- Solve equations and inequalities
- Simplify expressions
- Factor polynomials
- Graph equations and inequalities
- Advanced solvers
- All solvers
- Arithmetics
- Determinant
- Percentages
- Scientific Notation
- Inequalities

What can QuickMath do?
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students.
- The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and cancelling common factors within a fraction.
- The equations section lets you solve an equation or system of equations. You can usually find the exact answer or, if necessary, a numerical answer to almost any accuracy you require.
- The inequalities section lets you solve an inequality or a system of inequalities for a single variable. You can also plot inequalities in two variables.
- The calculus section will carry out differentiation as well as definite and indefinite integration.
- The matrices section contains commands for the arithmetic manipulation of matrices.
- The graphs section contains commands for plotting equations and inequalities.
- The numbers section has a percentages command for explaining the most common types of percentage problems and a section for dealing with scientific notation.
Math Topics
More solvers.
- Add Fractions
- Simplify Fractions

Game Central
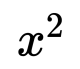
Get step-by-step explanations
Graph your math problems
Practice, practice, practice

Get math help in your language
How to Solve Algebra Problems Step-By-Step
- Pre Algebra & Algebra
- Math Tutorials
- Exponential Decay
- Worksheets By Grade
- B.B.A., Finance and Economics, University of Oklahoma
Solving Algebra word problems is useful in helping you to solve earthly problems. While the 5 steps of Algebra problem solving are listed below, the following will help you learn how to first identify the problem.
- Identify the problem.
- Identify what you know.
- Make a plan.
- Carry out the plan.
- Verify that the answer makes sense.
Identify the Problem
Back away from the calculator ; use your brain first. Your mind analyzes, plans, and guides in the labyrinthine quest for the solution. Think of the calculator as merely a tool that makes the journey easier. After all, you wouldn’t want a surgeon to crack your ribs and perform a heart transplant without first identifying the source of your chest pains.
The steps of identifying the problem are:
- Express the problem question or statement.
- Identify the unit of the final answer.
Express the Problem Question or Statement
In Algebra word problems, the problem is expressed as either a question or a statement.
- How many trees will John have to plant?
- How many televisions will Sara have to sell to earn $50,000?
- Find the number of trees John will have to plant.
- Solve for the number of televisions Sara will have to sell to earn $50,000.
Identify the Unit of the Final Answer
What will the answer look like? Now that you understand the word problem’s purpose, determine the answer’s unit. For example, will the answer be in miles, feet, ounces, pesos, dollars, the number of trees, or a number of televisions?
Algebra Word Problem
Javier is making brownies to serve at the family picnic. If the recipe calls for 2 ½ cups of cocoa to serve 4 people, how many cups will he need if 60 people attend the picnic?
- Identify the problem: How many cups will Javier need if 60 people attend the picnic?
- Identify the unit of the final answer: Cups
In the market for computer batteries, the intersection of the supply and demand functions determines the price, p dollars , and the quantity, q , of goods sold. Supply function: 80 q - p = 0 Demand function: 4 q + p = 300 Determine the price and quantity of computer batteries sold when these functions intersect.
- Identify the problem: How much will the batteries cost and how much will be sold when supply and demand functions meet?
- Identify the unit of the final answer: The quantity, or q , will be given in batteries. The price, or p , will be given in dollars.
- Proportions Word Problems Worksheet 1
- Proportions Word Problems Worksheet: Answers and Explanations
- How to Do Algebra Word Problems
- How to Solve Proportions to Adjust a Recipe
- Algebra Age-Related Word Problem Worksheets
- The Quantity Theory of Money
- Stoichiometry Definition in Chemistry
- Quiz 8th-Graders With These Math Word Problems
- Lesson Plan: Addition and Subtraction with Pictures
- How to Calculate an Equilibrium Equation in Economics
- 2nd Grade Math Word Problems
- Sixth Grade Word Problems
- Math Glossary: Mathematics Terms and Definitions
- 7th Grade Math Course of Study
- The Horse Problem: A Math Challenge
- Simple Interest Worksheets With Answers
Introduction to Algebra
Algebra is great fun - you get to solve puzzles!
What is the missing number?
OK, the answer is 6, right? Because 6 − 2 = 4 . Easy stuff.
Well, in Algebra we don't use blank boxes, we use a letter (usually an x or y, but any letter is fine). So we write:
It is really that simple. The letter (in this case an x) just means "we don't know this yet", and is often called the unknown or the variable .
And when we solve it we write:
Why Use a Letter?
So x is simply better than having an empty box. We aren't trying to make words with it!
And it doesn't have to be x , it could be y or w ... or any letter or symbol we like.
How to Solve
Algebra is just like a puzzle where we start with something like "x − 2 = 4" and we want to end up with something like "x = 6".
But instead of saying " obviously x=6", use this neat step-by-step approach:
- Work out what to remove to get "x = ..."
- Remove it by doing the opposite (adding is the opposite of subtracting)
- Do that to both sides
Here is an example:
To remove it, do the opposite , in this case add 2
Do it to both sides
Which is ...
Why did we add 2 to both sides?
To "keep the balance"....
Just remember this:
See this in action at the Algebra Balance Animation .
Another Puzzle
What we want is an answer like "x = ...", but the +5 is in the way of that! We can cancel out the +5 with a −5 (because 5−5=0)
Have a Try Yourself
Now practice on this Simple Algebra Worksheet and then check your answers. Try to use the steps we have shown you here, rather than just guessing!
Try the questions below, then read Introduction to Algebra - Multiplication

Get step-by-step solutions to your math problems

Try Math Solver

Get step-by-step explanations
Graph your math problems
Practice, practice, practice

Get math help in your language

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.29: Solving a System of Equations Algebraically
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 41230

- Samar ElHitti, Marianna Bonanome, Holly Carley, Thomas Tradler, & Lin Zhou
- CUNY New York City College of Technology & NYC College of Technology via New York City College of Technology at CUNY Academic Works
Suppose that Adam has 7 bills, all fives and tens, and that their total value is \(\$ 40 .\) How many of each bill does he have? In order to solve such a problem we must first define variables.
Let \(x\) be the number of five dollar bills.
Let \(y\) be the number of ten dollar bills.
Next, we write equations that describe the situation:
\(5 x+10 y=40 \quad:\) The combined value of the bills is \(\$ 40 .\)
That is, we must solve the following system of two linear equations in two variables (unknowns):
\(x+y=7 \quad\) : Adam has 7 bills.
\(5 x+10 y=40\) : The combined value of the bills is \(\$ 40 .\)
\[\left(\begin{align*} x+y &=7 \\ 5 x+10 y & =40 \end{align*}\right)\nonumber\]
This chapter deals with solving systems of two linear equations with two variable, such as the one above. We will consider two different algebraic methods: the substitution method and the elimination method.
The Substitution Method
In this section we solve systems of two linear equations in two variables using the substitution method . To illustrate, we will solve the system above with this method. We begin by solving the first equation for one variable in terms of the other. In this case we will solve for the variable \(y\) in terms of \(x\):
\[\begin{align*} & x+y=7 \\ \Longrightarrow & y=7-x \end{align*}\nonumber\]
Next, we substitute \(y=7-x\) into the second equation \(5 x+10 y=40:\)
\[5 x+10(7-x)=40\nonumber\]
The equation above can now be solved for \(x\) since it only involves one variable:
\[\begin{align*} 5 x+10(7-x) &=40 \\ 5 x+70-10 x &=40 \quad \text{distribute 10 into the parentheses} \\ -5 x+70 &=40 \quad \text{collect like terms} \\ -5 x &=-30 \quad \text{subtract 70 from both sides} \\ x &=6 \quad \text{divide both sides by −5} \end{align*}\nonumber\]
Hence, we get \(x=6 .\) To find \(y,\) we substitute \(x=6\) into the first equation of the system and solve for \(y\) (Note: We may substitute \(x=6\) into either of the two original equations or the equation \(y=7-x\) ):
\[\begin{array}{l} 6+y=7 \\ y=1 \text{subtract 6 from both sides} \end{array}\nonumber\]
Therefore the solution to the system of linear equations is
\[x=6, \quad y=1\nonumber\]
Before we are truly finished, we should check our solution. The solution of a system of equations are the values of its variables which, when substituted into the two original equations, give us true statements. So to check, we substitute \(x=6\) and \(y=1\) into each equation of the system:
\[\begin{array}{l} x+y=7 \Longrightarrow 6+1=7 \Longrightarrow 7=7 \text { true! } \\ 5 x+10 y=40 \Longrightarrow 5(6)+10(1)=40 \Longrightarrow 30+10=40 \Longrightarrow 40=40 \text { true! } \end{array}\nonumber\]
Hence, our solution is correct. To answer the original word problem - recalling that \(x\) is the number of five dollar bills and \(y\) is the number of ten dollar bills we have that:
\[Adam~has~6~five~ dollar~ bills~ and~ 1~ ten~ dollar~ bill.\nonumber\]
Example 27.1
\[\left(\begin{array}{l} 6 x+2 y=72 \\ 3 x+8 y=78 \end{array}\right)\nonumber\]
Again, here we solve the system of equations using substitution. First, solve the first equation \(6 x+2 y=72\) for \(y:\)
\[\begin{array}{rrr} & 6 x+2 y=72 \\ \Longrightarrow & 2 y=-6 x+72 & \text{subtract 6x from both sides} \\ \Longrightarrow & y=-3 x+36 & \text{divide both sides by 2} \end{array}\nonumber\]
Substitute \(y=-3 x+36\) into the second equation \(3 x+8 y=78\) :
\[\begin{align*} & 3 x+8 y=78 \\ \Longrightarrow & 3 x+8(-3 x+36)=78 \\ \Longrightarrow & x=10 \end{align*}\nonumber\]
Hence \(x=10 .\) Now substituting \(x=10\) into the equation \(y=-3 x+36\) yields \(y=6,\) so the solution to the system of equations is \(x=10, y=6 .\) The final step is left for the reader. It must be checked that \(x=10\) and \(y=6\) give true statements when substituted into the original system of equations.
To summarize the steps we followed to solve a system of linear equations in two variables using the algebraic method of substitution, we have:
Solving a System of Two Linear Equations in Two Variables using Substitution
- Solve one equation for one variable.
- Substitute the expression found in step 1 into the other equation.
- Solve the resulting equation.
- Substitute the value from step 3 back into the equation in step 1 to find the value of the remaining variable. 5
- Check your solution!
- Answer the question if it is a word problem.
A system of two linear equations in two variables may have one solution, no solutions, or infinitely many solutions. In Example 27.2 we will see a system with no solution.
Example 27.2
Solve the following system of equations by substitution.
\[\left(\begin{array}{l} x+y=1 \\ y=-x+2 \end{array}\right)\nonumber\]
The second equation is already solved for \(y\) in terms of \(x\) so we can substitute it directly into \(x+y=1\) :
\[x+(-x+2)=1 \Longrightarrow 2=1 \quad \text { False! }\nonumber\]
Since we get the false statement \(2=1,\) the system of equations has no solution.
The Elimination Method
A second algebraic method for solving a system of linear equations is the elimination method . The basic idea of the method is to get the coefficients of one of the variables in the two equations to be additive inverses, such as -3 and \(3,\) so that after the two equations are added, this variable is eliminated. Let's use one of the systems we solved in the previous section in order to illustrate the method:
\[\left(\begin{array}{l} x+y=7 \\ 5 x+10 y=40 \end{array}\right)\nonumber\]
The coefficients of the \(x\) variable in our two equations are 1 and \(5 .\) We can make the coefficients of \(x\) to be additive inverses by multiplying the first equation by \(-5\) and keeping the second equation untouched:
\[\left(\begin{array}{lllll} x & + &y & = & 7 \\ 5 x &+ & 10 y & = & 40 \end{array}\right) \Longrightarrow\left(\begin{array}{lllll} (-5)(x &+ & y) & = & (-5) 7 \\ 5 x & + & 10 y & = & 40 \end{array}\right)\nonumber\]
Using the distributive property, we rewrite the first equation as:
\[-5 x-5 y=-35\nonumber\]
Now we are ready to add the two equations to eliminate the variable \(x\) and solve the resulting equation for \(y\) :
\[\begin{array}{llll} & -5 x & - & 5 y & =& -35 \\ + & 5 x & + & 10 y & = & 40 \\ \hline & & & 5 y & = & 5 \\ & & \Longrightarrow & y & = & 1 \end{array}\nonumber\]
To find \(x,\) we can substitute \(y=1\) into either equation of the original system to solve for \(x:\)
\[x+1=7 \quad \Longrightarrow \quad x=6\nonumber\]
Hence, we get the same solution as we obtained using the substitution method in the previous section:
In this example, we only need to multiply the first equation by a number to make the coefficients of the variable \(x\) additive inverses. Sometimes, we need to multiply both equations by two different numbers to make the coefficients of one of the variables additive inverses. To illustrate this, let's look at Example 27.3.
Example 27.3
\[\nonumber\]
Lets aim to eliminate the \(y\) variable here. Since the least common multiple of 2 and 3 is \(6,\) we can multiply the first equation by 3 and the second equation by \(2,\) so that the coefficients of \(y\) are additive inverses:
\[\left(\begin{array}{lllll} -3 x & + & 2 y & = & 3 \\ 4 x & - & 3 y & = & -6 \end{array}\right) \Longrightarrow\left(\begin{array}{lllll} (3)(-3 x & + & 2 y & = & (3) 3 \\ (2)(4 x & - & 3 y & = & (2)(-6) \end{array}\right)\nonumber\]
Using the distributive property, we rewrite the two equations as:
\[\left(\begin{array}{lllll} -9 x & + & 6 y & = & 9 \\ 8 x & - & 6 y & = & -12 \end{array}\right)\nonumber\]
Adding them together gives:
\[-1 x=-3 \quad \Longrightarrow \quad x=3\nonumber\]
To find \(y,\) we can substitute \(x=3\) into the first equation (or the second equation) of the original system to solve for \(y:\)
\[-3(3)+2 y=3 \Longrightarrow-9+2 y=3 \Longrightarrow 2 y=12 \Longrightarrow y=6\nonumber\]
Hence, the answer to the problem is:
\[x=3 \quad y=6\nonumber\]
We can check the answer by substituting both numbers into the original system and see if both equations are correct.
The following steps summarize how to solve a system of equations by the elimination method:
Solving a System of Two Linear Equations in Two Variables using Elimination
- Multiply one or both equations by a nonzero number so that the coefficients of one of the variables are additive inverses.
- Add the equations to eliminate the variable.
- Substitute the value from step 3 back into either of the original equations to find the value of the remaining variable.
Exit Problem
Solve algebraically:
\(\begin{array}{lllll} 8 x & - & 4 y & = & 4 \\ 3 x & - & 2 y & = & 3 \end{array}\)
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Mathematics

How to Solve Word Problems in Algebra
Last Updated: December 19, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Daron Cam . Daron Cam is an Academic Tutor and the Founder of Bay Area Tutors, Inc., a San Francisco Bay Area-based tutoring service that provides tutoring in mathematics, science, and overall academic confidence building. Daron has over eight years of teaching math in classrooms and over nine years of one-on-one tutoring experience. He teaches all levels of math including calculus, pre-algebra, algebra I, geometry, and SAT/ACT math prep. Daron holds a BA from the University of California, Berkeley and a math teaching credential from St. Mary's College. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 70,749 times.
You can solve many real world problems with the help of math. In order to familiarize students with these kinds of problems, teachers include word problems in their math curriculum. However, word problems can present a real challenge if you don't know how to break them down and find the numbers underneath the story. Solving word problems is an art of transforming the words and sentences into mathematical expressions and then applying conventional algebraic techniques to solve the problem.
Assessing the Problem

- For example, you might have the following problem: Jane went to a book shop and bought a book. While at the store Jane found a second interesting book and bought it for $80. The price of the second book was $10 less than three times the price of he first book. What was the price of the first book?
- In this problem, you are asked to find the price of the first book Jane purchased.

- For example, you know that Jane bought two books. You know that the second book was $80. You also know that the second book cost $10 less than 3 times the price of the first book. You don't know the price of the first book.

- Multiplication keywords include times, of, and f actor. [9] X Research source
- Division keywords include per, out of, and percent. [10] X Research source
- Addition keywords include some, more, and together. [11] X Research source
- Subtraction keywords include difference, fewer, and decreased. [12] X Research source
Finding the Solution

Completing a Sample Problem

- Robyn and Billy run a lemonade stand. They are giving all the money that they make to a cat shelter. They will combine their profits from selling lemonade with their tips. They sell cups of lemonade for 75 cents. Their mom and dad have agreed to double whatever amount they receive in tips. Write an equation that describes the amount of money Robyn and Billy will give to the shelter.

- Since you are combining their profits and tips, you will be adding two terms. So, x = __ + __.

Expert Q&A

- Word problems can have more than one unknown and more the one variable. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 1
- The number of variables is always equal to the number of unknowns. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- While solving word problems you should always read every sentence carefully and try to extract all the numerical information. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ Daron Cam. Academic Tutor. Expert Interview. 29 May 2020.
- ↑ http://www.purplemath.com/modules/translat.htm
- ↑ https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/word-questions-solving.html
- ↑ https://www.wtamu.edu/academic/anns/mps/math/mathlab/int_algebra/int_alg_tut8_probsol.htm
- ↑ http://www.virtualnerd.com/algebra-1/algebra-foundations/word-problem-equation-writing.php
- ↑ https://www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/praxis-math/praxis-math-lessons/praxis-math-algebra/a/gtp--praxis-math--article--algebraic-word-problems--lesson
About This Article

To solve word problems in algebra, start by reading the problem carefully and determining what you’re being asked to find. Next, summarize what information you know and what you need to know. Then, assign variables to the unknown quantities. For example, if you know that Jane bought 2 books, and the second book cost $80, which was $10 less than 3 times the price of the first book, assign x to the price of the 1st book. Use this information to write your equation, which is 80 = 3x - 10. To learn how to solve an equation with multiple variables, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
James Carson
Sep 13, 2019
Did this article help you?

Lee Broadway
Aug 26, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter

- Mathematicians
- Math Lessons
- Square Roots
- Math Calculators
How to Do Algebra – Practical Tips for Mastering Equations
JUMP TO TOPIC
Understanding the Basics of Algebra
Solving common algebra problems, avoiding mistakes and building confidence, addition and subtraction, multiplication and division, working with fractions and decimals, graphs and functions in algebra, advanced algebraic concepts, applications of algebra.
As we begin our journey in algebra, it’s essential to foster confidence along the way, which comes from practice and the realization that algebra is a set of tools that empowers us to solve a variety of problems.
We recognize that each algebraic equation is a puzzle waiting to be solved, and just like any puzzle, there’s a method to approach it. Familiarity with the order of operations , the ability to manipulate algebraic expressions, and knowing how to handle fractions and decimals are all part of our toolkit.
Let’s join forces and demystify algebra, turning it from a feared subject into one where we can excel through patience and persistence. Stay tuned as we explore practical tips that will help us maneuver through the world of algebra together.
When we approach algebra, we’re engaging with a branch of mathematics where symbols, often called variables , take the place of numbers. These variables can represent numbers whose values are not yet known, allowing us to solve a wide range of problems.
In algebra, it’s crucial to get comfortable with variables. Think of a variable like a placeholder for a number we’re trying to find. For example, in the equation x – 2 = 4 , x is our variable.
Order of Operations Remembering the order of operations is key to solving algebraic equations. We use the acronym PEMDAS to recall this sequence:
- P arentheses
- M ultiplication and D ivision (from left to right)
- A ddition and S ubtraction (from left to right)
By sticking to this order, we ensure that we solve equations accurately.
Working with Equations Equations are like puzzles where we aim to isolate the variable and find its value. Let’s break this down:
- Identify what’s being added, subtracted, multiplied, or divided to the variable.
- Perform the opposite operation on both sides of the equation.
- Simplify until the variable stands alone with its value revealed.
Here’s a simple table to illustrate these steps with the equation x + 3 = 7 :
By applying these foundational concepts, we set ourselves up for success in solving algebraic problems. Remember, practice is our best friend in becoming proficient with algebra.
When tackling algebra problems , our first step is always to understand the problem at hand. For linear equations , we often have to find the value of a variable that makes the equation true. Let’s look at an example:

Problem: Solve for x: 2x + 3 = 7 Solution: First, subtract 3 from both sides to get 2x = 4. Next, divide both sides by 2 to find x = 2.
The Quadratic equations can be a bit trickier. These involve terms squared (like x²) and often require finding two solutions.
Problem: Solve for x: x² – 5x + 6 = 0 Solution: We can factor this equation to (x – 2)(x – 3) = 0, which gives us the solutions x = 2 and x = 3.
Word problems add another layer of complexity because we must translate a narrative into an equation. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Define variables: Let x represent what we’re solving for.
- Set up an equation: Use the given information to form an equation.
- Solve the equation: Use algebraic methods to solve for x.
- Verify your answer: Check if the solution makes sense in the context of the problem.
To ensure we’re solving problems efficiently, we adhere to the following best practices:
- Check for understanding: Ensure we grasp all aspects of the problem.
- Organize information: Write down what we know and what we need to find out.
- Break it down: Tackle the problem in smaller, more manageable steps.
- Check your work: Always review solutions for potential errors.
By following these strategies, we’ll be equipped to handle most algebra problems that come our way!
When we approach algebra, understanding the common pitfalls is as important as learning the concepts themselves. We will identify a few frequent mistakes and share strategies to bolster your confidence in algebra.
Order of Operations: A frequent mistake is not following the PEMDAS/BODMAS rules, where you perform calculations in this order: Parentheses/Brackets, Exponents/Orders, Multiplication and Division (from left to right), and Addition and Subtraction (from left to right). Remembering this acronym helps us avoid computation errors.
Variables and Equations: It’s easy to misinterpret variables or simplify equations incorrectly. We should always double-check our work, ensuring that we combine like terms and distribute coefficients properly.
Quadratic Equations: Solving these can be tricky. Remember to apply formulas and the factoring techniques correctly. Incorrect application could lead to wrong solutions.
To enhance our confidence, we must practice regularly. Working on various problems increases our familiarity with the types of questions that may appear on algebra tests.
Self-Teaching Guide: Make use of guides and textbooks. These resources often contain practice exercises and clear explanations for solving different types of algebra problems.
Use Technology Wisely: Incorporate educational technology where appropriate. Software and online platforms can provide interactive lessons and exercises that adapt to our skill level.
Study Groups: Working with peers can clarify doubts and reinforce learning. If someone else understands a concept, they can help explain it from a student’s perspective.
Regular Review: Finally, revisiting past topics periodically can help cement our understanding and contribute to long-term retention of algebra concepts. This habit ensures we’re always prepared for upcoming exams.
By staying mindful of these tips, we elevate our algebra skills and approach tests with greater assurance.
Exploring Algebraic Operations
In algebra, understanding how to manipulate numbers and variables through basic operations is essential. We’ll guide you through each process step by step.

When we’re dealing with algebraic expressions , addition and subtraction are about combining like terms. Here’s how we do it:
- Identify like terms : These are terms with the same variable raised to the same power.
- Combine them : Add or subtract their coefficients.
Example : (3x + 2x = (3+2)x = 5x) ($7y^2 – 4y^2$ = $(7-4)y^2 = 3y^2)$
For the multiplication of algebraic terms, we use the distributive property and laws of exponents.
- Distributive property : (a(b + c) = ab + ac)
- Multiplying exponents : When bases are the same, we add exponents. $(x^a \cdot x^b = x^{a+b})$
With division :
- Divide coefficients : If $( \frac{8x}{2x} )$, divide 8 by 2 to get 4.
- Subtract exponents : If $( \frac{x^3}{x^2} )$, subtract exponents (3 – 2 = 1), so our answer is $(x^1)$ or simply (x).
In algebra, we often encounter fractions and decimals in equations:
For fractions :
- Find a common denominator for addition and subtraction.
- Multiply straight across the numerator and denominator for multiplication.
- Flip the second fraction and multiply for division (reciprocal).
Example : $( \frac{3}{4} + \frac{1}{4} = \frac{3+1}{4} = \frac{4}{4} = 1 ) ( \frac{1}{3} \cdot \frac{3}{4} = \frac{1 \cdot 3}{3 \cdot 4} = \frac{3}{12} = \frac{1}{4} )$
With decimals , line up the decimal points for addition and subtraction. For multiplication, multiply normally and count decimal places from right to left in the product equal to the sum of the decimal places in the factors.
Practice these operations to build a strong foundation in algebra. Remember, step by step, we can solve even the most complex algebraic expressions.
When we work with functions in algebra, we often represent them visually using graphs. Graphs make understanding and interpreting functions easier because they provide a picture of what’s going on.
Function Notation is how we write functions algebraically. For example, if we have a function f that takes an input x, we write it as f(x) . This notation helps us quickly see how the output is connected to the input.
Function Transformations change the appearance of a graph. Here are the basic types:
To graph a function , we create a set of points where each point represents an input and its corresponding output . By connecting these points, we get the shape of the function, which helps us see patterns like linearity, curvature, and other important behaviors.
When interpreting functions , we look for specific characteristics like:
- The intercepts , where the graph crosses the axes .
- The slope , indicating steepness and direction for linear functions.
- The vertex for quadratic functions, which is the highest or lowest point.
Remember, different types of functions have different features, but once you master interpreting these features on graphs, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of how the function behaves across different values.
In short, familiarizing ourselves with graphing and interpreting functions equips us with the tools to tackle algebra problems more effectively.
In advanced algebra, we dive deeper into more sophisticated topics beyond the foundation we’ve built in basic algebra. To excel in these areas, it’s important to understand the following concepts:
Polynomials : We explore polynomials further by engaging with higher-degree equations and understanding the nuances of factoring polynomials . Factorization is key, allowing us to break down complex polynomials into simpler factors, which simplifies solving the equations.
Ratios and Proportion : We use ratios to compare two quantities and proportions to express that two ratios are equal. These are crucial when solving problems involving scale and in real-world applications such as in mixtures or map reading.
Inequalities : Expanding upon simple inequalities, we encounter systems of inequalities and learn to graph the solutions on a coordinate plane. We also explore absolute value inequalities which require careful attention as they introduce two potential ranges of solutions.
Factorials : Often represented with an exclamation point (n!), factorials are the product of all positive integers less than or equal to n. They are frequently found in permutations and combinations, which play a large role in probability and statistics.
Here’s a quick reference on how to denote various key elements:
- Absolute value : |x|
- Factorial of 5 : 5!
- Polynomial factorization : ( (x – r_1)(x – r_2)…(x – r_n) ), where each ( r ) is a root.
By grasping these concepts, we prepare ourselves for tackling algebraic challenges with confidence. Remember, practice is vital, so work through problems, and don’t hesitate to seek help when needed. Happy solving!
We encounter algebra in many situations, often without even realizing it! Here are a few practical tips on how we can apply algebra in our daily lives.
Budgeting: By creating equations to manage our incomes and expenses, we can keep our finances in check. It’s a practical application of solving for an unknown variable , our savings!
Cooking and Recipes: Altering a recipe? We use ratios and proportions, which are algebraic concepts, to adjust ingredient amounts whilst maintaining taste and consistency.
Shopping Discounts: Calculating discounts and sales prices is a day-to-day use of algebra. A price tag showing 20% off? No sweat, we just multiply the original price by 0.8 to find the new price.
When it comes to learning algebra, resources are plentiful:
Technology Tips: Websites like kastatic.org and kasandbox.org provide exercises and lessons to strengthen our algebra skills without the hassle of a web filter blocking our study. These resources usually load external resources so we can practice unblocked.
Programming: For those of us interested in technology, programming offers a direct connection to algebra. Understanding variables and logic in code requires algebraic thinking.
Projectile Motion: Sports enthusiasts use algebra intuitively when they calculate the best angle and force to throw a ball. It’s a real-world application of systems of equations !
If we need help, there’s a wealth of math lessons and exercises online that can assist us with our algebra studies. Remember, we’re not alone, and there are always more ways to make algebra both fun and relevant to our lives.
In our journey through algebra, we’ve equipped ourselves with an array of strategies to solve equations and understand mathematical expressions. We’ve learned that algebra is not just about finding the value of ‘x’, but about forming connections and developing problem-solving skills that are applicable far beyond the classroom.
Let’s recap the key takeaways:
- Practice regularly : Just like learning a new language, proficiency in algebra comes from consistent practice.
- Build from basics : Ensure your foundational math skills are solid, as they are the bedrock on which algebra stands.
- Understand the principles : Grasping the concepts behind the formulas makes it easier to apply them to different problems.
- Seek help when needed : Don’t hesitate to ask for assistance or use additional resources if concepts are unclear.
Remember, every equation represents a problem that can be dissected and conquered. By now, we should be better at identifying how algebra relates to real-world situations, which improves our analytical thinking.
As we continue to apply these skills in everyday scenarios, the versatility of algebra becomes increasingly clear. Whether budgeting finances, adjusting recipes or analyzing data, the power of algebra enhances our decision-making abilities and helps us approach complex problems with confidence.
- Pre Calculus
- Probability
- Sets & Set Theory
- Trigonometry
The Tech Edvocate
- Advertisement
- Home Page Five (No Sidebar)
- Home Page Four
- Home Page Three
- Home Page Two
- Icons [No Sidebar]
- Left Sidbear Page
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- My Speaking Page
- Newsletter Sign Up Confirmation
- Newsletter Unsubscription
- Page Example
- Privacy Policy
- Protected Content
- Request a Product Review
- Shortcodes Examples
- Terms and Conditions
- The Edvocate
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- Write For Us
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Assistive Technology
- Child Development Tech
- Early Childhood & K-12 EdTech
- EdTech Futures
- EdTech News
- EdTech Policy & Reform
- EdTech Startups & Businesses
- Higher Education EdTech
- Online Learning & eLearning
- Parent & Family Tech
- Personalized Learning
- Product Reviews
- Tech Edvocate Awards
- School Ratings
3 Simple Ways to Edit a WAV File
3 ways to cite video games, easy ways to treat an ice burn: 12 steps, 3 ways to put ink cartridges in a printer, 3 ways to log out of gmail, 4 ways to belay, how to become a successful runway model, 3 ways to create a filter in gmail, how to highlight blonde hair, 4 easy ways to extract specific data from pdf to excel, how to solve word problems in algebra.
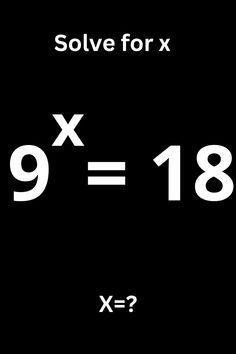
Introduction:
Word problems can be one of the most daunting aspects of algebra for many students. However, by following a few simple steps, you can master the art of solving word problems and improve your algebra skills. In this article, we will discuss the necessary steps to tackle word problems in algebra effectively.
Step 1: Read the problem carefully
The first step in solving any word problem is to read it thoroughly. Be sure to understand the problem’s context and the information provided. Look for clues and keywords that indicate relationships between variables.
Step 2: Identify the variables
Once you have a clear understanding of the problem, identify the unknown quantities or variables. For instance, if the problem involves finding the age of two siblings, you could represent their ages as “a” and “b.”
Step 3: Translate words into algebraic expressions
Convert the problem’s language into algebraic expressions involving variables and operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division. Look for key phrases like “sum,” “difference,” “product,” or “quotient” to guide your translation.
Step 4: Set up an equation (or equations)
Using your translated expressions from step 3, set up an equation that represents the given information. For more complex problems, you may need to write a system of equations that can be solved simultaneously.
Step 5: Solve the equation(s)
Now that you have an equation (or equations) to work with, use your algebra skills to solve for the unknown variable(s). You may need to perform steps like simplification, combining like terms, or using methods specific to linear equations or systems (e.g., substitution or elimination).
Step 6: Check your solution
Before accepting your answer as correct, take a moment to verify whether it makes sense within the context of the original problem. If you find any discrepancies or inconsistencies, revisit your steps to find the error and correct it.
Step 7: Write the final answer in a clear and concise manner
Once you are confident in your solution, present your final answer in a complete and easily understood form. Make sure to include any necessary units or labels to make your answer meaningful.
Conclusion:
By following these seven steps, you can efficiently solve word problems in algebra and boost your confidence in tackling these challenging problems. It takes time and practice but mastering this skill will make you more fluent in algebra and improve your overall mathematical abilities. Happy problem solving!
How to Breed Pit Bulls
How to say horse in spanish: 3 ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

3 Ways to Eat Granola

3 Ways to Get Pecs and Abs

How to Write a Thank You Note: 9 Steps

Simple Ways to Drink from a Coconut: 9 Steps
3 Ways to Keep Crappie in an Aquarium

Solver Title
Generating PDF...
- Pre Algebra Order of Operations Factors & Primes Fractions Long Arithmetic Decimals Exponents & Radicals Ratios & Proportions Percent Modulo Number Line Mean, Median & Mode
- Algebra Equations Inequalities System of Equations System of Inequalities Basic Operations Algebraic Properties Partial Fractions Polynomials Rational Expressions Sequences Power Sums Interval Notation Pi (Product) Notation Induction Logical Sets Word Problems
- Pre Calculus Equations Inequalities Scientific Calculator Scientific Notation Arithmetics Complex Numbers Polar/Cartesian Simultaneous Equations System of Inequalities Polynomials Rationales Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Coordinate Geometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Conic Sections Trigonometry
- Calculus Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series Fourier Transform
- Functions Line Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Conic Sections Transformation
- Linear Algebra Matrices Vectors
- Trigonometry Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify
- Statistics Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Average Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability Mid-Range Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal Distribution
- Physics Mechanics
- Chemistry Chemical Reactions Chemical Properties
- Finance Simple Interest Compound Interest Present Value Future Value
- Economics Point of Diminishing Return
- Conversions Roman Numerals Radical to Exponent Exponent to Radical To Fraction To Decimal To Mixed Number To Improper Fraction Radians to Degrees Degrees to Radians Hexadecimal Scientific Notation Distance Weight Time Volume
- Pre Algebra
- One-Step Addition
- One-Step Subtraction
- One-Step Multiplication
- One-Step Division
- One-Step Decimals
- Two-Step Integers
- Two-Step Add/Subtract
- Two-Step Multiply/Divide
- Two-Step Fractions
- Two-Step Decimals
- Multi-Step Integers
- Multi-Step with Parentheses
- Multi-Step Rational
- Multi-Step Fractions
- Multi-Step Decimals
- Solve by Factoring
- Completing the Square
- Quadratic Formula
- Biquadratic
- Logarithmic
- Exponential
- Rational Roots
- Floor/Ceiling
- Equation Given Roots
- Newton Raphson
- Substitution
- Elimination
- Cramer's Rule
- Gaussian Elimination
- System of Inequalities
- Perfect Squares
- Difference of Squares
- Difference of Cubes
- Sum of Cubes
- Polynomials
- Distributive Property
- FOIL method
- Perfect Cubes
- Binomial Expansion
- Negative Rule
- Product Rule
- Quotient Rule
- Expand Power Rule
- Fraction Exponent
- Exponent Rules
- Exponential Form
- Logarithmic Form
- Absolute Value
- Rational Number
- Powers of i
- Partial Fractions
- Is Polynomial
- Leading Coefficient
- Leading Term
- Standard Form
- Complete the Square
- Synthetic Division
- Linear Factors
- Rationalize Denominator
- Rationalize Numerator
- Identify Type
- Convergence
- Interval Notation
- Pi (Product) Notation
- Boolean Algebra
- Truth Table
- Mutual Exclusive
- Cardinality
- Caretesian Product
- Age Problems
- Distance Problems
- Cost Problems
- Investment Problems
- Number Problems
- Percent Problems
- Addition/Subtraction
- Multiplication/Division
- Dice Problems
- Coin Problems
- Card Problems
- Pre Calculus
- Linear Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Conversions

Most Used Actions
Number line.
- -x+3\gt 2x+1
- (x+5)(x-5)\gt 0
- 10^{1-x}=10^4
- \sqrt{3+x}=-2
- 6+11x+6x^2+x^3=0
- factor\:x^{2}-5x+6
- simplify\:\frac{2}{3}-\frac{3}{2}+\frac{1}{4}
- x+2y=2x-5,\:x-y=3
- How do you solve algebraic expressions?
- To solve an algebraic expression, simplify the expression by combining like terms, isolate the variable on one side of the equation by using inverse operations. Then, solve the equation by finding the value of the variable that makes the equation true.
- What are the basics of algebra?
- The basics of algebra are the commutative, associative, and distributive laws.
- What are the 3 rules of algebra?
- The basic rules of algebra are the commutative, associative, and distributive laws.
- What is the golden rule of algebra?
- The golden rule of algebra states Do unto one side of the equation what you do to others. Meaning, whatever operation is being used on one side of equation, the same will be used on the other side too.
- What are the 5 basic laws of algebra?
- The basic laws of algebra are the Commutative Law For Addition, Commutative Law For Multiplication, Associative Law For Addition, Associative Law For Multiplication, and the Distributive Law.
algebra-calculator
- Middle School Math Solutions – Equation Calculator Welcome to our new "Getting Started" math solutions series. Over the next few weeks, we'll be showing how Symbolab...
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.
Equation Solver
Enter the Equation you want to solve into the editor.
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students. The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and ...
Solve problems from Pre Algebra to Calculus step-by-step . Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Is there a step by step calculator for math? Symbolab is the best step by step calculator for a wide range of math problems, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus and linear algebra. It shows you the solution, graph, detailed steps and explanations ...
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. ... While we cover a very wide range of problems, we are currently unable to assist with this specific problem. I spoke with my team and we will make note of this for future training.
Get math help in your language. Works in Spanish, Hindi, German, and more. Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app.
Why we do the same thing to both sides: Variable on both sides. Intro to equations with variables on both sides. Equations with variables on both sides: 20-7x=6x-6. Equation with variables on both sides: fractions. Equation with the variable in the denominator.
In fact, solving an equation is just like solving a puzzle. And like puzzles, there are things we can (and cannot) do. Here are some things we can do: Add or Subtract the same value from both sides; Clear out any fractions by Multiplying every term by the bottom parts; Divide every term by the same nonzero value; Combine Like Terms; Factoring
Algebraic word problems are questions that require translating sentences to equations, then solving those equations. The equations we need to write will only involve. basic arithmetic operations. and a single variable. Usually, the variable represents an unknown quantity in a real-life scenario.
Algebra (all content) 20 units · 412 skills. Unit 1 Introduction to algebra. Unit 2 Solving basic equations & inequalities (one variable, linear) Unit 3 Linear equations, functions, & graphs. Unit 4 Sequences. Unit 5 System of equations. Unit 6 Two-variable inequalities. Unit 7 Functions. Unit 8 Absolute value equations, functions, & inequalities.
Solving Algebra word problems is useful in helping you to solve earthly problems. While the 5 steps of Algebra problem solving are listed below, the following will help you learn how to first identify the problem. Identify the problem. Identify what you know. Make a plan.
How to Solve. Algebra is just like a puzzle where we start with something like "x − 2 = 4" and we want to end up with something like "x = 6". But instead of saying "obviously x=6", use this neat step-by-step approach: Work out what to remove to get "x = ..." Remove it by doing the opposite (adding is the opposite of subtracting)
First, move everything that isn't under the radical sign to the other side of the equation: √ (2x+9) = 5. Then, square both sides to remove the radical: (√ (2x+9)) 2 = 5 2 =. 2x + 9 = 25. Now, solve the equation as you normally would by combining the constants and isolating the variable: 2x = 25 - 9 =. 2x = 16.
http://www.greenemath.com/In this lesson, we will cover how to solve algebra word problems. We will cover translating phrases to algebraic expressions, solvi...
Algebra Calculator. Graphing Calculator. Matrix Calculator. Draw, Scan, Solve, and Learn! ... Get step-by-step explanations. See how to solve problems and show your work—plus get definitions for mathematical concepts. Graph your math problems. Instantly graph any equation to visualize your function and understand the relationship between ...
Multiply one or both equations by a nonzero number so that the coefficients of one of the variables are additive inverses. Add the equations to eliminate the variable. Solve the resulting equation. Substitute the value from step 3 back into either of the original equations to find the value of the remaining variable.
The Algebra 1 course, often taught in the 9th grade, covers Linear equations, inequalities, functions, and graphs; Systems of equations and inequalities; Extension of the concept of a function; Exponential models; and Quadratic equations, functions, and graphs. Khan Academy's Algebra 1 course is built to deliver a comprehensive, illuminating, engaging, and Common Core aligned experience!
Putting everything together, you have . 2. Solve an equation for one variable. If you have only one unknown in your word problem, isolate the variable in your equation and find which number it is equal to. Use the normal rules of algebra to isolate the variable. Remember that you need to keep the equation balanced.
Solving algebra problems often starts with simplifying expressions. Here's a simple method to follow: Combine like terms: Terms that have the same variable can be combined. For instance, ( 3x + 4x = 7x ). Isolate the variable: Move the variable to one side of the equation. If the equation is ( 2x + 5 = 13 ), my job is to get ( x ) by itself ...
Problem: Solve for x: 2x + 3 = 7. Solution: First, subtract 3 from both sides to get 2x = 4. Next, divide both sides by 2 to find x = 2. The Quadratic equations can be a bit trickier. These involve terms squared (like x²) and often require finding two solutions. Problem: Solve for x: x² - 5x + 6 = 0.
Spread the loveIntroduction: Word problems can be one of the most daunting aspects of algebra for many students. However, by following a few simple steps, you can master the art of solving word problems and improve your algebra skills. In this article, we will discuss the necessary steps to tackle word problems in algebra effectively. Step 1: Read the problem carefully The first step in ...
Intro to equations with variables on both sides. (Opens a modal) Equations with variables on both sides: 20-7x=6x-6. (Opens a modal) Equation with variables on both sides: fractions. (Opens a modal) Equation with the variable in the denominator. (Opens a modal) Figuring out missing algebraic step.
This video shows how to solve 2 different word problems by setting up Algebraic equations. The second example requires setting up a a system of equations to...
To solve an algebraic expression, simplify the expression by combining like terms, isolate the variable on one side of the equation by using inverse operations. Then, solve the equation by finding the value of the variable that makes the equation true.
Algebra. Equation Solver. Step 1: Enter the Equation you want to solve into the editor. The equation calculator allows you to take a simple or complex equation and solve by best method possible. Step 2: Click the blue arrow to submit and see the result! The equation solver allows you to enter your problem and solve the equation to see the result.
Systems of equations word problems (with zero and infinite solutions) Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Quiz 3 Level up on the above skills and collect up to 400 Mastery points Start quiz
How to solve this nice exponential math algebra equation | Olympiad Problem | x=?#algebra #exponents #olympiad #integral #maths