

Fix Wi-Fi connection issues in Windows
Troubleshooting network problems in windows.
If you can’t get email, browse the web, or stream music, chances are you’re not connected to your network and can’t get onto the internet. To fix the problem, here are some things you can try.
Things to try first
Try these things first to help you fix or narrow down the connection problem.
Run Get Help to troubleshoot and fix common connection problems. Right click the network icon in the right side of the taskbar and select Diagnose network problems or open Get Help for Network & Internet
Make sure Wi‑Fi is turned on. Select the No internet icon on the right side of the taskbar, and make sure Wi-Fi is turned on. If it isn't, select it to turn it on. Also, make sure Airplane mode is turned off.
Select Manage Wi-Fi connections ( > ) on the Wi-Fi quick setting, see if a Wi-Fi network you recognize and trust appears in the list of networks. If it does, select the Wi-Fi network, and they try to connect to it. If it says Connected underneath the network name, select Disconnect , wait a moment, and then select Connect again.
Try connecting to a network on a different frequency band. Many consumer Wi-Fi routers broadcast at two different network frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. These will appear as separate networks in the list of available Wi-Fi networks. If your list of available Wi-Fi networks includes both a 2.4 GHz network and a 5 GHz network, try connecting to the other network. To learn more about the differences between 2.4 GHz networks and 5 GHz networks, check out Wi-Fi problems and your home layout .
Make sure the physical Wi‑Fi switch on your laptop is turned on. (An indicator light usually shows when it's on.)
Restart your modem and wireless router. This helps create a new connection to your internet service provider (ISP). When you do this, everyone that is connected to your Wi-Fi network will be temporarily disconnected. The steps you take to restart your modem and router can vary, but here are the general steps.
Note: If you have a cable modem/Wi-Fi router combo device, you only need to follow the steps for the single device.
Unplug the power cable for the router from the power source.
Unplug the power cable for the modem from the power source. Some modems have a backup battery. If you unplug the modem and lights stay on, remove the battery from the modem.
Wait at least 30 seconds or so. If you had to remove the battery from the modem, put it back in.
Plug the modem back into the power source. The lights on the modem will blink. Wait for them to stop blinking.
Plug your router back into the power source. Wait a few minutes for the modem and router to fully power on. You can usually tell when they’re ready by looking at the status lights on the two devices.
On your PC, try to connect again.
Narrow down the source of the problem
Connection problems can be due to a variety of reasons—problems with the website, your device, the Wi-Fi router, modem, or your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Try the following steps to help narrow down the source of the problem.
If the "Wi-Fi connected" icon appears on the right side of the taskbar, visit a different website. If the website opens, there might be a problem with the specific website. If you can't connect to another website, go to the next step.
On another laptop or phone, try to connect to the same network. If you can connect, the source of the problem is likely due to your device—go to the section Network troubleshooting on your device . If you can't connect to the network on any device, continue to the next step.
Check to see if there is a problem with the connection to your Wi-Fi router. Do this by using a ping test.
Select Search on the taskbar, and type command prompt . The Command Prompt button will appear. To the right of it, select Run as administrator > Yes .
At the command prompt, type ipconfig , and then select Enter . Look for the name of your Wi-Fi network within the results, and then find the IP address listed next to Default gateway for that Wi-Fi network. Write down that address if you need to. For example: 192.168.1.1
At the prompt, type ping <DefaultGateway> and then select Enter . For example, type ping 192.168.1.1 and select Enter . The results should be something like this:
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=64
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.1: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 4ms, Maximum = 5ms, Average = 4ms
If you see results like this and are getting a reply, then you have a connection to your Wi-Fi router, so there might be a problem with your modem or ISP. Contact your ISP or check online on another device (if you can) to see if there's a service outage.
If the results of the ping test indicate that you are not getting a reply from the router, try connecting your PC directly to your modem by using an Ethernet cable (if you can). If you can connect to the internet using an Ethernet cable, it confirms the connection problem is due to the Wi-Fi router. Make sure you've installed the latest firmware and see the documentation for your router.
Network troubleshooting on your device
Run network commands
Try running these network commands to manually reset the TCP/IP stack, release and renew the IP address, and flush and reset the DNS client resolver cache:
At the command prompt, run the following commands in the listed order, and then check to see if that fixes your connection problem:
Type netsh winsock reset and select Enter .
Type netsh int ip reset and select Enter .
Type ipconfig /release and select Enter .
Type ipconfig /renew and select Enter .
Type ipconfig /flushdns and select Enter .
Uninstall the network adapter driver and restart
If the previous steps didn’t work, try to uninstall the network adapter driver, and then restart your computer. Windows will automatically install the latest driver. Consider this approach if your network connection stopped working properly after a recent update.
Before uninstalling, make sure you have drivers available as a backup. Visit the PC manufacturer’s website and download the latest network adapter driver from there. If your PC can't connect to the internet, you'll need to download a driver on a different PC and save it to a USB flash drive so you can install the driver on your PC. You’ll need to know the PC manufacturer and model name or number.
Select Search on the taskbar, type device manager , and then select Device Manager from the list of results.
Expand Network adapters , and locate the network adapter for your device.
Select the network adapter, press and hold (or right-click), and then select Uninstall device > check the Attempt to remove the driver for this device check box > Uninstall .
After uninstalling the driver, select Start > Power > Restart .
After your PC restarts, Windows will automatically look for and install the network adapter driver. Check to see if that fixes your connection problem. If Windows doesn't automatically install a driver, try to install the backup driver you saved before uninstalling.
Check if your network adapter is compatible with the latest Windows Update
If you lost your network connection immediately after upgrading to or updating Windows 11, it's possible that the current driver for your network adapter was designed for a previous version of Windows. To check, try temporarily uninstalling the recent Windows Update:
Select Start > Settings > Windows Update > Update history > Uninstall updates .
Select the most recent update, then select Uninstall .
If uninstalling the most recent update restores your network connection, check to see if an updated driver is available:
Select the network adapter, press and hold (or right-click), then select Update driver > Search automatically for updated driver software , and then follow the instructions.
After installing the updated driver, select Start > Power > Restart if you're asked to restart, and see if that fixes the connection issue.
If Windows can’t find a new driver for your network adapter, visit the PC manufacturer’s website and download the latest network adapter driver from there. You’ll need to know the PC manufacturer and model name or number.
Do one of the following:
If you couldn’t download and install a newer network adapter driver, hide the update that’s causing you to lose your network connection. To learn how to hide updates, see Hide Windows Updates or driver updates .
If you could successfully install updated drivers for your network adapter, then reinstall the latest updates. To do this, select Start > Settings > Windows Update > Check for updates .
Use network reset
Using network reset should be the last step you try. Consider using it if the steps above don’t help to get you connected.
This can help solve connection problems you might have after upgrading from Windows 10 to Windows 11. It can also help to fix the problem where you can connect to the internet, but can't connect to shared network drives. Network reset removes any network adapters you have installed and the settings for them. After your PC restarts, any network adapters are reinstalled, and the settings for them are set to the defaults.
Select Start > Settings > Network & internet > Advanced network settings > Network reset . Open Network & Internet Status settings
On the Network reset screen, select Reset now > Yes to confirm.
Wait for your PC to restart, and see if that fixes the problem.
After using network reset, you might need to reinstall and set up other networking software you might be using, such as VPN client software or virtual switches from Hyper‑V (if you're using that or other network virtualization software).
Network reset might set each one of your known network connections to a public network profile. In a public network profile, your PC is not discoverable to other PCs and devices on the network, which can help make your PC more secure. However, if your PC is used for file or printer sharing, you’ll need to make your PC discoverable again by setting it to use a private network profile. To do this, select Start > Settings > Network & internet > Wi-Fi . On the Wi-Fi screen, select Manage known networks > the network connection you want to change. Under Network profile type , select Private .
Additional troubleshooting steps
Check your Wi-Fi settings
Wi-Fi adapter manufacturers might have different advanced settings you can change based on your network environment or connection preferences.
Check the Wireless Mode setting for your network adapter and make sure it matches the capabilities of the network you’re trying to connect to. If it doesn’t match, you won’t be able to connect, and the network might not appear in the list of available networks. The Wireless Mode will often be set to Auto or something similar by default, which enables connection for every kind of network that’s supported.
To find the wireless mode setting
In Device Manager, select Network adapters , and then double-click the network adapter name.
Select the Advanced tab and look for a Wireless Mode setting. Make sure it’s set to the mode your network is using.
Wi-Fi profile settings
Windows uses the Wi-Fi profile to save the settings that are needed to connect to a Wi-Fi network. These settings include the network security type, key, network name (SSID), and so on. If you can’t connect to a Wi-Fi network that you could connect to before, it’s possible that the network settings might have changed or the profile is corrupted.
To fix this, remove (or "forget") the network connection, then reconnect to the network. When you forget a network connection, it removes the Wi-Fi network profile from your PC.
To forget a network
Select Start > Settings > Network & internet .
Select Wi-Fi , then select Manage known networks .
Select the network you want to forget, then select Forget .
Afterwards, select the Wi-Fi icon on the taskbar and try to reconnect to the network to renew the network connection.
Check your home layout
Your Wi-Fi network might be affected by the network's frequency band, channel congestion, and/or signal strength. For more info, see Wi-Fi problems and your home layout .
Check for additional symptoms for the "No internet connection" icon.
There may be additional troubleshooting steps you can try, depending on which symptoms you're having. To view these steps, check out Wi-Fi connection icons and what they mean .
Related topics
Setting up a wireless network
How to find your wireless network password
Analyze the wireless network report
Wi-Fi tools and apps
Make a Wi-Fi network public or private in Windows

Afterwards, see if a Wi-Fi network you recognize and trust appears in the list of networks. If it does, select the Wi-Fi network, and they try to connect to it. If it says Connected underneath the network name, select Disconnect , wait a moment, and then select Connect again.
Try connecting to a network on a different frequency band. Many consumer Wi-Fi routers broadcast at two different network frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. These will appear as separate networks in the list of available Wi-Fi networks. If your list of available Wi-Fi networks includes both a 2.4 GHz network and a 5 GHz network, try connecting to the other network. To learn more about the differences between 2.4 GHz networks and 5 GHz networks, check out Wi-Fi problems and your home layout .
Run the Network troubleshooter. The Network troubleshooter can help diagnose and fix common connection problems.
To run the Network troubleshooter
Select the Start button > Settings > Network & Internet > Status . Open Network & Internet Status settings
Under Change your network settings , select Network troubleshooter .
Follow the steps in the troubleshooter, and see if that fixes the problem.
Restart your modem and wireless router. This helps create a new connection to your internet service provider (ISP).
When you do this, everyone that is connected to your Wi-Fi network will be temporarily disconnected. The steps you take to restart your modem and router can vary, but here are the general steps. ( Note : If you have a cable modem/Wi-Fi router combo device, you only need to follow the steps for the single device.)
If the "Wi-Fi connected" icon appears on the right side of the taskbar, visit a different website. If the website opens, there might be a problem with the specific website. If you can't connect to another website, go to the next step.
On another laptop or phone, try to connect to the same network. If you can connect, the source of the problem is likely due to your device—go to the section Network troubleshooting on your device . If you can't connect to the network on any device, continue to the next step.
Check to see if there is a problem with the connection to your Wi-Fi router. Do this by using a ping test.
In the search box on the taskbar, type command prompt . The Command Prompt button will appear. To the right of it, select Run as administrator > Yes .
At the command prompt, type ipconfig , and then select Enter . Look for the name of your Wi-Fi network within the results, and then find the IP address listed next to Default gateway for that Wi-Fi network. Write down that address if you need to. For example: 192.168.1.1
At the prompt, type ping <DefaultGateway> and then select Enter . For example, type ping 192.168.1.1 and select Enter . The results should be something like this:
Type netsh winsock reset and select Enter .
Type netsh int ip reset and select Enter .
Type ipconfig /release and select Enter .
Type ipconfig /renew and select Enter .
Type ipconfig /flushdns and select Enter .
In the search box on the taskbar, type device manager , and then select Device Manager from the list of results.
Expand Network adapters , and locate the network adapter for your device.
Select the network adapter, press and hold (or right-click), and then select Uninstall device > check the Attempt to remove the driver software for this device check box > Uninstall .
After uninstalling the driver, select the Start button > Power > Restart .
If you lost your network connection immediately after upgrading or updating Windows 10, it's possible that the current driver for your network adapter was designed for a previous version of Windows. To check, try temporarily uninstalling the recent Windows Update:
Select the Start button, then select Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update > View update history > Uninstall updates .
Select the most recent update, then select Uninstall .
Select the network adapter, select Update driver > Search automatically for updated driver software , and then follow the instructions.
After installing the updated driver, select the Start button > Power > Restart if you're asked to restart, and see if that fixes the connection issue.
If you couldn’t download and install a newer network adapter driver, hide the update that’s causing you to lose your network connection. To learn how to hide updates, see Hide Windows Updates or driver updates .
If you could successfully install updated drivers for your network adapter, then reinstall the latest updates. To do this, select the Start button, then select Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update > Check for updates .
This can help solve connection problems you might have after upgrading from a previous version of Windows to Windows 10. It can also help to fix the problem where you can connect to the internet, but can't connect to shared network drives. Network reset removes any network adapters you have installed and the settings for them. After your PC restarts, any network adapters are reinstalled, and the settings for them are set to the defaults.
Note: To use network reset, your PC must be running Windows 10 Version 1607 or later. To see which version of Windows 10 your device is currently running, select the Start button, then select Settings > System > About .
Select the Start button, then select Settings > Network & Internet > Status > Network reset . Open Network & Internet Status settings
On the Network reset screen, select Reset now > Yes to confirm.
Network reset might set each one of your known network connections to a public network profile. In a public network profile, your PC is not discoverable to other PCs and devices on the network, which can help make your PC more secure. However, if your PC is used for file or printer sharing, you’ll need to make your PC discoverable again by setting it to use a private network profile. To do this, select the Start button, then select Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi . On the Wi-Fi screen, select Manage known networks > the network connection you want to change > Properties . Under Network profile , select Private .
In Device Manager, select Network adapters , and then double-click the network adapter name.
Select the Advanced tab and look for a Wireless Mode setting. Make sure it’s set to the mode your network is using.
Select the Wi-Fi network icon on the right side of the taskbar, then select Network & Internet settings .
Select Wi-Fi , then select Manage known networks .
Select the network you want to forget, then select Forget .
Afterwards, select the Wi-Fi icon on the taskbar and try to reconnect to the desired network to renew the network connection.
Your Wi-Fi network might be affected by the network's frequency band, channel congestion, and/or signal strength. For more info, see Wi-Fi problems and your home layout .
There may be additional troubleshooting steps you can try, depending on which symptoms you're having. To view these steps, check out Wi-Fi connection icons and what they mean .
Make a Wi-Fi network public or private in Windows 10
Check the basics on your PC
Make sure Wi-Fi is turned on.
Swipe in from the right edge of the screen, select Settings , then select the Network icon.
Turn on Wi-Fi .
Make sure your PC isn’t in airplane mode.
Turn off Airplane mode .
Move closer to the router or access point if you can.
If you don’t see the network name at all, the router or access point might not be set to broadcast the network name. In this case, you’ll need to connect to it manually.
Swipe in from the right edge of the screen, and then select Settings .
Select the Network icon, and then select Hidden network .
Type the network name and select Next .
Type the password and select Next .
Follow any additional instructions to get connected.
The network will be added to your list of networks and will be available to connect to when your computer is in range of the network. To connect to the network, follow these steps:
Open Connect to a Network by selecting the network icon in the notification area.
Select Unnamed Network , select Connect , and then type the network information. The network will be added to your list of networks and will be available to connect to in the future when your computer is in range of the network..
Use the Network Troubleshooter
Let Windows try to help you fix the problem. Try running the Network troubleshooter to see if it can diagnose and fix the problem.
Select the Start button, start typing Network problems , and then select Identify and repair network problems in the list.
Run network commands after using the Network Troubleshooter
The Network Troubleshooter (mentioned above) can help diagnose and fix common connection problems. After using that, try running the network commands below because the combination of doing these two things can help you get connected.
If your problem isn’t fixed after running the Network troubleshooter, try to:
Reset the TCP/IP stack.
Release the IP address.
Renew the IP address.
Flush and reset the DNS client resolver cache.
Here's how to run networking commands in a command prompt:
Select the Start button, start typing cmd , right-click Command Prompt in the list, select Run as Administrator , and then select Yes .
At the command prompt, run the following commands in the listed order and then check to see if that fixes your connection problem:
Type netsh winsock reset and press Enter.
Type netsh int ip reset and press Enter.
Type ipconfig /release and press Enter.
Type ipconfig /renew and press Enter.
Type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter.
Restart your modem and router
This helps create a new connection to your Internet service provider (ISP). When you do this, everyone that is connected to your Wi-Fi network will be temporarily disconnected.
The steps you take to restart your modem and router can vary, but here are the general steps:
Unplug the power cable for the modem from the power source. Some modems have a backup battery. So if you unplug the modem and lights stay on, remove the battery from the modem.
See if it's a problem with your modem or your ISP
Make sure it’s not a problem with your cable modem or Internet service provider (ISP). If it is, contact your ISP.
At the command prompt, type ipconfig . Look for the IP address listed next to Default gateway . Write down that address if you need to. For example, 192.168.1.1.
At the prompt, type ping <Default gateway> and press Enter . For example, type ping 192.168.1.1 and press Enter . The result should be something like this: Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=64 Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=64 Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=64 Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=64 Ping statistics for 192.168.1.1: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 4ms, Maximum = 5ms, Average = 4ms
If the ping is successful and you see results similar to the results above, but you can’t connect to the Internet on your PC, there may be a problem with your modem or Internet service provider (ISP).
Check your network adapter
If you’re still having trouble connecting to a network, it might be related to your network adapter.
Try using the Network Adapter troubleshooter to automatically find and fix some problems. This troubleshooter will disable and re-enable the adapter, and try some other common repairs. Select the Start button, start typing Troubleshooting , and then select Troubleshooting in the list. Select View all > Network Adapter .
Update the network adapter driver. An outdated or incompatible network adapter driver can cause connection problems. Check to see if an updated driver is available.
Select the Start button, start typing Device Manager , and then select it in the list.
In Device Manager, select Network adapters , right-click your adapter, and then select Properties .
Select the Driver tab, and then select Update Driver .
Select Search automatically for updated driver software .
If Windows can’t find a new driver for your network adapter, visit the PC manufacturer’s website and download the latest network adapter driver from there. If your PC can't connect to the Internet, you'll need to download a driver on a different PC and save it to a USB flash drive so you can install the driver on your PC. You’ll need to know the PC manufacturer and model name or number.
Other steps to try on your router
Here are some things to check and try with your router if you’re at home and having trouble getting connected.
If you don't see the network name, sign in to your router and check to see if it’s set to broadcast the network name.
Connect your PC to your router using an Ethernet cable.
Open your web browser and type the IP address for your wireless router. (For example, 192.168.1.1 or 172.16.0.0—check the documentation for your router to find the default IP address.)
Sign in with your user name and password, then make sure an option labeled Enable SSID Broadcast , Wireless SSID broadcast , or something similar is turned on. This setting is often on a Wireless Settings page.
Check to see if your Wi-Fi network uses Media Access Control (MAC) address filtering for security. If it does, you’ll need to add the MAC address for your PC to the access list on your router before you can connect.
Select the Start button. Start typing cmd and right-click Command Prompt in the list. Select Run as Administrator , and then select Yes .
At the command prompt, type ipconfig /all . Write down the address that appears next to Physical Address for your wireless network adapter. This is the address you’ll need to add to the access list on your router.
To add the MAC address to the access list on your router:
Sign in with your user name and password, then look for a setting that says MAC Address Filter or something similar.
Add the MAC address you wrote down for your PC to the access list and save your changes.
On your PC, try to connect to the Wi-Fi network again.

Look in the Wireless Network section. If Wi-Fi is on, the button should say Turn wireless off .
Check and make sure your PC isn’t in airplane mode.
Select Add , and then select Manually create a network profile .
Type the network information.
If you want Windows to automatically connect when the network is in range, select the Start this connection automatically check box.
Select the Connect even if the network is not broadcasting check box, select Next , and then select Close .
Open the Network troubleshooter by right-clicking the network icon in the notification area and then selecting Troubleshoot problems .

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Find solutions to common problems or get help from a support agent.

Online support
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
- Best Mac Apps
- Unknown Caller
Digital Trends may earn a commission when you buy through links on our site. Why trust us?
Wi-Fi not working? How to fix the most common problems

Wi-Fi problems can strike anyone at any time, no matter how much networking experience you may have. But if you’ve not come across a particular Wi-Fi issue before, there’s no need to worry if you don’t know how to fix it. All you need are the right tools and a few tips, and you’ll be able to solve your Wi-Fi problem in no time.
Basic Wi-Fi troubleshooting checklist
Quick fixes for common problems, slow or no wi-fi or internet access in certain rooms, slow internet everywhere.
- One device can’t connect to the Wi-Fi
Nothing can connect to Wi-Fi
Connections drop at random times, wi-fi network disappears entirely, unknown devices on my wi-fi network, a recent update broke wi-fi.
- The satellite routers on my mesh network aren’t connecting
- My smart device isn’t connecting to Wi-Fi
- My console can’t connect to Wi-Fi
- Can’t connect to wireless printer
- Can’t connect to a guest Wi-Fi network that I set up
- Wi-Fi 6 or 6E isn’t working, even with a Wi-Fi 6 router
- Can’t find a router with Wi-Fi 7
Whether you’re experiencing problems with slow internet, Wi-Fi signal dropping, or you just can’t connect to Wi-Fi at all, here are some of the quickest and easiest fixes you can try. We’ll also cover some advanced advice on more troubling issues that would definitely result in your Wi-Fi not working at all, or at slower speeds.
If you have a non-specific problem with your Wi-Fi or don’t consider the problem serious enough to investigate more in-depth problems, consider the items on this list as a great way to start fixing your problem.
- Make sure your device’s Wi-Fi is on — Most laptops have a shortcut key that will turn off their Wi-Fi and it can be easy to press accidentally. Similarly, there is a quick toggle on most phones that will turn off the phone’s Wi-Fi capabilities.
- Restart your router — A quick restart of your router (achieved by unplugging it, waiting 30 seconds to 1 minute, and plugging it back in again) can fix many Wi-Fi difficulties.
- Check for an outage — Most ISP’s will have an outage map available on their website. Try using your phone’s data to check and see if an outage is reported in your area.
Forgot the Wi-Fi password
If you really can’t remember your Wi-Fi password, and there are no notes or cards with it written down somewhere, you’ll have to reset your router . Use a paperclip to press the hidden switch in the pinhole on the back of your router for 30 seconds. It should then default to factory settings.
- The 5 best Wi-Fi adapters for PC in 2024
- The most common motherboard problems, and how to fix them
- The most common Quest 3 problems and how to fix them
Use our guide to setting up a wireless router to get everything properly configured.
Wi-Fi connection lost when logging back into the computer
This problem can crop up on Windows 10 due to an issue with Fast Startup. Fast Startup keeps certain processes running so you can log back in very quickly. However, this can sometimes cause a bug with the wireless driver that prevents it from reconnecting to Wi-Fi properly. In the short term, you can turn off Fast Startup to prevent this problem . Search for Power Option s in your Windows 10 or Windows 11 search bar and go to this section of the Control Panel. Select Choose What the Power Button Does on the left-side menu, and then look at the new section Shutdown Settings . Find the option to Turn On Fast Startup and make sure it is deselected.
In the long term, you may need to update the driver for your wireless network adapter to fix any bugs causing this issue. You can follow our guide on how to update Windows 10 drivers for more information.
The network connects, but there’s no internet access
It might sound like a tired tip, but try resetting your modem by unplugging it and plugging it back in. If that’s no good, you can connect a laptop or desktop to your router with an Ethernet cable ( these are the best ones ) to see if it’s the router or your Wi-Fi that’s not working. If this works, then your best bet to get Wi-Fi working again is to reset your router . If there’s still no internet, though, you may have an outage. Contact your ISP.
Router crashes regularly and only restarting it helps
If your router needs to be restarted regularly, you should give your router a full reset . On most routers, you’ll find a Reset button that you can hold down with a paperclip. Do so for 30 seconds, and the router should default from factory settings. Use our guide to setting up a wireless router to get everything properly configured.
If that doesn’t work, your router may be on its way out. Your only real option is to return it if it is within its warranty period or to buy a new one.
Wi-Fi is made up of radio waves, meaning your Wi-Fi router broadcasts in all directions from a central location. If your router is in a far corner of your house, then you’re covering a great deal of the outside world unnecessarily. If you can, move your router to a more centralized location. The closer you can put your router to the center of your coverage area, the better reception will be throughout your home.
If you have external antennas, you can try adjusting those, too. Alternating between fully vertical and fully horizontal positions can help it reach in multiple directions.
If you live in an apartment building, other routers might be interfering with yours. Free software, like NetSpot on Mac, Windows, and Android, or Wi-Fi Analyzer for Android, can show you every wireless network nearby and what channel they’re using. If your router overlaps with nearby networks in particular rooms, consider switching to a less congested channel. If you need help switching, here’s our guide on how to change your Wi-Fi channel .
If none of that helps, your home might be too much for one router to handle. Consider purchasing a wireless repeater or setting up an old router to serve as one to extend the range of your main router. Upgrading to a whole-home mesh wireless system can also help with dead spots in certain areas of your home. Either way, it might be time to go and buy a new router .
If your Wi-Fi speed is slow no matter where you are, try plugging a laptop into your router directly and test your internet speed using one of the best internet speed tests . If speeds are still down, the problem is likely with your internet connection, not your router. Try some of these ways to improve your internet speed and contact your ISP.
If that’s not the issue, it could be that your current wireless channel is overcrowded by your devices or by those of other nearby networks. Consider changing the channel on your router in your router settings, by accessing the admin settings .
If that doesn’t help, performing a factory reset on your router and setting it up again may help. On most routers, there’s a Reset button that you can hold down with a paperclip. Do so for 30 seconds, and the router should default to factory settings. Use our guide to setting up a wireless router to get everything properly configured, and see if that helps.
If none of that works and your internet is fine on a wired connection, your router might be dying. Consider buying a new one: Here are the best routers we’ve reviewed and why they’re great picks. If the router seems fine, then it might instead be your modem, which could suffer connectivity issues if it’s on its way out, too. If you’re looking to upgrade your modem as a fix, we also have a guide on some of the top modem-router combos . Upgrading to a Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E router can also help ease issues with congestion and support faster speeds, provided that your broadband plan is capable of these boosted speeds.
One device can’t connect to the Wi-Fi
Sometimes you run into a Wi-Fi issue with one particular device. It’s probably just a momentary network issue, which is an easy fix. Try turning off the Wi-Fi on your device, then re-enabling it — or unplugging and replugging your Wi-Fi dongle. If that doesn’t work, restart the device and try again. Then try restarting the router itself.
If that doesn’t help, or if the problem reoccurs, consider deleting your current network from the list of saved networks on your device, then reconnect again.
If you’re running Windows 10 or 11, search for “wifi troubleshooting” and open the result, which should be Identify and Repair Network Issues . That will go through a series of diagnostics that may restore connectivity. On MacOS, you can run Wireless Diagnostics . Hold the Options key and click the AirPort (Wi-Fi) icon on the menu bar. Find Open Wireless Diagnostics , and then follow the on-screen instructions.
If you can’t connect to your Wi-Fi at all, plug your laptop into the router directly using an Ethernet cable, and see if you can connect that way. The particular type of Ethernet cable doesn’t matter, but there are some Ethernet cables that are better than others . If that works, your Wi-Fi is the problem and you should try some of the other fixes listed here. If it doesn’t work, then your internet may be down altogether. Check your ISP’s webpage and social accounts, or give them a call to see if they are reporting problems. Sometimes providers can be a little slow to note issues, so you can also check with a monitoring site like Downdetector and see if other users in your region are reporting problems.
Resetting your router can fix a myriad of issues, too, and an inability to connect is one of them. Press the Reset button on the back of the router with a paperclip for 30 seconds, and the router should default to factory settings. Use our guide to setting up a wireless router to get everything properly configured.
If that’s no use, you may need to consider buying a new router.
Is there some sort of pattern? Do connections drop whenever you use the microwave? Have you just installed a fish tank? It may sound weird, but some routers have trouble with these and other home hardware. The 2.5GHz band is readily interfered with by other devices, and 5GHz and 6GHz are notorious for being interrupted by physical objects. It could also be that you’re experiencing interference from other networks or devices. If your neighbors are heavy Wi-Fi users at a particular time each day, this could be slowing you down.
Changing your router’s channel might help. You can use NetSpot on Mac and Windows and Wi-Fi Analyzer for Android to show you every wireless network nearby. If yours overlaps with nearby networks, switching to a less congested channel in your router settings can help. We have a guide that will walk you through changing the channel on your router .
You can also try moving your router to a more accessible location so that there’s less distance (and interfering devices) between you and the router.
If that doesn’t work, try performing a factory reset on your router by pressing a paperclip into the miniature hole on it and following the reset steps as outlined in your manual.
If you lose track of your Wi-Fi network on any device, it’s possible that your router reset itself. Do you see an unprotected network named after your brand of router? That might be yours. Connect a laptop or desktop to it via an Ethernet cable, then use our guide to setting up a wireless router to get everything properly configured again.
If you don’t see such a network, plug your laptop into the router with an Ethernet cable, and see if you get a connection. Use our guide to finding your router’s IP address and login information for more help. Also, if you don’t have a cable, check out our guide on how to choose the right Ethernet cable .
Log into your Wi-Fi app or administrator settings (which you can find by searching your IP address on your browser ). Look for a list of currently connected devices and pinpoint the ones you don’t recognize.
First, make sure these don’t represent connections you didn’t realize you had — each smart device will have its own connection, for example, and they can have some strange titles if you didn’t name them. Game consoles and TVs may also be connected, and if you’ve had friends and family over recently they may have connected with unfamiliar devices.
If you’ve ruled out all familiar devices and there’s still a connection or two you don’t recognize, it’s possible someone else is hijacking your Wi-Fi network. In this case, look in your settings for an option to block these devices on your Wi-Fi and ban their MAC addresses, if possible. Then change your Wi-Fi password, and reboot your router. This may not stop especially determined hackers, but it’s usually enough to kick unwanted guests off your network.
If you want to take more drastic action, here are some steps for how to deal with someone stealing your Wi-Fi .
This can happen with some operating system updates. Windows 10 updates in mid-2020 had bugs that stopped some users from connecting to their Wi-Fi networks or even seeing a Wi-Fi connection at all. Similar updates to iOS, Android, and other platforms also have created bugs in the past that disrupt Wi-Fi connections.
When something like this happens, it’s best to wait for a patch that fixes the problem. In the meantime, remove the update and roll back your system to an earlier version to help get your online connectivity back.
While routers can last for years without needing a replacement, keep in mind that some problems can develop with age — a router may start lacking support for new device updates and similar issues that prevent it from working properly (as seen when Apple discontinued the AirPort Extreme, for example). That’s a sign that it’s time to look for a new router.
The satellite routers on my mesh network aren’t connecting
Make sure that your satellite devices are powered up and turned on. If they are, try unplugging and replugging the problematic device and see if it will connect to your network then. If your router app allows you to restart a Wi-Fi point (Google’s Home app, for example, allows this), then reboot that point and see if this helps, too.
Google also allows you to run a test to make sure the network is set up properly. You can find Wifi points on the Home app, under Test mesh . If the test comes back with a weak or failed connection, you should try repositioning your satellite routers to be closer to your primary router. This also is a good tactic for any mesh system that keeps dropping its satellite points — they could be too far away from the primary point.
You can also double-check to make sure that your satellite router devices have a different SSID than your primary router. If they were accidentally all assigned the same SSID, then the mesh network may not be able to coordinate properly.
If your router still seems unable to connect, then make sure that nothing significant has changed for your network settings. For example, if your ISP WAN (wide-area network) type changed for some reason, you may have to go back into the settings for the router and make sure that the right WAN setting is chosen.
There are additional special cases where certain Wi-Fi technology can interfere with mesh networks, so it’s also a good idea to contact router support directly and explain your situation if nothing is working.
My smart device isn’t connecting to Wi-Fi
First, make sure that your smart device and your router are both updated. Then try resetting your router and rebooting your smart device. You can either unplug and plug in the smart device or check its app for a reboot option — the Google Home app, for example, has a Reboot tool under each device section that you can use.
If the device still isn’t connecting properly, try moving it next to the router and seeing if it connects then — distance and interference can make a difference, especially for smaller smart devices. You should also double-check to make sure that your smart device doesn’t need a Zigbee hub to operate , which is more common among older smart devices but a problem that still occasionally crops up.
If your smart device keeps dropping a Wi-Fi signal, especially during busy times of the day, check to see if your router supports automatic band switching for devices. If it does, try turning this feature off. Sometimes a router will try to switch a smart device to a different band, but the device isn’t ready for that, causing it to lose a connection. There may also be issues with connecting to a mesh router, and you may have to be very specific about your network connection to make smart devices work.
It’s also a good idea to check if your particular device is suffering from temporary bugs that make connecting to Wi-Fi difficult or impossible. Nest minis and HomePod minis have both encountered such errors in the past. In these cases, a fix is usually patched in before too long, so keep making sure that your device is updated. Sometimes operating system updates, like a new iOS patch , also can affect smart device performance.
There are a number of other router settings that may block smart devices, but they are manufacturer dependent. If you can’t find what’s wrong, contact your router manufacturer’s support and explain that you think your router is having trouble connecting.
My console can’t connect to Wi-Fi
Check social media and Downdetector to make sure nothing is wrong with your gaming platform — sometimes your Xbox or PlayStation can get online just fine, but Xbox Live or Playstation Network is down for any number of reasons, but they’re typically back up again after a short period.
If everything looks all right there, reboot both your router and your game console and see if they can successfully connect. This is also a good time to test your internet connection. Major systems like Xbox and PlayStation have an option in their Settings menu to test your internet connection. On PlayStation, head to Settings , then Network , then select Test Internet Connection . On Xbox, go to Profile & System , select Settings , and in the General section, select Network Settings , where you will find an option to Test Network Speed & Statistics . This can provide more information about what’s going wrong and even tips on what you may need to change.
If your console and router seem to be acting properly but Wi-Fi keeps dropping, you may want to try moving the two devices closer to each other to see if the Wi-Fi signal improves. Try to remove any material or objects between the console and router: Placing both in a high, clear location often brings the best results. You can also try reducing the number of other devices on the network, especially if they’re streaming.
Can’t connect to wireless printer
First, make sure you are trying to connect to your Wi-Fi and not via Wi-Fi Direct — they are two different technologies. We also highly suggest the traditional routine of turning everything off and back on again, especially if your printer has connected to Wi-Fi successfully in the past. If your printer is far away from your router and keeps running into Wi-Fi errors, try moving it to a closer position.
If it looks like your printer is connected to Wi-Fi but you can’t get it to work, head into your printer settings on your computer and make sure the correct default printer is selected. Microsoft also has some troubleshooters you can run to see if they pick up on anything obviously awry.
It’s also a good idea to check your router security, firewalls, and VPN security to see if any of them are identifying the printer as a strange device and refusing a wireless connection. You may need to disable certain firewalls or reconfigure security protocols to use your printer successfully. When all else fails, uninstall your printer drivers and reinstall the more recent versions to see if this makes a difference.
And if your printer isn’t wirelessly enabled, consider upgrading to one that is. We have some recommendations for the best printers , laser printers , and multifunction printers that can be used wirelessly and connect to your home network.
Can’t connect to a guest Wi-Fi network that I set up
Guest Wi-Fi networks allow you to share your Wi-Fi with others in a secure way that helps prevent security issues. You’ve probably seen it on business routers, but it can be set up on home routers, too. If someone is having trouble connecting to the guest network but otherwise the Wi-Fi seems to be working, there are a few things you can try.
First, if you just set up your guest network, wait a few minutes. It may take a little time for the network to show up. If the guest network is visible, take a minute to head into your router app and check settings. Settings like Public Wi-Fi Active and Allow Guests to Access My Local Network should always be enabled. If it’s still not working, reset your router and try again.
Keep in mind, some guest networks have a stricter limit on how many devices can use them. If you have over a dozen people already on the guest network, others may not be able to log on.
Wi-Fi 6 or 6E isn’t working, even with a Wi-Fi 6 router
Wi-Fi 6 offers a host of improvements from older Wi-Fi standards, including improved performance, less latency, and better security. But if you don’t think you’re getting Wi-Fi 6 features from a router that supports it, something could be wrong with your setup.
Do you have any extenders on your network? If those aren’t compatible with Wi-Fi 6, you won’t be able to enjoy Wi-Fi 6 speed and features. If your device has picked up the signal from an extender, Wi-Fi 6 benefits may not be making the trip.
Additionally, most devices will need at least partial support for Wi-Fi 6 features to be able to use them. Devices that are several years old may not be compatible with any Wi-Fi 6 changes. That includes your phone and laptop, as well as smart devices that you might be using.
Even desktop computers may struggle with this. Internal Wi-Fi adapters may struggle to pick up on Wi-Fi 6 benefits when you switch to a new router, even if they are technically compatible. You should update your Wi-Fi drivers to fix any potential issues.
Can’t find a router with Wi-Fi 7
Wi-Fi 7 is the next generation of wireless technology, and it’s technical name is 802.11be. It’s the successor to existing Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E routers, and will offer much greater performance, with up to 36 Gbps data transfer rates — that’s more than three times faster than Wi-Fi 6 speeds. It also lets devices use multiple frequencies simultaneously to better utilize available network bandwidth.
The only downside to this is that Wi-Fi 7 routers aren’t yet available at competitive prices. There are some Wi-Fi 7 routers, like the impressive TP-Link Deco BE85 , but that’s a $1,500 mesh router system and complete overkill for just about anyone.
You can expect to see more Wi-Fi 7 routers with more approachable price tags in the coming months.
Editors' Recommendations
- How to change your router’s Wi-Fi password
- The most common GPU problems and how to fix them
- The most common Chromebook problems and how to fix them
- How to get Wi-Fi access anywhere at any time
- The most common Steam Deck problems and how to fix them
- Work From Home

If Slack is your office, not only will you want to know best Slack tips but also how to fix Slack issues. Nobody wants to look like a fool that can't navigate the office software without a tutorial from the manager, after all. And that goes doubly so if you work in tech, where these sorts of things are likely expected of you.
But there's not much to worry about. The program runs smoothly most of the time and we're here to help you for the times it does not. Here are our top tips to get you back in your Slack game and avert troubles. Trouble connecting to Slack
If it's not Slack or Teams, it's likely Google Meet. In today's post pandemic world, you're likely going to be using one of these programs for your next interview, office meeting, or big grant proposal. Getting prepared for these events today requires a lot more than dusting off a suit and picking out the office-suitable makeup. If you're using Google Meet, for example, you'll also want to pick out a professional 360-degree background and check to see that your camera and mic are working appropriately.
What if you do run into problems during your pre-interview checkup; or even worse, during the meeting? We've compiled a list of the most common Google Meet problems to get you looking smooth, professional, and ready to command the appropriate attention you deserve the next time you use Google Meet.
Microsoft Teams was introduced in 2017 as a unified communication and collaboration platform aimed at helping businesses and organizations get things done. Microsoft leveraged the company's existing Office software experience and created a unified experience between Teams, Office 365, and Skype for Business. However, as with all software, things don't always go according to plan. Sometimes you can run into Teams problems.
We're big Teams users here at Digital Trends -- it's our go-to communication and meeting tool -- and we've come across a few issues ourselves over the years. In the event you're having Microsoft Teams issues, here's how to fix some of the most common problems.
- Accessories
- Entertainment
- PCs & Components
- Wi-Fi & Networks
- Newsletters
- Digital Magazine – Subscribe
- Digital Magazine – Log in
- Smart Answers
- Best laptops
- Best antivirus
- Best monitors
- Laptop deals
- Desktop PC deals
When you purchase through links in our articles, we may earn a small commission. This doesn't affect our editorial independence .
Wi-Fi problems? Here’s how to diagnose your router issues

Whenever someone sends me a question about how to fix their Wi-Fi, I wince. It’s not that I dislike helping people with their router problems. In fact, there are few geeky endeavors I find more rewarding than fixing Wi-Fi connection issues at a friend or family member’s home.
But Wi-Fi has always felt more like a dark art than a science, and it’s an art that’s hard to conjure without being physically present. Potential points of failure are everywhere, and what works well in one home might not in another. Even the reviewers of networking gear can reach drastically different conclusions about the very same product.
Wi-Fi is fundamentally at odds, then, with my desire to answer questions with specific recommendations. The best I can do is walk your through how I diagnose Wi-Fi problems myself. That way, you can make better decisions on whether (and how) to upgrade your own gear.
Further reading: The best mesh Wi-Fi routers
Size up the Wi-Fi problem
The first step to solving Wi-Fi issues is to see if the slowdown is coming from your cable modem (which brings internet service into the home) or from the router (which distributes Wi-Fi connectivity throughout the home).
Start by plugging a computer directly into your modem with an ethernet cable and running a speed test. (The easiest way is to do a Google search for “speed test,” then hit the blue “Run Speed Test” button atop the search results.) A USB-to-Ethernet adapter will be necessary for testing on computers that don’t have an ethernet port, but if that’s too much trouble or you don’t have a proper computer at all, you can also try calling your internet provider and asking them to test your internet speed remotely.

Running speed tests throughout the house can help you figure out where the Wi-Fi trouble spots are.
Jared Newman / Foundry
If wired connection speeds are on par with your internet provider’s advertised speeds, the next step is to start running speed tests throughout the house. Measure speeds around the area where connectivity feels slow, then work your way back to where the router is located, running multiple tests in each area as you go.
The goal here is to figure out where your connection troubles are occurring. Consistently slow speeds throughout the house may be a sign of an outdated router, while dead zones or range issues may require a more powerful router or mesh Wi-Fi system. (More on that shortly.)
Find your Wi-Fi router’s 802.11 version
To figure out whether a router needs replacing, it helps to know how old it is. One way to do this to locate the router’s model number—it’s likely printed on the router itself—then search the web for info about which version of Wi-Fi it supports. Here are the major Wi-Fi versions to know about:
- 802.11a/b/g: Extremely old and almost certainly the source of all your Wi-Fi problems.
- 802.11a/b/g/n (or just 802.11n): Outdated at this point and a solid candidate for replacement. Many of these routers only support a single frequency band that’s slower and more congestion-prone, and “dual-band” variants have limited range on the faster 5 GHz frequency band.
- 802.11ac (also marketed as Wi-Fi 5): Not the latest standard, but still widely available even in some high-performance routers.
- 802.11ax (or Wi-Fi 6): Routers using this standard started shipping in late 2020, so your router is likely quite new.
- Wi-Fi 6E: Congrats, you probably just bought a new router .
Wi-Fi versions alone aren’t an indicator of quality—a cheap Wi-Fi 6 router can be worse than a high-end mesh system with Wi-Fi 5—but each successive version has introduced new features that improve connectivity, and we’ve generally seen a push toward better performance over time.
Try some smaller router fixes
Just to rehash a tip I discussed back in July , sometimes changing your router’s channel and bandwidth settings can work wonders for reducing Wi-Fi interference, especially if you’re seeing inconsistent speeds on devices that aren’t too far from the router. By digging into your router’s settings, you can bypass automatic channel selection and find a channel that might be less congested.
You can also try some other little tweaks, like getting your router off the ground and clearing some space around it—but I wouldn’t start rearranging your room for the router’s sake. Chances are the improvements will be minimal. Of course, moving your router to a more central location in the home can help, but that would likely require having the cable company rewire your home internet connection.
Wi-Fi extenders: a last resort

Because replacing a router is a pain, a lot of folks wonder if they can just solve their problems with a Wi-Fi extender or repeater , which take the wireless signal from a router and rebroadcast it farther away. (“Extender” sometimes refers to a device with a wired connection to the router, though I often see both terms used interchangeably.)
My experience with Wi-Fi extenders is hit or miss. Wireless repeaters will always degrade whatever signal they receive, so the benefits can cancel out if you’re trying to address a dead zone or interference from other nearby wireless devices. The same is true with powerline adapters , which send a wired ethernet connection from your router to another part of the house through your wall outlets. Depending on how your house is wired, this approach can give you a weak connection or not work at all.
I don’t tell people to avoid extenders outright, because they can work in some scenarios, but keep your expectations low and be prepared to return the device if it doesn’t help. Here’s how to set up a Wi-Fi extender if you decide to go that route.
Picking a new Wi-Fi router
Once you’ve concluded that it’s time to replace your router, then what?
our favorite mesh wi-fi system
Netgear orbi home wifi system (rbk50).

A mesh Wi-Fi system will be the surest way to solve your Wi-Fi problems, especially in larger homes or ones with lots of dead zones. These systems let you plug in multiple access points throughout the house, creating one big network. They’re better at managing connections than a router with an extender, and systems advertised as “Tri-Band” can connect each access point without congesting the rest of the network.
Such systems might not be necessary, though. If you haven’t replaced your router in a while, even a new standalone router might be enough to power through dead zones if they’re not too far away. Standalone routers are generally less expensive than mesh systems, and some have features that mesh systems lack, such as USB storage support or a large number of ethernet ports.
A supremely powerful gaming router
Tp-link gx90.

Ultimately, though, there’s no way to tell for sure if a new router will work without trying it yourself. You can read all sorts of reviews—PCWorld reviews both Wi-Fi mesh systems and the latest Wi-Fi 6E routers —but even the best advice isn’t one-size-fits-all. Buying a new router will always involve a leap of faith.
A note on modem/router combos
Finally, there’s one more complicating factor: Although cable companies used to distribute internet modems and routers separately—the former bringing in the internet from outside the house, and the latter to distributing Wi-Fi through the home—it’s increasingly common now to get both functions in one box. That makes installation easier for the cable company, but makes router replacement trickier for you.
If you have a combo box and are paying for it in rental fees, consider replacing it with two devices: A new router and a separate cable modem . But be aware that some companies—particularly fiber-optic internet providers such as AT&T and Verizon—make replacing the modem component difficult or impossible.
If replacing the modem isn’t possible or necessary, you can just disable its Wi-Fi features so they don’t interfere with your new router. The instructions for doing so can vary by provider, so expect to do some Googling of “modem mode” or “bridge mode” plus the name of your internet provider.
And if you’re still having Wi-Fi problems after all that, send me an email and I’ll do my best to help. You can also check out my Advisorator newsletter —where a version of this story first appeared—to get more practical tech advice every week.
Editor’s note: This article has been updated with up-to-date product recommendations.
Author: Jared Newman

Jared Newman has been helping folks make sense of technology for over a decade, writing for PCWorld, TechHive, and elsewhere. He also publishes two newsletters, Advisorator for straightforward tech advice and Cord Cutter Weekly for saving money on TV service.
Recent stories by Jared Newman:
- Wi-Fi 5 vs. Wi-Fi 6 vs. Wi-Fi 6E: Which router should you pick?
BroadbandNow is supported by commissions from some of the providers listed on our site. Learn More
The Ultimate Guide to Troubleshooting Home WiFi and Router Issues
- Tyler Cooper
- Restarting your router is the simplest way to solve Wi-Fi issues.
- Learning your router’s icons will help you diagnose any problems.
- Placing your router in a centralized and open area is essential for the best connection speed and stability.
- Speed tests and other diagnostic programs are useful tools for assessing your network connection.
- The best mesh Wi-Fi networks offer extensive coverage and the quickest speeds for your home.
Ninety-nine percent of home Wi-Fi issues can be fixed by unplugging the router, waiting five seconds, then plugging it back in. This resets the device and frequently improves the speed. But if that doesn’t fix your problem, this guide will provide you a to-the-point reference for dealing with some of the most common home Wi-Fi issues, such as the Wi-Fi not working, slowing down, disappearing, or not connecting with devices.
Keep reading to find out what to do if your connection is running slower than usual, as well as how to troubleshoot a network that won’t connect at all. We’ll also take a look at several tools you can use to help troubleshoot your connection no matter what problems crop up.
Table of Contents
Home wi-fi quick fix, understanding your router’s icons, how to troubleshoot wi-fi, tools for wi-fi troubleshooting, ways to boost your speeds or wi-fi reach, why does my computer keep disconnecting from wi-fi.
- If All Else Fails, Contact Your Service Provider
If your wireless connection suddenly stops working, restart your router before trying anything else. Here’s the process:
- Unplug or power off your router.
- Wait two to five minutes before plugging it back in.
- Wait five more minutes and retry the connection.
In most cases, this should fix your issue and allow you to get back online. If you go through these steps and something still isn’t working, you may need to contact your internet service provider for assistance.
Most routers have a series of icons that illuminate to convey different status messages at a glance. Though these can vary from brand to brand, most manufacturer’s include at least three primary status indicators:
Interpreting the Colors of Your Router’s Lights
Important note : In order to be clear on what your specific device is communicating to you, refer to the user manual for a more detailed explanation.
Pro tip: You can usually find a digital copy of your router’s manual by typing your device model number followed by “user manual” into Google.
If you’ve tried the quick fix above to no success, there are still several other ways you may be able to troubleshoot your Wi-Fi connection. In order to identify the technique most likely to actually help you, let’s break down some common issues:
“I’m experiencing slower-than-normal network speeds.”
Try this: Plug an ethernet cable directly into your router and test your internet speeds using our speed test tool . Next, test your speeds on the Wi-Fi connection. If they’re both slow, the issue is likely with your service provider and not your equipment. Give them a call.
If the hardwired connection is much faster than the wireless one, however, there may be more you can do to optimize your network. Wired connections will usually always be faster than wireless in some capacity, but the difference shouldn’t be so vast that your Wi-Fi is unusable. First, try moving your router to a more central location in your home. If that’s not an option, it may be worth exploring how to extend your Wi-Fi connection to all areas of your home.
Also, you might be encountering interference from networks adjacent to yours. If you think this may be the case, you can try changing the channel your router is broadcasting on. For starters, you’ll want to use the 5 GHz band whenever possible, if your router supports it. These tend to be less congested and therefore better performing than their 2.4 GHz counterparts.
“I have no internet connection at all.”
Try this: Plug an ethernet cable into your router and see if you’re able to get a signal on a desktop or laptop. If you can’t, your access has been cut and you should contact your ISP.
If you’re able to load web pages through a hardwired connection, there’s definitely something wrong with your Wi-Fi network. If restarting the router didn’t fix the issue, you may need to set it up again completely. Most routers have a small “reset” button that needs to be held down with a paperclip or other small object. Doing this will restore the device to factory settings and you’ll be able to go through the first-time setup once again.
If you’ve been through this process and still can’t get connected, you’ll likely need to contact your ISP for help. You could have an unpaid balance that has caused the company to suspend your account, or there might simply be an outage in your area.
“My Wi-Fi network disappeared completely.”
Try this: Check to see where your router is positioned. If it’s somewhere cramped, such as behind a couch or crammed into a storage closet, it might’ve overheated and shut down automatically to prevent any damage.
If you’re able to move your router to a place with more airflow, you should be able to solve the overheating issue. If you feel that your router is positioned in a good location and that overheating isn’t the problem, there are a few other things that could be happening.
For one, your network may have reset itself due to an update. Take a look at the default network name (usually printed somewhere on the router itself) and see if you recognize that network when looking for a connection.
“My phone/laptop/tablet won’t connect even though my other devices are fine.”
Try this: Turn off the offending device and turn it back on. You can also try turning the Wi-Fi off and on again in the settings of your device, just to be thorough.
If this doesn’t help, you may need to delete your network from the device entirely. On an iOS or Android device, you can simply click on the network name and hit “Forget This Network.” This means you’ll have to find the network again and put the password in like you did the first time you set it up, but it should solve any remaining connection issues in the process.
Our speed test tool allows you to see how your current network is performing in terms of both upload and download speeds. You can use this at any time to test the quality of your connection, and if you’re having any issues, you can use it to gauge your progress on getting them resolved. You can also use Speed Test periodically to see if you’re really getting the speeds that you’re paying for (look at your bill for payment info). Just remember that using Wi-Fi will always slow things down a little bit.
You can also run speed tests on different devices and from different locations. If the speed is sluggish on one device or in one location but not the others, that indicates an issue specific to the device or location.
Wireless Diagnostics (Mac)
The network diagnostics tool is a robust program that allows you to get a clear picture of your network health, as well as troubleshoot any issues you may be experiencing. You can find this program by hitting “command” plus “spacebar” and typing “Wireless Diagnostics” into the search bar.
When you first open the program, it will scan your immediate area for any available Wi-Fi networks. Once this is done, you’ll be presented with two options: monitor my Wi-Fi connection and continue to summary. Choose neither of these. Instead, at the top of your screen, select “Scan” from the Window drop-down menu. You will see a list of networks. Select “Scan Now.”
The service will then show you a full list of connections around you, including what channel they are operating on. The program will also show you the best channels for both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands based on network congestion. In order to actually change the channels your router is operating on, you’ll need to Google search the brand of the device followed by “IP address.” You will then type this in just like you would any regular website.
NirSoft (Windows)
NirSoft functions very similarly to the wireless diagnostics tools for Mac, scanning your Wi-Fi environment and displaying all available networks, as well as a number of useful statistics for each. You’ll still need to log into your router’s control panel to actually change its configuration.
NetSpot (Mac & Windows)
NetSpot is a fantastic alternative to both options above and even features some additional tools that intermediate users may find valuable. Above and beyond being able to view detailed information about your network, NetSpot also allows you to visualize its footprint in your home, showing you any dead zones and weak points that need to be patched up. Available as a free download, you’d be hard-pressed to find a more feature-complete troubleshooting program.
A little more speed or reach makes a big difference. To inject more oomph into your internet, try boosting your Wi-Fi signal and speeds with the following methods:
If your router is in a corner, closet, drawer, or non-central location, move it to a more open, central spot in the home (not the kitchen though. There is too much potential for liquid messes and signal interference from metal appliances). WiFi signals are stronger when they don’t have to travel through walls or floors, and a central location means better access to more devices. If your home is three floors, the central location is the middle of the second floor. Alternatively, adjust the angle of the antenna on your router, and see if that helps. Use compressed air to get gunk off your router, too. For more speed with heavy usage devices such as online gaming consoles and video-streaming laptops, keep them as close as possible to the router.
This method also gives you an idea whether neighbors, visitors, hackers, and others are connected to your network. The main step to see connected devices is to access your router’s admin panel. Another guide we wrote covers how to get into the admin panel. It’s easier than it may seem! Here are some other links that may help:
- Netgear login tutorial
- Linksys login tutorial
- Asus login tutorial
- TP-Link login tutorial
You may see a lot of devices connected to your WiFi, whether they’re on the 2.4GHz or 5GHz band. Smart speakers, smart thermostats, security cameras, and other smart home-type devices tend to be a better fit for 2.4GHz. PCs, laptops, gaming consoles for online gaming, and smart TVs that stream a lot of video should usually go on 5GHz.
2.4GHz band: This band has better range, works well through walls, and tends to be slower than 5GHz. It may slow down noticeably if “cluttered” with too many baby monitors, Bluetooth devices, garage door openers, smart home devices, holiday lights, etc. More than 20 of these devices might be too much, although some WiFi networks can have 200+ devices connected to them and perform just fine. If too many smart devices is an issue for your system:
- Reduce video/picture resolution on doorbell cameras and video devices to speed up the WiFi.
- Use a smart home hub to take traffic off WiFi and Bluetooth, which helps with congestion and speeds.
Routers tend to choose bands automatically depending on how far away the device is when you connect to the network. Reallocating devices to different bands depends on your router. With some routers, you do it through software. Others, you flip a switch on the router. A few, especially some mesh systems, aren’t super user-friendly in this regard. “Trickery” might be necessary. For instance, devices tend to connect to 5GHz as the default. If you want them on the other band and they’re portable (say, a group of smart light bulbs), you could go to the edges of your WiFi coverage, where they “flip” over to 2.4GHz since the range is better. Finish setting up there, then put the devices where they are supposed to be. They will stay on the 2.4GHz band. If the devices are not portable, then temporarily unplug the router closest to the device or separate the router and device as much as you can. These tricks often force the 2.4GHz band to be used.
Wi-Fi extenders work similarly to boosters and repeaters. Basically, they extend or amplify the main Wi-Fi network and create a second network. They’re useful if the main Wi-Fi signal is weak and you have just one dead zone (a mesh system may work better if the home has multiple dead zones). Extenders plug into outlets and resemble air fresheners. Extenders do create second networks, some with different names. It’s not always convenient to connect to two networks from the same house, so look for extenders that use the same network name when rebroadcasting. Also, while extenders extend the reach of your network, speeds may slow a bit. A mesh network enhances range without sacrificing speed and changing network names, so we touch on that in a bit.
It could be time for a change if you lived in a small apartment and took your router along to your new, much larger home. Bigger homes might need mesh routers or routers that can pair with repeaters/extenders to help WiFi signals reach farther. Before upgrading, though, especially if the space to cover has not changed, try moving the router if it’s in a closed location, and blast any dust buildup with compressed air.
>> Related Reading: The Best Wi-Fi Routers, Tested and Reviewed
Upgrading to mesh makes sense if your Wi-Fi connection is strong in some places but weak or dead in others. You may need mesh for coverage in large homes, multistory homes, and garages that are not close to the router. In a mesh network, a primary router and satellite nodes or modules coordinate to deliver speedy, efficient Wi-Fi. You put the nodes in different areas throughout your house, and each node is capable of broadcasting Wi-Fi. Mesh systems have become much more affordable, but you may be disappointed if you go entry-level. Plan to spend about $400 for impressive results. Look for two main features:
- Triband (three bands instead of two): The third band is another 5GHz band, and it’ll speed up communications between the primary router and the satellites.
- Wi-Fi 6: Wi-Fi 6 is more secure, efficient, and speedy compared with Wi-Fi 5. Wi-Fi 6 also handles traffic and congestion better. It has been available for a few years, but nowadays more and more devices support it. There’s also Wi-Fi 6E, which is even newer and stronger. Fewer devices support it, so don’t get your hopes up too much for that just yet (If you’re an avid online gamer, 6E can make a big difference and is worth further investigation).
If you live with a bunch of roommates or relatives who love streaming and gaming, all of you may need to agree on some guidelines or take turns using the internet connection. Of course, first try suggestions such as restarting the router, moving it to a central place, running speed tests, and using an extender for a dead zone. Do avoid putting your router in the kitchen, as microwaves and metal appliances can mess with the signal. So can liquids and food that get spilled on the router. Otherwise, here are ideas for Wi-Fi sharing and communication:
- Limit certain activities to certain times (perhaps downloading online games during the wee hours when everyone is asleep). Be aware that torrenting (while also being illegal) is a huge bandwidth hog.
- Give a heads up before hopping onto Zoom or any high bandwidth activity so that everyone else in the home doesn’t try to Zoom, FaceTime, and livestream classes all at once.
- If you live in a multi-family residence, ask your housemates to not share your Wi-Fi passwords with others in the building.
- Agree to dial back the graphics, for instance, by streaming in standard definition instead of 4K or Ultra HD.
- Pay a bit more money per resident for more bandwidth..
(more common if you’re in an apartment building and experiencing frequent Wi-Fi disconnects or out of range or weak Wi-Fi signals). By default, U.S. routers tend to be automatically set to channels 1, 6, and 11, especially 6. Assume that everyone else in the building is on these channels. Manually adjust your router so it is on channel 1, and retest your WiFi until you find a channel it works well on. Or, use a third-party app that shows the channels around you and helps find a less crowded channel.
If your internet plan has certain limits, then you are unlikely to get more. Say that you’ve been content with web surfing and some video streaming here and there at 25 Mbps max for the past few years. You’ve recently gotten into online gaming, and your new partner and stepchildren, all of whom love streaming movies, moved in. You may need a new plan that can support both online gaming and streaming in 4K, giving you speeds of 50 Mbps to 100 Mbps. Now, if you’re doing a lot of live streaming all of the sudden, perhaps taking online classes live every day or doing Twitch broadcasting, you might need speeds up to 150 Mbps or even 200 Mbps. However, if you cannot afford to upgrade your plan, you may still be able to improve your internet speeds. “If budget is a limiting factor, it’s best to call the service provider to see if there are faster plans that you can upgrade to,” said Mark Chen, founder and CEO of GetBillSmart. “Sometimes you’re stuck on a legacy plan that they can easily upgrade you to. You can also threaten to cancel to get a better deal and use those savings to get faster speeds.”
Once you’ve resolved the issue by following one of the above steps, make sure to secure your wireless home network to prevent hackers or neighbors from accessing your Wi-Fi.
If you find that you are consistently getting booted from your Wi-Fi network, there are a few things that could be happening. We recommend looking for any patterns in the service disruptions. Do they only happen at a certain time of the evening? Maybe it even drops when you pop something into the microwave? Believe it or not, there are many signals from Bluetooth devices, baby monitors, and smart lights constantly flowing through your home that can disrupt your internet connection.
If you’ve ruled out network interference using the tools listed above, you may need to try updating your router’s firmware. This is essentially the device’s “operating system,” and like any other piece of software, it needs to be updated from time to time to keep functioning properly.
If you’ve updated your firmware and are still getting disconnects, you may need to consider replacing the router outright, especially if it’s more than a few years old. Routers are computers, and computers unfortunately do tend to fail after a few years. If you’ve been renting a modem and router from your ISP, it might be better to invest in your own equipment since ISPs tend to rent out old hardware.
Firmware Updates by Brand
How to log into your router’s control panel.
Click on your router’s brand below to see in-depth instructions on how to log in to its configuration area, where you can adjust network passwords and names, as well as change the channels they are operating on.
- NETGEAR login tutorial
If All Else Fails, Contact Your Service Provider.
Though technical support from many companies can be a hit or miss experience, if you’ve tried everything above and nothing seems to be working, it might be best to simply reach out to request a tech to come to your home and sort the issue out directly. This may entail a service fee of some kind, but if it gets you back online, it’ll be worthwhile in the end.
Tech Support Phone Numbers for Common ISPs:
- AT&T Internet tech support: (800) 288-2020
- CenturyLink tech support: (888) 723-8010
- Cox tech support: (800) 234-3993
- Frontier tech support: (888) 884-0504
- HughesNet tech support: (866) 347-3292
- Mediacom Cable tech support: (800) 883-0145
- Rise Broadband tech support: (877) 910-6207
- Spectrum tech support: (855) 757-7328
- Suddenlink Communications tech support: (877) 794-2724
- TDS tech support: (866) 571-6662
- Verizon Fios tech support: (800) 837-4966
- Viasat tech support: (855) 463-9333
- Windstream tech support: (800) 347-1991
- WOW! tech support: (855) 496-9929
- XFINITY tech support: (800) 934-6489
- The Ultimate Guide to Troubleshooting Home Wi-Fi and Router Issues
Offer Detail
10 ways to troubleshoot and fix any Wi-Fi problems you're encountering
- When you encounter Wi-Fi problems, you can try troubleshooting your network or devices, check with your internet service provider, and more.
- Start by eliminating obvious problems and making sure you know whether it's related to the Wi-Fi network, internet connection, one device or all devices.
- Here are 10 ways to troubleshoot and solve Wi-Fi problems.
It can be hard to imagine or remember the days before Wi-Fi , when you had to run Ethernet cables throughout the house to connect computers to the internet and carry files around on CDs and portable hard drives (affectionately known as "sneakernet").
These days, we take Wi-Fi for granted – right up until it stops working and brings our modern connected household to a complete stop.
How to fix Wi-Fi problems
Here are 10 ways to troubleshoot and solve common Wi-Fi problems.
Basic check: Is the Wi-Fi router running?
It's not out of the question for the plug to have been accidentally pulled or the cat to have stepped on the power button. Make sure the Wi-Fi router's lights are on.
Is the issue related to one device or all devices?
Fixing computer problems like Wi-Fi connection issues often comes down to the process of elimination. That's why technical support technicians often start by asking silly and obvious questions like "is the computer plugged in?" Once you know the Wi-Fi is running, check to see if the problem happens on just one device or on all of them. If you can't connect on your laptop, for example, check your phone to see if you can see Wi-Fi signal strength bars.
Send a ping to Google
One other easy thing you can check for: is the connection problem related to your Wi-Fi network or to your internet service provider's internet signal? Your Wi-Fi network might be fine, for example, but the ISP's internet may be out. To find out, run a ping test using a computer.
1. On your PC, click the Start button search box and type "CMD," then press Enter.
2. In the Command Prompt window, type "ping Google.com."
3. Wait for the result.
If you see an error message, you might not have a working internet connection; continue troubleshooting in the next section. If you see a reply from Google, then you have a working internet connection and the problem lies elsewhere.
You can also log into your account for your internet service provider to check if there's an outage in your area. With many providers, a banner will appear at the top of your account page notifying you of an outage, or you can search for an outage map on the site.
Troubleshooting no service at all
This is unfortunately one of the more common problems people run into — the internet simply doesn't work at all. If none of the devices or computers on your Wi-Fi network can connect, reset both the internet router and Wi-Fi (this might be one device or two different ones). Unplug them, wait two minutes, and plug them back in. If your Wi-Fi doesn't start working again, the problem might be with your internet service provider — call customer service and let them troubleshoot.
Resolving slow or spotty internet in certain rooms
If your Wi-Fi drops out in certain parts of the house on a regular basis, the problem is almost certainly a "dead zone" caused by a router that can't reach everywhere. If possible, move the router to a more central location in the house. Alternatively, you can add a Wi-Fi extender to increase the range of your router.
Troubleshooting slow or spotty internet at certain times of day
If your connection problem isn't related to where you are in the house but is an intermittent problem at certain times of the day, the issue is likely related to a lack of bandwidth; too many devices are connected to the Wi-Fi network and using too much data. If three people are streaming Netflix on different devices at the same time, for example, there's your culprit. If possible, connect devices with an Ethernet cable so they aren't using Wi-Fi, or better yet, take one or more bandwidth hogs offline entirely.
Is your connection slow because of the Wi-Fi network or the ISP?
If you have a connection that's noticeably slow, it can also be helpful to figure out if your poor performance is being caused by a slow internet connection provided by your ISP or if the Wi-Fi network in your home is not working properly. You can do this by running an internet speed test . Run the test at speedtest.net in any browser (on a computer or mobile device). If the internet speed seems normal (at least 10Mbps, for example) the issue is related to your Wi-Fi network, not the internet. Read our detailed guide on how to check the strength of your Wi-Fi for more information.
How to resolve issues with your router
It can be challenging to know exactly what is causing a problem with your Wi-Fi connection, and the router itself has some settings and configurations that might be "breaking" your Wi-Fi network. If possible, check on and update your router's firmware. Most modern routers work with a simple mobile app you can use to check on the firmware and install any available updates. This can resolve issues with your connection reliability and speed. In addition, you can probably use the app to change the channels your router is using to broadcast on its various bands. If your connection is slow or intermittent, changing the channels might significantly improve your Wi-Fi service. For more information, read our article on how to boost your internet connection .
What to do if one device has trouble connecting
Make sure the device's software is up to date. And if your router is a dual-band or tri-band device, try connecting to one of the other Wi-Fi bands. There are any number of reasons why a laptop might connect more easily to one of the 5GHz radios rather than the other, for example.
What to do if your game console can't connect to Wi-Fi
Occasionally, consoles like the Xbox and PS4 can run into trouble connecting to Wi-Fi. Consoles can be affected by the same kind of glitches that affect PCs and mobile devices, but they generally only need to go to one internet location, so troubleshooting can be easier. Open a site like Downdetector in a web browser on your computer or a mobile device and use it to see if the Playstation Network or Xbox Live is down. If so, just wait for the site to come back up. Otherwise, reboot both the router and the console and move them closer together, if possible.
Related coverage from Tech Reference :
'why isn't my internet working': how to identify why you can't connect to the internet and troubleshoot accordingly, how to boost your internet speed at home in 8 ways, and make sure you're not being overcharged for low speeds, 'what is a good internet speed': the internet speeds you should aim for, based on how you use the internet, how to find out how fast your internet is using a free and accurate google speed test, 'why won't my pc connect to wi-fi': 6 ways to troubleshoot your windows computer's internet connection.
Watch: 10 inventions to fight your biggest fashion problems
- Main content
- Compare Providers
- Review Providers
Why is My Wi-Fi Not Working? How to Fix Your Internet
What to do when you have a Wi-Fi signal but no internet access.
These days, the little Wi-Fi symbol in the corner of your phone or laptop screen is so synonymous with internet connectivity that it’s easy to forget that Wi-Fi and internet aren’t the same thing. And it is possible to have one without the other. This guide will help you figure out why your Wi-Fi isn’t connected to the internet and what you can do to fix it.
The difference between Wi-Fi and internet signals
Wi-Fi is a radio broadcast signal transmitted by a router that allows devices like phones and laptops to connect to a network wirelessly. Internet signals are a connection to the world wide web. When both work properly, your Wi-Fi network is a wireless bridge that feeds your devices access to the internet.
Essentially, that little Wi-Fi icon on your device screen tells you that you’re connected to a router, not necessarily the internet. The wireless router needs to be connected to the internet for you to access the web via Wi-Fi. You can tell if you’re actually connected to the internet in your device’s Wi-Fi settings.
Reasons you’re connected to Wi-Fi but not internet
You’re on the wrong wi-fi network.
Go into your device’s Wi-Fi settings and make sure you’re connected to the right Wi-Fi network.
Since the Wi-Fi icons on devices don’t usually display a network name, you usually assume you’re on the right network. But there are a ton of Wi-Fi signals sharing the same space. You might be connected to a neighbor’s Wi-Fi, a Wi-Fi extender, or a hotspot.
Your modem or router needs a restart
Your networking equipment may not be connected to the internet, but it can still broadcast Wi-Fi signals. Oftentimes simply restarting your modem, router, or gateway (modem/router combo) clears up the issue.
Whether you have a separate modem and router or a gateway, the restart process is the same:
Step 1: Disconnect the power cable from the back of the equipment.
Step 2: Wait 60 seconds.
Step 3: Reconnect the power cable to the back of the equipment.
Step 4: Wait while the equipment reboots. This can take up to 20 minutes.
Restart your computer or device too
This is especially helpful with computers. A system restart is an easy cure-all that’s so effective it’s always worth a shot.
Give your internet connection a health check
Download our speed test app to see if your internet connection is running as it should.

Use our speed test to see if your internet connection is running as it should.

Try your PC’s Network troubleshooter (Windows only)
Windows PCs have a built-in network troubleshooter capable of repairing many internet issues on your computer. It’s really easy to run the Windows Network troubleshooter:
Step 1: Right-click the Wi-Fi icon in the lower-right corner of the screen.
Step 2: Click “Troubleshoot problems.”
Step 3: Select “All network adapters” and click Next.
Step 4: Wait while the troubleshooter searches for the problem.
Your ISP is down
Your internet service provider (ISP) may be experiencing an outage. Unfortunately, if that’s the case, there’s not much you can do about it besides waiting it out. It’s times like these when a mobile hotspot or smartphone tethering come in handy.
Most ISPs have mobile apps you can use to find out if there’s an outage in your area—some even give you an estimate of when service will be restored. You can also explore signing up for text alerts from your ISP to get notified of outages due to weather, construction, etc.
The website or service your attempting to use is down
Individual websites and services have outages too, and they can make it seem like your internet isn’t working. Try to access a different website or service on your device. If it works, you know your internet is fine, and the site’s down.
The sites downformeoreveryone.com and downdetector.com are useful for checking when your favorite sites and services are down.
Ready for a new internet provider?
Enter your zip code to see what internet providers are available in your area.
Your antivirus is blocking your internet connection
Antivirus software is designed to protect you against threats on the internet, but sometimes it can get in the way of your normal web activities. Try briefly disabling your antivirus software to see if doing so restores your internet access.
We don’t recommend using the internet without your security software turned on, so don’t spend any additional time on the web without it. But if your antivirus is blocking your connection, try updating it. Because web threats evolve so quickly, web security software requires frequent updates. It’s a good idea to switch on the auto-update feature of your software due to the frequency of essential updates.
You can also try adding an exception to your security software’s firewall for the program or service you’re attempting to use.
If your antivirus software is causing too much frustration, consider switching to a new one.
Third-party software is causing internet connectivity issues
You probably have a bunch of programs running in the background of your computer. Sometimes, one of these programs interferes with your internet connection. An easy way to rule out background program problems is to boot your computer in safe mode, which disables most third-party background software.
If you have a healthy internet connection after booting in safe mode, one of your programs is likely causing the issue.
Reboot in Safe Mode on Windows 10:
Step 1: Click the Start button, then the cog wheel icon to open the settings menu.
Step 2: Type “recovery options” into the settings search box at the top of the menu and press enter.
Step 3: Under the Advanced startup sections, click “Restart now.”
Step 4: Your PC will reboot and display an options menu. From the options menu, select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart.
Step 5: Your PC will reboot again, and you’ll see a list of options. To reboot with networking, press 5.
Step 6: Your PC will reboot into safe mode with networking. From here, test your internet connection. If it works, a background program may have been causing trouble with your internet connection.
Restart MacOS computers (with Apple processors) in Safe Mode:
Step 1: Shut down your computer.
Step 2: Hold down the power button until “Loading startup options” appears on the screen.
Step 3: Choose a volume.
Step 4: While holding the shift key, select “Continue in Safe Mode.”
Restart MacOS computers (with Intel processors) in Safe Mode:
Step 1: Restart your Mac and hold down the shift key as it boots up.
Step 2: Log in (you might have to log in twice).
Step 3: You should see a Safe Boot indicator in the menu bar.
Your networking cables are loose or damaged
The cables connecting your equipment to the internet can become loose over time, or they can be damaged after repeated stress. Look for tears, harsh twisting, kinking, pressure from furniture, and chew marks from pets.
First, check the line that connects to your modem or gateway (modem/router combo) from the wall outlet. For cable internet customers, look for a coaxial cable (the same kind used for cable TV). Other internet types use coaxial or Ethernet cables. Coaxial cable connections should be twisted hand tight to the back of the modem and the wall outlet. Ethernet cables should make an audible click when inserted in the socket on your equipment.
If you have a separate modem and router, check the Ethernet cable connecting them as well.
Still stumped?
If you’re still having trouble establishing an internet connection, try our other resources to get your internet running smoothly.
- No Internet Connection Troubleshooting Guide
- Why Does My Internet Keep Disconnecting?
- Improve Your Wi-Fi Speed in 10 Simple Steps
- Why is My Internet So Slow?
Author - Austin Aguirre
Austin worked as a broadband technician installing and troubleshooting countless home internet networks for some of the largest ISPs in the U.S. He became a freelance writer in 2020 specializing in software guides. After graduating with a BS in technical communication from Arizona State University, he joined the team at HighSpeedInternet.com where he focuses on home network improvement and troubleshooting.
Editor - Rebecca Lee Armstrong
Rebecca Lee Armstrong has more than six years of experience writing about tech and the internet, with a specialty in hands-on testing. She started writing tech product and service reviews while finishing her BFA in creative writing at the University of Evansville and has found her niche writing about home networking, routers, and internet access at HighSpeedInternet.com. Her work has also been featured on Top Ten Reviews, MacSources, Windows Central, Android Central, Best Company, TechnoFAQ, and iMore.
Related Posts

- Home Internet
The most common Wi-Fi problems and how to fix them
We my not have to disconnect from the Internet to make a phone call anymore, but Wi-Fi problems persist. Here are some of the common issues you will run into and how to fix them.

Internet speeds and Wi-Fi have both improved significantly over the last several years. Data speeds are faster across the board and wireless connections are more reliable than ever.
However, Wi-Fi isn't without issue. Hang out at a Starbucks long enough and you can experience it firsthand.
Once you've set up your home network , here are some very common issues you may run into with Wi-Fi and how to correct them.
Locating local internet providers
Slow connection
Despite faster speeds reaching most homes around the globe, wireless (and often wired) networks can get bogged down. If your Internet connection is still working but the speeds are slower than normal, there is usually a logical explanation that can usually be fixed.
Cause: The most obvious problem with Wi-Fi speeds slowing down is being too far from the router. The further you are from the router, the more unreliable the connection and its throughput will become.
Fix: To fix this, just get a little closer. If the router is located in a different room, try going into the room where the router is located and see if that fixes the issue. If this is a consistent issue, try to position your router higher (up on a shelf), away from other devices, which can interfere with it, and in a central location in your home.
If that doesn't work, consider purchasing a second router and a set of powerline network adapters to extend your network.
Cause: Another cause for slowdowns is a lack of bandwidth. If everyone is home and using their computers, phones and televisions for data-hungry applications, your typically speedy Internet is being spread thin and shared across multiple devices.
Fix: Disconnect any devices that you aren't actively using. If multiple people are trying to stream videos from, say, YouTube and Netflix, while someone else is trying to game online, you can try connecting one or more of the devices directly to the router using a Cat-5 ethernet cable to free up some of the wireless bandwidth. But the problem may be that you just don't have fast enough Internet speeds to support everything at once.
There is also the possibility that someone nearby is leeching off your Internet. To prevent this from happening, be sure to setup security for your network and give out the password sparingly.
11 ways to make your Wi-Fi faster

Cause: Interference can be a real issue, especially in crowded areas. When most people first get their Internet set up, they leave settings unchanged, which means default wireless frequency channels -- like 1, 6 and 11 -- become very crowded.
Fix: Fortunately, many newer model routers are capable of automatically selecting the least crowded frequencies upon rebooting. Perform a power cycle on your router or, log in to the admin panel and manually select a different channel.
Additionally, if you have a dual-band router, try enabling both 2.4GHz and 5GHz. Keep the 5GHz channel open for your most important connections.
Cause: During peak hours, Internet speeds can slow for everyone, especially in crowded, urban areas.
Fix: All you can really do when this is the case, if possible, is try to schedule your usage outside peak hours to get the best speeds.
Cause: Wireless technology has changed quite a bit over the last 10 years. New wireless standards have been put in place, speeds are faster than ever, fiber is being offered in more areas and devices you never thought would require an Internet connection need Wi-Fi -- televisions, speakers, refrigerator, printers, lights and more. The problem could easily be an outdated router.
Fix: If you think the limitation lies with your router, it may be time to start saving up for a new one. Upgrading your router every two years or so is good practice and can help you avoid certain issues altogether.
No Internet connection
Cause: Periodically, something glitches and the router or modem (or combination) just stop communicating. There isn't always an explanation. It just happens.
Fix: The best place to start is pulling the plug. Disconnect the modem and router from power and wait at least 30 seconds before restoring power to both.
Cause: For me, one of the most common problems that occurs with my Internet is the connection dropping completely -- not due to a hardware issue on my end, but rather a massive service outage.
Fix: Not much you can do here. You can go to the nearest coffee shop or get on the phone with your Internet service provider (ISP) and let them know you're affected. Sadly, this usually won't do much to speed up the recovery time, but it can help the ISP know more about which areas are affected by an outage.
Home Internet Guides
- Best Internet Providers in Los Angeles
- Best Internet Providers in New York City
- Best Internet Providers in Chicago
- Best Internet Providers in San Francisco
- Best Internet Providers in Seattle
- Best Internet Providers in Houston
- Best Internet Providers in San Diego
- Best Internet Providers in Denver
- Best Internet Providers in Charlotte NC
- Google Fiber Internet Review
- Xfinity vs Verizon Fios
- Verizon 5G vs. T-Mobile Home Internet
- Verizon Internet Review
- Xfinity Internet Review
- Best Rural Internet
- Best Cheap Internet and TV Bundles
- Best Speed Tests
- AT&T Home Internet Review
- Best Satellite Internet
- Verizon 5G Home Internet Review
- T-Mobile Home Internet Review
- Best Internet Providers
- Frontier Internet Review
- Best Mesh Wi-Fi Routers
- Eero 6 Plus Review
- TP-Link Review
- Nest Wi-Fi vs. Google Wi-Fi
- Best Wi-Fi Extender
- Best Wi-Fi 6 Routers
- Best Wi-Fi Routers
- What is 5G Home Internet?
- Home Internet Cheat Sheet
- Your ISP May Be Throttling Your Internet Speed
- How to Switch ISPs
- Internet Connection Types
- Internet for Apartments
- Top 10 Tips for Wi-Fi Security
- How to Save Money on Your Monthly Internet Bill
- How Much Internet Speed Do You Need?
- AT&T Internet Promo Codes
- Verizon Fios Discounts
- Comcast XFINITY Codes
Ad-free. Influence-free. Powered by consumers.
The payment for your account couldn't be processed or you've canceled your account with us.
We don’t recognize that sign in. Your username maybe be your email address. Passwords are 6-20 characters with at least one number and letter.
We still don’t recognize that sign in. Retrieve your username. Reset your password.
Forgot your username or password ?
Don’t have an account?
- Account Settings
- My Benefits
- My Products
- Donate Donate
Save products you love, products you own and much more!
Other Membership Benefits:
Suggested Searches
- Become a Member
Car Ratings & Reviews
2024 Top Picks
Car Buying & Pricing
Which Car Brands Make the Best Vehicles?
Car Maintenance & Repair
Car Reliability Guide
Key Topics & News
Listen to the Talking Cars Podcast
Home & Garden
Bed & Bath
Top Picks From CR
Best Mattresses
Lawn & Garden
TOP PICKS FROM CR
Best Lawn Mowers and Tractors
Home Improvement
Home Improvement Essential
Best Wood Stains
Home Safety & Security
HOME SAFETY
Best DIY Home Security Systems
REPAIR OR REPLACE?
What to Do With a Broken Appliance
Small Appliances
Best Small Kitchen Appliances
Laundry & Cleaning
Best Washing Machines
Heating, Cooling & Air
Most Reliable Central Air-Conditioning Systems
Electronics
Home Entertainment
FIND YOUR NEW TV
Home Office
Cheapest Printers for Ink Costs
Smartphones & Wearables
BEST SMARTPHONES
Find the Right Phone for You
Digital Security & Privacy
MEMBER BENEFIT
CR Security Planner
Take Action
How to Fix Your WiFi
Repairing electronic devices can be frustrating. Here's how to quickly get help with slow signals, dropped connections, and other potential router issues.
Home WiFi networks, which give internet access to the devices in your house, are notoriously glitchy. They can stop working and then restart, or work fine in some spots but badly in others. The challenge: figuring out where the problem resides—with your device (phone, smart TV, laptop), WiFi setup (modem and/or router), or internet service provider (ISP).
Before you start troubleshooting, keep in mind that it’s best to place your router in the center of your home. Try not to hide it in a closet; that slows the signal. Metal, glass, brick, microwaves, and Bluetooth speakers can interfere too.
Try This First Turn off your modem and router, wait a few minutes, then turn them back on. (Any service you call is going to ask you to try that, anyway.) Still not working? Go to your ISP’s website to see if there’s an outage in your area. If your WiFi is sluggish, use an Ethernet cable to connect the modem or router directly to a laptop. If that improves the speed to the laptop, the signal coming to your house is fine; you need either a new router or help adjusting the unit’s settings.
Get Online Help Google “ Spectrum support ,” “ Xfinity support ,” or the support for your own ISP to review your options. With Verizon , for example, you can communicate by phone, chat, or Facebook Messenger, and consult a drop-down menu for help with connection issues and identifying outages near you. A technician can walk you through a fix. If you’re comfortable following DIY steps, search online for “router problems” or “WiFi isn’t working.”
Get In-Person Help An ISP will send a technician to your home to restore service, replace a modem, etc., but it’s not always easy to schedule those appointments. Here are other options for timely on-site help.
Best Buy’s Geek Squad : If you’re enrolled in the My Best Buy Total plan, the Geek Squad will come to you to assist with troubleshooting, setups, and more. Cost: $50 for the first 90 minutes. Sign up at bestbuy.com .
Regional repair shops: If you live in one of the 18 states with NerdsToGo locations, you may be in luck. This support and repair service can fix slow WiFi connections remotely by accessing your computer (with your permission). You can also post the problem on the online marketplace Airtasker and get quotes and help from a local network troubleshooter.
Your Tech Support Toolkit
Want to stay cool when your devices let you down? Take a few minutes to prep for the next tech crisis before it begins. Here are three expert tips.
Have your info handy. Create a file with your tech receipts, manuals, and troubleshooting guides. Add serial numbers, log-ins, and passwords. Photograph the setups for your computer and router, so you know which cables go where.
Update your software. Device manufacturers use system updates to fix bugs and protect you from security threats, so don’t skip installing them. Laptops and smartphones will generally prompt you to do so, but routers are less helpful . Today’s models often have an automatic update feature that you can activate via a mobile app or the device’s settings.
Back up your data. If your laptop is lost or damaged, you’ll be thankful that your photos and files are preserved. Stow them on an external hard drive ($70 to $100), get a free (or paid) cloud storage backup plan such as Google Drive, or do both.
Editor’s Note: This article also appeared in the March 2024 issue of Consumer Reports magazine.
Jennifer Cook
Jennifer Cook is an award-winning freelance writer who contributes to Consumer Reports on health, wellness, mind-body, and environmental topics. She lives in New York's Hudson Valley in a farmhouse built in the 1840s. An avid walker and dancer, she feels fortunate to live near wetlands and wild things, and to have easy access to culture and good food.
Sharing is Nice
We respect your privacy . All email addresses you provide will be used just for sending this story.
Trending in Wireless Networking
Should You Buy a WiFi Extender?
How to Get a Stronger WiFi Signal
WiFi 7 May Be a Leap Forward, but No Need to Rush Out and Get It
How to Solve Your Wireless Printer Problems
TechRepublic
Account information.
Share with Your Friends
How to diagnose and fix Wi-Fi network problems using a Windows 10 PC
Your email has been sent
Good home Wi-Fi is a necessity for the modern professional. With more people working from home than ever before due to the COVID-19 pandemic, Wi-Fi can be the difference between a good day’s work and a frustrating, unproductive few hours.
Unfortunately, Wi-Fi has become the remote professional’s coronavirus paradox: It’s absolutely necessary for work, but more people working from home means more Wi-Fi networks congesting the average neighborhood, more bandwidth being used, and less Wi-Fi reliability.
SEE: Future of 5G: Projections, rollouts, use cases, and more (free PDF) (TechRepublic)
Luckily, some of the most common Wi-Fi problems are easily fixed. Not all of them, of course: If your connection is slow whether you’re wired or wireless, there’s probably too many people using the internet in your area, and no one short of your ISP can resolve that issue.
How to choose the right Windows 10 Wi-Fi analytics tool
Unlike macOS, Windows 10 doesn’t have a built-in wireless diagnostics tool . There are a lot of third-party options to choose from, but when it comes to doing something as sensitive as scanning all of the devices on a network and compiling data about the machine the app is running on you want a trusted program. For that, it’s best to look in the Microsoft Store , where apps have to pass a certification test prior to being published.
For this guide, I’m using one of the most popular wireless diagnostics tools for Windows 10, WiFi Analyzer by Matt Hafner ( Figure A ). WiFi Analyzer is free with premium options available, but all of the essential tools you need to diagnose common Wi-Fi problems are included with the free version.
How to assess your signal strength with WiFi Analyzer
When you open WiFi Analyzer you’ll be greeted with the screen in Figure B , which shows a variety of information about your Wi-Fi connection, like your network, its channel, your device ID, and other details. All of the data presented on this screen is displayed in real time.
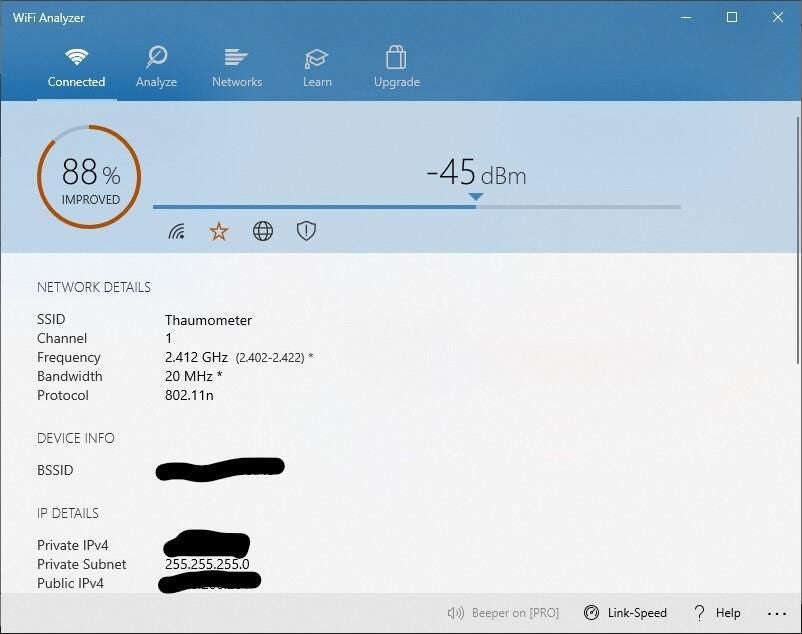
At the top of Figure B you’ll notice a circle that reports on the quality of your connection, a bar that shows your RSSI, and four icons. The icons are highlighted orange (from left to right) if WiFi Analyzer thinks you have a bad connection, are on a bad channel, don’t have internet access, or if your connection isn’t secure.
The circle with a percentage in it reflects whether or not your connection can be improved, and is a visual representation of the quality of your connection. If it appears orange (as it does in Figure B ), that’s because one of the four conditions shown in the icons isn’t met, or your RSSI is out of acceptable range.
RSSI is a reading of signal strength measured in dBm, and scales from 0, being the best, to -120, which is the worst. Typically, you’ll find signal ranges in the -80 dBm to -40 dBm. If you get much lower than -80 you’ll probably notice connection problems.
The information displayed on this screen updates in real time, so if you notice that your signal isn’t good try moving closer to your Wi-Fi router. The number on the bar should move toward 0. If your router isn’t in a good spot, and you can’t realistically move your computer, try moving the router to see if your signal strength gets stronger or weaker.
How to figure out what Wi-Fi channel to switch to
Wi-Fi channels are small slices of the overall Wi-Fi frequency band that routers can broadcast and computers can tune in to. Routers can simultaneously operate on the same channel, but the more routers on a single channel the more noise is generated, which can degrade signal strength and make internet connectivity spotty and unreliable.
You may have noticed that the star icon in Figure B was orange, indicating that my Wi-Fi wasn’t on the best channel.
If you click on the Analyze tab in WiFi Analyzer you’ll be shown a graph of all the Wi-Fi channels on your band (2.4GHz or 5GHz), and which networks are using them ( Figure C ).
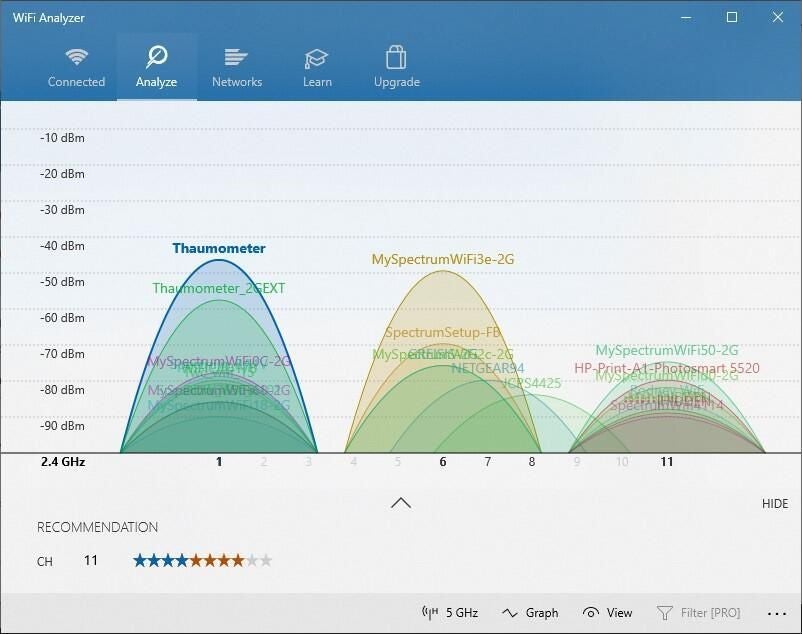
The Analyze screen is an excellent way to visualize which channels are crowded in your area, and it also recommends which channel to switch to, shown on the bottom of the screen. In Figure C , you can see that my current connection is the strongest on Channel 1, but also that Channel 1 is quite congested, as are channels 6 and 8. WiFi Analyzer recommends switching to channel 11, because even though there are several other networks using that channel their strength is fairly weak, meaning they’re less likely to interfere with my signal.
For this example I’m using a 2.4GHz network because it better illustrates network congestion. If you click on the 5GHz button on the bottom of the screen the view will switch over to nearby 5GHz signals ( Figure D ), but will only give a channel recommendation if you switch to a 5G connection.
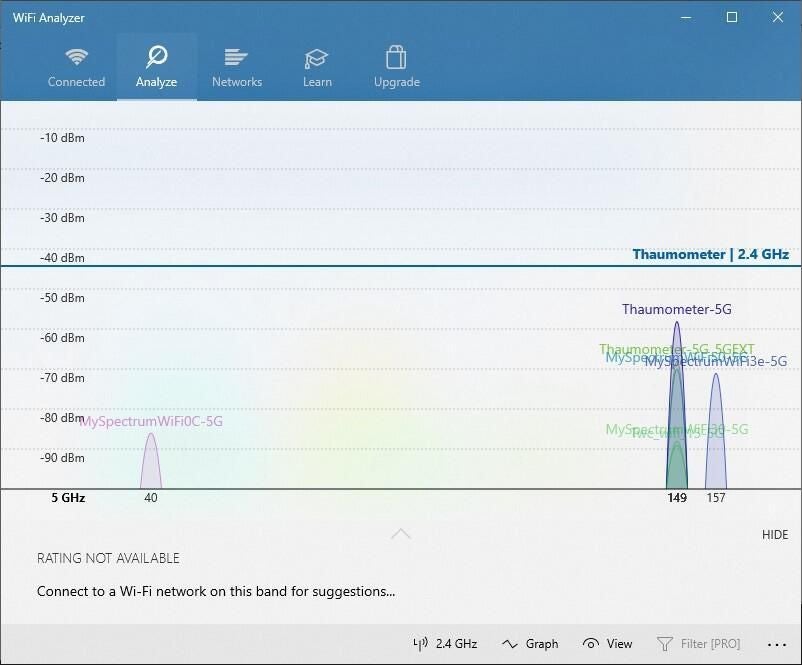
If WiFi Analyzer tells you that there’s a better channel to switch to there are two ways to go about doing it.
First, and easiest, is all dependent on the type of Wi-Fi router you have. Some routers are designed to search for the best channel whenever they power up, so the first thing you can try is rebooting your Wi-Fi router and checking to see what WiFi Analyzer says about your connection when it restarts.
SEE: Return to work: What the new normal will look like post-pandemic (free PDF) (TechRepublic)
If your router is configured to automatically search for the best channel you should see it on WiFi Analyzer’s recommended channel, or whichever one the router thinks is best. If a reboot doesn’t change the channel despite WiFi Analyzer showing it to be quite crowded then you probably don’t have automatic channel searching enabled or available on your router.
Without automatic channel finding, you’re stuck changing your router’s channel yourself. The way this is done is to log in to your Wi-Fi router using its IP address or login page URL, both of which vary based on the type of router you have. To find out how to log in to, and change settings on, your Wi-Fi router you’ll need to consult the manufacturer’s website or documentation that came with it.
If you want to learn more about how to read the various bits of information in WiFi Analyzer, be sure to click on the Learn tab, which will direct you to a variety of resources and WiFi Analyzer tutorials from Matt Haffner, who built the app.
Subscribe to the Innovation Insider Newsletter
Catch up on the latest tech innovations that are changing the world, including IoT, 5G, the latest about phones, security, smart cities, AI, robotics, and more. Delivered Tuesdays and Fridays
- How to become a network administrator: A cheat sheet
- 5G: What it means for IoT (free PDF)
- Network security policy
- What is SDN? How software-defined networking changed everything
- The best VPN services for 2020
- 5G: More must-read coverage
Create a TechRepublic Account
Get the web's best business technology news, tutorials, reviews, trends, and analysis—in your inbox. Let's start with the basics.
* - indicates required fields

Sign in to TechRepublic
Lost your password? Request a new password
Reset Password
Please enter your email adress. You will receive an email message with instructions on how to reset your password.
Check your email for a password reset link. If you didn't receive an email don't forgot to check your spam folder, otherwise contact support .
Welcome. Tell us a little bit about you.
This will help us provide you with customized content.
Want to receive more TechRepublic news?
You're all set.
Thanks for signing up! Keep an eye out for a confirmation email from our team. To ensure any newsletters you subscribed to hit your inbox, make sure to add [email protected] to your contacts list.
To revisit this article, visit My Profile, then View saved stories .
- Backchannel
- Newsletters
- WIRED Insider
- WIRED Consulting
Andrew Williams
How to fix your terrible Wi-Fi signal at home

There is a standard procedure to follow when home internet fails. Let your anger stew into a cortisol bouillabaisse, complain using exotic swears on Twitter and then let rip at an underpaid helpline worker, having spent 40 minutes listening to scratchy, old, big-band tunes while on hold.
But there may be an easy solution if the issue is down to range and signal quality, rather than a genuine failure of your ISP.
1. Finding the problem
A simple test lets you, in most cases, determine if the problem is ISP or range and signal quality related. Plug a laptop or desktop computer into your router using an Ethernet cable and run a speed test, such as the one found at speedtest.net . Performance still poor or non-existent? You may have deeper problems than those we’ll attempt to solve here.
Haven’t owned a computer with an ethernet port since 2012? Performing a Wi-Fi-based test right next to the router should give you an idea if the issue is range-related, if not eliminating every Wi-Fi issue as the culprit.
2. Move the router
Frustration has a habit of knocking out a certain foundational level of our cognitive abilities. In other words, we’re not calling you stupid, but have you tried moving your router?
A router’s antennae are designed to transmit signal in a roughly radial pattern, in their standard configuration. While most of us tend to place a router within a metre of the wall socket into which it is plugged, it makes more sense to put it somewhere between the rooms that need good Wi-Fi signal the most.
The problem? No ISP router comes with the cabling you’ll need to do this. For fibre internet an optical cable is needed. Standard broadband requires a normal ethernet cable. Ten-metre lengths of either cost just a few pounds online.
3. Change the channels used by your router
Changing the channel is another thing to try. Most routers these days transmit their Wi-Fi over 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies, using specific frequency bands in these spectrum classes.
Other wireless equipment you have in your home may interfere with the 2.4GHz signal in particular. Baby monitors , wireless speakers and just about any other wireless home gadgets have the potential to cause this, although we only tend to see it pop up in less well-designed products, like wireless speakers made by small companies.
Adrienne So

Nena Farrell

Aarian Marshall

Eric Ravenscraft
Live in a densely populated area, or one with several street Wi-Fi hotspots nearby, and the chance of this congestion issue increases. More routers mean more congestion.
To change the channel, you need to log into your router’s dashboard. This involves entering the IP address, usually printed on a sticker on the case, into the address bar and looking for the channel part of the interface. You’ll also need to enter admin login details. If they are not also on the case, you can usually find the standard login details for ISP routers online.
Most recent routers have an “Auto” mode that switches to channels with low interference. But one, six and 11 are the recommended ones for 2.4GHz Wi-Fi.
4. Update your router firmware
You may be used to updating the software on your phone and laptop, but there’s a good chance your router’s firmware has not been updated since you installed it. Some newer routers auto-update their software. Others, particularly older models, don’t. And you can understand why. Updating requires restarting the router, which can leave you without internet for several minutes and, crucially, lead to you thinking your internet is broken.
Security is the primary reason for updated firmware. However, router makers also fix bugs, some of which may affect Wi-Fi performance in certain cases. Software improvements may also have a big affect on traffic management, where a router judged the priority of the requests from your devices to improve all-round perceived performance, and other traffic juggling that falls under the router’s purview.
To update your router you’ll have to login to its dashboard, as mentioned in the “change the channel” section. Or use your router’s companion phone app, if it has one.
5. Get a repeater
A Wi-Fi repeater is one of the cheapest and simplest add-ons for adding Wi-Fi to the furthest room in your house. Most popular designs simply let you plug them into a power socket. They are unobtrusive, and don’t add to your home’s swamp of tangled cables. The TP-Link 300Mbps is a solid low-cost option. Check out our full guide to the best Wi-Fi extenders .
Performance is the potential problem here. You will usually see significantly reduced speeds and increased latency. A repeater is better for patching up annoying dead spots than supplying signal to PCs, games consoles and smart TVs (for this, see mesh networks, below).
Powerline tech may initially sound like something made up by an eight-year-old drunk on orange juice. These little boxes transmit your home internet through the electrical wiring of your home. They usually come in packs of two, one on each end of the handshake.
You attach one end to the router, with an ethernet cable, and a plug socket. The other box sits by whatever devices currently don’t get a strong enough signal from your router.
Most low-cost Powerline kits use wired ethernet ports at the other end, but you can buy sets that create their own Wi-Fi network, too. These are handy for home or garden offices packed with things that don’t have ethernet ports, on the other side of the house from the living room, where the router lives.
Powerline tech relies on your house’s wiring. If it was put together by a Dickens-era cowboy electrician, you may encounter some issues. But in most situations a Powerline setup will easily outperform a Wi-Fi repeater.
Read more: The best Wi-Fi extenders and mesh Wi-Fi routers
A mesh network is the latest, and currently best, way to solve Wi-Fi range problems. These are made up of two or more nodes that communicate with each other, in some cases over several frequency bands. And as the network operates with the nodes available to it, the whole thing does not fall apart if an issue arises with one of them, say if your partner unplugs one of the units.
Highly regarded mesh-style kits include Eero Mesh, Netgear Orbi, BT Whole Home Wi-Fi and Linksys Velop. Cost is the main issue here. A three-node mesh system may cost £300 or more. Check out our full guide to the best mesh Wi-Fi routers here .
Routers supplied by internet service providers are much better than they were a few years ago. They were once mostly dreadful. Now most are at least passable performers, particularly those supplied with fibre broadband contracts.
However, a solid third-party router will usually outperform them. They usually to have higher spec wireless systems, for one. Routers tend to be advertised by their top transmission speeds, such as AC1500 and AC1900.
This tells you they support Wi-Fi standards up to “ac”, and that when the bandwidth of their supported channels is added together, it adds up to a maximum potential speed of (for example) 1,900Mbps.
Today’s newest routers, such as the Asus RT-AX88U, already support next-gen Wi-Fi 6, also known as Wi-Fi ax. Only a few phones to date support ax, including the Samsung Galaxy S10, but high-spec routers like these often also have more powerful antennas, which means stronger, more reliable Wi-Fi signal for your house.
This article was originally published by WIRED UK

Matt Jancer

Parker Hall

Brenda Stolyar

WIRED COUPONS

Up to $58 Off TurboTax Online w/ TurboTax Service Code

$50 off in-person tax prep when you switch from TurboTax or another tax provider | H&R Block coupon

$25 off your first 3 orders with Exclusive Instacart Promo Code

1st Order: 25% Off DoorDash Promo Code ($15 minimum)

Take $10 Off Your Order - Finish Line Coupon Code

Groupon coupon: Extra 25% off sitewide

WiFi Keeps Disconnecting All The Time? Here’s How To Fix It
There are actually a lot of reasons for this
A patchy WiFi connection that keeps dropping out of service over and over again can be a major inconvenience.
The culprit could be anything from an out-of-date router and slow internet speeds to an incorrect computer setting or a huge outage on your internet service provider’s end.

To help you figure out why your WiFi keeps disconnecting, we’ve put together an explainer with a list of causes and solutions to help you bring that speedy WiFi service back to life.
Why Does My WiFi Keep Disconnecting?
Whether you’re trying to send an important email or you want to do a conference call on your PC or mobile device , a dropped WiFi connection can be an impediment to your life. Some of the main reasons why your WiFi keeps disconnecting include:
- Being in Airplane mode
- Slow speeds owing to signal, slow DNS server or packet loss
- Outdated WiFi driver software
- A recent update created bugs that disrupt the WiFi connection
- Power management issues
- Poorly configured wireless adapter
- Router is out of date or damaged
- Router is damaged or placed far from your device
- Interference on the network
- Massive service outage
- Being in an area with limited or no internet connection
- WiFi driver isn’t compatible with your the current version of your operating system

What to Do When Your WiFi Keeps Disconnecting
While there are varying reasons why your WiFi connection keeps dropping, you can troubleshoot most of them yourself. Before we go into more complex solutions, try some of these quick checks to get your WiFi back up and running again in no time.
Quick Checks
- Check whether your WiFi switch is set to On .
- Ensure that you’re using the correct WiFi connection.
- Make sure everything on your router is plugged in the way it should be.
- Check the lights on your router to see if any seem unusual or other than green. You can use your router manual to know what each light means and how to resolve any problems.
- Move your device closer to the router especially where there’s lots of interference. You can also get a WiFi range extender to boost your WiFi signal’s strength.
- Plug an Ethernet cable into your device and check if the connection is strong again. If it works, the issue is with the wireless signal.
- Check with your ISP whether there are any connection issues or service outages in your area.
- Remove any objects or electronics that could be interfering with your router.

- Change your router’s WiFi channel especially if your network tends to overlap with nearby networks.
- Restart your computer, mobile device or router to help reset the network settings and then try connecting to WiFi again.
- Check for any pending updates on your computer and install them.
- Remove and re-add the wireless network.
- Temporarily disable your security software (antivirus) as this could be conflicting with other software causing issues with your WiFi connection.
- Update your router’s firmware. If you’re not sure how to do this, check with your ISP.
- Run a network diagnostic to troubleshoot the problem. In Windows 10, right-click the WiFi icon on the taskbar and select Troubleshoot problems . On Mac, select Menu > System Preferences > Assist Me > Diagnostics and use the Network Diagnostics tool.
Update or Reinstall WiFi Adapter Driver
If your WiFi adapter driver is out of date, your device will keep disconnecting from WiFi. You can update or reinstall the driver to fix the problem.
- Right-click Start > Device Manager and then select Network Adapters to expand the category.
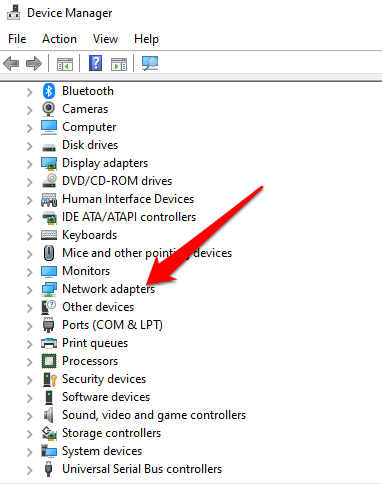
- Next, right-click your WiFi adapter and select Update Driver .
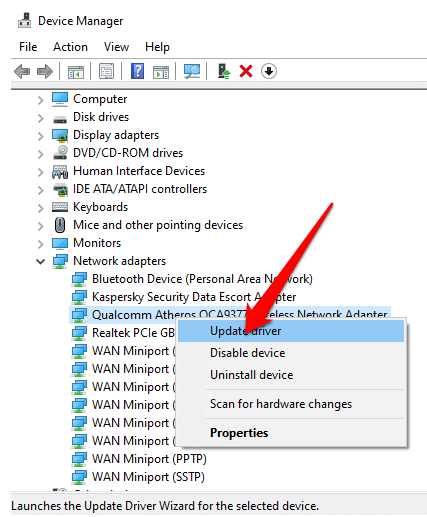
To reinstall the driver, right-click the adapter and select Uninstall driver . Restart your computer and Windows will download and install the latest version of the driver. Alternatively, you can download the latest driver online and install it on your computer.
Check Power Management Settings
Your computer’s Power Management settings may disable your wireless adapter and cause it to disconnect temporarily. You can make a small adjustment to your settings and resolve the problem.
- Right-click Start > Device Manager and expand the Network Adapters section.
- Double-click your WiFi adapter’s name, select the Power Management tab and uncheck the Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power box. Restart your computer and check if the WiFi works again.
Check DHCP Settings
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) automatically distributes IP addresses across the network so that your devices can connect and communicate over the web. If there’s a problem with the DHCP, your WiFi won’t work properly.
- In Windows 10, select Start > Settings > Network & Internet and then select Wifi .
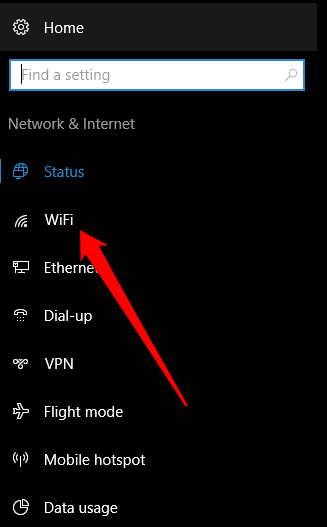
- Select your connection and then check whether the IP assignment option under IP Settings says Automatic (DHCP) . If it does, then DHCP is enabled, but if it doesn’t, select Edit > Automatic (DHCP) and then check if your WiFi is any better.
- On a Mac, select Menu > System Preferences > Network and ensure your network has a green dot next to it.
- Select Advanced > TCP/IP tab and check if the Configure IPv4 option is showing Using DHCP . If not, select the dropdown menu, choose the option and check whether your WiFi works again.
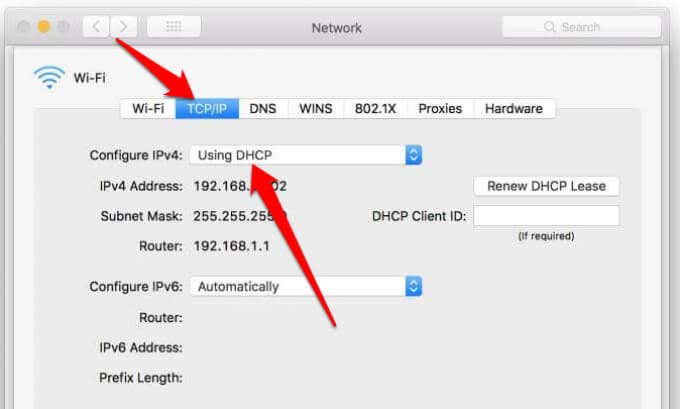
Resolve Dropped or Lost WiFi Connections
If your WiFi is still disconnecting even after trying the steps in this guide, you can factory reset your computer or your router to return them to out-of-the-box factory settings. You’ll lose all your settings and data during a factory reset so make sure you backup any data on your computer.
Once you reset your router , give it time to set itself up and check your WiFi connection again. If all else fails, contact your ISP for more guided assistance or get WiFi without an internet provider .
For more tips on WiFi issues, check out 10 ways to boost a weak WiFi signal and troubleshooting tips if your internet is connected but not working .
Elsie is a technology writer and editor with a special focus on Windows, Android and iOS. She writes about software, electronics and other tech subjects, her ultimate goal being to help people out with useful solutions to their daily tech issues in a simple, straightforward and unbiased style. She has a BCom degree in Marketing and currently pursuing her Masters in Communications and New Media. Read Elsie's Full Bio
Read More Posts:

Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Computers and Electronics
- Computer Networking
- Wireless Networking
How to Fix WiFi Connection Issues on a Laptop
Last Updated: January 24, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was written by Luigi Oppido and by wikiHow staff writer, Nicole Levine, MFA . Luigi Oppido is the Owner and Operator of Pleasure Point Computers in Santa Cruz, California. Luigi has over 25 years of experience in general computer repair, data recovery, virus removal, and upgrades. He is also the host of the Computer Man Show! broadcasted on KSQD covering central California for over two years. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 118,851 times.
Are you trying to figure out why your Windows laptop or MacBook isn't connecting to Wi-Fi? There's nothing more frustrating than not having internet access when you need it. But don't worry—there's usually an easy fix! This wikiHow article will teach you how to troubleshoot and fix your Wi-Fi connection on any PC or Mac laptop.
Windows Laptops

- Click the "No internet access" icon, which looks like a globe, on the taskbar near the clock. [1] X Trustworthy Source Microsoft Support Technical support and product information from Microsoft. Go to source If you don't see it, click the up-arrow to expand the overflow icons.
- If the Wi-Fi tile is gray or deactivated, click it to turn on Wi-Fi.
- While you're here, make sure Airplane Mode is disabled—if the tile is illuminated, click it to turn it off.

- If you're using Windows 11, after clicking the "No internet access" icon, click the right-arrow next to the Wi-Fi tile to bring up the list of networks.
- If you don't see the network you want to connect to, try moving closer to the wireless access point.
- If you are connected to a wireless network but unable to browse the web, click Disconnect on the network name, and then click Connect to reconnect.

- Right-click the "No internet access" icon near the clock and select Network and Internet Settings .
- Click Wi-Fi .
- Click Manage known networks .
- Click Forget on the network you can't connect to.
- Close this window, and then click the "No internet access" icon and try to connect to the network again. You will need to reenter the password.
- Move away from devices that use 2.4GHz or 5.0GHz bandwidths, such as microwaves, cordless phones, baby monitors, 2-way radios, some tablets, Wi-Fi cameras, and unshielded power or video cables.
- Try to minimize physical obstructions as well, especially walls and furniture made of concrete, brick, marble/stone, metal, reflective glass, water, or ceramic tile.

- For example, if your wireless network is called Centurylink1234 5G and you also see Centurylink1234 2.4, disconnect from the 5G network and try connecting to the 2.4 network.
- If you have access to the router, you might want to change the router's channel to a less busy channel.

- Click the Windows Start menu and select Settings (the gear icon).
- Click Network & Internet .
- Click Status .
- Click Network troubleshooter and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Click System .
- Click Troubleshoot .
- Click Other troubleshooters .
- Click Network Adapter .
- Click Run and follow the on-screen instructions to repair issues.
- If the troubleshooter repairs issues, you should be able to connect to Wi-Fi.
- If the troubleshooter doesn't find any issues, restart your PC.

- Unplug the power cable from both the router and modem (if separate).
- If the light on your modem stays on, it probably has battery backup. Remove the battery for now.
- (If you have a separate modem) After 30 seconds, plug the modem back in to the power source and wait for it to boot back up. When the lights stop blinking, continue.
- Plug the router back in and allow it to boot up. This can take several moments.
- Reconnect your laptop to the Wi-Fi network and try to browse the web.
- If other devices (such as your phone or tablet) can connect to this network but your laptop can't, continue with this method. If the network isn't available for any devices, contact your internet provider for troubleshooting.

- Press Windows key + S and type device .
- Click Device Manager in the search results.
- Expand the Network adapters menu and select your Wi-Fi adapter.
- Right-click adapter and select Uninstall device .
- Check the box next to "Attempt to remove the driver software for this device" and click Uninstall .
- Reboot your laptop. When it comes back up, Windows will automatically install a new generic driver for your Wi-Fi card.
- If this resolves your problem, it's possible that a recent Windows Update is incompatible with your Wi-Fi card. [3] X Trustworthy Source Microsoft Support Technical support and product information from Microsoft. Go to source You can try updating the drivers to see if that resolves the issue. If the issue comes back, uninstall the driver again and reboot to use the generic driver until a fix is available.

- Open the Windows Start menu and go to Network & Internet > Status (Windows 10) or Advanced network settings (Windows 11) > Network reset .
- Click Reset now and choose Yes to confirm.
- When your PC restarts, try connecting to the Wi-Fi network again.

- If you can't connect to any Wi-Fi networks, there's likely a hardware issue with your laptop, and you should contact the manufacturer for service.
- If you can connect at a café, try checking for and installing Windows Updates . Then, head home and try connecting to your Wi-Fi again. If you still can't connect, contact your internet provider for assistance.

- When Wi-Fi is on, you'll see a list of all available access points. Click the network you want to join.

- Close all open apps.
- Press and hold the Option key while you click the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar.
- Click Open Wireless Diagnostics .
- Follow the on-screen instructions to allow your Mac to test your wireless connection.
- If any issues are found, click the small "i" in a circle next to each issue found for instructions on how to proceed.

- Click the Apple menu and select System Preferences .
- Click Network .
- Click your Wi-Fi connection.
- Click Advanced and select TCP/IP .
- Click Renew DHCP Lease .

- Click Advanced .
- Select the Wi-Fi network and click the minus sign.
- Click Remove .
- Close all windows and then try to reconnect to the network. You will need to re-enter the Wi-Fi password if it was previously saved.

- If you can't connect at another location, there's likely a hardware issue with your MacBook, and you should contact Apple for service.
- If you can connect at a café, check for and install any updates . [7] X Research source Then, try to connect to the original network again. If you still can't connect, there's likely an issue with your home Wi-Fi router—contact your internet provider for assistance.
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/fix-wi-fi-connection-issues-in-windows-9424a1f7-6a3b-65a6-4d78-7f07eee84d2c#WindowsVersion=Windows_11
- ↑ https://www.dell.com/support/kbdoc/en-us/000150359/how-to-identify-and-reduce-wireless-signal-interference
- ↑ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/fix-wi-fi-connection-issues-in-windows-9424a1f7-6a3b-65a6-4d78-7f07eee84d2c#WindowsVersion=Windows_10
- ↑ https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT211786
- ↑ https://support.apple.com/guide/mac-help/use-wireless-diagnostics-mchlf4de377f/mac
- ↑ https://support.apple.com/guide/mac-help/set-the-date-and-time-mchlp2996/mac
About This Article

1. Check your laptop's Wi-Fi button or switch. 2. Make sure Wi-Fi is turned on. 3. Try disconnecting and reconnecting. 4. Reboot your computer. 5. Turn off your modem and router and turn them back on. 6. Forget and re-add the wireless network. 7. Run the network troubleshooter or wireless diagnostics. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Is this article up to date?

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Keep up with the latest tech with wikiHow's free Tech Help Newsletter
- Is a New iPad Pro Coming Soon?
- Get It Now: Spring Tech Deals at Amazon
How to Fix it When Your Wi-Fi Network Is Not Showing Up
Router, ISP, range, or device issues can create problems but it's possible a virus is at fault, too
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/TriciaGoss-c6bcd4d050f744c2b13efbf760819c9d.jpg)
- Pima College
In This Article
Jump to a Section
- Causes of the Problem
- Solutions to Try
- Frequently Asked Questions
When you can't connect to the internet because your Wi-Fi doesn't show up on your device, you have a problem. It helps if you know the cause, but you can take steps to remedy the situation even if you don't.
Causes for 'Wireless Network Not Showing Up' Issues
Problems with your router, ISP, or device could prevent your Wi-Fi network from showing up in the list of available networks. A few of the reasons that cause Wi-Fi connection problems include:
- Device not in router's range : Your device must be within the router's range. In most homes, that can be up to 30 feet from the router. You may be able to connect up to 50 feet away, but the speed is slower, and the connection often drops.
- Router not restored correctly : The router might not have been properly restored after losing power or being unplugged.
- Network adapter turned off/disabled : The Wi-Fi connection problem isn't always caused by the router; your device could be the culprit. If a restart doesn't help, your network adapter could be disabled, or its drivers may need updating.
- Virus : If your device has a virus, it could block your ability to connect to Wi-Fi. A quick virus scan and restart could help.
- Object interference : Large appliances, thick walls, or other wireless devices can interfere with your wireless connection.
Wi-Fi not showing up can be caused by these and more issues. Troubleshooting to find the problem is the key to fixing it.
How to Fix a Wi-Fi Network Not Showing Up
Try these troubleshooting steps in order until you resolve your issue. They are listed from easiest to most complex.
Troubleshoot your wireless connection . Before you begin trying to fix your Wi-Fi, make sure there is no problem with the device you are trying to connect.
If the issue is that your Wi-Fi network is not showing up on your laptop, for example, take a few minutes to make sure everything on the computer is as it should be. Are all cables connected to the device? Are they plugged in to a working outlet? Are you sure the Wi-Fi on the device is turned on? (This could be a physical switch, an internal setting, or both.) Ruling out the basics like this is the first place to start.
Properly restart the modem and router . Power cycling the router and modem can fix internet connectivity issues and resolve problems with wireless connections. It is important to reboot both the modem and the wireless router.
Check your network settings. The network could be hidden. Hiding a wireless network can be an effective way to protect privacy. However, it could result in the Wi-Fi network not showing up on a device. To connect with a hidden network , the SSID and other network details are required.
Access the Wi-Fi settings to add the network.
Look for interference. Interference is one of the many reasons Wi-Fi connections drop . Numerous objects around a home or office can interfere with a wireless router. Check for potential issues, such as appliances, microwaves or fluorescent lights, other wireless devices including wireless video game controllers or security cameras, and thick walls or columns.
Neighboring wireless networks could also interfere with your own. Changing your Wi-Fi channel number could resolve the issue.
Check with your ISP (Internet Service Provider) . If your troubleshooting efforts do not fix the problem, contact your internet service provider. There could be an area-wide issue of which you are unaware, or there might be a defect in the equipment provided by the company.
To fix slow Wi-Fi , close background programs, avoid signal interference, troubleshoot your network equipment, scan for malware, and contact your internet service provider.
To secure your Wi-Fi network , turn on WPA2 encryption, change the network name, create a strong password, turn on your router's firewall, and turn off admin privileges.
If you see the “Wi-Fi Doesn’t Have a Valid IP Configuration” error, restart your router, change the SSID and password, reset the firewall, or perform a network reset .
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
- How to Fix It When Samsung TV Apps Aren't Working
- How to Fix the PS5 'Cannot Connect to the Wi-Fi Network' Error
- How to Fix an Xbox That Won't Connect to Wi-Fi
- How to Measure Your Wi-Fi Signal Strength
- How to Fix It When Your PS5 Wi-Fi Is Slow
- How to Fix It When PS4 Won't Connect to Wi-Fi
- How to Fix It When Your PS4 Wi-Fi Is Slow
- How to Fix It When There's No Internet Connection
- How to Fix the PS4 'Cannot Connect to the Wi-Fi Network' Error
- How to Fix It When Nintendo Switch Won't Connect to Wi-Fi
- How to Fix a Poor Wi-Fi Signal on Your iPad
- How to Fix It When Fire Stick Won't Connect to Wi-Fi
- How to Fix Wi-Fi Authentication Problems on Android
- How to Increase Download Speed in Windows 10
- How to Fix Common Xbox 360 Wireless Networking Problems
- How to Fix it When Your iPhone Won't Connect to Wi-Fi
How-To Geek
How to fix when wi-fi keeps disconnecting on windows 11.
Put an end to your frustration!
Quick Links
Why does my wi-fi keep disconnecting, resolve an intermittent wi-fi connection on windows 11, key takeaways.
When your Wi-Fi keeps disconnecting on a Windows 11 PC, try restarting the router, forgetting and rejoining your network, making your network "Private," updating your network adapter drivers, using "Network Adapter" troubleshooter, or restarting "WLAN AutoConfig" service.
Does your PC automatically disconnect you from your Wi-Fi network every now and then? Your router may have an issue, or your PC's network settings might be incorrect. Here are a few ways to resolve this problem on your Windows 11 computer.
Just like when your phone is disconnecting from Wi-Fi , here are many possible reasons Windows 11 keeps disconnecting from your wireless network. Wi-Fi routers can have issues for all sorts of reasons, but your PC's network adapter may also be acting up, and on a laptop your power-saving plan may be limiting your wireless connection---to name a few causes.
In most cases, it's usually a software issue, which you can fix by changing a few options here and there on your PC.
Since there are so many possible reasons for the Wi-Fi disconnection issue on your Windows 11 PC, follow the most basic tips given below first, then try more advanced options if the basic ones don't fix your problem.
Restart Your Router
To rule out any possibility of a minor glitch on your router, restart your router . This will reboot all your router features, fixing any minor problems with them. Restarting your router also causes your PC to reconnect to your Wi-Fi network, which can help fix minor connection problems between your router and your computer.
Restarting a router is as easy as pressing the power button on the device. If yours doesn't have the button, feel free to unplug the device instead, waiting at least 10 seconds before plugging back in.
Forget and Reconnect to Your Wi-Fi Network
If your issue persists, delete your saved Wi-Fi network from your PC and then reconnect to it. This can resolve any issues with your connection sessions.
To do that, head into Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi > Manage Known Networks. Then, next to your network, click "Forget."
Rejoin your network by clicking the Wi-Fi icon in your system tray and choosing your network on the list. You'll have to enter your network password before you can establish a connection.
Choose Private Mode for Your Wi-Fi Network
By default, when you connect your Windows 11 PC to a Wi-Fi network, your PC uses "Public" mode . This is to ensure your PC is not discoverable on the network, thus keeping your privacy.
However, when you face a connectivity issue, it's worth changing that mode to "Private." This makes your PC discoverable on the network and enables file and printer sharing. As long as you're on a trusted network, you're safe using this mode. If you're on a public network, like a coffee shop, then you're better off skipping to the next fix .
To make that change, navigate to Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi > Manage Known Networks. Select your network on the list.
In the "Network Profile Type" section, choose "Private."
Update Your Network Adapter Drivers
Your network adapter may be using faulty or outdated drivers, causing the Wi-Fi connection drop issue. In this case, update drivers for your wireless adapter, and your issue will likely be fixed.
To do that, first, open Device Manager . Do this by right-clicking the "Start" menu and choosing "Device Manager."
On the Device Manager window, expand "Network Adapters." Then, right-click your wireless adapter and choose "Update Driver."
Select "Search Automatically for Drivers."
Install the available drivers, and you're done.
Use Network Adapter Troubleshooter
Windows 11 has many troubleshooters, one of which is a "Network Adapter" troubleshooter. You can use this tool when you're experiencing issues with your network connections. This tool finds the issues with your adapter and offers help to fix those issues.
To run the tool, navigate to Settings > Troubleshoot > Other Troubleshooters. Then, next to "Network Adapter," click "Run."
On the "Network Adapter" window, select "Wi-Fi" and click "Next."
Follow the on-screen instructions, and any issues with your network adapter will be fixed.
Restart Windows' WLAN AutoConfig Service
"WLAN AutoConfig" is a Windows service that runs in the background, allowing you to make network connections. This service is responsible for providing logic to your PC to connect to your wireless networks.
It's possible this service isn't working correctly or has stopped working, causing your PC to disconnect from your Wi-Fi network every now and then.
To fix that, restart the service. Do that by first opening "Run" using Windows+R. In the open box, type the following and press Enter:
services.msc
In the list on the right pane, find the "WLAN AutoConfig" service. Right-click it and choose "Restart."
Windows will stop and then start the service, then you can try connecting to Wi-Fi again.
Prevent Power Management From Turning Off Your Network Adapter
Windows 11's power management settings can turn off your various devices, including your network adapter, to save energy. You should disable this option for your network adapter when you're facing connectivity issues.
To do that, right-click the "Start" menu icon and choose "Device Manager." In the open window, expand "Network Adapters," right-click your adapter, and choose "Properties."
In "Properties," open the "Power Management" tab. Then, untick the "Allow the Computer to Turn Off This Device to Save Power" option. Save your changes by clicking "OK."
Change Power Settings for Your Network Adapter
Your PC's current power plan may be configured in such a way that it degrades your network adapter's performance, causing the disconnection issue. In this case, fix the issue by allowing your adapter to perform at its best in your power plan settings.
To do that, open "Start," find "Edit Power Plan", and click it. Then, select "Change Advanced Power Settings."
In the "Power Options" window, expand Wireless Adapter Settings > Power Saving Mode. Here, in the drop-down menus given next to "On Battery" and "Plugged In," choose "Maximum Performance."
Then, at the bottom, select "Apply" and "OK."
Your PC's power plan now won't affect your network adapter's performance, possibly resolving your Wi-Fi disconnection problem.
Reinstall Your Network Adapter Drivers
If your Wi-Fi connection still drops, uninstall and reinstall your network adapter drivers to fix any issues with them. Newer drivers often have patches for the bugs found in older drivers.
Start by opening Device Manager. Here, expand "Network Adapters," right-click your adapter, and choose "Uninstall Device."
Enable the "Attempt to Remove the Driver for This Device" option, then click "Uninstall."
Allow Device Manager to finish uninstalling your network adapter. Then, reboot your PC , and Windows will automatically install the required drivers for your adapter. You're then free to test your Wi-Fi connection again.
Reset Network Settings on Windows 11
If your PC still randomly disconnects you from your Wi-Fi network, there's a chance your network settings aren't correctly configured. Unless you know the exact setting causing the problem, reset all your network settings to the defaults to resolve your issue.
To do that, head into Settings > Network & Internet > Advanced Network Settings > Network Reset. Then, next to "Network Reset," click "Reset Now."
In the open prompt, choose "Yes." When your network settings are reset, reconnect to your Wi-Fi network.
If all of those fixes didn't work, it's possible you simply need to upgrade your network hardware. Many Wi-Fi problems come down to outdated routers , but you can easily fix that problem by shopping our guide to the best Wi-Fi routers available . There are also several excellent budget routers to choose from, if you want to save a few dollars.
Alternatively, if you think your router is not making the Wi-Fi disconnect, it's possible getting a new Wi-Fi adapter for your Windows 11 PC will make your connection more stable. You can also bypass the problem entirely by switching to an Ethernet connection ---you just need a good Ethernet cable and an available port.
- How to Features
- Fix Wi Fi Issues: How to Fix Slow Wi Fi, Connection Problems, Internet Speed
Fix Wi-Fi Issues: How to Fix Slow Wi-Fi, Connection Problems, Internet Speed
A slow internet speed can get really frustrating while doing something time-sensitive..

Nothing is more annoying than a slow Wi-Fi
- A slow internet speed could mean you’re having Wi-Fi connection issues
- You should place the Wi-Fi router at an optimal spot to fix slow Wi-Fi
- You can use a Wi-Fi analyser software to fix Wi-Fi issues
Slow Wi-Fi can be very annoying especially if you're studying or working from home. Slow internet speed can ruin your day whether you need to upload work-related files on the cloud or even if you need to stream your favourite show on Netflix. Thankfully slow Wi-Fi is a problem you can fix. In most cases slow Wi-Fi can be fixed in a few easy steps.. Follow this guide as we list out a few methods to fix Wi-Fi connection issues.
Slow Wi-Fi: How to fix
There are many factors at play that may result in slow Wi-Fi to be slow. These are some of the methods that you can follow to identify and fix Wi-Fi connection issues.
1. Do you have slow Internet speed?
Before jumping into conclusions that you're struggling with slow internet speed, make sure that the advertised speed of your internet plan matches with the internet speed that you're getting. To do that, visit any website that lets you measure internet speed such as speedtest.net or fast.com. If the speed results match with the advertised speed provided by your ISP (Internet Service Provider), we'd say that your connection is absolutely fine and in order to speed things up, you can always go for an upgraded plan that offers faster internet speeds.
- How to Password Protect a Word Document
2. Restart Wi-Fi router to fix Wi-Fi issues
Sometimes all you need to do with your Wi-Fi router is a quick restart to fix Wi-Fi connection problems. Simply turn off your Wi-Fi router and then turn it on after a few seconds and then check if you're still getting slow internet speeds. If that doesn't fix Wi-Fi issues, try restarting your computer, phone, or other devices. Sometimes the reason for slow Internet speed may just be one of your devices, and not the Internet connection.
3. Positioning the Wi-Fi router could fix slow Wi-Fi
Are you still facing slower internet speeds despite having a high-speed internet connection and a good enough Wi-Fi router? The problem could be with the positioning of your router. It is always recommended to place the router at a higher place, such as above the wardrobe. Besides, you can always place the Wi-Fi router at different spots in your house or workplace to see which area gets the best signal strength before finalising on a spot. Do note, generally Wi-Fi signals are able to pass through walls and other objects, but in some instances thicker walls or some metals do obstruct the signals. In such scenarios, it is always recommended to keep your router away from microwave ovens or refrigerators, and as we mentioned above, position the router at an elevation and an optimal spot.
4. Adjust the router's antennas
Positioning the antennas on a Wi-Fi router straight up redirects the Wi-Fi signals in a single direction. That's why you should always point the antennas in different directions. For instance, many Wi-Fi routers come with two or three antennas. In such a scenario, make sure to point the antennas in vertical and horizontal directions, so that the Wi-Fi signals can cover a wider area.
- How to Repost a Story on Instagram
5. Use a strong Wi-Fi security standard
If your Wi-Fi's security is not strong enough, it could be easy to gain access to the password. our neighbour might be stealing your Wi-Fi connection, and that may be why you have slow Wi-Fi. Therefore, it is always suggested to use WPA2 security protocol on your router. You can change this via your router's settings. To set a WPA2 password, access your Wi-Fi settings by entering your router's IP address in any browser on your phone or computer. You can find your router's IP address at the back of the router, or else you can also look for it by accessing your Wi-Fi's network settings on your phone or computer.
6. Single connection, multiple users
You might have a high-speed internet connection that's shared by multiple users in your house or your workplace, and while a Wi-Fi router doesn't slow the internet speeds when multiple people use it, your available bandwidth does get compromised. What this means is that you could be downloading files from the cloud, while your kid could be downloading that latest game from the PlayStation Network, all while your partner could be streaming their favourite movie or TV show. In such a scenario, all of you could face slow Wi-Fi since each device is using a significant chunk of the available bandwidth.
In this case you could try reducing the load on the Internet connection by pausing any one of the streams or downloads. This could lead to improved Wi-Fi speeds for others. Modern routers support technology that ensures equal bandwidth across all devices, and if you're facing issues even with one of those routers, the bottleneck may be your Internet speed.
- Google Forms: How to Create, Share, and Check Responses
7. Using QoS to fix slow Wi-Fi
One of the best tools available that is often overlooked is QoS or Quality of Service, whose job is to basically divide the available bandwidth on your Wi-Fi network between applications. With an optimum setting, you can watch that wildlife video on YouTube in 4K resolution without any stutter all while ensuring that your latest game gets downloaded on Steam. With QoS, you can decide which service to prioritise on your Wi-Fi network and hence dividing the bandwidth accordingly. Do note, there are different ways to access QoS settings for routers, which means the way to access QoS on a Netgear router will differ from that of a TP-Link router. To check your router's QoS settings, enter your router's IP address in a browser and look for the QoS tab to access the settings.
8. Update router's firmware to fix Wi-Fi connection issues
Software updates for your router are very important since they improve its stability, performance and security. Most of the routers available these days come with the ability to update themselves automatically, however if you're having an old router, you might have to install the software updates manually. Different routers have different ways to update the software. To find out more, enter your router's IP address in any browser on your phone or computer to access Wi-Fi settings for your router.
9. Changing the DNS server
Every ISP irrespective of their different internet plans uses a DNS (domain name system), which basically helps translate the IP address of servers into domain names such as youtube.com or facebook.com. Mostly, the default DNS server provided by ISPs is slow and unreliable, and this is why simply changing your DNS server can give you that sigh of relief and a much-needed gain in your internet speed and performance. To learn how to change DNS, you can check out our guides on how to change DNS on iOS , or on your computer . For those who use Android, go to the Wi-Fi settings on your phone and look for the Private DNS option. By default, it is turned off on most Android phones, but you can choose to set it on Automatic or you can even do the settings manually by hitting Private DNS provider hostname.
- How to Enhance Your iOS 14 Home Screen With Lovely Widgets
10. Use a Wi-Fi analyser
A Wi-Fi analyser app can be a potent tool in determining the best channel that's less crowded and offers minimal interference. There are two main bands used in Wi-Fi communications — 2.4GHz and 5GHz. The 5GHz band is less crowded but it has lower range, so keep that in mind when analysing the results of these tools. These bands are further divided into multiple channels and this is where a Wi-Fi analyser helps in finding out which Wi-Fi networks are broadcasting on the same channels so that you can opt for an alternate one. There are various free and paid Wi-Fi analyser apps available on the internet that can help you in solving such issues. You can check out some of the popular Wi-Fi analyser options for phone and computers such as NetSpot , InSSIDer , NetX and Network Performance Monitor to name a few.
11. Change your Wi-Fi channel
If you find out your router's IP address and use it to access your Wi-Fi settings in any browser, you'll come across channels under wireless settings. There are a total of 14 channels and the first thing you need to find out is which Wi-Fi channel is the most utlised in your area. Once you determine that, you can always try to find and choose a non-overlapping channel which is spaced far enough from the other channels. Most of the ISP's set the channel settings to automatic, but if you're having slower internet speeds then we'd say you fiddle around and find out the clearest channel for yourself for the best optimal experience.
12. Reset your device's network settings
If resetting your Wi-Fi router doesn't solve your problem, you should probably consider resetting your device's network settings. By resetting the network settings of your device, you'll basically be setting them to default. From there, you can reconfigure your Wi-Fi on all your devices and check if doing this solved your problem. The steps vary for each device and you will have to re-enter your Wi-Fi password to use the Internet. You can check our handy guide to finding your Wi-Fi password , in case you have forgotten it.
- How to Change Default Web Browser, Email Apps in iOS 14
13. Purchase a new Wi-Fi router
Getting a high-speed internet plan doesn't solve the quest for getting high internet speeds, instead your Wi-Fi router also has a big role to play. You see, you can get a high-speed internet plan, but you can't make the most out of it if your Wi-Fi router is old or doesn't comply with the new Wi-Fi standards. To fix this problem, try getting a new Wi-Fi router that supports 802.11ac (popularly known as Wi-Fi 5) or at least 802.11n (also known as Wi-Fi 4). However, if you're looking for a superfast Wi-Fi router, you can also purchase one that supports the latest 802.11ax standards (known as Wi-Fi 6). Although keep in mind that since this technology is still under development, routers that support Wi-Fi 6 standards are actually very expensive.
14. File a complaint with your ISP
If none of the methods mentioned above works out for you, then you should probably contact your ISP and let the professionals take care of the problem. Sometimes it is always better to simply call and file a complaint rather than trying to fix things on your own, and if your ISP has a good track record with customer service, your problem might be fixed in minimal time.
15. Change your ISP
If your current ISP isn't able to serve your needs in your area and you're still constantly dealing with slow internet speeds, then your last resort would be to look for a better connection and change to that. In such a scenario, it is always better to do some research and find out which connection provides the best price-to-performance ratio in your locality. It is also good to talk to your neighbours as well and see which connection they are using and how well it is serving them.
- How to Use Nearby Share on Android
- Microsoft Word: Transcribe or Dictate Audio with Word Online
- Don’t Let Amazon Collect Your User Data
- Got a New Windows Laptop? Install All Essential Apps in One Click
- Here’s How to Make WhatsApp Video Calls
For more tutorials, visit our How To section.
Will Xbox Series S, PS5 Digital Edition fail in India? We discussed this on Orbital , our weekly technology podcast, which you can subscribe to via Apple Podcasts , Google Podcasts , or RSS , download the episode , or just hit the play button below.
For the latest tech news and reviews , follow Gadgets 360 on X , Facebook , WhatsApp , Threads and Google News . For the latest videos on gadgets and tech, subscribe to our YouTube channel . If you want to know everything about top influencers, follow our in-house Who'sThat360 on Instagram and YouTube .

Related Stories

Advertisement

- Galaxy S24 Series
- Apple Vision Pro
- Apple iPhone 15
- OnePlus Nord CE 3 Lite 5G
- Xiaomi 14 Pro
- Oppo Find N3
- Tecno Spark Go (2023)
- Best Phones Under 25000
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Series
- Cryptocurrency
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Ultra
- Samsung Galaxy Z Flip 5
- Apple 'Scary Fast'
- Housefull 5
- GoPro Hero 12 Black Review
- Invincible Season 2
- HD Ready TV
- Laptop Under 50000
- Smartwatch Under 10000
- Latest Mobile Phones
- Compare Phones
- Samsung Galaxy M55 5G
- Vivo V40 SE 5G
- Motorola Edge 50 Pro
- Samsung Galaxy Book 4 (Intel Core 7)
- Samsung Galaxy Book 4
- Samsung Galaxy Tab S6 Lite (2024)
- Vivo Pad 3 Pro
- Fire-Boltt Oracle
- Honor Watch GS 4
- LG 65-inch 4K Ultra HD Smart LED TV 65UR7500PSC
- Xiaomi 32 Inch LED HD Ready Smart TV (L32M6-RA-L32M7-RA)
- Nintendo Switch (OLED Model)
- Microsoft Xbox Series S
- MarQ by Flipkart 1.5 Ton 4 Star Inverter Split AC (154IPG24WQ2)
- Lloyd 1 Ton 5 Star Inverter Split AC (GLS12I5FWGEV)
- WhatsApp's Bottom Navigation Tabs Are Now Rolling Out Widely on Android
- WhatsApp Rolls Out Bottom Navigation Tabs to All Android Smartphones
- OpenAI Previews 'Voice Engine' Audio Tool That Can Clone Human Voices With 15 Seconds of Audio
- HyperOS Update Schedule for Q2 2024 Announced by Xiaomi: See List of Eligible Xiaomi, Redmi Smartphones
- Redmi Note 13 Pro Turbo Specifications Leak, Could Debut Globally as Poco F6
- iPhone 16 Cases Surface Online, Hinting at Pill-Shaped Rear Camera Island
- Microsoft, OpenAI Plan $100 Billion Data Centre With 'Stargate' AI Supercomputer: Report
- Apple's New iPad Pro, iPad Air Models Likely to Launch in May: Mark Gurman
- Google to Show Token Balances in Wallets Running on Bitcoin, Polygon, Fantom Blockchains
- Vivo X Fold 3 Tipped to Launch in India Soon, Said to Be Country's Thinnest Foldable
- FATF Upset, Worried About Nations Being Slow in Regulating Crypto: Details

- Privacy Policy
- Editorial Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Complaint Redressal

Most Common Wi-Fi Issues and How To Fix Them
Encountering Wi-Fi issues is certainly a bad experience that is universally known by web users. However, navigating through these challenges doesn’t have to be daunting, especially if you haven’t encountered a specific problem before. With the right approach, armed with knowledge and effective troubleshooting techniques, resolving Wi-Fi woes becomes an attainable feat. Regardless of your situation, you shouldn’t be so alarmed. In this guide, we will help you to troubleshoot and fix some of the most common Wi-Fi issues.
Fixing the Most Common Wi-Fi Issues
Whether you’re grappling with sluggish internet speeds, erratic Wi-Fi signals, or the inability to establish a connection altogether, a plethora of troubleshooting methods exist to address these common issues. From basic fixes to more intricate solutions, we’ll explore a comprehensive range of strategies designed to restore your Wi-Fi connectivity to its optimal state. In addition to providing quick and easy fixes for common problems, we’ll delve into advanced troubleshooting advice tailored to tackle more stubborn issues. These include scenarios where Wi-Fi connectivity ceases entirely or operates at significantly reduced speeds, requiring a deeper understanding and nuanced approach to resolution.

Losing your Internet Connection or Wi-Fi can be seriously problematic when you’re seriously needing to stay online. A Lost Wi-Fi connection can break your workflow, ruin calls or conversations, and even drop you from an online game during a decisive moment. For PC users who have the computer directly attached to the router, this shouldn’t be a problem, but for devices that depend on Wi-Fi, losing the connection can certainly ruin the experience. Through this article, we will try to help you fix some of the most common Wi-Fi issues and restore your workflow.
Basic Wi-Fi Troubleshooting Checklist
When encountering a non-specific Wi-Fi issue or deeming the problem not severe enough to warrant in-depth investigation, it’s prudent to begin troubleshooting with a basic checklist. Consider the following items as an excellent starting point to address and resolve your Wi-Fi concerns effectively:
- Ensure that the Wi-Fi function on your device is enabled. Laptops often feature shortcut keys that may inadvertently deactivate Wi-Fi, while smartphones typically offer quick toggles to disable Wi-Fi capabilities.
- Perform a quick restart of your router by unplugging it from the power source, waiting for approximately 30 seconds to 1 minute, and then plugging it back in. This simple action can often rectify various Wi-Fi difficulties by resetting the router’s configurations.
- Investigate the possibility of an Internet service outage by consulting your Internet Service Provider’s (ISP) outage map, typically accessible on their website. Utilize your smartphone’s data connection to access this information if Wi-Fi is unavailable. A reported outage in your area could be the underlying cause of your Wi-Fi issues.
By systematically addressing these fundamental aspects of Wi-Fi troubleshooting, you can swiftly diagnose and resolve common connectivity issues, restoring your Wi-Fi network to optimal functionality.
Quick Fixes for Common Wi-Fi Issues:
Below you will find some of the most common Wi-Fi problems and some of the quick fixes you can try to recover your wireless connectivity.
1 – Forgot the Wi-Fi Password:
If you find yourself unable to recall your Wi-Fi password and there are no written records of it available, resetting your router is the next course of action. Follow these steps to reset your router to its factory settings:
- Step 1. Locate the reset button: Most routers feature a small pinhole button on the back or underside.
- Step 2. Use a paperclip: Straighten a paperclip and gently insert it into the reset button’s pinhole.
- Step 3. Hold the button: Press and hold the reset button for approximately 30 seconds. You may need to use some force, as the button is often recessed to prevent accidental resets.
- Step 4. Release the button: After holding the reset button for the specified duration, release it. The router will then restart and revert to its default factory settings.
- Step 5. Reconfigure your router: Once the router has restarted, you’ll need to reconfigure it, including setting up a new Wi-Fi password.
By following these steps, you can successfully reset your router and regain access to your Wi-Fi network, even if you’ve forgotten the password.
2 – Wi-Fi Connection Lost When Logging Back into the Computer:
Encountering Wi-Fi connection issues upon logging back into Windows 10 is a common occurrence, often attributed to a glitch associated with Fast Startup. Fast Startup is designed to expedite the login process by maintaining certain system processes running in the background. However, this feature can inadvertently trigger a bug within the wireless driver, preventing seamless reconnection to Wi-Fi networks.
For an immediate solution, consider disabling Fast Startup to mitigate this problem. Follow these steps to adjust the Fast Startup settings:
- Step 1. Search for “Power Options” in the Windows 10 or Windows 11 search bar and open the corresponding Control Panel section.
- Step 2. Within Power Options, navigate to “Choose What the Power Button Does” located on the left-side menu.
- Step 3. Explore the “Shutdown Settings” section and locate the option to “Turn On Fast Startup.”
- Step 4. Ensure that the option is selected to disable Fast Startup effectively.
In the long term, resolving this issue may necessitate updating the driver for your wireless network adapter. Updating drivers can rectify any underlying bugs causing the Wi-Fi connection problem. Refer to our comprehensive guide on updating Windows 10 drivers for detailed instructions on this process.
By implementing these solutions, you can effectively address Wi-Fi connection issues encountered during the login process on Windows 10, ensuring a smoother and more reliable networking experience.

3 – Network Connects, But There’s No Internet Access
Experiencing a network connection without internet access can be a frustrating ordeal. Here are some troubleshooting steps to address this issue effectively:
- 1. Reset Modem: Begin by resetting your modem. Simply unplug it from the power source, wait for a few seconds, and then plug it back in. This basic step can often resolve connectivity issues by refreshing the modem’s configurations.
- 2. Ethernet Connection Test: If resetting the modem doesn’t resolve the issue, try connecting a laptop or desktop directly to your router using an Ethernet cable. This direct connection eliminates potential Wi-Fi-related issues and helps determine whether the problem lies with the router or the Wi-Fi connection.
- 3. Router Reset: If the Ethernet connection test proves successful and confirms that the router is functioning correctly, your next step is to reset the router. Similar to the modem reset process, unplug the router, wait for a brief period, and then plug it back in. This action can help restore the router’s functionality and resolve internet access issues.
- 4. Contact ISP: If despite all efforts, you still encounter no internet access, there may be an outage in your area. Contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to inquire about any reported outages and seek assistance in resolving the issue.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can effectively diagnose and resolve network connectivity issues, restoring internet access and ensuring a seamless online experience.
4 – The Router Crashes Regularly and Only Restarting Helps
Experiencing regular router crashes can be disruptive to your internet connectivity and overall network stability. This certainly is among some of the most common Wi-Fi Issues. Here’s how to address this issue effectively:
Gizchina News of the week
- Perform a Full Reset: If your router requires frequent restarts to function properly, it may benefit from a full reset. Most routers feature a reset button typically located on the back or underside of the device. Using a paperclip or a similar tool, press and hold the reset button for approximately 30 seconds. This action will restore the router to its factory default settings. Following the reset, refer to our comprehensive guide for setting up a wireless router to ensure proper configuration.
- Assess Router Health: If the router continues to experience crashes even after a full reset, it may indicate a more serious hardware issue. Check for any signs of physical damage or overheating, as these factors can contribute to instability. Additionally, review the router’s firmware version and ensure it is up-to-date. Updating the firmware can sometimes resolve performance issues and bugs.
- Consider Warranty Coverage: If the router is still within its warranty period, consider reaching out to the manufacturer for assistance. You may be eligible for a replacement or repair at no additional cost. Be sure to provide details of the recurring crashes and any troubleshooting steps you’ve already taken.
- Explore Replacement Options: If the router is no longer under warranty or if the crashes persist despite troubleshooting efforts, it may be time to consider replacing the router. Invest in a reliable and reputable router model that meets your network requirements. Research customer reviews and technical specifications to make an informed decision.
By following these steps, you can effectively address router crashes and maintain a stable and reliable internet connection. Whether through troubleshooting or replacement, restoring router functionality is essential for uninterrupted network access.

Slow or Wi-Fi access in Certain Rooms
This is one of the most common Wi-Fi issues and is often a reason of complaint for Wi-Fi users. Encountering slow or nonexistent Wi-Fi or internet access in specific rooms can be frustrating, but there are several strategies to address this issue effectively:
- Optimize Router Placement: Wi-Fi signals propagate in all directions from the router, so its placement significantly impacts coverage. Consider relocating the router to a more centralized location within your home. Positioning it closer to the center of your coverage area can improve signal reception throughout your living space.
- Adjust Antenna Positioning: If your router features external antennas, experiment with adjusting their positions. Alternating between fully vertical and horizontal orientations can help broaden signal coverage in multiple directions, potentially improving connectivity in problematic areas.
- Mitigate Interference from Nearby Networks: In environments such as apartment buildings, neighboring routers may interfere with your Wi-Fi signal. Utilize Wi-Fi analysis tools like NetSpot or Wi-Fi Analyzer to identify nearby networks and the channels they’re using. If your router overlaps with these networks, consider switching to a less congested channel to minimize interference.
- Expand Coverage with Repeaters or Mesh Systems: If optimizing router placement and adjusting settings fail to resolve the issue, consider extending your Wi-Fi coverage using repeaters or mesh systems. Wireless repeaters amplify and rebroadcast Wi-Fi signals, effectively extending coverage to areas with poor connectivity. Alternatively, investing in a whole-home mesh wireless system can eliminate dead spots and provide seamless connectivity throughout your residence.
- Upgrade Your Router: If all else fails, it may be time to invest in a new router. Modern routers offer improved performance, enhanced features, and better coverage compared to older models. Evaluate your networking needs and research reputable router options that align with your requirements.
By implementing these strategies, you can effectively improve Wi-Fi coverage and resolve connectivity issues in specific rooms of your home, ensuring a seamless online experience for all occupants.
Slow Internet Regardless of Your Device or Place
Encountering slow internet speeds across all devices can be a frustrating experience, but there are several steps you can take to troubleshoot and resolve the issue:
- Test Wired Connection: Connect a laptop directly to your router using an Ethernet cable and perform an internet speed test. If speeds remain sluggish, the problem likely lies with your internet connection rather than the router. In such cases, explore ways to improve your internet speed and consider contacting your Internet Service Provider (ISP) for assistance.
- Check Wireless Channel Congestion: If the wired connection test yields satisfactory results, consider the possibility of wireless channel congestion. Access your router’s settings and navigate to the wireless channel configuration. Experiment with changing the channel to alleviate congestion caused by your devices or nearby networks.
- Perform Factory Reset: If adjusting the wireless channel fails to improve speeds, consider performing a factory reset on your router. Most routers feature a reset button that can be pressed using a paperclip. Hold down the reset button for approximately 30 seconds to restore the router to its factory default settings. Follow our guide to setting up a wireless router to reconfigure the device and assess if the reset resolves the issue.
- Consider Router Replacement: If none of the previous steps yield significant improvements and internet connectivity remains slow, it may indicate a failing router. Explore purchasing a new router, selecting from our list of reviewed top routers known for their reliability and performance. Alternatively, if the router appears to be functioning properly, consider the possibility of a problematic modem. Upgrading to a Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E router can also alleviate congestion and support faster speeds, provided your broadband plan supports these enhancements.
By systematically troubleshooting and implementing these solutions, you can identify and address the root cause of slow internet speeds, ensuring a smoother online experience for all users.
One Device Can’t Connect to Wi-Fi
Sometimes, the Wi-Fi issue will affect just one device. It can be frustrating when your smartphone is the only device having issues with the Wi-Fi connection. Fortunately, it’s perfectly possible to fix the issue and we will provide some valid tips to do so.
- Restart Wi-Fi on Device: Start by turning off the Wi-Fi on your device and then re-enabling it. Alternatively, if you’re using a Wi-Fi dongle, unplug it and then plug it back in. This simple step can often resolve momentary network issues.
- Restart Device and Router: If restarting the Wi-Fi connection doesn’t solve the problem, try restarting the device itself. After the device has rebooted, attempt to reconnect to the Wi-Fi network. Additionally, consider restarting the router to refresh its settings and potentially resolve any connectivity issues.
- Delete and Reconnect to Network: If the problem persists or reoccurs, delete the current network from the list of saved networks on your device. Then, reconnect to the network and test the connection again. This action can sometimes clear any lingering issues with the network profile.
- Run Network Diagnostics: On Windows 10 or 11, search for “wifi troubleshooting” and open the result labeled “Identify and Repair Network Issues.” This tool will run a series of diagnostics to identify and address any connectivity issues.If you’re using MacOS, you can run Wireless Diagnostics by holding the Options key and clicking the AirPort (Wi-Fi) icon on the menu bar. Select “Open Wireless Diagnostics” and follow the on-screen instructions to diagnose and troubleshoot Wi-Fi problems.
By following these steps and utilizing built-in network diagnostic tools, you can effectively troubleshoot and resolve Wi-Fi issues with a specific device, restoring connectivity and ensuring a seamless online experience.
Nothing Can Connect to Wi-Fi
If no device can get connected to the Wi-Fi, the issue is probably related to the router. You can try to connect your laptop directly using an Ethernet cable. If it starts to work after connecting, then the issue is related only to the Wi-Fi. Therefore, you can try some of the other fixes here. If it does not work, then your internet may be down altogether. Resetting your router can fix a myriad of issues, if it does not work even after a reset, you may be running into hardware issues and it’s better to consider a router replacement.
An update Broke Wi-Fi
This issue can happen sometimes with certain Operating System Updates. Some updates roll out at a fast pace, and some device-related bugs can escape during the rollout. Sometimes, the issue does not involve a bug within the software, but an incompatibility between the hardware and OS. The update can break the drivers, and there are a lot of other factors to consider. If you notice you’ve lost Wi-Fi shortly after updating your device, then you should consider rolling back your system to an earlier version.
There are a lot of scenarios to consider when you’re dealing with broken Wi-Fi. If your internet works when you’re attached to the router via cable, then the issue is related to the Wi-Fi. When it does not work, then it can be related to your ISP. Sometimes, your device has a faulty component that makes it unable to access Wi-Fi networks. Or, finally, your router is running into issues. Follow the tips above and learn how to solve some of the most common Wi-Fi issues. Try them to get your Wi-Fi back to an operational state.
Previous 4 Reasons why Android is a Better Choice than iOS
Next mastering google messages: customize your text bubble colors.
About the author Marco Lancaster Marco is the HARDWARE & OS EXPERT of Gizchina for the past 4 years. He is Fascinated for technology. He is constantly diving into the Software Development Field and is an expert in all kind of Hardware. He is passioned for the Chinese world of Smart Devices and an addict for technology in general.
Related Posts

A Guide to Maximize the Wi-Fi Experience on Your Android

Features that Make Microsoft Edge A Great Gaming Browser

Six Reasons Why Google Bard Takes the Lead in the AI Battle

Stay Connected Anywhere with Discounted Portable FIRSTNUM CPE WiFi Routers
- Roku Community
- Features, settings & updates
Wi-Fi & connectivity
- Channels & viewing
- Solving playback issues
- Roku mobile app
- Roku legacy products
- Issue Tracking Board
- Manufacturer support & warranty resources
- Discussions
- Using your smart home devices
- Cameras & doorbells
- Lights & power
- Smart home app
- Account, payments & subscriptions
- Community discussions
- Welcome to the Roku Community
- Announcements
- Roku Developer Program
- Roku Direct Publisher
- Roku TV Ready Certification Program
- Independent Developer Kit
- Streaming Players
- Wi-Fi & connectivity
Connecting Roku to WiFi Without a remote.
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Topic as New
- Mark Topic as Read
- Float this Topic for Current User
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Report Inappropriate Content
Can't connect to network
- Previous Topic
Re: Connecting Roku to WiFi Without a remote.
- Buffering 8
- Can't connect to network 94
- Connection issue 124
- Error code 14
- Ethernet 10
- General setup question 5
- Mobile hotspot 5
- Roku Smart Soundbar 1
- Wireless 64
- Wireless connection 1
- Wireless network compatibility 25

The most common iPhone 15 problems and how to solve them
Y ou rely on your iPhone 15 for everything. That includes music, movie, and TV show streaming, banking, smart home controls, calendars, reminders, and timers — which is only scratching the surface. Apple’s iOS namesake is faster, more durable, and packed with plenty of power, but that doesn’t mean it can’t run into trouble now and then. Not to worry though: for when a smartphone presents an issue, there’s usually a way to fix it.
And fortunately, a lot of these glitches are shared amongst iPhone owners. There’s a good chance that whatever’s causing your device to work incorrectly has happened to someone else, so today, we’re bringing you this roundup of the five most common iPhone problems, and what you can do to fix them.
iPhone 15 overheating issues
One of the biggest issues with the iPhone 15 has been overheating . However, this problem was originally reported around the release of the phone, when a lot of people were receiving their new iPhones and setting them up — that’s when most of the overheating issues occurred.
It’s pretty typical for a new phone to heat up more than usual when you’re getting everything set up and transferred over. When I got my iPhone 15 Pro and began the restoration process, which involves over 300GB of data, my device got very hot and was still getting warm over the next few days as everything was indexing.
However, the fix for this is pretty easy. Rebooting is the default solution for a lot of technical issues, and it usually works. Another quick fix involves enabling auto-brightness so it’s not always on maximum brightness and instead adjusts to ambient light. Other things that could help are turning off Bluetooth unless you need it, quitting apps that use location services, turning off Wi-Fi and AirDrop, or turning on airplane or Low Power mode.
You might also be using a case on your phone, which can trap excess heat. Removing it temporarily may help it cool down.
I also experienced my iPhone 15 Pro getting very hot in my hand while using it in direct sunlight. If you are outside often in sunny conditions, try to keep the iPhone out of direct sunlight, which would increase the air temperature and, as a result, the heat generated by your phone from normal processes.
Lastly, make sure you’re running the latest version of iOS. Apple was aware of the overheating issue and released a software update with iOS 17.0.3 , which “addresses an issue that may cause iPhone to run warmer than expected.”
If all of that still doesn’t help with the overheating issue, you might just want to give your phone (and yourself) a short break.
Titanium durability concerns
For the iPhone 15 Pro and iPhone 15 Pro Max, Apple made a change to the material used in the frame, going from stainless steel to brushed titanium. This change, along with a much more rounded design on the edges, means the iPhone 15 Pro is more lightweight and ergonomic.
However, as it turns out, the titanium design is actually not as durable as the previous stainless steel, as demonstrated in various drop tests over YouTube and elsewhere on the internet.
According to 9to5Mac , the flat design of the stainless steel frame on the iPhone 14 Pro could absorb the impact from a drop, which is a trait of the material. Titanium, however, is more rigid, so any impact needs to be dispersed to other areas on the device, which in this case would mean the front and back glass via spiderweb cracking.
Another issue with the titanium frame that people have noted is what appears to be “discoloration” from fingers touching the frame. This goes away with a simple wipe, though, so it’s not as big of an issue as many people made it appear to be.
Still, if you’re concerned about the durability of the titanium frame, the best fix is to put your iPhone 15 Pro or iPhone 15 Pro Max in a case. We have recommendations on the best cases for both the regular iPhone 15 Pro and the larger iPhone 15 Pro Max .
Another option is to get AppleCare+, which can cover unlimited incidents of accidental damage, as well as up to two incidents of theft or loss coverage, every 12 months depending on the plan you choose. There’s a cost for each incident, but if you don’t like to use cases, this is your best bet.
Burn-in issues with the iPhone 15 Pro Max
This issue has been popping up, mostly specific to owners of the most expensive iPhone 15 Pro Max model. The problem is OLED burn-in, which is not just an iPhone-specific problem since it can occur on any device with an OLED screen. However, it has become a concern for iPhone 15 Pro Max users.
What is OLED burn-in? It’s basically a ghosting effect, where remnants of whatever was on the screen remain on-screen even after you go to something else. For iPhone users, the burn-in problem shows remnants of keyboards, wallpaper images, app icons, videos, and other static visuals.
But what causes it? The primary cause for this is leaving a fixed image on the screen for an extended period of time, and this is only made worse if the display brightness goes higher. So unless you just constantly leave a static image on your iPhone 15 Pro Max screen for hours at a time, this should be a rare occurrence.
However, sometimes it’s just a defect in the display or a quality control issue. If you are experiencing burn-in issues on your iPhone 15 display, the only real fix is to take it to an Apple Store and get it repaired or replaced.
To make sure that this doesn’t happen to you, don’t leave an image on your screen for too long, especially when you’re outside and the brightness can go to max setting.
Poor battery life
This seems to happen every year, but the iPhone 15 Pro and iPhone 15 Pro Max have definitely had slightly poorer battery life than their predecessors.
If you’re experiencing not-so-great battery life on your iPhone 15, you could try a few things. Enabling auto-brightness can help, as this setting adjusts your screen brightness depending on ambient lighting, so you don’t need to have it on max brightness all the time, which would drain the battery faster. Having dark mode also helps reduce battery drain.
Other settings that can help extend battery life throughout the day are disabling background app refresh, turning off location services unless it’s absolutely necessary (Maps, for example), and disabling/limiting notifications. It’s also beneficial to use Wi-Fi as much as possible over cellular data since searching for a good cellular signal takes a toll on battery life.
If all else fails, you can also try restarting your iPhone 15 — a reboot usually helps for a lot of various situations. Lastly, there’s Low Power mode, which disables things like the always-on display and limits the display refresh rate to 60Hz on ProMotion devices to save battery power for essential tasks.
It’s also recommended to check your iPhone 15’s battery health by going to Settings > Battery > Battery Health and Charging . This will let you know what your battery’s maximum capacity is; a lower capacity can result in reduced battery life between charges. If it’s below 80% within the first year, then it’s most likely a defective battery, and Apple should replace it.
Camera launching with a black screen
The iPhone 15 Pro and iPhone 15 Pro Max have the new Action button , which replaced the silent/ring toggle. Though the default action for the button is still silent/ring, you can change it to something else if you prefer, and one of those actions is launching the Camera app. Of course, those who have the regular iPhone 15 or iPhone 15 Plus don’t have the Action button, but you can still quickly launch the Camera app from the lock screen shortcut.
But have you ever encountered a black screen once your camera launched? I have my Action button set to the Camera, and I’ve gotten that annoying black screen more than once in my time with the iPhone 15 Pro.
The only way to fix it is to quit the Camera app or lock the device and try again, unfortunately. It’s unclear why this happens in the first place, as it seems to be random. While the fix is easy enough, it is annoying to deal with as that moment you were trying to capture may be gone by the time you get the camera working again.
Wi-Fi connectivity issues
Many users have reported Wi-Fi connection issues with the iPhone 15. Cases range from slow internet performance to dropped connections, which is par for the course with many smartphones. Luckily, there’s a few things you can try to remedy your Wi-Fi woes.
First, simply try restarting your iPhone to see if a hard reset clears out the cobwebs. If your network issues persist, the next thing you should do (if you’re not using public Wi-Fi) is to reset your internet hardware. In most cases, this is just a modem/router combo. Once you’re back online, try using your iPhone again to see if it performs any better.
We’ve also heard a lot of talk about the iCloud Private Relay feature causing poor network performance. When enabled, Private Relay splits and encrypts your internet traffic, as a means of safeguarding your network. iCloud+ subscribers have this function toggled on by default, and it’s pretty easy to shut it down. Just go to Settings > iCloud > iCloud+ , then slide the toggle next to Private Relay to the off position.
The iPhone 15 series is great but not perfect
There’s always hype surrounding Apple’s new iPhone releases, and the iPhone 15 series is no exception. It seems to be a commercial success, but that doesn’t mean it’s perfect. As you can see, there have been several issues with the devices already, and it’s only been out for several months.
The good news is that most of the problems are pretty easy fixes that you can remedy yourself. The only one that we mentioned that requires a trip to the Apple Store is the burn-in issue, but that one should not be one to really worry about unless your display is defective.
Does the iPhone 15 come with a warranty?
Even if you didn’t purchase AppleCare+, and are having persistent issues with your iPhone 15, you may still be able to have the phone service under its manufacturer warranty. And whether you’re buying the base model or the iPhone 15 Pro Max, each model comes with a one-year limited warranty for hardware coverage, and 90 days of free technical support.

About iOS 17 Updates
iOS 17 brings big updates to Phone, Messages, and FaceTime that give you new ways to express yourself as you communicate. StandBy delivers a new full-screen experience with glanceable information designed to view from a distance when you turn iPhone on its side while charging. AirDrop makes it easier to share and connect with those around you and adds NameDrop for contact sharing. Enhancements to the keyboard make entering text faster and easier than ever before. iOS 17 also includes updates to Widgets, Safari, Music, AirPlay, and more.
For information on the security content of Apple software updates, please visit this website: https://support.apple.com/kb/HT201222
This update provides important bug fixes and security updates and is recommended for all users.
For information on the security content of Apple software updates, please visit this website:
https://support.apple.com/kb/HT201222
This update introduces new emoji, transcripts in Apple Podcasts and includes other features, bug fixes, and security updates for your iPhone.
New mushroom, phoenix, lime, broken chain, and shaking heads emoji are now available in the emoji keyboard
18 people and body emoji add the option to face them in either direction
Apple Podcasts
Transcripts let you follow an episode with text that highlights in sync with the audio in English, Spanish, French and German
Episode text can be read in full, searched for a word or phrase, tapped to play from a specific point and used with accessibility features such as Text Size, Increase Contrast, and VoiceOver
This update includes the following enhancements and bug fixes:
Music recognition lets you add songs you have identified to your Apple Music Playlists and Library, as well as Apple Music Classical
Siri has a new option to announce messages you receive in any supported language
Stolen Device Protection supports the option for increased security in all locations
Battery Health in Settings shows battery cycle count, manufacture date, and first use on iPhone 15 and iPhone 15 Pro models
Call Identification displays Apple-verified business name, logo, and department name when available
Business updates in Messages for Business provide trusted information for order status, flight notifications, fraud alerts or other transactions you opt into
Apple Cash virtual card numbers enable you to pay with Apple Cash at merchants that don’t yet accept Apple Pay by typing in your number from Wallet or using Safari AutoFill
Fixes an issue where contact pictures are blank in Find My
Fixes an issue for Dual SIM users where the phone number changes from primary to secondary and is visible to a group they have messaged
Some features may not be available for all regions or on all Apple devices. For information on the security content of Apple software updates, please visit this website:
This update provides bug fixes for your iPhone including:
Text may unexpectedly duplicate or overlap while typing
This update introduces additional security measures with Stolen Device Protection. This release also includes a new Unity wallpaper to honor Black history and culture in celebration of Black History Month, as well as other features, bug fixes, and security updates for your iPhone.
Stolen Device Protection
Stolen Device Protection increases security of iPhone and Apple ID by requiring Face ID or Touch ID with no passcode fallback to perform certain actions
Security Delay requires Face ID or Touch ID, an hour wait, and then an additional successful biometric authentication before sensitive operations like changing device passcode or Apple ID password can be performed
Lock Screen
New Unity wallpaper honors Black history and culture in celebration of Black History Month
Collaborate on playlists allows you to invite friends to join your playlist and everyone can add, reorder, and remove songs
Emoji reactions can be added to any track in a collaborative playlist
This update also includes the following improvements:
AirPlay hotel support lets you stream content directly to the TV in your room in select hotels
AppleCare & Warranty in Settings shows your coverage for all devices signed in with your Apple ID
Crash detection optimizations (all iPhone 14 and iPhone 15 models)
This update provides important bug fixes and is recommended for all users.
This update introduces Journal, an all-new way to reflect on life’s moments and preserve your memories. This release also includes Action button and Camera enhancements, as well as other features, bug fixes, and security updates for your iPhone.
Journal is a new app that lets you write about the small moments and big events in your life so you can practice gratitude and improve your wellbeing
Journaling suggestions make it easy to remember your experiences by intelligently grouping your outings, photos, workouts, and more into moments you can add to your journal
Filters let you quickly find bookmarked entries or show entries with attachments so you can revisit and reflect on key moments in your life
Scheduled notifications help you keep a consistent journaling practice by reminding you to write on the days and time you choose
Option to lock your journal using Touch ID or Face ID
iCloud sync keeps your journal entries safe and encrypted on iCloud
Action Button
Translate option for the Action button on iPhone 15 Pro and iPhone 15 Pro Max to quickly translate phrases or have a conversation with someone in another language
Spatial video lets you capture video on iPhone 15 Pro and iPhone 15 Pro Max so you can relive your memories in three dimensions on Apple Vision Pro
Improved Telephoto camera focusing speed when capturing small faraway objects on iPhone 15 Pro and iPhone 15 Pro Max
Catch-up arrow lets you easily jump to your first unread message in a conversation by tapping the arrow visible in the top-right corner
Add sticker option in the context menu lets you add a sticker directly to a bubble
Memoji updates include the ability to adjust the body shape of any Memoji
Contact Key Verification provides automatic alerts and Contact Verification Codes to help verify people facing extraordinary digital threats are messaging only with the people they intend
Precipitation amounts help you stay on top of rain and snow conditions for a given day over the next 10 days
New widgets let you choose from next-hour precipitation, daily forecast, sunrise and sunset times, and current conditions such as Air Quality, Feels Like, and wind speed
Wind map snapshot helps you quickly assess wind patterns and access the animated wind map overlay to prepare for forecasted wind conditions for the next 24 hours
Interactive moon calendar lets you easily visualize the phase of the moon on any day for the next month
This update also includes the following improvements and bug fixes:
Siri support for privately accessing and logging Health app data using your voice
AirDrop improvements including expanded contact sharing options and the ability to share boarding passes, movie tickets, and other eligible passes by bringing two iPhones together
Favorite Songs Playlist in Apple Music lets you quickly get back to the songs you mark as favorites
Use Listening History in Apple Music can be disabled in a Focus so music you listen to does not appear in Recently Played or influence your recommendations
A new Digital Clock Widget lets you quickly catch a glimpse of the time on your Home Screen and while in StandBy
Enhanced AutoFill identifies fields in PDFs and other forms enabling you to populate them with information such as names and addresses from your contacts
New keyboard layouts provide support for 8 Sámi languages
Sensitive Content Warning for stickers in Messages prevents you from being unexpectedly shown a sticker containing nudity
Qi2 charger support for all iPhone 13 models and iPhone 14 models
Fixes an issue that may prevent wireless charging in certain vehicles
This update provides important security fixes and is recommended for all users.
In rare circumstances, Apple Pay and other NFC features may become unavailable on iPhone 15 models after wireless charging in certain cars
Weather Lock Screen widget may not correctly display snow
This update introduces the ability for AirDrop transfers to continue over the internet when you step out of AirDrop range. This release also includes enhancements to StandBy and Apple Music, as well as other features, bug fixes, and security updates for your iPhone.
Content continues to transfer over the internet when you step out of AirDrop range
New options to control when the display turns off (iPhone 14 Pro, iPhone 14 Pro Max, iPhone 15 Pro, and iPhone 15 Pro Max)
Favorites expanded to include songs, albums, and playlists, and you can filter to display your favorites in the library
New cover art collection offers designs that change colors to reflect the music in your playlist
Song suggestions appear at the bottom of every playlist, making it easy to add music that matches the vibe of your playlist
Option to choose a specific album to use with Photo Shuffle on the Lock Screen
Home key support for Matter locks
Improved reliability of Screen Time settings syncing across devices
Fixes an issue that may cause the Significant Location privacy setting to reset when transferring an Apple Watch or pairing it for the first time
Resolves an issue where the names of incoming callers may not appear when you are on another call
Addresses an issue where custom and purchased ringtones may not appear as options for your text tone
Fixes an issue that may cause the keyboard to be less responsive
Fixes an issue that may cause display image persistence
https://support.apple.com/HT201222
This update provides important bug fixes, security updates, and addresses an issue that may cause iPhone to run warmer than expected.
This update provides important bug fixes, security updates, and fixes an issue that may prevent transferring data directly from another iPhone during setup.
Contact Posters let you customize how you appear on other people’s devices when you call them with a customized poster
Live Voicemail displays a live transcription as someone leaves a message and allows you to pick up the call
Stickers iMessage app brings all your stickers into one place including Live Stickers, Memoji, Animoji, emoji stickers, and your third party sticker packs
Live Stickers can be created by lifting the subject from photos or videos and stylizing them with effects like Shiny, Puffy, Comic, and Outline
Check In automatically notifies a family member or friend when you arrive at a destination safely and can share helpful information with them in case of a delay
Audio message transcription is available for audio messages you receive so you can read them in the moment and listen later
Search improvements help you find messages faster by allowing you to combine search filters such as people, keywords, and content types like photos or links to find exactly what you are looking for
Swipe to reply to a message inline by swiping to the right on any bubble
One-time verification code cleanup automatically deletes verification codes from the Messages app after using them with AutoFill in other apps
Leave a video or audio message to capture exactly what you want to say when someone does not pick up your FaceTime call
Enjoy FaceTime calls on Apple TV by using your iPhone as a camera (Apple TV 4K 2nd generation and later)
Reactions layer 3D effects like hearts, balloons, confetti, and more around you in video calls and can be triggered with gestures
Video effects allow you to adjust the intensity of Studio Lighting and Portrait mode
Full-screen experience with glanceable information like clocks, photos, and widgets designed to view from a distance when iPhone is on its side and charging in places such as your nightstand, kitchen counter, or desk
Clocks are available in a variety of styles including Digital, Analog, Solar, Float, and World Clock, with elements you can personalize like the accent color
Photos automatically shuffle through your best shots or showcase a specific album you choose
Widgets give you access to information at a distance and appear in Smart Stacks that deliver the right information at the right time
Night Mode lets clocks, photos, and widgets take on a red tone in low light
Preferred view per MagSafe charger remembers your preference for each place you charge with MagSafe, whether that’s a clock, photos, or widgets
Interactive widgets let you take actions, like mark a reminder as complete, directly from the widget by tapping it on the Home Screen, Lock Screen, or in StandBy
iPhone widgets on Mac enable you to add widgets from your iPhone to your Mac desktop
NameDrop lets you exchange contact information with someone new by bringing your iPhones close together
New way to initiate AirDrop allows you to share content or start a SharePlay session over AirDrop by bringing your iPhones close together
Improved autocorrect accuracy makes typing even easier by leveraging a powerful transformer-based language model (iPhone 12 and later)
Easier autocorrect editing temporarily underlines corrected words and lets you revert back to what you originally typed with just a tap
Enhanced sentence corrections can correct more types of grammatical mistakes when you finish sentences (iPhone 12 and later)
Inline predictive text shows single and multi-word predictions as you type that can be added by tapping space bar (iPhone 12 and later)
Safari and Passwords
Profiles keep your browsing separate for topics like work and personal, separating your history, cookies, extensions, Tab Groups, and favorites
Private Browsing enhancements include locking your private browsing windows when you’re not using them, blocking known trackers from loading, and removing identifying tracking from URLs
Password and passkey sharing lets you create a group of passwords to share with trusted contacts that stays up to date as members of the group make changes
One-time verification code AutoFill from Mail autofill in Safari so you can log in without leaving the browser
SharePlay makes it easy for everyone to control and play Apple Music in the car
Crossfade smoothly transitions between songs by fading out the currently playing song while fading in the next so the music never stops
Intelligent AirPlay device list makes finding the right AirPlay-compatible TV or speaker even easier by showing your devices in order of relevance, based on your preferences
Suggested AirPlay device connections are proactively shown to you as a notification to make it even more seamless to connect to your preferred AirPlay devices
Automatic AirPlay device connections are made between your iPhone and the most relevant AirPlay-compatible device so all you have to do is tap “Play” to begin enjoying your content
Adaptive Audio delivers a new listening mode that dynamically blends Active Noise Cancellation and Transparency to tailor the noise control experience based on the conditions of your environment (AirPods Pro (2nd generation) with firmware version 6A300 or later)
Personalized Volume adjusts the volume of your media in response to your environment and listening preferences over time (AirPods Pro (2nd generation) with firmware version 6A300 or later)
Conversation Awareness lowers your media volume and enhances the voices of the people in front of the user, all while reducing background noise (AirPods Pro (2nd generation) with firmware version 6A300 or later)
Press to mute and unmute your microphone by pressing the AirPods stem or the Digital Crown on AirPods Max when on a call (AirPods (3rd generation), AirPods Pro (1st and 2nd generation), or AirPods Max with firmware version 6A300 or later)
Offline Maps allow you to select an area you want to access, search, and explore rich information for places to download for use when your iPhone doesn’t have a Wi-Fi or cellular signal
EV routing improvements give you routes based on real-time EV charger availability for supported chargers
Option to say “Siri” in addition to “Hey Siri” for an even more natural way to make requests
Back-to-back requests can be issued without needing to reactivate Siri in between commands (iPhone 11 and later)
Visual Look Up
Expanded domains in Visual Look Up help you discover similar recipes from photos of food, Maps information from photos of storefronts, and the meaning of signs and symbols on things like laundry tags
Multiple or single subjects can be lifted from the background of photos and videos and placed into apps like Messages
Visual Look Up in Video helps you learn about objects that appear in paused video frames
Visual Look Up for subjects in photos enables you to look up information about objects you lift from photos directly from the callout bar
State of Mind reflection allows you to log your momentary emotion and daily mood, choose what factors are having the biggest impact on you, and describe your feelings
Interactive charts give you insights into your state of mind, how it has changed over time, and what factors may have influence such as exercise, sleep, and mindful minutes
Mental health assessments help you understand your current risk for depression and anxiety and if you might benefit from getting support
Screen Distance leverages the TrueDepth camera that powers Face ID to encourage you to increase the distance you view your device to reduce digital eye strain and can help reduce the risk of myopia in children
Sensitive Content Warnings can be enabled to prevent users from unexpectedly being shown images containing nudity in Messages, AirDrop, Contact Posters in the Phone app, and FaceTime messages
Expanded Communication Safety protections for children now detect videos containing nudity in addition to photos that children may receive or attempt to send in Messages, AirDrop, Contact Posters in the Phone app, FaceTime messages, and the system Photo picker
Improved sharing permissions give you even more control over what you share with apps, with an embedded photo picker and an add-only Calendar permission
Link tracking protection removes extra information from links shared in Messages, Mail, and Safari Private Browsing that some websites use in their URLs to track you across other websites, and links still work as expected
Accessibility
Assistive Access distills apps and experiences to their essential features in Phone and FaceTime, Messages, Camera, Photos, and Music, including large text, visual alternatives, and focused choices to lighten cognitive load
Live Speech lets you type what you want to say and have it be spoken out loud in phone calls, FaceTime calls, and for in-person conversations
Personal Voice enables users who are at risk of losing their voice to privately and securely create a voice that sounds like them on iPhone, and use it with Live Speech in phone and FaceTime calls
Point and Speak in Magnifier Detection Mode uses iPhone to read text out loud on physical objects with small text labels, such as keypads on doors and buttons on appliances
This release also includes other features and improvements:
Roadside Assistance via satellite lets you contact AAA to help you with vehicle issues when out of Wi-Fi or cellular range (iPhone 14, iPhone 14 Plus, iPhone 14 Pro, iPhone 14 Pro Max)
Pets in the People album in Photos surfaces individual pets in the album just like friends or family members
Photos Album widget lets you select a specific album from the Photos app to appear in the widget
Item sharing in Find My allows you to share an AirTag or Find My network accessory with up to five other people
Activity History in Home displays a recent history of events for door locks, garage doors, security systems, and contact sensors
Grid Forecast in Home shows when your electrical grid has cleaner energy sources available (Contiguous US only)
Grocery Lists in Reminders automatically group related items into sections as you add them
Inline PDFs and document scans in Notes are presented full-width, making them easy to view and mark them up
New Memoji stickers in Keyboard include Halo, Smirk, and Peekaboo
App Shortcuts in Spotlight Top Hit offer you app shortcuts to your next action when you search for an app
Redesigned Sharing tab in Fitness provides highlights of your friends’ activity like workout streaks and awards
Email or phone number sign-in lets you sign into your iPhone with any email address or phone number listed in your Apple ID account
New drawing tools in Freeform include a fountain pen, watercolor brush, ruler and more to create expressive boards
Crash Detection optimizations (iPhone 14, iPhone 14 Plus, iPhone 14 Pro, iPhone 14 Pro Max)
Some features may not be available for all regions or on all Apple devices. For more information, please visit this website:
https://www.apple.com/ios/ios-17
Some features may not be available for all regions or on all iPhone models. For information on the security content of Apple software updates, please visit this website:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Right click the network icon in the right side of the taskbar and select Diagnose network problems or open Get Help for Network & Internet. Make sure Wi‑Fi is turned on. Select the No internet icon on the right side of the taskbar, and make sure Wi-Fi is turned on. If it isn't, select it to turn it on. Also, make sure Airplane mode is turned off.
Restart your router — A quick restart of your router (achieved by unplugging it, waiting 30 seconds to 1 minute, and plugging it back in again) can fix many Wi-Fi difficulties. Check for an ...
A mesh Wi-Fi system will be the surest way to solve your Wi-Fi problems, especially in larger homes or ones with lots of dead zones. These systems let you plug in multiple access points throughout ...
Here's the process: Unplug or power off your router. Wait five more minutes and retry the connection. In most cases, this should fix your issue and allow you to get back online. If you go through these steps and something still isn't working, you may need to contact your internet service provider for assistance.
To find out, run a ping test using a computer. 1. On your PC, click the Start button search box and type "CMD," then press Enter. 2. In the Command Prompt window, type "ping Google.com." 3. Wait ...
Try Updating Your Wi-Fi Adapter's Driver If you're using a Windows or Linux PC with a Wi-Fi network adapter (whether built-in or otherwise), it's possible that updating the driver for the Wi-Fi adapter could solve your problem and allow you to connect to the Wi-Fi access point successfully. Related: How to Update Drivers on Windows 11
Step 1: Right-click the Wi-Fi icon in the lower-right corner of the screen. Step 2: Click "Troubleshoot problems.". Step 3: Select "All network adapters" and click Next. Step 4: Wait while the troubleshooter searches for the problem.
Perform a power cycle on your router or, log in to the admin panel and manually select a different channel. Additionally, if you have a dual-band router, try enabling both 2.4GHz and 5GHz. Keep ...
Go to your ISP's website to see if there's an outage in your area. If your WiFi is sluggish, use an Ethernet cable to connect the modem or router directly to a laptop. If that improves the ...
Cause of Wi-Fi Router Issues . Quite a few things can cause issues with your Wi-Fi router. The most common scenario is a wireless channel overcrowded by too many devices using too much bandwidth. The least likely scenario is a hardware failure with the router itself. There are also issues like malware on your device, a hacked router, and more.
Key Takeaways. Wi-Fi issues in Windows 11 can usually be resolved by resetting your Wi-Fi. To do so, follow this path: Settings > Network & internet > Advanced Network Settings > Network Reset. Interference from nearby devices like microwave ovens and cordless phones can also cause Wi-Fi problems.
If you get much lower than -80 you'll probably notice connection problems. The information displayed on this screen updates in real time, so if you notice that your signal isn't good try ...
The reboot process is simple on most routers -- unplug your router's power cable, wait a few seconds, and then plug it back in. If you have separate modem, you may also want to try unplugging your modem's power cable and plugging it back in after a few seconds. Some devices may have a power switch, but the unplug-and-plug-back-in method applies ...
To resolve Wi-Fi issues on Windows 10 automatically, use these steps: Open Settings on Windows 10. Click on Update & Security. Click on Troubleshoot. Click the Additional troubleshooters option. Select the Network Adapter option. Click the "Run the troubleshooter" button. Select the wireless adapter from the list.
Performing a Wi-Fi-based test right next to the router should give you an idea if the issue is range-related, if not eliminating every Wi-Fi issue as the culprit. 2. Move the router. Frustration ...
Add a new Wi-Fi network, select your home Wi-Fi, and type the correct password to connect. Reboot your Windows laptop or reboot your Mac. You can reboot a Linux laptop from the command line. Change your laptop's Wi-Fi channel. Most users keep their Wi-Fi adapter working on the 2.4 GHz band, but the 5 GHz band may be required to connect to your ...
You can make a small adjustment to your settings and resolve the problem. Right-click Start > Device Manager and expand the Network Adapters section. Double-click your WiFi adapter's name, select the Power Management tab and uncheck the Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power box. Restart your computer and check if the WiFi ...
Right-click the "No internet access" icon near the clock and select Network and Internet Settings. Click Wi-Fi. Click Manage known networks. Click Forget on the network you can't connect to. Close this window, and then click the "No internet access" icon and try to connect to the network again.
Ruling out the basics like this is the first place to start. Properly restart the modem and router. Power cycling the router and modem can fix internet connectivity issues and resolve problems with wireless connections. It is important to reboot both the modem and the wireless router. Check your network settings.
Open Settings on Windows 11. Click on Network & internet. Click the Advanced network settings tab on the right side. Under the "More settings" section, click the Network Reset tab at the bottom of the page. Click the Reset now button to fix the Wi-Fi problems on Windows 11. Click Yes to confirm. Click the Close button. Restart your computer.
To run the tool, navigate to Settings > Troubleshoot > Other Troubleshooters. Then, next to "Network Adapter," click "Run." On the "Network Adapter" window, select "Wi-Fi" and click "Next." Follow the on-screen instructions, and any issues with your network adapter will be fixed.
2. Restart Wi-Fi router to fix Wi-Fi issues. Sometimes all you need to do with your Wi-Fi router is a quick restart to fix Wi-Fi connection problems. Simply turn off your Wi-Fi router and then turn it on after a few seconds and then check if you're still getting slow internet speeds.
Step 1. Locate the reset button: Most routers feature a small pinhole button on the back or underside. Step 2. Use a paperclip: Straighten a paperclip and gently insert it into the reset button ...
I need to connect my Roku device to my WiFi but I don't have a remote. I can't use my Roku app as a remote because my Roku device isn't connected to the WiFi. So what can I do to solve the problem. It's impossible for me to do one thing without the other.
Y ou rely on your iPhone 15 for everything. That includes music, movie, and TV show streaming, banking, smart home controls, calendars, reminders, and timers — which is only scratching the surface.
About iOS 17 Updates. iOS 17 brings big updates to Phone, Messages, and FaceTime that give you new ways to express yourself as you communicate. StandBy delivers a new full-screen experience with glanceable information designed to view from a distance when you turn iPhone on its side while charging. AirDrop makes it easier to share and connect ...