Elevate Your Story
We are stinson: the presentation agency.
Our team of in-house presentation designers help companies around the world achieve their goals through effective storytelling. We deliver persuasive, engaging, and on-brand presentations that instill confidence and inspire action.

Explore Our Services
Multifaceted presentation design services for any client in any industry for any occasion.
We are the trusted presentation design partner for respected global brands and leading-edge startups since 2009.

Presentation Development
Our presentation designers transform dated PowerPoint and Keynote slides into visual stories that bring your key messages and data to life, whether you're speaking at a national sales conference or in the boardroom.
Content Consulting
Our consultants distill dense information to reveal what resonates most with your audience. We'll help you refine your story from beginning to end through strategic communications and a business-minded approach.
Template Systems
We analyze your brand and content to create custom designed templates for your teams. As a presentation company, we create functional templates to help users build consistent, on-brand slides for every presentation.
Presentation Training
Move your organization forward with presentation training that empowers you to build better presentations in less time. Master the tools of PowerPoint through hands-on learning and actionable feedback.
Find Your Solution
Discover custom presentation solutions for your unique business challenges.
Select your role to see how we can help you achieve your goals.
Sales & Marketing
Scientific & technical, analytical & research, teaching & development, executives & thought leaders, founders & investors, the stinson approach.
We design with purpose.
We work through three main phases to ensure every project is a success.
We kick off with a deep dive into your business, brand, and objectives, analyzing source material and defining key opportunities your target audience will care about.
We refine your content to establish a compelling narrative and conceptualize a visual story that aligns with your brand identity.
We combine our creative expertise and industry experience to build custom, high-impact presentations that bring your content to life.
Why Partner with Stinson?
We integrate story and design to help our clients achieve more.
89% of first-time clients come back to us for our presentation design services.
Over $300 million in funding raised through our focused pitch decks.
We helped ZoomInfo develop an interactive sales presentation with custom graphics and polished, sophisticated animations that reflect their modern branding and keep their audience engaged.
From one corporate PowerPoint template design back in 2015, our partnership with CrowdStrike has evolved into creating branded templates and collateral, and keynote presentations for their executive team.
We helped this financial services group redesign their existing investor presentation to better resonate with their audience. The resulting pitch deck is sleek and tells their business story to captivate investors.
We simplified dense scientific findings into a compelling narrative for healthcare professionals. Using graphics, photography, and brand elements brought the data-heavy presentation together into an easy-to-understand story.
The LearnWell Projects seeks to help colleges and universities eliminate academic-related retention problems. We helped them visualize complex and abstract concepts using animations and custom-made illustrations.
Concordia's Faculty of Fine Arts needed help visualizing survey data in way that is easy to understand and engaging to its readers. We developed an infographic to help educate the faculty staff and inspire action.
A very creative and collaborative process that made me change my thinking and approach; a worthwhile and rewarding experience.
Stinson is an expert at understanding information to visualize complex data and design clear text-heavy slides. They've helped improve the consistency of our presentations using a keen sense of brand and attention to detail. I'd recommend Stinson to anyone!
Stinson has a real talent for creating and honing presentations into first-class communication tools. We've used them repeatedly and are very happy with their skills and abilities.
We knew we had situations where our internal designs were no longer going to cut it. Finding and working with Stinson has elevated our external communications. The process is pain-free and quick. We have used Stinson on multiple designs, and plan to keep using them for upcoming design needs.
Whether helping to build a presentation deck, brochure, or short video, the Stinson team has been great to work with. They are creative problem solvers who help us take the complex and make it easier to understand. We really appreciate their initiative and level of service.
The team at Stinson did an excellent job and were able to turn our materials around within our tight timeline. The team catered to our specific needs and were a great partner. The updated design is fantastic and bold.
The team at Stinson understood so quickly what I was trying to show in my story, and made it so easy to tell it through graphics. I would use them again in a heartbeat.
We’re happy to answer your questions.
Let's Get Started!
Interested in a consultation or learning more about how we can work together?
Want insights from industry experts?
Sign up for our quarterly newsletter to receive presentation tips and communications.
Get Inspired
We’d love to hear about your project.
Complete the form below and one of our consultants will reach out within 24 hours.
Presentation design agency
We’re a presentation design agency. We design clear, compelling, and persuasive presentations. We also use our visual storytelling skills to create effective eLearning, and provide advanced PowerPoint, Google Slides, and presentation skills training.
Visual conversations, visible results
Presentation design and elearning.
You might not have known presentation design companies like BrightCarbon even existed.
But think about it…
All the time and opportunities wasted with awful bullet-point presentations and click-through eLearning. The boredom. The amateurishness.
Just imagine the value you could get from using compelling visual PowerPoint presentations. How thankful your audiences would be. How successful you could be.

Too much ugly text on slides and screens is a problem for audiences and learners alike. You just can't read and listen at the same time.

Beautiful compelling visuals, with a clear structure, help your audiences and learners to understand and remember your content.
Our services include / view all
Presentation creation.

Advanced PowerPoint Training

eLearning Creation

Presentation Helpdesk

Sales presentations
It's not always easy getting in the door to deliver a sales presentation. Yet some companies risk wasting opportunities with ugly and ineffective slides, and poorly prepared presenters. BrightCarbon's presentation design services can help you convert opportunities with amazing sales presentations and more.

Training presentations and eLearning
Most learning & development departments use text-heavy slides. For classroom training, for webinars, for storyboarding, and as the basis for rapid eLearning. But text-heavy slides don't work. We know how to use slides to tell visual stories, how to use visual storytelling for eLearning, and how to use great design to make learning effective.

Portfolio / view all

Presentation design
Jacobs – digitized construction execution.
BrightCarbon created a series of presentations for Jacobs for a large one-day event. We established a bespoke design style for the event, incorporating custom illustration and engaging animations to tell

Siemens – Metering managed services
We created this company presentation for Siemens, providing an overview of its managed services. The use of a tight grid system gives the PowerPoint presentation design a modern feel, and the mix of full-bleed imagery with iconography communicates the message clearly and concisely.

Pluto7 – Optimise supply and distribution management
For this project, BrightCarbon created a dynamic animation using playful visuals and a bold animation style to help explain the complexities of the Machine Learning product in a fun and engaging way.

Johnson & Johnson – Welcome and introduction
This company presentation for Johnson & Johnson uses a mix of cut-out and full-bleed photography, supported by iconography and animation, to tell the story. The visual presentation design used in this deck also translated well into online training content.
How to create beautiful and effective academic posters in PowerPoint
- 7th Jun 2022
- PowerPoint design
Your academic posters should be keeping pace with the rate science is moving, not trailing behind! It’s time to upgrade your template and create beautiful and effective academic posters using PowerPoint.

Google Slides: The ULTIMATE guide
- 22nd Jun 2023
- Google Slides , Presentation technology
As presentation nerds, we at BrightCarbon have had plenty of opportunity to get to know ins and outs of Google’s browser-based presentation tool. This guide will cover everything you need to know about Google Slides - from the very basics to the most advanced features - and will provide you with the know-how to make brilliant slides, quickly and easily.

Choosing a presentation design agency
- 26th Apr 2020
- PowerPoint design , Visual communication , Industry insights
Choosing a presentation design agency for your enterprise is a lot harder than buying a product. With presentation design services, you don’t know what you’re going to get until the project is nearly finished. What you get from the studio isn’t the exact same thing as what any other business ends up with. So how do you choose the right presentation design firm for your company?

Presentation agency or marketing agency?
- 3rd Mar 2022
- Industry insights
In the agency world, it’s fair to say that PowerPoint design sits somewhere at the bottom of the pile. Working with a specialist presentation design company will generally deliver better results, with less effort, and typically at lower cost. So why do some companies still not use presentation agencies for slide design?

Presentation design principles for better PowerPoint design
- 8th Feb 2022
- PowerPoint design , PowerPoint productivity
By applying some key principles of presentation design, you can make your PowerPoint design really standout and deliver both a more ‘popping’, but also more effective presentation.

14 sales presentation ideas
- 12th Aug 2021
- Sales presentations , Sales messaging
Sales presentations are important, but 1000s of people each day ignore the principles of sales presentation design and sales messaging and deliver material that is tired, ugly, and ineffective. These sales presentation ideas will help you to easily improve your sales presentation; stand out, engage your audience, and sell more.

How to make the ULTIMATE sales presentation
- 8th Jan 2022
- Sales presentations , Sales messaging , Visual communication
Sales presentations are the cornerstone of many companies’ sales efforts, yet so often they aren’t given the time and attention they deserve. Thrown together at the last-minute, often your sales reps stand up in front of a sales presentation that's nothing more than a glorified page of notes. Read this article for everything you need to make the ultimate sales presentation.

How to create visual presentations and eLearning
- 23rd Oct 2021
- PowerPoint design , Visual communication
Most presentations are a cascade of text-heavy Death-by-PowerPoint slides. Online learners suffer the torture of brochures converted to click-through-eLearning. Most people now recognize that using visuals is the way to go. But how do you make visual presentations and eLearning that work? We think there are six steps you need to follow.

Great work combined with amazing service, gracias Team BrightCarbon! Mila Johnson InComm

- Presentation Design
Impress your audience with high impact, effective & visually appealing presentations.
Since 2004, SodaPop Media ® has been providing expertise in designing and creating rich-media presentations for diverse industries and some of the most recognizable brands. We understand the importance of a strong initial impression, which is why our team of skilled presentation designers and multimedia experts are dedicated to crafting compelling presentations that leave a lasting impact.
- Fully custom, visual and dynamic
- Animation and interactivity
- Multimedia and voice-overs
- Powerful, effective, and attention-grabbing
- Fast turnaround

WorkSoft PowerPoint Presentation Design

Swiss‐American CDMO Interactive Presentation

KFC Marketing Presentation
SodaPop Media can help you save time by allowing you to focus on more important tasks and what you do best. Our designers will ensure that each slide aligns with your brand’s core values with a consistent tone, style, and color throughout your presentation. The PowerPoint presentations we create include custom graphics, icons, illustrations and animation to deliver the “wow factor” and add impact.

A high-impact, engaging presentation is the key to standing out and leaving a lasting impact. By striving to understand your brand, goals, personalities of the presenters, behavioral aspects of the target audience, the presentation environment, involvement of technology and your budget, we ensure that your presentation is tailored to your specific needs and equip you with the best-possible means of delivering your messages to the intended recipients. Don’t settle for a mediocre presentation. Let us help you make a statement and leave a lasting impression.
Contact us today and let our team of presentation design experts help you present your ideas and business in a winning way.
Presentation Design Service Includes:
- PowerPoint / Prezi Presentation Design
- Custom PowerPoint Template Design
- Corporate Business Presentation
- Executive Keynotes
- Marketing & Sales Presentation
- Company and Board Meeting Presentation
- Tradeshow Monitor Presentation
- Multimedia Show
- Litigation Presentation
- Training, Onboarding and Orientation
- Corporate and Investor Pitches
- Teaser Slide Decks
- Product Launches
- Interactive Product Demo
- On-Demand Online Interactive Presentation
- Annual Meeting & Business Event Presentation

Digital Generation Interactive Presentation
Our clients

“I am very impressed with the quality work that was applied throughout the project. The end product exceeded my expectations and I have had excellent feedback from peers and clients. I really feel that the SodaPop Media team is very creative and skilled at assisting the client to look at the creative process from outside the box. It definitely contributed to a quality product. Because of your superb organizational approach, management style and great processes all I can say is keep up the great work and service.”
“You guys are great! Thanks for all your help and dedication to great customer service! Highly recommend to others.”
“It's great to work with a company that is so committed to understanding what we trying to accomplish. We appreciate the work you've done for us so far and we are looking forward to having a great working relationship going forward.”
“Impeccable design. Superior customer service. My expectations are exceeded with every project.”
“Thanks for all your help with our new website. We couldn’t have don’t it without your team and support. You are an amazing group and we appreciate everyone’s patience while we figured out what we wanted. Everyone is very happy with the final result!”
“Thank you for all the work you guys do. It’s always top notch!”
“SodaPop Media is awesome! They are very professional, timely and always willing to help. I highly recommend their services. If you have the opportunity to work with them, consider yourself lucky!”
“For the past five years, we have worked with SodaPop Media on several website and digital marketing projects. The professionalism SodaPop Media brings to the table is amazing. We will continue to partner with SodaPop Media on projects in the future.”
“We just launched the first in the series of online courses SodaPop Media has produced for us and everyone is so pleased with how they turned out. Thank you so much for doing such a great job!”
“We really appreciate your partnership and your team has done an amazing job. We also value your flexibility and timeliness in project delivery.”
“I have worked with SodaPop Media on several executive-level presentations for various companies. Anyone who has done this type of assignment knows that these projects are often quick-turn and very hard to get unanimous approvals. SodaPop Media team is a genius with turning a simple PowerPoint presentation into an engaging rich-media presentation that captures the presenter's persona and tells a story. They're also great with following the client's direction and working under tight deadlines.”
“SodaPop Media team has exceeded any and all expectations and we look forward to working with your team again.”
“I have worked with SodaPop Media on multiple projects and have found that not only does SodaPop Media team produce a great product but is a joy to work with. In a world of extremely tight deadlines, and high client expectations, SodaPop Media team has always been willing to put in whatever effort is necessary for the project to succeed. I highly recommend SodaPop Media and always look forward to working with the team.”
“SodaPop Media has increased our future sales by delivering resources that our clients and prospective clients can access to learn about the company and our solutions.”
“SodaPop Media helped GlobeRanger to move and transition its website to the latest website technology.”
“I just wanted to thank all of you for your hard work. We are all super excited about the buzz that is being created as we speak. Just wanted to let you know that we appreciate your help and we couldn't have done it without you.”
“The website and our new marketing materials look outstanding. I wanted to thank you and your excellent team for the great work.”

- Our Clients
- Our Approach
- Our Process
- Our Commitment
- Giving Back
- Client Testimonials
- Website Design
- Web Development
- Interactive
- E-Learning Course Design
- Motion Graphics
- Graphic Design
- Digital Marketing
- Inbound Marketing
- Tradeshow Graphics
- Social Media Marketing
We're not around right now. But you can send us an email and we'll get back to you, asap.
Start typing and press Enter to search

Get AI + Human made PPT Presentations with our Presentation Design Service
We are a leading presentation design agency who can create engaging presentations that captivate your audience and leave a lasting impression. just share your requirements, we’ll do the rest..
Supporting 10K+ Customers Worldwide

Look what are the presentation services we’ve for you…
Round-the-clock design services to ensure your needs are always met.
Custom master templates that reflect your brand identity and simplify future presentations.
Professional presentations for corporate, with attention to brand guidelines.
Pitch decks that impress potential investors and secure funding for your business.
Choose a dedicated team for focused support or shared designers for flexibility.
A range of design services, including logos, brochures, and social media graphics.
4 simple steps to get your presentation ready
No hidden fees. Everything is transparent.
Step 1: Brief & Order
Tell us what you need, and we’ll take it from there. Our team of experts will work closely with you to ensure that we fully understand your expectations for the presentation.
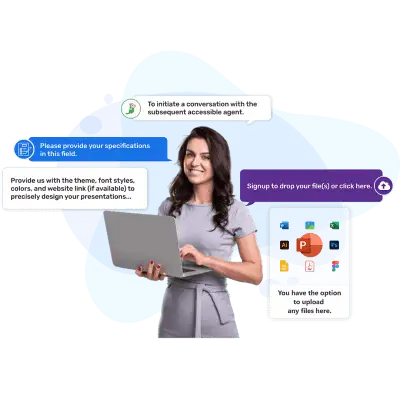
Step 2: Designing Process
We’ll keep you in the loop throughout the entire process, so you can review and provide feedback on the presentation. We’ll make any necessary corrections until you are completely satisfied.

Step 3: Live Monitoring
Once the presentation is finalized, you’ll be able to download it directly from our website. There are no hidden fees or extra charges – everything is transparent. Chat with us ad share your requirements
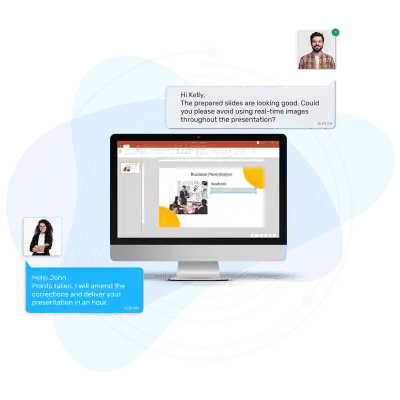
Step 4: Download & Present
Hurray! Your presentation is ready now. Just download your PPT and present anywhere with full confidence. We are battle ready for the next project too…

Starting Price
Slides Designed
Enterprise Customers

We have done it for many. You are the next!
Have a look at our presentation design company’s samples

Frequently Asked Questions
We offer 4, 24, and 48 hour turnaround times. You will receive the first draft of your presentation within the chosen timeframe, and we always strive to deliver high-quality work within the promised time.
Yes, we are available on weekends as well. Our representatives are available 24/7, so you can contact us anytime for support.
Yes, you can book a meeting or request a call with us during our operating hours. Our team is always ready to assist you with any questions or concerns you may have.
Share your requirements and we’ll do the magic for you

- PowerPoint Design Company
Join our PPT experts community
Meet and learn the tips and tricks from creators & companies who share how they use PowerPoint to create better presentations in minutes.
- Customer Testimonials
- PowerPoint Design Services
- Investor Pitch Decks
- Dedicated Designers
- Master Templates Design
- Enterprise Presentations
- Other Design Services
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Refund/Cancellation Policy
- Disclaimer Notice
Security Policies
- DMCA Policy
- GDPR Policy
- CCPA Policy
- Cookies Policy
Copyright © 2024 Deckez. All rights reserved.
Template egg.

Impactful Presentation Design for
Financial communications, sales enablement, conferences & events, sales & pitch decks, marketing communications, internal communications.
Welcome to SlideGenius. We’re a presentation design agency with one goal: to go beyond.
Our goal is to inspire audience action through engaging, meaningful, and memorable presentations. Whether you are a start-up or a Fortune 500 company, our elite presentation design team is here to deliver results at the speed you need. Our 24/7 services ensure that you have the support you need to succeed.
In a hurry? Call us now!
1.858.217.5144
Or fill out the form
Company Size None 1 2-10 10-100 100-1000 1000+
Trusted by 4,000+ Clients Globally
24 Hour Global Coverage
Quick Turnarounds
Customer feedback

Priscilla E.
Presentation Manager
I appreciate the amount of effort that went into optimizing this deck. It was quite an undertaking at over 100 slides, and your team was able to execute within a tight time frame.

Operations, Sports Licensed Division
Wanted to let you know your work has more than exceeded my expectations in all areas. Of all of the companies I work with, yours stands above the rest because of your professionalism, timeliness, and ability to communicate and consistently deliver a product that impresses.

Managing Director
The presentation was a huge success and we had many unsolicited comments on the format. I also want to mention the outstanding service provided by your team. I'm talking truly exceptional. Haven't seen something on that level of responsiveness in a long time.

Assistant VP, Corporate Communications
I want to extend a tremendous thank you for all your efforts over the past few days. It wasn’t an ideal timeframe and I really appreciate the speed at which you put together the materials we needed for tomorrow’s meeting. On behalf of everyone on our project team: a big thank you!

Katherine K.
Manager, Global Branding
I sincerely appreciate your fast response time and excellent visuals. This presentation is a keeper! We look forward to the next project in the very near future!
Director/National Sales & Marketing Leader
You all were wonderful. Thank you for getting the work done for me so quickly. I’m very pleased with what you created!

Product Marketing Manager
Thanks so much! REALLY appreciate the hustle...and it looks great!

Communication Specialist
You have done an outstanding job! Thanks so much for such a quick turnaround!
PowerPoint Design for Enterprise Business Executives
As a leading enterprise PowerPoint design agency, we’re equipped to handle any project. Whether you’re presenting in an upcoming virtual event, sales meeting, or in need of ongoing high-volume production support, SlideGenius can help.

Global Clients

Presentations Built

Presentation Designers
Global Coverage
We’ve worked with some of the world’s most impactful brands. View our presentation examples below.

In this presentation deck, SlideGenius showcases the humble beginnings of Adidas from its founding in the 1960s to its glorious...

American Airlines
When you think of world-class flight experience, American Airlines immediately comes to mind. This airline is one of the world’s...

American Express
American Express is a well-known brand for doing business with the largest and most vibrant consumers – and we wanted...

AT&T is a global leader in the Technology, Media, and Telecommunications industry. Their main purpose is to connect people with...

Blizzard Entertainment
SlideGenius showcases Blizzard’s strengths and other affiliations through this deck, tailored according to Blizzard’s brand identity.

The brand strives to deliver exceptional experience to each guest, employee, and investor. With over a century of being a...

NBCUniversal
NBCUniversal is a leader in the entertainment industry and so the presentation we created showcases some of its best productions,...

Spotify is one of today’s leading music streaming service providers. Here, there is something for everyone, which is why created...
IN A HURRY? START A PROJECT

CALL NOW 1.858.217.5144

LIVE CHAT ONLINE NOW
Presentation Services for Marketing Teams
Conferences & Events
Whether you’re hosting a national conference in-person or integrating webinars into your customer journey, SlideGenius delivers high-quality presentation support that empowers your team’s engagement. Our presentation design process has been refined over years of work and the results speak for themselves.

Investment Presentations
How can you stay ahead of the curve when the world of investments is always changing? A pitch deck you can take pride in will always be necessary to secure capital in any round of funding.
Our pitch deck specialists design a framework of success that makes you the beneficiary of over a decade’s worth of experience raising capital.

Sales & Pitch Decks
The sales landscape has changed dramatically in recent years and a high-quality sales deck is essential to obtaining B2B sales, both online and in-person.
Our team of sales deck design specialists work with you to create a framework of success through a proven strategy that we’ve developed over a decade’s worth of helping our clients sell more!

Team and vision presentations are an important component to building a culture of success. Whether it’s the CEO’s vision presentation or an executive’s off-site speaking engagement, we understand the importance of a clear and concise message to your team.

Enterprise Services
We never sleep. Whether your team needs a single presentation deck or hundreds the SlideGenius design team can accommodate any tight timeline. We work with some of the world’s largest companies delivering high-end design in quick turn environments.
Accessory Design Services
Video Design
We design and animate videos to help you with your marketing needs. The market is shifting to videos as a powerful means of shareability and brand exposure. Create a lasting impression with the power of video animation.
Graphic Design
An effective message stays with your audience even after the pitch is over. Reinforce your presentation with a striking print that expounds on your company’s strengths.

Infographic Design
SlideGenius has created hundreds of infographics for clients. Our expert staff will take your ideas and data and turn them into a cohesive and understandable infographics that can be shared for years to come.
- Scroll to top

Stunning, fast, & cost-effective presentations that get results.
PowerPoint presentation design agency.

Who our presentation design agency has helped.

We create incredible presentations. Our clients get extraordinary results.
Presentations that don’t convert are pointless..
No matter how great your deck looks, if it doesn’t engage, influence and ultimately sell, it’s a waste of money.
You need an inspiring presentation experience that gets stakeholder buy-in for your projects’ success.
Boring presentations don’t get results.
You only have one chance to get your clients excited about your pitch.
A lacklustre and forgettable presentation can hurt your business opportunity before it’s even begun.
You need a captivating presentation that wins investment and closes deals.
If you’re frustrated with your presentation branding inconsistencies, then so is your audience.
So you’ve got a slick website and beautiful brand guidelines.
If your presentation doesn’t match, it damages your brand and your chances of success.
You need to show brand harmony across your whole portfolio – especially your make-or-break presentation deck.
Writing, designing and building presentations is overwhelming.
Without in-house presentation experts, it’s hard to justify the time and resource it takes to make professional and consistent decks.
You need to outsource your presentation requirements to this presentation design company.
you should hire this presentation design agency to create a presentation that makes a difference to your bottom line.
Don’t let your company presentations let you down..
How you present your ideas can be the difference between success and failure.
Securing a pitch. Or being an also-ran. Getting investment funding . Or going home with nothing. Winning your company team over . Or failing to engage them at all.
So why run the risk of doing it yourself?
Let’s face it: you can’t spare the time. You can’t expend the effort. And you can’t afford the resource to do it in-house. Or you wouldn’t be reading this, right? That’s why you need a presentation design agency.
So, let’s talk about how we can help .

Our presentation services.
Presentation creation.

What’s your poison?
Whether you prefer to present in Microsoft PowerPoint, Google Slides or even Apple Keynote (if you must), we can craft your story, design your look and bring your ideas to life with animation and motion.
Investor / pitch decks

Stand out. Make an impact. Engage your audience.
We can help your pitch raise the funding you need – from seed funding to public launches.
Change the world with custom graphics. With strategic narrative flow. And with data storytelling techniques.
Presentation templates

Hype Presentation’s template development services create a framework that you can use for all future presentations – in Microsoft PowerPoint or Google Slides.
Layouts. Graphic assets. Colours. Fonts. Slide Master. All taken care of by a professional presentation design company. Sounds amazing, right?

Visual storytelling experts.
Discovery-led storytelling.
Our expert storytellers drill down into your big ideas – and your audiences’ needs – to uncover the essential components that will inspire the most engagement. Using classic storytelling techniques, we’ll craft a powerful, emotive and persuasive story to trigger maximum buy-in.
Spellbinding design
Great stories demand amazing imagery to back it up. Our presentation designers produce stunning visuals that not only look fantastic, but incorporate fundamental design theory to make complicated concepts simple to understand, convey meaning and emotion, and make your message impossible to forget.
Dynamic animation and motion
The final, essential element of a shop-stopping presentation is how it moves . Seamless transitions for total engagement, UX-led animation to help the audience follow complex ideas, and a premium wow-factor that will last long after your presentation has finished.
Presentation types.
Investor / pitch decks..
Investors want to know about demand. Your competition. Business model. Strategy. Projections. But the main thing they want to know is how you can make them money.
Of course – we’re a presentation design agency – so we’ll include all that information in your investor presentation. But we won’t stop there. We’ll create on-brand slide designs that draw your audience in – immersing them in your idea to see the true value.
Get them excited – and ready to join your adventure.
Sales presentations.
It makes no difference if you’re a start-up or Fortune 500 company.
If you’re pitching technology. Products. Services. Education.
Our presentation designers will work with you to understand your brand. Your ideas. And your requirements.
We’ll create a narrative that tells your story in a way that resonates with your audience. We’ll design beautiful visuals that respect and enhance your brand. And we’ll bring it all together into a persuasive sales presentation design experience.
Internal presentations
Some of the most important presentations you’ll ever make are to your own company. Maybe you’re pitching a new idea to the board Rolling out new processes to your teams. Presenting a whole new vision at a town hall event.
Either way – you can’t afford to make do with ‘ordinary’.
The same elements that make external presentations work are all still in play.
A compelling story. Stunning visuals Dynamic animation.
CPD presentations
Transform long-winded – ordinary – messaging into engaging and informative visual stories. That give your audience a competitive advantage. But doesn’t bore them to sleep in the process.
Get that all-important sign-off from your governing body.
We’re an experienced presentation design agency. So we’ll create a balanced argument. Visualise thorough research. Show your unique value. And highlight the precise technical detail that your audience will want to pay attention to.
Marketing presentations
A marketing presentation can be a more human way to generate leads. To get your brand name out there. To reach your goals.
But only when it’s done properly.
Our expert team will get to know your brand and your services as well as you do. We’ll use everything we learn about you to create highly-visual slides that do your business justice and draw out the real human stories buried in your brand.
And we’ll show your potential clients that they too can have all their problems solved by you. Every message will provide value – so you nestle your brand right at the forefront of their mind.
Conference presentations
When you get invited to give a conference presentation at a huge industry event, you only get one chance to nail it.
So the smart move is to work with a conference presentation agency that can handle everything when it comes to your keynote presentation.
Your narrative and your visual story. Audience interaction and motion design. We’ll tie it all together in an immersive presentation experience.
Product presentations
We’ll create an immersive product showcase presentation that won’t just tell your audience they need to buy your product – it will make them feel it.
Our presentation specialists will hit every pillar of persuasion and create an interactive presentation experience. So your audience can get to know the product that will change their lives.
Show your product off proudly: let the world see what you see.

What they say.
Software presentation.
“This might sound cheesy but do believe the Hype! We contacted them with a really urgent requirement and they delivered an amazing presentation and ultra fast. Knowing what we wanted and having the copy already drafted obviously helped but their team got our vision and brought it to life, and better than we expected. We will definitely work with them again and are already thinking about the next idea.”
Colin Brimson
CEO, d-flo Limited
Conference presentation
“Our conference presentation stood out as the best part, and presentation, of the day! The Rockstar section was the talk of the conference, with everyone asking our contact where they’d gone to produce that. Making noise at these events is how the individual brands cut through to the group heads and get more support and confidence where they need it.”
Gordon Donald
Senior Sponsorship and Promotions Manager, AG Barr
Sales presentation
“I highly recommend the team to anyone looking to elevate their communications and take their sales presentations to the next level.”
Stephanie Malham
Chief Operating Officer, Outright Games
CPD presentation
“The team guided us through the step-by-step process with ease, providing great insight and fresh new ideas, to create a more modern and engaging CPD for our audience.”
Andrew Hamilton
UK Specification and Marketing Director, FAAC
Investor deck
“The team helped us to create a first-class investor deck, which was instrumental to the success of our investment round. We ended up securing £585,000, which exceeded our expectations by 30%.”
Kirstine Newton
Co-founder, Altitude Gin
years of experience.
presentations created.
How can we help?
We empower brands with fast , cost-effective , results-driven presentations .
Frequently asked questions.

How do I get started with my presentation design project?
You’ve probably got deadlines to hit and want a fast turnaround. That’s why we make getting started as simple as putting a meeting in our calendar . We’ll meet over Teams to understand what you want to achieve, and discuss the best next steps for your project. Easy.
We’ll show you examples of our previous work that’s relevant to your project, and we’ll introduce the team, including your dedicated Google Slides or PowerPoint presentation designers.
From there, we’ll send you a proposal, explaining our costs and all the details, before you make any decisions.
Want to find out more? Get in touch .
How much will it cost to hire a presentation design agency?
We want to make our pricing as transparent and simple to understand as possible. Because we know that there’s nothing more frustrating than looking for a presentation design agency with no idea of how much it will cost before you start your enquiries.
So for a clear estimate, with no hidden extras, take a look at our costs .
How long does the presentation design process take?
Well, that depends. How long will your presentation last? Do you want help with the story, as well as design and animation? How complex – or simple – do you need it to be?
However you want the final deliverable to be, we’ll always try to work within your schedule.
Final delivery can be from as little as 24 hours for simple projects to a few weeks for a more in-depth presentation.
What software do you use to design presentations?
Our specialist presentation designers have years of experience in a huge range of presentation software. We tend to use PowerPoint, Google Slides, Prezi, or Keynote the most, but it really depends on the objectives your company needs to achieve and the platform you’re most comfortable using.
Meanwhile, our presentation designers are masters in the Adobe Suite, flexing their creative muscles in software including Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign, XD, and After Effects before we deliver the final file in a format that your team can easily access, use, and edit.
With this expansive skillset, we can offer the whole package: jaw-dropping presentations that don’t look like presentations, alongside professional supporting assets, such as digital brochures, bespoke video, print documents, and infographics. We’re a full-service presentation design agency.
Check out our full list of services to find out more.
Will I be protected by an NDA?
Absolutely. Our clients’ confidentiality is extremely important to us, and we have very strict measures in place. We’ll happily sign your NDA before we even have a consultation and, if you don’t have one to hand, you can use ours.
Do I need to provide the content for the presentation?
The best presentations follow strong themes that are consistent throughout the narrative, design and animation. In most cases, we’d recommend starting your project with a discovery workshop, where we unpick your brand story, your key messaging, as well as get to know your audience and their challenges. This not only help us to create a powerful narrative for your brand, but also allows us to step back and look at the big picture, making sure we recommend the right deliverable, software, and supporting assets to help you reach your goals.
If you have existing content that you’d like us to use as a starting point, that’s great. But if you’d like us to start from scratch, we can create a complete presentation with the findings from the workshop alone.
And, of course, if you’re happy with your company story, we can leave you to it and jump straight to design and experiential development.
Take a look at what we can do for you, whether you provide content, or we create it.
Will I be able to send the presentation to my audience after the meeting?
Of course you can, however, as expert presentation designers, we’d suggest you’re asking one document to do too much.
The more focused you can be, the more effective your communications.
So instead, we’d recommend creating a powerful presentation and a separate leave-behind document, allowing each to do their job properly.
Can each presentation be visually tailored to different audiences?
Oh yes. Creating personalised presentations, not only in narrative, but in visual style, is totally the right way to make a lasting impression. And it doesn’t have to be difficult.
We can create composite logo placeholders within your template, so you can simply drop in the logo of your prospective client next to your own and voilà.
Or we could go one step further, and create a design style based on integrating your brand colours with your prospects’ colours. Each time you present, you’d just need to find the colour value of their main brand colour, change the relevant elements within the template, and it will automatically apply to all those slides. Don’t worry, our presentation experts will walk you through it.
And of course, we’d love to help each time you confirm a new pitch, and our expert presentation designers will transform your presentation to bring together your brand and theirs. Don’t ask your audience to try and imagine your partnership.
Go one step further, and show them how your product would look with their branding, through image and video mock-ups, bespoke for each prospect.
How will you know what I like when it comes to design?
Graphic design isn’t all about how pretty something is. There’s a methodology and theory to it as well.
Over the last ten years, our specialist presentation designers have honed our presentation services and our design process to get them as close to an exact science as, we believe, is possible.
Our expert PowerPoint design process goes a little something like this:
1. Immersion
We take the time to deep dive into your brand guidelines, your previous company marketing collateral, your website, or just stuff you’ve seen that you like. Heck, even show us stuff you’ve seen that you didn’t like. It all helps.
Our specialist presentation designers burrow deep into anything you send us, getting to know you before they even get a chance to say hello.
2. Conversation
We’ve devised a thorough set of briefing questions, designed to get your opinions on how far we can push your brand, what you like, what you don’t like, how you need your company presentation to function, and what you want your audience to feel when they see it. We can even show mood boards at this stage, if you’re the visual type.
3. Initial look and feel
We’ll take just a small handful of your slides, and apply your brand-new design style to them, giving you the chance to review and make revisions. We just want to make sure you love it, before we go full steam ahead. We can even create multiple design routes at this stage, to give you some options. After all, you might not know what you like until you see it.
4. Roll out
Once you’re happy with the look and feel, we’ll roll it out across your unique slides within your presentation. At this stage, we’re still working in Adobe XD or Photoshop, and you’ll get another chance to review and give feedback, before we start building your bells-and-whistles professional presentation in PowerPoint.
We've uncovered the formula behind great presentations!
Starting is hard, let us make it easy.
Let’s get to know each other. We’ll gently steer the conversation just enough to establish effortless dialogue and deliver unparalleled results. Leave the hard stuff to us and take the credit—we don’t mind a bit.
Your story is a great launching pad.
Empathy is our connection point as human beings. We’ll put in time and effort to communicate clearly and make sure all of your final assets do the same. Let’s talk!
Kick start your momentum with us.
The right exchange of energies makes all the difference. We’ll tailor custom solutions that fit your project like a glove. Now step this way and we’ll get you fitted!
Our process is simple.
We'll help you craft the content of your presentation to maximize the impact of each idea.
We’ll create collateral that looks incredible, flows visually and tells the story you need told.
We’ll help you deliver with excellence through our custom training program , where we’ll equip you with the tools needed to knock your presentation out of the park.
15+ years experience helping some of the world's most admired brands
Emerge in the Spotlight
Take our Emerge Presenter Assessment and get an accurate breakdown of your virtual presentation strengths and weaknesses. This first-of-its-kind, skill-assessment system helps you discover what type of virtual presenter you naturally are whether it is leading a Zoom call or delivering an investor pitch.
Ready to get started?
Contact us today to speak to one of our experts.
Not quite ready?
Check out our blog for more resources.
"the designs are always amazing the team works tirelessly to cater the design to any specific requests we make and they always come through with something truly beautiful ".
– Matt Hull, Hill’s Pet Nutrition
Why all the praise?
© 2006-2024 Ethos3 – An Award Winning Presentation Design and Training Company ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Google Slides Presentation Design
- Pitch Deck Design
- Powerpoint Redesign
- Other Design Services
Expert help with design presentation to achieve your goals
We help business owners, startups, marketers, and educators present their ideas in the most appealing way.

Our presentation design services
Have your presentation redesigned, improved or created from scratch by our powerpoint service.

Explore our custom slide samples

Ballard Power Systems

Amazone Web Services Deck

Mixpanel Pitchdeck

Nursing Theory

String Theory is Retared

Blood Donation
Our services
At SlidePeak, we work with start-ups, managers, marketers, analysts, and other individuals to find their voice and tell their story through great designs in any software.
What is the power of a presentation design?
Your idea deserves a brilliant presentation design and pro help.
Whether it’s an academic project or business proposal, we can create a presentation that perfectly serves its purposes.
Delivering well-made presentations for all fields
Powerful, effective, and customized to your needs.
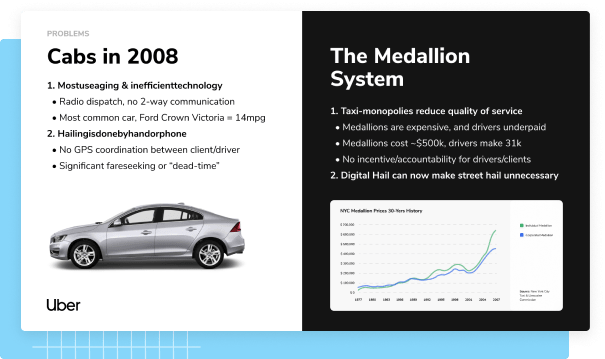
From designing one-page infographics to creating pitch decks — we cover all business-related topics and visualize data of all kinds.
We create custom-made presentations tailored specifically to your niche, precisely following your corporate style guide, tone of voice, and requirements. And a completely editable format allows you to update the delivered presentation by yourself.

We help educators present their study material in a more engaging way, accompanying lectures with professional, good-structured presentations.
Attention to detail, proper data visualization, clear structure, embedded videos, topic-based illustrations, and easy to edit slides is what makes our presentations so unique.
Having accumulated expertise while working with teachers of different disciplines and teaching for different academic levels, we know how to deliver a presentation that will meet all your needs.

We create presentations for almost all disciplines and academic levels: from Business to Healthcare, from BA to Ph.D.
If you need to present your research in the best way, meeting all academic standards, we can help you succeed. Our designers can organize your thoughts and your research in a clear and concise way by structuring slides, creating contrast, adding charts, graphs, and other visuals.
We can also advise you on content, edit, proofread, or redesign your presentation, and help with speaker notes.
Our customers' testimonials

Frequently asked questions
How fast can you do a powerpoint presentation.
The minimum possible deadline is under 12 hours. It is best suited for small orders, such as redesigning 3-5 slides without complex graphs and visuals. Sometimes, we can fulfill a larger order but must check your instructions first. In case of such a request, please get in touch with our 24/7 support team, and they’ll tell you whether it is realistic to accommodate it before your deadline.
A 24-hour deadline is perfect for urgent orders of approximately 10 slides. However, if you need 20-40 slides done within such a period, we’ll typically divide the order among several designers who’ll follow one style to ensure design consistency.
If you’re not in a rush, the recommended deadline for standard presentations of 10-20 slides is 3-5 days . This time is enough to approve the draft with you, finalize the presentation and, if necessary, make additional changes. Remember, the longer the deadline, the lower the cost of work.
Can you redesign a presentation in a language other than English?
Yes, that’s not a problem for our professional presentation company. We have extensive experience redesigning presentations in Spanish, French, Chinese, German, and other languages. However, as long as we don’t offer translation services, the content has to be provided by you.
I'm not sure about the style. How can you help me in such a case?
You can review the completed works on our website or request our portfolio to check other work samples not available online. Also, if you have any examples of the style you like, you can provide us with a link to the website or materials or describe it in writing.
In case you have any preferences regarding the color scheme or the list of colors that should not be used, upload it with the instructions, and the designer will consider your wishes. However, if you don’t know what exactly you would like to see, you can opt for a premium business presentation design service, and our experts will prepare several design options for you to choose the one that best fits your vision.
If you have a large presentation but are not sure that the final result will satisfy you, you can first order several slides, check the result, and then assign the rest to that designer.
Can I get a draft to approve the style?
Yes, of course. For non-urgent orders of 5 or more slides, we try to provide drafts for preliminary approval by default and take into account all comments before the order is completed. Therefore, if you want an initial draft of the PowerPoint presentation design, just indicate it when placing an order.
Please note that “draft” means 2-3 redesigned pages in PDF format.
What if I don't like the draft?
Such cases are extremely rare. However, should it happen, we clarify what exactly you don’t like about the draft and offer to let another designer redo it following your comments. In most cases, this is enough to hit the target.
What if I need to change something in the completed presentation?
If these are minor changes relating to the initial instructions, we will revise the presentation to perfection at no cost. That is the main reason why we usually provide a draft for general stylistic approval. Besides, in case of large orders, we can ask you to approve the completed presentation in parts so that the final result meets your expectations.
If changes are more significant and do not pertain to the initial instructions or require extensive amendments following updated guidelines, including designing extra slides, there can be an additional payment for the designer’s time and effort.
The significant advantage of our approach is that we always try to do our best so that you remain 100% satisfied with the final product.
What about the rights to images and illustrations? What sources do you usually use?
At our ppt presentation design company, we usually use images and illustrations that are provided by the client. Other sources generally include photo stocks (both paid and free) and open sources.
If the client has special requirements regarding copyright and use of images (e.g., commercial presentation design), we can either select images/illustrations that are allowed to be used for such purposes, buy the rights for such use, or provide the client with links to rights purchase.
I'm not a native speaker. Can you proofread the content for a presentation?
Yes, we can. We have experienced copywriters and editors on our team who can proofread the content, improve it, create content based on your materials, or, if necessary, do research, collect additional information, and write content from scratch.
For such a task, we recommend choosing the “Presentation from your material” option and describing your wishes regarding proofreading.
Do you help with content writing? What exactly can you do?
Yes, we have experienced copywriters who can help with writing, adaptation, and summarizing of content, both the one provided by the client or created from scratch by our team.
Please note that it is very important to choose the right type of work for such services. Here’s a brief description of available options:
- Presentation based on your material. This option is a good fit for cases when you have all the required information and just need to adapt it to the presentation, shorten it, identify the key ideas, summarize the data, or slightly refine the content.
- Presentation from scratch. As the name suggests, this service covers writing content from the ground up. It’s a perfect option for cases when the content needs to be radically revised or rewritten. As this type of work requires research, please ensure there’s enough freely available material on the topic before placing an order for PowerPoint presentation design services. However, should the creation of a presentation need narrow expertise in a specific niche, we recommend that you submit a preliminary request so that we can confirm whether we can fulfill the order.
Is it possible to incorporate my branding into a presentation redesign?
Yes, of course. Simply mention it in the instructions and provide related materials. It can be a link to the website, brand book, previously made slides, or a logo with a note to create a presentation in similar complementary colors.
Can we sign my company's NDA, or do you have your own agreement?
Yes, we can sign your company’s NDA or provide our agreement for signing. The advantage of our NDA is that it takes less time to approve it with the legal department, and both parties can sign it within 1-2 business days.
Please note that our legal department does not work on Saturdays and Sundays, so if you have an urgent presentation that needs to be designed over the weekend, our presentation design agency can take on the work and sign the agreement after the order is completed.
To sign our NDA, we require the following information from you:
- Company name (e.g., Trust Limited)
- Country of registration (e.g., USA)
- Registration number (e.g., CS513192014)
- Address (e.g., 205 East 42nd Street, New York)
- Printed name (e.g., John Smith)
- Title (e.g., Marketing Manager)
- Email address (e.g., [email protected] )
Signing your company’s NDA can take 2-4 business days, depending on the terms of the agreement and the comments of our lawyers.
Can I pay in installments?
Certainly! You can pay for just a part of the slides, wait for us to complete them, and then order the rest from the same designer.
Can I get an invoice?
Yes, you can download the invoice from the customer area, which will become available once you place an order. Here’s where you can find it:
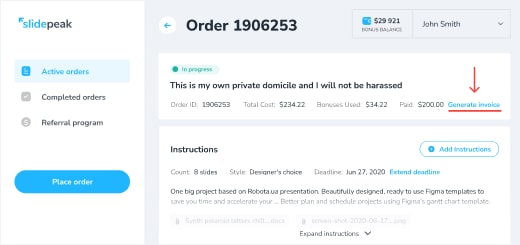
Alternatively, you can contact our support team , and they’ll email it to you.
SlidePeak presentation services: creating a story for your business
As an owner of a business idea, project, or service, you put a lot of time and dedication into every detail. Planning, analyzing the market, bringing a team of experts together – that’s always a tough challenge even for a seasoned pro.
So, by the time you have to pitch your huge project to investors or your target audience, you might already be quite exhausted and deeply buried in details. Recruit presentation design service to bring a fresh perspective and highlight the essentials in your custom slideshow.

Who will do my presentation content and design?
SlidePeak design services is a professional team with extensive experience in the market. We work as your partners, striving to boost your performance and provide you with the best visual representation of any project.
Who will be my copywriter? Our copywriters are experienced in producing short, on-point texts for any industry, topic, or project. They are here to make your speech memorable, well-argued, and convincing. Provide us with anything you've got – an old presentation, pieces of material, or just an inspiring idea – and they will help with crafting a whole story behind your project.
Who will be my designer? Our designers are well-trained experts in their field, able to create the best visuals of any complexity, impress your audience and make your presentation 100% engaging. They can integrate your corporate branding and your organization’s philosophy into the PPT slides, so it will be no different from in-house production. Also, if you are not sure what design style you are looking for, they can suggest options and help you choose the right style that meets your specific design needs.
Never lose your listeners’ attention with the A-level slideshow created under your custom request. Work alongside the presentation professionals and take over your target audience.

Light up the essentials with custom presentation design
Leading PowerPoint design services exist to create a solid ground for your presentation. What we do is take your brilliant idea and transform it into a well-crafted custom visual. The industry you work in, your target audience, the keynote, and your company – that’s what creates our framework. SlidePeak experts develop on-point content and perfect visuals to highlight the most important parts of your speech. Get the perfect balance of text and visuals crafted for you in due time by professional presentation design services.
Expertly designed presentations tailored to your specific needs
- Blog
- Client Login
- US/UK/Canada Mexico France Sweden Israel Germany Turkey

Global CAD Services
The global leader in on-demand cad services. contact us today for cad conversion, cad modeling, solar permit drawings, point cloud to cad conversion, and free auto-vectorization (e.g. using automated tools for pdf to dwg conversion )., cad & graphics experts.

- Access top quality CAD talent on demand
- Scale your business up and down as required
- Keep your fixed costs low and maintain maximum flexibility
- Keep your customers happy
- Maximize your profits
- Get a Quote
- Join our Team
- How we work
Our Services


100% satisfied and impressed by the service I received. All transaction aspects were completed online! My confidence in your company grew with each contact.
First let me say WOW! The conversions are absolutely perfect. My customer is going to be very pleased, as am I. Your company will continue to handle all our CAD conversion needs.
Thank you very much for the quick turnaround. Everything looks great once again you amaze me. I can’t wait for my customer to see them.
- The Benefits of 3D Modeling Services
- Impact of Industrial Revolution on Architectural Design
- Outsourcing CAD Support Works Well in AEC Industry
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

8 templates

solar eclipse
25 templates

ai technology
148 templates

55 templates

22 templates
Design Inspiration Business Meeting
Design inspiration business meeting presentation, free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
Download the "Design Inspiration Business Meeting" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Gone are the days of dreary, unproductive meetings. Check out this sophisticated solution that offers you an innovative approach to planning and implementing meetings! Detailed yet simplified, this template ensures everyone is on the same page, contributing to a productive and efficient meeting. Enhancing understanding and leaving room for innovative ideas, this tool has everything you need for an effective meeting of focused discussions and beneficial outcomes.
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- Different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

- Create a presentation Article
- Add and format Article
- Design a presentation Article
- Share and collaborate Article
- Give a presentation Article
- Set up your mobile apps Article
- Learn more Article

Create a presentation
Create a presentation in powerpoint for the web.

With PowerPoint for the web running in your web browser, you can:
Create presentations that include images, videos, transitions, and animations.
Get to your presentations from your computer, tablet, or phone.
Share and work with others, wherever they are.
If you're using the desktop version of PowerPoint on a Windows PC, see the PowerPoint Quick Start .
If you're using the desktop version of PowerPoint on a Mac, see Office for Mac Quick Start Guides and PowerPoint for Mac Help .
Create, open, and name a presentation
Go to powerpoint.office.com .

Select New blank presentation , open a Recent file, select one of the themes , or start with a presentation template .
To name the presentation, select the title at the top and type a name.
If you need to rename the presentation, select the title and retype the name.

Add a slide
Select the slide you want your new slide to follow.
Select Home > New Slide .
Select Layout and the you type want from the drop-down.

When working in PowerPoint for the web, your work is saved every few seconds. You can select File > Save a Copy to create a duplicate copy in another location.
Or choose File > Download As to save a copy to your device.

When you're online, AutoSave is always on and saves your changes as you work. If at any time you lose your Internet connection or turn it off, any pending changes will sync as soon as you’re back online.
Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
dissertation literature review themes
Have a language expert improve your writing.
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved March 25, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
Correct my document today
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 25 March 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

How to Write a Thematic Literature Review: A Beginner’s Guide

Literature reviews provide a comprehensive understanding of existing knowledge in a particular field, offer insights into gaps and trends, and ultimately lay the foundation for innovative research. However, when tackling complex topics spanning multiple issues, the conventional approach of a standard literature review might not suffice. Many researchers present a literature review without giving any thought to its organization or structure, but this is where a thematic literature review comes into play. In this article, we will explore the significance of thematic reviews, delve into how and when to undertake them, and offer invaluable guidance on structuring and crafting a compelling thematic literature review.
Table of Contents
What is a thematic literature review.
A thematic literature review, also known as a thematic review, involves organizing and synthesizing the existing literature based on recurring themes or topics rather than a chronological or methodological sequence. Typically, when a student or researcher works intensively on their research there are many sub-domains or associated spheres of knowledge that one encounters. While these may not have a direct bearing on the main idea being explored, they provide a much-needed background or context to the discussion. This is where a thematic literature review is useful when dealing with complex research questions that involve multiple facets, as it allows for a more in-depth exploration of specific themes within the broader context.

When to opt for thematic literature review?
It is common practice for early career researchers and students to collate all the literature reviews they have undertaken under one single broad umbrella. However, when working on a literature review that involves multiple themes, lack of organization and structure can slow you down and create confusion. Deciding to embark on a thematic literature review is a strategic choice that should align with your research objectives. Here are some scenarios where opting for a thematic review is advantageous:
- Broad Research Questions: When your research question spans across various dimensions and cannot be adequately addressed through a traditional literature review.
- Interdisciplinary Research: In cases where your research draws from multiple disciplines, a thematic review helps in synthesizing diverse literature cohesively.
- Emerging Research Areas: When exploring emerging fields or topics with limited existing literature, a thematic review can provide valuable insights by focusing on available themes.
- Complex Issues: Thematic reviews are ideal for dissecting complex issues with multiple contributing factors or dimensions.
Advantages of a Thematic Literature Review
With better comprehension and broad insights, thematic literature reviews can help in identifying possible research gaps across themes. A thematic literature review has several advantages over a general or broad-based approach, especially for those working on multiple related themes.
- It provides a comprehensive understanding of specific themes within a broader context, allowing for a deep exploration of relevant literature.
- Thematic reviews offer a structured approach to organizing and synthesizing diverse sources, making it easier to identify trends, patterns, and gaps.
- Researchers can focus on key themes, enabling a more detailed analysis of specific aspects of the research question.
- Thematic reviews facilitate the integration of literature from various disciplines, offering a holistic view of the topic.
- Researchers can provide targeted recommendations or insights related to specific themes, aiding in the formulation of research hypotheses.
Now that we know the benefits of a thematic literature review, what is the best way to arrange reviewed literature in a thematic format?
How to write a thematic literature review
To effectively structure and write a thematic literature review, follow these key steps:
- Define Your Research Question: Clearly define the overarching research question or topic you aim to explore thematically. When writing a thematic literature review, go through different literature review sections of published research work and understand the subtle nuances associated with this approach.
- Identify Themes: Analyze the literature to identify recurring themes or topics relevant to your research question. Categorize the bibliography by dividing them into relevant clusters or units, each dealing with a specific issue. For example, you can divide a topic based on a theoretical approach, methodology, discipline or by epistemology. A theoretical review of related literature for example, may also look to break down geography or issues pertaining to a single country into its different parts or along rural and urban divides.
- Organize the Literature: Group the literature into thematic clusters based on the identified themes. Each cluster represents a different aspect of your research question. It is up to you to define the different narratives of thematic literature reviews depending on the project being undertaken; there is no one formal way of doing this. You can weigh how specific areas stack up against others in terms of existing literature or studies and how many more aspects may need to be added or further looked into.
- Review and Synthesize: Within each thematic cluster, review and synthesize the relevant literature, highlighting key findings and insights. It is recommended to identify any theme-related strengths or weaknesses using an analytical lens.
- Integrate Themes: Analyze how the themes interact with each other, draw linkages between earlier studies and see how they contribute to your own research. A thematic literature review presents readers with a comprehensive overview of the literature available on and around the research topic.
- Provide a Framework: Develop a framework or conceptual model that illustrates the relationships between the themes. Present the most relevant part of the thematic review toward the end and study it in greater detail as it reflects the literature most relevant and directly related to the main research topic.
- Conclusion: Conclude your thematic literature review by summarizing the key findings and their implications for your research question. Be sure to highlight any gaps or areas requiring further investigation in this section.
- Cite and Reference: It is important to remember that a thematic review of literature for a PhD thesis or research paper lends greater credibility to the student or researcher. So ensure that you properly cite and reference all sources according to your chosen citation style.
- Edit and Proofread: Take some time to review your work, ensure proper structure and flow and eliminate any language, grammar, or spelling errors that could deviate reader attention. This will help you deliver a well-structured and elegantly written thematic literature review.
Thematic literature review example
In essence, a thematic literature review allows researchers to dissect complex topics into smaller manageable themes, providing a more focused and structured approach to literature synthesis. This method empowers researchers to gain deeper insights, identify gaps, and generate new knowledge within the context of their research.
To illustrate the process mentioned above, let’s consider an example of a thematic literature review in the context of sustainable development. Imagine the overarching research question is: “What are the key factors influencing sustainable urban planning?” Potential themes could include environmental sustainability, social equity, economic viability, and governance. Each theme would have a dedicated section in the review, summarizing relevant literature and discussing how these factors intersect and impact sustainable urban planning. Close with a strong conclusion that highlights research gaps or areas of investigation. Finally, review and refine the thematic literature review, adding citations and references as required.
In conclusion, when tackling multifaceted research questions, a thematic literature review proves to be an indispensable tool for researchers and students alike. By adopting this approach, scholars can navigate the intricate web of existing literature, unearth meaningful patterns, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their respective fields. We hope the information in this article helps you create thematic reviews that illuminate your path to new discoveries and innovative insights.
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading app that uses your interests to instantly create personalized reading feeds. Researchers can stay updated on the latest, most relevant content from its continually expanding library of 115M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex as well as prestigious publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more. The top-rated app in its space, R Discovery’s carefully curated features give you the power to choose what, where, and how you read research.
Try the app for free or upgrade to R Discovery Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to app-only features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, invite collaborators, auto sync with reference managers and more. It’s like having the world of research at your fingertips! Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Get R Discovery Prime now at just US$39 a year!
Related Posts

What is Inductive Reasoning? Definition, Types and Examples
How R Discovery achieved 2X engagement with GetFTR
What Is A Literature Review?
A plain-language explainer (with examples).
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) & Kerryn Warren (PhD) | June 2020 (Updated May 2023)
If you’re faced with writing a dissertation or thesis, chances are you’ve encountered the term “literature review” . If you’re on this page, you’re probably not 100% what the literature review is all about. The good news is that you’ve come to the right place.
Literature Review 101
- What (exactly) is a literature review
- What’s the purpose of the literature review chapter
- How to find high-quality resources
- How to structure your literature review chapter
- Example of an actual literature review
What is a literature review?
The word “literature review” can refer to two related things that are part of the broader literature review process. The first is the task of reviewing the literature – i.e. sourcing and reading through the existing research relating to your research topic. The second is the actual chapter that you write up in your dissertation, thesis or research project. Let’s look at each of them:
Reviewing the literature
The first step of any literature review is to hunt down and read through the existing research that’s relevant to your research topic. To do this, you’ll use a combination of tools (we’ll discuss some of these later) to find journal articles, books, ebooks, research reports, dissertations, theses and any other credible sources of information that relate to your topic. You’ll then summarise and catalogue these for easy reference when you write up your literature review chapter.
The literature review chapter
The second step of the literature review is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or thesis structure ). At the simplest level, the literature review chapter is an overview of the key literature that’s relevant to your research topic. This chapter should provide a smooth-flowing discussion of what research has already been done, what is known, what is unknown and what is contested in relation to your research topic. So, you can think of it as an integrated review of the state of knowledge around your research topic.

What’s the purpose of a literature review?
The literature review chapter has a few important functions within your dissertation, thesis or research project. Let’s take a look at these:
Purpose #1 – Demonstrate your topic knowledge
The first function of the literature review chapter is, quite simply, to show the reader (or marker) that you know what you’re talking about . In other words, a good literature review chapter demonstrates that you’ve read the relevant existing research and understand what’s going on – who’s said what, what’s agreed upon, disagreed upon and so on. This needs to be more than just a summary of who said what – it needs to integrate the existing research to show how it all fits together and what’s missing (which leads us to purpose #2, next).
Purpose #2 – Reveal the research gap that you’ll fill
The second function of the literature review chapter is to show what’s currently missing from the existing research, to lay the foundation for your own research topic. In other words, your literature review chapter needs to show that there are currently “missing pieces” in terms of the bigger puzzle, and that your study will fill one of those research gaps . By doing this, you are showing that your research topic is original and will help contribute to the body of knowledge. In other words, the literature review helps justify your research topic.
Purpose #3 – Lay the foundation for your conceptual framework
The third function of the literature review is to form the basis for a conceptual framework . Not every research topic will necessarily have a conceptual framework, but if your topic does require one, it needs to be rooted in your literature review.
For example, let’s say your research aims to identify the drivers of a certain outcome – the factors which contribute to burnout in office workers. In this case, you’d likely develop a conceptual framework which details the potential factors (e.g. long hours, excessive stress, etc), as well as the outcome (burnout). Those factors would need to emerge from the literature review chapter – they can’t just come from your gut!
So, in this case, the literature review chapter would uncover each of the potential factors (based on previous studies about burnout), which would then be modelled into a framework.
Purpose #4 – To inform your methodology
The fourth function of the literature review is to inform the choice of methodology for your own research. As we’ve discussed on the Grad Coach blog , your choice of methodology will be heavily influenced by your research aims, objectives and questions . Given that you’ll be reviewing studies covering a topic close to yours, it makes sense that you could learn a lot from their (well-considered) methodologies.
So, when you’re reviewing the literature, you’ll need to pay close attention to the research design , methodology and methods used in similar studies, and use these to inform your methodology. Quite often, you’ll be able to “borrow” from previous studies . This is especially true for quantitative studies , as you can use previously tried and tested measures and scales.

How do I find articles for my literature review?
Finding quality journal articles is essential to crafting a rock-solid literature review. As you probably already know, not all research is created equally, and so you need to make sure that your literature review is built on credible research .
We could write an entire post on how to find quality literature (actually, we have ), but a good starting point is Google Scholar . Google Scholar is essentially the academic equivalent of Google, using Google’s powerful search capabilities to find relevant journal articles and reports. It certainly doesn’t cover every possible resource, but it’s a very useful way to get started on your literature review journey, as it will very quickly give you a good indication of what the most popular pieces of research are in your field.
One downside of Google Scholar is that it’s merely a search engine – that is, it lists the articles, but oftentimes it doesn’t host the articles . So you’ll often hit a paywall when clicking through to journal websites.
Thankfully, your university should provide you with access to their library, so you can find the article titles using Google Scholar and then search for them by name in your university’s online library. Your university may also provide you with access to ResearchGate , which is another great source for existing research.
Remember, the correct search keywords will be super important to get the right information from the start. So, pay close attention to the keywords used in the journal articles you read and use those keywords to search for more articles. If you can’t find a spoon in the kitchen, you haven’t looked in the right drawer.
Need a helping hand?
How should I structure my literature review?
Unfortunately, there’s no generic universal answer for this one. The structure of your literature review will depend largely on your topic area and your research aims and objectives.
You could potentially structure your literature review chapter according to theme, group, variables , chronologically or per concepts in your field of research. We explain the main approaches to structuring your literature review here . You can also download a copy of our free literature review template to help you establish an initial structure.
In general, it’s also a good idea to start wide (i.e. the big-picture-level) and then narrow down, ending your literature review close to your research questions . However, there’s no universal one “right way” to structure your literature review. The most important thing is not to discuss your sources one after the other like a list – as we touched on earlier, your literature review needs to synthesise the research , not summarise it .
Ultimately, you need to craft your literature review so that it conveys the most important information effectively – it needs to tell a logical story in a digestible way. It’s no use starting off with highly technical terms and then only explaining what these terms mean later. Always assume your reader is not a subject matter expert and hold their hand through a journe y of the literature while keeping the functions of the literature review chapter (which we discussed earlier) front of mind.

Example of a literature review
In the video below, we walk you through a high-quality literature review from a dissertation that earned full distinction. This will give you a clearer view of what a strong literature review looks like in practice and hopefully provide some inspiration for your own.
Wrapping Up
In this post, we’ve (hopefully) answered the question, “ what is a literature review? “. We’ve also considered the purpose and functions of the literature review, as well as how to find literature and how to structure the literature review chapter. If you’re keen to learn more, check out the literature review section of the Grad Coach blog , as well as our detailed video post covering how to write a literature review .

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:
16 Comments
Thanks for this review. It narrates what’s not been taught as tutors are always in a early to finish their classes.
Thanks for the kind words, Becky. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This website is amazing, it really helps break everything down. Thank you, I would have been lost without it.
This is review is amazing. I benefited from it a lot and hope others visiting this website will benefit too.
Timothy T. Chol [email protected]
Thank you very much for the guiding in literature review I learn and benefited a lot this make my journey smooth I’ll recommend this site to my friends
This was so useful. Thank you so much.
Hi, Concept was explained nicely by both of you. Thanks a lot for sharing it. It will surely help research scholars to start their Research Journey.
The review is really helpful to me especially during this period of covid-19 pandemic when most universities in my country only offer online classes. Great stuff
Great Brief Explanation, thanks
So helpful to me as a student
GradCoach is a fantastic site with brilliant and modern minds behind it.. I spent weeks decoding the substantial academic Jargon and grounding my initial steps on the research process, which could be shortened to a couple of days through the Gradcoach. Thanks again!
This is an amazing talk. I paved way for myself as a researcher. Thank you GradCoach!
Well-presented overview of the literature!
This was brilliant. So clear. Thank you
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Writing the Dissertation - Guides for Success: The Literature Review
- Writing the Dissertation Homepage
- Overview and Planning
The Literature Review
- The Methodology
- The Results and Discussion
- The Conclusion
- The Abstract
- Getting Started
- Research Gap
- What to Avoid
Overview of writing the literature review
Conducting a literature review enables you to demonstrate your understanding and knowledge of the existing work within your field of research. Doing so allows you to identify any underdeveloped areas or unexplored issues within a specific debate, dialogue or field of study. This, in turn, helps you to clearly and persuasively demonstrate how your own research will address one or more of these gaps.
Disciplinary differences
Please note: this guide is not specific to any one discipline. The literature review can vary depending on the nature of the research and the expectations of the school or department. Please adapt the following advice to meet the demands of your dissertation and the expectations of your school or department. Consult your supervisor for further guidance; you can also check out Writing Across Subjects guide .
Guide contents
As part of the Writing the Dissertation series, this guide covers the most common expectations for the literature review chapter, giving you the necessary knowledge, tips and guidance needed to impress your markers! The sections are organised as follows:
- Getting Started - Defines the literature review and presents a table to help you plan.
- Process - Explores choosing a topic, searching for sources and evaluating what you find.
- Structure - Presents key principles to consider in terms of structure, with examples to illustrate the concepts.
- Research gap - Clarifies what is meant by 'gap' and gives examples of common types of gaps.
- What to Avoid - Covers a few frequent mistakes you'll want to...avoid!
- FAQs - Answers to common questions about research gaps, literature availability and more.
- Checklist - Includes a summary of key points and a self-evaluation checklist.
Training and tools
- The Academic Skills team has recorded a Writing the Dissertation workshop series to help you with each section of a standard dissertation, including a video on writing the literature review .
- Check out the library's online Literature Review: Research Methods training.
- Our literature reviews summary guide provides links to further information and videos.
- The dissertation planner tool can help you think through the timeline for planning, research, drafting and editing.
- iSolutions offers training and a Word template to help you digitally format and structure your dissertation.

What is the literature review?
The literature review of a dissertation gives a clear, critical overview of a specific area of research. Our main Writing the Dissertation - Overview and Planning guide explains how you can refine your dissertation topic and begin your initial research; the next tab of this guide, 'Process', expands on those ideas. In summary, the process of conducting a literature review usually involves the following:
- Conducting a series of strategic searches to identify the key texts within that topic.
- Identifying the main argument in each source, the relevant themes and issues presented and how they relate to each other.
- Critically evaluating your chosen sources and determining their strengths, weaknesses, relevance and value to your research along with their overall contribution to the broader research field.
- Identifying any gaps or flaws in the literature which your research can address.
Literature review as both process and product
Writers should keep in mind that the phrase 'literature review' refers to two related, but distinct, things:
- 'Literature review' refers, first, to the active process of discovering and assessing relevant literature.
- 'Literature review' refers, second, to the written product that emerges from the above process.
This distinction is vital to note because every dissertation requires the writer to engage with and consider existing literature (i.e., to undertake the active process ). Research doesn't exist in a void, and it's crucial to consider how our work builds from or develops existing foundations of thought or discovery. Thus, even if your discipline doesn't require you to include a chapter titled 'Literature Review' in your submitted dissertation, you should expect to engage with the process of reviewing literature.
Why is it important to be aware of existing literature?
- You are expected to explain how your research fits in with other research in your field and, perhaps, within the wider academic community.
- You will be expected to contribute something new, or slightly different, so you need to know what has already been done.
- Assessing the existing literature on your topic helps you to identify any gaps or flaws within the research field. This, in turn, helps to stimulate new ideas, such as addressing any gaps in knowledge, or reinforcing an existing theory or argument through new and focused research.
Not all literature reviews are the same. For example, in many subject areas, you are expected to include the literature review as its own chapter in your dissertation. However, in other subjects, the dissertation structure doesn't include a dedicated literature review chapter; any literature the writer has reviewed is instead incorporated in other relevant sections such as the introduction, methodology or discussion.
For this reason, there are a number of questions you should discuss with your supervisor before starting your literature review. These questions are also great to discuss with peers in your degree programme. These are outlined in the table below (see the Word document for a copy you can save and edit):
- Dissertation literature review planning table

Literature review: the process
Conducting a literature review requires you to stay organised and bring a systematic approach to your thinking and reading. Scroll to continue reading, or click a link below to jump immediately to that section:
Choosing a topic
The first step of any research project is to select an interesting topic. From here, the research phase for your literature review helps to narrow down your focus to a particular strand of research and to a specific research question. This process of narrowing and refining your research topic is particularly important because it helps you to maintain your focus and manage your material without becoming overwhelmed by sources and ideas.
Try to choose something that hasn’t been researched to death. This way, you stand a better chance of making a novel contribution to the research field.
Conversely, you should avoid undertaking an area of research where little to no work has been done. There are two reasons for this:
- Firstly, there may be a good reason for the lack of research on a topic (e.g. is the research useful or worthwhile pursuing?).
- Secondly, some research projects, particularly practice-based ones involving primary research, can be too ambitious in terms of their scope and the availability of resources. Aim to contribute to a topic, not invent one!
Searching for sources
Researching and writing a literature review is partly about demonstrating your independent research skills. Your supervisor may have some tips relating to your discipline and research topic, but you should be proactive in finding a range of relevant sources. There are various ways of tracking down the literature relevant to your project, as outlined below.
Make use of Library Search
One thing you don’t want to do is simply type your topic into Google and see what comes up. Instead, use Library Search to search the Library’s catalogue of books, media and articles.
Online training for 'Using databases' and 'Finding information' can be found here . You can also use the Library's subject pages to discover databases and resources specific to your academic discipline.
Engage with others working in your area
As well as making use of library resources, it can be helpful to discuss your work with students or academics working in similar areas. Think about attending relevant conferences and/or workshops which can help to stimulate ideas and allows you to keep track of the most current trends in your research field.
Look at the literature your sources reference
Finding relevant literature can, at times, be a long and slightly frustrating experience. However, one good source can often make all the difference. When you find a good source that is both relevant and valuable to your research, look at the material it cites throughout and follow up any sources that are useful. Also check if your source has been cited in any more recent publications.

Think of the bibliography/references page of a good source as a series of breadcrumbs that you can follow to find even more great material.
Evaluating sources
It is very important to be selective when choosing the final sources to include in your literature review. Below are some of the key questions to ask yourself:
- If a source is tangentially interesting but hasn’t made any particular contribution to your topic, it probably shouldn’t be included in your literature review. You need to be able to demonstrate how it fits in with the other sources under consideration, and how it has helped shape the current state of the literature.
- There might be a wealth of material available on your chosen subject, but you need to make sure that the sources you use are appropriate for your assignment. The safest approach to take is to use only academic work from respected publishers. However, on occasions, you might need to deviate from traditional academic literature in order to find the information you need. In many cases, the problem is not so much the sources you use, but how you use them. Where relevant, information from newspapers, websites and even blogs are often acceptable, but you should be careful how you use that information. Do not necessarily take any information as factual. Instead be critical and interpret the material in the context of your research. Consider who the writer is and how this might influence the authority and reliability of the information presented. Consult your supervisor for more specific guidance relating to your research.
- The mere fact that something has been published does not automatically guarantee its quality, even if it comes from a reputable publisher. You will need to critique the content of the source. Has the author been thorough and consistent in their methodology? Do they present their thesis coherently? Most importantly, have they made a genuine contribution to the topic?
Keeping track of your sources
Once you have selected a source to use in your literature review, it is useful to make notes on all of its key features, including where it comes from, what it says, and what its main strengths and weaknesses are. This way you can easily re-familiarise yourself with a source without having to re-read it. Keeping an annotated bibliography is one way to do this.
Alternately, below is a table you can copy and fill out for each source (see the Word document to save an editable copy for yourself). Software such as EndNote also allows you to keep an electronic record of references and your comments on them.
- Source evaluation table
Writing your literature review
As we explored in the 'Getting Started' tab, the literature review is both a process you follow and (in most cases) a written chapter you produce. Thus, having engaged the review process, you now need to do the writing itself. Please continue reading, or click a heading below to jump immediately to that section.
Guiding principles
The structure of the final piece will depend on the discipline within which you are working as well as the nature of your particular research project. However, here are a few general pieces of advice for writing a successful literature review:
- Show the connections between your sources. Remember that your review should be more than merely a list of sources with brief descriptions under each one. You are constructing a narrative. Show clearly how each text has contributed to the current state of the literature, drawing connections between them.
- Engage critically with your sources. This means not simply describing what they say. You should be evaluating their content: do they make sound arguments? Are there any flaws in the methodology? Are there any relevant themes or issues they have failed to address? You can also compare their relative strengths and weaknesses.
- Signpost throughout to ensure your reader can follow your narrative. Keep relating the discussion back to your specific research topic.
- Make a clear argument. Keep in mind that this is a chance to present your take on a topic. Your literature review showcases your own informed interpretation of a specific area of research. If you have followed the advice given in this guide you will have been careful and selective in choosing your sources. You are in control of how you present them to your reader.
There are several different ways to structure the literature review chapter of your dissertation. Two of the most common strategies are thematic structure and chronological structure (the two of which can also be combined ). However you structure the literature review, this section of the dissertation normally culminates in identifying the research gap.
Thematic structure
Variations of this structure are followed in most literature reviews. In a thematic structure , you organise the literature into groupings by theme (i.e., subtopic or focus). You then arrange the groupings in the most logical order, starting with the broadest (or most general) and moving to the narrowest (or most specific).
The funnel or inverted pyramid
To plan a thematic structure structure, it helps to imagine your themes moving down a funnel or inverted pyramid from broad to narrow. Consider the example depicted below, which responds to this research question:
What role did the iron rivets play in the sinking of the Titanic?
The topic of maritime disasters is the broadest theme, so it sits at the broad top of the funnel. The writer can establish some context about maritime disasters, generally, before narrowing to the Titanic, specifically. Next, the writer can narrow the discussion of the Titanic to the ship's structural integrity, specifically. Finally, the writer can narrow the discussion of structural integrity to the iron rivets, specifically. And voila: there's the research gap!

The broad-to-narrow structure is intuitive for readers. Thus, it is crucial to consider how your themes 'nest inside' one another, from the broad to the narrow. Picturing your themes as nesting dolls is another way to envision this literature review structure, as you can see in the image below.

As with the funnel, remember that the first layer (or in this case, doll) is largest because it represents the broadest theme. In terms of word count and depth, the tinier dolls will warrant more attention because they are most closely related to the research gap or question(s).
The multi-funnel variation
The example above demonstrates a research project for which one major heading might suffice, in terms of outlining the literature review. However, the themes you identify for your dissertation might not relate to one another in such a linear fashion. If this is the case, you can adapt the funnel approach to match the number of major subheadings you will need.
In the three slides below, for example, a structure is depicted for a project that investigates this (fictional) dissertation research question: does gender influence the efficacy of teacher-led vs. family-led learning interventions for children with ADHD? Rather than nesting all the subtopics or themes in a direct line, the themes fall into three major headings.
The first major heading explores ADHD from clinical and diagnostic perspectives, narrowing ultimately to gender:
- 1.1 ADHD intro
- 1.2 ADHD definitions
- 1.3 ADHD diagnostic criteria
- 1.4 ADHD gender differences
The second major heading explores ADHD within the classroom environment, narrowing to intervention types:
- 2.1 ADHD in educational contexts
- 2.2 Learning interventions for ADHD
- 2.2.1 Teacher-led interventions
- 2.2.2 Family-led interventions
The final major heading articulates the research gap (gender differences in efficacy of teacher-led vs. family-led interventions for ADHD) by connecting the narrowest themes of the prior two sections.
Multi-funnel literature review structure by Academic Skills Service
To create a solid thematic structure in a literature review, the key is thinking carefully and critically about your groupings of literature and how they relate to one another. In some cases, your themes will fit in a single funnel. In other cases, it will make sense to group your broad-to-narrow themes under several major headings, and then arrange those major headings in the most logical order.
Chronological structure
Some literature reviews will follow a chronological structure . As the name suggests, a review structured chronologically will arrange sources according to their publication dates, from earliest to most recent.
This approach can work well when your priority is to demonstrate how the research field has evolved over time. For example, a chronological arrangement of articles about artificial intelligence (AI) would allow the writer to highlight how breakthroughs in AI have built upon one another in sequential order.
A chronological structure can also suit literature reviews that need to capture how perceptions or understandings have developed across a period of time (including to the present day). For example, if your dissertation involves the public perception of marijuana in the UK, it could make sense to arrange that discussion chronologically to demonstrate key turning points and changes of majority thought.
The chronological structure can work well in some situations, such as those described above. That being said, a purely chronological structure should be considered with caution. Organising sources according to date alone runs the risk of creating a fragmented reading experience. It can be more difficult in a chronological structure to properly synthesize the literature. For these reasons, the chronological approach is often blended into a thematic structure, as you will read more about, below.
Combined structures
The structures of literature reviews can vary drastically, and for any given dissertation there will be many valid ways to arrange the literature.
For example, many literature reviews will combine the thematic and chronological approaches in different ways. A writer might match their major headings to themes or subtopics, but then arrange literature chronologically within the major themes identified. Another writer might base their major headings on chronology, but then assign thematic subheadings to each of those major headings.
When considering your options, try to imagine your reader or audience. What 'flow' will allow them to best follow the discussion you are crafting? When you are reading articles, what structural approaches do you appreciate in terms of ease and clarity?
Identifying the gap
The bulk of your literature review will explore relevant points of development and scholarly thought in your research field: in other words, 'Here is what has been done so far, thus here is where the conversation now stands'. In that way, you position your project within a wider academic discussion.
Having established that context, the literature review generally culminates in an articulation of what remains to be done: the research gap your project addresses. See the next tab for further explanation and examples.
Demystifying the research gap
The term research gap is intimidating for many students, who might mistakenly believe that every single element of their research needs to be brand new and fully innovative. This isn't the case!
The gap in many projects will be rather niche or specific. You might be helping to update or re-test knowledge rather than starting from scratch. Perhaps you have repeated a study but changed one variable. Maybe you are considering a much discussed research question, but with a lesser used methodological approach.
To demonstrate the wide variety of gaps a project could address, consider the examples below. The categories used and examples included are by no means comprehensive, but they should be helpful if you are struggling to articulate the gap your literature review has identified.
***P lease note that the content of the example statements has been invented for the sake of demonstration. The example statements should not be taken as expressions of factual information.
Gaps related to population or geography
Many dissertation research questions involve the study of a specific population. Those populations can be defined by nationality, ethnicity, gender, sexuality, socioeconomic class, political beliefs, religion, health status, or other factors. Other research questions target a specific geography (e.g. a country, territory, city, or similar). Perhaps your broader research question has been pursued by many prior scholars, but few (or no) scholars have studied the question in relation to your focal population or locale: if so, that's a gap.
- Example 1: As established above, the correlations between [ socioeconomic status ] and sustainable fashion purchases have been widely researched. However, few studies have investigated the potential relationship between [ sexual identity ] and attitudes toward sustainable fashion. Therefore...
- Example 2: Whilst the existing literature has established a clear link between [ political beliefs ] and perceptions of socialized healthcare, the influence of [ religious belief ] is less understood, particularly in regards to [ Religion ABC ].
- Example 3: Available evidence confirms that the widespread adoption of Technology XYZ in [ North America ] has improved manufacturing efficiency and reduced costs in the automotive sector. Using predictive AI models, the present research seeks to explore whether deployment of Technology XYZ could benefit the automotive sector of [ Europe ] in similar ways.
Gaps related to theoretical framework
The original contribution might involve examining something through a new lens. Theoretical framework refers, most simply, to the theory or theories a writer will use to make sense of and shape (i.e., frame ) their discussion. Perhaps your topic has been analysed in great detail through certain theoretical lenses, but you intend to frame your analysis using a theory that fewer scholars have applied to the topic: if so, that's a gap.
- Example 1: Existing discussions of the ongoing revolution in Country XYZ frame the unrest in terms of [ theory A ] and [ theory B ]. The present research will instead analyse the situation using [ theory C ], allowing greater insight into...
- Example 2: In the first section of this literature review, I examined the [ postmodern ], [ Marxist ], and [ pragmatist ] analyses that dominate academic discussion of The World According to Garp. By revisiting this modern classic through the lens of [ queer theory ], I intend to...
Gaps related to methodological approach
The research gap might be defined by differences of methodology (see our Writing the Methodology guide for more). Perhaps your dissertation poses a central question that other scholars have researched, but they have applied different methods to find the answer(s): if so, that's a gap.
- Example 1: Previous studies have relied largely upon the [ qualitative analysis of interview transcripts ] to measure the marketing efficacy of body-positive advertising campaigns. It is problematic that little quantitative data underpins present findings in this area. Therefore, I will address this research gap by [ using algorithm XYZ to quantify and analyse social-media interactions ] to determine whether...
- Example 2: Via [ quantitative and mixed-methods studies ], previous literature has explored how demographic differences influence the probability of a successful match on Dating App XYZ. By instead [ conducting a content analysis of pre-match text interactions ] on Dating App XYZ, I will...
Scarcity as a gap
Absolutes such as never and always rarely apply in academia, but here is an exception: in academia, a single study or analysis is never enough. Thus, the gap you address needn't be a literal void in the discussion. The gap could instead have to do with replicability or depth/scope. In these cases, you are adding value and contributing to the academic process by testing emerging knowledge or expanding underdeveloped discussions.
- Example: Initial research points to the efficacy of Learning Strategy ABC in helping children with dyslexia build their reading confidence. However, as detailed earlier in this review, only four published studies have tested the intervention, and two of those studies were conducted in a laboratory. To expand our growing understanding of how Learning Strategy ABC functions in classroom environments, I will...
Elapsed time as a gap
Academia values up-to-date knowledge and findings, so another valid type of gap relates to elapsed time. Many factors that can influence or shape research findings are ever evolving: technology, popular culture, and political climates, to name just a few. Due to such changes, it's important for scholars in most fields to continually update findings. Perhaps your dissertation adds value by contributing to this process.
For example, imagine if a scholar today were to rely on a handbook of marketing principles published in 1998. As good as that research might have been in 1998, technology (namely, the internet) has advanced drastically since then. The handbook's discussion of online marketing strategies will be laughably outdated when compared to more recent literature.
- Example: A wide array of literature has explored the ways in which perceptions of gender influence professional recruitment practices in the UK. The bulk of said literature, however, was published prior to the #MeToo movement and resultant shifts in discourse around gender, power imbalances and professional advancement. Therefore...
What to avoid
This portion of the guide will cover some common missteps you should try to avoid in writing your literature review. Scroll to continue reading, or click a heading below to jump immediately to that section.
Writing up before you have read up
Trying to write your literature review before you have conducted adequate research is a recipe for panic and frustration. The literature review, more than any other chapter in your dissertation, depends upon your critical understanding of a range of relevant literature. If you have only dipped your toe into the pool of literature (rather than diving in!), you will naturally struggle to develop this section of the writing. Focus on developing your relevant bases of knowledge before you commit too much time to drafting.
Believing you need to read everything
As established above, a literature review does require a significant amount of reading. However, you aren't expected to review everything ever written about your topic. Instead, aim to develop a more strategic approach to your research. A strategic approach to research looks different from one project to the next, but here are some questions to help you prioritise:
- If your field values up-to-date research and discoveries, carefully consider the 'how' and 'what' before investing time reading older sources: how will the source function in your dissertation, and what will it add to your writing?
- Try to break your research question(s) down into component parts. Then, map out where your literature review will need to provide extensive detail and where it can instead present quicker background. Allocate your research time and effort accordingly.
Omitting dissenting views or findings
While reviewing the literature, you might discover authors who disagree with your central argument or whose own findings contradict your hypothesis. Don't omit those sources: embrace them! Remember, the literature review aims to explore the academic dialogue around your topic: disagreements or conflicting findings are often part of that dialogue, and including them in your writing will create a sense of rich, critical engagement. In fact, highlighting any disagreements amongst scholars is a great way to emphasise the relevance of, and need for, your own research.
Miscalculating the scope
As shown in the funnel structure (see 'Structure' tab for more), a literature review often starts broadly and then narrows the dialogue as it progresses, ultimately bringing the reader to the dissertation's specific research topic (e.g. the funnel's narrowest point).
Within that structure, it's common for writers to miscalculate the scope required. They might open the literature review far too broadly, dedicating disproportionate space to developing background information or general theory; alternately, they might rush into the narrowest part of the discussion, failing to develop any sense of surrounding context or background, first.
It takes trial and error to determine the appropriate scope for your literature review. To help with this...
- Imagine your literature review subtopics cascading down a stairwell, as in the illustration below.
- Place the broadest concepts on the highest steps, then narrow down to the most specific concepts on the lowest steps: the scope 'zooms in' as you move down the stairwell.
- Now, consider which step is the most logical starting place for your readers. Do they need to start all the way at the top, or should you 'zoom in'?

The illustration above shows a stairwell diagram of a dissertation that aims to analyse Stephen King's horror novel The Stand through the lens of a specific feminist literary theory.
- If the literature review began on one of the bottom two steps, this would feel rushed and inadequate. The writer needs to explore and define the relevant theoretical lens before they discuss how it has been applied by other scholars.
- If the literature review began on the very top step, this would feel comically broad in terms of scope: in this writing context, the reader doesn't require a detailed account of the entire history of feminism!
The third step, therefore, represents a promising starting point: not too narrow, not too broad.
The 'islands' structure
Above all else, a literature review needs to synthesize a range of sources in a logical fashion. In this context, to synthesize means to bring together, connect, weave, and/or relate. A common mistake writers make is failing to conduct such synthesis, and instead discussing each source in isolation. This leads to a disconnected structure, with each source treated like its own little 'island'. The island approach works for very few projects.
Some writers end up with this island structure because they confuse the nature of the literature review with the nature of an annotated bibliography . The latter is a tool you can use to analyse and keep track of individual sources, and most annotated bibliographies will indeed be arranged in a source-by-source structure. That's fine for pre-writing and notetaking, but to structure the literature review, you need to think about connections and overlaps between sources rather than considering them as stand-alone works.
If you are struggling to forge connections between your sources, break down the process into tiny steps:
- e.g. Air pollution from wood-burning stoves in homes.
- e.g. Bryant and Dao (2022) found that X% of small particle pollution in the United Kingdom can be attributed to the use of wood-burning stoves.
- e.g. A study by Williams (2023) reinforced those findings, indicating that small particle pollution has...
- e.g. However, Landers (2023) cautions that factor ABC and factor XYZ may contribute equally to poor air quality, suggesting that further research...
The above exercise is not meant to suggest that you can only write one sentence per source: you can write more than that, of course! The exercise is simply designed to help you start synthesizing the literature rather than giving each source the island treatment.
Q: I still don't get it - what's the point of a literature review?
A: Let's boil it down to three key points...
- The literature review provides a platform for you, as a scholar, to demonstrate your understanding of how your research area has evolved. By engaging with seminal texts or the most up-to-date findings in your field, you can situate your own research within the relevant academic context(s) or conversation(s).
- The literature review allows you to identify the research gap your project addresses: in other words, what you will add to discussions in your academic field.
- Finally, the literature review justifies the reason for your research. By exploring existing literature, you can highlight the relevance and purpose of your own research.
Q: What if I don't have a gap?
A: It's normal to struggle with identifying a research gap. This can be particularly true if you are working in a highly saturated research area, broadly speaking: for example, if you are studying the links between nutrition and diabetes, or if you are studying Shakespeare.

The 'What to Avoid' tab explained that miscalculating the scope is a common mistake in literature reviews. If you are struggling to identify your gap, scope might be the culprit, particularly if you are working in a saturated field. Remember that the gap is the narrowest part of the funnel, the smallest nesting doll, the lowest step: this means your contribution in that giant academic conversation will need to be quite 'zoomed in':
This is not a valid gap → Analysing Shakespeare's sonnets.
This might be a valid gap → Conducting an ecocritical analysis of the visual motifs of Shakespeare's final five procreation sonnets (e.g. sonnets number thirteen to seventeen).
In the above example, the revised attempt to articulate a gap 'zooms in' by identifying a particular theoretical lens (e.g. ecocriticism), a specific convention to analyse (e.g. use of visual motifs), and a narrower object (e.g. five sonnets rather than all 150+). The field of Shakespeare studies might be crowded, but there is nonetheless room to make an original contribution.
Conversely, it might be difficult to identify the gap if you are working not in a saturated field, but in a brand new or niche research area. How can you situate your work within a relevant academic conversation if it seems like the 'conversation' is just you talking to yourself?

In these cases, rather than 'zooming in', you might find it helpful to 'zoom out'. If your topic is niche, think creatively about who will be interested in your results. Who would benefit from understanding your findings? Who could potentially apply them or build upon them? Thinking of this in interdisciplinary terms is helpful for some projects.
Tip: Venn diagrams and mind maps are great ways to explore how your research connects to, and diverges from, the existing literature.
Q: How many references should I use in my literature review?
A: This question is risky to answer because the variations between individual projects and disciplines make it impossible to provide a universal answer. The fact is that one dissertation might have 50 more references than another, yet the two projects could be equally rigorous and successful in fulfilling their research aims.
With that warning in mind, let's consider a 'standard' dissertation of around 10K words. In that context, referencing 30 to 40 sources in your literature review tends to work well. Again, this is not a universally accurate rule, but a ballpark figure for you to contemplate. If the 30 to 40 estimate seems frighteningly high to you, do remember that many sources will be used sparingly rather than being mulled over at length. Consider this example:
In British GP practices, pharmaceutical treatment is most often prescribed for Health Condition XYZ ( Carlos, 2019; Jones, 2020 ; Li, 2022 ). Lifestyle modifications, such as physical exercise or meditation practices, have only recently...
When writing critically, it's important to validate findings across studies rather than trusting only one source. Therefore, this writer has cited three recent studies that agree about the claim being made. The writer will delve into other sources at more length, but here, it makes sense to cite the literature and move quickly along.
As you search the databases and start following the relevant trails of 'research bread crumbs', you will be surprised how quickly your reference list grows.
Q: What if there isn't enough relevant literature on my topic?
A: Think creatively about the literature you are using and engaging with. A good start is panning out to consider your topic more broadly: you might not identify articles that discuss your exact topic, but what can you discover if you shift your focus up one level?
Imagine, for example, that Norah is researching how artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to provide dance instruction. She discovers that no one has written about this topic. Rather than panicking, she breaks down her research question into its component parts to consider what research might exist.
- First, dance instruction: literature on how dance has traditionally been taught (i.e., not with AI) is still relevant because it will provide background and context. To appreciate the challenges or opportunities that transition to AI instruction might bring, we need to understand the status quo. Norah might also search for articles that analyse how other technological shifts have affected dance instruction: for example, how YouTube popularized at-home dance study, or how live video services like Zoom enabled real-time interaction between dance pupils and teachers despite physical distance.
- Next, artificial intelligence used for instruction: Norah can seek out research on, and examples of, the application of AI for instructive purposes. Even if those purposes don't involve dance, such literature can contribute to illustrating the broader context around Norah's project.
- Could it be relevant to discuss the technologies used to track an actor's real-life movements and convert them into the motions of a video game character? Perhaps there are parallels!
- Could it be relevant to explore research on applications of AI in creative writing and visual art? Could be relevant since dance is also a creative field!
In summary, don't panic if you can't find research on your exact question or topic. Think through the broader context and parallel ideas, and you will soon find what you need.
Q: What if my discipline doesn't require a literature review chapter?
A: This is a great question. Whilst many disciplines dictate that your dissertation should include a chapter called Literature Review , not all subjects follow this convention. Those subjects will still expect you to incorporate a range of external literature, but you will nest the sources under different headings.
For example, some disciplines dictate an introductory chapter that is longer than average, and you essentially nest a miniature literature review inside the introduction, itself. Although the writing is more condensed and falls under a subheading of the introduction, the techniques and principles of writing a literature review (for example, moving from the broad to the narrow) will still prove relevant.
Some disciplines include chapters with names like Background , History , Theoretical Framework , etc. The exact functions of such chapters differ, but they have this in common: reviewing literature. You can't provide a critical background or history without synthesizing external sources. To illustrate your theoretical framework, you need to synthesize a range of literature that defines the theory or theories you intend to use.
Therefore, as stated earlier in this guide, you should be prepared to review and synthesize a range of literature regardless of your discipline. You can tailor the purpose of that synthesis to the structure and demands of writing in your subject area.
Q: Does my literature review need to include every source I plan to use in my discussion chapter?
A: The short answer is 'no' - there are some situations in which it is okay to use a source in your discussion chapter that you didn't integrate into your literature review chapter.
Imagine, for example, that your study produced a surprising result: a finding that you didn't anticipate. To make sense of that result, you might need to conduct additional research. That new research will help you explain the unexpected result in your discussion chapter.
More often, however, your discussion will draw on, or return to, sources from your literature review. After all, the literature review is where you paint a detailed picture of the conversation surrounding your research topic. Thus, it makes sense for you to relate your own work to that conversation in the discussion.
The literature review provides you an opportunity to engage with a rich range of published work and, perhaps for the first time, critically consider how your own research fits within and responds to your academic community. This can be a very invigorating process!
At the same time, it's likely that you will be juggling more academic sources than you have ever used in a single writing project. Additionally, you will need to think strategically about the focus and scope of your work: figuring out the best structure for your literature review might require several rounds of re-drafting and significant edits.
If you are usually a 'dive in without a plan and just get drafting' kind of writer, be prepared to modify your approach if you start to feel overwhelmed. Mind mapping, organising your ideas on a marker board, or creating a bullet-pointed reverse outline can help if you start to feel lost.
Alternately, if you are usually a 'create a strict, detailed outline and stick to it at all costs' kind of writer, keep in mind that long-form writing often calls for writers to modify their plans for content and structure as their work progresses and evolves. It can help such writers to schedule periodic 'audits' of their outlines, with the aim being to assess what is still working and what else needs to be added, deleted or modified.
Here’s a final checklist for writing your literature review. Remember that not all of these points will be relevant for your literature review, so make sure you cover whatever’s appropriate for your dissertation. The asterisk (*) indicates any content that might not be relevant for your dissertation. You can save your own copy of the checklist to edit using the Word document, below.
- Literature review self-evaluation checklist

- << Previous: Overview and Planning
- Next: The Methodology >>
- Last Updated: Feb 22, 2024 3:43 PM
- URL: https://library.soton.ac.uk/writing_the_dissertation

A Guide To Writing The Dissertation Literature Review
Tom Baldwin - Jan 22, 2024

Do you want to know a guide to writing the dissertation literature review? You are at the right place. This latest post will explore how to write a literature review, Purposes for writing a literature review, How to conduct a literature review and, most importantly, how to write a methodology for a literature review dissertation
And many more that can be helpful for you. So, without any delay, let’s get started.
Key Take Away
- Focused Scope: Clearly define your research question and key concepts to maintain focus and avoid information overload.
- Comprehensive Search: Use diverse sources and search techniques for a thorough literature review. Apply strict criteria for inclusion/exclusion to ensure relevance.
- Structured Presentation: Organize selected literature into themes and develop a concise thesis statement for a clear and guided narrative.
- Methodological Precision: Outline a rigorous methodology, detailing search strategy, inclusion/exclusion criteria, data extraction, and synthesis. Reflect on choices, acknowledging strengths and limitations.
Qualified Tutors

How To Write A Literature Review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing, evaluating, and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. Here’s a guide to help you:
1. Define Your Scope
Begin by explicitly defining the scope and parameters of your literature review. Clearly articulate the specific research question or topic you aim to explore.
Consider the key concepts, keywords, and terms relevant to your inquiry. This step is crucial for setting boundaries, ensuring focus, and avoiding information overload.
2. Search For Relevant Literature
Conduct a comprehensive literature search using a variety of sources such as academic databases , library catalogs, and search engines. Experiment with different combinations of keywords and synonyms related to your topic.
Use advanced search features and filters provided by databases to refine and narrow down your results. Be mindful of the inclusion and exclusion criteria to ensure relevance.
3. Select And Evaluate Sources
As you gather sources, critically evaluate each one. Examine the author’s credentials, institutional affiliations, and any potential biases. Consider the publication venue and its reputation within the field.
Pay attention to the publication date to ensure that you are incorporating recent and relevant research. Evaluate the research methodology employed in each study to assess the validity of the findings.
4. Organize The Literature
Organize the selected literature into themes or categories based on commonalities and differences. This can be achieved through the creation of an annotated bibliography or a matrix that categorizes studies based on key characteristics.
This organizational step will serve as the backbone of your literature review, providing a structured framework for presenting information.
5. Develop A Thesis Statement
Craft a clear and concise thesis statement that encapsulates the main theme, findings, or trends within the literature. This thesis statement should provide a roadmap for readers, guiding them through the overarching narrative of your literature review.
Ensure that the thesis aligns with the specific research question or objective you outlined in the initial stages.
6. Write An Introduction
In the introduction, contextualize the topic by providing background information, historical context, or relevant theoretical frameworks. Clearly state the purpose of your literature review and articulate the significance of the research question.
Transition smoothly from the general context to your specific focus, and conclude the introduction with your thesis statement.
7. Body Of The Review
Organize the body of your literature review logically. If following a thematic approach, discuss studies within each theme, summarizing their main findings, methodologies, and contributions to the field.
If following a chronological approach, trace the evolution of research over time. Ensure a coherent flow between paragraphs and sections, making connections between studies and highlighting key relationships.
8. Critical Analysis
Engage in a critical analysis of each source. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the studies, considering factors such as sample size, research design, and potential biases. Identify any conflicting findings or gaps in the literature.
Discuss how methodological choices in each study may have influenced the results and interpretations.
9. Synthesize Information
Synthesize information by identifying common themes, trends, or patterns across studies. Explore the relationships between different sources and offer insights into the cumulative knowledge generated by the literature.
Discuss how the collective findings contribute to the overall understanding of the topic and address your research question.
10. Write A Conclusion
Summarize the main findings and themes discussed in the body of the literature review. Reiterate your thesis statement and emphasize its significance.
Discuss the broader implications of the reviewed literature and its relevance to the field. Consider proposing areas for future research and potential avenues for exploration.
11. Cite Sources
Ensure proper citation of all sources using the designated citation style (e.g., APA, MLA). Adhere to formatting guidelines consistently throughout your literature review. Maintain accuracy in citing authors, publication years, and other relevant details.
12. Revise And Edit
Carefully review your literature review for clarity, coherence, and logical flow. Check for consistency in tone and style. Edit for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. Consider seeking feedback from peers, mentors, or writing support services to refine your work further.
Additional Tips
- Consider the cultural and geographical context of the studies you include.
- Be aware of any evolving debates or shifts in perspectives within the literature.
- Engage with your sources by offering critiques, connections, and reflections on the methodologies employed.
- Keep track of the publication status of the studies, as ongoing research might have been published after your literature search.
By following this detailed guide, you can create a comprehensive and nuanced literature review that not only summarizes existing research but also contributes valuable insights to the academic discourse in your field of study.
11 Purposes For Writing A Literature Review
Writing a literature review serves several important purposes within the academic and research context. Here are key reasons why researchers and scholars engage in the process of writing a literature review:
1. Establishing Context
Purpose: Provide background and context for a research study.
Explanation: A literature review helps situate a research project within the existing body of knowledge. By reviewing relevant studies, researchers establish a foundation for their work and demonstrate an understanding of the historical and theoretical context of their research.
2. Identifying Gaps In Knowledge
Purpose: Identify areas where further research is needed.
Explanation: By examining existing literature, researchers can pinpoint gaps, unanswered questions, or areas with conflicting findings. This identification of gaps helps justify the need for new research and contributes to the advancement of knowledge.
3. Demonstrating Scholarly Understanding
Purpose: Showcase a deep understanding of the subject matter.
Explanation: A well-crafted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with key concepts, theories, and empirical studies related to the research topic. It showcases the researcher’s expertise and positions them within the scholarly conversation.
4. Synthesizing Existing Knowledge
Purpose: Synthesize information from various sources to form a cohesive narrative.
Explanation: The literature review is an opportunity to synthesize information from diverse studies, presenting a comprehensive overview of existing knowledge. This synthesis helps researchers and readers understand the broader patterns, trends, and relationships in the literature.
5. Evaluating Methodologies
Purpose: Assess the strengths and weaknesses of research methodologies.
Explanation: Researchers critically evaluate the methodologies used in previous studies to understand the reliability and validity of their findings. This assessment informs the methodological choices in the current research and contributes to the overall research design.
6. Supporting Theoretical Frameworks
Purpose: Provide a theoretical foundation for the research.
Explanation: Literature reviews often explore and discuss theoretical frameworks relevant to the research topic. By doing so, researchers ground their work in established theories and frameworks, contributing to the theoretical development of their field.
7. Demonstrating Scope And Breadth
Purpose: Showcase a wide-ranging exploration of literature.
Explanation: Writing a literature review requires the exploration of a broad range of sources, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of the field. This demonstration of breadth adds credibility to the research and indicates a thorough examination of relevant scholarship.
8. Guiding Research Questions Or Hypotheses
Purpose: Inform the formulation of research questions or hypotheses.
Explanation: Through the review process, researchers gain insights into the existing gaps and patterns, helping them formulate specific and targeted research questions or hypotheses. This ensures that the research is purposeful and directly addresses gaps in the current knowledge.
9. Building A Conceptual Framework
Purpose: Construct a conceptual framework for the study.
Explanation: The literature review aids in the development of a conceptual framework by identifying key concepts, variables, and relationships explored in previous research. This framework serves as a theoretical foundation for the current study.
10. Informing Methodological Choices
Purpose: Guide decisions on research methods.
Explanation: Researchers can draw on the literature review to inform decisions about the most appropriate research methods. By understanding how previous studies were conducted, researchers can make informed choices regarding data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
11. Contributing To Academic Discourse
Purpose: Contribute to ongoing academic discussions.
Explanation: Writing a literature review is a scholarly contribution in itself. By summarizing, analyzing, and synthesizing existing research, researchers actively engage in the academic discourse of their field, adding their perspectives to the broader conversation.
A literature review serves as a critical component of the research process, enabling researchers to situate their work within the larger academic landscape, identify gaps, synthesize knowledge, and contribute to the ongoing scholarly conversation.
How To Write A Methodology For A Literature Review Dissertation

Writing the methodology for a literature review in a dissertation involves outlining the methods you will use to gather, organize, and analyze the literature. While a traditional research methodology might involve data collection and analysis.
The methodology for a literature review focuses on your approach to reviewing and synthesizing existing research. Here’s a guide on how to write the methodology section for a literature review dissertation.
1. Search Strategy
Describe your approach to searching for relevant literature. Include details such as the databases you used, keywords, and any specific criteria for inclusion or exclusion. This helps readers understand the comprehensiveness of your literature search.
2. Inclusion And Exclusion Criteria
Clearly outline the criteria you used to select or exclude studies. This might include factors such as publication date, study design, geographical location, or the type of participants. Justify your choices to demonstrate the rigour of your selection process.
3. Data Extraction
Explain how you extracted relevant information from the selected studies. Discuss the variables or themes you focused on and any tools or frameworks you used for data extraction.
4. Quality Assessment
If applicable, describe any criteria or tools you used to assess the quality of the studies included in your literature review. This is important for establishing the reliability and validity of your review.
5. Data Synthesis
Detail how you synthesized the information gathered from the literature. Discuss the methods you used to organize, categorize, and analyze the findings. This could involve thematic analysis, content analysis, or other qualitative synthesis methods.
6. Frameworks Or Models
If you used any theoretical frameworks or models to guide your literature review, explain them in this section. Discuss how these frameworks influenced your approach to analyzing and synthesizing the literature.
7. Categorization And Synthesis
Outline the process you followed to categorize the literature and synthesize key themes or concepts. This is the heart of your literature review methodology, so be specific about the steps you took to identify patterns and relationships in the literature.
8. Reflection On Methodological Choices
Reflect on the strengths and limitations of your methodology. Discuss any challenges you encountered and how you addressed them. This shows your awareness of potential biases and enhances the transparency of your work.
Conclude the methodology section by summarizing the key methods employed and how they contributed to the structure and content of your literature review. Remember to follow the specific guidelines provided by your institution and dissertation committee.
Adapt the above steps based on the requirements and expectations of your academic program.
1. What Is The Primary Purpose Of A Literature Review In A Dissertation?
A literature review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of existing research, establish context, identify gaps, and contribute to the scholarly discourse within a specific field.
2. How Do I Define The Scope Of My Literature Review?
Begin by clearly articulating your research question and identifying key concepts. This helps set boundaries, maintain focus, and avoid information overload.
3. What Criteria Should I Consider When Selecting And Evaluating Sources?
Evaluate author credentials, institutional affiliations, publication venue reputation, and research methodologies. Consider biases and the relevance of the publication date.
4. Why Is It Important To Organize The Literature Into Themes Or Categories?
Organizing literature helps create a structured framework for presenting information and highlights commonalities and differences between studies.
5. What Role Does A Thesis Statement Play In A Literature Review?
A thesis statement encapsulates the main theme, findings, or trends within the literature, providing a roadmap for readers and aligning with the research question.
In crafting a literature review for your dissertation, mastering the art of synthesizing existing research is key. By defining scope, organizing systematically, and critically analyzing sources
You contribute not only to your research but also to the broader academic conversation. Follow the methodology guide, employ purposeful writing, and create a compelling narrative to enrich your academic exploration.

I'm a prolific academic freelancer, has completed over 150 online classes and authored more than 600 essays, providing academic assistance to students globally.
Why Wait? Get Our Help Now!
- Let’s Get Started
Standard pricing starts from: $9.99
- How it works
How to Write a Dissertation Literature Review – Steps & Tips
Published by Anastasia Lois at August 12th, 2021 , Revised On October 17, 2023
From an academic standpoint, a dissertation literature review can be defined as a survey of the thesis, journal articles, books, and other academic resources on any given research title . This article provides comprehensive guidelines on how to write a dissertation literature review.
A literature review in a dissertation is of critical importance primarily because it provides insight into the key concepts, advancements, theories, and results of your research questions or research problem .
However, it is essential to note that; a first-class dissertation literature review focuses on summarizing the academic sources used for research and analysing, interpreting, and assessing them to determine the gaps and differences in opinions, judgments, themes, and developments.
A good literature review will further elaborate on existing knowledge concerning the research hypothesis or questions.
View dissertation literature review examples here.
When do you Write a Dissertation Literature Review?
Depending on your university’s guidelines, you might be required to include a literature review in the theoretical framework or the introduction.
Or you could also be asked to develop a standalone literature review chapter that appears before the methodology and the findings chapters of the dissertation.
In either case, your primary aim will be to review the available literature and develop a link between your research and the existing literature on your chosen topic.
Sometimes, you might be designated a literature review as a separate assignment . Regardless of whether you need to write a literature review for your dissertation or as a standalone project, some general guidelines for conducting literature will remain unchanged.
Here are the steps you need to take to write the literature review for a dissertation if you cannot write the literature review.
Steps of Writing a Literature Review
1. gather, assess, and choose relevant literature.
The first seed to take when writing your dissertation or thesis is to choose a fascinating and manageable research topic . Once a topic has been selected, you can begin searching for relevant academic sources.
If you are writing a literature review for your dissertation, one way to do this is to find academic sources relevant to your research problem or questions.
Without fully understanding current knowledge in the chosen study area, giving the correct direction to your research aim and objectives will be hard.
On the other hand, you will be expected to guide your research by developing a central question if you are writing a literature review as an individual assignment.
A notable difference here compared to the dissertation literature review is that you must answer this central question without conducting primary research (questionnaires, surveys, interviews). You will be expected to address the question using only the existing literature.
Dissertation Literature Review Research Question
How can company “A” improve its brand value through social media marketing?
Literature Review Research Question
What is the connection between social media marketing and brand value?
Stuck on a difficult dissertation? We can help!
Our Dissertation Writing Service Features:
- Expert UK Writers
- Plagiarism-free
- Timely Delivery
- Thorough Research
- Rigorous Quality Control

Use Keywords and References to Find Relevant Literature
Create a list of keywords that are relevant to the topic of research. Find journals, articles, and books using these keywords. Here are links to some recognised online academic libraries and databases;
- Inspec, (Computer science, engineering, physics, chemistry)
- EconLit, (Economics)
- Your university’s online research database
Finding relevant academic sources from “the reference list” of an article you have already found in a research database effectively discovers relevant studies.
Consider noting frequently appearing references as they are likely to be highly authentic and important publications even though they didn’t appear in the keyword search.
Journal articles or books that keep appearing with different keywords and phrases are the ones you should manually look out for.
The more times an article has been referenced, the more influential it is likely to be in any research field. Google Scholar lets users quickly determine how often a particular article has been referenced.
Also Read: How to Best Use References in a Dissertation
2. Weighing and Selecting Academic Sources
It won’t be possible for you to read every publication related to your topic. An excellent way to select academic sources for your dissertation literature review is to read the abstract , which will help you decide whether the source is supportive and relevant to your research hypothesis or research questions.
To help you select sources relevant to your study, here are some questions for you to consider before making the decision.
- What research questions has the author answered with their research work?
- What fundamental concepts have been defined by the author?
- Did the researcher use an innovative methodology or existing frameworks to define fundamental methods, models, and theories?
- What are the findings, conclusion, and recommendations in the source book or paper?
- What is the relevance between the existing literature and the academic sources you are evaluating?
- Does the source article challenge, confirm, or add to existing knowledge on the topic?
Any breakthrough studies and key theories relevant to your research topic should be recorded as you search for highly credible and authentic academic sources.
The method of your review of literature depends on your academic subject. If your research topic is in the sciences, you must find and review up-to-date academic sources.
On the other hand, you might look into old and historical literature and recent literature if your research topic is in the humanities field.
Looking for dissertation help?
Researchprospect to the rescue then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with dissertations across a variety disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

Recording Information and Referencing Sources
It is recommended that you start to write your literature review as you read articles, journals, and books. Take notes which can be later merged into the text of the literature review. Avoid plagiarism and record all sources used along with references.
A good way of recording information is to analyse each source, summarise the key concepts or theories and compile a complete list of references in the form of an annotated bibliography.
This is a beneficial practice as it helps to remember the key points in each academic source and saves you valuable time as you start the literature review write-up.
3. Identify Key Themes and Patterns
The next step is to look for themes and patterns in the chosen sources that would enable you to establish similarities and differences between their results and interpretations .
This exercise will help you to determine the structure and argument for your literature review. Here are some questions that you can think of when reading and recording information;
- Are any gaps in the existing literature?
- What are the weaknesses of the current literature that should be addressed?
- Were you able to identify any landmark research work and theories that resulted in the topic’s change of direction?
- What are the similarities and disagreements between these sources? Were you able to identify any contradictions and conflicts?
- What trends and themes were you able to identify? Are there any results, methods, or theories that lost credibility over time?
Also Read: How to Write a Dissertation – Step-by-Step Guide
4. Structure of Literature Review
There is no acclaimed literature review structure , which means that you can choose from a range of approaches (thematic, chronological, methodological, and theoretical) when deciding on the structure of the literature review .
However, before you begin to write the literature review , it is important to figure out the strategy that would work best for you. For long literature reviews, you might decide to use a combination of these strategies. For example, you could discuss each of the themes chronologically.
1: Theoretical
You can discuss various significant concepts, models, and theories in your literature review to form the basis of a theoretical framework . You could also combine a range of theoretical approaches to develop your theoretical framework or debate the significance of a particular theoretical framework.
2: Methodological
The methodological approach will require you to relate the findings of studies conducted in different research areas and use different research methods .
- You might discover that results from the quantitative research approach are not the same as qualitative research.
- You might split the selected academic sources based on their discipline – engineering, and sciences.
3: Thematic
You may also deploy a thematic approach, especially if you identified repeating key themes and patterns. If that is the case, you will be expected to put each aspect of the topic into different subsections within your literature review.
For example, if your research topic is “employment issues in the UK for international students,” you can divide the key themes into subsections; legal status, poor language skills, immigration policy, and economic turmoil.
4: Chronological
The most straightforward approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points, and critical debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
5. Writing your Literature Review
Whether it’s a dissertation literature review or a standalone literature review assignment you have been assigned, you will be expected to divide your literature review into three larger sections – introduction, main body, and a conclusion.
What you write under these three segments will depend on the aim of your study.
Section 1 – Introduction
Here you will be required to state the objectives of the literature review clearly;
Introduction to Dissertation Literature Review Recapitulate your research problem or questions with a summary of the sources you reviewed when the literature review is for your thesis or dissertation. Consider highlighting gaps in existing knowledge and stress the suitability of your topic.
For example:
Research problem A has been debated in many recent studies.
While the topic has been explored concerning A, the B aspect has not yet been explored.
Individual Literature Review Project When reviewing literature for an individual literature review assignment, make sure that you clearly state the purpose of the research and debate the scope of the literature (how recent or old are the academic sources you are reviewing).
Section 2 – Main Body
As previously mentioned, you can divide this section into further subsections depending on your literature review’s length. You can also have a separate heading for each research method, theme, or theory to help your readers better understand your research.
Here are some tips for you to write a flawless main body of literature review;
- Summarize and Combine ; Highlight the main findings from each academic source and organise them into one whole piece without losing coherence.
- Evaluate and interpret; Make sure you are giving opinions and arguments of your own where possible. Simply rephrasing what others have said will undermine your work. You will be expected to debate and discuss other studies’ results about your research questions or aim.
- Analytical Evaluation; It is essential to unmistakably present the literature you have reviewed and the merits and weaknesses of the literature.
- Make Use of Topic Sentences and Transitions; in organized subsections within the literature review to establish conflicts, differences, similarities, and relationships.
Example of How to Write a Dissertation Literature Review
The below example belongs to the body of a literature review on the effectiveness of e-recruitment in small and medium-sized enterprises in the United Kingdom’s IT sector.
E-recruitment means explicitly using digital technologies to recruit, select, and orient employees. The benefits of e-recruitment in the literature have been studied: increased access to a pool of candidates, time and cost savings, and greater flexibility for the organisation.
In contrast, the literature states that e-recruitment might not properly achieve the goal of retaining the workforce with the required skills to participate in the work environment (Lad & Das, 2016). Also, e-recruitment might be based on a flawed website design or poor application process, which might deter potential employees (Anand & Devi, 2016) .
This section of the study will focus on the existing studies linked to the effectiveness of e-recruitment. Human resource management is an essential function of business organisations because it manages the workforce.
The goal of HR should be to develop a strategic approach in which the organisation’s strategic goals can be attained efficiently and effectively. The advent of digital technologies has helped transform human resource management’s nature concerning recruiting and selecting employees for organisations.
The Internet’s benefits have reduced search time for candidates and significant cost savings for organisations. Finally, it offers a transparent method for obtaining information about specific candidates. E-recruitment helps organisations hire people from any part of the world as it promotes opportunities and benefits the organisation efficiently.
Sharma (2014) argues that 75% of human resource professionals in developed countries are now using e-recruitment to hire employees for their organisations. Additionally, some 2 out of 4 job seekers will use the Internet to source job opportunities.
Another evidence to support the rise of e-recruitment is a study by Holm (2014), which found that all Fortune 100 companies will be using some form of e-recruitment to advertise vacant positions.
The implications are that e-recruitment is a popular strategy for various positions, from blue-collar roles to white-collar and professional positions. The benefits of e-recruitment have been identified in the literature. Girard & Fallery (2009) argues that e-recruitment helps to save time for organisations and employees.
Employers can use several methods to post jobs in as little as 20 minutes. There are no limits to ad size, and they can receive resumes immediately. In contrast, the traditional methods require some time to appear, for example, in a newspaper, and might be there for a limited period.
Section 3 – Conclusion
When writing the dissertation literature review conclusion, you should always include a summary of the key findings which emerged from the literature and their relevance and significance to your research objectives.
Literature Review for Dissertation
If you are writing a dissertation literature review, you will be required to demonstrate how your research helped to fill an evident gap in research and contributed to the current knowledge in the field. Similarly, you can explain how you used the existing patterns, themes, and theories to develop your research framework.
Literature Review as an Individual Assignment
You can summarize your review of your literature’s significance and implications and provide recommendations for future work based on the gaps in existing knowledge you acknowledged.
6. Proofread
Finally, thoroughly proofread your literature review for grammatical, structural, spelling, and factual errors before submitting it to your university.
If you are unable to proofread and edit your paper, then you could take advantage of our editing and proofreading service , which is designed to ensure that your completed literature review satisfies each of your module or project’s requirements. We have Masters and PhD qualified writers in all academic subjects, so you can be confident that they will edit and improve the quality of your to 2:1 or First Class standard, as required.
Valuable Tips for Writing Dissertation Literature Review
Your literature review must systematically comply with your research area. Underneath, we are stating some essential guidelines for a compact literature review.
Contribute to the Literature
After carefully reviewing the literature, search for the gaps in knowledge and state how you have analysed the literature with a different perspective and contributed to your research area.
Keep your Argument Systematic & Consistent
Your arguments must be consistent and systematic while discussing theories and controversial and debatable content. Be logical in your review and avoid vague statements, not to make it complex for the readers.
Provide Adequate References
Don’t forget to provide references, as they are the soul of the dissertation. While discussing different aspects of the research, provide a reasonable number of references, as your discussion and interpretations must be backed up by relevant evidence. You can see an example provided in the sample paragraph above.
Be Precise While Writing a Review
You aren’t required to write every inch of information you have studied while reviewing the literature. You will be able to find tons of information that will correlate with your research area.
Be precise while writing the review, as writing unnecessary, irrelevant information won’t give a good impression. State the most reliable sources in your review without jumping into every possible source.
Don’t go Excessively for Direct Quotes
Direct quoting is required to make a point more impactful, but you should opt for it to a specific limit. Making excessive use of it won’t be a good idea.
The direct quote is mainly used when you think that the words being used by the actual author are so authentic in their meaning that you can’t replace or rephrase them. Try to avoid relying too much on a single author/s work.
Discussing their contributions and keeping the review going briefly would be better. While mentioning the points discussed by the prior researchers – link your arguments with their discussion. Don’t write the crux of their discussion, yet tell if your argument goes along with them.
Express your Analysis
The literature review is written to summarize your perspective, which should be backed up in light of the literature. Critically analyze literature with a rational approach and express your opinion on it.
Use the Correct Referencing Style
While referencing, one must use proper referencing styles, i.e., Harvard reference style, etc. Different referencing styles are used for in-text citations, while different for end-text citations.
Feeling overwhelmed by your literature review? Still unsure about how to write a dissertation literature review? There is no need to panic. Whether you are an undergraduate, postgraduate, or PhD student, our literature review writing service can help you have your literature review to the highest academic quality.
All papers completed by our writers are delivered along with a free anti-plagiarism report. We will amend your paper for free as many times as needed until you are delighted with the contents and the works’ quality as long as your original instructions and requirements remain unchanged.
FAQs About Dissertation Literature Review
How to find relevant literature for reference in a dissertation.
You must note down keywords related to the title of your dissertation and search journals, articles, and books using them.
How to select academic sources?
If you have found plenty of academic resources, you can select a few of them by reading the abstract of all the papers and separating the most relevant ones.
How to quote academic references?
It is recommended that you start to write your literature review as you read articles, journals and books. Take notes which can be later merged into the text of the literature review.
How should a literature review dissertation be written?
You should divide your literature review into three sections:
Introduction, main body, and conclusion.
You May Also Like
A list of glossary in a dissertation contains all the terms that were used in your dissertation but the meanings of which may not be obvious to the readers.
Do dissertations scare you? Struggling with writing a flawless dissertation? Well, congratulations, you have landed in the perfect place. In this blog, we will take you through the detailed process of writing a dissertation. Sounds fun? We thought so!
When writing your dissertation, an abstract serves as a deal maker or breaker. It can either motivate your readers to continue reading or discourage them.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Clinics (Sao Paulo)
Approaching literature review for academic purposes: The Literature Review Checklist
Debora f.b. leite.
I Departamento de Ginecologia e Obstetricia, Faculdade de Ciencias Medicas, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas, SP, BR
II Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Pernambuco, PE, BR
III Hospital das Clinicas, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Pernambuco, PE, BR
Maria Auxiliadora Soares Padilha
Jose g. cecatti.
A sophisticated literature review (LR) can result in a robust dissertation/thesis by scrutinizing the main problem examined by the academic study; anticipating research hypotheses, methods and results; and maintaining the interest of the audience in how the dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field. Unfortunately, little guidance is available on elaborating LRs, and writing an LR chapter is not a linear process. An LR translates students’ abilities in information literacy, the language domain, and critical writing. Students in postgraduate programs should be systematically trained in these skills. Therefore, this paper discusses the purposes of LRs in dissertations and theses. Second, the paper considers five steps for developing a review: defining the main topic, searching the literature, analyzing the results, writing the review and reflecting on the writing. Ultimately, this study proposes a twelve-item LR checklist. By clearly stating the desired achievements, this checklist allows Masters and Ph.D. students to continuously assess their own progress in elaborating an LR. Institutions aiming to strengthen students’ necessary skills in critical academic writing should also use this tool.
INTRODUCTION
Writing the literature review (LR) is often viewed as a difficult task that can be a point of writer’s block and procrastination ( 1 ) in postgraduate life. Disagreements on the definitions or classifications of LRs ( 2 ) may confuse students about their purpose and scope, as well as how to perform an LR. Interestingly, at many universities, the LR is still an important element in any academic work, despite the more recent trend of producing scientific articles rather than classical theses.
The LR is not an isolated section of the thesis/dissertation or a copy of the background section of a research proposal. It identifies the state-of-the-art knowledge in a particular field, clarifies information that is already known, elucidates implications of the problem being analyzed, links theory and practice ( 3 - 5 ), highlights gaps in the current literature, and places the dissertation/thesis within the research agenda of that field. Additionally, by writing the LR, postgraduate students will comprehend the structure of the subject and elaborate on their cognitive connections ( 3 ) while analyzing and synthesizing data with increasing maturity.
At the same time, the LR transforms the student and hints at the contents of other chapters for the reader. First, the LR explains the research question; second, it supports the hypothesis, objectives, and methods of the research project; and finally, it facilitates a description of the student’s interpretation of the results and his/her conclusions. For scholars, the LR is an introductory chapter ( 6 ). If it is well written, it demonstrates the student’s understanding of and maturity in a particular topic. A sound and sophisticated LR can indicate a robust dissertation/thesis.
A consensus on the best method to elaborate a dissertation/thesis has not been achieved. The LR can be a distinct chapter or included in different sections; it can be part of the introduction chapter, part of each research topic, or part of each published paper ( 7 ). However, scholars view the LR as an integral part of the main body of an academic work because it is intrinsically connected to other sections ( Figure 1 ) and is frequently present. The structure of the LR depends on the conventions of a particular discipline, the rules of the department, and the student’s and supervisor’s areas of expertise, needs and interests.

Interestingly, many postgraduate students choose to submit their LR to peer-reviewed journals. As LRs are critical evaluations of current knowledge, they are indeed publishable material, even in the form of narrative or systematic reviews. However, systematic reviews have specific patterns 1 ( 8 ) that may not entirely fit with the questions posed in the dissertation/thesis. Additionally, the scope of a systematic review may be too narrow, and the strict criteria for study inclusion may omit important information from the dissertation/thesis. Therefore, this essay discusses the definition of an LR is and methods to develop an LR in the context of an academic dissertation/thesis. Finally, we suggest a checklist to evaluate an LR.
WHAT IS A LITERATURE REVIEW IN A THESIS?
Conducting research and writing a dissertation/thesis translates rational thinking and enthusiasm ( 9 ). While a strong body of literature that instructs students on research methodology, data analysis and writing scientific papers exists, little guidance on performing LRs is available. The LR is a unique opportunity to assess and contrast various arguments and theories, not just summarize them. The research results should not be discussed within the LR, but the postgraduate student tends to write a comprehensive LR while reflecting on his or her own findings ( 10 ).
Many people believe that writing an LR is a lonely and linear process. Supervisors or the institutions assume that the Ph.D. student has mastered the relevant techniques and vocabulary associated with his/her subject and conducts a self-reflection about previously published findings. Indeed, while elaborating the LR, the student should aggregate diverse skills, which mainly rely on his/her own commitment to mastering them. Thus, less supervision should be required ( 11 ). However, the parameters described above might not currently be the case for many students ( 11 , 12 ), and the lack of formal and systematic training on writing LRs is an important concern ( 11 ).
An institutional environment devoted to active learning will provide students the opportunity to continuously reflect on LRs, which will form a dialogue between the postgraduate student and the current literature in a particular field ( 13 ). Postgraduate students will be interpreting studies by other researchers, and, according to Hart (1998) ( 3 ), the outcomes of the LR in a dissertation/thesis include the following:
- To identify what research has been performed and what topics require further investigation in a particular field of knowledge;
- To determine the context of the problem;
- To recognize the main methodologies and techniques that have been used in the past;
- To place the current research project within the historical, methodological and theoretical context of a particular field;
- To identify significant aspects of the topic;
- To elucidate the implications of the topic;
- To offer an alternative perspective;
- To discern how the studied subject is structured;
- To improve the student’s subject vocabulary in a particular field; and
- To characterize the links between theory and practice.
A sound LR translates the postgraduate student’s expertise in academic and scientific writing: it expresses his/her level of comfort with synthesizing ideas ( 11 ). The LR reveals how well the postgraduate student has proceeded in three domains: an effective literature search, the language domain, and critical writing.
Effective literature search
All students should be trained in gathering appropriate data for specific purposes, and information literacy skills are a cornerstone. These skills are defined as “an individual’s ability to know when they need information, to identify information that can help them address the issue or problem at hand, and to locate, evaluate, and use that information effectively” ( 14 ). Librarian support is of vital importance in coaching the appropriate use of Boolean logic (AND, OR, NOT) and other tools for highly efficient literature searches (e.g., quotation marks and truncation), as is the appropriate management of electronic databases.
Language domain
Academic writing must be concise and precise: unnecessary words distract the reader from the essential content ( 15 ). In this context, reading about issues distant from the research topic ( 16 ) may increase students’ general vocabulary and familiarity with grammar. Ultimately, reading diverse materials facilitates and encourages the writing process itself.
Critical writing
Critical judgment includes critical reading, thinking and writing. It supposes a student’s analytical reflection about what he/she has read. The student should delineate the basic elements of the topic, characterize the most relevant claims, identify relationships, and finally contrast those relationships ( 17 ). Each scientific document highlights the perspective of the author, and students will become more confident in judging the supporting evidence and underlying premises of a study and constructing their own counterargument as they read more articles. A paucity of integration or contradictory perspectives indicates lower levels of cognitive complexity ( 12 ).
Thus, while elaborating an LR, the postgraduate student should achieve the highest category of Bloom’s cognitive skills: evaluation ( 12 ). The writer should not only summarize data and understand each topic but also be able to make judgments based on objective criteria, compare resources and findings, identify discrepancies due to methodology, and construct his/her own argument ( 12 ). As a result, the student will be sufficiently confident to show his/her own voice .
Writing a consistent LR is an intense and complex activity that reveals the training and long-lasting academic skills of a writer. It is not a lonely or linear process. However, students are unlikely to be prepared to write an LR if they have not mastered the aforementioned domains ( 10 ). An institutional environment that supports student learning is crucial.
Different institutions employ distinct methods to promote students’ learning processes. First, many universities propose modules to develop behind the scenes activities that enhance self-reflection about general skills (e.g., the skills we have mastered and the skills we need to develop further), behaviors that should be incorporated (e.g., self-criticism about one’s own thoughts), and each student’s role in the advancement of his/her field. Lectures or workshops about LRs themselves are useful because they describe the purposes of the LR and how it fits into the whole picture of a student’s work. These activities may explain what type of discussion an LR must involve, the importance of defining the correct scope, the reasons to include a particular resource, and the main role of critical reading.
Some pedagogic services that promote a continuous improvement in study and academic skills are equally important. Examples include workshops about time management, the accomplishment of personal objectives, active learning, and foreign languages for nonnative speakers. Additionally, opportunities to converse with other students promotes an awareness of others’ experiences and difficulties. Ultimately, the supervisor’s role in providing feedback and setting deadlines is crucial in developing students’ abilities and in strengthening students’ writing quality ( 12 ).
HOW SHOULD A LITERATURE REVIEW BE DEVELOPED?
A consensus on the appropriate method for elaborating an LR is not available, but four main steps are generally accepted: defining the main topic, searching the literature, analyzing the results, and writing ( 6 ). We suggest a fifth step: reflecting on the information that has been written in previous publications ( Figure 2 ).

First step: Defining the main topic
Planning an LR is directly linked to the research main question of the thesis and occurs in parallel to students’ training in the three domains discussed above. The planning stage helps organize ideas, delimit the scope of the LR ( 11 ), and avoid the wasting of time in the process. Planning includes the following steps:
- Reflecting on the scope of the LR: postgraduate students will have assumptions about what material must be addressed and what information is not essential to an LR ( 13 , 18 ). Cooper’s Taxonomy of Literature Reviews 2 systematizes the writing process through six characteristics and nonmutually exclusive categories. The focus refers to the reviewer’s most important points of interest, while the goals concern what students want to achieve with the LR. The perspective assumes answers to the student’s own view of the LR and how he/she presents a particular issue. The coverage defines how comprehensive the student is in presenting the literature, and the organization determines the sequence of arguments. The audience is defined as the group for whom the LR is written.
- Designating sections and subsections: Headings and subheadings should be specific, explanatory and have a coherent sequence throughout the text ( 4 ). They simulate an inverted pyramid, with an increasing level of reflection and depth of argument.
- Identifying keywords: The relevant keywords for each LR section should be listed to guide the literature search. This list should mirror what Hart (1998) ( 3 ) advocates as subject vocabulary . The keywords will also be useful when the student is writing the LR since they guide the reader through the text.
- Delineating the time interval and language of documents to be retrieved in the second step. The most recently published documents should be considered, but relevant texts published before a predefined cutoff year can be included if they are classic documents in that field. Extra care should be employed when translating documents.
Second step: Searching the literature
The ability to gather adequate information from the literature must be addressed in postgraduate programs. Librarian support is important, particularly for accessing difficult texts. This step comprises the following components:
- Searching the literature itself: This process consists of defining which databases (electronic or dissertation/thesis repositories), official documents, and books will be searched and then actively conducting the search. Information literacy skills have a central role in this stage. While searching electronic databases, controlled vocabulary (e.g., Medical Subject Headings, or MeSH, for the PubMed database) or specific standardized syntax rules may need to be applied.
In addition, two other approaches are suggested. First, a review of the reference list of each document might be useful for identifying relevant publications to be included and important opinions to be assessed. This step is also relevant for referencing the original studies and leading authors in that field. Moreover, students can directly contact the experts on a particular topic to consult with them regarding their experience or use them as a source of additional unpublished documents.
Before submitting a dissertation/thesis, the electronic search strategy should be repeated. This process will ensure that the most recently published papers will be considered in the LR.
- Selecting documents for inclusion: Generally, the most recent literature will be included in the form of published peer-reviewed papers. Assess books and unpublished material, such as conference abstracts, academic texts and government reports, are also important to assess since the gray literature also offers valuable information. However, since these materials are not peer-reviewed, we recommend that they are carefully added to the LR.
This task is an important exercise in time management. First, students should read the title and abstract to understand whether that document suits their purposes, addresses the research question, and helps develop the topic of interest. Then, they should scan the full text, determine how it is structured, group it with similar documents, and verify whether other arguments might be considered ( 5 ).
Third step: Analyzing the results
Critical reading and thinking skills are important in this step. This step consists of the following components:
- Reading documents: The student may read various texts in depth according to LR sections and subsections ( defining the main topic ), which is not a passive activity ( 1 ). Some questions should be asked to practice critical analysis skills, as listed below. Is the research question evident and articulated with previous knowledge? What are the authors’ research goals and theoretical orientations, and how do they interact? Are the authors’ claims related to other scholars’ research? Do the authors consider different perspectives? Was the research project designed and conducted properly? Are the results and discussion plausible, and are they consistent with the research objectives and methodology? What are the strengths and limitations of this work? How do the authors support their findings? How does this work contribute to the current research topic? ( 1 , 19 )
- Taking notes: Students who systematically take notes on each document are more readily able to establish similarities or differences with other documents and to highlight personal observations. This approach reinforces the student’s ideas about the next step and helps develop his/her own academic voice ( 1 , 13 ). Voice recognition software ( 16 ), mind maps ( 5 ), flowcharts, tables, spreadsheets, personal comments on the referenced texts, and note-taking apps are all available tools for managing these observations, and the student him/herself should use the tool that best improves his/her learning. Additionally, when a student is considering submitting an LR to a peer-reviewed journal, notes should be taken on the activities performed in all five steps to ensure that they are able to be replicated.
Fourth step: Writing
The recognition of when a student is able and ready to write after a sufficient period of reading and thinking is likely a difficult task. Some students can produce a review in a single long work session. However, as discussed above, writing is not a linear process, and students do not need to write LRs according to a specific sequence of sections. Writing an LR is a time-consuming task, and some scholars believe that a period of at least six months is sufficient ( 6 ). An LR, and academic writing in general, expresses the writer’s proper thoughts, conclusions about others’ work ( 6 , 10 , 13 , 16 ), and decisions about methods to progress in the chosen field of knowledge. Thus, each student is expected to present a different learning and writing trajectory.
In this step, writing methods should be considered; then, editing, citing and correct referencing should complete this stage, at least temporarily. Freewriting techniques may be a good starting point for brainstorming ideas and improving the understanding of the information that has been read ( 1 ). Students should consider the following parameters when creating an agenda for writing the LR: two-hour writing blocks (at minimum), with prespecified tasks that are possible to complete in one section; short (minutes) and long breaks (days or weeks) to allow sufficient time for mental rest and reflection; and short- and long-term goals to motivate the writing itself ( 20 ). With increasing experience, this scheme can vary widely, and it is not a straightforward rule. Importantly, each discipline has a different way of writing ( 1 ), and each department has its own preferred styles for citations and references.
Fifth step: Reflecting on the writing
In this step, the postgraduate student should ask him/herself the same questions as in the analyzing the results step, which can take more time than anticipated. Ambiguities, repeated ideas, and a lack of coherence may not be noted when the student is immersed in the writing task for long periods. The whole effort will likely be a work in progress, and continuous refinements in the written material will occur once the writing process has begun.
LITERATURE REVIEW CHECKLIST
In contrast to review papers, the LR of a dissertation/thesis should not be a standalone piece or work. Instead, it should present the student as a scholar and should maintain the interest of the audience in how that dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field.
A checklist for evaluating an LR is convenient for students’ continuous academic development and research transparency: it clearly states the desired achievements for the LR of a dissertation/thesis. Here, we present an LR checklist developed from an LR scoring rubric ( 11 ). For a critical analysis of an LR, we maintain the five categories but offer twelve criteria that are not scaled ( Figure 3 ). The criteria all have the same importance and are not mutually exclusive.

First category: Coverage
1. justified criteria exist for the inclusion and exclusion of literature in the review.
This criterion builds on the main topic and areas covered by the LR ( 18 ). While experts may be confident in retrieving and selecting literature, postgraduate students must convince their audience about the adequacy of their search strategy and their reasons for intentionally selecting what material to cover ( 11 ). References from different fields of knowledge provide distinct perspective, but narrowing the scope of coverage may be important in areas with a large body of existing knowledge.
Second category: Synthesis
2. a critical examination of the state of the field exists.
A critical examination is an assessment of distinct aspects in the field ( 1 ) along with a constructive argument. It is not a negative critique but an expression of the student’s understanding of how other scholars have added to the topic ( 1 ), and the student should analyze and contextualize contradictory statements. A writer’s personal bias (beliefs or political involvement) have been shown to influence the structure and writing of a document; therefore, the cultural and paradigmatic background guide how the theories are revised and presented ( 13 ). However, an honest judgment is important when considering different perspectives.
3. The topic or problem is clearly placed in the context of the broader scholarly literature
The broader scholarly literature should be related to the chosen main topic for the LR ( how to develop the literature review section). The LR can cover the literature from one or more disciplines, depending on its scope, but it should always offer a new perspective. In addition, students should be careful in citing and referencing previous publications. As a rule, original studies and primary references should generally be included. Systematic and narrative reviews present summarized data, and it may be important to cite them, particularly for issues that should be understood but do not require a detailed description. Similarly, quotations highlight the exact statement from another publication. However, excessive referencing may disclose lower levels of analysis and synthesis by the student.
4. The LR is critically placed in the historical context of the field
Situating the LR in its historical context shows the level of comfort of the student in addressing a particular topic. Instead of only presenting statements and theories in a temporal approach, which occasionally follows a linear timeline, the LR should authentically characterize the student’s academic work in the state-of-art techniques in their particular field of knowledge. Thus, the LR should reinforce why the dissertation/thesis represents original work in the chosen research field.
5. Ambiguities in definitions are considered and resolved
Distinct theories on the same topic may exist in different disciplines, and one discipline may consider multiple concepts to explain one topic. These misunderstandings should be addressed and contemplated. The LR should not synthesize all theories or concepts at the same time. Although this approach might demonstrate in-depth reading on a particular topic, it can reveal a student’s inability to comprehend and synthesize his/her research problem.
6. Important variables and phenomena relevant to the topic are articulated
The LR is a unique opportunity to articulate ideas and arguments and to purpose new relationships between them ( 10 , 11 ). More importantly, a sound LR will outline to the audience how these important variables and phenomena will be addressed in the current academic work. Indeed, the LR should build a bidirectional link with the remaining sections and ground the connections between all of the sections ( Figure 1 ).
7. A synthesized new perspective on the literature has been established
The LR is a ‘creative inquiry’ ( 13 ) in which the student elaborates his/her own discourse, builds on previous knowledge in the field, and describes his/her own perspective while interpreting others’ work ( 13 , 17 ). Thus, students should articulate the current knowledge, not accept the results at face value ( 11 , 13 , 17 ), and improve their own cognitive abilities ( 12 ).
Third category: Methodology
8. the main methodologies and research techniques that have been used in the field are identified and their advantages and disadvantages are discussed.
The LR is expected to distinguish the research that has been completed from investigations that remain to be performed, address the benefits and limitations of the main methods applied to date, and consider the strategies for addressing the expected limitations described above. While placing his/her research within the methodological context of a particular topic, the LR will justify the methodology of the study and substantiate the student’s interpretations.
9. Ideas and theories in the field are related to research methodologies
The audience expects the writer to analyze and synthesize methodological approaches in the field. The findings should be explained according to the strengths and limitations of previous research methods, and students must avoid interpretations that are not supported by the analyzed literature. This criterion translates to the student’s comprehension of the applicability and types of answers provided by different research methodologies, even those using a quantitative or qualitative research approach.
Fourth category: Significance
10. the scholarly significance of the research problem is rationalized.
The LR is an introductory section of a dissertation/thesis and will present the postgraduate student as a scholar in a particular field ( 11 ). Therefore, the LR should discuss how the research problem is currently addressed in the discipline being investigated or in different disciplines, depending on the scope of the LR. The LR explains the academic paradigms in the topic of interest ( 13 ) and methods to advance the field from these starting points. However, an excess number of personal citations—whether referencing the student’s research or studies by his/her research team—may reflect a narrow literature search and a lack of comprehensive synthesis of ideas and arguments.
11. The practical significance of the research problem is rationalized
The practical significance indicates a student’s comprehensive understanding of research terminology (e.g., risk versus associated factor), methodology (e.g., efficacy versus effectiveness) and plausible interpretations in the context of the field. Notably, the academic argument about a topic may not always reflect the debate in real life terms. For example, using a quantitative approach in epidemiology, statistically significant differences between groups do not explain all of the factors involved in a particular problem ( 21 ). Therefore, excessive faith in p -values may reflect lower levels of critical evaluation of the context and implications of a research problem by the student.
Fifth category: Rhetoric
12. the lr was written with a coherent, clear structure that supported the review.
This category strictly relates to the language domain: the text should be coherent and presented in a logical sequence, regardless of which organizational ( 18 ) approach is chosen. The beginning of each section/subsection should state what themes will be addressed, paragraphs should be carefully linked to each other ( 10 ), and the first sentence of each paragraph should generally summarize the content. Additionally, the student’s statements are clear, sound, and linked to other scholars’ works, and precise and concise language that follows standardized writing conventions (e.g., in terms of active/passive voice and verb tenses) is used. Attention to grammar, such as orthography and punctuation, indicates prudence and supports a robust dissertation/thesis. Ultimately, all of these strategies provide fluency and consistency for the text.
Although the scoring rubric was initially proposed for postgraduate programs in education research, we are convinced that this checklist is a valuable tool for all academic areas. It enables the monitoring of students’ learning curves and a concentrated effort on any criteria that are not yet achieved. For institutions, the checklist is a guide to support supervisors’ feedback, improve students’ writing skills, and highlight the learning goals of each program. These criteria do not form a linear sequence, but ideally, all twelve achievements should be perceived in the LR.
CONCLUSIONS
A single correct method to classify, evaluate and guide the elaboration of an LR has not been established. In this essay, we have suggested directions for planning, structuring and critically evaluating an LR. The planning of the scope of an LR and approaches to complete it is a valuable effort, and the five steps represent a rational starting point. An institutional environment devoted to active learning will support students in continuously reflecting on LRs, which will form a dialogue between the writer and the current literature in a particular field ( 13 ).
The completion of an LR is a challenging and necessary process for understanding one’s own field of expertise. Knowledge is always transitory, but our responsibility as scholars is to provide a critical contribution to our field, allowing others to think through our work. Good researchers are grounded in sophisticated LRs, which reveal a writer’s training and long-lasting academic skills. We recommend using the LR checklist as a tool for strengthening the skills necessary for critical academic writing.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Leite DFB has initially conceived the idea and has written the first draft of this review. Padilha MAS and Cecatti JG have supervised data interpretation and critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read the draft and agreed with this submission. Authors are responsible for all aspects of this academic piece.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to all of the professors of the ‘Getting Started with Graduate Research and Generic Skills’ module at University College Cork, Cork, Ireland, for suggesting and supporting this article. Funding: DFBL has granted scholarship from Brazilian Federal Agency for Support and Evaluation of Graduate Education (CAPES) to take part of her Ph.D. studies in Ireland (process number 88881.134512/2016-01). There is no participation from sponsors on authors’ decision to write or to submit this manuscript.
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
1 The questions posed in systematic reviews usually follow the ‘PICOS’ acronym: Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes, Study design.
2 In 1988, Cooper proposed a taxonomy that aims to facilitate students’ and institutions’ understanding of literature reviews. Six characteristics with specific categories are briefly described: Focus: research outcomes, research methodologies, theories, or practices and applications; Goals: integration (generalization, conflict resolution, and linguistic bridge-building), criticism, or identification of central issues; Perspective: neutral representation or espousal of a position; Coverage: exhaustive, exhaustive with selective citations, representative, central or pivotal; Organization: historical, conceptual, or methodological; and Audience: specialized scholars, general scholars, practitioners or policymakers, or the general public.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.

OASIS: Writing Center
Common assignments: literature reviews, basics of literature reviews.
A literature review is a written approach to examining published information on a particular topic or field. Authors use this review of literature to create a foundation and justification for their research or to demonstrate knowledge on the current state of a field. This review can take the form of a course assignment or a section of a longer capstone project. Read on for more information about writing a strong literature review!
Students often misinterpret the term "literature review" to mean merely a collection of source summaries, similar to annotations or article abstracts. Although summarizing is an element of a literature review, the purpose is to create a comprehensive representation of your understanding of a topic or area of research, such as what has already been done or what has been found. Then, also using these sources, you can demonstrate the need for future research, specifically, your future research.
There is usually no required format or template for a literature review. However, there are some actions to keep in mind when constructing a literature review:
- Include an introduction and conclusion . Even if the literature review will be part of a longer document, introductory and concluding paragraphs can act as bookends to your material. Provide background information for your reader, such as including references to the pioneers in the field in the beginning and offering closure in the end by discussing the implications of future research to the field.
- Avoid direct quotations . Just like in an annotated bibliography, you will want to paraphrase all of the material you present in a literature review. This assignment is a chance for you to demonstrate your knowledge on a topic, and putting ideas into your own words will ensure that you are interpreting the found material for your reader. Paraphrasing will also ensure your review of literature is in your authorial voice.
- Organize by topic or theme rather than by author. When compiling multiple sources, a tendency can be to summarize each source and then compare and contrast the sources at the end. Instead, organize your source information by your identified themes and patterns. This organization helps demonstrate your synthesis of the material and inhibits you from creating a series of book reports.
- Use headings . APA encourages the use of headings within longer pieces of text to display a shift in topic and create a visual break for the reader. Headings in a literature review can also help you as the writer organize your material by theme and note any layers, or subtopics, within the field.
- Show relationships and consider the flow of ideas. A literature review can be lengthy and dense, so you will want to make your text appealing to your reader. Transitions and comparison terms will allow you to demonstrate where authors agree or disagree on a topic and highlight your interpretation of the literature.
Related Multimedia, Social Media, and Other Resources
Randolph, J. J. (2009). A guide to writing the dissertation literature review. Practical Assessment, Research and Evaluation , 14 (13), 1–13. https://scholarworks.umass.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1219&context=pare
Didn't find what you need? Search our website or email us .
Read our website accessibility and accommodation statement .
- Previous Page: Example
- Next Page: Synthesizing Your Sources
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: Mar 26, 2024 10:40 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Literature Reviews
- Choosing a Type of Review
- Developing a Research Question
- Searching the Literature
- Searching Tips
- ChatGPT [beta]
- Documenting your Search
- Using Citation Managers
- Concept Mapping
Outline of Review Sections
Strategies for writing.
- Help from UM Sweetland
- Further Resources
Avoiding Bias
Reporting bias.
This occurs when you are summarizing the literature in an unbalanced, inconsistent or distorted way .
Ways to avoid:
- look for literature that supports multiple perspectives, viewpoints or theories
- ask multiple people to review your writing for bias
Chemistry LitReviews

There is a short Canvas module on " Writing a Mini-Review " for those writing a literature review in chemistry. To access: 1 — log in to UM Canvas 2 — paste this url into browser

Contact author Yulia Sevryugina , Chemistry Librarian with questions.
Your Literature Review should not be a summary and evaluation of each article, one after the other. Your sources should be integrated together to create a narrative on your topic.
Consider the following ways to organize your review:
- By themes, variables, or issues
- By varying perspectives regarding a topic of controversy
- Chronologically, to show how the topic and research have developed over time
Use an outline to organize your sources and ideas in a logical sequence. Identify main points and subpoints, and consider the flow of your review. Outlines can be revised as your ideas develop. They help guide your readers through your ideas and show the hierarchy of your thoughts. What do your readers need to understand first? Where might certain studies fit most naturally? These are the kinds of questions that an outline can clarify.
An example outline for a Literature Review might look like this:
Introduction
- Background information on the topic & definitions
- Purpose of the literature review
- Scope and limitations of the review (what is included /excluded)
- Historical background
- Overview of the existing research on the topic
- Principle question being asked
- Organization of the literature into categories or themes
- Evaluation of the strengths and weaknesses of each study
- Combining the findings from multiple sources to identify patterns and trends
- Insight into the relationship between your central topic and a larger area of study
- Development of a new research question or hypothesis
- Summary of the key points and findings in the literature
- Discussion of gaps in the existing knowledge
- Implications for future research
ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY
An annotated bibliography collects short descriptions of each source in one place. After you have read each source carefully, set aside some time to write a brief summary. Your summary might be simply informative (e.g. identify the main argument/hypothesis, methods, major findings, and/or conclusions), or it might be evaluative (e.g. state why the source is interesting or useful for your review, or why it is not).
This method is more narrative than the Literature Matrix talked about on the Documenting Your Search page.
Taking the time to write short informative and/or evaluative summaries of your sources while you are researching can help you transition into the drafting stage later on. By making a record of your sources’ contents and your reactions to them, you make it less likely that you will need to go back and re-read many sources while drafting, and you might also start to gain a clearer idea of the overarching shape of your review.
READ EXTANT LIT REVIEWS CLOSELY
As you conduct your research, you will likely read many sources that model the same kind of literature review that you are researching and writing. While your original intent in reading those sources is likely to learn from the studies’ content (e.g. their results and discussion), it will benefit you to re-read these articles rhetorically.
Reading rhetorically means paying attention to how a text is written—how it has been structured, how it presents its claims and analyses, how it employs transitional words and phrases to move from one idea to the next. You might also pay attention to an author’s stylistic choices, like the use of first-person pronouns, active and passive voice, or technical terminology.
See Finding Example Literature Reviews on the Developing a Research Question page for tips on finding reviews relevant to your topic.
MIND-MAPPING
Creating a mind-map is a form of brainstorming that lets you visualize how your ideas function and relate. Draw the diagram freehand or download software that lets you easily manipulate and group text, images, and shapes.
Write down a central idea, then identify associated concepts, features, or questions around that idea. Make lines attaching various ideas, or arrows to signify directional relationships. Use different shapes, sizes, or colors to indicate commonalities, sequences, or relative importance.

This drafting technique allows you to generate ideas while thinking visually about how they function together. As you follow lines of thought, you can see which ideas can be connected, where certain pathways lead, and what the scope of your project might be. By drawing out a mind-map you may be able to see what elements of your review are underdeveloped and will benefit from more focused attention.
See the Concept Mapping section on the Organizing the Literature page of this guide for tools and inspiration in creating your own mind map.

- << Previous: Concept Mapping
- Next: Further Resources >>
- Last Updated: Feb 29, 2024 10:31 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.umich.edu/litreview

Literature review outline [Write a literature review with these structures]
Welcome to our comprehensive blog on crafting a perfect literature review for your research paper or dissertation.
The ability to write a literature review with a concise and structured outline is pivotal in academic writing.
You’ll get an overview of how to structure your review effectively, address your research question, and demonstrate your understanding of existing knowledge.
We’ll delve into different approaches to literature reviews, discuss the importance of a theoretical approach, and show you how to handle turning points in your narrative.
You’ll learn how to integrate key concepts from your research field and weave them into your paragraphs to highlight their importance.
Moreover, we’ll guide you through the nuances of APA citation style and how to compile a comprehensive bibliography. Lastly, we’ll walk you through the proofreading process to ensure your work is error-free.
As a bonus, this blog will provide useful tips for both seasoned researchers and first-time writers to produce a literature review that’s clear, informative, and engaging. Enjoy the writing process with us!
Structure of a Literature Review – Outline
When you write a literature review outline, you are laying the foundations of great work. Many people rush this part and struggle later on. Take your time and slowly draft the outline for a literature review.

The structure of a literature review consists of five main components:
- Introduction: Provide a brief overview of the chapter, along with the topic and research aims to set the context for the reader.
- Foundation of Theory or Theoretical Framework: Present and discuss the key theories, concepts, and models related to your research topic. Explain how they apply to your study and their significance.
- Empirical Research: Review and analyze relevant empirical related to your research question. Highlight their findings, methodologies, and any limitations they possess.
- Research Gap: Identify any gaps, inconsistencies, or ambiguities in the existing literature. This will help establish the need for your research and justify its relevance.
- Conclusion: Summarize the main findings from the literature review, emphasizing the importance of your research question and the identified research gap. Suggest potential avenues for future research in the field.
Sentence starters for each section of your literature review:
Literature review examples and types.
Based on the typology of literature reviews from Paré et al. (2015), the following list outlines various types of literature reviews and examples of when you’d use each type:
1. Conceptual Review: Analyzes and synthesizes the theoretical and conceptual aspects of a topic. It focuses on understanding key concepts, models, and theories.
Example use: When aiming to clarify the conceptual foundations and explore existing theories in a field, such as investigating the dimensions of job satisfaction.
2. Methodological Review: Evaluates and synthesizes the research approaches, methods, and techniques used in existing literature. It aims to identify methodological strengths and weaknesses in a research area.
Example use: When assessing data collection methods for researching user experiences with a new software application.
3. Descriptive Review: Provides a broad overview of studies in a research area. It aims to describe the existing literature on a topic and document its evolution over time.
Example use: When investigating the history of research on employee motivation and documenting its progress over the years.
4. Integrative Review: Combines and synthesizes findings from different studies to produce a comprehensive understanding of a research topic. It may identify trends, patterns, or common themes among various studies.
Example use: When exploring the links between work-life balance and job satisfaction, aggregating evidence from multiple studies to develop a comprehensive understanding.
5. Theory-driven Review: Examines a research topic through the lens of a specific theoretical framework. It focuses on understanding how the chosen theory explains or predicts phenomena in the literature.
Example use: When studying the impact of leadership styles on team performance, specifically using the transformational leadership theory as a basis for the analysis.
6. Evidence-driven Review: Aims to determine the effectiveness of interventions or practices based on the available research evidence. It can inform the decision-making process in practice or policy by providing evidence-based recommendations.
Example use: When assessing the effectiveness of telemedicine interventions for managing chronic disease outcomes, providing recommendations for healthcare providers and policymakers.
By understanding these types of literature reviews and their appropriate usage, researchers can choose the most suitable approach for their research question and contribute valuable insights to their field.
How to Write a Good Literature Review
To write a good literature review, follow these six steps to help you create relevant and actionable content for a young researcher.
1. Define the review’s purpose: Before starting, establish a clear understanding of your research question or hypothesis. This helps focus the review and prevents unnecessary information from being included.
2. Set inclusion and exclusion criteria: Use predefined criteria for including or excluding sources in your review. Establish these criteria based on aspects such as publication date, language, type of study, and subject relevance. This ensures your review remains focused and meets your objectives.
3. Search for relevant literature: Conduct a comprehensive search for literature relevant to your research question. Use databases, online catalogs, and search engines that focus on academic literature, such as Google Scholar, Scopus, or Web of Science. Consider using multiple search terms and synonyms to cover all related topics.
4. Organize and analyze information: Develop a system for organizing and analyzing the information you find. You can use spreadsheets, note-taking applications, or reference management tools like Mendeley, Zotero, or EndNote. Categorize your sources based on themes, author’s conclusions, methodology, or other relevant criteria.
5. Write a critique of the literature: Evaluate and synthesize the information from your sources. Discuss their strengths, weaknesses, and gaps in knowledge or understanding. Point out any inconsistencies in the findings and explain any varying theories or viewpoints. Provide a balanced critique that highlights the most significant contributions, trends, or patterns.
6. Structure the review: Organize your literature review into sections that present the main themes or findings. Start with an introduction that outlines your research question, the scope of the review, and any limitations you may have encountered. Write clear, concise, and coherent summaries of your literature for each section, and end with a conclusion that synthesizes the main findings, suggests areas for further research, and reinforces your research question or hypothesis.
Incorporating these steps will assist you in crafting a well-structured, focused, and informative literature review for your research project.
Here are some examples of each step in the process.
Top Tips on How to Write Your Literature Review
Here are the top tips on how to write your literature review, based on the Grad Coach TV video and advice from trusted coach Amy:
1. Develop a rough outline or framework before you start writing your literature review. This helps you avoid creating a jumbled mess and allows you to organize your thoughts coherently and effectively.
2. Use previous literature reviews as a guide to understand the norms and expectations in your field. Look for recently published literature reviews in academic journals or online databases, such as Google Scholar, EBSCO, or ProQuest.
3. Write first and edit later. Avoid perfectionism and don’t be afraid to create messy drafts. This helps you overcome writer’s block and ensures progress in your work.
4. Insert citations as you write to avoid losing track of references. Make sure to follow the appropriate formatting style (e.g. APA or MLA) and use reference management tools like Mendeley to easily keep track of your sources.
5. Organize your literature review logically, whether it’s chronologically, thematically, or methodologically. Identify gaps in the literature and explain how your study addresses them. Keep in mind that the structure isn’t set in stone and can change as you read and write.
Remember that writing your literature review is an iterative process, so give yourself room to improve and make changes as needed. Keep these actionable tips in mind, and you’ll be well on your way to creating a compelling and well-organized literature review.
Wrapping up – Your literature review outline
As we conclude this extensive guide, we hope that you now feel equipped to craft a stellar literature review.
We’ve navigated the intricacies of an effective literature review outline, given you examples of each section, provided sentence starters to ignite your writing process, and explored the diverse types of literature reviews.
This guide has also illustrated how to structure a literature review and organize the research process, which should help you tackle any topic over time.
Emphasizing key themes, we’ve shown you how to identify gaps in existing research and underscore the relevance of your work.
Remember, writing a literature review isn’t just about summarizing existing studies; it’s about adding your own interpretations, arguing for the relevance of specific theoretical concepts, and demonstrating your grasp of the academic field.
Keep the key debates that have shaped your research area in mind, and use the strategies we’ve outlined to add depth to your paper.
So, start writing, and remember, the journey of writing is iterative and a pivotal part of your larger research process.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider
- Public Lectures
- Faculty & Staff Site >>
From seminar paper to master of arts degree thesis to dissertation, the literature review provides both the foundation and the frame for your own research. Its preparation requires careful planning and a well-crafted presentation.
The purpose of the literature review
A literature review tells us what is known by sharing the results of prior studies related to your own.
A literature review places your study within a larger body of work. It shows how your study seeks to fill a gap in, or extend, our knowledge in this area.
A literature review offers a benchmark for assessing your own results. In the conclusion to your study you will revisit the literature review armed with your new findings.
Organizing the literature review
A good literature review is a synthesis of prior research presented in a way that adds value to our understanding of that work. So, it’s important to organize your review in a way that is coherent, relevant to your own study, and useful to other researchers. For example, you might cluster prior research by media type, communication situation, similar findings, key themes, respondent type, or other useful distinction.
Whatever organizing scheme you choose, it is typical to present the most important, relevant, or strongest collection of existing research first, and go from there. If not, there should be a narrative logic to the review presentation.
Another way to add value is to identify conceptual linkages among ideas and authors. Researchers often talk about the same processes — just in somewhat different ways.
It’s tempting to want to include every study that appeared in the key word search of your topic. Don’t. The challenge is to find the right balance between giving the reader confidence in your familiarity with literature and focusing on what’s most relevant for the study at hand.
Writing the literature review
Your synthesis of prior research should focus on key findings or conclusions with just enough information for the reader to discern the question and approach: “In her ethnographic study of Muslim immigrants’ perception of mainstream British media, Gillespie concluded…” The exception being if the study cited is significant because of its methodology — only then would you offer more methodological detail.
Not all ideas in the literature review are used to construct your study’s conceptual framework. So, at the end of each section, tell readers what key concept, finding, definition, or theme is most critical to “carry forward” into their reading of your study.
Don’t over-quote. It slows down your narrative. Direct quotations should only appear if the author said something in a unique, powerful, or precise way (e.g., a definition) that demands repeating in its exact form. Otherwise, use your own words.
Since a good review is a coherent, value-added organization of the literature, provide the reader with clear “signposts” through the instructive use of headings, introductions, transition phrases, and summary statements.
Finally, because people reading your paper or dissertation may not be familiar with your area of research, be careful not to weigh down your literature review in field-specific jargon. It is important that you write in clear and active prose.
by Nancy Rivenburgh, professor, Communication
A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Stellar Literature Review (with Help from AI)

Aren’t all of us mini versions of Sherlock Holmes when browsing data and archives for a research piece? As we go through the process, a comprehensive literature review is an essential toolkit to make your research shine.
A literature review consists of scholarly sources that validate the content. Its primary objective is to offer a concise summary of the research and to let you explore relevant theories and methodologies. Through this review, you can identify gaps in the existing research and bridge them with your contribution.
The real challenge is how to write an excellent literature review. Let’s learn.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is an introduction to your research. It helps you put your perspective to the table, along with a summary of the theme.
What does my literature review communicate?
- Explanation of your research: how the information was collected, the research method, the justification of the chosen data sources, and an overview of the data analysis.
- Framework: the journey from where the concept began and how it is presented.
- Connects the previous and current research:
It presents the broader scope of your research by connecting it to the existing data and debates and underlining how your content fits the prevailing studies.
In an era of information overload, a literature review must be well-structured.
Let’s learn all about the structure and style of a literature review that’ll help you strengthen your research.
Literature review– structure and style
Begin with a question and end it with the solution– the key to structuring a literature review. It resembles an essay’s format, with the first paragraph introducing the readers to the topic and the following explaining the research in-depth.
The conclusion reiterates the question and summarizes the overall insights of your research. There’s no word count restriction. —it depends on the type of research. For example, a dissertation demands lengthy work, whereas a short paper needs a few pages.
In a literature review, maintaining high quality is vital, with a focus on academic writing style. Informal language should be avoided in favor of a more formal tone.
The content avoids contractions, clearly differentiating between previous and current research through the use of past and present tense. Wordtune assists in establishing a formal tone, enhancing your work with pertinent suggestions. This AI-powered tool ensures your writing remains genuine, lucid, and engaging.

The option of refining the tonality offers multiple possibilities for rephrasing a single sentence. Thus, pick the best and keep writing.
Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
Your friendly step-by-step guide to writing a literary review (with help from AI)
Do you find it challenging to begin the literature review? Don’t worry! We’re here to get you started with our step-by-step guide.
1. Narrow down the research scope
Simply begin with the question: What am I answering through my research?
Whether it’s cooking or painting, the real challenge is the prep-up for it rather than performing the task. Once you’re done, it smoothly progresses. Similarly, for your literature review, prepare the groundwork by narrowing down the research scope.
Browse and scoop out relevant data inclining well with your research. While you can’t cover every aspect of your research, pick a topic that isn’t too narrow nor too broad to keep your literature review well-balanced.
2. Hunt relevant literature
The next question: Does this data align with the issue I’m trying to address?
As you review sources of information, hunt out the best ones. Determine which findings help in offering a focused insight on your topic. The best way to pick primary sources is to opt for the ones featured in reliable publications. You can also choose secondary sources from other researchers from a reasonable time frame and a relevant background.
For example, if your research focuses on the Historical Architecture of 18th-century Europe, the first-hand accounts and surveys from the past would hold more weight than the new-age publications.
3. Observe the themes and patterns in sources
Next comes: What is the core viewpoint in most of the research? Has it stayed constant over time, or have the authors differed in their points of view?
Ensure to scoop out the essential aspects of what each source represents. Once you have collected all this information, combine it and add your interpretations at the end. This process is known as synthesis.
Synthesize ideas by combining arguments, findings and forming your new version.
4. Generate an outline
The next question: How can I organize my review effectively? When navigating multiple data sources, you must have noticed a structure throughout the research. Develop an outline to make the process easier. An outline is a skeletal format of the review, helping you connect the information more strategically.
Here are the three different ways to organize an outline– Chronologically, Thematically, or by Methodology.You can develop the outline chronologically, starting from the older sources and leading to the latest pieces. Another way of organizing is to thematically divide the sections and discuss each under the designated sub-heading.
You can even organize it per the research methods used by the respective authors. The choice of outline depends on the subject. For example, in the case of a science paper, you can divide the information into sections like introduction, types of equipment, method, procedure, findings, etc. In contrast, it’s best to present it in divisions based on timelines like Ancient, Middle Ages, Industrial revolutions, etc., for a history paper.
If you’re confused about how to structure the data, work with Wordtune.

With the Generate with AI feature, you can mention your research topic and let Wordtune curate a comprehensive outline for your study.

Having a precise prompt is the key to getting the best results.
5. Start filling!
Your next question must be: Am I ready to compose all the parts of the literature review?
Once you’re ready with the basic outline and relevant sources, start filling in the data. Go for an introductory paragraph first to ensure your readers understand the topic and how you will present it. Ensure you clearly explain the section in the first sentence.
However, if beginning from the first paragraph seems intimidating, don’t worry! Add the main body content to the sub-headings, then jump to the introduction.
Add headings wherever possible to make it more straightforward and guide your readers logically through different sources. Lastly, conclude your study by presenting a key takeaway and summarizing your findings. To make your task easier, work with Wordtune. It helps align your content with the desired tone and refine the structure.
6. Give attention to detail and edit
The last question: Am I satisfied with the language and content written in the literature review? Is it easy to understand?
Once you’re done writing the first draft of a literature review, it’s time to refine it. Take time between writing and reading the draft to ensure a fresh perspective. It makes it easier to spot errors when you disconnect from the content for some time. Start by looking at the document from a bird's eye to ensure the formatting and structure are in order.
After reviewing the content format, you must thoroughly check your work for grammar, spelling, and punctuation. One of the best approaches to editing and proofreading is to use Wordtune . It helps simplify complex sentences, enhance the content quality, and gain prowess over the tonality.
The dos and don’ts of writing a literature review
Writing a stellar literature review requires following a few dos and don'ts. Just like Sherlock Holmes would never overlook a hint, you must pay attention to every minute detail while writing a perfect narrative. To help you write, below are some dos and don'ts to remember.

Composing a literature review demands a holistic research summary, each part exhibiting your understanding and approach. As you write the content, make sure to cover the following points:
- Keep a historical background of the field of research. Highlight the relevant relation between the old studies and your new research.
- Discuss the core issue, question, and debate of your topic.
- Theories lay the foundation of research. While you’re writing a literature review, make sure to add relevant concepts and ideas to support your statements.
- Another critical thing to keep in mind is to define complex terminologies. It helps the readers understand the content with better clarity.
Examples of comprehensive literature reviews
Aren’t good examples the best way to understand a subject? Let’s look into a few examples of literature reviews and analyze what makes them well-written.
1. Critical Thinking and Transferability: A Review of the Literature (Gwendolyn Reece)
An overview of scholarly sources is included in the literature review, which explores critical thinking in American education. The introduction stating the subject’s importance makes it a winning literature review. Following the introduction is a well-defined purpose that highlights the importance of research.
As one keeps reading, there is more clarity on the pros and cons of the research. By dividing information into parts with relevant subheadings, the author breaks a lengthy literature review into manageable chunks, defining the overall structure.
Along with other studies and presented perspectives, the author also expresses her opinion. It is presented with minimal usage of ‘I,’ keeping it person-poised yet general. Toward the conclusion, the author again offers an overview of the study. A summary is further strengthened by presenting suggestions for future research as well.
2. The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review
This literature review is thematically organized on how technology affects language acquisition. The study begins with an introduction to the topic with well-cited sources. It presents the views of different studies to help readers get a sense of different perspectives. After giving these perspectives, the author offers a personalized opinion.
One of the critical aspects that makes this a good literature review is a dedicated paragraph for definitions. It helps readers proceed further with a clear understanding of the crucial terminologies. There’s a comparison of the modern and previous studies and approaches to give an overall picture of the research.
Once the main body is composed, the author integrates recommendations for action-based tips. Thus, the literature review isn’t just summarizing the sources but offering actions relevant to the topics. Finally, the concluding paragraph has a brief overview with key takeaways.
Wordtune: your writing buddy!
A literature review demands the right balance of language and clarity. You must refine the content to achieve a formal tone and clear structure. Do you know what will help you the most? Wordtune !.
The real-time grammar checker leaves no scope for errors and lets you retain precision in writing. This writing companion is all you need for stress-free working and comprehensive literature review development.
Let the narrative begin
A literary review isn't just about summarizing sources; it's about seamlessly bringing your perspective to the table. Always remember to set a narrative for added interest and a brilliant composition. With structure and style being the pillars of a stellar literature review, work with Wordtune to ensure zero compromises on the quality.
Share This Article:

An Expert Guide to Writing Effective Compound Sentences (+ Examples)
How I Turned Clutter into Cash: 10 Proven Instagram Copywriting Hacks

How to Write a Wikipedia Page So It’ll Get Approved
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
Where instructors and editors talk writing.
- Literature Review Essentials: Identify Themes

Theme 1: Name or description of theme, which will eventually be made into a topic sentence Author Name (Year), Paraphrase of relevant material related to the theme Author Name (Year), Paraphrase of relevant material related to the theme Repeat as needed for all the sources you’ve found that deal with this theme Theme 2: Name or description of theme, which will eventually be made into a topic sentence Author Name (Year), Paraphrase of relevant material related to the theme Author Name (Year), Paraphrase of relevant material related to the theme Repeat as needed for all the sources you’ve found that deal with this theme Continue as needed, depending on how many themes you have identified in the literature and how many sources have information to contribute to the themes.

26 comments :

This was very helpful Jes! Thanks a lot.
We're glad you found this post helpful, Eniale!
Thank you Jes. I found your method to thematic literature review very useful and easy to understand. I am a Phd student in Education with the University of Durban.I am based in Zimbabwe.
We are glad you found this method useful!
I am having difficulties locating an example of a completed literature review outline. Where would I find additional examples? Thank you.
You’re welcome!
Hi is literature review writing same as writing a thematic summary after reading articles based on the given topic?
Great question! It depends on the assignment (what faculty want with the thematic summary assignment). For literature reviews, paragraphs revolve around themes within the literature as opposed to authors. So, when Jes uses the phrasing, "thematic literature reviews," she is referring to how literature reviews are about synthesizing themes across the literature as opposed to creating paragraphs that are summaries for each singular author/ source. You can read more about synthesis on our website http://bit.ly/2JEUK09
thank you, this one is useful.
I've been in a slump for weeks regarding a literature review assignment. This is very very helpful! Thank you!
We're happy this helped! Good luck with your literature review!
I'm doing a lit review for a post grad certificate and I have to discuss the findings using a framework analysis, can you lead me to the right section. Yours struggling
Hello, You might check with your professor regarding what is meant by “framework analysis” in relation to the finding of your literature review. While the Writing Center has some sources on components of writing literature reviews, it is best to speak with faculty regarding assignment specifics. You might also check out our page on literature reviews: https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/assignments/literaturereview We hope this helps!
i have found it useful, it has polished me some how, my problem in the literature review is how to formulate themes and subthemes for the topic. forexample dealing with solid waste skips monitoring and management for municpalities. what themes can i build on in the study. thank you dear.
Hello! I think creating an outline my help you identify some main themes and sub themes and then you can choose what themes and sub themes you want to focus on from there. You might check out our outlining page for tips on creating an outline: http://bit.ly/2WP3UCe. We hope this helps!
Thank you! My professor referenced this link/article for the literature review assignment in a research class. This was helpful.
So glad you found it helpful! Thank you for commenting!
This really was helpful. I feel so much better about tackling my lit review now. Thanks!
Helping writers gain confidence in their skills is one of our primary goals for this blog. Thank you for reaching out with this kind note to let us know we are on the right track! :)
Really informative study. It helped me in finding themes in literature. Plz if u can give me your email. It will be very helpful to me in writing my dissertation
This was very helpful; clear and concise. Thank you!
Oh Jes! you just sent me back to the drawing board, guilty of annotated bibliography. Thank you for this helpful writeup.
I'm sure you're not alone! And there is a reason this is a blog post topic. :) Kudos for identifying potential issues in your own writing and thank you so much for reading and commenting!
im failing to understand the concept themes
This can be a tricky concept to grasp, which is why we've created blog posts like this one. Basically, "themes" are ideas that connect so that writers are organizing based on themes rather than on sources. So instead of having one paragraph about one article, another paragraph about a different article, and a third paragraph about a third article, the paragraphs would be organized based on common ideas shared between two or three of the articles. You might check out our MEAL plan resources (https://academicanswers.waldenu.edu/faq/72800), or our resources for synthesis (https://academicanswers.waldenu.edu/faq/72694) for further clarification. Hope this helps! Thanks for reading!
Search the Blog
Featured posts.
- Expert Advice
- Writing Center Services
- Scholarly Writing
- Capstone Writing
- Grammar and Mechanics
- Writer's Workshop
- Social Change
- Literature Review
- International/Multilingual Students
- Passive Voice
WriteCast Podcast

Visit the Writing Center's Website

- About the Blog

Blog Archive
- ► May (1)
- ► April (1)
- ► February (1)
- ► January (1)
- ► December (1)
- ► November (1)
- ► September (1)
- ► July (1)
- ► June (1)
- ► March (2)
- ► October (2)
- ► September (2)
- ► August (2)
- ► July (2)
- ► June (2)
- ► April (2)
- ► March (3)
- ► January (3)
- ► November (3)
- ► October (3)
- ► September (4)
- ► August (4)
- ► July (5)
- ► June (5)
- ► May (5)
- ► April (9)
- ► March (7)
- ► February (8)
- ► January (9)
- ► December (9)
- ► November (9)
- ► October (9)
- ► September (8)
- ► August (7)
- ► July (8)
- ► June (8)
- ► May (7)
- ► March (9)
- ► December (8)
- ► August (9)
- ► July (6)
- ► June (6)
- ► May (9)
- ► April (8)
- Webinar Update: April Webinars!
- Literature Review Essentials: Align Problems
- Relaxation Reminder
- Literature Review Essentials: Construct Paragraphs
- WriteCast Episode 36: Social Change and Difficult ...
- Literature Review Essentials: A Five-Part Blog Series
- Literature Review Essentials: Curate Information
- March Webinar Update
- ► November (8)
- ► September (9)
- ► June (9)
- ► February (9)
- ► June (4)
- ► May (4)
- ► April (5)
- ► March (6)
- ► February (5)
- ► January (5)
- ► December (6)
- ► November (5)
- ► October (5)
- ► September (5)
- ► August (5)
- ► April (7)
- ► February (4)
- ► December (4)
- ► November (4)
- ► October (7)
- ► July (7)
- ► April (6)
- ► March (4)
- ► September (7)
- ► August (6)
- ► June (3)
- ► January (6)
- ► October (6)
- ► September (3)
- ► April (4)
- ► February (2)
- ► January (2)
- ► December (2)
- ► November (2)
- ► August (3)
© Walden University Writing Center SoraTemplates . Posts RSS . Comments RSS
- Words to pages
- Pages to words
Customer Reviews
Is essay writing service legal?
Essay writing services are legal if the company has passed a number of necessary checks and is licensed. This area is well developed and regularly monitored by serious services. If a private person offers you his help for a monetary reward, then we would recommend you to refuse his offer. A reliable essay writing service will always include terms of service on their website. The terms of use describe the clauses that customers must agree to before using a product or service. The best online essay services have large groups of authors with diverse backgrounds. They can complete any type of homework or coursework, regardless of field of study, complexity, and urgency.
When you contact the company Essayswriting, the support service immediately explains the terms of cooperation to you. You can control the work of writers at all levels, so you don't have to worry about the result. To be sure of the correctness of the choice, the site contains reviews from those people who have already used the services.

is here to help you!
Student years are the best time of one’s life. You are in the prime of your life and hopeful about the bright future ahead. This is the period that leaves the funniest photos, the sweetest memories, and gives you the most faithful friends. However, there is one thing that spoils all the fun – assignment writing. Have you ever struggled to write an essay or prepare a speech only to find that the deadline is getting closer, and the work is not ready yet? Are you desperate for someone to have your paper done? Ordering it online is a really convenient option, but you must be sure that the final product is worth the price. is one of the leading online writing centers that deliver only premium quality essays, term papers, and research papers.
Once you place an order and provide all the necessary instructions, as well as payment, one of our writers will start working on it. Be sure we won’t choose a person to do your paper at random. The writer assigned will hold an academic degree in the respective area of expertise, which makes it possible for him/her to find the relevant information, carry out exhaustive research, and develop a comprehensible and well-organized document. The final product will meet all your specifications regarding the content and formatting style. What is more, you will not have to proofread it for any grammatical or spelling errors, because our professionals have a really good command of the English language.

Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
By using themes! In this post, I share how you can structure your dissertation literature review using themes. There's also a link to a free PDF Theme Tracker Planner and my YouTube video on this topic! ... you have more themes than this, think about whether you can bring some of them together, consolidate them under one new theme. Literature ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
How To Structure Your Literature Review. Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components - an introduction, a body and a conclusion. Let's take a closer look at each of these. 1: The Introduction Section
When writing a thematic literature review, go through different literature review sections of published research work and understand the subtle nuances associated with this approach. Identify Themes: Analyze the literature to identify recurring themes or topics relevant to your research question. Categorize the bibliography by dividing them ...
The word "literature review" can refer to two related things that are part of the broader literature review process. The first is the task of reviewing the literature - i.e. sourcing and reading through the existing research relating to your research topic. The second is the actual chapter that you write up in your dissertation, thesis or ...
The literature review of a dissertation gives a clear, critical overview of a specific area of research. ... (i.e., near the bottom) warrants the most comprehensive attention in the literature review, whereas the broad themes at the top can be covered more quickly. The broad-to-narrow structure is intuitive for readers. Thus, it is crucial to ...
What Role Does A Thesis Statement Play In A Literature Review? A thesis statement encapsulates the main theme, findings, or trends within the literature, providing a roadmap for readers and aligning with the research question. Conclusion. In crafting a literature review for your dissertation, mastering the art of synthesizing existing research ...
Here, we look into how to conduct a successful literature review and thus write a high-quality thesis. 1. Define the scope of your review. Once you've decided on a specific research question, you have to decide on the comprehensiveness of your literature review. There are many factors you must decide on before you begin: What specific topics ...
Steps of Writing a Literature Review. 1. Gather, Assess, and Choose Relevant Literature. The first seed to take when writing your dissertation or thesis is to choose a fascinating and manageable research topic. Once a topic has been selected, you can begin searching for relevant academic sources. If you are writing a literature review for your ...
A sophisticated literature review (LR) can result in a robust dissertation/thesis by scrutinizing the main problem examined by the academic study; anticipating research hypotheses, methods and results; and maintaining the interest of the audience in how the dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field.
The final article in this issue is a review study by Ashutosh Kumar and Shreya Mishra. Through a combination of 'systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis', this study explored the current literature on rural mothers' empowerment. The aim was to identify under-researched issues related to the empowerment of rural mothers.
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels ...
Paraphrasing will also ensure your review of literature is in your authorial voice. Organize by topic or theme rather than by author. When compiling multiple sources, a tendency can be to summarize each source and then compare and contrast the sources at the end. Instead, organize your source information by your identified themes and patterns.
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
Consider the following ways to organize your review: By themes, variables, or issues. By varying perspectives regarding a topic of controversy. Chronologically, to show how the topic and research have developed over time. Use an outline to organize your sources and ideas in a logical sequence. Identify main points and subpoints, and consider ...
Take your time and slowly draft the outline for a literature review. The structure of a literature review consists of five main components: Introduction: Provide a brief overview of the chapter, along with the topic and research aims to set the context for the reader. Foundation of Theory or Theoretical Framework: Present and discuss the key ...
The purpose of the literature review. A literature review tells us what is known by sharing the results of prior studies related to your own. A literature review places your study within a larger body of work. It shows how your study seeks to fill a gap in, or extend, our knowledge in this area. A literature review offers a benchmark for ...
In an era of information overload, a literature review must be well-structured. Let's learn all about the structure and style of a literature review that'll help you strengthen your research. Literature review- structure and style. Begin with a question and end it with the solution- the key to structuring a literature review.
4. Consider the organisation of your work. In a dissertation literature review, organising your work goes beyond having an introduction, body and conclusion. You'll be reviewing a number of texts, so you'll also have to think clearly about how to organise themes, topics and your argument in general.
Literature reviews should be organized thematically because the purpose is to show, overall, what the literature has demonstrated. The goal is not to give the reader a summary of each article. That's what an annotated bibliography is: a series of summaries and analyses of sources, one listed after the other.With an annotated bibliography, readers are looking to have these questions answered ...
Dissertation Literature Review Themes. Level: College, High School, University, Master's, PHD, Undergraduate. Professional Writers Experts in their fields with flawless English and an eye for details. Gustavo Almeida Correia. #27 in Global Rating.
Exhibition stands contractors in Russia
Proekta has been involved in organizing promotional stands since 2012, with our specialists fulfilling a number of large projects for both Russian and foreign clients.
Participation in exhibitions is impossible without an exhibition stand contractor to create your brand’s business card and temporary office. There are two main types of exhibit stands – modular and exclusive stands. Almost every time there is a need for an exhibition booth, organizers will end up providing different additional services, including electricity, water, hanging installations, etc. Modular stands are built from pre-produced components, and this is the most cost-effective solution, as these components can be used many times. The more expensive and functional solution is an exclusive exhibit booth. It is assembled by combining materials based on a custom design. The exhibition stand arrangement is a multiple stage process where procedure is important because it addresses all significant nuances. Today’s exhibition stands at large events are real masterpieces that require complicated construction and solid experience. Exhibition stand building in Moscow is in-demand as there are many large, occurring business events in the area.
THE MAIN PROBLEMS
To make a promotional booth, you have make many decisions with your event manager during each stage of building. To get approval, consider the hall’s technical features and how to deal with logistics issues. Normally, construction time is limited, and any delay can negatively affect quality. Depending on the project’s complexity, equipment can be brought from other cities or countries, and all these details must be considered beforehand. Many advertising stands are part of a brand concept, so everything should be according to official branding. There are engineering designs featured at automobile exhibitions, where floor sturdiness should be considered. It is important to test the structural integrity of the venue when placing cars. Stand construction for exhibitions in Moscow should be entrusted to an experienced, responsible exhibition stand building professional with customer recommendations. That’s why it’s important that a builder has project delivery experience in the field of your exhibition. Also, you have to remember that different exhibition contractors offer different technologies and solutions, so some contractors may not fit your needs.

Building of the exhibition stand and exhibition management at MIAS 2016

Presentation of new models at Moscow International Automobile Salon

Exhibition set up on the Comtrans commercial vehicles show

Stand buildup for Golden Dragon Company on Comtrans exhibition
Moscow, Butyrskaya Street 62
+7 (499) 653-65-25 (Mon-Fri 10:00-18:00)
facebook.com/proekta
Saint Petersburg, St. Lva Tolstogo 1-3
Rostov-on-Don, St. Koroleva 5b
+7 (863) 333-21-96 (Mon-Fri 10:00-18:00)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Stinson is an expert at understanding information to visualize complex data and design clear text-heavy slides. They've helped improve the consistency of our presentations using a keen sense of brand and attention to detail. I'd recommend Stinson to anyone! - Ralph Torbay, Global Head of Haematology (Marketing), AstraZeneca.
Get a professional presentation designed by the world's most trusted presentation design company in PowerPoint, Google Slides, and more In October 2018, 24Slides became a Certified B Corporation which means we meet high standards of social and environmental impact, public transparency, and legal accountability to balance profit and purpose.
3) BrightCarbon. Bright Carbon is a PowerPoint presentation design company that puts a big emphasis on the message you want to deliver. Their designers and communication specialists will work on your content to be as effective as possible and help you visually explain your ideas. Timing: Around 4 weeks.
Presentation design Siemens - Metering managed services. We created this company presentation for Siemens, providing an overview of its managed services. The use of a tight grid system gives the PowerPoint presentation design a modern feel, and the mix of full-bleed imagery with iconography communicates the message clearly and concisely.
Our designers will ensure that each slide aligns with your brand's core values with a consistent tone, style, and color throughout your presentation. The PowerPoint presentations we create include custom graphics, icons, illustrations and animation to deliver the "wow factor" and add impact. Before & After Samples.
Join our PPT experts community. Meet and learn the tips and tricks from creators & companies who share how they use PowerPoint to create better presentations in minutes. Get the professional presentation design services from Deckez & engage your audience with stunning visuals and compelling narratives. Talk to us today!
Welcome to SlideGenius. We're a presentation design agency with one goal: to go beyond. Our goal is to inspire audience action through engaging, meaningful, and memorable presentations. Whether you are a start-up or a Fortune 500 company, our elite presentation design team is here to deliver results. at the speed you need.
Give your slides a complete makeover and stand out with an impactful presentation. $43 for 72 hours turnaround. Complete slides makeover using CVI, your company's brand guidelines or other style preferences. Adjust colors, fonts and text sizes. Adjust alignment of text and elements. Insert stock icons and images.
World-Class Presentation Design Company. At Presentation Geeks, we're a presentation design company that believe behind every great presentation lies an opportunity, an investment, a promotion, or more. That's why a PowerPoint slide should be more than just a beautiful graphic design, it's an opportunity to share your idea.
We've earned a reputation as one of the world's top presentation design companies — recognized by leaders in tech, healthcare, and financial services, to name a few. At 16X9, we deliver what our clients expect: perfection. In fact, our entire design team is Microsoft Certified in PowerPoint and quality is one of our greatest virtues ...
Our specialist presentation designers have years of experience in a huge range of presentation software. We tend to use PowerPoint, Google Slides, Prezi, or Keynote the most, but it really depends on the objectives your company needs to achieve and the platform you're most comfortable using.
Check out our blog for more resources. "The designs are always amazing! The team works tirelessly to cater the design to any specific requests we make and they always come through with something truly beautiful! Ethos3 is an award winning presentation design agency specializing in helping clients uncover the formula behind great presentations.
SlidePeak is a professional presentation design agency that helps business owners, marketers, educators, and individuals conduct research, structure and illustrate their ideas, and visualize data with high-quality, creative custom-made presentations designed in PowerPoint, Keynote and Google Slides.
Design Presentation Associates is a trusted partner for all types of CAD services. We enable you to: Access top quality CAD talent on demand. Scale your business up and down as required. Keep your fixed costs low and maintain maximum flexibility. Keep your customers happy. Maximize your profits. Design Presentation manages a vendor base of ...
Skip to start of list. 26,020 templates. Create a blank Presentation. Beige Scrapbook Art and History Museum Presentation. Presentation by Noisy Frame. Cream Neutral Minimalist New Business Pitch Deck Presentation. Presentation by Take Care Creative. Brown and Beige Aesthetic Modern Group Project Presentation.
Choose a design from our presentation templates or create your own from scratch. Customize your presentation with colors, fonts, and key information. Add animations, videos, images, illustrations. Use assets and other media content from your Brand Kit (Pro) to stay consistent with your business or school brand.
4,471 templates. Create a blank Company Presentation. Minimalist Beige Cream Brand Proposal Presentation. Presentation by Saga Design Studio. Creative and Minimal Portfolio Presentation. Presentation by Amit Debnath. Purple & white business profile presentation. Presentation by ARP Creation.
Download the "Design Inspiration Business Meeting" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Gone are the days of dreary, unproductive meetings. Check out this sophisticated solution that offers you an innovative approach to planning and implementing meetings!
Exhibition Stand Design And Build. NEGUS EXPO International is one of the leading Russian full service exhibition companies, operating since 1992. During this period we have built stands at over 3000 exhibitions in 89 countries and delivered our services to over 3600 companies.
Select New blank presentation, open a Recent file, select one of the themes, or start with a presentation template. To name the presentation, select the title at the top and type a name. If you need to rename the presentation, select the title and retype the name.
presentation designer jobs in London. Sort by: relevance - date. 820 jobs. Compliance Engineer. BSRIA Ltd. North London. £33,000 a year. Full-time +1. 8 hour shift +2. Driving Licence. Compliance: 1 year. United Kingdom. Easily apply: Responsive employer. Liaising with, and presentation of findings to clients and site management.... Today's top 178 Presentation Designer jobs in London ...
Industry exhibitions are always about competition. Those participating show off their products and services with a clear message about brand recognition and their superiority. An exclusive design, high-quality assembly, and premium materials undoubtedly makes your display stand out. We only use high-quality materials, state-of-the-art designs, and trusted suppliers.
Your message has been received. Troxel will not share or sell your contact information with any outside party. Call 901-877-6875or Contact Us today to learn more about The Troxel Company. Phone 901-877-6875• Fax 901-877-3439. 11495 Hwy. 57 • P.O. Box 276.