Join my VIP teacher email club!

If you are struggling with teaching the research report process, you are not alone. Seriously, we’ve all been there!
I spent several years avoiding research reports in my classroom or depending on the Library-Media Specialist to teach the research process.
One year, I decided to take the plunge and teach my students how to research a topic and write a research report.
The process was clunky at first, but I learned a lot about how students approach research and how to guide them from choosing a topic to completing their final copies.
Before we discuss the HOW , let’s talk about the WHY .

Why should you assign research reports to 5th and 6th grade students?
I have three main reasons for assigning research reports to my students.
First, the skill involved in finding reliable sources and citing sources is valuable.
Beginning in 5th grade, and possibly even before, students need to be able to discern the reliability of a source . They should be able to spot propaganda and distinguish between reputable sources and phony ones.
Teaching the procedure for citing sources is important because my 5th grade students need to grasp the reality of plagiarism and how to avoid it.
By providing information about the sources they used, students are consciously avoiding copying the work of authors and learning to give credit where credit is due.
Second, by taking notes and organizing their notes into an outline, students are exercising their ability to find main ideas and corresponding details.
Being able to organize ideas is crucial for young writers.
Third, when writing research reports, students are internalizing the writing process, including organizing, writing a rough draft, proofreading/editing, and writing a final draft.
When students write research reports about topics of interest, they are fine-tuning their reading and writing skills.

How to Teach Research Reports in Grades 5 & 6
As a veteran upper elementary teacher, I know exactly what is going to happen when I tell my students that we are going to start research reports.
There will be a resounding groan followed by students voicing their displeasure. (It goes something like this…. “Mrs Bazzit! That’s too haaaaaaard!” or “Ugh. That’s boring!” *Sigh* I’ve heard it all, lol.)
This is when I put on my (somewhat fictional) excited teacher hat and help them to realize that the research report process will be fun and interesting.

Step 1: Choose a Topic and Cite Sources
Students definitely get excited when they find out they may choose their own research topic. Providing choice leads to higher engagement and interest.
It’s best practice to provide a list of possible research topics to students, but also allow them to choose a different topic.
Be sure to make your research topics narrow to help students focus on sources. If students choose broad topics, the sources they find will overwhelm them with information.
Too Broad: American Revolution
Just Right: The Battle of Yorktown
Too Broad: Ocean Life
Just Right: Great White Shark
Too Broad: Important Women in History
Just Right: The Life of Martha Washington
Be sure to discuss appropriate, reliable sources with students.
I suggest projecting several examples of internet sources on your technology board. Ask students to decide if the sources look reliable or unreliable.
While teaching students about citing sources, it’s a great time to discuss plagiarism and ways to avoid it.
Students should never copy the words of an author unless they are properly quoting the text.
In fact, I usually discourage students from quoting their sources in their research reports. In my experience, students will try to quote a great deal of text and will border on plagiarism.
I prefer to see students paraphrase from their sources because this skill helps them to refine their summarization skills.
Citing sources is not as hard as it sounds! I find that my students generally use books and internet sources, so those are the two types of citations that I focus on.
How to cite a book:
Author’s last name, First name. Title of Book. City of Publication: Publisher, Date.
How to cite an internet article:
Author’s last name, First name (if available). “Title of Article or Page.” Full http address, Date of access.
If you continue reading to the bottom of this post, I have created one free screencast for each of the five steps of the research process!

Step 2: Take Notes
During this step, students will use their sources to take notes.
I do provide instruction and examples during this step because from experience, I know that students will think every piece of information from each source is important and they will copy long passages from each source.
I teach students that taking notes is an exercise in main idea and details. They should read the source, write down the main idea, and list several details to support the main idea.
I encourage my students NOT to copy information from the source but instead to put the information in their own words. They will be less likely to plagiarize if their notes already contain their own words.
Additionally, during this step, I ask students to write a one-sentence thesis statement. I teach students that a thesis statement tells the main point of their research reports.
Their entire research report will support the thesis statement, so the thesis statement is actually a great way to help students maintain a laser focus on their research topic.

Step 3: Make an Outline
Making an outline can be intimidating for students, especially if they’ve never used this organization format.
However, this valuable step will teach students to organize their notes into the order that will be used to write the rough draft of their reports.
Because making an outline is usually a new concept for my 5th graders, we do 2-3 examples together before I allow students to make their outlines for their research reports.
I recommend copying an outline template for students to have at their fingertips while creating their first outline.
Be sure to look over students’ outlines for organization, order, and accuracy before allowing them to move on to the next step (writing rough drafts).

Step 4: Write a Draft
During this step, each student will write a rough draft of his/her research report.
If they completed their outlines correctly, this step will be fairly simple.
Students will write their research reports in paragraph form.
One problem that is common among my students is that instead of writing in paragraphs, they write their sentences in list format.
I find that it’s helpful to write a paragraph in front of and with students to remind them that when writing a paragraph, the next sentence begins immediately after the prior sentence.
Once students’ rough drafts are completed, it’s time to proofread/edit!
To begin, I ask my students to read their drafts aloud to listen for their own mistakes.
Next, I ask my students to have two individuals look over their draft and suggest changes.

Step 5: Final Draft
It’s finally time to write final drafts!
After students have completed their rough drafts and made edits, I ask them to write final drafts.
Students’ final drafts should be as close to perfect as possible.
I prefer a typed final draft because students will have access to a spellchecker and other features that will make it easier to create their final draft.
Think of a creative way to display the finished product, because they will be SO proud of their research reports after all the hard work that went into creating them!
When grading the reports, use a rubric similar to the one shown in the image at the beginning of this section.
A detailed rubric will help students to clearly see their successes and areas of needed improvement.
Once students have completed their first research projects, I find that they have a much easier time with the other research topics assigned throughout the remainder of the school year.
If you are interested in a no-prep, step-by-step research report instructional unit, please click here to visit my Research Report Instructional Unit for 5th Grade and 6th Grade.

This instructional unit will guide students step-by-step through the research process, including locating reliable sources, taking notes, creating an outline, writing a report, and making a “works cited” page.
I’d like to share a very special free resource with you. I created five screencast videos, one for each step of the research report process. These screencasts pair perfectly with my Research Report Instructional Unit for 5th Grade and 6th Grade!
Research Report Step 1 Screencast
Research Report Step 2 Screencast
Research Report Step 3 Screencast
Research Report Step 4 Screencast
Research Report Step 5 Screencast
Hi, If i purchase your complete package on grade 5/6 writing does it come with your wonderful recordings on how to teach them? Thanks
Hi Gail! The recordings on this blog post can be used by anyone and I will leave them up 🙂 The writing bundle doesn’t come with any recordings but I did include step-by-step instructions for teachers. I hope this helps!
Thank you for sharing your information with everyone. I know how to write (I think, haha), but I wanted to really set my students up for success with their research and writing. Your directions and guides are just what I needed to jar my memory and help my students become original writers. Be blessed.
You are very welcome, Andrea! Thank you for this comment 🙂
Hi Andrea, I am a veteran teacher who has taught nothing but primary for 25 years. However, this is my first year in 5th. I’m so excited to have found your post. Can you direct me to how I can purchase your entire bundle for writing a 5-paragraph essay. Thanks, Sue
Sure, Susan, I can help with that! Here is the link for the 5th Grade Writing Bundle: https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/5th-Grade-Writing-Bundle-3611643

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
You may also enjoy...

Ben Franklin’s Fire Brigade – Free Lesson

Five Paragraph Essays – How to Teach & Grade

Tips for Teaching the Constitution in Upper Elementary

American Revolution Cloze Passages

Consistency for Upper Elementary Teachers

My Favorite “Student-Led” Open House Activity
What can i help you teach, find it here, let's connect, i'd love to connect with you.
Enter your first name and email address to join my exclusive VIP email club.
Copyright © 2020 | Thrive in Grade Five | All Rights Reserved
Quick Links

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Report Writing
- Updated on
- Nov 4, 2023

The term “report” refers to a nonfiction work that presents and/or paraphrases the facts on a specific occasion, subject, or problem. The notion is that a good report will contain all the information that someone who is not familiar with the subject needs to know. Reports make it simple to bring someone up to speed on a subject, but actually writing a report is far from simple. This blog will walk you through the fundamentals of report writing, including the structure and practice themes.
This Blog Includes:
What is a report, reporting formats, newspaper or magazine reports, business reports, technical reports, what is report writing, report writing: things to keep in mind, structure of report writing, magazine vs newspaper report writing format, report writing format for class 10th to 12th, report writing example, report writing for school students: practice questions, report writing slideshare.
- Report Writing in 7 steps
Also Read: Message Writing
A report is a short document written for a particular purpose or audience. It usually sets out and analyses a problem often recommended for future purposes. Requirements for the precise form of the report depend on the department and organization. Technically, a report is defined as “any account, verbal or written, of the matters pertaining to a given topic.” This could be used to describe anything, from a witness’s evidence in court to a student’s book report.
Actually, when people use the word “report,” they usually mean official documents that lay out the details of a subject. These documents are typically written by an authority on the subject or someone who has been tasked with conducting research on it. Although there are other forms of reports, which are discussed in the following section, they primarily fulfil this definition.
What information does reporting contain? All facts are appreciated, but reports, in particular, frequently contain the following kinds of information:
- Information about a circumstance or event
- The aftereffects or ongoing impact of an incident or occurrence
- Analytical or statistical data evaluation
- Interpretations based on the report’s data
- Based on the report’s information, make predictions or suggestions
- Relationships between the information and other reports or events
Although there are some fundamental differences, producing reports and essays share many similarities. Both rely on facts, but essays also include the author’s personal viewpoints and justifications. Reports normally stick to the facts only, however, they could include some of the author’s interpretation in the conclusion.
Reports are also quite well ordered, frequently with tables of contents of headers and subheadings. This makes it simpler for readers to quickly scan reports for the data they need. Essays, on the other hand, should be read from beginning to end rather than being perused for particular information.
Depending on the objective and audience for your report, there are a few distinct types of reports. The most typical report types are listed briefly below:
- Academic report: Examines a student’s knowledge of the subject; examples include book reports, historical event reports, and biographies.
- Identifies data from company reports, such as marketing reports, internal memoranda, SWOT analyses, and feasibility reports, that is useful in corporate planning.
- Shares research findings in the form of case studies and research articles, usually in scientific publications.
Depending on how they are written, reports can be further categorised. A report, for instance, could be professional or casual, brief or lengthy, and internal or external. A lateral report is for persons on the author’s level but in separate departments, whereas a vertical report is for those on the author’s level but with different levels of the hierarchy (i.e., people who work above you and below you).
Report formats can be as varied as writing styles, but in this manual, we’ll concentrate on academic reports, which are often formal and informational.
Also Read: How to Write a Leave Application?
Major Types of Reports
While the most common type of reports corresponds to the ones we read in newspapers and magazines, there are other kinds of reports that are curated for business or research purposes. Here are the major forms of report writing that you must know about:
The main purpose of newspaper or magazine reports is to cover a particular event or happening. They generally elaborate upon the 4Ws and 1H, i.e. What, Where, When, Why, and How. The key elements of newspaper or magazine report writing are as follows:
- Headline (Title)
- Report’s Name, Place, and Date
- Conclusion (Citation of sources)
Here is an example of a news report:
Credit: Pinterest
Business reports aim to analyze a situation or case study by implementing business theories and suggest improvements accordingly. In business report writing, you must adhere to a formal style of writing and these reports are usually lengthier than news reports since they aim to assess a particular issue in detail and provide solutions. The basic structure of business reports includes:
- Table of Contents
- Executive summary
- Findings/Recommendations
The main purpose of the technical report is to provide an empirical explanation of research-based material. Technical report writing is generally carried out by a researcher for scientific journals or product development and presentation, etc. A technical report mainly contains
- Introduction
- Experimental details
- Results and discussions
- Body (elaborating upon the findings)
Must Read: IELTS Writing Tips
A report is a written record of what you’ve seen, heard, done, or looked into. It is a well-organized and methodical presentation of facts and results from an event that has already occurred. Reports are a sort of written assessment that is used to determine what you have learned through your reading, study, or experience, as well as to provide you with hands-on experience with a crucial skill that is often used in the business.
Before writing a report, there are certain things you must know to ensure that you draft a precise and structured report, and these points to remember are listed below:
- Write a concise and clear title of the report.
- Always use the past tense.
- Don’t explain the issue in the first person, i.e. ‘I’ or ‘Me’. Always write in the third person.
- Put the date, name of the place as well as the reporter’s name after the heading.
- Structure the report by dividing it into paragraphs.
- Stick to the facts and keep it descriptive.
Must Read: IELTS Sample Letters
The format of a report is determined by the kind of report it is and the assignment’s requirements. While reports can have their own particular format, the majority use the following general framework:
- Executive summary: A stand-alone section that highlights the findings in your report so that readers will know what to expect, much like an abstract in an academic paper. These are more frequently used for official reports than for academic ones.
- Introduction: Your introduction introduces the main subject you’re going to explore in the report, along with your thesis statement and any previous knowledge that is necessary before you get into your own results.
- Body: Using headings and subheadings, the report’s body discusses all of your significant findings. The majority of the report is made up of the body; in contrast to the introduction and conclusion, which are each only a few paragraphs long, the body can span many pages.
- In the conclusion, you should summarize all the data in your report and offer a clear interpretation or conclusion. Usually, the author inserts their own personal judgments or inferences here.
Report Writing Formats
It is quintessential to follow a proper format in report writing to provide it with a compact structure. Business reports and technical reports don’t have a uniform structure and are generally based on the topic or content they are elaborating on. Let’s have a look at the proper format of report writing generally for news and magazines and the key elements you must add to a news report:
To Read: How to Learn Spoken English?
The report writing structure for students in grades 10 and 12 is as follows.
- Heading : A title that expresses the contents of the report in a descriptive manner.
- Byline : The name of the person who is responsible for drafting the report. It’s usually included in the query. Remember that you are not allowed to include any personal information in your response.
- (introduction) : The ‘5 Ws,’ or WHAT, WHY, WHEN, and WHERE, as well as WHO was invited as the main guest, might be included.
- The account of the event in detail : The order in which events occurred, as well as their descriptions. It is the primary paragraph, and if necessary, it can be divided into two smaller paragraphs.
- Conclusion : This will give a summary of the event’s conclusion. It might include quotes from the Chief Guest’s address or a summary of the event’s outcome.
Credit: sampletemplates.com
Credit: SlideShare
Now that you are familiar with all the formats of report writing, here are some questions that you can practice to understand the structure and style of writing a report.
- You are a student of Delhi Public School Srinagar handling a campus magazine in an editorial role. On the increasing level of global warming, write a report on the event for your school magazine.
- On the Jammu-Srinagar highway, a mishap took place, where a driver lost his control and skidded off into a deep gorge. Write a report on it and include all the necessary details and eyewitness accounts.
- As a reporter for the Delhi Times, you are assigned to report on the influx of migrants coming from other states of the country. Take an official statement to justify your report.
- There is a cultural program in Central Park Rajiv Chowk New Delhi. The home minister of India is supposed to attend the event apart from other delegates. Report the event within the 150-200 word limit.
- Write today’s trend of COVID-19 cases in India. As per the official statement. include all the necessary details and factual information. Mention the state with a higher number of cases so far.
- In Jawaharlal Nehru Stadium in New Delhi, a table tennis tournament was held between Delhi Public School New Delhi and DPS Punjab. Report the event in 250-300 words.
Also Read: Formal Letter Format, Types & Samples
Credits: Slideshare
Report Writ ing in 7 steps
- Choose a topic based on the assignment
- Conduct research
- Write a thesis statement
- Prepare an outline
- Write a rough draft
- Revise and edit your report
- Proofread and check for mistakes
Make sure that every piece of information you have supplied is pertinent. Remember to double-check your grammar, spelling, tenses, and the person you are writing in. A final inspection against any structural criteria is also important. You have appropriately and completely referenced academic work. Check to make sure you haven’t unintentionally, purposefully, or both duplicated something without giving credit.
Related Articles
Any business professional’s toolkit must include business reports. Therefore, how can you create a thorough business report? You must first confirm that you are familiar with the responses to the following three questions.
Every company report starts with an issue that needs to be fixed. This could be something straightforward, like figuring out a better way to organise procuring office supplies, or it could be a more challenging issue, like putting in place a brand-new, multimillion-dollar computer system.
You must therefore compile the data you intend to include in your report. How do you do this? If you’ve never conducted in-depth research before, it can be quite a daunting task, so discovering the most efficient techniques is a real plus.
Hopefully, this blog has helped you with a comprehensive understanding of report writing and its essential components. Aiming to pursue a degree in Writing? Sign up for an e-meeting with our study abroad experts and we will help you in selecting the best course and university as well as sorting the admission process to ensure that you get successfully shortlisted.
Ankita Mishra
A writer with more than 10 years of experience, including 5 years in a newsroom, Ankita takes great pleasure in helping students via study abroad news updates about universities and visa policies. When not busy working you can find her creating memes and discussing social issues with her colleagues.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Jump to navigation
- Inside Writing
- Teacher's Guides
- Student Models
- Writing Topics
- Minilessons
- Shopping Cart
- Inside Grammar
- Grammar Adventures
- CCSS Correlations
- Infographics
Get a free Grammar Adventure! Choose a single Adventure and add coupon code ADVENTURE during checkout. (All-Adventure licenses aren’t included.)
Sign up or login to use the bookmarking feature.
- 31 Writing Classroom Reports

Start-Up Activity
Take a "Stand-Up Poll." Say to your students, "I want you to stand up when I name something you care about." Then list the topics on this page: "Dolphins." After students stand, tell them to sit before the next category. "Spiders." Continue with the other topics: "Volcanoes." "Tornadoes." "Space." "Holidays." "Books."
Afterward, have all students sit and say, "What else do you care about that I haven't mentioned? Raise your hand, and when I call on you, stand up and say what you care about."
After students share their ideas, tell them that writing a report is an effective way to learn even more about topics that are important to them.
Think About It
“Life is abundant, and life is beautiful. And it's a good place that we're all in, you know, on this earth, if we take care of it.”
—Alice Walker
State Standards Covered in This Chapter
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.3.2
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.3.2.A
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.3.2.B
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.3.4
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.3.5
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.3.7
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.3.2.C
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.3.2.D
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.3.8
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.3.6
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RI.3.1
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RI.3.2
- CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RI.3.3
LAFS Covered in This Chapter
Lafs.3.w.1.2, lafs.3.w.2.4, lafs.3.w.2.5, lafs.3.w.3.7, lafs.3.w.3.8, lafs.3.w.2.6, lafs.3.ri.1.1, lafs.3.ri.1.2, lafs.3.ri.1.3, teks covered in this chapter, 110.5.b.12.b, 110.5.b.11.b.i, 110.5.b.11.b.ii, 110.5.b.11.a, 110.5.b.11.c, 110.5.b.11.d, 110.5.b.13.c, 110.5.b.13.d, 110.5.b.11.e, 110.5.b.6.b, 110.5.b.9.d, 110.5.b.9.d.i, 110.5.b.9.d.iii, page 160 from write on track, writing a report.
Provide students a general subject area that you have been studying. Then ask them to write down specific topics that interest them in that subject area. Help them realize they don't have to know all about their topics. They just need to be interested enough to learn more.
After students choose an interesting topic, have them write as many questions as they can think of about the topic. They can write their questions on paper, cards, or a gathering grid . (See page 162.)
Related Resource Tags
Click to view a list of tags that tie into other resources on our site
Page 161 from Write on Track
Writing a report (continued).
Encourage your students to find two or more sources of information about their topics. Have them read the sources listed on this page and select at least two.
As students study about their topics, have them write answers and source information beside the questions on their note cards, in their notebooks, or in their gathering grids. Tell them that if their reading brings up new questions, they should add them along with answers.
Page 162 from Write on Track
Gathering grid.
Use this page to help students create a gathering grid to guide their research. They can do so digitally with the download, or they can draw one by hand.
Page 163 from Write on Track
Writing a draft.
Once students complete their research, present to them the tips and examples for writing a strong beginning, middle, and ending. Then give them the time to create their first drafts.
Page 164 from Write on Track
Revising, editing, & proofreading.
After students complete the first drafts of their reports, lead them through the "Revising" material on this page. Have them use the questions to improve their work. Also, have peer reviewers use the same questions to read and respond to the reports.
Once revisions are complete, present the "Editing and Proofreading" material on this page. Students should check spelling, capitalization, and punctuation. Have them create a clean final copy, like the one shown on page 165.
Page 165 from Write on Track
Sample classroom report.
Have volunteers read each paragraph from the sample classroom report. Then lead a discussion about this report:
- How does the writer make you interested in the subject?
- How does the writer make you interested in details reported about the subject?
- How could you apply these same strategies to your own report?
- 01 Understanding Writing
- 02 One Writer's Process
- 03 Qualities of Writing
- 04 Selecting a Topic
- 05 Collecting Details
- 06 Writing a First Draft
- 07 Revising and Editing
- 08 Publishing Your Writing
- 09 Writing Basic Sentences
- 10 Combining Sentences
- 11 Writing Paragraphs
- 12 Understanding Text Structures
- 13 Writing in Journals and Logs
- 14 Writing Lists
- 15 Making Albums
- 16 Writing Notes and Emails
- 17 Writing Friendly Letters
- 18 Writing Personal Narratives
- 19 Writing Family Stories
- 20 Writing Realistic Stories
- 21 Writing Time-Travel Fantasies
- 22 Writing Tall Tales
- 23 Writing Alphabet Books
- 24 How-To Writing
- 25 Writing Information Essays
- 26 Writing Newspaper Stories
- 27 Writing Persuasive Essays
- 28 Writing Opinion Letters
- 29 Writing Book Reviews
- 30 Making Bookmarks
- 32 Writing Summaries
- 33 Writing Photo Essays
- 34 Writing Free-Verse Poetry
- 35 Traditional and Playful Poetry
- 36 Writing Plays
- 37 Using the Library
- 38 Using Technology
- 39 Reading to Understand Fiction
- 40 Reading to Understand Nonfiction
- 41 Reading Graphics
- 42 Reading New Words
- 43 Building Vocabulary Skills
- 44 Using Prefixes, Suffixes, Roots
- 45 Becoming a Better Speller
- 46 Learning to View
- 47 Giving Speeches
- 48 Performing Poems
- 49 Telling Stories
- 50 Learning to Interview
- 51 Listening to Learn
- 52 Using Graphic Organizers
- 53 Thinking Clearly
- 54 Thinking Creatively
- 55 Completing Assignments
- 56 Working in Groups
- 57 Taking Tests
- 58 Proofreader's Guide
- 59 Student Almanac
Ultimate Guide on How to Write a Report Tips and Sample

Defining a Report
A report is a type of writing that represents information, data, and research findings on a specific topic. The writer is expected to deliver a well-structured, credible, and informative text that dives into the small details of a certain topic, discussing its benefits and challenges.
Reports serve many important purposes. They provide recorded facts and findings. They are used to analyze data and draw insights that can be used for decision-making. Some reports serve as compliance checks to ensure that organizations meet certain standards and requirements. Also, reports are a formal way to communicate valuable information to decision-makers and stakeholders.
A report paper can be academic or about sales, science, business, etc. But unlike other texts, report writing takes much more than getting acquainted with the subject and forming an opinion about it. Report preparation is the most important stage of the writing process. Whether you are assigned to write an academic or a sales paper, before you start writing, you must do thorough research on the topic and ensure that every source of information is trustworthy.
Report writing has its rules. In this article, we will cover everything from how to start a report to how to format one. Below you will find a student research report sample. Check our paper writer service if you want one designed specifically for your requirements.
Student Research Report Sample
Before you read our article on how to write an act essay , see what an informative and well-structured report looks like. Below you will find a sample report that follows the format and tips we suggested in the article.
Explore and learn more about comprehensive but concise reports.
What are the Report Types
As mentioned, there are plenty of different types of report papers. Even though they are very formal, academic reports are only one of many people will come across in their lifetime. Some reports concentrate on the annual performance of a company, some on a project's progress, and others on scientific findings.
Next, we will elaborate more on different sorts of reports, their contents, and their purpose. Don't forget to also check out our report example that you can find below.

Academic Reports
An academic report represents supported data and information about a particular subject. This could be a historical event, a book, or a scientific finding. The credibility of such academic writing is very important as it, in the future, could be used as a backup for dissertations, essays, and other academic work.
Students are often assigned to write reports to test their understanding of a topic. They also provide evidence of the student's ability to critically analyze and synthesize information. It also demonstrates the student's writing skills and ability to simply convey complex findings and ideas.
Remember that the report outline will affect your final grade when writing an academic report. If you want to learn about the correct report writing format, keep reading the article. If you want to save time, you can always buy essays online .
Project Reports
Every project has numerous stakeholders who like to keep an eye on how things are going. This can be challenging if the number of people who need to be kept in the loop is high. One way to ensure everyone is updated and on the same page is periodic project reports.
Project managers are often assigned to make a report for people that affect the project's fate. It is a detailed document that summarizes the work done during the project and the work that needs to be completed. It informs about deadlines and helps form coherent expectations. Previous reports can be used as a reference point as the project progresses.
Sales Reports
Sales reports are excellent ways to keep your team updated on your sales strategies. It provides significant information to stakeholders, including managers, investors, and executives, so they can make informed decisions about the direction of their business.
A sales report usually provides information about a company's sales performance over a precise period. These reports include information about the revenue generated, the total number of units sold, and other metrics that help the company define the success of sales performance.
Sales report preparation is a meticulous job. To communicate information engagingly, you can put together graphs showing various information, including engagement increase, profit margins, and more.
Business Reports
If you were assigned a business report, something tells us you are wondering how to write a report for work. Let us tell you that the strategy is not much different from writing an academic report. A Strong thesis statement, compelling storytelling, credible sources, and correct format are all that matter.
Business reports can take many forms, such as marketing reports, operational reports, market research reports, feasible studies, and more. The purpose of such report writing is to provide analysis and recommendations to support decision-making and help shape a company's future strategy.
Most business reports include charts, graphs, and other visual aids that help illustrate key points and make complex information easy to digest.
Scientific Reports
Scientific reports present the results of scientific research or investigation to a specific audience. Unlike book reports, a scientific report is always reviewed by other experts in the field for its accuracy, quality, and relevance.
If you are a scientist or a science student, you can't escape writing a lab report. You will need to provide background information on the research topic and explain the study's purpose. A scientific report includes a discussion part where the researcher interprets the results and significance of the study.
Whether you are assigned to write medical reports or make a report about new findings in the field of physics, your writing should always have an introduction, methodology, results, conclusion, and references. These are the foundation of a well-written report.
Annual Reports
An annual report is a comprehensive piece of writing that provides information about a company's performance over a year. In its nature, it might remind us of extended financial reports.
Annual reports represent types of longer reports. They usually include an overview of a company's activities, a financial summary, detailed product and service information, and market conditions. But it's not just a report of the company's performance in the sales market, but also an overview of its social responsibility programs and sustainability activities.
The format of annual report writing depends on the company's specific requirements, the needs of its stakeholder, and the regulation of the country it's based.
Writing Reports Are Not Your Thing?
Our professional writers will get you any report type meeting your requirements in no time
Report Format
As we've seen throughout this article, various types of reports exist. And even though their content differs, they share one essential element: report writing format. Structure, research methods, grammar, and reference lists are equally important to different reports.
Keep in mind that while the general format is the same for every type, you still need to check the requirements of the assigned report before writing one. School reports, lab reports, and financial reports are three different types of the same category.
We are now moving on to discuss the general report format. Let's direct our attention to how to start a report.
Title : You need a comprehensive but concise title to set the right tone and make a good impression. It should be reflective of the general themes in the report.
Table of Contents : Your title page must be followed by a table of contents. We suggest writing an entire report first and creating a table of content later.
Summary : The table of contents should be followed by an executive report summary. To create a comprehensive summary, wait until you have finished writing the full report.
Introduction : A major part of the report structure is an introduction. Make sure you convey the main idea of the report in just a few words. The introduction section must also include a strong thesis statement.
Body : The central part of your work is called the report's body. Here you should present relevant information and provide supported evidence. Make sure every paragraph starts with a topic sentence. Here you can use bullet points, graphs, and other visual aids.
Conclusion : Use this part to summarize your findings and focus on the main elements and what they bring to the table. Do not introduce new ideas. Good report writing means knowing the difference between a summary and a conclusion.
Recommendations : A report is designed to help decision-makers or provide crucial information to the conversation, including a set of goals or steps that should be taken to further advance the progress.
Appendices : As a finishing touch, include a list of source materials on which you based the information and facts. If you want your report to get acknowledged, don't neglect this part of the report format.
How to Write a Report Like a PRO
Mastering the report writing format is only a fraction of the job. Writing an exceptional report takes more than just including a title page and references.
Next, we will offer report-writing tips to help you figure out how to write a report like a PRO. Meanwhile, if you need someone to review your physics homework, our physics helper is ready to take on the job.

Start With a Strong Thesis
A strong thesis is essential to a good paper because it sets the direction for the rest. It should provide a well-defined but short summary of the main points and arguments made in the report.
A strong thesis can help you collect your thoughts and ensure that the report has a course and a coherent structure. It will help you stay focused on key points and tie every paragraph into one entity.
A clear thesis will make your report writing sound more confident and persuasive. It will make finding supporting evidence easier, and you will be able to effectively communicate your ideas to the reader.
Use Simple Wording
Reports are there to gather and distribute as much information to as many people as possible. So, the content of it should be accessible and understandable for everyone, despite their knowledge in the field. We encourage you to use simple words instead of fancy ones when writing reports for large audiences.
Other academic papers might require you to showcase advanced language knowledge and extensive vocabulary. Still, formal reports should present information in a way that does not confuse.
If you are wondering how to make report that is easy to read and digest, try finding simpler alternatives to fancy words. For example, use 'example' instead of 'paradigm'; Use 'relevant' instead of 'pertinent'; 'Exacerbate' is a fancier way to say 'worsen,' and while it makes you look educated, it might cause confusion and make you lose the reader. Choose words that are easier to understand.
Present Only One Concept in Each Phrase
Make your reports easier to understand by presenting only one concept in each paragraph. Simple, short sentences save everyone's time and make complex concepts easier to digest and memorize.
Report writing is not a single-use material. It will be reread and re-used many times. Someone else might use your sales report to support their financial report. So, to avoid confusion and misinterpretation, start each paragraph with a topic sentence and tie everything else into this main theme.
Only Present Reliable Facts
You might have a strong hunch about future events or outcomes, but a research report is not a place to voice them. Everything you write should be supported by undisputed evidence.
Don't forget that one of the essential report preparation steps is conducting thorough research. Limit yourself to the information which is based on credible information. Only present relevant facts to the topic and add value to your thesis.
One of our report writing tips would be to write a rough draft and eliminate all the information not supported by reliable data. Double-check the credibility of the sources before finalizing the writing process.
Incorporate Bullet Points
When writing a research report, your goal is to make the information as consumable as possible. Don't shy away from using visual aids; this will only help you connect with a wider audience.
Bullet points are a great way to simplify the reading process and draw attention to the main concepts of the report. Use this technique in the body part of the report. If you notice that you are writing related information, use bullet points to point out their relation.
Incorporating bullet points and other visual aids in your report writing format will make a report easy to comprehend and use for further research.
While you are busy coming up with effective visual aids, you may not have enough time to take care of other assignments. Simply say, ' write my argumentative essay ,' and one of our expert writers will answer your prayer.
Review the Text for Accuracy and Inconsistencies
After completing report preparation and writing, ensure you don't skip the final stage. Even the greatest writers are not immune to grammatical mistakes and factual mix-ups.
Reviewing what you wrote is just as important as the research stage. Make sure there are no inconsistencies, and everything smoothly ties into the bigger scheme of events. Look out for spelling mistakes and word count.
If you want to further advance your writing skills, read our article about how to write a cover letter for essay .
Are You Looking for Help with Your Writing?
Our expert writers will provide top-notch assistance with any writing project
Related Articles
.webp)
- Skip to main content
- Writing Masterclass
- Math Masterclass
- Course Login
- YouTube Channel
- Facebook Group
- Search this website
Not So Wimpy Teacher
The Not So WImpy Teacher creates resources for busy teachers in grades 2-5 who are looking to deliver engaging and meaningful lessons without overwhelm and chaos.

Get my FREE Editing & Revising Centers
Get my free editing & revising centers.

Help your students master tricky writing skills with these FREE Editing and Revising Centers. Students in grades 2-5 will love this fun, collaborative way to practice editing and revising. Perfect for test prep and review.
We won't send you spam. Unsubscribe at any time.

Last updated on November 9, 2023 by Not So Wimpy Teacher
Teaching Informational Report Writing: 8 Must-Do Tips

One of the most important types of writing your students will learn is informational report writing. This writing genre will be used throughout their academic careers in a variety of different subjects like social studies and science.
But because informational report writing relies on research, it can be challenging for some kids. Today I’m breaking down the process with 8 must-do tips to help your kids learn how to write an engaging report.
1. Start with a pre-assessment
I always recommend starting with a pre-assessment. Give students a prompt and one writing period to respond to it the best they can. Use a simple rubric to score the sample, but don’t add the grade to the grade book.
Make sure you have realistic expectations for this assignment. Don’t get discouraged if your students don’t do very well. Remember, the point of the pre-assessment is to see what they know before you teach the genre. You can use this writing sample to plan your lessons, formulate conference groups, and serve as a baseline of where each student started. This allows you to measure their growth at the end of the unit.

2. Read a mentor text
I always read a mentor text to make it clear to students what informational report writing is. If you just tell 8-year-olds to write an informational report, they will stare at you like you have three heads. They don’t know what an informational report is.
Before you can expect students to write informational reports, you must provide examples of informational reports. You can show them two or three mentor text examples to help familiarize them with the genre.
I also use mentor texts in the next step of the informational report writing process when I teach them how to generate topics. I read a mentor text for each specific strategy I teach.
3. Teach students how to generate report topics
It can be very tempting to give students an assignment that relates to something you are learning in science or social studies. But don’t do it! At least not during writing. You want students to pick something that is interesting to them to write about. This will dramatically improve their writing motivation, enjoyment, and effort.

Most students don’t know what they want to write about. So you need to teach them strategies to help them generate topics that they are super excited to research and write about.
I like to teach two strategies to my students. The first one is to think of something you already know a lot about. Your students might play baseball or do gymnastics or raise chickens. Or they might pick something they’ve already learned about like dinosaurs or Fortnight. They will have tons of information to share on this topic that they are passionate about.
The second strategy is to think of something that they are curious about. Maybe they’ve always wanted to learn more about Antarctica or Lady Gaga or volcanoes. Because this is a topic that is interesting to them, they will enjoy doing the research and writing about it.
Have students record all these ideas in the research section of their notebooks. Once they have a bunch of ideas written down, tell them to choose the topic that is most interesting to them.
I also like to have a game plan for students who don’t have a topic after these lessons. Try a deskside conference and encourage them with some questions, or simply select an idea that they recorded on their sheet and express your interest in learning more about it. If neither of those ideas work, you can give them a list of prompts and give them five minutes to choose. It’s not the most ideal, but it’s better than letting them sit there for a week without choosing a topic.
4. Teach informational paraphrasing
An important lesson when teaching informational report writing is about paraphrasing and plagiarism. This is a tricky skill to learn, even for a lot of adults. So don’t worry if this seems tough for your students. They will practice it for years.
This is a serious lesson to teach, so you should approach it that way. Start by teaching students the word plagiarism, which is when someone steals someone else’s words. And be sure to emphasize that this is wrong.
When you write an informational report, you need to include facts and figures that you found during your research. But you can’t just write them down word for word. The key to doing this correctly is paraphrasing. Explain that paraphrasing is taking ideas and rewriting them in your own words.
Then, provide lots of examples of how to paraphrase facts and give students lots of opportunities to practice doing it together. I use an anchor chart to model how to paraphrase. One question I ask myself out loud is “What does this sentence actually mean?” Then, I try to restate it in my own words. I also model closing the book and writing my own sentence without looking at the facts.
Finally, I have students practice paraphrasing with a task card scoot. Remember, this is something you will have to practice a lot.
5. Show students how to research for informational reports

This is my favorite part of teaching informational report writing. Students get to look for books and articles about the topic they have chosen, and they love learning more.
I recommend taking your students to the school library if at all possible. You might even want to send a list of research topics to the school librarian ahead of time so he or she can point them in the right direction.
Sometimes it’s necessary to teach students how to search for articles on a child-safe search engine. Or you can always find appropriately leveled articles for your students. You don’t want them struggling with college-level material.
Use the first day of your research to just let them enjoy learning about their topic. No notebooks or pencils needed. This will help them choose which subtopics to focus on.
When it comes time to start note-taking, I have students use a printable to keep their research organized. This printable includes their topic and subtopics. As they read and find facts, they paraphrase them on Post-it notes and then add those notes to the correct section of their organizer. I encourage students to find 4-6 facts about each topic.
This method helps students when it’s time to start writing because they can easily shuffle the Post-it notes around on their desk in an order that makes sense.
Note-taking can be tough for struggling readers and writers. You might want to help guide students to the correct parts of their reference materials to find the information they need for each subtopic.
6. Practice writing and revising leads
Once students finish drafting, it’s time to start revising. One of the first revision lessons in teaching informational report writing is writing and revising leads.

I like to teach three different strategies for writing leads. The first one is to start with an interesting fact that makes people want to learn more about your topic. Sometimes this can be a really cool fact that students love but that doesn’t fit in with the subtopics they choose. This is one of the easier strategies for writing leads.
The second strategy is the question lead. It builds upon the fact strategy. But instead of just stating a fact, you ask a question that engages readers and makes them want to find out the answer.
The third strategy is the descriptive lead. It is a little more challenging because it uses a story to captivate readers and sets up the topic you are going to write about. You can always teach this strategy in a group conference with your more advanced writers if you prefer. Or save this strategy for your second masterpiece.
Be sure to show students an example of each strategy, read mentor texts, and model how to write them. Then have students practice writing leads in their notebooks. They can choose their favorite for their report.
7. Practice writing and revising conclusions
One of the last lessons in teaching informational report writing is how to revise the conclusion. Most students won’t even include a conclusion in their draft. That’s okay.
We can easily add in a conclusion during the revision process. I ask students to include three things in their conclusion:
- a transitional word or phrase like “in conclusion” or “in summary” to tell readers that they have come to the end
- a recap of the main idea from each subtopic paragraph
- a question, a fact, or a quote that they know their readers will love
8. Celebrate student writing

The final step in teaching informational report writing is to celebrate. After all the revisions are complete, students will publish their reports. Once the reports are published, students love to share their work with others.
There are tons of ways to celebrate writing. One idea is to combine all their reports into a class book and make a copy for each student. Then students can read their reports to buddies in a different class.
Or maybe you have a Research Party. Before the party, record an interview of each “researcher” presenting a piece of their research. They could read their favorite paragraph or summarize their subtopics. Then on the day of the celebration, you could put up some balloons and invite your students to dress up. Play the video on your whiteboard while students enjoy some sparkling punch and Cheez-Its or string cheese and crackers. You could even come up with silly awards to present to each researcher.
Students really look forward to these fun celebrations at the end of each writing unit.
Informational Report Writing Units

If you’d like even more help teaching informational report writing, my writing units may be just what you are looking for.
These units are available for grades 2-5 and come with EVERYTHING you need to teach informational report writing for 8 weeks. I’ve even included all the mentor texts you need. You don’t have to purchase any additional books or spend hours hunting in the library!
The lesson plans are simple. All you have to do is print and teach.
Students will learn all of the skills necessary to write a report with research: how to craft a strong lead, choose interesting details, write topic and concluding sentences, how to structure paragraphs…and so much more. There are digital anchor charts you can just project onto your whiteboard to save time.
Finally, these units make writing fun for your students. You may even find that your students beg for more writing time. And when students enjoy writing and get lots of practice, they perform better on standardized tests.
Shop This Post

Second Grade Informational Report Writing Unit

Third Grade Informational Report Writing Unit

Fourth Grade Informational Report Writing Unit

Fifth Grade Informational Report Writing Unit
You can also buy the informational report writing unit as a part of a writing bundle that also includes personal narrative, opinion, and fiction writing units.
Work With Me
I created the Not So Wimpy Writing Masterclass , an online professional development course specifically for teachers in grades 2-5 . The tips and strategies inside the course will help you ditch the overwhelm and become a more confident writing teacher who inspires students and transforms them into kids who love to write.
When you enroll in the Masterclass, you’ll learn tried and true strategies for how to teach writing , including how to:
- Teach writing in units
- Create manageable mini-lessons
- Keep students on task during independent writing time
- Implement a successful writing workshop without chaos and confusion
- Transform ALL your students into eager and excited writers who have the skills needed to perform well on standardized tests
This course will make teaching writing easier, more effective, and a heck of a lot more fun! And this professional development is easy! The course is completely online and self-paced. So you are in complete control of your schedule.
Registration for the Not So Wimpy Writing Masterclass is currently closed. Be sure to sign up for the Waitlist so you will be the first to know when we open it again. Sign up now so you don’t miss out!

Want tips for other types of writing? Read my tips for teaching personal narrative .
Have a Not So Wimpy Day,
You may also enjoy these posts

Reader Interactions
April 21, 2022 at 8:11 pm
I am very interested in your writing curriculum for 3rd and 4th grades. My administration is very big on research based programs. Do you have a spot on your website that shows your program is research based? Any information you can send me will help me convince my admin that this program is a necessity. Thanks!!
April 22, 2022 at 6:41 pm
Hi Jennifer, That’s a great question! Our writing units are based on the Writers Workshop model which is backed by a great deal of research.
November 26, 2022 at 1:16 pm
I purchased your writing bundle for 4th grade last year and loved it. Unfortunately, I was not able to use it (admin wanted another program). I am teaching 5th grade this year at a different school. Is there a noticeable difference between the 4th and 5th grade material?
December 2, 2022 at 10:56 am
Hi Susan, Thank you for your question. I answered your question through email so be sure to watch for it.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More than 400 helpful resources available in my shop!

Not So Wimpy Writing Masterclass
Do you struggle to find time to teach writing? Do you find it a challenge to deliver lessons that help all of your writers? Would you like to learn a simple and effective way to teach writing? The Not So Wimpy Writing Masterclass is an online professional development course for grades 2-5. In this course, you will go from feeling overwhelmed to feeling confident and excited about teaching writing.

Check out these recent podcast episodes:
- Connecting with Students Online with Jennifer Serravallo
- A Simple Problem-Solving Strategy That Works Every Time
- Giving Students Feedback About Their Writing
- Virtual and Socially Distant Valentine’s Day Activities for the Classroom
- How to Use Project-Based Learning in the Classroom
Grab a snack and join the discussion over on Facebook!
We have four separate groups for grades 2-5
Get even more great tips and tricks on my YouTube channel!

We LOVE and recommend these products!
Check out the books, supplies, and other products that we use in our own classrooms. We only recommend those things that we absolutely love and swear by!

Hello! I’m Jamie
- I believe that students need to be the leaders of the classroom. Even third graders are old enough to be held accountable and to take responsibility for their learning.
- I do not believe that kids were made to sit in seats. They need to get up and move around.
- Differentiated instruction is a must. I use guided reading and guided math groups to meet the individual needs of my students.
- Helping a student to discover their love for reading is a privilege that I never get tired of.
- School should be fun! We party in my class!
Follow Me Here

8.5 Writing Process: Creating an Analytical Report
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify the elements of the rhetorical situation for your report.
- Find and focus a topic to write about.
- Gather and analyze information from appropriate sources.
- Distinguish among different kinds of evidence.
- Draft a thesis and create an organizational plan.
- Compose a report that develops ideas and integrates evidence from sources.
- Give and act on productive feedback to works in progress.
You might think that writing comes easily to experienced writers—that they draft stories and college papers all at once, sitting down at the computer and having sentences flow from their fingers like water from a faucet. In reality, most writers engage in a recursive process, pushing forward, stepping back, and repeating steps multiple times as their ideas develop and change. In broad strokes, the steps most writers go through are these:
- Planning and Organization . You will have an easier time drafting if you devote time at the beginning to consider the rhetorical situation for your report, understand your assignment, gather ideas and information, draft a thesis statement, and create an organizational plan.
- Drafting . When you have an idea of what you want to say and the order in which you want to say it, you’re ready to draft. As much as possible, keep going until you have a complete first draft of your report, resisting the urge to go back and rewrite. Save that for after you have completed a first draft.
- Review . Now is the time to get feedback from others, whether from your instructor, your classmates, a tutor in the writing center, your roommate, someone in your family, or someone else you trust to read your writing critically and give you honest feedback.
- Revising . With feedback on your draft, you are ready to revise. You may need to return to an earlier step and make large-scale revisions that involve planning, organizing, and rewriting, or you may need to work mostly on ensuring that your sentences are clear and correct.
Considering the Rhetorical Situation
Like other kinds of writing projects, a report starts with assessing the rhetorical situation —the circumstance in which a writer communicates with an audience of readers about a subject. As the writer of a report, you make choices based on the purpose of your writing, the audience who will read it, the genre of the report, and the expectations of the community and culture in which you are working. A graphic organizer like Table 8.1 can help you begin.
Summary of Assignment
Write an analytical report on a topic that interests you and that you want to know more about. The topic can be contemporary or historical, but it must be one that you can analyze and support with evidence from sources.
The following questions can help you think about a topic suitable for analysis:
- Why or how did ________ happen?
- What are the results or effects of ________?
- Is ________ a problem? If so, why?
- What are examples of ________ or reasons for ________?
- How does ________ compare to or contrast with other issues, concerns, or things?
Consult and cite three to five reliable sources. The sources do not have to be scholarly for this assignment, but they must be credible, trustworthy, and unbiased. Possible sources include academic journals, newspapers, magazines, reputable websites, government publications or agency websites, and visual sources such as TED Talks. You may also use the results of an experiment or survey, and you may want to conduct interviews.
Consider whether visuals and media will enhance your report. Can you present data you collect visually? Would a map, photograph, chart, or other graphic provide interesting and relevant support? Would video or audio allow you to present evidence that you would otherwise need to describe in words?
Another Lens. To gain another analytic view on the topic of your report, consider different people affected by it. Say, for example, that you have decided to report on recent high school graduates and the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the final months of their senior year. If you are a recent high school graduate, you might naturally gravitate toward writing about yourself and your peers. But you might also consider the adults in the lives of recent high school graduates—for example, teachers, parents, or grandparents—and how they view the same period. Or you might consider the same topic from the perspective of a college admissions department looking at their incoming freshman class.
Quick Launch: Finding and Focusing a Topic
Coming up with a topic for a report can be daunting because you can report on nearly anything. The topic can easily get too broad, trapping you in the realm of generalizations. The trick is to find a topic that interests you and focus on an angle you can analyze in order to say something significant about it. You can use a graphic organizer to generate ideas, or you can use a concept map similar to the one featured in Writing Process: Thinking Critically About a “Text.”
Asking the Journalist’s Questions
One way to generate ideas about a topic is to ask the five W (and one H) questions, also called the journalist’s questions : Who? What? When? Where? Why? How? Try answering the following questions to explore a topic:
Who was or is involved in ________?
What happened/is happening with ________? What were/are the results of ________?
When did ________ happen? Is ________ happening now?
Where did ________ happen, or where is ________ happening?
Why did ________ happen, or why is ________ happening now?
How did ________ happen?
For example, imagine that you have decided to write your analytical report on the effect of the COVID-19 shutdown on high-school students by interviewing students on your college campus. Your questions and answers might look something like those in Table 8.2 :
Asking Focused Questions
Another way to find a topic is to ask focused questions about it. For example, you might ask the following questions about the effect of the 2020 pandemic shutdown on recent high school graduates:
- How did the shutdown change students’ feelings about their senior year?
- How did the shutdown affect their decisions about post-graduation plans, such as work or going to college?
- How did the shutdown affect their academic performance in high school or in college?
- How did/do they feel about continuing their education?
- How did the shutdown affect their social relationships?
Any of these questions might be developed into a thesis for an analytical report. Table 8.3 shows more examples of broad topics and focusing questions.
Gathering Information
Because they are based on information and evidence, most analytical reports require you to do at least some research. Depending on your assignment, you may be able to find reliable information online, or you may need to do primary research by conducting an experiment, a survey, or interviews. For example, if you live among students in their late teens and early twenties, consider what they can tell you about their lives that you might be able to analyze. Returning to or graduating from high school, starting college, or returning to college in the midst of a global pandemic has provided them, for better or worse, with educational and social experiences that are shared widely by people their age and very different from the experiences older adults had at the same age.
Some report assignments will require you to do formal research, an activity that involves finding sources and evaluating them for reliability, reading them carefully, taking notes, and citing all words you quote and ideas you borrow. See Research Process: Accessing and Recording Information and Annotated Bibliography: Gathering, Evaluating, and Documenting Sources for detailed instruction on conducting research.
Whether you conduct in-depth research or not, keep track of the ideas that come to you and the information you learn. You can write or dictate notes using an app on your phone or computer, or you can jot notes in a journal if you prefer pen and paper. Then, when you are ready to begin organizing your report, you will have a record of your thoughts and information. Always track the sources of information you gather, whether from printed or digital material or from a person you interviewed, so that you can return to the sources if you need more information. And always credit the sources in your report.
Kinds of Evidence
Depending on your assignment and the topic of your report, certain kinds of evidence may be more effective than others. Other kinds of evidence may even be required. As a general rule, choose evidence that is rooted in verifiable facts and experience. In addition, select the evidence that best supports the topic and your approach to the topic, be sure the evidence meets your instructor’s requirements, and cite any evidence you use that comes from a source. The following list contains different kinds of frequently used evidence and an example of each.
Definition : An explanation of a key word, idea, or concept.
The U.S. Census Bureau refers to a “young adult” as a person between 18 and 34 years old.
Example : An illustration of an idea or concept.
The college experience in the fall of 2020 was starkly different from that of previous years. Students who lived in residence halls were assigned to small pods. On-campus dining services were limited. Classes were small and physically distanced or conducted online. Parties were banned.
Expert opinion : A statement by a professional in the field whose opinion is respected.
According to Louise Aronson, MD, geriatrician and author of Elderhood , people over the age of 65 are the happiest of any age group, reporting “less stress, depression, worry, and anger, and more enjoyment, happiness, and satisfaction” (255).
Fact : Information that can be proven correct or accurate.
According to data collected by the NCAA, the academic success of Division I college athletes between 2015 and 2019 was consistently high (Hosick).
Interview : An in-person, phone, or remote conversation that involves an interviewer posing questions to another person or people.
During our interview, I asked Betty about living without a cell phone during the pandemic. She said that before the pandemic, she hadn’t needed a cell phone in her daily activities, but she soon realized that she, and people like her, were increasingly at a disadvantage.
Quotation : The exact words of an author or a speaker.
In response to whether she thought she needed a cell phone, Betty said, “I got along just fine without a cell phone when I could go everywhere in person. The shift to needing a phone came suddenly, and I don’t have extra money in my budget to get one.”
Statistics : A numerical fact or item of data.
The Pew Research Center reported that approximately 25 percent of Hispanic Americans and 17 percent of Black Americans relied on smartphones for online access, compared with 12 percent of White people.
Survey : A structured interview in which respondents (the people who answer the survey questions) are all asked the same questions, either in person or through print or electronic means, and their answers tabulated and interpreted. Surveys discover attitudes, beliefs, or habits of the general public or segments of the population.
A survey of 3,000 mobile phone users in October 2020 showed that 54 percent of respondents used their phones for messaging, while 40 percent used their phones for calls (Steele).
- Visuals : Graphs, figures, tables, photographs and other images, diagrams, charts, maps, videos, and audio recordings, among others.
Thesis and Organization
Drafting a thesis.
When you have a grasp of your topic, move on to the next phase: drafting a thesis. The thesis is the central idea that you will explore and support in your report; all paragraphs in your report should relate to it. In an essay-style analytical report, you will likely express this main idea in a thesis statement of one or two sentences toward the end of the introduction.
For example, if you found that the academic performance of student athletes was higher than that of non-athletes, you might write the following thesis statement:
student sample text Although a common stereotype is that college athletes barely pass their classes, an analysis of athletes’ academic performance indicates that athletes drop fewer classes, earn higher grades, and are more likely to be on track to graduate in four years when compared with their non-athlete peers. end student sample text
The thesis statement often previews the organization of your writing. For example, in his report on the U.S. response to the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, Trevor Garcia wrote the following thesis statement, which detailed the central idea of his report:
student sample text An examination of the U.S. response shows that a reduction of experts in key positions and programs, inaction that led to equipment shortages, and inconsistent policies were three major causes of the spread of the virus and the resulting deaths. end student sample text
After you draft a thesis statement, ask these questions, and examine your thesis as you answer them. Revise your draft as needed.
- Is it interesting? A thesis for a report should answer a question that is worth asking and piques curiosity.
- Is it precise and specific? If you are interested in reducing pollution in a nearby lake, explain how to stop the zebra mussel infestation or reduce the frequent algae blooms.
- Is it manageable? Try to split the difference between having too much information and not having enough.
Organizing Your Ideas
As a next step, organize the points you want to make in your report and the evidence to support them. Use an outline, a diagram, or another organizational tool, such as Table 8.4 .
Drafting an Analytical Report
With a tentative thesis, an organization plan, and evidence, you are ready to begin drafting. For this assignment, you will report information, analyze it, and draw conclusions about the cause of something, the effect of something, or the similarities and differences between two different things.
Introduction
Some students write the introduction first; others save it for last. Whenever you choose to write the introduction, use it to draw readers into your report. Make the topic of your report clear, and be concise and sincere. End the introduction with your thesis statement. Depending on your topic and the type of report, you can write an effective introduction in several ways. Opening a report with an overview is a tried-and-true strategy, as shown in the following example on the U.S. response to COVID-19 by Trevor Garcia. Notice how he opens the introduction with statistics and a comparison and follows it with a question that leads to the thesis statement (underlined).
student sample text With more than 83 million cases and 1.8 million deaths at the end of 2020, COVID-19 has turned the world upside down. By the end of 2020, the United States led the world in the number of cases, at more than 20 million infections and nearly 350,000 deaths. In comparison, the second-highest number of cases was in India, which at the end of 2020 had less than half the number of COVID-19 cases despite having a population four times greater than the U.S. (“COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic,” 2021). How did the United States come to have the world’s worst record in this pandemic? underline An examination of the U.S. response shows that a reduction of experts in key positions and programs, inaction that led to equipment shortages, and inconsistent policies were three major causes of the spread of the virus and the resulting deaths end underline . end student sample text
For a less formal report, you might want to open with a question, quotation, or brief story. The following example opens with an anecdote that leads to the thesis statement (underlined).
student sample text Betty stood outside the salon, wondering how to get in. It was June of 2020, and the door was locked. A sign posted on the door provided a phone number for her to call to be let in, but at 81, Betty had lived her life without a cell phone. Betty’s day-to-day life had been hard during the pandemic, but she had planned for this haircut and was looking forward to it; she had a mask on and hand sanitizer in her car. Now she couldn’t get in the door, and she was discouraged. In that moment, Betty realized how much Americans’ dependence on cell phones had grown in the months since the pandemic began. underline Betty and thousands of other senior citizens who could not afford cell phones or did not have the technological skills and support they needed were being left behind in a society that was increasingly reliant on technology end underline . end student sample text
Body Paragraphs: Point, Evidence, Analysis
Use the body paragraphs of your report to present evidence that supports your thesis. A reliable pattern to keep in mind for developing the body paragraphs of a report is point , evidence , and analysis :
- The point is the central idea of the paragraph, usually given in a topic sentence stated in your own words at or toward the beginning of the paragraph. Each topic sentence should relate to the thesis.
- The evidence you provide develops the paragraph and supports the point made in the topic sentence. Include details, examples, quotations, paraphrases, and summaries from sources if you conducted formal research. Synthesize the evidence you include by showing in your sentences the connections between sources.
- The analysis comes at the end of the paragraph. In your own words, draw a conclusion about the evidence you have provided and how it relates to the topic sentence.
The paragraph below illustrates the point, evidence, and analysis pattern. Drawn from a report about concussions among football players, the paragraph opens with a topic sentence about the NCAA and NFL and their responses to studies about concussions. The paragraph is developed with evidence from three sources. It concludes with a statement about helmets and players’ safety.
student sample text The NCAA and NFL have taken steps forward and backward to respond to studies about the danger of concussions among players. Responding to the deaths of athletes, documented brain damage, lawsuits, and public outcry (Buckley et al., 2017), the NCAA instituted protocols to reduce potentially dangerous hits during football games and to diagnose traumatic head injuries more quickly and effectively. Still, it has allowed players to wear more than one style of helmet during a season, raising the risk of injury because of imperfect fit. At the professional level, the NFL developed a helmet-rating system in 2011 in an effort to reduce concussions, but it continued to allow players to wear helmets with a wide range of safety ratings. The NFL’s decision created an opportunity for researchers to look at the relationship between helmet safety ratings and concussions. Cocello et al. (2016) reported that players who wore helmets with a lower safety rating had more concussions than players who wore helmets with a higher safety rating, and they concluded that safer helmets are a key factor in reducing concussions. end student sample text
Developing Paragraph Content
In the body paragraphs of your report, you will likely use examples, draw comparisons, show contrasts, or analyze causes and effects to develop your topic.
Paragraphs developed with Example are common in reports. The paragraph below, adapted from a report by student John Zwick on the mental health of soldiers deployed during wartime, draws examples from three sources.
student sample text Throughout the Vietnam War, military leaders claimed that the mental health of soldiers was stable and that men who suffered from combat fatigue, now known as PTSD, were getting the help they needed. For example, the New York Times (1966) quoted military leaders who claimed that mental fatigue among enlisted men had “virtually ceased to be a problem,” occurring at a rate far below that of World War II. Ayres (1969) reported that Brigadier General Spurgeon Neel, chief American medical officer in Vietnam, explained that soldiers experiencing combat fatigue were admitted to the psychiatric ward, sedated for up to 36 hours, and given a counseling session with a doctor who reassured them that the rest was well deserved and that they were ready to return to their units. Although experts outside the military saw profound damage to soldiers’ psyches when they returned home (Halloran, 1970), the military stayed the course, treating acute cases expediently and showing little concern for the cumulative effect of combat stress on individual soldiers. end student sample text
When you analyze causes and effects , you explain the reasons that certain things happened and/or their results. The report by Trevor Garcia on the U.S. response to the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 is an example: his report examines the reasons the United States failed to control the coronavirus. The paragraph below, adapted from another student’s report written for an environmental policy course, explains the effect of white settlers’ views of forest management on New England.
student sample text The early colonists’ European ideas about forest management dramatically changed the New England landscape. White settlers saw the New World as virgin, unused land, even though indigenous people had been drawing on its resources for generations by using fire subtly to improve hunting, employing construction techniques that left ancient trees intact, and farming small, efficient fields that left the surrounding landscape largely unaltered. White settlers’ desire to develop wood-built and wood-burning homesteads surrounded by large farm fields led to forestry practices and techniques that resulted in the removal of old-growth trees. These practices defined the way the forests look today. end student sample text
Compare and contrast paragraphs are useful when you wish to examine similarities and differences. You can use both comparison and contrast in a single paragraph, or you can use one or the other. The paragraph below, adapted from a student report on the rise of populist politicians, compares the rhetorical styles of populist politicians Huey Long and Donald Trump.
student sample text A key similarity among populist politicians is their rejection of carefully crafted sound bites and erudite vocabulary typically associated with candidates for high office. Huey Long and Donald Trump are two examples. When he ran for president, Long captured attention through his wild gesticulations on almost every word, dramatically varying volume, and heavily accented, folksy expressions, such as “The only way to be able to feed the balance of the people is to make that man come back and bring back some of that grub that he ain’t got no business with!” In addition, Long’s down-home persona made him a credible voice to represent the common people against the country’s rich, and his buffoonish style allowed him to express his radical ideas without sounding anti-communist alarm bells. Similarly, Donald Trump chose to speak informally in his campaign appearances, but the persona he projected was that of a fast-talking, domineering salesman. His frequent use of personal anecdotes, rhetorical questions, brief asides, jokes, personal attacks, and false claims made his speeches disjointed, but they gave the feeling of a running conversation between him and his audience. For example, in a 2015 speech, Trump said, “They just built a hotel in Syria. Can you believe this? They built a hotel. When I have to build a hotel, I pay interest. They don’t have to pay interest, because they took the oil that, when we left Iraq, I said we should’ve taken” (“Our Country Needs” 2020). While very different in substance, Long and Trump adopted similar styles that positioned them as the antithesis of typical politicians and their worldviews. end student sample text
The conclusion should draw the threads of your report together and make its significance clear to readers. You may wish to review the introduction, restate the thesis, recommend a course of action, point to the future, or use some combination of these. Whichever way you approach it, the conclusion should not head in a new direction. The following example is the conclusion from a student’s report on the effect of a book about environmental movements in the United States.
student sample text Since its publication in 1949, environmental activists of various movements have found wisdom and inspiration in Aldo Leopold’s A Sand County Almanac . These audiences included Leopold’s conservationist contemporaries, environmentalists of the 1960s and 1970s, and the environmental justice activists who rose in the 1980s and continue to make their voices heard today. These audiences have read the work differently: conservationists looked to the author as a leader, environmentalists applied his wisdom to their movement, and environmental justice advocates have pointed out the flaws in Leopold’s thinking. Even so, like those before them, environmental justice activists recognize the book’s value as a testament to taking the long view and eliminating biases that may cloud an objective assessment of humanity’s interdependent relationship with the environment. end student sample text
Citing Sources
You must cite the sources of information and data included in your report. Citations must appear in both the text and a bibliography at the end of the report.
The sample paragraphs in the previous section include examples of in-text citation using APA documentation style. Trevor Garcia’s report on the U.S. response to COVID-19 in 2020 also uses APA documentation style for citations in the text of the report and the list of references at the end. Your instructor may require another documentation style, such as MLA or Chicago.
Peer Review: Getting Feedback from Readers
You will likely engage in peer review with other students in your class by sharing drafts and providing feedback to help spot strengths and weaknesses in your reports. For peer review within a class, your instructor may provide assignment-specific questions or a form for you to complete as you work together.
If you have a writing center on your campus, it is well worth your time to make an online or in-person appointment with a tutor. You’ll receive valuable feedback and improve your ability to review not only your report but your overall writing.
Another way to receive feedback on your report is to ask a friend or family member to read your draft. Provide a list of questions or a form such as the one in Table 8.5 for them to complete as they read.
Revising: Using Reviewers’ Responses to Revise your Work
When you receive comments from readers, including your instructor, read each comment carefully to understand what is being asked. Try not to get defensive, even though this response is completely natural. Remember that readers are like coaches who want you to succeed. They are looking at your writing from outside your own head, and they can identify strengths and weaknesses that you may not have noticed. Keep track of the strengths and weaknesses your readers point out. Pay special attention to those that more than one reader identifies, and use this information to improve your report and later assignments.
As you analyze each response, be open to suggestions for improvement, and be willing to make significant revisions to improve your writing. Perhaps you need to revise your thesis statement to better reflect the content of your draft. Maybe you need to return to your sources to better understand a point you’re trying to make in order to develop a paragraph more fully. Perhaps you need to rethink the organization, move paragraphs around, and add transition sentences.
Below is an early draft of part of Trevor Garcia’s report with comments from a peer reviewer:
student sample text To truly understand what happened, it’s important first to look back to the years leading up to the pandemic. Epidemiologists and public health officials had long known that a global pandemic was possible. In 2016, the U.S. National Security Council (NSC) published a 69-page document with the intimidating title Playbook for Early Response to High-Consequence Emerging Infectious Disease Threats and Biological Incidents . The document’s two sections address responses to “emerging disease threats that start or are circulating in another country but not yet confirmed within U.S. territorial borders” and to “emerging disease threats within our nation’s borders.” On 13 January 2017, the joint Obama-Trump transition teams performed a pandemic preparedness exercise; however, the playbook was never adopted by the incoming administration. end student sample text
annotated text Peer Review Comment: Do the words in quotation marks need to be a direct quotation? It seems like a paraphrase would work here. end annotated text
annotated text Peer Review Comment: I’m getting lost in the details about the playbook. What’s the Obama-Trump transition team? end annotated text
student sample text In February 2018, the administration began to cut funding for the Prevention and Public Health Fund at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; cuts to other health agencies continued throughout 2018, with funds diverted to unrelated projects such as housing for detained immigrant children. end student sample text
annotated text Peer Review Comment: This paragraph has only one sentence, and it’s more like an example. It needs a topic sentence and more development. end annotated text
student sample text Three months later, Luciana Borio, director of medical and biodefense preparedness at the NSC, spoke at a symposium marking the centennial of the 1918 influenza pandemic. “The threat of pandemic flu is the number one health security concern,” she said. “Are we ready to respond? I fear the answer is no.” end student sample text
annotated text Peer Review Comment: This paragraph is very short and a lot like the previous paragraph in that it’s a single example. It needs a topic sentence. Maybe you can combine them? end annotated text
annotated text Peer Review Comment: Be sure to cite the quotation. end annotated text
Reading these comments and those of others, Trevor decided to combine the three short paragraphs into one paragraph focusing on the fact that the United States knew a pandemic was possible but was unprepared for it. He developed the paragraph, using the short paragraphs as evidence and connecting the sentences and evidence with transitional words and phrases. Finally, he added in-text citations in APA documentation style to credit his sources. The revised paragraph is below:
student sample text Epidemiologists and public health officials in the United States had long known that a global pandemic was possible. In 2016, the National Security Council (NSC) published Playbook for Early Response to High-Consequence Emerging Infectious Disease Threats and Biological Incidents , a 69-page document on responding to diseases spreading within and outside of the United States. On January 13, 2017, the joint transition teams of outgoing president Barack Obama and then president-elect Donald Trump performed a pandemic preparedness exercise based on the playbook; however, it was never adopted by the incoming administration (Goodman & Schulkin, 2020). A year later, in February 2018, the Trump administration began to cut funding for the Prevention and Public Health Fund at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, leaving key positions unfilled. Other individuals who were fired or resigned in 2018 were the homeland security adviser, whose portfolio included global pandemics; the director for medical and biodefense preparedness; and the top official in charge of a pandemic response. None of them were replaced, leaving the White House with no senior person who had experience in public health (Goodman & Schulkin, 2020). Experts voiced concerns, among them Luciana Borio, director of medical and biodefense preparedness at the NSC, who spoke at a symposium marking the centennial of the 1918 influenza pandemic in May 2018: “The threat of pandemic flu is the number one health security concern,” she said. “Are we ready to respond? I fear the answer is no” (Sun, 2018, final para.). end student sample text
A final word on working with reviewers’ comments: as you consider your readers’ suggestions, remember, too, that you remain the author. You are free to disregard suggestions that you think will not improve your writing. If you choose to disregard comments from your instructor, consider submitting a note explaining your reasons with the final draft of your report.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/8-5-writing-process-creating-an-analytical-report
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
How to Write a Progress Report for Students: A Step-by-Step Guide
Feeling behind on ai.
You're not alone. The Neuron is a daily AI newsletter that tracks the latest AI trends and tools you need to know. Join 250,000+ professionals from top companies like Microsoft, Apple, Salesforce and more. 100% FREE.
Providing feedback to students about their progress is an essential component of teaching and learning. Progress reports are an effective way to communicate with students, parents, and guardians about student performance throughout the academic year. In this step-by-step guide, we'll explore the purpose of progress reports, the essential components of a report, and how to write a clear and concise progress report for students.
Understanding the Purpose of a Progress Report
Progress reports serve several purposes. Firstly, they provide valuable feedback to students about their academic performance in each subject area, highlighting areas of strengths and weaknesses. Secondly, progress reports keep parents and guardians informed about their child's progress, helping them to be more involved and supportive of their child's learning. Finally, progress reports enable teachers to identify areas where they may need to modify teaching methods or provide additional support.
Evaluating Student Progress
Evaluating student progress is key to writing an effective progress report. Teachers should consider the student's achievement against the expected learning outcomes for the given grade level. This may involve using standardized tests, assessments, observations, and student work samples to determine whether the student is meeting expectations.
Communicating with Parents and Guardians
Progress reports are a critical communication tool for teachers to use with parents and guardians. They provide a snapshot of a student's academic progress, in addition to reports displaying their behavior in the classroom. Reports should be easily understood by parents, including specific feedback on areas where the student is struggling and where progress is being made. Teachers should make every effort to keep parents informed throughout the year and provide an opportunity for discussions about student progress.
Identifying Areas for Improvement
It is essential to identify areas for improvement when writing a progress report. This could include identifying a student's strengths, weaknesses, areas of growth, and where they need to improve. Teachers should use clear and concise language to communicate this information so that it is easily understood by both the student and parents or guardians. Clear reporting helps students to understand what they need to do to improve their academic performance.
Essential Components of a Progress Report
Student information.
Every progress report should begin with the student's name, grade, and the grading period covered in the report. Including this information upfront makes it easier for parents to view report cards if they have more than one student.
Grading Period
The grading period should also be included in the progress report. This provides readers with a timeline of when the student was evaluated and specifically how the student performed during that time.
Subject Areas
Progress reports should cover the various subject areas studied by students. This includes subject areas like mathematics, reading, writing, and science. Teachers should provide a summary that is based on the student's performance for each area, which includes information about how well the student is doing and how they compare to their peers in the same subject area.
Performance Indicators
Teachers should use performance indicators to identify specific areas of achievement or concern. Performance indicators help to describe what a student can do or what they need to improve further in different subject areas. Defining, these indicators is important as they help to paint a more complete picture of a student's performance.
Comments and Recommendations
Teachers are required to comment on a student's academic performance and behavior. These comments should be written in simple and concise language that describes the student's performance clearly. Teachers can point out areas for improvement, make recommendations for further study, and highlight areas where students excel, in order to give concise and constructive feedback to parents and students.
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Progress Report
Step 1: gather student data and information.
Before writing progress reports, teachers should ensure they have all the required information and data at their fingertips. This includes student work samples, test scores, observations, and any notes from previous parent-teacher meetings. Teachers should try to gather as much data as possible to clearly describe a student's progress throughout the year. This data makes it possible to write a balanced report that captures a student's strengths and areas of improvement.
Step 2: Analyze and Evaluate Student Performance
After gathering the student data, the teacher needs to analyze and evaluate the student's progress in each subject area. The teacher should determine whether the student has met the expected learning outcomes for the given grade level and identify areas where the student is excelling or needs more support. This step is critical to ensure that the resulting progress report is an accurate depiction of the student's performance throughout the grading period.
Step 3: Organize the Report
The next step is to organize the report in a clear and simple way so that it is easily understood by parents and guardians. Reports should include a brief introduction, the essential components of a progress report (as outlined above), and a summary of the student's performance. It is important to include information that parents can use to support student success inside and outside of the classroom. Organizing the report and writing it in a consistent format makes it easier for readers to follow and understand.
Step 4: Write Clear and Concise Comments
Upon analysis and evaluation, teachers should write clear and concise comments that describe the student's academic progress and behavior. These comments should be easy to understand, give specific details about progress, and target both positive achievements and areas that need improvement. Comments should be customized to each student to ensure that they reflect that individual's progress over time.
Step 5: Review and Edit the Report
Finally, it's always essential to review and edit reports before sending them out to parents. Review for accuracy, ensure that comments and recommendations are constructive and helpful. Finally, ensure that it follows the school's guidelines concerning the distribution of progress reports. Reviewing ensures that the report that is sent achieves its purpose of providing an accurate, constructive outlook on the student's performance in school.
ChatGPT Prompt for Writing a Progress Report for Students
Use the following prompt in an AI chatbot . Below each prompt, be sure to provide additional details about your situation. These could be scratch notes, what you'd like to say or anything else that guides the AI model to write a certain way.
Please compose a comprehensive and detailed update on the progress of students, including any improvements or setbacks, as well as any relevant observations or insights.
[ADD ADDITIONAL CONTEXT. CAN USE BULLET POINTS.]
Writing progress reports is an essential component of teaching. Progress reports provide valuable feedback to students, parents, and guardians about student academic performance throughout the academic year. By following the step-by-step guide outlined in this article, teachers can produce clear, concise, and meaningful progress reports that help students reach their full potential and improve their performance in the classroom and life.
You Might Also Like...

How to Write an Excellent Information Report
WRITING A HIGH-QUALITY INFORMATION REPORT
It is no surprise that informational texts are given a position of primary importance in most English curricula – we are in the information age, after all. From the ELA Standards of U.S. Common Core to the Literacy Requirements of the National Curriculum for England, non-fiction genres, in general, are given central positions in our teaching schedules. Acquiring the broad range of skills necessary to produce these texts competently takes time. Let’s look at the main features and organizational aspects of information reports to help set our students on the path to writing success.
Regardless of what genre we aim to teach our students, they must develop an awareness of the different approaches required when writing for various purposes. Students need to be able to select the correct tools and structures for the job, and this starts with the students defining the text’s purpose.
Information reports present factual information to inform the reader about a specific topic. Examples of information reports may be found in encyclopedias, reference books, technical texts, social studies books, science books, magazines, and even internet websites. These may all be classed as forms of information texts. Despite this very broad range, it is useful to describe information reports in relation to several standard features, which are explained below.

WHAT IS AN INFORMATION REPORT?

An information report provides readers with information on a chosen topic by providing them with facts.
INFORMATION REPORTS are also commonly known as INFORMATIONAL TEXTS and INFORMATIVE WRITING.
Generally, an information report is written to provide facts about a living or non-living object. It can be an individual object or a group of objects. Some suggestions are.
- Sea Creatures
- The Bald Eagle
- The Titanic
The challenge in writing a good information report is to provide the audience with plenty of facts and evidence about a topic without providing a personal opinion. If you do include personal opinion, essentially, you are writing a persuasive ( also known as an expository ) text. If you are writing about a class of objects, such as sharks, it is important to highlight the differences and similarities between the objects.
A COMPLETE TEACHING UNIT ON WRITING INFORMATION REPORTS

Get an entire unit on INFORMATIONAL TEXTS with no prep required. The editable DIGITAL & PRINT bundle offers a proven model based on research skills, writing strategies, and engaging content with 96 PAGES of material.
TYPES OF INFORMATION REPORTS
You will frequently encounter informational texts in your reading for both work and pleasure and whilst there are many variations, they generally fall into these three main categories.
Scientific Reports: Usually focuses on describing of appearance and behaviour of the subject of your report.
Technological Reports : Usually focus on two main categories of information. Those are the components and uses of the technology.
Social Studies Reports: Usually focuses on the description of people, places, history, geography, society, culture and economy.
STRUCTURE AND FEATURES OF AN INFORMATION REPORT
Information report structure.
INTRODUCTION Classify your topic, and describe the aspects, features or characteristics of the subject.
PARAGRAPHS Will be used to organise your information report. Use paragraphs to elaborate on your subject.
IMAGES Labelled diagrams such as maps, diagrams and pictures support and extend your written information.
SUBHEADINGS Keep your report in a logical state and ordered. It also helps the reader find key information quickly.
INFORMATION REPORT FEATURES
SPECIALIZED VOCABULARY Allows for more information to be shared with minimal text.
THIRD PERSON PERSPECTIVE Relays information from an impersonal position devoid of strong emotive language.
COMPARATIVE LANGUAGE Such as compared to, smaller than, greatest, different form is used to provide context
DEFINITIONS Of uncommon or unfamiliar language may be required in parts to assist the reader
RESEARCHING YOUR INFORMATION REPORT
Teaching students how to write information reports offers an excellent opportunity to introduce research skills to your students. For more advanced students, it creates opportunities for them to hone these important skills further. There are also several different processes students need to develop to ensure that they can filter their research for relevancy and accuracy. Let’s take a look at these:
1. Define the Scope of the Topic
If the scope of the topic is not defined precisely, considerable energy can be wasted at the research stage – especially if internet research is undertaken! Undoubtedly, you will know this from your own experience. How many man and woman hours have been wasted as our own research takes us down a pesky internet cul-de-sac?
2. Uncover Important Keywords and Phrases

The importance of keywords and subject-specific vocabulary in writing an information report has already been mentioned. However, generating these keywords and phrases is also crucial for the research stage when using the internet. Search engines are only as valuable as the terms that are searched. The research process will help students refine and filter the concepts and vocabulary they will use in writing their text.
3 Evaluate Sources
After selecting their search terms, students must look at and evaluate the returned sources. This is best achieved by the teacher reviewing various examples and modelling the criteria used to select the most valuable. Students are often not required to cite research papers at the school level, etc. But they should begin the process of ranking information in terms of its legitimacy. This is a long-term objective, but the teaching of this genre of writing offers ample opportunities for introducing this complex idea. Teaching this objective may involve lessons on things like distinguishing fact from opinion, how to spot bias, detecting fake news/satire, cross-referencing sources etc.
4 Develop Note-Taking Skills
The research stage of writing an information report affords students a valuable opportunity to develop their note-taking skills. The ability to mine information for the key points is an essential skill for a student to develop. Obviously, note-taking is a complex skill and will necessarily be differentiated according to the student’s age and abilities.

As an information report is a factual piece of writing focused on attention to detail, you must ensure your students are provided with an opportunity to research their topic. Ensure they use technical language when required and have a collection of useful facts to include.
The research will be a significant part of your lesson time, so please ensure you allow this before expecting them to contribute anything worthwhile.
Although we strongly encourage using visuals, leave this until all writing has been drafted, written and edited . It should support a robust written report first and foremost. Using grap hic organizers, planning tools, and writing checklists will greatly assist the planning and editing time. We have an in-depth article on student research strategies to explore here.
HOW TO WRITE AN INFORMATION REPORT
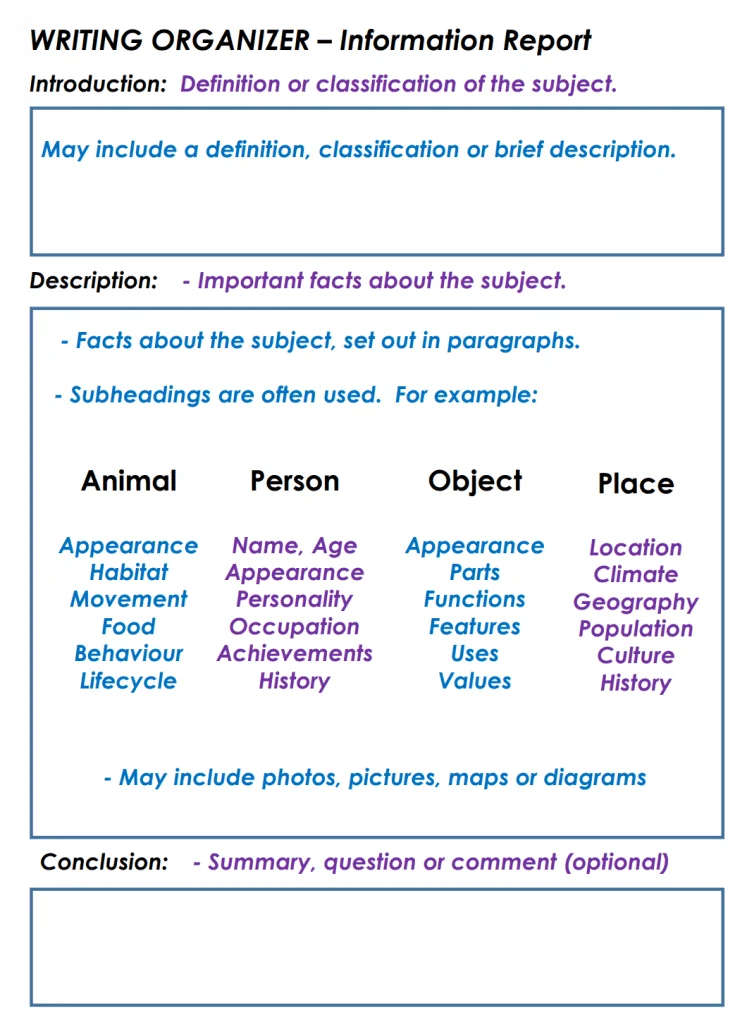
When considering how to organize the structure of an information report, the purpose of the text must be at the forefront of the student’s decision-making. The complexity of the textual organization will again depend on the student’s grade level and ability; however, the general structure will be as follows:
1. Table of Contents
A table of contents should be included for longer information texts. It should outline where specific information can be found in the document or the text. For longer texts, each section should correspond to a page number on the table of contents. For shorter texts, this may be numbered sections instead of page numbers. This will allow the reader to locate specific information that is being searched for without having to read through the whole text. Page numbers can be entered on the table of contents after the text is completed.
2. Introduction
As with other writing genres, information texts must first use a hook to grab the reader’s attention. This hook may take the form of an interesting fact or statistic, an anecdote or a question etc. Fundamentally, the introduction to the text must orientate the reader to the topic in question. It should outline what the reader can expect to learn within the body of the text.
3. Subheadings
The main job of the student when writing an informational text is to organize the information so that the reader can easily understand it. To help the reader achieve this, they need to organize their ideas into paragraphs and to help the reader locate the information on each of these ideas; each paragraph should contain a subheading. These subheadings can also provide titles for the table of contents.
Check out our complete guide to writing perfect paragraphs and sentence structure.
Subheadings are necessary to help your students organize their information by focusing on various aspects of the topic as a whole. For example, if the focus of the information report is an animal, then subsequent subheadings may be something along the lines of appearance , habitat , diet etc. Each subheading will consist of at least one paragraph that constitutes a separate section in the body of the text.
These subheadings often emerge organically as the student undertakes their research before writing. Subheadings may also be accompanied by relevant drawings, maps, tables etc., that summarize the information contained within.
The first sentence of each section should begin with a topic sentence expressing that paragraph’s main idea or topic. The following sentence will provide more detail on the topic sentence or main idea. The next sentence can provide an example or evidence regarding the main idea. Have your students practice this paragraph structure: Topic – Detail – Example.
4. Conclusion
The closing section of an information report can be used to summarize. The conclusion should focus on what the reader has learned in the text. It may also contain information on links or further reading the reader can undertake to find out more about the topic. For more advanced students, the opportunity to make cross-curricular links to IT skills (for example) can be taken by encouraging students to incorporate hyperlinks to further sources.
5. Glossary
The glossary will contain much of the subject-specific vocabulary identified at the prewriting stage. It will contain the words alphabetically and a definition that gives the word context in light of the topic. Some of the contents of the glossary will also be identified by the student reading over the body of the text they have written and selecting words that may pose difficulties for readers or need further contextualizing in terms of the topic. Sometimes, it is helpful to use bold fonts to emphasize the words in a text that will be defined in the glossary. This allows the reader to know they can turn to the glossary to find out further information on the definition of this word and its use in context. As with the other sections of an information report, illustrations, tables, and photographs can be used here to visually represent related ideas and concepts and reinforce the definitions provided.
And there it is, some meat on the bones of information reports. Choosing topics for your students to write about can be generated either by the interests of students themselves, which can significantly enthuse them, or you can select topics for your students that tie into other areas of their learning, thereby killing the proverbial two birds with one stone! It is quite a complex genre but a very important one, and it is advised that students are offered ample opportunity to read lots of information reports to internalize these features and structures. The reading of information reports not only helps our students to understand how to write them but also, wonderfully, helps our students learn lots of stuff about lots of things!
LANGUAGE FEATURES OF INFORMATION REPORTS
Present tense:.
Information reports are predominantly written in the present tense. This is because the information presented on the topic will generally be considered static knowledge. However, this is not always the case for all information texts; for example, autobiographies and biographies can be considered information texts but will more than likely be written in the past tense. For the purposes of this article, however, we will focus on the more formal genres of information texts.
Subject-Specific Vocabulary:
Depending on the topic of the text, vocabulary specific to the subject will typically be used. For example, if the text provides information on an animal, it will likely utilize related words and phrases such as ‘habitat’, ‘species’, ‘offspring’, ‘lifespan’ etc. A helpful exercise for preparation to write an information report is to have students brainstorm words and phrases related to that topic. This also helps ensure the student covers all relevant related material and helps them organize their material before writing. It will also provide useful search terms for internet researching of the topic and some of the vocabulary to be contained in the glossary – more on this later!
General Nouns:

Students need to realize that they should use general nouns when writing on their topic. The information in their text should be generally accurate, and this should be reflected in the generic noun classifying it; for example, Bees collect nectar from flowers.
Passive Voice:
Information reports are an example of formal non-fiction writing. In common with lots of formal writing, they often apply the passive voice. It is helpful to draw the student’s attention to how this differs from other more personal writing genres, such as fiction. When teaching narrative writing , we often encourage, even insist, our students name the doer of the action. In fiction writing, using the passive voice often takes the narrative drive out of a story, leaving it limp and weak in the hands of the reader. This is because the character and narrative voice are central to story writing . This is not the case in information report writing. Here, the passive voice draws attention away from the doer or speaker and firmly brings attention to the object.
For example:
“Every year, cars kill thousands of hedgehogs on our roads.”
Here the active voice is used. Read carefully; we can note a considerable amount of our attention goes to the ‘killer’ in this sentence, i.e. ‘cars’. This brings our attention away from what should be our primary focus and the topic of the report, ‘hedgehogs’.
If we instead use the passive voice to convey this information, it would look something like this:
“Every year, thousands of hedgehogs are killed on our roads.”
Now the same information is relayed to the reader while maintaining the sentence’s focus on the subject ‘hedgehogs’.
A valuable exercise to help students understand the difference between passive and active voices is to give them a list of sentences for them to identify whether the active or passive voice is being used. They can then rewrite active voice sentences as passive voice sentences and vice versa.
Information reports are also generally written in the third person for the same reason the passive voice is used. The third-person perspective creates an impersonal tone that maintains a formal tone appropriate to the genre.
Visual Information:
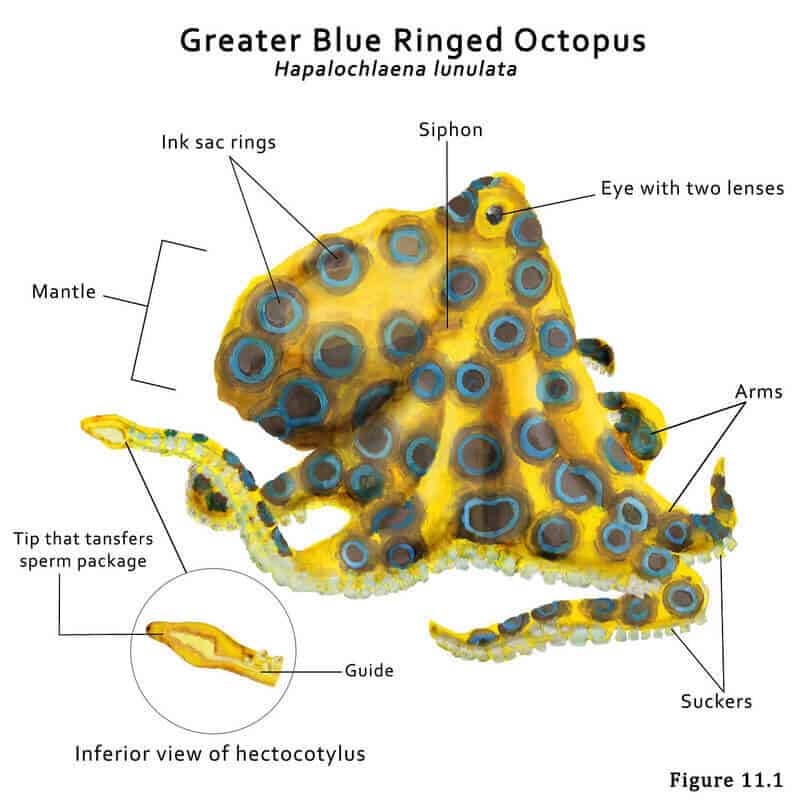
Visual presentations of the information to support the text, whether in the form of diagrams, photographs, graphs, maps, pictures, or tables, are extremely helpful to the reader. They help the reader to digest large amounts of information quickly. Remember too that pictures, photographs etc., should be labelled with captions explaining what they show.
Visual presentations should reinforce points made in the text, often in a condensed way. You may remember flicking through the pages of the World Book Encyclopedia or Encyclopedia Britannica as a child, and even if lacking the necessary literacy skills to actually read the articles, you likely picked up information just by looking at the colourful and well-presented illustrations and tables.
Browse any well-developed website, and the central role visual media plays in information sharing will quickly become apparent. Your student’s work should be no different in this regard. Depending on the age and ability of your students, they may wish to draw pictures or create graphs using computer software to accompany their text.
Fact vs Opinion:
As stated, the purpose of information reports is to present factual information on a topic. It is essential that students can consistently and accurately differentiate between what constitutes fact and what can be considered opinion. This is not always as straightforward as it may seem and will require some practice on the part of the student.
It can be helpful for students to have several sessions working on distinguishing fact from opinion before writing their information reports. Prepare a set of statements for the students in your class. It may be on the topic on which they are to write their reports or on an entirely unrelated topic. There should be a mixture of factual and opinion-based statements. After instructing the students on the differences between facts and opinions , have them go through each statement in their groups and discuss which they believe to be facts and which they believe to be opinions. They then categorize them accordingly.
Beyond the writing of information reports, identifying opinions and facts is an invaluable skill to inculcate in our students. You may wish to encourage them to apply it when watching TV news, reading newspapers etc.
TIPS FOR WRITING A GREAT INFORMATION REPORT
- Assume your readers are not as knowledgeable on the topic as you are. This means you must briefly explain your topic before getting into the body.
- Use the correct scientific and technical terms in your report.
- Find or create some labelled diagrams if possible.
- Use paragraphs effectively. Each new element of your information report should start with a new paragraph.
- Information reports are always written in the present tense and from a third-person perspective.
- You may ask questions or comment around your findings in the conclusion only. The rest of your report should be constructed purely of facts and evidence.
Be Technical and Descriptive
When putting together an information report, you need to know your topic well, so be sure to do your research beforehand. If you were writing an information report on the Titanic, you might want to discover some of the following facts.
- When & Where was Titanic built?
- What materials was it made from?
- Who was the captain, and were any other significant people involved?
- Explain the facts about Titanic’s maiden voyage, such as locations and dates.
- What caused the Titanic to sink ( Remember not to share opinions, just facts.)
- Any critical dates and statistics associated with Titanic.

INFORMATION REPORT GRAPHIC ORGANIZER TEMPLATE
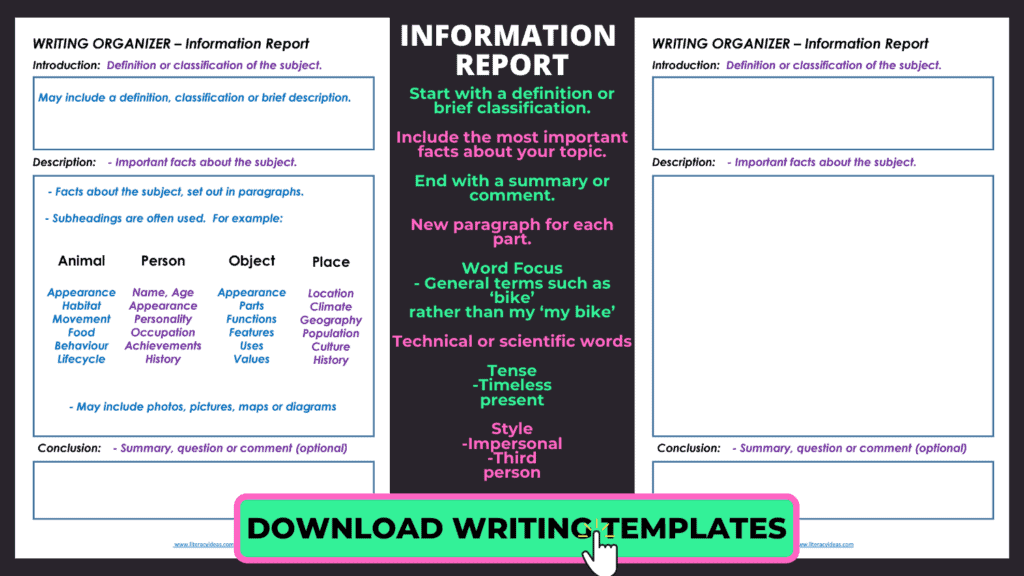
INFORMATION REPORT WRITING CHECKLIST
Information report example (student writing samples).
Below are a collection of information report examples for students. Click on the image to enlarge and explore them in greater detail. Please take a moment to read the information reports in detail and the teacher and student guides highlighting some critical elements of information report writing to consider before writing.
Please understand these student writing samples are not intended to be perfect examples for each age or grade level but a piece of writing for students and teachers to explore together to critically analyze to improve student writing skills and deepen their understanding of information report writing.
We recommend reading the example either a year above or below, as well as the grade you are currently working with, to gain a broader appreciation of this text type .

INFORMATION REPORT WRITING PROMPTS

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
We have several premium information report writing resources available that offer a complete, no-fuss and instant solution to producing excellent informative texts in the classroom and independently.
INFORMATION REPORT WRITING ANCHOR CHARTS & RUBRIC BUNDLE

INFORMATION REPORT WRITING VIDEO TUTORIALS

OTHER INFORMATION REPORT WRITING ARTICLES

Writing Documents for Classes
Progress reports.
Progress reports are common and critical documents in science and engineering, typically when you are part of a research team reporting to a funding agency about your progress on work you are doing for that agency. The basic point of a progress report is to summarize the status, progress, and likely future for a particular project. In a progress report you are often expected to commit to an exact schedule for the project completion, discuss the status of the materials being used and account for the money spent, and summarize concretely both the current findings and the predicted results. The professionalism of the progress report is often vital to the future of the project.
In classes and projects involving writing, progress reports are used as a way for you to summarize your progress to your teacher or advisor, who will typically give feedback on whether he or she is satisfied with your progress. These reports could feel like a mere formality or a waste of time to you, but they are an excellent opportunity to articulate some of the key sentences of your final report and even pose questions in writing to your audience. The rules for writing progress reports are a lot more flexible in a classroom or lab than they are on the job, with a lot less at stake, so you should take full advantage of the opportunity for practice.
For more ideas on writing progress reports, I recommend that you visit:
“Progress Reports” article from the Department of Engineering at Penn State
“Guidelines for Writing Reports” from networklearning.org
Style for Progress Reports
The following stylistic advice can be applied to most progress reports you write:
- Include a working title and the words “Progress Report” at the top of the page.
- Use section headings in the report to simplify both the writing and reading process.
- Open the report with a “Scope and Purpose” section, where you give a condensed version of your future report’s introduction and objective.
- Always include a section entitled, for example, “Progress,” which summarizes the work’s pace and progress and explains any snafus, dilemmas, or setbacks.
- Always include a section entitled, for example, “Remaining Work,” which honestly assesses the work that must still be completed. Think right on the page in this section, posing questions, speculating meaningfully, exploring your options.
- Always include a section that projects the expected results. Commit to a schedule for obtaining those results if possible.
- If necessary, include a section in which you directly solicit advice from your teacher or advisor. Be forthright and professional about the nature of the advice you need.
- Keep your paragraphs short and focused—just a few paragraphs per section, typically.
- Your tone can often be straightforward and familiar—therefore, as a rule, you can use “I” and “you” freely—but do not lapse into informality.
- Avoid being overly optimistic, pessimistic, apologetic, cocky, or self-deprecating.
- Style For Students Online. Authored by : Joe Schall. Provided by : The Pennsylvania State University. Located at : https://www.e-education.psu.edu/styleforstudents/ . Project : Penn State's College of Earth and Mineral Sciences' OER Initiative. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike

Report Writing: Format, Topics, and Examples

Learn the essentials of report writing with this comprehensive guide. Explore the proper format, find inspiring topics, and discover real-world examples to enhance your report writing skills.
What is Report Writing?
A Report Writing is a written account that helps us to know about an event, situation, or occurrence in detail that has already taken place.
Report Writing is a narrative of Events described in an impartial approach. Rules and Format of Report Writing are necessary to know for English report writing. Examples of Report Writing help us in doing this easily.
The Power of Effective Report Writing
Report writing is a skill that transcends industries and disciplines, playing a vital role in conveying information, analyzing data, and making informed decisions.
Whether you are a student, a researcher, a business professional, or someone looking to improve your communication abilities, mastering the art of report writing is essential for success.
This article will provide you with insights into the format, topics, and real-world examples of report writing to help you become a proficient report writer.
Understanding the Format of a Report
A well-structured report not only facilitates easy comprehension but also leaves a lasting impact on the reader. Understanding the proper format is the foundation of creating an effective report. In crafting a comprehensive and impactful report, one must carefully consider and include the following crucial elements. :
1. Title Page
The title page should include the report’s title, the name of the author or organization, the date of submission, and any relevant affiliations.
2. Abstract or Executive Summary
The abstract or executive summary is a concise overview of the report’s main points, providing the reader with a snapshot of the entire report’s content.
3. Table of Contents
The table of contents outlines the report’s structure, listing the headings and subheadings with corresponding page numbers.
4. Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the report, providing context, stating the purpose, and highlighting the significance of the topic.
5. Methodology
In research-oriented reports, the methodology section explains the approach taken to gather data, conduct experiments, or perform studies.
6. Findings
The findings section presents the data collected or the results of the research in a clear and organized manner, often using tables, graphs, or charts.
7. Discussion
The discussion section interprets the findings, provides insights, and offers explanations for observed patterns or trends.
8. Conclusion
The conclusion summarizes the main points, draws conclusions based on the findings, and may include recommendations for future actions.
9. Recommendations
In reports with actionable outcomes, the recommendations section suggests specific steps or strategies based on the findings.
10. References
The references section lists all the sources cited in the report, ensuring proper acknowledgment of external work and adding credibility.
Writing Tips for an Effective Sample Report
Creating a compelling report requires not just proper structure but also excellent writing skills. Here are some valuable tips to enhance your report writing:
1. Know Your Audience
Understanding your target audience is crucial when writing a report. Tailor your language, tone, and content to suit the reader’s level of expertise and interest.
2. Use Clear and Concise Language
Keep your writing clear, straightforward, and to the point. Avoid jargon and unnecessary technical terms that may confuse readers.
3. Organize Information Logically
Present information in a logical sequence, ensuring that each section flows smoothly into the next. Use headings and subheadings to provide a clear structure.
4. Support Claims with Evidence
Back up your statements with credible evidence and data. This adds credibility to your report and strengthens your arguments.
5. Edit and Proofread Thoroughly
Always review your report for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. A well-edited report shows professionalism and attention to detail.
6. Seek Feedback
Before finalizing your report, seek feedback from colleagues or peers. Fresh perspectives can help identify areas of improvement.
Selecting Engaging Report Writing Topics
Choosing the right topic is essential for crafting a compelling report. Whether it’s for academic, business, or research purposes, an engaging topic will capture the reader’s interest and keep them invested in your report. Here are some inspiring report writing topics:
1. The Impact of Technology on Modern Workplace s
Explore how technology has transformed traditional workplaces, affecting productivity, communication, and employee satisfaction.
2. Environmental Sustainability in Urban Cities
Examine the efforts made by urban cities to promote environmental sustainability, including green initiatives and waste reduction strategies.
3. The Rise of E-Learning: A Comprehensive Analysis
Analyze the growth of e-learning platforms, their effectiveness in education, and their potential to revolutionize the traditional learning system.
4. Cybersecurity Threats and Mitigation Strategies for Businesses
Investigate the latest cybersecurity threats faced by businesses and outline effective strategies to safeguard sensitive data and prevent cyber attacks.
5. Mental Health in the Workplace: Strategies for Employee Well-Being
Discuss the importance of addressing mental health issues in the workplace and propose strategies to support employee well-being.
Real-World Examples of Impactful Reports
To gain a deeper understanding of report writing’s practical applications, let’s explore some real-world examples:
1. World Health Organization (WHO) – Global Health Report
The WHO publishes comprehensive reports on global health issues, providing data on disease outbreaks, vaccination rates, and healthcare access worldwide. These reports play a crucial role in shaping global health policies and initiatives.
2. McKinsey & Company – Industry Research Reports
Management consulting firm McKinsey & Company produces insightful industry research reports that analyze market trends, consumer behavior, and business strategies. These reports serve as valuable resources for executives and decision-makers.
3. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) – Climate Assessment Reports
The IPCC releases periodic reports on climate change, assessing its impacts, causes, and potential solutions. These reports are instrumental in guiding environmental policies and international climate agreements.
A Sample Report Writing Format on A Bank Robbery.
The following points will make it easy to write a report easily shown below.
( Heading) DARING BANK ROBBERY
( Who Reported ) By a Special Correspondent
Where, When, What: Kolkata, August 14 (Introduction): A daring (CART) robbery took place today at 3 p.m. at the United Bank of India, Gariahat Branch, Kolkata.
How, why, Casualty: According to the Branch Manager, three men armed with pistols overpowered the security staff and locked the gate from the inside. One of the miscreants (710) herded the customers and the staff into one corner of the bank and kept them silent at gunpoint. The other two miscreants snatched the keys from the Manager.
Condition: Then they unlocked the vault and bagged cash and jewelry worth Rs. 40 lacks. They came out of the bank hurling bombs, jumped into a black Maruti Van, and sped away.
Reaction & Measures Taken (Conclusion): The police arrived within half an hour. No one has been arrested yet. Investigations are on, as the Deputy Commissioner of Police told the media.
People may also like
Report writing types in english:.
Basically, Report writing in English is of three types .
- General Report Writing: These reports give an account of a person’s experience of an event or an incident.
- Newspaper Report Writing: Newspaper reports are based on true incidents or accidents meant to express some information to the public.
- Business Report Writing: Business reports are made on orders based on observation, investigation, and analysis.
General Report Writing Examples
Example 1: Business Report – Market Analysis
Title: Market Analysis for XYZ Company’s Product Expansion
Executive Summary: The market analysis report assesses the potential of XYZ Company to expand its product line into a new market segment.
Introduction: This report aims to investigate the feasibility and potential challenges associated with XYZ Company’s entry into the youth-oriented consumer electronics market.
Methodology: Data was collected through a combination of surveys, focus groups, and secondary research from reputable industry reports.
Findings: The youth-oriented consumer electronics market is growing rapidly, with an annual growth rate of 12% over the past three years.
XYZ Company’s brand recognition is relatively low among the target audience.
The price sensitivity of the target market is a significant factor to consider.
- Analysis: The findings suggest that while there is a lucrative opportunity for XYZ Company to enter the market, it will require a focused marketing campaign and competitive pricing strategies to overcome initial brand awareness challenges.
- Discussion: By leveraging social media and influencers, XYZ Company can effectively reach the target audience and build brand loyalty. Additionally, offering a competitive pricing model will attract price-conscious customers.
- Recommendations:
- Collaborate with popular influencers to gain credibility and reach a wider audience.
Offer attractive introductory pricing and discounts to entice price-sensitive customers.
Conclusion: Entering the youth-oriented consumer electronics market presents a promising opportunity for XYZ Company. By implementing the recommended strategies, the company can capitalize on this potential growth and expand its product line successfully.
Remember that the specific format and content of a report may vary based on the requirements set by your institution, organization, or supervisor. Always check for any specific guidelines before starting your report writing.
Write a newspaper report on the “Annual Prize Distribution Ceremony in your school”
Annual Prize Distribution Ceremony in your school
By Staff Reporter
[City, Date]: The air was abuzz with excitement and anticipation as [Your School Name] hosted its grand Annual Prize Distribution Ceremony yesterday. The event, held in the school auditorium, was a momentous occasion that celebrated the academic excellence and achievements of the students.
Distinguished guests, parents, and faculty members graced the ceremony with their presence. The school principal, in his opening address, emphasized the significance of recognizing and applauding students’ efforts beyond academics.
The highlight of the event was the distribution of prizes to the meritorious students, acknowledging their outstanding performance in academics, sports, and extracurricular activities. The audience erupted with applause as the achievers walked up the stage to receive their awards.
The melodious music, vibrant dances, and thought-provoking skits captivated the audience.
The Annual Prize Distribution Ceremony concluded on a high note, leaving everyone inspired and motivated. It served as a testament to the school’s commitment to nurturing holistic development among its students.
[Your School Name] once again proved that it is not only a center of academic excellence but also a platform for nurturing well-rounded individuals.
By [Your Name]
Write a newspaper repot on “A terrible fire broke out in Kolkata”
Terrible fire breaks out in kolkata, causing extensive damage.
Kolkata, Date: A devastating fire broke out in a commercial area of Kolkata yesterday, causing widespread destruction and panic among residents and businesses. The incident occurred in the bustling market district, engulfing several multi-story buildings.
Eyewitnesses reported that the fire started in one of the shops due to an electrical short circuit and quickly spread to nearby establishments. Despite the immediate response from firefighters, the blaze proved challenging to control, as narrow streets hindered their access.
Local authorities and emergency services rushed to the scene, evacuating people from nearby buildings and providing medical assistance to those affected. Tragically, a few individuals sustained minor injuries in the process.
The fire caused extensive damage to properties, resulting in significant financial losses for business owners. The full extent of the damage is yet to be assessed.
Investigations into the incident are underway to determine the exact cause and potential safety lapses. As the city mourns the loss of properties and livelihoods, efforts are being made to extend relief and support to the affected residents.
1. Write a report for a newspaper about A Terrible Train Accident.
Odisha Train Accident / Coromandel Express Train Accident
Balasore, 3rd June 2023: At around 7 pm, 2nd June on Friday evening 10-12 coaches of the Shalimar-Chennai Coromandel Express derailed near Baleswar and fell on the opposite track. After some time, another train from Yeswanthpur to Howrah dashed into those derailed coaches resulting in the derailment of its 3-4 coaches. The train crash involving two passenger trains and a goods train in Odisha’s Balasore on Friday is said to be one of the deadliest rail accidents in India. More than 230 people have lost their lives in the accident and 900 have been injured. NDRF, ODRAF, and Fire Services are still working to cut the bogie and try to recover the living or the dead. Local people were seen helping the teams responsible for rescue and relief operations and they queued up to donate blood for the injured in Balasore. As a result, Local people became able to rescue 200-300 injured people A high-level committee has been declared to conduct an inquiry into the train accident. The Centre has announced an ex-gratia compensation of Rs 10 Lakh each to the kin of the deceased and Rs 2 Lakh to grievous and Rs 50,000 for minor injuries, Union Railways Minister Ashwini Vaishnav said.
2. Write a report for a newspaper about A Magic Show .
By Anik Dutta
On Friday, November 18: our school authority invited a magician to surprise the students of the school with a magic show. The magic show was a gift to the students from the school’s authoritative body as the school won the award for Best Disciplined School in Kolkata for the year 2015. The magic show was organized on the school’s open-air stage. The show went on for 2 hours, from 12 to 2 pm. The first magic shown by the great magician was pulling out of a rabbit from his hat which was absolutely empty when he wore it. The spectators were pleasantly surprised. He showed exciting magic tricks one after the other and ended the show with a message to the awestruck students, ‘Practice maths well, and you can do magic too as it is nothing but a game of calculation’. The show was immensely appreciated by all.
3. Write a report for a newspaper about Health Issues of the people of your District .
Health Issues of the People of Your District
By Ravi Yogi
On 20 May 2021: a health awareness campaign camp was organized in the Howrah district by the World Health Organisation. Some volunteers were chosen, who from then on, visit each house every month to remind people to get their children vaccinated. People now follow their instructions and keep their surroundings clean to avoid certain diseases. The volunteers distributed water purifiers at a cheap rate so that people could use them to get pure water. The mosquito-repellant sprays are used every month and mosquito nets are now used to keep mosquitoes away. If the volunteers arrange a blood donation camp every month it could help the people in need. Also, a free health checkup camp could be arranged for further health improvement of the people of the locality.
4. Write a report for a newspaper about the Annual sports Event of Your School .
Annual Sports Event of Your School
By Anwesha Das
The annual sports day of our school (St. Agnes H.S. School) was held on February 15 for the junior students at the school grounds. The event for the junior students started at 9:30 in the morning with a relay race. The next race they had was a tricycle race and the last one the junior students had was a treat to watch. The junior ones’ had to run wearing long gowns and they had to run the track without falling even once.
The juniors enjoyed the fun sporting events a lot, while the visitors’ race involving the parents remained the highlight of the day. At the end of the program Chief Guest Sourav Ganguly gave away the awards to the winners and the class teacher of each class distributed a box containing candies, a chocolate pastry, an orange, and two vanilla cream-filled wafer biscuits to every pupil of her class. The event turned out to be a joyful one with a smile on everyone’s face.
Newspaper Report Writing : Format, Topics, Examples
5. write a newspaper report on the first downpour of the season ..
FIRST DOWNPOUR OF THE SEASON
Kolkata, June 13: Today Kolkata experienced its first downpour during the season. The showers were brought about by a deep depression over the Gangetic West Bengal. There was incessant (WESO) rainfall accompanied by thunder and lightning. In Kolkata, it rained throughout the day with occasional breaks. The weather office at Alipore has recorded a rainfall of 20 cm. Many low-lying areas went underwater. Some of the major roads were waterlogged for several hours. There were traffic jams on many roads. The hand-pulled rickshaws had stopped. Train and air services were disrupted. There were cable faults in many parts of the city. Two persons were electrocuted. But they have not yet been identified, said the police officials.
6. As a Reporter for an English daily, write a report about A violent cyclonic storm .
A VIOLENT CYCLONIC STORM
By a Special Correspondent
Katak, August 12: A violent cyclonic storm ravaged the coastal areas of Odisha today. The cyclone started at about 6.45 p.m. It was said to have rushed at a speed of 80 km per hour. The worst-affected areas include Puri, Baleswar, and Paradip. The cyclone raised the sea to an alarming height. The high tidal waves submerged the low-lying coastal areas. It caused incalculable damage to life and property. More than 10,000 people were rendered homeless. Train services were totally disrupted. The State Government sent its rescue team along with central paramilitary forces to tackle the situation. A sum of Rs. 3 crores has been sanctioned for the relief and rehabilitation of the cyclone-hit people.
7. Write a report for a newspaper about A Serious Road Accident
A Serious Road Accident
Kolkata, January 18: As many as 20 persons including two women and a child were injured in an accident at about 8 pm, on M, G, Road yesterday. The accident took place when a speeding minibus, in a bid to overtake a private bus, skidded off the road. The vehicle carrying 45 passengers went straight into a shopping mall, after breaking the roadside railing, Persons inside the mall and the bus suffered serious injuries Local people started the rescue operation. The injured were taken to the nearest hospital. Locals got agitated and blocked the road causing the suspension of traffic for more than 3 hours. However, the police came and brought the situation under control.
8. Write a report within 100 words for an English daily about Cyclone hitting Coastal West Bengal .
Cyclone hits Coastal West Bengal
-By a Staff Reporter
Kolkata, June 12, 2013: A severe cyclone with a speed of 80 km. per hour hit the coastal areas of West Bengal yesterday evening at about 6-45 p.m. Caused by a deep depression in the Bay of Bengal, the cyclone ripped through the state resulting in huge damage to life and property. 60 persons have died and thousands have been rendered homeless. Train services have been disrupted leaving a number of people stranded. The state government has taken immediate steps to provide relief to the victims. More than 5000 people have been evacuated to temporary relief shelters. The Chief Minister has reviewed the situation and assured the people of all help.
9. Write a newspaper report on a road accident within 100 words .
BRAKE FAILURE BUS COLLIDES WITH A TRUCK
By a Staff Reporter
Kolkata, October 1, 2015: Yesterday at around 10:30 am an accident took place at Sinthi More when an Esplanade bound bus, of route no 78/1, suddenly collided with a truck. The report says the brake failure of the bus was the cause of this mishap. Five passengers were injured including a child and a woman. According to passengers, the ill-fated bus was moving at a great speed. Near Sinthi More the driver lost control and banged behind a truck. Local people rushed in, and took the injured to the nearest hospital where they were released after first aid. Traffic got disrupted. Cops reached the spot quickly, intervened, and normalcy was restored within an hour.
10. Write a report on a Railway accident.
A MAN DIED IN A RAILWAY ACCIDENT
By Kishore Ganguli
Kolkata, April 25: A man died after he had been hit by a Sealdah bound train close to Barrackpore station around 5.40 am today when the victim was returning home from a regular morning walk. According to an eyewitness, the man was trying to cross the tracks, got confused, and ended up on the track on which the train was coming on. Being hit on his head, he was hospitalized immediately. But the doctors declared him dead. The locals made a blockade on the railway tracks. The police came, dispersed the irate mob and the train service was restored. The railway authorities announced an exgratia payment of Rs 2 lakh to the next of kin of the deceased. The situation is tense till now.
FAQs about Report Writing
Q: what is the ideal length for a report.
Reports can vary in length depending on their purpose and complexity. However, a concise report of 10-20 pages is often preferred to keep the reader engaged.
Q: Can I use bullet points in my report?
Yes, using bullet points can enhance readability and make key information stand out. However, use them sparingly and only when appropriate.
Q: Should I include visuals in my report?
Yes, incorporating relevant visuals like graphs, charts, and images can make complex data easier to understand.
Q: Can I include my opinion in the report?
While reports should be objective and fact-based, there might be instances where your expert opinion is valuable. If so, clearly distinguish between facts and opinions.
Q: How can I make my executive summary compelling?
The executive summary should be concise yet informative. Highlight the most important findings and recommendations to pique the reader’s interest.
Q: Is it necessary to follow a specific report writing style?
Different organizations or fields may have their preferred report writing style. Always follow the guidelines provided by your institution or industry standards.
Q: What is the main purpose of a report?
A: The main purpose of a report is to present information, findings, and recommendations in a structured and organized manner.
A: Yes, bullet points can help present information concisely and improve readability.
Q: How long should an executive summary be?
A: An executive summary should be concise, typically ranging from one to two pages.
Q: Is it necessary to include visuals in a report?
A: Including visuals such as charts, graphs, and images can enhance the reader’s understanding of complex data.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid in report writing?
A: Common mistakes to avoid include using overly technical language, neglecting to cite sources properly, and lacking a clear structure.
Q: How can I make my report more engaging?
A: To make your report engaging, use real-life examples, incorporate visuals, and use a conversational tone when appropriate.
Students’ Progress Report – A Comprehensive Guide
Our students’ progress report pages are essential for students with special education IEPs.
As students progress through their academic careers, there are many 📝 factors that need to be taken into consideration when determining how well they are performing.
From grades and test scores to attendance and behavior, there are numerous metrics that can be used to assess a student’s progress.
But understanding how to interpret and analyze this information can be daunting for even the most experienced educators.
This comprehensive 📒 guide will help you navigate the complex world of student progress reporting.
In this blog post, we’ll explore what student progress reports are, why they’re important, and how to create a comprehensive report that accurately reflects a student’s performance.
We’ll also examine different methods of students’ progress report examples such as using rubrics.
I’ll also provide recommendations on the most effective strategies to use for different types of students.
Whether you’re a teacher, administrator, or parent, this guide will equip you with the tools you need to better understand how to 🕵️♀️ monitor and support students’ academic growth.
So, let’s get started!

Definition of a Progress Report
A progress report is a document that summarizes a student’s performance and accomplishments during a specific period, typically a 📆semester or year.
It aims to provide an overview of a student’s progress in their academic pursuits and highlights areas of improvement where necessary.
Progress reports serve as an essential communication tool between students, instructors, and parents.
Their purpose is to give an insight into a student’s 💪 strengths, weaknesses, and overall academic performance.
The students’ progress report should be comprehensive, transparent, and factual, reflecting the student’s academic efforts and performance over the reporting period.
A well-crafted progress report can help students 🎯 identify areas for further improvement.
Progress monitoring also provides important feedback to enhance their academic success.
Thus, it is crucial to ensure that a progress report is clear, concise, and accurately reflects a student’s academic progress.

The Purpose of Progress Reports
The purpose of progress reports is an important topic that needs to be 🤔 understood by both teachers and parents.
Progress reports provide an opportunity for teachers to update parents on their child’s academic performance, behavior, and/or any social or emotional issues.
Progress reports can help parents ✅ identify areas of strength and weakness in their child’s learning and provide a guide for areas that need more attention.
They also allow teachers to spot any potential challenges early on and work with parents to develop strategies to help the child succeed.
If students have been identified with a special education need, students’ progress report summaries are a required component of the IEP.
Documenting goals through 💻 progress reporting, typically quarterly, track the progress or lack of progress a student is making.
Furthermore, progress reports can also serve as a motivational tool for students, allowing them to reflect on their progress and set learning goals for the future.
Overall, progress reports are a critical tool in monitoring and supporting students’ academic success.
They ensure a collaborative effort between teachers and parents in achieving positive outcomes.

Types of Progress Reports
Effective progress 📋 tracking is essential part of any educational program to ensure students’ success.
Progress report is one of the important tools that provides regular assessment of student’s development in a given course.
It serves as an effective tool for communication between teachers, students, and parents to monitor academic progress, identify areas of improvement, and set future target goals.
There are three main types of students’ progress report documentations: narrative, single point, and rubric based.
Each of these reports have their own specific features and purposes that serve different needs of academic institutions.
I often use single 👉 point documentation as my go to as I can easily show the assessment score going up or down on a chart.
Parents seem to easily understand this type of students’ progress report.
Also, I add in a short 1-2 sentence narrative summarizing the progress.

Components of a Progress Report
A progress report is a document that provides information on the development and completion of a given project or task.
The report is designed to give a clear 🤳 picture of the status of a project or task and the progress that has been made towards its completion.
In order to create an effective progress report, it is important to include four essential components:
- The date of collection
- The assessment tool
- The students’ scores
- The baseline score
Each of these components provides specific information that is necessary for the progress report to be complete and informative.
Make sure you include all of the information when reporting out on students’ progress report summaries.
Correct documentation is important so that you are compliant with the laws associate with IEPs.
Having all of your documentation recorded properly is essential if there is ever a situation involving due process or educational lawsuits. 👩⚖️

When to Give Progress Reports
Giving ✉️ progress reports to parents and guardians is a crucial aspect of a teacher’s responsibility.
Progress reports communicate how students are performing in relation to their IEP goals.
The ⏳ frequency of progress reports will typically depend on your school district’s policies or the individual student’s needs.
However, it is generally recommended to provide students’ progress report summaries a few times a year.
This allows parents and guardians to have a clear understanding of their child’s continual progress and helps to 🛑 prevent any surprises during report card season.
In addition to regularly scheduled progress reports, it’s essential to consider special circumstances.
This includes changes in behavior or sudden dip in academic performance, necessitating that you share an update with parents or guardians.
Effective communication with parents and guardians through progress reports is a vital component of creating successful student-teacher-parent/guardian partnerships.

Tips for Writing a Progress Report
In order to create an effective progress report, it’s essential to 🏎️ follow a specific set of guidelines.
These guidelines will help ensure that the report is clear, concise, and provides all relevant information for the stakeholders involved.
Here are six tips for ⌨️ writing students’ progress report summaries:
1. Define the purpose and scope of the report: Before writing the report, it’s crucial to determine the purpose and scope. This includes identifying the stakeholders, explaining the goals, and outlining the timeframe.
2. Use a specific format: Decide on a format for the report that works best for the project or program. This could include a table, spreadsheet, or written summary.
3. Include quantitative data and qualitative 🧐 observations: Reports should include data to show progress towards goals. Qualitative observations help to contextualize these data points.
4. Use clear and concise language: Avoid using complex technical jargon or confusing language. Use clear and concise sentences to communicate the information effectively.
5. Include recommendations and future plans: Provide recommendations for next steps based on the report and any identified areas for improvement. This demonstrates a forward-thinking approach to the project.
6. Seek 🙋♀️ input from stakeholders: Before finalizing the report, seek input from the stakeholders involved. Their feedback will provide additional insights and help.
Want to see this set on Caroline’s TPT store? Click here to check it out.

Benefits of Progress Reports
Progress reports are an essential tool used in tracking and reporting students’ learning progress.
They act as a comprehensive guide towards the improvement of the 🎓 learning process and the eventual success of each student.
These reports allow students, parents, and educators to monitor progress, focus on strengths and weaknesses, and adjust strategies.
The benefits of progress reports include providing a transparent method of reporting progress, and creating a collaborative approach between educators, parents, and students.
Additionally, progress reports allow educators to provide feedback to students on their achievements.
This could open the door to provide more support and resources to students who might be struggling.
By using students’ progress report pages, educators can tailor their 👩🏫 instruction to meet the needs of each student.
A personalized learning experience that promotes academic success is what an IEP is all about.

Preparing and Presenting a Progress Report
Preparing and presenting a progress report is a crucial part of monitoring and evaluating the progress of students in any educational institution.
A progress report is designed to provide comprehensive information about the students’ 🏫 academic progress throughout a designated period.
As such, it requires thoughtful preparation and careful presentation to ensure its effectiveness.
It is essential to maintain a 📣 professional tone when writing a progress report to reflect respect and objectivity.
The guide will discuss the 🗝️ key components of a progress report, the importance of collecting and analyzing data, and best practices for presenting information clearly and effectively.
By following this guide, educators can create insightful and meaningful progress reports that support student learning and success.

Challenges of Writing Progress Reports
Writing progress reports is an essential part of special education teacher’s paperwork.
However, these reports can present certain challenges that must be addressed in order to provide accurate and meaningful feedback to parents or guardians.
One common challenge is ensuring that the report accurately reflects the student’s progress without being too ➕ positive or – negative.
Finding the right balance and tone is important.
Avoid giving too much praise as this leads to overlooking areas that need improvement.
Of course, always be careful of being overly critical as this can harm a student’s self-esteem and damage relationships.
Another challenge is ⌚️ time management, as teachers must balance writing detailed and informative reports with other responsibilities.
Ultimately, effective progress reports require educators to not only assess and report on a student’s academic progress, but also their emotional development and behavior in the classroom.

Best Practices for Writing Progress Reports
Writing ✏️ progress reports is an important skill that is essential for effective communication and feedback in academic and professional settings.
Progress reports are used to update stakeholders on project progress, identify issues and risks, and to set expectations for the next phase of work.
In order to write an effective progress report, there are several 🙌 best practices that you must follow.
These include clearly defining your goals and objectives, documenting your progress, highlighting achievements, identifying areas for improvement, communicating regularly, and using visuals to support your content.
This comprehensive guide provides the top ten best practices for writing progress reports that will help you to effectively communicate your progress and results to your stakeholders.
To conclude, a student’s progress report is an important document that 🪞 reflects their academic and non-academic growth.
It provides valuable information for parents, teachers and students to identify areas where improvement is needed and celebrate the areas of strength.
Regular 📧 communication and collaboration between parents, teachers and students can lead to better educational outcomes.
Therefore, it’s important for all stakeholders to understand the purpose and significance of students’ progress report to support the student’s holistic development.

- Special Education
- teaching resources
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Read More Blog Posts Here

Social Emotional Learning Activities for Every Classroom
Social emotional learning activities for teachers in elementary and secondary schools that help students learn how to regulate their feelings and behavior.

PLAAFP Examples to Create Comprehensive IEP Impact Statements
Get best practice tips and examples of PLAAFP so special education teachers can write quality, meaningful IEP impact statements.

Classroom Rules Poster Set to Rule the School
Each school year every teacher must have one essential item for a successful year of learning: a classroom rules poster set. There

Behavior Charts in the Classroom to Enhance Student Success
Behavior charts in the classroom for teachers to use as a method to communicate daily behavior to parents and caregivers.

IEP Accommodation Lists and Tracking for Special Educators
Special education IEP accommodations and 504 accommodations lists and documentation templates for documentation and tracking.

Cue Cards A Visual Behavior Tool for Autism
Cue cards, a remarkable tool for individuals with autism and their caregivers, truly hold the key to unlocking their potential. These magical

Hey, there! I'm Caroline.
I’m a special educator who helps students, teachers, and families live their best lives. I was born and raised on an Indiana farm that been in our family for over 150 years. I love all animals, people with autism, and hot chocolate.
Get your free IEP documents checklist and observation summary template.

Copyright 2015-2023 | Caroline Koehler | All Rights Reserved
Grab your FREE IEP documents checklist & summary template for your SPED paperwork!
Grab your free iep documents checklist & summary template for your sped paperwork.
Add your name and email address below for an instant FREE download.
Search form
Look at the report and do the exercises to improve your writing skills.
Instructions
Do the preparation exercise first. Then read the text and do the other exercises.
Preparation

Check your understanding: true or false
Check your writing: matching - useful language, check your writing: gap fill - making recommendations, worksheets and downloads.
Who would you like to come and visit your school?

Sign up to our newsletter for LearnEnglish Teens
We will process your data to send you our newsletter and updates based on your consent. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the "unsubscribe" link at the bottom of every email. Read our privacy policy for more information.
The Edvocate
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- Write For Us
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Assistive Technology
- Best PreK-12 Schools in America
- Child Development
- Classroom Management
- Early Childhood
- EdTech & Innovation
- Education Leadership
- First Year Teachers
- Gifted and Talented Education
- Special Education
- Parental Involvement
- Policy & Reform
- Best Colleges and Universities
- Best College and University Programs
- HBCU’s
- Higher Education EdTech
- Higher Education
- International Education
- The Awards Process
- Finalists and Winners of The 2022 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2021 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2020 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2019 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2018 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Finalists and Winners of The 2017 Tech Edvocate Awards
- Award Seals
- GPA Calculator for College
- GPA Calculator for High School
- Cumulative GPA Calculator
- Grade Calculator
- Weighted Grade Calculator
- Final Grade Calculator
- The Tech Edvocate
- AI Powered Personal Tutor
College Minor: Everything You Need to Know
14 fascinating teacher interview questions for principals, tips for success if you have a master’s degree and can’t find a job, 14 ways young teachers can get that professional look, which teacher supplies are worth the splurge, 8 business books every teacher should read, conditional admission: everything you need to know, college majors: everything you need to know, 7 things principals can do to make a teacher observation valuable, 3 easy teacher outfits to tackle parent-teacher conferences, 100 report card and progress report comments that teachers can use today.

Having difficulty with writing positive and constructive feedback on student report cards and progress reports? Use our ideas.
- The learner takes an active role in discussions.
- Learner consistently cooperates with the teacher and other students.
- Learner listens well and shares ideas frequently.
- The learner works democratically with peers.
- Learner shows self-confidence in…
- The learner works well in groups, planning and carrying out activities.
- Learner follows directions well.
- The learner is an enthusiastic learner who enjoys school.
- Learner tackles new challenges with a positive attitude.
- The learner has a positive attitude about school.
- Learner consistently makes good choices during the school day.
- Learner shows respect for peers and teachers.
- Learner transitions easily between classroom activities and is not a distraction to others.
- The learner is sensitive to the thoughts and opinions of others.
- The learner is a leader and positive role model for students .
- The learner is enthusiastic about participating.
- The learner takes an active part in discussions about (topic).
- Learner speaks with confidence.
- Learner volunteers often.
- The learner has a great sense of humor and enjoys our class assignments.
Needs Improvement
- The learner has difficulty staying focused and on task. · Needs to actively participate in classroom discussion.
- The learner needs to work on not distracting others during class.
- The learner is learning to be careful, cooperative, and fair.
- The learner needs to work on…
- One area for improvement is…
- The learner is eager to participate in class but needs to raise their hand.
- The learner is becoming more independent when completing class assignments.
- The learner needs frequent reminders to stay focused throughout the day.
- Learner, when motivated, does well on class assignments.
- The learner needs to work on following written and oral directions.
- Needs to actively participate in classroom discussions.
- The learner has frequent absences that are affecting (name’s) schoolwork.
- The learner needs to work on treating others with respect.
- The learner needs to work on completing homework assignments on time.
- Learner frequently comes to class unprepared .
- Learner often seems tired at school.
- The learner gets upset quickly when (topic).
- Although _____________’s growth in social skills and maturity is continuing, it is not consistent.
- _______ continues to make progress this year concerning their attitude in the classroom and on the playground.
Time Management/Work Habits
- The learner uses class time wisely.
- The learner is a self-motivated student.
- Learner completes work on time.
- The learner is very organized.
- Learner demonstrates problem-solving skills and is persistent.
- The learner has done a great job facing and overcoming significant challenges this year.
- The learner is very responsible and turns in work on time.
- The learner is flexible and adapts to changes quickly .
- The learner has made improvements in the area of…
- The learner has strengthened their skills in…
- The learner does not complete assignments on time. Seems unable to finish.
- The learner is encouraged to use time wisely to finish tasks in the time required.
- Learner struggles to stay organized and find appropriate materials (paper/pencil).
- The learner needs to slow down to improve the quality of their work.
- The learner is not working to their full potential.
- The learner is easily distracted.
- The learner needs to listen and follow directions more carefully .
- The learner needs more opportunities to…
- Learner grades are suffering because of missed assignments.
- The learner would benefit from…
Growth Mindset
- The learner has demonstrated excellent progress this year.
- The learner is learning how to be a better listener and takes direction well.
- The learner has worked very hard this year and has made substantial gains in the area of ______.
- The learner has shown significant improvement with ______.
- The learner is progressing nicely and shows consistent improvement in many areas of schoolwork, including ______.
- The learner is learning to be cooperative when working in groups.
- The learner is developing more positive ways to interact with others.
- The learner is listening to directions more carefully.
- The learner has continued to make steady progress with…
- The learner has shown noticeable improvement in…
General Subject Area Comments
- The learner has good reading and decoding skills.
- The learner is reading well at level…
- The learner uses reading strategies to increase their reading comprehension.
- The learner is reading smoothly and with good expression.
- Learner struggles with reading comprehension.
- The learner needs to read for 15 minutes each night.
- The learner is choosing books that are too simple for their level.
- The learner has difficulty using reading strategies to decode new words.
- The learner needs to learn essential sight words to improve decoding skills.
- The learner needs to build reading vocabulary.
- The learner uses various strategies to solve one- and two-step word problems.
- Learner demonstrates a good understanding of math concepts.
- Learner demonstrates problem-solving skills.
- The learner has strengthened their critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- The learner has difficulty understanding/solving word problems.
- The learner understands skills and strategie s but has a difficult time explaining processes.
- The learner would benefit from memorizing math facts.
- The learner has difficulty solving multi-step problems.
- The learner needs to slow down and check work.
- Learner memorizing basic math facts would be helpful to…
- The learner is willing to learn new writing skills and quickly applies these skills within their writing.
- The learner understands and applies the correct use of punctuation within the writing.
- Learner writing is clear and follows grammar and punctuation rules.
- Learner enjoys writing stories and can construct unique and exciting sentences.
- The learner can create precise and compelling writing that is interesting to read and easy to comprehend.
- The learner has shown significant improvement with their writing skills and consistently increases their writing comprehension and techniques.
- The learner has difficulty writing clear and understandable sentences.
- Learner words are often misplaced throughout their writing.
- Learner frequently displays grammatical errors within their writing.
- The learner needs to slow down and review their writing.
When To Take The MCAT
100 accommodations for students with learning and ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

How Effective Teachers Communicate Their Needs to Their Principal

Attributes of an Effective Teacher, Part 1: What You Need To Be

How can schools fight obesity AND unhealthy body image?

My Vision for the Future of Teacher Education
How to craft a culturally-responsive teaching approach.

Why teachers are unable to stop bias-based bullying
- Prodigy Math
- Prodigy English
From our blog
- Is a Premium Membership Worth It?
- Promote a Growth Mindset
- Help Your Child Who's Struggling with Math
- Parent's Guide to Prodigy
- Assessments
- Math Curriculum Coverage
- English Curriculum Coverage
- Game Portal
107 Report Card Comments to Use and Adapt

Written by Justin Raudys
Reviewed by Sarah Tino, M.Ed.
See your students' performance at a push of a button
With Prodigy's reports, teachers can easily track student progress and see their strengths and growth opportunities – all while the student has fun playing Prodigy Math!
- Teacher Resources
Learning skills (positive comments)
Learning skills (needs improvement), addition and subtraction, skip counting, place value, comparing numbers, addition with regrouping.
- Word problems
- Language (general)
Reading responses
Reading comprehension, response journal, note taking, distance learning.
- Tips for writing effective report cards
- Key considerations for effective end-of-year report cards
Just about every teacher agrees: report card comments are important to provide insights and next steps to students and families. But there are few who actually look forward to writing them.
Because every instructor knows working under tight deadlines to create upwards of 20 unique and detailed reports at the end of the year or term isn’t exactly straightforward (or particularly fun). That's especially true in the era of distance learning.
And while no one at your school knows your students better than you do, writing valuable report card comments for each of them can be a huge challenge.
That’s why we created a list of 107 sample report card comments — starters to help you find ideas, inspiration, and insights while writing your own report cards.
The 107 report card comments in this list will help you:
- Instill a growth mindset in students
- Build stronger home-to-school connections
- Write stronger leads and use livelier language
- Choose the right phrasing when writing positive and constructive report card comments
Report card comment starters
You'll notice that the report card comments below can act as a springboard for more fully developed ones. But don't worry, using them you'll be able to take some of these one-liners and turn them into insightful and actionable next steps!
For example, you'll be able to take a 1st grade number sense comment like "Your child is able to add and subtract numbers up to 20 using various manipulatives" and transform it into:
Your child is able to add and subtract numbers up to 20 using various manipulatives. This was evident when he was working independently to solve a real-world problem by adding toys in the classroom toy bin. As a next step, they should continue to add to larger numbers to encourage his skills. You can support him by asking him to add his own toy piles at home.
Or taking a responsibility-related learning skill comment from "Your child is able to take responsibility for her own actions both in and out of the classroom" to:
Your child is able to take responsibility for her own actions both in and out of the classroom. She often checks her agenda and day planner to make sure she has all of the necessary materials to complete work at home before leaving. During indoor recess, she takes time to tidy up everything she was playing with.
Notice the difference?
Compared to a single number or letter grade, report card comments can provide even more value to your students and their families. In other words, a number or letter or grade captures the what , while an accompanying comment captures the how .
Depending on the age group or grade level you teach, a letter or grade letter might be enough. However, research in Phi Delta Kappan, the professional journal for educators, suggests:
Comments that identify what students did well, what improvements they need to make, and how to make those improvements, provided with sensitivity to important contextual elements, can guide students on their pathways to learning success and ensure that all learn excellently.
Gather insights into student performance all year long and make report card writing easier with Prodigy, the adaptive math game that students love.
- ________ is confident, positive and a great role model for his/her classmates.
- ________ is frequently among the first to help and mentor other classmates. He/she is a valuable part of the classroom.
- ________ has shown excellent ability to set goals and be persistent in achieving them.
- ________ is interested in his/her own learning, listens attentively, and makes a solid effort to avoid distractions that could interrupt the learning process.
- ________ is accountable and responsible. He/she makes smart decisions, admits mistakes and listens to opportunities to improve.
- ________ relates well to classmates and is appreciative of different perspectives and experiences.
- ________ manages his/her emotions maturely and responds to feedback appropriately.
- ________ always looks for ways to be helpful in the classroom.
- ________ is dependable and reliable, follows directions effectively, and follows through on his/her commitments to him/herself and others.
- ________ is thoughtful, insightful and thorough in written and verbal communication, and has a talent for expressing his/her ideas clearly.
- ________ works well with classmates in group work and often takes a leadership role.
- ________ shows a positive attitude with classmates in group projects and activities, and both takes and gives suggestions and directions effectively.
- ________ shows maturity when solving problems with classmates and uses good communication.
- ________ excels at applying what he/she learns in the classroom to real-world and real-life situations.
- It has been a pleasure to have _______'s enthusiasm, positivity and maturity in my class.
- ________ is an enthusiastic member of the class and shows a willingness to learn.
- ________ shows responsible behavior, works well with a group and shows appreciation for the efforts of classmates.
- ________ is focused during classroom activities and willingly participated in class discussions.
- ________ performs independent work with confidence and focus.
- ________ works independently and takes pride in work done well.
- ________ is focused in class and willingly participates in group discussion.
- ________ is very conscientious and shows excellent effort and care with daily work.
- ________ demonstrates a willing and conscientious effort in his/her daily work.
- ________ shows a conscientious effort to learn.
- ________ has done a great job facing and overcoming big challenges this year. Please continue to nurture and encourage this behavior over the summer.
- ________ shows responsibility and follows directions whenever they are given.
- ________ listens to and follows directions precisely and attentively.
- ________ follows directions promptly and accurately.
- ________ is an active participant in class.
- ________ is a hard worker who calmly perseveres through challenging topics.
- ________ is encouraged to demonstrate more responsible attitudes and behavior in the classroom.
- ________ needs to show more appropriate behavior when interacting with classmates.
- ________ needs to pay attention to the use of appropriate language at all times
- ________ requires encouragement to listen attentively during group sharing times.
- ________ needs to listen to directions more attentively during lessons.
- ________ would benefit from showing a greater desire to contribute ideas in class.
- ________ needs frequent reminders to be attentive during instructions and lessons.
- ________ needs to improve his/her cooperation in group settings. He/she should work on voicing feelings and opinions and listening to others.
- ________ needs to improve his/her work with others. He/she must ensure to accept a share of the work when participating in a group assignment.
- ________ needs to improve on working independently and be sure to ask for assistance only when it is needed.
- ________ often struggles to focus in class, which harms his/her ability to engage well with class activities and assignments.
- ________ is encouraged to use time wisely to finish tasks in the time required.
- ________ is encouraged to be more responsible in completing tasks without needing regular reminders.
- ________ needs to show by the quality of work and use of class time that he/she is properly engaged in the learning process.
- ________ consistently needs reminders to focus on time management.
- ________ needs to follow classroom rules more closely throughout the school day.
Math (general comments)
- ________ is having considerable difficulty with math. I recommend he/she work on studying ________ and ________. This extra practice will help him/her feel more relaxed when doing math in the classroom. Please contact me if you need materials to get him/her started.
- ________ has a good understanding of all math concepts taught so far this year. He/she continues to turn in excellent assignments and especially enjoys hands-on math activities.
- ________ has a positive attitude towards math but continues to have trouble in a few key areas. He should practice every evening at home. Areas that need extra attention are ________ and ________ .
- ________ demonstrates a good understanding of all math concepts studied and communicates with clarity and good justification of reasoning.
- ________ needs to work on increasing his/her speed in math facts. He/she should continue with daily practice with a focus on addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
- ________ seems to need continuous encouragement in math. He/she continues to struggle with basic math concepts for his/her grade level.
- ________ is having a difficult time in certain areas of math. Areas in need of extra work are ________ . Working on these problem areas every night would help improve his/her learning outcomes.
- ________ is struggling to keep up in math. He/she could benefit from practicing the multiplication table and should also continue to practice the long division process.
- ________ is easily distracted during math lessons and behavioral issues are interfering with his/her learning. We will be working on more difficult subjects and he/she will struggle if he/she does not pay attention in class.
- ________ is having trouble with math tests. He/she does well on assignments, but does not seem to retain information for tests. I always give a week’s notice before tests, so please be sure ________ studies and adequately prepares for them as they approach.
- ________ is able to calculate addition and subtraction facts to 18 with confidence and accuracy.
- ________ is becoming more able to calculate addition and subtraction facts to 18 with confidence and accuracy.
- ________ requires more time and practice in calculating addition and subtraction facts to 18
- ________ needs to put more effort into learning to calculate addition and subtraction facts to 18.
- ________ is able to skip count forward and backward by twos, fives, tens, and hundreds to complete short patterns.
- ________ is learning to skip count forward and backward by twos, fives, tens, and hundreds to complete short patterns.
- ________ needs practice with skip counting forward and backward by twos, fives, tens, and hundreds to complete short patterns.
- ________ needs considerable practice with skip counting forward and backward by twos, fives, tens, and hundreds to complete short patterns.
- ________ is able to demonstrate place value concepts to give meaning to numbers from zero to 1000, identifying ones, tens, and hundreds.
- ________ is developing an understanding of place value concepts to give meaning to numbers zero to identifying ones, tens, and hundreds.
- ________ requires more time and practice to demonstrate place value concepts to give meaning to numbers 0 to 1000, identifying ones, tens, and 100s.
- ________ is able to compare numbers to 1000 using terms such as greater or less and greatest or least.
- ________ is learning to compare numbers to 1000 using terms such as greater or less and greatest or least.
- ________ requires support to compare numbers to 1000 using terms such as greater or less and greatest or least.
- ________ demonstrates a limited understanding in comparing numbers to 1000 using terms such as greater or less and greatest or least.
- ________ can demonstrate and explain the process of addition of whole numbers up to 100, with and without regrouping.
- ________ requires ongoing support to demonstrate and explain the process of addition of whole numbers up to 100 with and without regrouping.
- ________ requires considerable attention and individual instruction to demonstrate and explain the process of addition of whole numbers up to 100 with and without regrouping.
Word problems (math)
- ________ is able to complete word problems using one- and two-digit addition, showing his/her work and writing a full sentence answer.
- ________ is becoming more confident in his/her ability to complete word problems using one- and two-digit addition, showing his/her work and writing a full sentence answer.
As we move into language and literacy, the following sections include starter report card comments which cover reading, writing, oral communication and critical thinking skills.
Language arts (general)
- ________ ’s (comprehension, spelling, reading) has greatly improved, but he/she still needs extra work in (comprehension, spelling, reading). Please contact me if you need supplemental learning materials to use at home for practice.
- ________ is conscious of putting care into his/her daily writing work, and frequently goes beyond the minimum requirements for assignments.
- ________ has trouble with his handwriting. I believe he/she can form letters well, but has to slow down and take a little more time. Neater handwriting will improve his/her schoolwork overall.
- ________ makes a good effort to make his/her handwriting legible. He/she is able to print on the lines, use good spacing, and form letters correctly.
- ________ needs to focus on her spelling. More improvement is needed in the areas of (dictation, weekly spelling tests, sentence structure). Daily practice at home will help improve his/her results.
- ________ shows the ability to quickly use spelling, punctuation and grammar rules that were recently taught. He/she is able to quickly learn new skills and is eager to apply them to his/her writing.
- ________ is having considerable difficulty with reading, particularly with fluency and comprehension.
- ________ speaks well in front of the class, but requires improvement in written language. He/she is having trouble with (dictation, copying words correctly, story writing, creating logical sequences). Further practice is needed in this area.
- ________ continues to make excellent progress in spelling and reading. He/she works hard to submit work that is free of grammatical errors.
- ________ has difficulty remembering previously discussed writing skills and often makes errors with punctuation, grammar, and overall sentence structure. Basic writing skills need improvement.
- ________ is able to offer direct responses to his/her readings and supports ideas with sound reasoning and specific examples.
- ________ is learning to offer more direct responses to her reading experiences supported by reasons, examples, and details.
- ________ needs frequent support to offer direct responses to his/her reading experiences supported by reasons, examples, and details.
- ________ shows good ability when completing reading comprehension tests.
- ________ would benefit from extra practice with reading aloud and discussion of content.
- ________ consistently demonstrates comprehension of short spoken texts by answering questions, and explaining the events described.
- ________ consistently reads grade-level material independently.
- ________ uses good editing skills and correctly places capitals, quotation marks, question marks, apostrophes, commas, and periods.
- ________ is doing a good job of breaking a story into paragraphs
- ________ determines various forms of writing and identifies important ideas through the development of insightful questions and answers.
- ________ is able to analyze character actions, story plots, and shows strong fluency with reading.
- ________ uses correct spelling, grammar and punctuation when writing simple sentences.
- ________ is encouraged to show increased attention to the use of correct spelling, grammar and punctuation with general writing skills.
- ________ needs more time and practice in the use of correct spelling, grammar and punctuation with general writing skills.
- ________ requires considerable assistance to achieve the correct spelling, grammar and punctuation when writing simple sentences.
- ________ shows an excellent understanding of note taking from lectures and readings in preparation for tests and assignments.
- ________ requires ongoing support to develop an understanding of note taking from lectures and readings in preparation for tests.
- ________ was very engaged and focused during distance learning activities, and participated in class discussions.
- ________ stayed motivated to complete assignments during distance learning, and turned in all required materials on time.
- ________ needed some extra prompting to stay engaged during online lessons, but participated well in discussions when called upon.
- ________ modeled good online learning behavior for other students.
- ________ was disruptive during online learning and did not meaningfully participate in class discussions.
- ________ handled technical problems well and was always prepared.
- Although he/she couldn’t always access a device, _________ consistently completed online assignments and asked thoughtful questions.
- ________ should ask more questions during online discussions to avoid confusion later.
- ________’s attendance during online lessons was infrequent and assignments were not always completed.
- ________ worked well independently and in a group setting during distance learning activities.
- ________ is excellent at completing distance learning activities independently, but struggled to engage with his/her classmates during breakout sessions or class discussions.
- ________ is a technology superstar! He/she rarely needed assistance and even helped other classmates troubleshoot issues.
- ________ asks good questions and always reaches out proactively when he/she needs help with an assignment or lesson.
Tips for teachers to write more effective student report card comments
1. give yourself extra time and start writing comments early.

Somewhere around the halfway point to your deadline for report cards, you make your best effort to use time at the end of each week to reflect — and jot down notes — about your students’ performance and class week.
What are their strengths and weaknesses? How are their social skills developing with classmates? How is their class participation - are they an enthusiastic learner? Have they shown great improvement in one particular subject area? Are homework assignments getting done? Have any new challenges come up that affect learning?
Even just a few minutes of note-taking in the weeks preceding report card deadlines will help to ease your stress when the time comes to write your final comments.
Moreover, having a dated log of information detailed throughout the school year will help you remember how students are performing throughout each week, which can be valuable information come parent-teacher conference time.
This will also help to engage and reassure parents who want relevant and detailed commentary about their child’s performance at school.
2. Use free, curriculum-aligned apps for teachers
Use Prodigy to write insightful report cards with a minimum of hassle. Prodigy Math is an engaging math adventure for students where success depends on correctly answering adaptive math questions.
As students play, you’ll get insights into:
- Which skills students are practicing
- How far they’ve progressed through the curriculum
- What they’ve mastered and where they need more support
Use one of Prodigy’s eight reports to track student progress throughout the year. When the time comes to write report card comments, you’ll have detailed reports on all your students’ achievements.
Just getting started with Prodigy? No problem! The first time students explore the world of Prodigy Math, they’ll start completing the Placement Test — without even knowing. Once they’re done, you’ll have a snapshot of the grade level they’re at, what they know and specific skills they still need to work on.
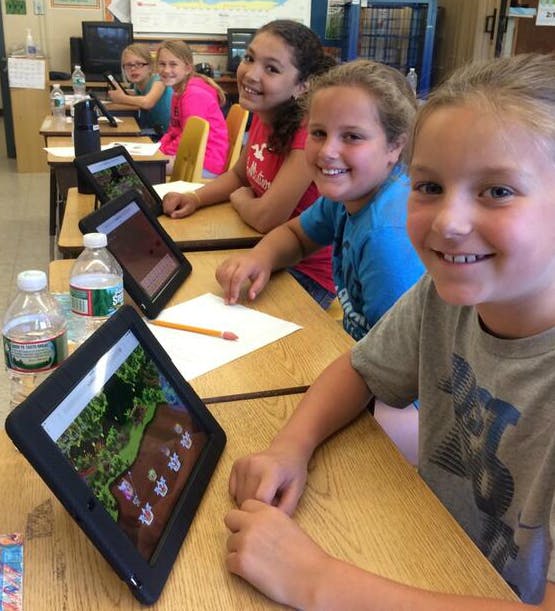

Spend more time teaching and less time grading
Prep for standardized tests, deliver adaptive skill practice or test students on a new skill — all while they play Prodigy Math, Prodigy English, or both!
3. Be encouraging, informational and professional

Although every report card cannot be glowingly positive, do strive to write in an encouraging and informational tone. As you write constructive report card comments, use encouraging language that focuses on the student’s opportunity for improvement.
For example, instead of describing a student struggling with listening as a “bad listener,” remark that the student “would benefit from listening more carefully.”
If appropriate, frame a negative comment in terms of what students are doing well -- and consider how this more successful characteristic can help them bolster performance in other areas.
4. Use a consistent format

Lead your report card comments with the positive comments, followed by areas that need more attention.
Choosing the right format for reporting information will simplify the entire process, while resulting in a clearer and more organized final product.
If you are unclear about your school’s format for report cards, request samples or consult with other teachers or staff members to clarify.
5. Be honest

Being open and honest about a student’s performance requires tact and consideration with regard to how you express those comments. Be transparent, and remain mindful that your goal is to improve your students’ learning experience.
Openness and honesty are key to ensuring that experience is the best it can be. If possible, discuss what intervention strategies you can use to help improve the student’s learning outcomes.
As elementary teacher Donna Donaghue remarks in her book A Guide for Beginning Elementary Teachers: Getting Hired and Staying Inspired :
If there is a problem, most parents will be grateful to you for telling them and will want to help you correct it as soon as possible. Many problems that show up at school are also problems noticed at home, so your comments will not surprise parents. Ideally, at some point prior to receiving the progress report, parents have already discussed the problem with you.
6. Move on if you get stuck
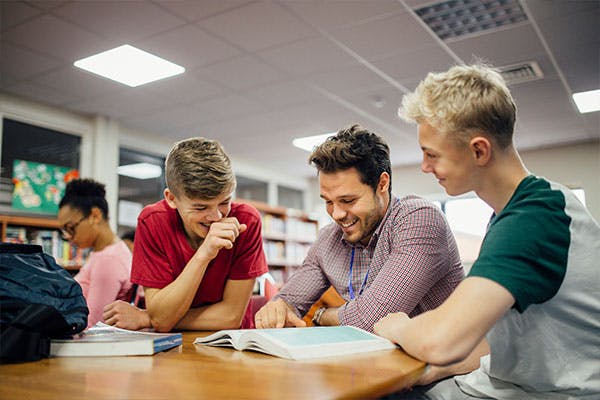

If you get stuck completing the comments for a particular student, move on to your other students and return to it later. You will likely have more trouble completing comments for students who have multiple areas needing further improvement and attention.
Feel free to move on and return to those students periodically or as you find the right language to express your insights.
7. Keep parents and guardians in mind

While every report card comment is ultimately about your student, think of your students’ parents or guardians as much as possible and offer suggestions for their participation.
In fact, if you can, keep parents up to date on an ongoing basis. This will help ensure they don't get caught off guard by any of your comments.
As you make note of your students’ strengths and weaknesses, endeavor to include practical insights into how parents can involve and support their child at home. If possible, make reference to how you use differentiated instruction to support the student in question.
Simple examples of tips for parents include:
- "Encourage your child to read. It doesn't have to be on your own either. Dedicating time before bed to read together can help make it seem like less of a chore."
- "Find homework help for your child if needed. Myself and other parents who are also getting homework help for their child are great resources to get started."
- "Ensure that your child completes their homework by creating a homework routine with your family where incentives like TV or computer time come after homework."
- "Help your child with organization skills at home. If a room in your house could be tidier, try using that as an opportunity to sort things like toys or dishes and utensils."
- "Help your child prepare for math tests by focusing their skills in addition and subtraction. If they don't like studying with traditional worksheets, try a digital game-based learning tool to help get them excited about the process."
As high school educator and teaching comprehension expert Anne Goudvis writes in her book Strategies That Work:
It is important that you include the parents in your comment so they know the child’s education is a joint mission. Sometimes you need to sound firm so that parents know you need their help and that you will not allow their child to continue inappropriate behavior.
8. Try not to repeat yourself

It is unlikely that your students or parents will compare their report card comments, but it is still a best practice to aim for unique commentary for each student that reflects each, individual learning outcome.
9. Proofread, even if you don’t want to
Report card time is perhaps your busiest period of the year, and it is understandable that you want to simply get them over with.
Despite this, you should make sure to double check all your comments before hitting print and handing them out. All your communications to parents are a reflection of you as a teacher, and should mirror the care and attention you show your students in class.
10. Notify parents

Make use of your school’s parent portal or email system to let parents know — as needed — that report card time is coming up.
This will help parents be prepared, and will also ensure that any important questions they may have are addressed before the final report cards are delivered.
Did you know?
If you're using Prodigy Math in your classroom, you can connect parents to follow their child's progress. A free parent account comes with a monthly report card and insights into classroom learning, helping them stay informed of how their child is doing in class. They can also send their child an encouraging message to cheer their child on as they play and practice skills in Prodigy!
11. Use specific examples with the help of direct observation
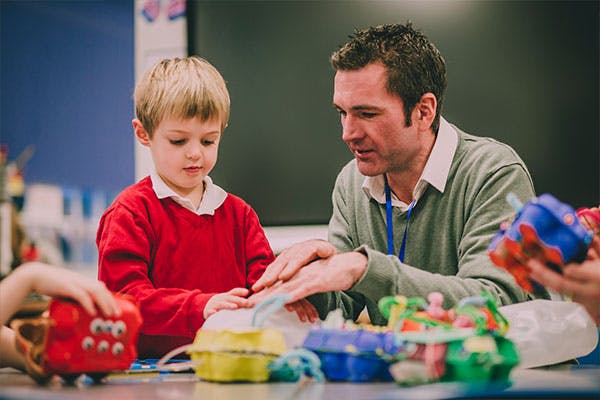

Record and use classroom anecdotes in your assessments. No matter how involved you are in your students’ progress, it can still be difficult to produce specific examples related to their performance if you haven’t recorded them along the way.
When you notice a positive or negative skill, ability, strength, or weakness in a class activity or assignment, be sure to note it down so that you may refer to it in your report card comments. Likewise, consider noting a sample of a student’s work every week or two.
To help with ease of access, keep ongoing files of this work in a personal folder or use a digital tool such as a Google Doc.
Putting this into practice is a time-saver and helps prevent last-minute stress. A strategy like direct observation and note-taking (as soon as possible) is far more reliable than trying to recall information and behaviors from weeks or months prior.
12. Try using tech to help
Writer's block happens to all of us, including teachers. If the report card comments in this article didn't help, fear not, there are still plenty of tools and resources to give you a helping hand.
One new option for teachers is using artificial intelligence (AI) to assist with report card ideas. For example, teachers can use tools like ChatGPT to generate examples for their specific needs.
When using chat technology, try to keep your prompt concise and easy to follow. A good template prompt to follow is:
"Write [number] report card comments for students studying [subject] in [grade]."
Here are some more specific examples to help get you started:
- Write 50 report card comments for students studying social studies in 5th grade.
- Generate 20 report card remarks commending a student for a positive attitude to learning.
- Create 10 report card comments that focus on a student needing to improve their attitude to learning.
Alternatively, you can use spreadsheets and report card builders to manually piece together a report card based on a template of comments.
Important tip: When using AI chat technology, make sure you don't submit any personal details about you or your students. Instead let the tool use a placeholder like "Student".
Key considerations for report card comments at the end of the year
Report card comments should aim to deliver feedback to students and parents that is personalized, detailed, and meaningful .

Writing report card comments doesn’t have to be stressful. Use these strategies to create livelier, more meaningful evaluations.
Effective report card comments emphasize and discuss:
- The specific, notable strengths that a student has shown and should attempt to continue to show
- The specific elements of knowledge, skills, and other outcomes recognized in the curriculum that are the most pertinent to a student’s achievement or development in the period of assessment
- The major next steps for improvement that will: identify the student’s most important learning needs, offer next steps for students and offer specific recommendations for how parents and guardians can help the student’s learning habits and skills (or the development of those habits and skills)
Effective report card comments are personalized – customized to each, individual student – and discuss:
- The student’s learning preferences, willingness to learn, and interests
- Detailed evidence of learning or skill-development gathered from in-class observations, and/or student assignments
Effective report card comments are expressed with clear and simple phrasing, using:
- An encouraging and/or positive tone
- Language that is easy to understand for both students and parents, as opposed to educational jargon used from the curriculum
Report Card Comments: Final Thoughts

Common Sense Education observes that "effective parent communication is crucial in helping students learn. But, for busy teachers it can be challenging just to keep up... Transparency and equity are key to managing any communication between home and school."
Personalized report card comments that are clear, precise, and meaningful are essential for informing students and their parents about what students have learned, what their strengths are and how they can effectively progress.
Among the pressure and deadlines of writing report cards, it can be helpful to keep these key goals in mind.
Get inspired by the report card comment examples — and strategies for success — above to ensure that precision, clarity, and meaning shine through in your report card comments.
When it comes time to hand out your report cards, you can do so with the full confidence that you are doing yourself — and each of your students — the justice your hard work deserves.
Gather student insights on Prodigy
Create or log in to your free teacher account on Prodigy — a standards-aligned, game-based learning platform that assesses student progress and performance as they play. Use Prodigy to motivate student learning, control the questions they answer as they play and collect student learning insights all year long.
How back-to-basics literacy and numeracy teaching transformed a struggling public school
When Manisha Gazula first took over as principal at one of Australia's most disadvantaged primary schools, a majority of students were moving on to high school with sub-par reading skills.
"If we were sending 100 kids to high school, 90 of them couldn't read or write as per their age — and that's failing those students," she said
Today Marsden Road Public School is a school transformed, with students achieving above the state average in writing and making above average progress in reading and numeracy.
Ms Gazula credits the shift to an approach to learning she calls the "Marsden Way".
About 90 per cent of the outer western Sydney school's students speak a language other than English and of those, 40 per cent have been speaking English for fewer than three years.
One in five students come from refugee backgrounds or have had "refugee-like experiences", Ms Gazula said.
"I've got students who have enrolled, 10 years old, and have never held a pencil or seen a book in their life," she added.
Today, every minute of the students' time is planned to make sure they make the most of their education.
At the beginning of the year all students get a two-week crash course in the Marsden Way, including basic skills such as learning to walk between classes quietly, in neat double lines, and to politely greet the teachers.
The time spent emphasising discipline has meant the school has one of the lowest suspension rates in the country.
"I don't accept mediocrity," Ms Gazula said.
"To say that our kids cannot perform, we cannot have the same expectations as the kids living on the other side of the bridge — I will not accept that."
Year 3 kids now outperforming the 'good schools'
The biggest change Ms Gazula made when she took over in 2016 was abandoning fashionable teaching practices like whole language.
Popular in the 1970s and still used in many schools today, whole learning's core philosophy is that reading is easy and natural, and students can teach themselves to read by being surrounded by good books.
Ms Gazula and many experts disagree, believing that reading is a difficult skill that must be explicitly taught.
"You wouldn't do that [whole learning] when you're trying to teach a child to play piano or to play any other instrument or to do something new — you would go step by step," Ms Gazula said.
"Yet when it comes to learning Maths or English, somehow we feel that different approaches are okay."
A recent Grattan Institute report sheeted home the blame for 30 per cent of Australian students not being able to read proficiently to whole language instruction.
It was no surprise to Ms Gazula, who adopted an explicit instruction teaching model known as the science of reading.
It takes the opposite approach to whole language – theorising that learning to read is hard and needs to be taught directly over two or three years.
The style incorporates old school practices — the teacher is firmly in charge — but it also incorporates the latest science on the way kids' brains best absorb new information.
Since adopting explicit instruction the school has transformed its NAPLAN results and sustained them, with life-changing results for students.
The school's year 3 and 5 students have outperformed the state in writing over the past three years, Ms Gazula said, and writing proficiency is over 60 per cent.
"So 60 per cent of year 3 kids — kids who couldn't speak English — are writing better than the so called good schools," Ms Gazula said.
Deputy Principal Troy Verey, who has been at the school for 11 years, said it was rewarding to see brighter futures.
"One of the aims at our school is we want a life of choice, not chance," he said.
"So if they know how to read and write and are numerate, they'll have more choices going ahead. Whether they want to be a tradie, whether they want to be a doctor."
Parents grateful for outstanding results
During a recent visit to the school the ABC met many parents who sung the Marsden Way's praises.
Ghanaian immigrant Victor Boateng is a huge fan of the school and what it has done for his four children.
"If they've got the good foundation, the numeracy and literacy, which is so important for them, you can go far," Mr Boateng said.
"Thanks to Marsden Road public school for helping me to shape my child, for helping me to bring up good kids."
Mum Ashty Fathi, pictured with her sons Omar (10) and Osman (5), likes the school's structure and routine.
Victor Boateng is a fan of what Marsden Road has done for his four children Anderson (year 6), Ruth (year 4), Alexander (year 2) and King George (kindergarten).
Mum Jaclina Trpeska, pictured with her son Sashe Andonov, initially planned to send her kids to private school, but is glad she chose Marsden Road.
After doing a work experience placement at Marsden Road, mum Ashty Fathi was so impressed she moved her oldest son to the school.
"I was determined to bring him here," she said.
"I wanted him to have the best education and I knew at Marsden Road they would provide that."
Mum Jaclina Trpeska is another thrilled parent, who is glad she didn't go through with her initial plan to send her two kids to private school.
"I have friends that live in the area and I've seen what their children do at school and when I show them what my kids are doing here they're shocked," she said.
"They say, 'Wow you're learning so much.'"
From struggling to 'punching above their weight'
The school also has some high-profile admirers like NSW Education Department Secretary Murat Dizdar, one of the most senior education bureaucrats in Australia.
He wants to replicate the Marsden Way elsewhere.
"The vast majority [of students] … are struggling with socio-economic complexity, and this school is punching above their weight," he said.
Mr Dizdar, a former teacher who went to public school himself, is passionate about the transformative effect of a good education.
As a young educator aiming to move on from his housing commission upbringing, he worked two jobs, picking up early morning shifts as a garbage collector before travelling to the high school where he taught.
"Post code, socio-economic disadvantage, English as an additional language, new arrivals, refugees … need not be a barrier or an inhibitor to having a rich education passport," he said.
"In fact, education is the greatest leveller."
ABC News can reveal Mr Dizdar is mandating that all teachers in New South Wales undertake explicit instruction training immediately after the Easter holidays.
"On day one, term two, which is a school development day, right across 2,200 schools, we will be undertaking explicit teaching learning, in every single school in New South Wales," Mr Dizdar said.
The teachers at Marsden Road hope it will lead to similar success at other schools.
"I tell the kids, 'I cannot change your family background or where you come from but what I can do is help you get out of that and make a better life for yourself'," Ms Gazula said.
"And parents want that too."
- X (formerly Twitter)
- Mathematics Education
- Public Schools
The Hechinger Report
Covering Innovation & Inequality in Education

OPINION: Artificial intelligence can be game-changing for students with special needs
Share this:
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
The Hechinger Report is a national nonprofit newsroom that reports on one topic: education. Sign up for our weekly newsletters to get stories like this delivered directly to your inbox. Consider supporting our stories and becoming a member today.
Get important education news and analysis delivered straight to your inbox
- Weekly Update
- Future of Learning
- Higher Education
- Early Childhood
- Proof Points
Much has been made of artificial intelligence’s potential to revolutionize education. AI is making it increasingly possible to break down barriers so that no student is ever left behind.
This potential is real, but only if we are ensuring that all learners benefit.
Far too many students, especially those with special needs, do not progress as well as their peers do academically. Meanwhile, digital media, heavily reliant on visuals and text, with audio often secondary, is playing an increasing role in education.
For a typical user in most cases, this is fine. But not for blind or deaf students, whose sensory limitations frequently impede their access to quality education. The stakes are much higher for these students, and digital media often underserves them.
That’s why the development of AI-powered tools that can accommodate all learners must be a priority for policymakers, districts and the education technology industry.
Related: ‘We’re going to have to be a little more nimble’: How school districts are responding to AI
Good instruction is not a one-way street where students simply absorb information passively. For learning content to be most effective, the student must be able to interact with it. But doing so can be especially challenging for students with special needs working with traditional digital interfaces.
A mouse, trackpad, keyboard or even a touch screen may not always be appropriate for a student’s sensory or developmental capabilities. AI-driven tools can enable more students to interact in ways that are natural and accessible for them.
For blind and low-vision students
For blind and low-vision students, digital classroom materials have historically been difficult to use independently. Digital media is visual, and to broaden access, developers usually have to manually code descriptive information into every interface.
These technologies also often impose a rigid information hierarchy that the user must tab through with keys or gestures. The result is a landscape of digital experiences that blind and low-vision students either cannot access at all or experience in a form that lacks the richness of the original.
For these students, AI-powered computer vision offers a solution — it can scan documents, scenes and apps and then describe visual elements aloud through speech synthesis. Coupled with speech recognition, this allows seamless conversational navigation without rigid menus or keyboard commands.
Free tools like Ask Envision and Be My Eyes demonstrate this potential. Using just an AI-enabled camera and microphone, these apps can capture and explain anything the user points them toward, and then answer follow-up questions.
These technologies have the potential to allow blind and low-vision students to get the full benefit of the same engaging, personalized ed tech experiences that their peers have been using for years.
For deaf and hard-of-hearing students
In some ways, the visually oriented world of digital media is an ideal fit for deaf and hard-of-hearing students. Audio is often a secondary consideration; particularly once users can read.
In cases in which audio is required for comprehension, like with video, the accommodation most digital developers provide is text-based captioning. Unfortunately, this means that a user must already be a proficient reader.
For younger learners, or any learner who does not read fluently or quickly, translation into sign language is a preferable solution. AI can be of service here, translating speech and text into animated signs while computer vision reads the user’s gestures and translates them into text or commands.
There are some early developments in this area, but more work is needed to create a fully sign language-enabled solution.
For the youngest learners
For young learners, even those without diagnosed disabilities, developmentally appropriate interactions with conventional desktop/mobile apps remain a challenge. A young child cannot read or write, which makes most text-based interfaces impossible for them. And their fine motor control is not fully developed, which makes using a mouse or keyboard or trackpad more difficult.
AI voice controls address these problems by enabling students to simply speak requests or responses, a more natural interaction for these pre-readers and -writers. Allowing a child to simply ask for what they want and verbally answer questions gives them a more active role in their learning.
Voice control may also enable a more reliable assessment of their knowledge, as there are fewer confounding variables when the student is not trying to translate what they understand into an input that a computer will understand.
Computer vision can smooth over text-based methods of interaction. For example, username/password login forms can be replaced with QR codes; many school-oriented systems have already done so.
Computer vision can also be used to enable interactions between the physical and digital world. A student can complete a task by writing or drawing on paper or constructing something from objects, and a computer can “see” and interpret their work.
Using physical objects can be more developmentally appropriate for teaching certain concepts. For example, having a child count with actual objects is often better than using digital representations. Traditional methods can also be more accurate in some cases, such as practicing handwriting with pencil and paper instead of a mouse or trackpad.
Even without physical objects, computer vision can enable the assessment of kinesthetic learning, like calculating on fingers or clapping to indicate syllables in a word.
Related : STUDENT VOICE: Teachers assign us work that relies on rote memorization, then tell us not to use artificial intelligence
A major hurdle in education is that although every student is unique, we have not had the tools or resources to truly tailor their learning to their individualized strengths and needs. AI technology has the potential for transformative change.
The responsibility falls on all of us — districts, policymakers and the ed tech industry — to collaborate and ensure that AI-powered accessibility becomes the norm, not the exception.
We must share knowledge and urgently advocate for policies that prioritize and fund the swift deployment of these game-changing tools to all learners. Accessibility can’t be an afterthought; it must be a top priority baked into every program, policy and initiative.
Only through concerted efforts can we bring the full potential of accessible AI to every classroom.
Diana Hughes is the vice president of Product Innovation and AI at Age of Learning .
This story about AI and special needs students was produced by The Hechinger Report , a nonprofit, independent news organization focused on inequality and innovation in education . Sign up for Hechinger’s newsletter .
Related articles
The Hechinger Report provides in-depth, fact-based, unbiased reporting on education that is free to all readers. But that doesn't mean it's free to produce. Our work keeps educators and the public informed about pressing issues at schools and on campuses throughout the country. We tell the whole story, even when the details are inconvenient. Help us keep doing that.
Join us today.
Letters to the Editor
At The Hechinger Report, we publish thoughtful letters from readers that contribute to the ongoing discussion about the education topics we cover. Please read our guidelines for more information. We will not consider letters that do not contain a full name and valid email address. You may submit news tips or ideas here without a full name, but not letters.
By submitting your name, you grant us permission to publish it with your letter. We will never publish your email address. You must fill out all fields to submit a letter.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Sign me up for the newsletter!
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
What the Data Says About Pandemic School Closures, Four Years Later
The more time students spent in remote instruction, the further they fell behind. And, experts say, extended closures did little to stop the spread of Covid.

By Sarah Mervosh , Claire Cain Miller and Francesca Paris
Four years ago this month, schools nationwide began to shut down, igniting one of the most polarizing and partisan debates of the pandemic.
Some schools, often in Republican-led states and rural areas, reopened by fall 2020. Others, typically in large cities and states led by Democrats, would not fully reopen for another year.
A variety of data — about children’s academic outcomes and about the spread of Covid-19 — has accumulated in the time since. Today, there is broad acknowledgment among many public health and education experts that extended school closures did not significantly stop the spread of Covid, while the academic harms for children have been large and long-lasting.
While poverty and other factors also played a role, remote learning was a key driver of academic declines during the pandemic, research shows — a finding that held true across income levels.
Source: Fahle, Kane, Patterson, Reardon, Staiger and Stuart, “ School District and Community Factors Associated With Learning Loss During the COVID-19 Pandemic .” Score changes are measured from 2019 to 2022. In-person means a district offered traditional in-person learning, even if not all students were in-person.
“There’s fairly good consensus that, in general, as a society, we probably kept kids out of school longer than we should have,” said Dr. Sean O’Leary, a pediatric infectious disease specialist who helped write guidance for the American Academy of Pediatrics, which recommended in June 2020 that schools reopen with safety measures in place.
There were no easy decisions at the time. Officials had to weigh the risks of an emerging virus against the academic and mental health consequences of closing schools. And even schools that reopened quickly, by the fall of 2020, have seen lasting effects.
But as experts plan for the next public health emergency, whatever it may be, a growing body of research shows that pandemic school closures came at a steep cost to students.
The longer schools were closed, the more students fell behind.
At the state level, more time spent in remote or hybrid instruction in the 2020-21 school year was associated with larger drops in test scores, according to a New York Times analysis of school closure data and results from the National Assessment of Educational Progress , an authoritative exam administered to a national sample of fourth- and eighth-grade students.
At the school district level, that finding also holds, according to an analysis of test scores from third through eighth grade in thousands of U.S. districts, led by researchers at Stanford and Harvard. In districts where students spent most of the 2020-21 school year learning remotely, they fell more than half a grade behind in math on average, while in districts that spent most of the year in person they lost just over a third of a grade.
( A separate study of nearly 10,000 schools found similar results.)
Such losses can be hard to overcome, without significant interventions. The most recent test scores, from spring 2023, show that students, overall, are not caught up from their pandemic losses , with larger gaps remaining among students that lost the most ground to begin with. Students in districts that were remote or hybrid the longest — at least 90 percent of the 2020-21 school year — still had almost double the ground to make up compared with students in districts that allowed students back for most of the year.
Some time in person was better than no time.
As districts shifted toward in-person learning as the year went on, students that were offered a hybrid schedule (a few hours or days a week in person, with the rest online) did better, on average, than those in places where school was fully remote, but worse than those in places that had school fully in person.
Students in hybrid or remote learning, 2020-21
80% of students
Some schools return online, as Covid-19 cases surge. Vaccinations start for high-priority groups.
Teachers are eligible for the Covid vaccine in more than half of states.
Most districts end the year in-person or hybrid.
Source: Burbio audit of more than 1,200 school districts representing 47 percent of U.S. K-12 enrollment. Note: Learning mode was defined based on the most in-person option available to students.
Income and family background also made a big difference.
A second factor associated with academic declines during the pandemic was a community’s poverty level. Comparing districts with similar remote learning policies, poorer districts had steeper losses.
But in-person learning still mattered: Looking at districts with similar poverty levels, remote learning was associated with greater declines.
A community’s poverty rate and the length of school closures had a “roughly equal” effect on student outcomes, said Sean F. Reardon, a professor of poverty and inequality in education at Stanford, who led a district-level analysis with Thomas J. Kane, an economist at Harvard.
Score changes are measured from 2019 to 2022. Poorest and richest are the top and bottom 20% of districts by percent of students on free/reduced lunch. Mostly in-person and mostly remote are districts that offered traditional in-person learning for more than 90 percent or less than 10 percent of the 2020-21 year.
But the combination — poverty and remote learning — was particularly harmful. For each week spent remote, students in poor districts experienced steeper losses in math than peers in richer districts.
That is notable, because poor districts were also more likely to stay remote for longer .
Some of the country’s largest poor districts are in Democratic-leaning cities that took a more cautious approach to the virus. Poor areas, and Black and Hispanic communities , also suffered higher Covid death rates, making many families and teachers in those districts hesitant to return.
“We wanted to survive,” said Sarah Carpenter, the executive director of Memphis Lift, a parent advocacy group in Memphis, where schools were closed until spring 2021 .
“But I also think, man, looking back, I wish our kids could have gone back to school much quicker,” she added, citing the academic effects.
Other things were also associated with worse student outcomes, including increased anxiety and depression among adults in children’s lives, and the overall restriction of social activity in a community, according to the Stanford and Harvard research .
Even short closures had long-term consequences for children.
While being in school was on average better for academic outcomes, it wasn’t a guarantee. Some districts that opened early, like those in Cherokee County, Ga., a suburb of Atlanta, and Hanover County, Va., lost significant learning and remain behind.
At the same time, many schools are seeing more anxiety and behavioral outbursts among students. And chronic absenteeism from school has surged across demographic groups .
These are signs, experts say, that even short-term closures, and the pandemic more broadly, had lasting effects on the culture of education.
“There was almost, in the Covid era, a sense of, ‘We give up, we’re just trying to keep body and soul together,’ and I think that was corrosive to the higher expectations of schools,” said Margaret Spellings, an education secretary under President George W. Bush who is now chief executive of the Bipartisan Policy Center.
Closing schools did not appear to significantly slow Covid’s spread.
Perhaps the biggest question that hung over school reopenings: Was it safe?
That was largely unknown in the spring of 2020, when schools first shut down. But several experts said that had changed by the fall of 2020, when there were initial signs that children were less likely to become seriously ill, and growing evidence from Europe and parts of the United States that opening schools, with safety measures, did not lead to significantly more transmission.
“Infectious disease leaders have generally agreed that school closures were not an important strategy in stemming the spread of Covid,” said Dr. Jeanne Noble, who directed the Covid response at the U.C.S.F. Parnassus emergency department.
Politically, though, there remains some disagreement about when, exactly, it was safe to reopen school.
Republican governors who pushed to open schools sooner have claimed credit for their approach, while Democrats and teachers’ unions have emphasized their commitment to safety and their investment in helping students recover.
“I do believe it was the right decision,” said Jerry T. Jordan, president of the Philadelphia Federation of Teachers, which resisted returning to school in person over concerns about the availability of vaccines and poor ventilation in school buildings. Philadelphia schools waited to partially reopen until the spring of 2021 , a decision Mr. Jordan believes saved lives.
“It doesn’t matter what is going on in the building and how much people are learning if people are getting the virus and running the potential of dying,” he said.
Pandemic school closures offer lessons for the future.
Though the next health crisis may have different particulars, with different risk calculations, the consequences of closing schools are now well established, experts say.
In the future, infectious disease experts said, they hoped decisions would be guided more by epidemiological data as it emerged, taking into account the trade-offs.
“Could we have used data to better guide our decision making? Yes,” said Dr. Uzma N. Hasan, division chief of pediatric infectious diseases at RWJBarnabas Health in Livingston, N.J. “Fear should not guide our decision making.”
Source: Fahle, Kane, Patterson, Reardon, Staiger and Stuart, “ School District and Community Factors Associated With Learning Loss During the Covid-19 Pandemic. ”
The study used estimates of learning loss from the Stanford Education Data Archive . For closure lengths, the study averaged district-level estimates of time spent in remote and hybrid learning compiled by the Covid-19 School Data Hub (C.S.D.H.) and American Enterprise Institute (A.E.I.) . The A.E.I. data defines remote status by whether there was an in-person or hybrid option, even if some students chose to remain virtual. In the C.S.D.H. data set, districts are defined as remote if “all or most” students were virtual.
An earlier version of this article misstated a job description of Dr. Jeanne Noble. She directed the Covid response at the U.C.S.F. Parnassus emergency department. She did not direct the Covid response for the University of California, San Francisco health system.
How we handle corrections
Sarah Mervosh covers education for The Times, focusing on K-12 schools. More about Sarah Mervosh
Claire Cain Miller writes about gender, families and the future of work for The Upshot. She joined The Times in 2008 and was part of a team that won a Pulitzer Prize in 2018 for public service for reporting on workplace sexual harassment issues. More about Claire Cain Miller
Francesca Paris is a Times reporter working with data and graphics for The Upshot. More about Francesca Paris

Cancer on campus: Over 150 students and staff at North Carolina university 'are diagnosed with host of tumors and disease' - as officials find lecture halls and classrooms teeming with toxic chemicals
- DID YOU ATTEND CLASSES IN POE HALL AND GET DIAGNOSED WITH CANCER? WRITE TO US AT [email protected]
More than 150 students, staff and alumni have reportedly been diagnosed with cancers and other diseases linked to a university building teeming with toxins.
Cases of lymphoma and thyroid and breast cancers have been reported among patients who spent time at Poe Hall, a class building at North Carolina State University in Raleigh.
The building closed in November 2023 amid reports of exposure to concerning levels of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), toxic chemicals linked to cancer .
An investigation the month before found that PCB levels in five rooms were more than 38 times the Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) building limit.
The university now faces lawsuits from some of the 152 patients who report falling sick with diseases linked to the toxins.
These include Sarah Glad, a 35-year-old mother-of-one who dreamed of using her degrees from NC State to run for office. However, her dreams were cut short when she died from stage four breast cancer, which her family claims is linked to attending classes in Poe Hall.
The dozens of cancer cases and their links to the university building were exposed by a months-long investigation by the local news station WRAL.
Mrs Glad attended NC State from 2007 to 2013, earning a bachelor's and master's degree.
Her husband, Robbie Glad, told WRAL , who investigated the cases, that his wife spent much of her master's program in Poe Hall.
Years later, within months of each other, Mrs Glad and a former classmate were both diagnosed with breast cancer. Mrs Glad was just 33 years old.
She was able to fulfill one dream and become a mother in August 2022, even as cancer ravaged her body.
However, in January 2024, at age 35, she died from the disease.
Now, Mr Glad is focused on raising awareness.
'I don’t care about money. I don’t care about compensation. I do care about being able to help other people,' he said.
NC State alumna Christie Lewis, who attended the university from 2007 to 2012, said that she started having night sweats while she was taking classes in Poe Hall. 'I could not figure out what was happening,' she told Fox News Digital .
'I was having to get up in the middle of night and change clothes completely. And then I would fall asleep. And I had to put a towel down.'
'It honestly took me weeks to even tell my husband about them because I kept on forgetting about it because it was just in the middle of the night.'
Around 2011-2012, Ms Lewis was diagnosed with thyroid cancer.
Months later, she discovered a lump on her neck, which turns out to be angosarcoma, a tumor found in the inner walls of blood and lymph vessels.
Though she initially thought it was just circumstance, she became suspicious after reading reports about a potential link between Poe Hall and cancer cases.
'Maybe my body isn’t the problem. Maybe I was actually exposed to something that caused this. I don’t know, it definitely shook me a little bit,' she said.
Jennifer Walter, who attended the university from 2004 to 2007, was diagnosed with thyroid cancer in 2017, followed by synovial sarcoma - which mainly attacks tissues near large joints like the knees - in 2022.
'There are such scary statistics that are tied with sarcoma. It’s just a lot more real,' she told Fox News Digital .
'They got it early, which I’m grateful for, but that fear never goes away. It’s something I’m going to have every day for the rest of my life.'
Ms Lewis said that she feels 'violated' because she thought she was 'getting a good education...in a safe place' before suddenly being 'put in unsafe conditions.'
She also fears she may have passed on PCB exposure to her children.
'It's made me feel just really nervous,' she said.
Poe Hall, which held education and psychology classes for 4,000 students, was constructed in 1971, when PCBs were commonly used in industrial products like oils, insulators, and electric appliances such as TV sets, lighting, and refrigerators.
PCBs, including those used to build Poe Hall, were largely mass produced by agricultural giant Monsanto until they were banned in 1979 amid concerns that they harmed humans and the environment.
WHAT ARE PCBs?
PCBs are classified by the World Health Organization as known human carcinogens. Their manufacture was banned in the US and UK four decades ago.
They were mass produced by agricultural giant Monsanto for 42 years before the decision was made to stop doing so.
Studies have shown that PCBs, of which there are around 210 variations, can alter liver function can even affect reproductive system.
Newcastle University researchers in 2017 found ‘extraordinary’ levels of the pollutant in the Mariana trench – the deepest part of the ocean.
Around 1.3 million tons of PCBs were produced before they were banned – but some scientists estimate a third of this has leaked into the environment.
According to the EPA, conclusive evidence has found that PCBs can cause cancer in animals, as well as harm their immune, reproductive, nervous, and endocrine systems.
The agency classifies these chemicals as 'probably carcinogenic' to humans.
According to the CDC, exposure to PCBs can lead to increased enzymes linked to liver damage, skin lesions, and respiratory issues.
Animal studies have shown effects such as weight loss, fatty liver, thyroid damage, and cancer.
NC State's investigation into Poe Hall began in August 2023 when an employee issued a complaint with the Occupational Safety and Health Division of the North Carolina Department of Labor (NCDOL).
The complaint 'alleged health and/or safety hazards related to Poe Hall,' according to the university's updates page for the investigation.
Health officials began sampling the seven-story building in October and found PCB levels more than 38 times the EPA's safe limits for construction.
The building officially closed in November, and the North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services (NCDHHS) recommended the university request a Health Hazard Evaluation (HHE).
An HHE is a federal investigation into a workplace to look for hazards such as carcinogens.
However, the investigation was called off in January by NC State's general counsel, according to the CDC.
Dr Dallas Shi, an official for the CDC's National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), wrote in a letter to WRAL detailing the agency's inability to move forward: 'I explained that the North Carolina State University’s Office of General Counsel has asked us to stop our evaluation.'
'The requestor expressed concerns over a lack of communication and general distrust in management’s actions. They also expressed concern about a lack of epidemiological analysis.'
'I offered to relay these concerns to the North Carolina State University’s Office of General Counsel in a confidential manner.'
According to WRAL , NC State University Chancellor Randy Woodson denied the CDC's report, with a lawyer writing: 'At no time has NC State requested that NIOSH close any HHE (Health Hazard Evaluation), and I’m reaching out to respectfully request a retraction of any statement to the contrary.'
Several NC state employees and students reached out the NCDHHS urging the agency to investigate.
'A wide-sweeping health assessment needs to be done to ensure students, staff, and faculty who worked and learned in Poe know how to manage their own health,' a former graduate student with noncancerous health issues wrote in an email to authorities.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Proofread first thing in the morning. Read your report card comments out loud and also silently. Read them slowly. Use a spell checker and grammar checker as a first screening, but don't depend on them. Keep a list of your most common errors and proof for these separately. Double-check the spelling of names.
Third, when writing research reports, students are internalizing the writing process, including organizing, writing a rough draft, proofreading/editing, and writing a final draft. When students write research reports about topics of interest, they are fine-tuning their reading and writing skills. How to Teach Research Reports in Grades 5 & 6
Report Writing Format for Class 10th to 12th. The report writing structure for students in grades 10 and 12 is as follows. Heading : A title that expresses the contents of the report in a descriptive manner. Byline: The name of the person who is responsible for drafting the report. It's usually included in the query.
Option 1: Assign "Plan Your Report.". Tell the students to choose a favorite topic and begin to fill out their clusters. Once they have the information they need, ask students to write their reports using "Write Your Report.". Option 2: Choose a specific topic and work through the entire report-writing process as a group.
A report is a well-structured and researched document that informs a specific audience on a particular problem or topic. The purpose of a report is to inform, guide or influence decision making and/or the outcome of a course of action. Writing reports is common in many workplaces. Thus, you often find this form of writing set as an assessment ...
As a teacher, writing student reports now places you on the other side of that equation, and it's a responsibility that carries a lot of weight. Step 1: Understand Your Audience. Step 2: Be Clear and Specific. Step 3: Provide Actionable Feedback. Step 4: Keep It Balanced.
I cover 31 topics structured into two themes: (a) Structure and content of an academic. report or paper and (b) General tips and tricks. E ach topic consists of two to five bullet. points where I ...
As students study about their topics, have them write answers and source information beside the questions on their note cards, in their notebooks, or in their gathering grids. Tell them that if their reading brings up new questions, they should add them along with answers. Select your writing standard type: CCSS. LAFS.
It also demonstrates the student's writing skills and ability to simply convey complex findings and ideas. Remember that the report outline will affect your final grade when writing an academic report. If you want to learn about the correct report writing format, keep reading the article. If you want to save time, you can always buy essays online.
Today I'm breaking down the process with 8 must-do tips to help your kids learn how to write an engaging report. 1. Start with a pre-assessment. I always recommend starting with a pre-assessment. Give students a prompt and one writing period to respond to it the best they can.
Some students write the introduction first; others save it for last. Whenever you choose to write the introduction, use it to draw readers into your report. ... The paragraph below, adapted from a report by student John Zwick on the mental health of soldiers deployed during wartime, draws examples from three sources. student sample text ...
Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Progress Report Step 1: Gather Student Data and Information. Before writing progress reports, teachers should ensure they have all the required information and data at their fingertips. This includes student work samples, test scores, observations, and any notes from previous parent-teacher meetings.
Teaching students how to write information reports offers an excellent opportunity to introduce research skills to your students. For more advanced students, it creates opportunities for them to hone these important skills further. There are also several different processes students need to develop to ensure that they can filter their research ...
The following stylistic advice can be applied to most progress reports you write: Include a working title and the words "Progress Report" at the top of the page. Use section headings in the report to simplify both the writing and reading process. Open the report with a "Scope and Purpose" section, where you give a condensed version of ...
Newspaper Report Writing: Newspaper reports are based on true incidents or accidents meant to express some information to the public. ... The magic show was a gift to the students from the school's authoritative body as the school won the award for Best Disciplined School in Kolkata for the year 2015. The magic show was organized on the ...
125 Report Card Comments. It's report card time and you face the prospect of writing constructive, insightful, and original comments on a couple dozen report cards or more. Here are 125 positive report card comments for you to use and adapt! Struggling Students?
Here are six tips for ⌨️ writing students' progress report summaries: 1. Define the purpose and scope of the report: Before writing the report, it's crucial to determine the purpose and scope. This includes identifying the stakeholders, explaining the goals, and outlining the timeframe. 2.
Students should take their notebook to note important things. Suitable present: Each class should write some poems or thank you card so that we can make a poster to give him as a present. For any class which wants to perform some dance or song they could register in the Dancing Club Recommendations: We will have a investigation with Bill Gates ...
Spread the loveHaving difficulty with writing positive and constructive feedback on student report cards and progress reports? Use our ideas. Positive The learner takes an active role in discussions. Learner consistently cooperates with the teacher and other students. Learner listens well and shares ideas frequently. The learner works democratically with peers. Learner shows self-confidence in ...
A book report, for example, is meant to show that a student has read a book and can give a summary of it to the class and the teacher. ... It's not a detailed visualization of microbes in a lab, but the report writing format is the same. Customize this report template and make it your own! Edit and Download.
"Write [number] report card comments for students studying [subject] in [grade]." Here are some more specific examples to help get you started: Write 50 report card comments for students studying social studies in 5th grade. Generate 20 report card remarks commending a student for a positive attitude to learning.
When students respond to each other's writing, it's often more helpful to the responders than the receivers, writes Patricia A. Dunn. Even before complications wrought by AI, faculty members and students alike have often dreaded college writing assignments—students because of painful past histories with the process and faculty because of time-consuming, often-frustrating, grading ...
The school's year 3 and 5 students have outperformed the state in writing over the past three years, Ms Gazula said, and writing proficiency is over 60 per cent.
The Hechinger Report is a national nonprofit newsroom that reports on one topic: education. ... Computer vision can also be used to enable interactions between the physical and digital world. A student can complete a task by writing or drawing on paper or constructing something from objects, and a computer can "see" and interpret their work
The more time students spent in remote instruction, the further they fell behind. And, experts say, extended closures did little to stop the spread of Covid. By Sarah Mervosh, Claire Cain Miller ...
President Joe Biden unveiled another round in his steady drip of student debt write-offs on Thursday, announcing that 78,000 public sector workers would not have to repay $6 billion in loans ...
More than 150 cancer cases have been linked to Poe Hall, a class building at North Carolina State University in Raleigh. Reports found high levels of the cancer-causing cehmicals PCBs.