- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →

Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Creative Problem-Solving & Why Is It Important?

- 01 Feb 2022
One of the biggest hindrances to innovation is complacency—it can be more comfortable to do what you know than venture into the unknown. Business leaders can overcome this barrier by mobilizing creative team members and providing space to innovate.
There are several tools you can use to encourage creativity in the workplace. Creative problem-solving is one of them, which facilitates the development of innovative solutions to difficult problems.
Here’s an overview of creative problem-solving and why it’s important in business.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Creative Problem-Solving?
Research is necessary when solving a problem. But there are situations where a problem’s specific cause is difficult to pinpoint. This can occur when there’s not enough time to narrow down the problem’s source or there are differing opinions about its root cause.
In such cases, you can use creative problem-solving , which allows you to explore potential solutions regardless of whether a problem has been defined.
Creative problem-solving is less structured than other innovation processes and encourages exploring open-ended solutions. It also focuses on developing new perspectives and fostering creativity in the workplace . Its benefits include:
- Finding creative solutions to complex problems : User research can insufficiently illustrate a situation’s complexity. While other innovation processes rely on this information, creative problem-solving can yield solutions without it.
- Adapting to change : Business is constantly changing, and business leaders need to adapt. Creative problem-solving helps overcome unforeseen challenges and find solutions to unconventional problems.
- Fueling innovation and growth : In addition to solutions, creative problem-solving can spark innovative ideas that drive company growth. These ideas can lead to new product lines, services, or a modified operations structure that improves efficiency.

Creative problem-solving is traditionally based on the following key principles :
1. Balance Divergent and Convergent Thinking
Creative problem-solving uses two primary tools to find solutions: divergence and convergence. Divergence generates ideas in response to a problem, while convergence narrows them down to a shortlist. It balances these two practices and turns ideas into concrete solutions.
2. Reframe Problems as Questions
By framing problems as questions, you shift from focusing on obstacles to solutions. This provides the freedom to brainstorm potential ideas.
3. Defer Judgment of Ideas
When brainstorming, it can be natural to reject or accept ideas right away. Yet, immediate judgments interfere with the idea generation process. Even ideas that seem implausible can turn into outstanding innovations upon further exploration and development.
4. Focus on "Yes, And" Instead of "No, But"
Using negative words like "no" discourages creative thinking. Instead, use positive language to build and maintain an environment that fosters the development of creative and innovative ideas.
Creative Problem-Solving and Design Thinking
Whereas creative problem-solving facilitates developing innovative ideas through a less structured workflow, design thinking takes a far more organized approach.
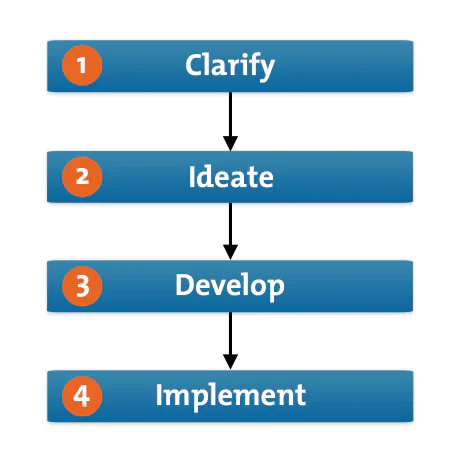
Design thinking is a human-centered, solutions-based process that fosters the ideation and development of solutions. In the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar leverages a four-phase framework to explain design thinking.
The four stages are:

- Clarify: The clarification stage allows you to empathize with the user and identify problems. Observations and insights are informed by thorough research. Findings are then reframed as problem statements or questions.
- Ideate: Ideation is the process of coming up with innovative ideas. The divergence of ideas involved with creative problem-solving is a major focus.
- Develop: In the development stage, ideas evolve into experiments and tests. Ideas converge and are explored through prototyping and open critique.
- Implement: Implementation involves continuing to test and experiment to refine the solution and encourage its adoption.
Creative problem-solving primarily operates in the ideate phase of design thinking but can be applied to others. This is because design thinking is an iterative process that moves between the stages as ideas are generated and pursued. This is normal and encouraged, as innovation requires exploring multiple ideas.
Creative Problem-Solving Tools
While there are many useful tools in the creative problem-solving process, here are three you should know:
Creating a Problem Story
One way to innovate is by creating a story about a problem to understand how it affects users and what solutions best fit their needs. Here are the steps you need to take to use this tool properly.
1. Identify a UDP
Create a problem story to identify the undesired phenomena (UDP). For example, consider a company that produces printers that overheat. In this case, the UDP is "our printers overheat."
2. Move Forward in Time
To move forward in time, ask: “Why is this a problem?” For example, minor damage could be one result of the machines overheating. In more extreme cases, printers may catch fire. Don't be afraid to create multiple problem stories if you think of more than one UDP.
3. Move Backward in Time
To move backward in time, ask: “What caused this UDP?” If you can't identify the root problem, think about what typically causes the UDP to occur. For the overheating printers, overuse could be a cause.
Following the three-step framework above helps illustrate a clear problem story:
- The printer is overused.
- The printer overheats.
- The printer breaks down.
You can extend the problem story in either direction if you think of additional cause-and-effect relationships.
4. Break the Chains
By this point, you’ll have multiple UDP storylines. Take two that are similar and focus on breaking the chains connecting them. This can be accomplished through inversion or neutralization.
- Inversion: Inversion changes the relationship between two UDPs so the cause is the same but the effect is the opposite. For example, if the UDP is "the more X happens, the more likely Y is to happen," inversion changes the equation to "the more X happens, the less likely Y is to happen." Using the printer example, inversion would consider: "What if the more a printer is used, the less likely it’s going to overheat?" Innovation requires an open mind. Just because a solution initially seems unlikely doesn't mean it can't be pursued further or spark additional ideas.
- Neutralization: Neutralization completely eliminates the cause-and-effect relationship between X and Y. This changes the above equation to "the more or less X happens has no effect on Y." In the case of the printers, neutralization would rephrase the relationship to "the more or less a printer is used has no effect on whether it overheats."
Even if creating a problem story doesn't provide a solution, it can offer useful context to users’ problems and additional ideas to be explored. Given that divergence is one of the fundamental practices of creative problem-solving, it’s a good idea to incorporate it into each tool you use.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a tool that can be highly effective when guided by the iterative qualities of the design thinking process. It involves openly discussing and debating ideas and topics in a group setting. This facilitates idea generation and exploration as different team members consider the same concept from multiple perspectives.
Hosting brainstorming sessions can result in problems, such as groupthink or social loafing. To combat this, leverage a three-step brainstorming method involving divergence and convergence :
- Have each group member come up with as many ideas as possible and write them down to ensure the brainstorming session is productive.
- Continue the divergence of ideas by collectively sharing and exploring each idea as a group. The goal is to create a setting where new ideas are inspired by open discussion.
- Begin the convergence of ideas by narrowing them down to a few explorable options. There’s no "right number of ideas." Don't be afraid to consider exploring all of them, as long as you have the resources to do so.
Alternate Worlds
The alternate worlds tool is an empathetic approach to creative problem-solving. It encourages you to consider how someone in another world would approach your situation.
For example, if you’re concerned that the printers you produce overheat and catch fire, consider how a different industry would approach the problem. How would an automotive expert solve it? How would a firefighter?
Be creative as you consider and research alternate worlds. The purpose is not to nail down a solution right away but to continue the ideation process through diverging and exploring ideas.

Continue Developing Your Skills
Whether you’re an entrepreneur, marketer, or business leader, learning the ropes of design thinking can be an effective way to build your skills and foster creativity and innovation in any setting.
If you're ready to develop your design thinking and creative problem-solving skills, explore Design Thinking and Innovation , one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses. If you aren't sure which course is the right fit, download our free course flowchart to determine which best aligns with your goals.

About the Author

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 10 min read
Creative Problem Solving
Finding innovative solutions to challenges.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Imagine that you're vacuuming your house in a hurry because you've got friends coming over. Frustratingly, you're working hard but you're not getting very far. You kneel down, open up the vacuum cleaner, and pull out the bag. In a cloud of dust, you realize that it's full... again. Coughing, you empty it and wonder why vacuum cleaners with bags still exist!
James Dyson, inventor and founder of Dyson® vacuum cleaners, had exactly the same problem, and he used creative problem solving to find the answer. While many companies focused on developing a better vacuum cleaner filter, he realized that he had to think differently and find a more creative solution. So, he devised a revolutionary way to separate the dirt from the air, and invented the world's first bagless vacuum cleaner. [1]
Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of solving problems or identifying opportunities when conventional thinking has failed. It encourages you to find fresh perspectives and come up with innovative solutions, so that you can formulate a plan to overcome obstacles and reach your goals.
In this article, we'll explore what CPS is, and we'll look at its key principles. We'll also provide a model that you can use to generate creative solutions.
About Creative Problem Solving
Alex Osborn, founder of the Creative Education Foundation, first developed creative problem solving in the 1940s, along with the term "brainstorming." And, together with Sid Parnes, he developed the Osborn-Parnes Creative Problem Solving Process. Despite its age, this model remains a valuable approach to problem solving. [2]
The early Osborn-Parnes model inspired a number of other tools. One of these is the 2011 CPS Learner's Model, also from the Creative Education Foundation, developed by Dr Gerard J. Puccio, Marie Mance, and co-workers. In this article, we'll use this modern four-step model to explore how you can use CPS to generate innovative, effective solutions.
Why Use Creative Problem Solving?
Dealing with obstacles and challenges is a regular part of working life, and overcoming them isn't always easy. To improve your products, services, communications, and interpersonal skills, and for you and your organization to excel, you need to encourage creative thinking and find innovative solutions that work.
CPS asks you to separate your "divergent" and "convergent" thinking as a way to do this. Divergent thinking is the process of generating lots of potential solutions and possibilities, otherwise known as brainstorming. And convergent thinking involves evaluating those options and choosing the most promising one. Often, we use a combination of the two to develop new ideas or solutions. However, using them simultaneously can result in unbalanced or biased decisions, and can stifle idea generation.
For more on divergent and convergent thinking, and for a useful diagram, see the book "Facilitator's Guide to Participatory Decision-Making." [3]
Core Principles of Creative Problem Solving
CPS has four core principles. Let's explore each one in more detail:
- Divergent and convergent thinking must be balanced. The key to creativity is learning how to identify and balance divergent and convergent thinking (done separately), and knowing when to practice each one.
- Ask problems as questions. When you rephrase problems and challenges as open-ended questions with multiple possibilities, it's easier to come up with solutions. Asking these types of questions generates lots of rich information, while asking closed questions tends to elicit short answers, such as confirmations or disagreements. Problem statements tend to generate limited responses, or none at all.
- Defer or suspend judgment. As Alex Osborn learned from his work on brainstorming, judging solutions early on tends to shut down idea generation. Instead, there's an appropriate and necessary time to judge ideas during the convergence stage.
- Focus on "Yes, and," rather than "No, but." Language matters when you're generating information and ideas. "Yes, and" encourages people to expand their thoughts, which is necessary during certain stages of CPS. Using the word "but" – preceded by "yes" or "no" – ends conversation, and often negates what's come before it.
How to Use the Tool
Let's explore how you can use each of the four steps of the CPS Learner's Model (shown in figure 1, below) to generate innovative ideas and solutions.
Figure 1 – CPS Learner's Model
Explore the Vision
Identify your goal, desire or challenge. This is a crucial first step because it's easy to assume, incorrectly, that you know what the problem is. However, you may have missed something or have failed to understand the issue fully, and defining your objective can provide clarity. Read our article, 5 Whys , for more on getting to the root of a problem quickly.
Gather Data
Once you've identified and understood the problem, you can collect information about it and develop a clear understanding of it. Make a note of details such as who and what is involved, all the relevant facts, and everyone's feelings and opinions.
Formulate Questions
When you've increased your awareness of the challenge or problem you've identified, ask questions that will generate solutions. Think about the obstacles you might face and the opportunities they could present.
Explore Ideas
Generate ideas that answer the challenge questions you identified in step 1. It can be tempting to consider solutions that you've tried before, as our minds tend to return to habitual thinking patterns that stop us from producing new ideas. However, this is a chance to use your creativity .
Brainstorming and Mind Maps are great ways to explore ideas during this divergent stage of CPS. And our articles, Encouraging Team Creativity , Problem Solving , Rolestorming , Hurson's Productive Thinking Model , and The Four-Step Innovation Process , can also help boost your creativity.
See our Brainstorming resources within our Creativity section for more on this.
Formulate Solutions
This is the convergent stage of CPS, where you begin to focus on evaluating all of your possible options and come up with solutions. Analyze whether potential solutions meet your needs and criteria, and decide whether you can implement them successfully. Next, consider how you can strengthen them and determine which ones are the best "fit." Our articles, Critical Thinking and ORAPAPA , are useful here.
4. Implement
Formulate a plan.
Once you've chosen the best solution, it's time to develop a plan of action. Start by identifying resources and actions that will allow you to implement your chosen solution. Next, communicate your plan and make sure that everyone involved understands and accepts it.
There have been many adaptations of CPS since its inception, because nobody owns the idea.
For example, Scott Isaksen and Donald Treffinger formed The Creative Problem Solving Group Inc . and the Center for Creative Learning , and their model has evolved over many versions. Blair Miller, Jonathan Vehar and Roger L. Firestien also created their own version, and Dr Gerard J. Puccio, Mary C. Murdock, and Marie Mance developed CPS: The Thinking Skills Model. [4] Tim Hurson created The Productive Thinking Model , and Paul Reali developed CPS: Competencies Model. [5]
Sid Parnes continued to adapt the CPS model by adding concepts such as imagery and visualization , and he founded the Creative Studies Project to teach CPS. For more information on the evolution and development of the CPS process, see Creative Problem Solving Version 6.1 by Donald J. Treffinger, Scott G. Isaksen, and K. Brian Dorval. [6]
Creative Problem Solving (CPS) Infographic
See our infographic on Creative Problem Solving .

Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of using your creativity to develop new ideas and solutions to problems. The process is based on separating divergent and convergent thinking styles, so that you can focus your mind on creating at the first stage, and then evaluating at the second stage.
There have been many adaptations of the original Osborn-Parnes model, but they all involve a clear structure of identifying the problem, generating new ideas, evaluating the options, and then formulating a plan for successful implementation.
[1] Entrepreneur (2012). James Dyson on Using Failure to Drive Success [online]. Available here . [Accessed May 27, 2022.]
[2] Creative Education Foundation (2015). The CPS Process [online]. Available here . [Accessed May 26, 2022.]
[3] Kaner, S. et al. (2014). 'Facilitator′s Guide to Participatory Decision–Making,' San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
[4] Puccio, G., Mance, M., and Murdock, M. (2011). 'Creative Leadership: Skils That Drive Change' (2nd Ed.), Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
[5] OmniSkills (2013). Creative Problem Solving [online]. Available here . [Accessed May 26, 2022].
[6] Treffinger, G., Isaksen, S., and Dorval, B. (2010). Creative Problem Solving (CPS Version 6.1). Center for Creative Learning, Inc. & Creative Problem Solving Group, Inc. Available here .
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
What is problem solving.
Book Insights
The Back of the Napkin: Solving Problems and Selling Ideas With Pictures
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Team Management
Learn the key aspects of managing a team, from building and developing your team, to working with different types of teams, and troubleshooting common problems.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

SWOT Analysis

How to Build a Strong Culture in a Distributed Team
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Top tips for delegating.
Delegate work to your team members effectively with these top tips
Ten Dos and Don'ts of Change Conversations
Tips for tackling discussions about change
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Heart, smarts, guts, and luck.
Expert Interviews
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.
10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
How to improve your creative skills for effective problem-solving

Jump to section
What’s creative thinking?
Creative thinking versus critical thinking
Creative thinking skills
How to develop creative thinking skills
4 creative thinking examples to include on your resume
Sharpen your creativity
Creative thinking is the key to unlocking innovation and problem-solving excellence.
In the whirlwind of everyday professional challenges, we’ve all encountered moments when fresh ideas feel elusive. If you’ve found yourself struggling to inspire your team or spinning out during a brainstorming session , it may be a sign you need to develop your creative skills. Plus, creative problem solving looks excellent on a resume .
As a leader or team member, your ability to think outside the box can ignite a spark of ingenuity that propels your team to new heights. Fan the flames of growth and learn how to improve your creative thinking (and highlight your new skills in your next job application).
What’s creative thinking?
Creative thinking is the dynamic process of transforming your ideas into actions. The skillset equips you to think differently and approach challenges from innovative angles.
At its core, creative thinking empowers you to break free from the constraints of the status quo and dream up fresh, original ideas. It breathes life into your decisions, encouraging you to embrace your imaginative instincts.
By daring to challenge traditional approaches, your creativity opens doors to uncharted innovations and groundbreaking solutions.
Creative thinking versus critical thinking
Although creative and critical thinking are both used in problem-solving , the two skills are marked by key differences.
Creative thinking is the catalyst for generating innovative ideas and crafting novel approaches to the challenges around them. With an open mind and a wild imagination, creative thinkers produce and explore unconventional solutions to the problems that stand in their way.
Critical thinking analyzes available information with an unbiased and rational approach. It involves questioning perceptions, ensuring that decisions are devoid of bias and reasoning remains grounded in sound judgment.
Creative thinking skills
When you look at creative thinking as a set of particular abilities, it becomes easier to develop and perfect. These creative skill examples can help you thrive inside and outside of the workplace:
1. Open-mindedness
When you’re open-minded, you can readily adapt to new information and look for fresh problem-solving approaches. You’re receptive to the opinions and ideas of others because you view them as constructive rather than criticizing . This openness also encourages you to freely share your creative ideas without fearing judgement.
2. Curiosity
You might find that you tap into creative potential the most when you’re challenging convention and posing new ways of thinking. Analyzing processes and asking yourself how you can improve them is an exciting way to make more efficient systems.
Whether you’re new to a job or have worked at the company for years, you may wonder why procedures are what they are — lean into this curiosity to develop new and better ways to work.

3. Ability to brainstorm
There are numerous ways to solve a problem, and brainstorming helps to get them onto paper so you can weigh their pros and cons. This way of lateral thinking encourages you to view solutions as multifaceted rather than a single, straightforward answer.
4. Experimentation
Creative people experiment with various ways of solving a problem before deciding on the best way to take action. Emulate this mindset in your projects and tasks. For instance, if you work in web design, you might try several page layouts before deciding on a final visual identity for your client.
5. Networking
Speaking with people from different professional backgrounds is an excellent way to stimulate creative thinking and develop new perspectives. When you network with professionals with diverse skill sets and experiences, they might influence you to look at the world differently or suggest an innovative way to tackle a problem.
6. Observation
It’s important to know when to take the backseat and listen in. Observing how others tackle complex issues might inspire you to make changes within your team. Always keep an eye out for opportunities to learn from more experienced peers and innovative colleagues.
7. Organization
Although some individuals claim to thrive in clutter, keeping your work organized creates an environment where you can work freely without distraction. This involves keeping your workspace tidy, creating clear to-do lists, and using visual maps to express your plans and processes.
8. Communication
Proper communication empowers you to share valuable insight and ideas with your teammates. You need strong verbal and written skills to pitch and describe your thoughts and actively listen to others’ feedback and advice.

9. Analysis
Before you can dream up a creative approach to an obstacle, you must fully understand the problem at hand. Without proper analysis, your solution may contain flaws, or you could miss important details of your problem. Practice sifting through every detail of the issue and pinpointing the causes.
10. Problem-solving
No matter your industry, problem-solving is always a valuable skill. Consider how to tackle a problem without asking the advice of others to see what creative solutions arise. This way, you can see what inventive ideas you can come up with before external opinions influence you.
Although some of your coworkers may seem to have a natural talent for creativity and creative thinking, it’s a skill anyone can develop and improve. Here are seven ways to advance your innovative problem-solving:
Reading is an effective way to exercise your mind, increase your vocabulary, and expose yourself to new ways of thinking. Whether your book is on a problem you’re facing at work or a new and exciting subject, reading is an excellent opportunity to learn. That’s right: simply cracking open a book can help you grow .
Keep a notepad nearby and write down thoughts and ideas as they arise. Writing helps you to process information, and you can revisit your musing whenever you need to get your creative juices flowing. If you’ve never tried journaling before, it’s an excellent way to process your thoughts and feelings in a safe and private space.
3. Exercise
Exercising improves your sleep and ability to cope with stress, making it easier to stay alert and contribute fresh ideas at work.

4. Listen to music
Music can affect your mood and place you in the mindset to solve problems. If you’re struggling with creative writing or creating a visual piece of work, listening to music could push you toward expressing yourself more meaningfully.
5. Ask for feedback
Collaboration and teamwork are key when developing creative solutions in the workplace. You can ask teammates or superiors for feedback on your ideas to gain insight into potential flaws in your reasoning and streamline your solutions.
6. Find a mentor or coach
Having an experienced person to bounce ideas off is a catalyst for creativity. A mentor or coach who’s dealt with similar obstacles can provide insight into what worked and what didn’t, saving you valuable brainstorming time.
7. Change your approach
If you’ve been approaching your tasks the same way, adjusting your processes may bring a fresh perspective and stimulate change. Ask yourself why you tackle work from a similar angle each time and consider more creative ways to conduct your day-to-day operations.

4 creative thinking examples to include on your resume
Employers want to add creative people to their teams because solving problems takes a lot of ingenuity. Use these four examples and bullet points for inspiration when listing creative thinking skills on your resume.
On a graphic designer’s resume:
- Collaborated on rebranding [company’s] visual identity and social media content strategy
- Developed unique and innovative branding material for [company A] , [company B] , and [company C]
On a copywriter’s resume:
- Revised [company’s] website and blog content to be more engaging, exciting, and SEO-focused
- Contributed original and innovative articles on [topic] to [publication A] and [publication B]
On a public relations specialist’s resume:
- Increased [company’s] brand awareness by planning [event] to launch [product]
- Collaborated with [brand] on [product’s] creative marketing strategy to reach a wider audience
On a teacher’s resume:
- Developed a novel approach to teaching [subject or class] to students with various learning styles and needs
- Introduced [extracurricular] , the first of its kind in [the school board] , to engage students in [activity]
Sharpen your creativity
Critical and creative thinking broaden your perspective and allow you to devise unique solutions to everyday problems. You can develop your creative skills by changing your environment, learning from others, and adjusting your approach to work.
Regardless of how you choose to spark creativity at work, don’t be afraid to step outside your comfort zone and confidently contribute your ideas. You never know — you might just come up with the next big company innovation.
Cultivate your creativity
Foster creativity and continuous learning with guidance from our certified Coaches.
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
How to develop critical thinking skills
6 ways to leverage ai for hyper-personalized corporate learning, self directed learning is the key to new skills and knowledge, the power of professional learning communities, why asynchronous learning is the key to successful upskilling, 8 creative solutions to your most challenging problems, why creativity isn't just for creatives and how to find it anywhere, the 10 best ted talks about life for inspiration and encouragement, can dreams help you solve problems 6 ways to try, similar articles, 10 problem-solving strategies to turn challenges on their head, thinking outside the box: 8 ways to become a creative problem solver, what is creative thinking and why does it matter, what are professional skills, and which should you add to your resume, the pomodoro technique: how a break can improve productivity and well-being, professional leadership skills to incorporate on your resume, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care™
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
What is creative problem-solving?
Table of Contents
An introduction to creative problem-solving.
Creative problem-solving is an essential skill that goes beyond basic brainstorming . It entails a holistic approach to challenges, melding logical processes with imaginative techniques to conceive innovative solutions. As our world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the ability to think creatively and solve problems with fresh perspectives becomes invaluable for individuals, businesses, and communities alike.
Importance of divergent and convergent thinking
At the heart of creative problem-solving lies the balance between divergent and convergent thinking. Divergent thinking encourages free-flowing, unrestricted ideation, leading to a plethora of potential solutions. Convergent thinking, on the other hand, is about narrowing down those options to find the most viable solution. This dual approach ensures both breadth and depth in the problem-solving process.
Emphasis on collaboration and diverse perspectives
No single perspective has a monopoly on insight. Collaborating with individuals from different backgrounds, experiences, and areas of expertise offers a richer tapestry of ideas. Embracing diverse perspectives not only broadens the pool of solutions but also ensures more holistic and well-rounded outcomes.
Nurturing a risk-taking and experimental mindset
The fear of failure can be the most significant barrier to any undertaking. It's essential to foster an environment where risk-taking and experimentation are celebrated. This involves viewing failures not as setbacks but as invaluable learning experiences that pave the way for eventual success.
The role of intuition and lateral thinking
Sometimes, the path to a solution is not linear. Lateral thinking and intuition allow for making connections between seemingly unrelated elements. These 'eureka' moments often lead to breakthrough solutions that conventional methods might overlook.
Stages of the creative problem-solving process
The creative problem-solving process is typically broken down into several stages. Each stage plays a crucial role in understanding, addressing, and resolving challenges in innovative ways.
Clarifying: Understanding the real problem or challenge
Before diving into solutions, one must first understand the problem at its core. This involves asking probing questions, gathering data, and viewing the challenge from various angles. A clear comprehension of the problem ensures that effort and resources are channeled correctly.
Ideating: Generating diverse and multiple solutions
Once the problem is clarified, the focus shifts to generating as many solutions as possible. This stage champions quantity over quality, as the aim is to explore the breadth of possibilities without immediately passing judgment.
Developing: Refining and honing promising solutions
With a list of potential solutions in hand, it's time to refine and develop the most promising ones. This involves evaluating each idea's feasibility, potential impact, and any associated risks, then enhancing or combining solutions to maximize effectiveness.
Implementing: Acting on the best solutions
Once a solution has been honed, it's time to put it into action. This involves planning, allocating resources, and monitoring the results to ensure the solution is effectively addressing the problem.
Techniques for creative problem-solving
Solving complex problems in a fresh way can be a daunting task to start on. Here are a few techniques that can help kickstart the process:
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a widely-used technique that involves generating as many ideas as possible within a set timeframe. Variants like brainwriting (where ideas are written down rather than spoken) and reverse brainstorming (thinking of ways to cause the problem) can offer fresh perspectives and ensure broader participation.
Mind mapping
Mind mapping is a visual tool that helps structure information, making connections between disparate pieces of data. It is particularly useful in organizing thoughts, visualizing relationships, and ensuring a comprehensive approach to a problem.
SCAMPER technique
SCAMPER stands for Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse. This technique prompts individuals to look at existing products, services, or processes in new ways, leading to innovative solutions.
Benefits of creative problem-solving
Creative problem-solving offers numerous benefits, both at the individual and organizational levels. Some of the most prominent advantages include:
Finding novel solutions to old problems
Traditional problems that have resisted conventional solutions often succumb to creative approaches. By looking at challenges from fresh angles and blending different techniques, we can unlock novel solutions previously deemed impossible.
Enhanced adaptability in changing environments
In our rapidly evolving world, the ability to adapt is critical. Creative problem-solving equips individuals and organizations with the agility to pivot and adapt to changing circumstances, ensuring resilience and longevity.
Building collaborative and innovative teams
Teams that embrace creative problem-solving tend to be more collaborative and innovative. They value diversity of thought, are open to experimentation, and are more likely to challenge the status quo, leading to groundbreaking results.
Fostering a culture of continuous learning and improvement
Creative problem-solving is not just about finding solutions; it's also about continuous learning and improvement. By encouraging an environment of curiosity and exploration, organizations can ensure that they are always at the cutting edge, ready to tackle future challenges head-on.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Creative Problem Solving Explained
Creative problem solving is based on the belief that everyone is creative and can enhance their creative abilities with discipline.
Creative problem solving is a deliberate approach to solving complex problems. While creativity is an innate part of creative problem solving, the process uses a variety of steps and strategies designed to bring to the table solutions that are actionable and effective.
It’s a proven approach to use innovative ideas and views of a problem to develop viable options that can be brought to bear on the challenge. It can also redefine the problem, coming at it from a new perspective that results in an effective solution.
It also has powerful applications for addressing your greatest workflow challenges. Using creative problem solving lets you identify, refine, iterate, and select the best options to improve workflows using new technologies like automation.
Fundamentals of Creative Problem Solving
Many people hear “creative problem solving” and think it’s about brainstorming answers. However, creative problem solving is about much more. Creative answers to problems do not just appear magically but are the result of deliberate processes.
To work well, creative problem solving is rooted in two assumptions:
- Everyone is creative in some manner
- You can learn and enhance someone’s creative abilities
Those are powerful assumptions. They help to dispel the idea that there are “creative types” and “noncreative types.” All participants can be empowered to engage in the process by supporting and reinforcing the innate presence of creativity.
Alex Osborn helped define and formalize the idea of creative problem solving. He believed that two types of thinking are critical to creative problem solving.
Convergent Thinking focuses on the norms of problem solving and focuses on finding a singular solution that's well defined. Divergent Thinking is the opposite, with multiple options being considered after fostering creativity as part of the problem solving process.
Both play a role and have value in problem solving. Typically, both are used as part of the process.
For example, divergent thinking can create multiple ideas for possible solutions. Convergent thinking can whittle those down to a few or one idea to implement.
Principles of Creative Problem Solving
Here is a closer look at some key tenets of creative problem solving.
Reframe the Problem as a Question
Begin by restating the problem as a question or series of open-ended questions. The problem becomes more approachable with multiple possibilities available, and participants can be invited into the process.
By contrast, problems presented as declarative statements are often met by silence. These statements often lead to a limited response or no response at all.
There's a shift when asked as a question rather than a statement. The challenge is not an obstacle but rather an opportunity to solve. It opens the door to brainstorming and ideation.
Suspend Judgment
All too often, ideas that are generated in problem solving spaces are quickly dismissed. This instantaneous judgment has short- and long-term impacts.
First, it immediately dismisses the presented idea and the presenter. What’s more, the dismissal can have a chilling effect on others, stymieing the idea generation process.
There’s a time when judging presented ideas – when convergent thinking is at play. In the beginning, immediate judgment should be suspended.
Even the most implausible ideas presented at the beginning of the process may play a role later as long as they are still considered viable. If poisoned early in the process, they will unlikely be given any value later.
‘Yes, And’ Instead of ‘No, But’
The word “no” can have a similarly stifling effect on the creative problem solving work. "But," whether preceded by "yes” or "no," can close the conversation. It acts to negate everything that has come before.
You can create and maintain a more positive, encouraging tone using "yes, and" language instead of "no, but" language.
More positive language helps build on previously generated ideas. It creates an additive approach to the process instead of a dismissive one.
One Approach to Creative Problem Solving
Having a clearly defined approach to solving problems helps participants understand the scope and scale of the work. While multiple approaches can be used, here is one way to frame the engagement.
1. Clarify the Problem
The most critical step to creative problem solving is identifying and articulating the problem or goal. While it may appear to be easy to do so, often, what people think the problem is is not the true problem.
The critical step is to break down the problem, analyze it and understand the core issue.
One approach is to use the "five whys." Start by asking yourself, "Why is this a problem?" Once you have the answer, ask, "Why else?" four more times.
This iterative process can often refine and revise to unearth the true issue that needs to be addressed. You can ask other questions to further refine, such as:
- Why is this problem important to us?
- What is stopping us from solving this problem?
- Where will we be differently 6-12 months after solving the problem?
2. Define Evaluation Criteria
The creative problem solving process is likely to generate many potential ideas. It’s important to establish the process by which the ideas will be evaluated and, if selected, deployed.
These processes may have important factors, such as budget, staffing and time. The process needs to address what you seek to accomplish, avoid and act on. The process should be articulated to the participants in the problem solving and those affected by the outcomes.
3. Research the Problem
You want a clear understanding of the problem, which may require lots or a little research. Understand the common problem, how others may deal with it, and potential solutions.
4. Develop Creative Challenges
Once the problem is articulated and researched, it’s time to frame them. “Creative challenges” are simple and brief, question-based concepts. For example, "How can we …" or “What would it mean if …" These challenges will form the basis of your problem solving. They should be broadly focused and not include any evaluation criteria.
5. Create Ideas
Idea generation is what most people envision when they think of brainstorming or solving problems.
Start by taking just one of the creative challenges. Give yourself or the team some time to build at least 50 ideas. That may seem like a lot, but it can spark conversation and construction.
The ideas may or may not solve the presented challenge. By capturing them on paper or a computer (many programs support idea generation), you can have them readily available to organize, expand on, evaluate, and flesh out.
Be sure to use the following rules in this stage:
- Write down every idea
- Ensure no one critiques presented ideas
- Don’t stop until you’ve reached 50
- Present the full list of ideas and then ask if anyone has anything else to add
- If you have time, sleep on the ideas and return the next day. Try to add 25 more.
6. Sort and Assess Ideas
Take a break and reconvene to look at the ideas using the evaluation criteria. Combine ideas, then use the evaluation criteria to whittle down the list.
Some ideas may be implementable immediately. Others may need further analysis to prioritize.
7. Create a Plan
When you have your shortlist, create an action plan that outlines the steps necessary to implement the ideas. By breaking down the ideas into actionable steps, you’ll be better able to put them into play and see the results.
Problem Solving Your Workflows
When it comes to coming up with creative answers to your workflow problems, we have a variety of resources for you listed below. In addition, we're always interested in providing objective, experienced ideas through our Customer Success and Services teams.
- Reframe Your Business Processes
- Process Redesign Tips
- What is Business Process Re-Engineering?
- Process Improvement Examples
- https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/what-is-creative-problem-solving
- https://www.mindtools.com/a2j08rt/creative-problem-solving
- https://www.creativeeducationfoundation.org/what-is-cps/
- https://innovationmanagement.se/2010/06/02/the-basics-of-creative-problem-solving-cps/
- https://asana.com/resources/convergent-vs-divergent
Tags creativity problem solving process improvement
Categories Business Ideas Workflow Ideas Project Management

Marketing the world's best workflow automation software and drinking way too much coffee. Connect with me on LinkedIn at https://www.linkedin.com/in/michaelraia/
Subscribe to Receive the Latest Workflow Automation Tips
Subscribe →
Business Ideas
Customer corner, department focus, employee spotlight, flowchart friday, industry focus, productivity points, productivity tips, project management, using integrify, workflow ideas.

The Palgrave Encyclopedia of the Possible pp 298–313 Cite as
Creative Problem-Solving
- Gerard J. Puccio 2 ,
- Barry Klarman 2 &
- Pamela A. Szalay 2
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2023
115 Accesses
Life and work in the beginning of the twenty-first century has been described as volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous. In this fast changing, innovation-driven environment, Creative Problem-Solving has been identified as a fundamental skill for success. In contrast to routine problem-solving, with straightforward and repeatable solution paths, today’s problems are described as being complex and wicked. To generate the possibilities that can effectively address complex problems, individuals need to draw on the highest level of human thought – creativity. Creative Problem-Solving explicitly draws on, and promotes, effective creative thinking. The purpose of this entry is to describe and distinguish Creative Problem-Solving from other forms of problems-solving. Moreover, as Creative Problem-Solving is a deliberate creativity methodology, this chapter also provides a description of the more specific thinking skills that are embodied by the higher-order skill of creative thinking and are explicitly called on in Creative Problem-Solving. Complex problems require complex thinking, and Creative Problem-Solving provides a structured process that allows individuals to more easily and efficiently deploy their creative thinking skills.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Anderson, L. W., & Krathwohl, D. R. (Eds.). (2001). A taxonomy for learning, teaching and assessing: A revision of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives: Complete edition . New York: Longman.
Google Scholar
Basadur, M. (1994). Simplex. Buffalo, NY: The Creative Education Foundation.
Brackett, M. (2019). Permission to feel: Unlocking the power of emotions to help our kids, ourselves, and our society thrive . New York: Celadon Books.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1990). Flow: The psychology of optimal experience . New York: HarperPerennial.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1996). Creativity: Flow and the psychology of discovery and invention . New York: HarperCollins.
Darwin, C. (2003). The origin of species: By means of natural selection of the preservation of favoured races in the struggle for life (p. 252). New York: Signet Classics.
Goleman, D. (1995). Emotional intelligence: Why it can matter more than IQ . New York: Bantam.
Isaksen, S. G., & Treffinger, D. J. (1985). Creative problem solving: The basic course. Buffalo, NY: Bearly Limited.
Isaksen, S. G., Dorval, K. B., & Treffinger, D. J. (1994). Creative approaches to problem solving. Dubuque, IA: Kendall/Hunt.
Isaksen, S. G., Dorval, K. B. & Treffinger, D. J. (2000). Creative approaches to problem solving (2nd ed.). Dubuque, IA: Kendall/Hunt Publishing.
Johnson, B. (1996). Polarity management: Identifying and managing unsolvable problem . Amherst: HRD Press.
Miller, J. C. (2004). The transcendent function: Jung’s model of psychological growth through dialogue with the unconscious . Albany: State University of New York Press.
Morriss-Kay, G. M. (2010). The evolution of human artistic creativity. Journal of Anatomy, 216 , 158–176.
Article Google Scholar
Mumford, M. D., Zaccaro, S. J., Harding, F. D., Jacobs, T. O., & Fleishman, E. A. (2000). Leadership skills for a changing world: Solving complex problems. Leadership Quarterly, 11 , 11–35.
Osborn, A. F. (1953). Applied imagination: Principles and procedures of creative problem-solving . New York: Scribner.
Osborn, A. F. (1963). Applied imagination: Principles and procedures of creative problem-solving (3rd ed.). New York: Scribner.
Otani, A. (2015, January). These are the skills you need if you want to be headhunted. Retrieved on 27 July 2015 from Osborn, A. F. (1953). Applied imagination: Principles and procedures of creative problem-solving . New York: Scribner.
Parnes, S. J. (1967). Creative behavior workbook. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons.
Parnes, S. J. (1988). Visionizing. East Aurora, NY: D.O.K. Publishers.
Parnes, S. J. (1992). Creative problem solving and visionizing. In S.J. Parnes (Ed.), Sourcebook for creative problem solving (pp. 133–154). Buffalo, NY: Creative Education Press.
Parnes, S. J., & Biondi, A. M. (1975). Creative behavior: A delicate balance. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 9 , 149–158.
Puccio, G. J. (2017). From the dawn of humanity to the 21st century: Creativity as an enduring survival skill. The Journal of Creative Behavior, 51 , 330–334. https://doi.org/10.1002/jocb.203 .
Puccio, G. J., Murdock, M. C., & Mance, M. (2005). Current developments in creative problem solving for organizations: A focus on thinking skills and styles. The Korean Journal of Thinking & Problem Solving, 15 , 43–76.
Puccio, G. J., Mance, M., & Murdock, M. (2011). Creative leadership: Skills that drive change (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks: SAGE.
Puccio, G. J., Mance, M., Switalski, B., & Reali, P. (2012). Creativity rising: Creative thinking and problem solving in the 21st century . Buffalo: ICSC Press.
Puccio, G. J., Burnett, C., Acar, S., Yudess, J. A., Holinger, M., & Cabra, J. F. (2018). Creative problem solving in small groups: The effects of creativity training on idea generation, solution creativity, and leadership effectiveness. The Journal of Creative Behavior . Advance online publication. [not sure of order]. https://doi.org/10.1002/jocb.381 .
Scott, G. M., Leritz, L. E., & Mumford, M. D. (2004). The effectiveness of creativity training: A meta-analysis. Creativity Research Journal, 16 , 361–388.
Stokes, P. D. (2013). Crossing disciplines: A constraint-based model of the creative/innovative process. The Journal of Product Innovation Management, 31 (2), 247–228. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12093 .
Trilling, B., & Fadel, C. (2009). 21st century skills: Learning for life in our times . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Vehar, J. R., Firestien, R. L., & Miller, B. (1997). Creativity unbound. Williamsville, NY: Innovation Systems Group.
Wagner, T. (2008). The global achievement gap: Why even our best schools don’t teach the new survival skills our children need – And what we can do about it . New York: Basic Books.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
International Center for Studies in Creativity, The State University of New York, Buffalo, NY, USA
Gerard J. Puccio, Barry Klarman & Pamela A. Szalay
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gerard J. Puccio .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Dublin City University, Dublin, Ireland
Vlad Petre Glăveanu
Section Editor information
No affiliation provided
Sergio Agnoli
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Puccio, G.J., Klarman, B., Szalay, P.A. (2022). Creative Problem-Solving. In: Glăveanu, V.P. (eds) The Palgrave Encyclopedia of the Possible. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90913-0_41
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-90913-0_41
Published : 26 January 2023
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-90912-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-90913-0
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
How to Use Creativity in Problem-Solving

Using creativity in problem-solving is a dynamic process that involves seeing challenges from unique perspectives, generating novel solutions , and redefining the status quo. It requires going beyond traditional methodologies and employing inventive thinking.
Table of Contents
Techniques such as brainstorming, lateral thinking, and mind mapping can help ignite your creative sparks. By cultivating a culture of creativity, you empower yourself and others to tackle issues innovatively, ensuring that the problem-solving process is effective but also exciting and rewarding.
What is the Role of Creativity in Problem-Solving?
Creative problem-solving is an approach that combines imagination, innovation, and a broad sense of flexibility to find solutions to problems. It’s about shunning the traditional mindset that restricts our thoughts to only known and accepted techniques and methods . Instead, it encourages thinking outside the box, leveraging all cognitive resources, and pushing beyond the boundaries of standard methodologies to arrive at unique and often more effective solutions.
At the heart of creative problem-solving is the understanding that problems are often not what they initially appear to be. An issue may seem like a stumbling block. Still, with creative problem-solving , it can be transformed into an opportunity for innovation and growth. It’s about not accepting the immediate, apparent problem at face value but delving deeper into uncovering the root cause and addressing that, often leading to a more comprehensive and long-lasting solution.

Stages of Creative Problem-Solving
To appreciate what is creative problem-solving, it is crucial to recognize its critical stages. First is problem identification, which involves understanding the problem from different angles and perspectives. This stage lays the groundwork for the creative process by opening up many possibilities.
Next comes idea generation. This stage is the crux of the creative process, where traditional thinking is left behind, and innovative ideas can flourish. Techniques like brainstorming, free writing, and mind mapping are commonly used to spur creativity and encourage various possible solutions.
Finally, there’s the evaluation and implementation of the solution. This stage involves critically assessing the proposed solutions, selecting the best one, and implementing them. It’s important to remember that the solution’s effectiveness should be evaluated and adjustments made, if necessary, to ensure the problem is resolved.
In essence, creative problem-solving is a process that welcomes innovation, embraces change, and turns problems into opportunities for creative growth. It’s not about finding a solution but about using creativity to discover the best solution. The beauty of creative problem-solving is that honing this skill is possible and can be developed, ultimately leading to better decision-making and problem-solving abilities in all areas of life.
How to Harness Creativity in Problem-Solving
Harnessing creativity is the cornerstone of innovative problem-solving. This involves challenging our usual thought patterns and opening ourselves to new ways of thinking. But how do we activate this creative engine within us? The answer lies in asking the right creative problem-solving questions.
Creative Problem-Solving Questions
Questions are the fuel that ignites the engine of creativity. They challenge our assumptions, expand our perspectives, and drive us to think outside the box. In problem-solving, creative questions can illuminate unseen possibilities and pathways toward innovative solutions.
The first step in harnessing creativity for problem-solving is understanding the problem in-depth. Questions such as “What is the core issue?” or “Why is this a problem?” can help identify the root cause rather than just dealing with symptoms. Understanding the problem at a granular level often reveals unique angles and opportunities for innovative solutions.
Once we deeply understand the problem, it’s time to generate ideas. Here, creative problem-solving questions are designed to push our thinking beyond usual boundaries. Questions like “What if the impossible were possible?” or “How would this problem be solved in a completely different context?” can spark unconventional ideas and unlock creative potential.
The next stage is about evaluating the solutions. Questions such as “What could be the potential impacts of this solution?” or “How can we improve this idea?” ensure we critically assess the proposed solutions from various angles. It’s vital to constructively challenge each idea’s viability, promoting further creativity and refinement.
Finally, we come to the implementation of the chosen solution. Questions like “What resources are needed to execute this solution?” and “What could be potential roadblocks, and how can we overcome them?” enable us to foresee any practical issues and address them proactively, thus ensuring a smooth execution of the solution.
Asking creative problem-solving questions can help unlock our inherent creative capabilities. By harnessing our creativity, we can drive innovative problem-solving and find solutions that are not just effective but also genuinely novel and groundbreaking. These questions are more than just tools; they are the catalysts that transform problems into opportunities for creative innovation.

What is the Connection between Creativity and Problem-Solving?
Creativity is an invaluable tool in the problem-solving process. It empowers us to develop unique solutions that resolve the issue and provide opportunities for growth and innovation. But how is creativity used in problem-solving? Let’s dive into the nuances of this connection.
At its core, problem-solving is about finding solutions to obstacles or challenges. Traditional problem-solving techniques often focus on logical reasoning and proven methodologies. However, these techniques may only sometimes be sufficient, especially when dealing with complex or unprecedented problems. This is where creativity steps in.
How is Creativity Used in Problem-Solving
Creativity in problem-solving starts with reframing the problem. It prompts us to see beyond the apparent and understand the problem from different perspectives. This is particularly helpful when dealing with intricate issues, as it helps identify underlying patterns and relationships that might not be immediately apparent.
Once the problem is reframed, the next step is idea generation. This is where the power of creativity truly shines. Creative thinking encourages us to break free from conventional thinking patterns and explore a broader spectrum of possibilities. Brainstorming, mind mapping, or even daydreaming can help stimulate creative thoughts and generate innovative ideas.
Creativity also plays a critical role in evaluating and selecting the best solution. It allows us to envision how each potential solution might play out, assess the risks and benefits, and choose the most effective and innovative option.
Finally, creativity is instrumental in the implementation of the solution. It encourages us to think on our feet, adapt to unexpected challenges, and continuously refine the solution until the problem is fully resolved.
Creativity fuels each stage of the problem-solving process, transforming it from a mundane task into an exciting journey of discovery and innovation. So, whether you’re dealing with a minor hiccup or a major hurdle, remember to tap into your creative side. You might be surprised at the great solutions that emerge.
How to Explore Techniques for Fostering Creativity in Problem-Solving
In the dynamic and competitive business world, a creative approach to problem-solving can be a significant differentiator. Now businesses require innovative solutions to keep up with rapidly changing environments and customer expectations. Here, we’ll explore techniques for fostering creative problem-solving in business.
How to Use Creative Problem-Solving in Business
Firstly, it’s crucial to cultivate an environment that encourages creativity. An open-minded culture supporting risk-taking and diverse perspectives can significantly enhance creative thinking. This includes welcoming all ideas during brainstorming sessions, regardless of how unconventional they seem, and celebrating successes and learning opportunities from failures.
Secondly, divergent thinking is a powerful tool for creative problem-solving. It involves generating multiple possible solutions to a problem rather than following a linear, logical path. Techniques like brainstorming or lateral thinking can stimulate divergent thinking, leading to more innovative problem-solving.
Another technique uses creative problem-solving frameworks, like the SCAMPER model (Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, Reverse). These frameworks provide structured methods for thinking creatively and can be particularly useful in a business setting.
Also, fostering creativity requires constant learning and development . Encouraging continuous learning, such as attending seminars, workshops, or online courses on creativity and innovation, can significantly enhance creative problem-solving skills. Also, exposure to different industries, cultures, and ways of thinking can provide new perspectives and ideas.
Creativity can also be enhanced by embracing technology. AI and machine learning, for example, can provide insights and patterns that would be hard to spot otherwise, opening new avenues for creative solutions.
Lastly, it’s essential to recognize the power of rest in fostering creativity. Downtime, hobbies, or simple walks in nature can rejuvenate the mind and often lead to ‘Eureka’ moments when least expected.
Fostering creative problem-solving in business is not a one-size-fits-all process. It requires a blend of culture, techniques, learning, technology, and well-being that suits your team’s unique needs and dynamics. However, the rewards – innovative solutions, competitive advantage, and team satisfaction – make it an investment worth making.

What are Some Successful Implementations of Creativity in Problem-Solving?
Applying creativity in problem-solving has led to groundbreaking solutions in various fields. In this context, we will explore several instances of creative problem-solving that resulted in successful and innovative outcomes.
Examples of Creative Problem-Solving
Accommodation: Let’s look at a classic example from the business world: Airbnb. In its early days, the company needed help to gain traction. The founders identified a key issue: the quality of listing photos could have been better, deterring potential renters. In a creative problem-solving move, they hired professional photographers to take pictures of the rentals. This innovative approach significantly improved the appeal of the listings, and the rest is history. Airbnb’s success illustrates how a creative solution can transform a problem into an opportunity.
Motor Industry: Consider the example of the automobile industry’s Tesla Motors . Confronted with the problem of fossil fuel dependency and its environmental impact, Tesla disrupted the conventional solution of tweaking existing fuel technologies. Instead, they creatively focused on developing high-performance electric vehicles, changing the industry’s perception and leading towards sustainable transportation.
Healthcare: Another example can be found in healthcare, particularly in the fight against polio. In the 1950s, the ‘iron lung’ was the primary treatment for polio-induced respiratory failure. It was a cumbersome and expensive solution. Dr. Bjørn Aage Ibsen , confronted with a polio outbreak, creatively proposed a new method: positive pressure ventilation. This involved manually ventilating the patient with a tube inserted into their trachea. This became the precursor to modern mechanical ventilation, demonstrating the impact of creative problem-solving in healthcare.
Education: Lastly, consider the example from education: the Khan Academy . Recognizing that traditional classroom education could not cater to each student’s pace and learning style, Salman Khan saw an opportunity to teach differently. He used technology creatively to provide free online educational videos, fundamentally transforming the access and delivery of education on a global scale.
The Impact of Creative Problem-Solving
In these cases, the key to successful problem-solving was applying creative thinking. These examples of creative problem-solving underscore the power of innovative thinking in transforming challenges into opportunities for growth and advancement. The ability to think creatively in problem-solving is a valuable skill and, in many cases, a game-changer.
How to Overcome Obstacles in Creativity in Problem-Solving
While creative problem-solving offers incredible potential for innovative solutions, it’s not without its challenges. However, these obstacles can often be overcome with a structured approach, such as the creative problem-solving model (CPS).
Creative Problem-Solving Model
The CPS model, initially developed by Alex Osborn and Sidney Parnes, provides a clear framework for navigating challenges that can arise during creative problem-solving. This model consists of four main steps: Clarify, Ideate, Develop, and Implement.
The first step, ‘Clarify,’ involves identifying the problem accurately and comprehensively. It’s easy to rush into solving a problem based on initial perceptions, which often results in treating symptoms rather than addressing the underlying issue. The CPS model emphasizes the importance of dedicating time to deeply understand the problem before jumping to solutions.
The second step, ‘Ideate,’ is generating various possible solutions. It’s common to experience blocks during this stage, such as sticking to familiar ideas or fearing judgment for unconventional thoughts. This step encourages divergent thinking, pushing past the initial, most apparent ideas to reach more unique and creative solutions.
Next, the ‘Develop’ stage involves converging on the most promising ideas and fleshing them into actionable solutions. Sometimes, the most creative ideas can seem risky or unrealistic. This stage, however, reminds us that these ideas often hold the most potential for innovative solutions and should be explored and developed rather than dismissed.
Finally, ‘Implement’ is about turning the solution into reality. Implementation can face many obstacles, from resistance to change, lack of resources, or unforeseen challenges. But the CPS model treats these not as dead ends but as parts of the problem-solving journey to be creatively overcome.
The creative problem-solving model provides a powerful tool to deal with the challenges of creative thinking. It offers a structured approach that fosters creativity, keeps the problem-solving process on track, and ultimately leads to innovative and effective solutions.

What are Some Tools and Strategies for Enhancing Creativity in Problem-Solving?
Creative problem-solving is a critical skill in today’s dynamic and complex world. It helps us navigate challenges with innovative and effective solutions. Various tools and strategies can enhance this process. Here, we delve into some of these creative problem-solving tools.
Creative Problem-Solving Tools
Brainstorming.
Brainstorming is the most familiar tool. It’s a freewheeling method to generate many ideas without immediate judgment or criticism. It invites and encourages wild and divergent thoughts, which are later sifted and refined. This tool is particularly effective in groups where diverse perspectives can spark unique ideas.
Mind Mapping
Mind Mapping, another powerful tool, visually represents thoughts and their interconnections. You can reveal unexpected connections by mapping the problem and related ideas and fostering innovative solutions. It’s an excellent tool for complex problems that involve multiple dimensions or for situations where a holistic view is needed.
The SCAMPER Method
The SCAMPER method (Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, Reverse) prompts users to ask specific questions about the problem. Each word in the acronym poses a different way to manipulate and think about the problem, leading to fresh insights and solutions.
Six Thinking Hats Technique
Then there’s the Six Thinking Hats technique by Edward de Bono. This tool urges users to assume different ‘hats’ or roles (like the optimist, devil’s advocate, creative, etc.) during problem-solving. This strategy ensures a comprehensive approach, capturing different perspectives and reducing bias in decision-making.
Alongside these tools, specific strategies can cultivate creativity in problem-solving. Encouraging a culture of openness, where diverse thoughts are valued, can lead to more prosperous, more creative problem-solving. Creating a safe space where risks are welcomed is beneficial, and failures are seen as learning opportunities rather than setbacks.
Moreover, taking regular breaks and engaging in different activities can stimulate creativity. Often, stepping away from a problem allows our subconscious minds to work on it, leading to unexpected insights.
Regularly practicing and using these tools and strategies can dramatically improve creative problem-solving abilities. They stimulate innovative thinking and help structure the process, making it more effective and efficient. By leveraging these creative problem-solving tools, we can transform how we approach problems, turning challenges into opportunities for innovation.
What is the Future of Creativity in Problem-Solving?
As we navigate through a world that is becoming progressively more complex and unpredictable, the importance of creativity in problem-solving cannot be overstated. While still valuable, traditional problem-solving methods often must catch up when dealing with unprecedented challenges. Creativity injects flexibility, innovation, and adaptability into problem-solving, making it a vital skill for the future. Here, we explore some trends and predictions of creativity in problem-solving.
Growing Creative Problem-Solving
Firstly, we will likely see greater recognition of the role of creativity in problem-solving across various sectors. From businesses to education systems, there’s a growing understanding that generating and implementing innovative solutions to problems for survival and growth is crucial. We can see more emphasis on fostering creativity in leadership roles and at all levels.
Tech-Enhanced Creative Solutions
Secondly, technology will continue to play a significant role in enhancing creativity in problem-solving. Advanced technologies like AI and machine learning can provide us with more data and insights, enabling us to understand problems better and develop more creative solutions. At the same time, technology can facilitate the creative problem-solving process through tools that stimulate creative thinking and collaboration.
However, as we increasingly rely on technology, there’s also a danger that we might limit our creativity by depending too much on algorithms and predefined solutions. Therefore, balancing technology and human creativity will be essential to future problem-solving.
Additionally, we expect to see more integration of diverse perspectives in problem-solving. As we face global problems across various fields and cultures, it’s becoming clear that the most creative and effective solutions often come from interdisciplinary and diverse teams.
Dynamic Problem Adaptation
Finally, resilience and adaptability in problem-solving will be emphasized as we move toward a more uncertain future. Creative problem-solving will be less about finding the correct answer and more about continuous learning and adapting to evolving situations.
The future of creativity in problem-solving looks bright, promising, and exciting. By recognizing the importance of creativity and harnessing it effectively, we can equip ourselves to navigate future challenges with innovative and effective solutions.
What is the role of creativity in problem-solving?
Creativity in problem-solving allows for the generation of unique, practical solutions. It involves thinking outside the box, challenging traditional assumptions, and viewing the problem from various perspectives. Creativity is crucial in problem-solving as it fosters innovation and adaptability.
How can creativity be harnessed in problem-solving?
Creativity can be harnessed in problem-solving by promoting a culture that supports risk-taking and values diverse perspectives, employing techniques like divergent thinking and creative problem-solving frameworks, engaging in continuous learning and development, embracing technology, and prioritizing well-being and rest.
What is the connection between creativity and effective problem-solving?
Creativity contributes to effective problem-solving by enabling the generation of numerous possible solutions, encouraging novel perspectives, and fostering flexibility and adaptability. These aspects, in turn, lead to more comprehensive and innovative solutions.
What challenges might one encounter in creative problem-solving?
Challenges in creative problem-solving include rushing to solve the problem without fully understanding it, experiencing blocks during the ideation stage, dismissing seemingly unrealistic or risky ideas, and encountering resistance or unforeseen challenges during the implementation stage.
How might the future of creativity in problem-solving look like?
The future will likely see greater recognition of the role of creativity in problem-solving across various sectors. Technology will play a significant role in enhancing creativity, but maintaining a balance with human creativity will be necessary. Integrating diverse perspectives and emphasis on resilience and adaptability will also characterize future problem-solving.

Learn How To Develop Launch-Ready Creative Products
Download How to Turn Your Creativity into a Product, a FREE starter kit.

Advertisement
Create a Memorable Social Media Experience
Get the content planner that makes social media 10x easier.

Invite Your Customers To A Whole New World
Create a unique user experience.

Maximize Your Brand and Make Your Mark
Custom brand assets will take you to new heights.

Niche Markets: How to Overcome Challenges

Magazine Page Layout: How to Use Digital Designs

Rank a Website: How to Use Guest Blogging for SEO

Anatomy of a Magazine: How to Shape Perception

Storytelling: How to Use it in Marketing

Business Landscape: How to Understand Trend Analysis
- About us
Creative problem solving: basics, techniques, activities
Why is creative problem solving so important.
Problem-solving is a part of almost every person's daily life at home and in the workplace. Creative problem solving helps us understand our environment, identify the things we want or need to change, and find a solution to improve the environment's performance.
Creative problem solving is essential for individuals and organizations because it helps us control what's happening in our environment.
Humans have learned to observe the environment and identify risks that may lead to specific outcomes in the future. Anticipating is helpful not only for fixing broken things but also for influencing the performance of items.
Creative problem solving is not just about fixing broken things; it's about innovating and creating something new. Observing and analyzing the environment, we identify opportunities for new ideas that will improve our environment in the future.
The 7-step creative problem-solving process
The creative problem-solving process usually consists of seven steps.
1. Define the problem.
The very first step in the CPS process is understanding the problem itself. You may think that it's the most natural step, but sometimes what we consider a problem is not a problem. We are very often mistaken about the real issue and misunderstood them. You need to analyze the situation. Otherwise, the wrong question will bring your CPS process in the wrong direction. Take the time to understand the problem and clear up any doubts or confusion.
2. Research the problem.
Once you identify the problem, you need to gather all possible data to find the best workable solution. Use various data sources for research. Start with collecting data from search engines, but don't forget about traditional sources like libraries. You can also ask your friends or colleagues who can share additional thoughts on your issue. Asking questions on forums is a good option, too.
3. Make challenge questions.
After you've researched the problem and collected all the necessary details about it, formulate challenge questions. They should encourage you to generate ideas and be short and focused only on one issue. You may start your challenge questions with "How might I…?" or "In what way could I…?" Then try to answer them.
4. Generate ideas.
Now you are ready to brainstorm ideas. Here it is the stage where the creativity starts. You must note each idea you brainstorm, even if it seems crazy, not inefficient from your first point of view. You can fix your thoughts on a sheet of paper or use any up-to-date tools developed for these needs.
5. Test and review the ideas.
Then you need to evaluate your ideas and choose the one you believe is the perfect solution. Think whether the possible solutions are workable and implementing them will solve the problem. If the result doesn't fix the issue, test the next idea. Repeat your tests until the best solution is found.
6. Create an action plan.
Once you've found the perfect solution, you need to work out the implementation steps. Think about what you need to implement the solution and how it will take.
7. Implement the plan.
Now it's time to implement your solution and resolve the issue.
Top 5 Easy creative thinking techniques to use at work
1. brainstorming.
Brainstorming is one of the most glaring CPS techniques, and it's beneficial. You can practice it in a group or individually.
Define the problem you need to resolve and take notes of every idea you generate. Don't judge your thoughts, even if you think they are strange. After you create a list of ideas, let your colleagues vote for the best idea.
2. Drawing techniques
It's very convenient to visualize concepts and ideas by drawing techniques such as mind mapping or creating concept maps. They are used for organizing thoughts and building connections between ideas. These techniques have a lot in common, but still, they have some differences.
When starting a mind map, you need to put the key concept in the center and add new connections. You can discover as many joints as you can.
Concept maps represent the structure of knowledge stored in our minds about a particular topic. One of the key characteristics of a concept map is its hierarchical structure, which means placing specific concepts under more general ones.
3. SWOT Analysis
The SWOT technique is used during the strategic planning stage before the actual brainstorming of ideas. It helps you identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of your project, idea, or business. Once you analyze these characteristics, you are ready to generate possible solutions to your problem.
4. Random words
This technique is one of the simplest to use for generating ideas. It's often applied by people who need to create a new product, for example. You need to prepare a list of random words, expressions, or stories and put them on the desk or board or write them down on a large sheet of paper.
Once you have a list of random words, you should think of associations with them and analyze how they work with the problem. Since our brain is good at making connections, the associations will stimulate brainstorming of new ideas.
5. Storyboarding
This CPS method is popular because it tells a story visually. This technique is based on a step-creation process. Follow this instruction to see the storyboarding process in progress:
- Set a problem and write down the steps you need to reach your goal.
- Put the actions in the right order.
- Make sub-steps for some steps if necessary. This will help you see the process in detail.
- Evaluate your moves and try to identify problems in it. It's necessary for predicting possible negative scenarios.
7 Ways to improve your creative problem-solving skills
1. play brain games.
It's considered that brain games are an excellent way to stimulate human brain function. They develop a lot of thinking skills that are crucial for creative problem-solving.
You can solve puzzles or play math games, for example. These activities will bring you many benefits, including strong logical, critical, and analytical thinking skills.
If you are keen on playing fun math games and solving complicated logic tasks, try LogicLike online.
We created 3500+ puzzles, mathematical games, and brain exercises. Our website and mobile app, developed for adults and kids, help to make pastime more productive just in one place.
2. Practice asking questions
Reasoning stimulates you to generate new ideas and solutions. To make the CPS process more accessible, ask questions about different things. By developing curiosity, you get more information that broadens your background. The more you know about a specific topic, the more solutions you will be able to generate. Make it your useful habit to ask questions. You can research on your own. Alternatively, you can ask someone who is an expert in the field. Anyway, this will help you improve your CPS skills.
3. Challenge yourself with new opportunities
After you've gained a certain level of creativity, you shouldn't stop developing your skills. Try something new, and don't be afraid of challenging yourself with more complicated methods and techniques. Don't use the same tools and solutions for similar problems. Learn from your experience and make another step to move to the next level.
4. Master your expertise
If you want to keep on generating creative ideas, you need to master your skills in the industry you are working in. The better you understand your industry vertical, the more comfortable you identify problems, find connections between them, and create actionable solutions.
Once you are satisfied with your professional life, you shouldn't stop learning new things and get additional knowledge in your field. It's vital if you want to be creative both in professional and daily life. Broaden your background to brainstorm more innovative solutions.
5. Develop persistence
If you understand why you go through this CPS challenge and why you need to come up with a resolution to your problem, you are more motivated to go through the obstacles you face. By doing this, you develop persistence that enables you to move forward toward a goal.
Practice persistence in daily routine or at work. For example, you can minimize the time you need to implement your action plan. Alternatively, some problems require a long-term period to accomplish a goal. That's why you need to follow the steps or try different solutions until you find what works for solving your problem. Don't forget about the reason why you need to find a solution to motivate yourself to be persistent.
6. Improve emotional intelligence
Empathy is a critical element of emotional intelligence. It means that you can view the issues from the perspective of other people. By practicing compassion, you can understand your colleagues that work on the project together with you. Understanding will help you implement the solutions that are beneficial for you and others.
7. Use a thinking strategy
You are mistaken if you think that creative thinking is an unstructured process. Any thinking process is a multi-step procedure, and creative thinking isn't an exclusion. Always follow a particular strategy framework while finding a solution. It will make your thinking activity more efficient and result-oriented.
Develop your logic and mathematical skills. 3500+ fun math problems and brain games with answers and explanations.

20 Problem Solving Activities to Improve Creativity

Creative problem solving requires creative problem solving activities. Even if you know all of the problem solving steps , it’s important to know exercises to actually execute each phase. These exercises are techniques on how to improve problem solving skills and the art of problem solving.
Listed below are 20 interactive exercises that will help you through each step of the problem solving process.
Problem Solving Activities
Note: For the sake of demonstration, we use the same example for each exercise, in this case, the difficult problem of opening a jar of peanut butter (to make a delicious peanut butter and jelly sandwich of course).
Step 1: Define the Problem
Problem solving activities that help you phrase and understand the problem you are trying to solve:
#1. Newspaper Headline – Try writing your problem as if it were a headline in a newspaper. You can write it as if the problem still exists, or as if the problem were already solved. Try Tabloid headlines for even more creative ideas.
Example: “Local man attempts to provide joy to the world by opening a jar of peanut butter.”
#2. Future Party – Imagine it’s one year from today; what did you solve in the last year? How is the world different based on the solution? What were the steps you took to solve the problem?
Example: “I can’t believe it’s been a year since we ate all the peanut butter from that crazy tight jar.”
#3. 40-20-10-5 – Explain your problem in up to 40 words. Then cut it down to 20 words; then to 10, then finally to only 5 words. These 5 words are the root of your problem (and likely the root of your solution as well).
Example: (Starting at 10 words) “I want to open up this jar of peanut butter.” -> “Open this peanut butter jar.”
#4. Explain Life I’m Five – Explain your problem as if you were talking to a 5-year old kid. Use basic language and simple metaphors if necessary. Inspired by the subreddit ELI5 .
Example: “There’s yummy-ness in this jar that I want to get out.”
Step 2: Brainstorm Ideas
Problem solving activities that help you generate a list of possible solutions that will solve your problem*:
#5. Ad Game – Have people mill about the room. When someone offers up an idea, everyone emphatically says “Yes!” and then the group continues to generate ideas, often building off the last idea that was just offered.
Example: “We should use a tool to open this jar.” “Yes!” “And it should not hurt our hands.” “Yes!” “And it’ll be nearly effortless.” “Yes!”
#6. Dumbest Idea First – Hold a contest to get the dumbest idea out first. Encourage everyone to think of the absolute dumbest possible solutions to the problem. After you have a long list, go back through and see which ones may not be all that dumb.
Example: “Let’s open it using C4 explosives.”
#7. What Would X Do – Pretend you’re someone famous (or someone you admire) and ask yourself how they would solve the problem, what options would they consider?
Example: (as Gandhi) “I will go on a hunger strike until the jar is ready to be open.”
#8. 10x10x10 Matrix – Generate a list of 10 ideas for solving the problem. Pick one of those ideas and generate 10 variations of that idea. Pick one idea from the new list and generate 10 more variations.
Example: (with just 5 ideas): –Round 1 (based on tools)–Dynamite, Power Drill, Vise grip, Scissors, Hammer. –Round 2 (based on vise grip)–Metal clamp, Pliers, Glue, Cement, Sticky Glove. –Round 3 (based on sticky glove)–Lots of tapping, Rubbing the seal, Punching, Soft caresses, Really strong hand.
*Note: Some of the exercises may not produce the perfect solution, but they can get you thinking differently.
Step 3: Decide on a Solution
Problem solving activities that help you narrow your list of possible solutions down to the best solution.
#9. Futures Wheel – Pick a possible solution and write it in the center of a piece of paper. List possible direct results/consequences of the solution around the center idea. List possible indirect results/consequences based on the direct results/consequences. Find more info here .
Example: Really strong hand leads to: ability to open other types of jars as well, big forearms, possible blisters, …
#10. Thiagi’s 35 – Use a point system to determine the preferred solution among your team, turning a possibly subjective discussion into an objective group decision. You can find a more detailed explanation on Thiagi’s site .
Example: Really strong hand – 7pts. Punching the jar – 3pts. A soft caress – 1pts.
#11. Idea Trial – When you can’t get agreement on which solution to choose, have the proponents of each idea represent them in “court.” Go through opening arguments, call witnesses and allow closing statements. Have the project board choose the winner.
Example: “Really strong hand, is it true you could also be used for terrible things, such as opening a can of sardines?”
#12. Coin-Flip – When deciding between two equally good solutions, flip a coin. When the coin is in the air, take note of what you secretly hope the result is and go with that (if you really can’t decide between the two, then go with the actual result of the coin-flip). Inspired by this poster.
Example: Heads is strong hands, tails is a soft cares. *Toss.* (I really don’t want to have to caress this jar of peanut butter…) Strong hands it is!
Step 4: Implement the Solution
Problem solving activities that help you implement the solution you have chosen:
#13. End in Mind – To create your plan, start with the end in mind and work backwards. Establish key milestones and dates in reverse order, starting with the end-of-project celebration and ending with today.
Example: Eat delicious PB&J sandwich (5pm), Make delicious PB&J sandwich (4:58pm), Open Peanut Butter Jar (4:57pm), Build up grip strength (4:47), …
#14. Idea Mock-ups – Create a mock-up of the solution. You can a create physical mock-up using the various supplies in your office or a virtual mock-up using images from around the web.
Example: Tell me you wouldn’t buy this incredible product .
#15. Gamification – Turn the completion of your project into a game. Establish rules for how you earn points, create badges to celebrate milestones and track game progress. Learn more about gamification .
Example: For each squeeze of the PB Gripper, you get 1 point. 100 points earns you the Gripper Badge, 500 points earns you a pudding cup. After 1,000 points you should be able to open the Peanut Butter jar.
#16. Be a Character – Add some fun to your work by executing your plan as if you were a fictional character. Think about how they would operate and get into character.
Example: (as the Incredible Hulk): HULK SMASH!
Step 5: Review the Results
Problem solving activities that help you review the results you achieved and the way you achieved them:
#17. Apply McLuhan – Answer McLuhan’s tetrad of questions in context of your solution: 1) What does your solution enhance? 2) What does it make obsolete? 3) What does it bring back that was once obsolete and 4) What does it flip into when taken to the extreme?
Example: Using a strong grip to open the jar: 1) The ability to get peanut butter, 2) Other tools for opening jars, 3) The joy of cooking my own food, 4) Only eating peanut butter and nothing else.
#18. Word on the Street – Conduct “word-on-the-street” type interviews with members of your team, asking them how they felt about the project and the solution.
Example: “Sir, what’s your opinion on this new development on the ability to consume delicious peanut butter?”
#19. Stop-Start-Continue – Review the way you completed your project and pick activities you should stop (things you did on this project that you don’t think are necessary for future projects), start (things you didn’t do on this project but that you should do on future projects) and continue (things you did on the project that you should do on future projects).
Example: STOP doing every single exercise for one solution. START finding snacks to eat while waiting to get to the solution. CONTINUE eating peanut butter.
#20. Find the Funny – Write a monologue or stand-up set that covers some of the funny moments or ideas from the project. Share it with your team.
Example: What’s the deal with airline peanut butter?
Creative Problem Solving
The purpose of the above problem solving activities is to get you to think about the problem in a different way and have some fun while solving it–both of which will enhance your creativity in finding and implementing a solution. And as Einstein ( probably ) said:”The significant problems we face cannot be solved at the same level of thinking we were at when we created them.”
Note: The example used may be a bit facetious but these exercises do work for tougher problems. I wanted to include an example to facilitate understanding and it happened to be around snack time.
THIS FREE 129 SECOND QUIZ WILL SHOW YOU
what is your humor persona?
Humor is a skill that can be learned. And when used correctly, it is a superpower that can be your greatest asset for building a happier, healthier and more productive life. See for yourself...
you might also be interested in...

5 Things a Corporate Master of Ceremonies Needs to Know
So you’ve got tapped to be the corporate MC for an event (or perhaps a wedding or conference). What do […]

Improve Your Public Speaking – 5 Ways to Energize an Audience
A tired audience is an impatient and distracted audience. To help ensure your presentation is actually heard, it’s important to […]

Announcing the 2019 Corporate Humor Awards
It’s now time for the 2019 Corporate Humor Awards! Nominate an individual or organization that is helping to keep the […]
9 thoughts on “20 Problem Solving Activities to Improve Creativity”
Thanks for sharing this article.
Pingback: Improving Problem Solving in the Workplace - LockHouse Games
Would you allow us to translate this (in Hungarian and Romanian) and use it in our class?
very good. on point!
i am a student doing my certificate in archives and records management, i hope this will help me and i think you too can help in in your class
can I use this for my class?
Pingback: Innovation Roundup | Avish Parashar | Motivational Improviser and Innovation Speaker
its wonderful
Pingback: The Carnival of HR: Emerging Trends in HR « Mumblr
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Humor Persona - Template B2B
I make an effort to appreciate the humor of everyday life....
This question helps us further the advancement of humor research to make it more equitable.
Humor Persona - Main B2C
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Overview of the Problem-Solving Mental Process
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
- Identify the Problem
- Define the Problem
- Form a Strategy
- Organize Information
- Allocate Resources
- Monitor Progress
- Evaluate the Results
Frequently Asked Questions
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything they can about the issue and then using factual knowledge to come up with a solution. In other instances, creativity and insight are the best options.
It is not necessary to follow problem-solving steps sequentially, It is common to skip steps or even go back through steps multiple times until the desired solution is reached.
In order to correctly solve a problem, it is often important to follow a series of steps. Researchers sometimes refer to this as the problem-solving cycle. While this cycle is portrayed sequentially, people rarely follow a rigid series of steps to find a solution.
The following steps include developing strategies and organizing knowledge.
1. Identifying the Problem
While it may seem like an obvious step, identifying the problem is not always as simple as it sounds. In some cases, people might mistakenly identify the wrong source of a problem, which will make attempts to solve it inefficient or even useless.
Some strategies that you might use to figure out the source of a problem include :
- Asking questions about the problem
- Breaking the problem down into smaller pieces
- Looking at the problem from different perspectives
- Conducting research to figure out what relationships exist between different variables
2. Defining the Problem
After the problem has been identified, it is important to fully define the problem so that it can be solved. You can define a problem by operationally defining each aspect of the problem and setting goals for what aspects of the problem you will address
At this point, you should focus on figuring out which aspects of the problems are facts and which are opinions. State the problem clearly and identify the scope of the solution.
3. Forming a Strategy
After the problem has been identified, it is time to start brainstorming potential solutions. This step usually involves generating as many ideas as possible without judging their quality. Once several possibilities have been generated, they can be evaluated and narrowed down.
The next step is to develop a strategy to solve the problem. The approach used will vary depending upon the situation and the individual's unique preferences. Common problem-solving strategies include heuristics and algorithms.
- Heuristics are mental shortcuts that are often based on solutions that have worked in the past. They can work well if the problem is similar to something you have encountered before and are often the best choice if you need a fast solution.
- Algorithms are step-by-step strategies that are guaranteed to produce a correct result. While this approach is great for accuracy, it can also consume time and resources.
Heuristics are often best used when time is of the essence, while algorithms are a better choice when a decision needs to be as accurate as possible.
4. Organizing Information
Before coming up with a solution, you need to first organize the available information. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? The more information that is available the better prepared you will be to come up with an accurate solution.
When approaching a problem, it is important to make sure that you have all the data you need. Making a decision without adequate information can lead to biased or inaccurate results.
5. Allocating Resources
Of course, we don't always have unlimited money, time, and other resources to solve a problem. Before you begin to solve a problem, you need to determine how high priority it is.
If it is an important problem, it is probably worth allocating more resources to solving it. If, however, it is a fairly unimportant problem, then you do not want to spend too much of your available resources on coming up with a solution.
At this stage, it is important to consider all of the factors that might affect the problem at hand. This includes looking at the available resources, deadlines that need to be met, and any possible risks involved in each solution. After careful evaluation, a decision can be made about which solution to pursue.
6. Monitoring Progress
After selecting a problem-solving strategy, it is time to put the plan into action and see if it works. This step might involve trying out different solutions to see which one is the most effective.
It is also important to monitor the situation after implementing a solution to ensure that the problem has been solved and that no new problems have arisen as a result of the proposed solution.
Effective problem-solvers tend to monitor their progress as they work towards a solution. If they are not making good progress toward reaching their goal, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies .
7. Evaluating the Results
After a solution has been reached, it is important to evaluate the results to determine if it is the best possible solution to the problem. This evaluation might be immediate, such as checking the results of a math problem to ensure the answer is correct, or it can be delayed, such as evaluating the success of a therapy program after several months of treatment.
Once a problem has been solved, it is important to take some time to reflect on the process that was used and evaluate the results. This will help you to improve your problem-solving skills and become more efficient at solving future problems.
A Word From Verywell
It is important to remember that there are many different problem-solving processes with different steps, and this is just one example. Problem-solving in real-world situations requires a great deal of resourcefulness, flexibility, resilience, and continuous interaction with the environment.
Get Advice From The Verywell Mind Podcast
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares how you can stop dwelling in a negative mindset.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
You can become a better problem solving by:
- Practicing brainstorming and coming up with multiple potential solutions to problems
- Being open-minded and considering all possible options before making a decision
- Breaking down problems into smaller, more manageable pieces
- Asking for help when needed
- Researching different problem-solving techniques and trying out new ones
- Learning from mistakes and using them as opportunities to grow
It's important to communicate openly and honestly with your partner about what's going on. Try to see things from their perspective as well as your own. Work together to find a resolution that works for both of you. Be willing to compromise and accept that there may not be a perfect solution.
Take breaks if things are getting too heated, and come back to the problem when you feel calm and collected. Don't try to fix every problem on your own—consider asking a therapist or counselor for help and insight.
If you've tried everything and there doesn't seem to be a way to fix the problem, you may have to learn to accept it. This can be difficult, but try to focus on the positive aspects of your life and remember that every situation is temporary. Don't dwell on what's going wrong—instead, think about what's going right. Find support by talking to friends or family. Seek professional help if you're having trouble coping.
Davidson JE, Sternberg RJ, editors. The Psychology of Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press; 2003. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511615771
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. Published 2018 Jun 26. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
A Cognitive Trick for Solving Problems Creatively
- Theodore Scaltsas

Mental biases can actually help.
Many experts argue that creative thinking requires people to challenge their preconceptions and assumptions about the way the world works. One common claim, for example, is that the mental shortcuts we all rely on to solve problems get in the way of creative thinking. How can you innovate if your thinking is anchored in past experience?
- TS Theodore Scaltsas is a Chaired Professor in Classical Philosophy at the University of Edinburgh in Scotland.
Partner Center
- Inspire & Impact Collection |
- 29 brainstorming techniques: effective ...
29 brainstorming techniques: effective ways to spark creativity

Bright ideas don’t come as easily as flicking on a light.
When it’s up to one individual to dream up a solution, it can be time-consuming and cause a lot of pressure. And when it comes to a group of people tasked with solving a problem, ideas might clash. Not to mention, everyone has a preferred method for their creative madness, making it difficult to get every team members’ wheels turning in the same direction.
That’s where brainstorming techniques come in. These techniques provide structure for brainstorming sessions, ignite creativity across all brainstormers, and ensure your ideas come to fruition. And luckily, there are lots of effective brainstorming techniques to choose from.
What is brainstorming?
Here’s a general brainstorming definition: it’s an approach taken by an individual or team to solve a problem or generate new ideas for the improvement of a product, organization, or strategy.
No matter your preferred method, most brainstorming techniques involve three steps:
Capture ideas
Discuss and critique the ideas
Choose which ideas to execute
Every brainstorming technique also involves the same ingredients. All you need is an individual or group of people, a problem to solve or an opportunity to address, and time.
Brainstorming challenges
The golden rule of all brainstorming sessions is quantity over quality. The more ideas you have, the better your chances are that one will be worthy of execution. For these reasons, especially in group brainstorming sessions, be sure all team members check their criticisms at the door and let it be known that the only bad ideas are no ideas.
Of course, not every brainstorming session will go off without a hitch. Some common brainstorming challenges include:
Unbalanced conversations, sometimes due to extroverts dominating discussions
The anchoring effect, meaning brainstormers cling to the first few ideas shared and don’t move on to others
Awkward silences, which often occur when participants are not prepared
Perhaps you’ve experienced some of these uncomfortable brainstorming sessions yourself. Thankfully, there are plenty of tried-and-true, and also some unorthodox, brainstorming techniques and tools that tackle just these issues.
Analytic brainstorming techniques
When you need to look at an idea from all angles or vet a problem thoroughly, analytic brainstorming techniques might be worth implementing. Consider the following brainstorming methods and tools to generate and qualify ideas.
1. Starbursting
A visual brainstorming technique, starbursting should be used once you or your team of brainstormers has homed in on a single idea. To begin starbursting, put an idea on the middle of a whiteboard and draw a six-point star around it. Each point will represent a question:
Consider every question and how it might pertain to your idea, such as, “Who will want to buy this product?” or, “When will we need to launch this program?” This will help you explore scenarios or roadblocks you hadn’t considered before.
Best for: large group brainstorms, vetting ideas thoroughly
2. The five whys, a.k.a. why analysis
Similar to starbursting, the five whys brainstorming technique helps you evaluate the strength of an idea. Challenge yourself to ask “why” questions about a topic or idea at least five times and consider what new problems you surface—and, importantly, note how you can address them. To help organize your thoughts, consider using a flowchart or fishbone diagram in hand with this brainstorming technique.
Best for: individual and group brainstorms, vetting ideas thoroughly
3. SWOT analysis
You might be familiar with SWOT analysis as it relates to strategic planning , and you might also be surprised to know that this concept can also be applied as a brainstorming exercise to help qualify an idea. The notion? Discuss the following aspects of your topic to determine whether it’s worth executing:
Strengths : how does the idea dominate or stand out from competitors?
Weakness : are there any flaws in the idea that could jeopardize its execution?
Opportunities : what else can you capitalize on based on this idea?
Threats : what are potential downfalls that could arise if the idea is launched?
4. How Now Wow
The How Now Wow brainstorming technique is all about categorizing ideas based on how unique they are and how easy they are to implement. Once you’ve collected several ideas, either individually or from team members, talk through where they fall in the How Now Wow spectrum:
How ideas are ideas that are original but not executable.
Now ideas are unoriginal ideas that are easily executable.
Wow ideas are never-been-pitched before ideas that are also easy to implement.
Obviously, you want as many “Wow” ideas as possible since these are executable but also because they might set you apart from competitors or dispel monotony in a company. To help organize your ideas, consider using a matrix of four squares with difficulty weighted on the Y-axis and innovation on the X-axis.
Best for: individual and group brainstorms, homing in on an executable solution
5. Drivers analysis
Just as the name implies, driver analysis is a brainstorming technique that analyzes the drivers or “causes” of a problem. To use this brainstorming technique, simply keep asking yourself or your team of brainstormers: “What’s driving [insert problem]?” and then, “What’s driving [insert answer to the previous question]?” Similar to why analysis, the deeper you dig into a problem, the more well-vetted it will be and the more confident you will be in executing solutions for those problems.
6. Mind mapping
Another visual brainstorming technique, mind mapping addresses the anchoring effect—a common brainstorming challenge where brainstormers fixate on the first ideas instead of coming up with new ones. Mind mapping does this by using the first idea to inspire other ideas.
You’ll need a large piece of paper or whiteboard to do this. Begin by writing down a topic and then drawing lines connecting tangential ideas to it. This essentially helps you paint a picture of your topic at hand and what might impact its execution or even expedite it.
Best for: individual and group brainstorms, visual thinkers
7. Gap filling, a.k.a. gap analysis
When you’re struggling with how to execute an idea, that’s where gap filling comes in—to address the obstacles standing in your way. Begin by starting with a statement of where you are and then a statement of where you want to be. For example, “Our company creates smart watches; we want to expand our portfolio to also include fitness trackers.”
It’s worth writing these out on a large piece of paper or a whiteboard for all of your brainstormers to see, perhaps using a flowchart or mind map to do so. Then, list obstacles that are preventing you from getting where you want to be and work through solutions for each of them. By the end of your brainstorming session, you should have a clearer plan of how to get where you want to be.
Best for: individual and group brainstorms, visual thinkers, honing in on an executable solution
Quiet async brainstorming techniques

Best for businesses that are crunched for time or teams with more introverted individuals, these quiet brainstorming techniques allow brainstormers to contribute ideas on their own time and often anonymously. Look to the following methods to get your creative juices flowing, especially for remote teams with frequent virtual meetings .
8. Brainwriting, a.k.a. slip writing
A nonverbal and in-person brainstorming technique, brainwriting addresses the brainstorming challenge of unbalanced conversations head-on. That’s because it requires participation and teamwork from every brainstormer, beginning with each person writing down three ideas relating to a topic on three separate slips of paper. Then everyone passes their ideas to the right or left and their neighbor builds on those ideas, adding bullet points and considerations.
The slips of paper continue to be passed around the table until they’ve made it all the way around. Then, the brainstorm facilitator can digest all of the ideas themselves, or the brainstormers can discuss each idea out loud and determine what’s worth pursuing. Pro tip: limit this brainstorming technique to no more than 10 people to not be overwhelmed with ideas or time constraints.
Best for: group brainstorms and introverted team members
9. Collaborative brainwriting
You can think of collaborative brainwriting like a herd of cows grazing in a field, except it’s brainstormers grazing on ideas throughout a week, anonymously jotting down thoughts or ideas. Oftentimes a brainstorming facilitator will kick off this technique by posting a large piece of paper, sticky notes, or sharing a cloud-based document to jot down a few brainstorming ideas.
From there, team members can build off of those ideas on their own time and anonymously provide feedback. Be sure to set a clear deadline of when the brainstorming session closes to ensure all brainstormers have an opportunity to chime in.
Best for: individual brainstorming
10. Brain-netting, a.k.a. online brainstorming
Great for remote teams, brain-netting is essentially a place for a team to brain dump their own ideas, whether that’s a Slack channel, Google Doc, or your project management tool .
The notion is that brainstormers can add ideas whenever inspiration strikes and that the list will be ever-evolving. Of course, the team leader might want to inform their team of brainstormers of any important dates or deadlines when they need solutions to a problem. They may also want to hold a meeting to discuss the ideas. All brainstormers’ identities can be left anonymous even in the meeting.
Best for: group brainstorms, introverted team members, remote teams
11. SCAMPER
The SCAMPER brainstorming technique encourages brainstormers to look at an idea from different angles and it uses its acronym to inspire each lens:
Substitute : consider what would happen if you swapped one facet of a solution for another.
Combine : consider what would happen if you combined one facet of a solution with another.
Adapt : consider how you could adapt an idea or solution in a new context.
Modify : consider how you can modify an idea to make it higher impact.
Put to another use : consider how else you could leverage your idea.
Eliminate : consider what you could remove from the idea or solution so that it’s simplified.
Reverse effective : finally, consider how you could reorganize an idea to make it most effective .
When used in a group brainstorming session, you might want to use templates to track responses or pair the SCAMPER method with a brainwriting session to encourage all brainstormers to evaluate ideas from every angle.
12. Lightning Decision Jam
Known as LDJ for short, the Lightning Decision Jam brainstorming technique requires 40 minutes to one hour to complete. What will you have by the end? Tangible results and buy-in from an entire team of brainstormers.
This brainstorming technique is great for remote team alignment . It all begins with writing down positives about a topic or what’s working regarding the topic, then writing down negatives and identifying what needs to be addressed most urgently. This is followed by a few minutes of reframing problems as questions, then brainstorming solutions for those problems.
Finally, your team uses a matrix to determine how high impact and how high effort your solutions are to decide which ideas are worth pursuing. For a more robust explanation of LDJ, watch this video by design agency AJ&Smart, which created the brainstorming technique.
Best for: group brainstorms, remote workforces, tight deadlines, honing in on an executable solution
13. The idea napkin
Similar to LDJ, the idea napkin is essentially a brainstorming template that distills a broad topic into tangible solutions. How it works: Every brainstormer has an “idea napkin” that they commit one idea to, beginning by writing down their idea, as well as an elevator pitch for it.
The idea napkin also includes a column for who the idea is targeting—meaning who you’re solving a problem for (customers, teammates, etc.)—and a column noting what problems your idea addresses. Brainstormers can fill out their napkins ahead of or during a brainstorming session, each is expected to present or share them. The final ideas will be placed on an impact and effort matrix to determine which are worth pursuing.
Best for: group brainstorms, honing in on an executable solution
Roleplaying brainstorm techniques

Drama lovers rejoice! These roleplay brainstorming techniques encourage brainstormers to figuratively walk in someone else’s shoes or put on their hat—or six hats, in one instance—to address a problem or dream up ideas from a new perspective. An added benefit of this? When brainstormers take on a personality that’s not their own, it lowers inhibitions since it’s technically not their point of view being brought to the table.
14. Six thinking hats
This brainstorming technique requires a minimum of six brainstormers to wear imaginary hats—hence the name— that require them to look solely at an idea from one specific angle. For instance, one brainstormer might be wearing an impact hat and only concern themselves with the impact of an idea and another might be wearing a constraints hat and only looking at the constraints of an idea.
You can pick and choose which angles are most important to your organization. And by the end of the group discussion, the whole brainstorming group should be able to hang their hats feeling confident about the ideas you’ll pursue.
Best for: group brainstorms (six or more people), introverted team members, vetting ideas thoroughly
15. Figure storming
Ever heard the phrase, “What would Abe do?” That’s pretty much the premise of this brainstorming technique in that brainstormers take on the identity of a famous or prominent figure, whether that’s a leader or celebrity, and put themselves in their brain space and how they’d approach an idea.
This helps teams look at a topic through a different lens and, in the case of group brainstorms, alleviates any nervousness that brainstormers will put out bad ideas. Because they’re not putting out their ideas—they’re sharing someone else’s. So go on and give yourself a new job title for the day.
Best for: individual and group brainstorms, extroverted team members
16. Role storming
Role storming is similar to figure storming in that brainstormers take on different personalities to dream up ideas, but with one dramatic twist—brainstormers act out those ideas.
Generally, brainstormers are asked to take on the role of an average person who will be affected by the idea or solution in question, whether that’s an employee, client, or another party, and they act out a scenario that could stem from the idea to help them decipher what problems might arise from it. Consider this brainstorming technique for more extroverted teams.
Best for: group brainstorms, extroverted team members
17. Reverse brainstorming
Reverse brainstorming is grounded in a little bit of chaos. It encourages brainstormers to play the role of disruptors by brainstorming problems first and then solutions. To kick off the brainstorming questions, a team leader will usually ask, “How do we cause [insert problem]?”
Once your team has listed the causes, they’ll have a new and different perspective for coming up with solutions to problems.
Best for: group brainstorms, idea generation, problem-solving
18. Reverse thinking
Reverse thinking is a bit of a mashup of the figure storming and six thinking hats brainstorming techniques. It encourages brainstormers to merely ask themselves, “What would someone else do in this situation?” Then, it prompts them to think through why that person’s solution would work or not and if your current solution is more effective.
Best for: group brainstorms, extroverted team members, vetting ideas thoroughly
Group brainstorm techniques

Most brainstorming techniques can be applied to groups of brainstormers, but these specific brainstorming techniques promote (and some even require) participation from everyone. When facilitated well, group brainstorming techniques not only yield more ideas but they can also:
Boost team morale through lighthearted brainstorming games and by involving participation in every step of the brainstorming process
Promote creative thinking, especially when brainstormers are given time to prepare their ideas and a structured approach to solve problems
Bring more diverse ideas together, thanks to the unique perspective each brainstormer has and their individual strengths
All this to say, group brainstorming techniques are all about putting people’s heads together.
19. Eidetic image method
The eidetic image method is grounded in setting intentions, and it begins with group members all closing their eyes to do just that. For example, if a company is setting out to design a new smartwatch, the brainstorming facilitator would encourage all brainstormers to close their eyes and quietly meditate on what smartwatches currently look like.
Then the group would discuss and close their eyes once more and quietly imagine new features to add to the device. They’d all open their eyes and discuss again, essentially layering on the possibilities for enhancing a product. This brainstorming technique is ideal for revamping or building on an existing product or solution.
Best for: visual thinkers, creating an idea anew
20. Rapid ideation
Great for teams that get sidetracked or have difficulty staying focused in meetings, the rapid ideation brainstorming technique encourages brainstormers to race against a clock and come up with as many ideas as possible—and importantly, not take themselves too seriously. This can be done by having brainstormers shout out ideas to a facilitator or write them on a piece of paper. You might find that some of the same ideas keep popping up, which likely means those are worth pursuing.
Best for: extroverted team members, tight deadlines
21. Round-robin brainstorming
Participation is required for the round-robin brainstorming technique. Everyone must contribute at least one idea before the entire group can give feedback or share a second idea.
Given the requirement that everyone must share an idea, it’s best to allow brainstormers time to prepare ideas before each round-robin brainstorming session. This brainstorming technique is great for introverted team members and also for larger groups to ensure everyone can contribute. Moreover, the round-robin brainstorming technique also promotes the notion that the only bad idea is no idea.
Best for: introverted team members and developing a surplus of ideas
22. Step-ladder brainstorming
Ideal for medium-sized groups of five to 15 people, the step-ladder brainstorming technique prevents ideas from being influenced by the loudest brainstormers of a group.
Here’s how it works: A brainstorming facilitator introduces a topic to their group of brainstormers and then dismisses all but two brainstormers from the room. The two brainstormers left in the room discuss their ideas for a few minutes and then one brainstormer is welcomed back into the room and shares their ideas before the original two brainstormers divulge their ideas.
Brainstormers are added back into the room one by one, with each new brainstormer sharing their ideas before the rest of the group divulges theirs, and so forth. Once the entire brainstorming group is back in the room, it’s time to discuss the ideas they’ve built together, step by step.
Best for: introverted team members, vetting ideas thoroughly, honing in on an executable solution
23. Charrette
You might want to book a few rooms for this one. The charette brainstorming technique helps break up a problem into smaller chunks and also breaks up your brainstormers into separate teams to address them.
For instance, you might reserve three rooms, write a topic or problem on a whiteboard, and have three sets of brainstormers walk into those rooms to jot down their ideas. Then, the sets of brainstormers rotate rooms and build off of the ideas of the group that was there before them. Consider it effective teamwork at its best.
Best for: vetting ideas thoroughly, honing in on an executable solution
More brainstorming techniques
For more unconventional approaches to get your individual or your team’s wheels turning, consider adding some of these brainstorming techniques to your arsenal of ways to ideate.
24. ‘What if’ brainstorming
A very off-the-cuff brainstorming technique, “what if” brainstorming is as simple as throwing out as many “what if” questions surrounding a topic as possible, similar to the rapid ideation brainstorming technique. For instance, “what if this problem occurred in a different country,” or, “what if this problem occurred in the 1800s?”
Walking through the scenarios might help spur new obstacles pertaining to your problem. Essentially, the “what if” brainstorming technique helps your team evaluate all the possibilities.
Best for: individual and group brainstorms, creating an idea anew, vetting ideas thoroughly
25. Change of scenery
It’s no secret that physical surroundings can impact your team workflow and even creativity. When your brainstorming session is in a rut, consider relocating to another location, perhaps a park, a walking meeting, or even a coffee shop.
Being in a new setting might spur new ideas and even loosen up your brainstormers so that they’re more open to sharing ideas and helping you achieve quantity over quality.
Best for: individual and group brainstorms, creating an idea anew
26. Random word picker
As this name implies, this brainstorming technique is a little random. Begin by tossing words into a hat and then pull them out and discuss how they relate to your brainstorming topic at hand. You may want to use a template to keep track of your thoughts and any new ideas the word association sparks.
To further organize your thoughts, consider pairing this brainstorming technique with word banking, meaning categorizing random words together and then drawing associations between their category and the brainstorming topic.
Best for: group brainstorms, creating an idea anew
27. Storyboarding
Turns out, storyboarding isn’t only for television and film. You can also apply this as a brainstorming technique, meaning illustrating or drawing a problem and possible solutions. Consider it another way to put yourself in someone else’s shoes, especially those your solution impacts. It’s also a means to visualize any roadblocks you might experience when executing a solution.
Best for: individual or group brainstorms, problem-solving, vetting ideas thoroughly
28. Wishing
Wishing is as simple as it sounds: You just wish for the solution you want to build. Think: “I wish our company was carbon neutral,” and then think of the possible ways in which you could achieve this, as well as areas that might be impossible to address for this. This will help uncover obstacles you might face and maybe even shed light on what you’re capable of overcoming.
Best for: individual or group brainstorms, creating an idea anew
29. Crazy eights
A short and fun brainstorming technique, crazy eights delivers on quantity by encouraging brainstormers to think quickly using a template that has eight boxes and only eight minutes on the clock to sketch out eight ideas. Once the timer stops, the group discusses their ideas.
For a larger group, consider having each brainstormer narrow in on only three ideas and give them a longer time limit of six minutes to sketch them out in more detail.
Best for: group brainstorms, visual thinkers, developing a surplus of ideas
8 tips for a productive brainstorming session
No matter which brainstorming technique is right for you and your team, consider the following best practices to brainstorm most effectively . Of course, it all begins with the brainstorming facilitator and how they set the tone for the session.
1. Allow time to prep
A brainstorming facilitator isn’t the only one in a brainstorming session who needs time to prepare for a meeting . They also should give brainstormers some context ahead of the session, such as in the form of a meeting agenda , to get in the correct mindset for the brainstorming session.
At least one day is standard but as little as two to 10 minutes is useful. Moreover, brainstorming facilitators should also have a few ideas in their back pocket for any creative ruts that might creep in.
2. Set a clear intention
The more context you can provide brainstormers from the get-go, the more fruitful ideas they can produce. For instance, clearly spell out what types of ideas you’re looking for. Whether it’s quickly executable ones or ones that are entirely pathbreaking, identify specific targets to address.
Additionally, be sure to let brainstormers know of any constraints you or your organization is operating under, including project timelines or budgets, so they’re generating executable ideas.
3. Invite new teammates and ideas
When the same people brainstorm together over and over, they can tend to produce the same ideas over and over. For this reason, consider introducing new people to your brainstorming session to shake up the usual and lend a fresh perspective—and hopefully fresh ideas—to your brainstorming topics. Invitees can be colleagues from different departments, customers or clients for a focus group, or an outside consultant.
4. Promote inclusivity
Every brainstorming session should be considered a safe space to share ideas—even unconventional ones. Remember, the only bad ideas are no ideas, and any idea shared shouldn’t be shot down or judged. In addition, the brainstorm facilitator should ensure every brainstormer is treated equally and given the same amount of time to talk. This might mean setting a timer for each brainstormer to talk and acknowledging those who are dominating conversations. Likewise, every brainstormer should be open and curious to ideas.
5. Think out of the box
Creative thinking begins with not taking ourselves too seriously. Just as you encourage inclusivity, encourage imperfections and out-of-the-box thinking, too. This could include anything from fun team building games to unique icebreaker questions. Hey, even a bevy of silly ideas to build off of is better than no ideas at all. Brainstorming techniques like wishing can encourage team members to open up.
6. Amplify creativity with music
Similar to how a change of scenery can inspire new ideas, even a little background music can promote creativity. Consider putting some on for your brainstorming session, and for the best results ensure it’s:
Instrumental
In a major key
On a fixed tempo and volume
7. Mix and match brainstorming techniques
Just as brainstorming techniques aren’t necessarily one-size-fits-all, they also aren’t all one-type-fits-every-session. Be prepared to pivot your brainstorming technique depending on what your group of brainstormers is most receptive to and also how many ideas you're juggling.
8. Execute your ideas
Coming up with bright ideas is great. But they’re pretty useless unless you effectively execute them. While some brainstorming techniques build the execution process into them, others might require you to follow up with brainstormers using project templates to map out a plan using creative solutions.
Brainstorming is about quantity over quality
When done right, a brainstorming session shouldn’t feel like a chore but rather an opportunity to create something together, especially when your brainstorming technique supports different styles of thinking and expression.
And whether you're operating as an individual or on a team, there’s something uniquely satisfying about seeing your ideas come to fruition. Get the creative ideas flowing, then customize your workflow management tool to turn those ideas into action.
Related resources
30-60-90 day plan: How to onboard new hires with ease

15 types of employee performance reviews
What is self-management? (7 skills to improve it)

Don’t like giving feedback? These 20 tips are for you
Want to boost your creativity? Switch off your smartphone and let your mind wander, say scientists

Being lost in your thoughts can also help with problem solving and creativity. Image: Unsplash/ bruce mars
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Victoria Masterson

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} Future of Work is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:, future of work.
Listen to the article
- Creativity and problem solving can happen when you let your mind wander, scientists in Germany have found.
- But smartphones mean we have mostly lost the habit of free thinking.
- Other studies have shown the phase just before falling asleep is highly creative, and that adapting to change forces us to think creatively.
- Creativity and problem solving are two of 10 key skills that will be needed in the world of work by 2025, according to the World Economic Forum.
Thinking about nothing in particular is more enjoyable than you’d imagine and can help in areas including creativity and problem solving, scientists have found.
At the University of Tübingen in southern Germany, psychologists studied more than 250 people who were “encouraged to engage in directionless contemplation or free-floating thinking ”, according to The Guardian newspaper.
The results, published in the Journal of Experimental Psychology, suggest humans find it hard to let their minds wander, but that this is an underused talent.
The wonders of a wandering mind
The psychologists found the benefits of free thinking include enhancing your imagination and making you feel better about yourself. Being lost in your thoughts can also help with problem solving and creativity, they said.
Participants in the study said they enjoyed letting their minds wander more than they had expected. But “some people simply found it hard to spend time with their own thoughts, especially if they tended towards negative thinking,” the Guardian reported.
Smartphones were concluded to be at least partly to blame - they are “distractions” that have “contributed to a loss of the habit of free thinking,” said the psychologists.
Take a nap to boost creativity
Other studies have shown the creative benefits of disengaging our brains. Researchers in France recently identified a point just before we fall asleep which is rich in creativity. Hypnagogia, or stage N1 was said to be used by the inventor Thomas Edison to plunder sleep-inspired ideas.
Scientists have found that creativity blends spontaneous and controlled thinking . This is the ability to “both spontaneously brainstorm ideas and deliberately evaluate them to determine whether they’ll actually work,” American neuroscientist Roger Beaty explains in an article for The Conversation.
Beaty makes the point that creativity isn’t just for geniuses. All of us use everyday creativity like drawing or making recipes, described by researchers as ‘little-c’ creativity. ‘Big-C’ creativity , on the other hand, tends to refer to creative breakthroughs in fields like science, technology, society and the arts.
Flexible thinking unlocks creativity
At the University of Cambridge in the UK, psychologists say “ cognitive flexibility ” is a crucial human skill in adapting to changing environments. COVID-19 essentially heralded a new era in flexible thinking – with most people, for example, having to cope with pandemic lockdowns. In the future, learning to use this flexible thinking will help us improve our resilience and wellbeing.
“Flexible thinking is key to creativity – in other words, the ability to think of new ideas, make novel connections between ideas, and make new inventions,” the Cambridge scientists say in an article for the World Economic Forum. “It also supports academic and work skills such as problem solving.”

Soft skills are key in the future world of work
In the Forum’s Future of Jobs Report 2020 , creativity and problem solving are two of 10 skills expected to be vital in the world of work by 2025.
“Core skills such as critical thinking, analysis and problem solving are consistently top of the reskilling and upskilling priorities for educators and businesses,” the report says.
Self-management skills like active learning, resilience, stress tolerance and flexibility are newly emerging skills on the list.
People skills like leadership and social influence are also vital, according to the report.
The World Economic Forum is working with Cabify, Deliveroo, Grab, MBO Partners, Postmates and Uber to improve working standards for the tens of millions of people who earn a living or top up their incomes through digital work/service platforms.
The chief executive officers from the six companies have signed The Charter of Principles for Good Platform Work , committing to ensure that platform workers receive fair conditions, treatment, benefits and training opportunities.
By collaborating with partners, the Forum is developing a comprehensive approach to provide clarity on platforms’ responsibilities to the workers who use their platforms, empower platform workers, promote their dignity and well-being, while supporting flexibility, innovation and the value offered by the platform economy to users and clients.
The Forum is looking for platform companies, regulatory bodies, workers’ organizations and independent experts globally who are committed to advancing working standards in the platform ecosystem, to collaborate on the next stage of the Promise of Platform Work initiative. Contact us to learn more.
Have you read?
The two things most likely to lead to creativity at work, 7 key soft skills of successful people, people with dyslexia have ‘enhanced abilities’, according to a new study, don't miss any update on this topic.
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Future of Work .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

Green job vacancies are on the rise – but workers with green skills are in short supply
Andrea Willige
February 29, 2024

Digital Cooperation Organization - Deemah Al Yahya

Why clear job descriptions matter for gender equality
Kara Baskin
February 22, 2024

Improve staff well-being and your workplace will run better, says this CEO

Explainer: What is a recession?
Stephen Hall and Rebecca Geldard
February 19, 2024

Is your organization ignoring workplace bullying? Here's why it matters
Jason Walker and Deborah Circo
February 12, 2024
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Learn Health Syst
- v.6(2); 2022 Apr

Creativity in problem solving to improve complex health outcomes: Insights from hospitals seeking to improve cardiovascular care
Amanda l. brewster.
1 Health Policy and Management, School of Public Health, University of California, Berkeley California, USA
Yuna S. H. Lee
2 Health Policy and Management, Columbia Mailman School of Public Health, New York New York, USA
Erika L. Linnander
3 Global Health Leadership Initiative, Yale School of Public Health, New Haven Connecticut, USA
Leslie A. Curry
4 Health Policy and Management, Yale School of Public Health, New Haven Connecticut, USA
Associated Data
Introduction.
Improving performance often requires health care teams to employ creativity in problem solving, a key attribute of learning health systems. Despite increasing interest in the role of creativity in health care, empirical evidence documenting how this concept manifests in real‐world contexts remains limited.
We conducted a qualitative study to understand how creativity was fostered during problem solving in 10 hospitals that took part in a 2‐year collaborative to improve cardiovascular care outcomes. We analyzed interviews with 197 hospital team members involved in the collaborative, focusing on work processes or outcomes that participants self‐identified as creative or promoting creativity. We sought to identify recurrent patterns across instances of creativity in problem solving.
Participants reported examples of creativity at both stages typically identified in problem solving research and practice: uncovering non‐obvious problems and finding novel solutions. Creativity generally involved the assembly of an “ecological view” of the care process, which reflected a more complete understanding of relationships between individual care providers, organizational sub‐units, and their environment. Teams used three prominent behaviors to construct the ecological view: (a) collecting new and diverse information, (b) accepting (rather than dismissing) disruptive information, and (c) employing empathy to understand and share feelings of others.
Conclusions
We anticipate that findings will be useful to researchers and practitioners who wish to understand how creativity can be fostered in problem solving to improve clinical outcomes and foster learning health systems.
1. INTRODUCTION
Improving performance often requires health care teams to employ creativity in problem solving, a key attribute of learning health systems. Creativity is defined the process of generating approaches that are both novel and useful. 1 , 2 Incorporating creativity into problem solving can help to address unique, site‐specific complexities that influence performance in health care, 3 , 4 and to enhance the positive impact of evidence‐based strategies adapted from outside the organization. 5 While some advances in health care can be applied generically across settings, researchers have documented the importance of innovation and adaptation by local implementation teams, 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 and customization to patients and context is a key part of patient‐centered, high‐quality care. 10 These observations from health care cohere with management research from other industries, which posits that when innovation depends on complex contextual information that is difficult to codify and transfer, innovation‐related problem solving needs to occur where that information is held, 11 and by the individuals who have agency to act on these solutions. 12 That is, key innovations must be made by staff located at each implementation site.
Despite the known importance of creativity in problem solving, relatively few studies detail how workers incorporate creativity into problem solving during the natural course of work—in health care or in other industries. 13 Prior research on creative problem solving in the workplace has been largely theoretical, 14 , 15 with some empirical research deriving from industries such as new product development 16 , 17 where novelty is an explicit goal of work. Such research also focuses on creative outcomes while neglecting processes that incorporate creativity as habit and routine, that is, as part of the organizational culture. 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 Detailed studies of front‐line problem solving in the automotive industry provide a useful framework for considering the dimensions of problem solving—including an important distinction between problem definition and generation of solutions 22 —but do not focus on creativity and innovation. More research is needed to better understand how creativity manifests during complex problem solving in health care. 18
Prominent learning and quality improvement models in health care assume that both problem definition and generation of solutions can be important sites of creativity. Models including Lean/Six‐Sigma, 23 the Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI) Model for Improvement, 24 the strategic problem‐solving process, 25 and user‐centered design 26 focus on uncovering nonobvious problems through an emphasis on root cause analysis and understanding user experience. More research is needed to understand the process by which creativity manifests when grappling with the complexity and customization that health care demands. 20
Even as more health care organizations seek to become learning organizations by implementing structured improvement interventions, 23 reports of such efforts highlight the fact that these improvement interventions do not always achieve intended results. Health care teams must overcome distinctive and substantial barriers to creativity, including strong hierarchies, aversion to risk, highly specialized professionals, and emphasis on standardization of care to promote reliability and quality. 27 , 28 There can be tension between creativity and health care performance improvement, as health care delivery often seeks to minimize variation, and the core of creativity is enhancing variation. 29 Yet, influencing performance in health care often requires moving beyond stability and the status quo, a process well served by incorporating creativity. 27 Accumulating grounded evidence on how creative problem solving manifests in a variety of health care contexts is important for advancing understanding of this phenomenon. 30
2. QUESTION OF INTEREST
To describe in detail how creativity emerges as health care workers engage in problem solving, we sought to characterize the processes through which creativity emerged in problem solving within hospitals seeking to reduce mortality from acute myocardial infarction (AMI) as part of a 2‐year performance improvement collaborative called leadership saves lives (LSL). Mortality for AMI, now publicly reported and included in the value‐based purchasing bundle, 31 is influenced by components of care delivery that cross multiple boundaries within and outside of the hospital. 32 , 33 One important contributor to lower AMI mortality is clinicians' ability to resolve open‐ended problems through creative thinking. 34 Creative problem solving is especially relevant to AMI care teams working to reduce mortality because of the multifaceted nature of the problem, which spans multiple units and levels of hierarchy within the hospital, and extends past hospital boundaries to pre‐hospital and post discharge systems. Each care setting is unique in numerous important ways, making it essential for teams to develop novel solutions that work in their own contexts (ie, apply creativity).
The LSL collaborative involved 10 hospitals in which AMI care teams engaged in a curriculum designed to foster group learning and problem solving. While teams were encouraged to be creative in their problem solving, the limitations of prior evidence meant that the intervention could not be prescriptive about exactly how creativity was expected to be cultivated. As described elsewhere, 35 participating hospital teams reported increased capacity for learning and problem solving, and their hospitals experienced significant decreases in risk‐stratified mortality rate (RSMR) over the course of the study period, suggesting that these hospitals would be an ideal context for examining multiple instances of creative problem solving and distilling common patterns. We anticipate that findings will be useful to researchers and practitioners who wish to understand how creativity can be fostered in problem solving to improve clinical outcomes.
3.1. Study design and setting
We conducted a qualitative study to understand how creativity was fostered during problem solving in the 10 hospitals that took part in the LSL collaborative from 2014 to 2016. As previously described, 35 hospitals were selected for participation from the membership of the Mayo Clinic Care Network (MCCN), a national group of medical systems committed to quality improvement through collaboration. From the 21 MCCN members (as of January 2014), hospitals were identified as candidates if they met all three eligibility criteria: (a) at least 200 AMI discharges per year to ensure sufficient experience in caring for patients with AMI, (b) average or below average national performance on 30‐day RSMR between January 07, 2009 and June 30, 2012 as reported by Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Hospital Compare in Spring 2014, suggesting opportunity for improvement, and (c) the largest hospital in the system, for hospitals in multihospital systems. From the list of 18 hospitals that met eligibility criteria, random sampling with a purposeful component 36 as used to select hospitals that were diverse in geography and teaching status. The first 10 hospitals were approached to determine receptivity; two declined and were replaced with sites similar in geography and teaching status. Hospital characteristics are presented in Table 1 .
Hospital characteristics (n = 10 hospitals)
3.2. LSL intervention
The LSL intervention, previously described in detail, 37 was implemented from June 2014 to June 2016. LSL was designed to foster reductions in AMI mortality by supporting the implementation of evidence‐based strategies and fostering improvements in domains of organizational culture related to hospital performance. Each hospital established a guiding coalition of approximately 15 staff involved in care of patients with AMI, representing multiple departments, and including senior executives as well as front‐line staff. Guiding coalition members participated in four, 1‐day workshops in which they were coached through a strategic problem‐solving methodology 25 to define a shared problem (ie, RSMR is too high) and objective (ie, reduce RSMR), and then use root cause analysis to generate, implement, and evaluate strategies designed to achieve the defined objective. Erika Linnander led intervention workshops at multiple LSL hospitals, and Erika Linnander and Leslie Curry engaged with guiding coalitions in three annual workshops that convened representatives of all 10 hospitals participating in LSL. LSL coalitions were encouraged to develop strategies that fit their unique contexts, through both tailoring existing evidence‐based practices and introducing completely novel approaches. The evidence‐based practices include monthly meetings with emergency medical services personnel to review AMI cases, identification of both physician and nurse champions for AMI care, nurses dedicated to the catheterization lab (not cross‐staffing from other units), pharmacist rounding on all inpatients with AMI, and creative problem solving. As noted earlier, the intervention did not prescribe specific approaches to cultivate creativity. Guiding coalitions were also encouraged to foster improvements in hospital culture related to AMI performance, focusing on domains of: learning environment, 38 psychological safety, 39 senior management support, 40 commitment to the organization, 41 and time for improvement efforts. 39
3.3. Data collection
We collected qualitative data about the use of creativity in problem solving in LSL hospitals using in‐depth, in‐person interviews 36 at the start of the LSL intervention, and at 6 months and 18 months into the 2‐year intervention. A team of interviewers who included individuals with backgrounds in qualitative research, health care management, and clinical care conducted interviews with staff involved in the guiding coalition as well as other clinicians and hospital executives, using a standardized interview guide ( Data S1 ). The interview guide asked about implementation of creative problem‐solving strategies as part of a broader set of interview questions examining the hospital's experience with LSL. Amanda Brewster and Leslie Curry were members of the team that conducted interviews. Interview participants were aware of the LSL intervention and aware that research was being conducted to understand the process of implementing the LSL intervention as well as its impact. Interviews took place at the hospitals where participants worked, generally in a quiet room. A total of 197 individuals participated in one or more interviews, with 162 interviews at baseline, 118 at 6 months, and 113 at 18 months into the intervention, for a total of 393 interviews (Table 2 ). The number of individual interviewees per hospital ranged from 15 to 26. Interviews lasted approximately 45 minutes and were audiotaped and professionally transcribed. The research procedures were reviewed and determined to be exempt by the Yale University Institutional Research Board.
Interview participant characteristics
3.4. Data analysis
Interview transcripts were analyzed by a 6‐member multidisciplinary team using the constant comparative method of analysis. 42 The current analysis of creative problem solving focused on content in which participants discussed work processes that they self‐identified as creative or promoting creativity, that is, ideas that were both novel and useful. Participants did not have to use the terms “creative” or “creativity” explicitly. Content could be coded as referring to creative problem solving if participants were providing examples in response to the structured interview questions on creative problem solving strategies, or if participants discussed processes for generating novel and useful ideas in response to other interview questions. We considered that participants would be best positioned to assess whether something was creative in the context of their environments, and therefore relied on participants' own judgements regarding novel and useful elements of the phenomenon. Each transcript was coded independently by at least three analysts, with discrepancies reconciled through negotiated consensus. A hybrid coding approach 43 in which we began with a small number of a priori codes based on key LSL program elements and added new codes as additional themes emerged during coding. Iterative coding and analysis occurred across each wave of data collection, with refinement and review by the full team of six analysts, until a final code structure was established and reapplied to the full dataset. We used Atlas.ti to facilitate coding and organization of data. The analysis team included members with diverse perspectives, representing expertise in health services research, management, organizational theory, social work, nursing, medicine, and anthropology. We sought to generate recurrent themes that characterize essential aspects of creative problem solving in hospital contexts, examining instances in which creativity emerged in uncovering nonobvious problems or finding novel solutions.
Across hospitals, participant descriptions of creativity in problem solving generally entailed the use of three prominent behaviors: (a) collecting new and diverse information, (b) accepting (rather than dismissing) disruptive information, and (c) employing empathy (ie, to understand or feel what another person is experiencing from within their frame of reference, that is, the capacity to place oneself in another's position). Each of the three behaviors appeared at times sufficient to advance creative problem solving by fostering a broad, inclusive new view of AMI care, which we term an “ecological view” (Figure 1 ). The following sections detail the three behaviors, followed by the emergent concept of an ecological view of AMI care.

Concepts identified as important to creative problem solving. Working from the right‐hand side of the figure, creativity in problem solving was promoted by the assembly of a new, ecological view of AMI care. At least one of three behaviors was typically used by LSL coalitions to foster this ecological view
4.1. Collecting new and diverse information
Collecting new and diverse information was a behavior that routinely contributed to creativity in problem solving for LSL coalitions. Sometimes the new information came from assembling new data or analyzing data in new ways; for example, conducting new analyses of mortality data helped LSL coalitions at several hospitals to expand their conception of their AMI mortality challenges to include non‐STEMI patients (patients with non‐ST segment elevation myocardial infarction). This was a significant shift, as most prior quality improvement efforts had focused exclusively on STEMI patients. As an example, a cardiologist on one hospital's team undertook a close and systematic review of AMI deaths, as part of a root cause analysis recommended in the LSL intervention, and noticed that non‐STEMI care seemed to offer greater opportunities for improvement, explaining:
With STEMI's there was never any waiting… but in non‐STEMIs [there were] delays… STEMI's, they all die after you've revascularized them. You've done everything you could… But the non‐STEMI's are coming in. Somebody thought they were stable, and then they deteriorate which makes you think you've got really more of an opportunity with them. (Hospital J, Physician).
In other cases, new and diverse information came from the LSL coalitions engaging personnel who had not previously been involved in problem solving related to AMI mortality. For example, an emergency medicine physician in one hospital described how input from personnel outside the LSL coalition informed plans for introducing a dedicated cardiology physician assistant (PA) role that would remain on site at all times. After the hospital's LSL coalition coalesced around the idea to add this role, the coalition sought out opinions from different stakeholders elsewhere in the organization, who brought to light a wide range of issues that would need to be worked out in order to successfully implement this solution. A physician on the LSL coalition described:
Then [a senior administrator] presented the other stuff, that I never thought of. Who technically has ownership of that PA?… How does the funding for that position come from everyone, if the revenue goes through one of our different cardiology groups?… I never thought of that. I said, “Give me a body, and have them there 24/7.”…Then the cardiologists say, “Well, it's great. What we do with the PAs when they're not in the cath lab?… That creative problem solving comes from listening to everyone's different opinions, and having the ability to separate me from the project. Taking out my own biases. (Hospital B, Emergency Medicine Physician).
Synthesizing diverse views allowed the team to gain a more accurate understanding of implementation challenges, enhancing the practical utility and likely impact of their ideas.
4.2. Accepting (rather than dismissing) disruptive information
Leveraging new and diverse information sources for creative problem solving typically required a second, distinct behavior: accepting (rather than dismissing) disruptive or unwelcome information. In describing instances where new information contributed to the development of novel and useful solutions, participants routinely described processes to overcome resistance to new information. For example, after the LSL coalition at Hospital J shifted to thinking about non‐STEMI care as a potential problem to address, team members identified another problem: high‐risk non‐STEMIs were difficult to identify. After getting input from other physicians and nurses and reviewing non‐STEMI risk guidelines from the American College of Cardiology, the LSL coalition recommended two major changes to improve care for patients with non‐STEMI AMI: a new protocol to equip nurses to initiate care for inpatients with evolving AMIs, and a new set of algorithms and procedures for attending cardiologists to more consistently review at‐risk cases. These new procedures met with initial resistance from other cardiologists within the hospital, but the opponents “knew that they couldn't just blow it off completely,” according to an LSL coalition member, because the LSL coalition had carefully documented a previously unrecognized pattern of non‐STEMI deaths pointing to the need for change. The LSL coalition helped to engineer this acceptance of information that diverged from prior beliefs by employing data, methodology, and a respected cardiologist as the messenger that would be compelling to the cardiologists.
In other situations, accepting disruptive information involved elevating the weight given to input from frontline personnel lower in the organizational hierarchy. The LSL guiding coalitions included perspectives not traditionally included in hospital process improvement discussions, such as EMS representatives external to the hospital. The perception that these representatives occupied positions that were more peripheral to the hospital and lower in the organizational hierarchy could have set up their perspectives to be dismissed. This risk was exemplified by the concerns of a paramedic on one LSL coalition, who reported initially feeling skeptical about the value he could add to a group that included high status individuals such as cardiovascular surgeons and department heads, who were seen as intimidating. (“I'm like, what's pre‐hospital's role? I mean this is a big, huge hospital system.”) Over time though, this paramedic saw that his perspective was actively accepted, and he was empowered to share his opinions with the group. Intentional emphasis on the importance of EMS by the LSL intervention facilitator aided this effort:
One of the first things [the team facilitator] brought up was the statistics on pre‐hospital, how much they're involved… Then I have [a physician] sitting right next to me, who looks at me and says, “What do you think about it? What can we do to improve the pre‐hospital side of things?” To me that brought me right into the team. (Hospital A, Paramedic).
Although hospital leaders were generally aware of the need to improve pre‐hospital processes, listening to and valuing the input from the EMS representative was key for the LSL coalition at Hospital A to understand the specific problems occurring at the interface of pre‐hospital and hospital care, a situation seen at other LSL hospitals as well. Once the problems had been identified, solutions could be introduced. In the case of Hospital A, the solution was for the hospital to hire an EMS liaison with experience as a paramedic to manage communication between pre‐hospital, emergency department, and other staff from the hospital who need to be activated to care for AMI patients. This solution was so widely recognized as effective in facilitating coordination across these systems that the hospital leadership agreed to fund a second liaison position.
Experience at another hospital illustrated how the hospital's senior management played an important role in getting team members to take new information seriously and thereby spurred creativity in problem solving. As part of the LSL project, this hospital started documenting the wait times for EKG results. These new data showed that slow EKG results routinely delayed AMI care. The EKG wait time measure represented new and disruptive information for the hospital, because EKG wait time had not previously been tracked or understood to delay AMI care. Senior managers within the hospital held firm on the need to substantially reduce EKG wait times, even after multiple barriers to solving this problem were identified: from limitations on which staff could perform EKGs, to transmission of results being slowed by wireless connectivity drops in different parts of the floor, to EKG results being printed in an area where they weren't immediately noticed. The stance of leaders, who were encouraging but very firm about the need to improve on the EKG wait time measure, forced ED teams to develop creative solutions rather than accept the inevitability of delays. The introduction of new, disruptive information about EKG wait times, coupled with active endorsement by multiple managers, represented a departure from previous quality improvement efforts in which teams were seen to resign themselves to the status quo. One manger explained:
[In earlier improvement efforts] I would hear an answer from one team that says, “No. This can't be done.” [Now] I think we have leaders who… are very good at saying, “Why not?” Then when we start looking at “why not,” we often find that, oh yeah, maybe it's possible… If [the leader] says I'm satisfied with, “This can't be done,” then you're not going to have much creative thinking. (Hospital I, Manager).
Taking the data on EKG wait times as a serious indicator of problems led to a variety of creative solutions being implemented in the ED over the course of the LSL project, including training new categories of staff members to perform EKGs, putting existing communication technologies to new uses, establishing a new space where EKGs could be performed when the ED was full, and printing EKGs in a new location, near the physicians who needed to interpret them. The changes were effective: the proportion of at‐risk patients receiving EKGs within the target time of 10 minutes rose from under 30% to 80%.
4.3. Employing empathy
Employing empathy—having problem‐solving staff consciously shift their mindsets to empathize with the experiences of colleagues or patients—was the third behavior regularly observed to foster creative problem solving for LSL coalitions. An example of empathizing with colleagues at referring facilities was reported by participants from Hospital F, which served as a referral center for AMI patients across a large region. As part of the LSL initiative, a nurse from the LSL coalition visited facilities that frequently transferred AMI patients to the hospital and followed the transfer process alongside providers at one referring facilities, which allowed her to experience the frustration of transfers from the referring facility's perspective (ie, empathize). She described the experience as follows:
I got myself involved in [a patient transfer] with their emergency physician, trying to help coordinate the transfer of that patient [from the outlying facility to our hospital]. It was amazing how complicated our system had made it to get a patient transferred. I was able to be that advocate and see it from that view and then experience that frustration from that provider standpoint. (Hospital F, Nurse).
Seeing transfers from the perspective of referring facilities revealed several flaws in the process, which were delaying patient care and led to the development of new approaches to streamline communication with referring facilities.
Another example of empathizing with colleagues was seen at Hospital D, where the director of cardiac services discussed the importance of understanding, in detail, the perspective of EKG technicians in order to address problems with EKG processes. He encouraged his team to go observe the EKG techs at work, to understand “steps to their job” and consider how to help them:
The first part is, don't be afraid to call and say, “I have a problem.” The second part is…go back, and [ask] what does the EKG tech do? They didn't know….[I said] maybe you ought to go with them for a while. You gotta go figure out…what are the steps to their job, and how can we make it more efficient, help them in quality? We learned together. We problem solve together. (Hospital D, Physician).
An example of empathizing with patients motivating creative problem solving was reported by a nurse coordinator explaining what happened when the LSL coalition reviewed the hospital's discharge education materials for patients with AMI. It was clear that the materials were inadequate to help patients effectively discharge (“It was horrid. I can't even believe that's what we were giving patients”). The team knew that improved materials were needed, but felt overwhelmed by the range of options. Ultimately, they took an approach of trying to put themselves in the patient's shoes, which led to the development of a patient education resource that was regarded as the best patient education tool in the hospital:
We just had to sit down and really problem solve and be the patient in the matter. What is going to make a difference? What's going to grab my attention as a patient to better adhere to my discharge instructions and understand them? All the praise goes to [three team members] because they put together the best patient education tools that we have in the hospital. (Hospital F, Nurse).
4.4. Ecological view
While we observed three distinctive behaviors fostering creative problem solving, as described in the sections above, the behaviors tended to accomplish the same thing: the assembly of a broad, inclusive new view of AMI care, which we term an “ecological view.” This ecological view, fostered by teams collecting new and diverse information, accepting (rather than dismissing) disruptive information, and employing empathy, routinely contributed to LSL coalitions creatively uncovering nonobvious problems and finding novel solutions. Figure 1 outlines our concept of how creativity in problem solving was driven by development of an ecological view of the care process.
We adopt the biological metaphor of ecology, which is often used in the study of organizations (Freeman 2006), 44 to connote the development of a shared understanding of AMI care that reflected the relationships among a wide range of different individual care providers, organizational sub‐units, and their environment. Organization scholars commonly analyze populations of organizations in an ecological context. We use the term “ecological view” to describe the emergence of self‐awareness inside the organization of this ecological context, as some of these providers and relationships were previously unknown, or known to only some but not all team members. The ecological view, in turn, infused the problem‐solving process with creativity—allowing team members to see the contours of problems that not previously been identified and to develop novel solutions.
5. DISCUSSION
In instances where creativity emerged during the problem‐solving process within LSL hospitals, a characteristic process was observed in which team members generated an ecological view of the AMI care process, reflecting a more complete understanding of relationships between care providers, organizational sub‐units, and their environment. The ecological view of AMI care sparked teams to define previously unrecognized problems, and to develop novel, tailored solutions. The experiences of the LSL hospitals indicated that identifying nonobvious problems represented an important site of creativity in the problem‐solving process. While our results stem from an initiative to improve AMI mortality, they could apply to initiatives to improve outcomes for other complex conditions involving care that spans disciplines, departments, and organizations, such as stroke, heart failure, and diabetes.
The emergence of the ecological view that supported creativity in problem solving was regularly fostered by at least three different behaviors: collecting new information, accepting disruptive information, and employing empathy. Although the role of the ecological view in creative problem solving was not theorized during the development or delivery of the LSL intervention, several of the LSL intervention components explicitly encouraged behaviors that we observed to promote an ecological view, and could be helpful for other hospitals seeking to promote creativity in problem solving. Specifically, the LSL intervention team facilitated the development of guiding coalitions with diverse membership, advised hospital teams to conduct root cause analyses, which fed the collection of new information, and coached on group processes to promote psychological safety to foster the process of surfacing disruptive information from individuals whose perspectives might not be known. Efforts to encourage empathy were not an intentional component of the LSL intervention although raising awareness of psychological safety could have heightened participants' focus on the feelings of others. Empathy—the exercise of intentionally placing oneself in a new perspective—emerged as an especially powerful tactic to leverage exposure to new information. This is consistent with prior research on problem solving in manufacturing, which identifies advantages of observing, first‐hand, a mechanical part in the situation where it is malfunctioning, as a way of getting richer information. 22 In the context of our study, the immersive quality of exercises in empathy may have provided richer information, and also emotional cues, which enhanced LSL coalition members' motivation to act on novel ideas that would have dissipated in the face of less compelling experiences. Intrinsic motivation has been theorized as an important contributor to individual creativity. 1
The behaviors we identified promoting an ecological view are not new to the quality improvement literature—other commonly used quality improvement models such as Lean and Six Sigma emphasize collection of new data and inclusion of diverse perspectives in understanding variability, waste, and poor performance. 45 , 46 Empathy for end‐users features as a component of the design‐thinking process, which is being used by some health care organizations for quality improvement. 26 Our results, however, provide real‐world examples of how these concepts foster creative problem solving in the context of a quality improvement intervention that targeted an outcome measure influenced by complex processes. While we reported the three behaviors that featured most prominently in participants' descriptions of examples where an ecological view emerged to promote creativity in problem solving during the LSL intervention, it is possible that other behaviors and supporting structures may promote the emergence of an ecological view in different settings. Notably, in the hospitals we studied, these three behaviors depended on support from a critical mass of team members in diverse clinical and managerial roles as well as hospital senior leadership. It is hard to say whether individual clinicians or staff members could enhance their own creative problem‐solving capabilities by applying these behaviors in isolation.
Our results should be interpreted in light of several study limitations. First, with 10 hospitals, our sample was relatively small, although hospitals were selected to be diverse in terms of geography, size, and teaching status, and each hospital tackled several dimensions of AMI care, thus accumulating a larger number of examples of problem solving. Further, the robust, longitudinal qualitative design allowed for deep characterization of the improvement process in each hospital. Second, hospitals in the study were exposed to a leadership development curriculum that encouraged a structured approach to problem solving; the process of creativity in problem solving may proceed differently in hospitals that had not been supported in this way. Third, we were not able to collect data on whether particular interventions introduced by the LSL hospitals were effective, or sustained over time beyond the study period, which prevents us from concluding whether solution quality was improved by creative problem solving in this study. We do know that LSL hospitals reduced AMI RSMR more quickly than the national average over the same time period, 35 suggesting that LSL hospitals did make changes that improved RSMR during the study period.
Our results provide a refined depiction of the creative problem‐solving process based on empirical observations across multiple hospitals. These findings suggest that health systems seeking to promote creative problem solving could encourage the three behaviors we have documented to advance an ecological view of care processes. As exploratory research, these findings point toward several opportunities for further study. First, it would be useful to examine the creative problem‐solving process in a different set of hospitals, working to improve a different outcome, to confirm the generalizability of our findings. A next step could include quantitatively testing the hypothesis that forming an ecological view is indeed constitutive of the creative problem‐solving process, and improves solution quality. Doing this could involve developing a survey‐based measure of the extent to which quality improvement teams have developed an ecological view of their target process, and evaluating the creativity and effectiveness of their solutions.
6. CONCLUSIONS
Creativity is crucial to performance improvement in health care, and evidence from other industries has linked individual traits such as motivation and values, as well as organizational traits such as leadership style, team climate, and decentralized structure to creative performance. 14 , 18 , 47 Seeking to illuminate the process by which creative problem solving occurs in health care, we observed a characteristic process that occurred across different hospitals, in which distinctive patterns of acquiring and processing new information contributed to creativity. These distinctive behaviors can be fostered by health care leaders seeking to improve performance on consequential clinical outcomes, including AMI mortality.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Supporting information
Data S1. Qualitative interview guide
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Funding for the Leadership Saves Lives (LSL) collaborative and its evaluation was provided through a research grant to Yale University from The Medicines Company, Parsippany, New Jersey. The authors thank the hospitals and guiding coalition members that participated in LSL for their time and dedication.
Brewster AL, Lee YSH, Linnander EL, Curry LA. Creativity in problem solving to improve complex health outcomes: Insights from hospitals seeking to improve cardiovascular care . Learn Health Sys . 2022; 6 ( 2 ):e10283. 10.1002/lrh2.10283 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
Funding information Medicines Company

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Its benefits include: Finding creative solutions to complex problems: User research can insufficiently illustrate a situation's complexity. While other innovation processes rely on this information, creative problem-solving can yield solutions without it. Adapting to change: Business is constantly changing, and business leaders need to adapt.
Key Points. Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of using your creativity to develop new ideas and solutions to problems. The process is based on separating divergent and convergent thinking styles, so that you can focus your mind on creating at the first stage, and then evaluating at the second stage.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis . Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another.
5. Ask for feedback. Collaboration and teamwork are key when developing creative solutions in the workplace. You can ask teammates or superiors for feedback on your ideas to gain insight into potential flaws in your reasoning and streamline your solutions. 6.
Six Thinking Hats: Edward de Bono's method involves using six different hats, each representing a specific thinking style, to approach the problem from various perspectives. 2. Mind Mapping ...
CPS is a comprehensive system built on our own natural thinking processes that deliberately ignites creative thinking and produces innovative solutions. Through alternating phases of divergent and convergent thinking, CPS provides a process for managing thinking and action, while avoiding premature or inappropriate judgment. It is built upon a ...
Creative problem-solving is an essential skill that goes beyond basic brainstorming. It entails a holistic approach to challenges, melding logical processes with imaginative techniques to conceive innovative solutions. As our world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the ability to think creatively and solve problems with fresh ...
Creative problem solving is based on the belief that everyone is creative and can enhance their creative abilities with discipline. Creative problem solving is a deliberate approach to solving complex problems. While creativity is an innate part of creative problem solving, the process uses a variety of steps and strategies designed to bring to ...
Creative problem-solving (CPS) is the mental process of searching for an original and previously unknown solution to a problem. To qualify, the solution must be novel and reached independently. The creative problem-solving process was originally developed by Alex Osborn and Sid Parnes.Creative problem solving (CPS) is a way of using creativity to develop new ideas and solutions to problems.
Humans are innate creative problem-solvers. Since early humans developed the first stone tools to crack open fruit and nuts more than 2 million years ago, the application of creative thinking to solve problems has been a distinct competitive advantage for our species (Puccio 2017).Originally used to solve problems related to survival, the tendency toward the use of creative problem-solving to ...
Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork. 1. Analysis. As a manager, you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first.
Creativity in problem-solving allows for the generation of unique, practical solutions. It involves thinking outside the box, challenging traditional assumptions, and viewing the problem from various perspectives. Creativity is crucial in problem-solving as it fosters innovation and adaptability.
7 Ways to improve your creative problem-solving skills. 1. Play brain games. It's considered that brain games are an excellent way to stimulate human brain function. They develop a lot of thinking skills that are crucial for creative problem-solving. You can solve puzzles or play math games, for example.
Step 4: Implement the Solution. Problem solving activities that help you implement the solution you have chosen: #13. End in Mind - To create your plan, start with the end in mind and work backwards. Establish key milestones and dates in reverse order, starting with the end-of-project celebration and ending with today.
Here are 8 creative problem-solving strategies you could try to bring creativity and fresh ideas to bear on any problem you might have. 1. Counterfactual Thinking. Counterfactual thinking involves considering what would have happened if the events in the past had happened slightly differently. In essence, it is asking 'what if' questions ...
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
A Cognitive Trick for Solving Problems Creatively. by. Theodore Scaltsas. May 04, 2016. Save. Many experts argue that creative thinking requires people to challenge their preconceptions and ...
1. Starbursting. A visual brainstorming technique, starbursting should be used once you or your team of brainstormers has homed in on a single idea. To begin starbursting, put an idea on the middle of a whiteboard and draw a six-point star around it. Each point will represent a question:
Creative problem-solving activities 6. The Hunt. Activity focus areas: Creativity, Team Decision-Making, Reasoning, Communication. Why creativity is important for problem-solving: Creativity is crucial for problem-solving because it allows individuals to think beyond conventional solutions and explore innovative approaches to challenges. By fostering creative thinking, problem-solvers can ...
Frame 2: She sees an ad on her laptop saying, "Unlock your creativity with Creativio - the ultimate app for creative problem-solving.". She clicks on the ad and downloads the app on her phone. Frame 3: She opens the app and sees a welcome screen: "Welcome to Creativio - the ultimate app for creative problem-solving.
Creativity and problem solving are two of 10 key skills that will be needed in the world of work by 2025, according to the World Economic Forum. Thinking about nothing in particular is more enjoyable than you'd imagine and can help in areas including creativity and problem solving, scientists have found.
Creativity is defined the process of generating approaches that are both novel and useful. 1 , 2 Incorporating creativity into problem solving can help to address unique, site‐specific complexities that influence performance in health care, 3 , 4 and to enhance the positive impact of evidence‐based strategies adapted from outside the ...