- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy

McGraw Hill My Math Grade 3 Chapter 12 Lesson 8 Answer Key Problem-Solving Investigation: Solve a Simpler Problem
All the solutions provided in McGraw Hill My Math Grade 3 Answer Key PDF Chapter 12 Lesson 8 Problem-Solving Investigation: Solve a Simpler Problem will give you a clear idea of the concepts.
McGraw-Hill My Math Grade 3 Answer Key Chapter 12 Lesson 8 Problem-Solving Investigation: Solve a Simpler Problem
Learn the Strategy

2. Plan I will collect and organize the data in a line plot. Then I will decide if Shane’s estimate is ________________. Answer: I will collect and organize the data in a line plot. Then I will decide if Shane’s estimate is reasonable.
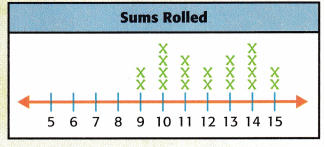
4. Check Does your answer make sense? Explain. Answer: Yes,because he only rolled 15 twice.
Practice the Strategy

1. Understand What facts do you know? Answer: From the given data, we know that Julina needs to make 100 favors for the family reunion and also about the estimate of relatives coming on friday and saturday. What do you need to find? Answer: We need to find the total number of relatives coming.
2. Plan Answer: Determine the total number of relatives coming.Add the relatives coming on friday and saturday and compare that too 100.
3. Solve Answer: Count of relatives coming on friday=62 Count of relatives coming on saturday = half the count of friday=62÷2=31 Therefore, the total count of relatives will be = 62+31=93
4. Check Does your answer make sense? Explain. Answer: Total 93 relatives will be attending, 93 is less than 100.So, Julina’s estimation of making 100 favors for the family reunion is resonable.
Apply the Strategy
Solve each problem by first solving a simpler problem.
Review the Strategies
Use any strategy to solve each problem.
- Solve a simpler problem.
- Determine reasonable answers.
- Make a table.
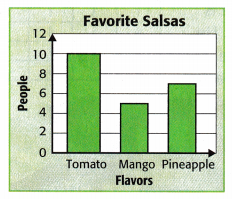
From the above data, How many fewer people chose mango salsa than pineapple or tomato salsa combined? Answer: The total number of people who like pineapple or tomato salsa combined will be 7+10=17 The fewer people who choose mango salsa than pineapple or tomato salsa combined will be 17-5=12
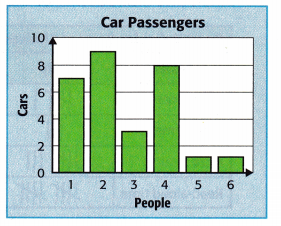
How many more cars had either 1 or 2 people rather than 4 people? Answer: Number of cars who had either 1 or 2 people will be 7+9=16 Number of cars who had either 4 people will be 8 Therefore, the number of cars who had either 1 or 2 people rather than 4 people will be 16-8=8
Question 5. Mathematical PRACTICE Reason Is it reasonable to say that about twice as many cars had 1 passenger than 3 passengers? Explain. Answer: Yes, that is reasonable to say because the number of cars with 1 passenger is 7 and twice of 3 passengers is 6. As 7 is greater than 6, the given statement is reasonable.
McGraw Hill My Math Grade 3 Chapter 12 Lesson 8 My Homework Answer Key
Problem Solving

Question 3. Mathematical PRACTICE Make Sense of Problems Look at Exercise 2. What is the simpler problem you solved first? Answer: The first simpler problem solved is to find out if the estimate is reasonable.I had to find the actual number of friends Elizabeth survyed.
Question 4. How many more students chose football and baseball together than basketball? Write an equation. Answer: The number of students who chose football and baseball together are 8+4=12 The number of students who chose basketball are 10 Therefore, the number of students chose football and baseball together than basketball will be 12-10=2 Let ‘a’ be the number of students chose football and baseball together than basketball. So, the equation will be 12-10=a=2
Question 5. Mathematical PRACTICE Model Math Write a problem about the data above that would take two steps to solve. Then solve. Answer: Is it reasonable to say that the number of Elizabeth’s friends who like football are twice that of baseball? From the above data, we know that the number of Elizabeth’s friends who like football are 8. The number of Elizabeth’s friends who like baseball are 4. As twice of 4 (2×4=8) is 8, the estimate is reasonable.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Please log in to save materials. Log in
- Resource Library
- 7th Grade Mathematics
Education Standards
Maryland college and career ready math standards.
Learning Domain: Expressions and Equations
Standard: Solve multi-step real-life and mathematical problems posed with positive and negative rational numbers in any form (whole numbers, fractions, and decimals), using tools strategically. Apply properties of operations as strategies to calculate with numbers in any form; convert between forms as appropriate; and assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies. For example: If a woman making $25 an hour gets a 10% raise, she will make an additional 1/10 of her salary an hour, or $2.50, for a new salary of $27.50. If you want to place a towel bar 9 3/4 inches long in the center of a door that is 27 1/2 inches wide, you will need to place the bar about 9 inches from each edge; this estimate can be used as a check on the exact computation.
Standard: Use variables to represent quantities in a real-world or mathematical problem, and construct simple equations and inequalities to solve problems by reasoning about the quantities.
Standard: Solve word problems leading to equations of the form px + q = r and p(x + q) = r, where p, q, and r are specific rational numbers. Solve equations of these forms fluently. Compare an algebraic solution to an arithmetic solution, identifying the sequence of the operations used in each approach. For example, The perimeter of a rectangle is 54 cm. Its length is 6 cm. What is its width?
Common Core State Standards Math
Cluster: Solve real-life and mathematical problems using numerical and algebraic expressions and equations
Reasonable Estimations & Exact Solutions

Students solve real-world problems by writing and solving equations. Students estimate the solution and determine if the estimate is reasonable before finding the exact solution. They write the solution as a complete sentence.
Students complete a Self Check.
Key Concepts
Students solve real-world problems by first estimating the solution and assessing the reasonableness of the solution. Next, they write an equation to solve the problem and then use the properties of equality to solve the equation. Students write the solution to the problem as a complete sentence.
Goals and Learning Objectives
- Write equations to solve multi-step real-life problems involving rational numbers.
- Solve equations using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of rational numbers.
- Use estimations strategies to estimate the solution and determine if the estimate is reasonable.
- Write the solution as a complete sentence.
Lesson Guide
Have students watch the video with a partner. Point out to students that their task is to write an equation to solve the problem posed in the video. Students can watch the video as many times as needed in order to find all information needed and write the equation.
As students are watching and listening to the video, they should take notes about any amounts given and label those amounts. They should make note of what they need to find out and use that information to define the variable in their equation.
Possible equation:
Let x equal the price in dollars of one pound of carrot raisin salad.
( 2 1 2 ⋅ 6.10 ) + ( 1 3 4 ⋅ 5 ) + 1 2 x = 28.25
SWD: Students with disabilities may have difficulty determining the relevant information for this task. Before they watch the video, provide students with a note-taking organizer that includes space for notes on how to write an equation.
Watch the video.
- Write an equation to find the cost per pound for the carrot raisin salad.
VIDEO: Best Deli
Math Mission
Discuss the Math Mission. Students will write equations to represent problem situations, make estimates, and solve the equations.
ELL: After defining the term estimation , explain that in solving math problems, we sometimes look for answers that are precise while other times estimation is sufficient. The context of the problem determines whether the answer should be precise or estimated.
Write equations, make estimates, and solve the equations.
Carrot Raisin Salad
Have students work in pairs. Ask a few questions to make sure that students understand the task.
SWD: Make sure all students understand the first task. Have students restate the task back to you in their own words so you can assess their understanding.
Preparing for Ways of Thinking
As students are working, have them record the ways in which they make their estimates so that they can share these during the Ways of Thinking discussion. Try to identify students who seem to have good estimation skills so that they can provide a good model for the class.
Remind students to always begin by identifying the variable in the equation.
Mathematical Practices
Mathematical Practice 1: Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them.
When students have finished solving the problem, they should go back to the problem and use the context of the problem to check their final answer. If the answer does not check, students need to rethink all of their steps. It may be that the equation they have written does not accurately represent the problem, or it may be they made an error in solving the equation.
Interventions
Student does not know what the variable should represent.
- What does the question ask you to find?
Student does not know where to begin to make an estimate.
- What are you being asked to find?
- Can you round 6.10 to a whole number?
- Think about 2 • 6.
- Think about 1 2 of 6.
Student does not understand how to check their answer.
- Read the problem again.
- Use the answer you got and calculate the total cost using the information in the problem.
- Does the total cost you calculated match the total cost in the problem?

Possible Answers
- Estimate: Total cost is $28.25. The fruit salad costs about $15; the potato salad costs about $8.00, so the carrot raisin salad should cost around $5.
- Equation solution: Let x equal the cost per pound in dollars of the carrot raisin salad.
( 2 1 2 ⋅ 6.10 ) + ( 1 3 4 ⋅ 5 ) + 1 2 x = $ 28.25 ( 15.25 ) + ( 8.75 ) + 1 2 x = $ 28.25 24.00 + 1 2 x = $ 28.25 1 2 x = $ 4.25 x = $ 8.50
The carrot raisin salad costs $8.50 per pound.
Look at the equation you wrote for the carrot raisin salad.
- Estimate the solution and decide whether your estimate makes sense.
- Solve the equation and write the answer as a complete sentence.
Use rounding and mental strategies to help you make an estimate.
The Deli and Other Situations
Have students work in pairs.
- What amounts could you round to help you estimate?
- 0.8 x + (2.5)(6.70) = 22.75
- Estimate: The total cost is about $23. The ham costs about $17, so 0.8 lb of turkey should cost about $6. Turkey should cost about $8 per lb.
- Equation solution: Let x equal the cost per pound of turkey.
0.8 x + ( 2.5 ) ( 6.70 ) = 22.75 0.8 x + 16.75 = 22.75 0.8 x = 6 x = 7.50
The turkey costs $7.50 per pound.
Mrs. Ortiz buys 0.8 lb of turkey and 2.5 lb of ham. The total cost is $22.75. The ham costs $6.70 per lb. What is the price per pound of the turkey?
- Write an equation to represent the problem.

Use the question in the problem to help you decide what quantity the variable in your equation should represent.
Three Salads
- 3(5.95 + 2 x ) + 3(5.95 + x ) = $48.75
- Estimate: The total cost of the salads and extra ingredients is $48.75. The salads alone cost about $36 ($6 × 6). The extra ingredients cost about $13. There were 9 extra ingredients, so each ingredient costs about $1.
- Let x equal the cost of each extra ingredient
3 ( 5.95 + 2 x ) + 3 ( 5.95 + x ) = $ 48.75 17.85 + 6 x + 17.85 + 3 x = $ 48.75 35.70 + 9 x = $ 48.75 9 x = $ 13.05 x = $ 1.45
Each extra ingredient costs $1.45.
Challenge Problem
- 3 x + 5 = 4 x + 1.25
- Estimate: The difference in the tips was about $4. Since one boy babysat for $3 per hour and the other for $4 per hour (a difference of $1 per hour), the difference in the tip should be the same as the number of hours each boy babysat. So, Jack and Marcus each babysat for about 4 hours.
- Let x equal the number of hours each boy babysat.
3 x + 5 = 4 x + 1.25 3 x − 3 x + 5 = 4 x − 3 x + 1.25 5 = x + 1.25 3.75 = x
Each boy babysat 3.75 hours.
A salad costs $5.95, plus an extra charge for each additional ingredient. You order 3 salads that each have 2 additional ingredients, and 3 salads that each have 1 additional ingredient. The total cost is $48.75. What is the cost of 1 additional ingredient?

Jack and Marcus both babysat for the same number of hours on Thursday and they both earned the same amount of money. However, Jack was paid $3 per hour and received a $5 tip, and Marcus was paid $4 per hour and received a $1.25 tip. How many hours did the boys babysit?
You will use the variable more than once in your equation.
Make Connections
Mathematics.
Facilitate the discussion to help students understand the mathematics of the lesson informally. As you discuss each of the problems, ask questions such as the following:
- How did you arrive at your estimate?
- Does your estimate make sense?
- How did you determine what quantity should be represented by the variable?
- What steps did you use to solve the equation?
- What properties of equality did you use in solving the equation?
- Does your solution make sense?
- How does your estimate compare to the solution?
- Is there another way to solve the problem?
ELL: During class discussions, make sure you provide wait time (5–10 seconds) and acknowledge student responses, both verbally and with gestures.
Performance Task
Ways of thinking: make connections.
Take notes about your classmates’ equations, estimates, and solutions.
As your classmates present, ask questions such as:
- How did you come up with your estimate?
- How close is your estimate to the final solution?
- How did you decide which quantity in the problem should be represented by the variable?
- Can you explain the steps you used to solve the equation?
- Does the solution to the equation make sense in terms of the problem situation?
- Why do you sometimes need to use both the addition property of equality and the multiplication property of equality to solve equations?
Write and Solve Equations
Have each student write a summary of the math in this lesson; then write a class summary. When done, if you think the summary is helpful, share it with the class.
A Possible Summary
In this lesson, we not only solved problems using equations, we first estimated the answers. To do this, we sometimes rounded decimal or fraction numbers, we sometimes had to rewrite numbers in a different form, and we used mental math.
We had several ways to check our answers. We could first compare our answer to our estimate, we could check that the solution to the equation made the equation true, and we could go back to the word problem and see if our answer matches the situation.
To solve equations like 4 x = 6, you need to use the multiplication property of equality; to solve equations like x + 6 = 10, you need to use the addition property of equality; but to solve equations like 3 x + 6 = 12, you need to use both properties.
Formative Assessment
Summary of the math: write and solve equations.
Write a summary about writing and solving equations.
Check your summary:
- Do you describe how to make an estimate?
- Do you discuss ways to check answers to problems?
- Do you explain how to determine which quantity in a problem should be represented by the variable?
What Is the Number?
This task allows you to assess students’ work and determine what difficulties they are having. The results of the Self Check will help you determine which students should work on the Gallery and which students would benefit from review before the assessment. Have students work on the Self Check individually.
Have students submit their work to you. Make notes on what their work reveals about their current levels of understanding and their different problem-solving approaches.
Do not score students’ work. Share with each student the most appropriate Interventions to guide their thought process. Also note students with a particular issue so that you can work with them in the Putting It Together lesson that follows.
Student applies operations in the wrong order—for example, chooses 4 x + 7 = 80 as an appropriate equation.
- In this expression, what is the first thing that happens to the number I am thinking of? Then what happens?
- What does x represent? What are you adding 7 to?
Student does not recognize all relevant expressions, for example, the student chooses 4( x + 7) = 80 as the only appropriate equation.
- How else could you write the expression 4( x + 7)?
Student calculates an incorrect value for x .
- If you substitute your value of x into the equation, do you get a true equation?
- How will you check whether your value for x is correct?
- 4( x + 7) = 80 and 4 x + 28 = 80 both represent the problem.
- The value of x represents the original number (in the statement, "I am thinking of a number...")
4 ( x + 7 ) = 80 4 x + 28 = 80 4 x + 28 − 28 = 80 − 28 4 x = 52 4 x 4 = 52 4 x = 13
Complete this Self Check by yourself.
I am thinking of a number. When I add 7 and then multiply by 4, the result is 80. What is my number?
- Which of the following equations represent this problem? Select all that apply, and justify your choices.
x + 28 = 80
4( x + 7) = 80
4 x + 7 = 80
4 x + 28 = 80
- For each equation that you identified, find the value of x and explain what it represents.
Three Consecutive Numbers
Student assumes that the three numbers are equal. For example, the student selects Total = x + 2 x + 3 x as an appropriate equation.
- What does consecutive mean?
- What does x represent?
- Can you try some numbers to check that this works?
Student does not multiply all terms in the parentheses. For example, the student selects Total = x + (2 x + 1) = (3 x + 2) as an appropriate equation.
- How do you write “one more than x ” using algebra? Now read the question again: What happens next? What happens if you add two of these numbers together?
Student does not correctly interpret the solution of the equation to solve the problem.
- You have found that x = 27. Read the question again. What are the three consecutive numbers?
- Both x + 2 x + 2 + 3 x + 6 and x + 2( x + 1) + 3( x + 2) correctly represent the situation.
- The value of x represents the first number, so the three numbers are 27, 28, and 29.
x + 2 ( x + 1 ) + 3 ( x + 2 ) = 170 x + 2 x + 2 + 3 x + 6 = 170 6 x + 8 − 8 = 170 − 8 6 x = 162 6 x 6 = 162 6 x = 27
The numbers 5, 6, and 7 are examples of consecutive numbers —that is, each number follows the previous one.
Suppose three consecutive numbers are used in the following way to get a total. The first number plus two times the second number plus three times the third number equals the total.
- Which of the following expressions represent this situation? Select all that apply, and justify your choices.
Total = x + 2 x + 3 x
Total = x + 2 x + 2 + 3 x + 6
Total = x + 2( x + 1) + 3( x + 2)
Total = x + (2 x + 1) + (3 x + 2)
- The total is 170. What are the three consecutive numbers? Explain your answer.
Reflect On Your Work
Have each student do a quick reflection before the end of the class. Review the reflections to determine where students might need some additional support in writing equations to solve problems.
Write a reflection about the ideas discussed in class today. Use the sentence starter below if you find it to be helpful.
Something I still don’t understand about writing equations to represent situations is …
- Online Student Edition
- Math Modeling with Applications
- Multilingual eGlossary
Textbook Resources
- Chapter Themes
- Chapter Test
- Extra Examples
- Concepts in Motion
- Personal Tutor
- Self-Check Quizzes
- Standardized Test Practice
- Vocabulary Review
Chapter Activities
Lesson Resources
- Educational Partners
- Meet the Authors
- National Resources
- Professional Development
- State Resources
- Teaching Today
- TechConnect
- 888-309-8227
- 732-384-0146
New User Registration
Forgot Password
Math Connects Course 2 Common Core, Grade: 7 Publisher: Glencoe McGraw-Hill
Math connects course 2 common core, title : math connects course 2 common core, publisher : glencoe mcgraw-hill, isbn : 78951305, isbn-13 : 9780078951305, use the table below to find videos, mobile apps, worksheets and lessons that supplement math connects course 2 common core., textbook resources.
- Call us toll-free
- FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
- Contact Lumos Learning – Proven Study Programs by Expert Teachers
Follow us: Lumos Learning -->
- 2024 © Lumos Learning
- Privacy Policy - Terms of Service - Disclaimers
PARCC® is a registered trademark of PARCC, Inc. Lumos Learning, is not owned by or affiliated in any fashion with PARCC, Inc... Read More
PARCC® is a registered trademark of PARCC, Inc. Lumos Learning, is not owned by or affiliated in any fashion with PARCC, Inc., the Partnership for the Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers, nor any state of the Union. Neither PARCC, Inc., nor The Partnership for the Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers, nor any member state has endorsed this product. No portion of any fees or charges paid for any products or services Lumos Learning offers will be paid or inure to the benefit of PARCC, Inc., or any state of the Union
SBAC is a copyright of The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, which is not aff... Read More
SBAC is a copyright of The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. The Regents of the University of California – Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
ACT® Aspire™ is a registered trademark of ACT Aspire LLC., which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. ACT Aspire LLC, was not... Read More
ACT® Aspire™ is a registered trademark of ACT Aspire LLC., which is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. ACT Aspire LLC,was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Florida Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Florida department of education, was not involved in the... Read More
Florida Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Florida department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Indiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Indiana department of education, was not involved in the... Read More
Indiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Indiana department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Mississippi Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Mississippi department of education, was not involved... Read More
Mississippi Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Mississippi department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Ohio Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Ohio department of education, was not involved in the prod... Read More
Ohio Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Ohio department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Tennessee Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Tennessee department of education, was not involved... Read More
Tennessee Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Tennessee department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Georgia Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Georgia department of education, was not involved... Read More
Georgia Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Georgia department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Missouri Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Missouri department of education, was not involved... Read More
Missouri Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Missouri department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
Louisiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Louisiana department of education, was not involved... Read More
Louisiana Department of Education is not affiliated to Lumos Learning. Louisiana department of education, was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse these products or this site.
- Exploratory
Customer Reviews
The various domains to be covered for my essay writing.
If you are looking for reliable and dedicated writing service professionals to write for you, who will increase the value of the entire draft, then you are at the right place. The writers of PenMyPaper have got a vast knowledge about various academic domains along with years of work experience in the field of academic writing. Thus, be it any kind of write-up, with multiple requirements to write with, the essay writer for me is sure to go beyond your expectations. Some most explored domains by them are:
- Project management

Chapter 7, Lesson 5: Problem-Solving Investigation: Determine Reasonable Answers
- Extra Examples
- Group Activity Cards
- Personal Tutor
- Self-Check Quizzes
The resource you requested requires you to enter a username and password below:
Please read our Terms of Use and Privacy Notice before you explore our Web site. To report a technical problem with this Web site, please contact the site producer .


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
McGraw Hill My Math Grade 5 Chapter 9 Lesson 8 My Homework Answer Key. Problem Solving. Mathematical PRACTICE 3 Check for Reasonableness Determine a reasonable answer to solve each problem. Question 1. Alyssa needs 7\(\frac{5}{8}\) inches of ribbon for one project and 4\(\frac{7}{8}\) inches of ribbon for another project.
Problem Solving Determine a reasonable answer for each problem. 1. Kevin can carry a basket 5 feet. Rachel can carry it 3 feet farther than Kevin. Daniel can carry the basket half as far as Rachel. Is it reasonable to say that they can carry it 15 feet with each person taking only one turn? 2. Josh and Anthony have a lemonade stand. They
All the solutions provided in McGraw Hill Math Grade 4 Answer Key PDF Chapter 3 Lesson 8 Problem-Solving Investigation: Reasonable Answers will give you a clear idea of the concepts. McGraw-Hill My Math Grade 4 Answer ... Problem Solving. Determine a reasonable answer for each problem. Question 1. Kevin can carry a basket 5 feet. Rachel can ...
Lesson 8: Problem Solving Investigation: Determine Reasonable Answers 1. Multi-step word problems: identify reasonable answers Lesson 9: Estimate Sums and Differences 1. Estimate sums and differences of mixed numbers 2. Round mixed numbers Lesson 9: Estimate Sums and ...
In this lesson we will solve Problem Solving exercises, using the strategy of reasonable answers. My Math book. ISBN 978--07-905763-1 ,McGraw-Hill
My Math 5 Volume 2 Common Core grade 5 workbook & answers help online. Grade: 5, Title: My Math 5 Volume 2 Common Core, Publisher: McGraw-Hill, ISBN: 21161968 ... Lesson 8: Problem-Solving Investigation: Determine Reasonable Answers. apps. videocam. create. Lesson 9: Estimate Sums and Differences. apps. videocam.
All the solutions provided in McGraw Hill My Math Grade 3 Answer Key PDF Chapter 12 Lesson 8 Problem-Solving Investigation: Solve a Simpler Problem will give you a clear idea of the concepts. ... Solve a simpler problem. Determine reasonable answers. Make a table. Question 3. Draw an example of a tally chart that may have been used to organize ...
For example, recognize an incorrect result 2/5 + 1/2 = 3/7 by observing that 3/7 < 1/2. (NO.3.6.4) Estimation: Estimate reasonable solutions to problem situations involving fractions and decimals Mathematical Practices: Use appropriate tools strategically. Attend to precision.
Lesson Objectives: When presented with a solution to word problem, students will determine if answer is reasonable at least eighty percent of the time. Time: Approximately 60 minutes Pre-instructional activities: Students will use QR code to choose a reasonable solution for a scenario set up by the teacher.
Cluster: Solve real-life and mathematical problems using numerical and algebraic expressions and equations Standard: Solve word problems leading to equations of the form px + q = r and p(x + q) = r, where p, q, and r are specific rational numbers. Solve equations of these forms fluently. Compare an algebraic solution to an arithmetic solution, identifying the sequence of the operations used in ...
Log In. The resource you requested requires you to enter a username and password below:
Chapter 3 Lesson 8Problem Solving Investigation.Learn the strategy, Apply the strategy using four steps: Understand, Plan, Solve and Check.Learn how multipli...
Math Connects Course 3 Common Core grade 8 workbook & answers help online. Grade: 8, Title: Math Connects Course 3 Common Core, Publisher: Glencoe McGraw-Hill, ISBN: 78951399 ... Problem-Solving Investigation: Determine Reasonable Answers. apps. videocam. create. Lesson 4: Convert Length, Weight/Mass, Capacity, and Time ... Lesson 8: Problem ...
Lesson Resources Extra Examples Group Activity Cards ... Online Calculators Study to Go. Mathematics. Home > Chapter 7 > Lesson 5. Math Connects: Concepts, Skills, and Problem Solving, Course 2 ... Lesson 5: Problem-Solving Investigation: Determine Reasonable Answers. Extra Examples; Group Activity Cards; Personal Tutor; Self-Check Quizzes; Log ...
Lesson 8: Problem Solving Skills: Use Logical Reasoning In this Lesson: Online Student Edition; Math Modeling with Applications; Multilingual eGlossary; Textbook Resources. Chapter Themes; Chapter Test; Extra Examples ... To report a technical problem with this Web site, ...
Write this amount in exponential form. 3. VOLUME To find the volume of a rectangular box you multiply the length times the width times the height. In a cube all sides are the same length. If the cube has length, width, and height of 6 inches, write the volume as a product. Then write it in exponential form. 4.
Lesson 8 Homework Practice Slope For Exercises 1 and 2, graph the data. Then find the slope. ... Lesson 8 Problem-Solving Practice Slope 1. GO-KARTS The graph shows the average speed of two go-karts in a race. What ... 8 1624324048566472 Length (in.) 0 20 40 60 80 1234 Packages Boxes 0 100 300 500 700 142 36758
create. Math Connects Course 2 Common Core grade 7 workbook & answers help online. Grade: 7, Title: Math Connects Course 2 Common Core, Publisher: Glencoe McGraw-Hill, ISBN: 78951305.
Monday (4/8): Review Lessons 1-5. Tuesday: Quiz, Lessons 1-5. Wednesday: Lesson 6, Use Models to Subtract Unlike Fractions. Thursday: Lesson 7, Subtract Unlike Fractions. Friday: Lesson 8, Problem Solving-Determine Reasonable Answers . Mrs. Heuer. We will move straight into our study of inequalities and I will cover functions in depth next year ...
Chapter 11, Lesson 5: Problem Solving Investigation: Determine Reasonable Answers. Extra Examples; Group Activity Cards; Personal Tutor; Self-Check Quizzes; Log In. ... To report a technical problem with this Web site, please contact the ...
Deadlines can be scary while writing assignments, but with us, you are sure to feel more confident about both the quality of the draft as well as that of meeting the deadline while we write for you. Charita Davis. #18 in Global Rating. 764. Finished Papers. 4.9/5. Custom essay writing service.
Lesson Resources Extra Examples Group Activity Cards ... Study to Go. Mathematics. Home > Chapter 7 > Lesson 5. California Mathematics: Concepts, Skills, and Problem Solving, Grade 6. Chapter 7, Lesson 5: Problem-Solving Investigation: Determine Reasonable Answers. Extra Examples; Group Activity Cards; Personal Tutor; Self-Check Quizzes; Log In ...
Chapter 8, Lesson 4 Problem-Solving Investigation Reasonable Answers. Is my answer reasonable? Fill in the blank with a fraction to make the statement true. The latter generalize The second you place your write an essay for me request, numerous writers will be bidding on your work. Find the experimental probability of landing on a 2.