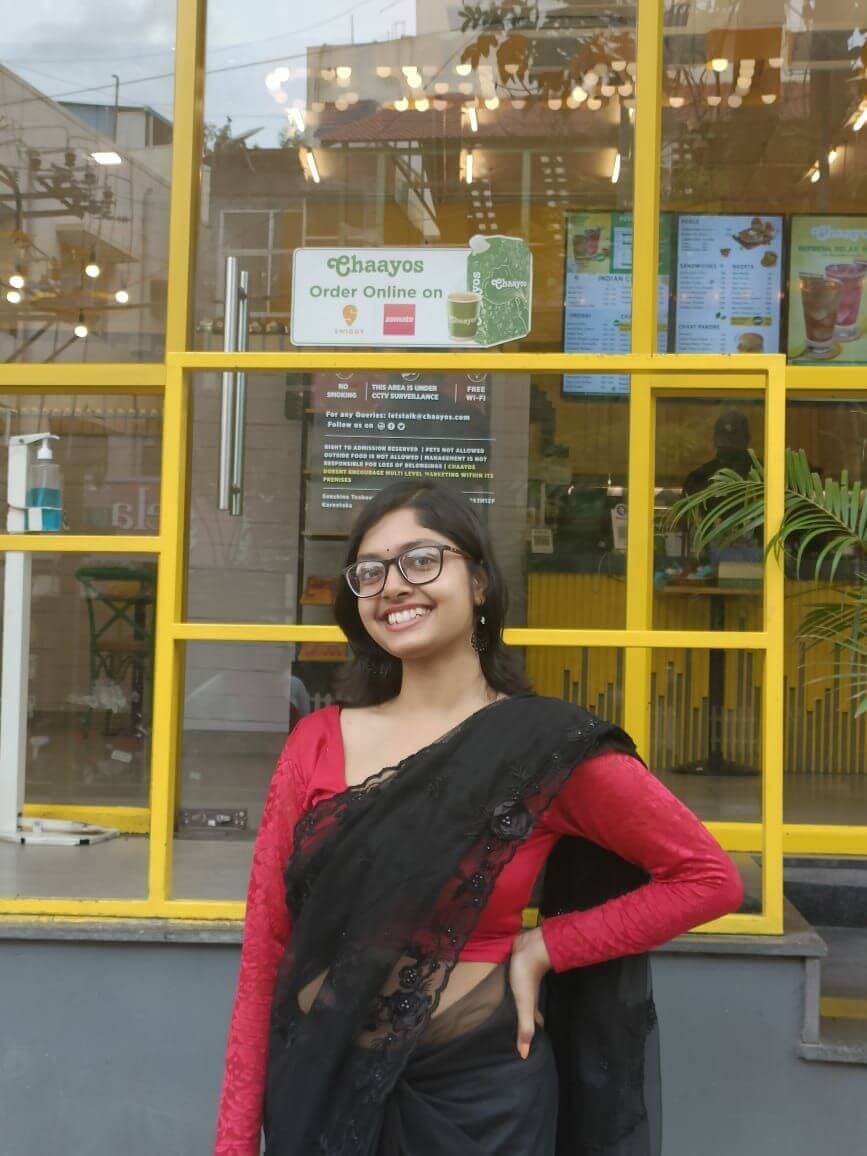
i) What are the parts of neuron?
Ans: Dendrite, nucleus, axon, nerve ending and a cell body.
ii) Which part of neuron receive the information first?
Ans: Dendritic tip receive the information first.
iii) At which place the electrical impulse get converted to a chemical impulse?
Ans: At synapse or a gap between nerve ending and a dendritic tip.
iv) What is neuromuscular junction?
Ans: The neuromuscular is made up of two words neuron & muscles, so it is the place where neuron and muscle fibre meet.
v) Draw the picture of neuron?
For more update follow net explanations page
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Last modified on: 1 year ago
- Reading Time: 5 Minutes
Question 1:
Read the case/passage and answer the questions given below.
To carry out a simple function such as eating food there has to be coordination of the eyes, hands and the mouth. The eyes have to focus on the food, the hands have to pick it up and take it to the mouth where it will be chewed. All these actions have to be coordinated in such a manner that they follow a particular sequence and the action is completed. A similar mechanism is also needed for internal functions of the body. This function is carried out by the nervous system. It is composed of (a) Specialised cells which can detect, receive and transmit different kinds of stimuli. These are called neurons. (b) Nerve fibres which are certain bundles of extended processes of nerve cells.
The individuals also have to adjust to the changing conditions around them and vary their responses. At the same time, the internal conditions of the body should be maintained constant. This is called homeostasis. The internal conditions of the body are maintained at a constant by controlling the physiology of the organisms.
(i) What will the correct sequence in which conduction of information through nerves take place? (ii) How homeostasis is said to maintain the equilibrium of the body? (iii) What function does the central nervous system perform? (iv) What happens when the dendrite tip of a nerve cell receives a signal?
Related Posts
Category lists (all posts).
All categories of this website are listed below with number of posts in each category for better navigation. Visitors can click on a particular category to see all posts related to that category.
- Full Form (1)
- Biography of Scientists (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions in Biology (37)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- DPP Biology for NEET (12)
- Blog Posts (35)
- Career Guidance (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths (12)
- Maths Formulas for Class 10 (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths (4)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 10 (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Science (23)
- HOTS for Class 10 Science (17)
- Important Questions for Class 10 Science (10)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Biology Solutions (4)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Chemistry Solutions (5)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Physics Solutions (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science (20)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science (15)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Science (4)
- Study Notes for Class 10 Science (17)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Social Science (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science (24)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science (3)
- Topicwise Notes for Class 10 Social Science (4)
- CBSE CLASS 11 (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (11)
- Free Assignments for Class 11 Chemistry (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (8)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Entrepreneurship (8)
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Entrepreneurship (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Formulas for Class 11 Maths (6)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths (17)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physical Education (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Physics (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physics (12)
- Class 11 Physics Study Notes (5)
- Concept Based Notes for Class 11 Physics (2)
- Conceptual Questions for Class 11 Physics (10)
- Derivations for Class 11 Physics (3)
- Extra Questions for Class 11 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- Numerical Problems for Class 11 Physics (4)
- Physics Formulas for Class 11 (7)
- Revision Notes for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- CBSE CLASS 12 (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology (13)
- Case Studies for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Business Studies (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (5)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (8)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry (16)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Economics (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 English (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Geography (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 History (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 History (13)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (5)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths (13)
- Maths Formulas for Class 12 (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Problems Based on Class 12 Maths (1)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physics (16)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- Class 12 Physics Conceptual Questions (16)
- Class 12 Physics Discussion Questions (1)
- Class 12 Physics Latest Updates (2)
- Derivations for Class 12 Physics (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Physics (4)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Physics (8)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics (18)
- Numerical Problems Based on Class 12 Physics (16)
- Physics Class 12 Viva Questions (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Physics (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Notes for Class 12 Political Science (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Worksheets for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Science (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science (9)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Social Science (26)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Maths (13)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science (19)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Maths (12)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science (18)
- NCERT Notes for Class 7 Science (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Maths (5)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science (18)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Science (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Science (19)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Social Science (30)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Maths (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Maths (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths (6)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science (11)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Science (2)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science (4)
- Numerical Problems for Class 8 Science (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 8 Science (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Social Science (27)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science (23)
- CBSE Class 9 English Beehive Notes and Summary (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths (11)
- NCERT Notes for Class 9 Maths (6)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths (12)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Maths (3)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Maths (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 9 (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 9 Science (22)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (11)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Science (1)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Science (15)
- Topic wise MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (2)
- Topicwise Questions and Answers for Class 9 Science (15)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Social Science (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science (19)
- CHEMISTRY (8)
- Chemistry Articles (2)
- Daily Practice Problems (DPP) (3)
- Books for CBSE Class 9 (1)
- Books for ICSE Class 10 (3)
- Editable Study Materials (8)
- Exam Special for CBSE Class 10 (3)
- H. C. Verma (Concepts of Physics) (13)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Biology (14)
- Extra Questions for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (1)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (5)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Maths (16)
- Important Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (4)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Physics (8)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Maths (7)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Physics (10)
- Topicwise Problems for IIT Foundation Mathematics (4)
- Challenging Physics Problems for JEE Advanced (2)
- Topicwise Problems for JEE Physics (1)
- DPP for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Chemistry (6)
- Chapterwise Questions for JEE Main Physics (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main Physics (8)
- Physics Revision Notes for JEE Main (4)
- JEE Mock Test Physics (1)
- JEE Study Material (1)
- JEE/NEET Physics (6)
- CBSE Syllabus (1)
- Maths Articles (2)
- NCERT Books for Class 12 Physics (1)
- NEET Chemistry (13)
- Important Questions for NEET Physics (17)
- Topicwise DPP for NEET Physics (5)
- Topicwise MCQs for NEET Physics (32)
- NTSE MAT Questions (1)
- Physics (1)
- Alternating Current (1)
- Electrostatics (6)
- Fluid Mechanics (2)
- PowerPoint Presentations (13)
- Previous Years Question Paper (3)
- Products for CBSE Class 10 (15)
- Products for CBSE Class 11 (10)
- Products for CBSE Class 12 (6)
- Products for CBSE Class 6 (2)
- Products for CBSE Class 7 (5)
- Products for CBSE Class 8 (1)
- Products for CBSE Class 9 (3)
- Products for Commerce (3)
- Products for Foundation Courses (2)
- Products for JEE Main & Advanced (10)
- Products for NEET (6)
- Products for ICSE Class 6 (1)
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance (1)
- Topic Wise Study Notes (Physics) (2)
- Topicwise MCQs for Physics (2)
- Uncategorized (138)
Test series for students preparing for Engineering & Medical Entrance Exams are available. We also provide test series for School Level Exams. Tests for students studying in CBSE, ICSE or any state board are available here. Just click on the link and start test.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Case Based Questions - Control and Coordination
Case study - 1.
In animals, such control and coordination are provided by nervous and muscular tissues. Touching a hot object is an urgent and dangerous situation for us. We need to detect it, and respond to it. How do we detect that we are touching a hot object? All information from our environment is detected by the specialised tips of some nerve cells. These receptors are usually located in our sense organs, such as the inner ear, the nose, the tongue, and so on. So gustatory receptors will detect taste while olfactory receptors will detect smell.
Q1: What are the parts of neuron? Ans: Dendrite, nucleus, axon, nerve ending and a cell body. Q2: Which part of neuron receive the information first? Ans: Dendritic tip receive the information first. Q3: At which place the electrical impulse get converted to a chemical impulse? Ans: At synapse or a gap between nerve ending and a dendritic tip. Q4: What is neuromuscular junction? Ans: The neuromuscular is made up of two words neuron & muscles, so it is the place where neuron and muscle fibre meet.
Case Study - 2
Body consists of dense networks of intricately arranged neurons. It sits in the forward end of the skull, and receives signals from all over the body which it thinks about before responding to them. Obviously, in order to receive these signals, this thinking part of the brain in the skull must be connected to nerves coming from various parts of the body.
Q1: What is reflex? Ans: It is the sudden action done in response to something in the environment. Q2: How does the nervous tissue cause action? Ans: When a nerve impulse reaches the muscles, the muscles fibres move by changing their shape and their arrangements in the cell. Q3: What is the function of the motor neuron? Ans: It transmits the impulses from spinal cord to skeletal muscles. Q4: What is reflex arc? Ans: It is the neural pathway that controls reflex starting from a sensory neuron and end at effector. Q5: What is the role of sensory neuron? Ans: It carry signals from outer part of body to central nervous system.
Case Study - 3
We also think about our actions. Writing, talking, moving a chair, clapping at the end of a programme are examples of voluntary actions which are based on deciding what to do next. So, the brain also has to send messages to muscles. This is the second way in which the nervous system communicates with the muscles. The communication between the central nervous system and the other parts of the body is facilitated by the peripheral nervous system consisting of cranial nerves arising from the brain and spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord. The brain thus allows us to think and take actions based on that thinking.
Q1: What are the three major parts of the brain? Ans: Forebrain, Midbrain and hindbrain. Q2: What are the function of medulla? Ans: It controls all the involuntary action such as blood pressure, salivation, vomiting, etc. Q3: Which fluid is present in our brain? Ans: Cerebrospinal fluid. Q4: What is the function of hypothalamus? Ans: It regulates homeostasis, releases hormones. Q5: What is the function of mid brain? Ans: The mid brain connects the forebrain and hindbrain.
Case Study - 4
Some plants like the pea plant climb up other plants or fences by means of tendrils. These tendrils are sensitive to touch. When they come in contact with any support, the part of the tendril in contact with the object does not grow as rapidly as the part of the tendril away from the object. This causes the tendril to circle around the object and thus cling to it. More commonly, plants respond to stimuli slowly by growing in a particular direction. Because this growth is directional, it appears as if the plant is moving.
Q1: How many type of tropism are shown by plants? Name them. Ans: Generally there are 6 type of tropism namely phototropism, gravitropism, chemotropism, thigmotropism, thermotropism and hydrotropism. Q2: The touch me not plant is an example of which tropism? Ans: It is an example of thigmotropism. Q3: Give one example of chemotropism? Ans: Growth of pollen tubes to wheels is one example of chemotropism. Q4: Name the plants hormone which promotes cell division? Ans: Cytokinins promotes cell division in plants. Q5: Name the plant hormone which inhibits growth? Ans: Abscisic acid
Case Study - 5
If the body design in the squirrel relied only on electrical impulses via nerve cells, the range of tissues instructed to prepare for the coming activity would be limited. On the other hand, if a chemical signal were to be sent as well, it would reach all cells of the body and provide the wideranging changes needed. This is done in many animals, including human beings, using a hormone called adrenaline that is secreted from the adrenal glands.
Q1: Which is the target organ for the adrenaline hormone? Ans: Heart is the target organ for the adrenaline hormone which increases the heartbeat rate. Q2: Which hormone is released by thyroid gland? Ans: Thyroxine is released by thyroid gland. Q3: What is the function of thyroxine hormone? Ans: It regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body and promote the best balance for growth. Q4: Name the hormone released by ovary? Ans: Estrogen and progesterone Q5: Name the three hormonal glands located in the brain? Ans: Pineal, pituitary and hypothalamus
Top Courses for Class 10
Important questions, previous year questions with solutions, past year papers, viva questions, extra questions, objective type questions, practice quizzes, shortcuts and tricks, sample paper, video lectures, semester notes, mock tests for examination, study material.

Case Based Questions: Control and Coordination Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions: control and coordination, case based questions: control and coordination notes, case based questions: control and coordination class 10, study case based questions: control and coordination on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country.
- Bihar Board
SRM University
Ap inter results.
- AP Board Results 2024
- UP Board Result 2024
- CBSE Board Result 2024
- MP Board Result 2024
- Rajasthan Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- CBSE Class 10
CBSE Class 10 Biology Control and Coordination Important Questions and Answers for 2023
All important cbse class 10 biology control and coordination questions, with answers, that could be asked in cbse class 10 science board exam 2023..

CBSE Class 10 Biology Control and Coordination Important Questions and Answers: This article will cover the important question and answers of the second chapter Control and Coordination under the unit World of Living. Although students will commonly find this as the seventh chapter in various resource materials, according to the latest syllabus by CBSE, it is Chapter 6 Control and Coordination.
Living organisms use systems that provide them control and coordination. In fact, in multicellular organisms, specialised tissues and systems provide these control and coordination to help them perform daily activities.
Chapter 7 Control and Coordination covers topics such as Tropic movements in plants; Introduction of plant hormones; Control and co-ordination in animals: Nervous system; Voluntary, involuntary and reflex action; Chemical co-ordination: animal hormones.
Important Questions from CBSE Class 10 Biology Control and Coordination
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Q.1. Which of the following statements is correct about receptors?
(a) Gustatory receptors detect taste while olfactory receptors detect smell
(b) Both gustatory and olfactory receptors detect smell
(c) Auditory receptors detect smell and olfactory receptors detect taste
(d) Olfactory receptors detect taste and gustatory receptors smell
- partly in A and B each
Q 3. In a synapse, chemical signal is transmitted from
(a) dendritic end of one neuron to axonal end of another neuron
(b) axon to cell body of the same neuron
(c) cell body to axonal end of the same neuron
(d) axonal end of one neuron to dendritic end of another neuron
Q.4. A doctor advised a person to take an injection of insulin because——-.
A) His blood pressure was low
B) His heart was beating slowly
C) He was suffering from goitre
D) His sugar level in blood was high
5. Which is the correct sequence of the components of a reflex arc?
(a) Receptors → Muscles → Sensory neuron → Motor neuron → Spinal cord
(b) Receptors → Motor neuron → Spinal cord → Sensory neuron → Muscle
(c) Receptors → Spinal cord → Sensory neuron → Motor neuron → Muscle
(d) Receptors → Sensory neuron → Spinal cord → Motor neuron → Muscle
- Muscles - receptor – brain
- Muscles - effector – brain
- Receptor - spinal cord – muscles
- Spinal cord - receptor – muscles
7. Posture and balance of the body is controlled by
(a) cerebrum
(b) cerebellum
(c) medulla
Q.8. Damage of cerebellum will mostly affect the career of :
A) architect
C) librarian
Q.9. The movement of shoot towards light is
(a) geotropism
(b) hydrotropism
(c) chemotropism
(d) phototropism
- Gibberellins
- Abscisic acid
Q.11. Which of the following is not associated with growth of plant?
(a) Auxin
(b) Gibberellins
(c) Cytokinins
(d) Abscisic acid
12.The plant hormone which is essential for cell division is
(A) Ethylene
(C) Gibberellin
(D) Cytokinin
Q.13. Choose the incorrect statement about insulin
(a) It is produced from pancreas
(b) It regulates growth and development of the body
(c) It regulates blood sugar level
(d) Insufficient secretion of insulin will cause diabetes
Q.14. The gap between two neurons is known as ___.
(A) synapse
(B) synopsis
(C) impulse
(D) synaptic node
Q.15. The shape of guard cells changes due to change in the
(a) protein composition of cells
(b) temperature of cells
(c) amount of water in cells
(d) position of nucleus in the cells
Q.17.The growth of pollen tubes towards ovules is due to
(a) hydrotropism
(b) chemotropism
(c) geotropism
18. In a synapse, chemical signal is transmitted from
(A) dendritic end of one neuron to axonal end of another neuron
(B) axon to cell body of the same neuron
(C) cell body to axonal end of the same neuron
(D) axonal end of one neuron to dendritic end of another neuron
Q.19. The substance that triggers the fall of mature leaves and fruits from plants is due to
(a) auxin
(b) gibberellin
(c) abscisic acid
(d) cytokinin
- hypothalamus
ASSERTION AND REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
Following questions consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Q.1. Assertion (A) : Insulin regulates blood sugar level.
Reason (R) : Insufficient secretion of insulin will cause diabetes.
Q.2. Assertion(A): A growing plant appears to bend towards the direction of light
Reason (R) : The plant hormone auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the root.
Q.3. Assertion (A) : The effect of auxin hormone on the growth of root is exactly opposite to that on a stem.
Reason (R) : Auxin hormone increases the rate of growth in root and decreases the rate of growth in stem.
Q.4. Assertion(A) : The use of iodised salt prevents risk of goitre.
Reason (R) : Iodised salt provides iodine needed by thyroid gland to make sufficient thyroxin for our body.
Q.5. Assertion (A) : The brain is also known as the central nervous system.
Reason (R) : Central nervous system controls and regulates the voluntary actions.
Q.6. Assertion (A) : Animals can react to stimuli in different ways.
Reason (R) : All animals have a nervous system and an endocrine system involving hormones.
Q.7. Assertion (A) : A receptor is a specialized group of cells in a sense organ that perceive a particular type of stimulus.
Reason (R) : Different sense organs have different receptors for detecting stimuli.
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
2. Write the name and functions of any two parts of the human hind-brain.
3. Which part of the nervous system controls reflex arcs?
5. Name the sensory receptors found in the nose and on the tongue.
6. List two body functions that will be affected if the cerebellum gets damaged.
7. Which gland secretes growth hormone in human beings?
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Q.1. Name the hormones secreted by the following endocrine glands and specify one function of each:
(a)Thyroid (b) Pituitary (c) Pancreas
Q.2. Write one example each of the following tropic movements :
(i) Positive phototropism (ii) Negative phototropism
(iii) Positive geotropism (iv) Negative geotropism
(v) Hydrotropism (vi) Chemotropism
Q.3. (a) An old man is advised by his doctor to take less sugar in his diet. Name the disease from which the man is suffering. Mention the hormone due to imbalance of which he is suffering from this disease. Which endocrine gland secretes this hormone?
(b) Name the endocrine gland which secretes growth hormone. What will be its effect on a person if there is: (i) Deficiency of growth hormones (ii) Excess secretion of growth hormones?
Q.4. What is Chemotropism? Give one example. Name any two plant hormones and mention their functions.
Q.5. (a) Name the part of brain which controls: (i) voluntary action (ii) involuntary action.
(b) What is the significance of the peripheral nervous system? Name the components of this nervous system and distinguish between the origin of the two.
Q.6. How does chemical coordination occur in plants? Explain with the help of three examples.
7. Draw and label a Neuron. Explain how it carries messages.
LONG ANSWER QUESTION
Q.1. a) Name chemical messenger of endocrine glands responsible for changes taking place in the body
b) Mention the gland which produces adrenalin and write its function
c) Name two phytohormones
2. Give the function(s) of the following plant hormones:
a. Auxins b. Gibberellins c. Cytokinins d. Abscisic acid e. Ethylene
Q 3. Smita’s father was complaining about frequent urination, pain in legs and a frequent weight loss to Smita’s mother and she discussed the things with her daughter when Smita returned from school. Listening to this Smita told her mother that her father should go and visit a doctor immediately. The doctor diagnosed that Smita’s father was having an elevated level of blood glucose. He should take care of his diet and should exercise regularly to maintain his normal glucose level.
On the basis of the text, answer the following questions:
(i) Name the disease he is suffering from and name the hormone whose deficiency causes it.
(ii) Identify the gland that secretes it and mention the function of this hormone.
(iii) Explain how the time and amount of secretion of this hormone is regulated in human system.
4. Mention one function for each of these hormones.
i) Thyroxine
ii) Insulin
iii) Estrogen
iv) Growth hormone
v) Testosterone.
CASE STUDY QUESTION
1 The human brain is a 3- pound (1.4-kilogram) mass of jelly-like fats and tissues—yet it'sthe most complex of all known living structures The human brain is more complex than any other known structure in the universe. Weighing in at three pounds, on average, this spongy mass of fat and protein is made up of two overarching types of cells—called glia and neurons— and it contains many billions of each. Neurons are notable for their branch-like projections called axons and dendrites, which gather and transmit electrochemical signals. Different types of glial cells provide physical protection to neurons and help keep them, and the brain, healthy. Together, this complex network of cells gives rise to every aspect of our shared humanity. We could not breathe, play, love, or remember without the brain.
1) Animals such as elephants, dolphins, and whales actually have larger brains, but humans have the most developed cerebrum. It's packed to capacity inside our skulls and is highly folded. Why our brain is highly folded?
- b) Learning
3) Which among these protects our brain?
a)Neurotransmitter
b) Cerebrospinal fluid
d) Grey matter
i) a, b & c
ii)b & c
iii)c & d
iv) b,c&d
- Humans respond to changes in their surrounding environment. The changes are known as _
a. activity
d. coordination
2. You close your eyes when your friend point the torchlight towards your eye. Which sensory organ is involved?
3. A baby cries when hears the thunder. What is the stimulus that is involved?
4. Based on the situation below, which situation shown human respond to stimuli?
I- A boy pulls his hand when touching a hot object.
II- A girl is reading a book.
III- A girl closes her ear when hearing the thunder.
IV- A boy is walking to school.
a. I and III
b. I and IV
c. II and III
d.II and IV
- A change in the environment that causes a reaction
- Something you write on a test
- A reaction to a change in the environment
- The way plants communicate
Q.1. Name two specialised tissues that provide control and coordination in multicellular organisms.
Ans. Nervous and muscular tissues.
Ans. Two parts of human hind-brain with their functions are as follows:
(i) Cerebellum: Controls & coordinates muscular movements, maintaining body posture and equilibrium. (ii) Medulla oblongata: which regulates the centre of swallowing, coughing, sneezing, salivation and vomiting.
Ans. Spinal cord.
Q.4. How does a touch – me – not plant respond on touching? What is this movement called?
Ans. Touch – me – not plant folds its leaflets on touching. This type of movement is called Growth independent movement (nastic movement)
Ans. Olfactory receptors, gustatory receptors.
Ans. a. Walking in a straight line.
Ans. Pituitary gland.
Ans. a. Thyroid: Secretes Thyroxine. It regulates metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
b. Pituitary: Secretes growth hormone. Growth hormone regulates growth and development of body.
c. Pancreas: Secretes insulin. Insulin lowers blood sugar level.
Ans. (i) Positive phototropism: shoots growing towards light.
(ii)Negative phototropism: roots growing away from light towards ground.
(iii) Positive geotropism: growth of roots towards earth due to the pull of the earth.
(iv)Negative geotropism: shoots growing away from the earth.
(v) Hydrotropism: roots growing towards the source of water.
(vi)Chemotropism: growth of pollen tubes towards the ovules.
Ans. a. The man is suffering with the disease Diabetes. Insulin is the hormone which is responsible for this disease. Pancreas secretes this hormone.
b. Pituitary gland.
(i) Deficiency of growth hormone causes dwarfism. (ii) Excess secretion of growth hormone cause gigantism in a person.
Ans. Chemotropism is the movement of a part of the plant in response to a chemical stimulus. It can be positive chemotropism or negative chemotropism. Example: The growth of pollen tube towards a chemical which is produced by an ovule during the process of fertilisation in a flower.
Two plant hormones with their functions are as follows:
Auxins promote growth, cell elongation, cell differentiation, root formation.
Gibberellins stimulate stem elongation, seed germination.
Ans.a. (i) Voluntary actions - cerebellum; (ii) Involuntary action — medulla oblongata.
b. The communication between the central nervous system and the other parts of the body is facilitated by the peripheral nervous system. Cranial nerves arise from the brain; spinal nerves arise from the spinal cord.
- Auxins secreted by growing tissues. They provide growth of plants.
- Gibberellins cause stem elongation, seed germination and flowering.
- Cytokinin’s present in areas of actively dividing cells like fruits, seeds. Promote cell division.
- Abscisic acid inhibits growth and respond to environmental stress.
Q. 7. Draw and label a Neuron. Explain how it carries messages.
Ans. Information from the environment is detected by dendritic tip of a neuron located in the sense organ. A chemical reaction sets off here and it creates an electrical impulse which travels from dendrite to cell body and then along the axon to its endings where it sets off the release of some chemicals. The chemicals cross the synapse and set off a similar electrical impulse in dendrites of next neuron.Another synapse at the end of its axon delivers the impulse to the other cells like muscles cells / glands (effector organs) which react to perform the action.
Ans: a) Hormone
b) Adrenal gland
- increases the blood pressure.
- increases heart beat rate.
- increases breathing rate.
- diverts blood to essential organs including the heart, brain and skeletal muscles by dilating their blood vessels and constricting those of less essential organs, such as the skin and digestive system.
c) auxin & gibberrellin
- Auxins promote cell elongation, root formation, cell division, etc. It also promotes fruit growth.
- Gibberellins stimulate stem elongation, seed germination and flowering.
- Cytokinins help in breaking the dormancy of seeds and buds. They delay ageing in leaves. They also promote the opening of stomata.
- Abscisic acid promotes falling of leaves and fruits.
- Ethylene promotes ripening of fruits
Q3. Smita’s father was complaining about frequent urination, pain in legs and a frequent weight loss to Smita’s mother and she discussed the things with her daughter when Smita returned from school. Listening to this Smita told her mother that her father should go and visit a doctor immediately. The doctor diagnosed that Smita’s father was having an elevated level of blood glucose. He should take care of his diet and should exercise regularly to maintain his normal glucose level.
Ans. (i) Disease-Diabetes, Hormone: Insulin
(ii) Gland-Pancreas: The blood glucose level is regulated by insulin hormone secreted by the pancreas.
(iii) Feedback Mechanism - Cells of pancreas secrete insulin hormone when level of blood glucose level increases in the blood. Insulin regulates the blood glucose level and its secretion gets reduced when blood glucose level falls down.
Ans. (i) Thyroxin – Control overall metabolic rate of the body (carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism)
(ii) Insulin – Conversion of glucose to glycogen in liver and muscles, thus decreases blood glucose level.
(iii) Estrogen – Development of female sex organ and secondary sexual characteristics like development of breast, pimples, shrill and a higher pitch voice
(iv) Growth hormone – Body growth and development of bones.
(v) Testosterone – Development of male sex organ and secondary sexual characteristics like moustache, beard & voice.
The human brain is a 3- pound (1.4-kilogram) mass of jelly-like fats and tissues—yet it'sthe most complex of all known living structures The human brain is more complex than any other known structure in the universe. Weighing in at three pounds, on average, this spongy mass of fat and protein is made up of two overarching types of cells—called glia and neurons— and it contains many billions of each. Neurons are notable for their branch-like projections called axons and dendrites, which gather and transmit electrochemical signals. Different types of glial cells provide physical protection to neurons and help keep them, and the brain, healthy. Together, this complex network of cells gives rise to every aspect of our shared humanity. We could not breathe, play, love, or remember without the brain.
Answer
1)Animals such as elephants, dolphins, and whales actually have larger brains, but humans have the most developed cerebrum. It's packed to capacity inside our skulls and is highly folded. Why our brain is highly folded?
To increase the surface area of the brain to receive sensory impulses from various receptors, interpret the sensory information with the information that is stored in the brain and respond accordingly
2)Which among this is not a function of cerebrum?
3)Which among these protects our brain?
a)Neurotransmitter b) Cerebrospinal fluid c)Meninges d) Grey matter
ii) b & c
2 All the living organisms (plants and animals) respond and react to changes in the environment around them. The changes in the environment to which the organisms respond and react are called stimuli (singular: stimulus). The living organisms show response to stimuli such as light, heat, cold, sound, smell, taste, touch, pressure, pain, water, and force of gravity, etc. The response of organisms to a stimulus is usually in the form of some movement of their body parts. For example, if a man touches a very hot utensil accidently, he quickly pulls his hand away from the hot utensil. Here, heat is the stimulus and the man reacts by moving his hand away from the hot utensil. Similarly, when the Sun is bright, we close our eyes. In this case, light is the stimulus and we react by closing the eyes.
1. Humans respond to changes in their surrounding environment. The changes are known as _
b. stimuli
a. sound
c. I and III
5. A response is ____
c. A reaction to a change in the environment
Biology is one of the natural sciences which involves the study of humans, plants and other living organisms, their structure, growth, function, evolution and so on under various specializations such as botany, zoology, molecular biology, microbiology, genetics, marine biology etc.
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- Where can I download Class 10th Control and Coordination Important Questions and Answers for CBSE Class 10 Science board exam 2023? + Get Important Questions and Answers from CBSE Class 10 Chapter Control and Coordination for 2023 CBSE board examination from this article by Jagran Josh.
- NDA Admit Card 2024
- TSPSC AE Answer Key 2024
- CTET Correction Window 2024
- NTA NITTT Result 2024
- APPSC Group 2 Result 2024
- CUET PG Answer Key 2024
- TN SET Application Form 2024
- CBSE Class 10 QnA
Latest Education News
COMEDK UGET 2024 Registrations Extended To April 10, Check Details Here
NDA Admit Card 2024 Live Updates: UPSC NDA 1 Hall Ticket Download Link on upsc.gov.in Soon
Click Here trend on Twitter: What is it?
2nd PUC Result 2024 Karnataka Date and Time: KSEAB 2nd Pre-University Certificate Results Expected in 3rd Week of April, Check Updates
The rising problem of unemployment: What does the India Employment Report 2024 suggest?
Total solar eclipse on April 8: What makes it so special?
OSSC CGL 2024 Registration Begins for 595 Posts: Direct Link to Apply Online
MP Board 10th, 12th Result 2024 Kab Aayega: एमपी बोर्ड की मूल्यांकन प्रक्रिया समाप्त, जानें कब तक आ सकता है परिणाम ?
AIESL Recruitment 2024: Apply Online For Aircraft Technician Posts at aiesl.in, Check Eligibility
Solar Eclipse 2024: List of Do’s and Don’ts During The Celestial Event
Solar Eclipse 2024: Google Doodle Celebrates the Celestial Event
MSDSU Result 2024 OUT at msdsu.ac.in, Direct Link to Download UG and PG Odd Semester Marksheet
JHC Clerk Assistant Recruitment 2024: झारखंड हाईकोर्ट में निकली क्लर्क और असिस्टेंट के 410 पदों पर भर्तियाँ
Magadh University Result 2024 OUT at magadhuniversity.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet PDF
Snapchat’s Solar System Feature: Know What it is and Why the Company is Disabling this feature
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Can You Spot A Magnet In This Beach Scene In 12 Seconds?
JEE Main Session 2 Question Paper 2024 Memory Based: Check Question Paper with Solutions April 8
Total Solar Eclipse 2024: Check Citywise Timings For The Rare Surya Grahan Of The Year
Sainik School Counselling 2024: Seat Allotment Result for AISSEE Class 6, 9 Soon, Required Documents
APSC Prelims Result 2024: Where will CCE Prelims Result be released? Check Previous Year Trends
Study Material
.webp)
Home > Class 10 Science Subject-wise Material
Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination

Class 10 Science Chapter 7 talks about how every living organism reacts as the changes occur around them taking not even a second. In the final examination, questions from control and coordination weigh at most 3 marks. The purpose of including Control and Coordination is to teach students about how organs and five senses in the human body; the receptors after receiving signals from the environment functions. The nervous system is mainly responsible for the control and coordination of animals and the human body.
Class Xth NCERT textbook covers control and coordination in-depth and with the help of the right study material, the student can understand the chapter in detail. Class 10 science chapter 7 notes, question banks, practice worksheets, and other study material provided by Educart, can significantly help in improving the exam preparation.
Table of Contents
Cbse class 10 control and coordination notes.
Below, we have provided the links to downloadable PDFs of Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Class 10 notes and get an in-depth explanation and understanding of the chapter.
<red> ➜ <red>Class 10 Control and Coordination Notes
📈 Trending: Class 10 CBSE Admit Card 2024
📺 Recommended: Important Questions PDFs for Class 10
📚 Don't Miss: CBSE Class 10 Sample Question Papers

CBSE Class 10 Control and Coordination DoE Worksheet
Below, we have provided the links to downloadable PDFs of DoE Worksheets for Control and Coordination Class 10 to practice more questions.
<red> ➜ <red>Worksheet 80EM
<red> ➜ <red>worksheet 81em, <red> ➜ <red>worksheet 82em, cbse class 10 control and coordination experiential activities.
Below, we have provided the links to downloadable PDFs of Experiential Learning Activity for ch 7 class 10 Science to help students implement their acquired knowledge in the real world.
<red> ➜ <red>Control and Coordination Experiential Activities
Cbse class 10 control and coordination important questions.
Below, we have provided Class 10 Science Important Questions that cover all the important questions in Control and Coordination.
<red> ➜ <red>Control and Coordination Important Questions(view)
Cbse class 10 control and coordination question bank.
Below, we have provided Class 10 Science Question Banks that cover every typology question with detailed explanations from various resources in one place.
<red> ➜ <red>Class 10 Life Processes CBSE Question Bank
<red> ➜ <red>class 10 life processes kendriya vidyalaya question bank, cbse class 10 control and coordination support material.
Below, we have provided Class 10 Science Support Materials that cover Case Study-based questions from the various concepts explained in Science NCERT chapters.
<red> ➜ <red>Control and Coordination Support Material
Why download these chapter-wise pdfs.
Students can do well on board examinations and other school tests, as well as college applications if they have the proper study materials in addition to the NCERT. For class 10, chapter 7 Control and Coordination, students may build a solid conceptual foundation by going through these chapter-by-chapter PDFs. For both instructors and students, accessing these Control and Coordination class 10 PDFs might be extremely beneficial.
- The study material Students may make a schedule and learn in an organized manner with PDF. Students may concentrate on a particular topic at a time and allocate considerable time to each subject by making a study timetable.
- Students may now have all of their study materials in a single place that they can access whenever they choose, eliminating the need for them to lug around bulky textbooks.
- Since PDFs may be browsed and downloaded on any device, downloading them is a convenient way to get content.
- To take notes and improve their test preparation, students can print educational materials.
How Can This Chapter-wise Material Help Students?
The Science Control and Coordination chapter-wise materials will assist in completing the chapter from the 10th NCERT textbook in addition to the extra study materials. Students may efficiently prepare for the chapter by downloading chapter notes, DoE worksheets, question banks, key questions, and a plethora of additional study resources.
- The science control and coordination class 10 notes cover the chapter in detail and include all of the key ideas. Pupils can comprehend the chapter more thoroughly.
- Students will benefit from using mind maps to make connections between the ideas they have learned. It is going to help bring previously held knowledge into line with recently learned information, enhancing comprehension of the chapter.
- Every type that will be tested in the 10th board exams may be prepared with the use of the DoE worksheets and question banks. When students fully grasp the subject, they may create a schedule and practice relevant questions.
- The recurrent questions and the idea questions you need to study for the test are among the Class 10 CBSE crucial questions. By practicing key questions, you could increase your chances of getting higher exam scores.
Teachers will help students thoroughly practice these issues by using the supplementary resources and questions that Educart has made available. All it takes to download these PDFs is a single click and identification by the user.
Extra 10% Discount

CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
Ncert books for class 10, cbse class 10 sample paper.
Buy Latest Books
Teacher's Corner

To Download PDF
Please verify your Whatsapp number first, so you can download unlimited pdfs for free
Please type a valid 10 digit whatsapp number

OTP sent, check your whatsapp
Your OTP is incorrect, Please enter valid OTP

- Mathematics (Standard)
- Mathematics (Basic)
- Social Science
- Computer Application
- Information Technology
- English Core
- Mathematics
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political Science
- Science (Hindi )
- Maths (Hindi)
- Social Science (Hindi )
- English (Hindi)
- Applied Maths
- Physical Education
- 40 Sample Papers
- English Language
- English Literature
- History & Civics
- 10 Year Solved Papers
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 English
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Math Standard
- Computer Applications
- Class 12 PCM Bundle
- Entrance Exam
- K-8 Raspberry Solutions
- K-8 Kiwi Solutions
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 7 - Control and Coordination 2023-24

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter-7 Important Questions with Answers - Free PDF Download
The important questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 control and coordination will help the students to prepare for their examination in an ordered way. These control and coordination Class 10 important questions are written in a simple and easy-to-understand way by the subject matter experts at Vedantu. To enable the students to get a fair idea of the chapter, students can rely on Chapter 7 Science Class 10 important questions . Students can use these for their exam preparation as important questions are made according to the priority of topics in the examination. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths and Science Students who are looking for better solutions can download Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions and Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions 2023-24 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions for other chapters:

Related Chapters
Study Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 - Control and Coordination
Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark)
1. Junctions of two neurons are called.
Synapsis
Ans: a) Synapse
2. Which of the following is a plant hormone?
Ans: d) Cytokinin
3. When a person is suffering from severe cold, he or she cannot –
Differentiate the taste of an apple from that of an ice – cream.
Differentiate red light from the green light.
Differentiate a hot object from a cold object.
Differentiate the smell of perfume from that of an agarbatti
Ans: (d) Differentiate the smell of perfume from that of an agarbatti.
4. What do you mean by geotropism?
Ans: The growth of a plant due to Gravitational force is called geotropism. Growth in the direction of the force (downward) is known as positive geotropism and the growth in the direction opposite to the force (upward) is known as negative geotropism.
5. Name the two sets of nerves that constitute the peripheral nervous system.
Ans: The two sets of nerves that constitute the peripheral nervous system are
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system.
6. The brain is lodged inside the cavity of the skull known as:
Ans: c) Cranium
7. The electrical impulse travels in a neuron from –
Dendrite $\to $ Axon $\to $ Axonal end $\to $ Cell body
Cell body $\to $ Dendrite $\to $ Axon $\to $ Axonal end
Dendrite $\to $ Cell body $\to $ Axon $\to $ Axonal end
Axonal end $\to $ Axon $\to $ Cell body $\to $ Dendrite
Ans: Dendrite $\to $ Cell body $\to $ Axon $\to $ Axonal end
8. Which hormone brings about the development of the mammary gland?
Progesterone
Ans: Estrogen
9. Name the hormone which promotes plant growth.
Ans: The hormone which promotes plant growth is auxin.
10. Which part of the brain maintains the posture and equilibrium of the body?
Ans: The part of the brain which maintains the posture and equilibrium of the body is the cerebellum.
11. Which one of the endocrine glands is known as the master gland?
Parathyroid
Ans: a) Pituitary
12. The growth of tendrils in pea plants is due to
effect of light
effect of gravity
rapid cell division in tendrillar cells in contact with the support
rapid cell divisions in tendrillar cells that are away from the support
Ans: d) rapid cell divisions in tendrillar cells that are away from the support
13. Dwarfism results by –
Excess secretion of thyroxin
Less secretion of growth hormone
less secretion of adrenaline
Excess secretion of growth hormone.
Ans: b) Less secretion of growth hormone.
14. Write the function of the hormone “thyroxine” produced in our body.
Ans: Thyroxine produced in our body controls the overall metabolic rate of the body, it plays a vital role in digestion, muscle function, brain development, heart, and maintenance of bones.
15. Name the hormones secreted by the pancreas.
Ans: The hormones secreted by the pancreas are:
16. The neurons that carry nerve impulses from the spinal cord to effectors are called –
Sensory neurons
motor neurons
Interneurons
spinal neurons
Ans: Motor neurons.
17. Select the mismatched pair
Adrenaline – Pituitary gland
Testosterone – Testes
Estrogen – Ovary
Thyroxine – Thyroid gland.
Ans: Adrenaline – Pituitary gland.
18. Which one of the following is a nastic movement in plants?
Bending of plants towards light
Growing of roots towards gravity.
Dropping of touch – me – not leaflets on touch
Movement of pollen tubes towards chemicals.
Ans: Dropping of touch – me – not leaflets on touch
19. What is the function of the occipital lobe?
Ans: The function of the occipital lobe is visual perception. It includes:
Depth perception
Color determination
Object recognition
Movement, etc.
20. Which part of the brain links the endocrine system with the nervous system?
Ans: Hypothalamus is the part of the brain which links the endocrine system with the nervous system.
21. The visceral nervous system controls and integrates the function of –
Urinary bladder
Blood vessels
All of the above
Ans: d) All of the above
22. Which of the following statements are true about the brain?
The main thinking part of the brain is the hindbrain.
Centers of hearing, smell, memory, sight, etc are located in the forebrain.
Salivation, vomiting, and blood pressure is controlled by the medulla in the hindbrain.
The cerebellum does not control the posture and balance of the body.
(i) and (ii)
(ii) and (iii)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
(iii) and (iv)
Ans: b) (ii) and (iii)
23. The substance that results in the fall of mature leave and fruits from plants is due to:
Gibberellins
Cytokinin
Ans: c) ABA
24. Name the structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
Ans: The structural and functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron (nerve cell).
25. Name one sex hormone.
Ans: An example of a sex hormone is testosterone.
26. Which part of the brain maintains the posture and equilibrium of the body?
Ans: The cerebellum is the part of the brain which maintains the posture and equilibrium of the body.
27. Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Ans: A plant hormone that promotes the growth of cells is auxin.
28. Which of the following is a plant hormone?
Ans: (d) Cytokinins
29. The gap between two neurons is called a
Synapse
Impulse
Ans: (b) synapse
30. The brain is responsible for
Thinking
Regulating the heartbeat.
Balancing the body
All of the above.
Ans: (d) all of the above.
31. What name is given to the microscopic gap between two adjacent neurons?
Ans: The microscopic gap between two adjacent neurons is known as the synapse.
32. If we step on something sharp accidentally, we move our foot away at once. What is this type of response known as?
Ans: This type of response is known as a reflex action.
33. Apart from the hindbrain, activities like walking, skating, riding a bicycle, and picking up a pencil are possible. Name this part of the hindbrain.
34. Name the plant hormone:
a. Which inhibits growth and causes wilting of leaves.
Ans: Abscisic acid inhibits growth and causes wilting of leaves.
b. Which promotes cell division.
Ans: Cytokinin promotes cell division.
35. Who transmits nerve impulses across the synapse?
Ans: Neurotransmitters are responsible for transmitting nerve impulses across the synapse.
36. Give the reason why endocrine glands release theft secretions into the blood?
Ans: Endocrine glands are ductless glands and hence instead of pouring their hormones into ducts , they release theft secretions into the blood.
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
1. How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Ans: Difference between reflex action and involuntary action is given below:
2. Why is the use of iodised salt advisable?
Ans: Iodine is a trace element and a necessary substrate for thyroid gland hormone synthesis. It is required by the thyroid gland to make thyroxine hormone. The use of iodised salt is advisable because it provides iodine needed by the thyroid gland to make sufficient thyroxine for our body that helps prevent risk of goitre.
3. Name the centre of the brain that controls
Ans: Medulla oblongata in hind brain controls swallowing.
Ans: Cerebrum in forebrain controls hearing.
4. Represent schematically the path of a reflex action.
Ans: The path of a reflex action is represented below:
5. Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Ans: Some patients of diabetes are treated by giving injections of insulin because insulin hormone regulates the levels of sugar in the blood. In diabetic patients, insulin hormone is not secreted by pancreas in the required amount and therefore blood sugar level rises.
6. Which signal will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
Ans: Spinal cord controls the reflex actions. And hence, the effects of spinal cord injury are:
Disturbed involuntary actions.
Disturbed reflex actions.
Inability of the quick response required to safeguard the body.
7. How does a touch – me – not plant respond to touching? What is this movement called?
Ans: Touch – me – no plant responds to touching by folding its leaflets and this type of movement is called growth independent movement i.e., the movement of plants that do not result in their growth.
8. What are phytohormones? Name them.
Ans: Phytohormones are synthesized at sites away from where they act. They diffuse to the area of action and help to co – ordinate growth, development and responses to the environment. Phytohormones are –
Gibberellins
Abscisic acid
9. What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Ans: A reflex action is a rapid and spontaneous action in response to any stimulus. It is controlled by the spinal cord. Example- Sudden jerky withdrawal of hand after touching something hot. T he reflex action is instant where thinking is not involved and hence the brain has no role. Although the information also goes on to the brain where the encounter remains the memory and makes us aware of our actions.
10. How is control and coordination between the environment and plants brought about?
Ans: Plants responses are of two types
Growth dependent – They are due to cell divisions.
Growth independent response – They are due to change in the amount of water.
Plants do not perform control & coordination like animals but they give responses to external stimuli like touch, light, and chemicals, etc.
11. Give two examples of functions in plants that are regulated by light.
Ans: The two functions in plants that are regulated by light are:
Seed germination - Breaking of dormancy
Photosynthesis – Respiration process
12. What is coordination? Give an example.
Ans: Coordination is a process through which two or more organs interact and complement the functions of one to adjust the vital activities of life. For example – under stressed conditions, the adrenal gland secretes the adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to face the emergency by increasing the breathing rate and heartbeat so that more oxygen can be supplied to the body.
13. How do endocrine glands help in maintaining feedback control?
Ans: The timing and amount of hormones released are regulated by the feedback mechanism. The endocrine system depends on the feedback system concerning hormones. There are two types of feedback systems –
Negative Feedback – This mechanism prevents deviation from the ideal mean value. For ex- less glucose levels in the blood do not induce the pancreatic cells to produce insulin so that less conversion of glucose to glycogen may occur.
Positive Feedback – These mechanisms promote deviation from the mean ideal value. For ex- High glucose level in the blood induces. The pancreatic cells produce insulin which converts glucose to glycogen.
14. Which types of glands in the human body secrete hormones? State any one location for them.
Ans: Three types of glands that secrete hormones in the human body are-
Exocrine gland – These types of glands have ducts that do not secrete their secretion into the blood. For example – the salivary gland.
Endocrine gland – These types of glands do not have ducts, they pour their secretion into blood. For example – The pituitary gland.
15. What is the result of hypothyroidism in children called?
Ans: The result of hypothyroidism in children is known as exophthalmic goiter. The exophthalmic goiter results in bulging of eyes, increased blood pressure, and heartbeat.
16. How is flowering affected in plants by various hormones?
Ans: Flowering is affected in plants by various hormones such as auxins and cytokinin promotes female flowers while gibberellins promote male flowers. Duration of light affects flowering in long-day plants and short-day plants.
17. Name the fluid-filled between the meninges of the brain. What are its functions?
Ans: The fluid-filled between the meninges of the brain is known as the cerebrospinal fluid. Its function is to protect the brain from mechanical shocks.
18. Name any two heterocrine glands and mention their function.
Ans: The two heterocrine glands are:
Pancreas – Its endocrine function is to produce insulin and glucagon. Its exocrine function is to produce digestive enzymes.
Ovaries – Its endocrine function is to produce estrogen and progesterone hormone. Its exocrine function is to produce female gametes.
19. What is the response of the stem towards light & gravity?
Ans: Plants' growth response to gravity is known as gravitropism and to light is phototropism. The stem shows a positive response toward the light i.e., it grows in the direction of the light and it shows a negative response toward gravity i.e., it grows in the opposite direction of gravity.
20. Name two activities that are regulated by plant pigments.
Ans: The two activities that are regulated by plant pigments are:
The response to the photoperiodic stimulus – due to some specialized pigments and phytochromes.
The control and coordination in plants with their environment.
21. How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick)?
Ans: Olfactory receptors help us detect the smell of an agarbatti. When you smell the scent of an incense stick, it first reaches your nose, where it is detected by the olfactory receptors. It is then sent to the forebrain in the form of electrical signals. The forebrain then interprets these electrical signals as the smell of an incense stick.
22. What are plant hormones?
Ans: Hormones are the chemicals that help to coordinate growth, and development. Plant hormones are the chemicals that help to coordinate growth, development, flowering and response to the environment in plants. For example – auxins, gibberellins, abscisic acid (ABA), cytokinin, etc.
23. How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
Ans: In the movement of leaves of sensitive plants, growth is not involved and movement is away from the source. Whereas, in the movement of shot towards light, growth is involved and movement is towards the source.
24. How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Ans: The chemical coordination in animals is maintained by hormones which are secreted by endocrine glands.
25. Give one example of a plant part.
Which is positively hydrotropic as well as positively geotropic.
Ans: Roots are positively hydrotropic as well as positively geotropic.
Which is positively phototropic but negatively geotropic.
Ans: Stem is positively phototropic but negatively geotropic.
26. The neck of a person appears to be swollen.
Name the disease this person is suffering from.
Ans: The person is suffering from goitre.
Name the mineral whose deficiency in the diet causes this disease.
Ans: Deficiency of iodine in the diet causes this disease.
27. Taking the example of heart beat, justify the antagonistic action of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nerves.
Ans: Antagonistic action of the sympathetic nerve – increases contraction and rhythm with respect to heart beat.
Antagonistic action of the parasympathetic nerve – decreases contraction and rhythm with respect to heart beat.
28. Why is abscisic acid known as stress hormone in plants?
Ans: Abscisic acid is known as a stress hormone in plants because unlike growth hormone, it inhibits growth and causes wilting of leaves.
29. Name the part of neuron
where information is acquired.
Ans: Dendrite is the part of the neuron where information is acquired.
through which information travels as an electrical impulse.
Ans: Axon is the part of the neuron through which information travels as an electrical impulse.
30. Why do leaves drop off seasonally?
Ans: The leaves drop off seasonally because of the cuts off supply of nutrients and water to leaves which happened due to stopped production of auxin.
31. A person suffered a head injury, due to which he faces breathing problems. No problem was detected with his respiratory system. What could be the cause of this problem?
Ans: A person suffered a head injury, faces breathing problems because he was injured in medulla oblongata. Medulla oblongata controls the respiratory system so he will be affected by breathing problems.
32. In a family of normal sized members, there are two exceptions, one member is dwarf and one is tall like “Khali”. What could be the cause of it?
Ans: Uneven heights in the family is caused due to malfunctioning of the growth hormone. In case of dwarfs, there is a deficiency of growth hormone whereas in case of giants there is an excess of growth hormone. Growth hormones are secreted from the pituitary gland.
33. Why do you blink your eyes as bright light is focused on you?
Ans: We blink our eyes as bright light is focused on us due to reflex action. It is done to protect the eye from bright light which otherwise would damage the retina. The amount of light that enters your eyes is controlled by the pupils. Hence, blinking the eyes cuts off the excessive light.
34. There is a polled plant in your drawing room, after a few days you notice that the plant has bent to one side. What could be the reason? How has this movement been coordinated?
Ans: The polled plant in your drawing room, after a few days bent to one side due to phototropic movement of the stem and it happens because of unequal growth of the stem on both sides which is initiated by the auxin hormone.
35. A leaf shaped gland is present above the intestine. The secretion of this gland regulates the metabolism of sugar in blood. Name the secretion and gland.
Ans: A leaf shaped gland that is present above the intestine and whose secretion regulates the metabolism of sugar in blood is the pancreas. The secretion is Insulin from special cells in it.
Short Answer Questions (3 Marks)
1. Mention three important functions of gibberellins.
Ans: Three important functions of Gibberellins are –
Stimulate stem elongation.
Help in breaking seed dormancy.
Promote production of male flowers.
2. What is the function of receptors in our body? What happens when receptors do not work properly?
Ans: The receptors detect information from the environment. If they do not work properly, the information will not be detected or will be detected late, due to which further process will be delayed and the signals will take time reaching the spinal cord or the brain. Hence, the response to the environmental stimulus will be delayed causing harm to the body.
3. What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Ans: Junctions of two neurons is called synapses. When a receptor detects a stimulus, chemicals is set off through the neurons. These electric signals travel from the dendrite of the presynaptic neuron to its cell body and then along its axon. At the end of axon of this neuron, the electrical impulse crosses the synapse and starts a similar electrical impulse in the dendrite of the next neuron.
4. What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
Ans: The control and coordination in an organism is needed for the proper functioning of the body. It handles appropriate movement in response to any external stimulus.
Multicellular organisms have a complex body and hence it coordinates with various organs of the body of an organism working together in a proper manner to produce proper reaction to stimulus. For example – under stressed conditions, the adrenal gland secretes the adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to face the emergency by increasing the breathing rate and heartbeat so that more oxygen can be supplied to the body.
5. Pituitary is a master endocrine gland. Justify this statement.
Ans: Pituitary gland is a master gland because it regulates the secretion of other endocrine glands such as -
Growth hormones
Thyroid stimulating hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Follicle stimulating hormone
Luteinizing hormone
Prolactin
Pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain and is attached to the hypothalamus by nerve fibres and blood vessels. The pituitary gland consists of Anterior lobe and Posterior lobe.
6. Draw the structure of the neuron and explain its function.
Ans: The basic structure of a neuron has three components –
Junctions of two neurons is called synapses. When a receptor detects a stimulus, chemicals is set off through the neurons. These electric signals travel from the dendrite of the presynaptic neuron to its cell body and then along its axon. At the end of axon of this neuron, the electrical impulse crosses the synapse and starts a similar electrical impulse in the dendrite of the next neuron.
7. How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
Ans: Adrenaline is a hormone which is involved in regulating visceral functions. Adrenaline is normally produced both by the adrenal glands and by a small number of neurons in the medulla oblongata. Under stressed conditions, the adrenal gland secretes the adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to face the emergency by increasing the breathing rate and heartbeat so that more oxygen can be supplied to the body. The blood supply decreases from the skin and digestive system and increases to skeletal muscles.
8. Where are Pons and medulla oblongata located? Write their functions.
Ans: Pons and medulla Oblongata are located in hindbrain.
Function of Pons – it acts as a bridge between the brain and spinal cord.
Function of Medulla oblongata – it controls activities like salivation, swallowing, vomiting, breathing, coughing, sneezing, heartbeat, sleep, consciousness and activities of the cerebrum.
9. List the function of testosterone and estrogen. Where are they secreted?
Ans: Testosterone is secreted in male bodies.
Function of testosterone – It is responsible for development of male sex organs and secondary sex characteristics like moustache, beard & voice.
Estrogen is secreted in male bodies.
Function of estrogen – it is responsible for development of female sex organs and secondary sex characteristics like mammary gland and uterine growth.
10. Define ‘nerve impulse’. Which structure in a neuron helps to conduct a nerve impulse?
Towards the cell body?
Ans: Nerve Impulse is a wave of the passing of information through neurons in the form of electrical and chemical signals. Dendrite helps to conduct a nerve impulse towards the cell body.
Away from the cell body?
Ans: Nerve Impulse is a wave of the passing of information through neurons in the form of electrical and chemical signals. Axon helps to conduct a nerve impulse away from the cell body.
11. Differentiate between axon and dendrites?
Ans: Difference between axon and dendrites is:
12. Mention the structure of the human brain.
Ans: The structure of human brain is outlined below,
13. What are tropic movements? Name the types of tropic movements in plants.
Ans: Tropic movement is the bending or movement of a part of a plant in response to the external stimulus. The types of tropic movements in plants are:
Phototropism – response to light.
Geotropism – response to gravity
Chemotropism - response to chemicals.
Hydrotropism – response to water.
14. Name the different lobes of cerebrum.
Ans: There are four lobes of cerebrum –
a) Frontal lobe – The part of the brain associated with reasoning.
b) Parietal lobe – The part of the brain associated with perception of general sensation s like pressure, touch and pain.
c) Occipital lobe – The part of the brain associated with visual perception.
d) Temporal lobe – The part of the brain associated with formation of memory and interpretation of sound and the language.
15. How do auxins promote the growth of tendril around a support?
Ans: Auxin present in the plants is a growth hormone. When the tip of a tendril touches a support, auxins in its tip move away from the support. Hence, the side of the tendril away from the support grows faster and becomes longer than the side which is in contact with the support and makes the tendril curve towards the support.
16. Write different between exocrine and endocrine glands.
Ans: Difference between endocrine and exocrine gland is given below:
17. What are the different kinds of neurons?
Ans: There are three different kinds of neurons –
Sensory neurons – their work is to convey impulses from receptors to the main nervous system.
Motor neurons – their work is to carry impulses from the main nervous system to an effector.
Connecting (Relay) neurons – their work is to connect sensory and motor centres.
18. You have touched a hot object. Represent diagrammatically the path that leads to a response, i.e., quickly pulling back the hand.
Ans: The diagrammatic representation of the path that leads to a response when we touch a hot object is as below,
19. Nervous and hormonal system together performs the functions of control and coordination in human beings. Justify the statement.
Ans: Nervous and hormonal systems together perform the function of control and coordination in human beings. Under stressed conditions, the stimulus is being perceived by the Central Nervous System which stimulates the adrenal gland that secretes the adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to face the emergency by increasing the breathing rate and heartbeat so that more oxygen can be supplied to the body. The blood supply decreases from the skin and digestive system and increases to skeletal muscles.
20. What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
Ans: Difference between reflex action and walking is given below:
21. Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
Ans: To demonstrate hydrotropism, take a tin box and make a hole its bottom. Fill the tin with moist saw dust and sow some gram seeds in it. In the next step, when the seed starts germinating, keep the tin box in a tilted position. After some time when you water the tin, you will observe that the radicle moves towards the wet saw dust which demonstrates positive hydrotropism.
22. How does phototropism occur in plants?
Ans: Movement of shoot towards light is called phototropism. This movement is caused due to more growth of cells towards the shaded side of the shoot as compared to the side of the shoot towards light. More growth of cells is due to secretion of auxin towards the shaded side.
23. How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Ans: Unlike animals, plants do not have a nervous system. Chemical coordination in plants is maintained by plant hormones also known as phytohormones. Some plant hormones are auxin, Gibberellins, Cytokinin etc. When sunlight falls on the side, the auxins hormone causes the shady side of the shoot to grow faster. Cytokinin is responsible for the cell division.
24. How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Ans: Difference between involuntary and reflex actions is given below:
25. Compare and contrast nervous system and hormonal control and coordination in animals.
Ans: Difference between nervous control and hormonal control is given below:
26. What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and movement in our legs?
Ans: Difference between movement in a sensitive plant and movement in our legs is given below:
27. On touching a hot plate, you suddenly withdraw your hand. Which category of neurons became active first and which one next?
Ans: Suddenly withdrawing the hand on touching a hot plate is an example of reflex action. Hence, first the sensory neurons are activated, which take the information to the spinal cord. After that, the motor neurons become active and bring the impulses from the brain to the muscles.
28. How does the plant shoot bends, when the plant is placed in a room having only one open window?
Ans: The shoot of the plant bends towards the direction of light when the plant is placed in such a room that has only one open window and this happens due to the auxin which is a plant growth hormone. Auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot and stimulates the cells to live longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light.
29. Give a reason to explain why
adrenaline helps in dealing emergency situations?
Ans: Under stressed conditions, the stimulus is being perceived by the Central Nervous System which stimulates the adrenal gland that secretes the adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to face the emergency by increasing the breathing rate and heartbeat so that more oxygen can be supplied to the body. The blood supply decreases from the skin and digestive system and increases to skeletal muscles.
secretions of growth hormone should be specific in the human body?
Ans: Secretions of growth hormone should be specific in the human body because if growth hormones are secreted in excess quantity then it will lead to gigantism while the less secretion of this hormone causes dwarfism.
30. A man becomes unconscious due to head injury. A pin is pricked on his foot, he withdraws his foot. Why? Explain.
Ans: Withdrawal of the foot when a pin is pricked on the foot is an example of the reflex action and reflex actions are controlled by the spinal cord and not by the brain. Hence, although being injured on the head, the person will withdraw his foot.
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks)
1. Compare nervous and hormonal mechanism for control
2. Mention one function for each of these hormones.
Ans: Thyroxine controls the overall metabolic rate of the body.
Ans: Insulin converts glucose to glycogen in liver and muscles and controls the blood sugar level.
Ans: Adrenaline increases heartbeat and blood pressure.
Growth hormone
Ans: Growth hormones are responsible for body growth and development of bones.
Testosterone.
Ans: Testosterone is the male hormone and develops male sex organs and secondary sex characteristics like moustache, beard and voice.
3. Write the following:
What are hormones?
Ans: Hormones are chemical substances which help in growth, control and coordination of a living organism. They are secreted in very small amounts by endocrine glands.
list four characteristics of hormones
Ans: Four characteristics of hormones are –
They are required in very less amounts.
Hormones are specific in their function.
They act away from the site of production.
Deficiency or over secretions of hormones have negative effects in the body.
4. Describe Nervous systems in humans.
Ans: A flow chart of the human nervous system is given below:

Download Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 PDF
Control and coordination class 10 important questions - summary.
Control and coordination Class 10 important questions include the topic namely nervous system muscular tissue correlation. This chapter also explains human brain anatomy, tissue protection, and nervous tissue action. It also gives brief information about animals and plants chemical coordination. The human body is a complex machine, which performs a ton of functions and processes to maintain and sustain human life. Living organisms must use systems providing chemical control and coordination. Keeping the general principles of body organisation in multicellular organisms. Specialised tissues are used to provide control and coordination activities.
Topics covered in Chapter 7 Science Class 10 important questions are - animal nervous system, reflex action, the human brain, coordination in the plant, response to the stimuli, movement due to growth, and also hormones in animals.
Nervous System - In the nervous system, neurons are the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. There are three parts in the neurons: dendrites, cyton/stoma/cell body and axon. Dendrites receive impulses from other neurons, cyton/soma processes the impulse. Axon transmits the impulse, either to another neuron or to muscles/glands, etc and it may be myelinated or unmyelinated. Nervous systems covered in the chapter are - central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, somatic nervous system, and autonomic nervous system.
Reflex Action - It is a sudden and involuntary reaction of the body in response to the stimuli. A reflex arc is a path followed by the electrical impulse during reflex action. The impulse travels from the receptor organ to the brain or spinal cord.
Plant Hormones and Movement - Control and coordination in plants is carried out by different hormones. Some of the plant hormones are auxin, cytokinin, gibberellins, abscisic acid and ethylene. There are two types of movement in plants: growth independent movements and growth-dependent movements. Growth related movements are also known as tropic movements. Some of the tropic movements are Phototropic movement (light dependent), Geotropic movement (gravity-dependent), Chemotropic movement (chemical-dependent), Hydrotropic movement (water-dependent), and Thigmotropic movement (touch dependent).
Endocrine System - Endocrine system in human secrets wide range of hormones for different functions. It consists of different glands like exocrine glands, endocrine glands, pituitary glands, thyroid gland, pancreas, adrenal gland, and gonads.
Benefits of Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 - Control and Coordination
Given below are a few benefits that students will gain by referring to the Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 .
The questions and solutions have been framed in a simple and easy-to-follow language. This has been done to aid students of all intellectual capabilities to ensure that they can prepare the chapter more effectively and perform excellently in their final exams.
Reading the chapter and learning the concepts are just the tip of the iceberg. To ensure you are prepared to score high marks in your exam, you need to practice the important questions of the chapter. This would in turn facilitate a better understanding of the topics covered in the chapter.
The questions and answers have been provided by our subject experts keeping in mind the latest CBSE exam pattern and updated syllabus to give you a real-time experience of the exams.
An important part of doing well in any exam is being good at time management skills. Solving the important questions while timing yourself will give you a fair idea of how prepared you are to appear for your actual exam.
To be sure that you aren’t taken by surprise when you face the actual question paper, it is strongly advisable that you solve the important questions. These important questions will help boost your confidence and improve your chances of scoring better marks in the exams.
After going through all Class 10 Science Ch 7 important questions , which provides fully solved solutions to all the questions, it helps the student to save time in their exam preparation. Class 10 Control and coordination important questions answers are designed in such a way that improves the confidence of the student by solving them. Before going through the important questions, let's go through the NCERT solutions of Class 10 Chapter 7. If you refer to all the Class 10 Science Chapter 7 important questions, you can easily score five marks in the board examinations.
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 10 Science

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 7 - Control and Coordination 2023-24
1. Explain the nervous system according to Chapter 7 of Class 10 Science.
The nervous system is considered to be the most complex part of the body. The main function of the nervous system is to transmit signals to and from different parts of the body, the nervous system coordinates all the actions and sensory information. It is made up of the brain which acts as the control centre, the spinal cord which is the highway from the brain and all the nerves which carry the messages. The nervous system reacts to all the changes inside and outside the body.
2. What is control and coordination according to Chapter 7 of Class 10 Science?
In class 10 science, one of the most compelling chapters is Control and coordination. It is the seventh chapter of the class 10 science NCERT textbook. According to this chapter, control refers to the power of restraining and regulating a process. It even refers to the power of regulating pace in order to go fast, slow down, or stop completely. Whereas, Coordination refers to the process of different systems of an organism working together in order to create an appropriate stimuli reaction.
3. How can I ace Chapter 7 of Class 10 Science?
Chapter 7 of Class 10 Science is one of the most important chapters. It is one of the most scoring chapters for the CBSE Students. The simplest way of acing this chapter is by understanding the topics thoroughly. Using Vedantu’s Chapter 7 of Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions, students will gain more perspective and it will enrich their skills of learning. Using NCERT Solutions, students can solve practice papers which will give them more clarity on topics each individual student needs to concentrate on. This way a student can achieve the goal easily.
4. What do you mean by Reflex action according to Chapter 7 of Class 10 Science?
Reflex action is an important concept for class 10 Science. Reflex action is a fast, involuntary, spontaneous reaction to stimuli. It helps to reduce the damage to the body from any potentially harmful conditions. An example of a reflex action is touching something hot. As soon as you touch something hot, you spontaneously move it away from the hot object (this is reflex action). It is a very essential action for the survival of many organisms. A reflex action does not need any input or thought.
5. What are the important questions for Chapter 7 of Class 10 Science?
Chapter 7 of Class 10 Science is a very important chapter from the examination point of view. Using Vedantu’s Class 10 Chapter 7 Science important questions, students will have an upper hand in understanding the concepts and covering all the important aspects of each chapter. This will help all students wanting to score maximum marks, as all the important concepts and topics are organised. This will help students to prioritise the topics they need to concentrate on and perform better. The solutions or any study materials provided by Vedantu are absolutely free of cost.
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions
Cbse study materials.
- RS Aggarwal
- ML Aggarwal
- Merchant of Venice
- NCERT Books
- Questions and Answers
- NCERT Notes
- Important Questions
Control and Coordination
Ncert revision notes for chapter 7 control and coordination class 10 science.
→ All the living organisms respond and react to changes in the environment around them.
→ The changes in the environment to which the organisms respond and react are called stimuli such as light, heat, cold, sound, smell, touch etc.
→ Both plants and animals respond to stimuli but in a different manner.
→ Control and Coordination in animals is done with the help of two main systems:
(i) Nervous system
(ii) Endocrine system
→ Control and coordination are provided by nervous and muscular tissues.
→ Nervous tissue is made up of an organized network of nerve cells or neurons which is specialized for conducting information via electrical impulses from one part of the body to another.
→ These are specialized tips of some nerve cells that detect the information from the environment. `These are located in our sense organs.
(i) Ear: It acts as phonoreceptors (receiving sound). It helps in hearing and maintaining the balance of body.
(ii) Eyes: It acts as photoreceptors (receiving light). It helps in seeing
(iii) Skin: It acts as thermoreceptors (feels temperature). It helps in feeling heat or cold and touch.
(iv) Nose: It acts as olfactory receptors (sense of smell). It helps in the detection of the smell.
(v) Tongue: It acts as Gustatory receptors (sense of test). It helps in the detection of taste.
It is the structural and functional unit of nervous system.
Functioning of Neuron
→ The information from receptors is acquired at the end of the dendritic tip of a nerve cell as chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse.
→ This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body and then at the end of the axon.
→ Chemicals are released at the end of the axon by the effect of electrical impulse.
→ These chemicals cross the gap (synapse) and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron.
→ The similar synapse finally allows delivery of such impulses from neurons to other cells, such as muscles cells or gland.
Parts of Neuron
(i) Dendrite: It acquires information.
(ii) Cell body: The information acquired by it travels as an electrical impulse.
(iii) Axon: It is the longest fibre on the cell body is called axon. It transmits electrical impulse from cell body to dendrite of next neuron.
Synapse: It is the gap between the nerve ending of one neuron and dendrite of the other neuron. Here, electrical signal is converted into chemical signal for onward transmission.
→ Reflex action is quick, sudden and immediate response of the body to a stimulus. Example: Knee jerk, withdrawal of hand on touching hot object.
→ Stimulus: It is observable or detectable change in the external or internal environment to which an organism reacts.
→ Reflex arc: The pathway through which nerve impulses pass during reflex action is called reflex arc.
→ Response: It is the final reaction after the reflex action.
Three types of responses:
(i) Voluntary: Controlled by fore brain. Example: talking, writing.
(ii) Involuntary: Controlled by mid and hind brain. Example: heart beat, vomiting, respiration.
(iii) Reflex action: Controlled by spinal cord. Example: withdrawal of hand on touching a hot object.
Need for Reflex Actions
→ In some situations such as touching a hot object, pinching etc. we need to act quickly, otherwise our body would be harmed. Here response is generated from spinal cord instead of brain. In this way, time for taking action is reduced which save us from injury.
→ Human nervous system consists of two parts, Central nervous system (CNS) and Peripheral nervous system (PNS) .
→ Central nervous system consists of Brain and Spinal Cord .
→ Peripheral nervous system consists of Cranial Nerves which arise from the brain and Spinal Nerves which arise from the Spinal cord.
→ Brain is the main coordinating center of the body. It has three major parts:
(i) Fore-brain
(ii) Mid-brain
(iii) Hind-brain
→ It is the most complex or specialised part of the brain. It consists of cerebrum.
→ Functions of Fore-brain:
(i) Thinking part of the brain.
(ii) Control the voluntary actions.
(iii)Store information (Memory).
(iv) Receives sensory impulses from various parts of the body and integrate it.
(v) Centre associated with hunger.
→ Controls involuntary actions such as change in pupil size and reflex movements of head, neck and trunk.
It has three parts:
(i) Cerebellum: Controls posture and balance. Precision of voluntary actions. Example: picking pen.
(ii) Medulla: Controls involuntary actions. Example: blood pressure, salivation, vomiting.
(iii) Pons: Involuntary actions, regulation of respiration.
Protection of Brain and Spinal Cord
→ Protection of Brain: Brain is protected by a fluid filled balloon which acts as shock absorber and is enclosed in cranium (skull or brain box).
→ Protection of Spinal Cord: Spinal cord is enclosed in vertebral column.
→ For taking place the voluntary actions, the brain has to send messages to muscles.
→ The communication between the central nervous system and the other parts of the body is facilitated by the peripheral nervous system consisting of cranial nerves arising from the brain and spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord.
→ The brain thus allows us to think and take actions based on that thinking. This is accomplished through a complex design, with different parts of the brain responsible for integrating different inputs and outputs.
Limitations of Electric communication/Nervous system
(i) Electric impulse will reach only to those cells that are connected by nervous tissue.
(ii) After generation and transmission of an electrical impulse, the cell takes some time to reset its mechanism before transmitting another impulse. So cells cannot continually create and transmit impulse.
(iii) Plants do not have any nervous system.
Chemical communication
→ It helps in overcoming the limitations of electric communication.
→ There are three types of movements in plants.
(i) Independent of growth
(ii) Dependent on growth
Independent of growth
→ Independent growth has immediate response to the stimulus.
• Plants use electrical-chemical means to convey information from cell to cell.
• For movement to happen, cells change their shape by changing the amount of water in them, resulting in swelling or shrinking of cells. Example: Drooping of leaves of ‘Touch-me-not’ plant on touching it.
Dependent on growth
→ These movements are tropic movements i.e., directional movements in response to stimulus.
• Tendrils: The part of tendril away from the object grows more rapidly as compared to the part near the object. This causes circulating of tendril around the object.
• Phototropism: Movement towards light.
• Geotropism: Movement towards/away from gravity.
• Chemotropism: Growth of pollen tube towards ovule.
• Hydrotropism : Movement towards water.
→ These are chemical compounds which help to coordinate growth, development and responses to the environment.
→ Main plant hormones are:
• Auxin: This hormones synthesized at shoot tip. It helps the cells to grow longer and involved in phototropism (response towards light).
• Gibberellin: It helps in the growth of the stem.
• Cytokinins: It promotes cell division. This is present in greater concentration in fruits and seeds
• Abscisic Acid: It inhibits growth. It also cause wilting of leaves and also known as stress hormone.
→ Hormones are the chemical substances which coordinate the activities of living organisms and also their growth.
• Endocrine glands: These glands secrete their product (hormone) into the blood and the main organ for releasing the hormones.
• The list of endocrine gland with the hormones names and their functions are given below:
(i) Thyroxine : This hormone is secreted by Thyroid. The Thyroid is located in Neck/Throat region. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
(ii) Growth hormones: This is secreted by Pituitary (master gland). This gland is located in Mid-brain. It regulates growth and development.
(iii) Adrenaline: This hormone is secreted by Adrenal. The adrenal gland is located above both kidneys. It regulates blood pressure (increasing), heart beat, carbohydrate metabolism (during emergency).
(iv) Insulin: This hormone is secreted by Pancreas. The pancreas is located below stomach. It reduces and regulates blood sugar level.
(v) Sex hormones:
(a) Testosteron in males: This hormone is secreted by testis. The testis is located in genital area. Its changes associated with puberty (Sexual maturity).
(b) Estrogen in females: This hormone is secreted by Ovaries. The ovaries are located in lower abdomen area. Its changes associated with puberty (Sexual maturity).
Diabetes is a disease in which blood sugar level increases.
Cause of Diabetes
The disease is caused due to the deficiency of insulin hormone secreted by pancreas that is responsible to control blood sugar levels.
Treatment of Diabetes
Injections of insulin hormone can help in the treatment of diabetes.
Feedback Mechanism
→ The excess or deficiency of hormones has a harmful effect on our body. Feedback mechanism makes sure that hormones should be secreted in precise quantity and at right time. Example: Feedback mechanism to control the sugar level in blood is as follows:
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialisation Class 10 History
Related chapters.
- Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Acids, Bases and Salts
- Metals and Non-metals
- Carbon and its Compounds
- Periodic Classification of Elements
Related Questions
- NCERT Solutions for Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Class 10 Science
Report a problem
- Question is incorrect
- Answer is Incorrect
- Spelling Mistakes
- Not explained in detail
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students
Control and Coordination Class 10 Extra Questions with Answers Science Chapter 7
In this page, you can find CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Extra Questions and Answers Control and Coordination Pdf free download, NCERT Extra Questions for Class 10 Science will make your practice complete.
Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Extra Questions and Answers Control and Coordination
Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination with Answers Solutions
Control and Coordination Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1. Mention the receptors for light and sound in animals. Answer: Sense organs are called receptors. The receptor of light in animals is calld photoreceptor. The receptor of sound in animals is called phonoreceptor.
Question 2. Which hormone regulates the concentration of sugar in the blood? Answer: Insulin secreted by Islets of Langerhans of pancreas.
Question 3. Define ‘reflex action.’ Answer: Reflex action is a rapid, automatic response to a stimulus which is not under the voluntary control of the brain.
Question 4. Name few involuntary actions controlled by the hindbrain. Answer: Involuntary actions controlled by hindbrain are vomiting, salivation and blood pressure.
Question 5. What is an axon? Answer: It is a large, single, unbranched nerve fibre arising from the cyton. It carries impulses from cyton located in CNS to effectors.
Question 6. Why are roots called positively geotropic? Answer: This is because the roots always grow towards the gravity of the Earth.
Question 7. What is the number of cranial nerves and spinal nerves in human beings? Answer: There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves in human beings.
Question 8. Name the largest cell present in the human body.’ Answer: Neuron.
Question 9. Which part of central nervous system controls reflexes? Answer: Spinal cord.
Question 10. Name the part of neuron (i) Where information is acquired. (ii) Through which information travels as an electrical impulse. Answer: (i) Dendrite, (ii) Axon.
Question 11. What will happen if intake of iodine in our diet is low? Answer:
- When iodine intake is low, release of thyroxine from thyroid gland will be less by which protein, carbohydrate and fat metabolisms will be affected.
- A person might suffer from goitre in case of iodine deficiency in the body.
Question 12. Which hormone controls the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in human beings? Answer: Parathyroid hormone (parathormone).
Question 13. Name the hormone, the secretion of which is responsible for dramatic changes in appearance in girls and boys when they approach 10-12 years of age. Answer: Oestrogen from the ovaries of girls and testosterone from testes of boys.
Question 14. Name two tissues that provide control and coordination in multicellular animals. Answer: The two tissues that provide control and coordination in multicellular animals are nervous tissue and muscular tissue.

Question 16. What do you understand by the sleep movement of plant organs? Answer: Sleep movement in plants e.g., in flowers is to protect the reproductive organs from the cold. Hence, sepals and petals of saffron flower close at sunset and open up in the morning.
Question 17. State the main function of abscistic acid in plants. Answer: Abscisic acid slows plant growth and inhibits division of cells.’ Question 18. What is spinal cord? Which body function is controlled by it? (U. P. 2018) Answer: Spinal cord is a long and cylindrical tube which is present in vertebral column. From its dorsal and ventral horn sensory and motor nerves originate which form spinal nerve. At the centre it contains neurocoel. Spinal cord is covered externally by three membranes. In this, H shaped grey matter is filled, which is surrounded by white matter. Lateral and dorsal sides have horns. Spinal cord: It serves as principal centre for almost all the reflexes and involuntary activities. It provide conduction pathway for nerves to transmit stimuli to brain.
Control and Coordination Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1. Define a synapse. Answer: Synapse is a very fine gap between telodendria of axon of one neuron and dendrites of another neuron. These two structures do not unite with each other but remain separated by a fine gap.
Question 2. Mention the functions of forebrain. Answer: The forebrain performs the following functions:
- It is responsible for intelligence, memory, consciousness, will power and voluntary actions.
- It has the centres for visual reception, hearing reception, touch, smell and temperature reception.
Question 3. Answer the following:
- Which hormone is responsible for the changes noticed in females at puberty?
- Dwarfism results due to deficiency of which hormone?
- Blood sugar level rises due to deficiency of which hormone?
- Iodine is necessary for the synthesis of which hormone?
- Growth hormone
Question 4. Name the hormones responsible for regulation of
- metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins
- balance of calcium and phosphate
- blood pressure
- water and electrolyte balance.
- Parathormone
- Vasopressin.
Question 5. What is a tropic movement? Explain with an example. Answer: The directional growth movement of plants due to external stimuli is called a tropic movement. It can be either towards the stimulus, or away from it. For example, in case of phototropic movement, shoots respond by bending towards light while roots respond by bending away from it.
Question 6. Why Mimosa pudica (touch-me-not) leaves droop down when touched? Answer: It is due to turgor pressure difference between the upper and lower halves of the base of petiole (pulvinus). Lower half cells lose water and upper half cells of pulvinus become turgid due to transfer of water from lower cells. Thus, the entire leaf droops down when touched.
Question 7. Why are the electrical-chemical signals not an efficient means of communication in plants? Answer: Unlike animals, where there is a nervous system for conduction of nerve impulses and circulatory system for conduction of hormones, there are no specialised tissues in plants. So, the electrical chemical signals are not an effective means of communication in plants.
Question 8. If a ripened fruit is kept in a basket of raw fruits, then what will happen? What causes it? Answer: The ripened fruit will release ethylene (hormone) which causes ripening of other raw. fruits kept in a basket.
Question 9. What is cerebrospinal fluid? What is its function? . Answer: Cerebrospinal fluid is the fluid found in the cavities of brain and central canal of spinal cord and in between arachnoid and pia mater. Function: It prevents the brain and spinal cord from mechanical shocks.
Question 10. Answer the following:
- Name the endocrine gland associated with a brain.
- Which gland secretes digestive enzymes as well as hormones?
- Name the endocrine gland associated with kidneys.
- Which endocrine gland is present in males but not in females?
Question 11. Describe the advantage of division of human heart in right and left parts. Answer: The advantage of division of human heart in right and left parts is that it prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.

Question 13. What is turgor movement? Answer: Turgor movement is the movement due to the difference of turgidity of the cells in the lower half and upper half of pulvinus (petiole of leaf). When leaf of touch-me-not plant (Mimosa pudica) is touched, the electrical signal send chemical signals from leaflets to pulvinus (petiole) of leaf. Cells in the lower half of pulvinus lose water and become flaccid, while cells in the upper half of pulvinus become turgid due to accumulation of more water. Hence, leaf droops down for a short time.
Question 14. Why do tendrils coil around hard rough objects? Answer: The growth movement of tendril in response to unilateral stimulus of touch is called thigmotropism. Tendrils of louki, tori, karela, and sweet pea plants coil around hard objects when they come in their contact. It occurs due to unequal growth of two sides of a tendril. The growth of the surface which comes in contact of the support is retarded, while it remains normal or increased on the other side, due to which tendril coils around the support.

Question 16. Nervous and hormonal system together perform the function of control and coordination in human beings. Justify the statement. Answer: Nervous and hormonal system together perform the function of control and coordination in human beings. Let us take an example, in the case of any emergency, stimulus is being perceived by CNS (Central nervous system). The stimulus is analysed and the response is sent to the effectors. Simultaneously, sympathetic nerves stimulate adrenal gland to release adrenaline which regulates blood pressure, increases heartbeat, constricts blood vessels and dilates pupil, etc. So, both nervous and endocrine systems interact and overcome the crisis together.
Question 17. How are the brain and spinal cord protected? Answer: (i) Brain: It is protected by the bony box called cranium. It is also called as skull. Also the membranes that surround the brain (meninges) are filled with cerebrospinal fluid that act as shock absorbers protecting the brain. (ii) Spinal cord: The vertebral column, commonly called backbone, protects the spinal cord.
Question 18. What are ductless glands? Answer: These ductless glands which form a group of tissues or cells in acting at distant sites of the body known as target organ or target cell.
Question 19. Name the hormone secreted by thyroid gland and describe its main functions. Answer: The glands which secrete hormones directly into blood are called ductless or endocrine glands. They reach their target cells through blood only and not through any duct. Thyroid gland is a bilobed structure situated at posterior surface of larynx. Its structure resembles ‘H’. Its weight in humans is about 25-30 g.
It mainly releases thyroxine or thyroid hormone which is a product of iodine. This hormone regulates metabolic activities in body. Its functions are to control the BMR rate, protein synthesis, increase heartbeat rate, uses of glucose. Lack of thyroid causes slowing of heartbeat, weak immune system and brain damage.

Control and Coordination Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1. Which hormone is released into the blood when its sugar level rises? Name the organ which produces the hormone and describe its effect on blood sugar level. Also name one digestive enzyme that this organ secretes and the function of this enzyme. Answer: Hormone: Hormones are released by stimulated cells are diffuse all around the original cell. Insulin hormone is released into the blood when its sugar level rises. Pancreas secretes the insulin hormone. The function of insulin hormone is to lower the blood sugar level.
Deficiency of insulin hormone in the body causes a disease known as diabetes. Diabetes is characterised by large quantities of sugar in the blood. The insulin hormone controls the metabolism of sugar. If due to some reason pancreas does not produce and secrete sufficient amount of insulin into blood.
then the sugar level in the blood rises. The high sugar level in the blood can cause many harmful effects to the body of person. The person having severe diabetes are treated by giving injection of insulin.
The pancreas secretes pancreatic juice which contains enzymes like trypsin for digesting proteins, lipase for breakdown of emulsified fats and amylase for breakdown of starch.

Question 3. (i) What are cranial and spinal nerves? Describe a spinal nerve. (ii) Draw a diagram of the human brain and label the following parts: (a) Cerebrum (b) Meninges (c) Medulla oblongata (d) Cerebellum Answer: (i) Cranial nerves are the nerves associated with the brain. These are 12 pairs in number and carries both sensory and motor nerves. Spinal nerves are the nerves connected with the spinal cord. These are 31 pairs in number. Spinal nerve arises in the form of dorsal root and ventral root and both unite in the neural canal to form a single branch. It comes out of the vertebral column through intervertebral canal and then divides into dorsal, ventral and visceral branches.

Question 4. Describe the central nervous system in human beings. or How many parts of brain are there? Sodden reactions like blood pressure, saliva secretion and vomating are controlled by which parts? Answer: The central nervous system in human beings consists of brain and spinal cord. (i) Brain: Brain is the highest coordinating centre in the body. It is covered by meaninges, which is made up of three layers. It is protected by cranium. Brain is broadly divided into:
(a) Forebrain: The forebrain includes cerebrum and olfactory lobes. Cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. It consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Sensory and motor receptors are present in the brain. There are various regions for reception of vision (occipital lobe), reception of sound (temporal lobe), touch, smell, temperature (parietal lobe) and muscular activities (frontal lobe). Olfactory lobes are one in pair and receives olfactory nerves.
(b) Midbrain: It is the small portion of the brian that connects cerebrum with the other parts of the brain and spinal cord.
(c) Hindbrain: It consists of cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata. Cerebellum is responsible for coordination and adjustment of movement and posture. Pons regulate respiration. Medulla oblongata regulates swallowing, coughing, sneezing and vomitting…
(ii) Spinal cord: Medulla oblongata extends downwards, enclosed in vertebral column to form a cylindrical structure known as spinal cord. It is also covered by meninges. It is the reflex centre of the body.
Question 5. Give the various functions performed by the plant hormones. Or Name various plant hormones. Also give their physiological effects on plant growth and development. Answer: The various functions performed by the plant hormones are: (i) Auxins promote cell enlargement and cell differentiation. They also promote growth.
(ii) Gibberellins promote cell enlargement and cell differentiation in the presence of auxin. It also help in breaking the dormancy in seeds and buds. It promote the growth in fruits.
(iii) Cytokinins promote cell division and help in breaking the dormancy of seeds and buds. It delay the ageing in leaves. It promotes the opening of stomata and also fruit growth.
(iv) Abscisic acid promotes the dormancy in seeds and buds. It promotes the closing of stomata and falling of leaves. It also inhibits growth, reverses the growth promoting effects of auxins and gibberellins. Its effects include wilting of leaves.
(v) Ethylene promotes the falling of leaves, ripening of fruits and helps in breaking bud dormancy.

- A receptor to perceive the stimulus.
- A sensory or afferent nerve which carries the message from the receptor to the spinal cord.
- The neurons of spinal cord transmit the impulse from afferent neurons to efferent neurons.
- The motor or efferent nerve carries messages from spinal cord to the muscles (effectors) that show the response.
Some examples of reflex actions are:
- Blinking of eyes when a foreign particle gets in them.
- Sneezing if an unwanted particle enters the nose.
- Watering of mouth at the sight or smell of good food.
- Withdrawl of foot if a nail comes in the way while walking and pricks the foot.
- Immediate withdrawl of hand on touching some hot thing.

- Soak some seeds of gram or moong in water for one day.
- Pierce slightly big holes (2 mm diameter) at the bottom of the cup.
- Fill it with 1 cm. thick layer of garden soil.
- Sprinkle soaked seeds (moong / gram) over the soil. Water the seeds.
- Put the cup on 2 pieces of wooden or stone slabs so that there is a little gap between the top of the table and bottom of the cup.
- Cover the lower part of the set-up with black paper.
- Water the seeds regularly with little water.
- You will observe that the roots come out from the holes and grow towards the Earth showing positive geotropism.
Question 8. Draw a well-labelled diagram of human brain and explain the functions of various parts. Answer: Structure and functions of human brain: It is the most important and delicate portion of the body. In an adult, its weight is 1300-1400 g. It remains enclosed in bony case called cranium. The brain is covered with three meninges. The outer meninx is called duramater and inner one is piamater.
In between these two arachnoid matter is present. A dense network of blood capillaries present in these meninges, which provide food and oxygen to the brain. In between the meninges, the space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (80%) which protects the brain against external shocks and mechanical injury.
1. Forebrain: The brain is divided into three parts-olfactory lobes, cerebrum and diencephalon. Cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. It is highly folded and convoluted which increases the surface area. The outer part of cerebrum is made up of grey matter while inner is made up of white matter. Cerebrum controls various activities of the body. Parts of Forebrain
- Olfactory lobes: These are concerned with sense of smell.
- Cerebrum: It is the centre of instinct thinking, memorising, reasoning, consciousness, learning, etc.
- Diencephalon: It is the centre of involuntary actions such as hunger, thirst, sleep, temperature, control, metabolism, etc.
2. Midbrain: It connect forebrain to hindbrains, many involuntary actions like change in size of pupil and auditory impulses are controlled by it.
3. Hindbrain: It consists of cerebellum, medulla oblongata and pons varolii. (i) Pons varolii: It is situated just below of cerebral peduncles like a lobe of 2.5 cm long. It provides control of activities like mastication, salivation, lacrimation and movement of eyeballs, etc. (ii) Cerebellum: It controls the body posture and equilibrium. It controls and coordinates the movement of voluntary muscles. (iii) Medulla oblongata: It is the posterior’most part of the brain which is cylindrical in shape. It controls involuntary activities such as respiration, heartbeat, circulation etc.
Question 9. What do you know about reflex action? Explain with the help of diagram. What is the importance of reflex actions? Answer: Reflex action The path followed by information or impulse in reflex action is called reflex arc. It is formed in the spinal cord and consists of two neurons:
- Sensory neurons containing dorsal horn.
- Motor neurons containing ventral horn.

- These are controlled by spinal cord and thus, minimise the burden on brain.
- These are very fast and accurate, wich minimise chances of mishappening.
Some examples of reflex actions:
- Sneezing: During this, the air from the lungs comes out forcefully.
- Coughing: When food particles enter the windpipe the air from the lungs comes out forcefully.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination In-Text Exercises Free PDF

The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination In-Text Exercises are provided below, in detailed and free to download PDF format. The solutions are latest , comprehensive , confidence inspiring , with easy to understand explanation . To download NCERT Class 10 Solutions PDF for Free, just click ‘ Download pdf ’.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination In-Text Exercise PDF
Check out solutions to other chapters.
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 Periodic Classification Of Elements
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce?
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
How should I study for my upcoming exams?
First, learn to sit for at least 2 hours at a stretch
Solve every question of NCERT by hand, without looking at the solution.
Solve NCERT Exemplar (if available)
Sit through chapter wise FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS
Practice MCQ Questions (Very Important)
Practice Assertion Reason & Case Study Based Questions
Sit through FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS involving MCQs. Assertion reason & Case Study Based Questions
After Completing everything mentioned above, Sit for atleast 6 full syllabus TESTS.
Comments are closed.
Contact Form
Privacy Policy
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – Control and Coordination Revision Notes
Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes
This article deals with control and coordination class 10 notes. Control and Coordination is the seventh chapter of CBSE Class 10 Science. First of all, we all know that the indication of being alive is that if something moves. Moreover, some of these movements are due to the result of growth. For example, when a seed germinates and grows, it pushes the soil and emerges out. Most noteworthy, these movements would not take place in case the growth of the plant were to be stopped.
An important question that can be raised is why we associate such movements with life. The answer to this is that movement is believed to be a response to change in an organism’s environment. Moreover, movement can also take place by living organisms to use environmental changes to their advantage. Therefore, this movement which takes place in response to the environment is carefully controlled. Living organisms must make use of systems that enable control and coordination.
Download Toppr app for Android and iOS or signup for free.
Sub-topics covered under Control and Coordination
- Coordination in Plants
- Hormones in Animals
- Human Brain
- Nervous System
- Reflex Action
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – Control and Coordination Revision Notes Free PDF Download

Why Should You Download Toppr?
Toppr is one of the best education apps out there. The platform boasts of really high-quality content. Furthermore, the preparation of this content has taken by teachers of a really high caliber. Moreover, the major unique selling point of Toppr is that it combines content along with efficient technology and design. Another important feature of Toppr is its adaptive platform which not like the test-centric platform of other education platforms. Also, it has comprehensive online classes as well.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 16 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 15 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 8 – How Do Organisms Reproduce? Revision Notes
One response to “CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 7 – Control and Coordination Revision Notes”
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Extra Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination
Get extra questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination with PDF. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These extra questions will be helpful to revise the important topics and concepts. You can easily download all the questions and answers in PDF format from our app.
Control And Coordination Class 10 Science Extra Questions with Answers
Question 1: Why is it advised to use iodised salt in our diet?
Answer: Iodine stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxin hormone. Deficiency of this hormone results in the enlargement of the thyroid gland. This can lead to goitre.
Question 2: Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes its growth. Where it is synthesized?
Answer: Plant hormone that promotes growth is auxin. It is synthesized at the tip of the plant stem.
Question 3: State the function of: (i) gustatory receptors, and (ii) olfactory receptors.
Answer: (i) Gustatory receptors – these are sensitive to taste (ii) Olfactory receptors – these are sensitive to smell.
Question 4: Name the part of the brain which controls posture and balance of the body.
Answer: Cerebellum in hind-brain controls the posture and balance of the body.
Question 5: Mention the part of the body where gustatory and olfactory receptors are located.
Answer: Gustatory receptors are located in Cerebrum of fore-brain. Olfactory receptors are located in Olfactory lobe of fore-brain.
Question 6: Smita’s father has been advised by a doctor to reduce his sugar intake. a) Name the disease he is suffering from and name the hormone whose deficiency is? b) Identify the gland that secretes it and mention the function of this hormone. c) Explain how the time and amount of secretion of this hormone is regulated in human system.
Answer: a) He is suffering from diabetes. Deficiency of insulin causes diabetes.
b) Pancreas secretes insulin. Insulin helps in regulating blood sugar.
c) When the sugar level in blood increases, it is detected by the a-cells of the pancreas which responds by producing more insulin. As the blood sugar level falls, insulin secretion is reduced.
Question 7: State the functions of plant hormones. Name four different types of plant hormones.
Answer: Plant hormones help to coordinate growth, development and responses in environment. Four different types of plant hormones are – Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins, Ethylene and Abscisic acid.
(i) Auxins control the tropic (growth related) movements of the plants in response to light, gravity, touch etc by increasing the size of cells. Under the influence of auxins, the plant stem bends towards unidirectional light whereas the roots bend away from it.
(ii) Gibberellins stimulate stem elongation and leaf expansion. Its application causes stem elongation in small plants such as cabbage. Spraying gibberellins on sugarcane plant increases the stem size and hence the yield.
(iii) Cytokinins are produced in regions of the plant body where rapid cell division occur, such as root tips, developing shoot buds, young fruits and seeds. Cytokinins promote growth by stimulating cell division. They also help in production of new leaves and chloroplasts in leaves.
(iv) Ethylene causes ripening of the fruits.
(v) Abscisic acid inhibits (i.e., slows down) the growth in different parts of the plant body. It also inhibits germination of seeds. It increases the tolerance of plant to different kinds of stresses such as temperature changes. So, it is also called the stress hormone in plants. It also causes the drying and falling of older leaves, flowers and fruits.
Question 8: (a) How is brain protected from injury and shock? (b) Name two main parts of hind brain and state the functions of each.
Answer: (a) Brain is covered by a three layered membrane called meninges. In between the layers of meninges and brain, cavity fluid named Cerebro Spinal Fluid (CSF) is filled. The hard skull covers the meninges. Thus Meninges, CSF and Skull protects our brain for a certain extent.
(b) Two main parts of hind-brain are — Medulla and Cerebellum. Their functions are: Medulla: Involuntary actions such as blood pressure, salivation and vomiting. Cerebellum: It is responsible for precision of voluntary actions and maintaining the posture and balance of the body.
Question 9: (a) Draw the structure of neuron and label cell body and axon. (b) Name the part of neuron: (i) where information is acquired (ii) through which information travels as an electrical impulse.
Answer: (a)
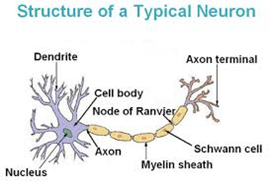
(b) (i) Dendrite (ii) Axon
Question 10: (a) Which plant hormone is present in greater concentration in the areas of rapid cell division? (b) Give one example of a plant growth promoter and a plant growth inhibitor.
Answer: (a) Cytokinin is present in greater concentration in the areas of rapid cell division.
(b) An example of a plant growth promoter is gibberellins and example of a plant growth inhibitor is abscisic acid.
Question 11: How is the spinal cord protected in the human body?
Answer: Spinal cord is enclosed in a bony cage called vertebral column.
Question 12: A potted plant is made to lie horizontally on the ground. Which part of the plant will show (i) positive geotropism? (ii) negative geotropism?
Answer: (i) Root (ii) Shoot.
Question 13: Mention the function of the hind-brain in humans.
Answer: Hind brain controls respiration, cardio-vascular reflexes and gastric secretions. It also modulates the motor commands initiated by the cerebrum.
Question 14: Mention the function of adrenaline hormone.
Answer: Adrenaline hormone is released into the blood from the adrenal gland during stimulation of the nervous system on seeing any adverse situation of fight or fright, it:
- increases the blood pressure.
- increases heart beat rate.
- increases breathing rate.
- diverts blood to essential organs including the heart, brain and skeletal muscles by dilating their blood vessels and constricting those of less essential organs, such as the skin and digestive system.
Question 15: A young green plant receives sunlight from one direction only. What will happen to its shoots?
Answer: Shoots will bend towards the light and roots away from the light.
Question 16: Name the plant hormones which help/promote (i) cell division (ii) growth of the stem and roots?
Answer: The plant hormones which help or promote: (i) Cell division — Cytokinins ii) Growth of the stem — Gibberellins
Question 17: What is the function of thyroxine hormone in our body?
Answer: Thyroxine hormone regulates the carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body so as to provide the best growth balance.
Question 18: Name two tissues that provide control and coordination in multicellular animals.
Answer: The two tissues that provide control and coordination in multicellular animals are nervous and muscular tissues.
Question 19: (i) Name the hormones that are released in human males and females when they reach puberty.
(ii) Name a gland associated with brain. Which problem is caused due to the deficiency of the hormone released by this gland?
Answer: (i) Testes in males produces hormone testosterone. Ovaries in females produces hormone oestrogen.
(ii) Pituitary gland present in the brain is responsible for body growth, development of bones and muscles (if excess-gigantism) (if less-dwarfism).
Question 20: Name the two main organs of our central nervous system. Which one of them plays a major role in sending command to muscles to act without involving thinking process? Name the phenomenon involved.
Answer: The two main organs of CNS are brain and spinal cord. Spinal cord plays a major role in sending command to muscles to act without involving thinking process. This phenomenon is called reflex action.
Question 21: Name the hormone secreted by human testes. State its functions.
Answer: Testes secrete male sex hormone called testosterone. The function of testosterone is to regulate male accessory sex organs and secondary sexual characters like moustache, beard and voice.
Question 22: Name and explain the function of the hormone secreted by the pituitary gland in humans.
Answer: Hormones secreted by pituitary gland along with their functions are:
- Growth hormone: It regulates growth and development of bones and muscles.
- Trophic hormone: It regulates secretion of hormones from other endocrine glands.
- Prolactin hormone: It regulates the function of mammary glands in females.
- Vasopressin hormone: It regulates water and electrolyte balance in the body,
- Oxytocin hormone: It regulates ejection of milk during lactation.
Question 23: What are ‘nastic’ and ‘curvature’ movements? Give one example of each.
Answer: Nastic movements: These are non-directional movements which are neither towards nor away from the stimulus. Example: Dropping of leaves.
Curvature movements : In such movements plant organs move towards or away from the stimulus. Example: Bending of shoot towards a source of light.
Question 24: Write the name and functions of any two parts of the human hind-brain.
Answer: Any two parts of human hind-brain with their functions are as follows: (i) Cerebellum, which controls the coordination of body movement and posture. (ii) Medulla oblongata, which regulates the centre of swallowing, coughing, sneezing and vomiting.
Question 25: What are plant hormones? Write two important functions of auxin.
Answer: Plant hormones can be defined as a chemical substance which is produced naturally in plants and are capable of translocation and regulating one or more physiological processes when present in low concentration. Two important functions of auxin are that it promotes cell elongation, root formation, cell division, etc.
Question 26: State how concentration of auxin stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light?
Answer: When light falls on the side of the shoot auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot. This concentration of the auxin stimulates the cell to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light. Thus, plant appears to bend towards light.
Question 27: What is synapse? In a neuron cell how is an electrical impulse created and what is the role of synapse in this context?
Answer: A synapse is the gap between the two neurons. Here the axon terminal of one neuron is in close proximity to the dendrite of the second neuron. When a nerve impulse reaches the knob like nerve ending of an axon, a tiny amount of a chemical substance is released in the synapse. This chemical substance is called as the neurotransmitter. At synapse the electrical signals converted into chemicals, that can easily cross over the gap and pass on to the next neurons where it again converted into electrical signals.
Question 28: Draw neat diagram of human brain and label on it the following parts: (i) Midbrain (ii) Pituitary gland
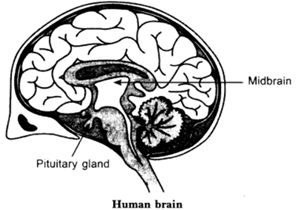
Question 29: Write one example each of the following tropic movements: (i) Positive phototropism (ii) Negative phototropism (iii) Positive geotropism (iv) Negative geotropism (v) Hydrotropism (vi) Chemotropism
Answer: (i) Positive phototropism: shoots growing towards light. (ii) Negative phototropism: roots growing away from light towards ground. (iii) Positive geotropism: growth of roots towards earth due to the pull of the earth. (iv) Negative geotropism: shoots growing away from the earth. (v) Hydrotropism: roots growing towards the source of water. (vi) Chemotropism: growth of pollen tubes towards the ovules.
Question 30: (a) Explain any three directional movements in plants. (b) How brain and spinal cord are protected in human? (c) Name the master gland present in the brain.
Answer: (a) Stimuli is responsible for the movement of the plant parts towards or away from it. This movement is called as Tropic Movement.
- Phototropism: movement of plant towards or away from the light.
- Geotropism: movement of plant parts towards the earth or away from it.
- Hydrotropism: movement of plant parts towards or away from any source of water.
(b) Both the brain and the spinal cord are protected by bone: the brain by the bones of the skull and the spinal cord is protected by a set of ring-shaped bones called vertebrae. They are both cushioned by layers of membranes called meninges as well as a special fluid called cerebrospinal fluid. This fluid helps to protect the nerve tissue to keep it healthy, and remove waste products.
(c) Pituitary gland present in the brain is known as the master gland.
Question 31: List in tabular form differences between nervous system and endocrine system.
Question 32: Which organ secretes a hormone when blood sugar rises in our body? Name the hormone and name one enzyme released by this organ.
Answer: Pancreas secretes a hormone when blood sugar rises in our body. Insulin is the hormone released by this organ and the name of the enzyme is pancreatic juice.
Question 33: Explain how auxins help in bending of plant stem towards light.
Answer: In plant shoots, the role of auxin is to cause a positive phototropism, i.e. to grow the plant towards the light. When light is incident on a plant from one direction, it causes the auxins to redistribute towards the shaded side of the plant. One function of auxin is to cause cell elongation. The redistribution causes the cells on the shaded side to elongate more than those on the side with the light shining on them. This causes the shoot to bend towards the light.
Question 34: What causes a tendril to encircle or coil around the object in contact with it is? Explain the process involved.
Answer: When a tendril comes in contact with any support, the part of the tendril in contact with the object does not grow as rapidly as the part away of the tendril away from the object. This cause the tendril to circle around the object and thus, cling to it.
Question 35: Name any three endocrine glands in human body and briefly write the function of each of them.
Answer: Three endocrine glands with their function in human body are as follows:
Thyroid gland: It secretes a hormone called thyroxine which regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the body and so provide the best balance for nutrients and mental ability.
Adrenal gland: It secretes two hormones-adrenalin and corticoid hormones regulate blood pressure, heartbeat, breathing rate and carbohydrate metabolism.
Pancreas: It secretes two hormones – insulin and glucagon. Insulin hormone lowers the blood glucose level. Glucagon hormone increases the blood glucose level.
Question 36: Which part of the brain controls involuntary actions? Write the function of any two regions of it.
Answer: Hind-brain controls the involuntary actions. Cerebellum controls the coordination of body movement and posture. Medulla oblongata regulates centre for swallowing, coughing, sneezing and vomiting.
Question 38: What is chemotropism? Give one example. Name any two plant hormones and mention their functions.
Answer: Chemotropism is the movement of a part of the plant in response to a chemical stimulus. It can be positive chemotropism or negative chemotropism. Example: The growth of pollen tube towards a chemical which is produced by an ovule during the process of fertilisation in a flower.
Two plant hormones with their functions are as follows:
- Auxins promote cell elongation, root formation, cell division, respiration and other physiological processes like protein synthesis, etc.
- Gibberellins stimulate stem elongation, seed germination and flowering.
Question 39: State the functions of any three of the structural and functional unit of nervous system.
Answer: The structural and functional unit of nervous system, i.e. neuron with their functions are as
- Cell body: Stimulus received from dendrite is changed into impulse in the cyton.
- Dendrites: They receive sensation or stimulus, which may be physical or chemical.
- Axon: It conducts impulse away from the cell body.
Question 40: What is ‘hydrotropism’? Describe an experiment to demonstrate ‘hydrotropism’.
Answer: ‘Hydrotropism’ is the directional growth of a plant part in response to water. For example: roots show hydrotropism as they grow towards water in the soil and are positively hydrotropic.
An experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism is as follows:
- A porous pot filled with water is taken and inserted in a tub filled with dry sand.
- A freshly germinated pea seedling is sowed in the sand.
- As water is not available in sand, the root growing will bend towards the porous pot filled with water.
- A hydrotropic curvature of the root is observed as it grows towards water.
- This bending of root shows the movement in response towards water.
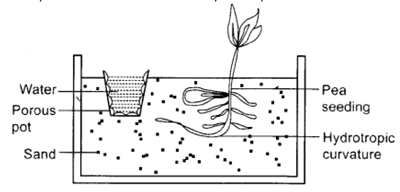
Question 41: What are ‘hormones’? State one function of each of the following hormones: (i) Thyroxine (ii) Insulin
Answer: Hormones are the chemical substances which coordinate and control the activities of living organisms and also their growth. The term hormone was introduced by Bayliss and Starling. (i) Function of Thyroxine: This hormone regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. (ii) Function of insulin: This hormone helps in regulating sugar level in the blood.
Question 42: What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of situation where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Answer: Receptors are present in our all parts of the body for example in skin, eye, nose tongue etc. They detect the signals and then send them to brain in the form of electrical signals. If these receptors are damaged then it they will not detect the input which leads to the harm for our body in dangerous situation.
Question 43: What is a reflex action? Describe the steps involved in a reflex action.
Answer: Reflex action: It is defined as an unconscious, automatic and involuntary response of effectors, i.e. muscles and glands, to a stimulus, which is monitored through the spinal cord.
Mechanism of reflex action: It involves the following steps:
- Receptor organ like skin perceives the stimulus and activates a sensory nerve impulse.
- Sensory organ carries message in the form of sensory impulse to the spinal cord.
- The spinal cord acts as modulator: The neurons of spinal cord transmit the sensory nerve impulse to motor neuron.
- Motor never conducts these impulses to the effectors like leg muscles which responds by pulling back the organ away from the harmful stimulus.
Question 44: (a) Name the two main constituents of the Central Nervous System in human beings. (b) What is the need for a system of control and coordination in human beings?
Answer: (a) The two main constituents of the Central Nervous System in human beings are the brain and the spinal cord.
(b) A living being does not live in isolation. It has to constantly interact with its external environment and has to respond properly for its survival. For example; when a hungry lion spots a deer, the lion has to quickly make a move so that it can have its food. On the other hand, the deer needs to quickly make a move to run for its life. The responses which a living being makes in relation to external stimuli are controlled and coordinated by a system; especially in complex animals. So, control and coordination . is essential in maintaining a state of stability and a steady state between the internal conditions of an organism and the external environment.
Question 45: (a) Name the hormone which is released into the blood when its sugar level rises. Explain the need of Chemical communication in multicellular organisms the organ which produces this hormone and its effect on blood sugar level. Also mention the digestive enzymes secreted by this organ with one function of each.
(b) Explain the need of Chemical communication in multicellular organisms.
Answer: (a) Glucose is needed by cells for respiration. It is important that the concentration of glucose in the blood is maintained at a constant level. Insulin is a hormone produced by the a-cells that regulates glucose levels in the blood.
In order for multicellular organisms to function properly, their cells must communicate. For instance, your muscles must contract when your brain sends a message to contract.
Pancreas produces insulin and p-cells which increase glucose in blood. It also – produces digestive enzyme (pancreatic amylase).
(b) Cell-to-cell signaling is a critical component of coordinating cellular activities. Through this communication, messages are carried from signaling cells to receiving cells, also known as target cells. This signaling occurs with proteins and other types of signaling molecules. Other things which happens in our body due to cell communication are – growth and development, cellular reproduction, tissue repair, sensing pain, etc.
- Biology Article
- Control And Coordination
Control and Coordination
Do we sleep every day? Yes, we do, unless we have an important event or examination coming up, we take a sound sleep. But how do we fall asleep? Does our brain shut down once we are asleep?
How are we able to react as soon as we dip our fingers into a hot cup of tea? How are we able to change paths while walking when we hear a car horn honk? Your answer to all these questions is that animals have a system which is responsible for all these sudden responses to stimuli. This system is called the Nervous system.

These series of actions that occurs within a fraction of seconds in response to a change or situation is what basically control and coordination.
Let us have a detailed look at the control and coordination in humans as well as plants.
Control and Coordination in Humans
In human beings, the control and coordination take place through the nervous system and the endocrine system that produce and secrete hormones. The five sense organs in our body, eyes, ears, nose, tongue and skin are called receptors and these organs functions by receiving information from the environment around us. Therefore, the response and coordination in both humans and animals involve the sense organs, the nervous system and hormones.
What is the Nervous system?
The nervous system consists of nerve fibres and nerve cells which transmit impulses of the nerve between different parts of the body.
It is a system found in animals that synchronizes its functions by passing signals to and from different parts of the body.
It is brought about by the nervous system after it detects any physical response on any part of the body due to various changes such as temperature, pressure, light, etc.
Furthermore, the nervous system coordinates with the endocrine system to react accordingly. This system of control and coordination is brought about after the involvement of various internal systems working in sync to respond in accordance.
The neuron is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. It receives and transmits electrical nerve impulses. A neuron comprises of :
The cell body consists of a nucleus and granular cytoplasm called Nissl’s granules.
Dendrites are several branched, finger-like projections that transmit nerve impulse towards the cell body.
The axon arises from the cell body which is branched at the distal end. The cells of the axon are called Schwann cells which are covered by a myelin sheath. The space between the myelin sheath is known as Nodes of Ranvier. The end of the axon contains bulb-like structures called the Synaptic Knob.
Parts of the Nervous System
Vertebrates have a distinct nervous system, which is divided into two main parts:
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Central Nervous System
It consists of the brain and spinal cord. Generation of sensory emotions takes place here. Thoughts and emotions are produced, leading to the formation of memories. It gathers information from all over the body and syncs its activity accordingly. Apart from sensory motions, it also controls the rate at which we breathe, heart rate, the temperature of the body, etc.
Explore more about Central Nervous System
Peripheral Nervous System
Everything apart from the brain and spinal cord constitutes the PNS. It includes nerves and everything that goes down the spinal cord. It is responsible for bringing information from all parts of the body to the brain. The nerves in the PNS are known as peripheral nerves, and these nerves connect our sense organs and all other organs, blood vessels, etc., to the CNS.
Explore more about Peripheral Nervous System
Organs of the Human Nervous System
The human nervous system consists of the following organs:
Spinal cord
Our brain controls all the actions of the body. It receives the signals from the sensory organs It comprises of three parts:
Forebrain helps in the control and coordination of all the voluntary functions and is the thinking part of the brain.
Midbrain transmits signals from the hindbrain and forebrain.
It helps in controlling the vision, hearing, temperature, etc.
The hindbrain controls and coordinates the heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, walking, sleeping, etc.
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a thick nerve located in the cavity of the backbone. Its upper end is connected to the brain. It is connected to all the parts of the body through nerves and controls all the functions of the body by transmitting the information received through the sensory organs to the brain.
The nerves connect the brain and spinal cord to all parts of the body. There are three types of nerves in our body:
Cranial Nerves connect all parts of the head to the brain.
Spinal Nerves connect all parts of the body to the spinal cord.
Visceral Nerves connect the spinal cord to the internal organs.
Functions of the Nervous System
The main function of a nervous system is the conduction and transmission of the nerve impulse.
Conduction and Transmission of Nerve Impulse
The information is carried in the form of a nerve impulse. It refers to any electrical, chemical, or mechanical disturbances created by a stimulus in a neuron. A nerve impulse is conducted across the synapse with the help of neurotransmitters.
A neuron is non-conducting. Its membrane is positive on the outside and negative on the inside. The resting potential of a neuron is 70 to 90. The membrane is thus said to be polarized.
Sodium-potassium pump operates to maintain the resting potential. The axon which is filled with axoplasm is immersed in the extracellular fluid. The sodium-potassium pump located on the membrane of the axon pumps 3 sodium ions from axoplasm to extracellular fluid and 2 potassium ions from extracellular fluid to axoplasm. The conduction is mediated by the enzyme Sodium-potassium ATPase.
When a stimulus is applied, the sodium ions start rushing inside and the potassium ions start rushing outside. This changes the permeability of the axon membrane and the pump stops operating. The resting potential inside the membrane is -70mV and the action potential is +30mV and the membrane is said to be depolarized. The action potential travels along the membrane and this is known as a nerve impulse.
After a certain time of action potential, the sodium-potassium pump operates again and the membrane of the axon gets repolarized by the resting potential.
Reflex Action and Reflex Arcs
Reflex action includes all the actions that are not under the control of our will. That means these actions are voluntary. For eg., sneezing, coughing, blinking, etc. It is an automatic response to a stimulus.
Reflex arc refers to the pathways taken by nerve impulses in a reflex action. There are two types of reflexes- spinal reflexes that involve only the spinal cord, and the cerebral reflexes that involve only the brain.
The sensory neurons transmit signals from the sensory organ to the relay neuron present in the spinal cord. These signals are sent back to the muscles through the motor neuron. The muscles attached to the sense organ move the organ away from danger.
Also refer Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
Hormones in Animals
The endocrine system in animals consists of endocrine glands and hormones . Hormones are chemical substances that are produced in the endocrine system and are responsible for passing signals/messages to different parts as a result of an occurrence in the body, which results in different parts reacting differently to the message from hormones. Not all cells in the body react to hormones, the cells who react are called target cells.
Functions of hormones in Animals
Ensures proper growth
Responsible to look after the maturing and development in a proper time frame
Makes sure reproduction happens at the right time
For instance, Thyroid secretes two hormones: Thyroxine (T4) and Thyronine (T3) which affects everyday metabolism.
Plants don’t possess the same organs and organ systems found in animals. However, they do have comparable systems to bring similar functions. Continue reading to know more about how plants bring about control and coordination in their systems.
Control and Coordination in Plants
Plants do coordinate, but in a different way than animals. Some plants are short, some are tall, some dense and some scanty. All these parameters are influenced by the presence of hormones called plant hormones. These hormones are also called phytohormones or Plant growth regulators. Phytohormones are responsible for control and coordination in plants. This movement is always in a controlled and organized environment.
Also read- Plant growth regulators
But if plants coordinate too, why are we not able to see any movement or change? This is because the response of plants to such reactions is practically too slow, slow to an extent that we see a change in plants may be weeks or months later. For example, once we stop watering a plant, it does not die or wither away in a day or two, it withers away after a fortnight or more.
Explore more information on Control and Coordination class 10 by visiting BYJU’S website. Alternatively, download BYJU’S app for further reference on any biology topics.
Further Reading

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
Wt is the importance of control and coordination? Pls give the direct ans for this
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case Study 1: Control and coordination are vital processes in living organisms that enable them to respond to their environment and maintain internal balance.In humans, the nervous system and the endocrine system work together to carry out these functions. The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, and it transmits signals through electrical impulses.
CBSE Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Control and Coordination. Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Control and Coordination. At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some ...
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Question 1: Read the case/passage and answer the questions given below. To carry out a simple function such as eating food there has to be coordination of the eyes, hands and the mouth. The eyes have to focus on the food, the hands … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and ...
The Case Based Questions: Control and Coordination is an invaluable resource that delves deep into the core of the Class 10 exam. These study notes are curated by experts and cover all the essential topics and concepts, making your preparation more efficient and effective.
B. VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS. Q.1. Name two specialised tissues that provide control and coordination in multicellular organisms. Ans. Nervous and muscular tissues. 2. Write the name and ...
Class Xth NCERT textbook covers control and coordination in-depth and with the help of the right study material, the student can understand the chapter in detail. Class 10 science chapter 7 notes, question banks, practice worksheets, and other study material provided by Educart, can significantly help in improving the exam preparation.
Control and Coordination Case Study Questions (CSQ's) Select the number of questions for the test: TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 10 Biology Control and Coordination chapter. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem-solving skills with expert advice.
Chapter 7 of Science NCERT Solutions for Class 10 explains some of the important hormones and their functions. Concepts were explained with a clear diagram showing the location of different glands in the human body and a table on the functions of different glands. Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Exercise 1.1 solution.
The Class 10 NCERT Solutions for Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination includes all the intext and exercise questions. Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination NCERT questions and answers help students to clear their doubts and to obtain good marks in Class 10 board exam. All the solutions provided in this article are strictly ...
Control and Coordination Class 10 Solutions perfectly follow these guidelines and also present the answers in a way that automatically grabs the teacher's attention. These solutions are accurately crafted by subject matter experts and based on CBSE instructions; hence students can easily rely on these while preparing for their exams.
An organism needs control and coordination system for the following functions : (i) To save the body of the organisms from the harmful changes in the environment. (ii) To control the speed of voluntary and involuntary actions. (iii) To have the capability to think and learn for responding to any stimuli. Question 10.
CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter-wise Notes. Chapter 1- Chemical Reactions and Equations Notes. Chapter 2- Acids, Bases and Salts Notes. Chapter 3- Metals and Non-Metals Notes. Chapter 4- Carbon and Its Compounds Notes. Chapter 5- Periodic Classification of Elements Notes. Chapter 6- Life Processes Notes.
FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 7 - Control and Coordination 2023-24. 1. Explain the nervous system according to Chapter 7 of Class 10 Science. The nervous system is considered to be the most complex part of the body. The main function of the nervous system is to transmit signals to and from different parts of the ...
In other words, living organisms must use systems providing control and coordination. In keeping with the general principles of body organisation in Multicellular organisms, specialised tissues are used to provide these control and coordination activities. (i) Coordination is needed for all human activities like, thinking and behaviour.
Answer. → Control and Coordination in animals is done with the help of two main systems: (i) Nervous system. (ii) Endocrine system. 3. Nervous System. Answer. → Control and coordination are provided by nervous and muscular tissues. → Nervous tissue is made up of an organized network of nerve cells or neurons which is specialized for ...
Control and Coordination Extra Questions Short Answer Type. Question 1. Define a synapse. Answer: Synapse is a very fine gap between telodendria of axon of one neuron and dendrites of another neuron. These two structures do not unite with each other but remain separated by a fine gap. Question 2.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination In-Text Exercises are provided below, in detailed and free to download PDF format. The solutions are latest, comprehensive, confidence inspiring, with easy to understand explanation.To download NCERT Class 10 Solutions PDF for Free, just click ' Download pdf '.
Students can access the Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination by downloading the pdf provided below. The pdf contains the important questions of Chapter 7, Control and Coordination, which are more likely to be asked in the board exam. Students are advised to go through these questions to prepare them well ...
This article deals with control and coordination class 10 notes. Control and Coordination is the seventh chapter of CBSE Class 10 Science. First of all, we all know that the indication of being alive is that if something moves. Moreover, some of these movements are due to the result of growth. For example, when a seed germinates and grows, it ...
Answer: (i) Spinal cord is protected with the help of the vertebral column. (ii) Brain is protected due to presence of a bony cavity which we call as skull in which brain is placed. This bony cavity is filled with a fluid which absorbs the shock and thus prevents the damage that may be caused to brain. Important Questions for Class 10 Science ...
Question 18: Name two tissues that provide control and coordination in multicellular animals. Answer: The two tissues that provide control and coordination in multicellular animals are nervous and muscular tissues. Question 19: (i) Name the hormones that are released in human males and females when they reach puberty.
The nervous system consists of nerve fibres and nerve cells which transmit impulses of the nerve between different parts of the body. It is a system found in animals that synchronizes its functions by passing signals to and from different parts of the body. It is brought about by the nervous system after it detects any physical response on any ...