
- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less

Computer Basics - What is a Computer?
Computer basics -, what is a computer, computer basics what is a computer.

Computer Basics: What is a Computer?
Lesson 2: what is a computer.
/en/computerbasics/about-this-tutorial/content/
What is a computer?
A computer is an electronic device that manipulates information, or data. It has the ability to store , retrieve , and process data. You may already know that you can use a computer to type documents , send email , play games , and browse the Web . You can also use it to edit or create spreadsheets , presentations , and even videos .
Watch the video below to learn about different types of computers.
Looking for the old version of this video? You can still view it here .
Hardware vs. software
Before we talk about different types of computers, let's talk about two things all computers have in common: hardware and software .

Everything you do on your computer will rely on both hardware and software. For example, right now you may be viewing this lesson in a web browser (software) and using your mouse (hardware) to click from page to page. As you learn about different types of computers, ask yourself about the differences in their hardware. As you progress through this tutorial, you'll see that different types of computers also often use different types of software.
What are the different types of computers?
When most people hear the word computer , they think of a personal computer such as a desktop or laptop . However, computers come in many shapes and sizes, and they perform many different functions in our daily lives. When you withdraw cash from an ATM, scan groceries at the store, or use a calculator, you're using a type of computer.

Desktop computers

Many people use desktop computers at work, home, and school. Desktop computers are designed to be placed on a desk, and they're typically made up of a few different parts, including the computer case , monitor , keyboard , and mouse .
Laptop computers

The second type of computer you may be familiar with is a laptop computer , commonly called a laptop. Laptops are battery-powered computers that are more portable than desktops, allowing you to use them almost anywhere.
Tablet computers

Tablet computers —or tablets —are handheld computers that are even more portable than laptops. Instead of a keyboard and mouse, tablets use a touch-sensitive screen for typing and navigation. The iPad is an example of a tablet.

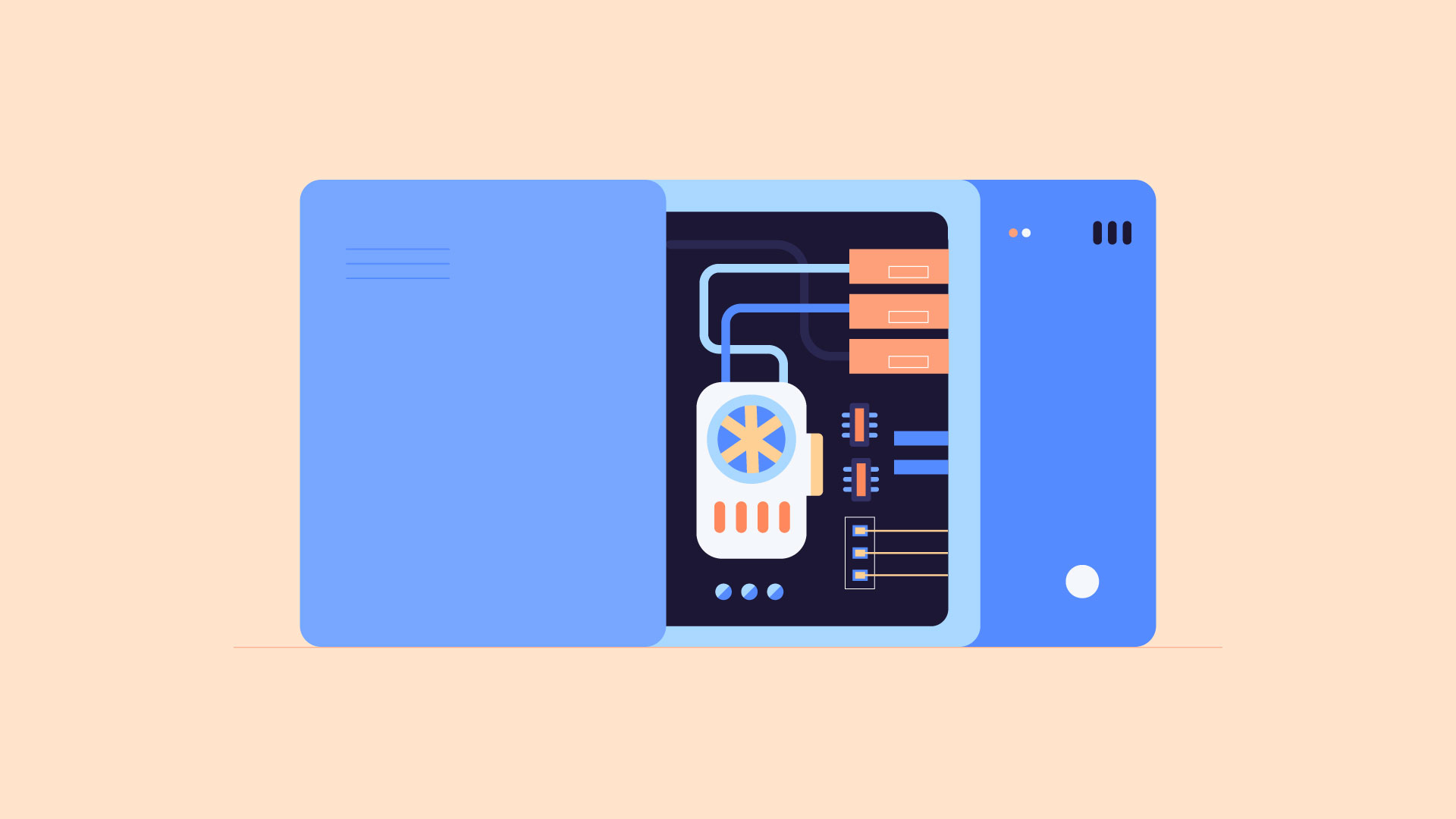
A server is a computer that serves up information to other computers on a network. For example, whenever you use the Internet, you're looking at something that's stored on a server. Many businesses also use local file servers to store and share files internally.
Other types of computers
Many of today's electronics are basically specialized computers , though we don't always think of them that way. Here are a few common examples.
- Smartphones : Many cell phones can do a lot of things computers can do, including browsing the Internet and playing games. They are often called smartphones .
- Wearables : Wearable technology is a general term for a group of devices —including fitness trackers and smartwatches —that are designed to be worn throughout the day. These devices are often called wearables for short.
- Game consoles : A game console is a specialized type of computer that is used for playing video games on your TV.
- TVs : Many TVs now include applications —or apps —that let you access various types of online content. For example, you can stream video from the Internet directly onto your TV.
PCs and Macs
Personal computers come in two main styles: PC and Mac . Both are fully functional, but they have a different look and feel, and many people prefer one or the other.
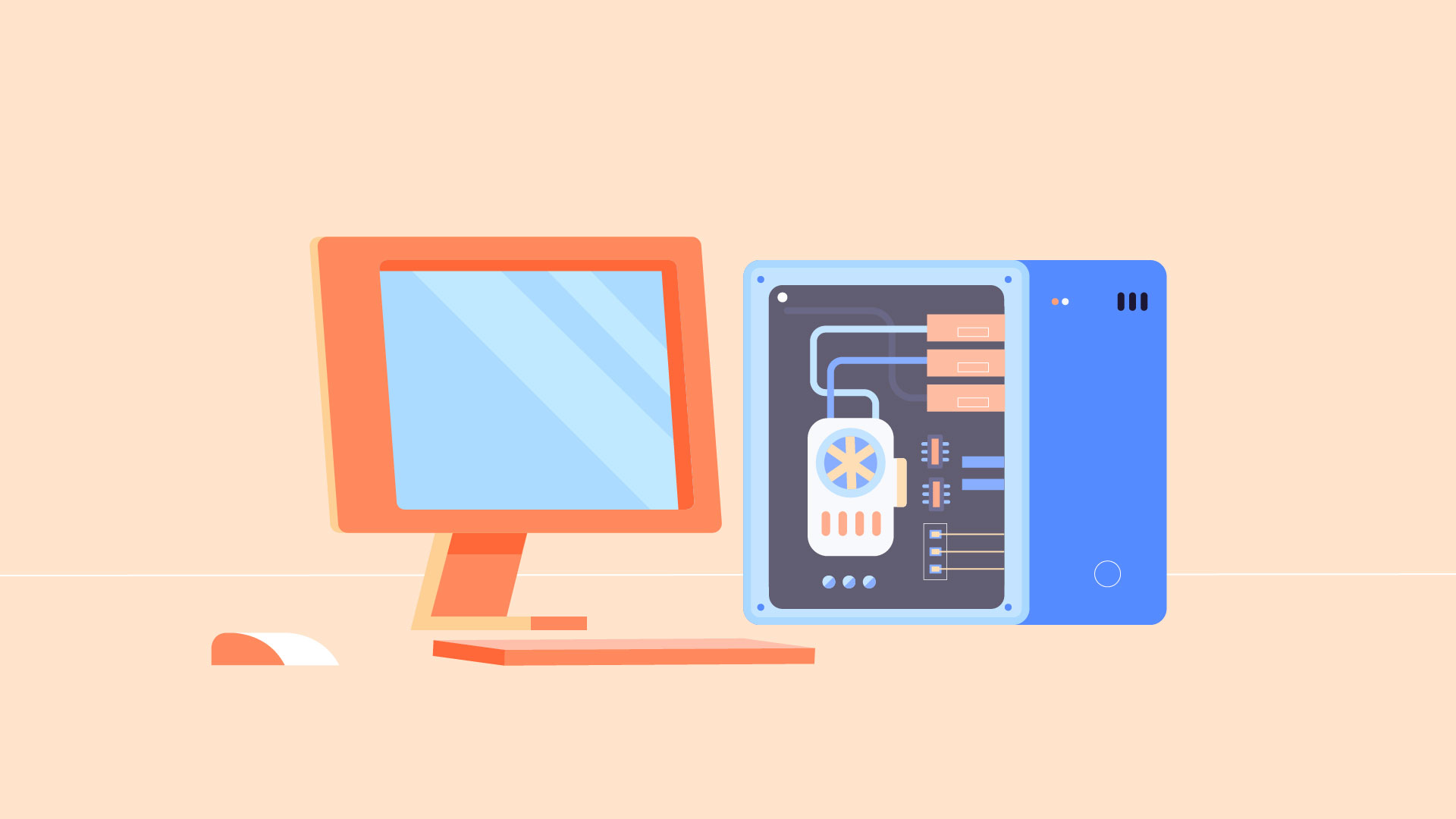

This type of computer began with the original IBM PC that was introduced in 1981. Other companies began creating similar computers, which were called IBM PC Compatible (often shortened to PC ). Today, this is the most common type of personal computer, and it typically includes the Microsoft Windows operating system.

The Macintosh computer was introduced in 1984, and it was the first widely sold personal computer with a graphical user interface, or GUI (pronounced gooey ). All Macs are made by one company ( Apple ), and they almost always use the Mac OS X operating system.
/en/computerbasics/basic-parts-of-a-computer/content/

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computer
Published by Rudy Brewer Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Chapter 1: Introduction to Computer"— Presentation transcript:

How Much Do I Remember? Are you ready to play.....

Basic Computer Vocabulary

Computer Skills Preparatory Year Presented by:

Computer Basics Whats that thingamagige?. Parts of a computer.

Chapter 1:Introduction to the world of computers

McGraw-Hill/Irwin ©2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved Plug-in B3 HARDWARE & SOFTWARE.

1 Jordan University of Science & Technology Faculty of Computer & Information Technology Department of Computer Science & Information Systems cs98.

An Overview of the Computer System

Hardware. Basic Computer System Central Processing Unit Input Devices Output Devices Backing Storage Devices.

Introduction to Computers

Computer Systems – Hardware

What Is A Computer System?

1 Hardware - devices for Input. 2 Hardware - devices for Input Processing.

1 System Software “Background software”, manages the computer’s internal resources.

1 Introduction to Computers Prof. Sokol Computer and Information Science Brooklyn College.

Computer Parts There are many parts that work together to make a computer work.

Introduction to Computers Essential Understanding of Computers and Computer Operations.

MIS 175 Spring Learning Objectives When you finish this chapter, you will: –Recognize major components of an electronic computer. –Understand how.

Computer Skills CIS-100 CH 1.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Mechanical Notes
Computer || Introduction, Definition, Parts & Types
Introduction of Computer A computer is a fast and accurate electronic machine that is designed to accept and store input…
Table of Contents
Introduction of Computer

- A computer is a fast and accurate electronic machine that is designed to accept and store input data, process them and produce output results, using the instructions of a stored program or data.
- A computer has some wonderful features that make it different from a human.
- It has become a critical piece of our lives.
- The word computer brings from the word ‘ compute ‘, that means to ‘ calculate .’
- The function performed by a PC is execution of program.
- A computer understand ‘ Binary ‘ language only.
- It produces 100 percent accurate results.
- Charles Babbage is considered as the dad of computer.
- He was an English mathematician and inventor.
Definition of Computer
- A computer is a fast data processing electronic machine in which a program is set of instruction or commands.
- It performs the arithmetical and logical operations on the input data and gives the desired output.
Working of Computer
- A computer works on the three basic steps:-
- This whole process is term as input- process- output cycle or I- P- O cycle.
Working of I- P- O cycle
- Let us learn with an example how I- P- O cycle works in a computer.
- Shilpa wants to add 18 and 17. So, she open the calculator on her computer and click on the buttons 18+ 17 =
- Input: The data and instructions that we enter into the computer are called as input. We input data using a keyboard and mouse.
- Here, data ( 18, 17 ) and instruction ( +, = ) acts as input.
- Process: Working on data is called as processing. The CPU works on data and does all the thinking and calculation.
- The computer finally gives the sum as 35.
- Output: The finally information we get is the output.
- The monitor shows the output.
Input:- 18, 17, +, =
Process:- 18 + 17 =
Output:- 35
Generations of Computer
- The term ” generation ” is generally used to characterise the major developments in the field of computer industry.
- There is no clear- cut separating line between the generations.
- Basically, the term generation is used to distinguish between different hardware technologies developed.
- Generations of a computers are divided into five categories. They are named as:-
1. First Generation of computer
2. Second Generation of computer
3. Third Generation of computer
4. Fourth Generation of computer
5. Future Generation of computer
- The 1st generation of computer is developed by Eckert and Mauchly in 1946 in the USA .
- They are named as Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator.
- In short ENIAC.
- It used high speed vacuum tubes as switching devices and had a tiny memory.
- The ENICA took about 200 microseconds to add two digits and about 2400 microseconds to multiple.
- In 1946 , Professor John V Neumann proposed the concept of stored programming that is the storage of machine instructions in the memory of the computer in 1949 known as EDSAC .
- EDSAC is represents Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator.
- It used mercury delay lines for storage.
- The 1st commercial production of stored electronic computers was UNIVAC .
- UNIVAC is stand for Universal Automatic Computer.
- During this period, PC writing computer programs was predominantly done in the machine language.
- Assembly language was presented during the early fifties.
Characteristics of 1st Generation of Computers
- It has a vacuum tube circuit.
- Continuous maintenance required.
- Punched card and paper tape utilized as secondary storage.
- Dump primary storage.
- Machine and symbolic language programming.
- Generated considerable heat.
- Poor reliability.
- Limited internal storage capacity.
- First commercial computer to be used.
- Slow input/output operations.
- Computer programmed with machine language.
- The 2nd generation of computers stared around 1956 .
- In this age, the computers used transistors instead of vacuum tubes.
- Transistors were made of germanium semi- conductor material.
- They were exceptionally solid when contrasted with tubes.
- Another major breakthrough during this period was the invention of magnetic core for storage.
- Developments of assembly language, assembler and procedural high- level language like Fortran, Cobol, Algol, Snobol, etc. were developed.
- Also, commercial applications like Payroll, Inventory Control and Production Planning and General Ledger System were developed.
Characteristics of 2nd Generation of Computers
- In a core element transistor circuit was used.
- Magnetic core primary storage.
- Secondary storage on tapes.
- Greater reliability and speed.
- Reduced generated heat.
- Smaller and more reliable.
- Faster than 1st generation computers.
- Required less power to operate.
- High level procedural languages Fortran and Cobol were utilized.
- Computers programmed in high level languages.
- The 3rd generation started in the year 1965 .
- In this generation, Germanium transistors were the core element replaced by silicon transistors.
- Here, the transistors were comprised of small scale integrated circuits, consisting of transistors, resistors, and capacitors, grown on a single chip of silicon.
- Hundred or even thousands of transistors could be manufactured on a single wafer of silicon.
- The size of main memory reached about 100 megabytes.
- FORTRANIV, COBOL- 68, PL/1 , etc. were other high level languages developed during this period.
- Additionally, the developments and usage of compiler and interpreter were used in programming languages.
- There are many important on line systems like airline reservation, dynamic production control, interactive query and integrated database management systems emerged on the global software scenario.
Characteristics of 3rd Generation of Computers
- Transistors were replaced by integrated circuits.
- Increased speed and reliability.
- Development of minicomputers.
- On line, real time processing.
- Multiprogramming operating system was introduced.
- It was faster than the previous generation.
- To improved input and output devices.
- The 4th generation was stared in the years 1976 – 1985 .
- This generation emerged with the large scale integrated circuits ( LSIC ) and very large integrated circuits ( VLSIC ) .
- There were packed about 50,000 transistors in a single chip.
- Personal computers were manufactured rapidly.
- Floppy disks served as low cost, high limit reinforcement peripherals.
- A significant development in software was the improvement of the most ambitious language ADA.
- And another development was in the field of interactive graphics.
Characteristics of 4th Generation of Computers
- The 4th generation computer used LSI and VLSI technology.
- Dramatic rise in hardware costs.
- Semi- conductor primary storage was used.
- Development of microcomputer or personal computer.
- Increased costs of software.
- Advancement of electronic spreadsheets and database management systems.
- Compact in size but faster speeds of processing.
- Microprocessor was used.
- An effective 5th generation computer would be highly complex and intelligent electronic device conceived with an idea of intelligence without going through the various stages of technical development.
- This idea of intelligence is called artificial intelligence or AI .
- The emphasis is now shifting developing reliable, faster, and smaller but dump machines to more intelligent machines.
Parts of Computer
- A computer is made up of different parts which are named as:-
1. The motherboard
2. The Central Processing Unit
3. A Graphics Processing Unit
4. A Random Access Memory
5. External Hard Drive
6. An Optical Drive
7. Solid State Drive
8. USB Flash Drive
9. Hard Disk Drive
10. A Card Reader
11. A Monitor
12. A keyboard
13. A mouse
14. Printer
15. Projector
16. Joystick

- The motherboard is the primary component of a PC.
- It is a board with integrated circuitry that interfaces different pieces of the PC including the CPU, RAM , disk drives just as any peripherals associated by means of the ports or the extension openings.
- It contains ports to interface every one of the inner parts.
- It carries a special port designed for power supply or fans.

- The central processing unit is written in short form as CPU.
- The CPU is called as the brain of the computer.
- This is where PC does all its processing work.
- It also controls all input, output and other devices.
- Inside CPU there is a box known as the CPU box.
- It is taken program guidelines from RAM , interprets and processes them and then sends back results so that the relevant components can easily carry out the instructions.
- They are usually cooled by a heat sink and fan, or water-cooling system.
- Most fresher CPU incorporates an on-die graphics preparing unit (GPU).
- The clock speed of CPU governs how quick it executes guidelines and is measured in GHz ; normal qualities lie between in the range of 1 GHz and 5 GHz.
- A Graphics Processing Unit is written in short form as GPU.
- A GPU is a chip or electronic circuit fit for rendering graphics for show on an electronic gadget which was acquainted with the more extensive market in year 1999 .
- It is best known for its use in providing the smooth graphics that consumers expect in modern games and videos.
- It comprise of polygonal directions that are changed over designs in recordings and games into bitmaps—a cycle called “ delivering “.
- And after that converted into signals that are shown on a screen.
- This transformation requires GPU to have a lot of processing power, which also makes GPUs valuable in machine learning, artificial knowledge, and different tasks that require a large number of complex and sophisticated computations.
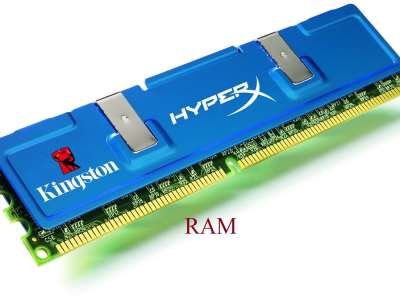
- A random access memory is written in short form as RAM.
- A RAM is a form of PC memory that can be read and changed in any order, regularly used to store working information and machine code.
- A RAM permits data items to be read or written in practically a similar amount of time independent of the actual area of data inside the memory.
- It stands out from other direct-access information storage media where the time needed to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their actual locations on the recording medium, because of mechanical limitations for example as media rotation speeds and arm movement.
- An external hard drive is a gadget that you plug into a PC port.
- An external hard drive gives you more extra space to keep your information.
- At the point when you store information on an outside hard drive, you can possibly get to it when the hard drive is connected to your PC .
- We can use an outer hard drive to store documents that you don’t get to every now and again for example, Old photographs or recordings, records and chronicled information, finished activities/portfolios and so on.
- An optical drive refers to a PC system that permits users to utilize DVDs, CDs and Blu-ray optical drives.
- The drive contains a couple of focal points that project electromagnetic waves that are liable for perusing and composing data on optical plates.
- An optical drives are fundamental pieces of hardware gadgets like VCD players, CD players, Blu-ray players, DVD players, and certain computer games control center like Microsoft Xbox one, Sony PlayStation 2, 3&4 and Nintendo Wii U .
- A solid-state drive is written in short form as SSD.
- A SSD is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit congregations to store information constantly, typically utilizing streak memory, and filling in as optional stockpiling in the order of PC amassing.
- It is likewise now and again called a solid-state device or a solid-state disk, even however SSDs do not have the physical spinning disks and movable read–compose heads used in hard plate drives (HDDs) and floppy circles.
- A USB flash drive is a data limit device that includes flash memory with an integrated USB interface.
- It is typically removable, rewritable and a lot more smaller than an optical disc.
- It is often used for storage, data back-up and transferring of PC files.
- A hard disk drive is written in short form as HDD.
- A PC HDD is a non-shaky memory equipment gadget that controls the arranging, perusing and composing of the hard plate, which outfits information stockpiling.
- It is commonly used as the main storage device in a PC.
- In a PC, HDD is generally found in the drive bay and is related with the motherboard through an ATA, SATA or SCSI connect.
- The HDD is likewise related to a power supply unit and can keep stored information while powered down.
- A card reader is a data input device that peruses data from a card-shaped storage medium.
- The first were punched card readers, which read the paper or cardboard punched cards that were utilized during the initial quite a few years of the PC business to store data and projects for PC frameworks.

- A monitor is an output device that shows data in pictorial construction.
- A monitor usually includes the visual display, circuitry, packaging, and power supply.
- It looks like a TV screen.
- Whatever we type with the help of keyboard can be seen on the monitor.
- It is also called as VDU.
- VDU stands for Visual Display Unit.
- The output we get on the monitor is called a soft copy .
- There are two types of monitor.
- LCD and CRT monitor.
- LCD is stand for Liquid Crystal Display and CTR is stand for Cathode Ray Tube.
- A keyboard is the most common input device used to enter data and instructions into the PC.
- A keyboard has many keys on it.
- There are various types of keyboard layouts manufactured based on the region and language utilized.

- A mouse is a hand held pointing device with two or three buttons on its top.
- It is used to select and point things on the monitor.
- It can also be used to draw pictures.
- A printer prints the output which we see on the PC screen on paper.
- The printer copy is called the hard copy.
- There are three main types of printer.
A. Dot matrix printer
B. Inkjet printer
C. Laser printer
- A dot matrix printer is an impact printer that prints utilizing a fixed number of pins or wires.
- In a dot matrix printer the pins or wires are organized in one or a few vertical segments.
- The pins strike an ink-covered lace and power contact between the lace and the paper, so that each pin makes a little dab on the paper.
- Thus mix of these specks shapes a spot lattice picture.
- They were also called as serial dot matrix printers .
- A Inkjet printing is a type of PC printing that reproduces a digital picture by impelling beads of ink onto paper and plastic substrates.
- These are the most commonly used type of printer, and reach from little reasonable customer models to costly expert machines.
- There are 2 main technologies which are in use in contemporary inkjet printers: continuous (CIJ) and drop-on-demand (DOD).
- A continuous inkjet means the flow is compressed and in a relentless stream.
- A drop-on-demand means the fluid is expelled from jet nozzle one drop at a time.
- This should be possible with a mechanical method with a push or some electrical technique.
- A Laser printing is an electrostatic computerized printing measure.
- It creates high-quality text and graphics by more than once passing a laser beam back and forth over a negatively charged cylinder called a “drum” to characterize a differentially charged image.
- The drum then, at that point specifically gathers electrically charged powdered ink, and moves the picture to paper, which is then heated in order to permanently fuse the text, imagery, or both, to the paper.
- Similarly as with digital photocopiers, laser printers employ a xerographic printing measure.
- A Laser printing differs from conventional xerography as carried out in simple scanners in that in the last mentioned, the image is formed by reflecting light off an existing document onto the uncovered drum.
- A projector is an optical device that takes pictures produced by a PC or Blu-beam player and reproduce them by projection onto a screen, wall, or another surface.
- The images may be movable or either slides.
- It is often about the size of a toaster and weighs only a few pounds.
- Real-time, Still images, Moving images are three categories of a projectors that are based on the type of their input.

- We use a joystick to play games on the PC.
- It helps us to control the movement of the pointer on the screen.
- It is stands for Uninterrupted Power Supply.
- It keeps the PC ON for some time even after the electricity goes OFF .
- It also saves the PC in case of high voltage or power problem.
Types of Computers
- On the basis of their performance and capacity computers are classified into 4 types. They are named as:-
1. Super computers
2. Mainframe computers
3. Mini computers
4. Microcomputers
- Super computers are the most powerful computers.
- They are also the most expensive PC.
- They are used for complex operations like astronomy, automobile designing, aircraft designing, space explorations, weather forecasting, etc.
- The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second rather than million instructions per second.
- Mainframe computers have a huge storage capacity.
- They can process data at a very high speed and they are also quite expensive.
- These PCs are generally used in large industries, banks and in scientific research centres.
- IBM-570 is a popular series of mainframe computers.
- Mini computers are less advanced as compared to mainframe computers in terms of speed and storage capacity.
- They are likewise more affordable than centralized server PCs.
- These PCs are mostly used as network servers and internet servers.
- PDP-8 and VAX PCs are examples of mini computers.
- Personal PCs, commonly used in schools, homes, offices, banks, etc. are known as microcomputers.
- These PCs are small with compact technology.
- The microcomputers were 1st developed by IBM corporation in 1981.
- Some other manufacturers are Dell, Apple, and HP .
- Desktop computers, laptops and palmtops are different types of microcomputers.
- Desktop PC are big in size and can be kept on a desk.
- Laptops as the name clearly indicates, are small enough to be carried easily while travelling.
- We can keep them on your lap and conveniently use them.
- These PC can be work with the help of batteries for a very long time.
- Tablets and palmtops are smaller than laptops and can be carried along easily.
Characteristics of a Computer
- There are 5th important characteristics of a computer which makes it a very special machine. They are as follows:-
2. Accuracy
3. Diligence
4. Versatility
5. Storage capacity
- A PC can perform operations at a very fast speed.
- It can perform thousands of mathematical operations in just a few seconds.
- The time it takes to perform these calculations is measured in the terms of nanoseconds or picoseconds.
1 second = 10 9 nanoseconds
1 seconds = 10 12 picoseconds
- A PC is considered to be 100% accurate, provided the data and instructions given to it by the user are up to the mark.
- A PC can work continuously for hours without getting tired.
- The speed and accuracy level also remains the same, even after it works for many hours.
- The same PC machine can be used for performing various jobs.
- It suits the needs of different kinds of people involved in different professions.
- A PC can store huge amount of data and information in its storage, called memory.
- This stored information can be kept and used for a long time.
Advantages of Using a Computer
- To increase our productivity.
- To connects us to the internet.
- It reduce waste and can store vast amount of data.
- To improves our employment options.
- To save the time.
- To assist the physical challenged.
- Also find your love in your life.
- To keep us entertained.
- To help us automate and monitor.
- To gave you a better understanding of data.
- They help us organize, sort and search through information .
Limitations of a Computer
- There are no decision making ability.
- It has no intelligence.
- They don’t have emotions and feelings.
External link
Realted Posts
Networking || definition,types, advantages, disadvantages & applications.
Networking Introduction Networking is referred as connecting computers electronically for the purpose of sharing information such as files, applications, etc….
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- CONSTRUCTION
- ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION
- GENERAL SCIENCE
- MANUFACTURING
- THERMODYNAMICS
Hello 👋 Chat now via Whatsapp
Looking for a Tutor Near You?

We use cookies
Our website use cookies, which help us to improve our site and enables us to deliver the best possible service and customer experience. By clicking accept you are agreeing to our cookies policy. Find out more
Choose Country Code
Ask a question.
- Bhubaneswar
- Gandhinagar
- Navi Mumbai
- Outside India
- Secundrabad
- Thiruchirappalli
- Thiruvananthapuram
- Visakhapatnam
PowerPoint Presentation Slides
Search our vast collection of PowerPoint presentations.

- 2D Animation
- 3D Printing
- Abacus / Brain Gym
- Accountancy
- Adobe Certification
- Advanced Excel
- Aeronautical
- Android Training
- Art & Craft Designing
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- AutoCAD Training
- B.Com Tuition
- B.Ed Tuition
- B.Sc Tuition
- Banking & Finance
- Basic Computer
- BCA Subjects
- BCA Tuition
- Big Data & Hadoop
- Bio Chemistry
- Biotechnology
- Business Management
- Business Studies
- C# (C Sharp)
- Cloud Computing
- Commerce Subjects
- Computer Science
- Cooking & Baking
- Cost Accounting and Financial Management
- Data Structures
- DBMS & RDBMS
- Digital Marketing
- Effective Communication
- Electronics
- Electronics And Communication
- Embedded Systems
- Enterprenuership
- Ethical Hacking
- Fashion Designing
- Financial Management
- Hardware Training
- Horticulture
- HR/Personnel
- HTML Training
- IIT JEE Mains
- Indirect Tax
- Information Technology and Strategic Management
- Instrumentation
- Java And J2EE
- Java Script
- Law, Ethics and Communication
- M.Sc Tuition
- Management Subjects
- Mass communication
- Mathematics
- MBBS Tuition
- Medical Entrance Exams
- MicroBiology
- Personality Development
- Pharma Training
- PHP And MySQL
- Political Science
- Public Administration
- Public Speaking
- Python Programming
- School level computer
- SEO for Ecommerce
- Social Studies
- Software Testing
- Spoken English
- SSC CGL Exams
- Web Development
- Wordpress Training
PPTs for Basic Computer

Presentation On What Is An Operating System?
Presentation On How A Computer Works

PPT On Excel Power Point For Excel Learner

PPT On Basic Knowledge Of Microsoft Excel

Email Etiquette PPT

Lunar Construction

Computer Network Security Basics

Basics Of The Computer

Storage Devices

Computer Fundamentals And C Language

Introduction To Computer

Fundamentals Of Computer
Optical Character Recognition

Binary No. System

Computer Basics

Basic Computer Course

Number System

Introduction To Linux Operating System

Computer - Number Conversion

Generations Of Computers

OPERATING SYSTEMS OVERVIEW

Computer Virus

Introduction About Computer
- Post Learning Requirement
- How it Works

Introduction to computer fundamentals
Nov 06, 2014
9.91k likes | 19.74k Views
Introduction to computer fundamentals. The Computer Defined. A computer is an electronic device that processes data, converting it into information that is useful to people. Analog and Digital Computer. Analog systems represent data as variable points along a continuous spectrum of values.
Share Presentation
- personal computer
- computer system
- personal computers
- computer perform tasks
- standard desktop personal computer

Presentation Transcript
The Computer Defined • A computer is an electronic device that processes data, converting it into information that is useful to people.
Analog and Digital Computer • Analog systems represent data as variable points along a continuous spectrum of values. • Early analog computers were mechanically devices, weighing several tons and using motors and gears to perform calculations.
Digital systems represents data as having one distinct value or another with no other possibilities. • Digital computers are so called because they work by the numbers.That is they break all types of information into tiny units and use numbers to represent those pieces of information.
Computers for individual users • Most computers are meant to be used by only one person at a time.Such computers are shared by several people,but only one user can work with the machine at any given moment.
Six primary types of computers • Desktop computers • Workstations • Notebook computers • Tablet computers • Handheld computers • Smart phones These systems are all examples of Personal Computers Personal computers are also called micro computers
Desktop Computers • The most common type of personal computer is the desktop computer…………….a PC that is designed to sit on a desk or table. • These computers you see in schools ,homes, offices. • These computers are used to communicate, produce music, edit photographs and videos, play sophisticated games and much more.
Workstations • A workstation is a speacialized,single user computer that typically has more power and features than a standard desktop personal computer. • These machines are popular among scientists,engineer who need a system with grater than average speed and the power to perform sophisticated tasks. • Workstations often have large high resolutions monitors and accelerated graphics handling capabilities.
Notebook Computer • Notebook computers as their name implies approximate the shape of an 8.5 by 11 inch notebook and easily fit inside a briefcase. • People frequently use these devices on their lap they are also called laptop computers.
Tablet PCs • The tablet PC is the newest development in portable , full featured computers. • Tablet PCs offer all the functionality of a notebook PC • They are lighter and can accept input from a special pen called a stylus or a digital pen.
Handheld PCs • Handheld personal computers are computing devices small enough to fit in your hands. • Personal digital assistant (PDA) is the type of handheld computers. • Size of PDA is no larger than small appointment book and is normally used for special applications • Displaying telephone numbers and addresses • Taking notes • Keeping track of dates or agendas
Smart phones • Some cellular phones double as miniature PCs • These phones offer advanced features ,that’s way they are called smart phones • These features can include • Web service • E-mail services • Special software such as personal organizers • Special hardware such as digital cameras or music players etc.
Computer for Organizations • Some computers handle the need of many users at the same time. • The largest organizational computers support thousands of individual users at the same time, from thousands of miles away.
Network servers • Today,most organization’s network are based on personal computer • Individual users have their own desktop computers which are connected to one or more centralized computers,called network servers. • Large organizations may have dozens or hundreds of individual servers working together at the heart of their network • When set up in such groups sometimes called clusters or server farms
In these large networks different group of servers may have different purposes • Handling printing tasks • Enabling internet communications • Accounting tasks • Word processing • Database management tasks
Mainframe computres • Mainframe computers are used in large organizations such as insurance companies and banks, where many people frequently need to use the same data. • In a traditional mainframe environment,each user access the mainframe’s resources through a device called a terminal
Types of terminal • A dumb terminal • An intelligent terminal
A dumb terminal • A dumb terminal does not process or store data • It is simply an input/output device that function as a window into a computer located somewhere else.
An intelligent terminal • An intelligent terminal can perform some processing operations but it usually does not have any storage.
The Parts of a Computer System • A complete computer system consists of four parts • Hardware • Software • Data • User
Hardware • The mechanical devices that make up the computer are called hardware • Hardware is any part of the computer you touch
Software • Software is a set of instructions that makes the computer perform tasks • The term program refers to any piece of software.
Data • Data consists of individual facts or pieces of information that by themselves may not make much sense to a person. • Tiny pieces of data in various form is actually the useful information.
Users • People are the computer operators, also known as users • No computer is totally autonomous
The information processing cycle • A computer converts data into information by performing various action. • During performing a mathematical operation on two numbers,then display the result.This is called the information processing cycle.
The information processing cycle has four parts • Input • Processing • Output • storage
Essential Computer hardware • A computer’s hardware devices fall into one of four categories • Processor • Memory • Input and Output • Storage
Processing devices • The processor is like the brain of the computer • It organizes and carries out instructions that come from either the user or software. • Processor usually consists of one or more speacialized chips called microprocessors. • Microprocessor is plugged into the computer’s motherboard • Motherboard is an example of circuit board • Many internal devices like sound card,videocard,disk controller are attached to the mother board.
Memory devices • In a computer, memory is one or more sets of chips that store data and program instructions either temporarily or permanently.
Random Access Memory • The most common type of memory is called random access memory(RAM) • RAM is like an electronic scratch pad inside the computer. • RAM holds data and program instructions while the CPU works with them. • When a program is launched it is loaded into and run from memory • RAM is also called read/write memory • RAM is made up of a set of chips mounted on a small circuit board. • RAM is also volatile ,meaning that it lost its contents when computer is shut off.
Read Only Memory • Unlike RAM ,read only memory (ROM) permanently stores its data, even when the computer is off. • RAM is called non volatile memory because it never lost its contents • ROM holds instructions that the computer needs to operate.
Input and Output devices • Input devices accept data and instructions from the user or from another computer • Out put devices return processed data to the user or to another system. • The most common input device is the keyboard,which accept letters,numbers and commands from the user. • Another type is mouse
Examples of input devices • The trackball and touchpad • The joystick • A scanner • A digital Camera • A microphone
The function of an output device is to present processed data to the user • The most common output devices are monitor and the printer
Storage Devices • The purpose of storage is to hold data permanently ,even when the computer is turned off. • Storage as an electronic file cabinet and RAM as an electronic worktable. • When you work with a program or set of data,the computer locates it in the file cabinet and puts a copy on the table.
What is storage and memory • There are three major distinctions between storage and memory • There is more room in storage than in memory • Contents are retained in storage but not in memory • Storage devices operate much slower than memory chips
Two types of storage • Magnetic storage • Optical storage
Magnetic storage • There are many types of computer storage but the most common is magnetic disk. • A disk is round, flat object that spins around its center.
Optical storage • Every computer sold today includes at least one form of optical storage • Devices that use lasers to read data from or write data to the reflective surface of an optical disc • The CD-ROM DRIVE is the most common type of optical storage device • An increasingly popular data storage technology is the digital video disc (DVD)
- More by User

Computer Fundamentals
Computer Fundamentals. Types Of Memories. Introduction.
425 views • 20 slides

Introduction to Computer
Introduction to Computer . Waqas Ali Sahito Lecturer Department of Computer Science. Subject Distribution. Theory 100 Marks Paper marks = 75 Sessional Marks = 25 Practical 50 Marks Objective = 10 Viva = 20 Sessional Marks = 20 Sessional Marks.
677 views • 41 slides

By Kiramat Rahman Department of Computer & Software Technology. Introduction to Computer. Input / Output (I/O) devices Commonly used input devices Commonly used output devices Other concepts related to I/O devices. Outline. Provide means of communication between a computer
878 views • 61 slides

INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER. EVOLUTION OF THE COMPUTER. EVOLUTION OF THE COMPUTER. The history and evolution of computer are divided into two eras : before 1940 after 1940. BEFORE 1940. In the beginning, human do calculation by fingers, stones, small woods etc.
532 views • 8 slides

Introduction to computer
Introduction to computer. Submitted by : aashish.c ashish.m Abhijeet.g Ankit.j abhay.j . CONTENT. WHAT IS COMPUTER? WHY COMPUTER? COMPUTER COMPONENT DATA & INFORMATION
843 views • 32 slides

INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER. Lecture #15 ARRAYS. By Shahid Naseem (Lecturer). ARRAYS DEFINITION. An array is a sequence of objects of same data type. The objects in an array are also called “elements of array”.
340 views • 16 slides

INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER. Lecture #9 OPERATING SYSTEM. By Shahid Naseem (Lecturer). LECTURE OUTLINES. DATA. A collection of raw (unprepared or unprocessed) facts ( things, people, objects, events) and figures, collected for a specific purpose is called data.
365 views • 19 slides

Computer Fundamentals. MSCH 233 Lecture 1. What is a computer?. A computer is an electronic machine which can accept data in a certain form, process the data and give the results of the process on a specific format as information. Where can computers be found and what are they used for ?.
530 views • 11 slides
Computer Fundamentals. Multimedia MSCH 233 Lecture 10. Who Use Multimedia Applications:. Teachers: To make video projects or to teach subjects Companies: To make Business Presentations Museums Banks Web designers Singers Movie maker. Etc. Types of multimedia. Audio Graphics Video.
287 views • 7 slides

Introduction to 7 Fundamentals
Introduction to 7 Fundamentals. PROSPECTING APPOINTMENT SETTING PRESENTATION OVERCOMING OBJECTIONS CLOSING RECRUITING & GETTING REFERRALS GETTING A LIST & GET NEW ASSOCIATE OFF TO FAST START. WHAT, WHY, HOW. Our Training System. The 7 Fundamentals Classes – 9 Weeks Total
853 views • 38 slides

Chapter-1. Computer Fundamentals. By: Mr. Birbal Jat PGT-Computer Sc . Kendriya Vidyalaya No 3 Jaipur. COMPUTER MEANS. C : Commonly O : Operator M : Machine P: Particular U: User T : Trade E : Education R: Research. The First in Computer World.
2.41k views • 35 slides

Computer Fundamentals. Input. Processing. Output. A Computer Is a System. Data is entered into the computer. The data is processed by adding, subtracting, and sorting. Becomes useful information. Input. Processing. Output. Example. Data for student registration.
1.08k views • 18 slides

Computer Science Fundamentals Course Introduction
Computer Science Fundamentals Course Introduction. How to learn stuff from Mr. Kramer. Class Flow. Lecture time I talk, you listen I demonstrate something raise hand for questions Open time Do the work I give help each other understand I’m wandering – raise hand or call me for help
360 views • 15 slides
Computer Fundamentals. MSCH 233 Lecture 7. Magnetic Drives. Types of Magnetic Drives: Floppy drive Hard disk Removable hard drive Tape drive Pocket-sized drive Microdrive. Floppy drive. Uses a high density floppy disk The floppy disk can store 1.44 MB of data It’s called drive A.
574 views • 17 slides

Computer Fundamentals. Northern College Diploma Philip Bird. Processor Architecture. Virtually every computer that has been built shares the same common layout. Von Neumann – programs and data both exist in the computers memory.
274 views • 9 slides

Computer Fundamentals. MDCS 134 Lecture 1. What is a computer?. A computer is an electronic machine which can accept data in a certain form, process the data and give the results of the process on a specific format as information. Where can computers be found and what are they used for ?.
554 views • 11 slides

Computer Fundamentals is not only useful topic for students it is also a must learn topic for all students. After the invention of computers life become more flexible for all human being. There are many computer languages for students to learn but before that they should learn all the simple Basic computer knowledge questions and answers from Mydearstudent website. Basic computer knowledge of anybody is a measure for today's job oppurtunities. For more details go through the website http://www.mydearstudent.com/basic-computers
282 views • 8 slides

14. Computer Fundamentals. Advanced Automotive Electricity and Electronics James D. Halderman. FIGURE 14.1 All computer systems perform four basic functions: input, processing, storage, and output.
385 views • 15 slides

COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS
COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS. Instructor: Fatima Naseem Lecture # 02 [email protected] http://web.uettaxila.edu.pk/CMS/AUT2010/cpCFbs/index.asp. Chapter 1B. Looking Inside the Computer System. Overview. Parts of Computer System > Hardware > Software
3.64k views • 58 slides

71. COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS. Figure 71-1 All computer systems perform four basic functions: input, processing, storage, and output. Figure 71-2 A potentiometer uses a movable contact to vary resistance and send an analog voltage right to the PCM.
295 views • 14 slides

COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALS. Instructor: Fatima Naseem Lecture # 01 [email protected] http://web.uettaxila.edu.pk/CMS/AUT2010/cpCFbs/index.asp. Course Book. “Introduction to Computers” by Peter Norton, 6th Edition. Contact. Fatima Naseem Room # 17, CED.
940 views • 45 slides
History of computers: A brief timeline
The history of computers began with primitive designs in the early 19th century and went on to change the world during the 20th century.

- 2000-present day
Additional resources
The history of computers goes back over 200 years. At first theorized by mathematicians and entrepreneurs, during the 19th century mechanical calculating machines were designed and built to solve the increasingly complex number-crunching challenges. The advancement of technology enabled ever more-complex computers by the early 20th century, and computers became larger and more powerful.
Today, computers are almost unrecognizable from designs of the 19th century, such as Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine — or even from the huge computers of the 20th century that occupied whole rooms, such as the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator.
Here's a brief history of computers, from their primitive number-crunching origins to the powerful modern-day machines that surf the Internet, run games and stream multimedia.
19th century
1801: Joseph Marie Jacquard, a French merchant and inventor invents a loom that uses punched wooden cards to automatically weave fabric designs. Early computers would use similar punch cards.
1821: English mathematician Charles Babbage conceives of a steam-driven calculating machine that would be able to compute tables of numbers. Funded by the British government, the project, called the "Difference Engine" fails due to the lack of technology at the time, according to the University of Minnesota .
1848: Ada Lovelace, an English mathematician and the daughter of poet Lord Byron, writes the world's first computer program. According to Anna Siffert, a professor of theoretical mathematics at the University of Münster in Germany, Lovelace writes the first program while translating a paper on Babbage's Analytical Engine from French into English. "She also provides her own comments on the text. Her annotations, simply called "notes," turn out to be three times as long as the actual transcript," Siffert wrote in an article for The Max Planck Society . "Lovelace also adds a step-by-step description for computation of Bernoulli numbers with Babbage's machine — basically an algorithm — which, in effect, makes her the world's first computer programmer." Bernoulli numbers are a sequence of rational numbers often used in computation.

1853: Swedish inventor Per Georg Scheutz and his son Edvard design the world's first printing calculator. The machine is significant for being the first to "compute tabular differences and print the results," according to Uta C. Merzbach's book, " Georg Scheutz and the First Printing Calculator " (Smithsonian Institution Press, 1977).
1890: Herman Hollerith designs a punch-card system to help calculate the 1890 U.S. Census. The machine, saves the government several years of calculations, and the U.S. taxpayer approximately $5 million, according to Columbia University Hollerith later establishes a company that will eventually become International Business Machines Corporation ( IBM ).
Early 20th century
1931: At the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Vannevar Bush invents and builds the Differential Analyzer, the first large-scale automatic general-purpose mechanical analog computer, according to Stanford University .
1936: Alan Turing , a British scientist and mathematician, presents the principle of a universal machine, later called the Turing machine, in a paper called "On Computable Numbers…" according to Chris Bernhardt's book " Turing's Vision " (The MIT Press, 2017). Turing machines are capable of computing anything that is computable. The central concept of the modern computer is based on his ideas. Turing is later involved in the development of the Turing-Welchman Bombe, an electro-mechanical device designed to decipher Nazi codes during World War II, according to the UK's National Museum of Computing .
1937: John Vincent Atanasoff, a professor of physics and mathematics at Iowa State University, submits a grant proposal to build the first electric-only computer, without using gears, cams, belts or shafts.

1939: David Packard and Bill Hewlett found the Hewlett Packard Company in Palo Alto, California. The pair decide the name of their new company by the toss of a coin, and Hewlett-Packard's first headquarters are in Packard's garage, according to MIT .
1941: German inventor and engineer Konrad Zuse completes his Z3 machine, the world's earliest digital computer, according to Gerard O'Regan's book " A Brief History of Computing " (Springer, 2021). The machine was destroyed during a bombing raid on Berlin during World War II. Zuse fled the German capital after the defeat of Nazi Germany and later released the world's first commercial digital computer, the Z4, in 1950, according to O'Regan.
1941: Atanasoff and his graduate student, Clifford Berry, design the first digital electronic computer in the U.S., called the Atanasoff-Berry Computer (ABC). This marks the first time a computer is able to store information on its main memory, and is capable of performing one operation every 15 seconds, according to the book " Birthing the Computer " (Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2016)
1945: Two professors at the University of Pennsylvania, John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert, design and build the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Calculator (ENIAC). The machine is the first "automatic, general-purpose, electronic, decimal, digital computer," according to Edwin D. Reilly's book "Milestones in Computer Science and Information Technology" (Greenwood Press, 2003).

1946: Mauchly and Presper leave the University of Pennsylvania and receive funding from the Census Bureau to build the UNIVAC, the first commercial computer for business and government applications.
1947: William Shockley, John Bardeen and Walter Brattain of Bell Laboratories invent the transistor . They discover how to make an electric switch with solid materials and without the need for a vacuum.
1949: A team at the University of Cambridge develops the Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator (EDSAC), "the first practical stored-program computer," according to O'Regan. "EDSAC ran its first program in May 1949 when it calculated a table of squares and a list of prime numbers ," O'Regan wrote. In November 1949, scientists with the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), now called CSIRO, build Australia's first digital computer called the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research Automatic Computer (CSIRAC). CSIRAC is the first digital computer in the world to play music, according to O'Regan.
Late 20th century
1953: Grace Hopper develops the first computer language, which eventually becomes known as COBOL, which stands for COmmon, Business-Oriented Language according to the National Museum of American History . Hopper is later dubbed the "First Lady of Software" in her posthumous Presidential Medal of Freedom citation. Thomas Johnson Watson Jr., son of IBM CEO Thomas Johnson Watson Sr., conceives the IBM 701 EDPM to help the United Nations keep tabs on Korea during the war.
1954: John Backus and his team of programmers at IBM publish a paper describing their newly created FORTRAN programming language, an acronym for FORmula TRANslation, according to MIT .
1958: Jack Kilby and Robert Noyce unveil the integrated circuit, known as the computer chip. Kilby is later awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for his work.
1968: Douglas Engelbart reveals a prototype of the modern computer at the Fall Joint Computer Conference, San Francisco. His presentation, called "A Research Center for Augmenting Human Intellect" includes a live demonstration of his computer, including a mouse and a graphical user interface (GUI), according to the Doug Engelbart Institute . This marks the development of the computer from a specialized machine for academics to a technology that is more accessible to the general public.

1969: Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie and a group of other developers at Bell Labs produce UNIX, an operating system that made "large-scale networking of diverse computing systems — and the internet — practical," according to Bell Labs .. The team behind UNIX continued to develop the operating system using the C programming language, which they also optimized.
1970: The newly formed Intel unveils the Intel 1103, the first Dynamic Access Memory (DRAM) chip.
1971: A team of IBM engineers led by Alan Shugart invents the "floppy disk," enabling data to be shared among different computers.
1972: Ralph Baer, a German-American engineer, releases Magnavox Odyssey, the world's first home game console, in September 1972 , according to the Computer Museum of America . Months later, entrepreneur Nolan Bushnell and engineer Al Alcorn with Atari release Pong, the world's first commercially successful video game.
1973: Robert Metcalfe, a member of the research staff for Xerox, develops Ethernet for connecting multiple computers and other hardware.
1977: The Commodore Personal Electronic Transactor (PET), is released onto the home computer market, featuring an MOS Technology 8-bit 6502 microprocessor, which controls the screen, keyboard and cassette player. The PET is especially successful in the education market, according to O'Regan.
1975: The magazine cover of the January issue of "Popular Electronics" highlights the Altair 8080 as the "world's first minicomputer kit to rival commercial models." After seeing the magazine issue, two "computer geeks," Paul Allen and Bill Gates, offer to write software for the Altair, using the new BASIC language. On April 4, after the success of this first endeavor, the two childhood friends form their own software company, Microsoft.
1976: Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak co-found Apple Computer on April Fool's Day. They unveil Apple I, the first computer with a single-circuit board and ROM (Read Only Memory), according to MIT .

1977: Radio Shack began its initial production run of 3,000 TRS-80 Model 1 computers — disparagingly known as the "Trash 80" — priced at $599, according to the National Museum of American History. Within a year, the company took 250,000 orders for the computer, according to the book " How TRS-80 Enthusiasts Helped Spark the PC Revolution " (The Seeker Books, 2007).
1977: The first West Coast Computer Faire is held in San Francisco. Jobs and Wozniak present the Apple II computer at the Faire, which includes color graphics and features an audio cassette drive for storage.
1978: VisiCalc, the first computerized spreadsheet program is introduced.
1979: MicroPro International, founded by software engineer Seymour Rubenstein, releases WordStar, the world's first commercially successful word processor. WordStar is programmed by Rob Barnaby, and includes 137,000 lines of code, according to Matthew G. Kirschenbaum's book " Track Changes: A Literary History of Word Processing " (Harvard University Press, 2016).
1981: "Acorn," IBM's first personal computer, is released onto the market at a price point of $1,565, according to IBM. Acorn uses the MS-DOS operating system from Windows. Optional features include a display, printer, two diskette drives, extra memory, a game adapter and more.

1983: The Apple Lisa, standing for "Local Integrated Software Architecture" but also the name of Steve Jobs' daughter, according to the National Museum of American History ( NMAH ), is the first personal computer to feature a GUI. The machine also includes a drop-down menu and icons. Also this year, the Gavilan SC is released and is the first portable computer with a flip-form design and the very first to be sold as a "laptop."
1984: The Apple Macintosh is announced to the world during a Superbowl advertisement. The Macintosh is launched with a retail price of $2,500, according to the NMAH.
1985 : As a response to the Apple Lisa's GUI, Microsoft releases Windows in November 1985, the Guardian reported . Meanwhile, Commodore announces the Amiga 1000.
1989: Tim Berners-Lee, a British researcher at the European Organization for Nuclear Research ( CERN ), submits his proposal for what would become the World Wide Web. His paper details his ideas for Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML), the building blocks of the Web.
1993: The Pentium microprocessor advances the use of graphics and music on PCs.
1996: Sergey Brin and Larry Page develop the Google search engine at Stanford University.
1997: Microsoft invests $150 million in Apple, which at the time is struggling financially. This investment ends an ongoing court case in which Apple accused Microsoft of copying its operating system.
1999: Wi-Fi, the abbreviated term for "wireless fidelity" is developed, initially covering a distance of up to 300 feet (91 meters) Wired reported .
21st century
2001: Mac OS X, later renamed OS X then simply macOS, is released by Apple as the successor to its standard Mac Operating System. OS X goes through 16 different versions, each with "10" as its title, and the first nine iterations are nicknamed after big cats, with the first being codenamed "Cheetah," TechRadar reported.
2003: AMD's Athlon 64, the first 64-bit processor for personal computers, is released to customers.
2004: The Mozilla Corporation launches Mozilla Firefox 1.0. The Web browser is one of the first major challenges to Internet Explorer, owned by Microsoft. During its first five years, Firefox exceeded a billion downloads by users, according to the Web Design Museum .
2005: Google buys Android, a Linux-based mobile phone operating system
2006: The MacBook Pro from Apple hits the shelves. The Pro is the company's first Intel-based, dual-core mobile computer.
2009: Microsoft launches Windows 7 on July 22. The new operating system features the ability to pin applications to the taskbar, scatter windows away by shaking another window, easy-to-access jumplists, easier previews of tiles and more, TechRadar reported .

2010: The iPad, Apple's flagship handheld tablet, is unveiled.
2011: Google releases the Chromebook, which runs on Google Chrome OS.
2015: Apple releases the Apple Watch. Microsoft releases Windows 10.
2016: The first reprogrammable quantum computer was created. "Until now, there hasn't been any quantum-computing platform that had the capability to program new algorithms into their system. They're usually each tailored to attack a particular algorithm," said study lead author Shantanu Debnath, a quantum physicist and optical engineer at the University of Maryland, College Park.
2017: The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is developing a new "Molecular Informatics" program that uses molecules as computers. "Chemistry offers a rich set of properties that we may be able to harness for rapid, scalable information storage and processing," Anne Fischer, program manager in DARPA's Defense Sciences Office, said in a statement. "Millions of molecules exist, and each molecule has a unique three-dimensional atomic structure as well as variables such as shape, size, or even color. This richness provides a vast design space for exploring novel and multi-value ways to encode and process data beyond the 0s and 1s of current logic-based, digital architectures."
2019: A team at Google became the first to demonstrate quantum supremacy — creating a quantum computer that could feasibly outperform the most powerful classical computer — albeit for a very specific problem with no practical real-world application. The described the computer, dubbed "Sycamore" in a paper that same year in the journal Nature . Achieving quantum advantage – in which a quantum computer solves a problem with real-world applications faster than the most powerful classical computer — is still a ways off.
2022: The first exascale supercomputer, and the world's fastest, Frontier, went online at the Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF) in Tennessee. Built by Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) at the cost of $600 million, Frontier uses nearly 10,000 AMD EPYC 7453 64-core CPUs alongside nearly 40,000 AMD Radeon Instinct MI250X GPUs. This machine ushered in the era of exascale computing, which refers to systems that can reach more than one exaFLOP of power – used to measure the performance of a system. Only one machine – Frontier – is currently capable of reaching such levels of performance. It is currently being used as a tool to aid scientific discovery.
What is the first computer in history?
Charles Babbage's Difference Engine, designed in the 1820s, is considered the first "mechanical" computer in history, according to the Science Museum in the U.K . Powered by steam with a hand crank, the machine calculated a series of values and printed the results in a table.
What are the five generations of computing?
The "five generations of computing" is a framework for assessing the entire history of computing and the key technological advancements throughout it.
The first generation, spanning the 1940s to the 1950s, covered vacuum tube-based machines. The second then progressed to incorporate transistor-based computing between the 50s and the 60s. In the 60s and 70s, the third generation gave rise to integrated circuit-based computing. We are now in between the fourth and fifth generations of computing, which are microprocessor-based and AI-based computing.
What is the most powerful computer in the world?
As of November 2023, the most powerful computer in the world is the Frontier supercomputer . The machine, which can reach a performance level of up to 1.102 exaFLOPS, ushered in the age of exascale computing in 2022 when it went online at Tennessee's Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF)
There is, however, a potentially more powerful supercomputer waiting in the wings in the form of the Aurora supercomputer, which is housed at the Argonne National Laboratory (ANL) outside of Chicago. Aurora went online in November 2023. Right now, it lags far behind Frontier, with performance levels of just 585.34 petaFLOPS (roughly half the performance of Frontier), although it's still not finished. When work is completed, the supercomputer is expected to reach performance levels higher than 2 exaFLOPS.
What was the first killer app?
Killer apps are widely understood to be those so essential that they are core to the technology they run on. There have been so many through the years – from Word for Windows in 1989 to iTunes in 2001 to social media apps like WhatsApp in more recent years
Several pieces of software may stake a claim to be the first killer app, but there is a broad consensus that VisiCalc, a spreadsheet program created by VisiCorp and originally released for the Apple II in 1979, holds that title. Steve Jobs even credits this app for propelling the Apple II to become the success it was, according to co-creator Dan Bricklin .
- Fortune: A Look Back At 40 Years of Apple
- The New Yorker: The First Windows
- " A Brief History of Computing " by Gerard O'Regan (Springer, 2021)
Sign up for the Live Science daily newsletter now
Get the world’s most fascinating discoveries delivered straight to your inbox.

Timothy is Editor in Chief of print and digital magazines All About History and History of War . He has previously worked on sister magazine All About Space , as well as photography and creative brands including Digital Photographer and 3D Artist . He has also written for How It Works magazine, several history bookazines and has a degree in English Literature from Bath Spa University .
The 7 most powerful supercomputers in the world right now
Computing 'paradigm shift' could see phones and laptops run twice as fast — without replacing a single component
Oladance OWS Pro Open-Ear Bluetooth Headphones review
Most Popular
By Anna Gora December 27, 2023
By Anna Gora December 26, 2023
By Anna Gora December 25, 2023
By Emily Cooke December 23, 2023
By Victoria Atkinson December 22, 2023
By Anna Gora December 16, 2023
By Anna Gora December 15, 2023
By Anna Gora November 09, 2023
By Donavyn Coffey November 06, 2023
By Anna Gora October 31, 2023
By Anna Gora October 26, 2023
- 2 'You could almost see and smell their world': Remnants of 'Britain's Pompeii' reveal details of life in Bronze Age village
- 3 Where does the solar system end?
- 4 Chemicals that make babies smell sweet and teens smell 'goat-like' revealed
- 5 'You probably didn't inherit any DNA from Charlemagne': What it means when your DNA 'matches' a historic person's
- 2 James Webb telescope confirms there is something seriously wrong with our understanding of the universe
- 3 How much does Earth weigh?
- 4 'You probably didn't inherit any DNA from Charlemagne': What it means when your DNA 'matches' a historic person's

Computer Science: Presenting
- Getting Started
- KU Library Resources
- Source Evaluation
Giving a Presentation
Here are a few tools and suggestions to help prepare you for getting up and presenting in front of a class. Hopefully, you'll be inspired to improve upon the traditional PowerPoint slideshow and integrate technology into your presentations.
Check out these articles for more advice on crafting an engaging and effective presentation:
- Designing Effective Virtual Presentations by KU Online
- What it Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- 1 0 Tips for Improving Your Public Speaking Skills
- Six Tips for Giving a Fabulous Academic Presentation
- 12 Reasons Your Presentation Sucks and How to Fix It
- 16 Useful Tips to Overcome Your Fear of Public Speaking
Sharing Your Presentation
Slideshare allows you to share presentations online. Slides are uploaded to Slideshare, searchable, and able to be shared or embedded across the internet.
Speaker Deck is another option for sharing your presentations online. It is similar to the style of Slideshare, but is ad free. Also, when you embed slideshows, they will automatically resize to the size of the space in which they are being embedded.
Library Resources
PowerPoint , one piece of the Microsoft Office Suite, is perhaps the best known tool for creating presentations. While everyone has seen dry presentations consisting primarily of text on slides, PowerPoint can do much more than this, including offering embedded content such as images, videos, audio files and even dynamic content from the internet.
These tools will help you to do more with your PowerPoint slides.
- 21 PowerPoint Add-ins and Plugins
- PowerPoint Twitter Tools These free tools allow users to interact with their audience via Twitter while presenting. You can poll the audience, take questions and feedback or auto-tweet your presentation all using these Twitter add-ons.
Prezi allows users to create dynamic "zooming" presentations. If you have already created a PowerPoint presentation, it also offers an option to import your existing slides to Prezi. Presentations are created, stored and delivered online.
Prezi offers a large number of tutorials to help you with every step of the process on their YouTube channel . The video below shows how to get started. You can also find examples of Prezis in their gallery .
Emaze is an online presentation platform built on HTML5 technology. Users can create, manage and share their presentations from any browser or mobile device. Emaze offers a variety of templates including formats using 3D animations and video backgrounds. Browse their gallery or view the sample presentation below:

Google Slides
Google Slides is to PowerPoint what Google Docs is to Word. It allows users with a free Google Drive account to create quick and easy presentations. While it doesn't have quite as many features as PowerPoint or others, it makes collaboration simple and works well for basic presentations. Google has a great tutorial to walk you through its features or you can watch the video below.
Thanks to Harvard Law School Library for inspiration in creating this LibGuide.
- << Previous: Plagiarism
- Next: Source Evaluation >>
- Last Updated: Feb 26, 2024 11:09 AM
- URL: https://libguides.kettering.edu/computerscience
IT Powerpoint Templates and Google Slides Themes
Discover a wide range of visually stunning and professionally designed presentation templates tailored specifically for the IT industry.
Explore Free IT Presentation Templates

2077 Futuristic City
Revamp your marketing or business project presentation with our Cyberpunk-Themed Business Presentation Toolkit! This futuristic design incorporates radiant shades of ... Read more

Neon Cyberpunk Style Theme
Present your next business initiative in a cutting-edge style using our Cyberpunk Powerpoint and Google Slides templates. Perfect for tech ... Read more

Cyberpunk Background Infographics
Dive into the future with our stunning, cyber-themed PowerPoint and Google Slides Templates. Perfect for educators and businesses in realms ... Read more

Illustrated Gaming Design Portfolio
Dive into the world of gaming design with our vibrant Cyberpunk style Google Slides and Powerpoint template. Specifically tailored for ... Read more

Cyber-Futuristic Cosplay Workshop
Unleash your innovative ideas with this Cyberpunk themed Powerpoint and Google Slides template. Ideal for educators in the field of ... Read more

Minimal Cybersecurity Agency
Experience the cutting-edge Cyberpunk themed Powerpoint and Google Slides templates specialized for the education sector. With a minimalistic yet modern ... Read more

Cyberpunk Metaverse Minitheme
Step into the future with our stylish and engaging Cyberpunk-themed Powerpoint and Google Slides templates. Designed to engage and impress ... Read more

Minimal AI Tool Pitch Deck
Unleash the power of AI technology in your next marketing or business presentation using these cutting-edge, minimalistic PowerPoint and Google ... Read more


Neon AI Newsletter
Harness the power of artificial intelligence marketing with our Premium Dark-Neon Powerpoint and Google Slides templates. Perfect for those in ... Read more

Retro SEO Specialist Resume
Boost your portfolio with our colourful, retro Y2K inspired PowerPoint template. This pastel-hued design is perfect for education, marketing, or ... Read more

Illustrated Information Technology Lesson
Elevate your technology lessons with our visually appealing, minimalistic Powerpoint and Google Slides templates, infused with a playful combination of ... Read more

Futuristic Tech Pitch Deck
Unveil next-gen innovations with our Advanced AI Powerpoint and Google Slides Templates. Tailored for businesses, it perfectly suits project strategy ... Read more

Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Project Proposal
Unleash your innovative marketing strategies with our AI-themed Powerpoint and Google Slides templates! Perfect for tech-forward audiences, these futuristic, neon-styled ... Read more

Simple AI Agency Pitch Deck
Kickstart your agency’s technology-forward journey with this modern, pastel-hued Powerpoint and Google Slides templates. Tailored for businesses wanting to showcase ... Read more

Futuristic Artificial Neural Networks Conference
Take your audience on a journey into the digital world with this modern, geometric-themed Powerpoint and Google Slides template. Its ... Read more
Professional designs for your presentations
SlidesCarnival templates have all the elements you need to effectively communicate your message and impress your audience.
Suitable for PowerPoint and Google Slides
Download your presentation as a PowerPoint template or use it online as a Google Slides theme. 100% free, no registration or download limits.
- Google Slides
- Editor’s Choice
- All Templates
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Google Slides Help
- PowerPoint help
- Who makes SlidesCarnival?
- What is PowerPoint? Video
- Create a presentation Video
- Choose the right view for the task Video
- Add and format text Video

What is PowerPoint?

Note: Microsoft 365 Copliot coming soon in PowerPoint.
With PowerPoint on your PC, Mac, or mobile device, you can:
Create presentations from scratch or a template.
Add text, images, art, and videos.
Select a professional design with PowerPoint Designer.
Add transitions, animations, and cinematic motion.
Save to OneDrive, to get to your presentations from your computer, tablet, or phone.
Share your work and work with others, wherever they are.
PowerPoint help
What's new in PowerPoint for Windows
Office Quick Start Guides
Get Microsoft presentation templates

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
- Generative AI
- Office Suites
- Collaboration Software
- Productivity Software
- Augmented Reality
- Emerging Technology
- Remote Work
- Artificial Intelligence
- Operating Systems
- IT Leadership
- IT Management
- IT Operations
- Cloud Computing
- Computers and Peripherals
- Data Center
- Enterprise Applications
- Vendors and Providers
- United States
- Netherlands
- United Kingdom
- New Zealand
- Newsletters
- Foundry Careers
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Copyright Notice
- Member Preferences
- About AdChoices
- E-commerce Affiliate Relationships
- Your California Privacy Rights
Our Network
- Network World

Presentation platform Pitch adds asynchronous video
Users of Pitch’s presentation software can now record and insert short videos directly into their presentations.

Presentation software maker Pitch has added a recordings feature so that users can now record and insert short videos directly into their presentations.
Users can record videos directly onto individual slides, with multiple collaborators all having the ability to add a recording into the same slide deck. The new feature has been built directly into the slide editing experience, with users simply needing to add a recording block, similar to the add text or image process, and then positioning it alongside the other content on the slide.
“We built recordings to transform presentations for the way work happens now,” Tomaž Štolfa, head of presentation experience at Pitch said. Štolfa believes that as collaboration is no longer confined to conference rooms or video calls, teams expect to be able to align asynchronously ahead of a big presentation, without being limited by schedules or physical locations.
Any member of a Pitch workspace can add recordings to slides, and anyone with access to a presentation can watch them. Users have the option to toggle recordings on and off and can also manage the playback speed of their videos. Comments and reactions allow teams to share updates and provide feedback inside the presentation environment.
Pitch has also integrated recordings into some of its most popular templates, and added two new templates, an async sales deck and async pitch deck.
Supporting asynchronous collaboration
As companies continue to embrace hybrid work models, asynchronous forms of communication have become increasingly popular, particularly among organizations that have teams working across multiple time zones.
Slack , Cisco , Dropbox , Asana and Trello all added video messaging features to their platforms in the latter half of 2021, while Loom, the which lets users create short videos that can be sent to colleagues and viewed whenever is convenient for them, has rapidly grown to a reported valuation above $1.5 billion.
Speaking to Computerworld in October 2021 , Angela Ashenden, principal analyst at CCS Insight said that many organizations “massively over-pivoted” towards real-time collaboration with video meetings and videoconferencing, which had adverse effects on lots of workers. “The growth of asynchronous is a realization that we need to manage our workloads better,” she said.
Related content
Just how good is ai-assisted code generation, the best ways to share files between windows pcs, windows 11 insider previews: what’s in the latest build, tech layoffs in 2024: a timeline, from our editors straight to your inbox.

Charlotte Trueman is a staff writer at Computerworld. She joined IDG in 2016 after graduating with a degree in English and American Literature from the University of Kent. Trueman covers collaboration, focusing on videoconferencing, productivity software, future of work and issues around diversity and inclusion in the tech sector.
More from this author
How blockchain can help tackle ticketing touts, tech talent charter lays out 2020 plan to make uk tech more inclusive, what is the circular economy and how can the it industry adopt it, how santander uk cut customer onboarding from days to hours, most popular authors.
- Howard Wen Contributing Writer

Show me more
Microsoft unbundles teams and office globally to avoid antitrust fight.

When the going gets tough, Apple’s Siri goes pro

Biggest problems and best practices for generative AI rollouts

Sam Bankman-Fried gets 25 years in prison

How to combat social media addiction

How social media companies are addicting adolescents

This is a potential security issue, you are being redirected to https://csrc.nist.gov .
You have JavaScript disabled. This site requires JavaScript to be enabled for complete site functionality.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
AI Risk and Threat Taxonomy
Description.
NIST’s Senior Researcher within the Computer Security Division provided a presentation on Artificial Intelligence Risk, the trustworthy attributes, and the adversarial challenges and risks associated with Machine Learning.
Event Details
Information Security and Privacy Advisory Board (ISPAB) March 2024 Meeting
Related Topics
Security and Privacy: risk management , security programs & operations
Technologies: artificial intelligence

Google Slides: How to add GIFs and stickers to your presentation
G oogle Slides helps you make impressive presentations with its diverse template library, collaboration options, and seamless integration with Google apps. You can use it on your Android phone, iPhone, desktop PC, laptop, or affordable Chromebook . Your audience might lose interest if your slides appear uninspired. Break the monotony by including an occasional GIF or sticker. This tutorial shows you how to add GIFs and stickers to Google Slides.
When to add GIFs and stickers to Google Slides
A GIF (Graphics Interchange Format) is an image file that uses a series of pictures to create an animated sequence. It's like a video without sound and is typically used to express reactions or make memes.
If you think your presentation might cause audience members to nod off to sleep, add a GIF or two to your Google Slides. There's a time and place for humor, so use it sparingly. For instance, a funny Star Wars GIF or sticker will attract your classmates' attention. But it might not fly during a board meeting presentation.
How to autoplay your Google Slides presentation
How to get gifs and stickers for your presentation.
If you can't find a particular GIF or sticker online, go to Giphy or Tenor.com and enter your search term. You can also explore the trending section to find popular GIFs. If you're using a phone, download the Giphy app from the Google Play Store or Apple App Store. You'll also find other third-party apps for Android and iOS.
How to add GIFs and stickers on desktop
We walk you through three ways of adding GIFs and stickers to Google Slides. The first method adds them from the web, the second accesses GIFs downloaded to your desktop PC, and the third uses a web link.
How to add GIFs and stickers from the web
- Open Google Slides .
- Click Insert from the toolbar.
- Select Image .
- Choose GIFs and stickers .
- Enter your search term.
- Select the GIF or sticker you want to add.
- Click Insert .
- To resize the image, click and drag any corner.
How to add GIFs and stickers saved on your computer
Adding GIFs and stickers from your computer is the easiest way to include them in your slideshow. You must download them to your PC before following these steps.
- Click Upload from computer .
How to add GIFs and stickers via URLs
First, keep your GIF or sticker's URL handy.
- Choose By URL .
- Paste the link.
- Click Insert image .
How to add GIFs and stickers on mobile
The Google Slides mobile app isn't as feature-rich as the desktop version. However, it will do in a pinch. First, download the GIFs or stickers you want on your phone. You can't add them to your presentation via URL.
The following steps work on Android and iOS. We use an Android smartphone in this tutorial, but iPhone users can follow along.
- Open the Google Slides app.
- Tap the plus icon in the upper-right corner.
- Select Image . Close
- Tap From photos .
- Choose a GIF or sticker from your gallery. Close
Why can't I add a GIF or sticker to Google Slides?
There are many reasons why your GIF or sticker might not load correctly despite following the steps listed above.
- Older versions of Google Slides might have issues with GIF playback, so get the latest update.
- GIFs and stickers may not appear as intended if you have poor internet connectivity. To avoid issues, download and add them to your slides instead of using URLs.
- Large GIF files may not work well with Slides. Compress the images or replace them with smaller files.
The best Google Slides templates for work, school, and home
How to edit gifs and stickers in google slides.
You can customize GIFs to match the theme of your presentation. You can add a border, crop, resize, and recolor images.
How to crop an image
- Double-click the GIF or sticker.
- Drag the black tabs until the image gets cropped to your preference.
- When you're happy with the final image, press Enter . If you aren't, type Ctrl + Z to undo the changes.
How to use formatting options
Use Google Slides' formatting options to change your GIF or sticker's orientation, size, color, opacity, and brightness.
- Select your GIF or sticker by clicking it.
- Select Format from the toolbar.
- Click Format options .
- Adjust the orientation or size from the Size and Rotation section.
- Change the tone of the image from the Recolor section.
- Customize your image's opacity, brightness, or contrast from the Adjustments section.
How to add a border
- Click the GIF or sticker.
- Select the pencil icon from the menu bar.
- Choose a border color.
- Click the border weight icon to adjust the thickness.
Get your point across with GIFs and stickers
If a picture is worth a thousand words, animated GIFS are worth even more. Pique your audience's interest by adding GIFs and stickers in Google Slides. If you want to make custom GIFs on Android, we have a guide for creating GIFs from stop-motion photos .

Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

solar eclipse
25 templates

academic writing
15 templates

8 templates

education technology
180 templates

32 templates

citizenship
14 templates
Computing Presentation templates
There are only 10 kinds of people in this world: those who know binary and those who don’t. if you’re among the ones who can, this selection of templates is the perfect match for you with these modern designs you can speak about data science, coding, computers or engineering in a modern, creative way that even the end users will understand.

Statistics and Data Analysis - 6th Grade
Download the Statistics and Data Analysis - 6th Grade presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. If you’re looking for a way to motivate and engage students who are undergoing significant physical, social, and emotional development, then you can’t go wrong with an educational template designed for Middle School by Slidesgo!...

Candycore Aesthetics Social Media Strategy
Download the Candycore Aesthetics Social Media Strategy presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. How do you use social media platforms to achieve your business goals? If you need a thorough and professional tool to plan and keep track of your social media strategy, this fully customizable template is your ultimate...

Work Program Project Proposal
Download the Work Program Project Proposal presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. A well-crafted proposal can be the key factor in determining the success of your project. It's an opportunity to showcase your ideas, objectives, and plans in a clear and concise manner, and to convince others to invest their...

Global Technology Investments Project Proposal Infographics
Download the Global Technology Investments Project Proposal Infographics template for PowerPoint or Google Slides to get the most out of infographics. Whether you want to organize your business budget in a table or schematically analyze your sales over the past year, this set of infographic resources will be of great...

Healthy Relationships and Communication Skills - 6th Grade
Download the Healthy Relationships and Communication Skills - 6th Grade presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and easily edit it to fit your own lesson plan! Designed specifically for elementary school education, this eye-catching design features engaging graphics and age-appropriate fonts; elements that capture the students' attention and make the...
Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access
Linear Grid Newsletter
Give an original touch to your employee newsletters with this grid design. It perfectly combines colors like green, yellow or orange with geometric icons to give dynamism to your news. You can use a different tone for each section, so they can be easily differentiated. Report on the latest company...

Computer Science Degree for College
Computer science degrees prepare students for the jobs of the future (and the present!). If you are interested in getting an education about coding, math, computers, and robots, this is the degree for you! Speak about it with this futuristic template that will take the viewers to another digital dimension....

Virtual Slides for Education Day
Digital learning is making its way into the world of education. For this reason, we've designed this new template so that the slides look like the screen of a laptop (complete with reflections!). Apart from graphs and infographics, the font is quite computer-esque and a perfect fit for this theme....
Silicon Valley Programmer Minitheme
No matter your actual profession, you can’t say you’ve never ever imagined being one of those fabled Silicon Valley programmers that make alternate realities come to life and can make us question the structures that govern our world. The good news: With this minitheme, you can join them for a...

Computer Science College Major
If you are a guru of computers, most likely you've studied computer science in college. Would you like to show others what a major in this field has to offer and what it could contribute to their professional development? Customize this template and let them feel the future, at least...

Soft Colors UI Design for Agencies
Agencies have the most creative employees, so having boring meetings with traditional Google Slides & PowerPoint presentations would be a waste. Make the most out of this potential with this creative design full of editable resources and beautiful decorations in calming, pastel tones. Let the creativity of your agency be...

Tech Startup Newsletter
Download the Tech Startup Newsletter presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Attention all marketers! Are you looking for a way to make your newsletters more creative and eye-catching for your target audience? This amazing template is perfect for creating the perfect newsletter that will capture your audience's attention from the...

Multimedia Software Pitch Deck
Download the Multimedia Software Pitch Deck presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Whether you're an entrepreneur looking for funding or a sales professional trying to close a deal, a great pitch deck can be the difference-maker that sets you apart from the competition. Let your talent shine out thanks to...

Web Project Proposal
We live in the internet era, which means that web design is currently one of the most demanded skills. This free template is perfect for those designers who want to present their web project proposal to their clients and see a preview of the final work.

Computer Science Proposal
A slide deck whose overall look and feel is very techie is what you need to put forward a proposal for a computer science project. And that’s what you’ll get with this template. The details on the backgrounds are so enticing and the neon tone used for the text contrasts...

How to Code Workshop
Are you an expert of Java? Yes, it's a beautiful island in Indonesia and more than half of the population of this country lives there... No! Well, yes, those facts are true, but we were talking about the programming language! We think workshops on how to code are a necessity,...
Robotic Workshop Infographics
Download the Robotic Workshop Infographics template for PowerPoint or Google Slides and discover the power of infographics. An infographic resource gives you the ability to showcase your content in a more visual way, which will make it easier for your audience to understand your topic. Slidesgo infographics like this set...

Software Testing Company
Software testing might not be the sexiest part of coding, but that doesn't mean it lacks intrigue or importance. After all, who wants to use a buggy app? It's software testing that ensures smooth operation and prevents annoying glitches from making it into the final product. Without it, our lives...
- Page 1 of 28
New! Make quick presentations with AI
Slidesgo AI presentation maker puts the power of design and creativity in your hands, so you can effortlessly craft stunning slideshows in minutes.

Register for free and start editing online
What is Good Friday? What the holy day means for Christians around the world

Christians around the world observe Good Friday two days before Easter, but what is it, and why do they commemorate the holy day?
The holiday is part of Holy Week, which leads up to Easter Sunday. Palm Sunday kicks off the series of Christian holy days that commemorate the Crucifixion and celebrate Jesus Christ's resurrection.
"Good Friday has been, for centuries now, the heart of the Christian message because it is through the death of Jesus Christ that Christians believe that we have been forgiven of our sins," Daniel Alvarez, an associate teaching professor of religious studies at Florida International University, told USA TODAY.
What is Holy Saturday? What the day before Easter means for Christians around the world
When is Good Friday?
Good Friday is always the Friday before Easter. It's the second-to-last day of Holy Week.
In 2024, Good Friday will fall on March 29.
What is Good Friday?
Good Friday is the day Christ was sacrificed on the cross. According to Britannica , it is a day for "sorrow, penance, and fasting."
"Good Friday is part of something else," Gabriel Radle, an assistant professor of theology at the University of Notre Dame, previously told USA TODAY. "It's its own thing, but it's also part of something bigger."
Are Good Friday and Passover related?
Alvarez says that Good Friday is directly related to the Jewish holiday, Passover.
Passover , or Pesach, is a major Jewish holiday that celebrates the Israelites’ exodus from Egypt.
"The whole Christian idea of atoning for sin, that Jesus is our atonement, is strictly derived from the Jewish Passover tradition," said Alvarez.
How is that possible?
According to the professor, Passover celebrates the day the "Angel of Death" passed over the homes of Israelites who were enslaved by the Egyptians. He said that the Bible states when the exodus happened, families were told to paint their doors with lamb's blood so that God would spare the lives of their firstborn sons.
Alvarez says this is why Christians call Jesus the "lamb of God." He adds that the symbolism of the "blood of the lamb" ties the two stories together and is why Christians believe God sacrificed his firstborn son. Because, through his blood, humanity is protected from the "wrath of a righteous God that cannot tolerate sin."
He adds that the stories of the exodus and the Crucifixion not only further tie the stories together but also emphasize just how powerful the sacrifice of the firstborn and the shedding of blood are in religion.
"Jesus is the firstborn, so the whole idea of the death of the firstborn is crucial," said Alvarez.
He adds that the sacrifice of the firstborn, specifically a firstborn son, comes from an ancient and "primitive" idea that the sacrifice unleashes "tremendous power that is able to fend off any kind of force, including the wrath of God."
Why Is Good Friday so somber?
Alavarez says people might think this holiday is more depressing or sad than others because of how Catholics commemorate the Crucifixion.
"I think [it's] to a level that some people might think is morbid," said Alvarez.
He said Catholics not only meditate on Jesus' death, but primarily focus on the suffering he faced in the events that led up to his Crucifixion. That's what makes it such a mournful day for people.
But, the professor says that Jesus' suffering in crucial to Christianity as a whole.
"The suffering of Christ is central to the four Gospels," said Alvarez. "Everything else is incidental."
According to the professor, statues that use blood to emphasize the way Jesus and Catholic saints suffered is very common in Spanish and Hispanic Countries, but not as prevalent in American churches.
Do you fast on Good Friday?
Father Dustin Dought, the executive director of the Secretariat of Divine Worship of the United States Conference of Catholic Bishops, previously told USA TODAY that Good Friday and Ash Wednesday are the two days in the year that Roman Catholics are obliged to fast.
"This practice is a way of emptying ourselves so that we can be filled with God," said Dought.
What do you eat on Good Friday?
Many Catholics do not eat meat on any Friday during Lent. Anything with flesh is off-limits. Dought says this practice is to honor the way Jesus sacrificed his flesh on Good Friday.
Meat that is off limits includes:
Instead, many Catholics will eat fish. According to the Marine Stewardship Council , this is allowed because fish is considered to be a different type of flesh.
Contributing: Jordan Mendoza ; USA TODAY

Spring 2024 Engineering and Computer Science Research Day Winners Announced

Master’s and doctoral students from across the College of Engineering and Computer Science presented their research at the 2024 ECS Research Day.
Master’s and doctoral students from across the College of Engineering and Computer Science (ECS) presented their research during the 2024 ECS Research Day, held at the National Veterans Resource Center. From fundamental studies to prototype development, a total of 113 posters and 20 oral presentations highlighted the broad research activities across the college.
A keynote address, “The Crucial Role of Strategic Decision-Making in Career Progression: A Personal Journey” was delivered by Melur K. “Ram” Ramasubramanian G’87, executive vice chancellor for academic affairs and provost at the State University of New York (SUNY) and the President of the SUNY Research Foundation. Ramasubramanian, who earned a Ph.D. in mechanical engineering from Syracuse University, shared his experience and insightful career advice with the attendees.
“ECS Research Day is a signature event that we organize every year to celebrate graduate research in our college. This year is particularly exciting with record participation and high-quality research presented. It showcases the strong scholarly work in many areas.” said Dacheng Ren, associate dean for research in ECS.
Below is a list of awards handed out during ECS Research Day:
ORAL PRESENTATION AWARDS
Communications and security.
First Place: Feng Wang. “Maximum Knowledge Orthogonality Reconstruction with Gradients in Federated Learning.” Advisor: Dr. M. Cenk Gursoy.
Second Place : Nandan Sriranga. “ Detection of Temporally Correlated Signals in Distributed Sensor Networks.” Advisor: Dr. Pramod Varshney.
Energy, Environment and Smart Materials
First Place: Johnson Agyapong. “ The Formation of Deterministic Wrinkle Morphologies via 4D Printing of Shape Memory Polymer Substrates.” Advisor: Dr. James Henderson.
Second Place: Ashok Thapa. “Passive Oscillating Heat Pipes for High-Heat Dissipation.” Advisor: Dr. Shalabh Maroo.
Health and Well-Being
First Place: Yikang Xu. “ A New Anti-Fouling Indwelling Urinary Catheter with Embedded Active Topography.” Advisor: Dr. Dacheng Ren.
Second Place: Natalie Petryk. “ Hydrolytic and Oxidative Degradation of Polyurethane Foams for Traumatic Wound Healing.” Advisor: Dr. Mary Beth Monroe.
Sensors, Robotics and Smart Systems
First Place: Yasser Alqaham. “Energetic Analysis on All Possible Bounding Gaits of Quadrupedal.” Advisor: Dr Zhenyu Gan.
Second Place: Zachary Geffert. “Multipath Projection Stereolithography for Rapid 3D Printing of Multiscale Devices.” Advisor: Dr. Pranav Soman.
POSTER PRESENTATION AWARDS
First Place: Omkar Desai. “A Caching System for Concurrent DNN Model Training.” Advisor: Dr. Bryan Kim.
Second Place (tied): Zifan Wang. “Catch You if Pay Attention: Temporal Sensor Attack Diagnosis Using Attention Mechanisms for Cyber-Physical Systems.” Advisor: Dr. Qinru Qiu.
Second Place (tied): Shreyas Aralumallige . “Chandregowda. Exploring the Role of Bio-Flocculant Interactions with Clay Minerals in Addressing Mining Industry Challenges.” Advisor : Dr. Shobha K Bhatia.
Third Place (tied): Matthew Qualters . “Experimental Flow Control Techniques on a Supersonic Multi-Stream Rectangular Jet Flow.” Advisor: Dr. Fernando Zigunov.
Third Place (tied): Pardha Nayani . “Unleashing Bandwidth: Passive Highly Dispersive Matching Network.” Advisor : Dr. Younes Ra’di.
Honorable Mention: Ziyang Jiao. “The Design and Implementation of a Capacity-Variant Storage System.” Advisor: Dr. Bryan Kim.
Honorable Mention: Ratnakshi Mandal . “The Dance of DNA and Histone Proteins: Molecular Insights Into Chromosome Formation.” Advisor: Dr. Shikha Nangia.
Alex Dunbar
- InclusiveU Program Celebrates 10 Years of Offering a Fully Inclusive College Experience to Students Tuesday, April 2, 2024, By Kelly Homan Rodoski
- Students Encouraged to Complete Survey That Will Inform Sexual and Relationship Violence Prevention and Response Tuesday, April 2, 2024, By Gabrielle Lake
- Experiencing the Solar Eclipse From an Animal’s Perspective Tuesday, April 2, 2024, By Dan Bernardi
- 2024 Syracuse University Scholars Announced Tuesday, April 2, 2024, By News Staff
- Spring 2024 Engineering and Computer Science Research Day Winners Announced Monday, April 1, 2024, By Alex Dunbar
More In STEM
Experiencing the solar eclipse from an animal’s perspective.
Awe, amazement and wonder are a few of the reactions humans have to a solar eclipse. The extremely rare occasion of being in the path of totality—where the moon’s disk completely blocks the sun for a few short moments—captivates audiences…
Caller ID of the Sea: Biologists Discover Link Between Whale Communication and Behavior
For researchers studying the acoustic behavior of whales, distinguishing which animal is vocalizing is like a teacher trying to figure out which student responded first when the entire class is calling out the answer. This is because many techniques used…
‘A Beautiful, Once-In-a-Lifetime Event’: The Total Solar Eclipse on April 8
Walter Freeman’s “Introduction to Astronomy” classes always end the same way they began, with Freeman advising his students that, ultimately, “we look at the stars because they are pretty and they illuminate who we are as humanity.” That humanity will…
Biology Professor Named University’s First Partnership for Undergraduate Life Sciences Education Fellow
Across the humanities and STEM disciplines in the College of Arts and Sciences (A&S), faculty thoughtfully develop course curricula and learning environments that incorporate their fields’ latest findings and pedagogical best practices. This careful attention ensures students benefit from a…
Machine Learning Gives Visibility to Underrepresented Authors
While fingerprint powder and microscopes are very important tools in forensics, machine learning is becoming one of the fastest emerging technologies in the field. This involves the use of algorithms and computing to perform efficient and effective investigations by analyzing…
Subscribe to SU Today
If you need help with your subscription, contact [email protected] .
Connect With Us
For the media.
Adobe Community
- Global community
- 日本語コミュニティ Dedicated community for Japanese speakers
- 한국 커뮤니티 Dedicated community for Korean speakers
- Lightroom Classic
- Discussions
How to retain order
Copy link to clipboard
never-displayed

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A computer is an electronic device that manipulates information, or data. It has the ability to store, retrieve, and process data. You may already know that you can use a computer to type documents, send email, play games, and browse the Web. You can also use it to edit or create spreadsheets, presentations, and even videos.
Download ppt "Chapter 1: Introduction to Computer". Computer A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory that can accept data (input), process the data according to specified rules, produce information (output), and store the information for future use.
A computer is a fast and accurate electronic machine that is designed to accept and store input data, process them and produce output results, using the instructions of a stored program or data.; A computer has some wonderful features that make it different from a human. It has become a critical piece of our lives. The word computer brings from the word ' compute ', that means to ...
Computer Basics 1. Computer Basic 1 includes two lessons: Lesson 1: Introduction to Computers Lesson 2: Common Computer Terminology. Lesson 1 - Introduction to Computer Objectives. After completing lesson 1, you will be able to: Describe the importance of computers in today's world. Download Presentation.
Welcome to Tech Sight. This is a basic presentation of computers. Here you will get an overview of computers and their history. It will help you to complete ...
Basic Computer (12 Slides) 6267 Views. 1. 2. Unlock a Vast Repository of Basic Computer PPT Slides, Meticulously Curated by Our Expert Tutors and Institutes. Download Free and Enhance Your Learning!
Presentation Transcript. Introduction to computer fundamentals. The Computer Defined • A computer is an electronic device that processes data, converting it into information that is useful to people. Analog and Digital Computer • Analog systems represent data as variable points along a continuous spectrum of values.
Download our Computer-related Google Slides themes and PowerPoint templates and create outstanding presentations Free Easy to edit Professional ... Use these Google Slides themes or download our PPT files for PowerPoint or Keynote to give a presentation about a Computer-related topic, including Information Technology. Filter by. Filters ...
His presentation, called "A Research Center for Augmenting Human Intellect" includes a live demonstration of his computer, including a mouse and a graphical user interface (GUI), according to the ...
CMU School of Computer Science
Blue Technology Illustration Education School Cute Workshop Computer Editor's Choice Internet Computing. Yes, computers can be your friend! Be at ease running your beginners' computer workshop with this fun Google Slides & PPT template with a desktop layout!
Mastering the Art of Oral Presentations by Don Fulop; John P. Stewart. ISBN: 9781119550105. Publication Date: 2019-03-27. Mastering the Art of Oral Presentations is your expert guide to delivering memorable and effective speeches and presentations. Projecting Enthusiasm: the Key to Dynamic Presentations for Professionals by Robert T. Tauber.
For an IT-themed slideshow presentation, you can insert elements like computer screens, circuit boards, binary code, server racks, and images of technology devices. Additionally, you can use icons representing programming languages, network diagrams, and cybersecurity symbols to enhance the relevance and visual appeal of your presentation.
Create a presentation. Open PowerPoint. In the left pane, select New. Select an option: To create a presentation from scratch, select Blank Presentation. To use a prepared design, select one of the templates. To see tips for using PowerPoint, select Take a Tour, and then select Create, . Add a slide.
Create presentations from scratch or a template. Add text, images, art, and videos. Select a professional design with PowerPoint Designer. Add transitions, animations, and cinematic motion. Save to OneDrive, to get to your presentations from your computer, tablet, or phone. Share your work and work with others, wherever they are.
Presentation software maker Pitch has added a recordings feature so that users can now record and insert short videos directly into their presentations.. Users can record videos directly onto ...
Computer Engineering Technology Presentation . Technology . Premium Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template . We dream of things, and then computer engineers come and make them into reality! Phones were just a dream a few decades ago, and now everyone has one on their pocket.
Presentations related to NIST's cybersecurity events and projects. Description. NIST's Senior Researcher within the Computer Security Division provided a presentation on Artificial Intelligence Risk, the trustworthy attributes, and the adversarial challenges and risks associated with Machine Learning.
Google Slides helps you make impressive presentations with its diverse template library, collaboration options, and seamless integration with Google apps. You can use it on your Android phone ...
Computer science degrees prepare students for the jobs of the future (and the present!). If you are interested in getting an education about coding, math, computers, and robots, this is the degree for you! ... Download the Tech Startup Newsletter presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Attention all marketers! Are you looking for a way to ...
Alvarez says this is why Christians call Jesus the "lamb of God." He adds that the symbolism of the "blood of the lamb" ties the two stories together and is why Christians believe God sacrificed ...
Master's and doctoral students from across the College of Engineering and Computer Science (ECS) presented their research during the 2024 ECS Research Day, held at the National Veterans Resource Center. From fundamental studies to prototype development, a total of 113 posters and 20 oral presentations highlighted the broad research activities across the college.
The rapid serial visual presentation-based brain-computer interface (RSVP-BCI) system achieves the recognition of target images by extracting event-related potential (ERP) features from electroencephalogram (EEG) signals and then building target classification models. Currently, how to reduce the training and calibration time for classification models across different subjects is a crucial ...
I am giving a presentation to my cameera club and will be using their computer. My catalog consists of 150 photos that I added to a Collection so I could reorder them as needed. I saved the collection as a catalog to an external drive to take to the venue, but the order in the new collection was wro...