- English Grammar
- English Tenses
- Present Tense
- Present Continuous Tense

Present Continuous Tense - Meaning, Definition, Formula, Uses, Structure with Examples
Are you wondering how the present continuous tense can be used? Well, fret no more. You just came across a sentence with the present continuous tense. In this article, you will learn all that you need to know about what the present continuous tense is, its definition, uses, structure and rules of usage. Along with these, with the examples and practice questions, you will surely be able to use the frame sentences using the present continuous tense accurately.

Table of Contents
Definition of the present continuous tense, structure of the present continuous tense, rules and points to remember when using the present continuous tense, uses of the present continuous tense, 10 sentences using the present continuous tense, test your understanding of the present continuous tense, frequently asked questions on present continuous tense, understanding the present continuous tense.
The present continuous tense, as the name suggests, is the form of tense that is used to denote an action that is ongoing or occurring in that current moment. It is also referred to as the present progressive tense as they represent the action that is progressing in the present. Let us now take a look at the definitions provided by various dictionaries about the present continuous tense.
The Cambridge Dictionary defines the ‘present continuous tense’ as “the verb form used for actions or events that are happening or developing now.” According to the Collins Dictionary, the present continuous tense is defined as “a verb form consisting of an auxiliary be in the present tense followed by a present participle and used especially to indicate that a present action or event is in progress, being repeated, or of a temporary nature or to express the future.” The present continuous tense is “the tense used to talk about actions or behaviour that are in progress now or planned for the future”, according to the Macmillan Dictionary.
There is definitely just one formula to mastering the present continuous tense and this is how it goes.
However, there is something more you should pay attention to. You should also learn how the sentences with the present continuous tense form of the verb are structured when they are positive, negative, interrogative and negative interrogative.
Have a look at the table given below to have a deeper understanding of the structure of the present continuous tense.
When using the present continuous tense, make sure you follow the sentence structure exactly.
- Always start with the subject when it is a positive or negative sentence and with the helping verb when it is in the interrogative format.
- A sentence with the present continuous tense consists of a helping verb (‘to be’ form of verbs) and a main verb . The helping verbs can be ‘am’ for the pronoun ‘I’, ‘is’ for singular subject and ‘are’ for a plural subject.
- Just note that like the other pronouns, the pronoun ‘am’ cannot be used in the negative form in an interrogative sentence. Instead of ‘amn’t’, ‘aren’t’ is used.
For example:
- Amn’t I reading a newspaper? Wrong
- Aren’t I reading a newspaper? Correct
- The present continuous tense can never be used with stative verbs .
Like the simple present tense , the present continuous tense is also generally used to talk about an action that is taking place in the present. The only difference is that it denotes an action that is continuing to happen or progressing at the current moment.
Take a look at the following points that elaborate on the more specific uses of the present continuous tense.
- It is used to represent an action that is happening or progressing in the moment that the speaker is speaking.
- My son is working on his science project.
- Santana is singing Don’t Rain on my Parade.
- It is used to depict a future event or arrangement.
- What are you planning to do tomorrow?
- I heard that Rachel is moving to Paris next month.
- It is used to denote an action that is going on or continuing at the time of speaking.
- Is she still working at the National Institute of Medical Sciences?
- I am currently taking guitar lessons so that I could play for your wedding.
Examples of Present Continuous Tense
Going through more and more examples can only make you an expert in the particular subject or topic. So , here you go. Check out the examples of sentences using the present continuous tense given below.
- My mom is cooking dinner.
- The band is playing all the classics.
- Monica and Rachel are going on a trip tomorrow.
- Sheethal is not practising for the final audition.
- I am trying out something new.
- They are not travelling to London next week.
- Are you watching a movie tonight?
- Is your phone working properly now?
- The children are loving the new park.
- Diana is playing the main role in the play.
Having gone through all the given examples, you should have understood really well. Check your understanding of the present continuous tense by filling in the blanks in the following sentence with the right form of tense using the verbs given in the brackets.
1. ______ the clock ________ (work)?
2. The teachers ___________ (plan) to dance to all the latest songs on Childrens Day.
3. ______ she ___________ (play – negative) the piano anymore?
4. The dog __________ (run) all around the garden.
5. We ____________ (go – negative) to the party tomorrow.
6. The Bellas ___________ (perform) the songs of the 80s.
7. Will, Smith and Sherlock ___________ (dance) well.
8. _______ I __________ (look) good today?
9. Trinita and Vinitha ____________ (ride) on their new cat.
10. _____ he still ________ (stand) there?
Ready to see if you got it all right. Check out the answers given below.
1. Is the clock working ?
2. The teachers are planning to dance to all the latest songs on Childrens Day.
3. Is she not playing the piano anymore?
4. The dog is running all around the garden.
5. We are not going to the party tomorrow.
6. The Bellas are performing the songs of the 80s.
7. Will, Smith and Sherlock are dancing well.
8. Am I looking good today?
9. Trinita and Vinitha are riding on their new cat.
10. Is he still standing there?
What is the present continuous tense?
The Present Continuous Tense, as the name suggests, is the form of tense that is used to denote the action that is ongoing or occuring in that current moment. It is also referred to as the present progressive tense as they represent the action that is progressing in the present.
What is the definition of the present continuous tense?
What is the formula to be followed when using the present continuous tense.
The formula to be kept in mind and used when writing or speaking a sentence in the present continuous tense is as follows: Subject + am/is/are + present participle (verb+ing) + the rest of the sentence
Give some examples of the present continuous tense.
Here are a few examples to show you how the present continuous tense is used.
What are the uses of the present continuous tense?
The present continuous tense can be used to talk about an action that
- is happening or progressing in the moment that the speaker is speaking.
- depicts a future event or arrangement.
- is going on or continuing at the time of speaking.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- English Grammar
- Present tense
Present continuous
Level: beginner
The present continuous is made from the present tense of the verb be and the –ing form of a verb:
We use the present continuous to talk about:
- activities at the moment of speaking :
I 'm just leaving work. I'll be home in an hour. Please be quiet. The children are sleeping .
Matching_MTYyNzM=
GapFillTyping_MTYyNzQ=
- future plans or arrangements:
Mary is going to a new school next term . What are you doing next week ?
Plans for next month
2nd (Sat.) – my birthday. Party! 4th – day off 10th (Sun.) – flight OS462 15.40 11th, 12th, 13th – conference, Vienna 15th – dentist 3 p.m. 22nd – Mum & Dad arrive, evening 23rd – Toni's Restaurant (make reservation!) 25th – Mum & Dad > home 29th – payday
TrueOrFalse_MTYyNzU=
GapFillTyping_MTYyNzY=
Present continuous questions
We make questions by putting am , is or are in front of the subject :
Are you listening? Are they coming to your party? When is she going home? What am I doing here?
ReorderingHorizontal_MTYyNzg=
GapFillTyping_MTYyNzk=
Present continuous negatives
We make negatives by putting not (or n't ) after am , is or are :
I 'm not doing that. You are n't listening. (or You ' re not listening. ) They are n't coming to the party. (or They ' re not coming to the party. ) She i s n' t going home until Monday. (or She 's not going home until Monday. )
GapFillDragAndDrop_MTYyODA=
GapFillTyping_MTYyODE=
Stative verbs
We do not normally use the continuous with stative verbs . Stative verbs include:
- verbs of thinking and feeling :
- verbs of the senses:
We normally use the simple instead:
I understand you. (NOT I am understanding you. ) This cake tastes wonderful. (NOT This cake is tasting wonderful. )
Level: intermediate
We also use the present continuous to talk about:
- something which is happening before and after a specific time :
At eight o'clock we are usually having breakfast. When I get home the children are doing their homework.
- something which we think is temporary :
Michael is at university. He 's studying history. I 'm working in London for the next two weeks.
- something which is new and contrasts with a previous state:
These days most people are using email instead of writing letters. What sort of clothes are teenagers wearing nowadays? What sort of music are they listening to?
- something which is changing, growing or developing:
The children are growing up quickly. The climate is changing rapidly. Your English is improving .
- something which happens again and again :
It 's always raining in London. They are always arguing . George is great. He 's always laughing .
Note that we normally use always with this use.
Matching_MTYyNzc=
Level: advanced
We can use the present continuous to talk about the past when we are:
- telling a story :
The other day I 'm just walking down the street when suddenly this man comes up to me and asks me to lend him some money. Well, he 's carrying a big stick and he looks a bit dangerous, so I 'm wondering what to do …
- summarising a book, film or play:
Harry Potter is a pupil at Hogwarts school. One day when he is playing Quidditch he sees a strange object in the sky. He wonders what is happening …
Hello teachers,
Is this sentence 'She is very careful' called a nominal sentence?
And if I want to use the sentence in present progressive form, which one is correct "She is very careful" or "she is being very careful"? Do they have different meanings?
Thank you very much in advance.
- Log in or register to post comments
Hi Risa warysha,
No, it's not a nominal sentence. It's a verbal sentence, because it includes a finite verb ("is"). A nominal sentence has no finite verb (e.g. The faster, the better. / How interesting! )
About your second question, they are both correct. Yes, they have different meanings. "She is being very careful" means that she is doing the current action carefully (but it does not say anything about whether she is generally careful or not, in other actions). On the other hand, "She is very careful" is about her actions in general.
I hope that helps.
LearnEnglish team
Can I say " She is lazy." for present progressive form because I think that "be" is a state verb?
And can I also say "She has been busy for the last 2 weeks." instead of "She has been being busy for the last 2 weeks."?
"Be" is a state verb, that's right. "She is lazy" is a perfectly good sentence but it's a present simple sentence, not the present progressive, because the present progressive is formed by be + - ing verb. The present progressive would be "She is being lazy", which also means a state but a temporary one, as mentioned above.
About your second question, it's very unusual to say "been being busy". The present perfect "She has been busy" already indicates a state that is temporary.
Hi Peter 1- can I use adverbs of frequency with Present continuous for ( temporary and changing, growing or developing and around now )
OR just I can use adverbs of frequency with Present continuous for (before and after a specific time and again and again ) ?
2- Is this grammatical or informal ? I use Present simple for future with (Instructions and directions) ? example - where do I pay ? - You take the train into the city centre and then you take a number five bus
Re: 1, if I understand you, I'd say adverbs of frequency aren't generally used with these meanings. But could you please give some specific examples? Just so we can be sure that we're talking about the same thing.
Re: 2, yes, these sentences are good examples of the present simple for instructions or directions. I wouldn't say there's any future sense here because in general, instructions were valid in the past, are valid now, and will be valid in the future.
All the best, Kirk LearnEnglish team
why my answers consider wrong i put is not instead of isn't . well does't they consider the same thing ?
Hi ashley_20,
Yes, right! "Is not" is the same as "isn't".
But if you are looking at the exercise "Present continuous negatives 2", the instruction says: Use contractions . That's why only "isn't" is accepted.
Why use "- ing" in this sentence? I usually say "I'll go...". How does "- ing" work?
Shall I pick up the laundry for you? Oh, no, don’t make a special journey. It’s OK. I'll be going to the shops anyway.
Hello again Jembut,
The form 'will be verb-ing' is often used when an action is seen as part of our day's itinerary. It's a little less formal than some other forms and is quite common in speech.
The LearnEnglish Team
I don't get the: "something which happens again and again". Isn't Present Simple the tense which we use to phrase repetitive, routine actions?
Hello Prodykcja,
You are right in thinking that we generally use the present simple to talk about routine actions. If we use the present continuous to talk about habitual actions, another layer of meaning is added.
Typically, it's one of two or three additional meanings. First, it can show that we're thinking of actions that continue for a specific period of time. For example, if you ask me to go running with you at 7 p.m., I might say, 'I'm sorry, but I'm just getting home from work then. I can't.' The specific period of time is the time it would take to go for a run starting at 7 p.m. Note that in this case, I could also answer using the present simple, but using the present continuous shows I'm not thinking so much of a schedule as what I'm normally doing at that time. This is not particularly important most of the time; it's more just how people sometimes think.
The second additional meaning the present continuous can express is an attitude of annoyance. We very often use time adverbials such as 'always' and 'all the time' when we want to express this meaning. The sentences in the explanation above are good examples of this.
The third (though not necessarily last) meaning expresses some kind of change. For example, let's say that for years your brother has had the habit of going running two days a week. Now he is training for a marathon, so you could tell your friends 'He's running every day now'.
As I've mentioned, there are other possible meanings -- you can see more on our Continuous aspect page -- but I'd say these are the most common ones.
Best wishes, Kirk LearnEnglish team
Hi, I learned that we can use the present continuous with some state verbs, but most of the time, those verbs describe ‘actions’ rather than ‘states.’ However, there is one example that baffles me, it is ‘Ella’s with us at the moment. The children are loving having her here.’ The state verb here describes emotion rather than action. And there is an explanation that the state verb in the aforementioned sentence emphasizes the situation for a period of time around the present. But, I am still confused about that. I think the present simple would be more proper, it should be ‘Ella’s with us at the moment. The children love having her here.’
Would you mind giving me further explanation about this case? As what I have been taught was that the state verb without ‘action’ meanings should be used in present simple to describe the states or feelings which are true at present.
Hello Bao Quach,
You certainly could use the present simple here, and there's really very little difference between the simple and continuous forms in this case. The use of continuous aspect here is very subjective and can communicate different things.
It could, for example, show that the speaker is trying to emphasise the temporary nature of the event, or it could be that it surprises her -- perhaps she expected the children not to enjoy having Ella at home. In this case, it would also be possible to use the simple 'don't like having her here' too, so it could again be a more emphatic way of saying it.
The continuous form is less matter-of-fact. If it were a simple observation about the children that isn't particularly important, the simple form would be the form the speaker would undoubtedly use. The fact they use the continuous form adds a more emotional or subjective flavour. I know that's very abstract, and I hope it's not confusing! It really depends on the speaker's intentions (which of course I don't know) and is difficult to describe.
But I hope that helps a little.
Thank you so much for your clear and insightful explanation; it helps a lot.
I have heard people say "I'm agreeing with you" or "I'm disagreeing with you". The word "to agree" or "to disagree" is a stative verb. Why is it used with the progressive?
Hello Selet,
As you say, these words are usually stative. However, if a person is in the middle of speaking and is interrupted then they might use them in a progressive form. For example:
John: I thought that film was really boring!
Sue: She's a really good director...
John: I know you'd argue!
Sue: Let me finish - I'm actually agreeing with you here! I was going to say that she's a really good director but this was a really bad film, not like her at all.
In a context like this the progressive is possible.
Can I ask a question using the question word "how long" in present continuous? How long are you doing this? Or How long have you been doing this? Which one would be correct?
Hello renu,
There might be a particular context in which the first sentence (with present continuous) is possible, but in general it's not correct. If you see someone doing something that they started doing sometime in the past, generally speaking 'How long have you been doing this?' is the correct question because we use this tense to speak about something that began in the past and is still relevant to the present.
This is a challenging point for many people learning English.
Can I mention a long period with the present continuous example this company is working in air port for 100 years
this company is working now
No, if you want to say for 100 years (or for + any time period), it should be the present perfect continuous: This company has been working in the airport for 100 years . You can read more about this on our Present perfect continuous page (linked) . I hope you find it useful.
I'm reading a book about AI. This sentence doesn't necessarily mean I'm reading the book at the moment of speaking, Could you check this pls?
Hi Khangvo2812,
Yes, that's right. We understand "reading a book" as an activity that can stop and start, but still all be the same activity. This includes at the moment of speaking. Even if you are not reading the book right now, if you have already started reading it and you intend to continue reading it in the future, then you can still say "I'm reading the book".
Hello, Sir! I wanted to know if the word "now" can be used with the present simple (excluding state verbs). I found an exercise where,I think, the options should have contained the present continuous form: - Melissa......... in a very busy office now. A. works B. has worked C. was working The answer is A (works). I think the sentence is about the action happening now. I was wondering why the present simple is used here. Thank you very much for your time. Best Wishes!
Hello Sokhomkim,
It's fine to use the present simple here provided you are describing a change to a permanent (or long-term) state. For example:
1. Melissa used to live in London, but now she lives in Madrid. 2. Melissa was living in London, but now she's living in Madrid.
The first sentence describes a change in Melissa's permanent/stable home; the second a change in her temporary living location.
I got it. Thanks you so much for your time, Sir. :)
Good morning teachers
When writing a sentence with for example “always, constantly, continually, forever” it means that something is irritating about the other people and more than normal? And can I use this form with “I”?
For example: A) My son is always staying up late. (Irritating for me and more than normal) B) My daughter is constantly studying. ( it is not irritating for me, but it’s more than normal)
C) I am forever losing my keys. (Irritating and more than normal)
Moreover, can I use this form to indicate an irritating behavior even if it doesn’t happen more than normal? For example: A) He is always play on his phone.( not more than normal, but irritating me)
So, these sentences are fine? Also, can I use other adverbs like(often, sometimes ) to give the same idea of always, forever and the other adverbs of this kind(always, constantly, endlessly…etc).
Thank you for your help and patience.
Hello khaledAl5,
The present progressive with always (forever, constantly etc) is often used for irritating habits but it can be used in other ways too. For example, it can be used to show something we find endearing or worrying as in your example B. It's context-dependent, of course, and the tone of voice or comments like 'it's so funny' signal the speaker's intent.
It's fine to use this form in the first person. Your example is a very good one.
Other adverbs of frequency like often, sometimes and so on are used with simple aspect rather than progressive. They don't have the same suggestion of impatience or irritation.
Hi, could you elucidate further about present continuous can be used for something which is happening before and after a specific time?
Hi nadiayunos,
For example, if you say:
At eight o'clock we are usually having breakfast.
It doesn't mean that the action happened only at eight o'clock, lasting for that moment only. The idea is that the action is ongoing at that specific moment - it started some time before eight o'clock, and went on after that moment.
Does that make sense?
Hello! I'm a bit confused with the irritating meaning of present continuous. Would you be so kind to explain these situations: 1. We can use always and some other words like constantly or continuously when we want to express irritation, but can we use words like never, rarely etc. ? 2. How can I express that someone doesn't do their homework using present continuous? Would it be correct to say 'You are always doing no homework!' or 'You are always not doing your homework!'?
Hello msh4x,
As far as I'm aware, this use of the present continuous is only used in the affirmative, not the negative. I certainly can't think of an example with 'never' or 'rarely' that sounds right to me.
The best form to use in general is the present simple. The present continuous is used when the action we're talking about is happening around the time of speaking, or at least the situation being described has just been discussed or is somehow relevant now.
Given all this, I'd recommend 'You never do your homework!' If you really wanted to use a continuous form, you could change it a bit and say something like 'You're always coming up with excuses for not doing your homework!'
Hope this helps.
Good point. One very common way we would express that meaning would be “You keep forgetting to”. You keep missing deadlines. You keep forgetting to turn in the work. You keep neglecting to do it. Etc.
Hi. I want to know the difference between: He don't play golf now. He is not playing golf now. Are both correct? or just one of them? Why?
Hi Darelia_1325,
The first sentence should be He doesn't play golf now (not don't).
We use the present simple ( He doesn't play... ] to describe habits. For example, I can say about myself that I go running . It doesn't mean I'm running right now but rather that running is my hobby - I do it regularly.
We use the present continuous ( He isn't playing ) to describe an activity right now. For example, I can say about myself that I am typing on my computer . It's what I am in the middle of right now.
Both sentences are possible:
He doesn't play golf now means that it was his hobby in the past but it's not his hobby any more.
He is not playing golf now means that he's doing something else - maybe he's at work or maybe he's driving his car.
He doesn’t play golf now = This is not a routine he has now. He no longer does this activity. He used to play golf but he doesn’t play any more because he has other hobbies or he isn’t able to play any more etc. But: “He is not playing golf now”” = He is not playing golf at this moment. For example “Can he come to the phone or is he playing golf?” “No, he isn’t playing golf. I will get him for you.” Do/Does play” is the simple present tense and describes routines or general facts. “Be + playing” is progressive and means at the moment/in progress.
Hello! It’s mentioned above that “We do not normally use the continuous with stative verbs”.
I thought I’d seen some words being used in that sense.
I don’t have the exact examples at the moment, but I strung some sentences together to show what I mean. I use the verbs ‘love’, ‘hate’, and ‘smell’.
• I’m loving it (LOL it’s McDonald’s but apart from that, I feel I’ve seen structures like this, as in, “I am not loving this moment right now”. • I’m hating this too much now to process any rational thoughts. • I was smelling the flower before a bee emerged from it and stung me.
Please advise, thank you!
Hello Elle_Y,
Yes, the explanation says 'normally' because there are exceptions. If you read through the comments below, you'll see many people have asked about this. Please have a look through the first few pages; I think our responses there should answer your questions. If not, please feel free to ask us again.
Yes, there are exceptions. We sometimes use stative verbs in the progressive to emphasize a currently changing or developing condition. For example: Kids grow fast. (General fact.) But “The kids are growing so fast!” Or “She often feels sick after eating sweets. (General or habitual condition.) But “I’m feeling a bit sick” emphasizes a change. “He is a bit temperamental.” (General routine or habit.) He is being especially difficult today. (Emphasizes deliberately acting in a particular way at the moment.)
We are not running tomorrow morning. Is that phrase right? If yes, could you explaing?
Hello Izabely Graebin,
Yes, that can be correct. If you regularly go running with a friend every morning, for example, then you could say this.
We very often use the present continuous to speak about future events that we've made some agreement or arrangement about. You can see more about this on our Talking about the future page, which explains the verb forms we use to speak about the future and their differences in meaning.
Hello,Sir. I was wondering if the sentence is right. e.g., More roads are being built every year. (Is it possible to use this sentence to talk about a process of changing?) Thank you for your precious time. Best Wishes!
Hello KimKH,
Yes, that sentence is perfect!
Hi guys. I have heard that the Present Continuous tense has way more importance in its action than the Present Simple tense regarding the speaker. Do you know why?
Hello leo15722,
I'm afraid I don't really understand what that statement means. I'm not saying it's wrong, but without understanding it or seeing an example of it, I don't know what to say!
All the best, Kirk The LearnEnglish Team
Hello sir, I have found this lesson very interesting and useful one?
I have come across a sentence in this lesson, "When I get home the children are doing their homework". I I'm finding it a bit difficult to understand.
Please explain whether that sentence implies: -
a) Routine action: Every day I get home (say from work), I found the children to be engaged in their homework or b) Regular action : On a particular day, whenever I get home (say I come to home multiple times may be from office, market etc), every time I found the children to be engaged in their homework. b) One-time action: On a particular day, when I get home (from work), I found the children to be engaged in their homework.
Mohit Gupta
Hello ismmohit,
Without any other information I would say that the correct interpretation is (c): the sentence tells use what the situation is at the time I get home on a particular occasion. It could be (b) if there was some other indication in the context such as an adverb (always, generally, typically etc).
Thanks a lot for your prompt response. Now, the meaning is clear to me but I still wonder when to use this sentence. Like we can use this sentence while telling a story or summarizing a book etc but other than that I haven't been able to figure out its usage.
I feel we can use its past form: "When I got home the children were doing their homework" or future form "When I get home the children will be doing their homework" more frequently.
What's your opinion on its usage?
Hello again,
It's very hard to say when the sentence is in isolation like this. It could be a present form used for a narrative, which is quite common in anecdotes and when relating stories informally, or it could be a typical action as I said. The verb forms have their normal meanings here, so the continuous aspect suggests something in progress etc.
Hi! That how I know if an action happens regulary, we use present simple, so in the following sentence given as an example: At eight o'clock we are usually having breakfast. Why is present continuous used?
Online courses

Group and one-to-one classes with expert teachers.

Learn English in your own time, at your own pace.

One-to-one sessions focused on a personal plan.

Get the score you need with private and group classes.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Present Continuous Tense | Examples & Exercises
Published on July 10, 2023 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on September 29, 2023.
The present continuous (also called the present progressive ) is a verb tense used to refer to a temporary action that is currently taking place. It can also describe future plans (e.g., “I am throwing a party next week”).
The present continuous is formed by combining a form of the auxiliary verb “be” with the present participle (“-ing” form) of another verb (e.g., “I am swimming”).
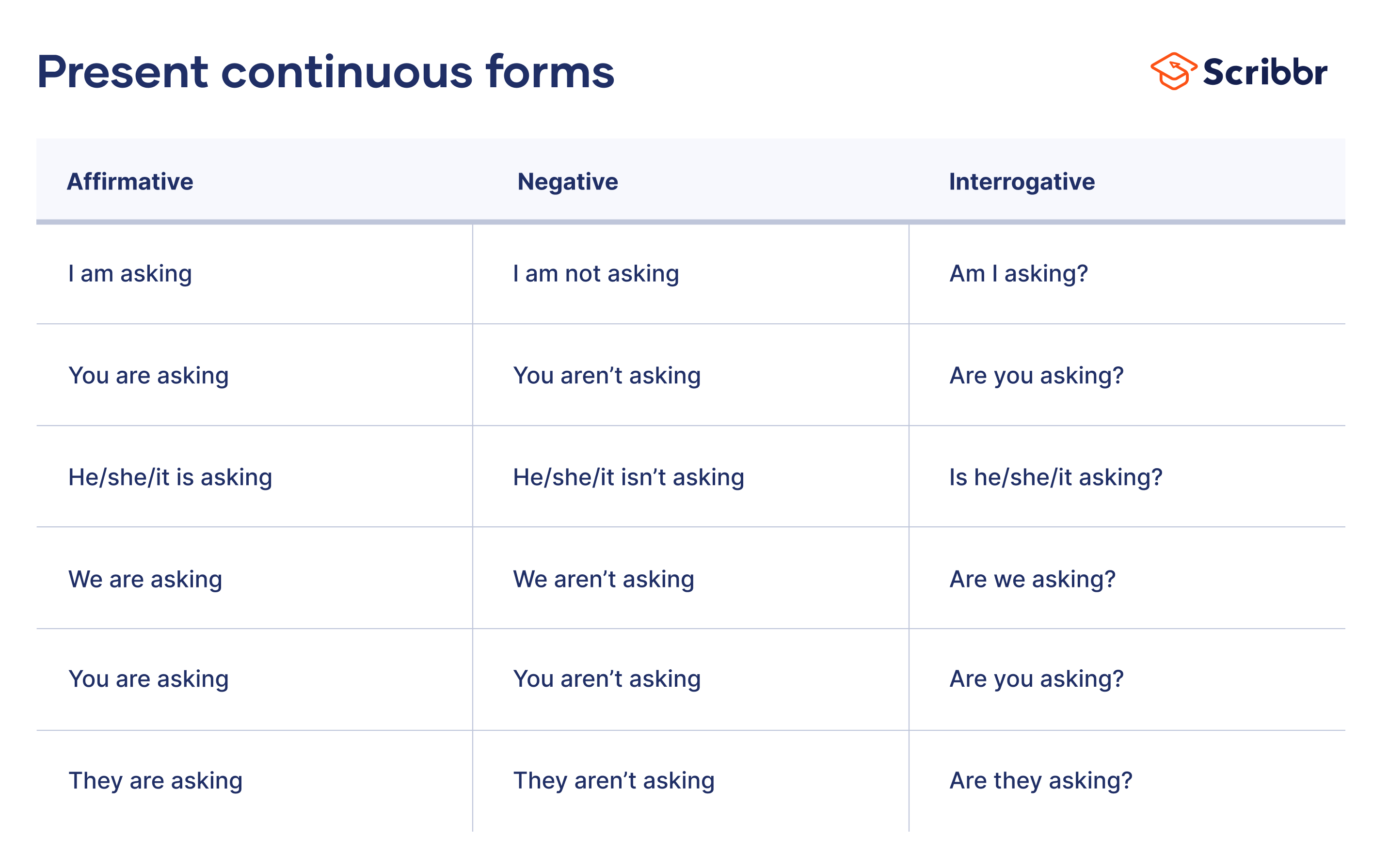
Table of contents
How to use the present continuous, when you shouldn’t use the present continuous, present continuous vs. present simple, present continuous vs. present perfect continuous, how to form negatives, how to form questions, how to form the passive voice, exercises: present simple vs. present continuous, other interesting language articles, frequently asked questions about the present continuous tense.
The present continuous uses different forms of the verb “be” depending on the person of the subject. The first person uses “am” the third person singular uses “is,” and all other persons use “are.” The verb is often contracted with the subject (e.g., “I’m,” “she’s,” “we’re”). The form of the other verb doesn’t change; it’s always the present participle (“-ing” form).
The present continuous describes an action or process that is ongoing (continuous). It is most commonly used to talk about actions that are currently happening and about future plans and intentions .
I am flying to Germany in three weeks.
We are investigating a crime.
There are also some other contexts where you may encounter the present continuous. It can be used to:
- Describe some new trend or development that differs from a past state
- Describe a process of change over time
- Emphasize (in combination with the adverb “always”) that something happens over and over again
My ankle is slowly recovering from a sprain.
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
You may have noticed that all the verbs used in the present continuous tense in the examples above describe an action or process—these are called dynamic verbs . The present continuous tense normally requires a dynamic verb.
Verbs that instead describe a state of being such as emotion, belief, perception, or possession are called stative verbs . Some examples include “prefer,” “appear,” “exist,” and “own.” Stative verbs should not be used in the present continuous tense.
- I am believing that love at first sight is existing .
- I believe that love at first sight exists .
- I am owning many books.
- I own many books.
Note that some verbs can be either stative or dynamic, depending on the specific sense in which they are used.
For example, the verb “think” may describe a fixed opinion or belief (in which case it’s stative) or a process of thought or consideration (in which case it’s dynamic).
- I am thinking that Rajit will arrive tomorrow.
- I think that Rajit will arrive tomorrow.
- I think about going for a bike ride at the weekend.
- I am thinking about going for a bike ride at the weekend.
If you’re unsure whether to use the present continuous (e.g., “is running”) or the present simple (e.g., “runs”) in a sentence, apply the following rules:
- To describe something that’s in the process of happening right now , use the present continuous .
- To describe a habit , general truth , or fixed situation or state , use the present simple .
I am good at math.
Toby is looking at the clouds.
When describing events in the near future, the two tenses can often be used interchangeably, but there are still some distinctions:
- The present continuous refers to an action someone is about to perform or to a future event or plan (not necessarily very specific or clearly defined).
- The present simple refers to a clearly defined and official plan for the (near) future or to a regularly scheduled event that will repeat in the future.
The party officially starts at 5:30 p.m., but some of us are meeting for drinks beforehand.
Another tense that’s sometimes confused with the present continuous is the present perfect continuous (e.g., “has been writing”). These tenses should not be used interchangeably.
Like the present continuous, the present perfect continuous also typically refers to an action that is currently ongoing. But there are two key differences that distinguish it from the present continuous:
- It emphasizes the fact that a current action extends into the past and is often used alongside an adverbial phrase that specifies when the action started (e.g., “since July” or “all week”).
- It can also refer to a completed action , as long as it was completed only recently .
It has been raining all day, but it just stopped.
You can create a negative statement in the present continuous by inserting the adverb not between the two verbs. The adverb is often contracted with the first verb (as “aren’t” or “isn’t”), but this is not done in the first person (“amn’t” is not a word in standard English).
Paulus isn’t paying attention to the teacher.
Yes–no questions are formed in the present continuous by placing the auxiliary verb (“is,” “are,” or “am”) first, followed by the subject and then the present participle (“-ing” verb).
Other kinds of questions are formed using wh-words ( interrogative pronouns such as “who” and interrogative adverbs such as “why”). Follow the same word order as above, but with the wh-word added at the start of the sentence.
Why am I worrying about things I can’t control?
The passive voice creates a sentence in which the subject is not the person or thing carrying out an action, but rather the person or thing being acted upon.
In the present continuous, the passive voice consists of the subject , a form of “be” (“is,” “are,” or “am”), the present participle “being,” and finally the past participle of the verb describing the action.
My house is being renovated next week.
Test your understanding of the difference between the present simple and the present continuous with the exercises below. Fill in one of the two options in each sentence.
- Practice questions
- Answers and explanations
- I _______ every morning before work. [run/am running]
- Kevin _______ the kitchen right now. [cleans/is cleaning]
- Humans _______ about 12 times per minute. [blink/are blinking]
- The train _______ at 12 p.m. every day. [leaves/is leaving]
- Allie _______ at the moment. [studies/is studying]
- “Run” is correct. In this instance, the present simple is used to refer to a habit.
- The present continuous form “is cleaning” is correct because it refers to a temporary action in the present.
- The present simple form “blink” is correct. In this instance, it’s used to express a fact.
- The present simple form “leaves” is correct. In this instance, it’s used to refer to a planned future event.
- The present continuous form “is studying” is correct because it refers to a temporary action that is currently taking place.
If you want to know more about nouns , pronouns , verbs , and other parts of speech , make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations and examples.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Possessive nouns
- Indefinite pronouns
- Relative pronouns
- Interrogative pronouns
- Present perfect tense
- Modal verbs
- Conditional sentences
- Subjunctive mood
- Imperative mood
- Interjections
- Determiners
- Prepositions
The “-ing” form of a verb is called the present participle . Present participles can be used as adjectives (e.g., “a thrilling story”) and to form the continuous verb tenses (e.g., the present continuous : “We are partying ”).
Gerunds also use the “-ing” form of a verb, but they function only as nouns (e.g., “I don’t enjoy studying ”).
We use the present continuous tense (also called the present progressive ) to describe a temporary action that is currently occurring (e.g., “I am gardening right now”) or sometimes a planned future event (e.g., “We are traveling to Greece this summer”).
It’s used differently from the simple present , which instead indicates a habit (e.g., “I garden on Tuesdays”), a general truth (e.g., “Bears hibernate in the winter”), or a fixed situation or state (e.g., “She speaks French and German”).
In the simple present tense , the stative verb “be” is used to describe temporary present situations (e.g., “I am tired”) and unchanging situations (e.g., “Laura is a doctor”). The form of the verb varies depending on the subject:
- The first person singular uses “am” (e.g., “I am”)
- The third person singular uses “is” (e.g., “he is,” “she is,” “it is”)
- All other subjects use “are” (e.g., “you are,” “we are,” “they are”)
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, September 29). Present Continuous Tense | Examples & Exercises. Scribbr. Retrieved March 29, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/verbs/present-continuous/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, simple present tense | examples, use & worksheet, what is a present participle | examples & definition, present perfect tense | examples & use, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Verb Tense Intro.
- Types of Verbs
- Active/Passive
- Simple Present
Present Continuous
- Simple Past
- Past Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perf. Cont.
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Cont.
- Simple Future
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect
- Future Perfect Cont.
- Would Always
- Future in the Past
The present continuous (also called present progressive) is a verb tense which is used to show that an ongoing action is happening now, either at the moment of speech or now in a larger sense. The present continuous can also be used to show that an action is going to take place in the near future. Read on for detailed descriptions, examples, and present continuous exercises.
Present Continuous Forms
The present continuous is formed using am/is/are + present participle . Questions are indicated by inverting the subject and am/is/are . Negatives are made with not .
- Statement: You are watching TV.
- Question: Are you watching TV?
- Negative: You are not watching TV.
Present Continuous Uses
Use the present continuous with normal verbs to express the idea that something is happening now, at this very moment. It can also be used to show that something is not happening now.
- You are learning English now.
- You are not swimming now.
- Are you sleeping ?
- I am sitting .
- I am not standing .
- Is he sitting or standing ?
- They are reading their books.
- They are not watching television.
- What are you doing ?
- Why aren't you doing your homework?
USE 2 Longer Actions in Progress Now
In English, now can mean different things: this second, today, this month, this year, this century, and so on. Sometimes, we use the present continuous to say that we are in the process of doing a longer action which is in progress; however, we might not be doing it at this exact second.
Examples: (All of these sentences can be said while eating dinner in a restaurant.)
- I am studying to become a doctor.
- I am not studying to become a dentist.
- I am reading the book Tom Sawyer.
- I am not reading any books right now.
- Are you working on any special projects at work?
- Aren't you teaching at the university now?
USE 3 Near Future
Sometimes, speakers use the present continuous to indicate that something will or will not happen in the near future.
- I am meeting some friends after work.
- I am not going to the party tonight.
- Is he visiting his parents next weekend?
- Isn't he coming with us tonight?
USE 4 Repetition and Irritation with Always
The present continuous with words such as always or constantly expresses the idea that something irritating or shocking often happens. Notice that the meaning is like simple present , but with negative emotion. Remember to put the words always or constantly between be and verb+ing .
- She is always coming to class late.
- He is constantly talking . I wish he would shut up.
- I don't like them because they are always complaining .
Present Continuous Tips
Remember non-continuous verbs / mixed verbs.
It is important to remember that non-continuous verbs cannot be used in any continuous tenses. Also, certain non-continuous meanings for mixed verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses. Instead of using present continuous with these verbs, you must use simple present .
- She is loving this chocolate ice cream. Not Correct
- She loves this chocolate ice cream. Correct
ADVERB PLACEMENT
The examples below show the placement for grammar adverbs such as always , only , never , ever , still , just , etc.
- You are still watching TV.
- Are you still watching TV?
ACTIVE / PASSIVE
- Right now, Tom is writing the letter. Active
- Right now, the letter is being written by Tom. Passive
More About Active / Passive Forms
Present Continuous Exercises
- Weekly Lesson
- Grammar Book
- Verb Tenses
- Conditionals
- Prepositions
- Mini-tutorials
- Irregular Verbs
- Reading Room
- Listening Lounge
- Phrasal Verb Dictionary
- Verb + Preposition Dictionary
Present Continuous Tense: Definition & Useful Examples in English
Present continuous tense in English with present continuous examples! Learn the definition and how to form the present continuous tense with useful examples and ESL printable infographics.
Present Continuous Tense
Present continuous definition.
The present continuous is a verb tense in which the action is on-going/still going on and hence continuous. The present continuous tense is used to talk about actions that are happening at this current moment.
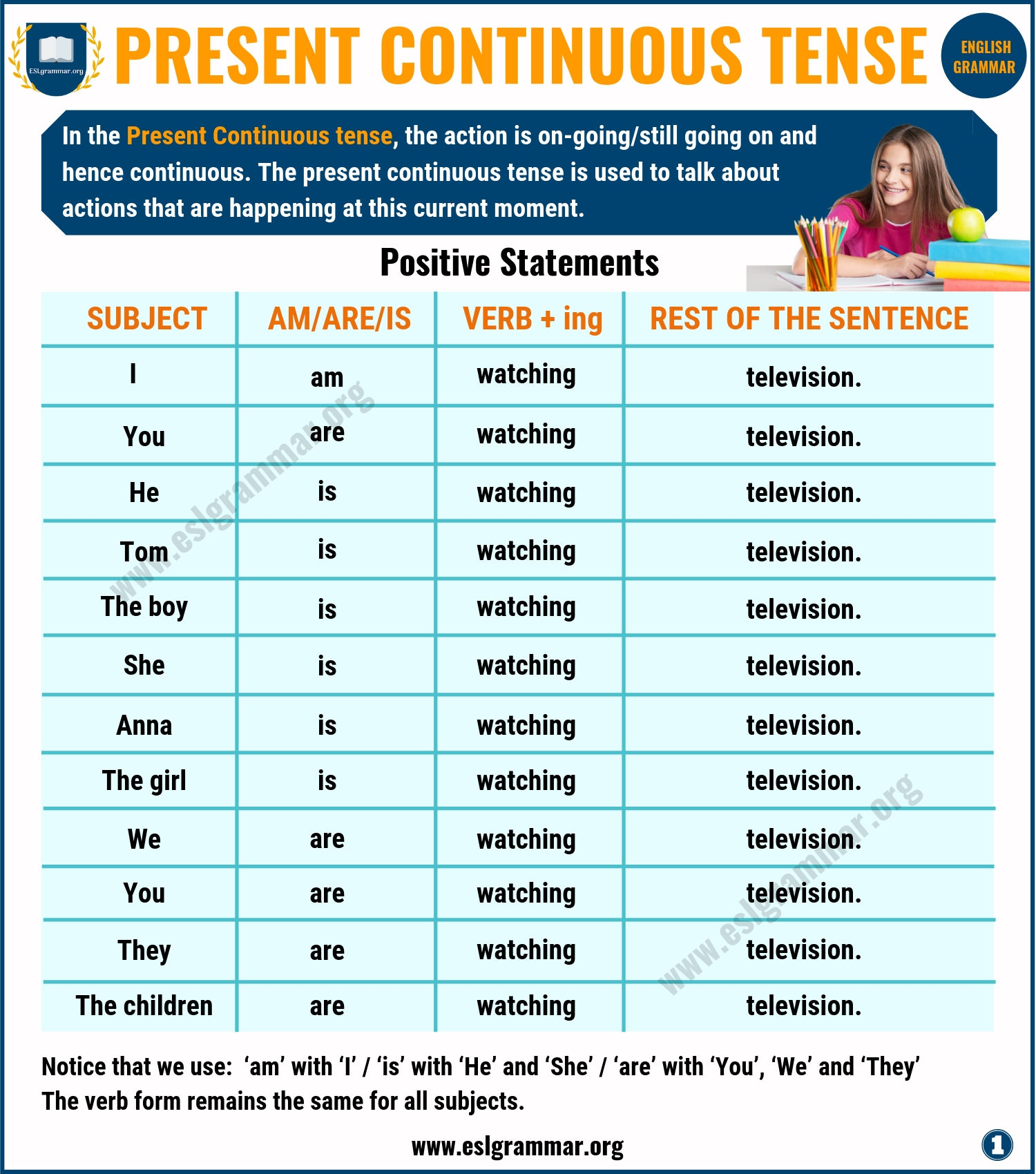
Forming Present Continuous Tense
Positive statements | present continuous.
Notice that we use:
- ‘am’ with ‘I’,
- ‘is’ with ‘He’ and ‘She’
- ‘are’ with ‘You’, ‘We’ and ‘They’
The verb form remains the same for all subjects.
Negative Statements | Present Continuous
- ‘am not’ with ‘I’,
- ‘is not’ with ‘He’ and ‘She’
- ‘are not’ with ‘You’, ‘We’ and ‘They’
Interrogative Statements/Questions | Present Continuous
Notice the structure of the interrogative statements. We use:
Present Continuous Chart
Present Continuous Quiz
Related posts:.

I know that Google is paradise.
tiene cosas que no
How do I download resources? I am specifically interested in resources relating continuous tenses to support my EALD learners. Thanks
the crowd was cheering for the players the players were playing very well please underline which is the helping verb and main verb in the above sentence.
Thank you for my help
yes i like your thoughts but you should make your explanation more clear
estas muy mal con el verbo ing el verboo ing tiene que tener ing
John e, ntine
Present Continuous

(also called Present Progressive)
We often use the Present Continuous tense in English. It is very different from the Present Simple tense, both in structure and in use.
How do we make the Present Continuous tense?
The structure of the Present Continuous tense is:
The auxiliary verb (be) is conjugated in the Present Simple: am, are, is
The main verb is invariable in present participle form: -ing
For negative sentences we insert not between the auxiliary verb and the main verb.
For question sentences, we exchange the subject and the auxiliary verb.
Look at these example sentences with the Present Continuous tense:
How do we use the Present Continuous tense?
We use the Present Continuous to talk about:
- action happening now
- action in the future
Present Continuous for action happening now
a) for action happening exactly now
Look at these images. Right now you are looking at this screen and at the same time...
b) for action happening around now
The action may not be happening exactly now, but it is happening just before and just after now, and it is not permanent or habitual.
Look at these examples:
- Muriel is learning to drive.
- I am living with my sister until I find an apartment.
Present Continuous for the future
We can also use the Present Continuous tense to talk about the future - if we add a future word !! We must add (or understand from the context) a future word. "Future words" include, for example, tomorrow , next year , in June , at Christmas etc. We only use the Present Continuous tense to talk about the future when we have planned to do something before we speak. We have already made a decision and a plan before speaking.
- We 're eating at Joe's Cafe tonight. We've already booked the table..
- They can play tennis with you tomorrow. They 're not working .
- When are you starting your new job?
In these examples, a firm plan or programme exists before speaking . The decision and plan were made before speaking.
How do we spell the Present Continuous tense?
We make the Present Continuous tense by adding -ing to the base verb. Normally it's simple: we just add -ing. But sometimes we have to change the word a little. Perhaps we double the last letter, or we drop a letter. Here are the rules to help you know how to spell the Present Continuous tense.
Back to 12 English Tenses
Present Continuous Games
Understanding Present Continuous Tense (Rules + Examples)

Among the many verb tenses, present continuous is one of the most commonly used tenses in English. It is used in daily conversations by people at large. Here is a brief breakdown of the present continuous. The article details the definition, different types of tenses, uses of present continuous tense, the structure of present continuous, and examples.
What Is Present Continuous Tense?
The present continuous, also known as the present progressive tense, refers to actions that are taking place now, these days, or nowadays. Here, the action hasn’t been completed yet. It is continuing and will do so for a little while.

For example: She is cleaning the house. Here, the person is cleaning the house right now and will continue to do so for a while . The action hasn’t ended yet.
Another example: The dog is barking at the birds. Here the action (barking) is taking place right now. In other words, it is a temporary action that will end soon.
What are the other tenses?
In English, there are three basic tenses . Each tense is further divided into four tenses. In total, the list comes to twelve verb tenses , and present continuous is one among them. Here is a full list of all the twelve tenses.
- The Simple Present
- The Present Continuous/Progressive Tense
- The Present Perfect
- The Present Perfect Continuous/Progressive Tense
- Simple Past
- The Past Continuous/Progressive Tense
- The Past Perfect
- The Past Perfect Continuous/Progressive Tense
- The Simple Future
- The Future Continuous/Progressive Tense
- The Future Perfect
- The Future Perfect Continuous/Progressive Tense
The table below explains each of these tenses with examples:
While these are all different types of tenses, the present simple, the past simple and the present perfect are the most commonly used.
Watch a short video lesson
How Is Present Continuous Different From Other Tenses?
Among many differences, the significant difference between the present continuous and other tenses is the structure. To understand them in detail, below is a comparison between present continuous with tenses like simple present and present perfect continuous .
Present Continuous vs. Simple Present
- The simple tense is used when talking about actions that are done consistently. In other words, it is used when performing things that are done routinely. For example: He plays football. In the sentence “He plays football,” the person plays football as a part of his daily life. It is not temporary instead it is a permanent routine.
On the other hand, present continuous talks about actions that are happening now and will end in a little while. For example: She is eating now. Here, the “eating” action is happening now. It is temporary and will soon end.
- In comparison to the simple present, forming a present continuous sentence is difficult. The structure of the present continuous is – subject + am/is/are + present participle (-ing).
On the other hand, the structure of the simple present is – subject + Verb1 + object.
- The most common time frame words used in the simple present are always, often, generally, every day, every week, sometimes, and never.
In comparison, the common time frame words used in the present continuous are now, still, right now, these days, and at the moment.
- All verbs are used in the simple present tense, whereas some verbs cannot be used in present continuous. Dynamic verbs are used, but stative verbs are not used in present continuous.
Present Continuous vs. Present Perfect Continuous
- In the present continuous, the action is happening now. For example: I am eating now. Here the action of “eating” is taking place now.
In comparison, the present perfect continuous indicates that the action has started in the past and is continuing in the present. For example: She has been learning Ballet since 2020. Here the person started learning ballet in 2020 and still continuing with it.
- The present continuous structure is – subject + am/is/are + present participle (-ing). On the other hand, the structure of present perfect continuous is – subject + have/has + been + present participle(ing).

How to Use Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous is used in many situations. It is used when:
- Talking about things that are taking place now.
- Describing an action that is in progress but takes a longer time to perform.
- Describing an action that will happen in the near future.
- Describing a repetitive, irritating action.
Action Taking Place Now
The tense is used when talking about an action that is happening now. The sentences have words like now, right now, and at the moment which indicates the action is taking place now.
- I am listening to music right now.
- They are dancing at the party now.
Longer Actions In Progress
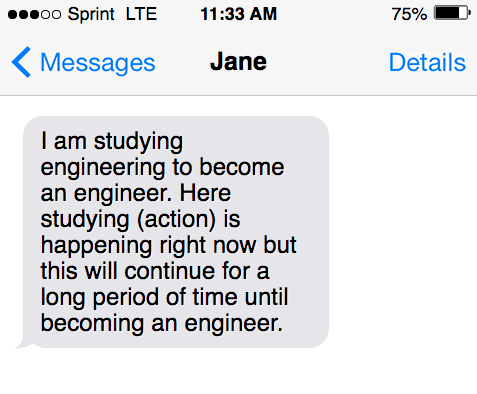
The present continuous is used to describe actions that are happening now but will take a longer time period to finish.
- I am studying engineering to become an engineer. Here studying (action) is happening right now but this will continue for a long period of time until becoming an engineer.
- I am practicing singing to become a classical singer.
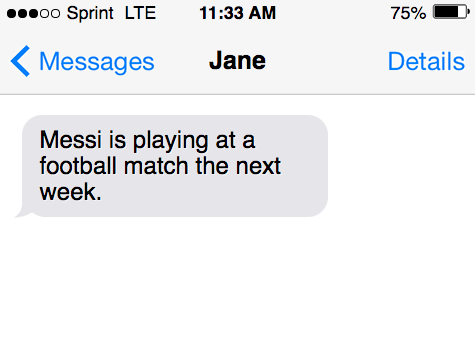
Near Future
It is used to describe events that are planned for the near future. The sentences have a “future word” in them. Words like tomorrow and next week are used.
- She is visiting the theatre tomorrow. Here, the person has planned to visit the theatre but will do it in the future which is tomorrow.
- Messi is playing at a football match the next week.
The tense is used to describe events that repeat and irritate.
- She is always complaining about her workplace. Here, the person is repeatedly complaining about her workplace.
- He is constantly coughing. I wish he takes some medicine.
Present Continuous Grammar Rules
- The present continuous is formed with the auxiliary verb and the present participle of the verb. The auxiliary verb comes in the form of am/is/are.
- At the end of the present particle of the verb, an “ing” is added. Here is the structure: subject + am/is/are + present participle (-ing).
- It is created using affirmative sentences as well as negative sentences.
- For negative sentences , there is a slight difference in the structure. The structure is – subject + am/is/are + not + present participle (-ing).
- It is also used in creating questions. But, when creating questions, there is a slight difference. The auxiliary verb and subject interchange their positions. The structure is – am/is/are + subject + present participle (ing).
Examples of Present Continuous
Here are examples of present continuous.
Affirmative Sentences
- He is riding a horse.
- She is swimming in the lake.
Negative Sentences
- I am not inviting her to my house. (I (subject) + am (auxiliary verb) + not (negative) + inviting (present participle with “ing”)).
- She is not eating an apple. (She (subject) + is (auxiliary verb) + not (negative) + eating (present participle with “ing”)).
- Is she laughing at me ? (Is (auxiliary verb) + she (subject) + laughing (present participle with “ing”)).
- Am I irritating you with my questions? (Am (auxiliary verb) + I (subject) + irritating (present participle with “ing”)).
- Why is he staring at me? (Is (auxiliary verb) + he (subject) + staring (present participle with “ing”)).

- Learning the English Present Continuous Tense?
- Present Simple Vs Present Progressive Tense Difference
- Difference Between Present Simple and Present Continuous
- Present Simple and Present Continuous | Learn English
- Present Continuous Tense (Present Progressive Tense)
- Present Continuous | Grammar | EnglishClub
- Present continuous | English grammar
Inside this article
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy
What Is the Present Continuous Tense? Definition, Usage & Examples
The present continuous tense is a verb tense used to describe actions that are currently happening and are in progress at the moment of speaking. This tense is formed by using the form of the verb “to be” (am, is, are) followed by the present participle (-ing) form of the verb.
This tense is also used to describe future plans that have been arranged or scheduled. For example, “I am meeting my friend at the park tomorrow.”
In this article, we will explore the present continuous tense in more detail, including its definition, usage, and examples.
Table of Contents
Definition of the Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense is a verb tense used to describe actions that are currently happening and are in progress at the moment of speaking. It can also be used to describe future plans that have been arranged or scheduled.
For example, “I am studying for my exam” or “She is watching a movie.”
Forming the Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense is formed by using a form of the verb “to be” (am, is, are) followed by the present participle (-ing) form of the verb.
The following table shows how to form the present continuous tense:
Usage of the Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense is used in the following situations:
- To describe actions that are currently happening at the moment of speaking. For example , “I am writing an article.”
- To describe temporary actions or situations that are happening now but may not be happening in the future. For example , “She is living in London for six months.”
- To describe future plans that have been arranged or scheduled. For example , “We are going to the beach this weekend.”
- To describe irritations or annoyances. For example , “He is always interrupting me when I’m talking.”
Examples of the Present Continuous Tense
- I am reading a book.
- They are playing football in the park.
- She is cooking dinner for us tonight.
- We are watching a movie at home.
- He is studying for his exams tomorrow.
Common Mistakes with the Present Continuous Tense
Here are some common mistakes that people make with the present continuous tense:
- Confusing it with the present simple tense.
- Using it incorrectly to describe permanent situations.
- Using it incorrectly to describe future plans that are not arranged or scheduled.
- Using it incorrectly to describe actions that are habitual or occur regularly.
It’s important to understand the proper usage of the present continuous tense to avoid these common mistakes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Present Continuous Tense:
- What is the difference between the present simple tense and the present continuous tense? The present simple tense is used to describe actions that are habitual or occur regularly, while the present continuous tense is used to describe actions that are currently happening or are in progress at the moment of speaking.
- Can the present continuous tense be used to describe future plans? Yes, the present continuous tense can be used to describe future plans that have been arranged or scheduled.
- Can the present continuous tense be used to describe permanent situations? No, the present continuous tense is not used to describe permanent situations. It is only used to describe temporary actions or situations that are happening now.
- What is the form of the present continuous tense? The present continuous tense is formed by using a form of the verb “to be” (am, is, are) followed by the present participle (-ing) form of the verb.
The present continuous tense is an important verb tense used to describe actions that are currently happening or are in progress at the moment of speaking. It’s important to understand the proper usage of this tense to avoid common mistakes and communicate effectively in English.
We hope this article has helped you to understand the definition, usage, and examples of the present continuous tense. With practice, you’ll be able to use this tense with confidence and ease in your everyday conversations.
Related Posts
Advise Verb Forms V1 V2 V3 Past Tense, Past Participle
Past Continuous Tense: Definition, Rules And Examples
Future Continuous Tense: Definition, Rules And Examples
Act Verb Forms v1 v2 v3: Past Tense and Past Participle
What Is the Past Perfect Tense? Definition, Usage & Examples
What Is the Future Perfect Tense? Definition, Usage & Examples
Add comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
The Complete Guide to the English Continuous Tense
What are you doing right now?
Are you reading ? Are you eating? Are you drinking coffee?
No, I know what you’re doing—you’re studying your English tenses!
If you answered my first question, though, there’s a good chance that you may have answered using one of the most common and useful English tenses of all—the English present continuous.
As you can see, the present continuous is a very important tense because we use it to talk about actions that are happening or that we’re doing right now.
Knowing how to use the present continuous tense is something you must do in order to improve your English.
And the good news is, it’s pretty easy to learn.
The clue to this tense is in the name— present means “right now” and continuous means “progressing” or “to keep going.”
In fact, some people like to call the present continuous tense the present progressive tense, so don’t get worried if you hear both terms. They’re the same thing!
But, as we say in English , there’s more than meets the eye (it’s deeper or more complicated than it appears) when it comes to this tense.
So let’s take a look at how to use the English present continuous, when to use it and some tips for how to master it.
Why It’s Important to Learn the English Present Continuous
What is the english present continuous, how to form the english present continuous, how to use the english present continuous to talk about ongoing actions, contractions and the english present continuous, how to form a negative using the english present continuous tense, how to form a question using the english present continuous, when to use the english present continuous tense, talking about an action that’s going to happen in the future, describing behavior and habits, the other continuous tenses in english, and one more thing....
Download: This blog post is available as a convenient and portable PDF that you can take anywhere. Click here to get a copy. (Download)
Like we already discussed, the present continuous is a very useful tense for natural-sounding conversations with English speakers. In fact, we use it daily and it has a number of different uses.
Another reason to learn it is that, if you want to know all the English tenses, the present continuous is a great place to start. Plus, you’ll need to know it in order to score high on your English tests.
Finally, as English learners, being able to switch between the tenses is an impressive and useful skill to develop.
Learning the English Present Continuous Tense? Your One-stop Guide to Nailing It
The present continuous is one of the four present tenses in the English language.
I like to call it the “what’s happening tense” or the “what are you doing tense,” as it’s a fun and simple way to get familiar with it.
Imagine you’re at home and your friend calls you.
You answer the phone.
You: “Hello?”
Friend: “What’s happening?”
You: “Not much, I’m eating my lunch. “
You might not have known it, but you responded in the present continuous tense. This is because you’re describing an action that you’re doing right now.
It’s important to note that the action hasn’t finished yet. Instead, it’s continuing at the time of the discussion.
If, for example, you answer with “Not much, I finished my lunch 10 minutes ago,” then you’d be answering in the past tense since the action is finished.
This is an important point and a key difference between the tenses.
Listen for it in popular English music, and you will start to pick up on the differences in a more natural way.
Learning the present continuous and the other five main continuous tenses in the English language might seem a bit overwhelming at first. But don’t stress! With the help…
It’s easy to form the present continuous tense. You simply need the correct conjugation of the verb to be :
- He/she/it is
Next, you need a present participle form of a verb to follow it.
I know that can sound scary, but it isn’t. An easier way to remember the present participle is to simply refer to it as an -ing verb .
It’s when we take the base form of a verb and add the suffix “-ing.”
And remember: if the verb ends with an -e, you need to remove it before adding “-ing.”
For example:
to drive → driving
If a short verb ( one syllable ) ends with a vowel, then the consonant should double before adding our -ing
to dig → dig g ing
to run → run n ing
Now, let’s take a look at how we actually form the present continuous.
We can do this simply by using the following pattern:
Subject + to be (conjugated) + -ing verb
She is driving. / She’s driving.
He is cooking dinner in the kitchen. / He’s cooking dinner in the kitchen.
The lady is dancing.
We are walking to school. / We’re walking to school.
I am writing my thesis. / I’m writing my thesis.
Something important to know about the English present continuous tense is that the action you’re describing can be ongoing, which means it lasts for a long time.
Take the very last example sentence, for example—”I’m writing my thesis.”
Writing a thesis doesn’t start and end on the same day. Instead, writing a thesis is an ongoing action that takes time. However, you can still use the present continuous tense to talk about it.
Let’s look at a few more examples of this:
I am studying law. / I’m studying law.
She is working in China. / She’s working in China.
They are living in their beach house for the summer. / They’re living in their beach house for the summer.
These examples show that the action could be occurring for years!
You might not be reading your law school textbooks right now, but “studying law” is still ongoing and unfinished. This means that since you haven’t earned your degree yet, you’re still studying law. So it’s correct to use the present continuous tense.
This is a common feature of the continuous tenses in the English language .
By now you’re probably asking yourself:
“I noticed that contractions are used for the subjects in the example sentences. Is this common?”
Contractions are commonly used in the present continuous form. Actually, they’re common to use in every continuous tense in English!
Without using contractions, your sentence might sound strange or rude. It’s kind of like you’re trying to clarify your point.
Since this tense is common for a general conversation , saying a sentence like “ I am studying law” can sound very formal and too strong. Saying “ I’m studying law” sounds a lot better!
Forming a negative in the present continuous is very simple. All you need to do is add the adverb not after the contraction of the subject and “to be.”
To make it even easier, follow this simple pattern:
Subject + to be (conjugated) + not + -ing verb
I am not running in the rain. / I’m not running in the rain.
Remember that wherever possible, contractions should be used. If you need to refresh your memory on how to form contractions, click here .
Now, let’s take a look at a few more examples that use contractions:
I’m not studying law.
He’s not swimming fast enough to win the race!
She isn’t coming to the meeting.
It isn’t raining.
To form a question in the present continuous tense, you just need to place the conjugated “to be” verb in front of the subject. These are the present simple forms of the root verb “to be.”
Are you studying law?
Is the train running late?
Am I speaking too fast?
As you might notice, this form is a great way to pose a polite question. To form a specific question related to time , place or meaning, just add a question word at the beginning of the sentence.
These are sometimes referred to as WH-words or WH-questions . They’re the question words when, where, why, how and what .
Let’s look at some examples:
Where are you studying law?
Why is the train running late?
What are you cooking for dinner?
Who are you dancing with?
There are a couple of different ways that the present continuous tense can be used that may at first seem opposite or contradictory to what we just learned.
But that’s also why it’s important to get a full and complete grasp of the tense !
Let’s take a look at some now.
Yes, the present continuous tense is used to talk about an action that’s going to take place in the future sometimes.
I know this may seem confusing. So, there are a few tips to help you know if you’ll need to use the present continuous in this way.
It’s also quite a specific situation. There are some “indicators” that’ll help you decide if you must use the tense to talk about the future, which makes it a bit easier.
The present continuous is used to talk about something happening in the future that seems to be definite, concrete and organized. It’s almost like a legal idea, as there must be some form of the intention behind it.
Take a look at the two sentences below:
I’m moving to Australia tomorrow .
I’m going to go to Australia.
The second sentence doesn’t provide as much detail. It doesn’t tell us when that person is going to move to Australia. It also doesn’t use the present continuous structure.
In the first example, the person says that they will move to Australia tomorrow. Therefore, there’s intention behind it, and going to Australia is something that the person has planned and organized.
Let’s take a look at another sentence like this:
She’s meeting with her doctor on Friday morning.
As you can see, these two sentences are very specific and talk about a moment in time. It shows us that the event (going to the doctor or moving to Australia) is planned and organized.
The present continuous tense is sometimes used in a negative way to describe behavior that you might consider annoying.
He’s always chewing with his mouth open!
They’re always arriving late, I can’t believe it.
She’s constantly complaining, I can’t deal with it!
He’s always forgetting his car keys!
When used like this, the sentence usually needs an adverb. Adverbs are words like “always” and “constantly” to show that the action happens frequently. By using the present continuous tense like this, the actions are portrayed as annoying or bad habits.
But you can also use it to compare.
You’re swimming a lot better than you were last year.
Or, an ongoing changing situation that doesn’t necessarily have to be negative:
She’s growing so quickly, I can’t believe it!
Don’t stop here! Next step is to master the other continuous tenses in English, they’re every bit as easy.
https://www.fluentu.com/blog/english/english-past-continuous/
The English future continuous tense is used to talk about actions that will continuously happen in the future. Find out more about what this tense is, how to form it, when…
How are you feeling now?
The present continuous doesn’t have to be scary. It’s a simple, useful and multifunctional tense that’s guaranteed to improve your English!
Use the continuous tense in conversations, and look out for it in English books, podcasts and movies. You can also use a program like FluentU to help you understand how to use tenses in context.
Once you’ve nailed it, you’ll be speaking more naturally , describing ongoing situations and talking about the future. And best of all, you’ll be on your way to covering all of the English tenses !
If you like learning English through movies and online media, you should also check out FluentU. FluentU lets you learn English from popular talk shows, catchy music videos and funny commercials , as you can see here:
If you want to watch it, the FluentU app has probably got it.
The FluentU app and website makes it really easy to watch English videos. There are captions that are interactive. That means you can tap on any word to see an image, definition, and useful examples.
FluentU lets you learn engaging content with world famous celebrities.
For example, when you tap on the word "searching," you see this:
FluentU lets you tap to look up any word.
Learn all the vocabulary in any video with quizzes. Swipe left or right to see more examples for the word you’re learning.
FluentU helps you learn fast with useful questions and multiple examples. Learn more.
The best part? FluentU remembers the vocabulary that you’re learning. It gives you extra practice with difficult words—and reminds you when it’s time to review what you’ve learned. You have a truly personalized experience.
Start using the FluentU website on your computer or tablet or, better yet, download the FluentU app from the iTunes or Google Play store. Click here to take advantage of our current sale! (Expires at the end of this month.)
Enter your e-mail address to get your free PDF!
We hate SPAM and promise to keep your email address safe

English Speaking Course
Present Continuous Tense – Definition, Formula & Examples

Explaining Present Continuous Tense
Present Continuous Tense: In the realm of English grammar, tenses play a crucial role in shaping the way we communicate. One of the fundamental tenses that allow us to express actions happening in the present is the Present Continuous Tense. In this article, we will delve deep into this tense, dissecting its structure and usage with real-life examples.
Learn more:
- English Sentences
- Modal Verbs
- English Grammar
- Questions & Answers
- Ways to say
Understanding the Basics
Before we dive into the intricacies, let’s establish a foundation by understanding what the Present Continuous Tense is all about.
What is Present Continuous Tense?
The Present Continuous Tense, also known as the Present Progressive Tense, is used to describe actions that are happening at the moment of speaking. These actions are in progress and not completed.
Structure of Present Continuous Tense
To form the Present Continuous Tense, you need two components: the present tense of the verb ‘to be’ and the base form of the main verb with the “-ing” suffix attached.
- Positive: Subject + am/is/are + base form of the verb + -ing (e.g., She is reading a book.)
- Negative: Subject + am not/isn’t/aren’t + base form of the verb + -ing (e.g., They aren’t watching TV.)
- Interrogative: Am/Is/Are + subject + base form of the verb + -ing? (e.g., Are you playing football?)
Present Continuous Tense in Action
Now that we have a grasp of the structure, let’s explore how the Present Continuous Tense is used in various situations.
1. Actions Happening Now
The primary use of the Present Continuous Tense is to describe actions taking place at the moment of speaking. For example:
- Example 1: “I am typing this article.”
- Example 2: “They are having dinner right now.”
2. Temporary Actions
This tense can also be used to indicate actions that are happening temporarily, not necessarily at the exact moment of speaking but in the present timeframe.
- Example 1: “She’s staying with her aunt for a few weeks.”
- Example 2: “He’s working on a project this month.”
3. Future Plans and Arrangements
Surprisingly, the Present Continuous Tense can also be employed to discuss future plans and arrangements when there’s a sense of intention or commitment.
- Example 1: “I’m meeting Jane at the café tomorrow.”
- Example 2: “They are flying to Paris next week.”

Present Continuous vs. Simple Present
It’s important to differentiate between the Present Continuous Tense and the Simple Present Tense, as they have distinct uses.
- The Present Continuous Tense describes actions in progress at the moment of speaking, while the Simple Present Tense expresses habitual actions or general truths.
- Present Continuous: “I am reading a book right now.” (action in progress)
- Simple Present: “I read books.” (habitual action)
Common Mistakes to Avoid
In the process of learning any new tense, certain common mistakes tend to crop up. Here are a few to watch out for:
1. Misplacing the ‘ing’
Ensure that the ‘-ing’ form is correctly attached to the verb. Mistakes such as “He is playingsoccer” should be corrected to “He is playing soccer.”
2. Neglecting the ‘to be’ Verb
Don’t forget to include the appropriate form of ‘to be’ (am/is/are) in your sentence structure. For instance, “She playing tennis” should be revised to “She is playing tennis.”
In conclusion, the Present Continuous Tense adds a dynamic element to our conversations, allowing us to express actions in progress with precision. By mastering this tense, you can elevate your English language skills and communicate more effectively.
1. When should I use the Present Continuous Tense?
- Use it to describe actions happening at the moment of speaking or actions occurring in the present timeframe.
2. Can I use the Present Continuous Tense for future plans?
- Yes, you can use it for future plans when there’s a sense of intention or commitment.
3. What’s the difference between Present Continuous and Simple Present?
- Present Continuous is for actions in progress, while Simple Present is for habitual actions or general truths.
4. Are there irregular verbs in the Present Continuous Tense?
- No, the verb form in the Present Continuous Tense is regular, with the ‘-ing’ suffix added to the base form.
5. How can I improve my understanding of English tenses?
- Practice, read, and engage in conversations to become more comfortable with using different tenses effectively.
Present Continuous Tense: Positive
1. She is reading a book. 2. They are playing soccer in the park. 3. I am writing an email. 4. He is cooking dinner. 5. We are watching a movie. 6. The cat is chasing the mouse. 7. They are dancing at the party. 8. She is singing a beautiful song. 9. I am studying for my exams. 10. He is fixing the car. 11. We are painting the walls. 12. They are discussing the project. 13. It is raining outside. 14. She is jogging in the park. 15. They are building a sandcastle on the beach. 16. I am talking to my friend on the phone. 17. He is playing the guitar. 18. We are traveling to Europe next week. 19. They are laughing at a joke. 20. She is taking a shower. 21. I am learning a new language. 22. He is waiting for the bus. 23. We are attending a concert tonight. 24. They are shopping for groceries. 25. She is driving to work. 26. I am meeting my colleague for lunch. 27. He is mowing the lawn. 28. We are cleaning the house. 29. They are studying together in the library. 30. She is cooking breakfast for her family.
Negative sentences
1. She is not reading a book. 2. They are not playing soccer in the park. 3. I am not writing an email. 4. He is not cooking dinner. 5. We are not watching a movie. 6. The cat is not chasing the mouse. 7. They are not dancing at the party. 8. She is not singing a beautiful song. 9. I am not studying for my exams. 10. He is not fixing the car. 11. We are not painting the walls. 12. They are not discussing the project. 13. It is not raining outside. 14. She is not jogging in the park. 15. They are not building a sandcastle on the beach. 16. I am not talking to my friend on the phone. 17. He is not playing the guitar. 18. We are not traveling to Europe next week. 19. They are not laughing at a joke. 20. She is not taking a shower. 21. I am not learning a new language. 22. He is not waiting for the bus. 23. We are not attending a concert tonight. 24. They are not shopping for groceries. 25. She is not driving to work. 26. I am not meeting my colleague for lunch. 27. He is not mowing the lawn. 28. We are not cleaning the house. 29. They are not studying together in the library. 30. She is not cooking breakfast for her family.
Interrogative sentences
1. Is she reading a book? 2. Are they playing soccer in the park? 3. Am I writing an email? 4. Is he cooking dinner? 5. Are we watching a movie? 6. Is the cat chasing the mouse? 7. Are they dancing at the party? 8. Is she singing a beautiful song? 9. Am I studying for my exams? 10. Is he fixing the car? 11. Are we painting the walls? 12. Are they discussing the project? 13. Is it raining outside? 14. Is she jogging in the park? 15. Are they building a sandcastle on the beach? 16. Am I talking to my friend on the phone? 17. Is he playing the guitar? 18. Are we traveling to Europe next week? 19. Are they laughing at a joke? 20. Is she taking a shower? 21. Am I learning a new language? 22. Is he waiting for the bus? 23. Are we attending a concert tonight? 24. Are they shopping for groceries? 25. Is she driving to work? 26. Am I meeting my colleague for lunch? 27. Is he mowing the lawn? 28. Are we cleaning the house? 29. Are they studying together in the library? 30. Is she cooking breakfast for her family?
Related posts:

Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Log In 0 The website uses cookies for functionality and the collection of anonymised analytics data. We do not set cookies for marketing or advertising purposes. By using our website, you agree to our use of cookies and our privacy policy . We're sorry, but you cannot use our site without agreeing to our cookie usage and privacy policy . You can change your mind and continue to use our site by clicking the button below. This confirms that you accept our cookie usage and privacy policy.
Free English Lessons
The present continuous verb tense – video.
Download PDF

In this lesson, you can learn about the present continuous verb tense in English.
Do you know to form and use the present continuous like many verb tenses in english , the present continuous has many different uses and meanings. you can learn more in this class., you’ll see all the possible meanings of the present continuous; whether you’re a beginner or an advanced learner, you’re sure to find something new., quiz: the present continuous verb tense.
Do you know how to form the present continuous tense and when to use it? Test yourself with this quiz.
It has 20 questions. If you see ‘Hint’, you can click it for more help. When you have finished, click ‘Finish Quiz’ to see your score.
After you get your score, you can choose ‘Restart Quiz’ to try again or ‘View Questions’ to review all the questions and answers.
Quiz Summary
0 of 20 Questions completed
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
0 of 20 Questions answered correctly
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), ( 0 )
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0 , ( 0 ) 0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0 )
- Not categorized 0%
Well done! You’ve finished!
That’s an excellent score! Congratulations!
A perfect score! Congratulations!
1 . Question
For the first five questions, you will see a sentence where the present continuous tense is not written correctly.
Write one word in the gap so that the second sentence is correct each time.
Incorrect: “He’s wash his car.” Correct: “He’s his car.”
Form the present continuous tense with be + the -ing form of the main verb.
2 . Question
Write one word in the gap so that the second sentence is correct.
Incorrect: “I’m no working on anything at the moment.” Correct: “I’m working on anything at the moment.”
Form a negative sentence with the word ‘not’.
3 . Question
Write one word in the gap so that the second sentence is correct. The word is a contraction of two words.
Incorrect: “He doesn’t coming with us tomorrow.” Correct: “He coming with us tomorrow.”
It would be grammatically correct to write ‘is not’ but this would sound very formal and unusual. You should write the contraction here – and use it when you’re speaking.
4 . Question
Incorrect: “You are coming to the cinema?” Correct: “Are coming to the cinema?”
The word order changes in questions.
5 . Question
Incorrect: “What you doing?” Correct: “What you doing?”
6 . Question
For the next five questions, choose the correct option to complete the rules about forming and using the present continuous tense.
To form the present continuous, use:
- the verb ‘be’ in any tense plus the -ing form of the main verb.
- the verb ‘be’ in the present simple tense plus the -ing form of the main verb.
If ‘be’ is in the past, you would form the past continuous!
7 . Question
Talking about things that are physically happening at the moment of speaking is:
- one of the uses of the present continuous.
- the only use of the present continuous.
8 . Question
If you are describing a picture, you should:
- use past tenses to describe it, because pictures show moments from the past.
- use the present continuous to describe it, even if the picture was taken a long time ago.
9 . Question
When you describe a picture, you should use the present continuous tense:
- to talk about everything you can see, including people, buildings and natural locations.
- to talk about the people in the picture, but use the present simple to describe things in the background.
10 . Question
If you want to use the present continuous to express that you find something strange or annoying, you should:
- use an adverb of opinion like 'annoyingly' or 'strangely'.
- use an adverb of frequency like 'always' or 'constantly'.
11 . Question
In the next five questions, you will see ten sentences that include the present continuous. Eight of them are correct uses and two are incorrect.
Match the sentences with the reasons for using the present continuous.
Sort elements
- "They’re having lunch at the moment."
- "I’m learning Swedish online in the evenings."
12 . Question
Match the sentences with the rules.
- "The two men in blue are smoking."
- "The tree in the background is being very big."
Even though we use the present continuous to talk about what people are doing in pictures, we use the present simple to describe places, natural locations and things that don’t move.
13 . Question
- "I’m living with my parents."
- "The world’s population is growing by millions every year."
14 . Question
- "I'm visiting my sister for a few days."
- "I'm finding the new job challenging."
15 . Question
- "Why are you always being rude to waiters?"
- "My mother’s being 70."
Even though someone’s age is temporary, not permanent, we use present simple to talk about it, because we consider it a true fact.
16 . Question
Now look at five more sentences and decide why the present continuous tense is used.
“She’s working from home today.”
The present continuous here shows:
- a changing situation.
- something happening now.
- something the speaker finds annoying.
- a feeling which the speaker is just starting to be aware of.
17 . Question
“What time are we meeting?”
- a future arrangement.
- something which has started, but not finished.
- a temporary situation.
18 . Question
“I’m doubting whether I can stay in the same company much longer.”
- something which the speaker finds annoying.
- something happening at this moment.
19 . Question
“They’re staying in a hotel until they can find a suitable apartment.”
- what people are doing in a picture.
20 . Question
“He’s always leaving the lights on all over the house!”
1. How Can You Form the Present Continuous?
To form the present continuous, you use:
- Be + verb + -ing
For example:
- He’s washing his car.
- They’re watching a film.
What about negatives and questions?
To make negatives, add not after be .
- She isn’t doing anything .
- I’m not working on that right now.
To make questions, move the verb be before the subject.
- Is he doing anything?
- Are you talking to me?
The same rule works if you ask a question with a question word like what, why, how, etc. Move the verb be before the subject.
- What are you watching?
- Where are they going?
You can see that to make questions in the present continuous, you don’t add anything. Don’t add words like do or did . Just change the order of the words!
So now you know how to form sentences and questions with the present continuous. But how do you use it?
Let’s look.
2. Something Happening Right Now
This is the most basic use of the present continuous.
These sentences are talking about something which is happening at this moment. He’s washing his car right now. They’re watching a film at this moment.
We can also use the present continuous to talk about:
3. Something which has Started but not Finished
This sounds similar to the last point. If we say:
This means he’s started washing his car, but he hasn’t finished yet.
That means they’ve started watching the film, but they haven’t finished yet.
So what’s the difference? Why is this separate to the last point?
It’s different because we can also use the present continuous in this way to talk about things which are not happening right now. For example:
- I’m reading a good book at the moment.
- She’s looking for a new apartment.
If I say I’m reading a good book at the moment , I don’t mean that I’m reading right now, at this minute. I mean that I’ve started a book and I haven’t finished it yet.
In the same way, She’s looking for a new apartment doesn’t mean that she’s out looking for an apartment this minute. It means she’s started looking for an apartment, but she hasn’t found one yet.
In these examples, we use the present continuous to talk about things happening around this moment, not necessarily at this specific moment.
4. Describing a Picture
If you have a picture or a photo, and you want to describe it to someone, you use the present continuous.
A picture or a photo is like a moment in time. That’s why we use the continuous form to talk about it.

Here, we can use the present continuous to talk about what we see:
- They are sitting on a beam, high above the city.
- The two men on the left are smoking.
- Some of them are eating sandwiches.
It doesn’t matter that the picture was taken a long time ago. We can still use the present continuous to describe it.
5. Talking about Temporary Situations
Another use of the present continuous is to show that something is temporary. Look at two sentences:
- He lives with his parents.
- He’s living with his parents.
What’s the difference? Why would you use the present continuous here?
In these sentences, the present continuous shows that the situation is temporary. If you say he lives with his parents , you mean that this is permanent.
If you say he’s living with his parents , you mean that this is a temporary situation. Maybe he’s living with his parents while he saves enough money to get his own place.
Let’s look at one more example here:
- She works in the marketing department.
- She’s working in the marketing department.

Is the difference clear now?
If you say she works in the marketing department , you mean that this is her permanent job.
If you say she’s working in the marketing department , you mean that she normally works somewhere else. She’s just working in the marketing department temporarily.
6. Talking About a Changing Situation
Yes, there are a lot of ways to use the present continuous! Remember that you don’t have to learn all of this at once. This video will still be here; take a break and review what we’ve done so far if you need to.
You can also use the present continuous to talk about a situation which is changing over time. For example:
- The population of our city is growing by around 5% a year.
- My English is slowly getting better.
- The river used to be really polluted, but it’s getting cleaner.
In all of these examples, we’re talking about a change which is happening over time, and which will probably continue into the future. If I say:
This means that I expect the population to continue growing, at least for the next few years.
OK, so you’ve seen how the present continuous can be used to talk about:
- Things happening now.
- Things which have started but not finished.
- Describing pictures.
- Temporary situations.
- Changing situations.
All of the meanings we’ve seen so far are similar. They are all about something happening around a moment in time. However, there are also some other ways to use the present continuous which are completely different.
Let’s look at a very important one.
7. Talking about Arrangements in the Future
Many English learners use will to talk about the future , but will can’t be used for everything. Actually, the present continuous is one of the most common ways to talk about the future in English.
If you have a solid plan or arrangement, meaning you know where and/or when something will happen, you can use the present continuous to talk about it. For example:
- We’re meeting outside the cinema at 8.00.
- They’re coming to ours for dinner on Saturday.
- What are you doing next weekend?
It’s very common to use the present continuous when you talk about plans for the near future, social plans, and so on.
8. Talking about Something Strange or Annoying
Now we’re getting to more specialised, less common uses of the present continuous.
Using the present continuous together with adverbs like always, constantly or continually can show that you find a repeated action annoying or strange. For example:
- He’s always forgetting to bring the things he needs.
- They’re constantly gossiping about me behind my back.
- My boss is continually interrupting me while I’m trying to work.
If you say:
You means that he often forgets to bring things, and you find this strange or annoying.
This use of the present continuous is unusual, because we’re using the present continuous to talk about a repeated action or a habit. We don’t normally do that.
You must use an adverb in these sentences. You can’t say:
- He’s forgetting to bring the things he needs. –> incorrect
- He’s always forgetting to bring the things he needs. –> correct
To give it the meaning of something which you find strange/annoying, you need an adverb. Always is the most common adverb to use in these sentences.
OK, we’re nearly there! One more to go:
9. Talking about New Feelings
Again, this is a very specialised, less common way to use the present continuous. What does it mean?
Think about these two sentences:
- I realise I made the wrong decision.
- I’m realising I made the wrong decision.
They’re both possible, but what’s the difference?
In the first sentence:
Your realisation is not a new feeling. But, when you say:
You mean that you are just starting to think about this. The feeling (= that you made the wrong decision) is still growing in you.
Let’s do one more example:
- I find it difficult to work with him.
- I’m finding it difficult to work with him.
Can you see the difference?
Again, if you say:
This is not something new for you. You generally find him difficult, and you dislike working with him.
This means that you are just starting to realise how difficult he is, and how you dislike working with him. These feelings are new to you.
Okay, that’s the end of the lesson. There’s a lot of information in this video, so you might find it useful to review some parts of the video again.
That’s all for now. Thanks very much for watching this spoken English lesson from Oxford Online English!
We Offer Video Licensing and Production
Use our videos in your own materials or corporate training, videos edited to your specifications, scripts written to reflect your training needs, bulk pricing available.
Interested?
More English Lessons
English grammar lessons.

- Facebook 21
- Odnoklassniki icon Odnoklassniki 1
- VKontakte 1
- Pinterest 0
- LinkedIn 15

When do you use the present continuous tense in English? - Easy Learning Grammar
- things that are happening now, at the time when we are talking.
- a temporary activity, even if it is not happening at the time when we are talking.
- a temporary situation in contrast to a permanent situation.
- a changing state or situation.
- the circumstances under which something is generally done.
- arrangements for future events along with a time adverb or phrase.
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5

Present Continuous Tense: Rules And Examples
- What Is Present Continuous Tense?
- When To Use It
- How To Form It
- How To Make It Negative
- Write With Grammar Coach
Right now, you are reading words. If you continue to read these words, you will learn a lot more about grammar. Specifically, we are going to learn about a neat way to use verbs . I am talking about the way that we use verbs to describe actions that are happening right now. So, let’s not waste any more time and check out a cool part of grammar known as the present continuous tense.

What is present continuous tense ?
We use verbs to refer to actions and states. To do so, we use many different types of verb tenses to say when actions occur or when states exist. The tense of a verb indicates when in time an event happened. Right now, we are going to look at a particular verb tense that refers to something that happens in the present but also keeps the fun going in the future: the present continuous tense. The present continuous tense , also called the present progressive tense , is a versatile verb tense that can refer to actions that are happening currently in the present and/or that happen in the future.
For example, the sentence I am washing my car expresses the thought that I am washing my car right now and I will continue to do so for some time in the future. The present continuous tense refers to actions and states that happen in the present but are continuous , that is, they still are ongoing and haven’t ended yet—that we know of right now, at least. I am obviously not going to wash my car forever!
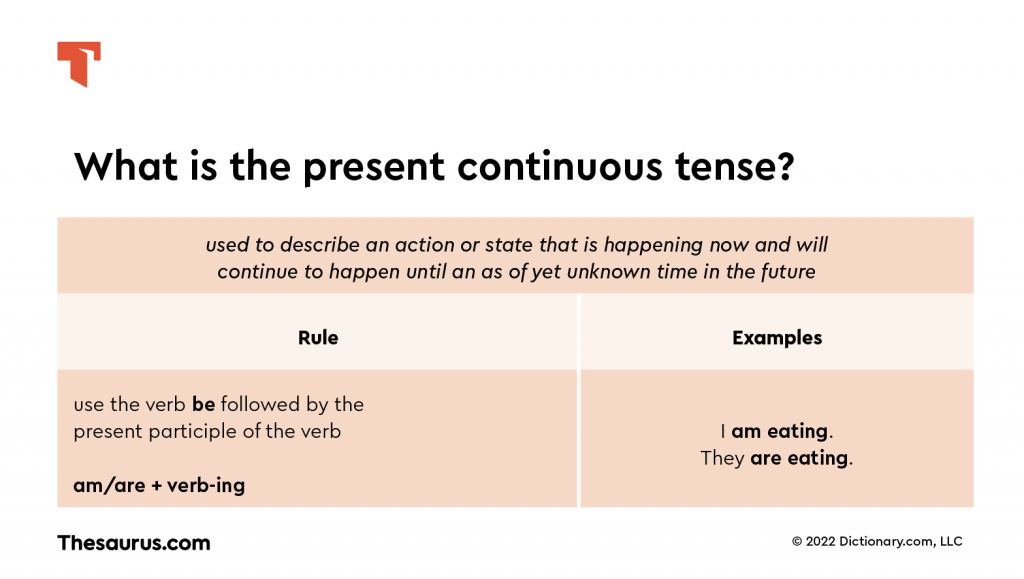
What’s funner than learning about grammar? Well, discussing if “funner” is a word or not! Find out here.
When do you use present continuous?
We often use the present continuous tense to refer to temporary states or actions. Putting it another way, we use the present continuous tense to describe an action or state that is happening now and will continue to happen until an as of yet unknown time in the future. Here are two examples of sentences that use the present continuous tense this way:
- Meghan is reading a book in the living room.
- My cat is watching the birds through the window.
Both of these sentences refer to actions that are being done for the moment but will stop when Meghan or that hungry cat does something else. We use the present continuous tense to indicate such a continuous action or state.
Because English grammar loves to make things difficult for us, we also often use the present continuous tense to refer to future events, especially ones that have been planned. When we do this, we often use adverbs of time to clarify that the present continuous tense is being used to refer to a future event rather than an event already in progress.
- I am going to Portugal this summer.
- We are celebrating Ben’s birthday next week.
There is one important caveat to keep in mind when using the present continuous tense. Typically, we don’t use the present continuous tense with stative verbs . Generally speaking, stative verbs describe states of existence rather than actions, so it usually doesn’t make sense to refer to them as being “in progress.” The following two sentences show incorrect use of the present continuous tense with stative verbs. You will probably notice how odd these sentences sound.
- That watch is looking cheap.
- My daughter is believing in Santa Claus.
Instead, we would use the simple present tense :
- That watch looks cheap.
- My daughter believes in Santa Claus.
Be careful of verbs that could be used as either stative or nonstative verbs depending on meaning or context.
For instance, we more commonly say Amanda appears sad today rather than Amanda is appearing sad today . On the other hand, we usually say The defendant is appearing in court tonight for such an upcoming event, rather than The defendant appears in court tonight.
Sometimes you need to a simple review to brush up your skills. Take a look at the simple present tense here.
How to form present continuous tense
To form the present continuous tense, we use the verb be followed by the present participle of the verb. The present participle is a form of a verb that ends in the suffix -ing. For example, the present participle of eat is eating. When using the present continuous tense, the verb be must be correctly conjugated so it agrees with the subject. For example:
- I am eating
- You are eating
- He/she/it is eating
- We are eating
- They are eating
Here are examples of the present continuous tense used in several sentences. Notice that the verb be is correctly conjugated to agree with the subject.
- I am studying for my algebra test.
- My lazy dog is snoring loudly.
- We are going to the beach during summer vacation.
How to make present continuous tense negative
In order to make the present continuous tense negative, all you need to do is put the word not between the verb be and the present participle. Contractions are also fine.
- I am not listening to his dumb jokes.
- She isn’t enjoying her time at the amusement park because of her toothache.
- Luckily, those hungry wolves aren’t heading this way.
No time like the present to improve your grammar!
You won’t mistake your verb tenses again when you check your writing on Thesaurus.com’s Grammar Coach ™. This writing tool uses machine learning technology uniquely designed to catch grammar and spelling errors. Its Synonym Swap will find the best nouns, adjectives, and more to help say what you really mean, guiding you toward clearer, stronger, writing.
Whether you’re writing about the past, present, or future, start writing smarter today!
Make Your Writing Shine!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
No matter the tense, do you know if "none" takes a singular or plural verb? Learn more about it here.

Ways To Say
Synonym of the day
- How it works
- Programmes and Methodology
- Schoolchildren

Present Continuous – definition, construction, use, and examples of Present Continuous verb tense
Present Continuous is one of 4 present verb tenses in English grammar . The Present Continuous verb tense indicates that an action or condition is happening now, frequently, and may continue into the future. However, it can be used in many situations, so that’s why today we’ll help you use the Present Continuous tense correctly and understand it generally.
Learn how to build sentences in Present Continuous, what is the definition of Present Continuous verb tense and when to use it in real life situations. Find out examples of sentences in Present Continuous form, as well as Present Continuous exercises and test!
Although verb tenses in English may seem tricky for beginner English learners, with Novakid approach to teaching English, you’ll see that Present Continuous can also become friendly. Soon, you’ll have no problem using it during real-life conversation with English native speakers.
In case you’re worried about confusing Present Continuous and Present Simple verb tenses, no worries. Sometimes, they overlap with each other in meaning, however, in such cases don’t worry – people should understand what you mean using either of the present tenses in English. Just in case, we are going to take a look at comparison of Present Continuous and Present Simple, so you’ll know which one is used to describe which situations.
Definition of Present Continuous
The Present Continuous tense, also known as the Present Progressive tense, is a grammatical form used in the English language to describe ongoing actions or situations that are happening at the present moment. It is formed by using the present tense of the auxiliary verb “to be” (am, is, are) followed by the present participle of the main verb (-ing form).
The use of Present Continuous in English
The primary function of the present continuous tense is to indicate actions that are currently taking place or unfolding in real-time, regardless of their duration. It emphasizes the temporary nature of the action, often implying that it is in progress but not yet completed. Additionally, the present continuous tense can be employed to convey future arrangements or plans that have already been decided.
It’s important to note that the Present Continuous tense is not limited to actions happening at the exact moment of speaking. It can describe ongoing actions occurring around the present time, even if they started before the moment of speaking and may continue after. Furthermore, the Present Continuous tense is not typically used for general truths, habitual actions, or permanent states, as it emphasizes temporary or current activities.
In summary, the Present Continuous tense is a grammatical construction used to express ongoing actions or situations happening at the present time. It highlights the temporary nature of the action and can also denote future plans or arrangements.
How to compose sentences in the Present Continuous?
Present Continuous tense is always composed of a suitable form of the verb “to be” , placed after the subject, and the gerund (which is a form of any verb with the “-ing” suffix added).
The structure of the Present Continuous tense varies depending on the subject of the sentence.
- For singular subjects: “I am” + present participle (e.g., “I am studying for my exam.”)
- For third-person singular subjects “he”, “she”, “it”: “He/She/It is” + present participle (e.g., “She is reading a book.”)
- For plural subjects and the pronouns “you,” “we,” and “they”: “They/You/We are” + present participle (e.g., “We are going to the park.”)
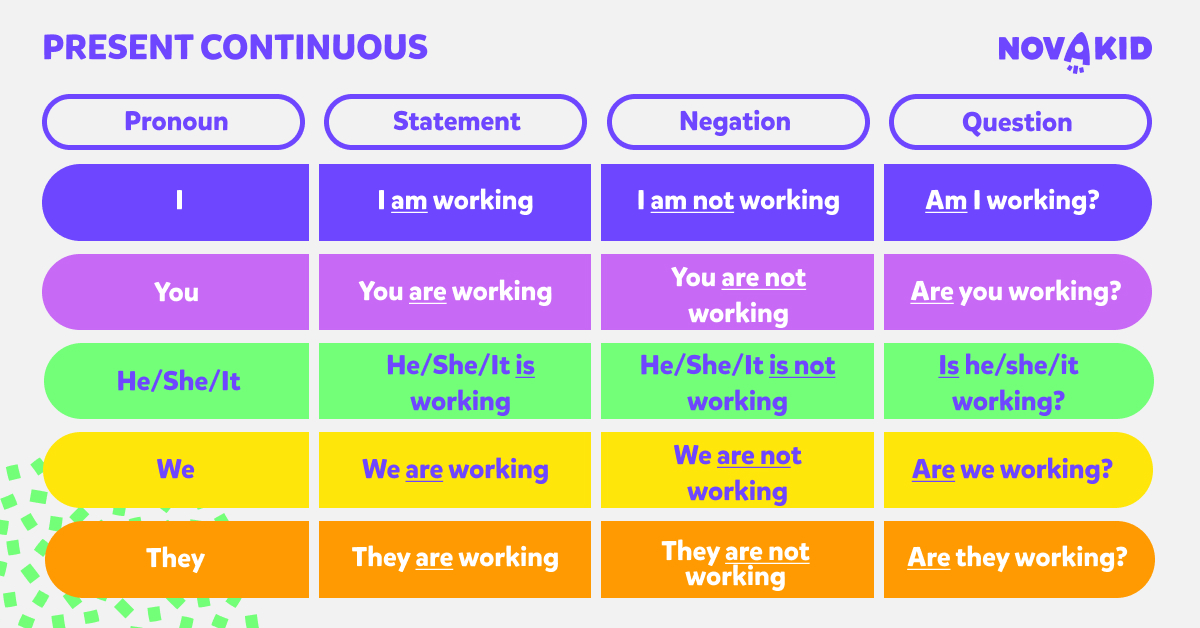
How to form sentences in the Present Continuous tense with examples
Let’s talk about building statements, negations, and questions in Present Continuous verb tense. See examples for each type of sentences below.
Construction of statements in Present Continuous
Singular subject: Subject + am/is/are + present participle (-ing form of the verb)
- Example 1: “I am studying for my exam.”
- Example 2: “She is reading a book.”
- Example 3: “The cat is sleeping on the couch.”
Third-person singular subject: Subject + is + present participle (-ing form of the verb)
- Example 1: “He is playing football with his friends.”
- Example 2: “She is cooking dinner in the kitchen.”
- Example 3: “The sun is shining brightly in the sky.”
Plural subjects and pronouns “you,” “we,” and “they”: Subject + are + present participle (-ing form of the verb)
- Example 1: “We are going to the park.”
- Example 2: “They are watching a movie at the cinema.”
- Example 3: “You are listening to music on your headphones.”
Construction of negations in Present Continuous
Singular subject: Subject + am/is/are + not + present participle
- Example 1: “I am not studying right now; I’m taking a break.”
- Example 2: “She is not attending the meeting; she is on vacation.”
- Example 3: “The dog is not barking; it’s sleeping peacefully.”
Third-person singular subject: Subject + is + not + present participle
- Example 1: “He is not working today; he has the day off.”
- Example 2: “She is not wearing a jacket because it’s warm outside.”
- Example 3: “The computer is not responding; there might be a technical issue.”
Plural subjects and pronouns “you,” “we,” and “they”: Subject + are + not + present participle
- Example 1: “We are not going to the party; we have other plans.”
- Example 2: “They are not studying for the test; they are playing video games.”
- Example 3: “You are not listening to me; you are distracted.”
Construction of questions in Present Continuous
Singular subject: Am/Is/Are + subject + present participle?
- Example 1: “Are you studying for the exam?”
- Example 2: “Is she coming to the party tonight?”
- Example 3: “Am I interrupting you?”
Third-person singular subject: Is + subject + present participle?
- Example 1: “Is he working on a new project?”
- Example 2: “Is she eating lunch right now?”
- Example 3: “Is it raining outside?”
Plural subjects and pronouns “you,” “we,” and “they”: Are + subject + present participle?
- Example 1: “Are we going to the beach this weekend?”
- Example 2: “Are they watching a movie at the theater?”
- Example 3: “Are you enjoying the party?”

How to recognize the Present Continuous tense?
Recognizing the Present Continuous tense in English is easier than you might think. One characteristic feature is the use of the present tense of the verb “to be” (am, is, are) followed by the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
To make it even simpler, there are some common adverbs that often accompany the Present Continuous tense, providing clues to help identify it. These adverbs include “now,” “at the moment,” “currently,” “right now,” and “temporarily.” Let’s see some examples:
- “I am studying now for my exam.” – The adverb “now” indicates that the action of studying is happening in the present moment.
- “She is currently working on a project.” – The adverb “currently” suggests that the action of working is ongoing at this time.
- “They are temporarily living in a hotel.” – The adverb “temporarily” signifies that the action of living in a hotel is temporary and happening now.
When to use the Present Continuous? Situational context for this present tense form
Situational context is another clue for recognizing the Present Continuous tense. It is often used to describe actions or situations that are happening right now or are in progress at the moment of speaking. It emphasizes the temporary nature of the action and implies that it is ongoing, but not necessarily completed. Some common situational contexts where the Present Continuous tense is used include:
- Something that is taking place at the moment of speaking:
- “He is listening to some music now.”
- “We are currently having dinner.”
- “They are singing perfectly right now.”
- Something that is planned for the near future:
- “I am going out tonight.”
- “She is leaving for London tomorrow.”
- “They are arriving at noon.”
- Something that is happening before and after a specific point in time:
- “At 5 o’clock they are drinking tea.”
- “We are sleeping at midnight.”
- “I am bathing right now.”
- Something which seems to be temporary:
- “He is staying just for the night.”
- “I am working only this evening.”
- “The kids are playing for now.”
- Something that is new:
- “People are now using smartphones to search the Internet.”
- “Why do people wear bandanas all of a sudden?”
- “The market crashed, and people are losing money.”
- Something which is changing, growing, or evolving:
- “The climate is changing.”
- “Your English is improving.”
- “This plant is growing so fast.”
7. Something that is happening again and again, perhaps with annoying regularity:
- “You are always forgetting your keys.”
- “It is always raining here.”
- “I am always losing in chess.”
The Present Continuous tense may also be used while telling a story or giving an account of a book, a movie, or a play.
When the present continuous should not be used?
It is not the right choice when speaking of something that happens regularly or periodically or has just occurred and it is no more. Also, it is not used with the verbs connected to thinking and feeling , such as: believe, dislike, know, like, love, hate, prefer, realise, recognise, remember, suppose, think (in the sense of to believe), understand, want, wish .
Other verbs that should not be used with present tense include: appear, feel, look, seem, smell, sound, taste (which are all verbs related to senses) and agree, be, belong, disagree, need, owe, own, possess (except that “to be” is sometimes used in present to express a state person is in) . These verbs are used in the present simple , if you want to speak about the present.
How to be sure that Present Continuous is the right choice?
If you want to express something that happens at the moment or the nature of such activity is continuous or you are simply telling a story, you may be pretty sure you want the Present Continuous tense to appear in the sentence.
However, the Present Continuous tense should not be used in certain contexts, and it can be helpful to compare it to the Future Simple and Present Simple to understand when to use them instead. Note that, if there is a verb related to thinking, feeling, or sensing anything, it is most likely that Present Simple is a better choice.
When the Present Continuous should not be used?
When discussing future events that are planned or scheduled, the Future Simple tense is more appropriate. For example, “I am going to the party tomorrow” should be “I will go to the party tomorrow.” The Future Simple tense indicates a specific future action.
On the other hand, when expressing general truths or habitual actions, the Present Simple tense is preferred over the Present Continuous tense. Stative verbs, which describe states or conditions, are often used in the Present Simple tense.
For instance, instead of saying “I am loving chocolate,” we say “I love chocolate” because it expresses a general truth. Similarly, instead of saying “He is understanding the concept,” we say “He understands the concept” as it describes a habitual understanding. The Present Continuous tense is most suitable for describing ongoing actions happening at the present moment.
Present Continuous and Simple Present and Future compared
Here are examples of sentences demonstrating the appropriate use of Future Simple and Present Simple instead of the Present Continuous tense.
- Present Continuous vs. Future Simple:
- Incorrect: “I am going to the beach next weekend.”
- Correct: “I will go to the beach next weekend.”
Explanation: The Future Simple tense (“will go”) is used here because the action of going to the beach is a planned future event.
- Present Continuous vs. Present Simple:
- Incorrect: “I am understanding the concept.”
- Correct: “I understand the concept.”
3. Explanation: The Present Simple tense is used (“understand”) because understanding is a state of knowledge, not an ongoing action.
- Incorrect: “She is hating broccoli.”
- Correct: “She hates broccoli.”
4. Explanation: The Present Simple tense (“hates”) is used here because “hating” describes a general dislike for broccoli, not an ongoing action.
- Incorrect: “He is having a new car.”
- Correct: “He has a new car.”
Explanation: The Present Simple tense (“has”) is used here to indicate possession of a new car, which is a state or condition.
Test your knowledge about Present Continuous
Here’s a simple test to check your knowledge of the correct use of Present Continuous verb tense in English. Each question consists of a sentence where you need to select the correct answer (a, b, or c). The sentences are designed to test your understanding of the Present Continuous tense. test your knowledge now!
- is listening
- will listen
- will be playing
Hey, what are your test results? Did you get all the answers right and your knowledge of Present Continuous verb tens has improved? Remember that with regular practice your English communication level will improve , and recognising and using the correct tense will allow you to speak clearly! Find out other ways to improve English language skills with native speaker teachers at Novakid , who transform each English lesson into an amazing adventure for your kids.
Did you like the content?
HELLO WOULD LOVE KNOW MORE THE TENSES.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Your message *

- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of the present continuous in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- 'I am cooking ' is an example of the present continuous .
- 'They're coming' is an example of the present continuous .
- bare infinitive
- non-progressive
- passivization
- phrasal verb
- subjunctive
- the active voice
- the past continuous
- the past tense
Translations of the present continuous
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
Hippocratic oath
a promise made by people when they become doctors to do everything possible to help their patients and to have high moral standards in their work

Sitting on the fence (Newspaper idioms)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun
- Translations
- All translations
Add the present continuous to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- School Guide
- English Grammar Free Course
- English Grammar Tutorial
- Parts of Speech
- Figure of Speech
- Tenses Chart
- Essay Writing
- Email Writing
- NCERT English Solutions
- English Difference Between
- SSC CGL English Syllabus
- SBI PO English Syllabus
- SBI Clerk English Syllabus
- IBPS PO English Syllabus
- IBPS CLERK English Syllabus
- What is Tense? Types, Definitions & Examples
Present Tense
- Simple Present Tense
- Present Continuous Tense - Meaning, Definition, Rules, Uses with Examples
- Present Perfect Tense: Definition, Rules, Examples, Sturcture
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Simple Past Tense - Definition, Structure, Rules and Examples
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Future Tense
- Simple Future Tense
- Future Continuous Tense
- Future Perfect Tense - Example, Formula, Rules, Structure
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense
- Rules of Tenses in Grammar
- Tense Chart in English - Rules, Examples, Types & Mind map
- English Grammar : Learn Rules of Grammar and Basics
- Parts of Speech: Definitions, Examples & 8 Types
- What is a Verb? Types, Uses, Examples
Present Continuous Tense – Meaning, Definition, Rules, Uses with Examples
Are you interested in finding methods to make your use of the English language more exciting and engaging? Using the present continuous tense is an extremely helpful piece of grammar that will allow you to add a touch of perceived loudness to both your written and spoken English. This is because the present continuous tense describes ongoing actions. Continue reading to find out how you should properly use it!
.png)
Present Continuous Tense
Table of Content
What is the Present Continuous Tense?
The present continuous tense: definition, structure of the present continuous tense, present continuous tense rules, present continuous tense examples, usage of present continuous tense, present continuous tense sentences, present continuous tense worksheet, present continuous tense exercises.
Present continuous tense is an important part of English grammar used to show actions or any situation happening in a time of speaking or around the current period. It is formed by combining the present tense of the verb “to be”(am, is, are) with the present particle form of the main verb(-ing form).
“The verb form used for actions or events that are happening or developing now” is how the Cambridge Dictionary describes the “present continuous tense.” “A verb form consisting of an auxiliary be in the present tense followed by a present participle and used especially to indicate that a present action or event is in progress, being repeated, or of a temporary nature, or to express the future,” is how the Collins Dictionary defines the present continuous tense. The Macmillan Dictionary defines the present continuous tense as “the tense used to talk about actions or behaviour that are in progress now or planned for the future.”
There is definitely just one formula to mastering the present continuous tense and this is how it goes.
Present Continuous Tense Formula
But you should be aware of something else as well. It’s important for you to understand the structure of positive, negative, interrogative, and negative interrogative phrases that contain the verb in the present continuous tense.
To have a better grasp of the present continuous tense’s construction, refer to the table that follows.
- Subject-Verb Agreement: The verb form “ to be “(am, is, are) should agree with the subject of the sentences. For singular subjects, use “ is “(he is, she is), and for plural subjects, use “are”(we are, they are).
- Present Participle Form: Add the “ -ing ” suffix to the base form of the verb to create the present participle. However, keep in mind that there are certain spelling rules to follow (e.g., drop the final “e” in words like “write” becomes “writing”).
- Time Indicators: The present continuous tense is commonly used with time expressions such as “ now ,” “ at the moment ,” “ currently, ” and “ right now ” to emphasize the ongoing nature of the action.
- I am writing an essay on my best friends.
- She is reading different kinds of novels.
- Kids are playing cricket outside now.
- Rohan is drinking coffee at the shop.
- We are going to the nearest library.
- Rick is eating his pizza at home.
- They are shopping at the fair for some refreshments
- I like listening to old classical songs.
- We are not quarreling with anyone.
- Are you planning to go to the movies tonight?
- Ongoing Actions: The present continuous tense is used to describe actions happening at the time of speaking. For example, “I am writing an article right now.”
- Temporary Situations: It is also used to describe temporary situations that are happening around the current period. For example, “She is living in London for a few months.”
- Future Plans: The present continuous tense can express future plans when combined with time expressions. For example, “We are meeting for lunch tomorrow.”
- Annoyance or Irritation: It can be used to express annoyance or irritation towards someone’s repeated actions. For example, “He is always interrupting me during meetings.”
Here are some examples of present continuous tense sentences:
- I am reading a book. This sentence shows an action (reading) that the speaker is currently doing.
- She is cooking dinner for the family. Here, the action (cooking) is happening right now.
- They are playing soccer in the park. This indicates that the action (playing) is taking place at the moment of speaking.
- We are planning our vacation for next month. Although the vacation is in the future, the planning is happening now.
- He is studying to become a doctor. This shows an ongoing action (studying) that is happening at present.
Part 1: Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verb in parentheses. I __________ (watch) a movie right now. She __________ (write) an email to her friend. They __________ (eat) lunch at the moment. We __________ (plan) our project work for next week. Part 2: Match the sentences to the correct pictures. (Here, you’d provide pictures depicting various actions and students would match sentences describing those actions in the present continuous tense.) Part 3: Change the sentences from present simple to present continuous. Example: He reads a book every night. -> He is reading a book right now. She sings beautifully. They run in the park every morning. We watch TV in the evenings. Part 4: Write your own sentences using the present continuous tense. Ask students to write five sentences about what they are doing today or what their plans are for the near future, using the present continuous tense.
1. We are _____ to Europe. 2. It ____very hard this evening. 3. Both Patrick and Shaun____ sheep fall asleep. 4. He____ more plants to the garden. 5. The builders ____a home for us. 6. A huge army of soldiers ____towards the north gate. 7. I _____the cake into ten slices. 8. You _____five eggs.
traveling is raining are counting is adding are building is marching am dividing are boiling
Also Read: Simple Past Tense – Definition, Structure, Rules and Examples Rules of Tenses in Grammar Past Perfect Tense Simple Present Tense
Present Continuous Tense – FAQs
1. what do you mean by present continuous tense.
The use of the present continuous verb tense denotes that an action or situation is occurring at the present time, on a regular basis, and may do so into the foreseeable future. The formula for the Present Continuous is to be [am, is, or are] plus the corresponding word in the present tense. While Scott searches for his new leather coat, his Aunt Victoria is warming up the vehicle.
2. What is the definition of Present Continuous Tense?
The use of the present continuous verb tense denotes that an action or situation is occurring at the present time, on a regular basis, and may do so into the foreseeable future. Persistent Existence in the Current.
3. What are the rules to be followed when using the Present Continuous Tense?
Followed by the present participle of the verb is what we use to create the present continuous tense. This is done by using the word “to be.” The present participle is a version of a word that is formed by adding the ending -ing to the end of the original verb.
4. What is the formula of Present Continuous Tense?
To write in the present continuous tense, simply combine the “be” verb (am, is, are…) with the appropriate present participle.
5. Give some examples of Present Continuous Tense.
Students are regularly coming to school. The boys and girls are playing in the park. Roy is crying out loud. It is raining now. I am cooking something special for lunch.
Please Login to comment...
- English Tenses
- SSC/Banking
- How to Delete Whatsapp Business Account?
- Discord vs Zoom: Select The Efficienct One for Virtual Meetings?
- Otter AI vs Dragon Speech Recognition: Which is the best AI Transcription Tool?
- Google Messages To Let You Send Multiple Photos
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

VIDEO
COMMENTS
Definition of the Present Continuous Tense. The Cambridge Dictionary defines the 'present continuous tense' as "the verb form used for actions or events that are happening or developing now." According to the Collins Dictionary, the present continuous tense is defined as "a verb form consisting of an auxiliary be in the present tense followed by a present participle and used ...
The present continuous (present progressive) tense is a way to convey any action or condition that is happening right now, frequently, and may be ongoing.It adds energy and action to writing, and its effect helps readers understand when the action is happening. Imagine Aunt Christine has surprised her nephew Scott for his birthday and is going to take him out to his favorite restaurant, Polly ...
Level: beginner. The present continuous is made from the present tense of the verb be and the -ing form of a verb: We use the present continuous to talk about: I'm just leaving work. I'll be home in an hour. Please be quiet. The children are sleeping. Mary is going to a new school next term.
The present continuous tense normally requires a dynamic verb. Verbs that instead describe a state of being such as emotion, belief, perception, or possession are called stative verbs. Some examples include "prefer," "appear," "exist," and "own.". Stative verbs should not be used in the present continuous tense.
Present continuous ( I am working ) - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
The present continuous (also called present progressive) is a verb tense which is used to show that an ongoing action is happening now, either at the moment of speech or now in a larger sense. The present continuous can also be used to show that an action is going to take place in the near future. Read on for detailed descriptions, examples ...
The present continuous tense is a verb tense that shows actions currently occurring. This tense also indicates when the event is temporary. Like other continuous tenses, present continuous uses the present participle form of a verb. Present continuous verbs include a helping verb or an auxiliary verb and the present participle form.
The present progressive is used: 1. To describe something which is happening at the exact moment of speech. Example: Jim is watching television at the moment. 2. To describe an action that is taking place now but not at the exact moment of speech. Example: John is working in London.
Present Continuous Definition. The present continuous is a verb tense in which the action is on-going/still going on and hence continuous. The present continuous tense is used to talk about actions that are happening at this current moment.
The structure of the Present Continuous tense is: The auxiliary verb (be) is conjugated in the Present Simple: am, are, is. The main verb is invariable in present participle form: -ing. For negative sentences we insert not between the auxiliary verb and the main verb. For question sentences, we exchange the subject and the auxiliary verb.
Among the many verb tenses, present continuous is one of the most commonly used tenses in English. It is used in daily conversations by people at large. Here is a brief breakdown of the present continuous. The article details the definition, different types of tenses, uses of present continuous tense, the structure of present continuous, and examples.
THE PRESENT CONTINUOUS definition: 1. the verb form used for actions or events that are happening or developing now: 2. the verb form…. Learn more.
Definition of the Present Continuous Tense. The present continuous tense is a verb tense used to describe actions that are currently happening and are in progress at the moment of speaking. It can also be used to describe future plans that have been arranged or scheduled. For example, "I am studying for my exam" or "She is watching a ...
How to Form a Negative Using the English Present Continuous Tense. Forming a negative in the present continuous is very simple. All you need to do is add the adverb not after the contraction of the subject and "to be.". To make it even easier, follow this simple pattern: Subject + to be (conjugated) + not + -ing verb.
The present continuous, also called the present progressive or present imperfect, is a verb form used in modern English that combines the present tense with the continuous aspect. [1] It is formed by the present tense form of be and the present participle of a verb. The present continuous is generally used to describe something that is taking ...
Structure of Present Continuous Tense. To form the Present Continuous Tense, you need two components: the present tense of the verb 'to be' and the base form of the main verb with the "-ing" suffix attached. Positive: Subject + am/is/are + base form of the verb + -ing (e.g., She is reading a book.)
Present continuous tense is a verb tense used to describe action happening right now, in the present moment and continuing. Some examples might be "I am reading a lesson," "Mike is riding his bike ...
The present continuous here shows: "I'm doubting whether I can stay in the same company much longer.". The present continuous here shows: "They're staying in a hotel until they can find a suitable apartment.". The present continuous here shows: "He's always leaving the lights on all over the house!".
We use the present continuous tense to talk about: things that are happening now, at the time when we are talking. Mum 's mowing the lawn, and I 'm doing my homework, but Isabel isn't doing anything.
Present continuous tense is used for actions that are happening in the present and/or in the future. Learn when to use the present continuous verb tense.
The Present Continuous tense, also known as the Present Progressive tense, is a grammatical form used in the English language to describe ongoing actions or situations that are happening at the present moment. It is formed by using the present tense of the auxiliary verb "to be" (am, is, are) followed by the present participle of the main ...
the present continuous meaning: 1. the verb form used for actions or events that are happening or developing now: 2. the verb form…. Learn more.
The Present Continuous Tense: Definition "The verb form used for actions or events that are happening or developing now" is how the Cambridge Dictionary describes the "present continuous tense." "A verb form consisting of an auxiliary be in the present tense followed by a present participle and used especially to indicate that a present action or event is in progress, being repeated ...