- The McKinsey Solve Assessment - 2023 Guide with Redrock Case Update

McKinsey’s Solve assessment has been making candidates sweat ever since it was initially trialled at the firm’s London office back in 2017 - and things have gotten even more difficult since the new version launched in Spring 2023 added the Redrock case study.
Since its initial roll-out, the Solve assessment is definitely the most idiosyncratic, but also the most advanced, of the screening tests used by the MBB firms.
It can be hard to understand how an ecology-themed video game can tell McKinsey whether you’ll make a good management consultant, let alone know how to prepare yourself to do well in that game. When you consider that McKinsey are potentially cutting 70%+ of the applicant pool based on this single test, you can hardly blame applicants for being worried.
Matters are definitely not helped by the dearth of reliable information about what could very well be - with a top-tier consulting job on the line - the most important test you will take over your entire career. This was already true with the version of Solve that had been around for a few years, let alone the new one.
What information is available online is then often contradictory. In particular, there is a huge amount of disagreement as to whether it is actually possible for you to meaningfully prepare for the Solve assessment - before you’ve even considered how to go about that preparation. There is also a lot of confusion and inaccuracy around the new Redrock Case - largely as it is so recent as an addition and individual test takers tend to misremember details.

Luckily, we at MCC have been interviewing test takers both before and after the Redrock Case rollout and following up to see which strategies and approaches actually work to push individuals through to interview.
Here, we’ll explain that it is indeed possible to prepare effectively for both versions of Solve and give you some ideas for how you can get started. Understanding how the Solve assessment works, what it tests you for and how is critical for all but the most hurried preparations.
This article makes for a great introduction to the Solve assessment. However, if you are going to be facing this aptitude test yourself and want full information and advice for preparation, then you should ideally get our full PDF guide:
MCC McKinsey Solve Guide

What is the McKinsey Solve assessment?

In simple terms, the McKinsey Solve assessment is a set of ecology-themed video games. In these games, you must do things like build food chains, protect endangered species, manage predator and prey populations and potentially diagnose diseases within animal populations or identify natural disasters.
Usually, you will be given around 70 minutes to complete two separate games, spending about the same amount of time on each.
Until recently, these games had uniformly been Ecosystem Building and Plant Defence. However, since Spring 2023, McKinsey has been rolling out a new version across certain geographies. This replaces the Plant Defence game with the new Redrock Case Study. Some other games have also been run as tests.
We’ll run through a little more on all these games below to give you an idea of what you’ll be up against for both versions and possible new iterations.
In the past, candidates had to show up to a McKinsey office and take what was then the Digital Assessment or PSG on a company computer. However, candidates are now able to take the re-branded Solve assessment at home on their own computers.
Test-takers are allowed to leverage any assistance they like (you aren’t spied on through your webcam as you would be with some other online tests), and it is common to have a calculator or even another computer there to make use of.
Certainly, we strongly advise every candidate to have at least a pen, paper and calculator on their desk when they take the Solve assessment.
Common Question: Is the Solve assessment the same thing as the PSG?
In short, yes - “Solve” is just the newer name for the McKinsey Problem Solving Game.
We want to clear up any potential confusion right at the beginning. You will hear this same screening test called a few different things in different places. The Solve moniker itself is a relatively recent re-branding by McKinsey. Previously, the same test was known as either the Problem Solving Game (usually abbreviated to PSG) or the Digital Assessment. You will also often see that same test referred to as the Imbellus test or game, after the firm that created the first version.
You will still see all these names used across various sites and forums - and even within some older articles and blog posts here on MyConsultingCoach. McKinsey has also been a little inconsistent on what they call their own assessment internally. Candidates can often become confused when trying to do their research, but you can rest assured that all these names refer to the same screening test - though folk might be referring to either the legacy or Redrock versions.
Why does the assessment exist?

As with Bain, BCG and other major management consulting firms, McKinsey receives far far more applications for each position than they can ever hope to interview. Compounding this issue is that case interviews are expensive and inconvenient for firms like McKinsey to conduct. Having a consultant spend a day interviewing just a few candidates means disrupting a whole engagement and potentially having to fly that consultant back to their home office from wherever their current project was located. This problem is even worse for second-round interviews given by partners.
Thus, McKinsey need to cut down their applicant pool as far as possible, so as to shrink the number of case interviews they need to give without losing the candidates they actually want to hire. Of course, they want to then accomplish this as cheaply and conveniently as possible.
The Problem Solving Test (invariably shortened to PST) had been used by McKinsey for many years. However, it had a number of problems that were becoming more pronounced over time, and it was fundamentally in need of replacement. Some of these were deficiencies with the test itself, though many were more concerned with how the test fitted with the changing nature of the consulting industry.
The Solve assessment has been developed and iterated by the specialist firm Imbellus ( now owned by gaming giant Roblox ) to replace the long-standing PST in this screening role and offers solutions to those problems with its predecessor.
We could easily write a whole article on what McKinsey aimed to gain from the change, but the following few points cover most of the main ideas:
- New Challenges: In particular, the changing demands of the consulting industry mean that McKinsey is increasingly seeking a new kind of hire. Previously, candidates were largely coming out of MBAs or similar business-focussed backgrounds, and so the PST’s quickfire business questions in a familiar GMAT-style format were perfectly sufficient to select consultants for what were fairly non-technical generalist consulting roles. However, clients have been bringing ever more technical projects to firms like McKinsey. This has led to the increasing internal segmentation of consulting firms - to create specialist digital divisions , for example. Even in generalist consulting, there is also now an increasing recognition of the utility of individuals with real depth of knowledge coming out of either industry or non-business academic routes like PhD programmes (you can read more about getting into consulting without an MBA here ). This feeds through to change what constitutes a good aptitude test for McKinsey. Without the once-crucial MBA, McKinsey can’t assume the same kind of detailed business knowledge. They also ideally want a single test that can be given to all kinds of prospective specialist consultants as well as generalists.
- Fairness and the Modern Context: The covid pandemic necessitated at-home aptitude testing. However, even before that, there were pressures for a move to a largely remote recruitment process. Online testing - versus real-life papers, sat on location - dramatically reduces the amount of travel required of candidates. This allows McKinsey to cast a wider net, providing more opportunities to those living away from hub cities, whilst also hugely reducing the carbon footprint associated with the McKinsey selection process.
- Gaming the System: More pragmatically, the Solve assessment promises to simply do the job of selecting the right candidates better than the PST. All things being equal, just increasing the candidate pool with an online test should lead to better quality candidates emerging to top the cohort. However, the Solve assessment also promises to do a better job at ranking those candidates in line with their actual abilities. A large part of this is that it is a much harder test to “game” than the PST was, where highly effective prep resources were available and readily allowed a bad candidate with good preparation to do better than a good candidate. The fact that game parameters change for every individual test-taker also cuts down the risk of some candidates having an unfair advantage by receiving details of the tests being used from those who have already taken them. The recent move towards the Redrock version also helps McKinsey stay ahead of those developing prep resources for the legacy Solve assessment.
- Cost Cutting: A major advantage of scrapping the old pen-and-paper PST is that the formidable task of thinning down McKinsey’s applicant pool can be largely automated. No test rooms and invigilation staff need to be organised and no human effort is required to devise, transport, catalogue and mark papers. This is especially impactful when we consider that the Solve assessment’s advanced “process scoring” function allows the kind of nuanced filtering of candidates that would usually require something like an essay-based exam to accomplish, rather than the multiple-choice PST. Imbellus has provided this without the huge time and effort from expert human markers that would usually be required - so McKinsey has gained ability whilst eliminating cost and inconvenience.
How is the Solve Assessment used by McKinsey?
McKinsey's own account of how the Solve assessment is used in selection can be seen in the following video:
Whilst some offices initially stuck with the old PST, the legacy Solve assessment was soon rolled out globally and is given universally to candidates for roles at pretty well every level of the hierarchy. Certainly, if you are a recent grad from a Bachelor’s, MBA, PhD or similar, or a standard experienced hired, you can expect to be asked to complete the Solve assessment.
Likewise, we can expect the new Redrock Case Study version to be rolled out globally - though at this point it seems you might be given either (especially as McKinsey has been having significant technical problems with this new online case study) and so should be ready for both.
At present, it seems that only those applying for very senior positions or perhaps those with particularly strong referrals and/or connections are allowed to skip the test. Even this will be office-dependent.
As noted above, one of the advantages of the Solve assessment is that it can be given to all of McKinsey’s hires. Thus, you can expect to be run into the same games whether you are applying as a generalist consultant or to a specialist consulting role - with McKinsey Digital , for example.
The takeaway here is that, if you are applying to McKinsey for any kind of consulting role, you should be fully prepared to sit the Solve Assessment!
Where does the Solve assessment fit into the recruitment process?
You can expect to receive an invitation to take the Solve assessment shortly after submitting your resume.
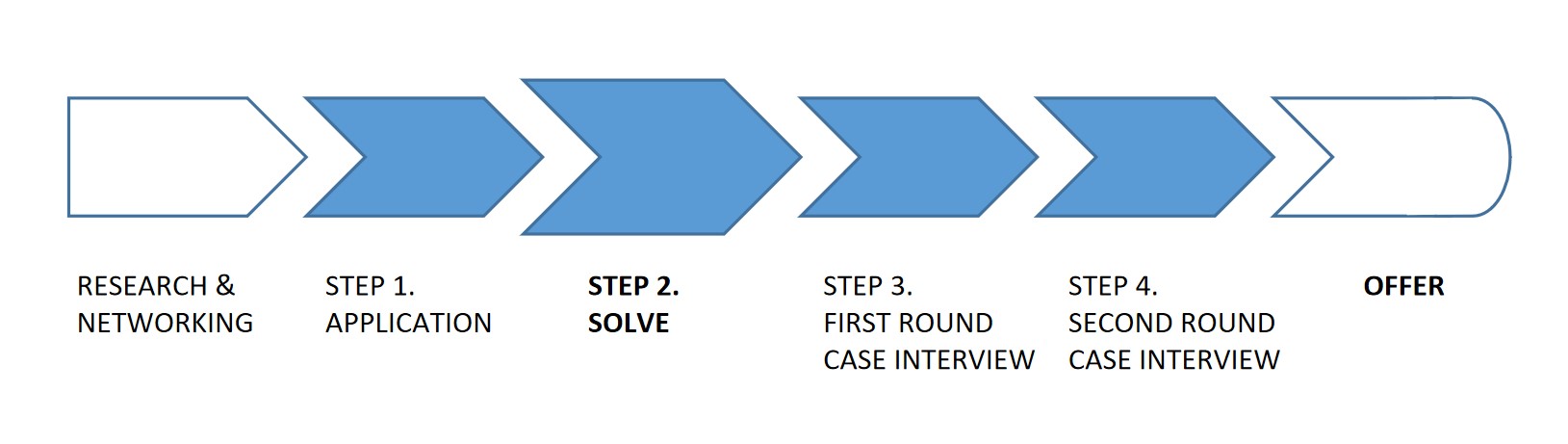
It seems that an initial screen of resumes is made, but that most individuals who apply are invited to take the Solve assessment.
Any initial screen is not used to make a significant cut of the candidate pool, but likely serves mostly to weed out fraudulent applications from fake individuals (such as those wishing to access the Solve assessment more than once so they practice...) and perhaps to eliminate a few individuals who are clearly far from having the required academic or professional background or have made a total mess of their resumes.
Your email invitation will generally give you either one or two weeks to complete the test, though our clients have seen some variation here - with one individual being given as little as three days.
Certainly, you should plan to be ready to sit the Solve assessment within one week of submitting your resume!
Once you have completed the test, McKinsey explain on their site that they look at both your test scores and resume (in more detail this time) to determine who will be invited to in-person case interviews. This will only be around 30% of the candidates who applied - possibly even less.
One thing to note here is that you shouldn’t expect a good resume to make up for bad test scores and vice versa. We have spoken to excellent candidates whose academic and professional achievements were not enough to make up for poor Solve performance. Similarly, we don’t know of anyone invited to interview who hadn’t put together an excellent resume.
Blunty, you need great Solve scores and a great resume to be advanced to interview.
Your first port of call to craft the best possible resume to land your invitation to interview is our excellent free consulting resume guide .
Impress your interviewer
What does the solve assessment test for.
Whilst information on the Solve assessment can be hard to come by, Imbellus and McKinsey have at least been explicit on what traits the test was designed to look for. These are:
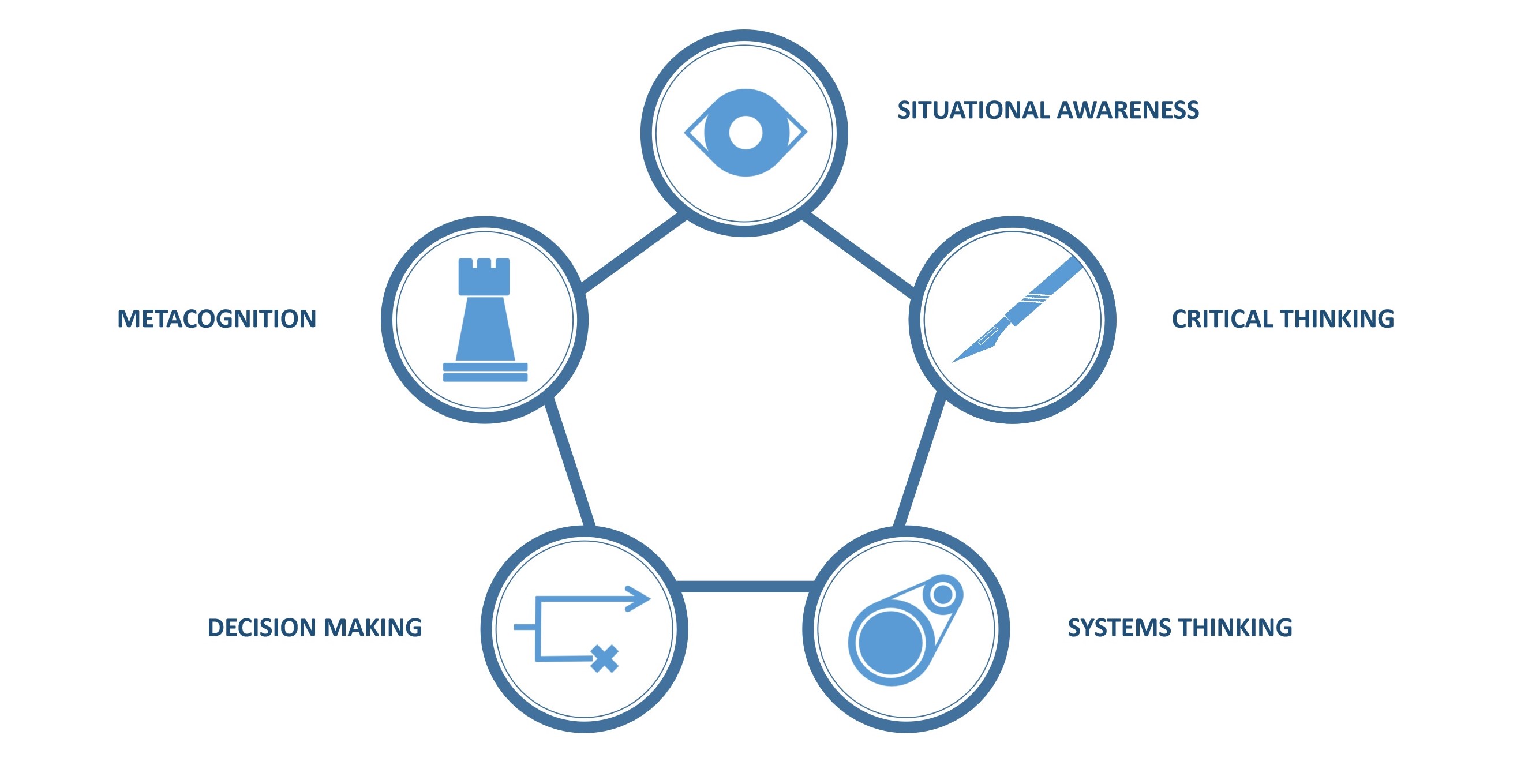
- Critical Thinking : making judgements based on the objective analysis of information
- Decision Making : choosing the best course of action, especially under time pressure or with incomplete information
- Metacognition : deploying appropriate strategies to tackle problems efficiently
- Situational Awareness : the ability to interpret and subsequently predict an environment
- Systems Thinking : understanding the complex causal relationships between the elements of a system
Equally important to understanding the raw fact of the particular skillset being sought out, though, is understanding the very idiosyncratic ways in which the Solve assessment tests for these traits. Let's dive deeper:
Process Scores
Perhaps the key difference between the Solve assessment and any other test you’ve taken before is Imbellus’s innovation around “process scores”.
To explain, when you work through each of the games, the software examines the solutions you generate to the various problems you are faced with. How well you do here is measured by your “product score”.
However, scoring does not end there. Rather, Imbellus’s software also constantly monitors and assesses the method you used to arrive at that solution. The quality of the method you used is then captured in your “process score”.
To make things more concrete here, if you are playing the Ecosystem Building game, you will not only be judged on whether the ecosystem you put together is self-sustaining. You will also be judged on the way you have worked in figuring out that ecosystem - presumably, on how efficient and organised you were. The program tracks all your mouse clicks and other actions and will thus be able to capture things like how you navigate around the various groups of species, how you place the different options you select, whether you change your mind before you submit the solution and so on.
You can find more detail on these advanced aspects of the Solve assessment and the innovative work behind it in the presentation by Imbellus founder Rebecca Kantar in the first section of the following video:
Compared to other tests, this is far more like the level of assessment you face from an essay-based exam, where the full progression of your argument towards a conclusion is marked - or a maths exam, where you are scored on your working as well as the final answer (with, of course, the major advantage that there is no highly qualified person required to mark papers).
Clearly, the upshot of all this is that you will want to be very careful how you approach the Solve assessment so you generally think before you act and show yourself in a very rational, rigorous, ordered light.
We have some advice for how to help look after your process score in our PDF Guide to the McKinsey Solve Assessment .
A Different Test for Every Candidate
Another remarkable and seriously innovative aspect of the Solve assessment is that no two candidates receive exactly the same test.
Imbellus automatically varies the parameters of the different games to be different for each individual test-taker so that each will be given a meaningfully different game to everyone else’s.
Within a game, this might mean a different terrain setting, having a different number of species or different types of species to work with or more or fewer restrictions on which species will eat which others.
Consequently, even if your buddy takes the assessment for the same level role at the same office just the day before you do, whatever specific strategy they used in their games might very well not work for you.
This is an intentional feature designed to prevent test takers from sharing information with one another and thus advantaging some over others. At the extreme, this feature would also be a robust obstacle to any kind of serious cheating.
If cheating seems far-fetched to some readers, remember how competitive the race to land jobs at top consulting firms is. We at MCC have previously been made aware of individuals purporting to sell the answers to consulting screening tests on the black market. If cheating is possible, there is always a risk it can happen.
To manage to give every candidate a different test and still be able to generate a reliable ranking of those candidates across a fundamental skillset, without that test being very lengthy, is a considerable achievement from Imbellus. At high level, this would seem to be approximately equivalent to reliably extracting a faint signal from a very noisy background on the first attempt almost every time.
Taking this level of trouble - and presumed additional expense - shows how seriously McKinsey take the task of ensuring reliable, fair selection by trying to eliminate anything like cheating, or even just normal information flow between candidates, that might have happened with something like the PST.
(Note that we are yet to confirm this also happens with the new Redrock Case Study, but it seems to be set up to allow for easy changes to be made to the numerical values describing the case, so we assume there will be the same kind of variation.)
What does it all mean for you?
Understanding what you are being tested for is obviously crucial in preparing yourself for any kind of assessment. For the Solve assessment, this is especially true the longer the time you have to prepare.
Over longer preps, an understanding of exactly the kind of traits being examined allows you to select skill-building activities that should actually show transference in boosting your test performance.
Of course, this begs the obvious question…
Can I Prepare for the McKinsey Solve Assessment?

In short, yes you can - and you should!
As noted previously, there has previously been a lot of disagreement over whether it is really possible to prep for the Solve assessment in a way that actually makes a difference.
Especially regarding the legacy version, there has been a widespread idea that the Solve assessment functions as something like an IQ test, so that preparation beyond very basic familiarisation to ensure you don’t panic on test day will not do anything to reliably boost your scores (nobody is going to build up to scoring an IQ of 200 just by doing practice tests, for example).
This rationale says that the best you can do is familiarise yourself with what you are up against to calm your nerves and avoid misunderstanding instructions on test day. However, this school of thought says there will be minimal benefit from practice and/or skill building.
The utility of preparation has become a little clearer with the addition of the Redrock Case Study to the new version of Solve. Its heavily quantitative nature, strong time pressure and structure closely resembling a traditional business case make for a clearer route to improvement.
However, as we explain in more detail in our PDF guide to the Solve assessment the idea that any aspect of either version of Solve can't be prepared for has been based on some fundamental misunderstandings about what kind of cognitive traits are being tested. Briefly put, the five key skills the Solve assessment explicitly examines are what are known as higher-order thinking skills.
Crucially, these are abilities that can be meaningfully built over time.
McKinsey and Imbellus have generally advised that you shouldn’t prepare. However, this is not the same as saying that there is no benefit in doing so. McKinsey benefits from ensuring as even a playing field as possible. To have the Solve test rank candidates based purely on their pre-existing ability, they would ideally wish for a completely unprepared population.

There has been a bit of variation in the games included in the Solve assessment/PSG over the years and what specific form those games take. Imbellus and McKinsey have experimented with whole new configurations as well as making smaller, iterative tweaks over time. That being said, the new 2023 Redrock case is by far the largest change to Solve since that assessment's genesis back in 2017.
Given that innovation seems to continue (especially with the lengthy feedback forms some candidates are being asked to sit after sitting the newest iteration), there is always the chance you might be the first to receive something new.
However, our surveys of, and interviews with, those taking the Solve assessment - both before and after recent changes - mean we can give you a good idea of what to expect if you are presented with either the legacy or the Redrock version of Solve.
We provide much more detailed explanation of each of the games in our Solve Assessment PDF Guide - including guidance on optimal scenarios to maximise your performance. Here, though, we can give a quick overview of each scenario:
Ecosystem Building
In this scenario, you are asked to assemble a self-sustaining ecosystem in either an aquatic, alpine or jungle environment (though do not be surprised if environments are added, as this should be relatively easy to do without changing the underlying mechanics).
The game requires you to select a location for your ecosystem. Several different options are given, all with different prevailing conditions. You then have to select a number of different plant and animal species to populate a functioning food chain within that location.
In previous versions of the game, you would have had to fit as many different species as possible into a functioning food chain. However, recent iterations of the Solve assessment require a fixed number of eight species to be selected.
Species selection isn’t a free-for-all. You must ensure that all the species you select are compatible with one another - that the predator species you select are able to eat the prey you have selected for them etc. All the species must also be able to survive in the conditions prevailing at the location you have selected.
So far, this sounds pretty easy. However, the complexity arises from the strict rules around the manner and order in which the different species eat one another. We run through these in detail in our guide, with tips for getting your food chain right. However, the upshot is that you are going to have to spend some significant time checking your initial food chain - and then likely iterating it and replacing one or more species when it turns out that the food chain does not adhere to the eating rules.
Once you have decided on your food chain, you simply submit it and are moved on to the next game. In the past, test takers were apparently shown whether their solution was correct or not, but this is no longer the case.
Test-takers generally report that this game is the easier of the two, whether it is paired with the Plant Defence game in the legacy Solve or the Redrock Case Study in the new version. Candidates will not usually struggle to assemble a functioning ecosystem and do not find themselves under enormous time pressure. Thus, we can assume that process scores will be the main differentiator between individuals for this component of the Solve assessment.
For ideas on how to optimise your process score for this game, you can see our PDF Solve guide .
Plant Defence
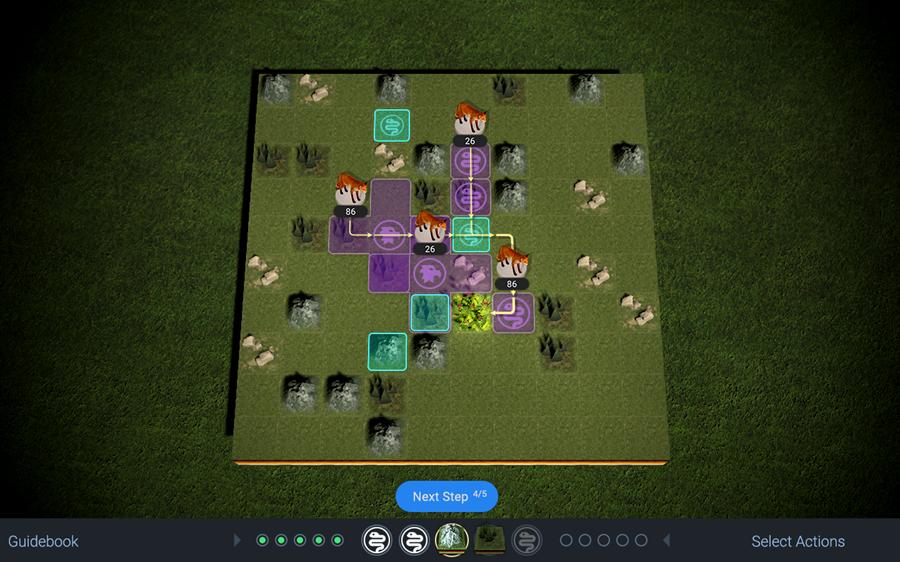
As mentioned, this game has been replaced with the Redrock Case Study in the new newer iteration of the Solve assessment, rolled out from Spring 2023. However you might still be asked to sit the legacy version, with this game, when applying to certain offices - so you should be ready for it!
This scenario tasks you with protecting an endangered plant species from invasive species trying to destroy it.
The game set-up is much like a traditional board game, with play taking place over a square area of terrain divided into a grid of the order of 10x10 squares.
Your plant is located in a square near the middle of the grid and groups of invaders - shown as rats, foxes or similar - enter from the edges of the grid before making a beeline towards your plant.
Your job then is to eliminate the invaders before they get to your plant. You do this by placing defences along their path. These can be terrain features, such as mountains or forests, that either force the invaders to slow down their advance or change their path to move around an obstacle. To actually destroy the invaders though, you use animal defenders, like snakes or eagles, that are able to deplete the groups of invaders as they pass by their area of influence.
Complication here comes from a few features of the game. In particular:
- You are restricted in terms of both the numbers of different kinds of defenders you can use and where you are allowed to place them. Thus, you might only have a couple of mountains to place and only be allowed to place these in squares adjacent to existing mountains.
- The main complication is the fact that gameplay is not dynamic but rather proceeds in quite a restricted turnwise manner. By this, we mean that you cannot place or move around your defences continuously as the invaders advance inwards. Rather, turns alternate between you and invaders and you are expected to plan your use of defences in blocks of five turns at once, with only minimal allowance for you to make changes on the fly as the game develops.
The plant defence game is split into three mini-games. Each mini-game is further split into three blocks of five turns. On the final turn, the game does not stop, but continues to run, with the invaders in effect taking more and more turns whilst you are not able to place any more defences or change anything about your set-up.
More and more groups of invaders pour in, and your plant will eventually be destroyed. The test with this “endgame” is simply how many turns your defences can stand up to the surge of invaders before they are overwhelmed.
As opposed to the Ecosystem Building scenario, there are stark differences in immediate candidate performance - and thus product score - in this game. Some test takers’ defences will barely make it to the end of the standard 15 turns, whilst others will survive 50+ turns of endgame before they are overwhelmed.
In this context, as opposed to the Ecosystem Building game typically preceding it, it seems likely that product score will be the primary differentiator between candidates.
We have a full discussion of strategies to optimise your defence placement - and thus boost your product score - in our Solve guide .
Redrock Case Study

This is the replacement for the Plant Defence game in the newest iteration of Solve.
One important point to note is that, where the Solve assessment contains this case study, you have a strict, separate time limit of 35 minutes for each half of the assessment. You cannot finish one game early and use the extra time in the other, as you could in the legacy Solve assessment.
McKinsey has had significant issues with this case study, with test takers noting several major problems. In particular:
- Glitches/crashes - Many test takers have had the Redrock Case crash on them. Usually, this is just momentary and the assessment returns to where it was in a second or two. If this happens to you, try to just keep calm and carry on. However, there are reports online of some candidates having the whole Solve assessment crash and being locked out as a result. If this happens, you should contact HR.
- Confusing interface - Candidates have routinely noted that Redrock's controls are confusing and seem poorly designed compared to the older Ecosystem Building game preceding it. This means that they can often lose time figuring out how to interact with the case.
- Confusing language - Related to the above is that the English used is often rather convoluted and sometimes poorly phrased. This can be challenging even for native English speakers but is even worse for those sitting Solve in their second language. It can make the initial instructions difficult to understand - compounding the previous interface problem. It can also make questions difficult, requiring a few readings to comprehend.
- Insufficient time - Clearly, McKinsey intended for Redrock to be time pressured. However, time is so scarce that pretty well nobody is getting through all the questions. This is plainly sub-optimal for McKinsey - as well as being stressful and disheartening for candidates. We would expect changes to be made to address this issue in future.
McKinsey are clearly aware of these issues, as they have been asking some test takers to complete substantial feedback surveys after sitting Redrock. Be aware, then, that this raises the likelihood of changes to the Redrock Case Study in the near term - meaning you should be ready to tackle something new.
For the time being, though, we can take you through the fundamentals of the current version of the Redrock Case Study. For more detail, see our freshly updated PDF Guide .
The Scenario
Whilst changes to the details are likely in future, the current Redrock Case Study is set on the Island of Redrock. This island is a nature reserve with populations of several species, including wolves and elk. Redrock's wolves are split into four packs, associated with four geographical locales. These packs predate the elk and depend upon them for food, such that there is a dynamic relationship between the population numbers of both species. Your job is to ensure ecological balance by optimising the numbers of wolves in the four packs, such that both wolves and elk can sustainably coexist.
The Questions
The Redrock case study's questions were initially split into three sections, but a fourth was later added. These sections break down as follows:
- Investigation - Here, you have access to the full description of the case, with all the data on the various animal populations. Your task is to efficiently extract all the most salient data points and drag-and-drop them to your "Research Journal" workspace area. This is important, as you subsequently lose access to all the information you don't save at this stage.
- Analysis - You must answer three numerical questions using information you saved in the Investigation section. This can include you dragging and dropping values to and from an in-game calculator.
- Report - Formerly the final section, you must complete a pre-written report on the wolf populations, including calculating numerical values to fill in gaps and using an in-game interface to make a chart to illustrate your findings. You will leverage information saved in the Investigation section, as well as answers calculated in the Analysis section.
- Case Questions - This section adds a further ten individual case questions. These are thematically similar to the preceding case, but are otherwise separate, not relying on any information from the previous sections. The ten questions are highly quantitative and extremely time pressured. Pretty well nobody finishes them before being timed out.
This is a very brief summary - more detail is available in our PDF Guide .
Other Games - Disease and Disaster Identification

There have been accounts of some test-takers being given a third game as part of their Solve assessment. At time of writing, these third games have always been clearly introduced as non-scored beta tests for Imbellus to try out potential new additions to the assessment. However, the fact that these have been tested means that there is presumably a good chance we’ll see them as scored additions in future.
Notably, these alternative scenarios are generally variations on a fairly consistent theme and tend to share a good deal of the character of the Ecosystem Building game. Usually, candidates will be given a whole slew of information on how an animal population has changed over time. They will then have to wade through that information to figure out either which kind of natural disaster or which disease has been damaging that population - the commonality with the Ecosystem Building game being in the challenge of dealing with large volumes of information and figuring out which small fraction of it is actually relevant.
Join thousands of other candidates cracking cases like pros
How to effectively prep for the solve assessment.

We discuss how to prep for the Solve assessment in full detail in our PDF guide . Here though, we can give you a few initial pointers to get you started. In particular, there are some great ways to simulate different games as well as build up the skills the Solve assessment tests for.
Playing video games is great prep for the legacy Solve assessment in particular, but remains highly relevant to the new Redrock version.
Contrary to what McKinsey and Imbellus have said - and pretty unfortunately for those of us with other hobbies - test-takers have consistently told us that they reckoned the Problem Solving Game and now the Solve assessment pretty robustly favours those with strong video gaming experience.
If you listened when your parents told you video games were a waste of time and really don’t have any experience, then putting in some hours on pretty much anything will be useful. However, the closer the games you play are to the Solve scenarios, the better. We give some great recommendations on specific games and what to look for more generally in our Solve guide - including one free-to-play game that our clients have found hugely useful as prep for the plant defence game!
PST-Style Questions
The inclusion of the Redrock case studies in the new version of Solve really represents a return to something like a modernised PST. Along with the similar new BCG Casey assessment, this seems to be the direction of travel for consulting recruitment in general.
Luckily, this means that you can leverage the wealth of existing PST-style resources to your advantage in preparation.
Our PST article - which links to some free PST questions and our full PST prep resources - is a great place to start. However, better than old-fashioned PDF question sets are the digital PST-style questions embedded in our Case Academy course . Conducted online with a strict timer running, these are a much closer approximation of the Solve assessment itself. These questions are indeed a subset of our Case Academy course, but are also available separately in our Course Exercises package .
Quick Mathematics With a Calculator
Again, specifically for the Redrock assessment, you will be expected to solve math problems very quickly. The conceptual level of mathematics required is not particularly high, but you need to know what you are doing and get through it fast using a calculator (and/or Excel, if you are already comfortable with that program).
Our article on consulting math is a great place to start to understand what is expected of you throughout the recruiting process, with our consulting math package (a subset of our Case Academy course) providing more in-depth lessons and practice material.
Learn to Solve Case Studies
With the Redrock Case Study clearly being an ecology-themed analogue to a standard business case study, it's pretty obvious that getting good at case studies will be useful.
However, the Solve assessment as a whole is developed and calibrated to be predictive of case interview performance, so you can expect that improving your case solving ability will indirectly bring up your performance across the board.
Of course, this overlaps with your prep for McKinsey's case interviews. For more on how to get started there, see the final section of this article.
Learning About Optimal Strategies for the Games
The first thing to do is to familiarise yourself with the common game scenarios from the Solve assessment and how you can best approach them to help boost your chances of success.
Now, one thing to understand is that, since the parameters for the games change for each test-taker, there might not be a single definitive optimal strategy for every single possible iteration of a particular game. As such, you shouldn’t rely on just memorising one approach and hoping it matches up to what you get on test day.
Instead, it is far better to understand why a strategy is sensible in some circumstances and when it might be different to do something else instead if the version of the game you personally receive necessitates a different approach.
In this article, we have given you a useful overview of the games currently included in the Solve assessment. However, a full discussion with suggested strategies is provided in our comprehensive Solve guide .
With the limited space available here, this is only a very brief sketch of a subset of the ways you can prep.
As noted, what will help with all of these and more is reading the very extensive prep guidance in our full PDF guide to the Solve assessment...
MCC Solve Assessment PDF Guide
Preparing for the Solve assessment doesn’t have to be a matter of stumbling around on your own. Whilst prep isn’t quite as straightforward as it would be for a more conventional test, there is still a lot you can do to increase your chances.
This article is a good start to get you up to speed. From here, though our new, updated PDF guide to the McKinsey Solve assessment is your first stop to optimise your Solve preparation.
This guide is based on our own survey work and interviews with real test-takers, as well as follow-ups on how the advice in the previous guide worked out in reality.
The MyConsultingCoach Solve guide is designed to be no-nonsense and straight to the point. It tells you what you need to know up front and - for those of you who have already received the invitation to interview and don’t have much time - crucial sections are clearly marked to read first, with specific advice for prepping in a hurry
For those of you starting early with more time to spare, there is also a fully detailed, more nuanced discussion of what the test is looking for and how you can design a more long-term prep to build up the skills you need - and how this can fit into your wider case interview prep.
All throughout, there is no fluff to bulk out the page count. The market is awash with guides at huge page counts, with appendices etc stuffed full of irrelevant material to boost overall document length. By contrast, we realise your time is better spent actually preparing than ploughing through a novel.
If this sounds right for you, you can purchase our PDF Solve guide here:
The Next Step - Case Interviews

So, you pour in the hours to generate an amazing resume and cover letter.
You prepare diligently for the Solve assessment. You go through our PDF guide , implementing all the suggestions. Accordingly, you pour more hours into gaming, skill building and practising with PST-style questions.
You feel great on the day itself and ace the test, building a perfect ecosystem and keeping your plant alive for 50+ turns or acing the calculations for the Redrock questions.
Your product and process scores are right at the top of your cohort and those plus your resume and cover letter are enough to convince McKinsey to invite you for a first-round case interview. Excellent!
Now the real work begins…
Arduous as application writing and Solve prep might have seemed, preparing for McKinsey case interviews will easily be an order of magnitude more difficult.
McKinsey tells candidates not to prepare for Solve, and it is quite possible that someone might pass that assessment without having done any work in advance. However, McKinsey explicitly expects candidates to have rigorously prepared for case interviews , and it is vanishingly unlikely that an unprepared interviewee could pass even first-round interviews.
The volume of specific business knowledge and case-solving principles, as well as the sheer complexity of the cases you will be given, mean that there is no way around knuckling down, learning what you need to know and practising on repeat.
McKinsey have internal mentoring programmes for promising individuals and we have even heard of HR staff there explicitly telling candidates to secure private coaching before their interviews (indeed, it seems MCC got directly recommended by at least one HR).
All this means that, if you want to get through your interviews and actually land that McKinsey offer, you are going to need to take things seriously, put in the time and learn how to properly solve case studies.
Unfortunately, not all case cracking methods are created equal. There are some older-but-still-well-known systems out there largely trading on brand recognition, but with dubious efficacy - especially in a world where interviewers know all about the frameworks they teach and how to select cases that don’t fit them.
The method we teach throws out generic frameworks altogether and shows you how to solve cases the way a real management consultant approaches a real engagement. Usefully, our method is based specifically on the way McKinsey train incoming consultants
The time you put into learning our approach to case cracking won't just be time down the drain memorising some cribs to be forgotten after the interview. Instead, the methods we teach should still be useful when you start the job itself, giving you a head start on becoming a top-performing consultant!
You can start reading about the MCC method for case cracking here . To step your learning up a notch, you can move on to our Case Academy course .
To put things into practice in some mock interviews with real McKinsey consultants, take a look at our coaching packages .
And, if all this (rightfully) seems pretty daunting and you’d like to have an experienced consultant guide you through your whole prep from start to finish, you can apply for our comprehensive mentoring programme here .
Looking for an all-inclusive, peace of mind program?
Candidates who sign up to our free services are 3 times more likely to land a job in one of their target firms . How?
- We teach how to solve cases like consultants , not through frameworks
- Our Meeting Board lets you practice with peers on 100+ realistic, interactive cases.
- Our AI mentor creates a personalised study roadmap to give you direction.
- All the advice you need on resume, cover letter and networking.
We believe in fostering talent, that’s why all of the above is free .
Account not confirmed
Get 25% off all test packages.
Get 25% off all test packages!
Click below to get 25% off all test packages.

McKinsey Tests
- https://www.mckinsey.com/careers/search-jobs
- New York, US
- 194 questions
McKinsey is one of the world’s leading management consultancy firms.
Careers at McKinsey and Co
McKinsey is a worldwide management consulting firm based in the U.S. It conducts qualitative and quantitative analysis to evaluate management decisions across public and private sector companies.
McKinsey offers a wide range of career paths, including consulting roles, research and analytics positions, digital and technology jobs, and support roles in areas such as finance, marketing, and human resources.
They are continually recruiting talented individuals from diverse backgrounds, including recent graduates, experienced professionals, and advanced degree holders.
As a consulting firm, McKinsey places a strong emphasis on problem-solving skills and critical thinking, and it seeks individuals who are able to work collaboratively and communicate effectively with clients and colleagues.
Careers at McKinsey & Company can offer a challenging and rewarding experience for individuals with a passion for problem-solving, a drive to learn and grow, and a desire to make a positive impact in the world.
McKinsey and Co Application Process
Online application, aptitude tests, problem solving test (pst), personal experience interview, problem solving game, mckinsey case interview, mckinsey fit interview, mckinsey online application.
To begin your Mckinsey online application you need to apply for your role via the Mckinsey career portal on their careers page.
You will be asked to provide information about your professional experience including a copy of your resume and cover letter.
Be sure to tailor your application to the role you’re applying for and emphasize any relevant skills, industry experience, or leadership positions that showcase your suitability.
McKinsey Aptitude Tests
If you meet the minimum requirements for the position and are successful in the application stage you will be invited to take part in a series of aptitude tests.
Tests vary depending on the role you’ve applied for so we’ve put together a comprehensive list of assessments you might be asked to take.
McKinsey Numerical Reasoning Tests
McKinsey uses numerical reasoning tests as part of its recruiting process to evaluate the quantitative skills of potential candidates. These tests are designed to assess a candidate’s ability to work with numerical data and to use quantitative reasoning to solve complex problems quickly.
The McKinsey numerical reasoning test typically consists of a series of multiple-choice questions that require candidates to perform basic arithmetic, analyze data sets, and use mathematical concepts to solve business problems. The test may also include questions related to probability, statistics, and financial analysis.
To prepare for the McKinsey numerical reasoning test, candidates should have a strong foundation in basic mathematical concepts, including arithmetic, algebra, geometry, and statistics.
During the test, candidates must manage their time effectively to ensure that they answer all questions within the allotted time. Candidates must also be able to work quickly and accurately under pressure, as the test is designed to be challenging.
With proper preparation and practice, candidates can improve their performance on these tests and increase their chances of success in the recruiting process.
McKinsey Verbal Reasoning Tests
McKinsey’s verbal reasoning test consists of a series of multiple-choice questions that require candidates to read and analyze passages of text and answer questions based on the information provided. The passages may cover a wide range of topics, but no prior knowledge of the topic is needed. Instead, you must focus on what you can comprehend from the written material.
To prepare for the McKinsey verbal reasoning test, candidates should have strong reading and comprehension skills and be able to analyze complex written material quickly and accurately. Candidates should also have a good understanding of sentence structure, vocabulary, and grammar.
From each passage of text, you will need to decide if a statement in the passage is true, or false or if you cannot tell.
McKinsey Problem Solving Test (PST)
The McKinsey Problem Solving Test (PST) is a standardized test used to assess the problem-solving skills of potential consultants. The test is designed to evaluate a candidate’s ability to analyze and solve complex business problems, and it is a key component of the recruiting process for McKinsey.
The test uses a multiple-choice format and may cover a range of topics, including data analysis, quantitative reasoning, logical reasoning, and critical thinking.
The skills assessed by the McKinsey PST include:
Analytical skills: Candidates must be able to analyze complex data and identify key patterns and trends.
Problem-solving skills: Candidates must be able to identify problems, develop hypotheses, and create solutions to solve complex business problems.
Time management skills: Candidates must be able to manage their time effectively, as the test is designed to be challenging and requires candidates to work quickly and efficiently.
Communication skills: Candidates must be able to communicate their findings and recommendations clearly and effectively, both in writing and in person.
You can practice some official example test questions for the Mckinsey PST test below:
- Example test questions 1
- Example test questions 2
- Example test questions 3
You can also try some free practice tests using our online platform.
Mckinsey Case Interview
The McKinsey Case Interview is a crucial component of the firm’s recruitment process, designed to assess a candidate’s problem-solving skills, business acumen, and communication abilities.
The interview typically lasts for 45 minutes to an hour, during which candidates are presented with a hypothetical business scenario or challenge.
These cases often reflect real-life client engagements, encompassing a wide range of industries and topics. Interviewers may also incorporate personal experience questions and the occasional brainteaser to gauge a candidate’s adaptability and critical thinking skills.
During the case interview, candidates are expected to ask clarifying questions, identify key issues, and develop a structured approach to address the problem at hand. Interviewers will evaluate the candidate’s ability to analyze data, synthesize information, and present logical and well-reasoned recommendations. Strong communication skills, active listening, and an ability to articulate one’s thought process are essential for success in this format.
To excel in a McKinsey Case Interview, candidates should practice with case materials and mock interviews to become familiar with various business problems and frameworks.
Additionally, staying up-to-date with industry trends, financial concepts, and market dynamics will provide a solid foundation for tackling cases. During the interview, demonstrate structured thinking, be hypothesis-driven, and actively engage with the interviewer. Finally, don’t forget to showcase your personal experience and interpersonal skills, as these are equally important to succeed in a consulting career at McKinsey.
Examples of case study scenarios include:
Market Entry Strategy: A leading pharmaceutical company is considering entering a new market with a groundbreaking drug. Evaluate the potential market size, competitive landscape, and regulatory environment to develop a comprehensive market entry strategy and provide recommendations on pricing, distribution channels, and marketing tactics.
Profitability Improvement: A major airline is experiencing declining profits due to increasing fuel costs, intensified competition, and changing customer preferences. Analyze the company’s financials, operational efficiency, and customer segments to identify areas of improvement and propose a detailed plan to optimize cost structure, enhance customer experience, and ultimately boost profitability.
Mergers and Acquisitions: A prominent consumer goods manufacturer is exploring the possibility of acquiring a smaller, niche competitor to expand its product portfolio and market share. Assess the strategic fit, financial performance, and potential synergies of the target company, and provide a recommendation on whether the acquisition should proceed, along with an integration plan for post-merger operations.
Digital Transformation: A large retail chain with brick-and-mortar stores is struggling to adapt to the rapidly evolving e-commerce landscape. Develop a comprehensive digital transformation strategy that includes revamping the company’s online presence, leveraging data analytics for personalized marketing, and reimagining the in-store experience to drive customer engagement and improve overall business performance.

Within two hours of practice I have improved my score from 50% correct to 88%.
Personal experience interview
The McKinsey Personal Experience Interview (PEI) is an essential part of the recruitment process, designed to evaluate a candidate’s interpersonal, leadership, and problem-solving skills.
This interview format aims to understand how a candidate has approached and navigated real-life challenges and situations, offering valuable insights into their potential fit within the McKinsey culture. The PEI typically lasts for 20-30 minutes, preceding or following the case interview, and focuses on assessing key qualities such as personal impact, entrepreneurial drive, and leadership capabilities.
To prepare for the McKinsey PEI, candidates should reflect on their past experiences and identify compelling stories that demonstrate their skills and personal attributes. These stories can be drawn from various aspects of a candidate’s life, including professional, academic, and extracurricular experiences. When sharing a personal experience story, it is crucial to follow the STAR (Situation, Task, Action, and Result) framework to ensure a structured and comprehensive response.
Candidates should be prepared to answer follow-up questions, as interviewers often delve deeper into the details of a story to better understand a candidate’s thought process and decision-making abilities. Practicing storytelling and effectively communicating one’s experiences can significantly contribute to a successful McKinsey PEI.
Questions you might be asked in a McKinsey PEI personal experience Interview include:
- Describe a time when you led a team through a challenging situation. How did you motivate the team and ensure a successful outcome?
- Can you provide an example of when you had to deal with a difficult or uncooperative team member? How did you handle the situation, and what was the outcome?
- Tell me about a time when you had to persuade a client or stakeholder to accept your proposal or idea. How did you approach the situation, and what was the result?
- Share an instance where you faced significant obstacles or setbacks in a project. How did you overcome these challenges, and what did you learn from the experience?
- Describe a time when you took a significant risk or pursued an entrepreneurial opportunity. What was your thought process, and what was the outcome?
Mckinsey Problem Solving Game (PSG)
The McKinsey Problem Solving Game (also known as the Imbellus Test) is a computer-based simulation game that McKinsey uses as part of its recruiting process to evaluate a candidate’s problem-solving skills. The game is designed to test a candidate’s ability to work collaboratively, analyze complex problems, and develop solutions to drive organizational change.
The games fall into one of 3 categories:
- Constrained optimization
- Strategy and adaption
- Cause vs. effect
To do well in each category of the game it’s important to prioritize your goals and remember the skills being tested. You should also be sure to read the instructions carefully and understand what you are required to do.
Constrained optimization game
For constrained optimization game types it’s important to ignore irrelevant data and focus on finding a solution to the optimization challenge and navigating the constraints.
Ecosystem design: candidates must decide on the optimal location and species to live in an environment as well as creating a sustainable ecosystem. Specific and plants have interrelationships i.e herbivores eat plants, omnivores eat herbivores and carnivores eat omnivores.
Animal relocation: a natural disaster is killing off an animal ecosystem. Your job is to discover which natural disaster is the cause and move the animal to a suitable location where they can thrive. You will need to analyze a large amount of data to reach a decision and identify key data.
Strategy and adoption game
Ecosystem survival: for this game, you must protect an ecosystem from invasive plant species. To be successful at this game you will need to introduce the right predators and protectors to manage the outbreak. The game tests how long you are able to delay the outcome of the invasion since they will inevitably take over.
Migration management: with limited resources, you must help a herd of animals to migrate - animals die and resources end at each turn; you must make the most optimal choices to keep as many alive with as many resources as possible by the end.
To be successful in both games read through new information at each stage, by comprehending the information slowly and adapting your approach with what you’ve learned.
Cause vs effect game
Disease Analysis: You will be required to analyze large amounts of data to identify why animals are dying in an ecosystem. You must find the problem and the right treatment required.
To be successful in this game, you need to start by identifying what the relevant and irrelevant information is. Then look for logical relationship patterns e.g. when X increases, Y decreases (something causes something else to happen).
The McKinsey fit interview helps recruiters evaluate a candidate’s cultural fit, motivation, and personal qualities. The fit interview is designed to assess a candidate’s alignment with McKinsey’s values, as well as their ability to work effectively in a team and communicate with clients.
The McKinsey fit interview typically consists of a series of behavioral questions that require candidates to provide specific examples of their experiences and achievements. The questions may cover a range of topics, including leadership, teamwork, problem-solving, communication skills, and more.
To prepare for the McKinsey fit interview, candidates should research the company and its culture, and be prepared to discuss their relevant experiences and achievements in detail. Candidates should also be familiar with McKinsey’s values and be able to demonstrate how their personal values align with those of the company.
Questions you might be asked in a McKinsey Fit Interview include:
- Why have you chosen to pursue a career in management consulting, and why McKinsey specifically?
- How do you see yourself contributing to McKinsey’s culture and mission?
- How do you handle stress and maintain a work-life balance in a demanding environment like management consulting?
Practice Aptitude Tests is not associated with McKinsey and Co. We provide preparation services for McKinsey and Co psychometric tests. Our tests are not designed to be identical to any style, employer or industry. Visit https://www.mckinsey.com/careers/search-jobs to find out more.
McKinsey Tests FAQs
How long is the mckinsey hiring process.
The length of the McKinsey hiring process can vary, but it typically takes 4-12 weeks from the initial application to a job offer.
How many people pass McKinsey's first round?
The number of people who pass the first round of the McKinsey interview process can vary depending on the job position and the number of applicants, but typically around 20-30% of applicants move on to the second round.
How long does it take to hear back from McKinsey's final round?
McKinsey usually informs candidates of the outcome within a few days after the final round of interviews.
How many interview rounds are there in McKinsey?
The number of interview rounds in McKinsey varies by position, but typically there are two to three rounds of interviews.
Enjoy what you’ve read? Let others know!
- Share on whatsapp
- Share on linkedin
- Share on twitter
- Share on facebook
- Share via email
Try McKinsey Tests for Free
Mckinsey & co 01.
20 Questions | 20 Minutes
McKinsey & Co 02
Mckinsey & co 03, improve your scores with our intelligent learning system.
Immediate access. Cancel anytime.
- 30 Numerical reasoning tests
- 30 Verbal reasoning tests
- 30 Diagrammatic reasoning tests
- 30 Situational judgement tests
- 34 Publisher packages e.g. Watson Glaser
- 252 Employer packages e.g. HSBC
- 29 Extra packages e.g Mechanical
- Dashboard performance tracking
- Full solutions and explanations
- Tips, tricks, guides and resources
- Access to free tests
- Basic performance tracking
- Solutions & explanations
- Tips and resources
Reviews of our McKinsey & Co tests
What our customers say about our McKinsey & Co tests
Saket Kumar
August 11, 2022
I like the difficulty level of the test. The questions are so analytical and they will definitely help in cracking the aptitude test.
Sunetra Ghewde
May 23, 2021
Medium difficult as time was running fast
Good application of aptitude required. Helpful. Would have performed better if I had more time.
Anjali Khandelwal
May 14, 2021
Speed of solving
Enjoyed solving the questions- I think more verbal reasoning questions should also be included
mustafa Alyagoub
Saudi Arabia
April 04, 2021
seems challenging
first time practicing the test, but the time is quiet challenging, still not relevant to these kind of test.
By using our website you agree with our Cookie Policy.

- Tests by Leading Employers
- Consulting Assessment Preparation
- McKinsey Problem Solving Game
McKinsey Problem Solving Game (Imbellus): a Complete Practice Guide to Pass the Digital Assessment
There is a lot of secrecy around the McKinsey Problem Solving Game, aka Imbellus.
This gamified assessment is used to filter out a large chunk of the many McKinsey applicants, and it’s supposedly crack-proof.
The internet is packed with blog posts, Reddit discussions, and forum threads about the McKinsey PSG, some even contradicting.
This information overload coupled with the huge importance of the test makes the whole preparation process nerve-wracking.
That’s why this practice guide strives to give you accurate and easy-to-digest information about your upcoming test.
It includes:
- A complete overview of the mini-games
- The best things to keep in mind while playing them
- The most helpful practice options available right now
- Useful tips and tactics to increase your chances of passing it
So, buckle up, and let’s get started.
Find out everything you need about the McKinsey Problem Solving Game , aka Imbellus, and prepare using actual simulations!

Gal , Expert on Game-Based Assessments at JobTestPrep .
What is the McKinsey Problem Solving Game (PSG)?
The McKinsey Problem Solving Game, also named McKinsey Imbellus, McKinsey Digital Assessment, and Solve, is a gamified test that replaces the previous assessment, PST, in the recruiting process. The PSG consists of two mini-games lasting for 70 minutes and evaluates candidates on five key cognitive abilities.
Only candidates who pass this stage are invited to the next hiring step, the case interviews.
What Skills Does the PSG Evaluate?
The PSG evaluates the consulting traits and qualifications of a candidate and then compares them to a real McKinsey consultant. If the applicant appears similar or better than the actual consultant, they'll pass the test.
Five main thinking skills are being assessed :
- Critical Thinking : The ability to solve problems by breaking them down into smaller parts.
- Decision-Making Process : The ability to take in large amounts of information and process it efficiently to make the best possible decision within time constraints.
- Meta Cognition : The ability to monitor your cognitive processes and improve them.
- Situational Awareness : The ability to keep track of several tasks or activities concurrently.
- Systems Thinking : The ability to identify the root causes of problems and possible solutions.
Do All Candidates Get the McKinsey Problem Solving Game?
As of 2024, almost all candidates for nearly all Mckinsey offices receive the Problem Solving Game. The PST, on the other hand, is no longer in use.
Get to Know the McKinsey PSG Format Inside Out
The Problem-Solving Game is sent to candidates once they pass the initial resume screening, making it the second hiring step.
McKinsey has created five mini-games, but you'll need to take only two of them. The most common ones are Ecosysystem Building and Redrock Study , and there are four other less common mini-games that only a fraction of the applicants receive (outlined below).
The time limit for the two common mini-games is 70 minutes , and for the others, it may range between 60 to 80 minutes. Each game will also have a tutorial, which is untimed.
Now, let's dive into each of the mini-games so you'll know what to expect on the test.
- Ecosystem Building
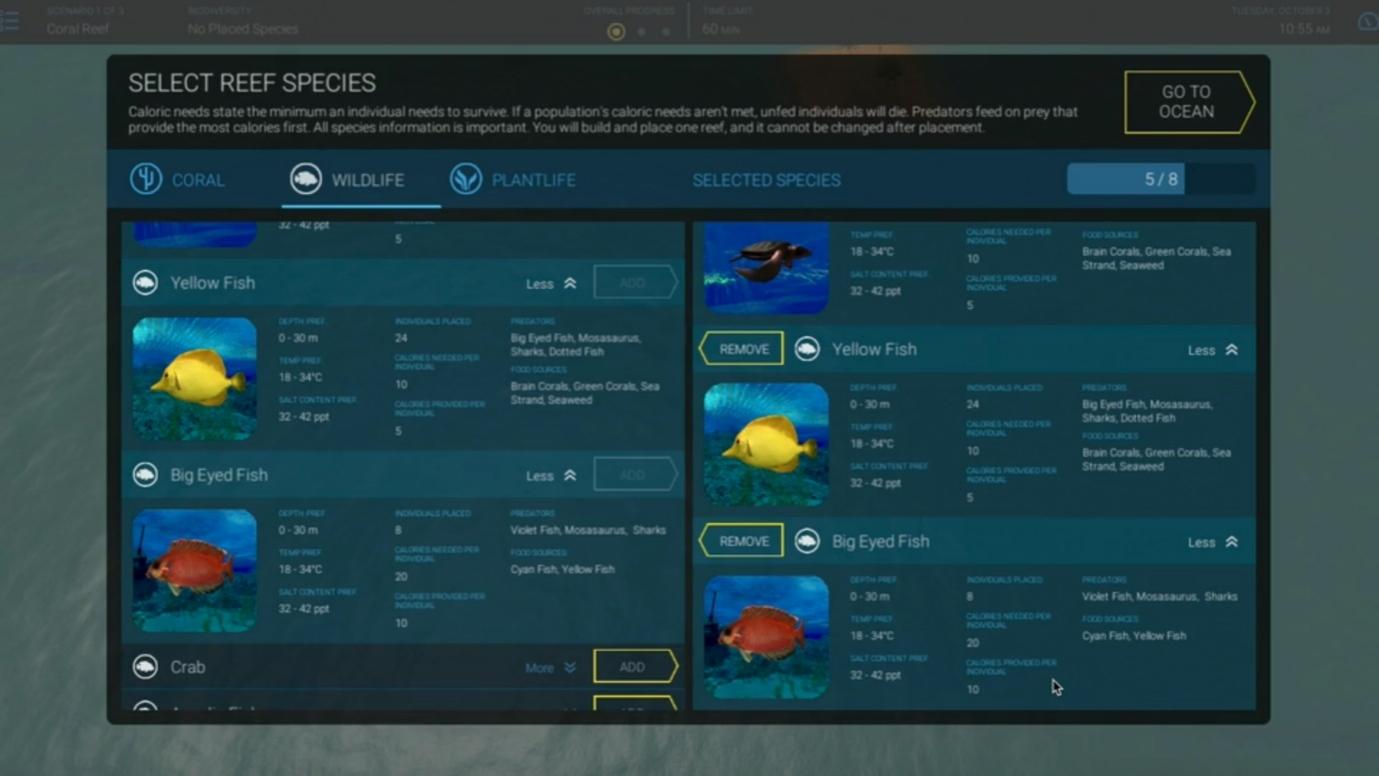
The first mini-game you'll need to pass is Ecosystem Building. In this game, you'll be randomly placed in either a mountain ridge or a coral reef scenario.

Your main objective in this mini-game is to build a sustainable ecosystem using exactly eight species from a collection of 39 species.
To achieve this goal successfully, you must strictly follow these guidelines:
- Terrain specs : The chosen location in the ecosystem must provide suitable living conditions for all eight species.
- Calories balance : Each species must be fed with enough calories from food to sustain itself.
- Food chain continuity : Each species must not be eaten into extinction by its predators.
The gaming platform provides specific information to help you meet these guidelines (some are seen in the game's "guidebook"):
Terrain Specs
Each location in the ecosystem has seven to eight terrain specs. You can choose a location using a pinpoint.
Of these seven or eight specs, only four can be displayed at any given time, using a checklist table in the upper-right corner of the screen:
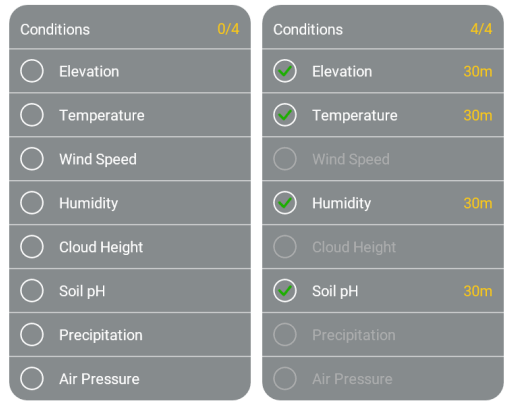
Now, here's what's crucial about these living conditions:
Each species has specific terrain specs that have to be met. If they aren't met, the species won't survive, and you won't achieve the game's main objective.
Luckily, the species' living conditions usually come in ranges, allowing you to be more flexible with the species you choose for your ecosystem.
Additionally, each species has only two to four terrain specs , when Depth/Elevation and Temperature appear for all species:
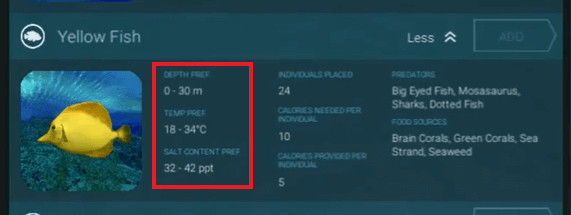
Knowing that you only need to look at specific terrain specs on the checklist table helps eliminate species or locations that are not suitable for creating a sustainable ecosystem.
Food Chain Continuity
The 39 species are divided into producers and consumers.
Producers are plants and fungi (in the Mountain scenario) and corals and seaweeds (in the Coral Reef scenario). They don't have any calorie needs, so their "calories needed" spec is always zero.
Consumers are animals that eat either plants, other animals, or both. Some consumers are at the top of the food chain and therefore not eaten by any other species.
While creating the food chain, it's important to ensure that no species is eaten to extinction. This can be monitored using the " calorie needed " and the " calorie provided " specs that each species has (shown below).
Calories Balance
Each species has a calorie needed and a calorie provided, as you can see below:
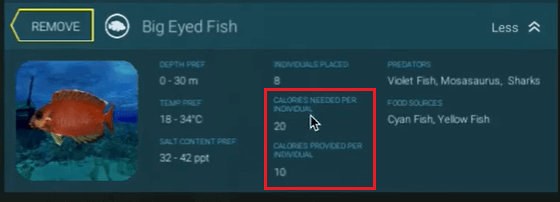
A species lives if its "calories needed" are less than the sum of the calories provided by other species it eats (other consumers or providers).
Furthermore, the species' "calories provided" must be higher than the sum of the calories needed by other species that eat it.
The Main Challenges of the Ecosystem Building Mini-Game
Ecosystem creation is first of all a decision-making game.
You get all the information you need to deliver correct decisions so there's no uncertainty or inaccurate details.
The problem is that you have a vast amount of information to absorb, calculate, analyze, and prioritize . This includes the specs of 39 species, the terrain specs of each location, and eating rules.
Some of the information is irrelevant and is there to distract you or tempt you to make assumptions . In this mini-game, you must not make any assumptions and you don't need to have any environmental, ecological, or zoological knowledge.
So, your ability to make quick and accurate calculations and ignore irrelevant data will have a great impact on your performance.
The preparation course we recommend on this page includes a replica of McKinsey's Ecosystem Building game. It enables you to practice using a like-for-like game experience and learn about every single rule, move, and item in detail. Plus, you’ll master calculation methods and other tactics to ensure the food chain survives in your chosen location.
Redrock Study
The second mini-game you'll most likely encounter is Redrock Study.
In the game's storyline, your task is to analyze the species inhabiting an island, which includes wolves and elks. The objective of your analysis is to formulate predictions and conduct various calculations , specifically focusing on percentages, by examining data on the evolution of the animal population.
The game has 4 sections:
- Investigation You will be presented with a written text that includes tables and graphs. Your task is to sort information and gather valuable data for the following test sections.
- Analysis You will be presented with 3 or 4 math problems ; each is separated into two parts. You will be given a calculator and a Research Journal to gather information relevant to the questions.
- Report You will be presented with two types of questions -
- 5 written questions regarding your findings in the analysis section
- 1 visual question in which you will need to choose a graph and use it to show what you found in the analysis.
- Cases You will be presented with 6 to 10 questions that are unrelated to the analysis you did so far.
You will have 35 minutes to complete all four sections , with a short, non-timed break before each one.
Alternative Mini-Games
As of 2024, the Ecosystem Building game is constant, but the second mini-game may vary in rare cases. This means that there's a slight chance you won't get the Plant Defense mini-game, but rather one of the three we show below.
Disaster Management
In the Disaster Management game, you have to identify what type of natural disaster has happened to an animal population in an ecosystem.
Then, based on the data and information given, you need to choose a different location that will ensure the survival of the ecosystem.
The Disaster Management mini-game has only one objective - the sustainability of the ecosystem, similar to the Ecosystem Building mini-game.
Disease Management
In the Disease Management mini-game, you have to identify patterns of a disease within an ecosystem and predict who will be infected next. You can then use the information given about each species to help you solve the problem.
Migration Management
Migration Management is a turn-based puzzle game. The candidate must direct the migration of 50 animals while helping them arrive at their destination with minimal casualties and with a pre-determined amount of resources.
- Plant Defense
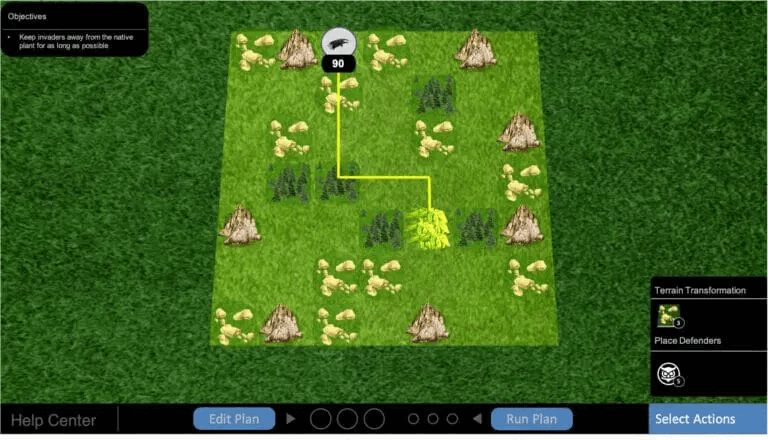
Plant Defense is a turn-based mini-game (similar to popular Tower Defense games). Your main objective is to defend a native plant that's located at the center of a 10x10, 10x14, or 12x12 grid from invader species, using defensive resources for as many turns as possible .
This mini-game consists of three maps, and each map is divided into two - the planning phase and the fast-forward phase. McKinsey recommends allocating 12 minutes per map, which makes it 36 minutes in total.
The 36-minute time limit is not fixed though, as it depends on how long it took you to finish the first mini-game, Ecosystem Building.
Many candidates mention that the Plant Defense game is more challenging than the Ecosystem creation. So, keep that in mind while taking the first one and plan your time wisely .
Now, let's take a closer look at the different elements and resources of this mini-game:
Your base is the native plant that you have to defend from invaders at all costs. Once an invader reaches the base, you lose the game.
Note that eventually, everyone loses, and you can't hold your base forever. But the more turns you manage to survive, the better .
There are two types of invaders in the game - Groundhog and Fox. Their movements on the map are the same, and the only difference between them is the terrain type that holds them back (more on terrains below).
Once an invader appears on your map, it will choose the shortest path to reach your base plant. This path will be shown as a yellow arrow .
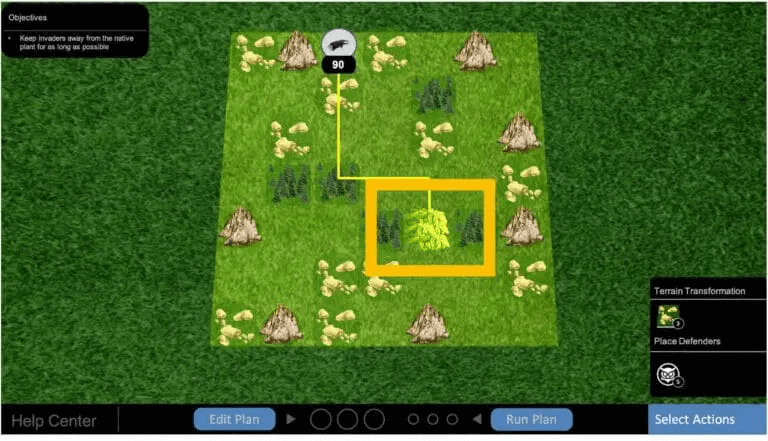
There are three types of terrains in the game:
- Forest : Slows down the Groundhog for one turn
- Rocky : Slows down the Fox for one turn
- Cliff : Blocks both the Fox and the Groundhog from passing this square
Each terrain holds one grid on the map, and you cannot place terrain on a grid that already has another terrain or a defender on it (more on defenders below).
As opposed to terrains, defenders don't just slow down or block an invader, they eliminate it for good.
There are several defenders you can use in the game: Bobcat, Falcon, Wolf, Python, and Coyote.
Note that you won't see all of the defenders at once.
Each defender has two important specs you must take into account:
Range : Each defender can cover a pre-determined number of grids on the map. For example, a Python can cover only one grid, while a Falcon can cover as many as 13 grids.
Damage : Each defender can cause specific forms of damage to an invader's population. When an invader attacks, you'll be able to see its population number and the damage that your defender can cause him. A Wolf, for example, has a damaging impact of 60, while a Falcon has only 20.
The Main Challenges of the Plant Defense Mini-Game
In this mini-game, you have to make decisions based on limited information and face unexpected events (like new invaders from any direction). Also, you must achieve two simultaneous objectives - survive each of the turns separately and for as long as possible.
This is the complete opposite of the Ecosystem Building game, in which you have all the data in front of you, and you have just one objective.
Two things that can help you overcome these challenges are (1) preparing for the unexpected events that will happen during the game and (2) planning low-risk solutions based on your resources (terrains and defenders).
The prep course that we recommend on this page has the closest simulation possible to the actual Plant Defense game. It has the same gameplay, invaders, and resources, and it's based on the same algorithm that appears in the McKinsey Problem Solving Game. This will enable you to learn the most effective tactics to ensure your base plant survives as many turns as possible.
How to Beat the McKinsey Problem Solving Game?
The proven way to beat the McKinsey PSG is by properly preparing beforehand.
There's no way around it. That’s because the mini-games include an immense amount of information, rules, and patterns you must master . And they require you to use tactics and strategies that are not obvious and take time to plan and execute.
All of that is under great time pressure and the high stakes of possibly failing it and losing an opportunity to work at McKinsey.
Now, there are a few practice options you can use to get a better understanding of the PSG and improve your chances of passing it, with the PSG Interactive Simulation being the most accurate one.
McKinsey Problem Solving Game Practice Options
PSG Interactive Simulation
The PSG Secrets simulation is an interactive platform that includes accurate practice for every part of McKinsey’s PSG. It mirrors what the actual game scenarios look like, what each button does, how the logic of the games works, how it generates the data, and more.
It has a full simulation option (two mini-games, 70 minutes), which includes:
- A full video course in 24 videos and 2h30m of content on Ecosystem, Redrock, and Plant Defense
- 2 excel solvers for the Ecosystem Game
- 10 Redrock test drills specifically for the case section
- 152 page-pdf guide
- 60-day money-back guarantee.
Tips to Improve Your Performance on the McKinsey Problem Solving Game
Here are several specific tips to help improve your overall performance on the test as well as tips to avoid any disturbances that could hurt your score:
#1 Sharpen Your Mental Math Abilities
The ability to make fast and accurate calculations can help a lot in this Problem-Solving Game. That’s because one wrong calculation might ruin your carefully built Ecosystem or cause an invader to reach your Native Plant.
There are several free apps and sites, like the renowned Khan Academy , that can help you improve your math skills quickly.
#2 Learn Fast Reading Skills
Mckinsey’s PSG requires you to absorb and analyze a tremendous amount of information under strict time constraints.
Fast reading skills come in handy in this test and can help reduce the amount of time needed to understand the numerous guidelines of the mini-games.
There are certain apps and browser extensions that allow you to practice this important skill , even on the go.
#3 Focus Only on What Matters
Don't get nervous when you first see the immense amount of data on the mini-games. That’s because a lot of the data is irrelevant, and you’ll be only using some particular parameters .
For example, in the Ecosystem game, you’ll only have to use specific species and terrain specs for your calculations, while ignoring others that are there only for distraction.
In the complete PSG Simulation Practice , you’ll see how to remove as much as 70% of the irrelevant data and remain just with the information that matters.
#4 Ignore Outside Information
While taking the assessment, especially the Ecosystem game, try to ignore any outside knowledge and information.
For example, if you’ve learned biology or zoology and you see that your food-eating rules don’t seem logical but the numbers are correct, always go with the numbers .
If you start to rely on previous knowledge, you might get confused and mess up your progress in the game.
#5 Learn to Solve Problems Like a Consultant
The PSG measures your consulting traits and compares them to a model McKinsey consultant.
That’s why learning to think and solve problems like a real consultant can help you pass this assessment.
Two main problem-solving skills you should practice are decision-making in fully controlled situations and with limited information.
Both of these skills can be trained using complex strategy games (examples are mentioned above) as well as practicing with the full PSG interactive simulation .
#6 Cut Down on Calculation Time Using Microsoft Excel
Mental math is an effective way to make calculations in the mini-games.
But as you’re only human, it’s not error-free. That’s why using a calculation tool, such as Excel formulas, can be a great way to make super fast and accurate calculations.
You can use it to gather all the relevant data, arrange it with columns and formulas (even in advance!), and turn the whole process into a no-brainer.
That said, you’ll need to use another monitor (preferably with a different browser) or another laptop since the assessment’s platform will take over your entire screen.
#7 Prep Your Hardware and Internet Connection
The last thing you want during the assessment is a “blue screen of death.”

It may happen if your hardware is not strong enough, since the McKinsey PSG is pretty demanding in its system requirements.
Any computer that is more than five years old or without an HD screen will likely encounter lags and performance drops.
Also, you must have a fast and stable internet connection. If you get disconnected in the middle of the test, you might need to start all over again or even reschedule for another testing date.
The PSG scores are divided into two types -
- Product score - the final outcome of your performance
- Process score - the efficiency (time and number of clicks) of your performance
If you get the PSG Practice Simulation , you’ll have a mock grading system that monitors your results and behavioral patterns.
This will allow you to track your progress while you practice for the test and see which areas demand improvement.
Why Did McKinsey Develop the Problem-Solving Game?
McKinsey created the Problem-Solving Game as an unbiased way to identify candidates from around the globe with strong cognitive abilities. The former assessment, Problem Solving Test (PST), was less challenging for candidates who were familiar with standardized tests, such as SAT and GMAT, or used the numerous mock tests found online.
The PSG, on the other hand, is supposedly crack-proof. That's because it takes into account the approach you use to solve the problems and not just the final solution. This seemingly removes any lucky guessing and shortcut techniques that were common on the McKinsey PST.
While on the PST you had just your final score, on the PSG your score is comprised of dozens of scoring criteria apart from your final result , including mouse movement, keystrokes, and clicks.
McKinsey can analyze these factors for every recorded candidate, which allows them to compare candidates more fairly.
What Does Imbellus Mean?
Imbellus is a company that creates immersive simulation-based assessments to assess cognitive processes. To develop a new testing format for the McKinsey recruitment process, they've teamed up with McKinsey consultants and UCLA Cresst psychologists.
In 2020, Imbellus was purchased by Roblox , an online gaming platform, to help sharpen its recruitment practices.
This was an in-depth prep guide for the McKinsey Problem Solving Game. It gave you an overview of the different mini-games, explained their main challenges, and offered some useful solving tips.
Additionally, you saw the best ways to prepare for the assessment, when the PSG Practice Simulation being the most realistic and accurate one.
Other JobTestPrep Assessments
- Free SHL questions
- What's on This Page
- What Is the McKinsey PSG?
- How to Beat the Games?
- Best Practice Options
- 7 Tips to Boost Your Performance

- Numerical Reasoning
- Verbal Reasoning
- In-Tray Exercises
- E-Tray Exercises
- What To Expect
- Group Exercises
- Presentations
- Assessment Centre Tips
- How To Prepare For An Interview
- How To Behave During An Interview
- Hope To Cope With Nerves
- PwC Assessment Centre
- KPMG Assessment Centre
- EY Assessment Centre
- BDO Assessment Centre & Online Ability Tests Guide
- IBM Assessment Centre & Study Guide
- GSK Assessment Centre
- Mastering the Teach First Assessment Centre 2024: Ultimate Prep Guide
- MI5 Assessment Centre
- Network Rail Assessment Centre
- Fast Stream Assessment Centre
- PSNI Assessment Centre
- Psychometric Tests
- Numerical Reasoning Test
- Verbal Reasoning Test
- Logical Reasoning Test
- Abstract Reasoning Test
- Inductive Reasoning Test
- Watson-Glaser Test
- How to Prepare for UKCAT Exam? – A Definitive Preparation Guide with Practice Tests, Tips & Tricks & More
- Mastering Mechanical Comprehension Tests: Tips, Practice, & Insights
- Diagrammatic Reasoning
- Spatial Reasoning Tests
- Numeracy Skills Test (QTS)
- Literacy Skills Test (QTS)
- SHL Numerical Test: 5 Essential Tips for Guaranteed Success
- RAF Aptitude Test
- Army BARB Test
- How to Prepare for Prison Officer Selection Test?
- Network Rail Online Tests
- PSNI Initial Selection Test
- Personality Tests

How to Successfully Pass the McKinsey Problem Solving Test?
If you would like to start a career in strategic consultancy, McKinsey & Company is one of the best options. This company has over 14, 000 employees in offices located throughout the world. is one of the top management consulting firms.
So, getting in can be very competitive. More than 80% of applicants are rejected by McKinsey based on their online aptitude tests. That is why it is important that you do your best at every step of the recruitment process.
In this article, we cover how to successfully pass McKinsey’s problem-solving test, online aptitude tests, the selection process, assessment center, and interviews.
Table of Contents
About McKinsey PST
The McKinsey Problem Solving Test (McKinsey PST) aims to test your logical thinking and problem-solving skills. It consists of a math computation, data interpretation, and critical reasoning test that are used by McKinsey to select the best candidates. The successful candidates will move onto the first round of case interviews.
The PST test is what differentiates the McKinsey recruiting process from its competitors. Another distinctive element is the Personal Experience Interview, or PEI. The McKinsey PST is one of the most challenging tests that you will come across in your life. It tests a wide range of skills and pushes you to work under tight time constraints.
McKinsey uses a PST because to be successful in consulting, there is a specific set of numerical computation and critical thinking skills that are required. It tests skills that you will be using on a daily basis as a consultant.
McKinsey PST Format
The McKinsey Problem Solving Test consists of 26 multiple-choice questions that need to be answered on paper. You have a 60 minute time limit. That gives you about two minutes per question. Most candidates fail because they run out of time.
The 26 questions are divided between three business cases. Each case study assesses how you would perform in the different stages of a consulting project: client interaction, problem solving, analytical work, problem definition, and implementation.
Every case study is based on real issues that consultants will be faced with in the field. This includes issues like profitability, market entry, or operational development.
In certain offices, non-native English speakers are given an extra 10 to 15 minutes to complete the test. You can find out from your McKinsey HR representative if you are allowed this additional time or not. No business knowledge is necessary to take the test. However, being familiar with common business knowledge terms is helpful.
You can use a pencil, a pen, and paper. You are not allowed to use a calculator or any commuting device during the PST test. You need to ensure that you have developed and practised the necessary skillset, especially time-saving skills.
McKinsey PST Questions
In the McKinsey Problem Solving Test, you will see a graph, chart, or table containing numerical data. This diagram will be followed by descriptive text about a company or industry.
The McKinsey PST test consists of 40% math word problems, 30% data interpretation, and 30% reading comprehension. You will be required to answer four to five questions that refer to the diagram. The two most challenging questions are math word problems and data interpretation.
McKinsey Math Word Problems
In math word problems, you will be given data in table X and required to calculate A, B, or C. These calculations may be profit margins. It may be calculating growth rates or the difference in sales from 2021 to 2019 for three different companies.
The point of these math word problems is to provide you with raw data presented in a text paragraph and assess whether you can figure out the math equation required to solve the problem.
Usually, the actual math word problem isn’t difficult to solve. It’s just addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, or growth rate calculations. The real challenge with the math word problems is time. The most common reason for errors in a math word problem is misunderstanding, misreading, or misinterpreting the data presented or the question being asked.
McKinsey Data Interpretation
The other tough PST test question is data interpretation. You will be presented with a chart or table with data and required to determine which variation of the question is correct. Some variations include: definitively correct, could be correct but you can’t be 100% certain, and definitely wrong.
You will need to use math to answer these questions, but they are not as computation-intensive as math word problems. They focus on assessing your logic and critical reasoning skills. You need to be able to examine the data and differentiate between a factual conclusion and a hypothesis suggested.
One common challenge is to quickly find information about different topics.

McKinsey Reading Comprehension
The last part of the McKinsey PST is a reading comprehension test. This section tests your ability to draw a conclusion based on a paragraph of text. This is similar to data interpretation, but it does not involve math. They test your ability to understand a situation based on the information provided. And then select the statement that is the most relevant.
You will encounter three types of answers: false conclusions, true conclusions, and unproven conclusions. With false conclusions, the answer will either be wrong or false. Even if the conclusion seems rational, the outcome may be incorrect.
True conclusions are statements that are logical and draw the correct conclusion. Unproven conclusions are those where the logic may be correct and the conclusion may seem rational. But they cannot be completely supported by the facts presented in the diagram or text.
McKinsey PST Passing Strategies
- First skim through the questions to understand what is being asked of you, and then read the table or chart with the data. This allows you to see what you should be paying attention to while you examine the data or read the text.
- Answer ALL questions on the PST test as there are no penalties for incorrect answers. If you are running out of time, it is better to guess an answer than leave it blank.
- Fill in the answer sheet as you progress. This may be obvious, but under stress, some candidates forget to note down their answers throughout the test.
- Carefully read through the questions and text descriptions.
- Provide what the questions are literally asking.
- If you need to sharpen your math computation skills, ensure you practise your math accuracy and speed. You won’t have enough time to double check all your computations. The more certain you are about your math skills, the more time you will have to answer all the other questions.
- For the data interpretation questions, be cautious of the multiple choice questions that seem consistent with the data but are not 100% supported by the data. The best way to tackle these questions is to instantly eliminate options that are obviously wrong. Then carefully examine the other options.
- In the data interpretation questions, you need to ask yourself whether the conclusion is correct under all scenarios. Although the conclusion may be true under the most common scenario, it doesn’t mean it is true under every scenario.
- Always remember that the conclusion that is true most of the time is not the same as the conclusion that is true every time.
- Wear a watch to stay track of time. Don’t assume that every testing room has a clock.
How to Prepare for the McKinsey PST

There are three different ways you can prepare for the McKinsey Problem Solving Test. JobTestPrep is a platform that offers resources, professional guides, and practise tests that can help you successfully pass the McKinsey PST.
The first prep tip for the PST is to practise math computations. You need to practise the accuracy and speed of your math. The test is timed, so you need to be skilled in arithmetic. Remember, the more you practice, the better you perform.
Use the selection technique to help you select calculations beforehand that are important to finding the answer.
The anchoring technique is another great time management method. When you are searching for the highest value among several potential answers, first calculate the first answer and then use that value as a benchmark as you work through others.
The second prep tip is to practise interpreting data. Be prepared to answer multi-paragraph stories with more than one diagram. Every chart is followed by four or five questions. You need to polish your ability to interpret data.
Another pro tip is to master quick percentage calculations. Growth rates and percentages are very common in the McKinsey PST test, but they require a lot of time to calculate.
Here are some useful time management tips. Firstly, with positive growth rates, the compound rate is generally underestimated. For example, we estimate 30%, but the real figure is actually 31%. On the other hand, with negative growth rates, this method will overestimate the compound value.
Another point to note is that the bigger the magnitude of the annual growth rate and the bigger the number of years for which it is applied, the less accurate this method becomes. The final prep tip is to take McKinsey PST practise tests. This will help show you what to expect on the actual test. You will find useful practise tests available on JobTestPrep .
McKinsey PST Score
McKinsey does not have an exact cut-off score for its PST. But according to research, the best estimate is that the PST has a cut-off score of 70%. This means that you need to get at least 19 out of the 26 questions correct.
Your success depends solely on your score. It does not depend on how well others perform on the test. If all the candidates in your PST session score above the cut-off score, then they will all go to the next round of interviews.
Most candidates think that scoring 70% will be sufficient to get them into the first round of interviews. However, scoring even higher can increase your chances of being hired by McKinsey.
In the final round, if you performed just as well as another candidate but only one position is available, McKinsey will choose the person who scored higher on the PST. So aim for 90% to set yourself apart from the other candidates.
McKinsey Aptitude Tests
You will need to pass three other aptitude tests, other than the McKinsey Problem Solving Test, to be a successful candidate. These are the McKinsey numerical reasoning test, verbal reasoning test, and the Excel test.
McKinsey Numerical Reasoning Test
The SHL numerical reasoning test aims to examine your arithmetic skills and ability to interpret data from diagrams. It tests your ability to examine an unfamiliar text passage and its data. You will need to solve basic math problems.
The challenge does not lie in the questions asked, but rather in the stress and time pressure. When taking the numerical reasoning test, you will only have a minute to read the question, analyse the data, and do the necessary calculations.
The most effective way to prepare for this numerical test is to take practise tests. These practise test questions will help show you the types of questions you will encounter on the actual test.
McKinsey Verbal Reasoning Test
McKinsey’s verbal reasoning test aims to assess how well you can extract information from an unfamiliar passage of text. And then use this information to determine whether the statements that follow are true, false, or impossible to say.
The verbal reasoning test evaluates your comprehension level.
The McKinsey verbal reasoning test can be more difficult for non-native English speakers. The most effective preparation tip to pass a verbal reasoning test is to take practise tests. These verbal reasoning practise test questions will help you determine how texts are created and questions are asked.
McKinsey Excel Test

The McKinsey Excel Test is another important test that you will encounter during the examination stage of your interview process.
Regardless of what position or role you hold, you will most likely be working with Excel. That is why a lot of companies have an exam during the assessment stage. In Excel practise tests, you will find graphs and tables that display data. You will be required to answer the questions in a multiple-choice format.
McKinsey Selection Process
The McKinsey interview process can be nerve-wracking with its intensive application process. However, equipped with the right preparation, you are likely to impress McKinsey’s upper management. We have included a breakdown of what you can expect during your selection process at McKinsey.
McKinsey CV Submission
Most McKinsey applicants apply online for vacant positions directly on the McKinsey website. You will find an online application form that you can fill in and attach your CV to. You will find a list of current available positions and their locations.
McKinsey Online Assessment Tests
After completing and submitting your McKinsey online application form, you will be invited to take some of the McKinsey aptitude tests. These include numerical reasoning, verbal reasoning, Excel, and problem-solving tests.
Pre-Employment Telephone Screening
During the telephone conversation, you will be required to answer McKinsey behavioural interview questions. These questions are similar to situational judgement test questions. You will be given a scenario and asked particular questions about what you will do in that situation.
McKinsey Job Interview
The last stage in the McKinsey selection process is the in-person interview. You need to know a little about the company and show interest. The interview questions are best answered using the STAR (situation, task, action, and result) method. This is a concise way of answering and allows you to outshine your competition.
McKinsey Assessment Centre
At the McKinsey Assessment Centre event , you will attend presentations about the company.
You may be asked to participate in presentation exercises that assess your verbal and non-verbal communication skills. You will be assessed on your body language and tone to see how well you can cope with delivering professional presentations. A few tips are to stand straight, make eye contact with the audience, and don’t speak too fast.
At the McKinsey Assessment Centre, you may be invited to join a group exercise. This evaluates your ability to communicate and work together as a team to reach conclusions. You will be assessed in this exercise. So, demonstrate your strengths and share your ideas.
Show that you are open to building on someone else’s input and able to persuade others towards your options. We advise you to remain calm and speak with confidence and clarity.
You will also engage in role-playing games. These are games where you are allocated 20 minutes to work in a pair and analyse information. You and your partner will need to prepare your response.
In the second part, your interviewer will play the role of a client, and you will be the McKinsey representative. You need to demonstrate your teamwork, negotiation skills, and critical thinking.
You may also have to take further assessment tests, participate in group interviews, and have a one-on-one direct interview.
McKinsey Advanced Professional Degree Interviews

The McKinsey Advanced Professional Degree (APD) Interview consists of three interviews. The first two are 45-minute, one-on-one interviews. Both of these interviews will include a personal experience interview (PEI) and a McKinsey case interview to assess your problem-solving skills .
In the personal experience interview, you will be asked questions about the specific role you have experience in and how you contributed to the success of the company. You will also be asked questions that focus on your motivations. These are generally CV-based questions that are competency-based.
In the McKinsey case interview, you will need to answer questions based on a business case study. You need to demonstrate how you interpret the information presented, select key elements, and back your reasoning. In the end, you need to arrive at a conclusion and be able to back your decision.
The final interview will happen in the specific office you have applied to. The format of the interview varies depending on the office, so you will receive detailed information before your assessment day.
During this interview, ask your interviewer about their own experiences within McKinsey and their career path. They want to see how interested you are in McKinsey.
Who Has to Take the McKinsey PST?
Not every candidate is required to take the McKinsey Problem Solving Test. People who have extensive experience and those hired from top-tier business schools generally don’t have to take the test.
However, most people who are applying for an entry-level business analyst role will be required to take and successfully pass the McKinsey PST test to be considered.
If you are uncertain about whether you need to take the PST, you should assume that you will. You can ask the HR team at the office you are applying to for confirmation.
What Is the McKinsey PST Success Rate?
According to surveys, the common PST pass rate is 33%. The majority of candidates fail because they did not work efficiently or effectively manage their time.
One of the main contributors to failure is that candidates run out of time at the end of the test to fill in the PST answer sheet.
The McKinsey PST is a skills test that you should practise for beforehand. It is not an assessment where you can walk in and use your natural intelligence to pass. You need to be aware of the strategies and time-saving techniques before you approach the test.
McKinsey PST vs. GMAT
If you’ve taken a GMAT before, then this point can be helpful. Most candidates who have prepared for and taken the GMAT believe that the PST is the same test with a different name.
They believe the tests are very similar. However, even though the tests share a similar format, they are very different. They both require you to have good math skills. But the PST requires a less academic style of math. In the PST, you need to estimate and prioritise calculations.
You need to treat the PST as an entirely separate test and prepare for it accordingly.
Final Thoughts
If you want to get your dream job at McKinsey, then you need to prepare for the selection process. As we highlighted earlier, there are a few assessment tests and interviews that you will need to pass to be a successful candidate. You can get the practise you need with the resources available on JobTestPrep.
Sarah is an accomplished educator, researcher and author in the field of testing and assessment. She has worked with various educational institutions and organisations to develop innovative evaluation methods and enhance student learning. Sarah has published numerous articles and books on assessment and learning. Her passion for promoting equity and fairness in the education system fuels her commitment to sharing insights and best practices with educators and policymakers around the world.

Visit our Contact Page
AssessmentCentreHQ Unit 57 Minerva Ave, Chester, CH1 4QL
- NUMERICAL REASONING
- VERBAL REASONING
- ASSESSMENT CENTRES
- APTITUDE TESTS
- PRIVACY POLICY
Featured On

© Copyright 2023 AssessmentCentreHQ – All Rights Reserved
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

McKinsey Problem Solving Test

Related Papers
Abhinandan dole
Journal of Tourism History, 1 (2009), 49-66
Gordon Pirie
Few air travellers along Britain’s Empire air routes in the 1930s were intentional holidaymakers. Survey data, and passenger profiles culled from other contemporary sources, show that most commercial airline passengers flew on work assignment. High fares deterred leisure travel by air, but air passengers flying long-distance on paid business or public service errands incidentally became tourists by virtue of the slow, low altitude, daylight flights that stopped frequently for refuelling: infant aeronautical technology and air travel economics created tourism of sorts along new routes. Sightseeing from the air and on the ground was integral to Empire air journeys. Unpredictability added to the adventure value of flying; the novelty of aerial views added to its scenic value. Airline publicity, documentary films, and passenger accounts and diaries, stressed this in-flight and en-route experience: flying was a new way of seeing and experiencing foreign and historic places and landscapes, and for spotting game. Flying was not just a way of reaching a destination.
Felix Faulhaber
Markus Schuckert
Tara Duncan
The Travel Catering Research Centre (TCRC) is only one of its kind in the world. It is supported by the International Flight Catering Association (IFCA). Founded in 2002, the Centre aims to generate and disseminate knowledge to academics and industrialists in support of ...
European Physical Journal C
Asian Journal of Management Cases
Rizal Ahmad
Journal of Air Transport Management
David Warnock-Smith
HRidoy Khan
Andy Theodore
RELATED PAPERS
Climate change and aviation: Issues, challenges and solutions
Paul Upham , Stefan Gössling , Alice Larkin (aka Bows)
Richard Farr
Ioulia Poulaki , Eleni Kitrinou
Ajoy Rajeev
romano pagliari
Gui Lohmann
Journal of Air Transport Studies
Michelle Galvão
Nikolaos Iason Koufodontis , Eleftherios Katarelos
Professor Andreas Papatheodorou
jason jasmin
Thúy Ngọc Trần
Tio Rico Mc Pato
Cláudia Ribeiro de Almeida
Sireesh PALLIKONDA
Aviation Systems
Andreas Wittmer
Jeremy Toner , Abigail Bristow
Professor Dimitrios Buhalis
alaa massoud
Matin Bagherpour
Amitabh Upadhya
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Resources >
Mckinsey approach to problem solving.
McKinsey and Company is recognized for its rigorous approach to problem solving. They train their consultants on their seven-step process that anyone can learn.
This resource guides you through that process, largely informed by the McKinsey Staff Paper 66. It also includes a PowerPoint Toolkit with slide templates of each step of the process that you can download and customize for your own use.
You can click any section to go directly there:
Overview of the McKinsey Approach to Problem Solving
Problem solving process.
- Problem Definition & Problem Statement Worksheet
Stakeholder Analysis Worksheet
Hypothesis trees, issue trees, analyses and workplan, synthesize findings, craft recommendations, distinctiveness practices, harness the power of collaboration, sources and additional reading, download the umbrex toolkit on the mckinsey approach to problem solving.
Problem solving — finding the optimal solution to a given business opportunity or challenge — is the very heart of how consultants create client impact, and considered the most important skill for success at McKinsey.
The characteristic “McKinsey method” of problem solving is a structured, inductive approach that can be used to solve any problem. Using this standardized process saves us from reinventing the problem-solving wheel, and allows for greater focus on distinctiveness in the solution. Every new McKinsey associate must learn this method on his or her first day with the firm.
There are four fundamental disciplines of the McKinsey method:
1. Problem definition
A thorough understanding and crisp definition of the problem.
2. The problem-solving process
Structuring the problem, prioritizing the issues, planning analyses, conducting analyses, synthesizing findings, and developing recommendations.
3. Distinctiveness practices
Constructing alternative perspectives; identifying relationships; distilling the essence of an issue, analysis, or recommendation; and staying ahead of others in the problem-solving process.
4. Collaboratio n
Actively seeking out client, customer, and supplier perspectives, as well as internal and external expert insight and knowledge.
Once the problem has been defined, the problem-solving process proceeds with a series of steps:
- Structure the problem
- Prioritize the issues
- Plan analyses
- Conduct analyses
- Synthesize findings
- Develop recommendations
Not all problems require strict adherence to the process. Some steps may be truncated, such as when specific knowledge or analogies from other industries make it possible to construct hypotheses and associated workplans earlier than their formal place in the process. Nonetheless, it remains important to be capable of executing every step in the basic process.
When confronted with a new and complex problem, this process establishes a path to defining and disaggregating the problem in a way that will allow the team to move to a solution. The process also ensures nothing is missed and concentrates efforts on the highest-impact areas. Adhering to the process gives the client clear steps to follow, building confidence, credibility, and long-term capability.
Problem Definition & Problem Statement Worksheet
The most important step in your entire project is to first carefully define the problem. The problem definition will serve the guide all of the team’s work, so it is critical to ensure that all key stakeholders agree that it is the right problem to be solving.
Problem Statement Worksheet
This is a helpful tool to use to clearly define the problem. There are often dozens of issues that a team could focus on, and it is often not obvious how to define the problem. In any real-life situation, there are many possible problem statements. Your choice of problem statement will serve to constrain the range of possible solutions.
- Use a question . The problem statement should be phrased as a question, such that the answer will be the solution. Make the question SMART: specific, measurable, action-oriented, relevant, and time-bound. Example: “How can XYZ Bank close the $100 million profitability gap in two years?”
- Context . What are the internal and external situations and complications facing the client, such as industry trends, relative position within the industry, capability gaps, financial flexibility, and so on?
- Success criteria . Understand how the client and the team define success and failure. In addition to any quantitative measures identified in the basic question, identify other important quantitative or qualitative measures of success, including timing of impact, visibility of improvement, client capability building required, necessary mindset shifts, and so on.
- Scope and constraints . Scope most commonly covers the markets or segments of interest, whereas constraints govern restrictions on the nature of solutions within those markets or segments.
- Stakeholders . Explore who really makes the decisions — who decides, who can help, and who can block.
- Key sources of insight . What best-practice expertise, knowledge, and engagement approaches already exist? What knowledge from the client, suppliers, and customers needs to be accessed? Be as specific as possible: who, what, when, how, and why.
The problem definition should not be vague, without clear measures of success. Rather, it should be a SMART definition:
- Action-oriented
Example situation – A family on Friday evening
Scenario: A mother, a father, and their two teenage children have all arrived home on a Friday at 6 p.m. The family has not prepared dinner for Friday evening. The daughter has lacrosse practice on Saturday and an essay to write for English class due on Monday. The son has theatre rehearsal on both Saturday and Sunday and will need one parent to drive him to the high school both days, though he can get a ride home with a friend. The family dog, a poodle, must be taken to the groomer on Saturday morning. The mother will need to spend time this weekend working on assignments for her finance class she is taking as part of her Executive MBA. The father plans to go on a 100-mile bike ride, which he can do either Saturday or Sunday. The family has two cars, but one is at the body shop. They are trying to save money to pay for an addition to their house.
What is the problem definition?
A statement of facts does not focus the problem solving:
It is 6 p.m. The family has not made plans for dinner, and they are hungry.
A question guides the team towards a solution:
1. What should the family do for dinner on Friday night?
2. Should the family cook dinner or order delivery?
3. What should the family cook for dinner?
4. What should the family cook for dinner that will not require spending more than $40 on groceries?
5. To cook dinner, what do they need to pick up from the supermarket?
6. How can the family prepare dinner within the next hour using ingredients they already have in the house?
In completing the Problem Statement Worksheet, you are prompted to define the key stakeholders.
As you become involved in the problem-solving process, you should expand the question of key stakeholders to include what the team wants from them and what they want from the team, their values and motivations (helpful and unhelpful), and the communications mechanisms that will be most effective for each of them.
Using the Stakeholder Analysis Worksheet allows you to comprehensively identify:
- Stakeholders
- What you need from them
- Where they are
- What they need from you
The two most helpful techniques for rigorously structuring any problem are hypothesis trees and issue trees. Each of these techniques disaggregates the primary question into a cascade of issues or hypotheses that, when addressed, will together answer the primary question.
A hypothesis tree might break down the same question into two or more hypotheses.
Example: Alpha Manufacturing, Inc.
Problem Statement: How can Alpha increase EBITDA by $13M (to $50M) by 2025?
The hypotheses might be:
- Alpha can add $125M revenues by expanding to new customers, adding $8M of EBITDA
- Alpha can reduce costs to improve EBITDA by $5M
These hypotheses will be further disaggregated into subsidiary hypotheses at the next level of the tree.
The aim at this stage is to structure the problem into discrete, mutually exclusive pieces that are small enough to yield to analysis and that, taken together, are collectively exhaustive.
Articulating the problem as hypotheses, rather than issues, is the preferred approach because it leads to a more focused analysis of the problem. Questions to ask include:
- Is it testable – can you prove or disprove it?
- It is open to debate? If it cannot be wrong, it is simply a statement of fact and unlikely to produce keen insight.
- If you reversed your hypothesis – literally, hypothesized that the exact opposite were true – would you care about the difference it would make to your overall logic?
- If you shared your hypothesis with the CEO, would it sound naive or obvious?
- Does it point directly to an action or actions that the client might take?
Quickly developing a powerful hypothesis tree enables us to develop solutions more rapidly that will have real impact. This can sometimes seem premature to clients, who might find the “solution” reached too quickly and want to see the analysis behind it.
Take care to explain the approach (most important, that a hypothesis is not an answer) and its benefits (that a good hypothesis is the basis of a proven means of successful problem solving and avoids “boiling the ocean”).
Often, the team has insufficient knowledge to build a complete hypothesis tree at the start of an engagement. In these cases, it is best to begin by structuring the problem using an issue tree.
An issue tree is best set out as a series of open questions in sentence form. For example, “How can the client minimize its tax burden?” is more useful than “Tax.” Open questions – those that begin with what, how, or why– produce deeper insights than closed ones. In some cases, an issue tree can be sharpened by toggling between issue and hypothesis – working forward from an issue to identify the hypothesis, and back from the hypothesis to sharpen the relevant open question.
Once the problem has been structured, the next step is to prioritize the issues or hypotheses on which the team will focus its work. When prioritizing, it is common to use a two-by-two matrix – e.g., a matrix featuring “impact” and “ease of impact” as the two axes.
Applying some of these prioritization criteria will knock out portions of the issue tree altogether. Consider testing the issues against them all, albeit quickly, to help drive the prioritization process.
Once the criteria are defined, prioritizing should be straightforward: Simply map the issues to the framework and focus on those that score highest against the criteria.
As the team conducts analysis and learns more about the problem and the potential solution, make sure to revisit the prioritization matrix so as to remain focused on the highest-priority issues.
The issues might be:
- How can Alpha increase revenue?
- How can Alpha reduce cost?
Each of these issues is then further broken down into deeper insights to solutions.
If the prioritization has been carried out effectively, the team will have clarified the key issues or hypotheses that must be subjected to analysis. The aim of these analyses is to prove the hypotheses true or false, or to develop useful perspectives on each key issue. Now the task is to design an effective and efficient workplan for conducting the analyses.
Transforming the prioritized problem structure into a workplan involves two main tasks:
- Define the blocks of work that need to be undertaken. Articulate as clearly as possible the desired end products and the analysis necessary to produce them, and estimate the resources and time required.
- Sequence the work blocks in a way that matches the available resources to the need to deliver against key engagement milestones (e.g., important meetings, progress reviews), as well as to the overall pacing of the engagement (i.e., weekly or twice-weekly meetings, and so on).
A good workplan will detail the following for each issue or hypothesis: analyses, end products, sources, and timing and responsibility. Developing the workplan takes time; doing it well requires working through the definition of each element of the workplan in a rigorous and methodical fashion.
This is the most difficult element of the problem-solving process. After a period of being immersed in the details, it is crucial to step back and distinguish the important from the merely interesting. Distinctive problem solvers seek the essence of the story that will underpin a crisp recommendation for action.
Although synthesis appears, formally speaking, as the penultimate step in the process, it should happen throughout. Ideally, after you have made almost any analytical progress, you should attempt to articulate the “Day 1” or “Week 1” answer. Continue to synthesize as you go along. This will remind the team of the question you are trying to answer, assist prioritization, highlight the logical links of the emerging solution, and ensure that you have a story ready to articulate at all times during the study.
McKinsey’s primary tool for synthesizing is the pyramid principle. Essentially, this principle asserts that every synthesis should explain a single concept, per the “governing thought.” The supporting ideas in the synthesis form a thought hierarchy proceeding in a logical structure from the most detailed facts to the governing thought, ruthlessly excluding the interesting but irrelevant.
While this hierarchy can be laid out as a tree (like with issue and hypothesis trees), the best problem solvers capture it by creating dot-dash storylines — the Pyramid Structure for Grouping Arguments.
Pyramid Structure for Grouping Arguments
- Focus on action. Articulate the thoughts at each level of the pyramid as declarative sentences, not as topics. For example, “expansion” is a topic; “We need to expand into the European market” is a declarative sentence.
- Use storylines. PowerPoint is poor at highlighting logical connections, therefore is not a good tool for synthesis. A storyline will clarify elements that may be ambiguous in the PowerPoint presentation.
- Keep the emerging storyline visible. Many teams find that posting the storyline or story- board on the team-room wall helps keep the thinking focused. It also helps in bringing the client along.
- Use the situation-complication-resolution structure. The situation is the reason there is action to be taken. The com- plication is why the situation needs thinking through – typically an industry or client challenge. The resolution is the answer.
- Down the pyramid: does each governing thought pose a single question that is answered completely by the group of boxes below it?
- Across: is each level within the pyramid MECE?
- Up: does each group of boxes, taken together, provide one answer – one “so what?” – that is essentially the governing thought above it?
- Test the solution. What would it mean if your hypotheses all came true?
Three Horizons of Engagement Planning
It’s useful to match the workplan to three horizons:
- What is expected at the end of the engagement
- What is expected at key progress reviews
- What is due at daily and/or weekly team meetings
The detail in the workplan will typically be greater for the near term (the next week) than for the long term (the study horizon), especially early in a new engagement when considerable ambiguity about the end state remains.
It is at this point that we address the client’s questions: “What do I do, and how do I do it?” This means not offering actionable recommendations, along with a plan and client commitment for implementation.
The essence of this step is to translate the overall solution into the actions required to deliver sustained impact. A pragmatic action plan should include:
- Relevant initiatives, along with a clear sequence, timing, and mapping of activities required
- Clear owners for each initiative
- Key success factors and the challenges involved in delivering on the initiatives
Crucial questions to ask as you build recommendations for organizational change are:
- Does each person who needs to change (from the CEO to the front line) understand what he or she needs to change and why, and is he or she committed to it?
- Are key leaders and role models throughout the organization personally committed to behaving differently?
- Has the client set in place the necessary formal mechanisms to reinforce the desired change?
- Does the client have the skills and confidence to behave in the desired new way?
Great problem solvers identify unique disruptions and discontinuities, novel insights, and step-out opportunities that lead to truly distinctive impact. This is done by applying a number of practices throughout the problem-solving process to help develop these insights.
Expand: Construct multiple perspectives
Identifying alternative ways of looking at the problem expands the range of possibilities, opens you up to innovative ideas, and allows you to formulate more powerful hypotheses. Questions that help here include:
- What changes if I think from the perspective of a customer, or a supplier, or a frontline employee, or a competitor?
- How have other industries viewed and addressed this same problem?
- What would it mean if the client sought to run the company like a low-cost airline or a cosmetics manufacturer?
Link: Identify relationships
Strong problem solvers discern connections and recognize patterns in two different ways:
- They seek out the ways in which different problem elements – issues, hypotheses, analyses, work elements, findings, answers, and recommendations – relate to one another.
- They use these relationships throughout the basic problem-solving process to identify efficient problem-solving approaches, novel solutions, and more powerful syntheses.
Distill: Find the essence
Cutting through complexity to identify the heart of the problem and its solution is a critical skill.
- Identify the critical problem elements. Are there some issues, approaches, or options that can be eliminated completely because they won’t make a significant difference to the solution?
- Consider how complex the different elements are and how long it will take to complete them. Wherever possible, quickly advance simpler parts of the problem that can inform more complex or time-consuming elements.
Lead: Stay ahead/step back
Without getting ahead of the client, you cannot be distinctive. Paradoxically, to get ahead – and stay ahead – it is often necessary to step back from the problem to validate or revalidate the approach and the solution.
- Spend time thinking one or more steps ahead of the client and team.
- Constantly check and challenge the rigor of the underlying data and analysis.
- Stress-test the whole emerging recommendation
- Challenge the solution against a set of hurdles. Does it satisfy the criteria for success as set out on the Problem Statement Worksheet?
No matter how skilled, knowledgeable, or experienced you are, you will never create the most distinctive solution on your own. The best problem solvers know how to leverage the power of their team, clients, the Firm, and outside parties. Seeking the right expertise at the right time, and leveraging it in the right way, are ultimately how we bring distinctiveness to our work, how we maximize efficiency, and how we learn.
When solving a problem, it is important to ask, “Have I accessed all the sources of insight that are available?” Here are the sources you should consider:
- Your core team
- The client’s suppliers and customers
- Internal experts and knowledge
- External sources of knowledge
- Communications specialists
The key here is to think open, not closed. Opening up to varied sources of data and perspectives furthers our mission to develop truly innovative and distinctive solutions for our clients.
- McKinsey Staff Paper 66 — not published by McKinsey but possibly found through an internet search
- The McKinsey Way , 1999, by Ethan M. Rasiel
For consultants
© Copyright 2023 by Umbrex
Designed by our friends at Filez
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
"The McKinsey Way" Book: A Comprehensive Summary
The McKinsey Way is a book by Ethan M. Rasiel , published in 1999, about what McKinsey&Company does, how McKinsey organizes and what working at McKinsey is like.
20 years after publication, the book still holds significant value, offering timeless insights into the world’s most prestigious management consulting firm: McKinsey&Company. In this article, we’ll provide a detailed summary of all the lessons and insights from The McKinsey way . We’ll re-organize the content and occasionally insert supporting insights to make it more friendly to the reader.
The McKinsey Way has 5 Parts (Sections) with 180 pages:
- Part 1: The Problem Solving Methodology of McKinsey
Part 2: Logistics of how a McKinsey project works
Part 3: insights into the actual works of consultants, part 4: how to excel as a junior consultant, part 5: exit opportunities and life after mckinsey.
Table of Contents
Part 1: The McKinsey problem-solving methodology
The McKinsey problem-solving process can be summarized in the 5 steps: define the problems, find the root cause, use “hypothesis-driven” process, analyze with “issue tree” and propose solutions.
1. Define the problem: Every consulting project revolves around a “problem”. But the “problem” is NOT always the problem!
One symptom may have different causes and we as doctors should never rely on the patient to diagnose.
So, always dig deeper. Get facts. Asks questions. Poke around. Challenge the client… until you find the real problem.
2. Find the root cause: Don’t jump straight to the solution, because you might just be fixing the symptoms. The problem will come back if the root cause is not properly dealt with.
3. Use “hypothesis-driven” process: Make educated guesses of possible root-cause A B C and test with data (a.k.a: facts). We’ll sometimes call this a fact-based process.
4. Break down and structure the analysis with the “ issue tree ” framework: A “hypothesis-driven” process may take forever as there are millions of possible root-causes. We need to test hypotheses from the top to the bottom of the issue tree – a top-down fashion. These issue trees need to be MECE.
5. Propose solutions: When the root causes are identified, consultants propose solutions targeting them directly.
A few notes when using this methodology
No.1: Don’t force the facts to say what you want.
When you propose or work extensively with a running hypothesis , it’s easy to get emotionally attached and turn the problem-solving process into a proving exercise. So keep an open mind and listen to what the data have to say.
No.2: Let the hypothesis come to you naturally.
You will not be able to form an initial hypothesis every time. The clients may not even know their problems. The scope of the project is often large and vague. So, dive in, gather facts, conduct analyses, and the hypotheses will show themselves.
No.3: Don’t reinvent the wheel.
Business problems often resemble each other more than they differ. With suitable techniques, you can apply what you and the firm learned from other projects. After all, one of the values consulting firms bring is to provide the “best practice” – what the top players in the game are doing
No.4: Make sure your solution fits your client.
The most brilliant solution is useless without proper implementation. So know your client’s weaknesses, strengths, and capabilities and tailor your solutions accordingly.
No.5: Be mindful of politics.
There are always politics in projects. Many times, McKinsey gets involved in fights between corporate factions. This creates friction that prevents you from doing your job (late data; rejected interviews, etc.).
So think about how your solutions affect the players in an organization and always build a consensus along the way. If consensus requires you to change your solution, try to compromise. It’s no good devising the ideal solution if the client refuses to accept it.
It’s highly recommended that you refer to the following video for a general view on how McKinsey organizes and a better understanding of the insights from this part.
There is a whole system behind how McKinsey solve a business problem. In this part of The McKinsey Way, Ethan Rasiel describes how the company sells their projects, builds a team and manages its hierarchy.
Selling a study/project
McKinsey typically does not sell. The firm does marketing through a constant stream of books, articles, and scholarly journals like the McKinsey Quarterly, etc. The Firm also invites organize press releases and generates quite some coverage by journalists.
These publications help McKinsey Partners build and nurture a vast network of informal contacts with potential clients. And when a problem arises, the client knows who to contact.
Assembling a team
Almost all projects need a full-time team of consultants. Typically, the process goes like this:
- The ED (a.k.a: Project Owner) signs a contract with the client
- The ED hires an EM from within the McKinsey network, from any offices (a.k.a: Project CEO)
- The EM then hires a group of staff, consisting of BAs (a.k.a: Business Analyst) and Associates.
It’s solely the EM’s responsibility to keep the team happy and functional. McKinsey projects have a few common practices to do so:
- A monthly “team-bonding”.
- A “team temperature” (a.k.a: morale) weekly survey.
The hierarchy
The chain of command in McKinsey is very clear and strict. So is the responsibility funnel. In the ED’s eyes, the EM is responsible for everything in the project. In the EM eyes, the BA is responsible for everything within the assigned workstream. Even when a BA messes things up, to the ED, it’s not the BA’s fault, but the EM.
To provide the best solution for the clients, consultants need tons of skills in preparing presentations; conducting researchs and interviews; presenting the final products in a simple structure; communicating with clients; and brainstorming.
Making presentations, a.k.a: the final deliverable documents
Most consultants spend a big portion of their time making presentations (often in PowerPoint). Utilize the support team! Keep it structured, from top to bottom, from end to end.
Note that there are diminishing marginal returns to your effort, meaning that the last miles toward perfection are always much harder than the beginning. So, resist the temptation to tweak your presentation at the last minute. Try to assess its gains vs those of a good night’s sleep for you and the supporting cast.
Visualizing data with charts and exhibits
We subconsciously admire the people who talk in sophisticated language, so we make complex charts. However, simple and easy-to-follow charts go a long way in consulting. Charts are just a means of getting your messages across, not a Ph.D. project.
Also, don’t forget to:
- Write clear chart titles
- List out units of measurement in all axes
- Mark legends and side notes
- Provide data sources
Managing internal communications
- Over-communication is always better. Keep that information flowing. Make sure that your team is up to date with at least the broad outlines of your workstream and your boss up to date with your team’s progress. There are many channels for this: email, voicemail, messaging, small talks during cigarette breaks, meetings, etc.
- Keep your communication brief, yet comprehensive and structured.
- Look over your shoulder – always. You never know who is listening. Remember that your client’s confidentiality is a must.

Working with clients
This is a big one as the true hierarchy at McKinsey is “Client -> Firm -> and then You”. The client is your biggest boss.
There are many tips on client management, but the general principle is to bring the client to your side. You never win by opposing the client. Remind them about mutual benefits. Do it everyday!
Some of the client members can be “liabilities”. There are 2 types of them:
- the merely “useless”.
- the hostile ones.
With both types, the number 1 option is to subtly trade them out of your realm. When that is not possible, the next best option is to play ignorant. Leak out information only with the right “secret audience”.
No matter what, engage the client members in the process. The more they feel everybody is on the same boat, the more they would support you.
You should also get buy-ins throughout the organization along the process. Every important party has to agree with you. Ideally, the final document has already been discussed many times through many rounds with the client before the official presentation.
Doing research
Don’t reinvent the wheel! Whatever you are doing, chances are that someone, somewhere has done something similar. Building upon someone’s work is the best way to save time and energy while achieving the highest standard.
Besides, here are some research tips:
- Start with the annual report. All public companies have them available on their website.
- Look for abnormal patterns (things that are especially good or bad). That’s where all the insights lie.
- Last but not least, look for the best practice. Find out what the best performers in the field are doing and learn from them.
Conducting interviews
This is one of the most effective ways to gather qualitative facts during a project. You will find yourself interviewing multiple industry and function experts as well as key client leaders.
Here are a few tips:
- Be prepared. Know exactly what you want to get out of it. Know as much as you can about the interviewee. Writing an interview brief for yourself is not a bad idea.
- If possible, have the interviewee’s boss set up the meeting.
- Start with some general and open-ended questions then move on to specific ones. Let the content flow naturally.
- Sometimes, it’s useful to use the indirect style. Take time to make the interviewee comfortable with you and the interview process.
- Include some questions you know the answer to. This gives insights into the interviewee’s style, knowledge, and honesty.
- Don’t ask too much. Focus on what you really need (what you prioritize in the interview brief).
- Listen and let the interviewee know you are doing so.
- Paraphrase what you hear in your own words. Confirm whether you understand correctly. This also gives chances for the interviewee to add or amplify important points.
- Near the end, use this last trick to flush out any possible missing insights: “Is there anything else you would like to tell or any question I forgot to ask…?”.
- Adopt the Columbo tactic. Wait until a day or two passes, then drop by the interviewee’s office. “I was just passing by and remembered a question I forgot to ask”. This is a less threatening way to keep the conversation going.
- Lastly, always write a thank-you note. A short and sincerely one always does the work.
Brainstorming at McKinsey
In McKinsey, we often use the word “Problem-Solving” interchangeably with brainstorming sessions. It’s a very topic-focus meeting within the McKinsey team, consisting of the consultant in-charge, the EM, and sometimes even the ED and experts.
Before the session, prepare in advance as much supporting data as possible. It will come handy in the process.Inside the White room: Start with tabula rasa — a clean slate. When you get your team into the room, leave your preconceptions at the door. Bring in only the facts, and find new ways of looking at them.
Management consulting is an interesting yet challenging job. To survive and thrive at McKinsey, here are some advices for you:
Tip 1: Find your own mentor
At McKinsey, every consultant is officially assigned a mentor, who may not be in the same office. How much you benefit from the official mentor is pretty much a matter of luck. If you want great guidance, you have to go out and get your own. Get a few too, don’t stick to just one.
Tip 2: Survive the road
Business travel can be exhausting and difficult, here are some note you can take to deal with it:
- Look at business travel as an adventure.
- Do proper planning. These simple logistics can make a big difference
- Treat everyone with tremendous respect
Tip 3: Have a list of items to bring when traveling
Here is the list:
- Clothing: extra shirts or blouses, spare ties, spare shoes, casual clothes, cashmere sweaters
- Tools: writing pad, copy of whatever you send to the client, calculator
- Personal care Items
- Things to keep you organized and in touch
Tip 4: Treat your assistant well
Having a good assistant is a lifeline. Treat them well. Be clear about what you want. Give them room to grow. Take time to train them well. Answering their questions and showing them the ropes.
Tip 5: Have boundaries to keep your life balance
Since you have a large amount of work to cover as a consultant, there is almost no work-life balance. However, if you want a life, lay down some rules. For example:
- Make one day a week to be completely free of work, both physically and mentally. Tell your boss about it! He/she will respect it. And so should you.
- Don’t take work home. When you are home, you are home!
- Plan long ahead, especially when you travel.

Tip 6: The 80 / 20 Rule
80% of the wealth is owned by just 20% of the population. 80% of the output can be produced by 20% of the effort. 20% of the problems can cause 80% of the trouble.
So if you wanna save time and effort. Always try to find those 20% and act upon them!
Tip 7: Don’t try to analyze everything
If you don’t take shortcuts, there is simply too much to do. Be selective. Find the key drivers. Focus on the core problem, then apply analysis. This helps avoid going down blind alleys and boiling the ocean.
Tip 8: The Elevator Test
Concise communication is crucial in consulting. Anytime the EM asks you for your workstream status, you have to be able to give him a 30 seconds summary. Short yet insightful. This skill takes practice. Try doing it every day in various contexts!
Tip 9: Pluck the Low-Hanging Fruit
Solving only part of the problem can still mean increased profits. Those little wins help you and your customers. Try to see such opportunities and grab them first.
Tip 10: Hit singles
Get your job and only your job done, don’t try to do the work of the whole team.
It’s impossible to do everything yourself all the time. Even if you manage to pull it off once, you raise unrealistic expectations and once you fail, it is difficult to get back credibility.
Tip 11: Look at the big picture
When you are feeling swamped, take a step back, figure out what you are trying to achieve, and then look at what you are doing. “Does this really matter?”
Probably not! All of these troubles will go away!

Tip 12: Just say “I don’t know”
The firm pounds the concept of professional integrity: Honesty. If you don’t know something, just say “I DON’T KNOW” in an empowering fashion. Admitting that is a lot less costly than bluffing.
“Leaving McKinsey is never a question of whether—it’s a question of when”
There are not many people who stay with McKinsey for their whole career life. In the last part of The McKinsey Way , Ethan Rasiel and other ex-McKinsey consultants share their valuable lessons and memories from working at the company.
- “Structure, structure, structure. MECE, MECE, MECE. Hypothesis-driven, Hypothesis-driven, Hypothesis-driven.” – Former associate in Dusseldorf and San Francisco offices
- “The quality of the people. In the corporate world, the average-caliber employee is far below McKinsey’s least intelligent.” – Wesley Sand
- “What stays with me is the rigorous standard of information and analysis, the proving and double-proving of every recommendation, combined with the high standard of communication both to clients and within the Firm.” – Former associate in the Boston and New York offices
- “When faced with an amorphous situation, apply structure to it.” – Kristin Asleson, New York office, 1990-93; now working in Silicon Valley
- “Execution and implementation are the key. A blue book is just a blue book, unless you do something with it. Getting things done is the most important thing.” – Former EM in the New York office
Scoring in the McKinsey PSG/Digital Assessment
The scoring mechanism in the McKinsey Digital Assessment
Related product
/filters:quality(75)//case_thumb/1669802837683_mc_kinsey_comprehensive_bundle.png)
McKinsey Comprehensive Package
Unlock all materials helping you land the next job in McKinsey!
Among MBB firms, people tend to say McKinsey is slightly better than the other two in three factors: prestige, people, practices, and offices
At McKinsey, the salary for entry-level consultants ranges from $90,000 to $110,000/year, while the figure for experienced Associates can go up to $233,000
McKinsey hiring process including 3 phases: resume screening, PST test, and case interview. Each candidate will have to undergo 4-6 interviews during 4-8 weeks

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This practice test has been developed to provide a sample of the actual McKinsey Problem Solving Test used for selection purposes. This test assesses your ability to solve business problems using deductive, inductive, and quantitative reasoning. This practice test contains a total of 26 questions. The actual test contains 26
This practice test has been developed to provide a sample of the actual McKinsey Problem Solving Test used for selection purposes. This test assesses your ability to solve business problems using deductive, inductive, and quantitative reasoning. This practice test contains a total of 26 questions. The actual test contains 26
The McKinsey Problem Solving Test (or PST) is a paper-based test used at McKinsey & Company to select candidates for the case interviews. The PST is conducted after resume screening; it has 6 types of question, testing the candidate on 3 crucial problem-solving skills - data interpretation, mental calculations and logical reasoning.
¶ The test contains 1 business case. The case has two "teams", each with five questions, making a total of ten questions in the test. Ensure that you read the background to the case carefully. ¶ The questions are multiple choice. You must select one correct answer for each question. ¶ Mark your answer by circling it on the answer sheet ...
The Problem Solving Test (invariably shortened to PST) had been used by McKinsey for many years. However, it had a number of problems that were becoming more pronounced over time, and it was fundamentally in need of replacement. ... This article is a good introduction. From here, though our new, updated PDF guide to the McKinsey Solve ...
Practice Test Overview and Instructions This practice test has been developed to provide a sample of the actual McKinsey Problem Solving Test used for selection purposes. This test assesses your ability to solve business problems using deductive, inductive, and quantitative reasoning. This practice test contains a total of 13 questions.
McKinsey PST: an adaptive learning approach to pass the test The McKinsey Problem Solving Test (McKinsey PST) is a data interpretation and critical number reasoning test used by McKinsey to select candidates to be admitted to the first round of case interviews.The use of the PST is the main difference between the McKinsey recruiting process and those of its main competitors.
News. The McKinsey Solve Assessment - 2023 Guide with Redrock Case Update. McKinsey's Solve assessment has been making candidates sweat ever since it was initially trialled at the firm's London office back in 2017 - and things have gotten even more difficult since the new version launched in Spring 2023 added the Redrock case study.
The book includes over 40 strategy cases, a number of case starts exercises, several human capital cases, a section on marketing cases and 21 ways to cut costs. Yeah, reviewing a book Mckinsey Problem Solving Test could go to your near links listings. This is just one of the solutions for you to be successful.
The PST test is a multiple-choice test. These problem-solving skills will include logical reasoning, interpreting data and mental calculations. Officially, McKinsey & Company has never mentioned a passing score or an acceptance rate for the PST test. But there is a rough estimate of 30 to 35% for an acceptance rate, and the pass mark of being ...
The McKinsey Problem Solving Test (PST) is a standardized test used to assess the problem-solving skills of potential consultants. The test is designed to evaluate a candidate's ability to analyze and solve complex business problems, and it is a key component of the recruiting process for McKinsey. The test uses a multiple-choice format and ...
practice-test-A-1-17 - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. McKinsey
The McKinsey Problem Solving Game, also named McKinsey Imbellus, McKinsey Digital Assessment, and Solve, is a gamified test that replaces the previous assessment, PST, in the recruiting process. The PSG consists of two mini-games lasting for 70 minutes and evaluates candidates on five key cognitive abilities. Only candidates who pass this stage ...
The McKinsey Problem Solving Test consists of 26 multiple-choice questions that need to be answered on paper. You have a 60 minute time limit. That gives you about two minutes per question. Most candidates fail because they run out of time. The 26 questions are divided between three business cases.
McKinsey Solve (formerly called Problem-Solving Game, Digital Assessment, or colloquially the "Imbellus Game") is a gamified test designed by Imbellus for the McKinsey & Company. In the McKinsey recruitment process, the Solve Game sits between the resume screening and the case interviews, serving the same purpose as the paper-based tests ...
If you only use the pdf document on a screen, you will not experience the real test conditions. 2. ... Use of "McKinsey", "McKinsey PST", "McKinsey Problem Solving Test" or any other variations do not imply any affiliation with or endorsement by McKinsey & Company. The information provided on igotanoffer.com and its related products ...
McKinsey and Company is recognized for its rigorous approach to problem solving. They train their consultants on their seven-step process that anyone can learn. This resource guides you through that process, largely informed by the McKinsey Staff Paper 66. It also includes a PowerPoint Toolkit with slide templates of each step of the process ...
Problem statements should commence with a question or a firm hypothesis. Be specific, actionable and focus on what the decision maker needs to move forward. Break a problem into component parts so that problems can be divided and allocated. The parts should be MECE. Do it as a team, share with Experts and client to get input and alignment.
McKinsey Problem Solving Game FAQs All technical issues should be directed from you (the candidate) to [email protected]. You can email the support team directly, or use the live chat function. The support team will be able to run diagnostics on your link and help solve any issues directly
The McKinsey problem-solving process can be summarized in the 5 steps: define the problems, find the root cause, use "hypothesis-driven" process, analyze with "issue tree" and propose solutions. 1. Define the problem: Every consulting project revolves around a "problem". But the "problem" is NOT always the problem!