- For educators
- Go to my projects
- Português (PT)
- Português (BR)

BibGuru ISBN Citation Generator
Cite websites, books, articles, ...
What is an ISBN citation generator and how can it help you?
Getting citations and reference lists correctly done can be very confusing and time-consuming.
The good news is that our ISBN citation generator can do it automatically for you and it is FREE to use! 🎉
Not convinced yet? Here are 5 reasons why you are going to love the BibGuru ISBN citation maker :
😌 No flood of distracting ads
👌 Simple and intuitive interface
🎓 APA, MLA, Chicago, Turabian, and thousands of other citation styles
🥇 Most accurate citation data
With BibGuru we have made a citation tool that truly helps students to focus on the content of their work instead of worrying about how to get their reference list correctly done.
BibGuru can turn the ISBN number of any book into a correctly formatted APA citation or MLA citation in seconds! Those days of wasting time entering data manually or losing grades on incorrect bibliographies are finally gone!
If you need to know more about ISBNs check out our What is the ISBN? section.
Why, when, and what do I have to cite?
Why The broad scientific knowledge we have today is the accomplishment of many researchers over time. To put your own contribution in context , it is important to cite the work of the researchers who influenced you. Cited sources can provide key background information, support or dispute your thesis, or offer important definitions and data. Citing also shows that you have personally read the work.
When In addition to crediting the ideas of others that you used to build your own argument, you need to provide documentation for all facts and figures that are not common knowledge. Common knowledge is knowledge that is known by everyone, or nearly everyone, and can basically concern any subject. An example for common knowledge would be "There are seven days in a week".
What The number of sources you cite in your work depends on the intent of the paper. In most cases, you will need to cite one or two of the most representative sources for each key point. However, if you are working on a review article, the aim is to present to the readers everything that has been written on a topic, so you will need to include a more exhaustive list of citations.
What is the ISBN number?

An ISBN, or International Standard Book Number , is a numeric commercial book identifier, which is a number unique for every book including e-books and audio books.
ISBNs are calculated using a specific mathematical formula and include a check digit to validate the number. They are used by publishers, booksellers, libraries, and other retailers worldwide in the marketing and buying of books.
On most books, the ISBN number can be found on the back cover, next to the barcode. You most likely have seen them many times.
ISBNs usually start with 978 followed by 10 digits or 9 digits plus an X. An ISBN can be split into blocks of digits giving information about the language of the book and publisher.
How do I cite with ISBN?
With BibGuru, you can automatically create a citation in thousands of different citation styles just entering the ISBN of your book. All you need to do is pick a citation style and then search for the ISBN of your book. BibGuru will then automatically create an accurate citation in the style you chose.
While all the specific rules of the ISBN citation style might sound very complicated, you don't need to worry about getting them wrong with BibGuru.
Use our ISBN citation generator above to create the fastest and most accurate ISBN citations possible.
With the BibGuru ISBN citation generator, you can create a citation in thousands of different citation styles by entering the ISBN of your book. All you need to do is pick a citation style and then search for the ISBN of your book. BibGuru will then automatically create an accurate citation in the style you chose.
Yes, the BibGuru ISBN citation generator is free.
Yes, the BibGuru ISBN citation generator stores all your references. Once you are done adding all your references, you only have to copy and paste the list into your paper.
The easiest way to cite an ISBN is to simply use BibGuru . Just enter the ISBN of your book in the search box and BibGuru will automatically create an accurate citation in the style you chose.
ISBNs are not included in the Works Cited list in the MLA citation style for a number of reasons. If you want more information on that topic, the MLA Style Center is a good resource.
Yes, every major and most minor publishers will automatically assign an ISBN to any book they publish. Only self-published books are most likely not going to have an ISBN. Also, ISBNs were developed only in the second half of the twentieth century, so older books won’t have them.
No, they are not the same thing. ISBNs are used to identify each unique publication whether in the form of a physical book or related materials such as eBooks or software. A DOI, or Digital Object Identifier, is a string of numbers, letters and symbols used to permanently identify an article or document and link to it on the web.
On most books, the ISBN number can be found on the back cover, next to the barcode.
Citation generators
Citation guides, alternative to.
- NoodleTools
- Getting started
From our blog
- 📚 How to write a book report
- 📝 APA Running Head
- 📑 How to study for a test
Citation Generator
Powered by chegg.
- Select style:
- Archive material
- Chapter of an edited book
- Conference proceedings
- Dictionary entry
- Dissertation
- DVD, video, or film
- E-book or PDF
- Edited book
- Encyclopedia article
- Government publication
- Music or recording
- Online image or video
- Presentation
- Press release
- Religious text
What Is Cite This For Me's Citation Generator?
Cite This For Me’s open-access generator is an automated citation machine that turns any of your sources into citations in just a click. Using a citation generator helps students to integrate referencing into their research and writing routine; turning a time-consuming ordeal into a simple task.
A citation machine is essentially a works cited generator that accesses information from across the web, drawing the relevant information into a fully-formatted bibliography that clearly presents all of the sources that have contributed to your work.
If you don’t know how to cite correctly, or have a fast-approaching deadline, Cite This For Me’s accurate and intuitive citation machine will lend you the confidence to realise your full academic potential. In order to get a grade that reflects all your hard work, your citations must be accurate and complete. Using a citation maker to create your references not only saves you time but also ensures that you don’t lose valuable marks on your assignment.
Not sure how to format your citations, what citations are, or just want to find out more about Cite This For Me’s citation machine? This guide outlines everything you need to know to equip yourself with the know-how and confidence to research and cite a wide range of diverse sources in your work.
Why Do I Need To Cite?
Simply put, referencing is the citing of sources used in essays, articles, research, conferences etc. When another source contributes to your work, you have to give the original owner the appropriate credit. After all, you wouldn’t steal someone else’s possessions so why would you steal their ideas?
Any factual material or ideas you take from another source must be acknowledged in a reference, unless it is common knowledge (e.g. President Kennedy was killed in 1963). Failing to credit all of your sources, even when you’ve paraphrased or completely reworded the information, is plagiarism. Plagiarizing will result in disciplinary action, which can range from losing precious points on your assignment to expulsion from your university.
What’s more, attributing your research infuses credibility and authority into your work, both by supporting your own ideas and by demonstrating the breadth of your research. For many students, crediting sources can be a confusing and tedious process, but it’s a surefire way to improve the quality of your work so it’s essential to get it right. Luckily for you, using Cite This For Me’s citation machine makes creating accurate references easier than ever, leaving more time for you to excel in your studies.
In summary, the referencing process serves three main functions:
- To validate the statements and conclusions in your work by providing directions to other sound sources that support and verify them.
- To help your readers locate, read and check your sources, as well as establishing their contribution to your work.
- To give credit to the original author and hence avoid committing intellectual property theft (known as ‘plagiarism’ in academia).
How Do I Cite My Sources With The Cite This For Me's Citation Machine?
Cite This For Me’s citation generator is the most accurate citation machine available, so whether you’re not sure how to format in-text citations or are looking for a foolproof solution to automate a fully-formatted works cited list, this citation machine will solve all of your referencing needs.
Referencing your source material doesn’t just prevent you from losing valuable marks for plagiarism, it also provides all of the information to help your reader find for themselves the book, article, or other item you are citing. The accessible interface of this citation builder makes it easy for you to identify the source you have used – simply enter its unique identifier into the citation machine search bar. If this information is not available you can search for the title or author instead, and then select from the search results that appear below the citation generator.
The good news is that by using tools such as Cite This For Me, which help you work smarter, you don’t need to limit your research to sources that are traditional to cite. In fact, there are no limits to what you can reference, whether it be a YouTube video, website or a tweet.
To use the works cited generator, simply:
- Select from APA, MLA, Chicago, ASA, IEEE and AMA * styles.
- Choose the type of source you would like to cite (e.g. website, book, journal, video).
- Enter the URL , DOI , ISBN , title, or other unique source information into the citation generator to find your source.
- Click the ‘Cite’ button on the citation machine.
- Copy your new reference from the citation generator into your bibliography or works cited list.
- Repeat for each source that has contributed to your work.
*If you require another referencing style for your paper, essay or other academic work, you can select from over 7,500 styles.
Once you have created your Cite This For Me account you will be able to use the citation machine to generate multiple references and save them into a project. Use the highly-rated iOS or Android apps to create references in a flash with your smartphone camera, export your complete bibliography in one go, and much more.
What Will The Citation Machine Create For Me?
Cite This For Me’s citation maker will generate your reference in two parts; an in-text citation and a full reference to be copied straight into your work.
The citation machine will auto-generate the correct formatting for your works cited list or bibliography depending on your chosen style. For instance, if you select a parenthetical style on the citation machine it will generate an in-text citation in parentheses, along with a full reference to slot into your bibliography. Likewise, if the citation generator is set to a footnote style then it will create a fully-formatted reference for your reference page and bibliography, as well as a corresponding footnote to insert at the bottom of the page containing the relevant source.
Parenthetical referencing examples:
In-text example: A nation has been defined as an imagined community (Anderson, 2006).* Alternative format: Anderson (2006) defined a nation as an imagined community.
*The citation machine will create your references in the first style, but this should be edited if the author’s name already appears in the text.
Bibliography / Works Cited list example: Anderson, B. (2006). Imagined Communities. London: Verso.
Popular Citation Examples
- Citing archive material
- Citing artwork
- Citing an audiobook
- Citing the Bible
- Citing a blog
- Citing a book
- Citing a book chapter
- Citing a comic book
- Citing conference proceedings
- Citing a court case
- Citing a database
- Citing a dictionary entry
- Citing a dissertation
- Citing an eBook
- Citing an edited book
- Citing an email
- Citing an encyclopedia article
- Citing a government publication
- Citing an image
- Citing an interview
- Citing a journal article
- Citing legislation
- Citing a magazine
- Citing a meme
- Citing a mobile app
- Citing a movie
- Citing a newspaper
- Citing a pamphlet
- Citing a patent
- Citing a play
- Citing a podcast
- Citing a poem
- Citing a presentation
- Citing a press release
- Citing a pseudonym
- Citing a report
- Citing Shakespeare
- Citing social media
- Citing a song
- Citing software
- Citing a speech
- Citing translated book
- Citing a TV Show
- Citing a weather report
- Citing a website
- Citing Wikipedia article
- Citing a YouTube video
What Are Citation Styles?
A citation style is a set of rules that you, as an academic writer, must follow to ensure the quality and relevance of your work. There are thousands of styles that are used in different academic institutions around the world, but in the US the most common are APA, MLA and Chicago.
The style you need to use will depend on the preference of your professor, discipline or academic institution – so if you’re unsure which style you should be using, consult your department and follow their guidelines exactly, as this is what you’ll be evaluated on when it comes to grading.
Referencing isn’t just there to guard against plagiarism – presenting your research in a clear and consistent way eases the reader’s comprehension. Each style has a different set of rules for both page formatting and referencing. Be sure to adhere to formatting rules such as font type, font size and line spacing to ensure that your work is easily legible. Furthermore, if your work is published as part of an anthology or collected works, each entry will need to be presented in the same style to maintain uniformity throughout. It is important to make sure that you don’t jump from one style to another, so follow the rules carefully to ensure your reference page and bibliography are both accurate and complete.
If you need a hand with your referencing then why not try Cite This For Me’s citation builder? It’s the quickest and easiest way to reference any source, in any style. The citation generator above will create your references in MLA format style as standard, but this powerful citation machine can generate fully-formatted references in thousands of the widely used global college styles – including individual university variations of each style. So, whether your subject requires you to use the APA citation , or your professor has asked you to adopt the Chicago style citation so that your work includes numbered footnotes, we’re sure to have the style you need. Cite This For Me also offers a citation machine and helpful formatting guide for styles such as ASA , IEEE or AMA . To access all of them, simply create your free account and search for your specific style.
Popular Citation Styles
- ACS Referencing Generator
- AMA Citation Generator
- APA Citation Generator
- APSA Referencing Generator
- ASA Citation Generator
- Bluebook Citation Generator
- Chicago Style Citation Generator
- Harvard Referencing Generator
- IEEE Referencing Generator
- MHRA Referencing Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Nature Referencing Generator
- OSCOLA Referencing Generator
- Oxford Referencing Generator
- Turabian Citation Generator
- Vancouver Referencing Generator
How Do I Format A Works Cited List Or Bibliography?
Drawing on a wide range of sources greatly enhances the quality of your work, and reading above and beyond your recommended reading list – and then using these sources to support your own thesis – is an excellent way to impress your reader. A clearly presented works cited list or bibliography demonstrates the lengths you have gone to in researching your chosen topic.
Typically, a works cited list starts on a new page at the end of the main body of text and includes a complete list of the sources you have actually cited in your paper. This list should contain all the information needed for the reader to locate the original source of the information, quote or statistic that directly contributed to your work. On the other hand, a bibliography is a comprehensive list of all the material you may have consulted throughout your research and writing process. Both provide the necessary information for readers to retrieve and check the sources cited in your work.
Each style’s guidelines will define the terminology of ‘ works cited ’ and ‘ bibliography ’, as well as providing formatting guidelines for font, line spacing and page indentations. In addition, it will instruct you on how to order your works cited list or bibliography – this will usually be either alphabetical or chronological (meaning the order that these sources appear in your work). Before submitting your work, be sure to check that you have formatted your whole paper – including your reference page and bibliography – according to your style’s formatting guidelines.
Sounds complicated? Referencing has never been so easy; Cite This For Me’s citation machine will automatically generate fully-formatted references for your works cited page or bibliography in your chosen style. Sign in to your Cite This For Me account to save and export your bibliography straight into Microsoft Word, Evernote, EndNote and more. If that sounds like too much work.
How Do Citations Actually Work?
Although the citation generator will create your bibliography and works cited list for you in record time, it is still useful to understand how this system works behind the scenes. Understanding how a citation machine actually generates references will greatly increase the quality of your work.
As well as saving you time with its citation maker, Cite This For Me provides the learning resources to help you fully understand the citing process and the benefits of adopting great referencing standards.
The referencing process:
- Find a book, journal, website or other source that will contribute to your work.
- Save the quote, image, data or other information that you will use in your work.
- Save the source information that enables you to find it again (i.e. URL, ISBN, DOI etc.).
- Format the source information into a reference.
- Copy and paste the reference into the body of the text.
- Repeat for each source that contributes to your work.
- Export or copy and paste the fully-formatted reference into your bibliography.
Manage all your citations in one place
Create projects, add notes, cite directly from the browser and scan books’ barcodes with a mobile app.
Sign up to Cite This For Me – the ultimate citation management tool.
- Plagiarism and grammar
- School access
Cite a Book in APA
- powered by chegg.

Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper
Consider your source's credibility. ask these questions:, contributor/author.
- Has the author written several articles on the topic, and do they have the credentials to be an expert in their field?
- Can you contact them? Do they have social media profiles?
- Have other credible individuals referenced this source or author?
- Book: What have reviews said about it?
- What do you know about the publisher/sponsor? Are they well-respected?
- Do they take responsibility for the content? Are they selective about what they publish?
- Take a look at their other content. Do these other articles generally appear credible?
- Does the author or the organization have a bias? Does bias make sense in relation to your argument?
- Is the purpose of the content to inform, entertain, or to spread an agenda? Is there commercial intent?
- Are there ads?
- When was the source published or updated? Is there a date shown?
- Does the publication date make sense in relation to the information presented to your argument?
- Does the source even have a date?
- Was it reproduced? If so, from where?
- If it was reproduced, was it done so with permission? Copyright/disclaimer included?
- EasyBib® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style Format
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
OttoBib is no longer operational (in service from 2005 - 2022)
Bibliography and works cited resources:
- https://owl.purdue.edu/[...]/evaluating_bibliographic_citations.html
- https://tippie.uiowa.edu/how-write-bibliography
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
Cite a Book in MLA

Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper
Citing books in mla.
How do you cite a book? What information do you need to include and where does it go? Citation Machine citing tools can help you easily create formatted citations for your research paper.
First, find your book using the search box above. The book’s author, title, or ISBN will work. If there are books with similar titles, authors, different editions, etc., you will be shown all possibilities, so you can choose the correct book. From there, the citing tools will automatically pull information on the source and help you create a citation.
Books aren’t just in print. They can be electronic, too. You can find them in online databases, websites, audiobooks, and other forms of media. Citation Machine citing tools can handle those, as well.
Standard book citation:
Collins, Suzanne. The Hunger Games. Scholastic, 2008.
Translated works in MLA format:
If the focus was on the text, rather than the actual translation, cite the source like this:
Vila-Matas, Enrique. Never Any End to Paris. Translated by Anne McLean, New Directions, 2011.
If the focus was on the translation, include the translator’s name first in the citation.
McLean, Anne, translator. Never Any End to Paris. By Enrique Vila-Matas, New Directions, 2011.
Wish you had an automatic MLA citation generator to do all of the heavy lifting for you? Try out our generator, at the top of this page.
How to cite a textbook in print:
To cite a full textbook in print in MLA format, you’ll need to find the following pieces of information:
- Name of the author(s) or editor(s)
- Title of the textbook, including any subtitles
- Version of the textbook (such as a numbered edition or revised edition)
- Name of the publisher
- Year the textbook was published
Place the pieces of information in this format:
Last name, First name of the author or Last name, First name, editor. Title of the Textbook. Version, Publisher, Year published.
If the textbook was compiled by an editor, use this format at the beginning of the citation:
Last name, First name, editor.
Examples of how to cite a textbook in print:
Lilly, Leonard S. Braunwald’s Heart Disease: Review and Assessment . 9th ed., Elsevier Saunders, 2012.
Cherny, Nathan, et al., editors. Oxford Textbook of Palliative Medicine . 5th ed., Oxford UP, 2015.
E-books in MLA format:
Citing an e-book (a digital book that lacks a URL and that you use software to read on a personal e-reader):
Alcott, Louisa May. Little Women. E-book ed., Barnes & Noble Classics, 2004.
In the “version” section of the citation, include “E-book ed.” to specify that you used an e-book version of a printed book.
You can also use the “final supplemental” section of the citation to specify the file type of the electronic edition of the work if you know the work varies by file format.
Alcott, Louisa May. Little Women. E-book ed., Barnes & Noble Classics, 2004. EPUB.
If you’re citing a book available from a website, here’s an example in MLA format:
Doyle, Arthur Conan. “A Scandal in Bohemia.” The Complete Sherlock Holmes, Internet Archive, archive.org/details/deysayan844_gmail_Cano/mode/2up?ref=ol&view=theater&q=119.
The website is the container, which is found in the third position of the citation, in italics.
Wish you had a second set of eyes to review your citations? Use our MLA citation generator and compare the output to yours.
Featured links:
MLA Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interviews | PDFs
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
Cite a Book
- powered by chegg.

Check your paper before your teacher does!
Avoid plagiarism — quickly check for missing citations and check for writing mistakes., is your source credible don’t forget to consider these factors., purpose : reason the source exists.
- Is the point of the information to inform, persuade, teach, or sell?
- Do the authors/publishers make their intentions clear?
- Does the information appear to be fact or opinion?
- Does the point of view seem impartial? Do they identify counter-arguments?
Authority - Author: Source of the information
- Who is the author? What are their credentials or qualifications?
- What makes the author qualified to write on this topic?
- Is there clearly defined contact information for the author?
Authority - Publisher: Source of the information
- Who is the publisher? Is it a non-profit, government agency, or organization? How might this affect their point of view?
- What makes the publisher qualified to generate works on this subject?
- What can the URL tell you about the publisher? For instance, .gov may signify that it is a government agency.
Relevance : Importance of the information to your topic
Currency : timeliness of the information.
- When was the information published? When was it last updated? Does it reflect the most current information available?
- How does your topic fit in with this source’s publication date? Do you need current information to make your point or do older sources work better?
Comprehensiveness
- Does the source present one or multiple viewpoints on your topic?
- Does the source present a large amount of information on the topic? Or is it short and focused?
- Are there any points you feel may have been left out, on purpose or accidentally, that affect its comprehensiveness?
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
Scribbr Harvard Referencing Generator
Accurate Harvard references, verified by experts, trusted by millions.
Save hours of repetitive work with Scribbr's Harvard Referencing Generator.
Stop wasting hours figuring out the correct citation format. With Scribbr's referencing generator , you can search for your source by title, URL, ISBN, or DOI and generate accurate Harvard style references in seconds.
Rely on accurate references, verified by experts.
You don’t want points taken off for incorrect referencing. That’s why our referencing experts have invested countless hours perfecting our algorithms. As a result, we’re proud to be recommended by teachers worldwide.
Enjoy the Harvard Referencing Generator with minimal distraction.
Staying focused is already challenging enough. You don’t need video pop-ups and flickering banner ads slowing you down. At Scribbr, we keep distractions to a minimum while also keeping the Harvard Referencing Generator free for everyone.
Referencing Generator features you'll love
Search for your source by title, URL, DOI, ISBN, and more to retrieve the relevant information automatically.
Cite Them Right 12th ed.
Scribbr's Harvard Referencing Generator supports the most commonly used versions: Cite Them Right (12th edition).
Export to Bib(La)TeX
Easily export in BibTeX format and continue working in your favorite LaTeX editor.
Export to Word
Reference list finished? Export to Word with perfect indentation and spacing set up for you.
Sorting, grouping, and filtering
Organize the reference list the way you want: from A to Z, new to old, or grouped by source type.
Save multiple lists
Stay organized by creating a separate reference list for each of your assignments.
Choose between Times New Roman, Arial, Calibri, and more options to match your style.
Industry-standard technology
The Scribbr Referencing Generator is built using the same citation software (CSL) as Mendeley and Zotero, but with an added layer for improved accuracy.
Explanatory tips help you get the details right to ensure accurate citations.
Secure backup
Your work is saved automatically after every change and stored securely in your Scribbr account.
- Introduction
Reference examples
Missing information, citation examples, tools and resources, how to reference in harvard style.

Harvard referencing is a widely used referencing style (especially in UK universities) that includes author-date in-text citations and a complete reference list at the end of the text.
There are many versions of Harvard referencing style. Our guidance reflects the rules laid out in Cite Them Right: The Essential Referencing Guide (12th edition) by Richard Pears and Graham Shields.
Scribbr’s free reference generator can create flawless Harvard style references for a wide variety of sources.
- Cite a webpage
- Cite a book
- Cite a journal article

Harvard reference entries
The reference list appears at the end of your text, listing full information on all the sources you cited. A Harvard reference entry generally mentions the author , date , title , publisher or publication that contains the source, and URL or DOI if relevant.
You’ll include different details depending on the type of source you’re referencing, as some information is only relevant to certain kinds of publications.
The format of a reference entry varies based on source type. Apart from the information included, formatting details such as the use of italics also depend on what you’re referencing. The tabs below show formats and examples for the most commonly referenced source types.
The suggested information won’t necessarily all be available for the source you’re referencing. To learn how to work around missing information in your references, check the table below.
Harvard Referencing Generator
Generate accurate Harvard style references in seconds
Get started
Harvard in-text citations
Harvard referencing style uses author-date in-text citations, which means including the author’s last name and the publication year of the source, like this: (Smith, 2019). This citation points the reader to the corresponding entry in the reference list.
Always include an in-text citation when you quote or paraphrase a source. Include a page number or range when available and relevant to indicate which part of the source you’re drawing on. Using material from other sources without acknowledging them is plagiarism.
In-text citations can be parenthetical (author and date both in parentheses) or narrative (author name mentioned in the sentence, date in parentheses). A source may also have more than one author. If there are four or more, name only the first, followed by “ et al. ”
As with reference entries, it’s good to be aware of how to deal with missing information in your in-text citations.
Scribbr offers a variety of other tools and resources to help with referencing and other aspects of academic writing:
- Referencing generator : Scribbr’s free referencing generator can also create flawless citations in other styles, such as APA and MLA .
- Free plagiarism checker : Detect and fix plagiarism issues with the most accurate plagiarism checker available, powered by Turnitin.
- Proofreading services : Make sure your writing is clear and professional with the help of an expert editor.
- Guide to Harvard style : Understand the rules of Harvard referencing style, and learn how to cite a variety of sources.
- Guides and videos : Explore our Knowledge Base, our YouTube channel, and a wide variety of other educational resources covering topics ranging from language to statistics.
Jessie Ball duPont Library
Citation management tools.
- Creating Citations
- Zotero Help
- Word Plugin
- Citation Machine
Citation Builder
- Generate citations automatically
- Microsoft Word
Subject Guide

Citation Machine is a citation generator that allows users to create citations by filling in information about the source. It supports MLA, APA, Turabian, and Chicago style formatting. Also it has an ISBN look-up that will generate a citation based on a book's ISBN number. CM helps create citations for A LOT of different source types.
- Make a bibliography. It's free, easy and OttoMatic
Ottobib is a fairly simple citation generator that uses the ISBN of a book to create the citation. It supports MLA, APA, and Chicago/Turabian formats. It's perfect for citing books but has no feature to cite electronic sources.
- OttoBib Homepage
- Citation Builder Includes APA 6, MLA 7 & 8, Chicago, and CSE/CBE (Author/Date) styles. From North Carolina State University Libraries.
CiteFast is a user-friendly citation generator that supports MLA, APA, and Chicago formatting. Also helps users generate a title page.
- CiteFast Link
KnightCite was created by the Hekman Library of Calvin College as a reliable and efficient means of citing sources for its students. The generator is provided free of charge, and there is an option to create an account so you have more access privileges such as saving citations for later and alphabetizing them. Supports MLA, APA, and Chicago style formatting. Also cites a wide variety of sources including books, anthologies, multimedia, periodicals, communications, and online sources.
- KnightCite Homepage
- << Previous: Word Plugin
- Next: Microsoft Word >>
- Last Updated: Oct 7, 2021 3:18 PM
- URL: https://library.sewanee.edu/citetools
Research Tools
- Find Articles
- Find Research Guides
- Find Databases
- Ask a Librarian
- Learn Research Skills
- How-To Videos
- Borrow from Another Library (Sewanee ILL)
- Find Audio and Video
- Find Reserves
- Access Electronic Resources
Services for...
- College Students
- The School of Theology
- The School of Letters
- Community Members
Spaces & Places
- Center for Leadership
- Center for Speaking and Listening
- Center for Teaching
- Floor Maps & Locations
- Ralston Listening Library
- Research Help
- Study Spaces
- Tech Help Desk
- Writing Center
About the Library
- Where is the Library?
- Library Collections
- New Items & Themed Collections
- Library Policies
- Library Staff
- Friends of the Library
Jessie Ball duPont Library, University of the South
178 Georgia Avenue, Sewanee, TN 37383
931.598.1664

Scribbr Citation Generator
Description.
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition
Title: move anything with layered scene diffusion.
Abstract: Diffusion models generate images with an unprecedented level of quality, but how can we freely rearrange image layouts? Recent works generate controllable scenes via learning spatially disentangled latent codes, but these methods do not apply to diffusion models due to their fixed forward process. In this work, we propose SceneDiffusion to optimize a layered scene representation during the diffusion sampling process. Our key insight is that spatial disentanglement can be obtained by jointly denoising scene renderings at different spatial layouts. Our generated scenes support a wide range of spatial editing operations, including moving, resizing, cloning, and layer-wise appearance editing operations, including object restyling and replacing. Moreover, a scene can be generated conditioned on a reference image, thus enabling object moving for in-the-wild images. Notably, this approach is training-free, compatible with general text-to-image diffusion models, and responsive in less than a second.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Scribbr MLA Citation Generator
Accurate MLA citations, verified by experts, trusted by millions.
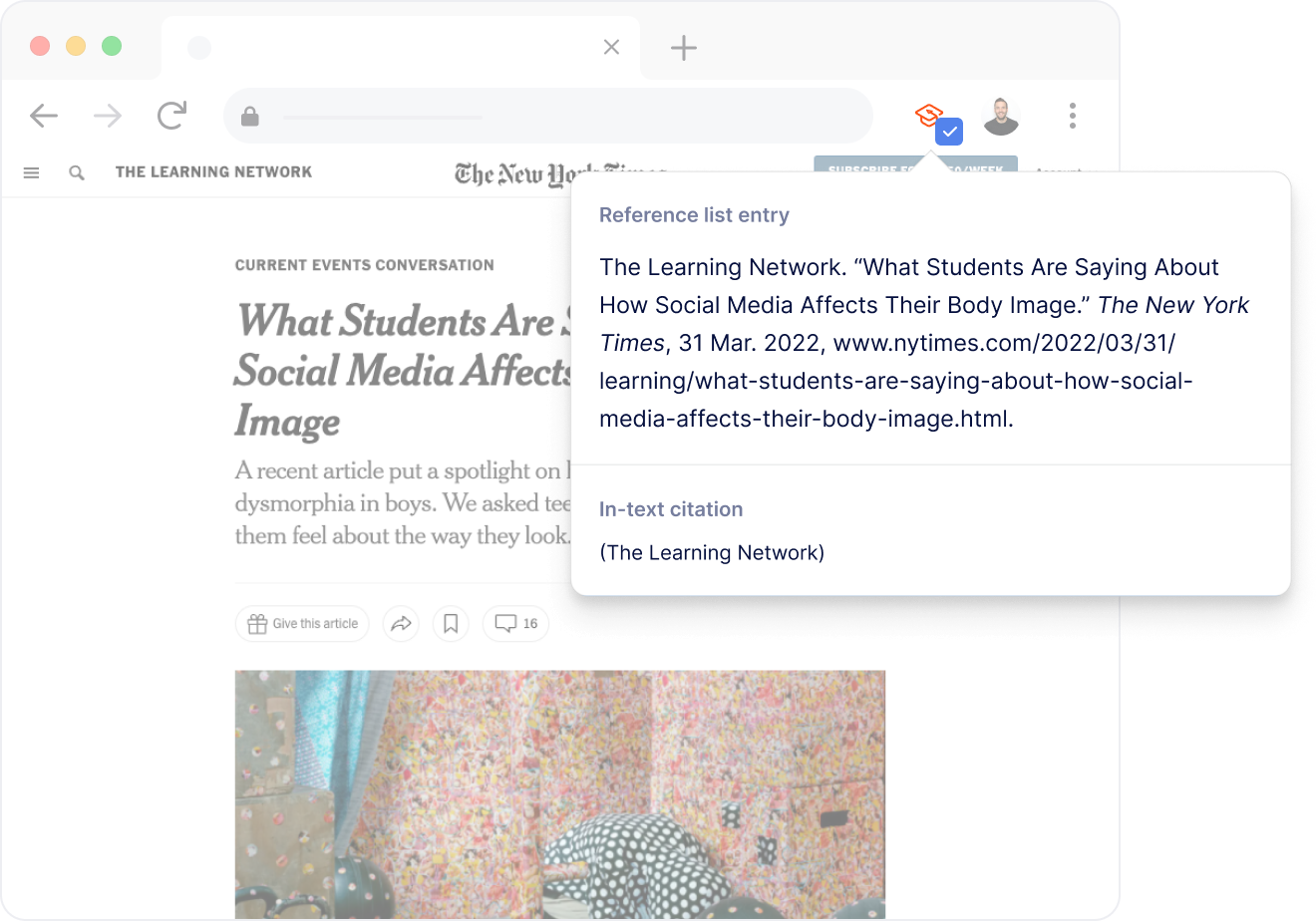
Scribbr's MLA Citation Generator for Chrome
Effortlessly cite any page or article directly from your browser with just one click. Our extension simplifies the citation process by automatically retrieving essential details such as the title, author(s), and publication date , ensuring accurate MLA citations in seconds.

Trust in expert-verified MLA citations
Avoid the risk of losing points due to incorrect citations. Our MLA citation experts have meticulously refined our algorithms, ensuring precision and reliability. This dedication has earned us recognition and recommendations from educators worldwide.
Experience distraction-free citation
Focus on your work without interruptions. Our citation generator provides a clean interface, free from distracting video pop-ups and flashing ads. Best of all, it's completely free for everyone.
Features you'll love
Search for your source by title, URL, DOI, ISBN, and more to retrieve the relevant information automatically.
MLA 8th & 9th edition
Scribbr's Citation Generator supports both MLA 8 and MLA 9 (as well as APA and Harvard ). No matter what edition you're using, we’ve got you covered!
Export to Bib(La)TeX
Easily export in BibTeX format and continue working in your favorite LaTeX editor.
Export to Word
Reference list finished? Export to Word with perfect indentation and spacing set up for you.
Sorting, grouping, and filtering
Organize the reference list the way you want: from A to Z, new to old, or grouped by source type.
Save multiple lists
Stay organized by creating a separate reference list for each of your assignments.
Choose between Times New Roman, Arial, Calibri, and more options to match your style.
Industry-standard technology
Scribbr's citation generator is built using the same citation software (CSL) as Mendeley and Zotero, but with an added layer for improved accuracy.
Annotations
Create perfectly formatted MLA Style annotated bibliographies with just a few clicks.
Explanatory tips help you get the details right to ensure accurate citations.
Citation guides
Getting to grips with citation is simple with the help of our highly rated MLA citation guides and videos .
Secure backup
Your work is saved automatically after every change and stored securely in your Scribbr account.
- Introduction
- Missing information
- No page numbers
- Scroll to top
How to cite in MLA format

MLA is one of the most common citation styles used by students and academics. This quick guide explains how to cite sources according to the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook . You can also use Scribbr’s free citation generator to automatically generate references and in-text citations.
An MLA citation has two components:
- In-text citation : Every time you quote or paraphrase a source, you cite the author and the page number in parentheses.
- Works Cited : At the end of your paper, you give a full reference for every source you cited, alphabetized by the author’s last name.
MLA Works Cited list
The list of Works Cited (also known as the bibliography or reference page) gives full details of every source you cited in your text. Each entry is built from nine core elements:
Following this format, you can create a citation for any type of source—for example, a book , journal article , website , or movie . You only include information that’s relevant to the type of source you’re citing.
Missing information in MLA citations
Regardless of the source type, the most important elements of any MLA citation are the author , the source title , and the publication date. If any of these are missing from the source, the Works Cited entry will look slightly different.
MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate MLA citations in seconds
Get started
MLA in-text citations
MLA in-text citations are brief references that direct your reader to the full source entry. You include them every time you quote , block quote , paraphrase or summarize a source.
The in-text citation must match the first word of the Works Cited entry—usually the author’s last name . It also includes a page number or range to help the reader locate the relevant passage.
If you already named the author in your sentence, include only the page number in parentheses:
Sources with no page numbers
If the source has no page numbers, you either use an alternative locator, or leave the page number out of the citation:
Tools and resources
Besides the MLA Citation Generator, Scribbr provides many more helpful tools and resources;
- Citation generator : Generate flawless APA , MLA , and Harvard citations in seconds
- Free plagiarism checker : Detect and correct plagiarism with the most accurate plagiarism checker for students
- AI Proofreader : Upload and improve unlimited documents and earn higher grades on your assignments. Try it for free!
- Paraphrasing tool: Avoid accidental plagiarism and make your text sound better.
- Grammar checker : Eliminate pesky spelling and grammar mistakes.
- Summarizer: Read more in less time. Distill lengthy and complex texts down to their key points.
- AI detector: Find out if your text was written with ChatGPT or any other AI writing tool. ChatGPT 2 & ChatGPT 3 supported.
- Proofreading services : Hire a professional editor to improve your writing
- Citation checker : Check your work for citation errors and missing citations.
- Guides and videos : Explore hundreds of articles, bite-sized videos, time-saving templates, and handy checklists that guide you through the process of research, writing, and citation.
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Original research article, the application of virtual synchronous generator technology in inertial control of new energy vehicle power generation.

- 1 College of Transportation Engineering, Changzhou Vocational Institute of Mechatronic Technology, Changzhou, China
- 2 Component Testing and Research Department, China Automotive Technology and Research Center Co., Ltd., Changzhou, China
Introduction: With the rapid development of human society and economy, the power generation technology of various new energy vehicles has begun to receive widespread attention.
Methods: Due to the lack of inertia and frequency stability in the new energy vehicle power generation system, this paper proposes a power generation control method that combines linear active disturbance rejection control technology and virtual synchronous generator technology. This method first introduces the control strategy and inertial response of the virtual synchronous generator. Then, it uses linear active disturbance rejection control technology to improve the virtual synchronous generator technology to deal with the uncertainty and external interference in the system.
Results: The results showed that when the virtual inertia coefficient was 0, and the new energy vehicles would hardly intervene in the regulation of the grid voltage. When the virtual inertia coefficient was 5, the decline rate of the DC bus voltage of new energy vehicles had slowed down. When the virtual inertia coefficient increased, the power output of new energy vehicles can be increased to the grid. When the load suddenly increased, and the corresponding DC bus voltage decreased more slowly. In the VSG output power comparison, under the research method, the frequency fluctuation only increased by 0.09 Hz and returned to the rated frequency of 50 Hz. Additionally, the dynamic process of the system output power was the shortest, lasting only 0.05 s.
Discussion: The above results show that the research method has significant superiority and effectiveness in improving the inertial response and overall stability of the new energy vehicle power system.
1 Introduction
With the transformation of the global energy structure and the increasing requirement for environmental protection, the new energy vehicles (NEVs) are becoming a global trend. Meanwhile, the rapid growth of renewable energy resources (RES) causes the power system operate stable uncertainly. In this context, how to effectively integrate NEVs and power systems has become one of the hot research topics in the current energy field ( Chang et al., 2021 ; Mitra and Nguyen, 2022 ). Especially in the inertial control of power generation in the power system, NEVs play an increasingly important role. At present, most research focuses on the application of VSG technology in fixed power systems, while there is relatively little research on the specific application scenarios of mobile power systems, especially NEVs. At the same time, traditional power systems rely on large synchronous generators to provide the necessary inertia to maintain system frequency stability. However, with the widespread integration of RES, the number of traditional generators in the system has decreased, leading to a decrease in grid inertia and thus affecting the stability of the grid. In this situation, virtual synchronous generator (VSG) technology has attracted widespread attention in recent years as an innovative solution ( Muhtadi et al., 2021 ; Choudhuri et al., 2023 ). VSG technology can simulate the dynamic features of traditional synchronous generator (SG), such as inertia and damping, which is particularly important for power sources without rotating mass such as photovoltaics, wind power, and NEVs. By implementing behaviors similar to SG, VSG technology provides a useful way to enhance the stability and adaptability of the power grid, especially in the face of large-scale RES integration and load fluctuations ( Zeng et al., 2021 ). However, applying VSG to NEVs power generation systems (PGS) still faces challenges, especially in dealing with uncertainty and external disturbances. In view of this, this experiment proposes to use linear active disturbance rejection controller (LADRC) technology to improve VSG and apply it to the inertial control of NEVs in the PGS, aiming to improve the operational stability of the PGS.
The experiment focuses on two innovative points. Firstly, the mathematical model of SG is established, and then the basic model of virtual synchronous machine is extended. This model is combined with the topology structure of the NEV converter to obtain the charging and discharging control strategy of the converter. Secondly, second-order active disturbance rejection control is introduced to improve the traditional VSG model, and the performance of the improved control model is analyzed. Meanwhile, the conclusions are supported through simulation comparison and verification with different methods.
2 Related works
The application of VSG technology in inertial control of NEVs power generation (IC-NEVsPG), especially in improving the stability and flexibility of power systems, has attracted widespread attention from many scholars. Rathore et al. proposed a damping control method based on VSG to enable real-time adjustment of equation parameters. It utilized VSG to control the inertia and damping factor, and the effectiveness of this technology has been verified through simulation. By adjusting the inertia and damping factors, the dynamic frequency variation of micro-grids could be effectively controlled ( Rathore et al., 2021 ). Elizabeth Michael N and other scholars proposed a compensatory technique based on VSG to control the frequency fluctuations of electric vehicle inverters. It analyzed the construction of direct current (DC) and electric vehicle batteries, and verified the bidirectional power flow between the proposed virtual power plant and the power grid through case studies. Ultimately, it enabled the power grid to have higher penetration capabilities ( Elizabeth Michael et al., 2020 ). Tinajero’s team proposed a nonlinear optimal controller for PGSs based on electronic power inverters to simulate the inertia. In addition, the analysis program predefined the inertia constant of the inverter, which must consider the rated power of the generator during the formulation process. This method was effective ( Tinajero et al., 2022 ). Zhang et al. proposed a control method that integrates fuzzy inference system and VSG to achieve a multi VSG parallel system for micro-grid alternating current (AC). This method utilized fuzzy logic rules to adjust the virtual inertia and damping factor to achieve coordinated control between the two. This method could effectively suppress power frequency oscillations ( Zhang et al., 2022 ). Terazono et al. proposed an improved intelligent motor control method to effectively enhance the inertia of future power grids. By utilizing this system, it was possible to effectively control mechanism updates and temporarily utilize the kinetic energy stored in rotating loads. The proposed method for suppressing power grid frequency fluctuations had significant effectiveness ( Terazono et al., 2020 ).
In addition, scholars have analyzed other control strategies for micro-grids. Rasool et al. analyzed two methods, sag control strategy and low inertia micro-grid stability control strategy, and verified the effectiveness and sharing of this method from theory and practice. The charging control of electric vehicles could provide sufficient inertia and damping for the micro-grid, and extend the lifespan of electric vehicle batteries ( Rasool et al., 2020 ). Jafari et al. proposed an induction charging method based on modulation grid power supply to improve the stability of power supply frequency. This method could effectively adjust the charging station and virtual inertia using a controller, thereby controlling the frequency of power grid fluctuations and improving the control efficiency of the controller ( Jafari et al., 2020 ). Magdy et al. proposed a vehicle networking control method based on VSG to control the load frequency of AC islanded micro-grids. It also used an improved heuristic optimization algorithm to adjust the controller parameters, and finally verified the feasibility and effectiveness of this method ( Magdy et al., 2021 ). The team of scholars Khokhar and Dahiya proposed a bio inspired SSO and fuzzy PID control method to reduce the minimum frequency of electric vehicle battery operation. The experiment found that the controller has good robustness and the system has high stability under this technology ( Khokhar et al., 2020 ). Albert et al. proposed an optimization method that integrates adaptive hybrid particle swarm optimization and grey wolf algorithm to improve the charging efficiency of fast charging stations for hybrid vehicles. This method limited the quantity of charging stations installed while minimizing the overall pricing cost, significantly improving the charging capacity of stations and minimizing charging costs ( Albert et al., 2022 ).
To sum up, most current research focuses on fixed power systems. Relevant research on mobile power systems, especially the specific application scenario of new energy electric vehicles, is still relatively scarce. The dynamic working environment and changing load demands of NEVs place higher requirements on the adaptability and control strategies of power generation technology. In view of this, the paper proposes an improved virtual synchronous power generation technology and applies it to new energy PGSs, hoping to improve the stability of automobile PGSs.
3 The application of VSG technology in IC-NEVsPG
The aim of this experiment is to explore the application of VSG technology in IC-NEVsPG and further optimize the control strategy by combining LADRC technology. An in-depth analysis is conducted on the working principle and control strategy of VSG technology, especially its implementation and effectiveness in NEVs, and the application of LADRC technology in VSG systems is explored.
3.1 Control strategy and inertial response of VSG
The development of VSG mainly addresses some challenges encountered in distributed energy systems, such as the large fluctuations, lack of inertia, and complex power allocation problems that arise when using traditional power electronic devices. This type of system typically includes new energy generation units, energy storage systems, and VSG inverters that play a core role ( Idan et al., 2023 ). Figure 1 shows the topology of VSG.
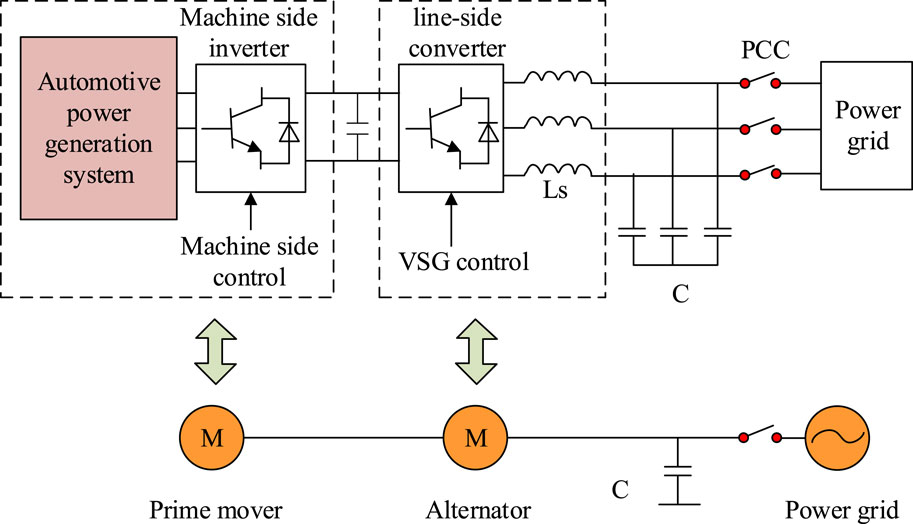
Figure 1 . Structure of VSG.
The synchronous machine model in virtual synchronous machine technology can adopt different levels of simulation models. Although higher-order models theoretically have more precise accuracy, their value in practical applications is limited due to their complexity and high computational costs ( Salem et al., 2023 ). Therefore, the experiment adopts a second-order hidden pole synchronous machine model as the core of VSG, while assuming that the model does not include the magnetic saturation effect of the iron core and rotor damping. The corresponding operational structure of the SG is Figure 2 .
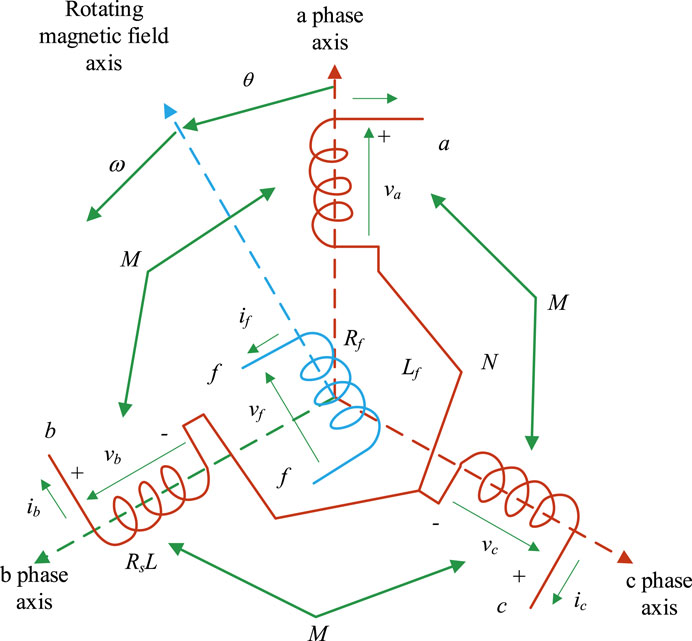
Figure 2 . Operating structure of SG.
Assuming that variable DC current source i f provides power to the rotor winding of VSG. When the system is stable, it is assumed that the value of i f remains unchanged, then d j f / d t = 0 . The corresponding calculation of the back electromotive force of the synchronous machine is Eq. 1 .
In Eq. 1 , e a , e b , and e c all represent the back electromotive force of the generator. i f represents the rotor excitation current of the SG. M f represents the max-mutual inductance between the stator-winding and the rotor-winding. Furthermore, the calculation of the active power (AP) P and reactive power (RP) Q of VSG at the inverter bridge arm is Eq. 2 .
The above equation and the principle of VSG indicate that frequency stability is a key indicator for the operation of automotive power systems. Its fluctuations not only reduce the operational efficiency of power grid equipment, but may also affect the entire system’s stability. If the frequency deviation is not corrected in a timely manner, it may seriously interfere with the normal operation of the car, and even lead to the collapse of the power grid frequency. In traditional SGs, the static characteristic equation between the AP and frequency of the generator, as well as the mechanical equation, can be established through a speed controller. The specific calculation is Eq. 3 .
In Eq. 3 , P m is the mechanical power input to the generator. P e represents the electromagnetic power output by the generator. ω r e f represents the angular frequency (AF) reference value of the generator. ω g represents the AF of the generator rotor. K f represents the frequency adjustment coefficient. J s represents the moment of inertia of the generator rotor. T m , T e and D represent the mechanical torque, electromagnetic torque, and damping coefficient of the generator, respectively. P r e f represents the reference value of the given AP of the SG. Next, this experiment combines the damping coefficient and droop coefficient under the active frequency modulation of VSG, and the corresponding control equation is Eq. 4 .
In Eq. 4 , J represents the virtual moment of inertia. P s e t represents the given AP reference value. D p represents the virtual damping coefficient. The reactive voltage regulation of VSG can be established through the reactive voltage control characteristics of SGs, and the droop coefficient of reactive voltage can be obtained, as shown in Eq. 5 .
In Eq. 5 , Q s e t represents the reference value of RP. Q represents the actual RP output of VSG. U m is the voltage amplitude at the PCC point of the LCL inverter. U r e f represents the reference value of VSG output voltage amplitude. D p is the RP voltage coefficient. The process of VSG’s AP control and RP control is Figure 3 .
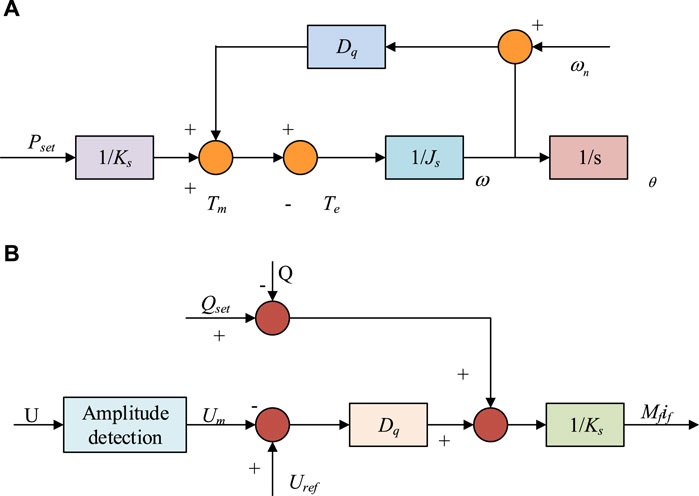
Figure 3 . Flow of VSG AP control and reactive voltage control. (A) VSG active power control diagram (B) VSG reactive voltage control diagram.
In VSG design, inertia and damping are crucial for the inertial response of VSG. The larger the inertia time constant, the more difficult it is for the generator rotor to accelerate, and the corresponding natural oscillation angle frequency and damping coefficient will be smaller. The inertia time constant is usually defined based on the rated capacity of the generator and is used to obtain the dynamic response time, as shown in Eq. 6 .
In Eq. 6 , ω n is the AF of natural oscillation. ξ represents the damping coefficient. t r is the dynamic response time. δ represents power-frequency response. Therefore, when calculating the equivalent inertia time constant of the power grid, the output power of the generator can be linked to the inertia constant, thereby obtaining the virtual inertia constant K of the system. When determining the parameters of the VSG model, it is necessary to avoid power overshoot during transient processes and ensure the equipment’s safety and stable operation.
3.2 IC-NEVsPG based on VSG
The suppression of frequency fluctuations at the grid connection point in this study plays a crucial role in the grid connection stability of NEVs. In islanding mode, the output voltage of NEVs will vary with the load, making it difficult to maintain a stable rated frequency. To reduce frequency fluctuations at the grid connection point, improve the dynamic response of NEVs converters, and achieve seamless frequency modulation in islanding mode, this experiment proposes to improve the VSG control strategy using LADRC. By linearizing the controller and linking various parameters in the system with the bandwidth of the controller and observer, the problem of parameter tuning is simplified ( Wu et al., 2023 ). At the same time, the tracking differential part in ADRC is omitted, and the extended state observer (ESO) and nonlinear state error feedback (NLSEF) are linearized and transformed into Linear Extended Star Observer (LESO) and linear state error feedback (LSEF). Among them, ESO is used to observe the output of the system and estimate its existence of disturbances. NLSEF is used to receive the results of ESO observations, control system errors, and compensate for disturbances. LESO is an observer used in control systems, whose core function is to estimate the system state, especially in situations where the system state is difficult to measure directly. The design purpose of LESO is to quickly and accurately observe unknown disturbances and states in the system, and it plays an important role in active disturbance rejection control (ADRC) technology. Taking second-order LADRC as an example, its structure is shown in Figure 4 .
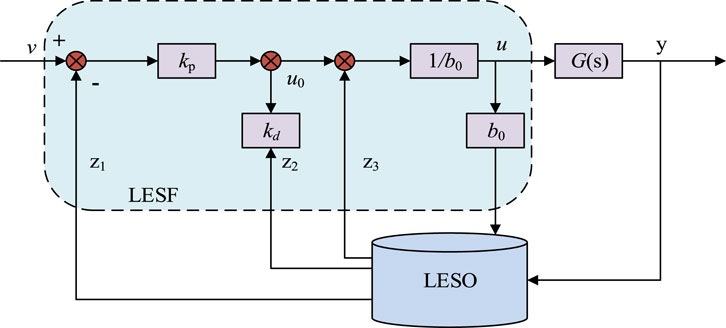
Figure 4 . Second order LADRC.
When the PGS of NEVs is considered as a second-order controlled object, the differential equation y ¨ = − a 1 y ˙ − a 2 y + w + b u can be obtained. In this equation, u and y represent the inputs and outputs of the controlled object in the system. w represents the external disturbance of the system. a 1 and a 2 both are system parameters. b represents the system gain parameter. This experiment guarantees b ≈ b 0 and considers b 0 as the nominal value of b . Assuming x 2 = y ˙ , x 1 = y , the system’s total disturbance can be obtained as x 3 = f y , y ˙ , w = − a 1 y − a 2 y + w + b − b 0 u . After optimization, the system’s state equation can be obtained, and then the state equation of the Linear Extended Star Observer (LESO) is constructed, as shown in Eq. 7 .
In Eq. 7 , x 1 , x 2 , x 3 represents the state variables of the system. β 1 , β 2 , β 3 represents the gain value of the undetermined observer in the system. z 1 , z 2 , z 3 represents the observation value of observer LESO on the state variable x 1 , x 2 , x 3 . LADRC will feed back the system disturbance estimated by LESO to the controller for compensation; and after compensation, the controlled NEV system can be equivalent to an integral series structure. Since the proportional-derivative controller (PD controller, PD) has zero steady-state error, strong anti-interference ability, and better stability and maximum peak overshoot than the integral controller, the PD controller was used to control the automotive PGS in the experiment. The composition of the differential equation and LSEF that can be obtained is shown in Eq. 8 .
In Eq. 8 , k p and k d both represent the proportional and differential coefficients of the PD controller, and both parameters are to be quantified. ω c represents the controller bandwidth. ξ represents the damping ratio. During the operation of NEVs, their PGS is considered as a second-order controlled object, while LESO is a third-order controlled object. The characteristic equation of the third-order LESO and the expression of the gain value of the system’s undetermined observer can be obtained through synthesis, as shown in Eq. 9 .
In Eq. 9 , s represents a complex frequency domain operator. ω 0 represents the observer bandwidth. To lift the dynamic response capability of power output and maintain the stability of system frequency, this experiment then introduces the second-order linear active disturbance rejection control algorithm (SO-LADRC) in the AP frequency link. Before introducing LADRC, the AP frequency loop control of VSG is Figure 5 .
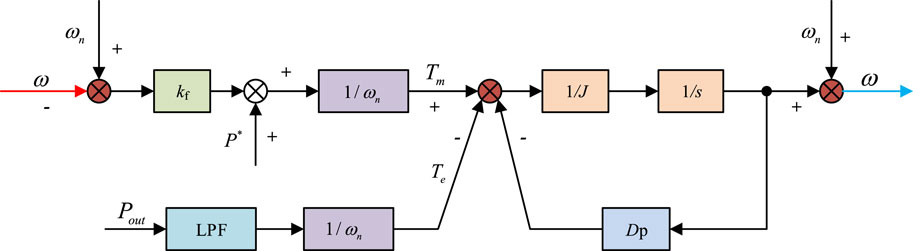
Figure 5 . VSG active frequency loop control process.
In Figure 5 , K f is the frequency droop coefficient, which is used to obtain the primary frequency modulation power based on the deviation between the VSG output AF and the rated AF. D p is responsible for providing damping for the system, and low-pass filter (LPF) is the output power feedback first-order low-pass filtering link. Using the process in Figure 5 to improve the VSG control system can effectively respond to the response and stability of the power grid’s dynamic changes. The closed-loop transfer function of the AP-frequency loop can be obtained through Figure 5 . After performing the inverse Laplace transform, the total disturbance calculation of d 2 ω d t 2 and the system can be obtained, as shown in Eq. 10 .
In Eq. 10 , τ p represents the time constant of LPF. ω n represents input. ω represents the integrated series controlled object of the output. It is very consistent with the control form of LADRC and can be combined with VSG. In summary, the designed VSG control structure based on LADRC is Figure 6 .
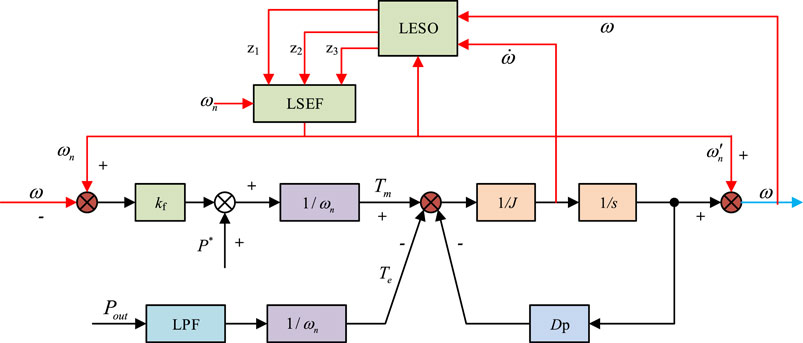
Figure 6 . VSG control based on LADRC.
In summary, the transfer function of z 1 , z 2 , z 3 and the composition of LSEF can be obtained. By combining the two, the transfer function of the control input U s of the controlled NEVs can be obtained. The calculation is Eq. 11 .
In Eq. 11 , V s represents the reference input of ADRC. Y s represents the specific form of the output of the controlled object in the complex frequency domain. Then, it is combined with the control input of the controlled NEVs, and the system output AP P o u t and the set value of AP P * are obtained. Furthermore, the closed-loop transfer function from the given VSG’s AF value to the VSG output AF can be obtained, as displayed in Eq. 12 .
In Eq. 12 , a 1 ∼ a 6 represents the coefficients. The final verification of the stability of the control system for NEVs can be based on the Lienard Chipard stability criteria. This standard is applied to the control strategy of the design. Since a 1 ∼ a 6 is all positive, the stability of NEVs PGSs can be evaluated using odd order Herwitz determinant. The calculation of parameters is Eq. 13 .
Eq. 13 constrains ω 0 and ω c in terms of stability and can serve as a reference for adjusting these two parameters. In addition, simulation software is utilized for numerical analysis of the stability of new energy generation systems.
4 Performance testing and application effects of the IC-NEVsPG system
With the rapid growth of NEVs worldwide, the operation of their PGSs has become an undeniable topic. Especially in terms of power grid stability and energy efficiency, the control technology of NEVs PGSs is particularly important. Therefore, this experiment aims to explore the practical effects and potential advantages of improving VSG technology in NEVs through comprehensive performance testing and practical application case analysis.
4.1 Performance testing of IC-NEVsPG system
To test and analyze the proposed control strategy, a model of an AC-DC hybrid micro-grid containing electric vehicles is built using PSCAD/EMTDC software, as shown in Figure 7 .
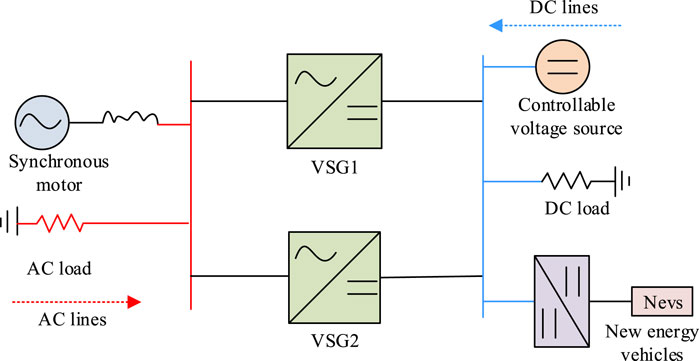
Figure 7 . Testing of AC/DC hybrid power grid.
In Figure 7 , in the test system, the AC power supply is equivalent to a synchronous motor, and the DC power supply is equivalent to a controllable voltage source. Energy conversion is realized on both sides of AC and DC through two VSG connections, and a certain amount of load is connected. The electric vehicle is connected to the DC bus through a bidirectional DC/DC converter. Table 1 shows the PGS parameters.
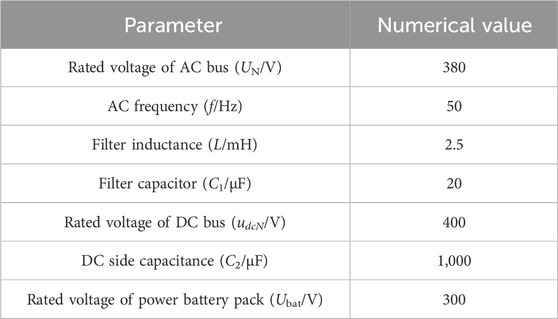
Table 1 . Partial parameters of new energy generation system.
Based on the above experimental setup, ignoring the impact of NEVs access, load fluctuation testing of the PGS is started. When the time is 3s, the load of the system is suddenly increased by 10 kW. The entire process of frequency variation during system load fluctuations during this process is Figure 8 .
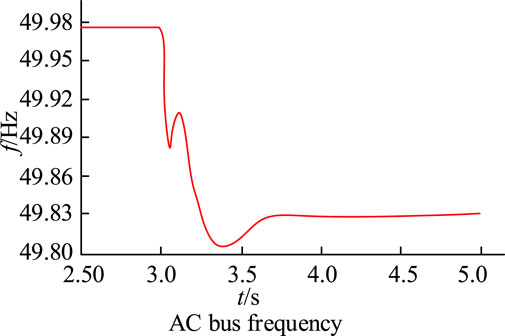
Figure 8 . AC bus frequency.
The variation of the curve in Figure 8 shows that the frequency of the system begins to slowly decrease during load fluctuations, and it can overcome the shortcomings of inertia in traditional control strategies during power generation, effectively enhancing the frequency stability. Under the virtual inertial control strategy, NEVs can give voltage support for the DC power grid. This support can be controlled by adjusting the value of the virtual inertia coefficient (VIC). Different coefficients have different effects on the voltage response of the system when the load suddenly changes. When the load of 10 kW is suddenly increased for 3s, the changes in DC bus voltage (DC-BV) and NEVs power can be obtained as shown in Figure 9 .
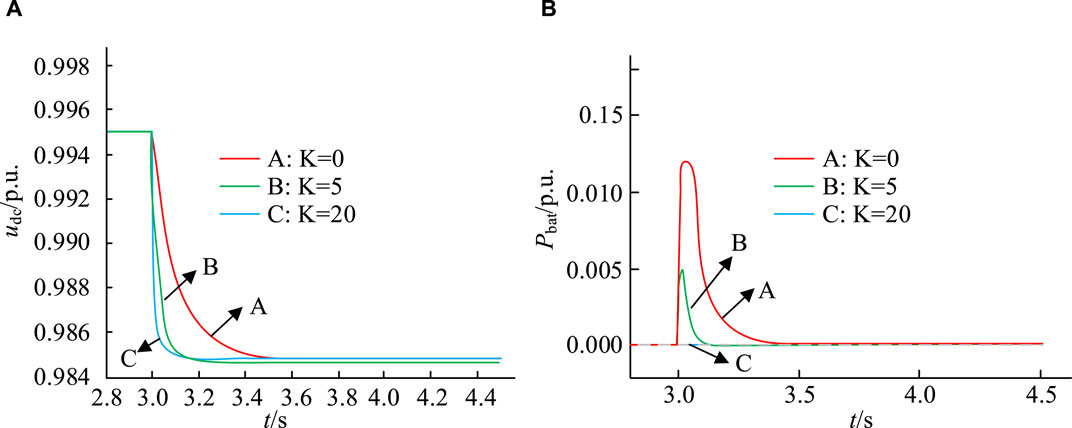
Figure 9 . Changes in DC-BV and NEVs power. (A) Changes in DC bus voltage (B) Changes in the power of new energy vehicles.
The three waveforms in Figure 9A show the changes in DC-BV under the conditions of VICs of 0, 5, and 20, respectively. The three waveforms in Figure 9B represent the changes in power of NEVs. In waveform A, when the VIC is 0, under the droop control, the DC-BV will rapidly decrease when the load suddenly increases, and NEVs will hardly intervene in the regulation of the grid voltage. In waveform B, after introducing the VIC K = 5, the decrease rate of the DC-BV of NEVs slows down, indicating that NEVs will increase the power output of the grid when the load suddenly increases. Waveform C further shows that increasing the VIC can improve the output of NEVs to the grid power during sudden load increases, making the decrease rate of DC-BV slower. The above results indicate that under virtual inertial control, NEVs can effectively provide voltage support for the DC network of micro-grids. By adjusting the VIC, the degree to which NEVs participate in voltage support can be controlled. However, when the VIC exceeds a certain limit value, virtual inertia control may cause system instability, so it is necessary to choose an appropriate VIC.
To test the effectiveness of the virtual inertia control strategy, this experiment selects the DC micro-grid voltage regulation method based on fractional order virtual inertia method (VRM-DC), the electric vehicle V2G technology based on inverter and optimal non integer model virtual inertia control (OAIM-VIC), and the constructed LADRC-VSG method for load fluctuation comparison ( Khooban, 2020 ; Long et al., 2022 ). The above three methods are respectively referred to as strategies A, B, and C. Similarly, when the time is 3 s, the load of the system is suddenly increased by 10 kW. When the time is 4 s, the load begins to return to normal. The obtained load test results are shown in Figure 10 .
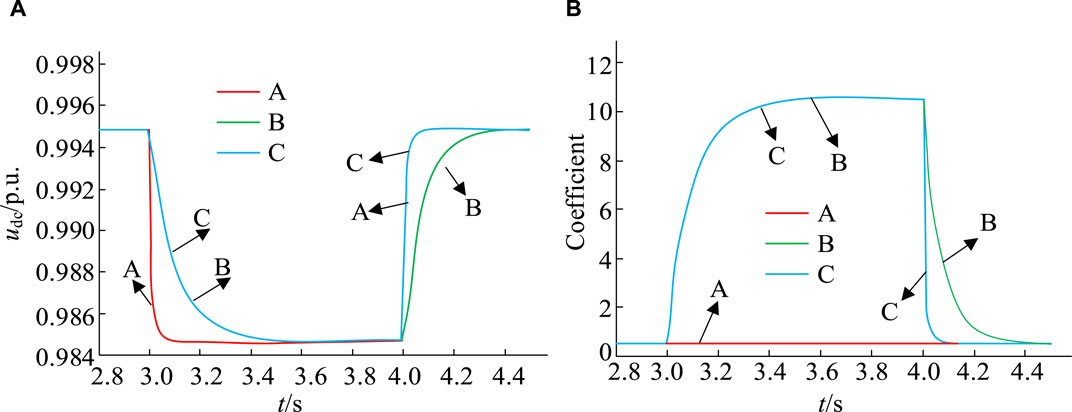
Figure 10 . Changes in DC-BV and VIC. (A) Changes in DC bus voltage (B) Comparison of virtual inertia coefficient.
Figure 10A, B show the changes in DC-BV and VIC under different strategy operations. Analyzing the changes in waveform A in Figure 10 , under the VRM-DC strategy, when the value of the VIC is very small or close to 0, the voltage drop rate of the DC network is faster. The inertia of DC voltage is small, and NEVs are hardly involved in voltage regulation. Under the OAIM-VIC strategy, the VIC will change according to the specific fluctuation of the grid voltage, allowing NEVs to participate in the regulation of the grid voltage. Waveform B represents the dynamic response change of the DC-BV. The speed of the decrease in DC-BV is significantly slowed down, and the stability of the voltage is significantly improved. In waveform C, the LADRC-VSG method can not only slow down voltage fluctuations, but also accelerate recovery speed and improve voltage stability. The above analysis indicates that adjusting the VIC appropriately can slow down voltage fluctuations while maintaining recovery speed, thereby enhancing the stability of the DC network.
4.2 Simulation results of grid connection modes for different virtual inertial control strategies
The correctness of the proposed NEVs power generation strategy is verified and simulated in MATLAB R2020b/Simulink environment. The experiment is carried out with a NEV as the research object, and ANOVA test is used to select the test. At the beginning of the experiment, NEVs are connected to the grid with an AP of -4kW, achieving single power factor charging. When the time reaches 0.6s, the AP setting of NEVs is adjusted to 4kW, and it is converted to discharge to the grid at a unit power factor. By monitoring the frequency fluctuations and power output changes of the grid connection points in the monitoring system, simulation results are exhibited in Figure 11 .
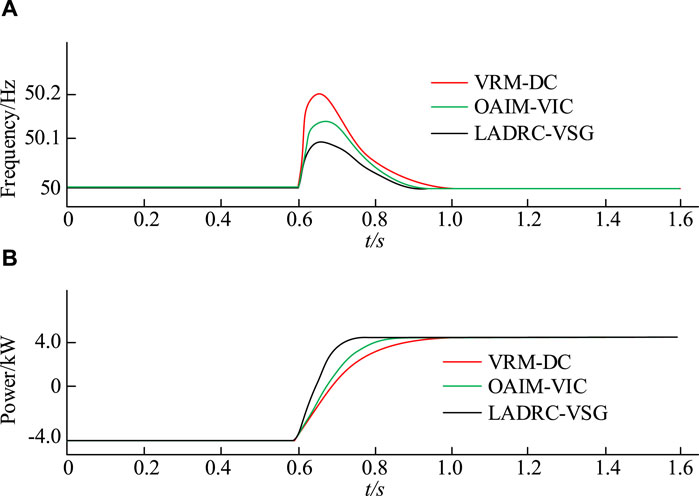
Figure 11 . Frequency and AP output of grid connection points. (A) Grid connection point frequency (B) Active power output.
Figure 11A shows the frequency variation of NEVs at the grid connection point. The comparison of different VSG control strategies shows that the frequency fluctuations at the grid connection points of VRM-DC, OAIM-VIC, and LADRC-VSG are 0.18Hz, 0.14Hz, and 0.08Hz, respectively. Compared to VRM-DC and OAIM-VIC, LADRC-VSG significantly reduces the frequency of grid connection by 55% and 43%. Figure 11B shows the output variation of AP of NEVs. When given a change in AP, the dynamic process of VRM-DC’s grid connected output power lasts for 0.33 s. Under the control of OAIM-VIC and LADRC-VSG, the dynamic process of grid connected output power lasts for 0.22 s and 0.16 s, respectively. The comparison shows that the LADRC-VSG strategy has significant advantages in terms of disturbance resistance and dynamic performance. Then, under the initial conditions, the system load is set to 12kW, which means the initial given AP P * of NEVs is 12 kW. When the time is 0.7 s, the load of the system suddenly decreases to 4 kW, and the variation of the output frequency and AP of the simulated system is Figure 12 .
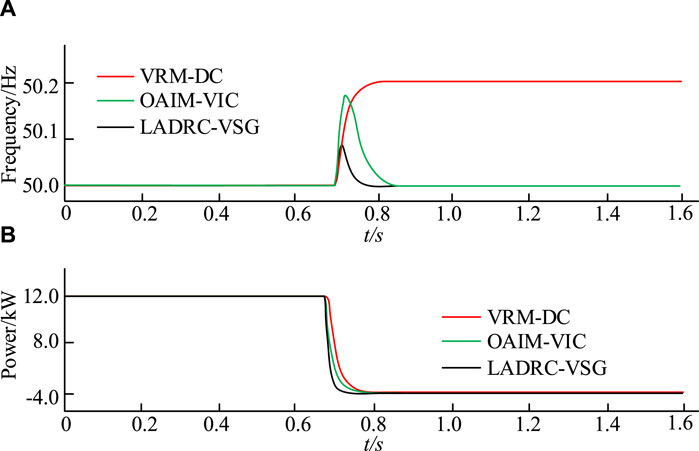
Figure 12 . Simulation results in island mode. (A) VSG output frequency (B) VSG output active frequency.
Figure 12A shows the VSG output power. Under VRM-DC control, the fluctuation of system output frequency caused by load changes ultimately increases by 0.2 Hz and tends to stabilize. When using OAIM-VIC control, the frequency fluctuation increases by 0.18 Hz and then returns to the rated frequency of 50 Hz. Under LADRC-VSG, the frequency fluctuation only increases by 0.09 Hz to restore to the rated frequency of 50 Hz. In Figure 12B ), after a sudden load change under three control strategies, the output AP of the system decreases from 12 kW to 4 kW. However, under LADRC-VSG, the duration of the dynamic process of system output power is the shortest, only 0.05 s. Under VRM-DC control and OAIM-VIC control, the duration is 0.1 s and 0.08 s, respectively. This indicates that the LADRC-VSG strategy performs better in terms of dynamic performance and frequency regulation ability.
Based on the above results, compared to the VRM-DC control proposed in reference ( Long et al., 2022 ) and the OAIM-VIC control strategy proposed in reference ( Khooban, 2020 ), the LADRC-VSG strategy has very superior performance in improving new energy electric vehicles. To emphasize the superiority of the research method, the performance results of the three methods are compared. The results are shown in Table 2 .
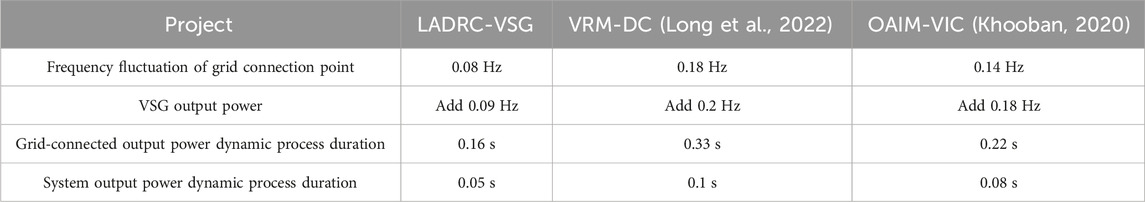
Table 2 . Comparison results.
5 Conclusion
The widespread application of NEVs PGSs has led to a series of problems such as inertia loss in automotive PGSs, and has brought adverse effects on the stable operation of the system. Therefore, this study proposed an IC-NEVsPG strategy that integrates LADRC and VSG. Firstly, an analysis was conducted on the VSG strategy, followed by the improvement of VSG using LADRC technology, which was jointly applied to the inertial control of NEVs PGSs. The results showed that adjusting the VIC appropriately could control the degree to which NEVs participate in voltage support. Under the LADRC-VSG strategy, voltage fluctuations could be effectively reduced and recovery speed could be accelerated. The changes in the frequency of NEVs at the grid connection point showed that the frequency fluctuations of VRM-DC and OAIM-VIC strategies at the grid connection point were 0.18 Hz and 0.14 Hz, respectively. The frequency fluctuation of the grid connection point under LADRC-VSG operation was 0.08 Hz. In the comparison of AP, under the control of VRM-DC, OAIM-VIC, and LADRC-VSG strategies, the dynamic process of grid connected output power lasted for 0.33 s, 0.22 s, and 0.16 s, respectively. The above data all indicate that the LADRC-VSG strategy not only provides new theoretical and technical support for the effective integration of the power grid and NEVs, but also provides practical guidance for further improving the stability and reliability of smart grids. In the future, the charging and discharging of electric vehicles will become more large-scale and orderly with the construction of large-scale charging stations, the unification of electric vehicle battery standards, and the gradual adoption of battery replacement charging methods. This will enable electric vehicles to participate in the frequency and voltage regulation of the power grid. The ability will be stronger, and the proposed control strategy will be more practical and economical. However, the experiment was analyzed and tested solely through the constructed simulation model, without any physical tests being conducted. Additionally, due to time constraints and lack of experimental conditions, only the effectiveness of the improved VSG electric vehicle charge and discharge control method was verified. This experiment failed to further verify the control effect of multiple electric vehicles participating in charging and discharging.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
MD: Data curation, Writing–original draft. HM: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
HM was employed by the China Automotive Technology and Research Center Co., Ltd.
The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Albert, J. R., Selvan, P., Sivakumar, P., and Rajalakshmi, R. (2022). An advanced electrical vehicle charging station using adaptive hybrid particle swarm optimization intended for renewable energy system for simultaneous distributions. J. Intelligent Fuzzy Syst. 43 (4), 4395–4407. doi:10.3233/jifs-220089
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Chang, J., Du, Y., Lim, E. G., Wen, H., Li, X., and Jiang, L. (2021). Coordinated frequency regulation using solar forecasting based virtual inertia control for islanded microgrids. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 12 (4), 2393–2403. doi:10.1109/tste.2021.3095928
Choudhuri, S., Adeniye, S., and Sen, A. (2023). Distribution alignment using complement entropy objective and adaptive consensus-based label refinement for partial domain adaptation. Artif. Intell. Appl. 1 (1), 43–51. doi:10.47852/bonviewaia2202524
Elizabeth Michael, N., Hasan, S., and Mishra, S. (2020). Virtual inertia provision through data centre and electric vehicle for ancillary services support in microgrid. IET Renew. Power Gener. 14 (18), 3792–3801. doi:10.1049/iet-rpg.2020.0217
Idan, R. F., Mahdi, A. J., and Abdul Wahhab, T. M. (2023). Review on virtual inertia control topologies for improving frequency stability of microgrid. Eng. Technol. J. 41 (2), 1–14. doi:10.30684/etj.2022.136217.1304
Jafari, H., Moghaddami, M., Olowu, T. O., Sarwat, A. I., and Mahmoudi, M. (2020). Virtual inertia-based multipower level controller for inductive electric vehicle charging systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 9 (6), 7369–7382. doi:10.1109/jestpe.2020.3032898
Khokhar, B., Dahiya, S., and Singh Parmar, K. P. (2020). A robust cascade controller for load frequency control of a standalone microgrid incorporating electric vehicles. Electr. Power Components Syst. 48 (6-7), 711–726. doi:10.1080/15325008.2020.1797936
Khooban, M. H. (2020). An optimal non-integer model predictive virtual inertia control in inverter-based modern ac power grids-based v2g technology. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 36 (2), 1336–1346. doi:10.1109/tec.2020.3030655
Long, B., Zeng, W., Rodriguez, J., Guerrero, J. M., Hu, J., and Chong, K. T. (2022). Enhancement of voltage regulation capability for dc-microgrid composed by battery test system: a fractional-order virtual inertia method. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 37 (10), 12538–12551. doi:10.1109/tpel.2022.3171556
Magdy, G., Ali, H., and Xu, D. (2021). Effective control of smart hybrid power systems: cooperation of robust LFC and virtual inertia control systems. CSEE J. Power Energy Syst. 8 (6), 1583–1593. doi:10.17775/CSEEJPES.2020.05230
Mitra, J., and Nguyen, N. (2022). Grid-scale virtual energy storage to advance renewable energy penetration. IEEE Trans. Industry Appl. 58 (6), 7952–7965. doi:10.1109/tia.2022.3202515
Muhtadi, A., Pandit, D., Nguyen, N., and Mitra, J. (2021). Distributed energy resources based microgrid: review of architecture, control, and reliability. IEEE Trans. Industry Appl. 57 (3), 2223–2235. doi:10.1109/tia.2021.3065329
Rasool, A., Yan, X., Rasool, U., Abbas, F., Numan, M., Rasool, H., et al. (2020). Enhanced control strategies of VSG for EV charging station under a low inertia microgrid. IET Power Electron. 13 (13), 2895–2904. doi:10.1049/iet-pel.2019.1592
Rathore, B., Chakrabarti, S., and Srivastava, L. (2021). ARI and ARID control of virtual synchronous generator for frequency response improvement. IET Renew. Power Gener. 15 (3), 664–675. doi:10.1049/rpg2.12054
Salem, R. B., Aimeur, E., and Hage, H. (2023). A multi-party agent for privacy preference elicitation. Artif. Intell. Appl. 1 (2), 98–105. doi:10.47852/bonviewaia2202514
Terazono, D., Liu, J., Miura, Y., Sakabe, S., Bevrani, H., and Ise, T. (2020). Grid frequency regulation support from back-to-back motor drive system with virtual-synchronous-generator-based coordinated control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 36 (3), 2901–2913. doi:10.1109/tpel.2020.3015806
Tinajero, M. Z., Ornelas-Tellez, F., and Garcia-Barriga, N. (2022). Optimal control of an inverter-based virtual synchronous generator with inertial response. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 20 (5), 780–786. doi:10.1109/tla.2022.9693562
Wu, Z., Zhao, Y., and Zhang, N. (2023). A literature survey of green and low-carbon economics using natural experiment approaches in top field journal. Green Low-Carbon Econ. 1 (1), 2–14. doi:10.47852/bonviewglce3202827
Zeng, W., Li, R., Huang, L., Liu, C., and Cai, X. (2021). Approach to inertial compensation of HVDC offshore wind farms by MMC with ultracapacitor energy storage integration. IEEE Trans. Industrial Electron. 69 (12), 12988–12998. doi:10.1109/tie.2021.3134092
Zhang, L., Zheng, H., Cai, G., Zhang, Z., Wang, X., and Koh, L. H. (2022). Power-frequency oscillation suppression algorithm for AC microgrid with multiple virtual synchronous generators based on fuzzy inference system. IET Renew. Power Gener. 16 (8), 1589–1601. doi:10.1049/rpg2.12461
Keywords: virtual synchronous generator, inertia, new energy, automobile power generation, control system, smart grid, stability
Citation: Du M and Mei H (2024) The application of virtual synchronous generator technology in inertial control of new energy vehicle power generation. Front. Mech. Eng 10:1382664. doi: 10.3389/fmech.2024.1382664
Received: 06 February 2024; Accepted: 22 March 2024; Published: 10 April 2024.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2024 Du and Mei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hailong Mei, [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are 5 reasons why you are going to love the BibGuru ISBN citation maker: 🚀 Fast. 😌 No flood of distracting ads. 👌 Simple and intuitive interface. 🎓 APA, MLA, Chicago, Turabian, and thousands of other citation styles. 🥇 Most accurate citation data. With BibGuru we have made a citation tool that truly helps students to focus ...
MyBib is a free bibliography and citation generator that makes accurate citations for you to copy straight into your academic assignments and papers. ... websites, and videos just by searching for a title or identifier (such as a URL or ISBN). Plus, we're using the same citation formatting engine as professional-grade reference managers such as ...
Generate APA style citations quickly and accurately with our FREE APA citation generator. Enter a website URL, book ISBN, or search with keywords, and we do the rest! Updated with APA 7th Edition!
Citation Generator: Automatically generate accurate references and in-text citations using Scribbr's APA Citation Generator, MLA Citation Generator, Harvard Referencing Generator, and Chicago Citation Generator. Plagiarism Checker: Detect plagiarism in your paper using the most accurate Turnitin-powered plagiarism software available to ...
Style selection. Format your bibliography using APA, MLA, Chicago / Turabian, Harvard, or any of the 10,000+ other CSL styles.. Copy Citation / Note. As you're writing, you can quickly generate parenthetical citations or footnotes /endnotes to paste into your document without typing names or dates by hand.
This is the total package when it comes to MLA format. Our easy to read guides come complete with examples and step-by-step instructions to format your full and in-text citations, paper, and works cited in MLA style. There's even information on annotated bibliographies.
An ISBN or International Standard Book Number is a 13 digit number that identifies published books. Ex: 978-3-16-148410-. ... APA Citation Generator | Website | Books | Journal Articles | YouTube | Images | Movies | Interview | PDF. Home > APA Citation Generator > Cite a Book. Company. Blog; Chegg Inc.
Referencing your sources is important because it: The most common citation styles in the UK are APA, MLA, Harvard, Vancouver, MHRA, and Oscola. Each citation style has specific rules for formatting citations. Scribbr's free Reference Generator can generate perfect references and in-text citations in both APA and MLA styles.
How to create APA citations. APA Style is widely used by students, researchers, and professionals in the social and behavioral sciences. Scribbr's free citation generator automatically generates accurate references and in-text citations.. This citation guide outlines the most important citation guidelines from the 7th edition APA Publication Manual (2020).
Enter the URL, DOI, ISBN, title, or other unique source information into the citation generator to find your source. Click the 'Cite' button on the citation machine. Copy your new reference from the citation generator into your bibliography or works cited list. Repeat for each source that has contributed to your work.
We cite according to the 9th edition of MLA, 7th edition of APA, and 16th edition of Chicago (8th edition Turabian). Cite a book in apa7 with EasyBib. Automatically create your works cited page and format your bibliography.
Generate bibliographies/works cited pages for books - just enter the ISBN(s) of the book(s) you've cited in your paper. Bibliography and Works Cited Generator for MLA, APA, Wikipedia and Bibtex - OttoBib.com
An ISBN or International Standard Book Number is a 13 digit number that identifies published books. Ex: 978-3-16-148410-. Powered by . ... Wish you had an automatic MLA citation generator to do all of the heavy lifting for you? Try out our generator, at the top of this page.
An ISBN or International Standard Book Number is a 13 digit number that identifies published books. Ex: 978-3-16-148410-
A Chicago Citation Generator is a software tool that automatically generates citations and bibliographies in the Chicago citation style. Citations can be created by entering an identifying piece of information about a source, such as a website URL, book ISBN, or journal article DOI to the generator. The generator will then create a fully ...
Save hours of repetitive work with Scribbr's Chicago Citation Generator. Stop wasting hours figuring out the correct citation format. With Scribbr's citation generator, you can search for your source by title, URL, ISBN, or DOI and generate accurate Chicago style citations in seconds. No experience needed. ⚙️ Styles.
Save hours of repetitive work with Scribbr's Harvard Referencing Generator. Stop wasting hours figuring out the correct citation format. With Scribbr's referencing generator, you can search for your source by title, URL, ISBN, or DOI and generate accurate Harvard style references in seconds.
Citation Machine is a citation generator that allows users to create citations by filling in information about the source. It supports MLA, APA, Turabian, and Chicago style formatting. Also it has an ISBN look-up that will generate a citation based on a book's ISBN number. CM helps create citations for A LOT of different source types.
Search by title, URL, DOI, or ISBN: Perfectly formatted references every time. Inaccurate citations can cost you points on your assignments, so our seasoned citation experts have invested countless hours in perfecting Scribbr's citation generator algorithms. ... Citation Generator: Automatically generate accurate references and in-text ...
Scribbr's free citation generator for Edge lets you instantly generate accurate citations for any online source in APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard and any other style. In addition, it extracts key sentences¹, complete with proper citations, and generates a comprehensive summary². With millions of users every month, students, teachers, and ...
Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form. The generator will produce a formatted MLA ...
Citation Generator Check your Citations Cite with Chrome. AI Writing. AI Proofreader Paraphrasing Tool Grammar Checker Summarizer AI Detector. ... Improve your in-text citations and references for errors and inconsistencies using Scribbr's AI technology or human experts. Run a free check.
Learning to Plan and Generate Text with Citations. Constanza Fierro, Reinald Kim Amplayo, Fantine Huot, Nicola De Cao, Joshua Maynez, Shashi Narayan, Mirella Lapata. The increasing demand for the deployment of LLMs in information-seeking scenarios has spurred efforts in creating verifiable systems, which generate responses to queries along with ...
Diffusion models generate images with an unprecedented level of quality, but how can we freely rearrange image layouts? Recent works generate controllable scenes via learning spatially disentangled latent codes, but these methods do not apply to diffusion models due to their fixed forward process. In this work, we propose SceneDiffusion to optimize a layered scene representation during the ...
A Harvard Referencing Generator is a tool that automatically generates formatted academic references in the Harvard style. It takes in relevant details about a source -- usually critical information like author names, article titles, publish dates, and URLs -- and adds the correct punctuation and formatting required by the Harvard referencing ...
How to cite in MLA format. MLA is one of the most common citation styles used by students and academics. This quick guide explains how to cite sources according to the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook.You can also use Scribbr's free citation generator to automatically generate references and in-text citations.. An MLA citation has two components:
Keywords: virtual synchronous generator, inertia, new energy, automobile power generation, control system, smart grid, stability. Citation: Du M and Mei H (2024) The application of virtual synchronous generator technology in inertial control of new energy vehicle power generation. Front. Mech. Eng 10:1382664. doi: 10.3389/fmech.2024.1382664